Preparation and Properties of Chitosan Salicylaldehyde Hydrogel Loaded with Anthocyanins
-
摘要: 在蓝莓花色苷(ACNs)存在下,以水杨醛为交联剂原位构筑了负载ACNs的壳聚糖水凝胶(ACNs/CS-SA),表征了其结构和形貌,研究了其稳定性、溶胀性能和缓释性能。FT-IR和XRD表征结果表明ACNs通过物理包埋均匀分散在水凝胶三维网络结构中;TG-DTG表征结果表明凝胶包埋显著提高了ACNs的热稳定性;ACNs/CS-SA的溶胀性能和缓释性能均展现出pH响应性;在pH2.7、4.6、6.7介质中,ACNs/CS-SA 24 h累计释药率分别为74.28%±4.58%、40.72%±4.04%和15.70%±1.71%;释放过程符合Weibull方程,R2分别为0.99405、0.95165和0.99712。鉴于ACNs/CS-SA的pH响应性能和对ACNs热稳定性的提高,本研究有望为新型药物包封材料的开发和ACNs的应用提供理论和实验基础。Abstract: In the presence of blueberry anthocyanins (ACNs), chitosan hydrogel crosslinking with salicylaldehyde (ACNs/CS-SA) was constructed. The structure and morphology of ACNs/CS-SA were characterized. The stability, swelling properties and ACNs controlled-release behaviors for the ACNs/CS-SA were investigated in the media of different pH. ACNs were uniformly dispersed in three-dimensional network structure of CS-SA hydrogel by physical embedding, which was confirmed by FT-IR and XRD characterization. The thermal stability of ACNs was significantly improved due to gelation, which was confirmed by TG-DTG characterization. Both the swelling properties and ACNs controlled-release behaviors for the ACNs/CS-SA exhibited pH response. In buffer media of pH2.7, 4.6 and 6.7, the cumulative release rates of ACNs for 24 h were 74.28%±4.58%, 40.72%±4.04% and 15.70%±1.71%, and the release process followed Weibull equation with the correlation coefficients R2 0.99405, 0.95165 and 0.99712, respectively. This study lays a theoretical and experimental foundation for the development of novel drug encapsulation materials and the application of ACNs owing to the ACNs/CS-SA pH responsiveness and ACNs thermal stability improvement.
-
Keywords:
- anthocyanins /
- chitosan hydrogel /
- stability /
- pH response /
- sustained release properties /
- dynamics
-
花色苷(anthocyanins,ACNs)是一种广泛存在于自然界的类黄酮化合物,由花青素与葡萄糖、半乳糖、阿拉伯糖、鼠李糖等,以糖苷键形式结合而成。ACNs具有颜色鲜艳、无毒、抗氧化活性、抑菌等特点,在食品、药品、保健品等领域应用广泛[1-3]。ACNs以C6(A环)-C3(C环)-C6(B环)为基本骨架,结构中多个酚羟基使其具有抗氧化活性,但也容易受温度、光照、氧气、pH等条件影响,使含量、颜色和活性等发生变化[4],极大地限制了其应用。此外ACNs容易受到胃肠道pH和消化酶的影响,导致生物利用度较低[5-6]。
构筑包封体系实现ACNs的有效控释是提高其稳定性和生物利用度的有效方法。水凝胶与生物组织结构类似,具有独特的三维交联网状结构,能够吸收大量水和体液而不溶解[7],是构筑药物包封体系的常见载体。Xie等[8]利用ACNs与硫酸软骨素的共色作用强化颜色,以卡拉胶构筑水凝胶载体,提高了ACNs在温度、pH和金属离子等多种条件下的稳定性。混合魔芋葡甘聚糖和黄原胶形成的协同水凝胶增强ACNs在多种pH(3.0、6.0和9.0)下的热稳定性[9]。明胶和低酰基结冷胶复合水凝胶(8/2,w/w)在模拟消化过程中可调节ACNs的释放,且对正常大鼠肠上皮细胞的增殖没有抑制作用,表明该复合水凝胶的安全性[10]。
壳聚糖是自然界中存在的唯一碱性多糖,具有良好的生物相容性、生物降解性、生物粘附特性和渗透增强效应,使壳聚糖逐渐成为理想的封装和输送材料[11]。壳聚糖分子链上含有大量氨基,易与醛基化合物发生缩合反应,基于动态亚胺键构筑pH响应型水凝胶[12],其冻干后微观形貌通常为多孔海绵状,微米级孔径为药物的负载提供了大量空间[13];良好的溶胀和pH响应性能使药物释放行为具有可控性[14]。以壳聚糖和醛为原料有望构筑出具有缓释性能的pH响应型水凝胶。水杨醛是天然存在于荞麦种子[15]、菊科植物[16]和食草叶甲虫防御分泌物[17]中的一元醛,具有更好的生物安全性。本文以水杨醛与壳聚糖构筑水凝胶(CS-SA)包埋蓝莓ACNs,得到花色苷/壳聚糖-水杨醛水凝胶(ACNs/CS-SA),并对其缓释性能、稳定性、溶胀性能进行评价,以期利用亚胺键的响应性实现ACNs的可控释放、提高ACNs的稳定性,并为壳聚糖基天然缓释材料的开发提供更多选择。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
壳聚糖(脱乙酰度95%,粘度100~200 mPa·s) 萨恩化学技术(上海)有限公司;水杨醛(98%,分析纯) 北京伊诺凯科技有限公司;蓝莓提取物冻干粉(花色苷含量25%) 西安隆择生物工程有限责任公司;矢车菊-3-O-葡萄糖苷标准品(>95%) 上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;磷酸二氢钾、无水乙醇、冰醋酸、氯化钾、无水碳酸钠、醋酸钠均为分析纯 天津市永大化学试剂有限公司;磷酸氢二钠(分析纯) 天津市化学试剂六厂;浓盐酸(分析纯) 天津标准科技有限公司。
FA2004N型电子天平 上海精密科学仪器有限公司;PHSJ-3F型实验室pH计 上海雷磁仪器厂;RCT Basic型IKA磁力加热搅拌器 艾卡(广州)仪器设备有限公司;is5型傅里叶变换红外光谱仪 赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司;UV-2600型紫外可见分光光度计 岛津企业管理(中国)有限公司;TM3030型台式扫描电镜 日本株式会社日立高新技术那珂事业所;TD3000型X-射线衍射仪 丹东通达科技有限公司;ZRY-2P高温综合热分析仪 上海精密科学仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 CS-SA的制备
水杨醛溶液的制备:取146 μL水杨醛,用无水乙醇定容至10 mL,备用。
壳聚糖溶液的制备:称取2.0 g壳聚糖溶解于100 mL的1%(V/V)醋酸水溶液中,制得2%壳聚糖溶液,密封静置24 h,备用。
CS-SA的制备:量取2.0 mL的壳聚糖溶液于螺口玻璃瓶中,室温下磁力搅拌,转速700 r/min,缓慢滴加1.0 mL水杨醛溶液,得到CS-SA[14]。
1.2.2 ACNs/CS-SA的制备
ACNs溶液的制备:分别称取0.0080、0.0160、0.0320、0.0400、0.0600、0.1200 g蓝莓提取物冻干粉,溶解于1.0 mL去离子水中,超声匀质,得不同质量浓度的ACNs溶液,避光,4 ℃冷藏,备用。
不同负载量ACNs/CS-SA的制备:分别量取2.0 mL壳聚糖溶液于螺口玻璃瓶中,室温下磁力搅拌,转速700 r/min,迅速加入1.0 mL不同浓度的ACNs溶液,同时缓慢滴加1.0 mL水杨醛溶液,制得负载量(以水杨醛质量计)分别为20%、40%、80%、100%、150%和300%的ACNs/CS-SA,并采用倒管实验[14]考察不同负载量对凝胶行为的影响。
1.2.3 表征方法
采用红外光谱(FT-IR)、紫外-可见光谱(UV-Vis)、X-射线衍射(XRD)、扫描电子显微镜(SEM)进行结构和形貌表征,表征方法参考文献[14],并稍作修改;采用热重分析(TG-DTG)进行热稳定性表征,表征方法参考文献[18],并稍作修改。具体表征方法如下:
1.2.3.1 FT-IR表征
取适量水凝胶,加入少量无水乙醇,用磁力搅拌器打碎至形成均匀溶液,倒入模具,自然干燥后制得水凝胶薄膜,测绘FT-IR图谱。取少量蓝莓提取物冻干粉与适量KBr粉末混合,充分研磨,装入模具,15 MPa下压片1 min,测绘FT-IR图谱。采集参数:分辨率4 cm−1,扫描范围4000~500 cm−1,扫描次数16次。
1.2.3.2 UV-Vis表征
取少量水凝胶于0.1 cm石英比色皿上涂抹均匀,测绘UV-Vis图谱。取2 mL以醋酸溶液调至pH4.2的ACNs溶液于1 cm石英比色皿中,测绘UV-Vis图谱。设置波长范围200~700 nm。
1.2.3.3 XRD表征
取适量水凝胶,加入少量无水乙醇,用磁力搅拌器打碎至形成均匀溶液,少量多次均匀涂于载玻片上,自然干燥,测绘XRD图谱。取适量蓝莓提取物冻干粉充分研磨、压片,测绘XRD图谱。XRD采用Cu-ka(λ=0.15406 nm)辐射,扫描速率0.01°/s,扫描范围3~50°,电压30 kV,电流20 mA。
1.2.3.4 SEM表征
分别将蓝莓提取物冻干粉、不同负载量的ACNs/CS-SA冷冻干燥至恒重,得ACNs/CS-SA冻干凝胶。用裁纸刀快速切割ACNs/CS-SA冻干凝胶,得到平整的横截面,粘贴到导电胶上,喷金60 s,观察水凝胶形貌。
1.2.3.5 热重分析表征
分别称取少量蓝莓提取物冻干粉、CS-SA冻干凝胶粉末、负载量为100%的ACNs/CS-SA冻干凝胶粉末于坩埚中,记录40~640 ℃范围内加热过程中样品失重曲线(升温速率10 ℃/min)。
1.2.4 溶胀性能测定方法
分别将CS-SA和负载量100%的ACNs/CS-SA置于培养皿中,自然干燥48 h,制得干凝胶片。分别取pH2.7的醋酸溶液、pH4.6、6.7的NaAc-HAc缓冲溶液和pH11.7的Na2CO3溶液20 mL于50 mL小烧杯中,将称量后的干凝胶片置于其中,每隔一段时间取出凝胶片,用滤纸将表面擦干,称重,记录,重复以上操作。每个实验平行三次,计算平均值。溶胀率SR按(1)计算:
SR(%)=mt−m0m0×100 (1) 式中:m0为干凝胶片质量,g;mt为溶胀后凝胶片质量,g。
1.2.5 缓释性能测定方法
标准曲线的绘制:将5 mg矢车菊-3-O-葡萄糖苷标准品溶解于pH2.7的醋酸溶液中,转移至100 mL容量瓶定容,得储备液,避光备用。依次量取不同体积的储备液至10 mL容量瓶中,定容,得到浓度分别为0.004、0.008、0.012、0.016、0.020 mg/mL的溶液,在最大吸收波长512 nm处依次测定上述各浓度溶液的吸光度值,绘制标准曲线:y=2.921x+0.0321,R2=0.99982。参照以上步骤,分别在最大吸收波长521 nm处绘制pH4.6的NaAc-HAc缓冲溶液标准曲线:y=0.651x+0.00803,R2=0.99948;在最大吸收波长540 nm处绘制pH6.7的NaAc-HAc缓冲溶液标准曲线:y=0.696x+0.0115,R2=0.99911。
缓释性能测定方法:取一定质量的100% ACNs/CS-SA干凝胶片,称重,记录,浸于200 mL pH2.7的醋酸溶液中,每间隔一定时间,取2 mL溶液于石英比色皿中,测定吸光度值,利用标准曲线计算浓度,平行做三组实验,计算ACNs累计释放率。参照以上步骤,分别测定pH4.6、6.7的NaAc-HAc缓冲溶液中ACNs累计释放率。ACNs累计释放率Q按(2)计算:
Q(%)=cn×Vm×100 (2) 式中:cn为第n次溶液中ACNs的浓度,mg/mL;V为浸泡溶液的体积,mL;m为凝胶中负载的ACNs质量,mg。
释放动力学的拟合:分别利用准一级动力学方程、准二级动力学方程、Higuchi方程、Weibull方程和Pepaas方程拟合释放过程,见式(3)~(7),研究不同pH对ACNs/CS-SA中ACNs释放行为的影响。
准一级动力学方程:ln(1−QQe)=−kt (3) 准二级动力学方程:tQ=1kQ2e+tQe (4) Higuchi方程:Q=kt1/2+b (5) Weibull方程:Q=A{1−e−[k(t−τ)]d} (6) Pepaas方程:Q=ktn (7) 式中:Q为t时刻ACNs的累计释放率;Qe为平衡时ACNs的释放率;t为释放时间,min;k为动力学常数;τ为位置参数;n为形状参数;kd为尺度参数;A、b为参数。
1.3 数据处理
溶胀和缓释性能测定实验重复3次,数据结果用“平均值±标准差”表示,Origin2018软件绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 负载量对凝胶行为的影响
制备了不同负载量的ACNs/CS-SA,结果如图1。负载量20%、40%、80%、100%、150%的ACNs/CS-SA均成胶;负载量150%的ACNs/CS-SA边缘有少量ACNs溶液渗出;负载量300%的ACNs/CS-SA质地较软,且成胶时间大于24 h。
2.2 ACNs/CS-SA的表征
2.2.1 FT-IR表征
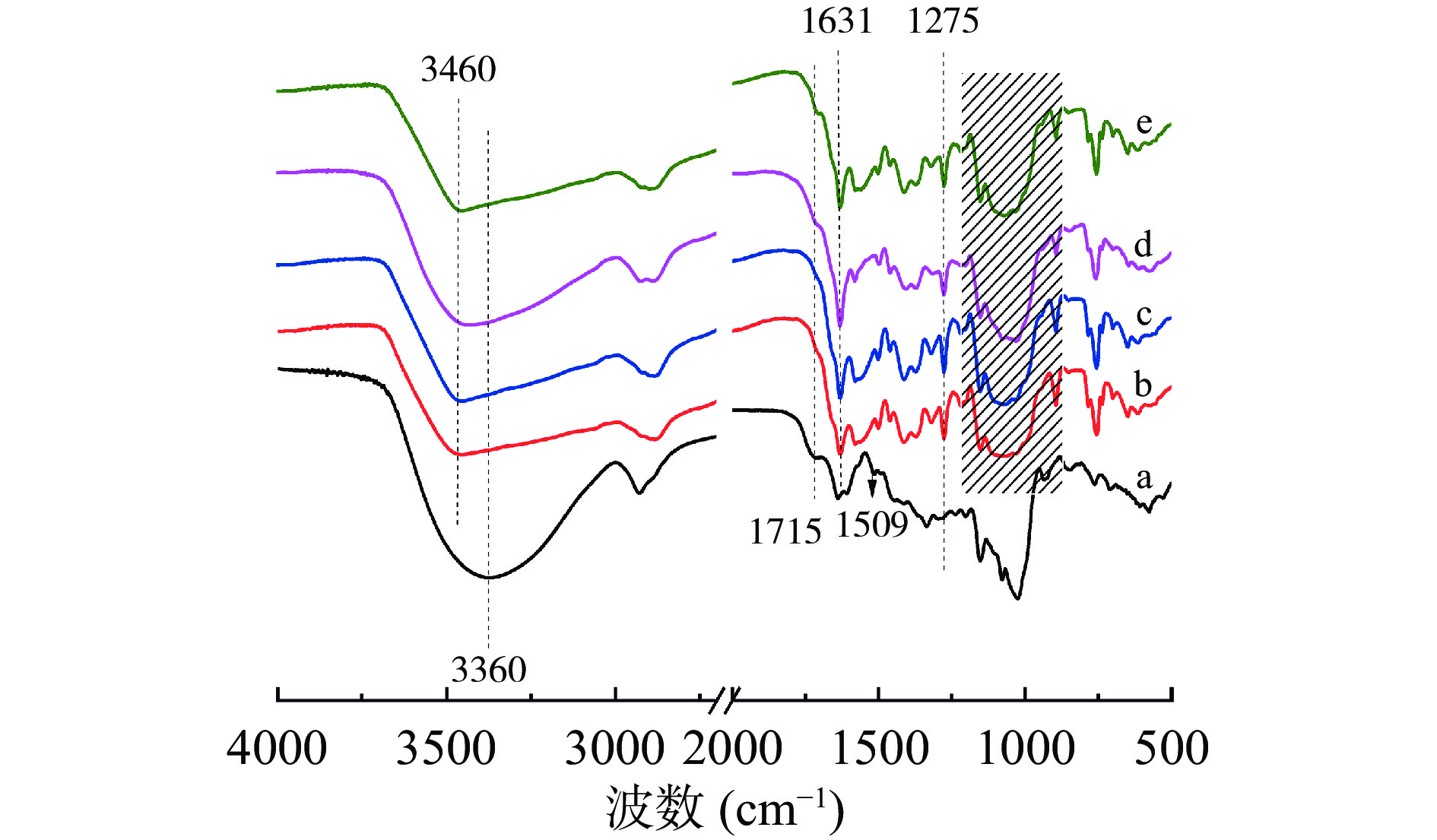
由ACNs的FT-IR表征(图2a)可知:3360 cm−1处出现宽且强的羟基伸缩振动特征峰,是由于ACNs的多羟基结构形成分子内氢键,导致羟基特征吸收峰红移并加宽;1715 cm−1处为苯环上的α-羰基结构特征峰,说明花色苷中存在酚酸结构,1509 cm−1处的苯并吡喃芳香环振动特征峰为黄烊衍生物的典型特征峰[19]。由CS-SA的FT-IR表征(图2b)可知:3460 cm−1处出现O-H伸缩振动特征峰,CS-SA于1631 cm−1 处出现强的尖峰,归属于亚胺键基团伸缩振动峰,说明水杨醛的醛基与壳聚糖的氨基反应生成了亚胺键。由不同负载量ACNs/CS-SA的FT-IR表征(图2c~2e)可知:随着ACNs的增加,1715 cm−1处开始出现ACNs苯环上α-羰基结构特征峰,且该峰的强度随负载量的增加而增加。ACNs/CS-SA保留着CS-SA中1631 cm−1处亚胺键的特征峰,1152、1078、1018 cm−1(图2阴影区)分别属于糖环上C-O-C、仲羟基、伯羟基的C-O特征峰和1275 cm−1处对应酚羟基特征峰,未出现新的特征振动峰,说明ACNs通过物理作用锚定到水凝胶网络结构中。
2.2.2 UV-Vis表征
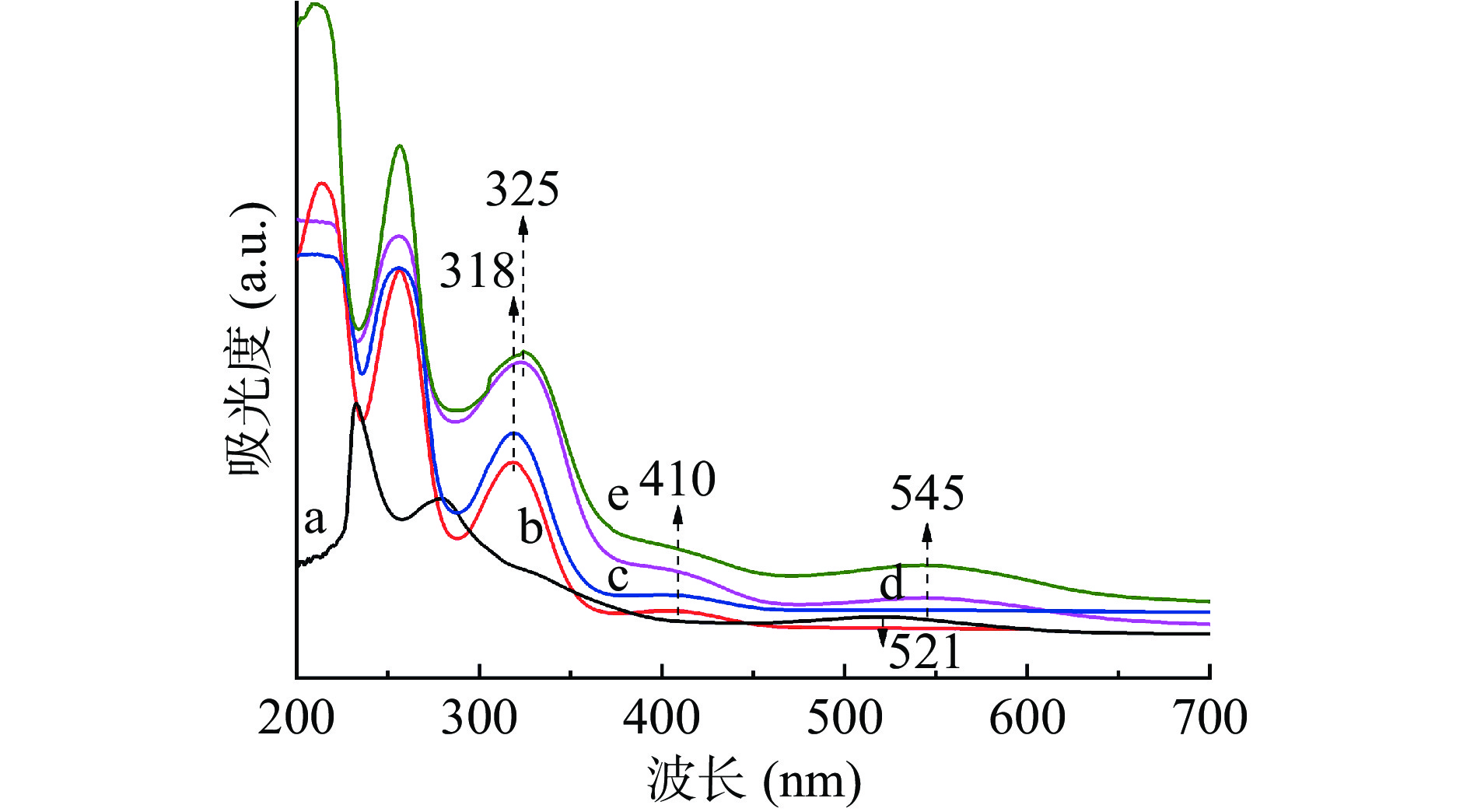
由图3a可知:ACNs水溶液分别在波长280 nm和521 nm处出现特征峰,与多羟基黄酮类化合物紫外特征吸收峰一致[20]。由图3b可知:CS-SA在410 nm吸收峰归属于SA-亚胺的酮胺。由图3c~3e可知:随负载量增加,ACNs/CS-SA保留410 nm处CS-SA的吸收峰,545 nm处ACNs特征吸收峰逐渐增强;CS-SA 318 nm处苯环吸收峰和ACNs 521 nm处吸收峰分别红移至325 nm和545 nm,说明CS-SA负载ACNs过程中,苯环和ACNs黄烊盐发色团(糖苷配基发色团)发生J-聚集[21]。
2.2.3 XRD表征
由ACNs的XRD表征(图4a)可知,ACNs的XRD图谱为无定型“馒头”峰,说明ACNs是无定形结构。由CS-SA的XRD表征(图4b)可知,CS-SA在2θ=6.5°、14.6°和20.6°处有较强衍射峰,依据布拉格方程2dsinθ=nλ计算出d=13.58 Å,6.06 Å,4.31 Å,分别对应相邻糖链(包含水杨醛和花色苷分子)、相邻苯环之间的距离和相邻糖链(不包含水杨醛和花色苷分子)之间的距离[12]。ACNs/CS-SA组装示意图如图5所示。由ACNs/CS-SA的XRD表征(图4c~4f)可知,负载量20%、100%、150%的ACNs/CS-SA与CS-SA的XRD谱图没有明显区别,说明ACNs进入凝胶层间,可能以微米级均匀分散于凝胶体系[13]。
2.2.4 SEM表征及负载机理
由ACNs的SEM表征(图6a)可以看出:ACNs冻干粉表面呈不规则形貌。由CS-SA的SEM表征(图6b)可以看出:冷冻干燥的CS-SA呈孔状结构,为ACNs的包埋提供了空间。由不同负载量ACNs/CS-SA的SEM表征(图6c~6e)可以看出:随着ACNs负载量的增加,孔径越来越小,ACNs未出现分相现象。正如图5所示,ACNs均匀分散在CS-SA三维网络结构中。通过放大倍率SEM图可以发现,随着ACNs负载量的增加,负载量为20%、100%、150%的ACNs/CS-SA纤维结构逐渐明显,说明ACNs参与凝胶超分子自组装过程,正如紫外光谱表征(图3)发现,水杨醛的苯环和黄烊盐发色团之间发生J-聚集。
2.2.5 TG和DTG表征
结合2.1负载量对凝胶行为的影响,选择凝胶稳定、包埋完全的ACNs/CS-SA进行TG和DTG表征,结果如图7:ACNs、CS-SA和ACNs/CS-SA的热分解均经历了三个阶段,ACNs在40~260 ℃出现的缓慢失重现象,主要与水分挥发和糖苷键断裂有关;260~330 ℃出现的迅速失重,归因于开环反应使ACNs降解为酚酸和醛;330~530 ℃的失重与糖类热解有关[22-23]。CS-SA在40~250 ℃出现水分蒸发及初步热分解,此阶段失重较少;250~330 ℃,其经历氧化反应产生CO2、H2O和有机中间产物;继续加热至580 ℃,热解完全[24]。ACNs/CS-SA在40~250 ℃的缓慢失重现象主要与吸附在水凝胶中的结合水挥发和ACNs多糖的脱除有关;250~330 ℃迅速失重与CS-SA的热分解及ACNs的降解有关,DTG曲线显示失重速率为12.58%/min,小于ACNs在该温度段的失重速率25.03%/min;330~580 ℃范围内,CS-SA和ACNs/CS-SA的TG曲线斜率近似,二者的DTG曲线均出现宽峰,且DTG曲线显示失重速率小于ACNs,最大失重速率对应温度明显升高。由此可见,凝胶包埋可以显著提高ACNs的热稳定性。正如先前研究[9],凝胶行为可以避免ACNs暴露于热辐射,提高其稳定性。
2.3 ACNs/CS-SA的溶胀性能
ACNs/CS-SA在不同pH介质中的溶胀性能见图8。由图8可以看出,ACNs/CS-SA、CS-SA溶胀性能展现出明显的pH响应性。在酸性介质中溶胀率均较大,pH2.7时,二者溶胀率最大,133 min时分别为1167.47%±92.57%和1145.18%±7.42%。在中性、碱性介质中二者溶胀率较小,这是由于CS氨基的去质子作用(CS pKa6.5)使氢键作用增强,溶胀率下降。ACNs/CS-SA在pH11.7介质中溶胀率高于pH6.7介质中的溶胀率,这可能由于ACNs结构中存在大量酚羟基,在碱性介质中去质子化。
2.4 ACNs/CS-SA的缓释性能
不同pH条件下,ACNs/CS-SA的缓释性能见图9。由图9可知,pH2.7时ACNs/CS-SA累计释药率较高,随pH增加,ACNs/CS-SA累计释药率减少。在pH2.7、4.6和6.7的缓冲溶液中,ACNs/CS-SA 24 h累计释药率分别为74.28%±4.58%、40.72%±4.04%和15.70%±1.71%。ACNs累计释药率呈现先增大后趋于平衡的规律,结合图8可以看出,ACNs/CS-SA缓释性能与溶胀性能曲线趋势一致,展现了pH响应性能。pH2.7时,ACNs/CS-SA 24 h累计释药率高,这是由于强酸性条件下,亚胺键部分断裂,CS氨基被质子化,高分子链伸展[25],凝胶溶胀,有利于ACNs的释放;pH6.7时,ACNs累计释药率低,亚胺键在中性介质中稳定性较高,壳聚糖氨基部分去质子化,ACNs/CS-SA的疏水单元能够更有效地排序,凝胶溶胀性能差,阻止了ACNs的释放。
在pH2.7和4.6的缓冲溶液中,ACNs/CS-SA开始60 min ACNs释放速率均较快,累计释药率分别为28.31%±1.48%和20.98%±7.74%,这主要是由于开始阶段ACNs/CS-SA缓释溶胀速率快,凝胶表面的ACNs释放到缓冲溶液中。原位凝胶使ACNs分子和基质之间产生较强的物理作用力,克服了明显突发释放的缺点,使ACNs在前60 min的中度突发释放和随后1 d的延长释放之间达到了良好的平衡,适用于药物控释系统的设计[26]。
一般认为亲水性药物的释放主要受扩散过程控制,但其他因素,如基质的物理作用力和基质侵蚀也起着重要作用[27]。为了进一步探讨ACNs的释放行为,分别利用准一级动力学方程、准二级动力学方程、Higuchi方程、Pepaas方程和Weibull方程对不同pH条件下ACNs/CS-SA中ACNs释放行为进行拟合,结果见表1。由表1可见,不同pH条件下,Weibull方程均对ACNs/CS-SA释放过程有较好拟合,R2分别为0.99405、0.95165、0.99712。但Weibull方程为经验方程,无法充分描述药物的溶出动力学性质。准二级动力学方程、Higuchi方程、Pepaas方程对pH2.7时ACNs/CS-SA释放过程也有较高的相关系数(R2=0.91015~0.95904),说明pH2.7时ACNs/CS-SA释放机制复杂,受许多因素控制。Higuchi方程表明ACNs分子在凝胶中的扩散在其释放过程中起着重要作用。Pepaas方程中n<0.45,说明ACNs的扩散为Fick扩散[28]。
表 1 100% ACNs/CS-SA释放动力学模型分析Table 1. Release dynamics model analysis of 100% ACNs/CS-SA模型 方程 R2 pH2.7 准一级 Q=64.22519×[1−exp(−0.00683t)] 0.89566 准二级 Q=1/(0.01328+1.63956/x) 0.95617 Higuchi Q=1.94371t1/2+12.00928 0.91015 Weibull Q=77.49016×{1−e−[0.00362(t+15.10121)]0.7096} 0.99405 Pepaas Q=6.90565t0.33862 0.95904 pH4.6 准一级 Q=34.54011×[1−exp(−0.01705t)] 0.81687 准二级 Q=1/(0.02534+1.21956/x) 0.91344 Higuchi Q=0.94346t1/2+13.24074 0.76389 Weibull Q=46.15881×{1−e−[0.00613(t−7.72996)]0.40212} 0.95165 Pepaas Q=7.594t0.24816 0.88208 pH6.7 准一级 Q=16.46357×[1−exp(−0.00273t)] 0.96812 准二级 Q=1/(0.0473+19.09845/x) 0.94464 Higuchi Q=0.46828t1/2+0.02852 0.83522 Weibull Q=15.6828×{1−e−[0.00289(t+29.80457)]1.63029} 0.99712 Pepaas Q=0.61095t0.45867 0.84236 Xie等[8]研究了卡拉胶构筑水凝胶包埋ACNs,结果表明,随着介质pH增加,ACNs累计释药率逐渐增大,在pH1.0介质中ACNs累计释药率为41.3%;在pH6.0介质时累计释药率为93.4%。如前所述,ACNs/CS-SA展现了相反的pH响应释药性能,随着pH增加ACNs累计释药率逐渐减小,酸性条件下ACNs累计释药率最大。也有研究表明,水杨醛及衍生物交联壳聚糖构筑的水凝胶对大鼠的免疫系统、血液生化指标和组织器官等没有不良影响[27]。ACNs/CS-SA不仅具有良好的pH响应性,并能提高ACNs的稳定性,而且可能具有复合水凝胶的安全性[10],有望为ACNs应用提供新载体。
3. 结论
在蓝莓ACNs存在下,以水杨醛为交联剂,原位构筑了载药水凝胶ACNs/CS-SA。ACNs/CS-SA不仅提高了ACNs的热稳定性,而且ACNs释放行为展现出控释性能和pH响应性。在pH2.7、4.6、6.7介质中,100% ACNs/CS-SA 24 h累计释药率分别为74.28%±4.58%、40.72%±4.04%和15.70%±1.71%,随着介质pH增加,ACNs累计释药率逐渐减小。ACNs/CS-SA溶胀性能和释放动力学研究表明,ACNs/CS-SA的控释性能与其溶胀性能展现相同的规律,溶胀率增加ACNs释放率增大;Higuchi方程表明ACNs分子在凝胶中的扩散行为是释放过程的重要影响因素,主要可能由于亚胺键和壳聚糖氨基的酸碱响应,在不同pH介质中ACNs/CS-SA结构发生变化,从而使ACNs的释放展现pH响应性。ACNs/CS-SA制备方法简单、绿色,具有良好的pH响应性,并能提高ACNs的稳定性,为新型药物包封材料的开发和ACNs的应用提供了理论和实验基础。
-
表 1 100% ACNs/CS-SA释放动力学模型分析
Table 1 Release dynamics model analysis of 100% ACNs/CS-SA
模型 方程 R2 pH2.7 准一级 Q=64.22519×[1−exp(−0.00683t)] 0.89566 准二级 Q=1/(0.01328+1.63956/x) 0.95617 Higuchi Q=1.94371t1/2+12.00928 0.91015 Weibull Q=77.49016×{1−e−[0.00362(t+15.10121)]0.7096} 0.99405 Pepaas Q=6.90565t0.33862 0.95904 pH4.6 准一级 Q=34.54011×[1−exp(−0.01705t)] 0.81687 准二级 Q=1/(0.02534+1.21956/x) 0.91344 Higuchi Q=0.94346t1/2+13.24074 0.76389 Weibull Q=46.15881×{1−e−[0.00613(t−7.72996)]0.40212} 0.95165 Pepaas Q=7.594t0.24816 0.88208 pH6.7 准一级 Q=16.46357×[1−exp(−0.00273t)] 0.96812 准二级 Q=1/(0.0473+19.09845/x) 0.94464 Higuchi Q=0.46828t1/2+0.02852 0.83522 Weibull Q=15.6828×{1−e−[0.00289(t+29.80457)]1.63029} 0.99712 Pepaas Q=0.61095t0.45867 0.84236 -
[1] ZHANG Y Z, YIN L Q, HUANG L, et al. Composition, antioxidant activity, and neuroprotective effects of anthocyanin-rich extract from purple highland barley bran and its promotion on autophagy[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,339(3):127849.
[2] MILENKOVIC D, KRGA I, DINEL A L, et al. Nutrigenomic modification induced by anthocyanin-rich bilberry extract in the hippocampus of ApoE-/-mice[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2021,85(10):104609.
[3] GARCIA C, BLESSO C N. Antioxidant properties of anthocyanins and their mechanism of action in atherosclerosis[J]. Free Radical Biology and Medicine,2021,172(8):152−166.
[4] GHAREAGHAJLOU N, HALLAJ-NEZHADI S, GHASEMPOUR Z. Red cabbage anthocyanins: Stability, extraction, biological activities and applications in food systems[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,365(12):130482.
[5] PIMENTA INADA K O, REVOREDO SILVA T B, ARAUJO LOBO L, et al. Bioaccessibility of phenolic compounds of jaboticaba (Plinia jaboticaba) peel and seed after simulated gastrointestinal digestion and gut microbiota fermentation[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2020,67(4):103851.
[6] LEE J Y, JO Y U, SHIN H, et al. Anthocyanin-fucoidan nanocomplex for preventing carcinogen induced cancer: Enhanced absorption and stability[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics,2020,586(8):119597.
[7] GUYOT C, CERRUTI M, LEROUGE S. Injectable, strong and bioadhesive catechol-chitosan hydrogels physically crosslinked using sodium bicarbonate[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:C,2021,118(1):111529.
[8] XIE C J, WANG Q, YING R F, et al. Binding a chondroitin sulfate-based nanocomplex with kappa-carrageenan to enhance the stability of anthocyanins[J]. Food Hydrocolloid,2020,100(3):105448.
[9] JIN W P, XIANG L, PENG D F, et al. Study on the coupling progress of thermo-induced anthocyanins degradation and polysaccharides gelation[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2020,105(8):105822.
[10] LIU L Y, ZHANG D D, SONG X X, et al. Compound hydrogels derived from gelatin and gellan gum regulates the release of anthocyanins in simulated digestion[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,127(6):107487.
[11] LI L, ZHANG P, LI C C, et al. In vitro/vivo antitumor study of modified-chitosan/carboxymethyl chitosan “boosted” charge-reversal nanoformulation[J]. Carbohyd Polymers,2021,269(10):118268.
[12] IFTIME M M, MORARIU S, MARIN L. Salicyl-imine-chitosan hydrogels: Supramolecular architecturing as a crosslinking method toward multifunctional hydrogels[J]. Carbohyd Polymers,2017,165(2):39−50.
[13] IFTIME M M, AILIESEI G L, UNGUREANU E, et al. Designing chitosan based eco-friendly multifunctional soil conditioner systems with urea controlled release and water retention[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2019,223(11):115040.
[14] LIU C X, DONG C F, LIU S H, et al. Multiple chiroptical switches and logic circuit based on salicyl-imine-chitosan hydrogel[J]. Carbohyd Polymers,2021,257(4):117534.
[15] BARDA C, GRAFAKOU M E, KALPOUTZAKISA E, et al. Chemical composition of Crepis foetida L. and C. rubra L. volatile constituents and evaluation of the in vitro anti-inflammatory activity of salicylaldehyde rich volatile fraction[J]. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology,2021,9(6):104256.
[16] JANES D, KREFT S. Salicylaldehyde is a characteristic aroma component of buckwheat groats[J]. Food Chemistry,2008,109(2):293−298. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.12.032
[17] SCHMIDT L, WIELSCH N, WANG D, et al. Tissue-specific profiling of membrane proteins in the salicin sequestering juveniles of the herbivorous leaf beetle, Chrysomela populi[J]. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology,2019,109(6):81−91.
[18] 王洪玲, 崔维真, 刘强, 等. 水杨醛交联壳聚糖构筑新型壁材包囊花椒油研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(8):199−204. [WANG Hongling, CUI Weizhen, LIU Qiang, et al. New wall material prepared by salicylaldehyde crosslinking chitosan encapsulated Zanthoxylum bungeanum oil[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022,48(8):199−204. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.029885 [19] 谢凤英, 李凤凤, 张爽, 等. 黑米花色苷酰化修饰红外光谱分析[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2018,38(8):2386−2389. [XIE Fengying, LI Fengfeng, ZHANG Shuang, et al. Analysis of acylation modification of black rice anthocyanins using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR)[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2018,38(8):2386−2389. [20] 薛宏坤, 李鹏程, 钟雪, 等. 高速逆流色谱分离纯化桑葚花色苷及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(15):96−104. [XUE Hongkun, LI Pengcheng, ZHONG Xue, et al. Separation and purification of anthocyanins from mulberry fruit by high-speed counter-current chromatography and their antioxidant activity[J]. Food Science,2020,41(15):96−104. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190715-193 [21] 王锋, 邓洁红, 谭兴和, 等. 花色苷及其共色作用研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2008,29(2):472−476. [WANG Feng, DENG Jiehong, TAN Xinghe, et al. Research progress on anthocyanins and copigmentation[J]. Food Science,2008,29(2):472−476. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2008.02.104 [22] WANG D, MA Y, ZHANG C, et al. Thermal characterization of the anthocyanins from black soybean (Glycine max L.) exposed to thermogravimetry[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2014,55(2):645−649. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2013.10.007
[23] WEN Y Y, LIU J, JIANG L, et al. Development of intelligent/active food packaging film based on TEMPO-oxidized bacterial cellulose containing thymol and anthocyanin-rich purple potato extract for shelf life extension of shrimp[J]. Food Packaging and Shelf Life,2021,29(9):100709.
[24] HERAS-MOZOS R, HERNANDEZ R, GAVARA R, et al. Dynamic covalent chemistry of imines for the development of stimuli-responsive chitosan films as carriers of sustainable antifungal volatiles[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,125(4):107326.
[25] 董翠芳, 王洪玲, 刘长霞, 等. pH响应的壳聚糖-糠醛水凝胶的构筑及自愈合性能[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程,2020,36(11):127−133,138. [DONG Cuifang, WANG Hongling, LIU Changxia, et al. Fabrication of pH responsive chitosan-furfural hydrogel and its self-healing abilit[J]. Polymer Materials Science & Engineering,2020,36(11):127−133,138. doi: 10.16865/j.cnki.1000-7555.2020.0253 [26] IFTIME M M, TARTAU L M, MARIN L. New formulations based on salicyl-imine-chitosan hydrogels for prolonged drug release[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,160(10):398−408.
[27] CRACIUN A M, TARTAU L M, PINTEALA M, et al. Nitrosalicyl-imine-chitosan hydrogels based drug delivery systems for long term sustained release in local therapy[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2019,536(2):196−207.
[28] 刘中垒, 李国玉, 谭勇, 等. 红花黄色素缓释骨架片的研制及其体外释放度的研究[J]. 石河子大学学报(自然科学版),2009,27(3):328−333. [LIU Zhonglei, LI Gongyu, TAN Yong, et al. The preparation of safflower yellow sustained-release matrix tablets and their drug release in vitro[J]. Journal of Shihezi University (Natural Science),2009,27(3):328−333. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7383.2009.03.014 -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 曾臻,上官雪茹,蔡依婕,丰艳,吴伟菁,吴兰兰,何义姝,林木丁,谭强来. 新型重组海洋抗菌肽制备与评价的综合实验设计. 食品与药品. 2025(02): 185-190 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 曾臻,罗家英,蔡依婕,上官雪茹,黄艺虹,李雅婷,李婉褀,谭强来. 四联鲎抗菌肽Tachyplesin Ⅱ毕赤酵母重组质粒构建及其表达. 科技创新与应用. 2024(07): 47-50 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 苏琰,李融. 抗菌肽的食品保鲜应用及生物合成研究进展. 食品与机械. 2024(07): 208-215 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)













 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:



