Research Progress of Antibacterial Hydrogels in the Food Field
-
摘要: 水凝胶是由亲水性三维网络结构组成的一种高分子材料,可以迅速吸水溶胀并保持溶胀状态,避免大量水流失。它能够提供足够的容量来容纳各种材料,包括小分子、聚合物和颗粒等,其中表现出抗菌性能的被称为抗菌水凝胶。抗菌水凝胶已被广泛应用于生物医学、纺织、化工、农业以及组织工程等多个领域。其在食品包装、食品质量指示以及食品保鲜等方面有很大的应用潜力却没有引起人们足够的重视。据活性成分的类型,抗菌水凝胶可分为3类:天然高分子抗菌水凝胶;载有无机/有机抗菌物质的水凝胶;载有光激活或光响应材料的水凝胶。本综述分别阐述了这3类抗菌水凝胶的抗菌机理及其应用现状,以期为抗菌水凝胶在食品领域上发挥抗菌功效的应用提供更广阔的思路。Abstract: Hydrogel is a polymer material composed of a hydrophilic three-dimensional network structure, which can quickly absorb water, swell, and maintain the swollen state to avoid significant water loss. It can provide sufficient capacity to accommodate a variety of materials, including small molecules, polymers and particles, among which, those that exhibit antibacterial properties are called antibacterial hydrogels. Antibacterial hydrogels have been widely used in many fields, such as biomedicine, textile, chemical industry, agriculture, and tissue engineering. They have great application potential in food packaging, food quality indication, and food preservation, but have not attracted enough attention. According to the type of active ingredients, antibacterial hydrogels can be divided into three categories: Natural polymer antibacterial hydrogel, hydrogels loaded with inorganic/organic antibacterial substances, and antibacterial hydrogels containing light-activated or light-responsive materials. This review expounds on the antibacterial mechanism and application status of these three types of antibacterial hydrogels, in order to provide a broader idea for the application of hydrogels in the field of food to exert its antibacterial effect.
-
Keywords:
- hydrogel /
- bacteriostasis /
- antibacterial mechanism /
- food packaging /
- food preservation
-
近年来,微生物污染严重危害了食物安全和人体健康,抗生素应运而生,已经成为现代医学的基石。然而,持续的使用和滥用抗生素导致耐药性细菌也随之出现。传统抗菌剂的抗菌机理大多是通过破坏细菌细胞内部的酶活性来抑制细菌的生长,易导致细菌产生耐药性,进而逐渐变为耐药菌株[1]。因此,当前迫切需要开发新的抗菌剂并急需寻找新的、高效的抗菌材料来解决这一问题。抗菌材料应当具有安全无毒、优异的抗菌性和生物相容性等特征,为了满足这些要求,一些新型的抗菌材料,如碳纳米管[2]、金属纳米颗粒[3]、聚合物[4]、多肽[5]、水凝胶[6]的潜在应用价值已经显现出来。在这些抗菌材料中,水凝胶因具有其独特的优势,受到广泛关注。
“水凝胶”一词于1894年第一次出现在文献中[7],水凝胶是亲水性或水溶性高分子通过一定的物理或化学交联所形成的三维(3D)网络结构的凝胶,其中水为分散介质并且至少占凝胶重量的70%,因此,水凝胶具有很强的吸水性和保水性。此外,基于天然高分子材料的水凝胶还具有其他很多特性,比如具有生物相容性和生物可降解性、较小的硬度和较高的弹性,这就决定了水凝胶具有多种商业用途。事实上,对于合成功能性水凝胶的研究已经十分成熟,如自愈水凝胶[8]、抗菌水凝胶[9]、形状记忆水凝胶[10]以及组织粘合剂水凝胶[11]等。
水凝胶凭借其独特的三维结构,能够提供足够的容量容纳小分子、聚合物和颗粒等材料,已然成为一种具有实用前途的抗菌材料,广泛应用于生物医学、化妆品、纺织、化工、建筑、农业以及组织工程等多个领域,是目前研究的热点[12]。相比于其他抗菌材料,水凝胶成本低且容易获得,因此,抗菌水凝胶的应用对人类生活产生了巨大的积极影响。然而,抗菌水凝胶在食品领域上的应用没有引起人们足够的重视。关于抗菌水凝胶在食品领域上的应用类综述也未有发表。
目前,根据其活性成分的类型,抗菌水凝胶主要可分为3大类:天然高分子抗菌水凝胶,例如纤维素基抗菌水凝胶、壳聚糖基抗菌水凝胶和淀粉基抗菌水凝胶等;载有无机/有机抗菌物质的水凝胶,例如银纳米粒子(NPs)、氧化锌/季铵盐等;载有光激活或光响应材料的水凝胶,这类水凝胶可以借助光介导发挥抗菌的功能。这3类抗菌水凝胶各有优缺点,其中,将光激活或光响应材料结合到具有良好生物相容性的水凝胶里,所制备出的光介导抗菌水凝胶由于其优异的抗菌性能而引起了人们的广泛兴趣[13]。根据不同活性成分抗菌水凝胶的优缺点,选择安全且合适的抗菌水凝胶应用于食品领域是切实可行的。本综述分别阐述了这3类抗菌水凝胶的抗菌机理及其应用现状,以期为抗菌水凝胶在食品领域上发挥抗菌功效的应用提供更广阔的思路。
1. 水凝胶的形成机理
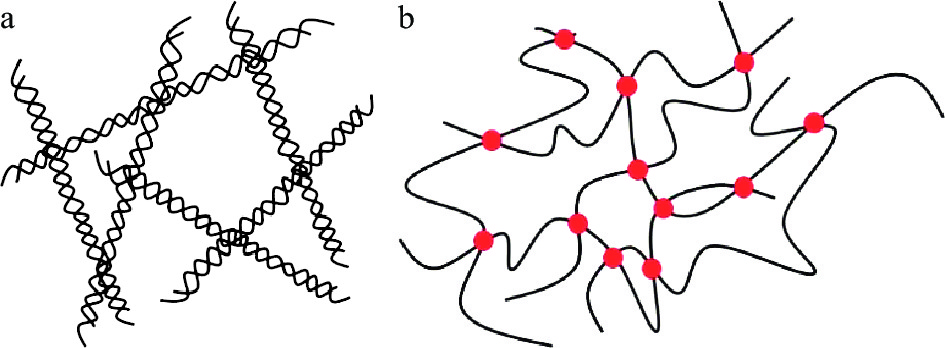
由于水凝胶基本上是由交联网络构成的,因此,根据水凝胶形成时不同的交联方式,可简单分为物理交联水凝胶和化学交联水凝胶两大类[14](见图1)。
1.1 物理交联水凝胶
物理交联水凝胶在凝胶形成过程中不涉及化学反应,通过聚合物链间的弱相互作用力形成,如疏水相互作用[15]、氢键[16]、离子相互作用[17]等,由于分子之间的作用力不强,通过改变一些物理条件,如pH、温度等,就可以破坏物理交联水凝胶的结构。
1.1.1 疏水相互作用
以亲水单体和少量疏水单体的共聚反应为基础,同时在反应体系中加入表面活性剂作为水凝胶网络的交联点,最终可得到稳定的疏水缔合水凝胶。近年来,疏水作用水凝胶在抗菌敷料领域受到越来越多的关注。Li等[18]采用丙烯酸、1-乙烯基-3-丁基咪唑鎓、羧基改性阿拉伯树胶和氯化铝一步法制备了一种抗菌水凝胶敷料。由于疏水相互作用,该水凝胶在吸水后的力学性能得到改善。因此,这种新型水凝胶在伤口敷料领域具有广阔的应用前景。
1.1.2 氢键
氢键是一种非共价相互作用力,具有独特的可调节性、特异性和方向性。虽然单个氢键的解离能很低,但多个氢键的聚集体形成的强键合能与共价键相当[19]。所以,利用氢键作为交联点制备水凝胶成为新的趋势。Zhang等[20]通过开环聚合(ROP)技术制备了水溶性三嵌段共聚物,由于特殊的锯齿形氢键的存在,形成一个致密的疏水核,由此开发了一种具有超拉伸性、坚韧性和可自愈性的水凝胶。该项工作为通过增强高密度氢键开发聚合物水凝胶提供了一种新策略,具有优异的机械性能,并显示出其广泛的应用潜力。
1.1.3 离子相互作用
离子交联水凝胶是一类由离子与聚合物侧链形成离子键的水凝胶。例如:Zhou等[21]通过三嵌段共聚物胶束和离子相互作用的双重交联,获得了高度柔韧、坚韧和自修复的水凝胶,动态的离子相互作用赋予水凝胶自愈性能。其中,海藻酸钠与钙离子通过离子相互作用形成的离子交联水凝胶是最常见的离子交联水凝胶。例如,Li等[22]成功开发了具有促血管生成和抗菌特性的钙离子(Ca2+)交联海藻酸钠(SA)水凝胶。通过细胞毒性试验和菌落形成试验可知,该水凝胶不仅具有良好的生物相容性还能够有效地抑制大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌。
1.2 化学交联水凝胶
化学交联水凝胶是由共价键构成的具有三维网络结构的凝胶,它的聚合物链(共价键)之间呈现出强而持久的相互作用力,导致其交联过程不可逆,所以这类水凝胶具有结构稳定等特点,但是也可以通过特殊的物理方式、水解或酶解来破坏其三维结构。通常,化学交联水凝胶多是通过添加小分子化学交联剂、引发剂等形成的,具有上述优点的同时也具有非环境友好和有毒等缺点,因此,限制了其在食品领域的应用。
化学交联水凝胶的制备一般分为两步:首先要制备前体物质,然后再选择不同的交联方式进行凝胶化。根据不同的交联方式可分为交联剂交联水凝胶[23],辐射交联水凝胶[24],光交联水凝胶[25]等。在不使用有细胞毒性的化学试剂的前提下,所制备的辐照交联水凝胶和光交联水凝胶在食品领域的应用也是具有可行性的。Chang等[26]以明胶和透明质酸为基质,通过化学交联并进一步负载作为抗菌因子的扁柏醇抗菌剂,成功制备了一种具有抗菌作用的水凝胶。通过化学交联可以增强水凝胶的机械性能、结构稳定性及其抗降解性能,成功开发了具有良好机械强度、抗菌性能和无细胞毒性的可生物降解的再生水凝胶。由此可见,选择合适的化学交联方法,也可以制备出适用于食品领域的抗菌水凝胶。
2. 抗菌水凝胶的分类
高分子水凝胶可分为天然高分子水凝胶和合成高分子水凝胶[27]。天然高分子水凝胶大多具有一定的抗菌性,而合成高分子水凝胶通常没有抗菌性,需要额外再嵌入抗菌物质,如无机物质、有机物质、光激活或光响应材料等[28]。因此,根据活性成分的类型,抗菌水凝胶主要可分为3类[29]:天然高分子抗菌水凝胶,此类抗菌水凝胶具有良好的生物相容性和可降解性,是应用于食品领域的首要选择;载有无机/有机抗菌物质的水凝胶,例如银纳米粒子(NPs)、氧化锌/季铵盐等;载有光激活或光响应材料的抗菌水凝胶。他们的优缺点见表1。
2.1 天然高分子抗菌水凝胶
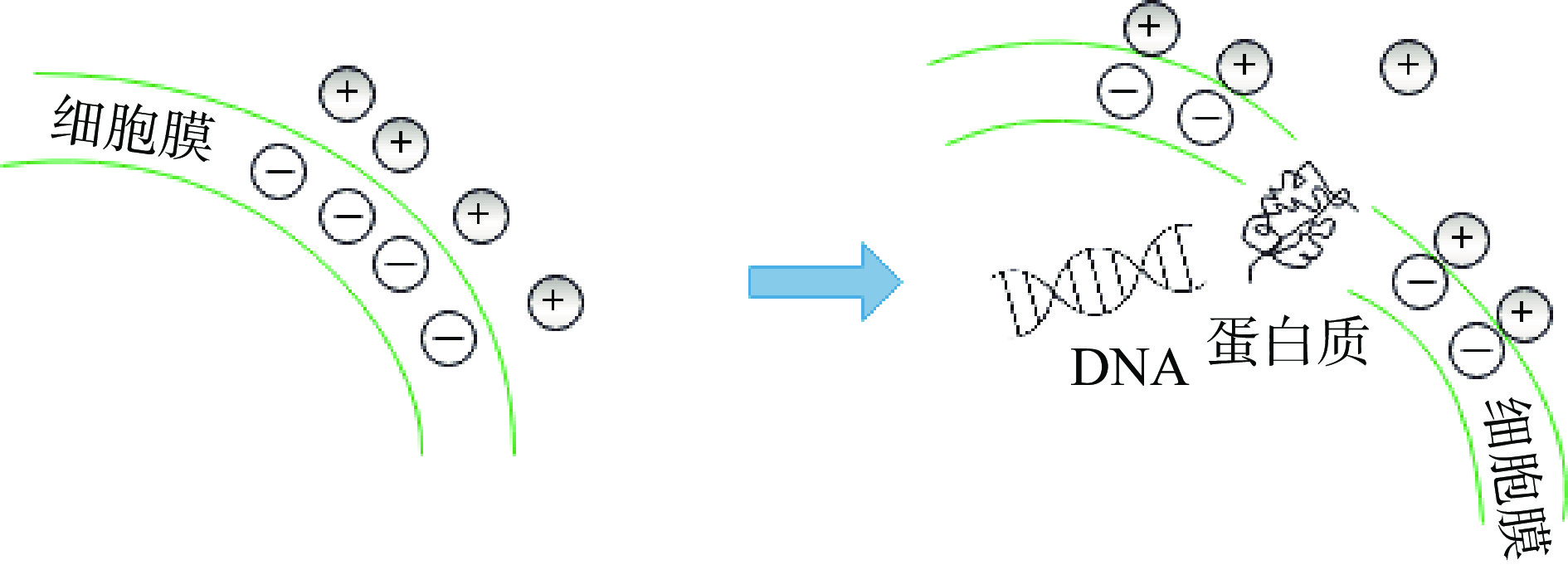
制备天然高分子水凝胶的基材有很多,如壳聚糖、海藻酸钠、纤维素、蛋白质和明胶等,大多都具有一定的抗菌特性。其中天然多糖因其具有抗微生物和粘膜粘附等特性而优于其他天然高分子水凝胶基材[32]。因此,天然高分子多糖基抗菌水凝胶的实际应用相比于其他基材制备的天然高分子水凝胶更加广泛。天然高分子多糖基抗菌水凝胶的抗菌机理为:多糖在液体中解离而产生带正电荷的基团与带负电荷的致病菌膜成分的结合,破坏细胞膜结构,导致细胞质泄漏,从而抑制微生物的生长繁殖。其主要抗菌机理见图2。天然高分子多糖基抗菌水凝胶可分为3类:纤维素基抗菌水凝胶、壳聚糖基抗菌水凝胶和淀粉基抗菌水凝胶。
2.1.1 纤维素基抗菌水凝胶
纤维素是地球上最丰富的可再生资源,其具有丰富的羟基,易于形成氢键连接的网络结构,是用于制备水凝胶的优质材料[34]。可以通过化学改性纤维素或者添加金属纳米颗粒使纤维素具有抗菌性能。
Shaghaleh等[35]基于小麦秸秆的氧化纳米原纤化纤维素(TOCNFs)与食品级阳离子改性聚合物(N-异丙基丙烯酰胺-共-丙烯酰胺)开发了一种用于水果包装的pH/温度响应水凝胶薄膜。该水凝胶薄膜具有抗菌性能和pH/热响应性能,能够智能递送防腐剂(NA)延缓水果腐烂,具有安全、可回收、可行性和抑菌的功效。抑菌结果表明,该抗菌水凝胶薄膜可以抑制约40%的大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的菌落生长,证明了其在水果包装领域中巨大的应用潜力。
2.1.2 壳聚糖基抗菌水凝胶
壳聚糖具有多种生物学特性,是具有良好生物相容性、生物降解性、无毒和抑菌性的碱性天然多糖[36]。壳聚糖的抗菌性能和作为水凝胶基材均是目前研究的热点。壳聚糖对革兰氏阳性与革兰氏阴性细菌的抗菌机理不同,前者的主导杀菌机理为:壳聚糖分子中的正电荷与细胞表面带负电荷的细菌、真菌或者其他聚合物发生静电作用,形成多层结构或静电络合物,一方面阻碍营养物质的输送,另一方面改变细菌细胞膜的渗透性,使胞内物质流出,达到抗菌的目的。后者的主导杀菌机理为:壳聚糖通过渗透进入微生物细胞内,吸附胞内阴离子物质,干扰细胞正常的生理活动,从而起到杀菌的目的[37]。由于壳聚糖本身具有良好的抗菌性,又是制备水凝胶的良好基材,因此,壳聚糖通过简单的物理和化学方法,与合适的试剂共混或交联可以制备出具有抗菌性能的壳聚糖基水凝胶。
基于壳聚糖制备而成的水凝胶是目前研究最多的一种由天然抗菌成分组成的抗菌型水凝胶。Chen等[38]制备了与明胶微球结合的抗菌海藻酸盐/壳聚糖水凝胶,具有抗菌性和可生物降解性。凝胶化的机制归因于氧化海藻酸钠(OAlg)的醛基和羧甲基壳聚糖(CMCS)的氨基基团之间的反应。结果表明,该抗菌水凝胶有效抑制大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌至少2个数量级的细菌数,在抑菌方面具有广阔的前景。Kang等[39]利用壳聚糖(CS)和水溶性2,3-二醛纤维素(DAC),在不添加有毒的化学交联剂的情况下,制备出了一种绿色抗菌水凝胶。该水凝胶对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌具有良好的抑菌作用,并且抑菌直径随着DAC用量的增加而增加。采用该方法所制备的绿色抗菌水凝胶有望在食品储存等多个领域应用。
2.1.3 淀粉基抗菌水凝胶
淀粉是一种具有优异生物相容性的天然大分子多糖。淀粉基水凝胶易受温度、pH和离子强度等多种因素的影响,其缺点是容易被微生物污染、均一性以及力学性能较差,限制了淀粉基水凝胶的应用。然而,通过化学修饰、物理修饰和酶修饰等方法对淀粉改性、添加抗菌物质或金属纳米粒子可以改善这些问题[40]。
Chin等[41]将柠檬酸、淀粉、聚乙烯醇(PVA)和聚乙二醇(PEG)通过冻融技术,在不使用任何刺激性溶剂和化学品的条件下进行物理交联制备抗菌淀粉-柠檬酸水凝胶。抗菌活性的基本原理是淀粉-柠檬酸盐水凝胶中存在羧酸分子,它可以通过破坏细菌膜来抑制细菌的增殖。该淀粉-柠檬酸水凝胶对大肠杆菌、化脓性葡萄球菌、鼠李氏沙门氏菌和金黄色葡萄球菌等多种细菌表现出优异的抗菌活性。结果表明,淀粉-柠檬酸盐水凝胶作为一种经济高效的绿色抗菌载体具有很高的潜力。
2.2 载有无机/有机抗菌物质的水凝胶
2.2.1 载有无机抗菌物质的水凝胶
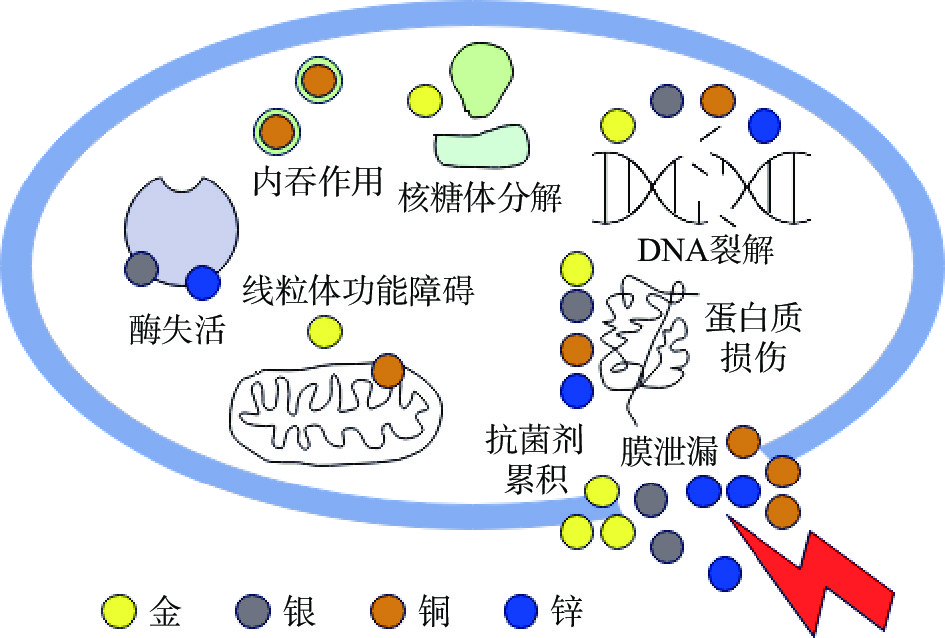
与抗生素相比,无机抗菌材料由于其具有适用于广谱微生物、稳定性高、安全性高等优点而被广泛应用于抗菌领域。载有无机抗菌物质的水凝胶通常是在水凝胶的基体中掺入金属离子或金属氧化物,常用的金属离子有金(Au)、银(Ag)和铜(Cu)等,金属氧化物有氧化锌(ZnO)、二氧化钛(TiO2)和氧化镍(NiO)等,都是具有很好的抗菌活性的材料。不同种类的无机抗菌物质的抗菌机理不同:金属离子或金属氧化物可以与细菌或霉菌的活性酶结合,可以作用于细胞内的DNA、蛋白质、核糖体以及线粒体,破坏其结构,使得细菌细胞死亡[42]。无机抗菌剂可能的抗菌机理如图3所示。
其中,银是一种具有代表性的抗菌材料,可抑制细菌、真菌以及病毒的生长发育[44]。银离子通过静电作用可以与细菌膜蛋白上带负电荷的巯基(-SH)结合,从而引起蛋白质变性,最终导致细菌的细胞凋亡。随着细菌的凋亡,结合在膜蛋白上的银离子会被还原为银原子,使银元素能够发挥持续杀菌的作用[45]。Boccalon等[46]对基于聚乙烯醇、海藻酸钠和硼砂的水凝胶进行了适当的改性,形成了可以负载银离子纳米颗粒的活性分子的网络。经抗菌实验结果表明,该水凝胶对革兰氏阳性菌、革兰氏阴性菌和酵母菌有显著的抗菌活性。
2.2.2 载有有机抗菌物质的水凝胶
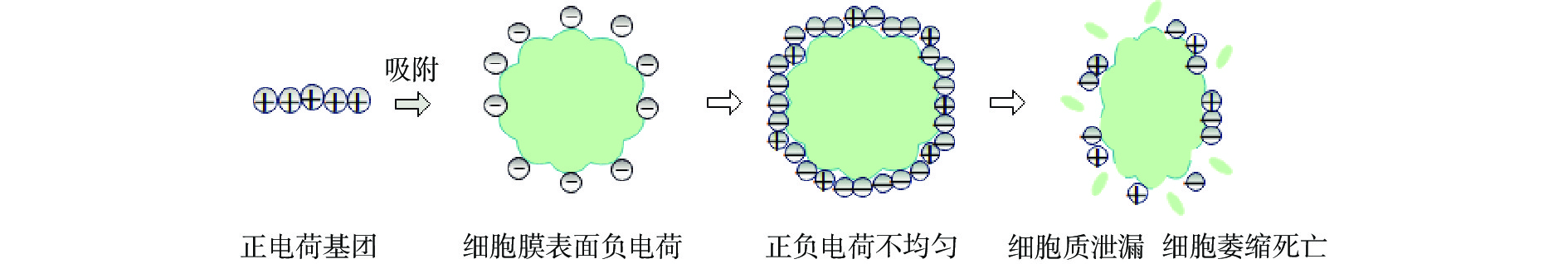
有机抗菌剂大多是从合成药物或自然资源中提取的,化学合成的有机抗菌剂主要包括醛类、醇类和有机酸类等[47]。有机抗菌物质的抗菌机理主要是通过吸附微生物细胞膜表面的阴离子,与之结合后破坏细胞膜或蛋白质的合成系统,抑制微生物的繁殖。其抗菌机理见图4。
其中,广泛存在于真菌、细菌和动物等生物中的季铵盐不仅来源丰富而且功能多样,已经在食品、工业、农业和医学等领域中广泛应用。Zhang等[48]通过壳聚糖季铵盐与环氧氯丙烷反应,成功获得了一系列新型交联壳聚糖季铵盐负载硫酸庆大霉素的水凝胶,这种季铵盐类型的水凝胶显示出优异的杀菌性能,测定了该水凝胶对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的理化性质、硫酸庆大霉素释放行为、细胞毒性和抗菌活性,结果表明该水凝胶具有良好的水稳定性、热稳定性、药物释放能力以及抗菌性能,对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的抑菌圈可达30 mm左右。
2.3 载有光激活或光响应材料的抗菌水凝胶
尽管化学合成的抗菌水凝胶具有很好的抑菌性,但是在实际应用中依然存在各自固有的局限性。比如天然抗菌成分组成的水凝胶基本上都是属于接触型杀菌水凝胶,只能达到表面杀菌的作用,杀菌效果并不理想;负载无机抗菌剂的水凝胶具有生物相容性差和细胞毒性等缺点;负载有机抗菌剂的水凝胶具有抑菌时间短和耐药性等缺点。
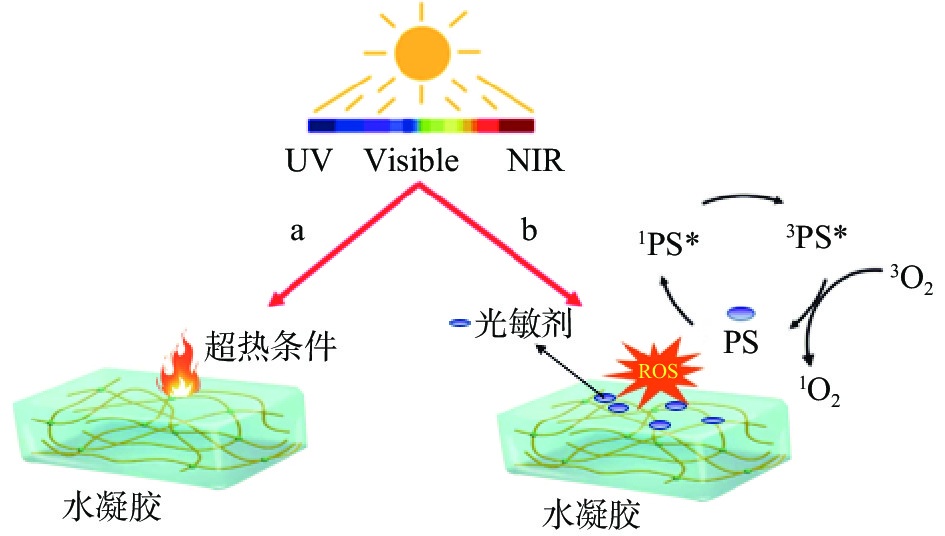
因此,近年来广大科研工作者致力于寻找更加快速有效的抗菌方法,其中微波光谱疗法、声动力学疗法和光介导疗法的应用最为广泛[49]。载有光激活或热响应材料的抗菌水凝胶,又叫光介导的抗菌水凝胶,该类水凝胶需要借助外源性抗菌技术---光介导发挥抗菌的功能。光介导疗法可分为基于热疗的光热疗法(PTT)和基于活性氧(ROS)的光动力疗法(PDT),这是两种常用的抗菌疗法,因其优异的杀菌能力和光可控性而受到广泛关注。光敏剂和光热剂作为光转化的核心,分别对PDT和PTT的效果有很大影响[50]。光介导的抗菌水凝胶是指将光敏抗菌水凝胶或光热抗菌水凝胶与外源性抗菌技术结合起来的水凝胶。即在适当的光谱波长的照射下,水凝胶内部的光热材料或光敏材料能够吸收光能而被激发,从而实现杀菌的目的。PTT和PDT之间的一个显著区别是前者通常使用近红外(NIR)照射进行刺激,而后者通常需要使用可见光照射[51]。基于PTT和PDT抗菌水凝胶的机理如图5所示。
2.3.1 基于PTT的抗菌水凝胶
基于PTT的抗菌水凝胶,是将光热剂(PTA)与水凝胶结合,在光的刺激下,PTA可以将光能转变为热能,导致局部温度升高从而破坏细菌细胞膜的通透性,最终导致细菌死亡。基于PTT的两个重要先决条件是光热剂(PTA)和近红外辐射(NIR)[55]。这种抗菌水凝胶适用于广谱微生物抗菌且不易产生耐药性。
Tao等[56]报道了一种由甲基丙烯酸甲酯修饰的明胶(Gel-MA)和N,N-双(丙烯酰基)胱胺(BACA)螯合的铜纳米粒子(Cu NPs)通过自由基聚合与光引发剂组成的复合水凝胶。由于局部表面存在等离子体共振(LSPR)效应,Cu NPs能够有效地将近红外激光照射(808 nm)能量转化为局部热量,从而实现光热治疗。体外抗菌实验表明,该混合水凝胶对革兰氏阳性菌(金黄色葡萄球菌)和革兰氏阴性菌(大肠杆菌)均表现出良好的抗菌效果。
2.3.2 基于PDT的抗菌水凝胶
基于PDT的光敏抗菌水凝胶,是将光敏剂(PS)与水凝胶交联或接枝结合在一起,在适当的波长的照射下PS吸收光子并转变为单重激发态,然后通过系统间的交叉成功地转变为三重激发态,并与基态氧反应产生活性氧(ROS),以达到快速杀死细菌并不产生耐药性的目的[57]。它需要三个同时存在的因素:光敏剂(PS)、光源和氧分子[58]。大量的研究表明,PS对革兰氏阳性菌和革兰氏阴性菌均有良好的杀菌效果[59-60]。
董建成等[61]利用蒙脱土(MMT)分别吸附3种阳离子光敏剂(PS),通过紫外光交联法制备出相应的光敏MMT/PS水凝胶。研究了3种光敏抗菌水凝胶对金黄色葡萄球菌的抗菌作用。抗菌结果表明,复合了3种阳离子光敏剂Zn-TMPyP、TMPyP和MB的水凝胶,在可见光照射条件下(λ≥420 nm)细菌的存活率分别为1.51%、47.26%和74.58%,三者对金黄色葡萄球菌均具有一定的杀灭效果,其中负载Zn-TMPyP的水凝胶在光照条件下对金黄色葡萄球菌的杀菌率达到98.49%。
3. 抗菌水凝胶在食品领域的应用
3.1 智能食品包装系统
随着消费者食品安全意识的提升,抗菌型水凝胶在智能食品包装行业中的潜力(见图6)引起人们的广泛关注。水凝胶被认为是一种有效的食品包装材料,具有理想的防潮性能、抗菌和抗氧化活性以及生物可降解性,广泛用于保鲜蔬菜水果、肉类和牛奶。
3.1.1 食品包装
根据功能的不同,食品包装可分为三类:传统食品包装、活性食品包装和智能食品包装。在包装应用中,水凝胶可以提供抗菌活性并控制食品水分含量,从而形成活性包装,提高食品的质量和安全性,并延长食品的储存期[62]。且水凝胶作为包装材料具有可以降低食品的水分活度、抑制有害细菌和腐败菌、保持良好的机械能力、低成本和易于制备以及良好的生物降解性以减少环境污染等特点。
国内外许多研究者均发现水凝胶可以在肉类以及蔬菜水果中发挥保鲜抑菌的作用。El-mekawy等[63]以虾壳制备的壳聚糖为原料制成响应刺激性壳聚糖水凝胶作为肉类和鸡肉的智能包装材料。Bandyopadhyay等[64]开发了一种基于细菌纤维素和瓜尔胶(BC-GG)的聚乙烯吡咯烷酮-羧甲基纤维素(PVP-CMC)水凝胶薄膜,用于包装保鲜浆果(例如蓝莓)。结果表明,水凝胶薄膜具有一定的抗菌性,可以在15 d内保鲜蓝莓。李瑶瑶等[65]研究了壳聚糖水凝胶对青霉菌(Penicillium italicum)的抑制及其对脐橙的保鲜效果。结果表明不同浓度壳聚糖水凝胶对脐橙采后P.italicum均有一定的抑制作用,其中以2.0%的壳聚糖水凝胶效果最优。由此可知,水凝胶可以被用作多功能食品的包装材料,以延长食品的保质期。
3.1.2 食品质量指示
食品质量的检测在食品运输、储存和售卖过程中至关重要。食品质量特征包括食品的外观、质地、颜色、风味和营养成分等。传统的监测食品质量的分析方法,如色谱法和质谱法等,具有检测成本昂贵、复杂且不便于携带等缺点。因此,生物传感器作为一种快速的食品质量检测方法,具有灵敏度高、成本低和便携等优点,已广泛用于检测食品中的营养成分或有害物质[66]。它可以通过检测食品中某些物质的存在及其含量来监控食品的新鲜或变质程度,从而控制食品的安全和质量。然而,食品中的水分会影响生物传感器的灵敏性。因此,基于天然高分子材料的水凝胶在食品质量检测等食品领域的应用潜力逐渐显示出来,具有高亲水性、保水性和生物相容性的水凝胶,可以很好地降低食品水分的干扰,成为开发生物传感器和指示器的理想材料[67]。
食品腐败是一个复杂的过程,不同食品的腐败后的产物也不同。因此,通过检测温度、湿度、pH和氧气含量等来评估食品的腐败程度是一种可行的方法[68]。温度是影响大多数食品质量的关键因素之一,温度过高或波动很大不利于食品储存,易造成食品变质。湿度对食品的影响也很大,水分活度高的食品,如肉类、水果、蔬菜等生鲜产品,若包装内的湿度过低,就会失去水分而变干;若包装内的湿度过高,食品会吸收水分并变质[69]。最重要的是,许多食品的质量变化伴随着其pH和氧气含量的变化。因此,对食品包装内的温度、湿度、pH和氧气含量等指标进行实时监测可以有效反映食品的腐败情况。
其中,在水凝胶基质中添加pH响应染料,用于检测食品新鲜度的研究最为广泛。Lu等[67]以甘蔗渣纤维素纤维为原料制备出纳米纤维素,然后与锌(Zn)交联形成了更加牢固的水凝胶基质。该水凝胶作为pH响应染料(溴百里酚蓝/甲基红)的载体,可作为比色新鲜度指示剂,根据鸡肉样品的新鲜度而改变颜色。Tirtashi等[70]在纤维素-壳聚糖基质水凝胶中加入胡萝卜花青素作为化学反应染料比色pH指示剂,用于监测巴氏杀菌牛奶的腐败程度。由此可见,水凝胶在食品质量检测方面的应用具有很大的潜力。
3.2 食品保鲜
伴随着人们对食品质量要求的提升,食品保鲜方面的标准也开始越来越高。除了食品包装材料可以进行保鲜以外,人们往往会使用冰块对食品进行保鲜,抑制微生物的生长。尽管,冰块能够有效地降低周围环境的温度,达到食品保鲜的功效,但冰块的使用还是存在很大的弊端:冰块的不可重复利用性对水资源造成了很大的浪费,且冰的融水性易导致食品交叉污染。
虽然利用抗菌冰块和酸性电解水冰来代替传统冰块是一个有效的方法[71],但是其厚塑料外壳会降低冷却效率并带来环境负担。因此,开发一种新型坚固、可重复使用、抗微生物以及无塑料污染的食品冷却介质至关重要。此时,基于水凝胶而制备成的冰块展现出它巨大的应用潜力。
相对于传统保鲜冰块,基于天然高分子材料的水凝胶冰块的保水性好,不易融水而造成交叉污染,且不需要类似于冰袋的塑料包装,可以与食品直接接触,实现零塑料无污染[72]。此外,该类水凝胶冰块成分天然、安全且用料便宜,易于获得和回收,具有可持续性和可生物降解性,是传统冰块最有前途的替代品。Zou等[73]首次以高亲水性的明胶作为水凝胶的基质材料,制备了一种基于明胶-甲萘醌亚硫酸氢钠水凝胶的新型固定冷却介质“果冻冰块”(JIC),其冷却效率与传统冰块的冷却效率接近,并且可以实现抗微生物、可重复使用和可堆肥等目的。在十个应用周期中观察到异常稳定的冷却效率和强大的机械强度,对细菌、真菌和酵母菌均具有稳定的抗菌功能。在JIC的生命周期结束时,可以堆肥或用作土壤处理剂以促进植物生长。新型JIC有望成为传统冰块和冰袋的更安全、更环保以及更有前途的替代品。这也是抗菌水凝胶应用于食品领域上的一次新的创新,给未来抗菌水凝胶的应用发展提供了新的思路。
4. 结语与展望
微生物污染严重威胁了人类健康,作为新型抗菌材料,水凝胶因其独特的优势,在抑菌领域的应用研究受到密切关注。本综述简要介绍了水凝胶的概念以及形成机理,重点概述了抗菌水凝胶的分类、机理以及在智能食品包装以及食品保鲜领域的应用研究。抗菌水凝胶是理想的抗菌生物材料,由于其优异的刺激响应性和吸水性等特征,在食品包装材料、食品质量指示剂和食品保鲜等各个领域都有广泛的应用。然而,值得注意的是,抗菌水凝胶的抑菌范围尚未充分了解,难以利用单一的材料来达到预期广谱抗菌的目标,并且抗菌水凝胶在食品领域的应用了解不够深入、发展的较为局限且具有挑战性。因此,未来应该聚焦于开发具有多功能性的广谱抗菌水凝胶,设计制备多种高强度且抗菌性能优异的复合型水凝胶应用于更广泛的食品领域将是研究方向。
-
-
[1] 刘艺楠. 传统抗菌剂与新型抗菌剂对细菌生长及细菌耐药的影响[D]. 石家庄: 河北科技大学, 2019 LIU Y N. Effects of traditional antibacterial agents and new antibacterial agents on bacterial growth and bacterial resistance[D]. Shijiazhaung: Hebei University of Science & Technology, 2019.
[2] MOCAN T, MATEA C T, POP T, et al. Carbon nanotubes as anti-bacterial agents[J]. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences,2017,74(19):3467−3479. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2532-y
[3] AMIN R M, MAHMOUD R K, GADELHAK Y, et al. Gamma irradiated green synthesized zero valent iron nanoparticles as promising antibacterial agents and heavy metal nano-adsorbents[J]. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management,2021,16:100461.
[4] ZHANG Z, HAN X. Polymer antibacterial agent immobilized polyethylene films as efficient antibacterial cling films[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:C,2019,105:110088. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2019.110088
[5] DEBBABI S, GROLEAU M, LÉTOURNEAU M, et al. Antibacterial properties of the pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide: A new human antimicrobial peptide[J]. PLOS ONE,2018,13(11):e207366.
[6] XIE Y, WANG X, SUN M, et al. Heterochiral peptide-based biocompatible and injectable supramolecular hydrogel with antibacterial activity[J]. Journal of Materials Science,2022,57(8):5198−5209. doi: 10.1007/s10853-022-06982-7
[7] RIZWAN M, RUBINA GILANI S, IQBAL DURANI A, et al. Materials diversity of hydrogel: Synthesis, polymerization process and soil conditioning properties in agricultural field[J]. Journal of Advanced Research,2021,33:15−40. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2021.03.007
[8] DING H, LIANG X, ZHANG X N, et al. Tough supramolecular hydrogels with excellent self-recovery behavior mediated by metal-coordination interaction[J]. Polymer,2019,171:201−210. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2019.03.061
[9] STENSTRÖM P, FAN Y, ZHANG Y, et al. UV-cured antibacterial hydrogels based on PEG and monodisperse heterofunctional Bis-MPA dendrimers[J]. Molecules,2021,26(8):2364. doi: 10.3390/molecules26082364
[10] LI X, LIU W, LI Y, et al. Mechanically robust enzymatically degradable shape memory polyurethane urea with a rapid recovery response induced by NIR[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B,2020,8(23):5117−5130. doi: 10.1039/D0TB00798F
[11] LI M, ZHANG Z, LIANG Y, et al. Multifunctional tissue-adhesive cryogel wound dressing for rapid nonpressing surface hemorrhage and wound repair[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2020,12(32):35856−35872.
[12] JAYAKUMAR A, JOSE V K, LEE J M. Hydrogels for medical and environmental applications[J]. Small Methods,2020,4(3):1900735. doi: 10.1002/smtd.201900735
[13] HAN D, LI Y, LIU X, et al. Rapid bacteria trapping and killing of metal-organic frameworks strengthened photo-responsive hydrogel for rapid tissue repair of bacterial infected wounds[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,396:125194. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.125194
[14] SHARMA S, TIWARI S. A review on biomacromolecular hydrogel classification and its applications[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,162:737−747. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.110
[15] LIU X, HE X, YANG B, et al. Dual physically cross-linked Hydrogels incorporating hydrophobic interactions with promising repairability and ultrahigh elongation[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2021,31(3):2008187. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202008187
[16] SHAO C, MENG L, WANG M, et al. Mimicking dynamic adhesiveness and strain-stiffening behavior of biological tissues in tough and self-healable cellulose nanocomposite hydrogels[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2019,11(6):5885−5895.
[17] YU H C, LI C Y, DU M, et al. Improved toughness and stability of κ-carrageenan/polyacrylamide double-network hydrogels by dual cross-linking of the first network[J]. Macromolecules,2019,52(2):629−638. doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.8b02269
[18] LI D, FEI X, WANG K, et al. A novel self-healing triple physical cross-linked hydrogel for antibacterial dressing[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B,2021,9(34):6844−6855. doi: 10.1039/D1TB01257F
[19] WANG W, ZHANG Y, LIU W. Bioinspired fabrication of high strength hydrogels from non-covalent interactions[J]. Progress in Polymer Science,2017,71:1−25. doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2017.04.001
[20] ZHANG R, FU Q, ZHOU K, et al. Ultra stretchable, tough and self-healable poly (acrylic acid) hydrogels cross-linked by self-enhanced high-density hydrogen bonds[J]. Polymer,2020,199:122603. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2020.122603
[21] ZHOU H, ZHANG M, CAO J, et al. Highly flexible, tough, and self-healable hydrogels enabled by dual cross-linking of triblock copolymer micelles and ionic interactions[J]. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering,2017,302(2):1600352. doi: 10.1002/mame.201600352
[22] LI S, WANG X, CHEN J, et al. Calcium ion cross-linked sodium alginate hydrogels containing deferoxamine and copper nanoparticles for diabetic wound healing[J]. Int J Biol Macromol,2022,202:657−670. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.01.080
[23] BERMEJO-VELASCO D, AZEMAR A, OOMMEN O P, et al. Modulating thiol pKa promotes disulfide formation at physiological pH: An elegant strategy to design disulfide cross-linked hyaluronic acid hydrogels[J]. Biomacromolecules,2019,20(3):1412−1420. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.8b01830
[24] SONG Y, XU L, XU L, et al. Radiation cross-linked gelatin/sodium alginate/carboxymethylcellulose sodium hydrogel for the application as debridement glue paste[J]. Polym Bull (Berl),2022,79(2):725−742. doi: 10.1007/s00289-020-03525-5
[25] FU S, ZHOU L, ZENG P, et al. Antibacterial chitosan-gelatin hydrogel beads cross-linked by riboflavin under ultraviolet a irradiation[J]. Fibers and Polymers,2021,23(2):315−320.
[26] CHANG K, CHEN W, CHEN C, et al. Chemical cross-linking on gelatin-hyaluronan loaded with hinokitiol for the preparation of guided tissue regeneration hydrogel membranes with antibacterial and biocompatible properties[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: C,2021,119:111576. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.111576
[27] LEE S C, KWON I K, PARK K. Hydrogels for delivery of bioactive agents: A historical perspective[J]. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews,2013,65(1):17−20. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2012.07.015
[28] 许雨芩, 杨建军, 吴庆云, 等. 抗菌型高分子水凝胶研究进展[J]. 化工新型材料,2022,50(9):218−224, 228. [XU Y Q, YANG J J, WU Q Y, et al. Research progress of antibacterial polymer hydrogels[J]. New Chemical Materials,2022,50(9):218−224, 228. [29] ZHANG R, YU B, TIAN Y, et al. Diversified antibacterial modification and latest applications of polysaccharide-based hydrogels for wound healthcare[J]. Applied Materials Today,2022,26:101396. doi: 10.1016/j.apmt.2022.101396
[30] 周春才, 袁跃, 苏小凯. 抗菌水凝胶研究进展[J]. 化学世界,2016,57(1):51−55. [ZOU C C, YUAN Y, SU X K. Progress in synthesis of antibacterial hydrogel[J]. Chemical World,2016,57(1):51−55. [31] LIU L, SHI J, SUN X, et al. Thermo-responsive hydrogel-supported antibacterial material with persistent photocatalytic activity for continuous sterilization and wound healing[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2022,229:109459. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.109459
[32] 章紫英, 邓利珍, 戴涛涛, 等. 多糖基水凝胶载体及其干燥方式研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(23):438−446. [ZHANG Z Y, DENG L Z, DAI T T, et al. Research progress of polysaccharide-based hydrogel carriers and their drying method[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(23):438−446. [33] 何天盈, 殷娴, 孙博, 等. 抑菌型表面活性剂抑菌机理及应用[J]. 日用化学工业,2018,48(7):408−414. [HE T Y, YIN X, SUN B, et al. Antimicrobial mechanisms and applications of antimicrobial surfactants[J]. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics,2018,48(7):408−414. [34] CHANG C, ZHANG L. Cellulose-based hydrogels: Present status and application prospects[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2011,84(1):40−53. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.12.023
[35] SHAGHALEH H, HAMOUD Y A, XU X, et al. Thermo-/pH-responsive preservative delivery based on TEMPO cellulose nanofiber/cationic copolymer hydrogel film in fruit packaging[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,183:1911−1924. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.05.208
[36] SHARIATINIA Z, JALALI A M. Chitosan-based hydrogels: Preparation, properties and applications[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,115:194−220. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.04.034
[37] 夏金兰, 王春, 刘新星. 抗菌剂及其抗菌机理[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版),2004(1):31−38. [XIA J L, WANG C, LIU X X. Research on antimicrobial agents and their mechanisms of actions[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology),2004(1):31−38. [38] CHEN H, XING X, TAN H, et al. Covalently antibacterial alginate-chitosan hydrogel dressing integrated gelatin microspheres containing tetracycline hydrochloride for wound healing[J]. Materials Science & Engineering C,2017,70(Pt1):287−295.
[39] KANG X, DENG L, YI L, et al. A facile method for preparation of green and antibacterial hydrogel based on chitosan and water-soluble 2, 3-dialdehyde cellulose[J]. Cellulose,2021,28(10):6403−6416. doi: 10.1007/s10570-021-03879-7
[40] 刘玉华, 魏宏亮, 李松茂, 等. 淀粉基水凝胶的研究进展[J]. 化工进展,2021,40(12):6738−6751. [LIU Y H, WEI H L, LI S M, et al. Research progress of starch-based hydrogels[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2021,40(12):6738−6751. [41] CHIN S F, ROMAINOR A N B, PANG S C, et al. Antimicrobial starch-citrate hydrogel for potential applications as drug delivery carriers[J]. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology,2019,54:101239. doi: 10.1016/j.jddst.2019.101239
[42] 肖九梅. 解读食品抗菌剂包装材料的性能特点及其应用机理[J]. 塑料包装,2017,27(6):22−28. [XIAO J M. Reading performance characteristics and the application mechanism of food antimicrobial packaging materials[J]. Plastics Packaging,2017,27(6):22−28. [43] SAIDIN S, JUMAT M A, MOHD AMIN N A A, et al. Organic and inorganic antibacterial approaches in combating bacterial infection for biomedical application[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: C,2021,118:111382. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.111382
[44] HAMAD A, KHASHAN K S, HADI A. Silver nanoparticles and silver ions as potential antibacterial agents[J]. Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials,2020,30(12):4811−4828. doi: 10.1007/s10904-020-01744-x
[45] DAI T, WANG C, WANG Y, et al. A nanocomposite hydrogel with potent and broad-spectrum antibacterial activity[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2018,10(17):15163−15173.
[46] BOCCALON E, PICA M, ROMANI A, et al. Facile preparation of organic-inorganic hydrogels containing silver or essential oil with antimicrobial effects[J]. Applied clay Science,2020,190:105567. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2020.105567
[47] 马超, 吴瑛. 抗菌剂抗菌机理简述[J]. 中国酿造,2016,35(1):5−9. [MA C, WU Y. Research on antimicrobial agents and their mechanism of actions[J]. China Brewing,2016,35(1):5−9. [48] ZHANG J, TAN W, LI Q, et al. Preparation of cross-linked chitosan quaternary ammonium salt hydrogel films loading drug of gentamicin sulfate for antibacterial wound dressing[J]. Marine Drugs,2021,19(9):479. doi: 10.3390/md19090479
[49] ALVES F, GOMES GUIMARÃES G, MAYUMI INADA N, et al. Strategies to improve the antimicrobial efficacy of photodynamic, sonodynamic, and sonophotodynamic therapies[J]. Lasers in Surgery and Medicine,2021,53(8):1113−1121. doi: 10.1002/lsm.23383
[50] CUI Q, YUAN H, BAO X, et al. Synergistic photodynamic and photothermal antibacterial therapy based on a conjugated polymer nanoparticle-doped hydrogel[J]. ACS Applied Bio Materials,2020,3(7):4436−4443. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.0c00423
[51] FEDATTO ABELHA T, RODRIGUES LIMA CAIRES A. Light-activated conjugated polymers for antibacterial photodynamic and photothermal therapy[J]. Advanced NanoBiomed Research,2021,1(7):2100012. doi: 10.1002/anbr.202100012
[52] 刘东亮, 饶璐, 赵媛, 等. 光敏抗菌复合水凝胶的辐射制备及应用现状[J]. 辐射研究与辐射工艺学报,2021,39(6):4−12. [LIU D L, RAO L, ZHAO Y, et al. Radiation preparation and application status of photosensitive antibacterial composite hydrogel[J]. Journal of Radiation Research and Radiation Processing,2021,39(6):4−12. [53] 陈鹏, 杨凤英, 顾志鹏, 等. 抗氧化水凝胶的研究进展[J]. 功能高分子学报,2021,34(2):182−194. [CHEN P, YANG F Y, GU Z P, et al. Recent progress in antioxidant hydrogels[J]. Journal of Functional Polymers,2021,34(2):182−194. [54] ZHU S, SONG Y, PEI J, et al. The application of photodynamic inactivation to microorganisms in food[J]. Food Chemistry: X,2021,12:100150. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2021.100150
[55] KUMAR A V P, DUBEY S K, TIWARI S, et al. Recent advances in nanoparticles mediated photothermal therapy induced tumor regression[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics,2021,606:120848. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.120848
[56] TAO B, LIN C, DENG Y, et al. Copper-nanoparticle-embedded hydrogel for killing bacteria and promoting wound healing with photothermal therapy[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B,2019,7(15):2534−2548. doi: 10.1039/C8TB03272F
[57] CHEN L, CHEN M, ZHOU Y, et al. NIR photosensitizer for two-photon fluorescent imaging and photodynamic therapy of tumor[J]. Frontiers in Chemistry,2021:9.
[58] DENG K, LI C, HUANG S, et al. Recent progress in near infrared light triggered photodynamic therapy[J]. Small, 2017, 13(44): 1702299.
[59] UCUNCU M, MILLS B, DUNCAN S, et al. Polymyxin-based photosensitizer for the potent and selective killing of Gram-negative bacteria[J]. Chemical Communications,2020,56(26):3757−3760. doi: 10.1039/D0CC00155D
[60] YANG Z, QIAO Y, LI J, et al. Novel type of water-soluble photosensitizer from Trichoderma reesei for photodynamic inactivation of Gram-positive bacteria[J]. Langmuir,2020,36(44):13227−13235. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c02109
[61] 董建成, 葛孝栋, 王清清, 等. 阳离子光敏抗菌型水凝胶的制备及性能表征[J]. 材料工程,2019,47(2):56−61. [DONG J C, GE X D, WANG Q Q, et al. Preparation and property characterization of cationic photo antimicrobial hydrogel[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering,2019,47(2):56−61. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2017.000588 [62] BATISTA R A, ESPITIA P J P, QUINTANS J D S S, et al. Hydrogel as an alternative structure for food packaging systems[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2019,205:106−116. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.10.006
[63] EL-MEKAWY R E, ELHADY H A, AL-SHAREEF H F. Highly stretchable, smooth, and biodegradable hydrogel films based on chitosan as safety food packaging[J]. Polymers & Polymer Composites,2021,29(6):563−573.
[64] BANDYOPADHYAY S, SAHA N, BRODNJAK U V, et al. Bacterial cellulose and guar gum based modified PVP-CMC hydrogel films: Characterized for packaging fresh berries[J]. Food Packaging and Shelf Life,2019,22:100402. doi: 10.1016/j.fpsl.2019.100402
[65] 李瑶瑶, 李喜宏, 邓玉璞, 等. 脐橙新型壳聚糖水凝胶抑菌保鲜研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2013,34(23):328−332. [LI Y Y, LI X H, DENG Y P, et al. Study on the inhibition and preservation of new chitosan hydrogel in Navel orange[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2013,34(23):328−332. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2013.23.063 [66] YE Y, GUO H, SUN X. Recent progress on cell-based biosensors for analysis of food safety and quality control[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2019,126:389−404. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2018.10.039
[67] LU P, YANG Y, LIU R, et al. Preparation of sugarcane bagasse nanocellulose hydrogel as a colourimetric freshness indicator for intelligent food packaging[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2020,249:116831. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116831
[68] CHENG H, XU H, JULIAN MCCLEMENTS D, et al. Recent advances in intelligent food packaging materials: Principles, preparation and applications[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,375:131738. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131738
[69] GAIKWAD K K, SINGH S, AJJI A. Moisture absorbers for food packaging applications[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters,2019,17(2):609−628. doi: 10.1007/s10311-018-0810-z
[70] EBRAHIMI TIRTASHI F, MORADI M, TAJIK H, et al. Cellulose/chitosan pH-responsive indicator incorporated with carrot anthocyanins for intelligent food packaging[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,136:920−926. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.06.148
[71] ZHAO L, ZHANG Z, WANG M, et al. New insights into the changes of the proteome and microbiome of shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) stored in acidic electrolyzed water ice[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2018,66(19):4966−4976. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b00498
[72] ZOU J, WANG L, SUN G. Sustainable and reusable gelatin-based hydrogel "Jelly Ice Cubes" as food coolant. I: Feasibilities and challenges[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2021,9(46):15357−15364.
[73] ZOU J, SBODIO A O, BLANCO ULATE B, et al. Novel robust, reusable, microbial-resistant, and compostable protein-based cooling media[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2022:2201347.
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 孙静,刘梅,杨晓珺,贾添慧. 淀粉制品中铝残留量的测定. 现代食品. 2024(03): 189-193 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 韩子德,张华,燕立媛,王红对. 食品添加剂检测技术存在的问题与改进措施. 食品安全导刊. 2024(28): 161-163 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 陈亚军,雷雨. 定西特色食品马铃薯淀粉制品抽检问题分析及发展建议. 中外食品工业. 2024(19): 96-98 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 刘慧,孙秀兰. 微波消解-电感耦合等离子体质谱(ICP-MS)法测定韭菜中11种元素. 中国无机分析化学. 2023(12): 1459-1465 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 常薇,汪瑾,刘李婷,杨婧妍. 陕西省魔芋制品铝残留问题现状及分析. 粮食加工. 2023(06): 115-116 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



