Immunity Enhancement Activity and Mechanism of Ganoderma lucidum-Panax quiquefolium L.-Cordyceps sinensis compound Based on Network Pharmacology
-
摘要: 本研究系统评价了灵芝西洋参冬虫夏草复方(以下简称“复方”)的增强免疫力功能,并采用网络药理学探究其作用机制。分别考察复方的NK细胞活性、迟发型变态反应、脾淋巴细胞增殖能力和单核-巨噬细胞吞噬能力以评估其增强免疫力活性。体外和体内结果表明:复方低、中、高剂量组(0.4、0.8、2.4 g/kg)均可以显著增加NK细胞活性(P<0.001),中、高剂量组均能显著增加迟发型变态反应(P<0.001),低剂量组可以显著增加巨噬细胞吞噬能力(P<0.05)。利用多个在线数据库收集复方的活性成分、作用靶点及疾病靶点。使用Cytoscape、STRING 等软件构建复方-靶点-疾病网络与蛋白质相互作用网络,并运用Metascape对靶点基因进行GO与KEGG富集分析。网络药理学分析结果表明:该复方通过花生四烯酸、过氧麦角甾醇、胆固醇棕榈酸酯、PQ-2、环氧灵芝醇C、麦角甾-7,9,22-三烯-3-醇、麦角甾烷-7,22-二烯-3β-醇等活性物质,作用于NK细胞和T细胞的蛋白激酶B(AKT1)、表皮生长因子受体(EGFR)、非受体酪氨酸激酶(SRC)等靶点,调控肿瘤、FOXO、Th17、NK细胞等信号通路协同发挥增强免疫力作用。同时本研究初步揭示了复方增强免疫力的多组分、多靶点、多通路的协同作用机制,为后续深入研究其分子机制和应用提供了新思路和理论依据。Abstract: In this study, the immunity enhancement activity of Ganoderma lucidum-Cordyceps sinensis-Panax quiquefolium L. compound (here in after referred to as "compound") was systematically evaluated, and its mechanism was explored by network pharmacology. The NK cell activity, delayed allergic reaction, spleen lymphocyte proliferation and monocyte-macrophage phagocytosis of compound were investigated to evaluate its immunity enhancement activity. The results in vivo and in vitro indicated the low, medium and high dose groups (0.4, 0.8, 2.4 g/kg) of compound could significantly increase NK cell activity (P<0.001), the medium and high dose groups could significantly increase the delayed allergic reaction activity (P<0.001), and the low dose group could significantly increase the phagocytic index of monocyte-macrophage (P<0.05). The active ingredients, action targets and disease targets of the compound were collected by multiple online databases and document retrieval. Cytoscape and STRING were utilized to construct the interaction network between compound-target-disease network and protein, GO and KEGG enrichment analysis of target genes performed by Metascape. The results of network pharmacological analysis indicated that the compound could act on 94 targets such as protein kinase B (AKT1), epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and non-receptor tyrosine kinase (SRC) of NK cells and T cells by active substances such as arachidonic acid, peroxyergosterol, cholesterol palmitate, PQ-2, epoxy ganoderma alcohol C, ergosterol-7,9,22-triene-3-alcohol, ergosteran-7,22-diene-3β-alcohol and other active compounds, regulate 1382 GO items, including tumor regulation, FOXO, Th17 and NK cells and 171 signal channel to synergistically enhance immunity. Meanwhile, this study preliminarily revealed the synergistic mechanism of multi-components, multi-targets and multi-pathways of the compound to immunity enhancement, which could provide new ideas and theoretical basis for further study in its molecular mechanism and application.
-
免疫系统是人体健康的重要防线,能够识别和清除体内衰老、死亡,甚至发生变异的肿瘤细胞等,从而维持机体的稳定[1]。免疫系统功能失调严重影响身体健康,甚至发生疾病,因此对免疫系统调节对健康的维持非常关键[2]。免疫调节功能的保健食品开发是目前的研究热点,据统计,在所有保健食品中,增强免疫力保健食品数量排名第一位[3-4]。
灵芝是我国传统食疗宝库中的瑰宝,研究表明其富含多糖、三萜及甾醇等多种活性成分,具有抗炎、抗衰老、抗氧化及增强免疫力等多种功能[5-6]。西洋参,又名花旗参,富含皂苷和多糖等活性成分,现代研究表明具有增强免疫力作用[7-9]。冬虫夏草富含腺苷和多糖等活性成分,研究显示冬虫夏草多糖和腺苷具有增强免疫力的作用[10]。虽然灵芝西洋参复方[11],冬虫夏草西洋参复方[12]的增强免疫力研究报道较多,但灵芝、西洋参、冬虫夏草三者复配的增强免疫力活性及作用机制的研究暂未见报道。近些年,灵芝、西洋参、冬虫夏草已经均被用于保健食品开发,其中灵芝和西洋参进入药食同源试点[3-4]。
基于复方原料多成分、多靶点和途径复杂等特点,本研究利用网络药理学方法[13]研究复方增强免疫力的物质基础和作用机制,为进一步开发灵芝-西洋参-冬虫夏草复方功能产品和保健食品的研发提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
SPF级健康成年昆明小鼠 150只,合格证号为430727211100934021和430727211100995338。体质量18~22 g,购自湖南斯莱克景达实验动物有限公司,实验动物许可证号SCXK(湘)2021-0002,审查批文号:IAEC-K-210420-01。饲养环境条件为温度18~29 ℃,相对湿度40%~70%,12 h/12 h明暗交替,自由摄食和饮水。动物经适应性饲养1周后开始实验。灵芝-西洋参-冬虫夏草复方(批号:SHS2108262-2) 由东莞市东阳光冬虫夏草研发有限公司提供;BCCB9502二硝基氟苯 美国Sigma公司;12007145蓖麻油酸 上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;2020042202丙酮 Keshi;印度墨汁 西基(上海)生物科技有限公司;B2025019 Na2CO3 上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;SZ604 LDH试剂盒 东仁化学科技(上海)有限公司。
CKX41生物倒置显微镜 日本奥林巴斯公司;ST16离心机 赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司;PHERASatarFS酶标仪 德国BMGLABTECH有限公司;HERAcell® 150i细胞培养箱 赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司;Cellometer AutoT4细胞计数仪 上海厦泰生物科技有限公司;SW-CJ超净操作台 苏州安泰空气技术有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 剂量与实验设计
灵芝-西洋参-冬虫夏草复方制备方法:取灵芝400 g,料液比1:10,沸水提取2 h,重复两次,过滤后合并滤液,真空干燥后制得灵芝粉。西洋参200 g、冬虫夏草(繁育品)100 g粉碎,过100目筛,分别得西洋参和冬虫夏草粉。将上述三种粉末加入适当辅料混合,制备得到复方480 g。灵芝西洋参胶囊购买于药店(作为实验阳性对照物);以上样品根据实验需求称取适量,用蒸馏水稀释至所需浓度。
根据李立等[11]、邱涵等[12]对灵芝洋参复合物、冬虫夏草西洋参复合物增强免疫力功能实验研究,复方成人每日推荐用量为4.8 g,成人以60 kg计,则人的用量为0.8 g/kg体重,依据药效研究中人与小鼠给药剂量的换算方法[14],即复方低、中、高剂量为0.4、0.8、2.4 g/kg/d,分别对应人体剂量的5、10、30倍,灌胃给药。灵芝西洋参胶囊,按照日推荐剂量0.4 g*4粒/d/60 kg,即26.7 mg/kg/d,对小鼠按照10倍人体剂量灌胃给药,即267 mg/kg/d。正常组每天灌胃给纯净水,给药组每天给药,连续30 d,根据《保健食品功能评价方法(2020年版)(征求意见稿)》[15]评价复方的增强免疫力活性,检测小鼠NK细胞活性、迟发型变态反应、脾淋巴细胞增殖能力和单核-巨噬细胞吞噬能力。
1.2.2 检测实验方法
检测方法参考《保健食品功能评价方法(2020年版)(征求意见稿)》。
1.2.2.1 NK细胞活性测定实验
按要求将各项加入96孔培养板中,于37 ℃、5% CO2培养箱中培养4 h后,按LDH检测试剂盒步骤加入反应液及终止液,酶标仪490 nm处测定OD值。
1.2.2.2 迟发型变态反应(耳肿胀)
给药第25 d,小鼠腹部剃毛,范围约3 cm×3 cm,用二硝基氟苯(DNFB)溶液50 μL均匀涂抹致敏。5 d后,用DNFB溶液10 μL均匀涂抹于小鼠右耳(两面)再次致敏。24 h后处死小鼠,剪下左耳和右耳。用打孔器取下直径8 mm的耳片,称重。
1.2.2.3 小鼠碳廓清实验
用生理盐水将印度墨汁原液稀释4倍。按体重从小鼠尾静脉注入稀释的印度墨汁(10 mL/kg),待墨汁注入,立即计时。注入墨汁后2、10 min,分别从内眦静脉丛取血20 μL,并立即将其加到2 mL 0.1%Na2CO3溶液中。以Na2CO3溶液作空白对照,在600 nm波长处测光密度(OD)值。处死小鼠,取肝脏和脾脏,用滤纸吸干脏器表面血污,分别称重。
1.2.2.4 脾淋巴细胞提取
无菌取脾,置于盛有适量磷酸缓冲盐溶液(PBS)的平皿中,用注射器吸取PBS冲洗脾脏表面及内部至脾脏发白,用镊子轻轻将脾撕碎,用注射器内芯将脾脏研磨制成单个细胞悬液。经200目筛网过滤,用PBS液洗1次,1500 r/min离心5 min。细胞沉淀中加入红细胞裂解液5~10 mL,混匀静置5 min,加入PBS至50 mL混匀,200目筛网过滤,1500 r/min离心5 min,弃上清,重复操作一次;然后将细胞悬浮于20 mL完全培养液中,活细胞计数,离心重悬后,分别调整细胞浓度为2×107和2×106个/mL。
1.2.2.5 脾淋巴细胞增殖
取细胞密度为2×106个/mL的脾细胞悬液200 μL分别加入96孔培养板中,一孔加ConA液15 μL,另一孔作为对照,设3个平行孔,置37 ℃,5% CO2培养箱中培养48 h。采用CCK-8法检测细胞增殖情况,用酶标仪在450 nm处测定吸光度。
1.2.3 复方活性化合物筛选
利用中药系统药理学数据库与分析平台(TCMSP)平台[16](http://tcmspw.com/tcmsp.php),检索西洋参、灵芝和冬虫夏草的成分信息,以药代动力学(ADME)参数中的口服利用度(oral bioavailability,OB)≥30%和药物相似性(drug-likeness,DL)≥0.18作为筛选指标。将初筛结果通过Pubchem数据库(https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov),确定其2D分子结构,并保存为SDF格式。
1.2.4 复方潜在作用靶点获取
通过Pharmmapper药物靶点数据库[17-18](http://www.lilab-ecust.cn/pharmmapper),对筛选后的复方活性成分所作用的靶点进行预测。利用Uniprot数据库(https://www.uniprot.org),选择生物物种为“Homo sapiens”,对所作用的蛋白质靶点信息统一规范化。将复方有效成分及其靶点信息整理导入软件Cytoscape 3.6.1,构建复方活性成分-靶点网络图。
1.2.5 免疫力相关靶点筛选
以“immunity”为关键词,挖掘GeneCards数据库(https://www.genecards.org/)、Drugbank数据库[19](https://www.drugbank.ca/)、OMIM数据库(https://www.omim.org/),收集与免疫相关的所有受体及基因信息。利用R语言将复方靶点信息与免疫力靶点信息进行对比分析,找到共同靶点,并绘制维恩图,将其标记为复方活性成分增强免疫功能的潜在作用靶点。
1.2.6 蛋白-蛋白相互作用网络构建与分析
将二者的交集靶点提交至STRING version 11.0数据库[20](https://string-db.org/),设定生物种类为“Homo sapiens”,置信度为0.4,保存TSV格式结果。将全部节点信息导入Cytoscape 3.6.1构建蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用(protein-protein interaction,PPI)网络模型,借助Network Analysis进行拓扑参数特性分析。节点(node)大小和颜色反映度值(degree)的大小,边(edge)的粗细反映结合分数的大小。
1.2.7 GO富集分析与KEGG通路分析
将靶点信息导入生物信息资源Metascape数据库[21](https://metascape.org/),设定生物物种为“Homo sapiens”,对复方增强免疫力功能靶点参与的主要的生物学过程与代谢通路并进行富集分析。对GO数据各筛选前20条,KEGG数据筛选前20条通路信息,利用bioinformatics平台(http://www.bioinformatics.com.cn/)进行可视化处理。
1.2.8 复方“药物成分-作用靶点-作用通路”网络构建
将上述的活性成分、靶点预测结果、通路分析结果导入Cytoscape 3.6.1,构建复方的成分-靶点-通路网络图,借助Cytoscape 3.6.1进行拓扑分析,预测复方增强免疫力的潜在核心靶点及发挥药效的主要活性成分。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 增强免疫力活性实验
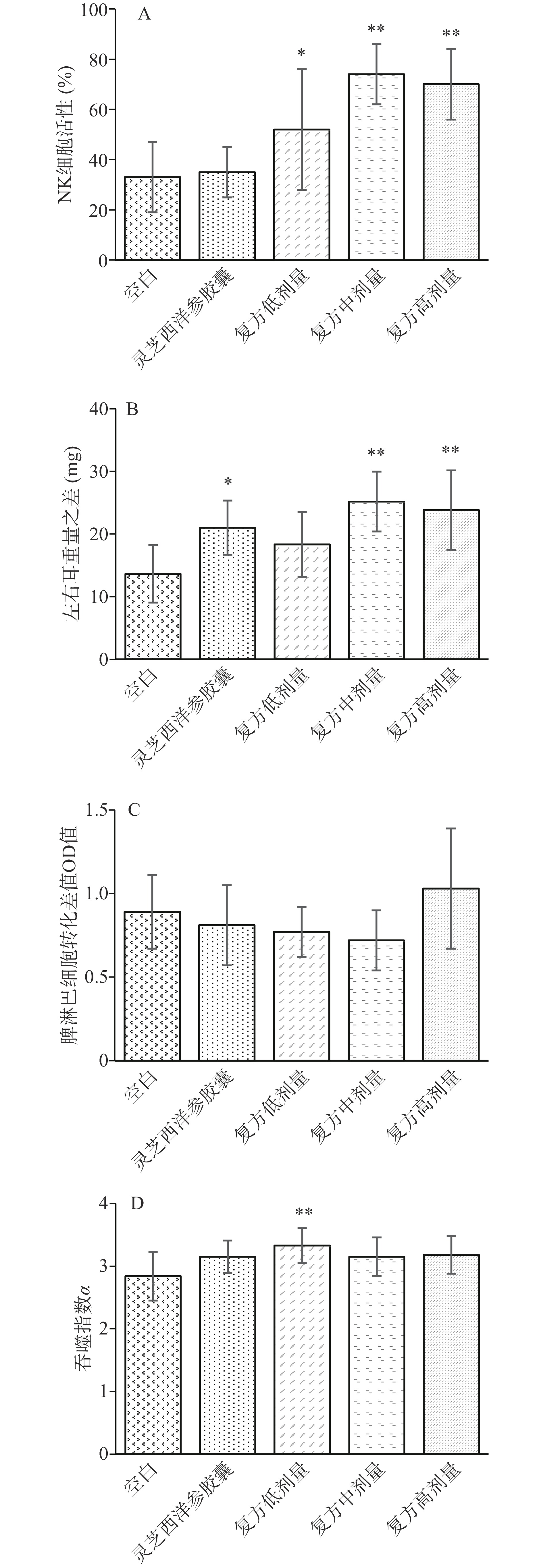
自然杀伤细胞(NK)可以直接杀伤靶细胞,它不依赖抗体和补体而直接实现免疫功能,有免疫调节作用,并可以达到直接杀伤靶细胞的目的,所以NK 细胞的活性是衡量机体免疫的重要指标[22]。如图1所示,在NK细胞活性实验中,与空白组相比,实验组复方低(P<0.05)、中(P<0.001)、高(P<0.001)剂量组均可以增加小鼠NK细胞活性,且实验组免疫力活性随给药浓度的上升呈现一定的剂量依赖性,其中复方中、高剂量可以极显著增加小鼠NK细胞活性。
吞噬实验是通过观察巨噬细胞对异物颗粒的吞噬能力,来评价吞噬细胞的功能和反映非特异性免疫应答能力,从而反映机体的天然免疫防御功能。机体内巨噬细胞、中性粒细胞等都具有吞噬功能,这些细胞的功能正常与否关系到免疫应答的抗原提呈过程和抗原清除能力[23]。在吞噬指数实验中,复方低剂量组可以显著增加小鼠巨噬细胞对墨汁的吞噬指数(P<0.001),灵芝西洋参胶囊组和复方中、高剂量组对小鼠巨噬细胞吞噬能力也有一定增强作用,但统计学结果不显著。
二硝基氟苯(DNFB)稀释液可与腹壁皮肤蛋白结合成完全抗原,由此刺激T 淋巴细胞增殖成致敏淋巴细胞。4~7 d后再将其涂抹于耳部进行抗原攻击,使局部肿胀,一般在抗原攻击后24~48 h达高峰,其肿胀程度可以反映迟发型变态反应程度。在迟发型变态反应实验中,灵芝西洋参胶囊组(P<0.05)和复方中(P<0.001)、高(P<0.001)剂量组均能显著增加小鼠迟发型变态反应,复方低剂量组虽然也可以增加小鼠迟发型变态反应,但统计学结果不显著(P>0.05)。
脾脏淋巴细胞中含有T淋巴细胞和B淋巴细胞,它们均是机体的免疫活性细胞,其增殖是反映细胞免疫最直接的指标[24]。在脾淋巴细胞增殖实验中,复方高剂量组小鼠脾淋巴细胞增殖能力高于正常组,但无统计学意义,灵芝西洋参和复方低、中剂量组小鼠脾淋巴细胞增殖能力与空白组无显著差异(P>0.05)。
因此从复方增强免疫力活性实验结果来看:复方可以提高NK细胞活性和促进迟发型变态反应。
根据《保健食品功能评价方法(2020年版)(征求意见稿)》规定及评价方法,在NK 细胞活性实验中,有两个剂量阳性,可以判定复方的NK细胞活性实验结果阳性;复方在迟发型变态反应中有两个剂量阳性,可以判定细胞免疫功能实验结果为阳性。综合以上实验结果判定:复方具有增强免疫力功能。复方具有可进一步开发为增强免疫力的保健食品的潜力。
2.2 复方活性成分筛选
通过TCMSP平台与相关文献[25-28]中的冬虫夏草化合物,共计筛选出复方有效活性成分79个(西洋参11个,灵芝54个,冬虫夏草14个),其中三者共有化合物1个,灵芝与冬虫夏草共有化合物4个,具体化合物信息见表1。
表 1 复方活性成分信息Table 1.Active ingredients information of compound Mol ID 分子名称 分子质量 OB(%) DL Source ID MOL001645 Linoleyl acetate 乙酸亚油醇酯 308.56 42.10 0.20 Cordyceps sinensis CS1 MOL001439 Arachidonic acid 花生四烯酸 304.52 45.57 0.20 Cordyceps sinensis CS2 MOL008999 Cholesteryl palmitate 胆固醇棕榈酸酯 625.19 31.05 0.45 Cordyceps sinensis CS3 MOL012269 Stigmasta-5,22-dien-3-ol-acetate 醋酸豆甾醇 454.81 46.44 0.86 Cordyceps sinensis CS4 MOL001973 Sitosteryl acetate β-谷甾醇乙酸酯 456.83 40.39 0.85 Cordyceps sinensis CS5 MOL000449 Stigmasterol 豆甾醇 412.77 43.83 0.76 Cordyceps sinensis CS6 MOL000359 Sitosterol 谷甾醇 414.79 36.91 0.75 Cordyceps sinensis CS7 MOL001510 24-Epicampesterol 24-表甾醇 400.76 37.58 0.71 Cordyceps sinensis CS8 MOL002224 Aurantiamide acetate 金色酰胺醇酯 444.57 58.38 0.59 Cordyceps sinensis CS9 MOL002140 Perlolyrine 川芎哚 264.3 65.95 0.27 Cordyceps sinensis CS10 MOL011125 (+)-Ganoderic acid Mf 灵芝酸F 512.8 32.62 0.82 Ganoderma lucidum GL1 MOL011127 (+)-Methyl ganolucidate A 赤灵芝酸甲酯A 514.77 31.14 0.82 Ganoderma lucidum GL2 MOL011129 Methyl lucidenate F 赤芝酸甲酯F 470.66 32.67 0.81 Ganoderma lucidum GL3 MOL011135 22,23-Dimethylene ganodermic acid S 灵芝酸 578.86 33.61 0.71 Ganoderma lucidum GL4 MOL011137 Campesta-7,22E-dien-3beta-ol 星鱼甾醇 398.74 43.51 0.72 Ganoderma lucidum GL5 MOL011156 Epoxyganoderiol A 环氧灵芝醇A 472.78 33.78 0.83 Ganoderma lucidum GL6 MOL011157 Epoxyganoderiol B 环氧灵芝醇B 454.76 42.3 0.83 Ganoderma lucidum GL7 MOL011158 Epoxyganoderiol C 环氧灵芝醇C 456.78 37.7 0.83 Ganoderma lucidum GL8 MOL011160 Ganodesterone 灵芝固醇 408.68 47.86 0.77 Ganoderma lucidum GL9 MOL011162 Ergosta-7,22-dien-3beta-yl palmitate 麦角甾-7,22-
三烯-3β-醇棕榈酸酯637.2 37.60 0.43 Ganoderma lucidum GL10 MOL011164 Ergosta-7,22-dien-3β,5α,6α-triol 啤酒甾醇 430.74 31.43 0.77 Ganoderma lucidum GL11 MOL011165 Ergosta-7,22-diene-3beta-yl linoleate 麦角甾-7,22-
二烯-3β-醇亚油酸酯661.22 45.11 0.37 Ganoderma lucidum GL12 MOL011167 Ergosta-7,22-diene-3beta-yl Pentadecanoate 麦角甾-7,22-
二烯-3β-醇十五酸酯623.17 38.25 0.47 Ganoderma lucidum GL13 MOL011168 Ergosta-7,9(11),22-trien-3β,5α,6α-triol 麦角甾醇 442.75 46.95 0.78 Ganoderma lucidum GL14 MOL011171 Ganoderal B 灵芝醇B 440.73 42.56 0.81 Ganoderma lucidum GL15 MOL011172 Ganoderan B 灵芝多糖B 454.76 42.19 0.81 Ganoderma lucidum GL16 MOL011189 Ganoderic acid DM 灵芝酸DM 468.74 38.8 0.83 Ganoderma lucidum GL17 MOL011206 Ganoderic acid Me灵芝酸Me 554.84 31.16 0.76 Ganoderma lucidum GL18 MOL011209 Ganoderic acid Mi 灵芝酸Mi 528.85 34.4 0.81 Ganoderma lucidum GL19 MOL011214 Ganoderic acid R 灵芝酸R 554.84 31.46 0.77 Ganoderma lucidum GL20 MOL011215 Ganoderic acid S 灵芝酸S 512.8 34.37 0.83 Ganoderma lucidum GL21 MOL011218 Ganoderic acid TQ 灵芝酸TQ 524.81 36.30 0.78 Ganoderma lucidum GL22 MOL011219 Ganoderic acid TR 灵芝酸TR 468.74 36.23 0.83 Ganoderma lucidum GL23 MOL011221 Ganoderic acid V 灵芝酸V 528.8 30.19 0.80 Ganoderma lucidum GL24 MOL011222 Ganoderic acid V1 灵芝酸V1 512.75 30.18 0.80 Ganoderma lucidum GL25 MOL011224 Ganoderic acid X 灵芝酸X 512.8 33.55 0.81 Ganoderma lucidum GL26 MOL011225 Ganoderic acid Y 灵芝酸Y 454.76 38.64 0.82 Ganoderma lucidum GL27 MOL011226 Ganoderic acid Z 灵芝酸Z 456.78 37.67 0.82 Ganoderma lucidum GL28 MOL011229 Ganoderic aldehyde A 灵芝醛A 454.76 42.26 0.81 Ganoderma lucidum GL29 MOL011235 Ganoderiol F 灵芝醇F 454.76 38.12 0.82 Ganoderma lucidum GL30 MOL011241 Ganodermanondiol 灵芝酮二醇 456.78 37.64 0.80 Ganoderma lucidum GL31 MOL011243 Ganodermatriol 灵芝三醇 456.78 30.46 0.82 Ganoderma lucidum GL32 MOL011244 Ganodermenonol 灵芝萜酮三醇 438.76 44.69 0.80 Ganoderma lucidum GL33 MOL011245 Ganodermic acid R 灵芝酸R 554.84 31.16 0.76 Ganoderma lucidum GL34 MOL011247 Ganodermic acid T-Q 灵芝酸T-Q 512.8 33.55 0.81 Ganoderma lucidum GL35 MOL011248 Ganodermic acid T-O 灵芝酸T-O 512.8 32.62 0.82 Ganoderma lucidum GL36 MOL011250 Ganodermnonol 灵芝萜烯酮醇 438.76 44.69 0.80 Ganoderma lucidum GL37 MOL011251 Ganoderol A 灵芝醇A 438.76 44.69 0.80 Ganoderma lucidum GL38 MOL011256 Ganolucidic acid E 灵芝酸E 484.74 32.85 0.82 Ganoderma lucidum GL39 MOL011258 Ganosporelactone B 灵芝内酯B 530.72 31.21 0.33 Ganoderma lucidum GL40 MOL011266 Lucialdehyde A 灵芝醛A 438.76 44.78 0.80 Ganoderma lucidum GL41 MOL011267 Lucialdehyde B 灵芝醛B 452.74 43.12 0.81 Ganoderma lucidum GL42 MOL011268 Lucialdehyde C 灵芝醛C 454.76 42.26 0.81 Ganoderma lucidum GL43 MOL011270 Lucidenic acid A 赤芝酸A 458.65 30.34 0.79 Ganoderma lucidum GL44 MOL011287 Lucidone A 赤芝酮A 402.58 37.22 0.64 Ganoderma lucidum GL45 MOL011290 Lucidumol A 赤芝萜醇A 458.8 34.75 0.8 Ganoderma lucidum GL46 MOL011303 Methyl Ganoderic acid DM 甲基灵芝酸DM 482.77 39.55 0.83 Ganoderma lucidum GL47 MOL011304 Methyl Ganoderic acid TR 甲基灵芝酸TR 482.77 39.82 0.83 Ganoderma lucidum GL48 MOL011309 Methyl lucidenate Q 赤芝酸甲酯Q 474.7 30.19 0.81 Ganoderma lucidum GL49 MOL000282 Stellasterol 星鱼甾醇 398.74 43.51 0.72 Ganoderma lucidum GL50 MOL011394 Ginsenoside F2 人参皂苷 F2 785.14 36.43 0.25 Panax ginseng PG1 MOL011434 Polyacetylene PQ-2 聚乙炔PQ-2 306.44 36.74 0.20 Panax ginseng PG2 MOL011435 PQ-2 306.44 36.74 0.19 Panax ginseng PG3 MOL011442 Stigmasta-3,5-dien-7-one 豆甾烯醇 410.75 43.87 0.75 Panax ginseng PG4 MOL011455 20-Hexadecanoylingenol 殷金醇棕榈酸酯 418.58 32.70 0.65 Panax ginseng PG5 MOL005344 Ginsenoside rh2 人参皂苷 rh2 622.98 36.32 0.56 Panax ginseng PG6 MOL006774 Stigmast-7-enol 豆甾醇-7-烯醇 414.79 37.42 0.75 Panax ginseng PG7 MOL006980 Papaverine 罂粟碱 339.42 64.04 0.38 Panax ginseng PG8 MOL008173 Daucosterol_qt 胡萝卜甾醇 414.79 36.91 0.75 Panax ginseng PG9 MOL008397 Daturilin 白曼陀罗灵 436.64 50.37 0.77 Panax ginseng PG10 MOL000358 Beta-sitosterol β-谷甾醇 414.79 36.91 0.75 PQ/GL/CS CoMol1 MOL011169 Peroxyergosterol 过氧化麦角甾醇 428.72 44.39 0.82 GL/CS CoMol2 MOL011159 Ergosta-4,6,8(14),22-tetraene-3-one 麦角甾烯酮 406.71 48.32 0.75 GL/CS CoMol3 MOL008998 Cerevisterol 啤酒甾醇 432.76 39.52 0.77 GL/CS CoMol4 2.3 复方活性成分靶点关系网络构建
对2.2中检索的81个化合物分别导入Pharmmapper服务器,收集匹配度(Norm fit)≥0.95的靶点信息,合并后剔除重复值共得到靶点306个。利用Cytoscape 3.6.1对上述数据集构建化合物靶点关系网络,见图2。
2.4 免疫力相关靶点数据构建
以“immunity”为关键词在GeneCards数据库初步筛选出17418个候选基因,根据经验,设定多次Relevance score值大于等于中位数,以Relevance score≥10.11的基因为免疫力相关的潜在靶点,共806个。同时,以“immunity”为关键词在OMIM数据库筛选出潜在靶点11个,Drugbank数据库筛选出潜在靶点34个,Therapeutic Target Database (TTD) 数据库筛选出潜在靶点10个。合并后删除重复值,最终得到851个与免疫力相关的潜在靶点。将2.2中收集的复方活性成分靶点与免疫力靶点取交集,并绘制韦恩图,得到成分-疾病共同靶点94个,见图3。
2.5 复方增强免疫力的PPI网络分析
将相关靶点导入STRING version 11.0数据平台,分析蛋白-蛋白相互作用关系,将结果导入软件Cytoscape 3.6.1构建蛋白相互作用关系网络,见图4。经Network Analyzer分析网络拓扑学参数,其网络中聚类系数为0.644,共有94个节点(靶点蛋白)、1208条边(蛋白相互作用),蛋白与蛋白之间线条表示靶点之间相互作用关系,线条越多表示关联度越大。结果表明,AKT1、EGFR、SRC、ALB、HSP90AA1度值较大,分别为72、70、70、69、60,其为5个关键靶点。
2.6 生物信息学GO分析
应用Metascape数据平台对复方增强免疫力的相关靶点进行GO-BP(生物过程)、GO-CC(细胞组分)、GO-MF(分子功能)分析,将GO条目按照-log10(P) value进行排序,分别选取各类别的前20绘制富集泡泡图,见图5。由结果分析可见,复方参与的免疫力相关的生物过程(Biological Process, BP)可能主要参与蛋白质磷酸化(protein phosphorylation)、对激素的反应(response to hormone)、细胞对脂质的反应(cellular response to lipid)、转移酶活性的正向调节(positive regulation of transferase activity)和细胞粘附的调节(regulation of cell adhesion)等多条生物过程;相关的细胞组分(Cellular Component)可能主要涉及膜筏(membrane raft)、受体复合物(receptor complex)和囊泡腔(vesicle lumen)等组分;相关的分子功能(Molecular Function, MF)可能主要参与蛋白丝氨酸/苏氨酸/酪氨酸激酶活性(protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity)、激酶结合(kinase binding)和蛋白酪氨酸激酶活性(protein tyrosine kinase activity)等功能。
2.7 代谢通路的富集分析
应用Metascape数据平台对潜在作用靶点进行KEGG代谢通路富集分析,按照P-vlaue进行排序,选取前20条通路,通过bioinformatics平台对富集结果绘制气泡图,见表2和图5。由结果可见,复方发挥增强免疫力功能的潜在代谢通路可能主要涉及肿瘤通路(Pathways in cancer)、FOXO通路、Th17细胞分化(Th17 cell differentiation)、IL-17信号通路(IL-17 signaling pathway)、新型冠状病毒通路(Coronavirus disease - COVID-19)、NK细胞活性(Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity)等多条信号通路。
表 2 TOP20潜在靶点KEGG通路富集Table 2. TOP20 potential targets were enriched in KEGG pathwaysGO Description Count -log (P) Genes hsa05200 Pathways in cancer 42 47.79 ABL1, AKT1, AKT2, XIAP, AR, BCL2L1, BMP2, CASP3, CCNA2, CDK2, EGFR, ESR1, FGFR1, GRB2, GSK3B, HMOX1, HSP90AA1, IGF1, IGF1R, IL2, JAK2, JAK3, KIT, MDM2, MET, MMP1, MMP2, MMP9, NOS2, PIK3R1, PPARG, PRKACA, MAPK1, MAPK8, MAPK10, MAP2K1, RARA, RXRA, STAT1, TGFB2, TGFBR1, TGFBR2 hsa05417 Lipid and atherosclerosis 24 30.14 AKT1, AKT2, BCL2L1, CASP1, CASP3, MAPK14, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, GSK3B, HSPA8, HSP90AA1, JAK2, MMP1, MMP9, NOS3, PDPK1, PIK3R1, PPARG, MAPK1, MAPK8, MAPK10, RXRA, SELP, SRC hsa04068 Foxo signaling pathway 20 27.90 AKT1, AKT2, CDK2, MAPK14, EGFR, GRB2, IGF1, IGF1R, INSR, MDM2, PDPK1, PIK3R1, PLK1, MAPK1, MAPK8, MAPK10, MAP2K1, TGFB2, TGFBR1, TGFBR2 hsa04914 Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation 17 24.39 AKT1, AKT2, CCNA2, CDK2, MAPK14, HSP90AA1, IGF1, IGF1R, PGR, PIK3R1, PLK1, PRKACA, MAPK1, MAPK8, MAPK10, MAP2K1, AURKA hsa04659 Th17 cell differentiation 16 22.09 MAPK14, HSP90AA1, IL2, JAK2, JAK3, LCK, PRKCQ, MAPK1, MAPK8, MAPK10, RARA, RXRA, STAT1, TGFBR1, TGFBR2, ZAP70 hsa05145 Toxoplasmosis 16 21.82 AKT1, AKT2, XIAP, BCL2L1, CASP3, MAPK14, HSPA8, JAK2, NOS2, PDPK1, PIK3CG, MAPK1, MAPK8, MAPK10, STAT1, TGFB2 hsa04520 Adherens junction 12 17.36 CSNK2A1, EGFR, FGFR1, IGF1R, INSR, MET, MAPK1, PTPN1, SRC, TGFBR1,
TGFBR2, WAShsa05171 Coronavirus disease - COVID-19 15 15.18 CFB, CASP1, MAPK14, ACE, EGFR, IL2, MMP1, PIK3R1, MAPK1, MAPK8, MAPK10, SELP, STAT1, SYK, ADAM17 hsa04657 IL-17 signaling pathway 11 14.09 CASP3, MAPK14, GSK3B, HSP90AA1, LCN2, MMP1, MMP9, MAPK1,
MAPK8, MAPK10, S100A9hsa05202 Transcriptional misregulation in cancer 13 13.42 BCL2L1, CCNA2, ELANE, IGF1, IGF1R, MDM2, MET, MMP9, PLAU, PPARG, RARA, RXRA, TGFBR2 hsa05203 Viral carcinogenesis 12 11.72 CASP3, CCNA2, CDK2, CHEK1, GRB2, JAK3, MDM2, PIK3R1, PRKACA,
MAPK1, SRC, SYKhsa04650 Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity 10 10.96 CASP3, GRB2, ITGAL, LCK, PIK3R1, MAPK1, MAP2K1, PTPN11, SYK, ZAP70 hsa04213 Longevity regulating pathway - multiple species 8 10.72 AKT1, AKT2, HSPA8, IGF1, IGF1R, INSR, PIK3R1, PRKACA hsa04064 NF-kappa B signaling pathway 9 10.4 PARP1, XIAP, BCL2L1, CSNK2A1, LCK, PLAU, PRKCQ, SYK, ZAP70 hsa04930 Type II diabetes mellitus 7 9.96 GCK, INSR, PIK3R1, PKLR, MAPK1, MAPK8, MAPK10 hsa04928 Parathyroid hormone synthesis, secretion and action 8 8.82 EGFR, FGFR1, PDE4D, PRKACA, MAPK1, MAP2K1, RXRA, VDR hsa04670 Leukocyte transendothelial migration 7 7.15 MAPK14, ITGAL, ITK, MMP2, MMP9, PIK3R1, PTPN11 hsa04360 Axon guidance 8 6.97 ABL1, GSK3B, MET, PDPK1, PIK3R1, MAPK1, PTPN11, SRC hsa03320 PPAR signaling pathway 6 6.88 MMP1, PDPK1, PPARA, PPARG, RXRA, NR1H3 hsa04020 Calcium signaling pathway 7 4.98 EGFR, FGFR1, KDR, MET, NOS2, NOS3, PRKACA 2.8 复方增强免疫力的“成分-靶点-通路”网络分析
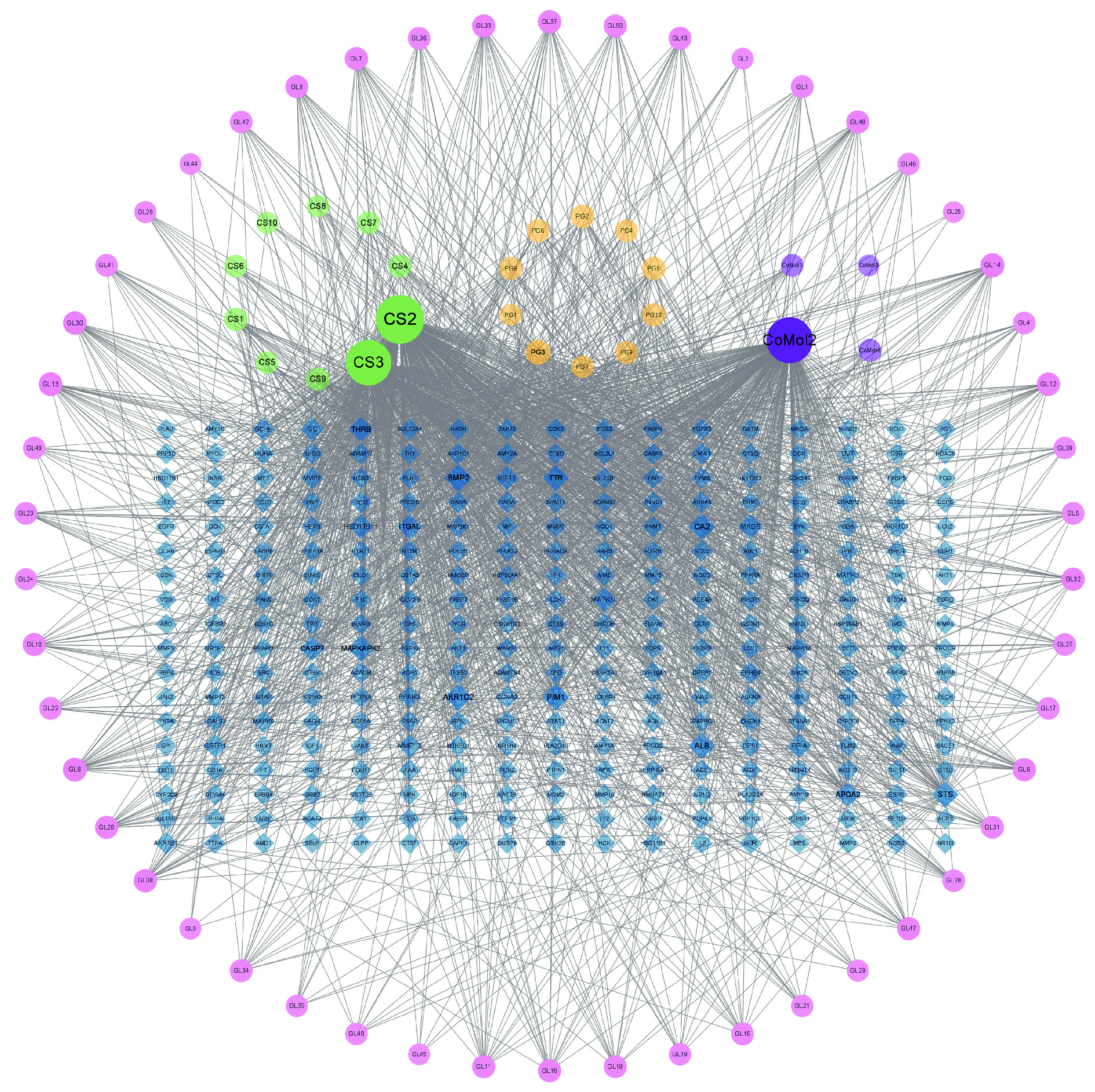
将上述成分、靶点和代谢通路数据导入Cytoscape 3.6.1构建复方增强免疫力的成分-靶点-通路网络,见图6。通过Cytoscape 3.6.1内置的Network Analyzer进行复方增强免疫力的网络拓扑学分析。该网络包含有89个节点(41个活性成分、28个靶点、20条通路)和1132条边,菱形图标代表复方的化学成分,圆形图标代表靶点,倒三角图标代表代谢通路。对连接度值(degree)进行排序,花生四烯酸、过氧麦角甾醇、胆固醇棕榈酸酯、PQ-2、环氧灵芝醇C、麦角甾-7,9,22-三烯-3-醇、麦角甾烷-7,22-二烯-3β-醇等成分可能是复方增强免疫力的重要活性成分,见表3。
表 3 潜在活性成分的网络节点特征参数Table 3. Network node characteristic parameters of potential active ingredients编号 化合物名称 连接度 中间中心度 接近中心度 来源 CS2 花生四烯酸 53 0.1035 0.6327 冬虫夏草 CoMol2 过氧麦角甾醇 53 0.1030 0.6327 冬虫夏草/灵芝 CS3 胆固醇棕榈酸酯 51 0.0919 0.6000 冬虫夏草 PG3 PQ-2 35 0.0297 0.5254 西洋参 GL8 环氧灵芝醇C 26 0.0119 0.4733 灵芝 GL13 麦角甾烷-7,22-二烯-3β-醇 25 0.0125 0.4806 灵芝 GL14 麦角甾-7,9,22-三烯-3-醇 23 0.0097 0.4769 灵芝 药理实验结果表明:复方具有增强免疫力功能,尤其NK细胞活性和迟发型变态发育效果显著。运用网络药理学的研究方法,从整体的角度研究成分与功能之间的关联性,构建了复方增强免疫力的“成分-靶点-通路”网络,筛选出41个潜在活性成分,28个作用靶点,20条免疫相关的KEGG代谢通路(见图7),初步揭示了该复方增强免疫力功效的潜在物质基础和作用机制。
研究表明,中药中分离的单体化合物,其活性测试显示单体成分的抗肿瘤活性低于原药材的作用[29]。“有效成分”不应指单体化合物,有效组分相比单体化合物,不是简单的成分堆积,其成分相对稳定,而且有相对固定组成和含量比例关系,能通过多靶点、多通路发挥其功效[30]。本文通过网络药理学进一步分析发现:在复方中与免疫力功能关联度较高成分为:花生四烯酸、过氧麦角甾醇、胆固醇棕榈酸酯PQ-2、麦角甾-7,9,22-三烯-3-醇、环氧灵芝醇C、麦角甾烷-7,22-二烯-3β-醇等,这可能是复方的重要“有效组分”,见表3(其中表3的8种化合物对应图7中排名前8的物质)。研究表明:灵芝中具有免疫调节的活性成分为甾醇、三萜和多糖,其中甾醇和三萜具有直接细胞毒作用使肿瘤细胞死亡,多糖组分通过免疫调节发挥抗肿瘤作用[31-32];西洋参中的免疫活性成分为皂苷和多糖[33];冬虫夏草中免疫活性成分有多糖、核苷、甾醇等[34]。综合以上结果来看:过氧麦角甾醇、麦角甾-7,9,22-三烯-3-醇、麦角甾烷-7,22-二烯-3β-醇隶属于甾醇类化合物,主要来自于复方的冬虫夏草和灵芝,而环氧灵芝醇C属于三萜类化合物,来自于灵芝[30];西洋参中的聚乙炔类化合物PQ-2具有免疫调节活性[32]。除表3中的7种物质外,其余34种成分也是复方中的重要的物质基础;复方的增强免疫力活性在以上41个潜在活性成分的协同作用下发挥功能。与此同时,网络药理学尚未能阐明其余常见的具有增强免疫力活性成分如:多糖、皂苷等,可能受限于组分特性、研究深度及网络药理学本身的局限性[35],未来随着物质基础、量效关系研究的逐渐深入,将会进一步通过网络药理学充分揭示复方的有效组分。
通过蛋白-蛋白相互作用分析发现,蛋白激酶B(AKT1)、表皮生长因子受体(EGFR)、非受体酪氨酸激酶(SRC)、白蛋白(ALB)、热休克蛋白(HSP90AA1)等可能是复方发挥免疫作用的主要作用靶点[36]。AKT是一种57 kDa的丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶,哺乳动物体内含有3种AKT基因,分别为AKT1、AKT2和AKT3。其中AKT1基因定位于染色体14q32位置,且在脑组织、心脏组织和肺组织中表达最多[37]。磷酸化的AKT1从细胞膜附近转移到细胞质和细胞核,可调控下游蛋白的磷酸化来控制细胞的凋亡、侵袭、血管生成等过程[37]。EGFR由1186个氨基酸组成的受体酪氨酸蛋白激酶,在正常的生理状态下EGFR与相应配体表皮生长因子、转化生长因子、双调蛋白等结合,引起受体的二聚化,二聚化的受体发生交联磷酸化介导激活细胞增殖、分化、迁移等生命现象[37-38]。SRC蛋白激酶是一种酪氨酸的专一性蛋白激酶,它广泛存在于各种细胞胞质中,通过相关信号通路参与了细胞的发育、增殖和凋亡等,在多种免疫因子的转录和表达中起调控作用[39]。ALB在人体内含量最高(通常占血浆蛋白总含量的50%以上),且含有585种氨基酸残基的一种单链多肽。它是血浆中存在的最小蛋白质之一,分子量约为66458[40]。同时,白蛋白也是一种通用的大分子载体,有利于帮助溶解度有限的各种内源性化合物(包括脂肪酸和胆素),在全身循环中的运输。HSP90AA1,热休克蛋白家族的一员,是具有维持细胞稳态的关键分子伴侣蛋白,作为非应激细胞中最丰富的细胞质蛋白之一,其可在应激不利的条件下(如热、缺氧、酸中毒等),提高细胞对外界应激的抵抗力[41-42]。
KEGG通路富集分析表明,复方增强免疫力的主要靶点是肿瘤相关通路(Pathways in cancer)、FOXO通路、Th17细胞分化(Th17 cell differentiation)、IL-17信号通路(IL-17 signaling pathway)、新型冠状病毒通路(COVID-19)和NK细胞活性(Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity)等多条信号通路。其中肿瘤相关通路一直是近几十年的研究热点,新型冠状病毒作用靶点研究是近3年的研究热点;二者均有作用靶点丰富、多变、通路机理复杂的特点。FOXO即细胞转录因子,其中FOXO3a可通过促进PI3K/AKT信号通路中p-PI3K、p-AKT蛋白的表达,介导炎症因子TNF-α对滋养细胞增殖、侵袭能力抑制并促进其发生凋亡[43]。Th17即辅助T细胞,主要通过分泌IL-17A、IL-17F、IL-21、IL-22、IL-26 等因子发挥生物学效应,其中IL-17A为其标志性细胞因子,IL-17A已被证实在炎症反应如迟发型变态反应及自身免疫性疾病中发挥重要作用[44]。IL-17是一个主要的促炎性细胞因子并发挥多种介质细胞功能,能刺激成纤维细胞和表皮细胞产生IL-6、IL-8、细胞间黏附分子、粒细胞-巨噬细胞克隆刺激因子;还能刺激如TNF-α和IL-1β等促炎性细胞因子的产生,并和这些细胞诱导产生大量的炎性因子;也可通过激活丝裂原活化蛋白激酶及NF-κB等下游信号通路发挥生物学效应[45]。COVID-19病毒入侵人体后涉及两个免疫应答路径:分泌干扰素(IFN)以及趋化因子(IL-6、IL-8等),分别用于抑制病毒增殖和召集白细胞攻击病毒。COVID-19病毒进入人体后,免疫系统会启动模式识别受体(PRR)来激活相关通路,其中IFN-I 和IFN-III 是最重要的免疫感应通路,经PRR 激活,下游信号传递会导致细胞因子的分泌,降低机体炎症因子表达,减少氧化应激自由基堆积和细胞凋亡,改善机体免疫功能[46-48]。
NK细胞即自然杀伤细胞,在机体内可直接识别并杀伤肿瘤细胞;可分泌细胞因子募集树突状细胞(Dendritic cells),促进DCs 成熟,增强免疫应答;可杀伤肿瘤干细胞与循环肿瘤细胞, 维持肿瘤细胞休眠, 抑制肿瘤转移[49-51],从而维持人体免疫系统的稳定。复方增强免疫力机制所涉及的主要成分、靶点、通路见图7。
综上所述,复方可能的增强免疫力机制为,其中的活性成分花生四烯酸、甾醇类、皂苷、多糖等多种活性物质通过AKT1、EGFR、SRC、ALB、HSP90AA1等靶点作用于免疫细胞:NK细胞和T细胞(Th17);一方面可直接提升NK细胞活性,杀死肿瘤细胞,促进免疫应答;另一方面也可促进Th17细胞释放IL17、IL-6、TNF-α等细胞因子,可通过PI3K/AKT信号通路、JAK-STAT信号通路、ACT信号通路、IKKS细胞通路、NF-κ
B信号通路,FOXO等多重信号通路,协同促进免疫细胞因子释放,间接发挥免疫作用,最终达到增强免疫力效果。 3. 结论
本研究结果表明,与空白组相比,复方中剂量0.8 g/kg(P<0.001)、高剂量2.4 g/kg(P<0.001)均能显著增加小鼠NK 细胞活性,中剂量0.8 g/kg(P<0.001)、高剂量2.4 g/kg(P<0.001)剂量组均能显著增加小鼠迟发型变态反应,在吞噬指数实验中,复方低剂量0.4 g/kg可以显著增加小鼠巨噬细胞吞噬指数(P<0.001),因此复方具有开发为增强免疫力功能保健食品的潜力。本文首次通过网络药理学构建复方的“成分-靶点-通路”,对其增强免疫力活性机制系统研究;结果表明复方的增强免疫力作用机制可能是通过复方中花生四烯酸、过氧麦角甾醇等41种活性物质,作用于NK细胞、T细胞等免疫细胞的AKT1、EGFR、SRC等94个靶点,调控肿瘤、FOXO、Th17、NK细胞等1382个GO条目与171条信号通路发挥增强免疫力作用。该结论为复方的增强免疫力物质基础和作用机制研究提供了新的理论依据。后续将继续开展相关试验对活性成分、核心靶点及通路进行验证,以揭示其分子机制。
-
表 1 复方活性成分信息
Table 1
Active ingredients information of compound Mol ID 分子名称 分子质量 OB(%) DL Source ID MOL001645 Linoleyl acetate 乙酸亚油醇酯 308.56 42.10 0.20 Cordyceps sinensis CS1 MOL001439 Arachidonic acid 花生四烯酸 304.52 45.57 0.20 Cordyceps sinensis CS2 MOL008999 Cholesteryl palmitate 胆固醇棕榈酸酯 625.19 31.05 0.45 Cordyceps sinensis CS3 MOL012269 Stigmasta-5,22-dien-3-ol-acetate 醋酸豆甾醇 454.81 46.44 0.86 Cordyceps sinensis CS4 MOL001973 Sitosteryl acetate β-谷甾醇乙酸酯 456.83 40.39 0.85 Cordyceps sinensis CS5 MOL000449 Stigmasterol 豆甾醇 412.77 43.83 0.76 Cordyceps sinensis CS6 MOL000359 Sitosterol 谷甾醇 414.79 36.91 0.75 Cordyceps sinensis CS7 MOL001510 24-Epicampesterol 24-表甾醇 400.76 37.58 0.71 Cordyceps sinensis CS8 MOL002224 Aurantiamide acetate 金色酰胺醇酯 444.57 58.38 0.59 Cordyceps sinensis CS9 MOL002140 Perlolyrine 川芎哚 264.3 65.95 0.27 Cordyceps sinensis CS10 MOL011125 (+)-Ganoderic acid Mf 灵芝酸F 512.8 32.62 0.82 Ganoderma lucidum GL1 MOL011127 (+)-Methyl ganolucidate A 赤灵芝酸甲酯A 514.77 31.14 0.82 Ganoderma lucidum GL2 MOL011129 Methyl lucidenate F 赤芝酸甲酯F 470.66 32.67 0.81 Ganoderma lucidum GL3 MOL011135 22,23-Dimethylene ganodermic acid S 灵芝酸 578.86 33.61 0.71 Ganoderma lucidum GL4 MOL011137 Campesta-7,22E-dien-3beta-ol 星鱼甾醇 398.74 43.51 0.72 Ganoderma lucidum GL5 MOL011156 Epoxyganoderiol A 环氧灵芝醇A 472.78 33.78 0.83 Ganoderma lucidum GL6 MOL011157 Epoxyganoderiol B 环氧灵芝醇B 454.76 42.3 0.83 Ganoderma lucidum GL7 MOL011158 Epoxyganoderiol C 环氧灵芝醇C 456.78 37.7 0.83 Ganoderma lucidum GL8 MOL011160 Ganodesterone 灵芝固醇 408.68 47.86 0.77 Ganoderma lucidum GL9 MOL011162 Ergosta-7,22-dien-3beta-yl palmitate 麦角甾-7,22-
三烯-3β-醇棕榈酸酯637.2 37.60 0.43 Ganoderma lucidum GL10 MOL011164 Ergosta-7,22-dien-3β,5α,6α-triol 啤酒甾醇 430.74 31.43 0.77 Ganoderma lucidum GL11 MOL011165 Ergosta-7,22-diene-3beta-yl linoleate 麦角甾-7,22-
二烯-3β-醇亚油酸酯661.22 45.11 0.37 Ganoderma lucidum GL12 MOL011167 Ergosta-7,22-diene-3beta-yl Pentadecanoate 麦角甾-7,22-
二烯-3β-醇十五酸酯623.17 38.25 0.47 Ganoderma lucidum GL13 MOL011168 Ergosta-7,9(11),22-trien-3β,5α,6α-triol 麦角甾醇 442.75 46.95 0.78 Ganoderma lucidum GL14 MOL011171 Ganoderal B 灵芝醇B 440.73 42.56 0.81 Ganoderma lucidum GL15 MOL011172 Ganoderan B 灵芝多糖B 454.76 42.19 0.81 Ganoderma lucidum GL16 MOL011189 Ganoderic acid DM 灵芝酸DM 468.74 38.8 0.83 Ganoderma lucidum GL17 MOL011206 Ganoderic acid Me灵芝酸Me 554.84 31.16 0.76 Ganoderma lucidum GL18 MOL011209 Ganoderic acid Mi 灵芝酸Mi 528.85 34.4 0.81 Ganoderma lucidum GL19 MOL011214 Ganoderic acid R 灵芝酸R 554.84 31.46 0.77 Ganoderma lucidum GL20 MOL011215 Ganoderic acid S 灵芝酸S 512.8 34.37 0.83 Ganoderma lucidum GL21 MOL011218 Ganoderic acid TQ 灵芝酸TQ 524.81 36.30 0.78 Ganoderma lucidum GL22 MOL011219 Ganoderic acid TR 灵芝酸TR 468.74 36.23 0.83 Ganoderma lucidum GL23 MOL011221 Ganoderic acid V 灵芝酸V 528.8 30.19 0.80 Ganoderma lucidum GL24 MOL011222 Ganoderic acid V1 灵芝酸V1 512.75 30.18 0.80 Ganoderma lucidum GL25 MOL011224 Ganoderic acid X 灵芝酸X 512.8 33.55 0.81 Ganoderma lucidum GL26 MOL011225 Ganoderic acid Y 灵芝酸Y 454.76 38.64 0.82 Ganoderma lucidum GL27 MOL011226 Ganoderic acid Z 灵芝酸Z 456.78 37.67 0.82 Ganoderma lucidum GL28 MOL011229 Ganoderic aldehyde A 灵芝醛A 454.76 42.26 0.81 Ganoderma lucidum GL29 MOL011235 Ganoderiol F 灵芝醇F 454.76 38.12 0.82 Ganoderma lucidum GL30 MOL011241 Ganodermanondiol 灵芝酮二醇 456.78 37.64 0.80 Ganoderma lucidum GL31 MOL011243 Ganodermatriol 灵芝三醇 456.78 30.46 0.82 Ganoderma lucidum GL32 MOL011244 Ganodermenonol 灵芝萜酮三醇 438.76 44.69 0.80 Ganoderma lucidum GL33 MOL011245 Ganodermic acid R 灵芝酸R 554.84 31.16 0.76 Ganoderma lucidum GL34 MOL011247 Ganodermic acid T-Q 灵芝酸T-Q 512.8 33.55 0.81 Ganoderma lucidum GL35 MOL011248 Ganodermic acid T-O 灵芝酸T-O 512.8 32.62 0.82 Ganoderma lucidum GL36 MOL011250 Ganodermnonol 灵芝萜烯酮醇 438.76 44.69 0.80 Ganoderma lucidum GL37 MOL011251 Ganoderol A 灵芝醇A 438.76 44.69 0.80 Ganoderma lucidum GL38 MOL011256 Ganolucidic acid E 灵芝酸E 484.74 32.85 0.82 Ganoderma lucidum GL39 MOL011258 Ganosporelactone B 灵芝内酯B 530.72 31.21 0.33 Ganoderma lucidum GL40 MOL011266 Lucialdehyde A 灵芝醛A 438.76 44.78 0.80 Ganoderma lucidum GL41 MOL011267 Lucialdehyde B 灵芝醛B 452.74 43.12 0.81 Ganoderma lucidum GL42 MOL011268 Lucialdehyde C 灵芝醛C 454.76 42.26 0.81 Ganoderma lucidum GL43 MOL011270 Lucidenic acid A 赤芝酸A 458.65 30.34 0.79 Ganoderma lucidum GL44 MOL011287 Lucidone A 赤芝酮A 402.58 37.22 0.64 Ganoderma lucidum GL45 MOL011290 Lucidumol A 赤芝萜醇A 458.8 34.75 0.8 Ganoderma lucidum GL46 MOL011303 Methyl Ganoderic acid DM 甲基灵芝酸DM 482.77 39.55 0.83 Ganoderma lucidum GL47 MOL011304 Methyl Ganoderic acid TR 甲基灵芝酸TR 482.77 39.82 0.83 Ganoderma lucidum GL48 MOL011309 Methyl lucidenate Q 赤芝酸甲酯Q 474.7 30.19 0.81 Ganoderma lucidum GL49 MOL000282 Stellasterol 星鱼甾醇 398.74 43.51 0.72 Ganoderma lucidum GL50 MOL011394 Ginsenoside F2 人参皂苷 F2 785.14 36.43 0.25 Panax ginseng PG1 MOL011434 Polyacetylene PQ-2 聚乙炔PQ-2 306.44 36.74 0.20 Panax ginseng PG2 MOL011435 PQ-2 306.44 36.74 0.19 Panax ginseng PG3 MOL011442 Stigmasta-3,5-dien-7-one 豆甾烯醇 410.75 43.87 0.75 Panax ginseng PG4 MOL011455 20-Hexadecanoylingenol 殷金醇棕榈酸酯 418.58 32.70 0.65 Panax ginseng PG5 MOL005344 Ginsenoside rh2 人参皂苷 rh2 622.98 36.32 0.56 Panax ginseng PG6 MOL006774 Stigmast-7-enol 豆甾醇-7-烯醇 414.79 37.42 0.75 Panax ginseng PG7 MOL006980 Papaverine 罂粟碱 339.42 64.04 0.38 Panax ginseng PG8 MOL008173 Daucosterol_qt 胡萝卜甾醇 414.79 36.91 0.75 Panax ginseng PG9 MOL008397 Daturilin 白曼陀罗灵 436.64 50.37 0.77 Panax ginseng PG10 MOL000358 Beta-sitosterol β-谷甾醇 414.79 36.91 0.75 PQ/GL/CS CoMol1 MOL011169 Peroxyergosterol 过氧化麦角甾醇 428.72 44.39 0.82 GL/CS CoMol2 MOL011159 Ergosta-4,6,8(14),22-tetraene-3-one 麦角甾烯酮 406.71 48.32 0.75 GL/CS CoMol3 MOL008998 Cerevisterol 啤酒甾醇 432.76 39.52 0.77 GL/CS CoMol4 表 2 TOP20潜在靶点KEGG通路富集
Table 2 TOP20 potential targets were enriched in KEGG pathways
GO Description Count -log (P) Genes hsa05200 Pathways in cancer 42 47.79 ABL1, AKT1, AKT2, XIAP, AR, BCL2L1, BMP2, CASP3, CCNA2, CDK2, EGFR, ESR1, FGFR1, GRB2, GSK3B, HMOX1, HSP90AA1, IGF1, IGF1R, IL2, JAK2, JAK3, KIT, MDM2, MET, MMP1, MMP2, MMP9, NOS2, PIK3R1, PPARG, PRKACA, MAPK1, MAPK8, MAPK10, MAP2K1, RARA, RXRA, STAT1, TGFB2, TGFBR1, TGFBR2 hsa05417 Lipid and atherosclerosis 24 30.14 AKT1, AKT2, BCL2L1, CASP1, CASP3, MAPK14, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, GSK3B, HSPA8, HSP90AA1, JAK2, MMP1, MMP9, NOS3, PDPK1, PIK3R1, PPARG, MAPK1, MAPK8, MAPK10, RXRA, SELP, SRC hsa04068 Foxo signaling pathway 20 27.90 AKT1, AKT2, CDK2, MAPK14, EGFR, GRB2, IGF1, IGF1R, INSR, MDM2, PDPK1, PIK3R1, PLK1, MAPK1, MAPK8, MAPK10, MAP2K1, TGFB2, TGFBR1, TGFBR2 hsa04914 Progesterone-mediated oocyte maturation 17 24.39 AKT1, AKT2, CCNA2, CDK2, MAPK14, HSP90AA1, IGF1, IGF1R, PGR, PIK3R1, PLK1, PRKACA, MAPK1, MAPK8, MAPK10, MAP2K1, AURKA hsa04659 Th17 cell differentiation 16 22.09 MAPK14, HSP90AA1, IL2, JAK2, JAK3, LCK, PRKCQ, MAPK1, MAPK8, MAPK10, RARA, RXRA, STAT1, TGFBR1, TGFBR2, ZAP70 hsa05145 Toxoplasmosis 16 21.82 AKT1, AKT2, XIAP, BCL2L1, CASP3, MAPK14, HSPA8, JAK2, NOS2, PDPK1, PIK3CG, MAPK1, MAPK8, MAPK10, STAT1, TGFB2 hsa04520 Adherens junction 12 17.36 CSNK2A1, EGFR, FGFR1, IGF1R, INSR, MET, MAPK1, PTPN1, SRC, TGFBR1,
TGFBR2, WAShsa05171 Coronavirus disease - COVID-19 15 15.18 CFB, CASP1, MAPK14, ACE, EGFR, IL2, MMP1, PIK3R1, MAPK1, MAPK8, MAPK10, SELP, STAT1, SYK, ADAM17 hsa04657 IL-17 signaling pathway 11 14.09 CASP3, MAPK14, GSK3B, HSP90AA1, LCN2, MMP1, MMP9, MAPK1,
MAPK8, MAPK10, S100A9hsa05202 Transcriptional misregulation in cancer 13 13.42 BCL2L1, CCNA2, ELANE, IGF1, IGF1R, MDM2, MET, MMP9, PLAU, PPARG, RARA, RXRA, TGFBR2 hsa05203 Viral carcinogenesis 12 11.72 CASP3, CCNA2, CDK2, CHEK1, GRB2, JAK3, MDM2, PIK3R1, PRKACA,
MAPK1, SRC, SYKhsa04650 Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity 10 10.96 CASP3, GRB2, ITGAL, LCK, PIK3R1, MAPK1, MAP2K1, PTPN11, SYK, ZAP70 hsa04213 Longevity regulating pathway - multiple species 8 10.72 AKT1, AKT2, HSPA8, IGF1, IGF1R, INSR, PIK3R1, PRKACA hsa04064 NF-kappa B signaling pathway 9 10.4 PARP1, XIAP, BCL2L1, CSNK2A1, LCK, PLAU, PRKCQ, SYK, ZAP70 hsa04930 Type II diabetes mellitus 7 9.96 GCK, INSR, PIK3R1, PKLR, MAPK1, MAPK8, MAPK10 hsa04928 Parathyroid hormone synthesis, secretion and action 8 8.82 EGFR, FGFR1, PDE4D, PRKACA, MAPK1, MAP2K1, RXRA, VDR hsa04670 Leukocyte transendothelial migration 7 7.15 MAPK14, ITGAL, ITK, MMP2, MMP9, PIK3R1, PTPN11 hsa04360 Axon guidance 8 6.97 ABL1, GSK3B, MET, PDPK1, PIK3R1, MAPK1, PTPN11, SRC hsa03320 PPAR signaling pathway 6 6.88 MMP1, PDPK1, PPARA, PPARG, RXRA, NR1H3 hsa04020 Calcium signaling pathway 7 4.98 EGFR, FGFR1, KDR, MET, NOS2, NOS3, PRKACA 表 3 潜在活性成分的网络节点特征参数
Table 3 Network node characteristic parameters of potential active ingredients
编号 化合物名称 连接度 中间中心度 接近中心度 来源 CS2 花生四烯酸 53 0.1035 0.6327 冬虫夏草 CoMol2 过氧麦角甾醇 53 0.1030 0.6327 冬虫夏草/灵芝 CS3 胆固醇棕榈酸酯 51 0.0919 0.6000 冬虫夏草 PG3 PQ-2 35 0.0297 0.5254 西洋参 GL8 环氧灵芝醇C 26 0.0119 0.4733 灵芝 GL13 麦角甾烷-7,22-二烯-3β-醇 25 0.0125 0.4806 灵芝 GL14 麦角甾-7,9,22-三烯-3-醇 23 0.0097 0.4769 灵芝 -
[1] 周悦芳, 范培红. 中药免疫调节作用研究进展[J]. 时珍国医国药,2017,28(1):204−207. [ZHOU Y F, FAN P H. Research progress of immunomodulatory effect of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Shizhen Traditional Chinese Medicine and Traditional Chinese Medicine,2017,28(1):204−207. [2] HWANG Y Y, MCKENZIE A N. Innate lymphoid cells in immunity and disease[C]//New York: Crossroads Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity, 2013, 785: 9-26.
[3] 萨翼, 陈广耀, 王进博, 等. 已批准增强免疫力功能的中药类保健食品现状及监管建议[J]. 中国中药杂志,2019(5):885−890. [SA Y, CHEN G Y, WANG J B, et al. Current status and regulatory recommendations of approved Chinese medicine health food for immunity enhancement[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2019(5):885−890. [4] 王昊, 单宇, 孙志蓉. 冬虫夏草应用及市场现状分析[J]. 现代中药研究与实践,2016,30(6):4. [WANG H, SHAN Y, SUN Z R. Analysis on application and market status of Cordyceps sinensis[J]. Research and Practice of Modern Chinese Medicine,2016,30(6):4. [5] 李卫东, 林志彬. 灵芝的扶正固本及对“亚健康”者的保健作用[J]. 食药用菌,2016,24(1):29−32. [LI W D, LIN Z B. The effects of Ganoderma lucidum on the strengthening the body and improving sub-health[J]. Edible and Medicinal Mushrooms,2016,24(1):29−32. [6] 尚金燕, 李桂荣, 邵明辉, 等. 西洋参的药理作用研究进展[J]. 人参研究,2016(6):49−51. [SHANG J Y, LI G R, SHAO M H, et al. Advances in pharmacological effects of American Ginseng[J]. Ginseng Research,2016(6):49−51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1521.2016.06.016 [7] WANG M, GUILBERT L J, LI J, et al. A proprietary extract from North American ginseng (Panax quinquefolium) enhances IL-2 and IFN-g productions in murine spleen cells induced by ConA[J]. Int Immunopharmacol,2004,4(2):311−315. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2003.12.002
[8] 于永超, 张佳丽, 林兵, 等. 西洋参多糖对钴-60辐照小鼠的免疫调节作用[J]. 现代预防医学,2012,39(11):2685−2687. [YU Y C, ZHANG J L, LIN B, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of American ginseng polysaccharide on cobalt-60 irradiated mice[J]. Modern Preventive Medicine,2012,39(11):2685−2687. [9] MCELHANEY J E, SIMOR A E, MCNEIL S, et al. Efficacy and safety of CVT-E002, a proprietary extract of Panax quinquefolius in the prevention of respiratory infections in influenza vaccinated community dwelling adults: A multicenter, randomized, double-Blind, and placebo controlled trial[J]. Influenza Res Treat,2011,2011:1−8.
[10] 李如意, 林也, 魏艳霞, 等. 冬虫夏草对免疫抑制模型小鼠免疫功能调节作用的研究[J]. 湖南中医药大学学报,2017,37(12):1316−1319. [LI R Y, LIN Y, WEI Y X, et al. Study on the regulation of Cordyceps sinensis on immune function in immunosuppressive mice[J]. Journal of Hunan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2017,37(12):1316−1319. [11] 李立, 王亚东, 王海玉, 等. 灵芝洋参复合物对小鼠免疫功能的影响[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志,2019,29(24):2963−2965. [LI L, WANG Y D, WANG H Y, et al. Effects of Ganoderma lucidum and ginseng complex on immune function in mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Health Laboratory Science,2019,29(24):2963−2965. [12] 邱涵, 吕晓君, 张鹏. 冬虫夏草西洋参复合物增强免疫力功能实验研究[J]. 中国医药导报,2016,13(9):18−22. [QIU H, LV X J, ZHANG P. Experimental study on Cordyceps sinensis and Panax quincefolium compound enhancing immune function[J]. China Medical Review,2016,13(9):18−22. [13] 解静, 高杉, 李琳, 等. 网络药理学在中药领域中的研究进展与应用策略[J]. 中草药,2019,50(10):2257−2265. [XIE J, GAO S, LI L, et al. Research progress and application strategy of network pharmacology in TCM[J]. Chinese Herbal Medicine,2019,50(10):2257−2265. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2019.10.001 [14] 陈奇. 中药药理研究方法学[M]. 3 版 . 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2011: 28. CHEN Q. Methodology of pharmacological research on traditional chinese medicine [M]. 3rd Ed. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2011: 28.
[15] 国家市场监督管理总局. 关于公开征求《允许保健食品声称的保健功能目录 非营养素补充剂(2020年版)(征求意见稿)》意见的公告[EB/OL]. (2020-11-24) [2022-08-26] https://www.samr.gov.cn/hd/zjdc/202011/t20201124_323851.html State Administration for Market Regulation. Notice on public solicitation of comments on Non-Nutrient Supplements (2020) of the List of Health Functions Allowed to Be Claimed by Health Food (Draft) [EB/OL]. (2020-11-24) [2022-08-26] https://www.samr.gov.cn/hd/zjdc/202011/t20201124_323851.html
[16] RU J, LI P, WANG J, et al. TCMSP: A database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines[J]. Journal of Cheminformatics,2014,6(1):13. doi: 10.1186/1758-2946-6-13
[17] WANG X, SHEN Y, WANG S, et al. PharmMapper 2017 update: A web server for potential drug target identification with a comprehensive target pharmacophore database[J]. Nucleic Acids Research,2017,45(1):356−360.
[18] LIU X F, OUYANG S S, YU B, et al. Pharm mapper server: A web server for potential drug target identification using pharmacophore mapping approach[J]. Nucleic Acids Research,2010,38:609−614. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq300
[19] DAVID S WISHART, YANNICK D FEUNANG, AN C GUO, et al. DrugBank 5.0: A major update to the DrugBank database for 2018[J]. Nucleic Acids Research,2018,46:1074−1082. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1037
[20] DAMIAN SZKLARCZYK, ANNIKA L GABLE, DAVID LYON, et al. String V11: Protein–protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets[J]. Nucleic Acids Research,2019,47(1):607−613.
[21] ZHOU Y Y, ZHOU B, LARS Pache , et al. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets [J] Nat Commun, 2019, 10(1): 1523.
[22] 赵宏宇, 崔林虎, 张伟云. 蛹虫草对小鼠体液免疫功能和NK细胞活性的影响[J]. 园艺与种苗,2020,40(2):3−5,49. [ZHAO H Y, CUI L H, ZHANG W Y. Effects of Cordyceps militaris on humoral immune function and NK Cell activity in mice[J]. Horticulture and Seedlings,2020,40(2):3−5,49. [23] 周会芳, 徐倩, 边育红, 等. 小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞吞噬功能实验的改进[J]. 天津中医药大学学报,2015,34(5):279−282. [ZHOU H F, XU Q, BIAN Y H, et al. Improvement of phagocytic function of mouse peritoneal macrophages[J]. Journal of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2015,34(5):279−282. [24] 朱科学, 聂少平, 李文娟, 等. 黑灵芝多糖对小鼠脾淋巴细胞增殖及诱生细胞因子的影响[J]. 食品科学,2010,31(19):351−354. [ZHU K X, NIE S P, LI W J, et al. Effects of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide on proliferation and inducing cytokines of splenic lymphocytes in mice[J]. Food Science,2010,31(19):351−354. [25] 钱正明, 李文庆, 孙敏甜, 等. 冬虫夏草化学成分分析[J]. 菌物学报,2016,35(4):476−490. [QIAN Z M, LI W Q, SUN M T, et al. Chemical composition analysis of Cordyceps sinensis[J]. Chinese Journal of Fungi,2016,35(4):476−490. [26] 钱正明, 孙敏甜, 李文庆, 等. 冬虫夏草不同生长阶段甾醇类含量分析[J]. 菌物学报,2019,38(4):539−544. [QIAN Z M, SUN M T, LI W Q, et al. Analysis of sterol content in Cordyceps sinensis at different growth stages[J]. Chinese Journal of Fungi,2019,38(4):539−544. [27] 梅全喜, 李文佳. 鲜冬虫夏草的研究与应用[M]. 北京: 中国中医药出版社, 2020: 1-481. MEI Q X, LI W J. Study and application of fresh Cordyceps sinensis[M]. Beijing: China Traditional Chinese Medicine Press, 202: 1-481.
[28] YANG M L, KUO P C, HUANG Z L, et al. Anti-inflammatory principles from Cordyceps sinensis[J]. Journal of Natural Products,2011,74(9):1996−2000. doi: 10.1021/np100902f
[29] 韩飞, 彭珍, 周志渝, 等. 功效性分类中药对提高机体免疫功能的究进展[J]. 中草药,2016,47(11):2549−2555. [HAN F, PENG Z, ZHOU Z Y, et al. Research progress of efficacy classification of traditional Chinese medicine to improve the immune function of the body[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Medicines,2016,47(11):2549−2555. [30] 李小江, 邬明歆, 孔凡铭, 等. 中药有效成分抗肿瘤活性及作用机制研究进展[J]. 中草药,2020,51(9):2587−2592. [LI X J, WU M X, KONG F M, et al. Research progress on antitumor activity and mechanism of effective components of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Chinese Herbal Medicine,2020,51(9):2587−2592. [31] 曾祥丽, 包海鹰. 灵芝三萜类成分与药理学研究进展[J]. 菌物研究,2004(1):68−77. [ZENG X L, BAO H Y. Research progress of triterpenoids from Ganoderma lucidum and their pharmacology[J]. Fungus Research,2004(1):68−77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3538.2004.01.010 [32] 陆慧, 贾晓斌, 陈彦, 等. 灵芝甾醇类活性成分及其抗肿瘤作用机制的研究进展[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2011,26(2):325−329. [LU H, JIA X B, CHEN Y, et al. Research progress of sterols from Ganoderma lucidum and their antitumor mechanism[J]. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2011,26(2):325−329. [33] 吴首蓉, 郭晓宇, 屠鹏飞, 等. 西洋参化学成分、生物活性、品质评价及产品开发研究进展[J]. 药学学报,2022(6):57. [WU S R, GUO X Y, TU P F, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents, biological activity, quality evaluation and product development of Panax quinquefolium[J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmacy,2022(6):57. [34] 王敦. 冬虫夏草活性成分研究进展[J]. 环境昆虫学报,2021,43(4):779−787. [WANG D. Research progress on active components of Cordyceps sinensis[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Entomology,2021,43(4):779−787. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0858.2021.04.1 [35] 任艳, 邓燕君, 马焓彬, 等. 网络药理学在中药领域的研究进展及面临的挑战[J]. 中草药,2020,18(15):4789−4797. [REN Y, DENG Y J, MA H B, et al. Research progress and challenges of network pharmacology in traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Chinese Herbal Medicine,2020,18(15):4789−4797. [36] 王言森, 曹洪丽. 肺腺癌组织中 PI3K、p-AKT1 蛋白表达的变化及意义[J]. 山东医药,2017,57(29):65−67. [WANG Y S, CAO H L. Expression of PI3K and P-AKT1 protein in lung adenocarcinoma and its significance[J]. Shandong Medicine,2017,57(29):65−67. [37] T LIAKAKOS, E FATOUROU, D ZIOGAS, et al. Targeting VEGF, EGFR, and other interacting pathways for gastric cancerpromises and reality[J]. Ann Surg Oncol,2008,15(10):2981−2985. doi: 10.1245/s10434-008-9870-9
[38] SARTORE-BIANCHI A, BENCARDINO K, DI NICOLANTONIO F, et al. Integrated molecular dissection of the epidermal growthfactor receptor (EFGR) oncogenic pathway to predict response to EGFR-targeted monoclonal antibodies in metastatic colorectal cancer[J]. Target Oncol,2010,5(1):19−28. doi: 10.1007/s11523-010-0138-5
[39] 胡睿, 朱曙东. SRC蛋白激酶活性的调节机制[J]. 生物化学与生物物理,2016,43(11):1061−1069. [HU R, ZHU S D. Regulation of SRC protein kinase activity[J]. Biochemistry and Biophysics,2016,43(11):1061−1069. [40] 朱珊珊, 陈鑫, 颜巧妍, 等. 抗肿瘤药物的临床应用进展[J]. 中国现代医生,2019,57(9):164−168. [ZHU S S, CHEN X, YAN Q Y, et al. Progress in clinical application of antitumor drugs[J]. Chinese Journal of Modern Physicians,2019,57(9):164−168. [41] O'NEILL S, ROSS J A, WIGMORE S J, et al. The role of heat shock protein 90 in modulating ischemia-reperfusion injury in the kidney[J]. Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs,2012,21(10):1535−1548. doi: 10.1517/13543784.2012.713939
[42] 李润玖, 李锐, 张彧. 热休克蛋白生物学功能及其在肾损伤中作用的研究进展[J]. 中国急救复苏与灾害医学杂志,2008(2):121−125. [LI R J, LI R, ZHANG Y. Research progress on biological function of heat shock protein and its role in renal injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Emergency resuscitation and Disaster Medicine,2008(2):121−125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-6966.2008.02.025 [43] 张孝丽, 车立群, 吴红敬, 等. FOXO3a 通过PI3K/AKT 信号通路介导炎症因子TNF-α抑制滋养细胞的增殖、侵袭及促进细胞发生凋亡[J]. 免疫学杂志,2020,36(6):482−489. [ZHANG X L, CHE L Q, WU H J, et al. FOXO3a mediates the inflammatory factor TNF-α through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway to inhibit trophotropin cell proliferation, invasion and promotion of cell apoptosis[J]. Journal of Immunology,2020,36(6):482−489. [44] KRSTIC J, OBRADOVIC H, KUKOLI T, et al. An overview of interleukin-17A and interleukin-17 receptor a structure, interaction and signaling[J]. Protein Pept Lett,2015,22(7):570−580. doi: 10.2174/0929866522666150520145554
[45] 朱闽, 何清湖. 中医药通过调节 Th17 细胞分化在自身免疫性炎症性疾病中作用的研究进展[J]. 湖南中医药大学学报,2016,36(8):82−86. [ZHU M, HE Q H. Research progress on the role of traditional Chinese medicine in autoimmune inflammatory diseases by regulating Th17 cell differentiation[J]. Journal of Hunan University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2016,36(8):82−86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-070X.2016.08.023 [46] 李莉娟, 韩莉. 新型冠状病毒SARS-CoV-2免疫机理及疫苗开发[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学,2020,39(8):3890−3898. [LI L J, HAN L. Immune mechanism and vaccine development of novel Coronus SARS-CoV-2[J]. Genomics & Applied Biology,2020,39(8):3890−3898. [47] BLANCO-MELO D, NILSSON-PAYANT B E, LIU W C, et al. Imbalanced host response to SARS-CoV-2 drives development of COVID-19[J]. Cell,2020,181(5):1036−1045. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.026
[48] 张岩, 唐德志, 舒冰, 等. 基于文献探讨中药干预新型冠状病毒肺炎的作用机制[J]. 中医杂志,2020,61(13):1110−1117. [ZHANG Y, TANG D Z, SHU B, et al. Study on the mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine in the intervention of COVID-19 based on literature[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2020,61(13):1110−1117. [49] ZHOU Y, ZHANG Y T, LIAN X C, et al. Therapeutic target database update 2022: facilitating drug discovery with enriched comparative data of targeted agents[J]. Nucleic Acids Research,2022,50(D1):1398−1407. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab953
[50] DEMARIA O, CORNEN S, DAERON M, et al. Harnessing innate immunity in cancer therapy[J]. Nature,2019,574:45−56. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1593-5
[51] CORREIA A L, GUIMARAES J C, AUF D M P, et al. Hepatic stellate cells suppress NK cell-sustained breast cancer dormancy[J]. Nature,2021,594:566−571. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03614-z
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 张根生,黄昕钰,李琪,李月明,韩冰,费英敏. 植物清蛋白的制备、功能特性及其在食品中的应用进展. 中国调味品. 2023(05): 202-207 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张宇涵,周靖萱,张南海,赵亮,张列兵,周峰. 胶原蛋白肽与弹性蛋白肽对改善皮肤光老化的研究进展. 食品研究与开发. 2023(11): 208-216 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王娟娟,刘勋,周学,罗欢,赵国建. 胶原蛋白的研究进展及其应用. 中国皮革. 2022(07): 1-7 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 赵琼瑜,胡鉴,陈雨欣,李彩燕,宋伟. 中华鳖背甲脱钙工艺优化及其胶原蛋白结构表征. 食品与机械. 2022(10): 151-157+223 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 赵琼瑜,胡鉴,李彩燕,徐树杰,宋伟. 超声波辅助鳖甲脱钙工艺优化及其对胶原蛋白生化特征的影响. 食品工业科技. 2022(22): 39-51 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(6)





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:



