Research Progress of Modification Methods for Improving Emulsifying Properties of Polysaccharides
-
摘要: 天然多糖因其结构稳定、分子量高、具有多种生物活性、安全性高等优点而表现出良好的乳化和增稠作用,被作为乳化剂广泛应用于食品工业。然而,多糖的高亲水性、难溶解性等特点导致其在高温、高盐等条件下乳化性能较差,限制了其广泛应用。通过对多糖进行修饰可以改变其分子量、结构、疏水性等功能特性,提升其乳化性能。本文综述了物理、化学和生物等修饰方法对多糖分子结构、乳化性能等的影响及修饰多糖在乳状液中应用的研究现状和进展,分析了目前修饰方法中存在的问题,并对未来发展趋势进行了展望,旨在为改善多糖乳化性能的进一步研究和拓宽其应用领域提供理论依据。Abstract: Natural polysaccharides have numerous biological activities, a stable structure, a large molecular weight, and a high level of safety, making them a popular choice for use as emulsifiers in the food business. However, polysaccharides' strong hydrophilicity and insolubility caused them to perform poorly during emulsification in high-temperature and high-salt environments, restricting their widespread use. To improve their ability to form emulsions, polysaccharides can have their molecular weight, structure, hydrophobicity, and other functional qualities altered. This paper reviews the effects of physical, chemical, and biological modification methods on the molecular structure and emulsification properties of polysaccharides, as well as the status and progress of research on the use of modified polysaccharides in emulsions, and also analyzes the issues with the current modification methods and forecasts the future development trend, with the goal of providing a theoretical foundation for further research on improving the emulsification property and broadening their application fields.
-
Keywords:
- polysaccharides /
- modification method /
- emulsion /
- stability /
- application
-
乳化剂是一种表面活性剂,可吸附至油水界面上,通过降低界面张力形成保护涂层,是形成和稳定食品乳剂的关键成分[1]。食品工业中常用的乳化剂主要包括蛋白质、多糖、磷脂等[2]。与其他乳化剂相比,多糖基乳化剂的优点十分显著。首先,多糖是一类来源广泛的天然聚合物,在自然界中资源丰富,具有可再生性[3];其次,多糖的稳定结构使乳剂在一定的离子强度、pH和温度范围内可保持稳定[4];第三,多糖具有高分子质量和高粘度,可通过增加乳液的粘度来提高乳液稳定性[5];第四,多糖具有多种生物活性,如抗氧化和抑菌活性,有助于乳液在长期贮存中维持其稳定性[6]。然而,只有分子链上附着蛋白或疏水基团的多糖可以作为乳化剂,但自然界中大多数多糖都是高亲水分子,缺乏表面活性,只能作为乳剂的稳定剂,这限制了多糖在相关领域的发展。多糖的乳化性能与自身的分子量、疏水基团和分支程度密切相关[7],物理、化学和生物等修饰方法可以改变多糖的分子量和结构,从而影响多糖的相关性能,因此人们致力于探究多种多糖修饰方法来优化其性能。
目前,大量研究证实通过修饰多糖可以提高其乳化性能[8-10]。然而,关于不同修饰方法及其对改性多糖相关性能影响的综述较少。本文旨在归纳总结多糖的修饰方法及其对多糖乳化性能的影响,同时,总结多糖及其衍生物在乳状液中的应用情况,旨在为改善多糖乳化性能的进一步研究和拓宽其应用领域提供理论依据。
1. 多糖的修饰方法
1.1 多糖的物理修饰方法
多糖的分子质量是决定其功能特性的重要因素[11]。目前,超声法和辐射法是多糖修饰最常用的两种物理方法,这两种方法主要是通过破坏多糖分子间的作用力来降解多糖,从而影响其理化性质和功能特性。
1.1.1 超声法
超声波处理多糖溶液可以改善多糖的理化性质和功能特性。由于超声波的空化效应,多糖颗粒附近的气体分子和气泡会发生振动,与介质之间存在一个高压梯度,产生高强度的剪切力,从而破坏多糖颗粒的结构,使多糖发生降解,其分子量和聚合度均会下降。Wu等[12]利用超声波成功制备出三种不同分子质量(1.90×105、8.27×104和4.65×104 Da)的秋葵果胶多糖降解产物,其表观粘度、旋转半径和分支度明显降低,但酯化程度明显提高。Xiao等[13]用超声波处理金针菇多糖,发现其溶液构象发生改变,部分三重螺旋结构的稳定性遭到破坏,黏度和凝胶强度均显著降低,但其热稳定得到了改善,并表现出较好的益生元活性。此外,超声处理对多糖的范德华力和氢键等分子间作用力影响较大,而对多糖的化学键、官能团、结晶结构和分子构象基本不起作用。如超声处理后的天然黄茶多糖有部分降解,但单糖组成没有改变[14]。超声法处理芋头果皮水溶性非淀粉多糖样品与未处理多糖样品一样均含有阿拉伯糖、半乳糖、葡萄糖和甘露糖,并且在它们的红外光谱中均有类似的无定形的官能团[15]。利用超声法降解含蛋白质或阿魏酸等疏水基团的高分子质量多糖,可以很大程度保留对乳化性能有贡献的基团,同时低分子量能显著降低界面张力。两亲性多糖在吸附在油滴表面后会产生较厚的界面层,超声功率的空化可将多糖降解为更小的尺寸,它可以更快地吸附到油滴表面形成一层界面膜,这可能有助于降低界面张力[16]。在特定的超声功率下,多糖混合物中能形成小而稳定的油滴,界面致密的膜可以阻止油滴的聚集[17]。不同的超声强度和处理时间对多糖的降解有影响,这可能与多糖组分的分子质量分布有关,在高功率长时间处理下,多糖组分的分子量分布均匀,油水乳状液的表观粘度过低,容易失稳;经短时间低功率处理后的油水乳状液具有较高的表观粘度,并抗聚集[18]。因此,超声是降解多糖提高其乳状液稳定性的有效手段。
1.1.2 辐射法
辐照法修饰多糖分子主要是利用电离辐射(γ射线、X射线以及电子束等)诱导其发生聚合、交联、接枝或降解等变化[19-20]。与其他化学和生物修饰方法相比,电离辐射法具有操作简单,条件易控的优点,且在短时间内可以很容易地获得几种具有不同功能的衍生物[21]。电离辐射主要通过破坏分子间和分子内氢键和切割糖苷键来降解多糖,同时在这个过程会产生RCHO、RCOOH、CO2和CO等副产物。许多研究表明,辐照处理对多糖的乳化性能有积极的影响,多糖中糖苷键的断裂可能暴露出更多的亲水和疏水部分。例如,经辐照处理的海洋多糖可以增加其水溶性并降低其粘度[22]。辐照处理还能显著改善淀粉和葡聚糖的水溶性和流变特性[23]。辐照处理酵母-D-葡聚糖会导致多糖链中-OH、-CO、-CH等官能团的暴露,可提高其溶解度、降低粘度,并增加其发泡能力和胆汁酸结合的能力[24]。综上,电离辐射是改善多糖乳化特性等相关性能的有效方法。
1.2 多糖的化学修饰方法
多糖的化学修饰是指通过化学方法对其结构进行改性,获得功能特性改善的多糖衍生物,其修饰程度用取代度(DS)来表示。取代度定义为每个脱水葡萄糖单位的平均取代基数,主要由滴定法确定[25],此外,核磁共振波技术(NMR)也可以测定取代度。多糖的化学修饰可以通过引入具有高活性的官能团来使多糖降解,改变MW,提高其溶解度,改变其功能特性[26]。化学修饰法主要包括硫酸化、乙酰化、辛酰基琥珀酸酐酯化、磷酸化、羧甲基化、氧化、硒化以及烷基化等[27]。其中硫酸化、羧甲基化、乙酰化以及辛酰基琥珀酸酐酯化等方法均能改善多糖的乳化性能。
1.2.1 硫酸化修饰
硫酸基团与多糖链上的羟基之间的相互作用,使得天然多糖具有两亲性性质,此时硫酸化多糖表面的羟基可以锚定到油水界面,降低界面张力,同时高强度的酸水解使多糖具有高的硫酸基团覆盖率和高电位,能产生足够的静电斥力来阻止乳液液滴的团聚,显著提高乳化效率[28]。因此,硫酸基团对多糖表面羟基基团的取代度,对多糖基乳液的乳化稳定性具有十分重要的作用。不同硫酸化方法对其修饰的多糖的乳化特性具有显著影响。氯磺酸-吡啶法、浓硫酸法和三氧化硫吡啶法是常用的三种硫酸化方法。
氯磺酸-吡啶法由氯磺酸提供硫酸基团[29],具有高取代度和高产率,是最常用的硫化改性方法。但该方法的缺点是氯磺酸带剧毒、具有强刺激性,其反应过程剧烈、难以控制。通过自带冷凝器和搅拌装置的三颈烧瓶来制备硫酸盐试剂,即向处于冰浴条件下的吡啶中加入氯磺酸,充分混合,当烧瓶中出现大量淡黄色固体时,除去冰水浴。将多糖粉末溶于有机溶剂,加入硫酸盐试剂在一定温度下反应,反应结束后置于冰水中冷却至室温,用氢氧化钠中和后用乙醇醇沉,收集沉淀物,用蒸馏水复溶,复溶液经透析后冷冻干燥即得硫化多糖[30]。硫化多糖取代度主要与反应温度、反应时间和试剂比例有关,通常会通过设计单因素实验和响应面来确定最佳反应条件。Xu等[31]通过响应面优化确定了最佳反应参数:氯磺酸/吡啶的比值为1.3:1,反应持续时间为3.4 h,反应温度为65 ℃,此条件下可得到DS值最高,即DS值为0.99±0.02的迷果芹硫酸盐多糖。其中,反应温度是影响DS值最重要的因素,其次是反应时间和试剂比例。
浓硫酸法与氯磺酸法的改性操作相似,在冰浴条件下,按照一定的比例将正丁醇和浓硫酸在烧瓶中充分混合,加入硫酸铵,并使溶液温度保持在0 ℃以下,随后加入多糖粉末,搅拌一定时间后通过NaOH溶液调节pH7结束反应,用95%乙醇沉淀,沉积物用水重新溶解,经透析冷冻干燥后即得硫酸化多糖[32]。高爽等[33]研究发现反应时间是影响甜玉米芯多糖硫酸酯化DS值的重要因素,其次是硫酸铵和浓硫酸用量,在最佳条件下获得的硫酸酯化多糖DS值高达1.1478,且具有较好的溶解性。DS值与硫化多糖的功能特性密切相关,如硫酸化玉竹多糖的羟基自由基的清除能力随着取代度的增加不断增强[34]。浓硫酸法具有操作方便、反应速度快、试剂安全等优点,但因其浓硫酸的强酸性质易使多糖降解和炭化,且产率也较低,故此法较少使用[35]。
三氧化硫吡啶法改性多糖的步骤是将多糖粉末溶于无水DMSO或N,N-二甲基甲酰胺中,在反应温度下搅拌30 min形成均相溶液,加入三氧化硫吡啶配合物,在适当的温度下反应,结束后将混合物冷却至室温,用氢氧化钠水溶液中和至中性,最后,经乙醇沉淀、透析和冻干,即可获得硫酸化多糖[36]。经此法制备的硫酸化油菜胞外多糖的DS值为0.29,取代度较低,但其生物活性有明显提高[37]。Liu等[38]通过控制反应温度、时间和三氧化硫-吡啶配合物(SO3·Pyr)用量成功获得了具有不同取代度和链构象的硫酸多糖,发现其反应温度显著影响菌丝多糖的取代度和产率,其中中等取代度的硫化多糖具有最好的抗氧化和抗凝能力,过度取代可能破坏三螺旋结构,导致抗氧化和抗凝能力急剧下降。此外,所有硫化多糖均表现出比天然多糖更好的抗氧化和抗凝能力。三氧化硫吡啶法操作简单方便,但因其使用的试剂较为昂贵,不适合大规模应用。
1.2.2 羧甲基化修饰
羧甲基化修饰是将羧甲基引入多糖分子链中,增强多糖的水溶性,有利于分子向油水界面的快速扩散形成界面膜;羧甲基的引入还可以增强糖链的亲水性,增加乳化微粒表面水化层的厚度。此外,羧甲基带有负电荷,可以增强乳化微粒间的静电排斥作用,这些因素均有利于增强多糖的乳化性能[39-40]。羧甲基化具有成本低、操作简单、反应过程温和、产率高以及产物低毒或无毒的优点[41]。羧甲基化过程是将多糖与一定比例的异丙醇混合,搅拌均匀后滴入相应比例的20%氢氧化钠溶液。在室温下搅拌3 h,加入羧基甲基化剂(一定比例的氯乙酸、氢氧化钠和异丙醇的混合物),在60℃下继续反应4 h。将溶液冷却至室温后,用0.5 mol/L盐酸将溶液的pH调至7,离心后透析上清液,冷冻干燥获得羧甲基化衍生物[42]。通过控制氯乙酸的用量可以获得不同取代度的羧甲基化衍生物[43]。取代度的高低会影响羧甲基化多糖的功能特性,羧甲基化修饰适用于水溶性差,表面活性低且不含蛋白的多糖,因其反应的碱性条件易使蛋白变性,从而弱化其乳化性能[39]。
1.2.3 乙酰化修饰
乙酰化主要修饰多糖的支链结构,将乙酰基团引入到天然多糖链上羟基的位置上发生亲核取代反应,在适当的条件下可以产生相应的多糖衍生物[44]。乙酰基的接入使得多糖具有两亲性,增强了多糖在油-水界面的乳化作用,同时多糖的分子链之间发生缠结,体系的网络结构增强。分子质量大、高分子长链较多,且乙酰基含量较多的乙酰化多糖在油-水界面舒展产生的空间位阻作用足以达到阻止油滴聚集从而稳定乳液的作用,对多糖的静电作用力依赖性较小。乙酰化过程将多糖溶解在蒸馏水中,搅拌至溶液均匀,用氢氧化钠调整pH至9.0,在一定温度下搅拌4 h,而后添加所需量的醋酸酐,用氢氧化钠使溶液的pH保持在8.0~8.4之间,并不断搅拌。反应后,用盐酸中和以终止反应,透析后醇沉,蒸馏水复溶后冷冻干燥即得到乙酰化多糖[45]。通过在衍生过程中控制乙酰化试剂(乙酸酐)可获得不同DS的乙酰化衍生物,其中添加吡啶作为催化剂可以增加取代度,而乙酸酐的用量影响不大[46]。
1.2.4 辛烯基琥珀酸酐修饰
辛烯基琥珀酸酐(OSA)的酯化涉及到羟基与疏水取代基的部分取代,从而使多糖具有两亲性和界面性质[47-49]。目前,合成OS-多糖最广泛使用的方法是将多糖以颗粒状悬浮在蒸馏水中,滴加OSA,不断搅拌的同时用NaOH保持pH在8.0左右。反应温度通常在25~35 ℃之间,持续反应至浆液pH稳定,用HCl中和。反应结束后,将混合物过滤或离心,产物用水和丙酮或乙醇洗涤,最后干燥、研磨。这种多糖与OSA酯化反应途径已被广泛研究。研究者们对反应条件进行了优化,如使用超声波、高静压和等离子辐射等辅助,可以提高反应效率,缩短反应时间,使酯基在颗粒内和/或产物内分布更均匀[50-52]。针对淀粉的修饰主要是为了打开淀粉颗粒的紧密结构,增加其表面积,降低其结晶度,降低OSA液滴大小以及分散淀粉分子,从而使OSA更容易接近羟基,并使最终产品中的OS基团分布更均匀[53-55]。通过修饰使淀粉的一些结构和功能性质发生了改变,其反应效率也得到提高。琼脂糖经OSA改性后,多孔网络结构致密,纤维变薄,且具有新的物理性能,包括低凝胶、低熔化温度以及高透明度[56]。同样的,改性后的罗勒籽胶的界面张力降低,接触角和分子量增加,zeta电位的负值增加。所有分散体均表现出剪切变薄行为,修饰后表观粘度增加[57]。这些多糖改性后具备的凝胶性能和新引入的两亲性特性,使其有望作为功能性材料应用于食品工业中。
1.3 多糖的生物修饰方法
生物修饰多糖中酶法也是通过改变多糖的分子量来影响其相关性能。
酶处理是通过各种生物酶来处理多糖,过程较为温和,主要机理是利用不同的糖苷酶破坏多糖相应的糖苷键来修饰多糖,降低其分子质量和乳液的界面张力从而改善乳化稳定性[58]。研究发现酶降解能有效去除山药多糖中的蛋白质,同时降低分子量和粘度,增大粒径,其性质随着结构的改变而改变[59]。经酶水解的桑叶多糖的刚性结构被分解为更灵活的短链结构,这增加了多糖的表面活性,促进了界面上的吸附,从而降低了表面张力、表观粘度和热稳定性,但其触变性能和结构恢复能力,以及抗氧化活性有所提高[60]。大豆种皮多糖为亲水性物质,其主链连接的蛋白质经蛋白酶处理后亲水性增强,使得乳化剂整体更为亲水,且在pH为3.0时,蛋白质带正电,与带负电荷的大豆种皮多糖因静电引力互相吸引,使其锚点数量增加,乳化性增强。酶改性是一种有效的多糖加工方法。与其他修饰方法相比,酶处理耗能更少,但由于试剂较为昂贵,所以只能小范围的应用,同时由于酶具有专一性,只会作用于相同的糖苷键,所以经酶处理的多糖具有较高的均一性。
2. 不同修饰方法对多糖乳化性能的影响
多糖的修饰会对其结构产生重要的变化,导致修饰多糖物理化学性质的变化[61]。大量研究证实,多糖修饰对其乳化性能有重要的影响。
2.1 物理修饰法对多糖乳化性能的影响
分子量是多糖基乳状液稳定作用的关键。分子量越低,其吸附到油水界面的速度就越快[62]。物理修饰主要是通过改变多糖的分子量来影响其乳化性能。多糖分子量的变化会影响其分子尺寸、黏度、溶解度、界面活性以及亲疏水基团,从而影响多糖乳化性能[63]。
研究表明在含有阿拉伯胶的沙拉酱中,超声处理后的阿拉伯胶颗粒尺寸减小,形成了更稳定的水包油乳剂,从而使沙拉酱乳剂更稳定[64]。超声处理虽然会降低多糖分子量,但不会破坏多糖的致密结构。分子量较低的多糖具有较小的团聚尺寸和较高的水迁移率,从而提高了界面容量,形成了更紧密的界面层,致密的结构使表面活性基团的可及性更好,提高了乳液在高温下的稳定性[64]。不同的超声条件对多糖乳化性能的影响也不同。Wang等[65]研究了不同振幅和超声处理时间对含黄原胶的橄榄油乳剂的影响,方法 A 采用 70% 振幅超声 2 min,方法 B 采用 70% 振幅超声3 min,接着90%振幅超声1 min(共4 min)。结果显示,振幅或处理时间的增加均显著降低了黄原胶的黏度,增加了其界面活性,提高了乳液的稳定性。使用不同频率(28、40、50、135 kHz)的超声处理海藻酸钠,随超声频率的增加,Mn先增加后降低,可诱导ALG降解和重排,还可降低M/G比值,提高海藻酸钠的疏水作用和界面活性[66]。此外,通过其他方法协同超声对多糖进行改性也有较好的效果。Wang等[67]用微流态化和超声波相结合处理后的改性柑橘果胶稳定乳剂,比超声处理后的果胶和原果胶稳定的乳剂具有更高的离心稳定性和热稳定性。
经高能辐射处理,多糖中糖苷键的断裂会导致多糖链解聚,其致密结构被破坏,从而暴露出更多可能的亲水性和疏水性部分,这是辐射法提高多糖乳化性能的一个可能的原因[66]。相关研究表明多糖的吸水性、乳化性、溶胀性和溶解度指数等功能特性会随辐照剂量(0~5 kGy)的增加而增加[68]。Asma等[69]的研究也显示,随着5~50 kGy辐照剂量的增加,酵母β-D-葡聚糖的乳化性能逐渐增加,在50 kGy辐照剂量时乳化力最高,为79.24%。然而,并不是辐照处理多糖的剂量越高,其乳化性能越好。Han等[70]研究了γ射线辐照对辛烯基琥珀酰化水稻淀粉和高直链淀粉玉米淀粉乳化性能的影响,发现淀粉的乳化能力和稳定性随着辐照剂量的增加而增加,最终在10 kGy时达到稳定,在30和50 kGy时降低。这可能是由不同多糖自身结构和分子质量的差异所引起的。乳化剂的分子尺寸太小,则会形成单分子界面膜,从而不能最大限度地提高乳液的稳定性[71]。因此,高剂量辐照的过度降解可能会降低乳状液的容量和多糖的稳定性。两亲性材料的乳化性能与其粒径密切相关,不同多糖在适合的辐照剂量下才能形成最适合乳化的链大小。
2.2 化学修饰法对多糖乳化性能的影响
一些天然多糖的亲水链上附着非极性基团或蛋白,因此具有良好的乳化性能,常见的有阿拉伯胶、果胶和半乳糖类多糖等[72]。然而,自然界大多数多糖是高亲水分子,几乎不具备表面活性,因此无法作为良好的乳化剂,更倾向于通过增强连续相的粘度来增强乳液的稳定性[73]。这种类型的多糖可以通过化学法将疏水基团附着在其亲水骨架上使其具有表面活性,疏水基团如乙酰基、羧甲基、辛烯基琥珀酸酐和硫酸基等均可有效提高多糖的乳化性[74]。
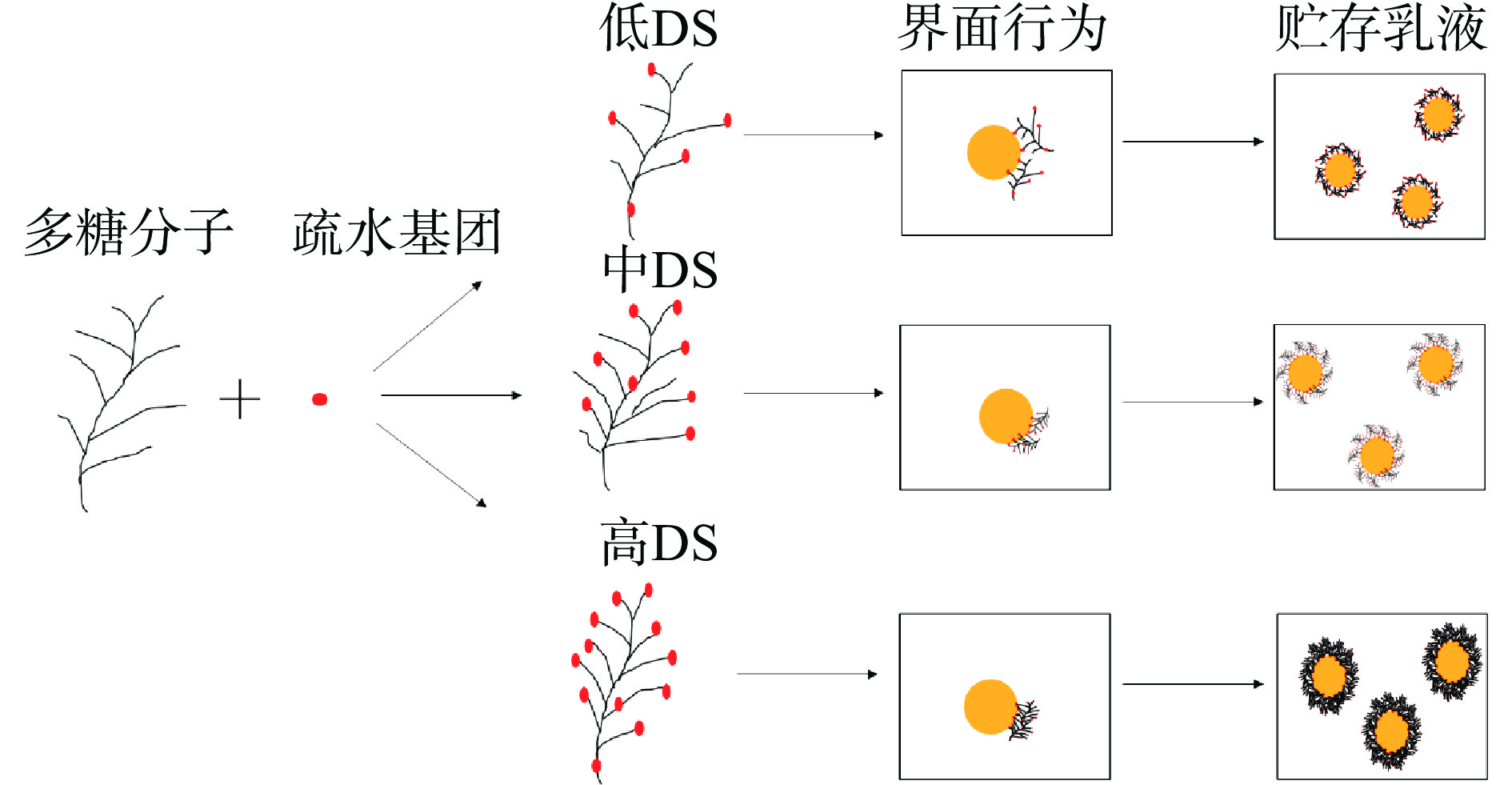
如图1所示,化学修饰对多糖乳化性能的影响与疏水基团取代度密切相关[75-76]。具体分为两种情况,当疏水基团取代度较低时,多糖的降解起主要作用,多糖的分子量和黏度显著降低,此时多糖具有一定的表面活性,但缺乏足够的作用力来稳定乳剂,乳化效果较差;当疏水基团取代度较高时,多糖的分子量和黏度随着取代度的增加而增加,此时多糖的疏水性增加,高分子量也提供一定的空间位阻阻止液滴的聚集和絮凝,乳化效果显著改善。Li等[76]对沙蒿多糖进行乙酰化修饰,发现其分子量和黏度随取代度的增加而先降低后增加,较高取代度的乙酰化沙蒿多糖可更大程度降低表面张力,显示出更小的液滴尺寸,使沙蒿多糖具有较好的乳化性能。乙酰化修饰能显著降低界面张力,提高了牛大力多糖的乳化性能,且中取代度和高取代度的乙酰牛大力多糖比阿拉伯胶具有更好的乳化能力[77]。同样的,硫酸盐基团的含量越高,所形成的纳米晶体乳化液的粒径越小,粘度越高,其乳化能力也越强[28]。此外,经羧甲基化修饰的木质素对水包油乳剂具有更高的稳定性[78]。Lin等[79]研究表明OSA修饰淀粉稳定的乳剂的胃稳定性取决于取代程度。OSA修饰淀粉取代程度的增加有助于提高乳液对胃液中离子强度、低pH和酶等的稳定性,液滴大小的增加程度与取代程度呈负相关。其他的研究也表明了OSA修饰对多糖的乳化性能具有良好的改善效果[80-81]。此外,使用一些手段辅助多糖进行化学改性,其乳化性能会更好。用乙基二甲基氯硅辅助合成C-3辛二酸改性玉米淀粉,结果发现,与OSA改性淀粉相比,C-3辛二酸改性淀粉制备的乳液平均粒径和zeta电位显著降低,更适用于乳剂的稳定[82]。
2.3 生物修饰法对多糖乳化性能的影响
与物理修饰法相似,生物修饰法中的酶法同样通过改变多糖的分子质量来影响其乳化性能,较小的分子质量可以促进乳化性能的改善。Li等[83]用木聚糖酶水解沙蒿多糖,其分子质量和回转半径减小,而分子构象增大,水解物具有更强的降低油水界面张力的能力,在油/水乳液中形成较好的液滴。木聚糖酶对沙蒿多糖的降解主要破坏主干结构,不影响侧链结构。同样的,α-1,4-聚半乳糖内酯酶对甜菜果胶的降解也是发生在主干上[84],这是由于酶的高选择性和专一性所决定的。因此,与物理修饰法不同,生物修饰法可以选择合适的酶来降解多糖,保留其对乳化贡献高的部分,提高多糖的乳化性能。从海参中提取硫酸化岩藻聚糖,通过酶法水解降解为不同分子量(2000~100 kDa),产生的多糖的尺寸随着分子量的降低而降低。由MW最高的岩藻聚糖制成的多层乳液对NaCl(0~100 mmol/L)具有更好的稳定性。较高分子量的硫酸化岩藻聚糖能显著提高包封脂质的初始消化率[85]。基于此,可以根据需要生产具有特定功能的多糖乳化剂。此外,通过酶法修饰多糖,还可以提高多糖的疏水性。使用α-淀粉酶修饰藜麦淀粉,疏水性随酶解时间的增加而增加,粒径减小,淀粉断裂和淀粉接触角增大,藜麦淀粉乳液的乳化指数值增大,油滴尺寸减小,当最小粒径和接触角最接近90°时,其乳化性能最好[86]。藜麦淀粉疏水性的增加可能是酶解后其结晶增加、层状结构含量变高、分形结构更紧凑的原因。以往的研究中,提高多糖疏水性的方法大多是通过化学修饰来实现的[87],酶解对多糖疏水性增加的相关报道较少,这对相关的多糖修饰方法提供了一个新的思路。
3. 多糖及其修饰多糖在乳状液中的应用
许多研究人员已经探索了多糖基乳剂在食品工业中的潜力,本文就以下较常见的应用展开讨论。
3.1 生物活性化合物的封装和传递
多酚、类胡萝卜素和精油等疏水化合物具有抗氧化、抗炎、抗癌和抗菌等多种有益活性,但因其水溶性、化学稳定性以及生物利用度都较差,在实际中的应用也受到限制[88]。多糖基乳剂因其无毒、易于消化、生物相容性高,并可以在宽泛的pH和温度下保持稳定等优点引起了广泛关注[24]。多糖基乳剂可用于封装和保护油滴内的疏水活性物质,并使其在食物和胃肠道中保持稳定。研究表明,多糖稳定的乳剂具有较高的包封效率和良好的包封稳定性,例如,含叶黄素的玉米纤维胶(CFG)稳定乳剂表现出良好的理化性质、稳定性和体外生物可及性,在贮藏过程中,所载叶黄素含量稳定,在光、高温条件下可避免降解。用CFG稳定的乳剂包裹13.8%~32.4%后,提高了叶黄素的生物可及性[89]。而经过修饰的多糖也具有比天然多糖更好的效果,乳改性淀粉稳定咖啡乳剂可在一定程度上控制香气释放,可用于速溶咖啡香气富集[90]。Pan等[91]制备了OSA改性姜黄素包封,发现姜黄素在糊精稳定乳液中的包封效率约为57.93%,而在OSA改性糊精稳定乳液中的包封效率提高到85.41%。OSA改性糊精稳定的糊乳的乳化稳定性显著提高。
3.2 脂质消化和调节
脂质消化是一个界面过程,主要是由脂酶和胆盐吸附在乳化脂滴表面控制的。研究表明应用多糖稳定乳剂传递食品生物活性物质时,多糖会阻止胆盐的竞争性置换或延迟脂肪酶向疏水脂质核心的运输,从而有效延缓脂质分解[92]。多糖基乳剂可以通过控制胃肠道中脂质的消化和吸收来增加饱腹感和降低食欲,因而可针对特殊人群开发相应的功能性食品。纤维素纳米晶体已被证明通过降低脂肪酶到达油滴的能力来抑制皮克林乳剂中的脂质消化[93]。壳聚糖可与胆盐结合,诱导液滴絮凝,增加胃肠道液体黏度,从而延缓乳化脂类的消化[94]。海藻酸盐可与钙离子和脂肪酸结合,诱导耗尽絮凝的发生,调节胃肠液体流变学,从而延缓乳化脂质的消化[95]。在模拟胃肠道条件下,纤维素纳米晶体稳定的玉米水油乳剂可以防止口腔和胃环境中的液滴合并[96]。不同种类的多糖由于表面活性、结合特性、增稠和凝胶行为的不同,会通过不同的机制影响乳化脂类的消化[97-98]。综上所述,这些研究表明,基于多糖的乳剂可以被设计来调节脂质消化,它们调节脂质消化的能力可以促进功能食品的发展,这些功能食品可以通过增加饱腹感来控制饮食行为,或将生物活性物质传递到胃肠道的特定区域,以实现不同的需求。
4. 结论与展望
乳化剂是食品工业中最重要的食品添加剂之一,而多糖作为其中最重要的来源之一,具有巨大的发展潜力。通过物理、化学或生物方法修饰表面活性较低的多糖,可以改变其性质,从而表现出较好的表面活性,进一步增强其乳化性能。在目前修饰天然多糖的方法中,仍存在以下问题:a.物理方法所使用的设备较为昂贵,难以大批量生产;化学修饰方法易污染环境且存在安全性等问题;生物修饰方法产物均一性好,但成本较高。b.关于修饰多糖改善其乳化性能的构效关系研究还不够深入,不同修饰多糖的乳化性能与其一级、二级结构的关系尚不明确。随着相关仪器设备的更新换代和多糖修饰方法的不断开发与完善,乳化成本、环境污染等限制将得到解决,不同加工方式对多糖结构和改善其乳化性能的机制也将得到阐明。今后,更高效、更安全且易于产业化的多糖修饰方法将不断被开发,并将其应用于药物递送、乳饮料等行业,在食品、医药、化工等领域具有广阔的发展前景。
-
[1] OZTURK B, MCCLEMENTS D J. Progress in natural emulsifiers for utilization in food emulsions[J]. Current Opinion in Food Science,2016,7:1−6.
[2] ZHANG Y, SUN T, JIANG C. Biomacromolecules as carriers in drug delivery and tissue engineering[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B,2018,8(1):34−50. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2017.11.005
[3] HUANG G, CHEN F, YANG W, et al. Preparation, deproteinization and comparison of bioactive polysaccharides[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2021,109:564−568.
[4] RICHA R, CHOUDHURY A R. Exploration of polysaccharide based nanoemulsions for stabilization and entrapment of curcumin[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,156:1287−1296. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.11.167
[5] 李秀秀, 尚静, 杨曦, 等. 多糖的增稠, 胶凝及乳化特性研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(15):300−308. [LI X X, SHANG J, YANG X, et al. Research progress in thickening, gelling and emulsifying properties of polysaccharides[J]. Food Science,2021,42(15):300−308. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200617-239 [6] HUANG H, HUANG G. Extraction, separation, modification, structural characterization, and antioxidant activity of plant polysaccharides[J]. Chem Biol Drug Des,2020,96(5):1209−1222. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13794
[7] KUMAR M, TOMAR M, SAURABH V, et al. Delineating the inherent functional descriptors and biofunctionalities of pectic polysaccharides[J]. Carbohydr Polym,2021,269:118319. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118319
[8] LI X L, TU X F, THAKUR K, et al. Effects of different chemical modifications on the antioxidant activities of polysaccharides sequentially extracted from peony seed dreg[J]. Int J Biol Macromol,2018,112:675−685. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.01.216
[9] TANG S, WANG T, HUANG C, et al. Sulfated modification of arabinogalactans from Larix principis-rupprechtii and their antitumor activities[J]. Carbohydr Polym,2019,215:207−212. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.03.069
[10] LI Y, YUAN Y, LEI L, et al. Carboxymethylation of polysaccharide from Morchella angusticepes Peck enhances its cholesterol-lowering activity in rats[J]. Carbohydr Polym,2017,172:85−92. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.05.033
[11] SHEN S G, LIN Y H, ZHAO D X, et al. Comparisons of functional properties of polysaccharides from nostoc flagelliforme under three culture conditions[J]. Polymers,2019,11(2):263. doi: 10.3390/polym11020263
[12] WU D T, HE Y, FU M X, et al. Structural characteristics and biological activities of a pectic-polysaccharide from okra affected by ultrasound assisted metal-free Fenton reaction[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,122:107085. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107085
[13] XIAO J, CHEN X, ZHAN Q, et al. Effects of ultrasound on the degradation kinetics, physicochemical properties and prebiotic activity of Flammulina velutipes polysaccharide[J]. Ultrason Sonochem,2022,82:105901. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2021.105901
[14] WANG H, CHEN J, REN P, et al. Ultrasound irradiation alters the spatial structure and improves the antioxidant activity of the yellow tea polysaccharide[J]. Ultrason Sonochem,2021,70:105355. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105355
[15] ANWAR M, BABU G, BEKHIT A E D. Utilization of ultrasound and pulse electric field for the extraction of water-soluble non-starch polysaccharide from taro (Colocasia esculenta) peel[J]. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies,2021,70:102691.
[16] CUI R, ZHU F. Ultrasound modified polysaccharides: A review of structure, physicochemical properties, biological activities and food applications[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2021,107:491−508.
[17] LI Y, XIANG D, WANG B, et al. Oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by ultrasonic degraded polysaccharide complex[J]. Molecules,2019,24(6):1097. doi: 10.3390/molecules24061097
[18] ZHOU L, ZHANG J, XING L, et al. Applications and effects of ultrasound assisted emulsification in the production of food emulsions: A review[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2021,110:493−512.
[19] 路欣彤, 齐欣, 高雪峰, 等. 辐照处理对桦褐孔菌多糖抗疲劳作用的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(3):351−357. [LU X T, QI X, GAO X F, et al. Effects of irradiation treatment on anti-fatigue effect of polysaccharides from Phorus betulinus[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(3):351−357. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021050192 [20] 周鑫, 舒晓燕, 李鑫奎, 等. 白芷粗多糖的提取工艺优化及辐照对其含量和活性的影响[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2021,12(21):8508−8516. [ZHOU X, SHU X Y, LI X K, et al. Optimization of extraction technology of crude polysaccharides from Angelica dahurica and effects of irradiation on its content and activity[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection,2021,12(21):8508−8516. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2021.21.spaqzljcjs202121030 [21] HUANG S, CHEN F, CHENG H. Modification and application of polysaccharide from traditional Chinese medicine such as Dendrobium officinale[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,157:385−393. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.04.141
[22] BALJIT SINGH, BALDEV SINGH. Developing a drug delivery carrier from natural polysaccharide exudate gum by graft-copolymerization reaction using high energy radiations[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,127:450−459. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.01.075
[23] KHANDAL D, MOHAMAD S F, COQUERET X. Recent advances in the radiation chemistry of destructured starch and other glucans as model compounds[J].Carbohydrate Chemistry: Chemical and Biological Approaches, 2021, 45: 664.
[24] B Y C A, C M C B. Influence of emulsifier type on the in vitro digestion of fish oil-in-water emulsions in the presence of an anionic marine polysaccharide (fucoidan): Caseinate, whey protein, lecithin, or Tween 80[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2016,61:92−101. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2016.04.047
[25] KHOSHDOUNI FARAHANI Z, MOUSAVI M, SEYEDAIN ARDEBILI S M, et al. Modification of sodium alginate by octenyl succinic anhydride to fabricate beads for encapsulating jujube extract[J]. Curr Res Food Sci,2022,5:157−166. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2021.11.014
[26] XU Y, WU Y J, SUN P L, et al. Chemically modified polysaccharides: Synthesis, characterization, structure activity relationships of action[J]. Int J Biol Macromol,2019,132:970−977. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.213
[27] SIMSEK M, ASIYANBI-HAMMED T T, RASAQ N, et al. Progress in bioactive polysaccharide-derivatives: A review[J]. Food Reviews International,2021:1−16.
[28] ZHANG H, QIAN Y, CHEN S, et al. Physicochemical characteristics and emulsification properties of cellulose nanocrystals stabilized O/W pickering emulsions with high -OSO3− groups[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2019,96:267−277. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.05.023
[29] XIAO H, FU X, CAO C, et al. Sulfated modification, characterization, antioxidant and hypoglycemic activities of polysaccharides from Sargassum pallidum[J]. Int J Biol Macromol,2019,121:407−414. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.09.197
[30] CHEN L, HUANG G. Antioxidant activities of sulfated pumpkin polysaccharides[J]. Int J Biol Macromol,2019,126:743−746. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.12.261
[31] XU Y, SONG S, WEI Y, et al. Sulfated modification of the polysaccharide from Sphallerocarpus gracilis and its antioxidant activities[J]. Int J Biol Macromol,2016,87:180−190. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.02.037
[32] 肖恩来, 马永强, 王鑫, 等. 响应面优化硫酸法改性甜玉米芯多糖研究[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2019,30(2):71−76. [XIAO E L, MA Y Q, WANG X, et al. Modification of sweet corn cob polysaccharide by response surface optimization with sulfuric acid method[J]. Chinese Food Additives,2019,30(2):71−76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2513.2019.02.004 [33] 高爽, 王鑫, 马永强, 等. 硫酸酯化甜玉米芯多糖的制备[J]. 哈尔滨商业大学学报(自然科学版),2016,32(5):537−541. [GAO S, WANG X, MA Y Q, et al. Preparation of sulfated sweet corn cob polysaccharide[J]. Journal of Harbin University of Commerce (Natural Science Edition),2016,32(5):537−541. [34] 霍达. 水溶性玉竹多糖的分离纯化、结构表征、硫酸化修饰及活性研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2020 HUO D. Isolation, purification, structure characterization, sulfuration modification and activity of water-soluble Polygonatum polysaccharide[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2020.
[35] XIE L, SHEN M, HONG Y, et al. Chemical modifications of polysaccharides and their anti-tumor activities[J]. Carbohydr Polym,2020,229:115436. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115436
[36] 王瑞芳, 陈发河, 吴光斌, 等. 三氧化硫吡啶法酯化修饰海参岩藻聚糖硫酸酯的研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(4):113−117, 124. [WANG R F, CHEN F H, WU G B, et al. Study on the esterification of fucoidan sulfate ester of sea cucumber by thiopyridine trioxide method[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(4):113−117, 124. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.022219 [37] ZHANG Z, LIU Z, TAO X, et al. Characterization and sulfated modification of an exopolysaccharide from Lactobacillus plantarum ZDY2013 and its biological activities[J]. Carbohydr Polym,2016,153:25−33. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.07.084
[38] LIU Y, TANG Q, DUAN X, et al. Antioxidant and anticoagulant activities of mycelia polysaccharides from Catathelasma ventricosum after sulfated modification[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2018,112:53−60. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.10.064
[39] 石华乐, 秦玉昌, 姚怡莎, 等. 羧甲基化改性对不同分子量水溶性大豆多糖乳化性的影响[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2015,6(5):1790−1798. [SHI H L, QIN Y C, YAO Y S, et al. Effects of carboxymethylation modification on emulsification of water-soluble soybean polysaccharides with different molecular weights[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection,2015,6(5):1790−1798. doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2015.05.047 [40] 燕文胜, 张亮亮, 李焕洋, 等. 化学改性对连翘不溶性膳食纤维理化性质、结构及乳化稳定性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(19):61−68. [YAN W S, ZHANG L L, LI H Y, et al. Effects of chemical modification on physicochemical properties, structure and emulsification stability of forsythia insoluble dietary fiber[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(19):61−68. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021120175 [41] LIU W, HU C, LIU Y, et al. Preparation, characterization, and α-glycosidase inhibition activity of a carboxymethylated polysaccharide from the residue of Sarcandra glabra (Thunb.) Nakai[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2017,99:454−464. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.02.065
[42] LIU Y, LU K, HU X, et al. Structure, properties and potential applications of phytoglycogen and waxy starch subjected to carboxymethylation[J]. Carbohydr Polym,2020,234:115908. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.115908
[43] LI Y T, CHEN B J, WU W D, et al. Antioxidant and antimicrobial evaluation of carboxymethylated and hydroxamated degraded polysaccharides from Sargassum fusiforme[J]. Int J Biol Macromol,2018,118(Pt B):1550−1557.
[44] KRISZTINA H, KUTTEL M M, GIANLUIGI D B, et al. O-acetylation of typhoid capsular polysaccharide confers polysaccharide rigidity and immunodominance by masking additional epitopes[J]. Vaccine,2020:3866−3875.
[45] 邵珠领, 吴艳丽, 张宇, 等. 桦褐孔菌多糖的乙酰化修饰及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(9):73−77. [SHAO Z L, WU Y L, ZHANG Y, et al. Acetylation modification and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Porus betulinus[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(9):73−77. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2019.09.014 [46] ABUDUWAILI A, NUERXIATI R, MUTAILIFU P, et al. Isolation, structural modification, characterization, and bioactivity of polysaccharides from Folium isatidis[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2022,176:114319. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.114319
[47] XU T, JIANG C, ZHOU Q, et al. Preparation and characterization of octenyl succinic anhydride modified waxy maize starch hydrolyzate/chitosan complexes with enhanced interfacial properties[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2021,267:118228. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118228
[48] 杨雪, 王姝雯, 刘庆庆, 等. 大米抗性辛烯基琥珀酸淀粉酯的制备及特性分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(11):167−174. [YANG X, WANG S W, LIU Q Q, et al. Preparation and property analysis of rice octenyl succinate resistant starch ester[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(11):167−174. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021090064 [49] CHEN H, CHEN F, XIAO Q, et al. Structure and physicochemical properties of amphiphilic agar modified with octenyl succinic anhydride[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2021,251:117031. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117031
[50] ZHANG Y, DAI Y, HOU H, et al. Ultrasound-assisted preparation of octenyl succinic anhydride modified starch and its influence mechanism on the quality[J]. Food Chem X,2020,5:100077. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2020.100077
[51] JI S, XU T, HUANG W, et al. Atmospheric pressure plasma jet pretreatment to facilitate cassava starch modification with octenyl succinic anhydride[J]. Food Chem,2022,370:130922. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130922
[52] SILVA E K, ANTHERO A, EMERICK L B, et al. Low-frequency ultrasound-assisted esterification of Bixa orellana L. seed starch with octenyl succinic anhydride[J]. Int J Biol Macromol,2022,207:1−8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.02.090
[53] LIU X, DING S, WU J, et al. Molecular structures of octenyl succinic anhydride modified starches in relation to their ability to stabilize high internal phase emulsions and oleogels[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,120:106953. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.106953
[54] PUNIA S, SANDHU K S, DHULL S B, et al. Dynamic, shear and pasting behaviour of native and octenyl succinic anhydride (OSA) modified wheat starch and their utilization in preparation of edible films[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,133:110−116. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.04.089
[55] SWEEDMAN M C, TIZZOTTI M J, SCHÄFER C, et al. Structure and physicochemical properties of octenyl succinic anhydride modified starches: A review[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2013,92(1):905−920. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.09.040
[56] XIAO Q, WENG H, CHEN G, et al. Preparation and characterization of octenyl succinic anhydride modified agarose derivative[J]. Food Chem,2019,279:30−39. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.11.133
[57] GAHRUIE H H, ESKANDARI M H, KHALESI M, et al. Rheological and interfacial properties of basil seed gum modified with octenyl succinic anhydride[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2020,101:105489. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.105489
[58] SHOKRI Z, SEIDI F, SAEB M R, et al. Elucidating the impact of enzymatic modifications on the structure, properties, and applications of cellulose, chitosan, starch and their derivatives: A review[J]. Materials Today Chemistry,2022,24:100780. doi: 10.1016/j.mtchem.2022.100780
[59] ZOU M, CHEN Y, SUN D, et al. Immunomodulatory acidic polysaccharides from Zizyphus jujuba cv. Huizao: Insights into their chemical characteristics and modes of action[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,258:35−42. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.03.052
[60] HU T G, ZOU Y X, LI E N, et al. Effects of enzymatic hydrolysis on the structural, rheological, and functional properties of mulberry leaf polysaccharide[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,355:129608. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129608
[61] WANG Z, XIE J, SHEN M, et al. Sulfated modification of polysaccharides: Synthesis, characterization and bioactivities[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2018,74:147−157.
[62] ZHANG R, BELWAL T, LI L, et al. Recent advances in polysaccharides stabilized emulsions for encapsulation and delivery of bioactive food ingredients: A review[J]. Carbohydr Polym,2020,242:116388. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116388
[63] SHAO P, FENG J, SUN P, et al. Recent advances in improving stability of food emulsion by plant polysaccharides[J]. Food Res Int,2020,137:109376. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109376
[64] GAVAHIAN M, CHEN Y M, MOUSAVI KHANEGHAH A, et al. In-pack sonication technique for edible emulsions: Understanding the impact of acacia gum and lecithin emulsifiers and ultrasound homogenization on salad dressing emulsions stability[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,83:79−87. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.04.039
[65] WANG L, DING J, FANG Y, et al. Effect of ultrasonic power on properties of edible composite films based on rice protein hydrolysates and chitosan[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2020,65:105049. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105049
[66] FENG L, CAO Y, XU D, et al. Molecular weight distribution, rheological property and structural changes of sodium alginate induced by ultrasound[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2017,34(Complete):609−615.
[67] WANG W, FENG Y, CHEN W, et al. Citrus pectin modified by microfluidization and ultrasonication: Improved emulsifying and encapsulation properties[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2021,70:105322. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105322
[68] HAMDANI A M, WANI I A, GANI A, et al. Effect of gamma irradiation on physicochemical, structural and rheological properties of plant exudate gums[J]. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies,2017,44:74−82.
[69] KHAN A A, GANI A, MASOODI F A, et al. Structural, thermal, functional, antioxidant & antimicrobial properties of beta-D-glucan extracted from baker's yeast (Saccharomyces cereviseae) effect of gamma-irradiation[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2016,140:442−450. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.01.003
[70] HAN J A, LIM S T. Effect of γ-irradiation on pasting and emulsification properties of octenyl succinylated rice starches[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2012,90(4):1480−1485. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.07.018
[71] DICKINSON E. Hydrocolloids acting as emulsifying agents-How do they do it?[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,78:2−14. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.01.025
[72] MCCLEMENTS D J, BAI L, CHUNG C. Recent Advances in the utilization of natural emulsifiers to form and stabilize emulsions[J]. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol,2017,8:205−236. doi: 10.1146/annurev-food-030216-030154
[73] PRASHER P, SHARMA M, MEHTA M, et al. Current-status and applications of polysaccharides in drug delivery systems[J]. Colloid and Interface Science Communications,2021,42:100418. doi: 10.1016/j.colcom.2021.100418
[74] USMAN M, ZHANG C, PATIL P J, et al. Potential applications of hydrophobically modified inulin as an active ingredient in functional foods and drugs: A review[J]. Carbohydr Polym,2021,252:117176. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117176
[75] LIU C M, GUO X J, LIANG R H, et al. Alkylated pectin: Molecular characterization, conformational change and gel property[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2017,69:341−349. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.03.008
[76] LI J, HU X, LI X, et al. Effects of acetylation on the emulsifying properties of Artemisia sphaerocephala Krasch polysaccharide[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2016,144:531−540. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.02.039
[77] HUANG Z, ZONG M H, LOU W Y. Effect of acetylation modification on the emulsifying and antioxidant properties of polysaccharide from Millettia speciosa Champ[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,124:107217. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107217
[78] LI S, WILLOUGHBY J A, ROJAS O J. Oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by carboxymethylated lignins: Properties and energy prospects[J]. Chem Sus Chem,2016,9(17):2460−2469. doi: 10.1002/cssc.201600704
[79] LIN Q, LIANG R, ZHONG F, et al. Effect of degree of octenyl succinic anhydride (OSA) substitution on the digestion of emulsions and the bioaccessibility of β-carotene in OSA-modified-starch-stabilized-emulsions[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,84:303−312. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.05.056
[80] LI J, LI Y, ZHONG J, et al. Effect of cellulose nanocrystals on the formation and stability of oil-in-water emulsion formed by octenyl succinic anhydride starch[J]. LWT,2021,151:112214. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112214
[81] PAN Y, WU Z, ZHANG B, et al. Preparation and characterization of emulsion stabilized by octenyl succinic anhydride-modified dextrin for improving storage stability and curcumin encapsulation[J]. Food Chem,2019,294:326−332. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.05.053
[82] GAO W, LIU P, WANG B, et al. Synthesis, physicochemical and emulsifying properties of C-3 octenyl succinic anhydride-modified corn starch[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,120:106961. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.106961
[83] LI J, HU X, YAN X, et al. Effects of hydrolysis by xylanase on the emulsifying properties of Artemisia sphaerocephala Krasch. polysaccharide[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,76:158−163. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2016.12.015
[84] CHEN H M, FU X, LUO Z G. Effect of molecular structure on emulsifying properties of sugar beet pulp pectin[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2016,54:99−106. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.09.021
[85] SHI F, TIAN X, MCCLEMENTS D J, et al. Influence of molecular weight of an anionic marine polysaccharide (Sulfated fucan) on the stability and digestibility of multilayer emulsions: Establishment of structure-function relationships[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,113:106418. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.106418
[86] ZHANG L, XIONG T, WANG X F, et al. Pickering emulsifiers based on enzymatically modified quinoa starches: Preparation, microstructures, hydrophilic property and emulsifying property[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,190:130−140. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.08.212
[87] AI C, MENG H, LIN J, et al. Emulsification properties of alkaline soluble polysaccharide from sugar beet pulp: Effect of acetylation and methoxylation[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,124:107361. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107361
[88] WANI T A, SHAH A G, WANI S M, et al. Suitability of different food grade materials for the encapsulation of some functional foods well reported for their advantages and susceptibility[J]. C R C Critical Reviews in Food Technology,2016,56(15):2431−2454. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2013.845814
[89] FENG H, CHAO L, TAN C P, et al. Physicochemical properties and in vitro bioaccessibility of lutein loaded emulsions stabilized by corn fiber gums[J]. RSC Advances,2017,7:38243−38250. doi: 10.1039/C7RA04943A
[90] LEE L W, LIU X, WONG W, et al. Effects of sucrose monopalmitate (P90), Tween 80 and modified starch on coffee aroma retention and release in coffee oil-based emulsions[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2017,66(MAY):128−135.
[91] PAN Y, WU Z, ZHANG B, et al. Preparation and characterization of emulsion stabilized by octenyl succinic anhydride-modified dextrin for improving storage stability and curcumin encapsulation[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,294(OCT.1):326−332.
[92] ESPINAL-RUIZ M, RESTREPO-SANCHEZ L P, NARVAEZ-CUENCA C E, et al. Impact of pectin properties on lipid digestion under simulated gastrointestinal conditions: Comparison of citrus and banana passion fruit (Passiflora tripartita var. mollissima) pectins[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2016,52(JAN):329−342.
[93] SARKAR A, LI H, CRAY D, et al. Composite whey protein–cellulose nanocrystals at oil-water interface: Towards delaying lipid digestion[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,77:436−444. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.10.020
[94] QIN D, YANG X, GAO S, et al. Influence of hydrocolloids (dietary fibers) on lipid digestion of protein-stabilized emulsions: Comparison of neutral, anionic, and cationic polysaccharides[J]. Journal of Food Science,2016,81(7):C1636−C45. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.13361
[95] 孙瑞. 用于固定脂质微纳米载体的水凝胶珠的制备与评价[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2021 SUN R. Preparation and evaluation of hydrogel beads for immobilization of lipid micro/nano carriers[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2021.
[96] BAI L, LÜ S, XIANG W, et al. Oil-in-water Pickering emulsions via microfluidization with cellulose nanocrystals: 2. In vitro lipid digestion[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2019,96:709−716. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.04.039
[97] INFANTES-GARCIA M R, VERKEMPINCK S H E, DEL CASTILLO-SANTAELLA T, et al. In vitro gastric lipid digestion of emulsions with mixed emulsifiers: Correlation between lipolysis kinetics and interfacial characteristics[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,128:107576. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2022.107576
[98] TAN Y, ZHANG Z, MURIEL MUNDO J, et al. Factors impacting lipid digestion and nutraceutical bioaccessibility assessed by standardized gastrointestinal model (INFOGEST): Emulsifier type[J]. Food Research International,2020,137:109739. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109739
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 刘家欣,梁梦茜,张群利. 生物基可降解包装材料在果蔬保鲜中的研究进展. 包装工程. 2025(03): 10-18 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 鞠阳,郑秀霞,段嘉婧,范蓓,王凤忠,孙玉凤. 淀粉醛强化大豆分离蛋白/槲皮素复合膜制备及性能研究. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2024(01): 135-145 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 卢奕如,倪辉,朱艳冰,姜泽东,李清彪,郑明静. 卡拉胶/速溶琼胶包埋体系负载茶多酚的特性. 中国食品学报. 2024(09): 40-50 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 刘娅妮,王飞宇,孙鹏伟,高虹,范秀芝,殷朝敏,于巍,史德芳,方尚玲. 物理活性包装对香菇贮藏品质、呼吸及能量代谢的影响. 食品工业科技. 2024(24): 301-310 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 张军,张凯,张娜,刘梦娇,张人平,王晨,刘文婧,霍柳炎. 赖氨酸-葡萄糖美拉德反应产物对杏鲍菇采后品质的影响. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2023(22): 181-189 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 杨旭,乔恒,王宇临,胡代花,陈旺. 不同波段紫外线照射处理对香菇生理特性及贮藏品质的影响. 食品科技. 2023(11): 56-63 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



