Effects of Sodium Citrate, Sodium Tartrate Substitution of Sodium Chloride on the Quality of Squid Surimi Gel
-
摘要: 本文以不同比例柠檬酸钠(Sodium Citrate,SC)和酒石酸钠(Sodium Tartrate,ST)替代氯化钠(Sodium Chloride,NaCl)制备鱿鱼鱼糜凝胶,通过对其胶凝过程、感官特性、理化性质以及蛋白分子特性等分析,探索有机盐替代对鱿鱼鱼糜凝胶品质的影响。结果表明,当柠檬酸钠、酒石酸钠与NaCl的配比为2:1时,鱿鱼鱼糜凝胶强度、硬度、持水性均显著大于(P<0.05)其它复配组。两种有机盐(SC与ST)与NaCl配比结果表明,鱼糜凝胶的弹性和内聚性与鱼糜凝胶强度变化规律一致。盐复配添加使得鱼糜凝胶中疏水相互作用显著(P<0.05)低于对照组,并在SC、ST与NaCl配比为1:1时,疏水相互作用含量分别达至最低值(0.59、0.43 g/L)。流变学结果可以看出,有机盐添加显著缩短(40~57 ℃缩短至40~52 ℃)鱿鱼鱼糜热诱导过程中由于内源性蛋白酶导致的凝胶劣化。鱼糜凝胶的二级结构结果表明SC、ST与NaCl进行复配,α-螺旋和β-折叠含量呈现上升趋势,β-转角含量在复配比1:1时显著(P<0.05)高于对照组。低场核磁共振结果表明有机盐和NaCl的配比为2:1时,鱼糜凝胶相比其他配比组更容易固定水分,并且自由水含量更少。综上,有机盐和NaCl的配比为2:1时,可在一定程度上代替纯有机盐的添加。Abstract: In this study, the squid surimi gel was prepared by sodium citrate (SC) and sodium tartrate (ST) which substituted of sodium chloride (NaCl) in different proportions and the effect of organic salts on the properties changes of squid surimi gel was investigated through rheological properties, physicochemical properties and protein characteristics. From the results, the gel prepared by addition of organic salt and NaCl by the ratio of 2:1 significantly improved (P<0.05) the gel strength, hardness, and water holding capacity compared to other groups. Meanwhile, the elasticity and cohesiveness of surimi gel were consistent with the change trend of surimi gel strength. The mixed addition of organic salts and NaCl inhibited the generation of hydrophobic interactions, and the inhibition effect reached the minimum value of 0.59 g/L (SC) and 0.43 g/L (ST) when the ratio was 1:1. The results of rheological properties demonstrated that the addition of organic salts significantly shortened (40~57 °C to 40~52 °C) the gel degradation due to endogenous proteases during heat process of squid surimi. The secondary structure results showed that the content of α-helix and β-sheet increased when organic salts were added with NaCl, and the relative content of β-turn was significantly (P<0.05) higher than other groups by the ratio of 1:1. The low-field NMR results showed that when the ratio of organic salt and NaCl was 2:1, the gel contained more immobilized water and less free water than the other groups. All results showed that addition of organic salt and NaCl at ratio of 2:1 could keep the high gel quality of squid and provided the scientific basis to prepare the squid products by using organic salts.
-
Keywords:
- squid /
- surimi /
- organic salt /
- substitution /
- gel properties
-
鱿鱼属于软体动物门(Mollusca)头足纲(Cephalopoda),广泛分布于世界各大洋,尤其是太平洋和印度洋[1]。因其资源丰富、产量大、营养价值高、肉厚色白,具有作为鱼糜制品原料的重要前景[2],但是由于鱿鱼肌肉不同于其他鱼类的特殊性,蛋白酶活性强,凝胶性能差,限制了鱿鱼鱼糜产品的开发[3-4]。因此,提高其产品品质成为热点方向之一。王冬妮等[5]利用不同淀粉及蛋白类添加物对鱿鱼鱼糜凝胶性的改良研究中发现,淀粉类中红薯淀粉、玉米淀粉、木薯淀粉和马铃薯淀粉及蛋白类中大豆分离蛋白、大豆浓缩蛋白和蛋清蛋白均可提高鱿鱼鱼糜的凝胶强度,增强保水性,使其组织结构更加紧密。徐安琪等[4]报道利用紫菜粉,通过影响肌原纤维蛋白二级结构,可以改善鱿鱼鱼糜凝胶品质。
在鱿鱼体内,除了相较于普通鱼类含有更多的水解蛋白酶外,还含有一种强水解酶—金属蛋白酶(Metalloproteases,MMPs)。有报道称MMP可以降解鱿鱼体内胶原蛋白并且参与其死后的肌肉软化进程[6]。当轻链肌球蛋白(Light meromyosin,LMM)以及重链肌球蛋白(Heavy meromyosin,HMM)在盐溶作用下曝露在环境中时可以与MMP结合进行水解反应[7]。通常情况下,大部分水解蛋白酶(例如组织蛋白酶、天冬氨酸蛋白酶、丝氨酸蛋白酶)在加热至60 ℃左右才会表现出水解活性,然而MMP在较低温度下就表现出较强活性,使得加热后蛋白结构遭到破坏,导致鱿鱼鱼糜凝胶性能降低,严重影响鱿鱼鱼糜制品的质量和市场价值。在前期研究中发现,鱿鱼鱼糜凝胶在低温加热过程中(20~40 °C)会产生较强水解反应,导致鱿鱼鱼糜的凝胶劣化过程贯穿整个加热进程[8]。金属蛋白酶作为影响其凝胶性能的主要内源蛋白酶,其可通过金属螯合作用进行酶活性抑制[9-10]。通过螯合剂类产品对酶活性进行抑制,使凝胶形成的关键蛋白-肌球蛋白的降解得到一定程度上的控制。
肌原纤维蛋白(Myofibrillar proteins,MPs)作为凝胶形成中最重要的蛋白质,为使其充分溶解,通常加入2%~3%的NaCl,既可以调节鱼糜制品的风味,还可以提高鱼糜制品的凝胶特性[11]。然而,盐摄入过多可能会对人类健康产生不利影响,特别是对那些患有高血压和心血管疾病的人群[12]。因此,减盐鱼糜制品的开发也成为了迫切需要解决的问题[13]。柠檬酸钠(Sodium Citrate,SC)和酒石酸钠(Sodium Tartrate,ST)是一类具有强金属螯合性的羟基羧酸盐类食品添加剂,能够螯合大多数二价和三价金属离子,因此推测其能通过对MMPs活性位点上的金属离子进行螯合进而抑制鱿鱼肉蛋白的水解和HMM的降解。同时,SC和ST作为盐类,可使鱼糜中MPs的结构展开、肌球蛋白溶出,从而代替NaCl在鱼糜中的作用。
然而,纯有机盐添加使得产品呈现苦涩味,NaCl添加能够适当增加产品风味,故有机盐与NaCl的不同配比对鱼糜制品的研究有着重要的现实意义。此外,SC、ST对MPs的溶出以及MMPs的活性和肌球蛋白的降解的抑制作用,可为提高鱼糜制品的品质提供新思路。因此,本研究将采用2.5%的盐制备样品,将有机盐(SC和ST)和NaCl进行不同配比,综合探讨有机盐与NaCl复配对鱿鱼鱼糜凝胶制品品质的影响,为鱿鱼加工产业的多样化发展提供新理论、新技术和新方法。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
秘鲁鱿鱼(平均长度:61.04±7.21 cm;平均质量:383.09±131.08 g) 购自中国浙江省舟山市的沈家门渔市,将购买的鱿鱼运回实验室用流水解冻,去除头、尾、皮,留其酮体,并将其酮体置于密封袋中,置于−80 ℃冰箱中储藏备用;氯化钠、柠檬酸钠(SC)、硫酸铜、四水合酒石酸钠、碘化钾、氢氧化钠、尿素、三氯乙酸 国药化学试剂有限公司;酒石酸钠(ST) 阿拉丁生化技术有限公司;β-巯基乙醇 索莱宝科技有限公司。
T18匀浆机 IKA集团;Multifuge X1R型高速冷冻离心机、DXR 2Xi显微激光共聚焦拉曼光谱仪 赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司;2600UV/VIS紫外可见分光光度计 尤尼柯(上海)仪器有限公司;FP 3010型食品加工机 上海博朗有限公司;HH-W420电热恒温水浴锅 北京长安科学仪器有限公司;HR-20旋转流变仪 美国TA仪器;TA XTplus型食品物性测定仪 英国SMS公司;CS-210精密色差仪 杭州彩谱科技有限公司;MDF-U53V冰箱 日本三洋公司;PQ001低场核磁分析仪 上海纽迈电子有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 鱼糜糊和鱼糜凝胶样品制备
鱿鱼酮体流水解冻并擦去表面水分,将其切碎后放入食品加工机中空斩1 min,加入盐(盐总量为2.5%,有机盐(SC与ST)按不同比例分别与NaCl进行1:2、1:1、2:1(w/w)复配)后斩拌2 min。斩拌期间中,每隔30 s停一次,期间不断用冰水降温以控制温度不超过10 ℃,水分含量达到为78%,斩拌后的成品即为鱼糜糊。将斩拌好的鱼糜糊灌入塑料肠衣(直径2.5 cm)内,采用一段式水浴加热(90 ℃、30 min)制成鱼糜凝胶样品。将加热后的鱼糜凝胶制品放置在冰上降温30 min后置于4 ℃冰箱中冷藏待测。有机盐与NaCl分别以1:2、1:1、2:1量添加,凝胶配方如表1所示。纯有机盐添加作为对照组。
表 1 鱼糜凝胶配方Table 1. Ingredient of surimi gels处理组(有机盐:NaCl) 2.5%盐(g) 肉(g) 冰水(g) 总量(g) SC(ST) NaCl 1:2 4.17 8.33 426.51 60.99 500 1:1 6.25 6.25 426.51 60.99 500 2:1 8.33 4.17 426.51 60.99 500 1.2.2 凝胶强度测定
参照Huang等[14]的方法并稍作修改。采用食品物性测定仪的P-5S金属探头进行测定。测前先将高度为2.5 cm的鱼糜凝胶圆柱体在室温静置30 min,以使鱼糜凝胶的中心温度达到室内温度。测试参数为:检测速度为1 mm/s,测试距离40 mm;穿刺距离10 mm;触发力0.1 N。
1.2.3 全质构测定
将高2.5 cm凝胶圆柱体在室温下平衡30 min后放在载物台上。使用柱形探头P/50测定,测定时将样品放在探头正下方的样品台上。物性测试仪的起始力为0.6 N,其中测试速度为3.0 mm/s,形变量为30%,获得样品的硬度、黏聚性、弹性、咀嚼性等质构参数。
1.2.4 持水性测定
持水性(Water-holding capacity,WHC)测定参考Manat等[15]的方法略微修改。将鱼糜凝胶切成5 mm厚的薄片并电子天平准确称取1 g(±0.1 g)并记为M1,将样品用三层滤纸包好后放入50 mL离心管中,用离心机以8000×g的转速在4 ℃下离心15 min。离心后的样品质量记录为M2。每组样品平行测量3组,结果取其平均值[16],WHC(%)的计算公式如下:
WHC(%)=M2M1×100 (1) 式中:M1表示离心前的样品质量,g;M2表示离心后的样品质量,g。
1.2.5 白度的测定
用色差仪检测其横截面的亮度值(L*)、红度值(a*)和黄度值(b*)。白度的计算方法为[17]:
白度=100[(100−L∗)2+a∗2+b∗2]12 (2) 1.2.6 化学作用力测定
参考Gómez-Guillén[18]和Tan等[19]的方法,并略有修改。将2 g凝胶样品与10 mL溶液8000 r/min均质30 s,4 ℃静置1 h,在4 ℃、8000×g下离心10 min,取上清液保存在4 ℃待测。其中,样品经S4溶液处理过后保留沉淀并加入溶液S5,重复以上操作。向含有S5的上清液中加入等体积的20%三氯乙酸溶液(TCA),在4 ℃,8000×g离心10 min,弃去上清液。沉淀再次使用TCA溶液进行漂洗和收集。将收集到的沉淀物加入1 mL的1 mol/L的NaOH进行溶解。蛋白质浓度采用双缩脲法进行测定。鱼糜凝胶溶解液分别是S1(0.05 mol/L NaCl)、S2(0.6 mol/L NaCl)、S3(0.6 mol/L NaCl+1.5 mol/L尿素)和S4(0.6 mol/L NaCl+8 mol/L尿素)和S5(0.6 mol/L NaCl+8 mol/L尿素+0.5 mol/L β-巯基乙醇)。结果以每升溶液中所溶出的蛋白质的浓度(C)来表示(g/L)。离子键、氢键、疏水相互作用和二硫键的计算如下:
离子键(g/L)=CS2−CS1 (4) 氢键(g/L)=CS3−CS2 (5) 疏水相互作用(g/L)=CS4−CS3 (6) 二硫键(g/L)=CS5 (7) 式中:溶解于S1、S2的蛋白含量之差表示离子键的大小,g/L;溶解于S2、S3的蛋白含量之差表示氢键的大小,g/L;溶解于S3、S4的蛋白含量之差表示疏水作用的大小,g/L;溶解于S5的蛋白含量表示二硫键的大小,g/L。
1.2.7 流变学特性的测定
流变学特性参照Xue等[20]的方法并稍作修改。实验采用直径为40 mm的夹具进行测定。将鱼糜糊样品均匀地涂布在测试平台上,外周涂一层薄薄的硅油以防止水分蒸发。试验测试参数为:采用温度扫描模式,振荡频率为1 Hz,应变为2%,平行板间距1000 um,升温扫描范围20~90 ℃,升温速率4 ℃/min,测定升温过程中储能模量(G')和损耗模量(G'')的变化。
1.2.8 拉曼光谱测定
拉曼光谱的测定参考Guo等[21]的方法,并略微修改。取厚度为3 mm左右的凝胶薄片在785 nm激发激光束下进行100~3400 cm−1范围的扫描。其中激光功率为6.0 mW,曝光时间为10 s,每1 cm−1收集一次数据。由于1003 cm−1附近的苯丙氨酸环对微环境不敏感,因此将该附近的伸缩振动强度作为内标进行归一化。使用Peakfit v4软件对1600~1700 cm−1范围的数据进行了高斯反卷积拟合,并计算蛋白质各个二级结构(α-螺旋、β-折叠、β-转角和无规卷曲)的百分比。
1.2.9 低场核磁共振测定
将高2.5 cm的凝胶样品置于核磁管中进行测定,采用Carr-Purcell-Meiboom-Gill(CPMG)测量横向弛豫时间常数T21、T22和T23,利用Multi Exp Inv Analysis软件对低场核磁共振弛豫曲线进行成多指数曲线拟合,得到各峰位横向松弛时间,并根据各峰面积计算不同类型水分含量的比例。
1.3 数据处理
各指标均进行3次独立试验,并用平均值±标准差来表示测试结果。采用SPSS 26.0中的单因素方差分析(Duncan)进行数据统计分析。P < 0.05表示数据具有统计学意义上的差异。利用Origin 2021软件进行图形处理。
2. 结果与分析
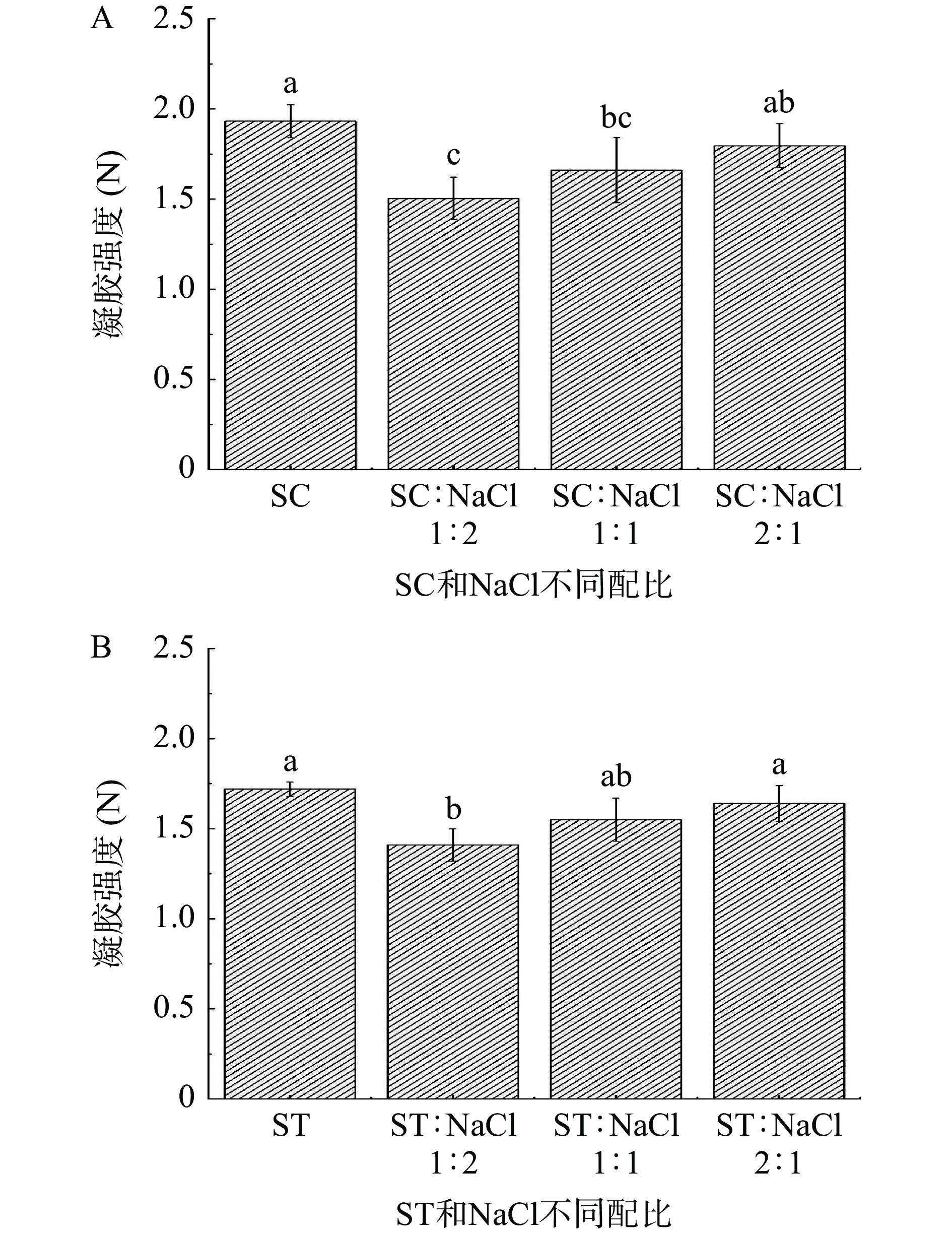
2.1 鱿鱼鱼糜凝胶强度分析
凝胶强度测定是使用最广泛的评估鱼糜凝胶品质的方法,从图1中可以看出,两种有机盐(SC和ST)与NaCl不同配比下的鱿鱼鱼糜的凝胶强度变化结果相似,这与有机盐的结构以及金属螯合作用相似有关[8]。ST添加的凝胶强度(1.72±0.04 N)要低于SC添加组(1.93±0.09 N),主要原因是SC对蛋白的溶解度以及肌球蛋白降解的抑制作用大于ST。与有机盐纯替代相比,不同配比下的鱼糜凝胶强度都发生了不同程度的下降,并且在有机盐与NaCl的配比为1:2时,鱼糜凝胶强度达到最低值(P<0.05)。但当有机盐与NaCl的配比为2:1时,鱿鱼鱼糜凝胶强度与对照组相比,并无显著差异(P>0.05),表现出较好的可替代性。结果显示,鱼糜凝胶强度受有机盐添加含量的效果明显,随着有机盐含量的增加,鱼糜凝胶强度逐渐增强。Chu等[8]报道相较于NaCl,SC及ST添加能显著增加鱿鱼凝胶力。张崟等[22]报道称,SC能显著提高罗非鱼鱼糜的凝胶强度。有机盐可能通过增加其金属螯合性来抑制MMPs活性,进而减缓肌球蛋白降解,达到改善鱼糜凝胶强度的目的。结果表明,在不同有机盐(SC和ST)与NaCl配比中,柠檬酸钠、酒石酸钠分别与NaCl的配比为2:1时,可替代NaCl的纯添加。
2.2 鱿鱼鱼糜凝胶全质构特性分析
不同有机盐与NaCl配比下的鱿鱼鱼糜凝胶的质地特性如表2和表3所示。鱼糜凝胶的质地特性受不同盐配比的显著影响(P < 0.05)。在两组有机盐配比中,不同SC和ST配比组的硬度、粘附性、内聚性以及咀嚼性均小于对照组,与赵宏蕾等[23]研究的SC与碳酸氢钠协同作用下的法兰克福香肠的质地特性低于碳酸氢钠组的结论相似。在SC与NaCl的不同配比添加中,当SC与NaCl的配比为2:1时,鱿鱼鱼糜凝胶的硬度与对照组并无显著差异(P > 0.05)。随着SC添加量的逐渐减少,鱼糜凝胶硬度逐渐降低。这与赵宏蕾等[23]报道的SC添加量的增加,会降低法兰克福香肠的硬度和咀嚼性的结论不同,这种差异可能是鱼糜凝胶的制备工艺和法兰克福香肠不同导致的。不同于鱼糜凝胶的硬度,鱼糜凝胶的粘附性在SC与NaCl的配比为2:1时达到最小值。同时,鱼糜凝胶的弹性也随着SC含量的增加出现下降趋势,并在SC与NaCl的配比为2:1时达到最小值。陈海华等[24]认为,鱼糜凝胶的弹性受鱼糜的破断距离的影响,与鱼糜受力时的形变有关。鱼糜凝胶的内聚性以及咀嚼性则随着SC添加量的增加而增加。在ST与NaCl的不同配比添加中,鱼糜的质地特性与SC和NaCl的配比结果相似,但是鱼糜凝胶的弹性、内聚性以及咀嚼性则随着ST添加的增加而增加,在ST完全添加时达到最大值。
表 2 SC和NaCl不同配比下鱿鱼鱼糜凝胶质地特性Table 2. Texture properties of squid surimi gels with different ratios of SC and NaCl处理组(有机盐:NaCl) 硬度(N) 粘附性(g·s) 弹性 内聚性 咀嚼性 SC 14.75±0.46a −4.01±0.61a 0.81±0.00b 2.74±0.09a 3326.36±166.79a 1:2 12.41±0.34b −7.24±0.74b 0.82±0.00a 2.62±0.02a 2715.05±65.14b 1:1 12.82±0.38b −7.17±0.86b 0.82±0.00a 2.67±0.11a 2867.15±208.33b 2:1 14.38±0.73a −13.15±0.72c 0.79±0.00c 2.30±0.06b 2668.33±89.79b 注:同列字母不同样品组的质地特性存在显著差异表(P<0.05);表3同。 表 3 ST和NaCl不同配比下鱿鱼鱼糜凝胶质地特性Table 3. Texture properties of squid surimi gels with different ratios of ST and NaCl处理组(有机盐:NaCl) 硬度(N) 粘附性(g·s) 弹性 内聚性 咀嚼性 ST 13.56±0.88a −1.92±0.29a 0.81±0.01a 2.91±0.01a 3258.37±181.28a 1:2 11.27±0.70b −13.24±0.66c 0.77±0.00b 2.27±0.10c 2006.89±56.67d 1:1 12.36±0.56ab −7.35±0.55b 0.81±0.01a 2.63±0.09b 2687.67±86.44b 2:1 13.10±0.27a −14.69±1.01d 0.78±0.01b 2.22±0.12c 2318.28±180.24c 2.3 鱿鱼鱼糜凝胶持水性分析
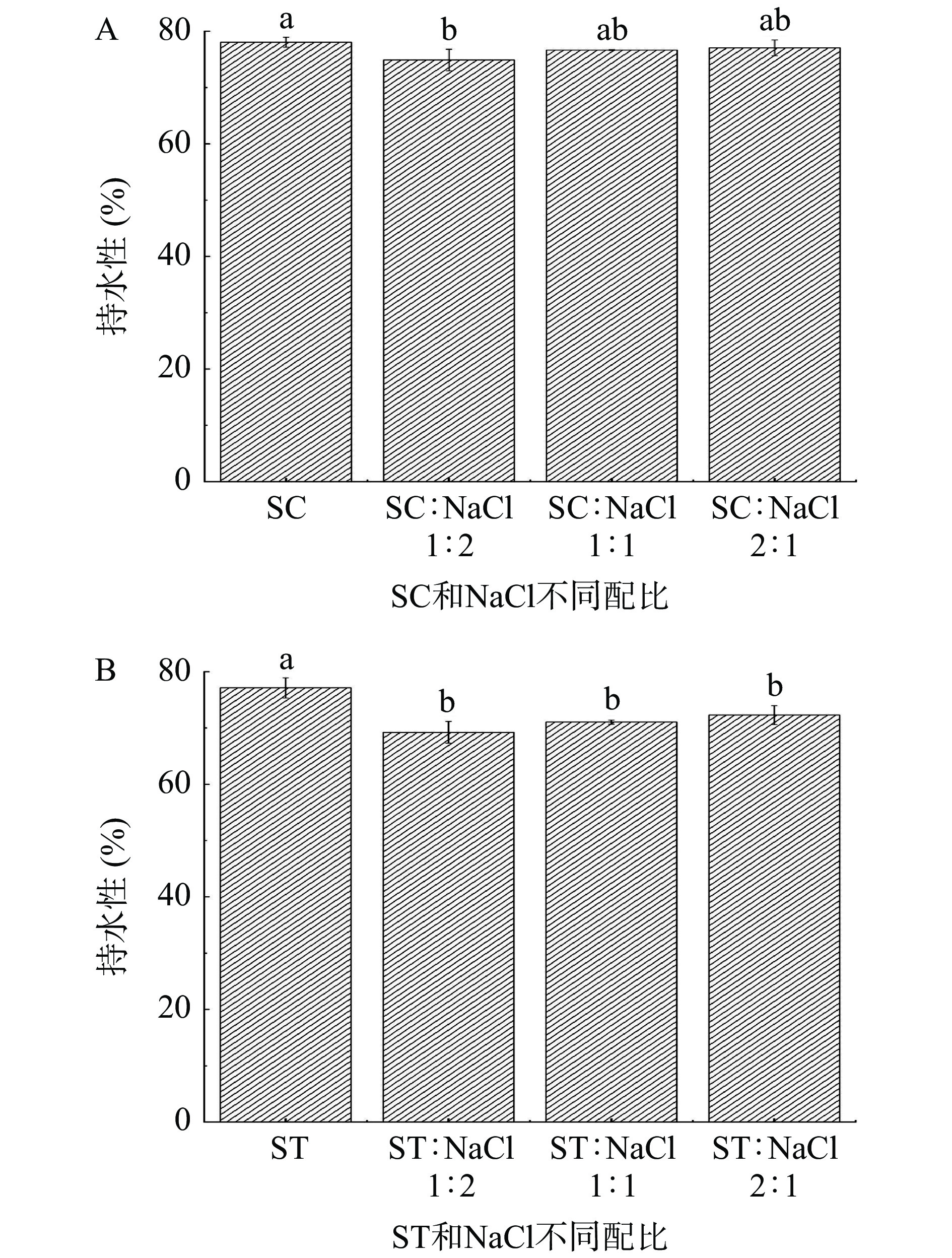
如图2所示,不同配比下SC和ST处理组的鱼糜凝胶WHC发生了不同程度的下降。在图2A中,随着有机盐SC添加量的不断变化,SC与NaCl配比添加为1:2时,鱼糜凝胶的WHC显著性降低(P<0.05)。随SC添加量的进一步增长,SC与NaCl配比添加达到2:1时,凝胶WHC与对照组无显著差异(P>0.05)。图2B中复配组鱼糜凝胶WHC显著低于(P<0.05)对照组,且与SC不同配比下的鱼糜凝胶的WHC的结果相似。该结果与上述鱼糜凝胶强度、硬度等结果趋势相似,推测可能是有机盐对鱿鱼肌肉中的MMPs进行了抑制,进而缓解了肌球蛋白的降解,促进了鱼糜凝胶品质的提高。
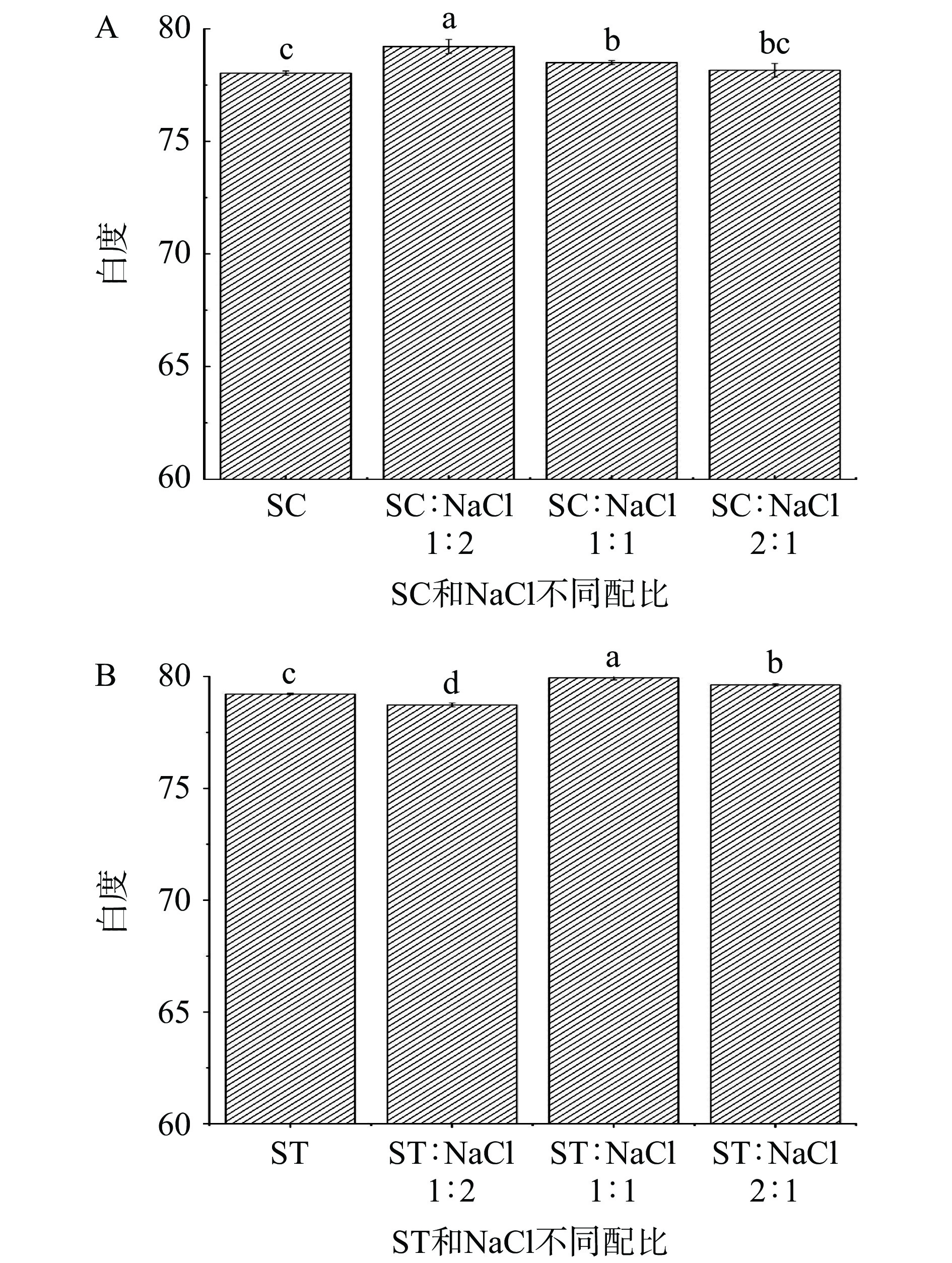
2.4 鱿鱼鱼糜凝胶白度分析
在图3A中,与对照组相比,不同配比组的鱼糜凝胶白度均有所提高,并在SC与NaCl配比为1:2时,鱼糜凝胶的白度值达到最大值。随着SC含量的逐渐增加,鱼糜凝胶的白度值逐渐降低,因为SC具有调节鱼糜肉pH的作用,高含量的SC促进了鱼糜肉的pH升高,使鱼糜凝胶的白度值下降。这与Holmer等[25]报道的SC溶液处理过的奶牛肌肉颜色更暗的结论一致。张崟等[22]研究发现SC对罗非鱼鱼糜凝胶白度无显著作用,这种结果的差异可能是因为鱼种的不同造成的。图3B中,当ST与NaCl的配比为1:2时,鱼糜凝胶的白度值最低。由于ST添加量较少时,鱿鱼鱼糜在加热过程中ST对美拉德褐变和油脂受热降解后的着色反应的抑制作用较低,导致色素大量沉积。随着ST添加量的增加,鱼糜凝胶的白度值呈现先增加再下降的趋势,并在两者配比为1:1时,白度值达到最大值。据报道,鱼糜蛋白质间的变性、聚合、交联等作用共同影响着凝胶制品的白度[26]。当ST和NaCl的配比为1:1时,NaCl的加入会促进的MPs的溶解度增加,同时ST对鱼糜中的美拉德褐变和油脂高温下热降解着色都有一定程度的抑制作用,从而使鱼糜凝胶的白度值增高。随着ST含量的进一步增加,鱼糜凝胶白度值降低,可能由于NaCl的减少而导致鱼糜中MPs溶出率的减少。因此,在ST中适量增加NaCl可以促MPs的增溶,进而提高鱼糜凝胶的白度值。
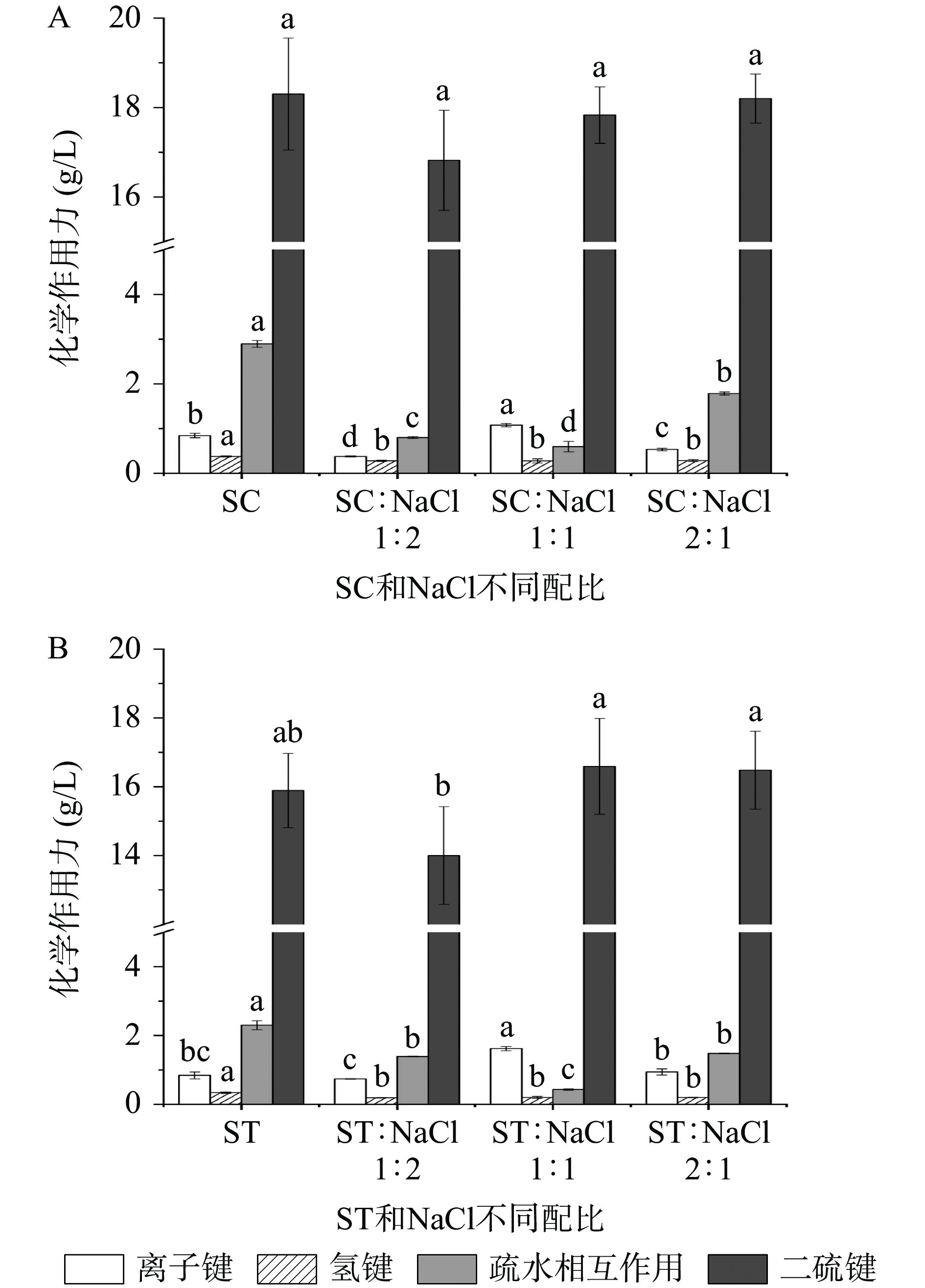
2.5 鱿鱼鱼糜凝胶化学作用力分析
有机盐与NaCl不同配比对鱼糜凝胶中的化学作用力产生了显著影响(P < 0.05)。随着NaCl添加量的增加,鱼糜凝胶中的离子键含量下降(图4)。由于NaCl能促进更多蛋白质的溶出,在加热过程中蛋白质的结构因受热舒展暴露出更多离子键,并在高温作用下被破坏,从而含量逐渐降低。两种有机盐配比下的鱼糜凝胶中的氢键均低于对照组(P < 0.05),而不同配比组间并没有显著差异(P > 0.05)。疏水相互作用和二硫键作为维持鱼糜凝胶的主要贡献作用力[27],对鱼糜凝胶的网络形成有着重要影响。相比于对照组,两种有机盐配比的疏水相互作用显著降低(P < 0.05),并在有机盐与NaCl为1:1添加时,鱼糜凝胶中的疏水相互作用含量达到最低值,这可能是有机盐和NaCl的混合添加抑制了疏水相互作用的生成。当有机盐与NaCl的配比为2:1时,鱼糜凝胶中的疏水相互作用远高于有机盐与NaCl的配比为1:2时的添加。这与Zhang等[28]和Xiong等[29]报道的羟基能促进疏水相互作用生成的结果一致。二硫键的变化则随着有机盐的添加量的增加而增加,其变化与鱼糜凝胶强度的结果基本一致(P > 0.05),这表明鱼糜凝胶网络结构主要依赖于二硫键。该结果与钟坦君和文献[27-30]报道的二硫键是是维持凝胶网络结构的主要化学作用力的结论一致。
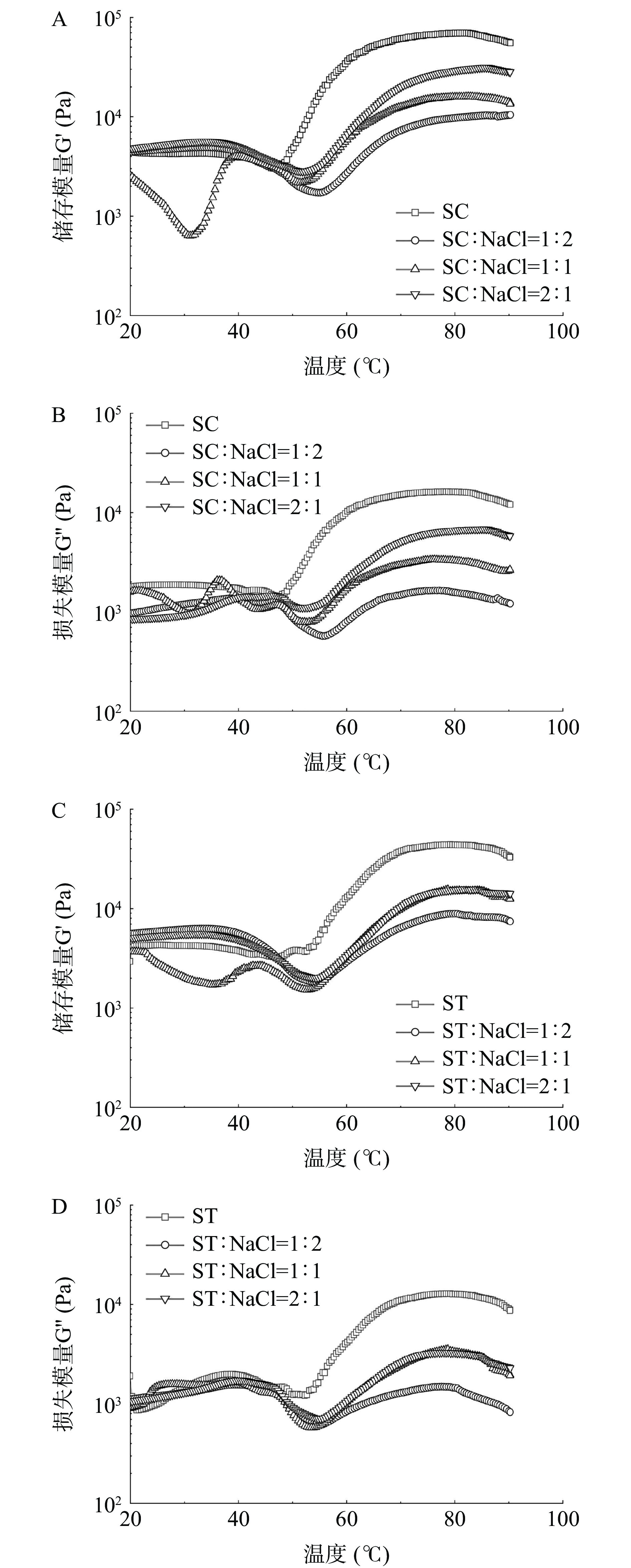
2.6 鱼糜凝胶流变学特性的变化
有机盐与NaCl不同配比下的鱿鱼鱼糜糊在加热过程中流变学特性如图5所示。在相对较低的温度下,G'和G''逐渐增加,并在40 ℃左右达到峰值,表明网络凝胶结构形成[31]。而后,随着温度到达内源性蛋白酶最佳活性温度,G'和G''开始下降,导致凝胶网络结构分解(凝胶劣化)[32]。LMM和HMM是鱼糜凝胶网络形成的主要蛋白,其降解会造成鱼糜凝胶的无法成型以及凝胶解胶,进而降低鱼糜凝胶强度。随着有机盐SC和ST含量的逐渐增加,有机盐的金属螯合和性也逐渐增强,通过对鱿鱼体内的金属离子进行螯合,以降低MMPs的活性,使鱼糜糊快速通过凝胶劣化温度段,并最终提高G'和G''。在图5A和图5B中,随着SC含量的逐渐减少,鱼糜糊在热诱导过程中的凝胶劣化温度逐渐延长(从40~52 °C延长至40~57 °C),表明了SC添加对鱿鱼肌肉内的主要内源酶-MMPs的活性进行了抑制,并缩短了鱼糜在热诱导过程的凝胶劣化温度段。而在ST与NaCl的不同配比添加中,鱼糜凝胶劣化温度段的差异并不大,这可能是因为ST对MMPs活性的抑制作用低于SC所造成的结果的不同[33]。在图5B和图5D中,G''在相对较低的温度段内随着温度的逐渐升高逐渐增大,这是因为随着温度的逐渐增高,鱼糜蛋白相互聚集并交联形成弱凝胶,使鱼糜蛋白的流动性逐渐减小,粘性逐渐增大。而后随着凝胶劣化的发生,G''也随着G'发生下降,说明鱼糜蛋白以及弱凝胶网络遭到内源性蛋白酶的水解,导致其弱凝胶体系崩溃解体,并造成蛋白流动性增加。
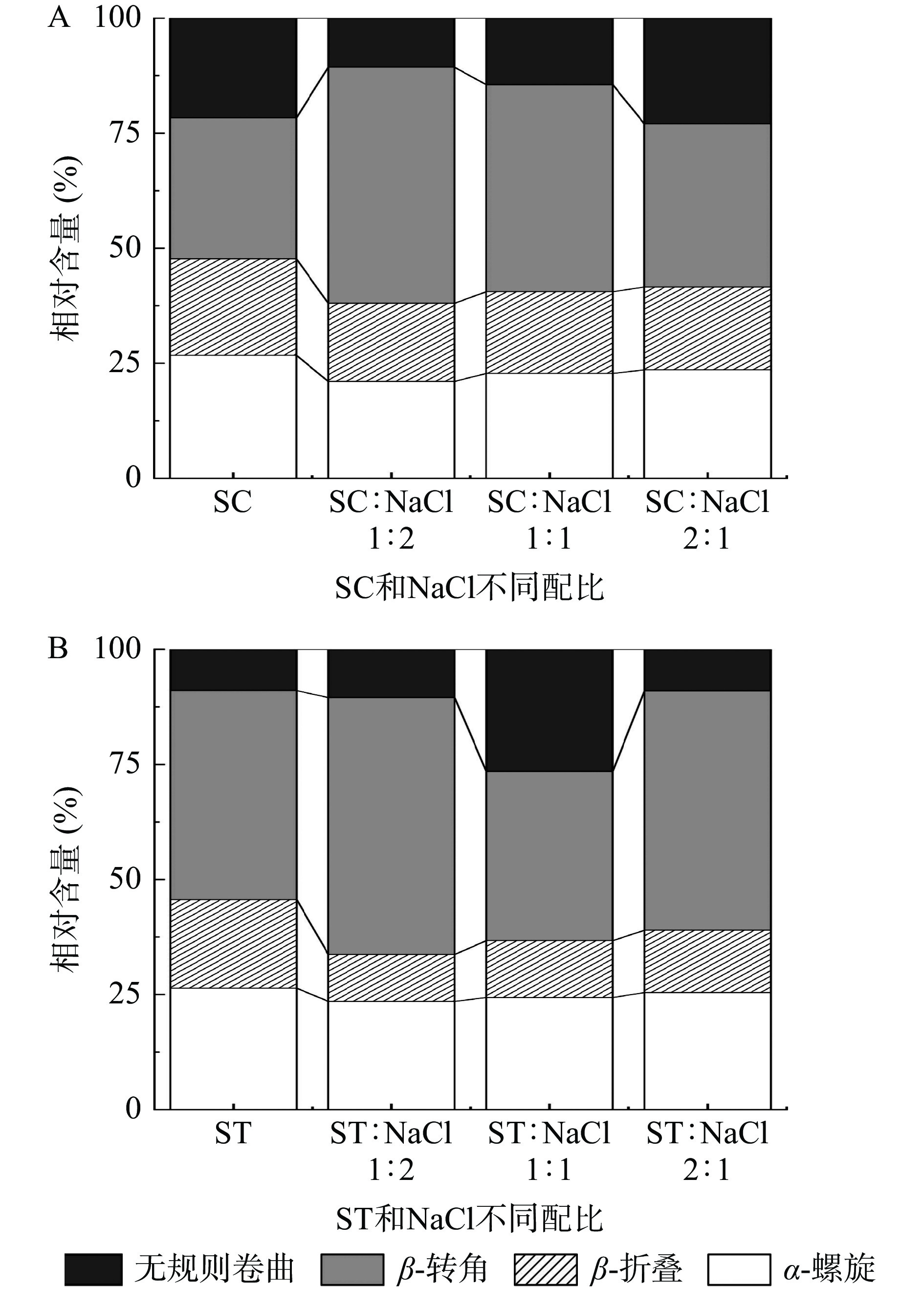
2.7 鱿鱼鱼糜凝胶蛋白二级结构的变化
不同有机盐配比添加对鱼糜凝胶中蛋白质的二级结构产生了影响(图6)。在两种有机盐配比中,随着有机盐添加量的增加,鱼糜凝胶中α-螺旋和β-折叠都逐渐增加。这与Liu等[34]报道的β-折叠的增加常伴随着α-螺旋的减少的结论不同。这可能是有机盐主要依靠抑制已溶出的MPs的降解来提高鱼糜凝胶品质。而有机盐对蛋白质的溶解度低于NaCl,因此随着有机盐添加量的逐渐增加,鱼糜蛋白质的溶解度逐渐降低,导致鱼糜蛋白在加热后含有更多的α-螺旋结构,而β-折叠的增多则可能是依赖于有机盐对已溶出MPs结构的α-螺旋的更多地转化成了β-折叠。与对照组相比,SC、ST与NaCl复配比1:1时,β-转角含量分别上升20.66%和10.41%,复配比2:1时,则分别上升4.82%和6.60%。α-螺旋和β-转角相对含量的增加,使得凝胶网络结构更紧密。
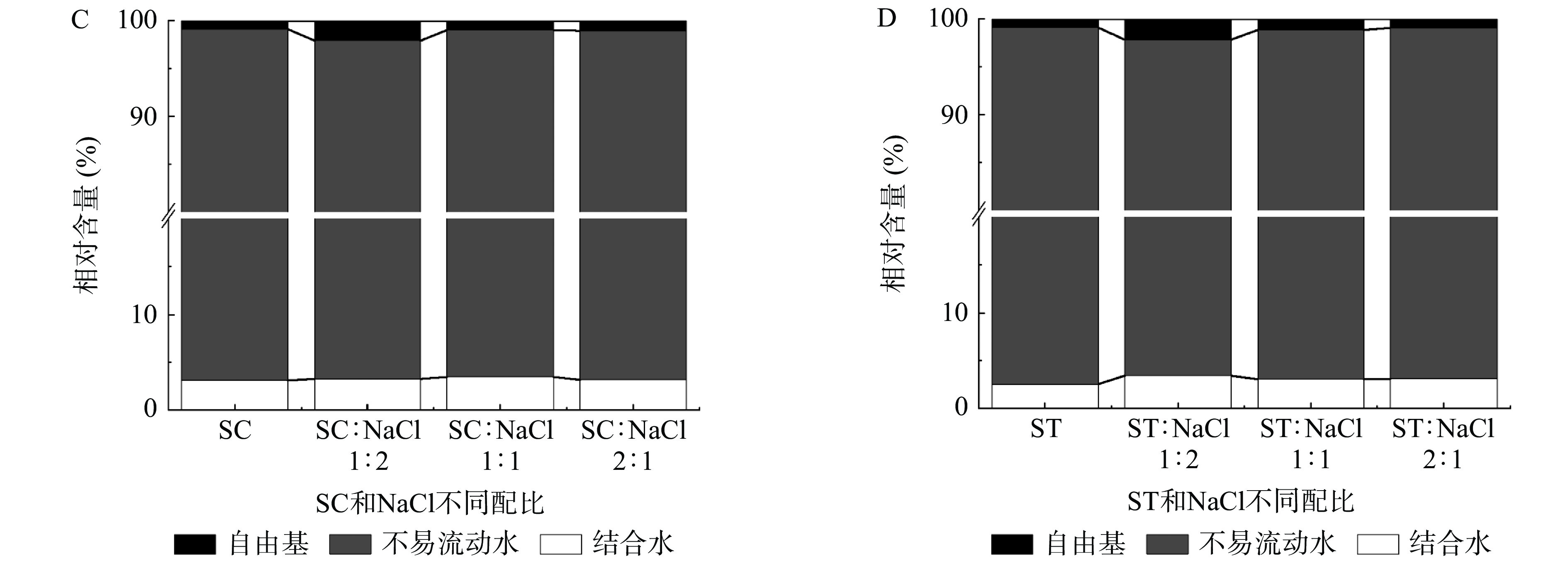
2.8 鱿鱼鱼糜凝胶水分迁移的变化
鱼糜中的MPs在高温作用下结构展开,内部蛋白相互交联成为具有拦截水分流失能力的三维网状弹性凝胶结构,因此鱼糜凝胶中的水分评判对评价鱼糜凝胶品质具有重要意义。在图7A中,随着SC添加量的增加,T22逐渐左移,同时相应的峰面积也逐渐增高,表明鱼糜凝胶中的不易流动水与凝胶网络的连接更加牢固。与其他配比组相比,当SC与NaCl的配比为2:1时,可观察到T22的左移以及相对较高的峰面积,表明该配比下的鱼糜凝胶与其他配比组相比具有较好的水分拦截能力。图7C中,相比对照组与其他配比组,SC与NaCl的配比为1:2时,可观察到鱼糜凝胶内含有较高的自由水。随着SC添加量的进一步增加,鱼糜凝胶体系中的自由水含量减少,不易流失水分含量增加。在ST与NaCl的不同配比中,可观察的相似的结果(图7B、图7D)。这表明SC和ST的添加在一定程度上改善了鱼糜凝胶内部体系结构。王红妮等[35]认为,蛋白质由于NaCl的加入,会导致其组织结构收缩而变性,从而导致水分结合能力减弱,自由水含量升高。而MPs在SC的作用下,组织结构逐渐松散,亲水集团逐渐暴露,水分则在亲水集团的作用被拦截在鱼糜凝胶网络中。
3. 结论
研究结果表明柠檬酸钠、酒石酸钠与NaCl的配比为2:1时,鱼糜的凝胶强度、硬度以及持水性与对照组相比,均无显著差异(P>0.05)。因此,当柠檬酸钠、酒石酸钠分别与NaCl的配比为2:1时,鱼糜凝胶与纯有机盐组无显著性差异,且比配比1:2时分别提高21%(SC)和23%(ST),在改善鱿鱼鱼糜凝胶性的同时,减少NaCl在鱼糜中的含量。SC和ST作为低钠盐,在食品方面的研究非常有限,在鱼糜制品上的研究报道更加少见,该研究为SC和ST在鱼糜制品以及低钠食品研究中提供了新思路。然而,本文仅从较为宏观的角度提出SC和ST改善鱿鱼鱼糜凝胶的可能性,没有从微观分子结构上进行分析,未来工作中则需要着重于有机盐对相应水解蛋白酶的抑制机理研究。
-
表 1 鱼糜凝胶配方
Table 1 Ingredient of surimi gels
处理组(有机盐:NaCl) 2.5%盐(g) 肉(g) 冰水(g) 总量(g) SC(ST) NaCl 1:2 4.17 8.33 426.51 60.99 500 1:1 6.25 6.25 426.51 60.99 500 2:1 8.33 4.17 426.51 60.99 500 表 2 SC和NaCl不同配比下鱿鱼鱼糜凝胶质地特性
Table 2 Texture properties of squid surimi gels with different ratios of SC and NaCl
处理组(有机盐:NaCl) 硬度(N) 粘附性(g·s) 弹性 内聚性 咀嚼性 SC 14.75±0.46a −4.01±0.61a 0.81±0.00b 2.74±0.09a 3326.36±166.79a 1:2 12.41±0.34b −7.24±0.74b 0.82±0.00a 2.62±0.02a 2715.05±65.14b 1:1 12.82±0.38b −7.17±0.86b 0.82±0.00a 2.67±0.11a 2867.15±208.33b 2:1 14.38±0.73a −13.15±0.72c 0.79±0.00c 2.30±0.06b 2668.33±89.79b 注:同列字母不同样品组的质地特性存在显著差异表(P<0.05);表3同。 表 3 ST和NaCl不同配比下鱿鱼鱼糜凝胶质地特性
Table 3 Texture properties of squid surimi gels with different ratios of ST and NaCl
处理组(有机盐:NaCl) 硬度(N) 粘附性(g·s) 弹性 内聚性 咀嚼性 ST 13.56±0.88a −1.92±0.29a 0.81±0.01a 2.91±0.01a 3258.37±181.28a 1:2 11.27±0.70b −13.24±0.66c 0.77±0.00b 2.27±0.10c 2006.89±56.67d 1:1 12.36±0.56ab −7.35±0.55b 0.81±0.01a 2.63±0.09b 2687.67±86.44b 2:1 13.10±0.27a −14.69±1.01d 0.78±0.01b 2.22±0.12c 2318.28±180.24c -
[1] XIE J, TAO L, WU Q, et al. Mercury and selenium in squids from the Pacific Ocean and Indian Ocean: The distribution and human health implications[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin,2021,173:112926. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2021.112926
[2] 孔文俊, 刘鑫, 薛勇, 等. 不同蛋白添加剂对秘鲁鱿鱼鱼糜凝胶特性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2015,36(14):119−122. [KONG W J, LIU X, XUE Y, et al. Effect of different protein additives on surimi gelation from Peruvian squid surimi[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2015,36(14):119−122. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2015.14.015 [3] 赵艳秋, 刘俊荣, 王伟光, 等. 北太平洋鱿鱼肌肉蛋白质凝胶特性的研究[J]. 水产科学,2009,28(3):122−125. [ZHAO Y Q, LIU J R, WANG W G, et al. Gelling properties of muscle proteins in red oceanic squid[J]. Fisheries Science,2009,28(3):122−125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1111.2009.03.002 [4] 徐安琪, 杨镕, 朱煜康, 等. 紫菜粉添加对鱿鱼鱼糜凝胶特性及其蛋白结构的影响[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(2):46−52. [XU A Q, YANG R, ZHU Y K, et al. Effect of laver (Porphyra umbilicalis) powder on gel properties and protein structure of giant squid (Dosidicus gigas) surimi[J]. Food Science,2021,42(2):46−52. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191110-121 [5] 王冬妮, 范馨茹, 祁立波, 等. 淀粉和蛋白类添加物对鱿鱼鱼糜凝胶特性的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2018,18(4):65−71. [WANG D N, FAN X R, QI L B, et al. Effect of starch and non-muscle protein on gel properties of squid (Illex argentinus) surimi[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2018,18(4):65−71. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2018.04.010 [6] XU C, WANG C, CAI Q, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2) plays a critical role in the softening of common carp muscle during chilled storage by degradation of type I and V collagens[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2015, 63: 10948−10956.
[7] PARK S, CHO S, YOSHIOKA T, et al. Influence of endogenous proteases and transglutaminase on thermal gelation of salted squid muscle paste[J]. Journal of Food Science,2003,68:2473−2478.
[8] CHU Y J, DENG S G, LV G C, et al. Improvement of gel quality of squid (Dosidicus gigas) meat by using sodium gluconate, sodium citrate, and sodium tartrate[J]. Foods,2022,11(2):73.
[9] NYAISABA B M, MIAO W H, HATAB S, et al. Effects of cold atmospheric plasma on squid proteases and gel properties of protein concentrate from squid (Argentinus ilex) mantle[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,291(SEP.1):68−76.
[10] 梁高丽, 谢占玲. 微生物源金属蛋白酶的研究进展[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志,2017,47(3):45−48. [LIANG G L, XIE Z L. Advances in metalloproteinases from microorganisms[J]. Chinese Qinghai Journal of Animal and Veterinary Sciences,2017,47(3):45−48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7950.2017.03.017 [11] 李艳青, 孔保华, 夏秀芳. 鱼糜凝胶形成机理及提高鱼糜凝胶特性的添加物研究新进展[J]. 食品科技,2012,37(7):140−144. [LI Y Q, KONG B H, XIA X F. Gel formation mechanism of surimi and research progress on new additives of enhancing gel properties of surimi[J]. Food Science and Technology,2012,37(7):140−144. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2012.07.068 [12] DEYSI C, HELEN M, MORENO A, et al. Combined effect of high hydrostatic pressure and lysine or cystine addition in low-grade surimi gelation with low salt content[J]. Food and Bioprocess Technology,2016,9(8):1391−1398. doi: 10.1007/s11947-016-1728-8
[13] 汪雪娇. 微波处理对鱼肉制品咸度感知的增强作用与减盐鱼糜的加工适应性[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2021. WANG X J. Saltiness perception enhancement of fish products by microwave treatment and processing adaptability in salt-reduced surimi[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2021.
[14] HUANG J, YE B, WANG W, et al. Incorporation effect of inulin and microbial transglutaminase on the gel properties of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) surimi[J]. Food Meas Charact,2021,15(1):1−11. doi: 10.1007/s11694-020-00604-z
[15] MANAT C J, WORAWAN P, SOOTTAWAT B. Physicochemical properties and gel-forming ability of surimi from three species of mackerel caught in Southern Thailand[J]. Food Chemistry,2009,121(1):85−92.
[16] 米红波, 王聪, 苏情, 等. 变性淀粉对白鲢鱼鱼糜凝胶特性和蛋白构象的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2021,21(1):72−80. [MI H B, WANG C, SU Q, et al. Effect of modified starch on gel properties and protein conformation of surimi from sliver carp[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2021,21(1):72−80. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2021.01.009 [17] 罗小迎, 孙晓欢, 戈春东, 等. 斩拌时间和凝胶化时间对微波熟制鱼饼品质的影响[J]. 肉类研究,2019,33(10):22−28. [LUO X Y, SUN X H, GE C D, et al. Effects of chopping time and gelation treatment time on the quality of microwave cooked fish cake[J]. Meat Research,2019,33(10):22−28. [18] GÓMEZ-GUILLÉN M C, BORDERı́AS A J, MONTERO P. Chemical interactions of nonmuscle proteins in the network of sardine (Sardina pilchardus) muscle gels[J]. Food Science and Technology,1997,30(6):602−608.
[19] TAN F J, LAI K M, HSU K C. A comparative study on physical properties and chemical interactions of gels from tilapia meat pastes induced by heat and pressure[J]. Journal of Texture Studies,2010,41(2):153−170. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-4603.2010.00219.x
[20] XUE S, YANG H, YU X, et al. Applications of high pressure to pre-rigor rabbit muscles affect the water characteristics of myosin gels[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,240:59−66. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.07.096
[21] GUO J, ZHOU Y, YANG K, et al. Effect of low-frequency magnetic field on the gel properties of pork myofibrillar proteins[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,274(15):775−781.
[22] 张崟, 曾庆孝, 朱志伟, 等. 柠檬酸盐对罗非鱼鱼糜的凝胶性及抗冻性的影响(英文)[J]. 陕西科技大学学报(自然科学版),2009,27(1):14−19,36. [ZHANG Y, ZENG Q X, ZHU Z W, et al. Effects of trisodium citrate and tricalcium citrate on the gel forming and cryoprotective properies of tilapia (Sarotherodon nilotica) surimi[J]. Journal of Shaanxi University of Science & Technology,2009,27(1):14−19,36. [23] 赵宏蕾, 辛莹, 刘美月, 等. 柠檬酸钠协同碳酸氢钠替代磷酸盐对法兰克福香肠品质的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(10):94−103. [ZHAO H L, XIN Y, LIU M Y, et al. Effect of sodium citrate combined with sodium hydrogen carbonate on the quality of phosphate-free frankfurters[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(10):94−103. [24] 陈海华, 薛长湖. 漂洗条件和热处理对大头狗母鱼鱼糜凝胶特性的影响(英文)[J]. 食品科学,2010,31(3):11−18. [CHEN H H, XUE C H. Effects of washing media and thermal treatment on gel properties of painted lizardfish (Trachinocephalus myops) surimi[J]. Food Science,2010,31(3):11−18. [25] HOLMER S F, KUTZLER L W, MCKEITH F K, et al. Sodium citrate as a replacement for sodium chloride in a brine solution when evaluated in cows of different backfat thickness[J]. Meat Science,2009,81(2):349−356. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2008.08.012
[26] YAN B, JIAO X, ZHU H, et al. Chemical interactions involved in microwave heat-induced surimi gel fortified with fish oil and its formation mechanism[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2020,105:105779. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.105779
[27] 钟坦君, 洪鹏志, 周春霞, 等. 没食子酸对金线鱼鱼糜凝胶特性及其体外消化产物活性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(14):76−84. [ZHONG T J, HONG P Z, ZHOU C X, et al. Effect of gallic acid on gel properties and in vitro activity of digested products of Nemipterus virgatus surimi[J]. Food Science,2022,43(14):76−84. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20211022-239 [28] ZHANG T, LI Z, WANG Y, et al. Effects of konjac glucomannan on heat-induced changes of physicochemical and structural properties of surimi gels[J]. Food Research International,2016,83:152−161. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2016.03.007
[29] XIONG G, CHENG W, YE L, et al. Effects of konjac glucomannan on physicochemical properties of myofibrillar protein and surimi gels from grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella)[J]. Food Chemistry,2009,116(2):413−418. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.02.056
[30] WANG X, XIA M, ZHOU Y, et al. Gel properties of myofibrillar proteins heated at different heating rates under a low-frequency magnetic field[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,321:126728. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126728
[31] TAN L, TIAN L, ZHANG X, et al. Effects of γ-polyglutamic acid on the physicochemical properties and microstructure of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) surimi during frozen storage[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2020,134:109960. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109960
[32] GAO Y P, HIDETO F, DENG S G, et al. Effect of pH and heating conditions on the properties of Alaska pollock (Theragra chalcogramma) surimi gel fortified with fish oil[J]. Journal of Texture Studies,2018,49(6):595−603. doi: 10.1111/jtxs.12365
[33] GENG J T, TAKAHASHI K, KAIDO T, et al. The effect of organic salts on the browning of dried squid products processed by air-drying[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,269:212−219. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.06.129
[34] LIU R, ZHAO S, XIE B, et al. Contribution of protein conformation and intermolecular bonds to fish and pork gelation properties[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2011,25(5):898−906. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2010.08.016
[35] 王红妮, 刘会平, 刘平伟, 等. 糟蛋减压加工过程中蛋黄蛋白质二级结构的变化研究[J]. 现代食品科技,2013,29(6):1262−1265. [WANG H N, LIU H P, LIU P W, et al. Changes in yolk protein secondary structure of the preserved egg in wine during low pressure-vacuum processing[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2013,29(6):1262−1265. doi: 10.13982/j.mfst.1673-9078.2013.06.051 -
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 张月,杨新玥,黄莉,马帅宇,胥畅,杨腊梅,裴慧洁,何维,杨勇. 乳酸菌复配发酵对川味香肠品质及酪胺含量的影响. 食品与发酵工业. 2025(06): 83-90 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 牟燕,赖茂佳,易宇文,范文教. 微生物发酵剂对川味牦牛肉香肠品质的影响. 中国酿造. 2024(02): 188-193 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李晓,王成,郭楠楠,潘道东. 嗜酸乳杆菌发酵鸭肉脯工艺优化及品质分析. 肉类研究. 2024(01): 36-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 赵志磊,李昊轩,牛晓颖,陈萌,庞艳苹. γ射线辐照结合VC、烟酰胺对卤驴肉中亚硝酸盐的降解效果. 食品科学. 2024(16): 197-203 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 文静,许恒毅,甘蓓,周渊坤,张锦峰. 混合菌株发酵板鸭的研究进展. 江西科学. 2024(04): 710-715 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)





 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:



