Antioxidant Activity and Tyrosinase Inhibitory Activity of Three Phenolic Compounds from Quezui Tea
-
摘要: 为深入挖掘雀嘴茶的利用价值,本文以其中含量丰富的6'-O-咖啡酰熊果苷(CA)、β-熊果苷和绿原酸三大酚类成分为研究对象,对其抗氧化活性和酪氨酸酶抑制活性进行分析。结果表明,雀嘴茶三大酚类成分均表现出较好的抗氧化活性,6'-O-咖啡酰熊果苷(CA)、β-熊果苷和绿原酸清除DPPH自由基的IC50值分别为13.56±0.14、104.41±6.52和8.42±0.21 μg/mL,清除ABTS+自由基的IC50值分别为18.01±0.06、50.60±1.25和26.93±0.38 µg/mL,清除OH自由基的IC50值为2.64±0.06、>10.00和<1.00 mg/mL,对铁离子总还原能力的强度依次为绿原酸>CA>β-熊果苷;雀嘴茶三大酚类成分对酪氨酸酶的抑制活性差异较大,CA对酪氨酸酶兼具单酚酶和二酚酶抑制作用,其IC50值分别为1.114±0.035和95.198±1.117 μmol/L,β-熊果苷仅有单酚酶抑制作用,IC50值为681.335±17.975 μmol/L,绿原酸既无单酚酶抑制作用,也无二酚酶抑制作用。研究结果为雀嘴茶中活性成分的开发利用提供了重要参考。
-
关键词:
- 雀嘴茶 /
- 6'-O-咖啡酰熊果苷 /
- 抗氧化活性 /
- 酪氨酸酶抑制剂
Abstract: In order to deeply explore the utilization value of Quezui tea, the antioxidant activity and tyrosinase inhibitory activity of its three phenolic compounds including 6'-O-caffeoylarbutin (CA), β-arbutin, and chlorogenic acid were analyzed in this study. The results indicated that all three phenolic compounds of Quezui tea had excellent antioxidation activity. The IC50 values of CA, β-arbutin, and chlorogenic acid on DPPH radical scavenging were 13.56±0.14, 104.41±6.52 and 8.42±0.21 μg/mL, respectively. The IC50 values of ABTS+ radical scavenging were 18.01±0.06, 50.60±1.25 and 26.93±0.38 µg/mL, respectively. The IC50 values of OH radical scavenging were 2.64±0.06, >10.00 and <1.00 mg/mL, respectively. The intensity of total iron reduction was in the order of chlorogenic acid>CA>β-arbutin. In addition, the inhibitory activities of all three phenolic compounds of Quezui tea were significantly different. CA had inhibitory effects on both monophenolase and diphenolase activities with IC50 values of 1.114±0.035 and 95.198±1.117 μmol/L, respectively. β-arbutin only had inhibitory effects on monophenolase activities with IC50 value of 681.335±17.975 μmol/L, and chlorogenic acid had no inhibitory effect on either monophenolase activity or diphenolase activity. The results would provide an important foundation for the development and utilization of the active compounds from Quezui tea.-
Keywords:
- Quezui tea /
- 6'-O-caffeoylarbutin /
- antioxidant activity /
- tyrosinase inhibition
-
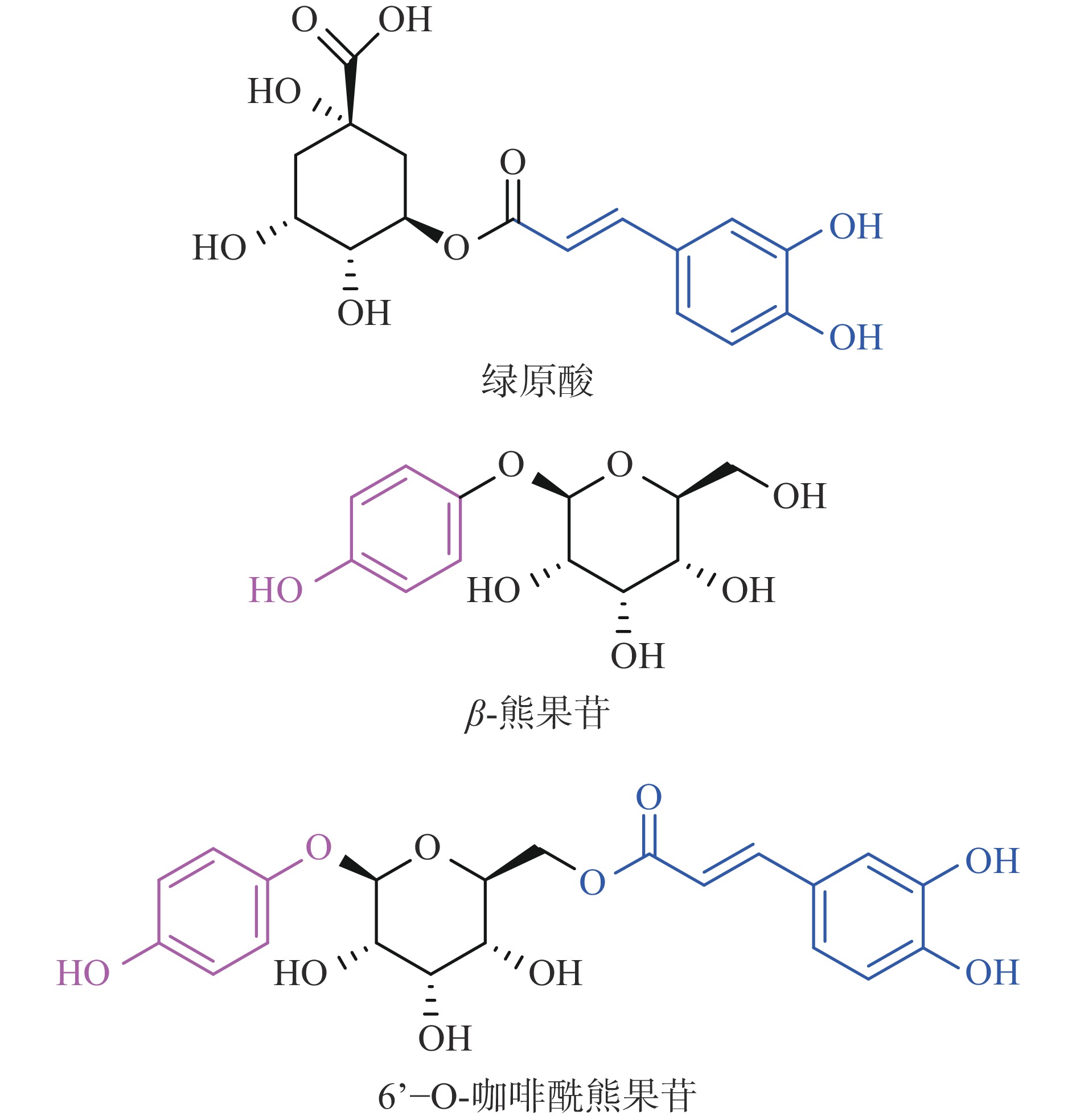
“雀嘴茶”由野生樟叶越桔(Vaccinium dunalianum Wight)顶芽或幼嫩叶[1]经杀青、干燥后炮制而得,在云南滇中彝族民间历来作为保健茶品,常饮有降血脂血压、软化血管、清热解毒、祛风除湿、舒筋活络的功效[2-3]。Wang等[4]发现雀嘴茶提取物有效地保护乙酰氨基酚的肝脏毒性,Zhang等[5]发现雀嘴茶可以减轻高脂食品引发的非酒精性脂肪肝,Gao等[6]发现雀嘴茶提取物抑制细胞凋亡以及维持细胞形态,具有潜在的神经保护活性。然而提取物成分复杂,难以深入研究药效机制,有必要从中挖掘具有明确分子结构的活性物质。Zhao等[7-10]最早从雀嘴茶中分离出10余种具有咖啡酰基的酚类化合物,并发现6'-O-咖啡酰熊果苷(CA,20%~25%)、β-熊果苷(12%~18%)和绿原酸(4%~8%)是其中含量较高的三个酚类化合物,对应的结构如图1所示。
根据三个化合物的结构,可以发现CA的结构中同时具有β-熊果苷的对苯酚结构、绿原酸的邻苯二酚结构和共轭结构。大多数酚类物质具有很强的抗氧化活性,可清除机体新陈代谢产生的大量自由基,防止器官被氧化损伤,及时将毒素排出体外,有效预防高血脂、高血糖、心脑血管疾病。许多学者也对CA的生物活性进行了研究,Liu等[11]发现CA对血小板聚集有抑制作用,具有抗血栓栓塞的作用,凌琳[12]发现CA可以降低血清尿酸,孔令朋[2]发现CA可以改善I型糖尿病的血糖水平,具有保护肝脏、肾脏和胰腺的作用。此外,Xu等[13-14]发现CA具有比β-熊果苷更强的黑色素抑制活性、更低的毒性和更高的安全性,作为β-熊果苷的替代资源极具挖掘潜力。目前国内外对于雀嘴茶的研究报道相对集中于活性成分分析、种质资源调查及快速繁殖体系建立、基因克隆等[15-16],对其主要活性成分的生物活性和作用机制几乎空白。本文通过研究雀嘴茶中三个主要酚性成分CA、β-熊果苷和绿原酸的抗氧化活性和酪氨酸酶抑制能力,从而进一步深入了解雀嘴茶主要活性成分的价值,以期为雀嘴茶的深度开发利用提供数据支撑和理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
CA、β-熊果苷、绿原酸 经高效液相色谱检测纯度均>90%,实验室自制;丙酮、乙酸乙酯、甲醇(色谱纯)、石油醚、二氯甲烷、甲醇(分析纯) 天津市致远化学试剂有限公司;无水乙醇、过硫酸钾、七水合硫酸亚铁(>99%)、水杨酸、30%过氧化氢、磷酸盐缓冲液(pH6.6)、铁氰化钾、三氯乙酸、氯化铁 分析纯,广东光华科技股份有限公司;硅胶(分析纯)、2,2-二苯基-1-苦基肼(DPPH)(>98%)、2,2-联氮-二(3-乙基-苯并噻唑-6-磺酸)二铵盐(ABTS)(>98%)、蘑菇酪氨酸酶(EC 1.14.18.1)、L-多巴(>99%)、L-酪氨酸(>99%)、抗坏血酸(分析纯) 上海泰坦科技股份有限公司;去离子水 实验室自制。
Agilent 1260 Infinity高效液相色谱仪 美国安捷伦科技(中国)有限公司;SpectraMax® 190光吸收型全波长酶标仪 美谷分子仪器(上海)有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 雀嘴茶中CA、β-熊果苷和绿原酸的分离
根据文献[7]的方法稍做修改。经粉碎的雀嘴茶粉末首先于室温中于水-丙酮(4:6,v/v)混合溶液中浸提过夜,提取液经浓缩除去丙酮、乙酸乙酯脱脂后放置过夜即得CA;剩余滤液经柱层析即得β-熊果苷和绿原酸。
1.2.2 抗氧化活性研究
1.2.2.1 DPPH自由基清除能力
参照文献[17-18]报道的方法稍做修改。以乙醇为溶剂配制成浓度为0.10 mg/mL的DPPH自由基溶液,在96孔板中加入100 µL待测试样溶液和100 µL DPPH自由基溶液混合均匀,避光反应30 min,设定波长为517 nm测定吸光度,每个样品平行测定三次。以抗坏血酸为阳性对照。按下式(1)计算DPPH自由基清除率,并计算出其半数清除质量浓度(IC50):
DPPH自由基清除率(%)=[1−(As1−Ab1)∕Ac1]×100 (1) 式中:As1为实验组(样品溶液与DPPH自由基溶液)的吸光度;Ab1为空白实验组(样品溶液与无水乙醇)的吸光度;Ac1为对照实验组(水与DPPH自由基溶液)的吸光度。
1.2.2.2 ABTS+自由基清除能力
参照文献[17-18]报道的方法稍做修改。将7.4 mmol/L ABTS溶液和2.45 mmol/L过硫酸钾溶液混合避光12~16 h,获得ABTS+自由基溶液,用蒸馏水稀释,使其在734 nm处吸光值达到0.70±0.02。在96孔板中加入40 µL待测试样溶液和160 µL的ABTS+自由基溶液,室温避光反应8 min在734 nm处测得吸光值,每个样品平行测定三次,按下式(2)计算ABTS+自由基清除率,并计算出其半数清除质量浓度(IC50):
ABTS+自由基清除率(%)=[1−(As2−Ab2)/Ac2]×100 (2) 式中:As2为实验组(样品溶液与ABTS+自由基溶液)的吸光度;Ab2为空白实验组(样品溶液与水)的吸光度;Ac2为对照实验组(水与ABTS+自由基溶液)的吸光度。
1.2.2.3 羟基自由基清除能力
参照文献[19]报道的方法稍做修改。在离心管中加入50 µL 9.0 mmol/L的硫酸亚铁溶液、50 µL 9.0 mmol/L水杨酸和50 µL 8.8 mmol/L 30%的过氧化氢溶液,再加入50 µL样品,充分混合后室温反应1 h,在510 nm处测得吸光值,每个样品平行测定三次,按下式(3)计算羟基自由基清除率,并计算出其半数清除质量浓度(IC50):
羟基自由基清除率(%)=[1−(As3−Ab3)∕Ac3]×100 (3) 式中:As3为实验组(样品溶液)的吸光度;Ab3为空白实验组(样品溶液与氧化氢溶液)的吸光度;Ac3为对照实验组(水)的吸光度。
1.2.2.4 铁离子还原能力
参照文献[20]报道的方法稍做修改。在反应体系中加入200 µL待测溶液与200 µL的0.1 mmol/L磷酸盐缓冲液的0.1%氯化铁溶液,然后将反应液避光静置10 min后,在700 nm波长下读取吸光度。
1.2.3 酪氨酸酶抑制活性研究
参照文献[21-22]的方法稍做修改以测定酪氨酸酶的抑制活性。将150 μL 1 mmol/L的L-酪氨酸(单酚酶抑制活性)或0.5 mmol/L L-多巴(二酚酶抑制活性)分别与30 μL样品充分混合均匀后,加入30 ℃孵育的31.25 U/mL酪氨酸酶溶液(溶于PBS溶液中),在475 nm(ε=3600 mol−1·L·cm−1)处测得吸光值。按式(4)计算酶活抑制率,并计算出其半数抑制质量浓度(IC50):
酶活抑制率(%)=(1−R/R0)×100 (4) 式中:R为有抑制剂反应得到的反应动力学方程的斜率;R0为无抑制剂反应得到的反应动力学方程的斜率。
1.3 数据处理
所有测试均做3组平行实验,并采用Origin软件进行数据处理分析,处理结果以平均值±标准差表示。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 抗氧化活性研究
2.1.1 DPPH自由基清除能力
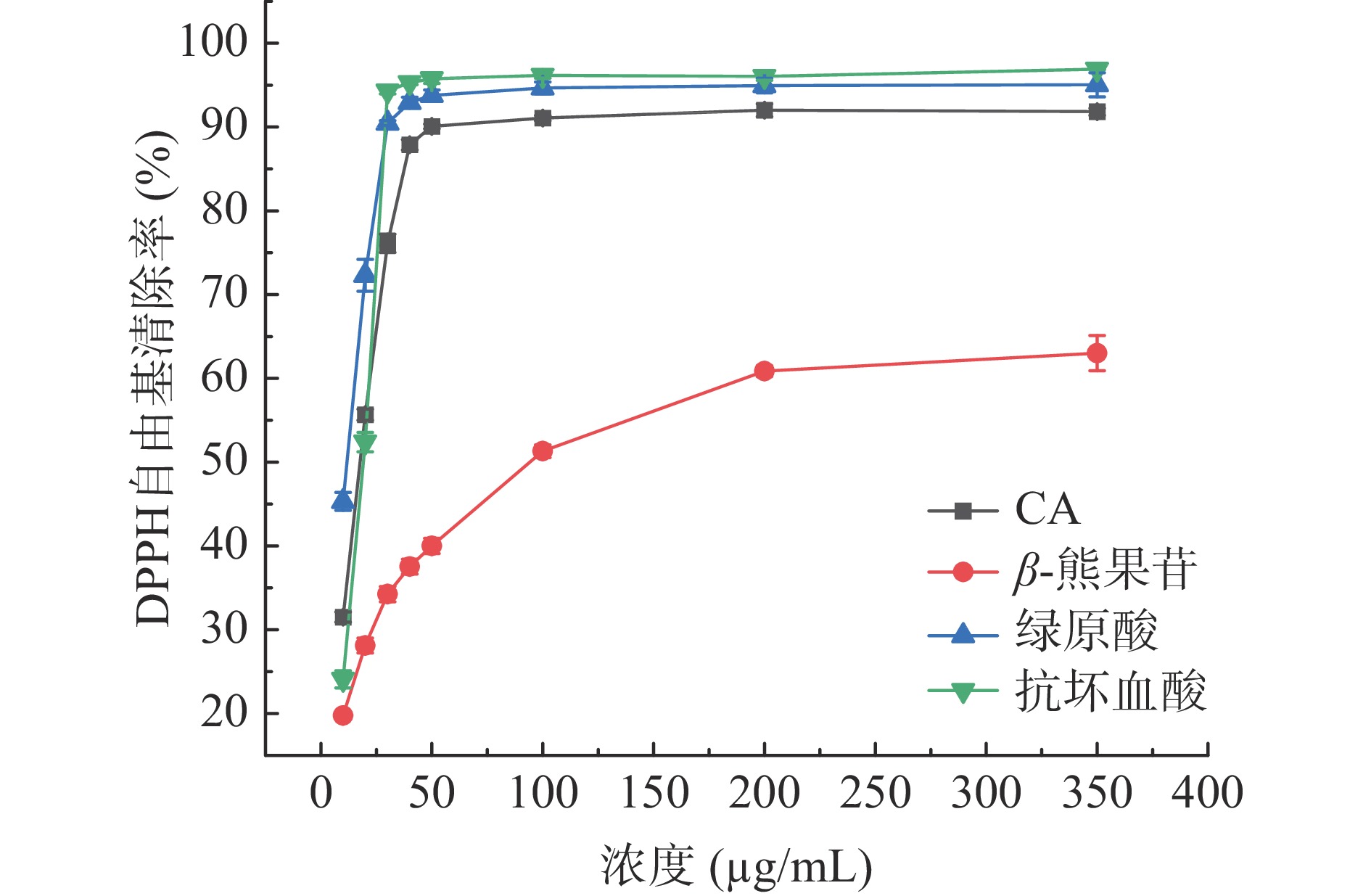
对CA、β-熊果苷和绿原酸清除DPPH自由基的实验结果如图2所示。
根据计算可得CA、β-熊果苷、绿原酸与抗坏血酸清除DPPH自由基的IC50分别是13.56±0.14、104.41±6.52、8.42±0.21和15.09±0.05 μg/mL。结果表明,CA和绿原酸的DPPH自由基清除率优于对照品抗坏血酸,而且随着浓度的增加,CA、绿原酸和抗坏血酸的DPPH自由基清除率逐渐增加,当浓度增加到350 μg/mL时,清除率分别达到92%、95%和97%。相较而言,β-熊果苷的清除能力较弱,浓度350 μg/mL时,清除率仅为63%。酚类化合物的酚羟基易提供质子氢给自由基,从而阻止自由基的反应,达到清除自由基的目的。CA、β-熊果苷、绿原酸的结构中均有酚羟基,但其位置和数量的差异会影响化合物的供氢能力,进而极大影响自由基清除能力,其中位置的影响最大,数量次之[23]。因此,有邻位羟基的CA和绿原酸表现出较好的DPPH自由基清除能力,只有一个对位酚羟基的β-熊果苷由于供氢能力较弱而表现出较低的清除能力。
2.1.2 ABTS+自由基清除能力
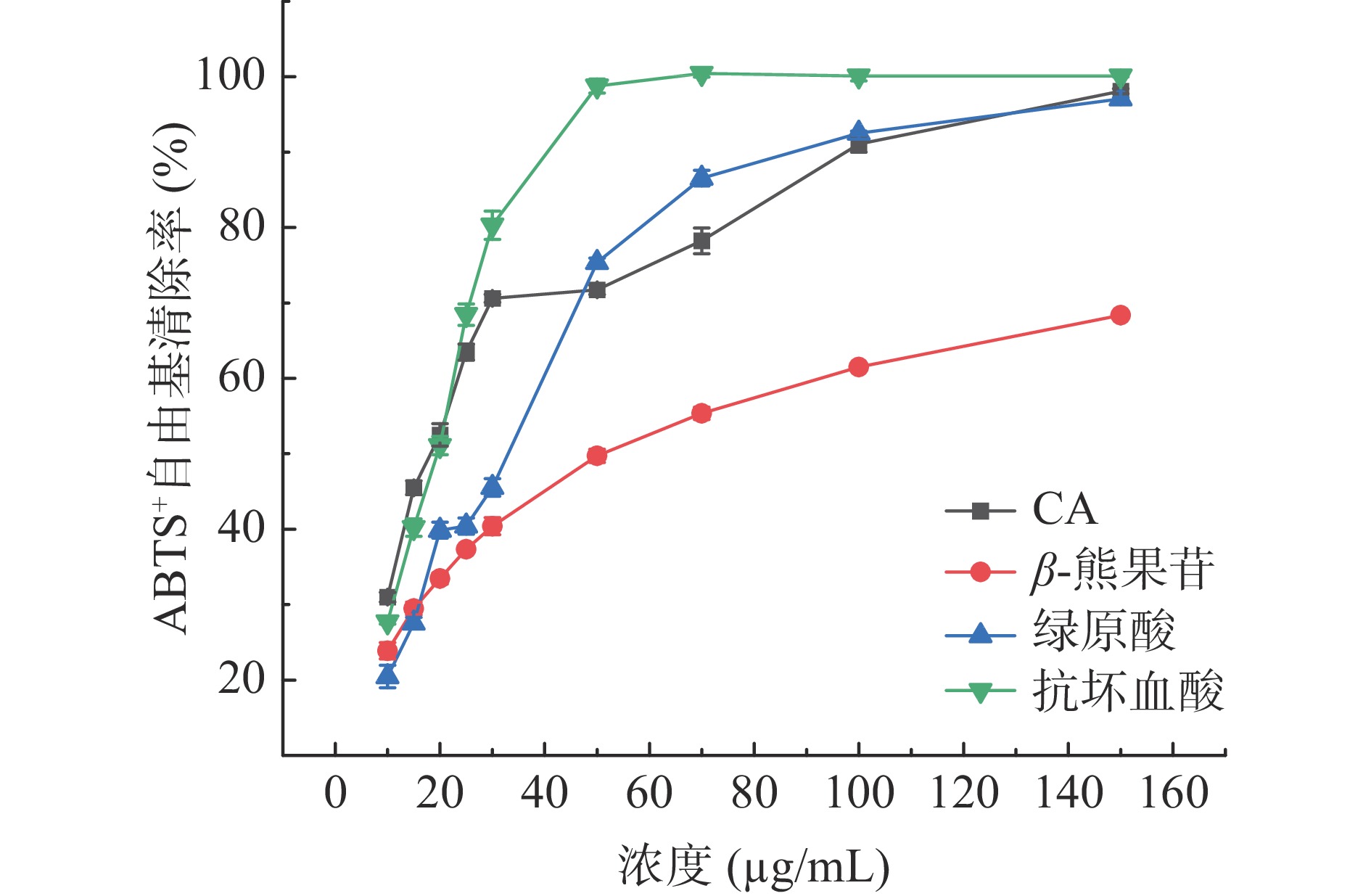
对CA、β-熊果苷和绿原酸清除ABTS+自由基的实验结果如图3所示。
根据计算可得CA、β-熊果苷、绿原酸与抗坏血酸清除ABTS+自由基的IC50分别为18.01±0.06、50.60±1.25、26.93±0.38和17.20±0.09 µg/mL。由图3可知,抗坏血酸的ABTS+自由基清除能力优于CA、绿原酸和β-熊果苷。在10~50 µg/mL的低浓度范围内,CA的ABTS+自由基清除率较好,与抗坏血酸接近,且高于绿原酸,可能CA相对较多的酚羟基有关。但随着浓度继续升高,CA对ABTS+自由基清除能力降低,主要是因为CA溶解较差,进而影响了其对ABTS+自由基清除能力。当浓度增加到150 µg/mL时,CA、绿原酸和抗坏血酸的ABTS+自由基清除率分别达到98%、97%和100%,β-熊果苷对ABTS+自由基清除的能力较弱,浓度为150 µg/mL时,清除率仅为68%。
2.1.3 OH自由基清除能力
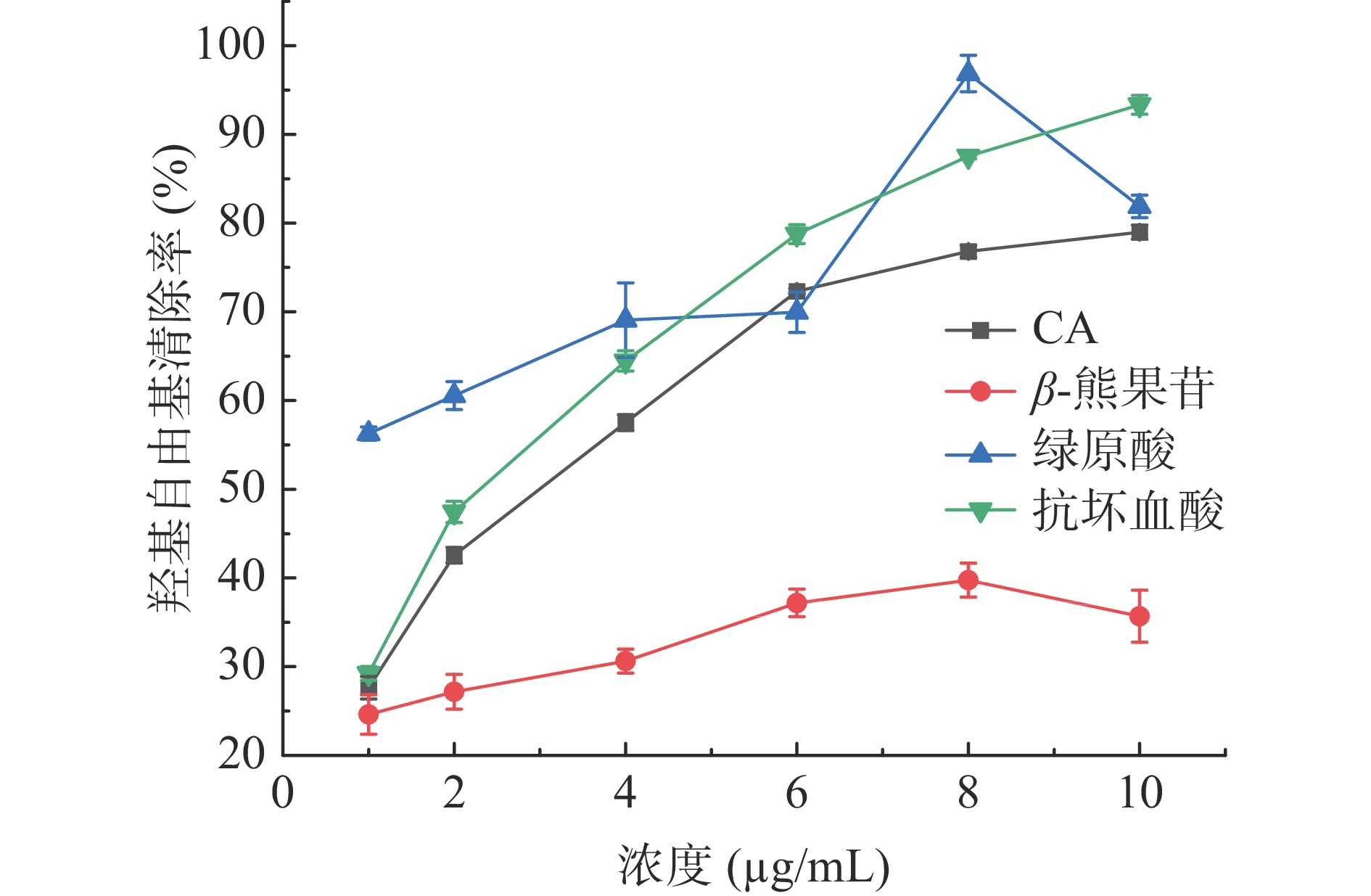
CA、β-熊果苷和绿原酸清除OH自由基的实验结果如图4所示。
根据计算可得CA、β-熊果苷、绿原酸与抗坏血酸清除OH自由基的IC50分别为2.64±0.06、>10.00、<1.00和2.12±0.03 mg/mL。结果表明,CA、绿原酸和抗坏血酸对OH自由基清除率远高于β-熊果苷,当浓度达到10 mg/mL时,清除率分别为78%、82%和93%,而β-熊果苷的浓度达10 mg/mL时,清除率仅为35%。羟基自由基是体内最活泼的活性氧,可诱导多种病理变化,虽然绿原酸对OH自由基清除率随着浓度的升高有一定的波动,但根据IC50值和图4中浓度在4 mg/mL之前的OH自由基清除率来看,绿原酸对羟基自由基清除能力要高于CA、β-熊果苷与抗坏血酸,主要可能是因为绿原酸不仅具有较多的供氢体,从而使具有高度氧化性的自由基还原,同时在清除OH自由基的同时不会产生二级自由基分子[24]。
2.1.4 铁离子还原能力
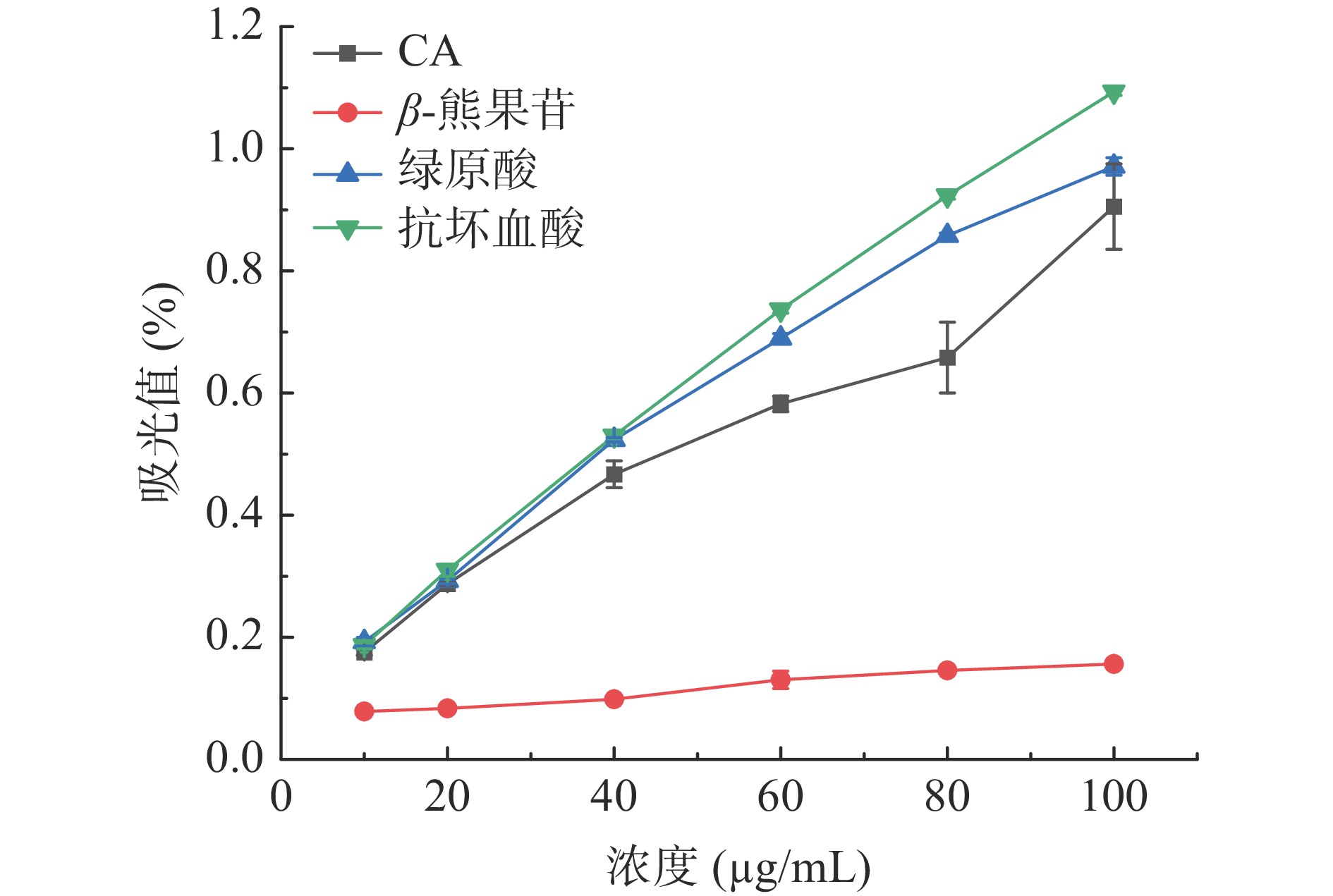
对CA、β-熊果苷和绿原酸的铁离子还原能力实验结果如图5所示。
由图5可知,随着CA、β-熊果苷、绿原酸与抗坏血酸浓度增加,吸光值也在增加,表明其还原能力与浓度正相关。在低浓度时,CA、绿原酸与抗坏血酸的吸光值差异不大,但随着浓度增加,差异逐渐增加,当浓度为100 µg/mL时,抗坏血酸吸光值>绿原酸吸光值>CA吸光值。对于β-熊果苷,吸光度随着化合物浓度变化较小,与其他三个化合物表现出大的吸光值差异。由此反映出抗氧化能力由高到低依次为:抗坏血酸>绿原酸>CA>β-熊果苷。CA、β-熊果苷和绿原酸三者均能供氢,但在该情况下均不及抗坏血酸,而β-熊果苷只有一个酚羟基供氢能力远不如CA与绿原酸。
酚类化合物作为氢供体,是应用最广泛的抗氧化剂。CA、β-熊果苷、绿原酸的结构中具有还原性羟基功能基团,自由基能从苯酚结构中捕获氢而生成氢过氧化物得以清除。张华等[25]、袁博等[26]发现酚类化合物的抗氧化活性主要取决于其含有的酚羟基数目和空间位阻。绿原酸与CA拥有比β-熊果苷更多的酚羟基。因此,CA和绿原酸具有较强的DPPH、ABTS+、OH自由基清除能力和铁离子还原能力,β-熊果苷而对自由基清除能力和铁离子还原能力相对于CA和绿原酸较弱。此外,绿原酸与其他抗氧化剂不同的是在清除羟基自由基的同时不会产生二级自由基分子,因此绿原酸清除羟基自由基能力高于其他抗氧化剂。
2.2 酪氨酸酶抑制活性研究
为深入挖掘具有明确分子结构的酪氨酸酶抑制剂,进一步对雀嘴茶提取物中的三个主要活性成分CA、β-熊果苷和绿原酸进行了酪氨酸酶抑制活性研究,结果如表1所示。结果表明CA和β-熊果苷具有较好的酪氨酸酶抑制活性,而绿原酸对酪氨酸酶没有抑制活性。
表 1 雀嘴茶三大酚类成分抑制酪氨酸酶活性IC50值Table 1. IC50 values of tyrosinase inhibition capacity of three phenolic compounds from Quezui tea样品名称 单酚酶
(μmol/L)二酚酶
(μmol/L)CA 1.114±0.035 95.198±1.117 β-熊果苷 681.335±17.975 无抑制 绿原酸 无抑制 无抑制 2.2.1 单酚酶抑制活性
为进一步考察CA和β-熊果苷浓度与其抑制酪氨酸酶活性的关系,首先以L-酪氨酸为底物,不同浓度CA和β-熊果苷为抑制剂,测定单酚酶抑制活性。结果如图6a和图6b所示,由表1和图6可知,CA和β-熊果苷对酪氨酸酶表现出较好的单酚酶抑制活性。当CA的浓度为0.02 μmol/L时,对单酚酶的抑制作用为85%以上,但随着浓度的增高,CA对单酚酶的抑制率反而减小,其IC50值为1.114±0.035 μmol/L。当β-熊果苷浓度为2500 μmol/L时,熊果苷对单酚酶的抑制率为76%左右,IC50为681.335±17.975 μmol/L,远低于CA。
2.2.2 二酚酶抑制活性
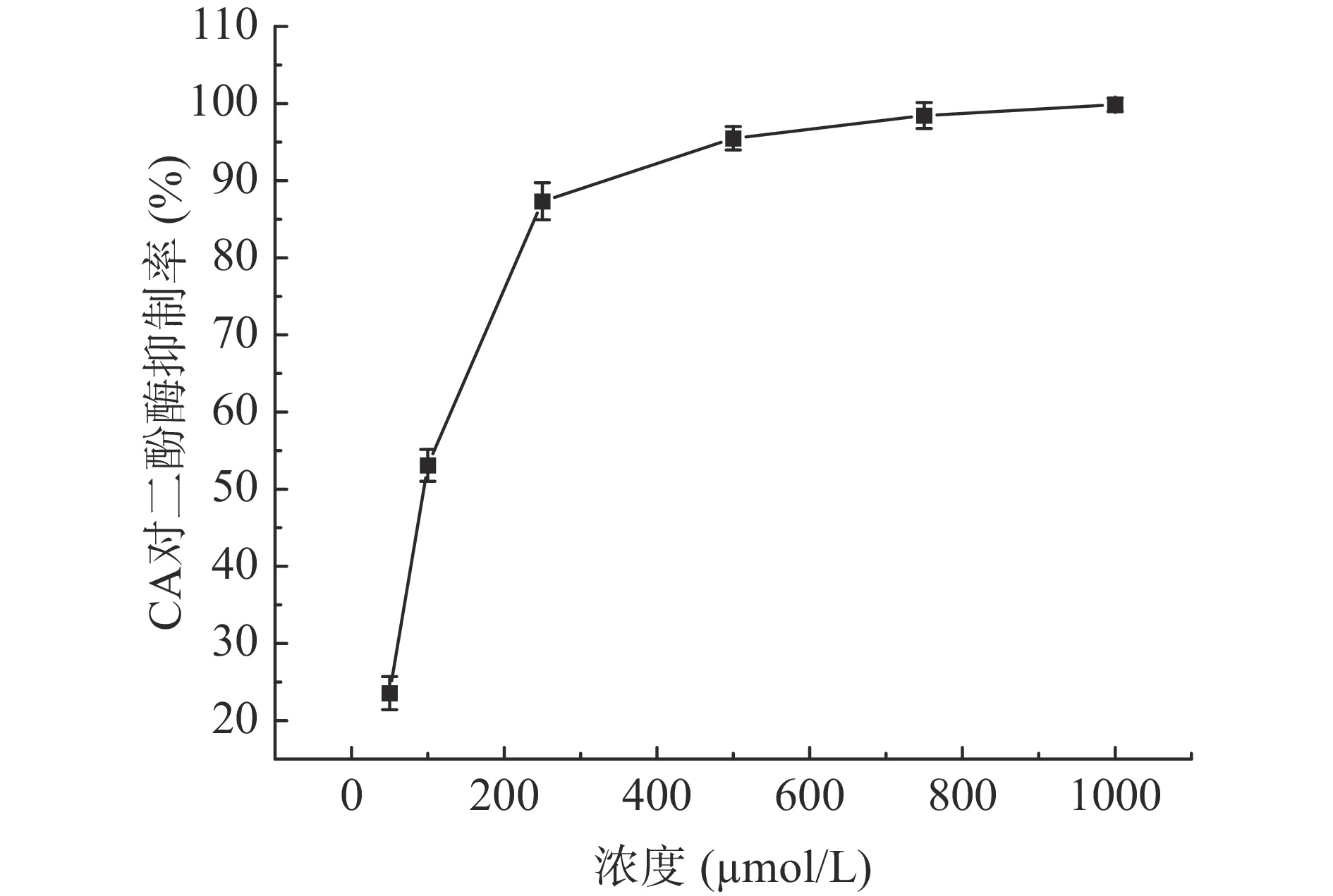
其次以L-多巴为底物,不同浓度CA为抑制剂,测定二酚酶抑制活性,结果如图7所示。
由表1可知CA对酪氨酸酶表现出较好的二酚酶抑制活性,其IC50数值是95.198±1.117 μmol/L。β-熊果苷与绿原酸无二酚酶抑制活性。由图7可知,随着CA的浓度的增加,对酪氨酸酶酶活的抑制率也在增加,其浓度与酪氨酸酶抑制率成正相关。当CA浓度达1000 μmol/L时,对酪氨酸酶酶活的抑制作用大于99.8%。
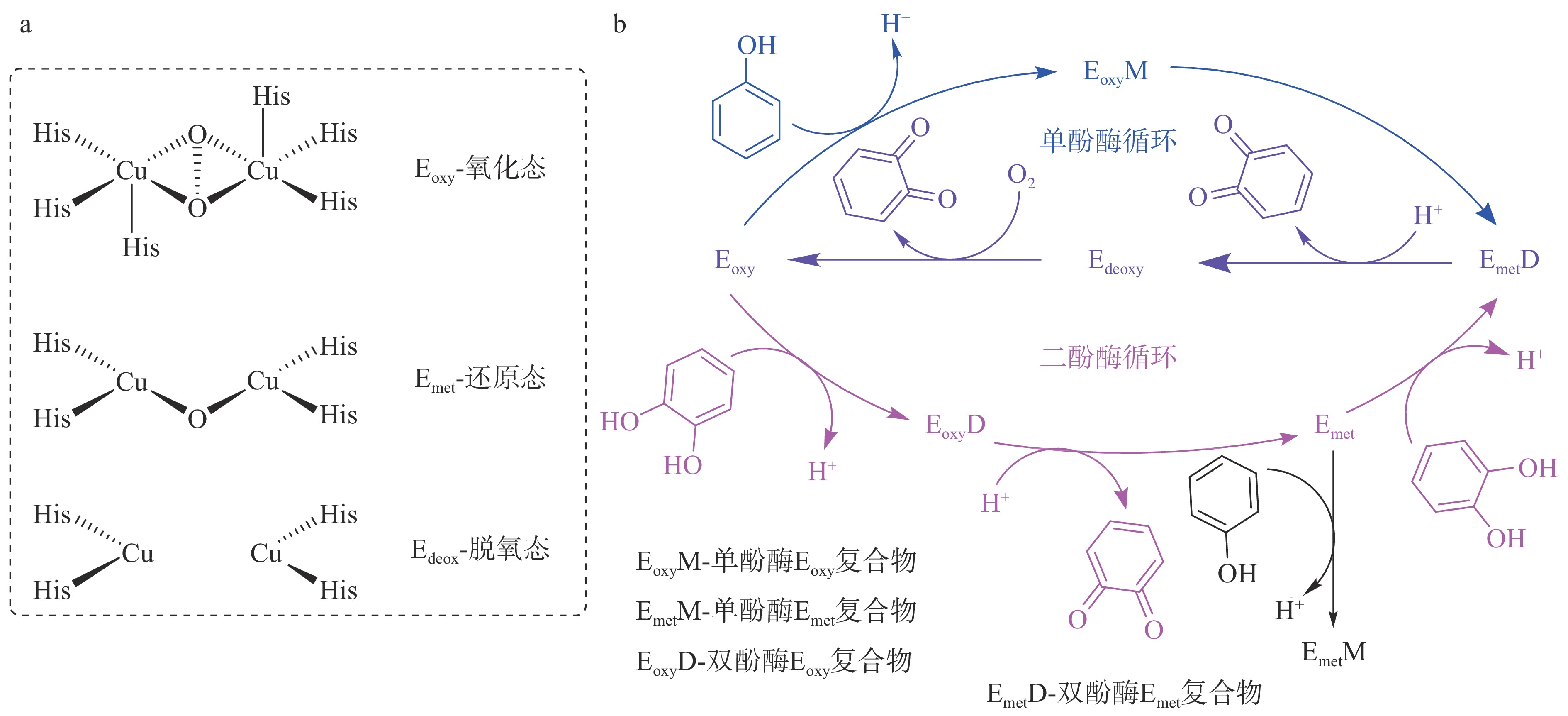
酪氨酸酶是一种多酚氧化酶(Polyphenol Oxidase,PPO),属氧化还原酶类,在哺乳动物中称为酪氨酸酶[27-28],在昆虫中称为酚氧化酶(Phenol Oxidase,PO),作为一种III型铜蛋白家族的疏水性膜结合蛋白,酪氨酸酶的活性中心含有2个通过内源桥基连接的Cu2+,每个Cu2+分别与3个组氨酸配位结合,其双核Cu2+在酶促反应中以氧化态、还原态和脱氧态3种不同形式传递氧(图8a),具有单酚酶和二酚酶活性(图8b),通过单酚酶循环催化一元酚羟基化生成邻二羟基化合物,通过二酚酶循环邻二酚氧化成邻二苯醌,且两个循环中均需氧自由基参与反应[29]。CA、β-熊果苷的结构[30]中均有单酚结构,因此可参与单酚循环,CA中还具有二酚酶结构,还可进一步参与到二酚酶循环中,而绿原酸只有二酚结构,无法参与单酚酶循环,无法启动该循环反应而不具有酪氨酸酶抑制活性。结果与CA、β-熊果苷和绿原酸对酪氨酸酶的抑制活性相符,即CA不仅具有优异的单酚酶抑制活性,还有较好的二酚酶抑制活性,β-熊果苷只具有较好的单酚酶抑制活性,绿原酸不具有酪氨酸酶抑制活性。
3. 结论
本文研究了雀嘴茶三个主要成分CA、β-熊果苷和绿原酸的抗氧化活性以及对酪氨酸酶活性的抑制作用。CA、绿原酸具有优异的抗氧化活性。CA清除DPPH自由基的能力优于抗坏血酸,清除ABTS+自由基和OH自由基的能力与抗坏血酸相当。绿原酸清除DPPH自由基和OH自由基的能力优于抗坏血酸,但清除ABTS+自由基的能力较抗坏血酸低。β-熊果苷具有一定的抗氧化活性,但相对于CA和绿原酸其抗氧化活性较弱。在对酪氨酸酶抑制活性的实验中发现CA与β-熊果苷均具有单酚酶抑制活性,并且实验结果显示CA不但对单酚酶有优异的抑制活性,还具有良好的二酚酶抑制活性。因此,在天然产物中CA是理想的酪氨酸酶抑制剂,可作为美白产品的理想天然绿色添加剂。雀嘴茶中富含CA、β-熊果苷和绿原酸,具有较好的抗氧化活性,且一些成分具有良好的对酪氨酸酶抑制活性,因此具有较高的开发和应用价值。
-
表 1 雀嘴茶三大酚类成分抑制酪氨酸酶活性IC50值
Table 1 IC50 values of tyrosinase inhibition capacity of three phenolic compounds from Quezui tea
样品名称 单酚酶
(μmol/L)二酚酶
(μmol/L)CA 1.114±0.035 95.198±1.117 β-熊果苷 681.335±17.975 无抑制 绿原酸 无抑制 无抑制 -
[1] 罗旭璐. 樟叶越桔原植物及其组织培养系的化学成分分析[D]. 昆明: 西南林业大学, 2015 LUO X L. Analysis of chemical constituents of the original plant of bilberry camphor and its tissue culture line[D]. Kunming: Southwest Forestry University, 2015.
[2] 孔令朋. 雀嘴茶化学成分及其生物活性研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2019 KONG L P. Study on chemical constituents and biological activities of Vaccinium dunalianum wight[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2019.
[3] KAZAZIC M, ALIMAN J, DJOGIC S, et al. Phenol content and antioxidant activity of different blueberry species from prozor region[J]. IFMBE Proceedings,2020,78:268−274.
[4] WANG Y, TIAN L, WANG Y, et al. Protective effect of Que Zui tea hot-water and aqueous ethanol extract against acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice via inhibition of oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis[J]. Food & Function,2021,12(6):2468−2480.
[5] ZHANG J K, ZHOU X L, WANG X Q, et al. Que Zui tea ameliorates hepatic lipid accumulation and oxidative stress in high fat diet induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Food Research International,2022,156:111196. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111196
[6] GAO S H, ZHAO T R, LIU Y P, et al. Phenolic constituents, antioxidant activity and neuroprotective effects of ethanol extracts of fruits, leaves and flower buds from Vaccinium dunalianum wight[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,374:131752. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131752
[7] ZHAO P, TANAKA T, HIRABAYASHI K, et al. Caffeoyl arbutin and related compounds from the buds of Vaccinium dunalianum[J]. Phytochemistry,2008,69(18):3087−3094. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2008.06.001
[8] LUO X L, LI N, XU M, et al. HPLC simultaneous determination of arbutin, chlorogenic acid and 6’-O-caffeoylarbutin in different parts of Vaccinium dunalianum wight[J]. Natural Product Research,2015,29(20):1963−1965. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2015.1013472
[9] LI N, ZENG W L, LUO X L, et al. A new arbutin derivative from the leaves of Vaccinium dunalianum wight[J]. Natural Product Research,2018,32(1):65−70. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2017.1333993
[10] XU W H, LIANG Q, ZHANG Y J, et al. Naturally occurring arbutin derivatives and their bioactivities[J]. Chemistry and Biodiversity,2015,12(1):54. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201300269
[11] LIU F F, LIU H L, CAO J X. Effect of Vaccinium dunalianum glycoside on platelet aggregation in animals[J]. Advanced Materials Research,2013,2203(634-638):1229−1235.
[12] 凌琳. 雀嘴茶降低血清尿酸的物质基础及机制研究[D]. 福州: 福建医科大学, 2021 LING L. The treatment and mechanism study of Vaccinium dunalianum W. in lowering serum uric acid[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Medical University, 2021.
[13] XU M, LAO Q C, ZHAO P, et al. 6'-O-caffeoylarbutin inhibits melanogenesis in zebrafish[J]. Natural Product Research,2014,28(12):932−934. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2014.883395
[14] 张颖君, 李春启, 许敏, 等. 6'-O-咖啡酰基熊果苷及其衍生物和复方在制备化妆品或药物中的应用: 云南, CN103120624A[P]. 2013-05-29 ZHANG Y J, LI C Q, XU M, et al. Application of 6'-O-caffeoyl arbutin and its derivatives and compounds in the preparation of cosmetics or medicines: Yunnan, CN103120624A[P]. 2013-05-29.
[15] 李娜, 但汉龙, 刘云, 等. 雀嘴茶咖啡酰熊果苷水提工艺的优化[J]. 食品工业科技,2015,36(17):140−144,149. [LI N, DAN H L, LIU Y, et al. Optimization of the water extraction process of 6'-O-caffeoylarbutin from Vaccinium dunalianum[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2015,36(17):140−144,149. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2015.17.028 [16] 尹继庭, 孙浩, 丁勇, 等. 樟叶越桔ITS序列及6'-O-咖啡酰熊果苷含量分析[J]. 西部林业科学,2013,42(4):52−57. [YI J T, SHUN H, DING Y, et al. ITS sequence analysis of 6'-O-caffeoylarbutin in high-yielding plant of Vaccinium dunalianum var. dunalianum[J]. Journal of Western China Forestry Science,2013,42(4):52−57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8246.2013.04.009 [17] 张孟琴, 徐路, 张俊波, 等. 三叶木通果皮主要营养成分, 活性成分含量测定及果皮提取物抗氧化活性评价[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(10):388-394. [ZHANG M Q, XUE L, ZHANG J B, et al. Determination of contents of the main nutritional components, functional components of Akebia trifoliata pericarp and the antioxidant activity of its extracts[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(10):388-394. [18] 马妮, 刘慧燕, 方海田, 等. 红枣多酚提取工艺优化, 成分及抗氧化活性分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(16):246−254. [MA N, LIU H Y, FANG H T, et al. Optimization of polyphenol extraction process, analysis of components and antioxidant activity of jujube[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(16):246−254. [19] 刘晓丽, 杨冰鑫, 陈柳青, 等. HPLC测定余甘子茶中3种多酚成分及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(13):315−320,327. [LIU X L, YANG B X, CHEN L Q, et al. Determination of three polyphenol components in Phyllanthus emblica L. tea by high performance liquid chromatography and their antioxidant activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(13):315−320,327. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020.13.050 [20] 普天磊, 韩学琴, 邓红山, 等. 辣木抗氧化成分提取方法和抗氧化能力研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(19):310−315. [PU T L, HAN X Q, DENG H S, et al. Research progress of extraction method of antioxidant components and antioxidant activity of Moringa oleifera[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(19):310−315. [21] YU Q, FAN L, DUAN Z. Five individual polyphenols as tyrosinase inhibitors: Inhibitory activity, synergistic effect, action mechanism, and molecular docking[J]. Food Chem,2019,297:124910. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.05.184
[22] YANG Y, SUN X, NI H, et al. Identification and characterization of the tyrosinase inhibitory activity of caffeine from Camellia pollen[J]. J Agr Food Chem,2019,67(46):12741−12751. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b04929
[23] 杨怡萌, 陈星宇, 吴娅, 等. 蒲公英黄酮抗氧化活性的构效关系分析[J]. 化学通报,2020,83(11):7. [YANG Y M, CHEN X Y, WU Y, et al. Structure and antioxidant activities relationship of dandelion flavonoids[J]. Chemistry,2020,83(11):7. doi: 10.14159/j.cnki.0441-3776.2020.11.011 [24] 梁洁怡, 王志强, 徐阳纯, 等. 棠梨果实中绿原酸提取工艺的优化及抗氧化作用[J]. 食品工业,2021,42(4):4. [LIANG J Y, WANG Z Q, XU Y C, et al. Optimization of extraction technology of chlorogenic acid from Pyrus calleryana decne and antioxidant activity[J]. The Food Industry,2021,42(4):4. [25] 张华, 周志钦, 席万鹏. 15种柑橘果实主要酚类物质的体外抗氧化活性比较[J]. 食品科学,2015,36(11):64−70. [ZHANG H, ZOU Z Q, XI W P. Comparison of antioxidant activity in vitro of 15 major phenolic compounds in citrus fruits[J]. Food Science,2015,36(11):64−70. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201511013 [26] 袁博, 曹健, 秦朗, 等. 四种酚类化合物体外抗氧化活性的比较研究[J]. 食品工业,2018,39(9):200−204. [YUAN B, CAO J, QIN L, et al. Study on the comparison of antioxidant activity in vitro of four phenolic compounds[J]. The Food Industry,2018,39(9):200−204. [27] 李莉莉, 邢蕊, 邓阳阳, 等. 酪氨酸酶抑制剂的研究新进展[J]. 食品工业,2016,37(8):235−239. [LI L L, XING R, DENG Y Y, et al. New developments of tyrosinase inhibitors[J]. The Food Industry,2016,37(8):235−239. [28] HRIDYA H, AMRITA A, SANKARI M, et al. Inhibitory effect of brazilein on tyrosinase and melanin synthesis: Kinetics and in silico approach[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2015(81):228−234.
[29] LVARO SÁNCHEZ-FERRER, JN RODRÍGUEZ-LÓPEZ, F GARCÍA-CÁNOVAS, et al. Tyrosinase: A comprehensive review of its mechanism[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Protein Structure and Molecular Enzymology,1995,1247(1):1−11. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(94)00204-T
[30] 胡治明. 氢醌及其结构类似物抑制皮肤黑素生成和抗氧化作用研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2011 HU Z M. Effects of hydroquinone and its structural analogues on melanogenesis and antioxidation[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2011.
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 唐基涛,帅良,廖玲燕,曲德智,殷菲胧,何妹英,刘云芬. α-熊果苷处理对采后龙眼果皮褐变及活性氧代谢的影响. 核农学报. 2025(04): 784-792 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 字雨欣,刘艺兰. 乡村振兴视域下凤仪雀嘴茶茶膏制作技艺传承发展研究. 福建茶叶. 2025(03): 172-174 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 夏海梅,王莉,陆中云,瞿广城. 红雀嘴茶不同药用部位浸出率比较及安全性研究. 云南中医中药杂志. 2024(04): 92-95 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 马雯芳,吴剑丽,张秀丽,蓝昌斌,甘洁雪,周华锋,王剑. 壮药蛇尾草HPLC指纹图谱及抗氧化活性的谱效关系. 湖北农业科学. 2024(05): 84-90 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 唐勇,吴化雨,赵平,王芳,邓佳. 6’-O-咖啡酰熊果苷处理通过激活苯丙烷代谢提高采后蓝莓果实对灰霉病的抗性. 食品科学. 2024(13): 256-263 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 李楚然,王卫华,武波晓,杨晓琴,刘云,赵平. 樟叶越橘化学成分及其生物活性研究进展. 林产化学与工业. 2024(05): 199-209 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 姚传慧,谢东,赵平,徐俊明,何远平,杨晓琴. 不同地域引栽樟叶越橘嫩叶中有效成分含量及其抗氧化活性差异分析. 林产化学与工业. 2024(06): 38-46 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 李远飞,曾婷,丁钟慧,冯楠,韦振,李丽梅. 酸叶胶藤化学成分及其抗氧化活性研究. 西南民族大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(03): 282-288 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:



