Antifungal Activity of Bacillus Fermentation Broth,and Gene Cloning, Prokaryotic Expression of Endoglucanase
-
摘要: 通过液培法和菌丝生长速率法,探究茯苓粉培养基(ABP培养基)诱导芽孢杆菌CmRh1产葡聚糖酶的发酵上清液对苹果炭疽病菌的抑制作用;采用PCR技术克隆葡聚糖内切酶基因,异源表达并初步验证其功能;采用在线生物信息学对芽孢杆菌葡聚糖酶的理化性质、信号肽、跨膜区、保守结构域、二级和三级结构、亚细胞定位等进行预测。结果表明:茯苓粉培养基(ABP培养基)诱导的芽孢杆菌CmRh1发酵上清液对苹果炭疽病菌具有一定的抑菌效果,抑菌率分别为16.07%和14.03%;从芽孢杆菌CmRh1菌株克隆到1个葡聚糖内切酶基因(Glu4),开放阅读框(Open Reading Frame,ORF)为1500 bp,编码499 aa。生物信息学预测,Glu4是1个含有信号肽和1个跨膜结构域稳定的亲水性蛋白质,其分子量约为55 kDa,理论等电点为7.14;保守结构域预测,Glu4属于GH5型纤维素酶家族;二级结构元件主要包括α螺旋、延伸链、β转角和无规则卷曲,三级结构为典型的β-三明治结构,符合葡聚糖内切酶的结构特征;Glu4亚细胞定位于细胞外,是一个典型的分泌蛋白。SDS-PAGE结合Western blot结果显示,Glu4能在大肠杆菌中表达,其蛋白大小与理论值55 kDa基本相符。重组工程菌具有分泌葡聚糖内切酶能力,为后期葡聚糖内切酶的纯化、酶学性质分析及探究Glu4对苹果炭疽病菌的抑菌活性奠定基础。Abstract: Liquid culture method and mycelial growth rate method were performed to explore the antifungal activity of Bacillus sp. CmRh1 fermentation broth induced by Agar buffered Pachyman (ABP) medium against Colletotrichum gloeosporioides in this study. The endoglucanase gene was cloned by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technique, heterologously expressed in Escheria coli and functionally analyzed. Physicochemical properties, signal peptide, transmembrane region, conserved domain, secondary and tertiary structure, and subcellular location of endoglucanase from Bacillus sp. CmRh1 were predicted by the online bioinformatics tools. The results showed that Bacillus sp. CmRh1 possessed the ability to produce β-1,3 glucanase and β-1,4 glucanase, and the fermentation broth containing glucanase displayed a certain antifungal activity against C. gloeosporioides mycelial growth. Besides, an endoglucanase gene (Glu4) from Bacillus sp. CmRh1 was cloned, and its open reading frame (ORF) was 1500 bp encoding a protein of 499 amino acid residues. Bioinformatics predicted that Glu4 was a stable hydrophilic protein containing a signal peptide and a transmembrane domain. The relative molecular weight of Glu4 was 55 kDa, and its theoretical isoelectric point was 7.14. Glu4 belonged to the glycoside hydrolase family (GH5) containing the carbohydrate-binding module (CBM_3). The secondary structural elements mainly include α helix, β turn, extended strand, and random coil. The tertiary structure was a typical β-sandwich structure, which was consistent with the structural characteristics of endoglucanase. It was predicted that Glu4 was located outside the cell. The results of combined SDS-PAGE with western blot showed that Glu4 was successfully expressed in E. coli, and its molecular weight was consistent with the prediction. In conclusion, E. coli BL21(DE3)/pEB-Glu4 had the ability to secrete endoglucanase, which would be beneficial to purifying, analyzing characterization of endoglucanase, and exploring antifungal activity of endoglucanase against C. gloeosporioides.
-
苹果炭疽病是全球苹果产区普遍发生的一种主要危害果实的病害[1],每年造成巨大的经济损失。化学杀菌剂是防治苹果炭疽病害的主要措施,但其应用中暴露出的环境及安全问题日益凸显,如毒性强、污染环境、易产生抗药性、危害人类健康等[2]。因此,亟需开发高效、绿色环保、无公害的生物杀菌剂来防治苹果炭疽病。
芽孢杆菌作为理想的生防菌,已在国内外广泛研究和防治植物病害[3]。据报道,除了脂肽类物质[4-5]、聚酮类物质[6]、环肽[7]和挥发性化合物[8]等主要抑菌物质,很多芽孢杆菌还能诱导合成真菌细胞壁降解酶发挥生防作用。丝状真菌的细胞壁主要由几丁质、葡聚糖、甘露聚糖和糖蛋白组成,其中葡聚糖作为细胞壁主要结构多糖,包括β-1,3-葡聚糖、β-1,4-葡聚糖、β-1,3-β-1,4-葡聚糖和β-1,6-葡聚糖等[9]。由于芽孢杆菌的抑菌机理较为复杂,通常是多种抑菌机制协同发挥作用,且葡聚糖酶抑菌机理较为简单清晰,使其在生防领域的研究相对较少。芽孢杆菌(Bacillus sp.)ABLF-18、ABLF-50和类芽孢杆菌(Paenibacillus sp.)ABLF-90具有合成葡聚糖酶能力,且体外抑菌实验证实它们均对棉花黄萎病菌(Verticillium dahliae)具有不同程度的抑菌作用[10]。贝莱斯芽孢杆菌(Bacillus velezensis)和枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis)合成的几丁质酶和β-1,3-葡聚糖酶对香蕉镰刀菌属(Fusarium sp.)和链格孢属(Alternaria sp.)2种病原真菌均具有抑菌作用[11]。国慧[12]克隆了萎缩芽孢杆菌SF1中的β-1,3葡聚糖酶基因,并在大肠杆菌中进行异源表达,发现β-1,3葡聚糖酶对尖孢镰刀菌胡麻专化型的抑菌率达45%,占菌株SF1总抑菌率的61.9%。假单胞菌(Pseudomonas sp.)EA6抑制植物病原真菌Phytophthora parasitica的主要活性物质是β-1,4-葡聚糖酶和β-1,3-葡聚糖酶,协同作用降解P. parasitica细胞壁,且二者具有相似的抑菌活性[13]。然而,芽孢杆菌葡聚糖酶对苹果炭疽病菌的研究目前尚未见报道。
课题组前期从高山草甸大花杓兰根际土壤分离到1株芽孢杆菌CmRh1,并证实该菌株产生的挥发性物质和脂肽类粗提物均对苹果炭疽病菌具有不同程度的抑制作用(暂未发表)。为初步探究芽孢杆菌葡聚糖酶对苹果炭疽病菌的抑制作用,本研究采用液培法和菌丝生长速率法分别测定ABP培养基诱导培养芽孢杆菌CmRh1的发酵上清液对苹果炭疽病菌的抑菌活性;采用PCR技术克隆葡聚糖内切酶基因、异源表达及在ABP和CMC琼脂平板进行功能验证,为后期葡聚糖酶的分离纯化和体外抑菌研究奠定基础,进而为全面阐明CmRh1的抑菌机理提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
芽孢杆菌CmRh1 本研究室保存;苹果炭疽病菌(Colletotrichum gloeosporioides) 国家微生物资源平台——中国农业微生物菌种保藏管理中心;Escheria coli BL21(DE3)感受态细胞、表达载体pEASY-Blunt E1 北京全式金;E. coli TOP10感受态细胞、克隆载体pLB-Simple Vector 北京天根;茯苓粉培养基(ABP培养基) 河北本元生物,按说明书配制;即用型LB肉汤琼脂、LB肉汤培养基 上海生工,按说明书配制;PDA培养基、PD培养基 参照杨薇红等[14]配制;羧甲基纤维素培养基(CMC培养基) 参照余丽等[15]方法配制;细菌DNA提取试剂盒、PCR扩增试剂盒 北京艾德莱;DNA凝胶回收试剂盒 上海碧云天;SDS-PAGE变性丙烯酰胺凝胶快速制备试剂盒、TMB显色试剂盒、小鼠抗6X His单克隆抗体、HRP标记的山羊抗小鼠IgG、预染和非预染蛋白Marker 上海生工;质粒小提试剂盒、DNA Marker 北京天根;3,5-二硝基水杨酸(DNS) 北京索莱宝;试剂琼脂糖、刚果红、氨苄青霉素 河北本元生物。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 芽孢杆菌CmRh1产葡聚糖酶的平板鉴定
将−80 ℃甘油管保存的芽孢杆菌CmRh1划线于LB培养基,37 ℃过夜培养。随机挑取活化的CmRh1单菌落分别接种在ABP培养基和CMC培养基上,30 ℃培养5~6 d,观察并记录CmRh1菌落周围是否出现透明水解圈。
1.2.2 芽孢杆菌CmRh1发酵上清液的抑菌活性测定
1.2.2.1 ABP选择性培养基诱导发酵液的制备
挑取CmRh1单菌落接种至LB液体培养基,37 ℃培养至对数生长期,作为种子液;按1%接种量接种CmRh1至100 mL ABP培养基中,30 ℃培养5~6 d;4 ℃ 12000 r/min离心10 min后,上清液经0.22 μm无菌针孔过滤器过滤除菌,即获得无菌发酵上清液。
1.2.2.2 发酵上清液的抑菌活性测定
液培法[16]:将直径为5 mm苹果炭疽病菌的菌饼分别接种到含4 mL上述制备的发酵上清液(处理组)和4 mL无菌水(对照组)的100 mL PD培养基中,25 ℃振荡培养5 d。试验设3个重复。收集苹果炭疽病菌的菌丝球,105 ℃烘干至恒重,计算抑菌率。
抑菌率 (%)= 对照菌丝干重 − 处理菌丝干重 对照菌丝干重 ×100 菌丝生长速率法[17]:将直径为5 mm苹果炭疽病菌的菌饼接种到含/不含发酵上清液的PDA培养基中(发酵上清液:PDA=2:8作为处理组;无菌水:PDA=2:8为对照组),25 ℃培养5 d,试验设3个重复。十字交叉法分别测量处理组和对照组苹果炭疽病菌的菌落直径,计算抑菌率。
抑菌率 (%)= 对照组苹果炭疽病菌菌落直径 − 处理组苹果炭疽病菌菌落直径 对照组苹果炭瘨病菌菌落直径 − 菌块直径 ×100 葡聚糖酶活力测定:采用DNS法测定发酵上清液中葡聚糖酶活力。参照DNS试剂说明书方法制作葡萄糖标准曲线。0.5%葡聚糖底物用醋酸-醋酸钠缓冲液配制(0.1 mol/L,pH5.2)。1 mL 0.5%葡聚糖于50 ℃预热5 min,加0.5 mL发酵上清液,50 ℃反应30 min,再加2 mL DNS试剂,沸水浴10 min。对照管于50 ℃反应20 min后,加2 mL DNS试剂,再加0.5 mL发酵上清液,沸水浴10 min。样品管和对照管冷却后,补蒸馏水至10 mL,540 nm测定吸光度值。根据葡萄糖标准曲线获得发酵上清液中还原糖含量,计算酶活力。在50 ℃、pH5.2条件下,每分钟葡聚糖被酶解产生1.0 μg还原糖所需的酶量,即为1个酶活力单位(U)。
1.2.3 葡聚糖内切酶基因的克隆
参照细菌DNA提取试剂盒的说明书提取产葡聚糖内切酶CmRh1菌株DNA。根据已报道细菌葡聚糖内切酶基因的核苷酸序列,合成1对引物PJTF和PJTR[18]。以CmRh1的DNA为模板,PJTF和PJTR为引物,PCR扩增CmRh1菌株葡聚糖内切酶基因。PCR扩增体系(25 μL):2×A8 PCR Mix 12.5 μL,PJTF和PJTR各1 μL,DNA 1 μL,ddH2O 9.5 μL。PCR反应程序:94 ℃ 5 min;94 ℃ 30 s、60 ℃ 30 s、72 ℃ 30 s,循环30次;72 ℃ 10 min。1.0%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测。PCR产物经DNA凝胶回收试剂盒切胶纯化后,克隆至零背景克隆载体pLB-Simple Vector中,氯化钙法转化至E. coli TOP10,37 ℃过夜培养。菌落PCR和质粒PCR鉴定阳性的转化子送上海生工进行双向测序。序列经拼接、校对后,进行Blastn和Blastp分析,以明确克隆的基因确实为葡聚糖内切酶基因。成功构建的重组质粒命名为pLB-Glu4。
1.2.4 Glu4编码蛋白的生物信息学分析
采用ProtParam软件(http://www.expasy.org/tools/protparam. html)对葡聚糖内切酶的一级结构及理化性质进行分析[19],包括氨基酸数量、分子量、理论上的等电点、不稳定性指数、亲疏水性等;TMpred软件(https://embnet.vital-it.ch/software/TMPRED_form.html)预测蛋白质的跨膜结构域[20];SignalP-5.0 Server软件(http://www.cbs.dtu. dk/services/SignalP/)对信号肽进行预测分析[21];NCBI保守结构域数据库分析蛋白序列的保守结构域[22];SOPMA软件(https://npsa-prabi.ibcp.fr/cgi-bin/npsa_automat.pl?page=/NPSA/npsa_sopma.html)对蛋白质的二级结构预测[23];FoldIndex软件(https://fold.weizmann.ac.il/fldbin/findex)对蛋白质固有无序化进行分析[24];SWISS-MODEL软件(http://swissmodel.expasy.org/)对蛋白质的三级结构预测[25];葡聚糖内切酶的亚细胞定位采用PredSL(http://aias.biol.uoa.gr/PredSL/input.html)[26]和CELLO v2.5 server(http://cello.life.nctu.edu.tw/)[27]进行预测。
1.2.5 重组工程菌的构建
根据获得的葡聚糖内切酶基因序列,重新设计1对特异性引物PJT-eF和PJT-eR。以pLB-Glu4质粒为模板,PJT-eF和PJT-eR为引物进行PCR扩增,其PCR体系和程序同上述葡聚糖内切酶基因的克隆。PJT-eF:5'-ATGAAACGGTCAATTTCTATTTTTATTACGTG-3';PJT-eR:5'-CTAATTGGGTTCTGTACCCCAAATC-3'。PCR产物经1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳和切胶纯化后,直接克隆至表达载体pEASY-Blunt E1,氯化钙法转化E. coli BL21(DE3)。PCR鉴定的潜在阳性转化子送上海生工进行DNA测序,测序引物为表达载体上的T7 Promoter Primer和T7 Terminator Primer。将核苷酸序列无突变且插入方向正确的重组质粒命名为pEB-Glu4。含pEB-Glu4重组质粒的工程菌子命名为E. coli BL21(DE3)/pEB-Glu4。
1.2.6 Glu4的诱导表达及检测
挑取工程菌E. coli BL21(DE3)/pEB-Glu4接种于含Amp的LB液体培养基,37 ℃振荡过夜培养。按1%的接种量将过夜培养物转接于新鲜的含Amp的LB液体培养基中,37 ℃振荡培养至OD600约为0.6。菌液加入0.5 mmol/L IPTG,分别于20 ℃培养过夜和37 ℃条件下培养6 h,以未加IPTG诱导的菌液作为阴性对照。所有菌液12000 r/min,离心2 min,收集菌体。菌体重悬于PBS缓冲液(pH7.4),超声波细胞破碎仪破碎菌体,离心收集上清和沉淀。沉淀用等量的缓冲液(8 mol/L Urea,50 mmol/L Tris-HCl,300 mmol/L NaCl,pH8.0)进行充分溶解。上清和沉淀分别加入SDS Loading Buffer,充分混匀;沸水煮沸5 min后进行SDS-PAGE(12%分离胶,5%浓缩胶)检测。
1.2.7 Western blot检测重组蛋白Glu4
12% SDS-PAGE电泳后,首先将胶中的蛋白质转印到PVDF膜上,用含5%脱脂奶粉的TBS溶液进行封闭;TBST洗膜3次后,1:5000稀释的小鼠抗6X His单克隆抗体覆盖膜,37 ℃轻柔振荡孵育2 h;TBST洗涤膜3次,再加入1:3000稀释的HRP标记的山羊抗小鼠IgG,37 ℃孵育1 h;TBST洗膜3次、TBS洗膜2次,将膜转移到阴暗处。最后按照TMB显色试剂盒说明书的操作步骤进行显色反应。
1.2.8 重组葡聚糖内切酶的ABP和CMC平板验证
将重组工程菌E. coli BL21(DE3)/pEB-Glu4按1%接种量接种至含Amp的100 mL LB液体培养基中,37 ℃、200 r/min振荡培养至OD600为0.5,加入终浓度为0.5 mmol/L的IPTG,37 ℃条件下培养4 h。将已诱导和未诱导的重组工程菌E. coli BL21(DE3)/pEB-Glu4以及E. coli BL21(DE3)分别点种到ABP培养基和CMC培养基中,观察菌落周围是否出现水解圈。
1.3 数据处理
本研究所有实验对照组和处理组均设置3个重复。测得的数据利用IBM SPSS Statistics 20 进行分析处理。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 芽孢杆菌CmRh1发酵上清液的抑菌活性测定
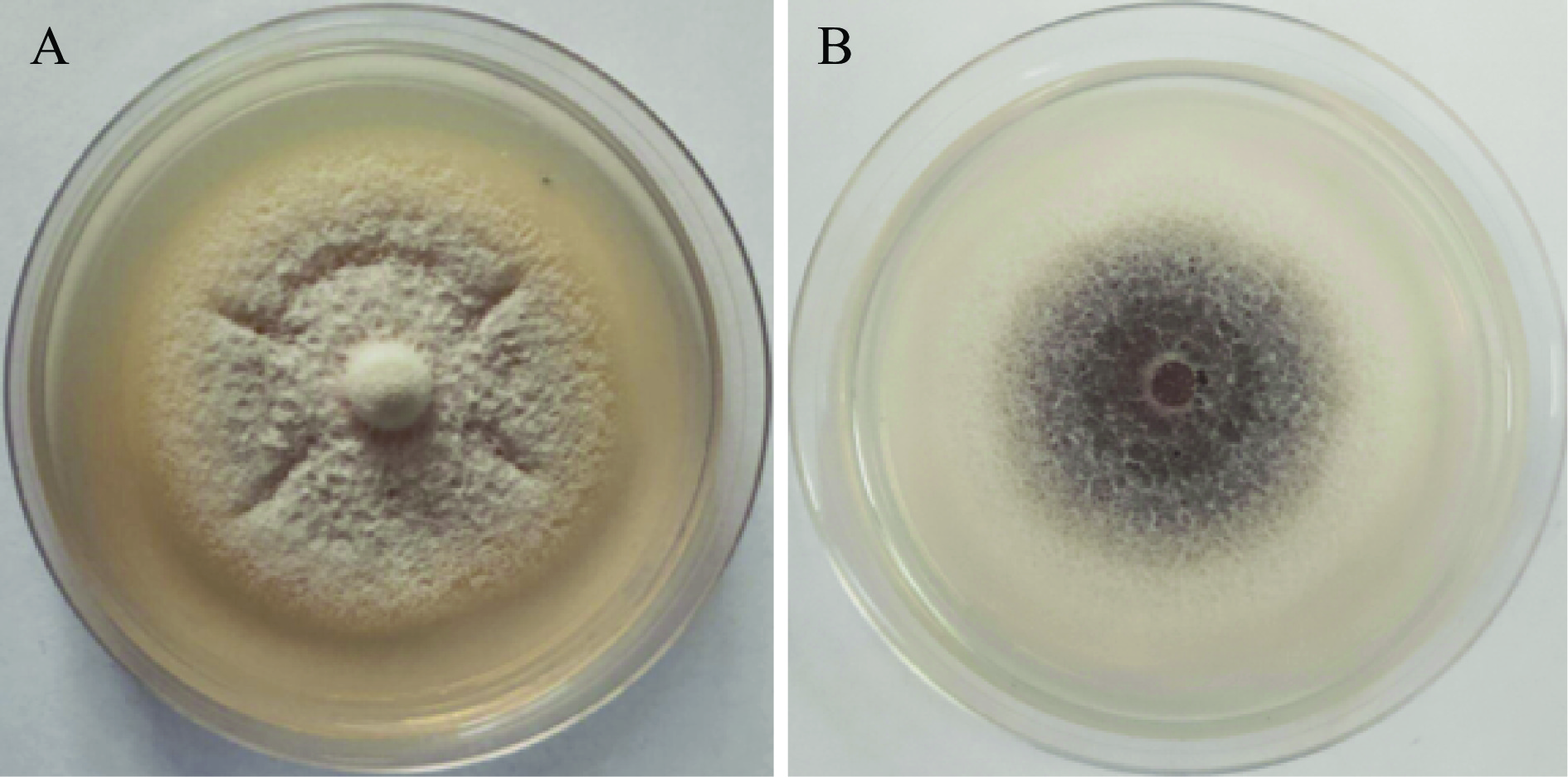
CmRh1菌株在ABP培养基和CMC培养基上均能生长,且菌落周围均出现明显的透明水解圈(图1),表明CmRh1菌株具有产葡聚糖内切酶的能力。在CMC平板,透明水解圈直径(D)与CmRh1菌落直径(d)比值为8.33,而在ABP平板中,D/d比值为1.4,初步判断芽孢杆菌CmRh1利用羧甲基纤维素的能力优于茯苓多糖。
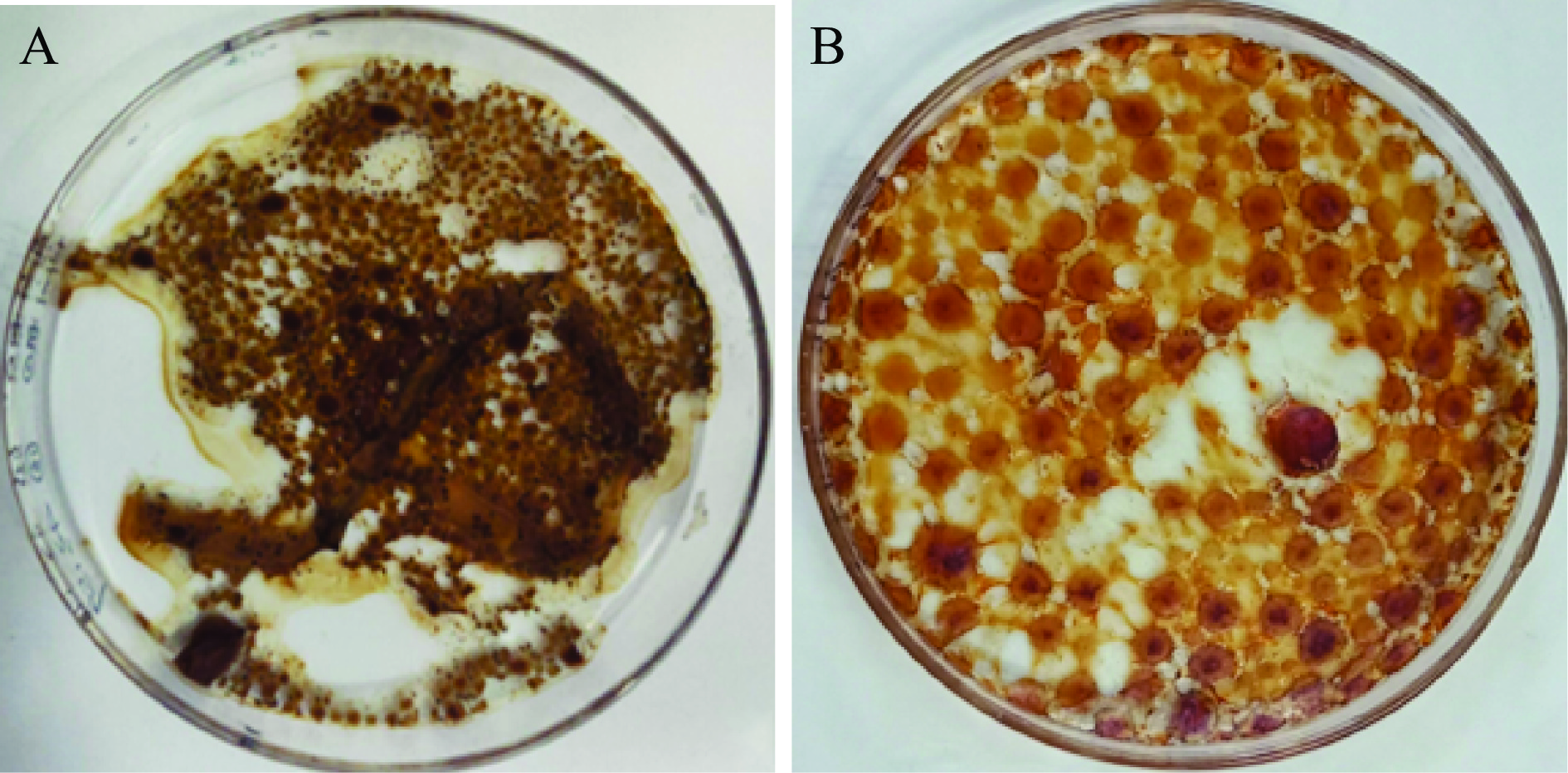
ABP培养基诱导培养法制备的CmRh1菌株发酵上清液的葡聚糖酶活力为26.41 U/mL,且对苹果炭疽病菌菌丝生物量和菌丝生长均有一定抑制作用(图2和图3),抑菌率分别为16.07%和14.03%。从图2可以看出,相比对照组,发酵上清液处理组的菌丝球直径更小,且菌丝球呈黑褐色。推测其原因如下:a. 以ABP培养基中的茯苓粉作为诱导物,诱导芽孢杆菌CmRh1产生葡聚糖酶[16]。葡聚糖酶抑制丝状真菌菌丝生长,菌丝可能出现断裂和膨胀,不利于菌丝相互缠绕形成较大的菌丝球;b. 苹果炭疽病菌可能通过产生黑色素来提高其对葡聚糖酶的抵抗作用[28]。
![]() 图 2 液培法测定CmRh1发酵液对苹果炭疽病菌的抑制作用注:A.处理组A;B.对照组;图3同。Figure 2. Determination of antifungal activity of fermentation broth against C. gloeosporioides by liquid culture method
图 2 液培法测定CmRh1发酵液对苹果炭疽病菌的抑制作用注:A.处理组A;B.对照组;图3同。Figure 2. Determination of antifungal activity of fermentation broth against C. gloeosporioides by liquid culture method从图3可以看出,对照组和处理组真菌长势差异较大,但菌落直径差异并不明显。推测原因可能为ABP培养基诱导法制备的发酵上清液对苹果炭疽病菌菌丝生长具有一定抑制作用,同时发酵上清液可能存在促进菌丝生长的物质,使得处理组菌落直径较小,但菌丝生长更加浓密;而对照组菌丝生长快,老龄菌丝产生黑色素、菌丝老化自溶,使其菌落直径较大,但菌丝更加稀疏。
2.2 葡聚糖内切酶基因Glu4的克隆
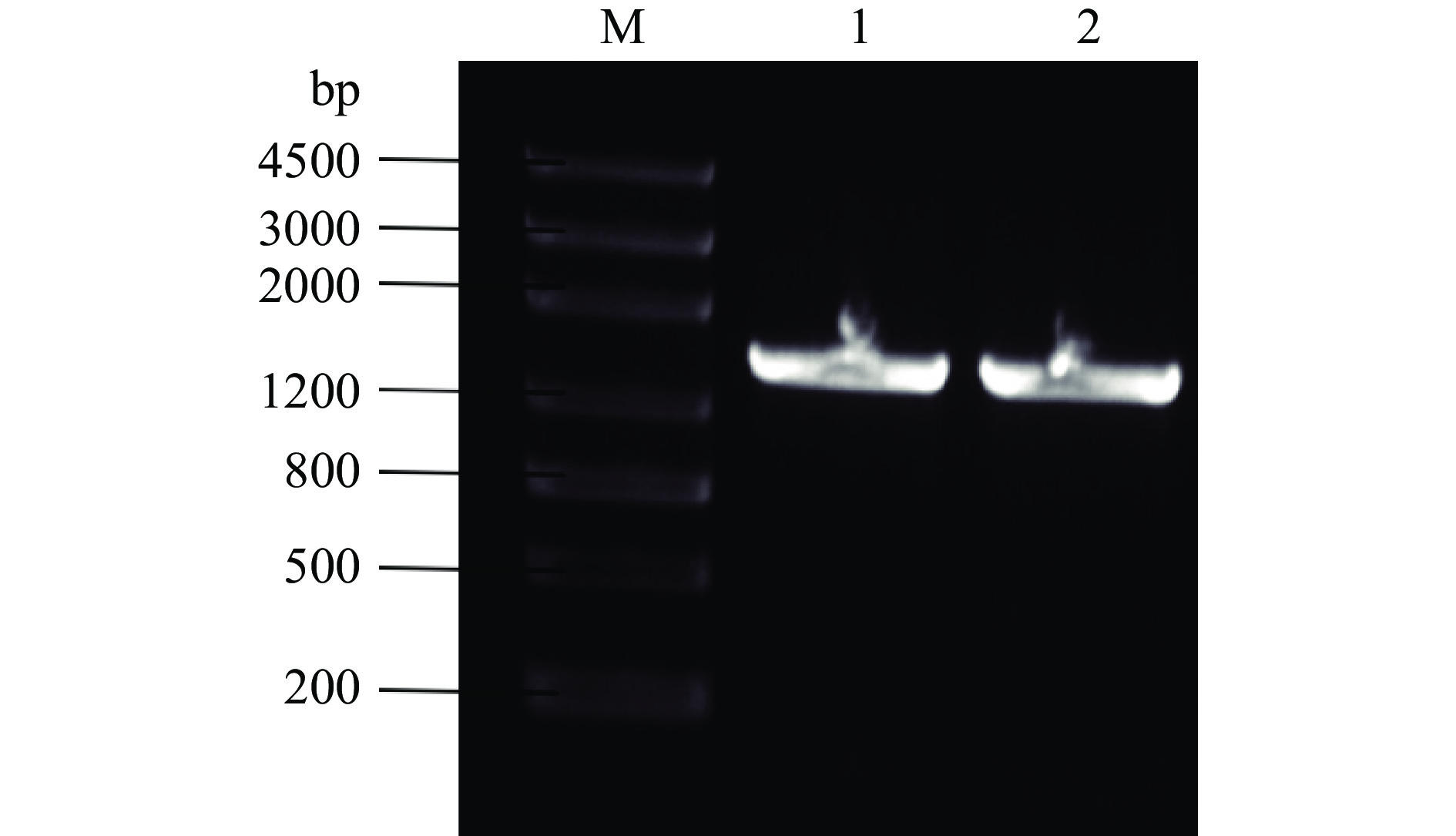
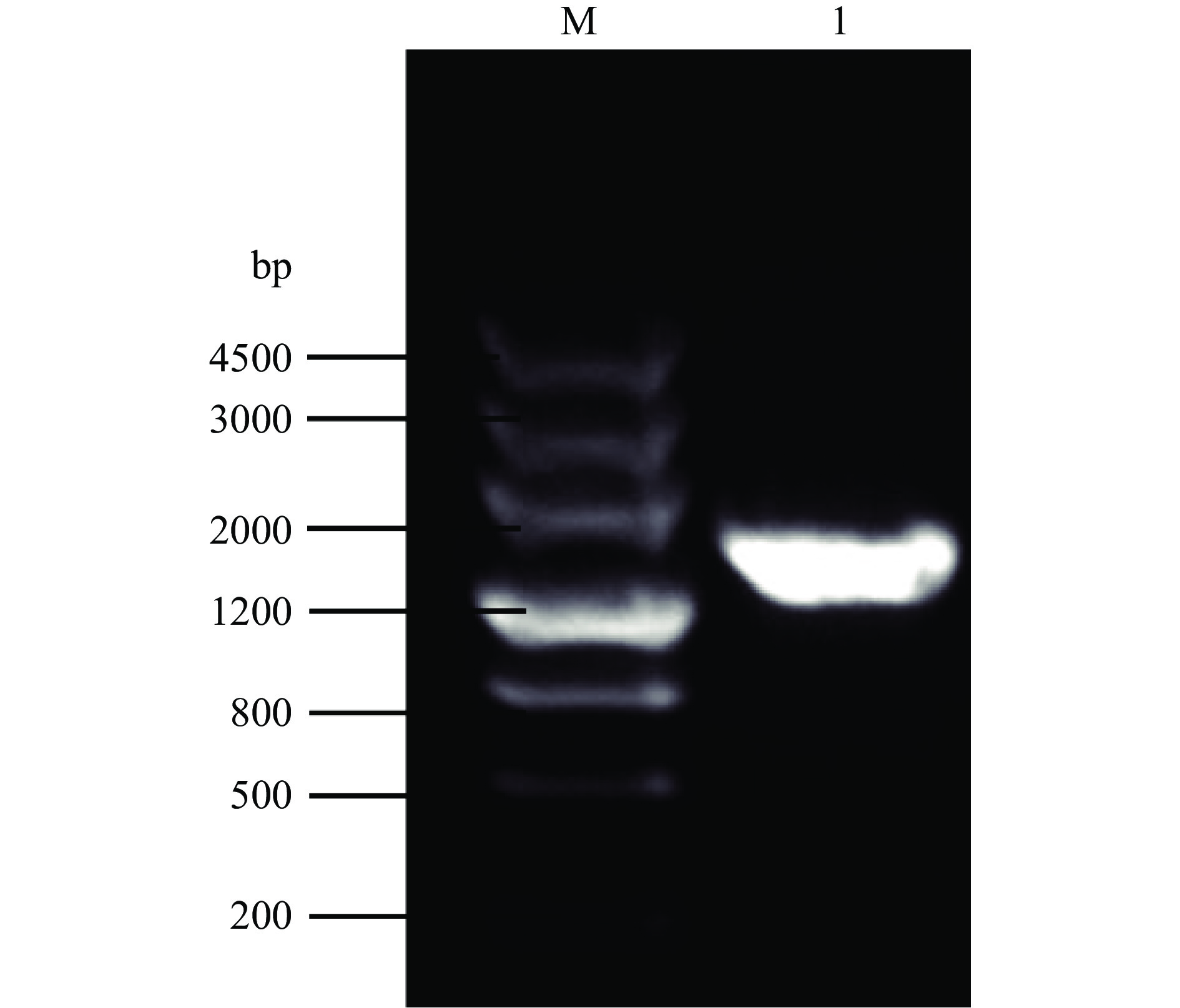
以CmRh1基因组DNA为模板,扩增到1条单一明亮、大小介于1200~2000 bp的特异性条带,与预期的葡聚糖内切酶基因大小基本相符(图4)。克隆测序结果表明,本研究克隆到的Glu4基因大小为1500 bp,与GenBank数据库中Bacillus velezensis WRN014中cellulase family glycosylhydrolase(Accession No. CP041361.1)的核苷酸序列同源性为99.73%。该基因编码的氨基酸序列与Bacillus amyloliquefacien GH5(glycosyl hydrolase family 5)型纤维素酶(Accession No. WP_079004861.1)的同源性达99.8%。综上,插入到克隆载体pLB-Simple Vector的基因确实为葡聚糖内切酶基因,重组质粒命名为pLB-Glu4。
2.3 葡聚糖内切酶Glu4的生物信息学分析
2.3.1 Glu4的基本理化性质
Glu4基因的ORF为1500 bp,编码499 aa。ProtParam预测Glu4的分子量为55 kDa,理论等电点为7.14。带负电荷的残基总数(Asp+Glu)为54,带正电荷的残基总数(Arg+Lys)为54,不稳定性指数为32.55(<40),亲水性平均系数为−0.601,说明Glu4为稳定的亲水性蛋白质。Glu4含有丝氨酸(23个)、苏氨酸(19个)和酪氨酸(10个)共52个潜在的磷酸化位点。NetOGlyc 4.0预测Glu4含有15个潜在的糖基化位点,其中10个为丝氨酸和苏氨酸残基上形成O-糖基化,5个为天冬酰胺残基上形成的N-糖基化。
2.3.2 Glu4的信号肽、跨膜结构域及亚细胞定位
TMPred和TMHMM预测Glu4含有1个跨膜结构域,其中1~4 aa位于膜内侧,5~27 aa为跨膜螺旋,28~499 aa位于膜外侧。SignalP 5.0 Server预测Glu4含有信号肽,且信号肽的剪切位点位于第29和第30氨基酸之间。CELLO v2.5 server预测Glu4定位于细胞外的可靠性为4.562,而定位于细胞壁、细胞膜和细胞质的可靠性分别为0.154、0.238和0.046。PredSL预测Glu4含有分泌通路信号肽,且得分为0.95467。因此,综合CELLO v2.5 server和PredSL预测结果,推测Glu4亚细胞定位于细胞外,是一个典型的分泌蛋白。
2.3.3 Glu4的保守结构域、二级及三级结构
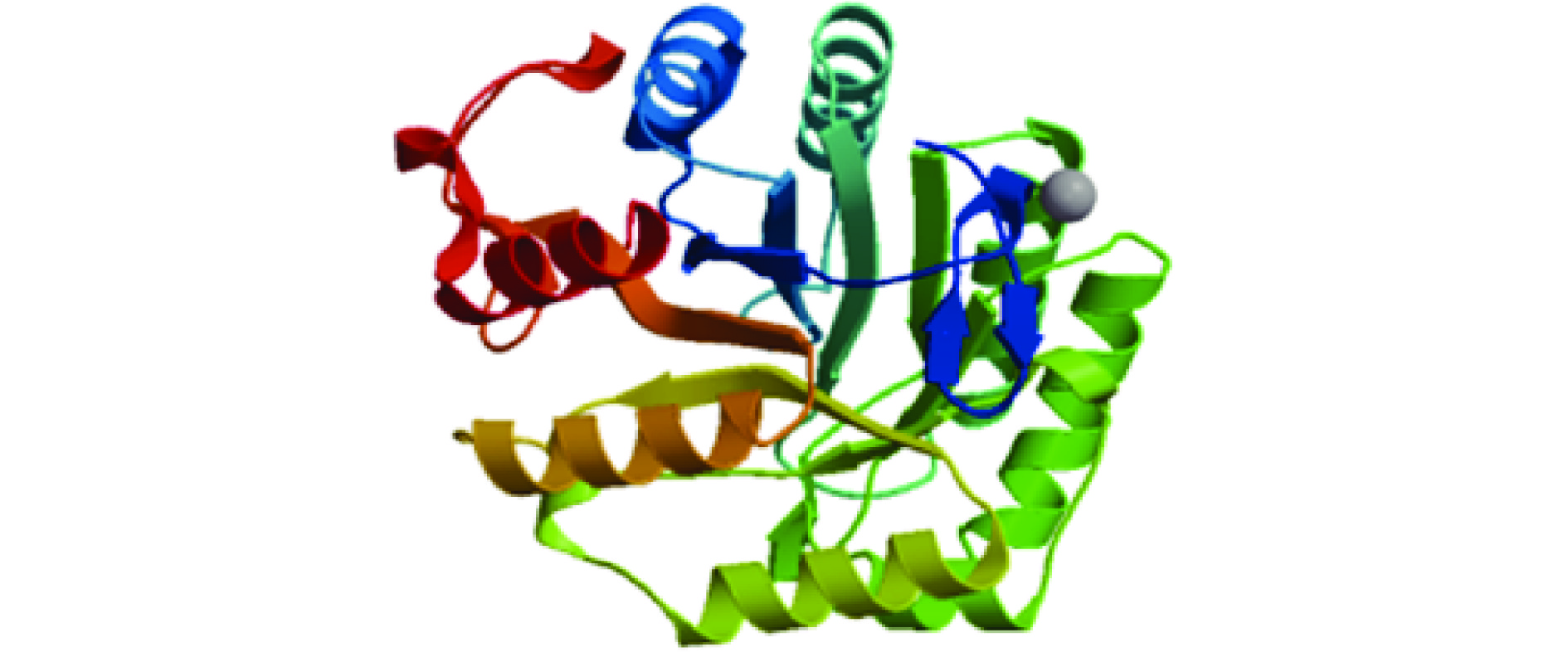
保守结构域预测显示,Glu4属于GH5型纤维素酶家族(pfam00150,50~296 aa),且356~437 氨基酸残基为CBM_3纤维素酶结合域(图5)。图6展示了Glu4二级结构元件主要包括117个氨基酸残基组成α-螺旋(α-helix)、123个氨基酸残基组成延伸链(extended strand)、42个氨基酸残基组成β-转角(β-turn)和217个氨基酸残基组成无规则卷曲(random coil)。以枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis)的内切葡聚糖酶(3pzt.1.A)为模板,利用SWISS-MODEL在线程序对Glu4的三级结构进行同源建模,发现其三级结构包含无规卷曲、α-螺旋和β-转角等二级结构元件,且Glu4三级结构为典型的β-三明治结构(图7),符合葡聚糖酶内切酶的结构特征[29]。
2.3.4 Glu4编码蛋白无序化分析
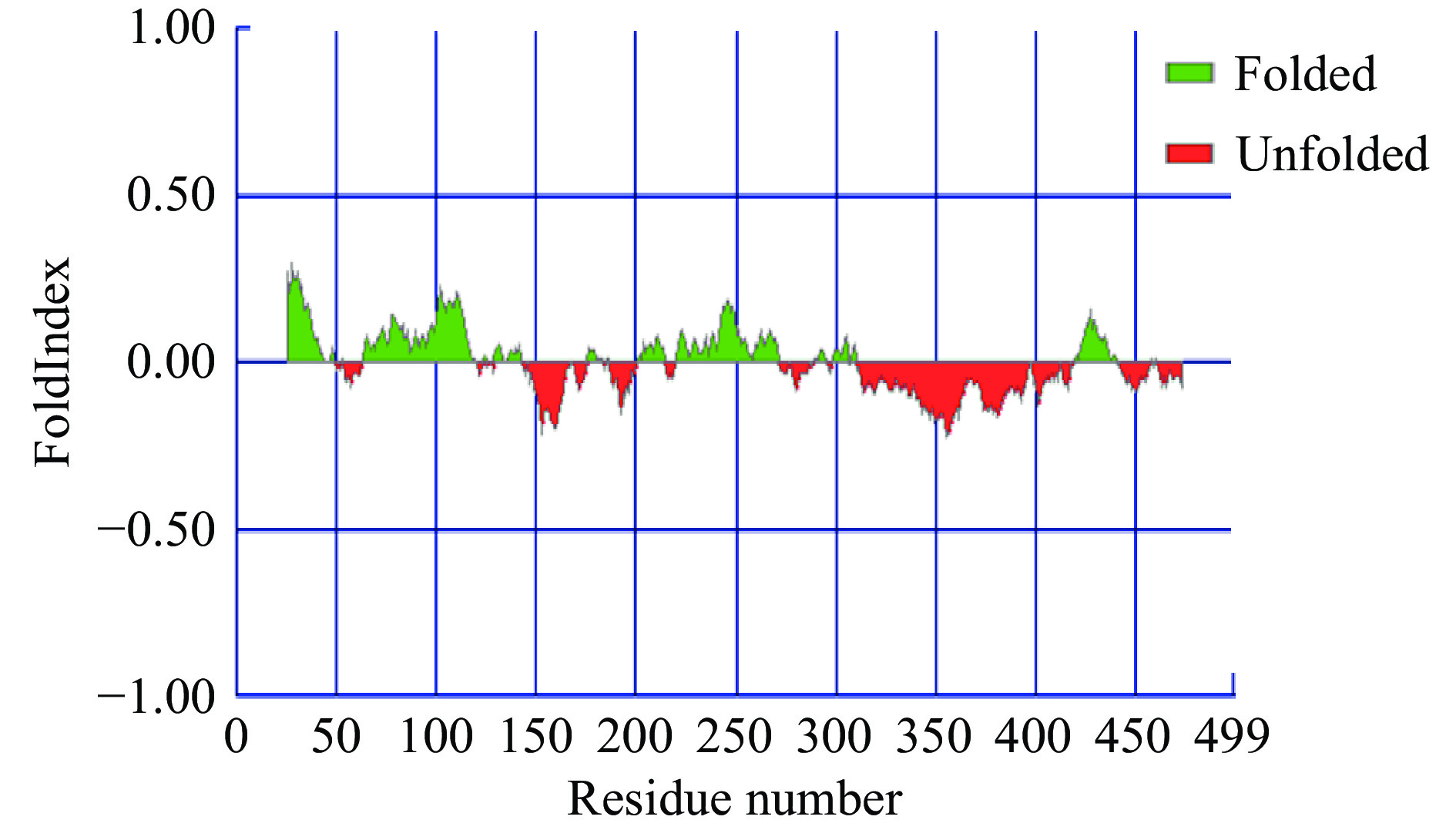
无序化特征预测结果表明,Glu4蛋白存在11处无序区,最长无序区包含101个氨基酸残基(图8)。Glu4蛋白共499个氨基酸,其中无序氨基酸236个,占比47.29%。对最长无序区的氨基酸残基(311~411 bp)进行分析,发现该无序区刚好位于纤维素结合结构域(CBM),且该区域富含甘氨酸、丙氨酸、天冬氨酸、天冬酰胺、赖氨酸、谷氨酰胺和苏氨酸,推测该区域氨基酸的无序化特征可能与CBM与不同类型底物的识别和结合能力密切相关。
2.4 含Glu4重组工程菌的构建
以pLB-Glu4为模板,PJT-eF和PJT-eR为引物,PCR扩增到1条1500 bp特异性条带。PCR产物经切胶纯化后,直接连接至表达载体pEASY-Blunt E,转化E. coli BL21(DE3)。PCR对潜在阳性转化子进行鉴定,结果成功扩增单一清晰目的片段,其大小与理论值相一致(图9)。重组质粒测序结果显示,Glu4基因的核苷酸序列无突变且插入方向正确,表明原核表达载体构建成功,命名为pEB-Glu4。含pEB-Glu4质粒的重组子命名为E. coli BL21(DE3)/pEB-Glu4。
2.5 Glu4的诱导表达、检测
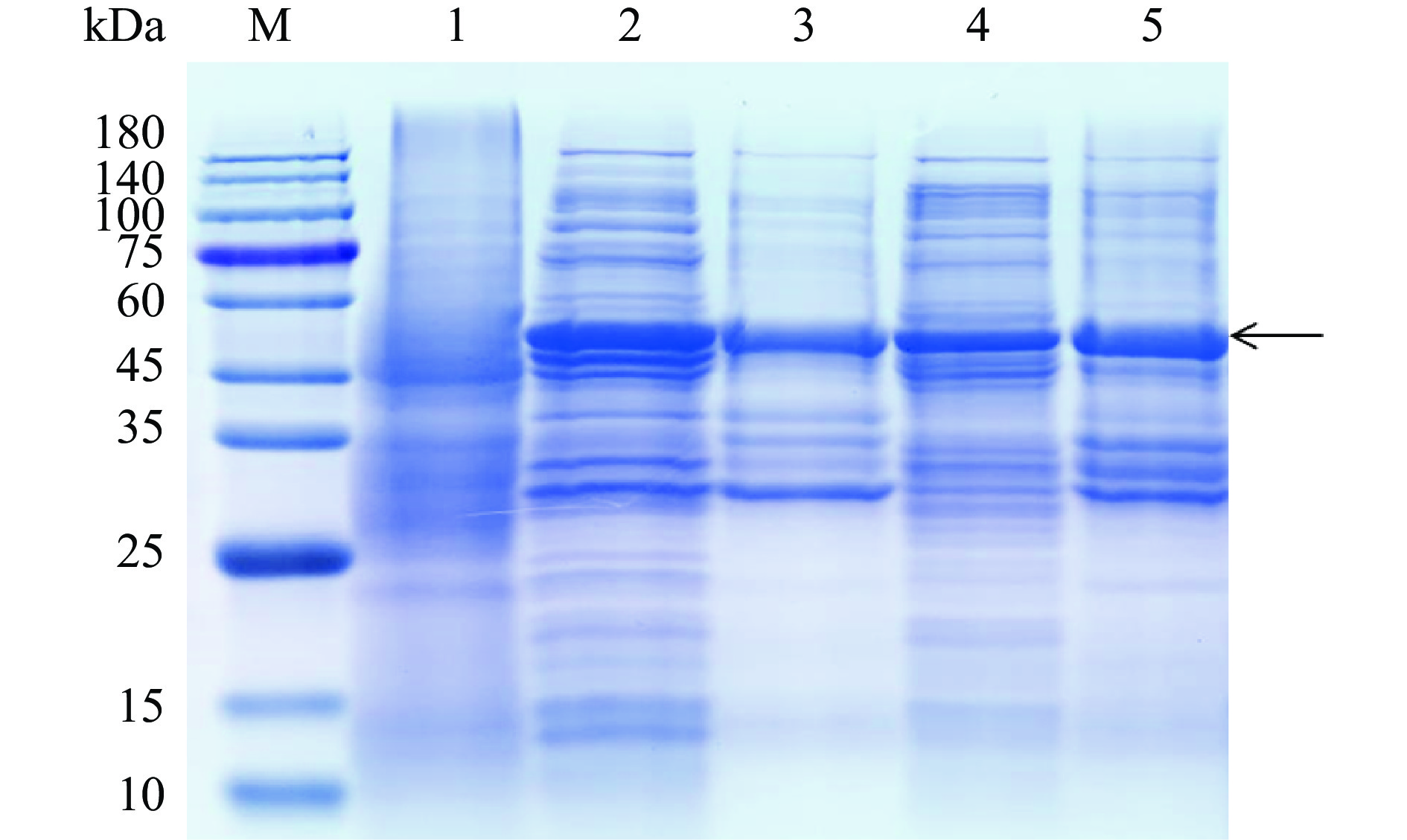
重组质粒pEB-Glu4转化至E. coli BL21(DE3),0.5 mmol/L IPTG分别于20和37 ℃进行诱导表达。SDS-PAGE检测结果如图10显示,相对未诱导菌体总蛋白,重组工程菌在IPTG诱导后均有特异性蛋白条带,其分子量大小与Glu4的理论值(55 kDa)相符,表明His标签融合的Glu4蛋白能在大肠杆菌中高效表达。此外,Glu4蛋白在工程菌上清和沉淀均有表达,说明该蛋白以可溶性和包涵体两种形式存在。相比37 ℃,20 ℃诱导的上清Glu4蛋白表达量有所增加,说明低温诱导更有利于Glu4的可溶性表达。
![]() 图 10 Glu4重组蛋白表达的SDS-PAGE图谱注:M:Protein Marker; 1:诱导前总蛋白;2:20 ℃ 上清;3:20 ℃ 沉淀;4:37 ℃ 上清;5:37 ℃ 沉淀;图11同。Figure 10. Expression analysis of Glu4 recombinant protein by SDS-PAGE
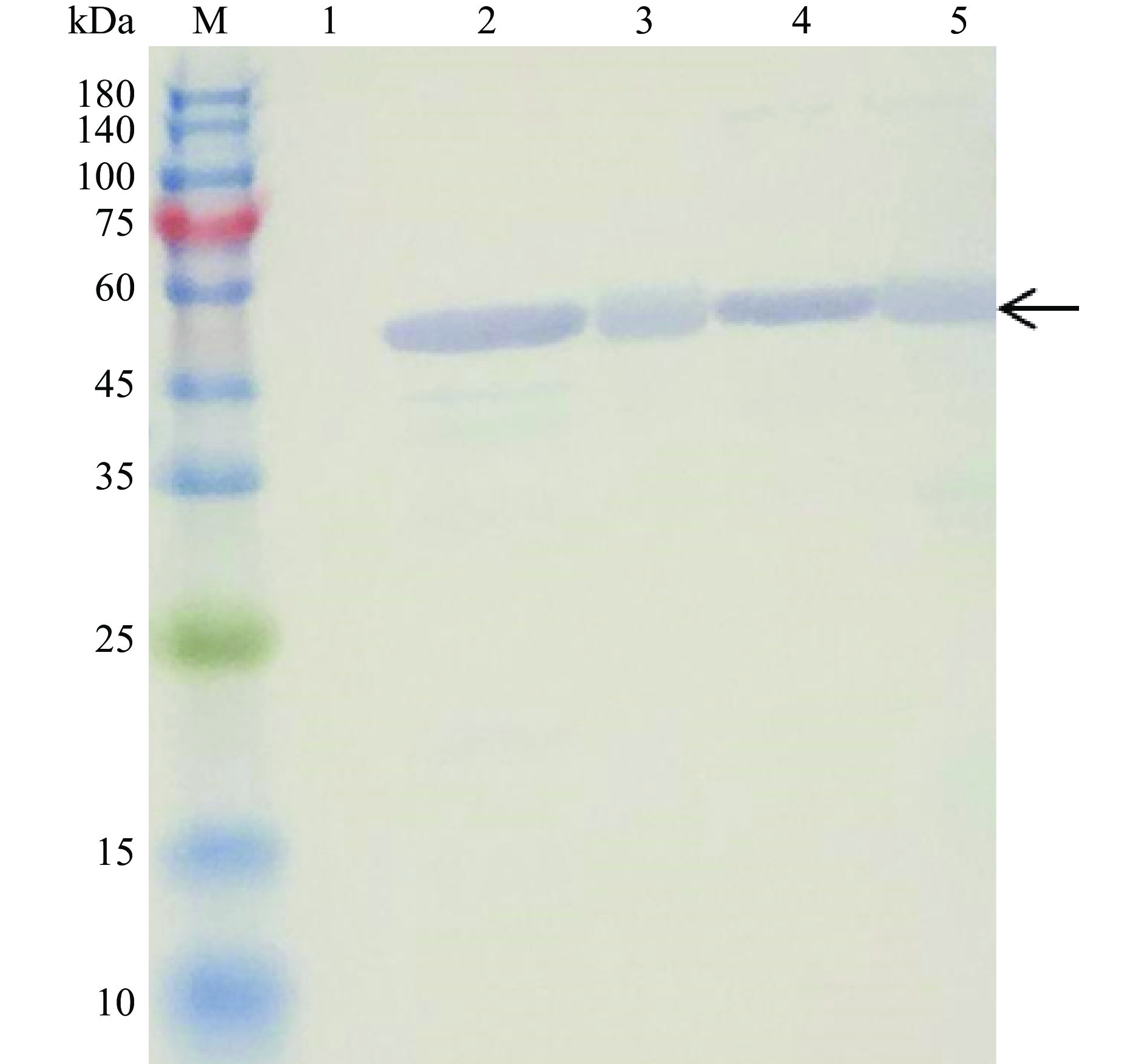
图 10 Glu4重组蛋白表达的SDS-PAGE图谱注:M:Protein Marker; 1:诱导前总蛋白;2:20 ℃ 上清;3:20 ℃ 沉淀;4:37 ℃ 上清;5:37 ℃ 沉淀;图11同。Figure 10. Expression analysis of Glu4 recombinant protein by SDS-PAGE为进一步确定Glu4蛋白是否表达,将上述诱导表达蛋白进行Western blot分析,结果均出现大小约为55 kDa的单一蛋白条带(图11),表明上述诱导表达的蛋白确实为His标签融合的Glu4蛋白。
2.6 重组葡聚糖内切酶的ABP和CMC平板验证
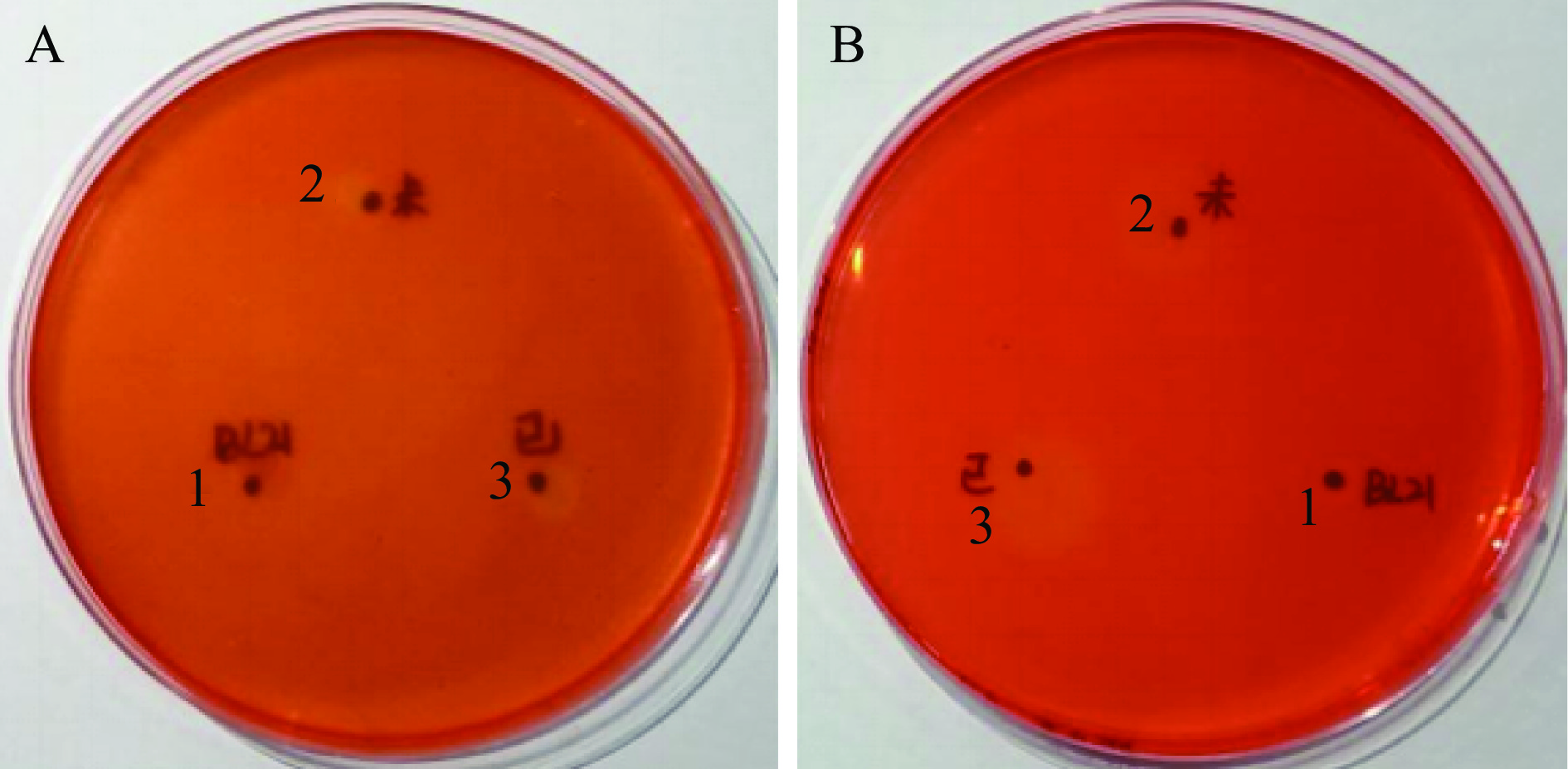
将IPTG诱导/未诱导的重组工程菌E. coli BL21(DE3)/pEB-Glu4和E. coli BL21(DE3)分别点种到ABP培养基和CMC培养基。本研究所用原核表达载体为pEASY-Blunt E1,该载体与pET载体骨架相似,具有T7lac启动子,理论上能严谨调控外源蛋白的表达,但研究中确实发现IPTG未诱导的重组菌也有较小透明水解圈(图12)。推测可能原因如下:a.芽孢杆菌Glu4蛋白在大肠杆菌中有弱的本底表达;b.微生物代谢过程中,产生微量葡聚糖酶,分解培养基中的羧甲基纤维素和茯苓多糖。但相比E. coli BL21(DE3)和未诱导的重组工程菌,IPTG诱导的重组工程菌在ABP和CMC平板均出现更为明显的透明水解圈(图12),表明大肠杆菌中表达的Glu4具有合成β-1,3葡聚糖酶和β-1,4葡聚糖酶能力。
Glu4属于GH5型纤维素酶家族,且重组工程菌E. coli BL21(DE3)/pEB-Glu4对CMC培养基中羧甲基纤维素(β-1,4葡聚糖[30])的水解效果好于ABP培养基中的茯苓多糖(主要是β-1,3葡聚糖[31])(图12),推测大肠杆菌中表达的Glu4可能主要是β-1,4葡聚糖酶活性。
3. 讨论
近年来,微生物来源的葡聚糖酶防治植物真菌病害的研究备注关注。葡聚糖酶是一种诱导酶,通常需要特定的底物诱导合成,且葡聚糖酶对多种植物病原真菌均具有一定的抑制作用[16,32-34]。本研究采用羧甲基纤维素(β-1,4葡聚糖)和茯苓粉(茯苓多糖主要是β-1,3葡聚糖)作为诱导物,发现大花杓兰根际芽孢杆菌CmRh1在含茯苓粉ABP平板和含羧甲基纤维素的CMC平板上均能生长,且菌落周围均出现明显的透明水解圈,初步揭示了CmRh1菌株具有合成β-1,3葡聚糖酶和β-1,4葡聚糖酶能力。液培法和菌丝生长速率法证实ABP培养基诱导培养法制备的CmRh1发酵上清液对苹果炭疽病菌(Colletotrichum gloeosporioides)的生物量和菌丝生长具有一定的抑制作用,但抑菌效果不理想。推测其可能原因如下:a.菌株产酶能力弱,使得葡聚糖酶合成量少或活性较低;b.培养基配方或发酵条件不是最佳产酶条件;c.葡聚糖酶可能不是CmRh1抑制C. gloeosporioides的主要机制。前期研究发现CmRh1产生的脂肽类物质和挥发性物质在实验室条件下对苹果炭疽病菌(C. gloeosporioides)均有一定抑制作用(暂未发表)。综上,笔者认为CmRh1对C. gloeosporioides的抑菌机制较为复杂,至少是多种机制的协同作用,抑菌活性物质包括脂肽类物质、挥发性物质和真菌细胞壁降解酶等。
本研究利用PCR技术克隆到1个葡聚糖内切酶基因(Glu4),开放阅读框ORF为1500 bp,编码499 aa,分子量约为55 kDa,理论等电点为7.14。Glu4基因与贝莱斯芽孢杆菌内切葡聚糖酶基因CMCase[35]和芽孢杆菌S6的内切葡聚糖酶基因(glu)[18]的ORF大小一致,且编码蛋白的氨基酸相似性高达96%,表明克隆到的Glu4在芽孢杆菌中高度保守。SDS-PAGE结合Western blot结果显示,Glu4基因能在大肠杆菌中高效表达,其蛋白大小与理论值55 kDa基本相符。另外,透明圈法初步证实原核表达的Glu4具有葡聚糖内切酶活性。
保守结构域预测,Glu4属于GH5糖苷水解酶家族,且包含CBM_3纤维素酶结合域(356~437 aa)。据报道,GH5是最大的糖苷水解酶家族,其酶序列在碳水化合物活性酶数据库超过12000个,且绝大多数GH5糖苷水解酶为内切酶[36]。碳水化合物结合组件CBM分为83个家族,其中CBM_2、CBM_3和CBM_6目标底物是纤维素[37]。Lee等[38]采用基因枪法从Bacillus sp. KD114克隆1个编码496个氨基酸的β-1,4-葡聚糖基因(cel5L)属于GH5家族,并证实Cel5L中CBM_3可能影响酶的热稳定性、酶和底物的亲和力、底物特异性。微泡菌属(Microbulbifer sp.)中β-1,4-葡聚糖酶基因MaCel5A[39]也属于GH5家族,2个几丁质结合结构域(chitin-binding domains)取代了CBM;大肠杆菌异源表达的MaCel5A对羧甲基纤维素和大麦β-葡聚糖有选择性的作用。来自Rhizosphere Metagenomic Library的β-1,4内切葡聚糖酶也属于GH5家族,但没有碳水化合物结合组件CBM;该酶对可溶形式的纤维素(如羧甲基纤维素和羟乙基纤维素等)作为底物表现出良好的活性[40]。本研究发现,芽孢杆菌CmRh1和重组大肠杆菌对CMC(β-1,4葡聚糖)的利用现象比茯苓多糖(主要是β-1,3葡聚糖)更加明显。因此,结合上述报道和本研究结果,推测本研究异源表达的Glu4可能主要具有内切β-1,4葡聚糖酶活性。下一步将对E. coli表达的Glu4进行纯化、酶学性质分析、探究Glu4对C. gloeosporioides的抑菌活性。本研究工作的开展,为将来全面阐明CmRh1对C. gloeosporioides的抑菌机理、研发生防菌剂来防治苹果炭疽病害奠定基础。
-
图 2 液培法测定CmRh1发酵液对苹果炭疽病菌的抑制作用
注:A.处理组A;B.对照组;图3同。
Figure 2. Determination of antifungal activity of fermentation broth against C. gloeosporioides by liquid culture method
图 10 Glu4重组蛋白表达的SDS-PAGE图谱
注:M:Protein Marker; 1:诱导前总蛋白;2:20 ℃ 上清;3:20 ℃ 沉淀;4:37 ℃ 上清;5:37 ℃ 沉淀;图11同。
Figure 10. Expression analysis of Glu4 recombinant protein by SDS-PAGE
-
[1] VELHO A C, ALANIZ S, CASANOVA L, et al. New insights into the characterization of Colletotrichum species associated with apple diseases in southern Brazil and Uruguay[J]. Fungal Biology,2015:229−244.
[2] HAHN M. The rising threat of fungicide resistance in plant pathogenic fungi: Botrytis as a case study[J]. Journal Chemical Biology,2014,7(4):133−141. doi: 10.1007/s12154-014-0113-1
[3] SHAFI J, TIAN H, JI M. Bacillus species as versatile weapons for plant pathogens: A review[J]. Biotechnology & Biotechnology Equipment,2017,31(3):446−459.
[4] 王珺, 郭庆港, 苏振贺, 等. 脂肽类抗生素fengycin对大丽轮枝菌孢子萌发和微菌核形成的影响[J]. 植物病理学报,2020,50(6):739−747. [WANG J, GUO Q G, SU Z H, et al. Effect of fengycin produced by Bacillus subtilis NCD-2 on the conidial germination and microsclerotia formation of Verticillium dahlia[J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica,2020,50(6):739−747. [5] CHEN L, ZHANG H, ZHAO S, et al. Lipopeptide production by Bacillus atrophaeus strain B44 and its biocontrol efficacy against cotton rhizoctoniosis[J]. Biotechnology Letters,2021,43:1183−1193. doi: 10.1007/s10529-021-03114-0
[6] 桑建伟, 杨扬, 陈奕鹏, 等. 内生解淀粉芽孢杆菌BEB17脂肽类和聚酮类化合物的抑菌活性分析[J]. 植物病理学报,2018,48(3):402−412. [SANG J W, YANG Y, CHEN Y P, et al. Antibacterial activity analysis of lipopeptide and polyketide compounds produced by endophytic bacteria Bacillus amyloliquefaciens BEB17[J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica,2018,48(3):402−412. [7] CHOUB V, MAUNG C E H, WON S J, et al. Antifungal activity of cyclic tetrapeptide from Bacillus velezensis CE100 against plant pathogen Colletotrichum gloeosporioides[J]. Pathogens,2021,10(2):209. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10020209
[8] RAJAOFERA M J N, WANG Y, DAHAR G Y, et al. Volatile organic compounds of Bacillus atrophaeus HAB-5 inhibit the growth of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides[J]. Pesticide Biochemistry Physiology,2019,156:170−176. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2019.02.019
[9] BOWMAN S M, FREE S J. The structure and synthesis of the fungal cell wall[J]. Bioessays,2006,28(8):799−808. doi: 10.1002/bies.20441
[10] SU X, WU S, LIU L, et al. Potential antagonistic bacteria against Verticillium dahlia isolated from artificially infested nursery[J]. Cells,2021,10(12):3588. doi: 10.3390/cells10123588
[11] WIN T T, BO B, MALEC P, et al. The effect of a consortium of Penicillium sp. and Bacillus spp. in suppressing banana fungal diseases caused by Fusarium sp. and Alternaria sp.[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology,2021,131:1890−1908. doi: 10.1111/jam.15067
[12] 国慧. 生防萎缩芽孢杆菌β-l, 3-葡聚糖酶拮抗功能的研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2017 GUO H. Study on the antagonistic function of the biocontrogenic Bacillus β-l, 3-glucanase[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University, 2017.
[13] EL-SAYED A S A, AKBAR A, IQRAR I, et al. A glucanolytic Pseudomonas sp. associated with Smilax bona-nox L. displays strong activity against Phytophthora parasitica[J]. Microbiological Research,2018,207:140−152. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2017.11.018
[14] 杨薇红, 童斌, 张小华, 等. 发芽马铃薯PDA培养基对几种霉菌培养效果的影响[J]. 农产品加工(上半月),2017(3):22−24. [YANG W H, TONG B, ZHANG X H, et al. Influence on culture effect of several moulds of germination of potato PDA medium[J]. Academic Periodical of Farm Products Processing,2017(3):22−24. [15] 余丽, 晏爱芬. 高黎贡山土壤中纤维素分解菌的筛选[J]. 生物学杂志,2012,29(2):34−36,76. [YU L, YAN A F. A study of microorganisms in Gaoligong Mountains—screening of celluloytic microbes[J]. Journal of Biology,2012,29(2):34−36,76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1736.2012.02.034 [16] 高小宁, 涂璇, 黄丽丽, 等. 产β-1,3-葡聚糖酶植物内生放线菌的筛选及抑菌活性研究[J]. 微生物学通报,2009,36(8):1189−1194. [GAO X N, TU X, HUANG L L, et al. The screen of plant endophytic actinomycetes producing β-1,3-glucanase and antifungal activity of β-1,3-glucanase[J]. Microbiology,2009,36(8):1189−1194. [17] 李琪敏, 周婷婷, 秦春秀, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌HAB-8菌株分离筛选鉴定及抑菌机理初步研究[J]. 黑龙江农业科学,2019(2):28−36. [LI Q M, ZHOU T T, QIN C X, et al. Isolation, screening, identification and antimicrobial mechanism of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain HAB-8[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences,2019(2):28−36. [18] 陈宁宁, 单秋丽, 郝委委, 等. 芽孢杆菌S6内切葡聚糖酶基因的克隆及功能鉴定[J]. 济南大学学报(自然科学版),2018,32(4):305−309. [CHEN N N, SHAN Q L, HAO W W, et al. Cloning and functional identification of endo-glucanase gene of Bacillus subtilis S6[J]. Journal of University of Jinan (Science and Technology),2018,32(4):305−309. [19] 焦文强, 刘运超, 邢广旭, 等. 猴源葡萄糖调节蛋白78生物信息学分析及其真核表达[J]. 中国畜牧兽医,2021,48(4):1170−1178. [JIAO W Q, LIU Y C, XING G X, et al. Bioinformatics analysis and eukaryotic expression of Chlorocebus sabaeus glucose regulatory protein 78[J]. China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine,2021,48(4):1170−1178. [20] 戴姿薇, 唐标. 新型冠状病毒相关TMPRSS2蛋白结构特征和抗原表位分析[J]. 微生物学杂志,2021,41(1):58−68. [DAI Z W, TANG B. Protein structural characteristics and antigen epitopes analysis of TMPRSS2 correlated with SARS-CoV-2[J]. Journal of Microbiology,2021,41(1):58−68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7021.2021.01.008 [21] ALMGRO ARMENTEROS J J, TSIRIGOS K D, SONDERBY C K, et al. SignalP 5.0 improves signal peptide predictions using deep neural networks[J]. Nature Biotechnology,2019,37(4):420−423. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0036-z
[22] MARCHLER-BAUER A, BO Y, HAN L, et al. CDD/SPARCLE: functional classification of proteins via subfamily domain architectures[J]. Nucleic Acids Research,2017,45(D1):D200−D203. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw1129
[23] 刘月, 张宇飞, 张亚坤, 等. 绵羊肺腺瘤病毒NM株囊膜蛋白的二级结构及其B细胞抗原表位预测[J]. 动物医学进展,2013,34(1):29−33. [LIU Y, ZHANG Y F, ZHANG Y K, et al. Prediction of secondary structure and B cell epitope for envelope protein of OPAV-NM strain[J]. Progress in Veterinary Medicine,2013,34(1):29−33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5038.2013.01.007 [24] 游韩莉, 袁义杭, 李长江, 等. 青杄MYB转录因子基因PwMYB20的克隆及表达分析[J]. 林业科学,2017,53(5):23−32. [YOU H L, YUAN Y H, LI C J, et al. Cloning and expression analysis of MYB homologous gene PwMYB20 from Picea wilsonii[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae,2017,53(5):23−32. doi: 10.11707/j.1001-7488.20170504 [25] 陈煜文. 水稻纹枯病菌内切葡聚糖酶基因EG146的克隆与表达[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2020 CHEN Y W. Cloning and expression of endoglucanase gene EGl46 fromo Rhizoctonia solani, the pathogen of rice sheat blight [D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2020.
[26] 冯伟科. 拟南芥维生素K环氧化物还原酶的亚细胞定位和拓扑结构研究[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2011 FENG W K. Subcellular localization and membrane topology of Arabidopsis vitamin K epoxide reductase[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2011.
[27] YU C S, CHEN Y C, LU C H, et al. Prediction of protein subcellular localization[J]. Proteins: Structure, Function and Bioinformatics,2006,64:643−651. doi: 10.1002/prot.21018
[28] 曹志艳, 杨胜勇, 董金皋. 植物病原真菌黑色素与致病性关系的研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报,2006(1):154−158. [CAO Z Y, YANG S Y, DONG J G. A review on relation between pathogenicity and melanin of plant fungi[J]. Microbiology China,2006(1):154−158. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2654.2006.01.031 [29] 王圆, 张朝晖, 王蓓, 等. 细菌产β-1,3-1,4-葡聚糖酶的结构、功能及应用的研究进展[J]. 饲料工业,2005,26(2):18−20. [WANG Y, ZHANG Z H, WANG B, et al. Advance in the study of structure, function and application of β-1,3-1,4-glucanase produced by bacteria[J]. Feed Industry,2005,26(2):18−20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-991X.2005.02.005 [30] 侯进慧, 张翔, 乔高翔. 菠萝泛菌β-1, 4-内切葡聚糖酶基因克隆、表达与酶活性分析[J]. 食品科学,2016,37(23):211−215. [HOU J H, ZHANG X, QIAO G X. Cloning, expression and activity of an endo-1, 4-β-D-glucanase from Pantoea ananatis[J]. Food Science,2016,37(23):211−215. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201623035 [31] 张年, 李兆星, 李娟, 等. 茯苓的化学成分与生物活性研究进展[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化,2019,21(2):220−233. [ZHANG N, LI Z X, LI J, et al. Advances in the research of constituents and pharmacological effects of Poria cocos (Schw.) Wolf[J]. World Science and Technology-Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2019,21(2):220−233. [32] 李纪顺, 陈凯, 李红梅, 等. 通过染色体整合β-1,4-葡聚糖酶基因glu14提高绿色木霉对小麦纹枯病的防治效果[J]. 植物病理学报,2013,43(4):393−400. [LI J S, CHEN K, LI H M, et al. Enhanced bio-control activity of Trichoderma viride against wheat sheath blight (Rhizoctonia cerealis) through chromosomal integration of Bacillus megaterium β-1,4-glucanase gene glu14[J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica,2013,43(4):393−400. [33] 黄大野, 杨丹, 曹春霞. 链霉菌HEBRC45958防控番茄棒孢叶斑病研究[C]// 病虫防护与生物安全——中国植物保护学会2021年学术年会论文集, 2021: 113 HUANG D Y, YANG D, CAO C X. Studies on the control of tomato cladospora leaf spot disease by Streptomyces HEBRC45958[C]// Pest prevention and biosafety-Proceedings of the 2021 academic annual meeting of the Chinese plant protection society, 2021: 113.
[34] 范青, 田世平, 刘海波, 等. 两种拮抗菌β-1, 3-葡聚糖酶和几丁酶的产生及其抑菌的可能机理[Z]. 中国科学院植物研究所, 2009-01-01 FAN Q, TIAN S P, LIU H B, et al. Production of two antagonistic bacteria β-1, 3-glucanase and chitinase and their possible inhibitory mechanism [Z]. Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2009-01-01.
[35] 陈龙, 吴兴利, 闫晓刚, 等. 贝莱斯芽孢杆菌的内切葡聚糖酶基因的克隆、表达及其酶学性质分析[J]. 中国畜牧杂志,2019,55(9):100−108. [CHEN L, WU X L, YAN X G, et al. Cloning and expression of β-1,4-endoglucanase gene from Bacillus velezensis and its enzymatic properties[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science,2019,55(9):100−108. [36] BERLEMONT R, MARTINY A C. Phylogenetic distribution of potential cellulases in bacteria[J]. Applied Environmental Microbiolology,2013,79(5):1545−1554. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03305-12
[37] TALAMANTES D, BIABINI N, DANG H, et al. Natural diversity of cellulases, xylanases, and chitinases in bacteria[J]. Biotechnol Biofuels,2016,9:133. doi: 10.1186/s13068-016-0538-6
[38] LEE J P, SHIN E S, CHO M Y, et al. Roles of carbohydrate-binding module (CBM) of an endo-β-1,4-glucanase (Cel5L) from Bacillus sp. KD1014 in thermostability and small-substrate hydrolyzing activity[J]. Journal of Microbiology Biotechnology,2018,28(12):2036−2045. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1802.10001
[39] LI H, HU Q, HONG X, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of a thermostable and halotolerant endo-β-1,4-glucanase from Microbulbifer sp. ALW1[J]. 3 Biotech,2021,11(5):250. doi: 10.1007/s13205-021-02801-z
[40] WIERZBICKA-WOS A, HENNEBERGE R, BATISTA-GARCIA R A, et al. Biochemical characterization of a novel monospecific belonging to GH family 5 from a rhizosphere metagenomic library[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2019,10:1342. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01342
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 石启龙,刘静,赵亚. 基于温度分布和水分状态分布的扇贝柱蛋白质加热变性数值模拟. 食品工业科技. 2025(05): 239-247 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 李晓燕,丁奕涵,矫佳伟,巩雪,李立,王天娜. 农产品超声辅助热泵干燥技术的研究进展. 包装工程. 2024(09): 53-61 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘静,赵亚,石启龙. 果蔬和水产品新型干燥预处理技术研究进展及未来展望. 食品工业科技. 2022(10): 32-42 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 刘静,赵亚,石启龙. 渗透剂预处理对扇贝柱热泵干燥动力学及品质特性的影响. 食品科学技术学报. 2022(03): 145-156 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 赵亚,朱智壮,石启龙,刘静. 成膜预处理提高扇贝柱超声波辅助热泵干燥效率及品质. 农业工程学报. 2022(18): 274-283 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 吴紫茼,金婧彧,马亚娟,王佳荣,王阳阳,刘亚琼,王颉. 海湾扇贝柱(Argopecten irradians)干制过程中蛋白质变化对品质特性的影响. 食品科技. 2021(10): 115-121 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)








 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



