Comparison of Antioxidant Activities of Three Kinds of Juices and Their Protective Effects on Oxidative Damage of Colon Cell NCM460
-
摘要: 比较刺梨汁(Rosa roxburghii Tratt juice,RRTJ)、石榴汁(Pomegranate juice,PJ)以及蓝莓汁(Blueberry juice,BJ)的活性成分含量以及抗氧化活性,探究三种果汁对葡聚糖硫酸钠盐(Dextran sulfate sodium,DSS)诱导人正常结肠上皮细胞NCM460氧化损伤的保护作用。结果表明,三种果汁中共同含有的生物活性成分有28种,其中刺梨汁的总多酚、总黄酮含量显著高于石榴汁和蓝莓汁(P<0.05),分别为22.77和12.04 mg/mL;同时,刺梨汁对ABTS+·、DPPH·的清除能力显著高于石榴汁和蓝莓汁(P<0.05),半数清除率(Half scavenging rate,IC50)分别为4.00±0.32和10.03±0.51 μL/mL;Pearson相关性分析表明果汁的总多酚含量与ABTS+·清除能力呈正相关(P<0.05)。此外,刺梨汁缓解DSS诱导NCM460细胞氧化损伤的能力最强,2 μL/mL刺梨汁即能使氧化损伤的NCM460细胞活力恢复到与对照组相当的水平,降低DSS引起的细胞中活性氧(Reactive oxygen species,ROS)水平。实验表明果汁中的总多酚含量与抗氧化能力呈正相关;刺梨汁的总多酚和总黄酮含量高于蓝莓汁和石榴汁,抗氧化活性和缓解DSS诱导NCM460细胞氧化损伤的能力最强,具有深入研究开发的潜力。Abstract: To compare the contents of active ingredients and antioxidant activity of Rosa roxburghii Tratt juice (RRTJ), pomegranate juice (PJ) and blueberry juice (BJ) and investigate the protective effects of three kinds of fruit juices against dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced oxidative damage in human normal colonic epithelial cells NCM460. There were 28 bioactive components in the three juices. The total polyphenols and total flavonoids of RRTJ were significantly higher than those in the PJ and BJ (P<0.05), 22.77 and 12.04 mg/mL, respectively. Meanwhile, the ABTS+· and DPPH· scavenging abilities of the juice were significantly higher than those in the PJ and BJ (P<0.05), and the half scavenging rate (IC50) was 4.00±0.32 and 10.03±0.51 μL/mL, respectively. Pearson correlation analysis indicated that the total polyphenol content of the juice was positively correlated with the ABTS+· scavenging ability (P<0.05). In addition, RRTJ had the strongest ability to alleviate DSS-induced oxidative damage in NCM460 cells, and 2 μL/mL RRTJ could restore the viability of oxidatively damaged NCM460 cells to a level comparable to the control and reduce the level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in DSS-induced cells. The results showed that the content of total polyphenols in fruit juice was positively correlated with antioxidant capacity. The content of total polyphenols in juice was positively correlated with antioxidant capacity, and the antioxidant activity and the ability to alleviate DSS-induced oxidative damage in NCM460 cells were the strongest in vitro, which had the potential for in-depth research and development.
-
氧化应激是源于抗氧化剂和氧化剂水平之间的生理失衡。在受到有害刺激时,机体中ROS水平会增加,耗尽抗氧化剂,并最终导致氧化应激[1],氧化应激与多种疾病的发生相关,如心血管疾病、糖尿病、代谢紊乱、炎症性肠病(Inflammatory bowel disease,IBD)等。IBD是由氧化应激引起的一类代表性疾病[2-3],包括特发性慢性和复发性肠道炎症性疾病,2017年全球病例达到680万例[4],已成为全球公共的健康问题。由于胃肠道是消化食物的主要器官,易受到外源饮食(高碳水、高糖基化等食物)的刺激导致炎症[5],因此通过减少肠道ROS的产生可以缓解肠道炎症能有效达到预防和治疗IBD的效果。
多酚、黄酮类物质具有较高抗氧化性,在植物性食物中普遍存在,研究表明膳食多酚、黄酮作为高效的自由基清除剂[6],可以通过调节细胞凋亡、氧化还原平衡信号传导、免疫系统调节等细胞过程来维持机体ROS水平[7-9],发挥抗氧化作用。果蔬是活性酚类化合物和维生素C(Vitamin C,VC)的主要来源[10],每日适量摄入果蔬有助于降低患氧化应激相关疾病的风险[6, 11],2022发布的最新膳食指南中也推荐每日需保证摄入200~350 g的水果,有助于保护人体健康。
刺梨、石榴和蓝莓是常见的富含功能性成分的水果[12-14]。刺梨是我国西南地区特有的水果,以高VC、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)和类黄酮含量而闻名[12,15],具有提高免疫、抗氧化、抗衰老、抗炎和降低癌症等药理作用[16-17],是膳食补充剂、开发功能性食品甚至药物开发的潜在来源。石榴原产于伊朗,富含有维生素、黄酮、多酚等物质[18-19],是生物活性化合物的宝贵来源,被认为是最佳功能性食物之一[14]。蓝莓是一种原产于北美的浆果类水果,富含花青素、维生素、多酚等活性成分化合物[20],在抗氧化、抗衰老以及增强免疫力等方面功效显著[21],具有较高的经济价值和广阔的发展前景。目前三种水果都被证实具有良好的抗氧化性和功效作用,但是,鲜见三者的果汁成分与抗氧化能力及缓解肠道氧化损伤能力的比较。因此,本研究将在探究刺梨汁(RRTJ)、石榴汁(PJ)和蓝莓汁(BBJ)的生物活性成分的基础上对其总多酚、总黄酮含量、抗氧化活性以及对IBD细胞模型氧化损伤的保护作用进行分析比较,以期为水果的深入开发以及在食品保健、预防氧化应激性疾病等领域的应用提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
金刺梨 2019年9月采摘于贵州安顺金刺梨种植基地;秘鲁Camposol蓝莓 2019年9月购于电商;四川会理突尼斯软籽石榴 2020年9月由成都云上唯果农林科技有限公司提供;芦丁、绿原酸 成都德斯特生物技术有限公司;亚硝酸钠、硝酸铝 成都科隆化工试剂厂;福临酚试剂、ROS试剂盒 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;2,2-二苯基-1-苦基肼(DPPH)、2,2'-联氮-二(3-乙基-苯并噻唑-6-磺酸)二铵盐(ABTS)、乙酸钠、过硫酸钾、硫酸亚铁、水杨酸 上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium(DMEM)高糖培养基 美国 Hyclone公司;胎牛血清 美国Gibco公司。
Thermo Scientific Q Exactive液相质谱联用仪、C18色谱柱(2.7 μm,2.1×100 μm) 德国Thermo Fisher公司;U-3900H双光束紫外分光光度计 日本HITACHI公司;1510型全波长酶标仪 德国塞默飞世尔科技有限公司;Novo cyte型安捷伦流式细胞仪 美国ACEA Biosciences 公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 果汁制备
金刺梨和蓝莓清洗晾干后去除果蒂和果萼,切小榨汁;石榴用无菌纱布包裹石榴手工挤压出汁。三种果汁再用无菌纱布过滤、离心5 min(3500 r/min,4 °C),收集上清液,用0.22 μm滤膜过滤,避光条件下−80 ℃分装保存。
1.2.2 果汁活性成分分析
样品制备:取1 mL果汁,加入甲醇定容至10 mL,经0.22 μm有机滤膜过滤后上机检测。
液相色谱条件:流动相A:0.1 %甲酸水溶液;B相:乙腈;柱温:40 °C:进样量为5 μL;流速:0.3 mL/min,见表1。
表 1 梯度洗脱程序Table 1. Gradient elution procedure序号 时间 A相(%) B相(%) 1 0 95 5 2 2 70 30 3 5 30 70 4 7 10 90 5 8 10 90 6 8.1 95 5 7 10 95 5 质谱条件:离子源:H-ESI;源温:320 °C;检测模式:Full Scan-dd MS2;扫描范围:100~800(m/z);蒸发器温度:350 °C;喷雾电压:Positive Ion:3.5 kv,Negative Ion:3.2 kv;鞘气流速:50 Arb;辅助气流速:15 Arb;Intensity Threshold:1.0
× 104。1.2.3 总多酚含量测定
参照He等[15]方法略有修改。以绿原酸为标准品制作标准曲线,取1 mL果汁滤液,75%乙醇定容至10 mL,室温超声辅助提取30 min,为待测液。待测液稀释10倍后取1 mL进行测定,加入1.5 mL福林酚试剂和1 mL 7.5% Na2CO3溶液,蒸馏水定容至10 mL,摇匀后室温避光30 min,765 nm处测定吸光度,根据标曲y=0.0049x+0.0264(R²=0.9964)计算果汁总多酚含量,结果以每毫升果汁中的绿原酸当量表示。
1.2.4 总黄酮含量测定
参照He[15]、Mohammad[22]等方法略有修改。以芦丁为标准品制作标准曲线,取1 mL果汁滤液,75%乙醇定容至10 mL,室温超声辅助提取30 min,为待测液。待测液稀释10倍后取1 mL进行测定,加入0.4 mL 5% NaNO2溶液,摇匀静置5 min,再加入0.4 mL 10% Al(NO3)3溶液,摇匀反应5 min后,加入4 mL 1 mol/L的NaOH溶液,用30%乙醇定容至10 mL,10 min后于510 nm处测定吸光度,根据标曲y=0.0012x+0.0001(R2=0.9992)计算果汁总黄酮含量,结果以每毫升果汁中的芦丁当量表示。
1.2.5 ABTS+·清除能力
参照刘翰飞[23]的方法略有修改,将果汁稀释为不同浓度的待测液,在96孔板中加入195 μL的ABTS工作液,再加入5 μL的待测液,室温避光反应5 min,于734 nm处测定吸光度A1,等量20 mmol/L乙酸钠溶液代替ABTS工作液为空白对照,测出的吸光度为A2,等量蒸馏水代替待测液为测出的吸光度为A0,重复三次。按如下公式计算ABTS+·的清除率:
ABTS+⋅清除率(%)=(1−A1−A2A0)×100 1.2.6 DPPH·清除能力
参考刘翰飞[23]、He[24]的方法略有修改,将果汁稀释为不同浓度的待测液,取待测样品5 μL和195 μL DPPH工作液(0.035 mg/mL,无水乙醇配制)加入96孔板中,混匀后避光反应30 min,517 nm处测定吸光度A1,等量无水乙醇代替DPPH工作液为空白组测得吸光度A2,等量蒸馏水代替样品溶液测得吸光度A0,重复三次。按如下公式计算DPPH·的清除率:
DPPH⋅清除率(%)=(1−A1−A2A0)×100 1.2.7 OH·清除能力
参考Chen等[25]的方法略有修改,将果汁稀释为不同浓度的待测液,取待测液、7.5 mmol/L的FeSO4溶液、6 mmol/L水杨酸醇溶液(无水乙醇配制)、0.3% H2O2水溶液各250 μL混匀,37 ℃水浴反应30 min,520 nm处测定吸光度A1,等量蒸馏水代替0.3 % H2O2溶液为空白对照测得吸光度A2,等量蒸馏水代替样品液测得吸光度A0,重复三次。按如下公式计算·OH的清除率:
⋅OH清除率(%)=(1−A1−A2A0)×100 1.2.8 细胞增殖活性
将对数期的NCM460细胞接种到96孔板中,贴壁后参照Ding[26]及Sumit[27]等方法,使用DSS诱导NCM460造成氧化损伤,探究三种果汁对NCM460细胞的保护作用。用MTT法检测细胞增殖活性。造模:加入不同浓度DSS干预12 h。果汁阴性:加入不同浓度的果汁干预24 h。对照组:只加DMEM完全培养基培养24 h;模型组:加入DMEM完全培养基培养12 h后,再加入30 mg/mL DSS培养12 h;样品组:先加入不同浓度的果汁干预12 h后,再加入30 mg/mL DSS培养12 h。
1.2.9 细胞ROS水平
按照1.2.8中不同的干预方式处理后,弃去上清,用不含EDTA的胰酶消化后收集到流式管中,按照ROS试剂盒方法操作,上机用FITC通道检测。
1.3 数据处理
通过Excel和Prism 9对数据进行单因素方差分析(One-way ANOVA),并采用Pearson进行相关性分析,P<0.05表示有显著差异,P<0.01表示有极显著差异。结果均用“平均值±标准偏差”表示。
液相质谱数据用Thermo Xcalibur Qual Browser软件进行处理,Compound Discoverer 3.1.1.12软件结合mzVault数据库、mzCloud数据库用于成分分析及匹配。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 三种果汁的成分鉴定及总多酚总黄酮含量测定
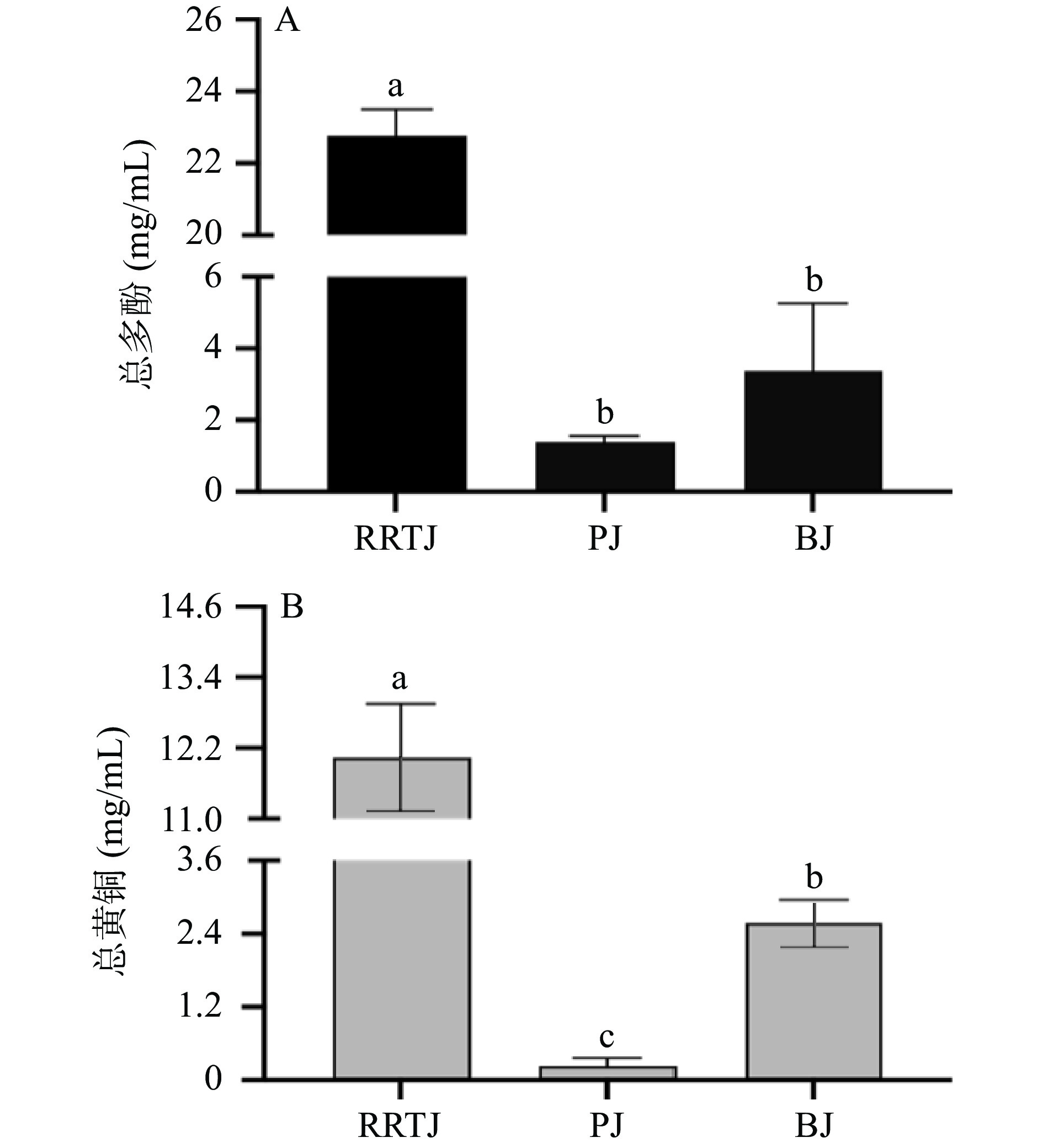
利用HPLC-Q-Exactive Orbitrap-MS分析了刺梨汁、石榴汁、蓝莓汁中的可能的成分。如表2所示,三种果汁中共含有的潜在生物活性成分有28种,包括10种酚酸,8种有机酸类,5种氨基酸,3种黄酮类,1种生物碱,1种糖苷类。通过三种果汁的相对峰面积比较,发现刺梨汁中儿茶素、对香豆酸、鞣花酸、新绿原酸、紫云英苷、富马酸、DL-苹果酸、VC、柠檬酸、长寿花糖甙的峰面积大于石榴汁和蓝莓汁,可半定量得到刺梨汁中这些生物活性物质含量高于石榴汁和蓝莓汁。多酚黄酮是水果中重要的生物活性来源,因此检测了三种果汁总多酚和总黄酮含量,其含量如图1所示。刺梨汁的总多酚、总黄酮含量与蓝莓汁和石榴汁存在显著性差异(P<0.05)。其中刺梨汁的总多酚和总黄酮含量最高,其含量分别为22.77±0.73和12.04±0.91 mg/mL,分别是石榴汁的16.38和52.35倍,蓝莓汁的6.78和4.67倍。综上,刺梨中活性物质总多酚和总黄酮含量最高,其次是蓝莓汁,最低的为石榴汁。
表 2 三种果汁中的活性成分Table 2. Active ingredients in three kinds of fruit juices序号 分类 化合物 分子式 分子量 保留时间(min) 质荷比(m/z) 模式 峰面积比:RRTJ/RRTJ 峰面积比:PJ/RRTJ 峰面积比:BJ/RRTJ 1 酚酸 儿茶素 C15H14O6 290.07896 4.557 289.0718 [M-H]− 1 0.0185381 0.0047719 2 酚酸 对香豆酸 C9H8O3 164.04727 4.627 163.0401 [M-H]− 1 0.3546840 0.0243441 3 酚酸 异香草酸 C8H8O4 168.04224 3.102 170.0964 [M+H]+ 1 21.1876641 18.9522201 4 酚酸 咖啡酸 C9H8O4 180.04226 3.793 179.0349 [M-H]− 1 0.9439670 9.4652850 5 酚酸 阿魏酸 C10H10O4 194.05783 5.681 193.0870 [M-H]− 1 1.6777904 47.0191357 6 酚酸 芥子酸 C11H12O5 224.06844 4.527 225.1495 [M+H]+ 1 11.227866 142.189311 7 酚酸 鞣花酸 C14H6O8 302.00618 5.593 303.0133 [M+H]+ 1 0.1997369 0.0140473 8 酚酸 对香豆酰奎尼酸 C16H18O8 338.10026 4.889 337.0930 [M-H]− 1 0.0588202 1.5330073 9 酚酸 新绿原酸 C16H18O9 354.09494 3.74 353.0879 [M-H]− 1 0.0036370 0.5928340 10 酚酸 表儿茶素 C15H14O6 290.07893 4.953 289.0718 [M-H]− 1 0.0641652 0.0731626 11 黄酮类 紫云英苷 C21H20O11 448.1004 4.401 447.0569 [M-H]− 1 0.0021714 0.0020716 12 黄酮类 芦丁 C27H30O16 610.1536 5.657 609.1976 [M-H]− 1 0.3958080 56.4030733 13 黄酮类 染料木苷 C21H20O10 432.10564 4.756 433.1677 [M+H]+ 1 372.1262714 3.4947074 14 生物碱 葫芦巴碱 C7 H7NO2 105.02136 0.827 136.8267 [M-H]− 1 35.9551281 1.2682148 15 有机酸 富马酸 C4H4 O4 116.01081 0.879 115.0039 [M-H]− 1 0.2096278 0.0881666 16 有机酸 衣康酸 C5 H6 O4 130.0266 0.948 129.0192 [M-H]− 1 1.03847909 1.2074671 17 有机酸 DL-苹果酸 C4H6O5 134.02149 1.061 133.0143 [M-H]− 1 0.7183395 0.1855467 18 有机酸 反乌头酸 C6 H6 O6 174.01642 0.912 173.0095 [M-H]− 1 1.5748353 1.8560623 19 有机酸 维生素C C6 H8 O6 174.01636 1.49 175.0247 [M-H]− 1 0.4208721 0.6294469 20 有机酸 柠檬酸 C6 H8 O7 192.0633 1.278 191.0197 [M-H]− 1 0.1741608 0.6592146 21 有机酸 奎宁酸 C7 H12 O6 192.06341 0.832 191.0560 [M-H]− 1 0.0798837 8.4139563 22 有机酸 脱落酸 C15 H20 O4 264.13628 7.092 265.1047 [M+H]+ 1 0.3879990 5.3032785 23 糖苷 长寿花糖甙 C19 H30 O8 386.19405 5.108 385.1862 [M-H]− 1 0.1444265 0.7048008 24 氨基酸 赖氨酸 C6 H14N2O2 146.10549 0.695 145.0983 [M-H]− 1 17.3911049 4.8403282 25 氨基酸 組氨酸 C6 H9 N3 O2 155.06944 0.703 154.4484 [M-H]− 1 15.7036029 4.4824619 26 氨基酸 L-酪氨酸 C9 H11 N O3 181.07389 1.294 163.0400 [M-H]− 1 8.3561917 1.5198959 27 氨基酸 DL-精氨酸 C6H14N4O2 174.11154 0.715 173.0093 [M-H]− 1 5.3336296 52.6650510 28 氨基酸 异亮氨酸 C6H13NO2 131.09461 1.379 130.0876 [M-H]− 1 1.5481378 0.8577223 ![]() 图 1 三种果汁的总多酚和总黄酮含量注:不同果汁(RRTJ:刺梨汁;PJ:石榴汁;BJ:蓝莓汁)同一指标标不同小写字母表示具有显著性差异(P<0.05);表3同。Figure 1. Total polyphenol and total flavonoid contents of three kinds of fruit juices
图 1 三种果汁的总多酚和总黄酮含量注:不同果汁(RRTJ:刺梨汁;PJ:石榴汁;BJ:蓝莓汁)同一指标标不同小写字母表示具有显著性差异(P<0.05);表3同。Figure 1. Total polyphenol and total flavonoid contents of three kinds of fruit juices2.2 果汁的抗氧化能力及与活性成分的相关性
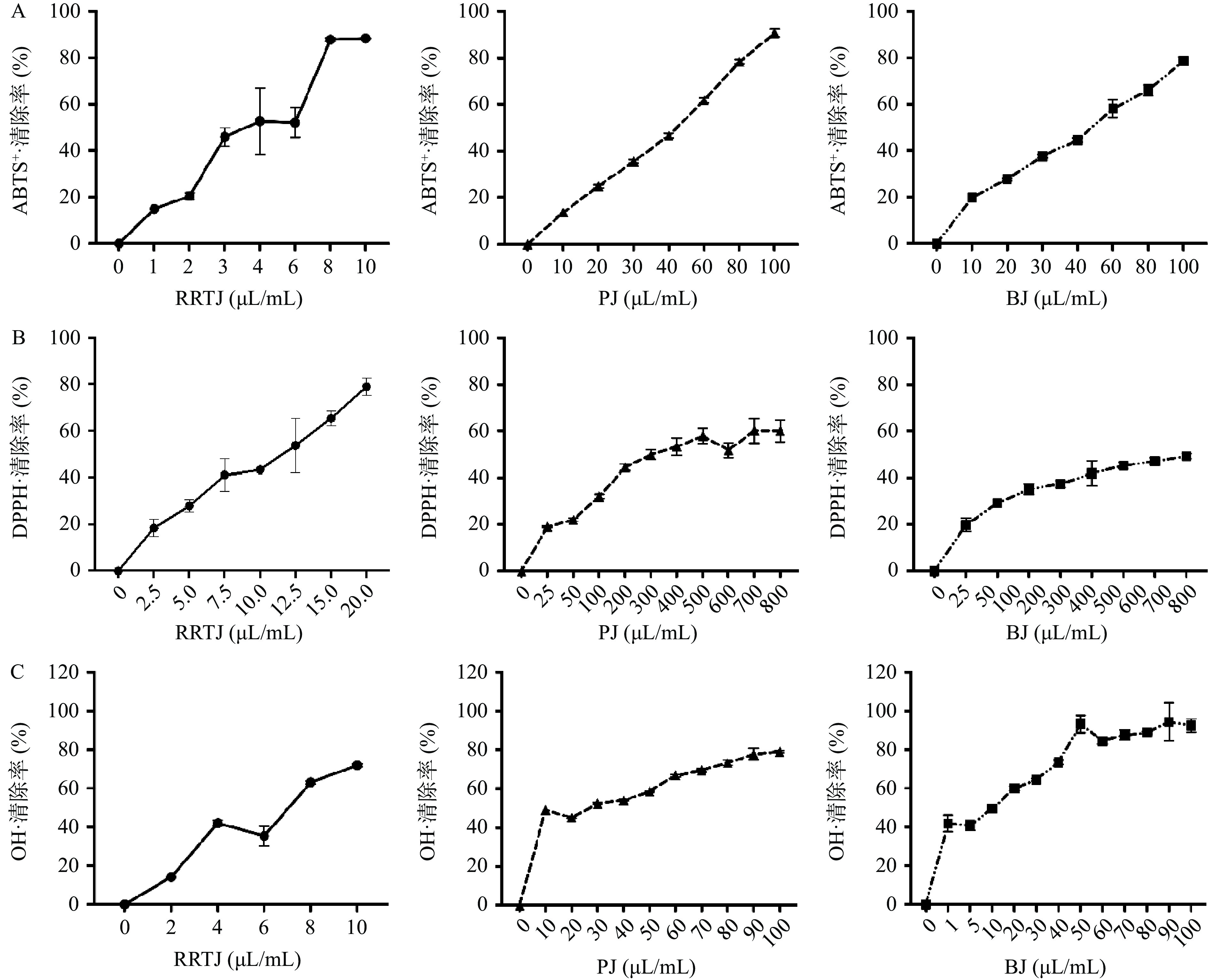
三种果汁的ABTS+·、DPPH·、·OH的清除能力如图2和表3所示,ABTS+·、DPPH·、·OH的清除率与果汁浓度相关,在一定浓度范围内,ABTS+·、DPPH·、·OH的清除率随果汁浓度的增加而上升。抗氧化能力越强,果汁清除ABTS+·、DPPH·、·OH的IC50就越小。从表3可看出,三种果汁中,刺梨汁清除ABTS+·、DPPH·的IC50最小,分别为4.00±0.32和10.03±0.51 μL/mL,显著低于石榴汁和蓝莓汁的IC50(P<0.05),是石榴汁IC50的9.82%、2.76%,是蓝莓汁IC50的10.16%、1.19%;刺梨汁和蓝莓汁清除·OH的IC50显著低于石榴汁(P<0.05),但二者之间无显著性差异(P>0.05)。综合比较下,三种果汁中刺梨汁的抗氧化能力最强。
表 3 三种果汁抗氧化活性的IC50Table 3. IC50 of antioxidant activity of three kinds of fruit juicesIC50(μL/mL) RRTJ PJ BJ ABTS+· 4.00±0.32b 40.74±0.72a 39.37±0.74a DPPH· 10.03±0.51c 362.77±71.48b 840.43±73.57a ·OH 5.92±0.46b 19.79±0.85a 5.67±0.82b 由表4可知,果汁中总多酚和总黄酮与ABTS+·、DPPH·、·OH的IC50均存在较强的相关性(r<−0.05),并且总多酚与ABTS+·的IC50存在显著负相关性(r=−0.999,P<0.05)。由此可表明果汁中生物活性含量与其抗氧化能力存在正相关性,与上述实验得到的结论一致,三种果汁中刺梨汁的总多酚总黄酮含量最高,其ABTS+·、DPPH·的清除能力最强。
表 4 活性成分含量与抗氧化之间的相关性Table 4. Correlation between active ingredient content and antioxidationr 总多酚 总黄酮 IC50 of ABTS+· IC50 of DPPH· IC50 of ·OH 总多酚 1.000 总黄酮 0.994 1.000 IC50 of ABTS+· −0.999* −0.988 1.000 IC50 of DPPH· −0.769 −0.697 0.800 1.000 IC50 of ·OH −0.558 −0.642 0.512 −0.102 1.000 注:*表示存在显著性,P<0.05。 2.3 果汁对NCM460细胞氧化损伤的保护作用
2.3.1 建立NCM460细胞损伤模型
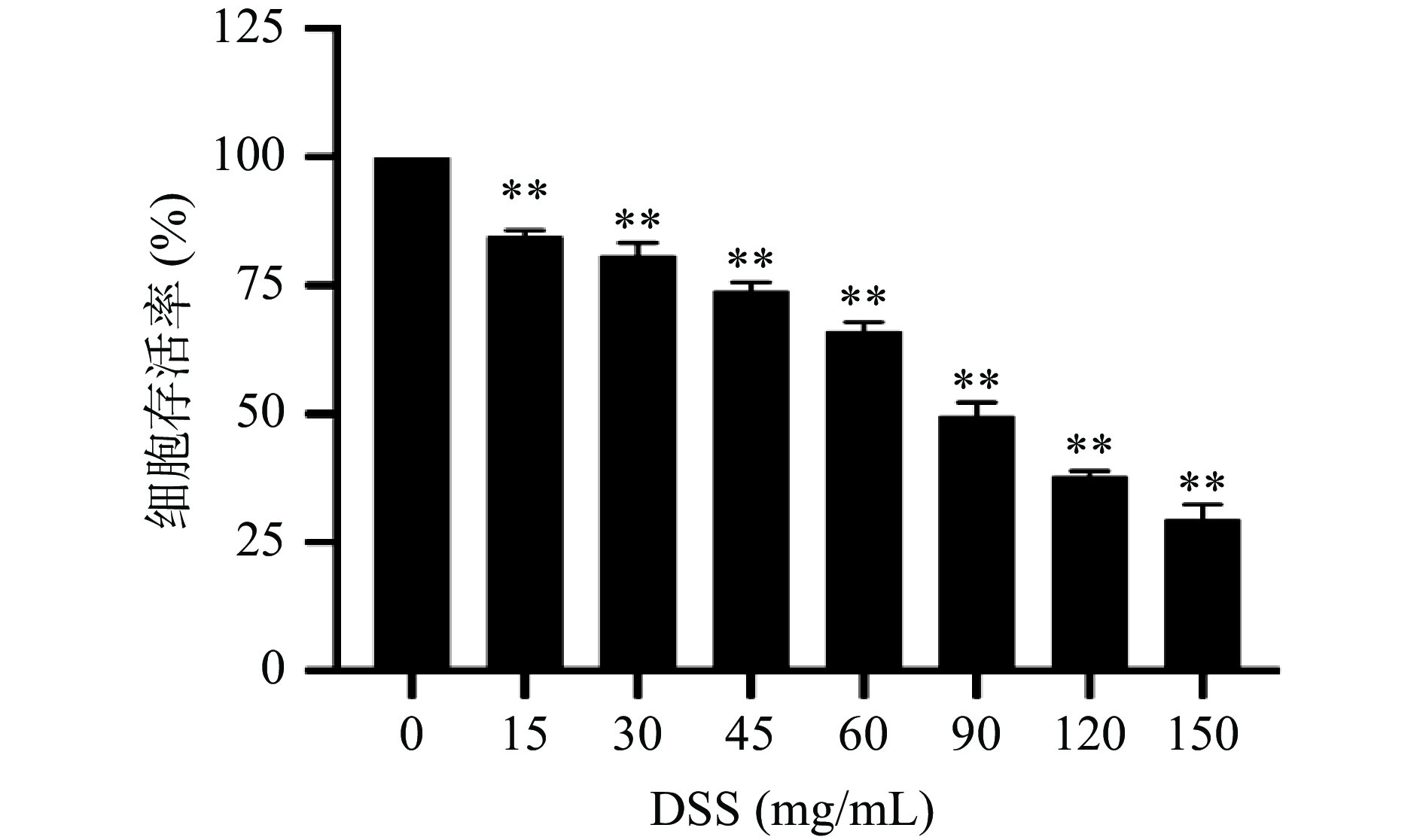
利用DSS诱导人正常结肠上皮细胞NCM460,建立细胞损伤模型。DSS诱导12 h后,NCM460细胞的存活率如图3所示。随着DSS浓度的增大,NCM460细胞存活率越来越小;30 mg/mL DSS诱导12 h后,细胞存活率为80.84%。已有研究[26]表明IC80左右的DSS浓度会导致NCM460细胞的凋亡水平升高,产生过量的ROS,造成氧化损伤。因此本实验后续研究采用30 mg/mL DSS诱导NCM460细胞12 h建立细胞氧化损伤模型。
![]() 图 3 DSS对NCM460细胞存活率的影响注:*表示与对照相比存在显著性差异,P<0.05;**表示与对照相比存在极显著性差异,P<0.01;图4同。Figure 3. Effect of DSS on the survival rate of NCM460 cells
图 3 DSS对NCM460细胞存活率的影响注:*表示与对照相比存在显著性差异,P<0.05;**表示与对照相比存在极显著性差异,P<0.01;图4同。Figure 3. Effect of DSS on the survival rate of NCM460 cells2.3.2 果汁对NCM460细胞增殖的影响
三种果汁干预后NCM460细胞的存活率如图4所示。当0~20 μL/mL的刺梨汁、0~125 μL/mL的石榴汁、0~100 μL/mL蓝莓汁干预24 h后,NCM460细胞存活率与对照组相比并没有显著的下降(P>0.05),并且与对照组相比,0~10 μL/mL的刺梨汁干预后,能显著促进细胞增殖(P<0.05)。由此表明刺梨汁、石榴汁和蓝莓汁分别在0~20、0~125、0~100 μL/mL浓度范围内对NCM460细胞无毒性作用。因此,后续实验选择无毒剂量范围内的果汁进行对细胞保护作用的探索。
2.3.3 果汁对DSS损伤NCM460细胞活力的保护作用
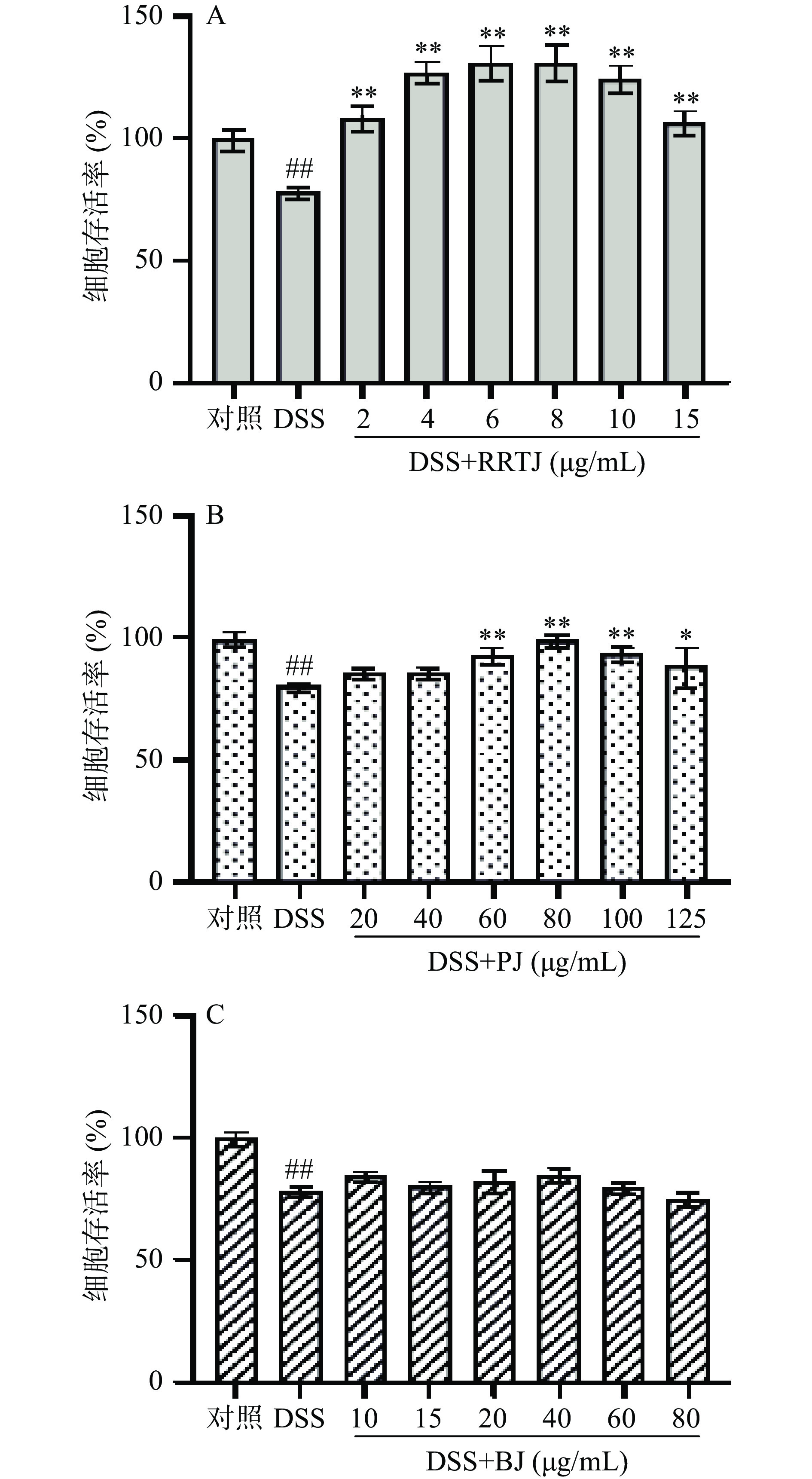
三种果汁对DSS诱导NCM460细胞损伤的保护作用如图5所示。与DSS组相比,刺梨汁在0~15 μL/mL范围内,能显著提高NCM460细胞的存活率(P<0.05),并且在2 μL/mL的刺梨汁干预后细胞活率升高至107.92%,恢复到与对照组相当的水平,8 μL/mL的刺梨汁干预后,细胞增殖得最快,活率达到130.94%;石榴汁在60~100 μL/mL范围内能显著提高NCM460细胞的存活率(P<0.05),但在80 μL/mL时,细胞活率仅可恢复到98.88%;而0~80 μL/mL浓度范围内的蓝莓汁干预后受损细胞活率与DSS组无显著差异(P>0.05)。由此可表明在三种果汁中,刺梨汁对NCM460细胞损伤的保护作用最强。后续ROS测定选择使细胞活力恢复到正常水平的果汁浓度进行实验,蓝莓汁选取最大无毒剂量。
![]() 图 5 三种果汁对NCM460细胞氧化损伤的保护作用注:#表示与对照组相比具有显著性差异(P<0.05),##表示与对照组相比具有极显著性差异(P<0.01);*表示与DSS组相比具有显著性差异(P<0.05),**表示与DSS组相比具有极显著性差异(P<0.01);图6同。Figure 5. Protective effects of three kinds of fruit juices on oxidative damage in NCM460 cells
图 5 三种果汁对NCM460细胞氧化损伤的保护作用注:#表示与对照组相比具有显著性差异(P<0.05),##表示与对照组相比具有极显著性差异(P<0.01);*表示与DSS组相比具有显著性差异(P<0.05),**表示与DSS组相比具有极显著性差异(P<0.01);图6同。Figure 5. Protective effects of three kinds of fruit juices on oxidative damage in NCM460 cells2.3.4 果汁对DSS诱导NCM460细胞内ROS水平的影响
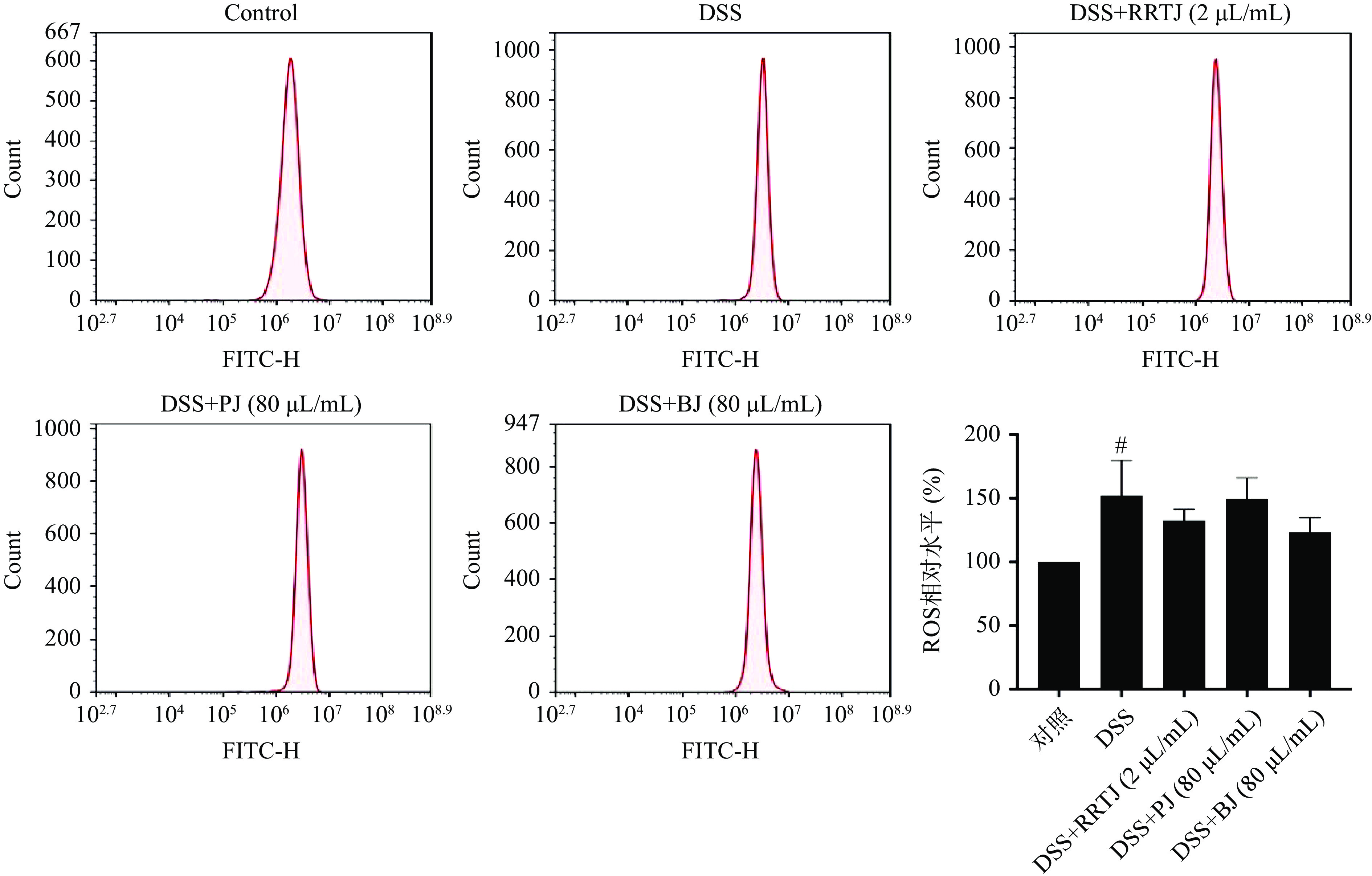
利用DCFH-DA荧光探针检测NCM460细胞内ROS水平,其结果如图6所示。荧光信号越强表明细胞内ROS水平越高。与对照组相比,30 mg/mL DSS 诱导12 h后,NCM460细胞内ROS水平显著增加(P<0.05),为对照组的1.52倍。而经过2 μL/mL的刺梨汁、80 μL/mL的蓝莓汁干预后,均能抑制DSS诱导的ROS水平升高。刺梨汁用量较少,可能是由于刺梨汁中含有更多的生物活性物质,其抗氧化作用能更好的清除自由基,达到保护细胞氧化损伤的作用。
3. 讨论
水果中含有各种生物活性物质,其中以多酚、黄酮类物质等天然抗氧化物质为主。已有研究报道,刺梨、石榴和蓝莓含有儿茶素、绿原酸、咖啡酸、阿魏酸等酚类物质[15,28-30],并且生物活性物质含量与体外抗氧化活性存在较强的相关性[28]。研究发现[31]刺梨中的许多物质如VC、SOD、胡萝卜素以及三萜类等物质都高于普通水果(苹果、梨、柑橘等)且抗氧化能力也更强。Qiong等[32]比较了刺梨、蓝莓、柠檬、菠菜等11种果蔬的多酚、抗坏血酸等物质含量和ABTS+·、DPPH·清除能力,发现刺梨中的多酚、抗坏血酸等物质含量远高于其他果蔬,同时还表现出最强的ABTS+·、DPPH·清除能力。本实验也得到了与之相似的结果,三种果汁中均含有多种生物活性物质,并且刺梨汁中儿茶素、咖啡酸、鞣花酸、对香豆酰奎宁酸、新绿原酸、VC等物质含量高于石榴汁和蓝莓汁;且总多酚含量与ABTS+·清除能力呈显著正相关(P<0.05)。刺梨汁的抗氧化活性更强可能就是由于其含有更多的抗氧化物质(总多酚、总黄酮等),可以为自由基提供氢原子,并转化为稳定的酚类自由基,从而抑制过氧化链反应的发展。
ROS(包括超氧化物阴离子、过氧基和·OH等[2-3])的积累所引起的氧化应激会损伤肠道上皮细胞[1],富含抗氧化物质的果蔬是重要的外源性抗氧化剂,90%左右的膳食多酚会到达结肠,能起到抗炎、维护肠道稳态的作用[33],因而本研究选择人正常结肠上皮细胞NCM460的炎症模型来探究三种果汁缓解氧化应激的能力。当机体受到有害刺激时,细胞稳态会被打破,产生大量ROS,造成生物分子损伤,因而细胞中ROS含量可以反应细胞氧化损伤的程度[34]。刺梨含有丰富的VC、SOD、儿茶素[35]等物质,石榴中含有安石榴苷、鞣花酸等[36]以及蓝莓中含有的花青素[37]等都具有较强的抗氧化活性,可以通过消除自由基的产生,调节Nrf2或者NF-κB通路,降低ROS、脂质过氧化及TNF-α、TGF-β和IL-6等炎症因子,增加体内SOD、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(glutathione peroxidase, GSH-Px)等抗氧化酶[37-39]来发挥抗氧化应激的作用,恢复机体稳态[40]。卢薇等[41]比较了刺梨汁、蓝莓汁等果汁的抗氧化及抗肿瘤细胞HepG2增殖活力的能力,发现它们都具有一定抗细胞氧化能力并且刺梨汁的抗细胞氧化能力最强。本实验中也同样发现,相较于石榴汁和蓝莓汁,刺梨汁在2 μL/mL低浓度下就能恢复DSS诱导的NCM460细胞活力下降并降低细胞内ROS水平,对NCM460细胞氧化损伤有良好的保护作用。由此可进一步证实在本实验条件下,刺梨汁缓解氧化损伤的能力强,其结果与前面成分鉴定出的刺梨汁中生物活性物质含量最高和体外抗氧化能力最强相一致。虽然实验得到刺梨汁中的生物活性成分含量最多、抗氧化应激效果最好,但是健康效益的差异是具体某种生物活性物质起关键作用还是植物化学物质的协同作用还有待阐明。
4. 结论
刺梨汁、石榴汁和蓝莓汁中均含有许多生物活性物质,如儿茶素、阿魏酸、新绿原酸、VC等。刺梨汁的总多酚和总黄酮含量最高,分别为22.77和12.04 mg/mL;体外抗氧化活性和缓解DSS诱导NCM460细胞氧化损伤的能力最强,在2 μL/mL的低浓度下就能恢复NCM460细胞活率并且降低细胞内ROS水平。该研究证明了刺梨的营养和药用价值,可为西南地区特有的刺梨水果资源在食品保健及医药领域的开发应用提供理论依据。
-
图 1 三种果汁的总多酚和总黄酮含量
注:不同果汁(RRTJ:刺梨汁;PJ:石榴汁;BJ:蓝莓汁)同一指标标不同小写字母表示具有显著性差异(P<0.05);表3同。
Figure 1. Total polyphenol and total flavonoid contents of three kinds of fruit juices
图 3 DSS对NCM460细胞存活率的影响
注:*表示与对照相比存在显著性差异,P<0.05;**表示与对照相比存在极显著性差异,P<0.01;图4同。
Figure 3. Effect of DSS on the survival rate of NCM460 cells
图 5 三种果汁对NCM460细胞氧化损伤的保护作用
注:#表示与对照组相比具有显著性差异(P<0.05),##表示与对照组相比具有极显著性差异(P<0.01);*表示与DSS组相比具有显著性差异(P<0.05),**表示与DSS组相比具有极显著性差异(P<0.01);图6同。
Figure 5. Protective effects of three kinds of fruit juices on oxidative damage in NCM460 cells
表 1 梯度洗脱程序
Table 1 Gradient elution procedure
序号 时间 A相(%) B相(%) 1 0 95 5 2 2 70 30 3 5 30 70 4 7 10 90 5 8 10 90 6 8.1 95 5 7 10 95 5 表 2 三种果汁中的活性成分
Table 2 Active ingredients in three kinds of fruit juices
序号 分类 化合物 分子式 分子量 保留时间(min) 质荷比(m/z) 模式 峰面积比:RRTJ/RRTJ 峰面积比:PJ/RRTJ 峰面积比:BJ/RRTJ 1 酚酸 儿茶素 C15H14O6 290.07896 4.557 289.0718 [M-H]− 1 0.0185381 0.0047719 2 酚酸 对香豆酸 C9H8O3 164.04727 4.627 163.0401 [M-H]− 1 0.3546840 0.0243441 3 酚酸 异香草酸 C8H8O4 168.04224 3.102 170.0964 [M+H]+ 1 21.1876641 18.9522201 4 酚酸 咖啡酸 C9H8O4 180.04226 3.793 179.0349 [M-H]− 1 0.9439670 9.4652850 5 酚酸 阿魏酸 C10H10O4 194.05783 5.681 193.0870 [M-H]− 1 1.6777904 47.0191357 6 酚酸 芥子酸 C11H12O5 224.06844 4.527 225.1495 [M+H]+ 1 11.227866 142.189311 7 酚酸 鞣花酸 C14H6O8 302.00618 5.593 303.0133 [M+H]+ 1 0.1997369 0.0140473 8 酚酸 对香豆酰奎尼酸 C16H18O8 338.10026 4.889 337.0930 [M-H]− 1 0.0588202 1.5330073 9 酚酸 新绿原酸 C16H18O9 354.09494 3.74 353.0879 [M-H]− 1 0.0036370 0.5928340 10 酚酸 表儿茶素 C15H14O6 290.07893 4.953 289.0718 [M-H]− 1 0.0641652 0.0731626 11 黄酮类 紫云英苷 C21H20O11 448.1004 4.401 447.0569 [M-H]− 1 0.0021714 0.0020716 12 黄酮类 芦丁 C27H30O16 610.1536 5.657 609.1976 [M-H]− 1 0.3958080 56.4030733 13 黄酮类 染料木苷 C21H20O10 432.10564 4.756 433.1677 [M+H]+ 1 372.1262714 3.4947074 14 生物碱 葫芦巴碱 C7 H7NO2 105.02136 0.827 136.8267 [M-H]− 1 35.9551281 1.2682148 15 有机酸 富马酸 C4H4 O4 116.01081 0.879 115.0039 [M-H]− 1 0.2096278 0.0881666 16 有机酸 衣康酸 C5 H6 O4 130.0266 0.948 129.0192 [M-H]− 1 1.03847909 1.2074671 17 有机酸 DL-苹果酸 C4H6O5 134.02149 1.061 133.0143 [M-H]− 1 0.7183395 0.1855467 18 有机酸 反乌头酸 C6 H6 O6 174.01642 0.912 173.0095 [M-H]− 1 1.5748353 1.8560623 19 有机酸 维生素C C6 H8 O6 174.01636 1.49 175.0247 [M-H]− 1 0.4208721 0.6294469 20 有机酸 柠檬酸 C6 H8 O7 192.0633 1.278 191.0197 [M-H]− 1 0.1741608 0.6592146 21 有机酸 奎宁酸 C7 H12 O6 192.06341 0.832 191.0560 [M-H]− 1 0.0798837 8.4139563 22 有机酸 脱落酸 C15 H20 O4 264.13628 7.092 265.1047 [M+H]+ 1 0.3879990 5.3032785 23 糖苷 长寿花糖甙 C19 H30 O8 386.19405 5.108 385.1862 [M-H]− 1 0.1444265 0.7048008 24 氨基酸 赖氨酸 C6 H14N2O2 146.10549 0.695 145.0983 [M-H]− 1 17.3911049 4.8403282 25 氨基酸 組氨酸 C6 H9 N3 O2 155.06944 0.703 154.4484 [M-H]− 1 15.7036029 4.4824619 26 氨基酸 L-酪氨酸 C9 H11 N O3 181.07389 1.294 163.0400 [M-H]− 1 8.3561917 1.5198959 27 氨基酸 DL-精氨酸 C6H14N4O2 174.11154 0.715 173.0093 [M-H]− 1 5.3336296 52.6650510 28 氨基酸 异亮氨酸 C6H13NO2 131.09461 1.379 130.0876 [M-H]− 1 1.5481378 0.8577223 表 3 三种果汁抗氧化活性的IC50
Table 3 IC50 of antioxidant activity of three kinds of fruit juices
IC50(μL/mL) RRTJ PJ BJ ABTS+· 4.00±0.32b 40.74±0.72a 39.37±0.74a DPPH· 10.03±0.51c 362.77±71.48b 840.43±73.57a ·OH 5.92±0.46b 19.79±0.85a 5.67±0.82b 表 4 活性成分含量与抗氧化之间的相关性
Table 4 Correlation between active ingredient content and antioxidation
r 总多酚 总黄酮 IC50 of ABTS+· IC50 of DPPH· IC50 of ·OH 总多酚 1.000 总黄酮 0.994 1.000 IC50 of ABTS+· −0.999* −0.988 1.000 IC50 of DPPH· −0.769 −0.697 0.800 1.000 IC50 of ·OH −0.558 −0.642 0.512 −0.102 1.000 注:*表示存在显著性,P<0.05。 -
[1] LIU P, LI Y, WANG R, et al. Oxidative stress and antioxidant nanotherapeutic approaches for inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Biomedicines,2021,10(1):85. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10010085
[2] LIGUORI I, RUSSO G, CURCIO F, et al. Oxidative stress, aging, and diseases[J]. Clinical Interventions in Aging,2018,13:757−772. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S158513
[3] SIES H, JONES D P. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) as pleiotropic physiological signalling agents[J]. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology,2020,21(7):363−383. doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-0230-3
[4] ALATAB S, SEPANLOU S G, IKUTA K, et al. The global, regional, and national burden of inflammatory bowel disease in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017[J]. The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology,2020,5(1):17−30.
[5] GEICU O I, STANCA L, VOICU S N, et al. Dietary AGEs involvement in colonic inflammation and cancer: Insights from an in vitro enterocyte model[J]. Scientific Reports,2020,10(1):2754. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-59623-x
[6] RUDRAPAL M, KHAIRNAR S J, KHAN J, et al. Dietary polyphenols and their role in oxidative stress-induced human diseases: Insights into protective effects, antioxidant potentials and mechanism(s) of action[J]. Front Pharmacol,2022,13:806470. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.806470
[7] ZHOU G, CHEN L, SUN Q, et al. Maqui berry exhibited therapeutic effects against DSS-induced ulcerative colitis in C57BL/6 mice[J]. Food Function,2019,10(10):6655−6665. doi: 10.1039/C9FO00663J
[8] PACHECO M T, VEZZA T, DIEZ-ECHAVE P, et al. Anti-inflammatory bowel effect of industrial orange by-products in DSS-treated mice[J]. Food Function,2018,9(9):4888−4896. doi: 10.1039/C8FO01060A
[9] VALKO M, LEIBFRITZ D, MONCOL J, et al. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease[J]. International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology,2007,39(1):44−84.
[10] EBRAHIMI P, LANTE A. Polyphenols: A comprehensive review of their nutritional properties[J]. The Open Biotechnology Journal,2021,15(1):164−172. doi: 10.2174/1874070702115010164
[11] DIREITO R, ROCHA J, SEPODES B, et al. Phenolic compounds impact on rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease and microbiota modulation[J]. Pharmaceutics,2021,13(2):145. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13020145
[12] XU J, VIDYARTHI S K, BAI W, et al. Nutritional constituents, health benefits and processing of Rosa roxburghii: A review[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2019:60.
[13] GIMÉNEZ-BASTIDA J A, ÁVILA-GÁLVEZ M Á, ESPÍN J C, et al. Evidence for health properties of pomegranate juices and extracts beyond nutrition: A critical systematic review of human studies[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2021,114:410−423.
[14] EL NEWEHY N M, ABD-ALHASEEB M M, OMRAN G A, et al. Comparative metabolomics reveal intraspecies variability in bioactive compounds of different cultivars of pomegranate fruit (Punica granatum L.) and their waste by-products[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2022,102(13):5891−5902. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.11940
[15] HE J Y, ZHANG Y H, MA N, et al. Comparative analysis of multiple ingredients in Rosa roxburghii and R. sterilis fruits and their antioxidant activities[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2016,27:29−41. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2016.08.058
[16] LI H, FANG W, WANG Z, et al. Physicochemical, biological properties, and flavour profile of Rosa roxburghii Tratt, Pyracantha fortuneana, and Rosa laevigata Michx fruits: A comprehensive review[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,366:130509. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130509
[17] 赵斯尘, 王永刚. 药食同源刺梨的研究进展[J]. 食品工业,2022,43(3):186−191. [ZHAO S C, WANG Y G. Research progress of edible Rosa roxburghii Tratt[J]. The Food Industry,2022,43(3):186−191. [18] MATHON C, CHATER J M, GREEN A, et al. Quantification of punicalagins in commercial preparations and pomegranate cultivars, by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2019,99(8):4036−4042. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.9631
[19] MANDAL A, BHATIA D, BISHAYEE A. Anti-inflammatory mechanism involved in pomegranate-mediated prevention of breast cancer: The role of NF-kappa B and Nrf2 signaling pathways[J]. Nutrients,2017,9(5):436. doi: 10.3390/nu9050436
[20] PEREZ R, LACA A, LACA A, et al. Environmental behaviour of blueberry production at small-scale in Northern Spain and improvement opportunities[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2022:339.
[21] ZHOU L, XIE M H, YANG F, et al. Antioxidant activity of high purity blueberry anthocyanins and the effects on human intestinal microbiota[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2020:117.
[22] QNEIBI M, HANANIA M, JARADAT N, et al. Inula viscosa (L.) Greuter, phytochemical composition, antioxidant, total phenolic content, total flavonoids content and neuroprotective effects[J]. European Journal of Integrative Medicine,2021:42.
[23] 刘翰飞. 刺梨抗氧化抑菌作用的谱效关系研究 [D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2020. LIU H F. Study on the spectrum-effect relationship of anti-oxidation and bacteriostasis of Rose roxburghii [D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2020.
[24] HE J M, YIN T P, CHEN Y, et al. Phenolic compounds and antioxidant activities of edible flowers of Pyrus pashia[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2015,17:371−379. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2015.05.045
[25] CHEN G, KAN J. Characterization of a novel polysaccharide isolated from Rosa roxburghii Tratt fruit and assessment of its antioxidant in vitro and in vivo [J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2018, 107(Pt A): 166-174.
[26] DING A, WEN X. Dandelion root extract protects NCM460 colonic cells and relieves experimental mouse colitis[J]. Journal of Natural Medicines,2018,72(4):857−866. doi: 10.1007/s11418-018-1217-7
[27] BHATTACHARYYA S, DUDEJA P K, TOBACMAN J K. ROS, Hsp27, and IKKbeta mediate dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) activation of IkappaBa, NFkappaB, and IL-8[J]. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases,2009,15(5):673−683. doi: 10.1002/ibd.20821
[28] 熊颖, 禹霖, 柏文富, 等. 不同品种蓝莓果实品质特征和抗氧化能力及多酚组成的比较[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报,2022,42(2):119−128. [XIONG Y, YU L, BAI W F, et al. Evaluation of quality characteristics, antioxidant ability and polyphenol composition of different blueberry cultivars[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology,2022,42(2):119−128. [29] BRIGHENTI V, GROOTHUIS S F, PRENCIPE F P, et al. Metabolite fingerprinting of Punica granatum L. (pomegranate) polyphenols by means of high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array and electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry detection[J]. Journal of Chromatography A,2017,1480:20−31. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2016.12.017
[30] BECKER PERTUZATTI P, TEIXEIRA BARCIA M, GOMEZ-ALONSO S, et al. Phenolics profiling by HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS(n) aided by principal component analysis to classify Rabbiteye and Highbush blueberries[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,340:127958. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127958
[31] WANG L T, LV M J, AN J Y, et al. Botanical characteristics, phytochemistry and related biological activities of Rosa roxburghii Tratt fruit, and its potential use in functional foods: A review[J]. Food Function,2021,12(4):1432−1451. doi: 10.1039/D0FO02603D
[32] YANG Q Q, ZHANG D, FARHA A K, et al. Phytochemicals, essential oils, and bioactivities of an underutilized wild fruit Cili (Rosa roxburghii)[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2020,143:11928.
[33] CHIU H F, VENKATAKRISHNAN K, GOLOVINSKAIA O, et al. Gastroprotective effects of polyphenols against various gastro-intestinal disorders: A mini-review with special focus on clinical evidence[J]. Molecules,2021,26(7):2090. doi: 10.3390/molecules26072090
[34] PISOSCHI A M, POP A. The role of antioxidants in the chemistry of oxidative stress: A review[J]. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry,2015,97:55−74. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.04.040
[35] LIU C, CHAN L P, LIANG C H. The anti-aging activities against oxidative damages of Rosa roxburghii and multi-fruit concentrate drink[J]. Journal of Food and Nutrition Research,2020,7(12):845−850. doi: 10.12691/jfnr-7-12-5
[36] TOPALOVIC A, KNEZEVIC M, IVANOVIC L, et al. Phytochemical screening of wild pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) juices from the market[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2021:100.
[37] YANG W J, GUO Y X, LIU M, et al. Structure and function of blueberry anthocyanins: A review of recent advances[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2022:88.
[38] FELGUS-LAVEFVE L, HOWARD L, ADAMS S H, et al. The effects of blueberry phytochemicals on cell models of inflammation and oxidative stress[J]. Advances In Nutrition,2022,13(4):1279−1309. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmab137
[39] ALI H, JAHAN A, SAMRANA S, et al. Hepatoprotective potential of pomegranate in curbing the incidence of acute liver injury by alleviating oxidative stress and inflammatory response[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology,2021,12:694607. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.694607
[40] POUNIS G, COSTANZO S, BONACCIO M, et al. Reduced mortality risk by a polyphenol-rich diet: An analysis from the Moli-sani study[J]. Nutrition,2018,48:87−95. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2017.11.012
[41] 卢薇, 费建军, 沈晓梅, 等. 五种果汁的酚类组成及其抗氧化、抗肿瘤细胞增殖活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,43:365−371. [LU W, FEI J J, CHEN X M, et al. Phenolic profiles, antioxidant and antiproliferative activities towards tumor cells of five fruit juices[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,43:365−371. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021070043 -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 李娜,郭莹莹,朱文嘉,姚琳,江艳华,蒋昕,王联珠. SC/T 3407—2022《食用琼胶》制定内容解析. 中国渔业质量与标准. 2023(06): 26-31 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 魏甜甜,文昌典,于金哲. 琼脂基环保包装材料的研究进展. 农产品加工. 2022(17): 107-108+111 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:



