Effects of Jointed Treatment with Enzymatic Hydrolysis and Fermentation on the Components and Biological Activity of Auricularia auricula
-
摘要: 为探究黑木耳液经过酶解与发酵联合处理后的成分和生物活性的变化,将黑木耳液利用纤维素酶、果胶酶酶解,再利用接种比例1:1的植物乳杆菌(L. plantarum)与发酵乳杆菌(L. fermentum)进行发酵,测定经酶解与发酵联合处理前后木耳液的成分变化,通过傅立叶红外光谱(FTIR)和原子力显微镜(AFM)表征其结构;对其抗氧化活性,体外抑制α-淀粉酶和α-葡萄糖苷酶活性进行评价;建立H2O2诱导RAW264.7细胞氧化损伤模型,通过检测抗氧化酶含量来评价不同质量浓度木耳发酵液对细胞氧化损伤的保护作用,以及对RAW264.7细胞增殖、吞噬效果及细胞因子释放量的影响。结果表明,木耳发酵液中总糖含量由未处理木耳液的170.57 mg∙g−1提高到539.14 mg∙g−1,同时,蛋白质含量由未处理木耳液的15.00 mg∙g−1提高到81.28 mg∙g−1;FTIR光谱分析结果表明,木耳发酵液中-OH峰明显变宽;原子力显微镜结果显示,木耳发酵液的三维结构呈密集的谷堆状,木耳中的多糖水解生成了较多小分子的糖,支链含量增多并聚集成团;黑木耳发酵液质量浓度为0.5 mg/mL时,其α-淀粉酶抑制率较木耳液相比提高了2.39倍;在黑木耳发酵液质量浓度为5 mg/mL时,其胆酸盐结合能力是黑木耳酶解液和木耳液结合胆酸盐能力的1.37倍和2.66倍。木耳发酵液显著提高了RAW264.7细胞的增殖和吞噬能力,并对氧化损伤的RAW264.7细胞具有保护效应。酶解与发酵联合处理显著提高了黑木耳活性成分的功能,为黑木耳产品的深入开发研究提供了理论依据。
-
关键词:
- 酶解发酵黑木耳液 /
- 抗氧化活性 /
- α-淀粉酶抑制率 /
- α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制率 /
- 胆酸盐结合能力
Abstract: In order to investigate the changes of components and biological activities of Auricularia auricula liquid after enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation, the Auricularia auricula liquid was firstly subjected to enzymatic hydrolysis using cellulase and pectinase, followed by joint fermentation using Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus fermentum with inoculation ratio of 1:1. The components of the Auricularia auricula liquid before and after enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation treatment was monitored. Their structure was characterized by Fourier infrared spectrum (FTIR) and atomic force microscopy (AFM). The antioxidant activity, anti-α amylase and anti-α- glucosidase activities in vitro were evaluated. The oxidative damage model of RAW264.7 cells induced by H2O2 was established, and the protective effect of different concentrations of Auricularia auricula fermentation broth on cell oxidative damage was evaluated by detecting the content of antioxidant enzymes. The effects of the fermentation broth on RAW264.7 cell proliferation, phagocytosis and cytokine release were also determined. Results showed that the total sugar content in the fermentation broth of Auricularia auricula increased to 539.14 mg∙g−1 from 170.57 mg∙g−1 in the untreated Auricularia auricula liquid, and the protein content increased from 15.00 mg∙g−1 in the untreated Auricularia auricula liquid to 81.28 mg∙g−1 simultaneously. The FTIR suggested that there were significant increase in -OH vibrations of polysaccharide in Auricularia auricula liquid after enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation treatment. The results of atomic force microscope showed that the three-dimensional structure of the fermentation broth of Auricularia auricula was in dense grain piles-like structure, and the polysaccharides in Auricularia auricula were hydrolyzed to produce more small molecules of sugars, and the content of branched chains increased and agglomerated. Compared with the untreated Auricularia auricula liquid, the α-amylase inhibition rate of the Auricularia auricula fermentation broth increased by 2.39 times when the concentration was 0.5 mg/mL. And 5 mg/mL of Auricularia auricula fermentation broth increased the bile salt binding capacity by 1.37 and 2.66 times of the Auricularia auricula hydrolysate and untreated Auricularia auricula liquid. The fermentation broth improved the proliferation and phagocytosis of RAW264.7 cells and showed protective effect on oxidative damaged cells. The jointed treatment by enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation greatly improved the functions of the active components of Auricularia auricula, which provided a theoretical basis for the further development and research of Auricularia auricula products. -
黑木耳(Auricularia auricula),被誉为“素中之王”和“菌中瑰宝”[1],富含多糖、蛋白质、膳食纤维、人体必需氨基酸、多种微量元素等营养物质[2]。作为一种药食同源的食用菌,具有抗氧化、抗炎、降血糖、降血脂、抗肿瘤等功效[3]。属于大型真菌的黑木耳细胞壁是由β-葡聚糖、甘露聚糖、蛋白质和几丁质组成的复杂交联聚合物[4]。若要提高黑木耳子实体中活性成分的生物利用度,需采取措施将其从细胞中释放出来。主要方法有物理法、化学法、生物法等。但物理方法往往效率低且费时;化学方法通常使用大量的溶剂且耗能,而生物修饰因其操作简单、效率高、环境友好而受到越来越多的关注[5]。在食用菌类、豆类和谷类等食品加工过程中,生物修饰中的酶解法和发酵法改变细胞壁结构并促进可溶性成分的释放,其效果已得到证实,其中酶解可以增加细胞壁通透性,有利于活性成分的释放。益生菌发酵也能促进食品中活性成分的释放及提高其功能性[6]。
现已有大量文献报道经酶解处理或乳酸菌发酵来提高食物等的生物活性。Tong等[7]用果胶酶、木聚糖酶混合水解藜麦可显著增加酚类化合物的含量,从而提高藜麦的抗氧化活性和抗炎活性。Quines等[8]研究发现经过细胞壁水解酶和含有β-葡萄糖苷酶活性的乳酸菌发酵仙人掌,其抗氧化活性和降血糖活性得到增强。Wang等[9]利用植物乳杆菌发酵杏鲍菇,提高了总酚含量,增加了抗氧化能力;此外,发酵还促进了醇类、酯类物质释放,赋予杏鲍菇更好的风味。可见,酶解法和乳酸菌发酵是改善食品的营养品质和生物活性的重要加工技术手段。目前,关于黑木耳的加工利用集中在黑木耳多糖、黑色素等成分的提取及功能性的研究,而对黑木耳进行生物修饰,从而提高生物活性的研究较少。因此,本研究旨在通过酶解与发酵联合处理黑木耳,使黑木耳活性成分释放出来,探讨酶解与发酵联合处理对黑木耳成分、结构及其生物活性的影响。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
黑木耳 产自黑龙江省大兴安岭地区;植物乳杆菌(Lactobacillus plantarum)、发酵乳杆菌(Lactobacillus fermentum) 黑龙江大学微生物重点实验室保存菌种;纤维素酶、果胶酶、2,2’-联氨-双-(3-乙基苯并噻唑啉-6-磺酸)ABTS、3,5-二硝基水杨酸(DNS)、脂多糖(LPS) 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;BCA蛋白浓度测定试剂盒 碧云天生物技术有限公司;模拟胃液、模拟肠液、α-淀粉酶、α-葡萄糖苷酶、4-硝基苯基-α-D-吡喃葡萄糖苷(PNPG) 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;小鼠单核巨噬细胞RAW264.7 江苏菲亚生物科技有限公司;DMEM培养基 美国GIBCO有限公司;Cell Counting Kit-8试剂盒 东仁化学科技(上海)有限公司;谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GPX)试剂盒、过氧化氢酶(CAT)试剂盒、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)试剂盒、小鼠白细胞介素6检测试剂盒、小鼠白细胞介素β检测试剂盒、小鼠肿瘤坏死因子α检测试剂盒 上海酶联生物科技有限公司。
H1850型台式高速离心机 湖南湘仪实验室仪器开发有限公司;UV-1200D型紫外分光光度计 北京普析通仪器有限责任公司;AVATAR370型傅里叶红外光谱仪 美国赛默飞世尔科技公司;NU-5500E型CO2细胞培养箱 奥林巴斯公司;VersaMAX型酶标仪 PLUS; MLS-3781-PC型高压蒸汽灭菌器 日本松下健康医疗器械。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 黑木耳酶解液与发酵液的制备
按照牟佳红等[10]方法制备。木耳酶解液的制备方法:将黑木耳用40 ℃自来水泡发2 h,清洗,使用胶体磨研磨制成木耳液,加入质量比为2:3,总加酶量为3.2%(w/w 按木耳浆液质量计)的果胶酶与纤维素酶,在50 ℃,pH5.5条件下酶解3.5 h后即为木耳酶解液。木耳发酵液的制备方法:将酶解液灭菌(121 ℃,15 min),冷却到室温,接入3%的复合菌液(植物乳杆菌:发酵乳杆菌=1:1),37 ℃条件下发酵8 h,3823×g离心15 min,取上清液为黑木耳发酵液。将制得的木耳液、酶解液与发酵液冷冻干燥制得冻干粉,4 ℃保存,用于后续实验。
1.2.2 营养成分和活性成分的测定
蛋白质的测定:BCA试剂盒测定;总糖的测定:按照国家标准GB/T 15672-2009《食用菌中总糖含量的测定》;灰分的测定:按照国家标准GB 5009.4-2016《食品中灰分的测定》;总酚的测定:按照国家标准GB 8313-2018《茶叶中茶多酚和儿茶素含量的检测方法》。
1.2.3 结构表征
1.2.3.1 原子力显微镜观察
参考Li等[11]方法略作改动,以硅片(规格为8 mm×8 mm)为载体,硅片浸在乙醇中,超声波震荡2.5 h,取出后用脱脂棉轻轻擦除表面酒精,过程中一定要避免硅片亮面出现划痕。分别将木耳液、酶解液、发酵液冻干粉用纯水溶解,配制成10 μg/mL的稀溶液,在硅片上滴一滴,均匀涂抹开,自然晾干。原子力显微镜下观察:轻敲模式(Tapping Mode)下对样品进行扫描观察。
1.2.3.2 傅里叶红外光谱测定
参考Song等[12]方法,分别取木耳液、酶解液、发酵液冻干粉2.0 mg,使其与200 mg恒重后的溴化钾粉末混合均匀,研磨后压片,利用傅里叶红外光谱仪进行扫描,扫描范围为4000~500 cm−1。
1.2.4 体外降糖、降脂活性的测定
1.2.4.1 体外吸附油脂能力的测定
参考吕冰冰等[13]的方法并略有改动,称取0.50 g木耳液、酶解液、发酵液冻干粉(m0)放入离心管中,加入10.0 mL的0.01 mol/L盐酸溶液,样品溶解后,称重记为m1。再加入3.0 g的花生油,在37 ℃恒温振荡1 h,用0.1 mol/L的NaOH溶液调节pH至7.0,37 ℃恒 温振荡1 h,1698×g离心15 min,吸取上层脂肪于干燥烧杯中,称重记为m2,将其置于120 ℃烘箱中2 h,取出冷却,称量记为m3,将下层溶液与离心管称重记为m4。按照式(1)计算脂肪吸附能力。
脂肪吸附量(g/g)=m4+(m3−m2)−m1m0 (1) 1.2.4.2 体外吸附胆固醇能力的测定
参考孙凯峰等[14]方法并有修改。取新鲜鸡蛋的蛋黄与蒸馏水按照1:9的比例混合。取蛋黄液50.0 g和2.0 g木耳液、酶解液、发酵液冻干粉加入三角瓶中,调pH7.0,1698×g离心30 min,取上清液,在550 nm波长处下测OD值,利用胆固醇标准曲线:y=0.7509x+0.0918,R2=0.9962,计算反应体系当中的胆固醇含量。胆固醇的吸附量计算公式如下:
胆固醇吸附量(mg/g)=A1−A2M1 (2) 式中:A1-吸附前胆固醇量,单位为mg;A2-吸附后上清液中胆固醇量,单位为mg;M1-样品质量,单位为g。
1.2.4.3 体外胆酸盐结合能力的测定
参考唐茹萌等[15]的方法并略有改动。取1 mL不同质量浓度的木耳液、酶解液、发酵液冻干粉于玻璃具塞试管中,加入1 mL模拟胃液,涡旋混匀,37 ℃水浴消化1 h,取出,调pH至6.3,再加入4 mL模拟肠液,37 ℃水浴消化1 h。每支试管再分别加入4 mL牛磺胆酸盐溶液,37 ℃水浴反应1 h后,1698×g离心10 min,取2.5 mL上清液,加入3倍体积的硫酸溶液,混匀后70 ℃水浴20 min,取出冰浴5 min,反应体系中以水代替牛磺胆酸盐溶液作为空白,测定387 nm波长处吸光度,利用胆酸盐含量计算标准曲线:y=1.9920X−0.0229,R2=0.996,按式(3)计算牛磺胆酸盐结合率。
牛磺胆酸盐结合率(%)=(1−A0A1)×100 (3) 式中:A0-样品组的吸光度;A1-空白组的吸光度。
1.2.4.4 α-淀粉酶抑制率测定
参考陈玥彤等[16]方法,将木耳液、酶解液、发酵液冻干粉溶解于PBS(pH6.8),添加淀粉溶液(0.1 mL,1%,w/v)和α-淀粉酶(0.2 mL,6 U/mL)。在37 ℃活化10 min。加入DNS溶液终止反应,将反应体系在沸水浴5 min后,加10 mL蒸馏水,在540 nm处测定反应体系OD值,通过式(4)计算α-淀粉酶抑制率。
α-淀粉酶抑制率(%)=A0−(A1−A2)A0×100 (4) 式中:A0-磷酸盐缓冲液的吸光值;A1-反应体系的吸光值;A2-α-淀粉酶酶促反应体系的吸光值。
1.2.4.5 α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制率测定
参考刘萌[17]和姚旭等[18]方法并略作修改。将木耳液、酶解液、发酵液冻干粉配制成10 mg/mL溶液,分别取50 μL与250 μL α-葡萄糖苷酶混匀,37 ℃水浴10 min,加入250 μL PNPG (5 mmol/L),37 ℃水浴10 min,加入450 μL Na2CO3溶液(0.2 mmol/L)终止反应,在405 nm波长处测定OD值,按式(5)计算α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制率,重复实验3次。
α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制率(%)=(1−A1−A2A0)×100 (5) 式中:A1-空白的吸光值,A2-样品的吸光值,A0-用蒸馏水代替PNPG的样品的吸光值。
1.2.5 抗氧化活性测定
1.2.5.1 ABTS+自由基清除活性的测定
参考Xu等[19]方法并改进,在96孔板中按表1添加各试剂。
表 1 各试剂添加量Table 1. Addition amount of each reagent分组 样品(μL) ABTS+工作液(μL) 蒸馏水(μL) 乙醇溶液(μL) 样品组(A2) 20 180 − − 对照组(A0) − − 20 180 空白组(A1) − 180 20 − 按上表添加试剂后,混匀,30 ℃反应10 min,在734 nm处用酶标仪测定吸光值。ABTS+自由基清除率计算见式(6):
ABTS+自由基清除率(%)=(1−A2−A0A1)×100 (6) 式中:A0-蒸馏水与乙醇混匀的OD值;A1-蒸馏水代替样品的OD值;A2-样品与ABTS+工作液混匀的OD值。
1.2.5.2 羟基自由基清除活性的测定
参考张雪娇等[20]方法,配制6 mmol/L硫酸亚铁、6 mmol/L过氧化氢及6 mmol/L水杨酸乙醇溶液。在96孔板中按表2添加各试剂。
表 2 羟基自由基清除活性测定各试剂添加量Table 2. •OH free radical scavenging activity determination of addition amount of each reagent分组 FeSO4
(μL)水杨酸乙醇
(μL)H2O2
(μL)蒸馏水
(μL)样品
(μL)样品组(A2) 50 50 50 − 50 对照组(A1) 50 50 − 50 50 空白组(A0) 50 50 50 50 − 加入样品、硫酸亚铁溶液及过氧化氢溶液后,37 ℃预热10 min,再加入水杨酸乙醇溶液,37 ℃预热30 min,在510 nm处用酶标仪测定吸光值。羟基自由基清除率计算见式(7):
羟基自由基清除率(%)=(1−A2−A0A1)×100 (7) 式中:A0-蒸馏水代替样品的OD值;A1-蒸馏水代替过氧化氢溶液的OD值;A2-样品与硫酸亚铁、过氧化氢和水杨酸乙醇溶液混匀的OD值。
1.2.5.3 超氧阴离子自由基清除活性的测定
参考Zhang等[21]的方法并略作改动。取48孔板,每孔中加入450 μL的Tris-HCl溶液(50 mmol/L、pH8.2)预热25 min,然后加入100 μL木耳液、酶解液、发酵液和40 μL的6 mmol/L邻苯三酚溶液,在25 ℃下准确反应4 min后加入50 μL的8 mol/L盐酸溶液终止反应,用酶标仪于320 nm波长处测定溶液体系OD值。以蒸馏水代替样品溶液作为空白,蒸馏水代替邻苯三酚溶液作为样品对照,超氧阴离子自由基清除率按式(8)计算。每个样品平行3次,结果取平均值。
超氧阴离子自由基清除率(%)=(1−A2−A0A1)×100 (8) 式中:A0-蒸馏水代替样品的OD值;A1-蒸馏水代替邻苯三酚的OD值;A2-样品与邻苯三酚反应的OD值。
1.2.6 RAW264.7细胞氧化损伤保护效应
1.2.6.1 RAW264.7 细胞的培养
参考 Fang等[22]的方法对细胞进行复苏及培养处理。将含有RAW264.7冻存管在 37 ℃ 水浴中迅速摇晃解冻,加入DMEM培养基,离心去上清,补加DMEM完全培养基后吹匀。将所有细胞悬液加入培养瓶中培养过夜,换培养基并检查细胞密度。当细胞密度达80%~90%,即可进行传代培养。先弃去培养基上清,用 PBS缓冲液润洗 1~2 次,再加 1~2 mL 胰酶,置于37 ℃、5% CO2培养箱中消化1~2 min,加DMEM完全培养基终止消化。然后轻轻吹打细胞,完全脱落后吸出,离心弃去上清液,补加 1~2 mL 培养液后吹匀。最后按 5~6 mL 每瓶补加 DMEM 培养液,将细胞悬液按1:2分到新的含5~6 mL培养液的新瓶中。
1.2.6.2 RAW264.7细胞的毒性作用
参考Wu等[23]的方法进行改进,采用CCK-8法进行细胞毒性实验。取对数生长期的RAW264.7细胞,用新鲜培养基将细胞稀释至2×105细胞/mL,向96孔板内圈的60孔中每孔加入100 μL,外圈加入150 μL无菌PBS,在37 ℃、5% CO2培养箱中培养24 h。弃上清,PBS清洗,向96孔板中加入100 μL不同浓度(100、200、400、600、800和1000 μg/mL)的样品,在37 ℃,5% CO2培养箱中培养24 h,向其每个孔中加入10% CCK8溶液100 μL,于37 ℃,5% CO2培养箱中孵育1~4 h,用酶标仪在450 nm处测定OD值(A2)。其中完全培养液代替样品的OD值为对照(A0);完全培养液和CCK8但不加细胞的OD值为空白(A1)。细胞存活率检测采用细胞增殖-毒性检测试剂盒(Cell Counting Kit-8)测定,按公式(9)计算细胞存活率:
细胞存活率(%)=A2−A1A0−A1×100 (9) 式中:A0-完全培养液代替样品的OD值;A1-完全培养液和CCK8但不加细胞的OD值;A2-样品反应的OD值。
1.2.6.3 RAW264.7细胞氧化损伤模型的建立
参考李伟等[24]方法进行改进,培养方法按1.2.6.2进行,H2O2浓度选择为200、400、600、800、1000 µg/mL。细胞存活率按公式(9)进行测定。
1.2.6.4 RAW264.7细胞氧化损伤的保护效应
培养方法按1.2.6.2进行,样品浓度选择为100、200、400、600、800、1000 μg/mL,H2O2浓度为400 µmol/L。细胞存活率按公式(9)进行测定。
1.2.6.5 RAW264.7细胞的SOD、CAT、GPX含量测定
具体步骤按照上海酶联生物试剂盒进行测定。
1.2.7 RAW264.7细胞免疫测定
1.2.7.1 细胞培养
按照1.2.6.1进行培养。
1.2.7.2 细胞增殖率测定
方法同1.2.6.2。
1.2.7.3 细胞吞噬率测定
参考Bao等[25]方法并进行改进,实验组:样品100 μL/孔;空白组:DMEM培养液100 μL/孔;LPS组:100 ng/mL LPS溶液100 μL/孔处理细胞,置于培养箱中继续培养24 h后,弃上清,用PBS清洗,每孔内加入0.075%的中性红溶液100 μL,继续培养1 h。弃上清,PBS清洗,去除游离的中性红。然后每孔中加入100 μL细胞裂解液,室温放置过夜,在540 nm波长下测吸光度。细胞吞噬率计算公式如式(10)所示:
吞噬率(%)=A样品A空白×100 (10) 1.2.7.4 细胞免疫因子TNF-α、IL-β、IL-6测定
具体步骤按照上海酶联生物试剂盒进行。
1.3 数据处理
利用Origin9.1软件对实验所得数据进行处理,实验数据测定重复3次,所有数据以平均值±标准误差的形式表示。采用单因素方差分析(ANOVA)对数据进行分析,显著性比较采用Fisher检验,显著性水平为P<0.05。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 成分分析
黑木耳中的主要成分是多糖、蛋白质和酚类物质,具有很强的抗氧化活性[26]。由表3中的结果表明,黑木耳发酵液和黑木耳酶解液的总糖和蛋白质含量显著高于木耳液(P<0.05),黑木耳中的灰分主要是无机盐和矿物质元素,在经过酶解与发酵后无显著变化。发酵食品中的酚类化合物作为一种天然抗氧化剂,可以清除过量的活性氧(ROS),防止氧化损伤。本研究中黑木耳酶解液和黑木耳发酵液的总酚含量分别为7.46和6.04 mg∙g−1,发酵液中的总酚含量有所下降,这与Zielinski等[27]研究结果类似,这可能因为在有氧发酵过程中,部分酚类物质被氧化导致。
表 3 黑木耳液、酶解液、发酵液中总糖、蛋白质、灰分和总酚的含量Table 3. Contents of total sugar, protein, ash and total phenol in liquid, enzymatic hydrolysate and fermentation broth of Auricularia auricularia成分 木耳液 黑木耳酶解液 黑木耳发酵液 总糖(mg∙g−1) 170.57±11.67c 531.39±55.84b 539.14±44.58a 蛋白质(mg∙g−1) 15.00±2.02c 83.65±1.27a 81.28±2.19b 灰分(mg∙g−1) 2.05±0.05b 2.14±0.97a 2.08±1.33ab 总酚(mg∙g−1) 5.11±0.35c 7.46±2.15a 6.04±2.03b 注:同一行不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),表4同。 2.2 结构表征
2.2.1 红外光谱分析
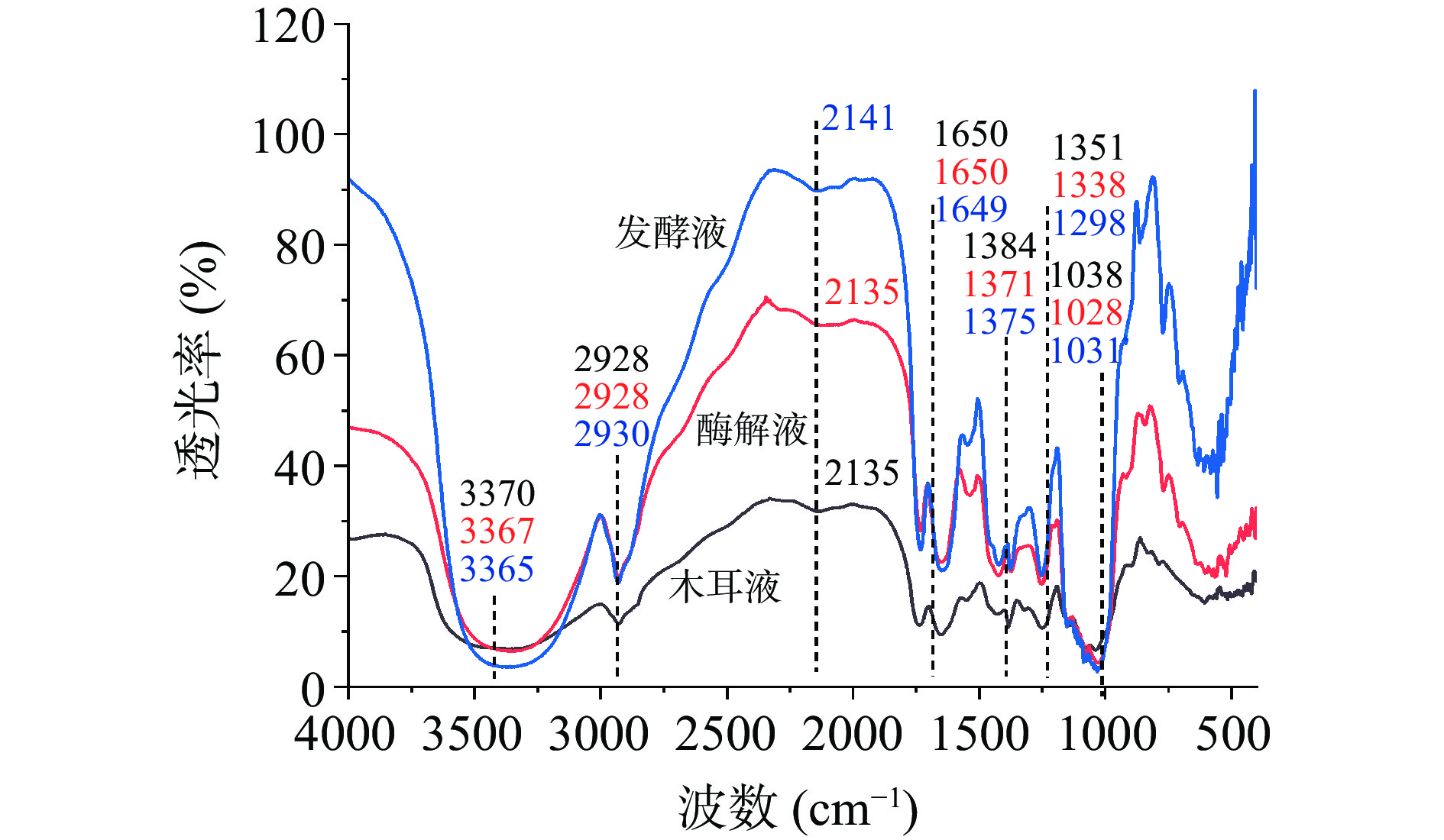
FT-IR光谱可以检测多糖的结构,如单糖类型、糖苷键和官能团,还可以用来评价分子的振动和不同原子之间的极性键[28]。由图1可知,与未处理的木耳液相比,木耳发酵液在3200~3600 cm−1范围内的-OH振动峰增强,其中3370和3365 cm−1处出现较宽吸收峰,是由N-H键和O-H键的伸缩振动引起的[29],表明经酶解处理后,有更多的亲水基团暴露;在2928和2930 cm−1处的吸收峰是由C-H键的伸缩振动引起的[30],且在1656 cm−1附近的CO-NH2-振动峰更加尖锐。1650 cm−1附近的吸收峰归属于酰胺类化合物的伸缩带,1384、1371 cm−1处伸缩和弯曲振动是由-CH键引起的,1200~1000 cm−1是由于糖类的C-O-C键的存在,说明发酵液中的多糖含有吡喃苷键[31-32]。此外,在1400~1250 cm−1的吸收峰是由于C-N键的伸缩振动所致。
2.2.2 原子力显微镜分析
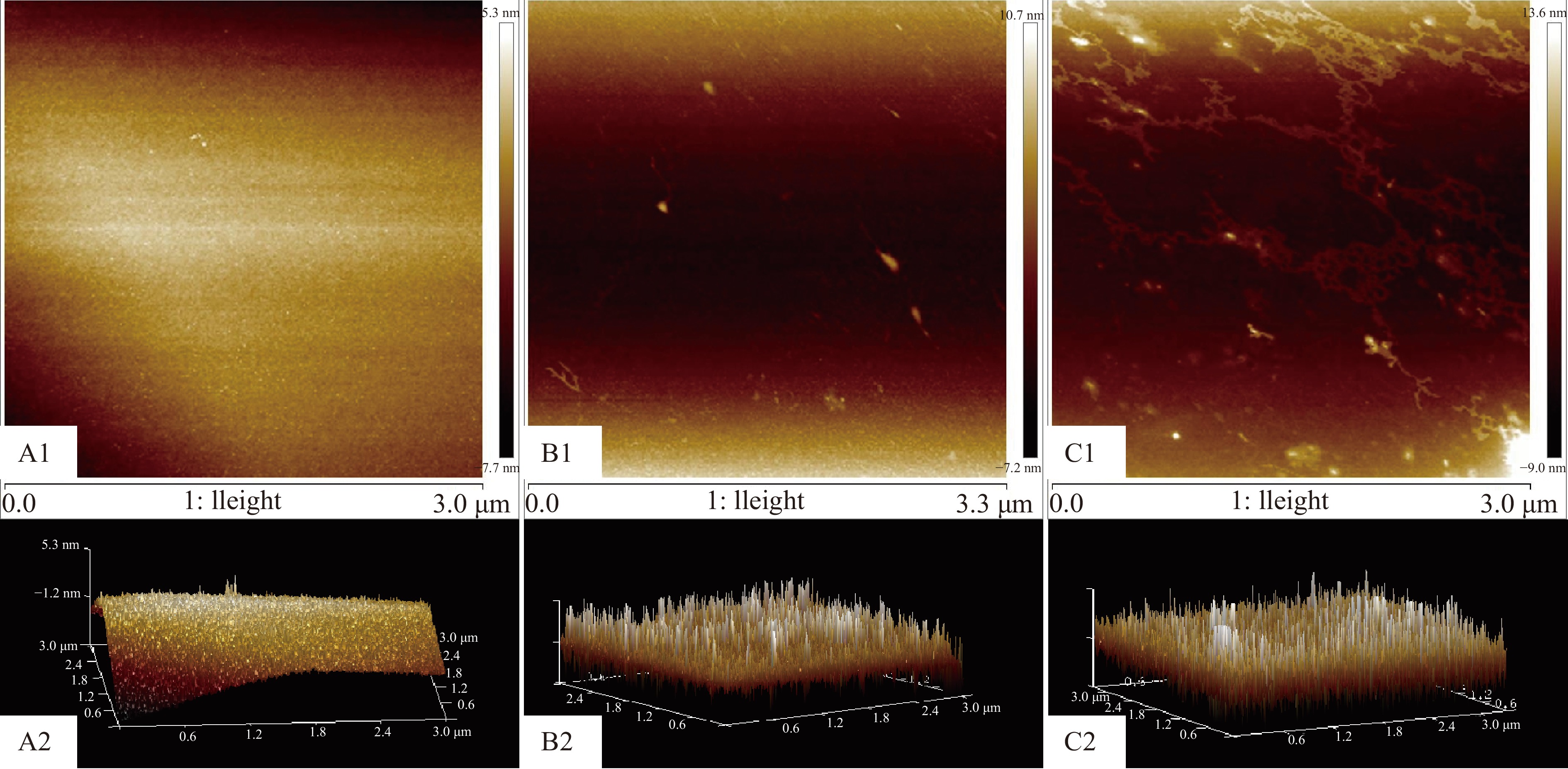
图2为木耳液、酶解液、发酵液的原子力平面和三维立体图,由图可知,图A1呈较为光滑平面,图B1、C1形态呈球状,部分球状分子聚集,在一起成为链状结构,其中C1表面形貌较为粗糙。图A2的三维结构呈高的尖头和许多不规则的突起,B2、C2的三维结构呈密集的谷堆状,这说明经过酶解与发酵处理后,木耳中的多糖支链含量增多,糖分子容易聚集在一起,从而形成了团状、岛屿状和谷堆状[33]。
2.3 体外降糖降脂活性
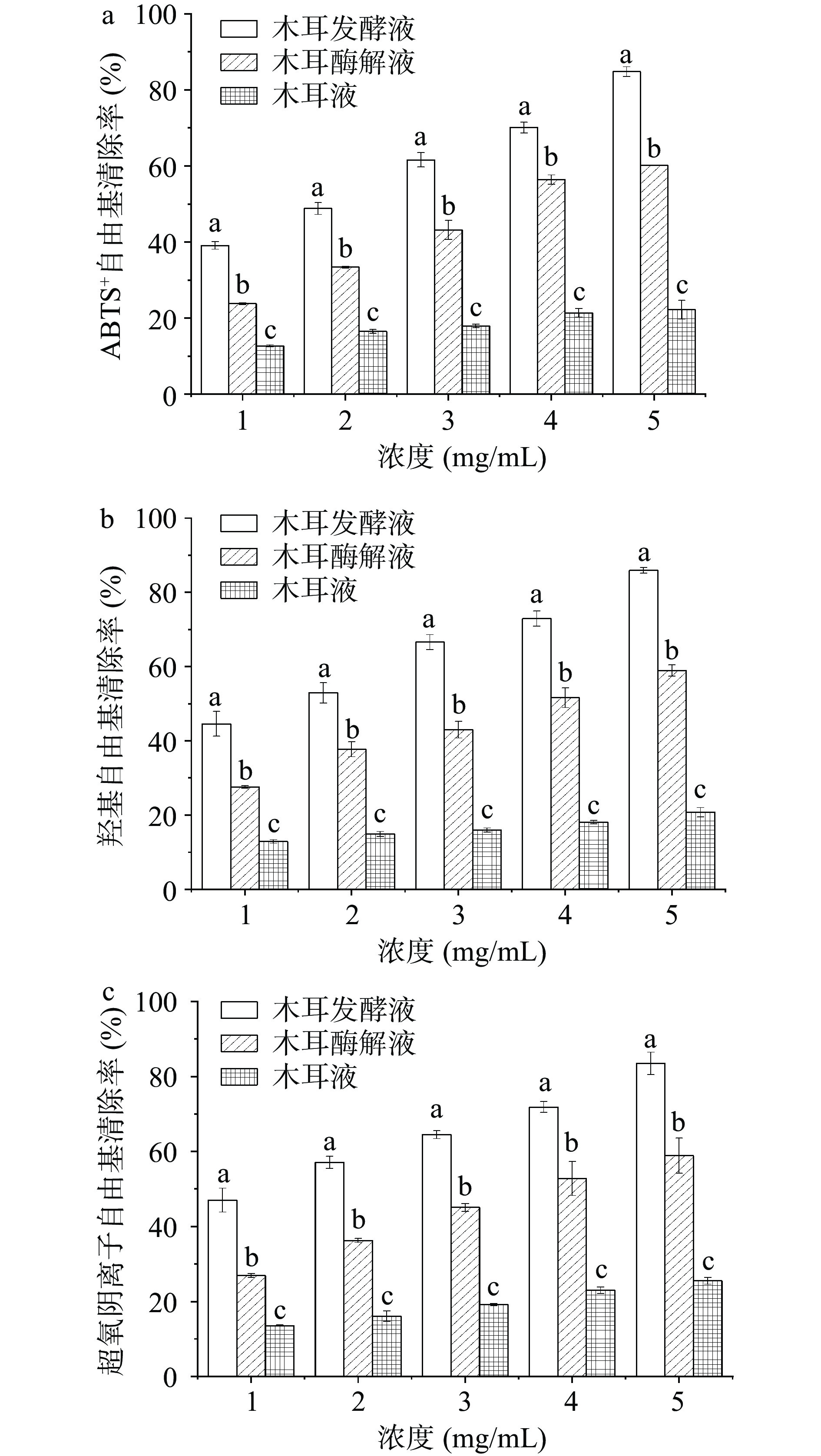
图3(a)和(b)分别为木耳液、黑木耳酶解液和黑木耳发酵液对α-淀粉酶、α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制作用的结果。由图可知,随着样品浓度逐渐增加,抑制率也逐渐上升。黑木耳发酵液的抑制率均高于黑木耳酶解液和木耳液,当质量浓度为0.5 mg/mL时,黑木耳发酵液的α-淀粉酶抑制率为43.30%±1.84%,是木耳液抑制率的3.39倍;α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制率为62.93±1.87%,而酶解液和木耳液分别为43.22%±0.93%和25.21%±0.93%。结合原子力显微镜结果,分析其原因可能是发酵后木耳液中含有较多的低分子多糖,对α-淀粉酶及α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制作用更强。
胆酸盐结合能力是衡量降脂效果的一个指标,如图3(c)所示,随着黑木耳发酵液浓度增加,其胆酸盐结合能力无明显变化;而黑木耳酶解液和木耳液随着浓度的增加胆酸盐结合能力逐渐增加。但胆酸盐结合能力大小为黑木耳发酵液>黑木耳酶解液>木耳液。在5 mg/mL时,黑木耳发酵液的胆酸盐结合能力为76.53%±0.63%,黑木耳酶解液和木耳液分别为55.98%±1.44%和28.74%±1.36%,黑木耳发酵液是黑木耳酶解液和木耳液结合胆酸盐能力的1.37倍和2.66倍。
木耳液、酶解液和发酵液对油脂和胆固醇的吸附能力见表4,其中胆固醇标准曲线为y=0.7509x+0.0918,R2=0.9962。在中性条件下的胆固醇吸附量高于酸性条件下,且黑木耳发酵液>黑木耳酶解液>木耳液。可能由于酸性条件下蛋白质、酚类等物质变性,胆固醇吸附能力降低。胆固醇参与胆酸合成,胆酸降低,有助于减少胆固醇的堆积;木耳中的多糖、纤维素等物质具有结合胆酸钠的能力,可减少胆酸重吸收,促进胆固醇分解,具有降脂的作用[34]。
表 4 黑木耳液、酶解液、发酵液对油脂和胆固醇的吸附能力Table 4. Adsorption capacity of Auricularia auricula liquid, enzymatic hydrolysate and fermentation broth for oil and cholesterol指标 木耳液 黑木耳酶解液 黑木耳发酵液 胆固醇吸附量(mg∙g−1) 91.75±3.07c 148.19±4.05b 152.31±5.72a 脂肪吸附量(g∙g−1) 4.95±0.41c 5.21±0.22b 5.33±0.34a 2.4 抗氧化活性
据报道,微生物发酵可以产生更多的生物活性物质,从而增强抗氧化活性[35]。图4(a)显示了黑木耳发酵液、黑木耳酶解液和木耳液的ABTS+自由基清除作用,黑木耳发酵液以1至5 mg/mL的不同浓度与ABTS+自由基发生反应,其表现出浓度依赖性,在样品浓度为5 mg/mL,黑木耳发酵液的ABTS+自由基清除率为84.79%±1.29%,IC50值为2.03 mg/mL,黑木耳发酵液的ABTS+自由基清除率高于黑木耳酶解液和木耳液,可能是由于木耳中的多糖、蛋白质和酚类等活性成分具有清除自由基的能力[36],经微生物发酵后,黑木耳发酵液含有较多的具有供氢能力的活性成分,可以清除ABTS+自由基。
羟基自由基穿过细胞膜,通过与碳水化合物、蛋白质、脂质和DNA的反应导致组织损伤和细胞死亡,因此清除羟基自由基至关重要。图4(b)结果显示,黑木耳发酵液的•OH消除能力远高于黑木耳酶解液和木耳液。•OH清除率随着样品浓度的增加而增加。在5 mg/mL时,黑木耳发酵液清除率达到85.89%±0.75%,此时黑木耳发酵液的IC50值为1.58 mg/mL。黑木耳发酵液比酶解液和木耳液具有更高的清除能力,这可能是由于发酵导致木耳中多糖、多酚等分子量降低时对羟基自由基的清除能力更强,这与Wang等和Wu等[37-38]文献报告相似。
超氧阴离子自由基是一种有毒物质,由许多生物和光化学反应产生,可进一步参与活性氧ROS形成的反应[39],在细胞及生物体中具有很强的氧化毒性。如图4(c)所示,黑木耳发酵液具有较高的超氧阴离子自由基清除能力,超氧阴离子自由基清除能力与浓度具有一定的依赖性,在5 mg/mL时,黑木耳发酵液的O2-•清除率达到83.48%±2.98%,此时黑木耳发酵液的IC50值为1.29 mg/mL。Miao等[40]研究了天然木耳多糖(AAP)和绿色木霉发酵后的木耳多糖(D-AAP-I~D-AAP-VII)的抗氧化效果,结果表明,与天然AAP相比,D-AAP-VI具有更高的抗氧化活性,与本实验结果相似。因此,生物发酵法可能是提高天然多糖抗氧化活性的有效途径。
2.5 对RAW264.7细胞氧化损伤保护效应
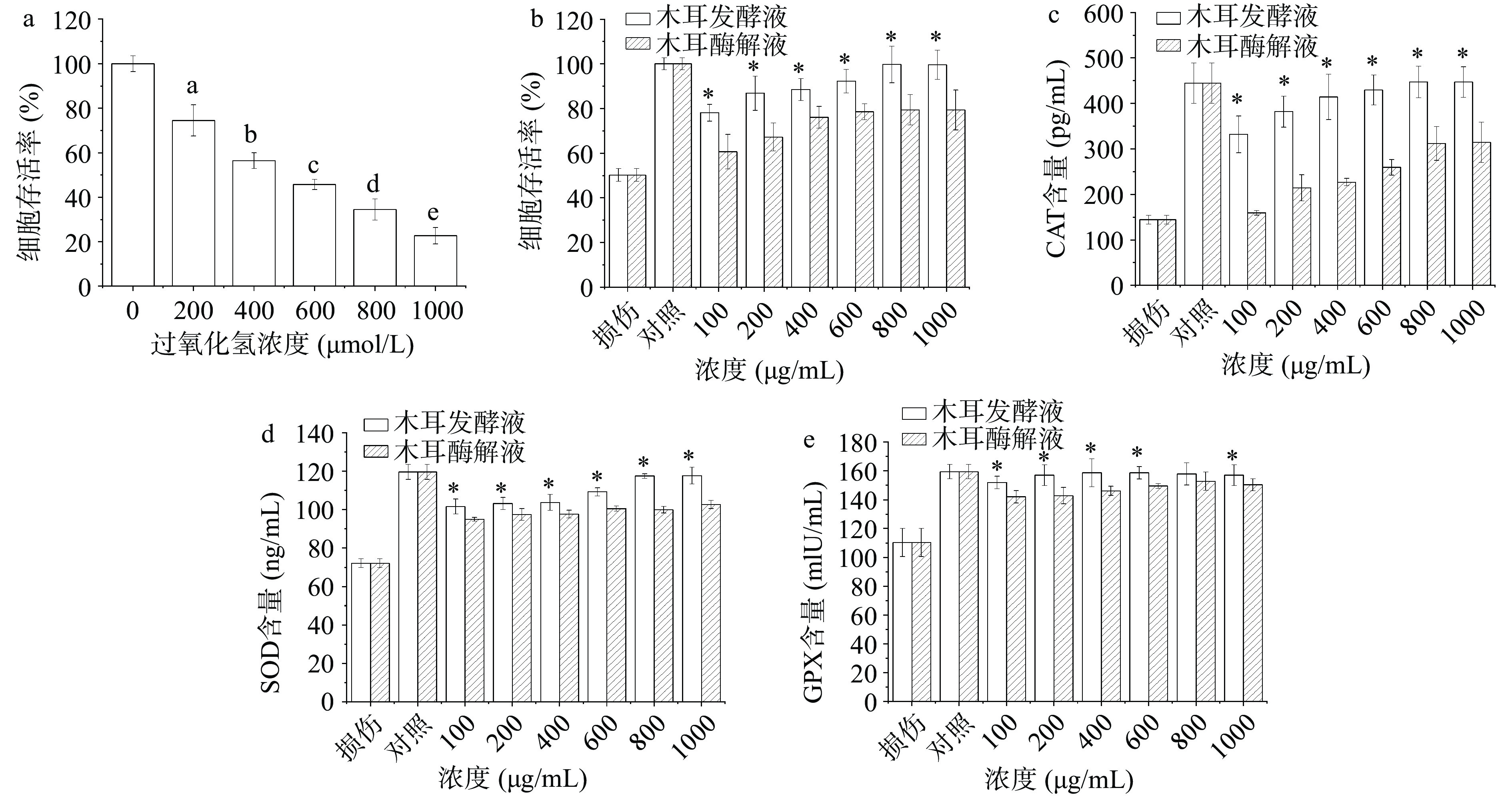
氧化应激是自由基生成和清除之间的动态平衡,由过氧化氢诱导的细胞氧化损伤模型被广泛用于研究氧化应激抑制活性[41]。在确定细胞氧化损伤的过程中,通常选择存活率为50%至70%的损伤浓度作为最佳浓度,考虑到细胞存活率过低,细胞易受诱导物过度损伤,不利于细胞的后期修复作用,因此存活率选择60%左右较为合适[42]。由图5(a)可知,当H2O2浓度在400 μmol/L时,细胞存活率达到59.79%,与其它组别具有显著性差异(P<0.05)。因此H2O2成功诱导建立了RAW264.7细胞氧化损伤模型。
由表3成分分析可知,黑木耳酶解液与发酵液各成分含量均显著高于木耳液(P<0.05),因此选用不同浓度的黑木耳发酵液、酶解液进行细胞实验,通过测定对H2O2诱导的RAW264.7细胞氧化损伤模型的氧化应激抑制活性,评价酶解与发酵处理木耳液的抗氧化活性。
如图5(b)所示,只加H2O2处理的损伤组细胞存活率约为对照组的52.45%±2.17%,与对照组有显著性差异(P<0.05);黑木耳发酵液和黑木耳酶解液对细胞存活率的影响呈现浓度依赖性,随着黑木耳发酵液浓度的增加,细胞存活率从78.10%±3.73%增加到99.71%±6.57%,与损伤组差异显著(P<0.05),当样品浓度为800 μg/mL时,黑木耳发酵液组细胞活力为99.71%±6.57%,与1000 μg/mL浓度时的细胞存活率差异不显著,而黑木耳酶解液组在1000 μg/mL时细胞存活率达到79.38%±8.96%,证明黑木耳发酵液和黑木耳酶解液对氧化损伤的细胞均有保护作用,但黑木耳发酵液对细胞保护效果高于黑木耳酶解液,在样品浓度为1000 μg/mL时细胞活力达到最高且与对照组不具有显著性差异,证明实验组细胞在黑木耳发酵液保护作用下,存活率基本恢复到了对照组的水平。
如图5(c)所示,与损伤组相比,随着黑木耳发酵液和黑木耳酶解液浓度增加,CAT含量明显上升。同时黑木耳发酵液的CAT含量显著高于黑木耳酶解液(P<0.05)。当黑木耳发酵液浓度在1000 μg/mL时,CAT含量为447.00±33.66 pg/mL,高于损伤组(144.5 pg/mL);而黑木耳酶解液浓度为100 μg/mL时,与损伤组无显著差异;随着黑木耳酶解液浓度逐渐增加,CAT释放量也逐渐增加,在800 μg/mL达到最高,此时CAT含量为312.00±44.25 pg/mL,与黑木耳发酵液和对照组差异显著;与1000 μg/mL的黑木耳酶解液差异不显著。
由图5(d)可知,与损伤组相比,随着浓度增加,黑木耳发酵液组SOD含量逐渐增加,而黑木耳酶解液组趋于稳定,且黑木耳发酵液组的SOD含量高于黑木耳酶解液组,与损伤组差异显著。当样品浓度为1000 μg/mL时,SOD的含量高达117.67±4.38 ng/mL,黑木耳酶解液组为102.68±2.13 ng/mL,分别高于损伤组45.54和30.54 ng/mL。Xu等[43]用碱法提取的黑木耳多糖能在一定程度上提高SOD和CAT活性,利用中性蛋白酶酶解得到的黑木耳多糖也能提高抗氧化酶活性。与前人的研究结果一致。
谷胱甘肽还原酶(GPX)是维持细胞内还原型谷胱甘肽含量的主要黄素酶,在防止血红蛋白氧化和维持巯基蛋白活性方面起着重要作用[44]。由图5(e)可知,与损伤组相比,随着样品浓度增加,黑木耳发酵液组GPX含量先增加后趋于稳定,在1000 μg/mL时,GPX含量为157.83±7.21 mIU/mL,黑木耳酶解液为152.83±15.15 mIU/mL。黑木耳酶解液组的GPX含量与其浓度无剂量关系;而黑木耳发酵液与对照组无显著差异,不同浓度黑木耳发酵液对于GPX含量影响效果相似,这也为验证黑木耳发酵液对H2O2诱导的RAW264.7细胞氧化损伤的保护作用提供了佐证。Xiao等[45]研究表明,黑木耳多糖分子中含有活性中心,具有增强GPX活性的作用,在发酵过程中,木耳多糖的活性基团会暴露出来,从而提高抗氧化酶活性。
2.6 对RAW264.7细胞免疫活性影响
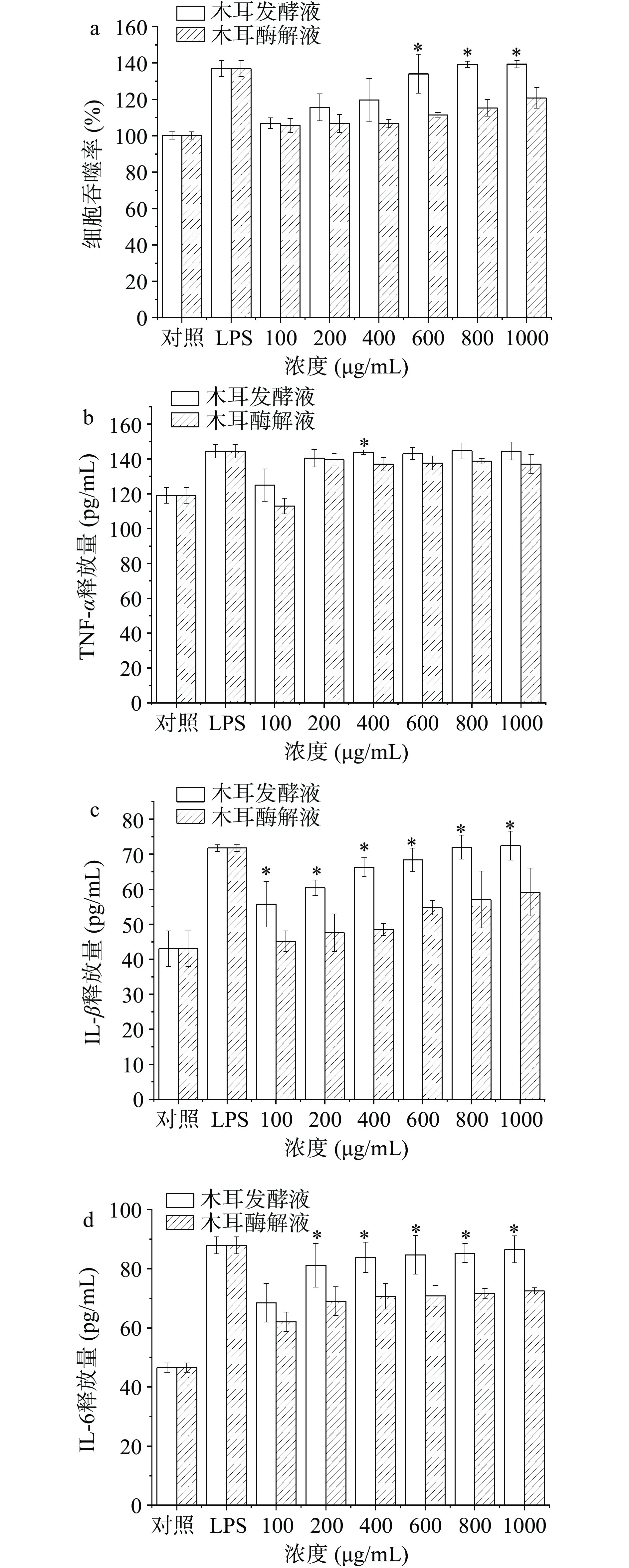
细胞的吞噬能力是细胞活性的关键指标。木耳样品细胞吞噬能力结果如图6(a)所示,所有的水解物在100~1000 μg/mL的浓度范围内都对巨噬细胞吞噬中性红有影响。各水解物的吞噬速率随样品浓度的增加而增加,且呈剂量依赖性;当样品浓度为100~800 μg/mL时,所有样品组的吞噬速率均呈缓慢上升趋势。当样品浓度增加到1000 μg/mL时,黑木耳发酵液的吞噬率最高,达到139.34%±1.99%,这意味着黑木耳发酵液可以增加RAW264.7巨噬细胞的吞噬能力。实验还表明在一定浓度范围内的黑木耳发酵液对巨噬细胞无毒害作用,可显著提高该细胞的增殖活力,可用于后续实验,这与Zhang等[46]结果相似。
细胞因子作为免疫系统中细胞与细胞间相互作用的信号分子,起着重要的作用。TNF-α可杀死或抑制肿瘤细胞,能够加强免疫反应并诱导其它免疫因子的分泌;IL-β可进一步激活巨噬细胞,参与抗体产生,其分泌量可直接反映免疫功能状况[47]。如图6(b)、(c)、(d)所示,黑木耳发酵液和黑木耳酶解液以浓度依赖性方式显著诱导细胞因子IL-β的分泌,但对于IL-6和TNF-α样品无浓度依赖性。在浓度为1000 μg/mL时,木耳发酵液的IL-6含量为86.52±1.27 pg/mL,IL-β和TNF-α的产生量分别为72.50±1.29 pg/mL和144.61±3.04 pg/mL,与空白对照相比,增加约1.3和1.16倍,与LPS阳性对照无显著差异。因此,可以得出结论,黑木耳发酵液可以作为潜在的免疫刺激剂来诱导促炎细胞因子如TNF-α和IL-β的产生。据报道,来自其他乳酸杆菌菌株的胞外多糖在对小鼠巨噬细胞产生炎症介质的影响方面显示出免疫调节潜力[48]。多糖通过识别并结合巨噬细胞表面的特定受体来激活巨噬细胞,从而引发免疫反应并发挥免疫调节作用。
3. 结论
本研究探索了酶解与乳杆菌发酵联合处理对黑木耳液成分和结构的变化及其抗氧化、体外降血糖降血脂活性、细胞免疫活性的影响。由结果可知,与未处理的黑木耳液相比,酶解与乳杆菌发酵联合处理可显著提高黑木耳发酵液中总糖、蛋白质及总酚的含量,增强对α-淀粉酶、α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制活性以及体外胆固醇吸附、胆酸盐结合能力,具有潜在的辅助治疗糖尿病和减缓肥胖等慢性疾病的功效。此外,黑木耳发酵液在一定浓度下还可以保护细胞氧化损伤,提高RAW264.7细胞的吞噬能力,促进细胞免疫因子TNF-α、IL-β、IL-6的释放,具有潜在的免疫效果。由此可见,酶解与发酵联合处理可以作为一种有效的食品加工技术, 增强黑木耳的生物活性。本研究为黑木耳精深加工的开发利用、为研发高附加值健康食品提供科学依据。但发酵过程变化非常复杂,菌种发酵特异性和具体作用机制还亟需进一步研究,功能强化相关性以及可能存在的协同增效作用也需进一步阐明。
-
表 1 各试剂添加量
Table 1 Addition amount of each reagent
分组 样品(μL) ABTS+工作液(μL) 蒸馏水(μL) 乙醇溶液(μL) 样品组(A2) 20 180 − − 对照组(A0) − − 20 180 空白组(A1) − 180 20 − 表 2 羟基自由基清除活性测定各试剂添加量
Table 2 •OH free radical scavenging activity determination of addition amount of each reagent
分组 FeSO4
(μL)水杨酸乙醇
(μL)H2O2
(μL)蒸馏水
(μL)样品
(μL)样品组(A2) 50 50 50 − 50 对照组(A1) 50 50 − 50 50 空白组(A0) 50 50 50 50 − 表 3 黑木耳液、酶解液、发酵液中总糖、蛋白质、灰分和总酚的含量
Table 3 Contents of total sugar, protein, ash and total phenol in liquid, enzymatic hydrolysate and fermentation broth of Auricularia auricularia
成分 木耳液 黑木耳酶解液 黑木耳发酵液 总糖(mg∙g−1) 170.57±11.67c 531.39±55.84b 539.14±44.58a 蛋白质(mg∙g−1) 15.00±2.02c 83.65±1.27a 81.28±2.19b 灰分(mg∙g−1) 2.05±0.05b 2.14±0.97a 2.08±1.33ab 总酚(mg∙g−1) 5.11±0.35c 7.46±2.15a 6.04±2.03b 注:同一行不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),表4同。 表 4 黑木耳液、酶解液、发酵液对油脂和胆固醇的吸附能力
Table 4 Adsorption capacity of Auricularia auricula liquid, enzymatic hydrolysate and fermentation broth for oil and cholesterol
指标 木耳液 黑木耳酶解液 黑木耳发酵液 胆固醇吸附量(mg∙g−1) 91.75±3.07c 148.19±4.05b 152.31±5.72a 脂肪吸附量(g∙g−1) 4.95±0.41c 5.21±0.22b 5.33±0.34a -
[1] 李定金, 段秋霞, 段振华, 等. 黑木耳功能性成分及其干燥技术研究进展[J]. 保鲜与加工,2020,20(6):233−237. [LI D J, DUAN Q X, DUAN Z H, et al. Research progress in functional components and drying technology of Auricularia auricula[J]. Storage and Process,2020,20(6):233−237. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6221.2020.06.036 [2] TAHIDUL I, KUMAR G, XU B Y. Insights into health-promoting effects of Jew's ear (Auricularia auricula-judae)[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2021,114:552−569.
[3] CHEN N N, ZHANG H, ZONG X, et al. Polysaccharides from Auricularia auricula: Preparation, structural features and biological activities[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2020,247:116750. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116750
[4] PAK S, CHEN F, MA L Y, et al. Functional perspective of black fungi (Auricularia auricula): Major bioactive components, health benefits and potential mechanisms[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2021,114:245−261.
[5] TIAN W N, DAI L W, LU S M, et al. Effect of Bacillus sp. DU-106 fermentation on Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide: Structure and immunoregulatory activities[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,135:1034−1042. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.203
[6] KWAW E, MA Y K, TCHABO W, et al. Effect of lactobacillus strains on phenolic profile, color attributes and antioxidant activities of lactic-acid-fermented mulberry juice[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,250:148−154. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.01.009
[7] TANG Y, ZHANG B, LI X, et al. Bound phenolics of quinoa seeds released by acid, alkaline, and enzymatic treatments and their antioxidant and α-glucosidase and pancreatic lipase inhibitory effects[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2016,64(8):1712−1719. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b05761
[8] QUINES V C, JEONG B G, KERR W L, et al. Antioxidative properties of eastern prickly pear (Opuntia humifusa) fermented with lactic acid bacteria and cell wall-hydrolyzing enzymes[J]. Food Science and Technology,2020,122:109029.
[9] WANG B Y, ZHAO N, LI J, et al. Selenium-enriched Lactobacillus plantarum improves the antioxidant activity and flavor properties of fermented Pleurotus eryngii[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,45:128770.
[10] 牟佳红, 梁安雯, 覃超琳, 等. 酶解与发酵联合处理对黑木耳还原糖含量及抗氧化性能的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(7):139−147. [MU J H, LIANG A W, QIN C L, et al. Effect of enzymatic hydrolysis combined with fermentation treatment on reducing sugar content and antioxidant performance of Auricularia auricula[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(7):139−147. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021070175 [11] LI J, GU F F, CAI C, et al. Purification, structural characterization, and immunomodulatory activity of the polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidum[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,143:806−813. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.09.141
[12] SONG S, LIU X Y, ZHAO B T, et al. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum fermentation on the chemical structure and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from bulbs of Lanzhou lily[J]. ACS omega,2021,6(44):29839−29851. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c04339
[13] 吕冰冰, 谢笔钧, 孙智达. 红肉番石榴果胶的理化特性及其体外降脂作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(20):51−60. [LÜ B B, XIE B J, SUN Z D. Physical and chemical properties of red-flesh guava pectin and its lipid-lowering effectin vitro[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(20):51−60. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021010091 [14] 孙凯峰, 包怡红. 微生物发酵对黑木耳总糖含量和体外调脂活性的影响[J]. 中草药,2018,49(16):3781−3787. [SUN K F, BAO Y H. Effect of microbial fermentation on total sugar content and in vitro hypolipidemic effect of Auricularia auricula[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2018,49(16):3781−3787. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2018.16.009 [15] 唐茹萌, 焦文雅, 桑亚新, 等. 裙带菜多糖体外和体内降血脂活性[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(1):142−149. [TANG R M, JIAO W Y, SANG Y X, et al. In vitro and in vivo hypolipidemic effect of Undaria pinnatififida polysaccharide[J]. Food Science,2022,43(1):142−149. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20210108-087 [16] 陈玥彤, 张闪闪, 李文意, 等. 黑木耳多糖的磷酸化修饰、结构表征及体外降糖活性[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(8):29−35. [CHEN Y T, ZHANG S S, LI W Y, et al. Structural characterization and hypoglycemic effect in vitro of phosphorylated Auricularia auriculata polysaccharide[J]. Food Science,2022,43(8):29−35. [17] 刘萌. 香菇多糖结构特征及降糖作用研究[D]. 西安: 陕西科技大学, 2020. LIU M. Study on the structural characteristics and hypoglycemic effect of lentinan[D]. Xi'an: Shaanxi University of Science & Technology, 2020.
[18] 姚旭, 郦萍, 顾青. 4种甜橙皮黄酮类化合物体外抗氧化活性及降糖降脂功能研究[J]. 中国食品学报,2022,22(1):49−57. [YAO X, Li P, GU Q. Study on antioxidant activity, hypoglycemic and lipid-lowering function of four flavonoids from sweet orange peel in vitro[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2022,22(1):49−57. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2022.01.006 [19] XU Y Y, SHEN M, CHEN Y D, et al. Optimization of the polysaccharide hydrolysate from Auricularia auricula with antioxidant activity by response surface methodology[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,113:543−549. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.02.059
[20] 张雪娇, 刘登勇, 王惠民. 羟脯氨酸小肽的体外抗氧化活性[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(5):55−60. [ZHANG X J, LIU D Y, WANG H M. Antioxidant activity in vitro of hydroxyproline peptides[J]. Food Science,2021,42(5):55−60. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200310-172 [21] ZHANG Q A, WANG X, SONG Y, et al. Optimization of pyrogallol autoxidation conditions and its application in evaluation of superoxide anion radical scavenging capacity for four antioxidants[J]. Journal of AOAC International,2016,99(2):504−511. doi: 10.5740/jaoacint.15-0223
[22] FANG Y, CHEN X, LUO P Z, et al. The correlation between in vitro antioxidant activity and immunomodulatory activity of enzymatic hydrolysates from selenium-enriched rice protein[J]. Journal of Food Science,2017,82(2):517−522. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.13595
[23] WU J H, LI M X, LIU L, et al. Nitric oxide and interleukins are involved in cell proliferation of RAW264.7 macrophages activated by viili exopolysaccharides[J]. Inflammation,2013,36(4):954−961. doi: 10.1007/s10753-013-9626-y
[24] 李伟, 叶嘉宜, 陈运娇, 等. 桉叶多酚提取物体内外抗氧化活性评价[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(5):160−168. [LI W, YE J Y, CHEN Y J, et al. Antioxidant activity of eucalyptus leaf polyphenol extract in vitro and in vivo[J]. Food Science,2021,42(5):160−168. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200130-289 [25] BAO Z J, YAO L Q, ZHANG X Y, et al. Isolation, purification, characterization, and immunomodulatory effects of polysaccharide from Auricularia auricula on RAW264.7 macrophages[J]. Journal of Food Biochemistry,2020,44(12):e13516.
[26] ISLAM T, YAO F J, KANG W Y, et al. A systematic study on mycochemical profiles, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory activities of 30 varieties of Jew’s ear (Auricularia auricula-judae)[J]. Food Science and Human Wellness,2022,11(4):781−794. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2022.03.005
[27] ZIELINSKI H, SZAWARANOWAK D, BACZEK N, et al. Effect of liquid-state fermentation on the antioxidant and functional properties of raw and roasted buckwheat flours[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,271:291−297. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.07.182
[28] WU Z Z, XU E B, LONG J, et al. Use of attenuated total reflectance mid-infrared spectroscopy for rapid prediction of amino acids in Chinese rice wine[J]. Journal of Food Science,2015,80(8):C1670−C1679. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.12961
[29] TANG J, NIE J, LI D P, et al. Characterization and antioxidant activities of degraded polysaccharides from Poria cocos sclerotium[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2014,105:121−126. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.01.049
[30] NGUYEN T L, WANG D Y, HU Y L, et al. Immuno-enhancing activity of sulfated Auricularia auricula polysaccharides[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2012,89(4):1117−1122. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.03.082
[31] MA G X, KIMATU B M, ZHAO L Y, et al. In vivo fermentation of Pleurotus eryngii polysaccharide and its effects on fecal microbiota composition and immune response[J]. Food & Function,2017,8(5):1810−1821.
[32] WANG Z B, PEI J J, MA H L, et al. Effect of extraction media on preliminary characterizations and antioxidant activities of Phellinus linteus polysaccharides[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2014,109:49−55. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.03.057
[33] HE P F, ZHANG A Q, ZHANG F M, et al. Structure and bioactivity of a polysaccharide containing uronic acid from Polyporus umbellatus sclerotia[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2016,152:222−230. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.07.010
[34] 黄尚林. 西藏黑木耳粗多糖降血脂活性的研究[D]. 林芝: 西藏农牧学院, 2021. HUANG S L. Study on hypolipidemic activity of crude polysaccharide from Xizang Auricularia auriculata[D]. Linzhi: Tibet Agricultural and Animal Husbandry University, 2021.
[35] KATALINIC V, MILOS M, KULISIC T, et al. Screening of 70 medicinal plant extracts for antioxidant capacity and total phenols[J]. Food Chemistry,2004,94(4):550−557.
[36] DIEZOZAETA I, ASTIAZARAN O J. Fermented foods: An update on evidence-based health benefits and future perspectives[J]. Food Research International,2022,156:111133. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111133
[37] WANG Y, ANDRUKHOV O, RAUSCH-FAN X. Oxidative stress and antioxidant system in periodontitis[J]. Frontiers in Physiology,2017,8:910. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00910
[38] WU Q, QIN D D, CAO H X, et al. Enzymatic hydrolysis of polysaccharide from Auricularia auricula and characterization of the degradation product[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,162:127−135. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.098
[39] NIEVESCORDONES M, LOPEZDELACALLE M, RODENAS R, et al. Critical responses to nutrient deprivation: A comprehensive review on the role of ROS and RNS[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany,2019,161:74−85. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.10.039
[40] MIAO J N, WANG S, ZHANG J Q, et al. Response surface methodology for the fermentation of polysaccharides from Auricularia auricula using Trichoderma viride and their antioxidant activities[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,155:393−402. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.03.183
[41] LIU J B, CHEN Z F, HE J, et al. Anti-oxidative and anti-apoptosis effects of egg white peptide, Trp-Asn-Trp-Ala-Asp, against H2O2-induced oxidative stress in human embryonic kidney 293 cells[J]. Food & Function,2014,5(12):3179−3188.
[42] HAN J H, JIN C N, ZHONG Y J, et al. Involvement of NADPH oxidase in patulin-induced oxidative damage and cytotoxicity in HEK293 cells[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2021,150:112055. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2021.112055
[43] XU S Q, ZHANG Y J, JIANG K. Antioxidant activity in vitro and in vivo of the polysaccharides from different varieties of Auricularia auricula[J]. Food & Function,2016,7(9):3868−3879.
[44] LU A X, YU M G, FANG Z Y, et al. Preparation of the controlled acid hydrolysates from pumpkin polysaccharides and their antioxidant and antidiabetic evaluation[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,121:261−269. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.09.158
[45] XIAO B, CHEN S, HUANG Q Q, et al. The lipid lowering and antioxidative stress potential of polysaccharide from Auricularia auricula prepared by enzymatic method[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,187:651−663. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.07.138
[46] ZHANG Y, ZENG Y, MEN Y, et al. Structural characterization and immunomodulatory activity of exopolysaccharides from submerged culture of Auricularia auricula-judae[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,115:978−984. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.04.145
[47] SEILLET C, BELZ G T, MIELKE L A. Complexity of cytokine network regulation of innate lymphoid cells in protective immunity[J]. Cytokine,2014,70(1):1−10. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2014.06.002
[48] CISZEKLENDA M, NOWAK B, SROTTEK M, et al. Immunoregulatory potential of exopolysaccharide from Lactobacillus rhamnosus KL37: Effects on the production of inflammatory mediators by mouse macrophages[J]. International Journal of Experimental Pathology,2011,92(6):382−391. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2613.2011.00788.x
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 卯明娟,洪鹏,刘迪,陆源添,侯立娟. 黑木耳菌株活力检测及优良菌株筛选. 中国瓜菜. 2025(02): 66-74 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)










 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:



