Optimization of Fermentation Technology of Integrated Fruit and Vegetable Enzyme and Evaluation of Its Function of Nourishing Bowel and Defecating
-
摘要: 目的:确定综合果蔬酵素发酵工艺,并探究其润肠通便功能。方法:通过调整发酵时间、发酵温度、低聚异麦芽糖添加量、燕麦麸皮添加量,以感官评分为评价指标,优化综合果蔬酵素的制备工艺,测定酵素产品的特征性成分,建立小鼠便秘模型,探究综合果蔬酵素不同剂量(低剂量5 mL/kg,中剂量10 mL/kg,高剂量15 mL/kg)对小鼠小肠墨汁推进率和排便的影响。结果:应用响应面法优化出综合果蔬酵素的配方为发酵时间为72 h,发酵温度为37 ℃,低聚异麦芽糖添加量为3%,燕麦麸皮添加量为3%,在此条件下感官评分为95.33分。特征性成分检测中综合果蔬酵素中富含1100 mg/kg乳酸、γ-氨基丁酸100 mg/kg、120 mg/100 g的游离氨基酸,小鼠试验中,高剂量的综合果蔬酵素的墨汁推进率高达66.7%,与对照组相比极显著(P<0.01)提升,6 h内排便粒数高剂量组达到33.16粒,极显著(P<0.01)高于模型对照组,有效缩短了粪便在小肠内的滞留时间,起到润肠通便的作用。结论:优化后的综合果蔬酵素具有较好的感官评分和润肠通便作用,具有一定的应用前景。Abstract: Objective: To determine the fermentation technology of dietary fiber enzyme, and to explore its function of nourishing intestine and defecating. Methods: By adjusting the fermentation time, fermentation temperature, the amount of isomaltose and oat bran, the sensory score of integrated fruit and vegetable enzyme was optimized, the characteristic components of the enzyme products were determined. To establish a constipation model in mice, and to explore the effects of different doses of Integrated fruit and vegetable enzymes (low dose 5 mL/kg, medium dose 10 mL/kg, high dose 15 mL/kg) on small intestinal ink propulsion rate and defecation in mice. Results: The formula of integrated fruit and vegetable enzyme was optimized by response surface method. The fermentation time was 72 h, the fermentation temperature was 37 ℃, the amount of isomaltose added was 3%, and the amount of oat bran added was 3%. In the mouse experiment, the ink advance rate of high-dose integrated fruit and vegetable enzyme was as high as 66.7%, compared with the control group, it was significantly improved (P<0.01), and the number of defecation grains within 6 h reached 33.16 in the high-dose group, it was significantly higher than the model control group (P<0.01) , which effectively shortened the retention time of feces in the small intestine, and played the role of moistening the intestine. Conclusion: The optimized integrated fruit and vegetable enzyme of fruits and vegetables has better sensory score and nourishing bowel function, so it has certain application prospect.
-
Keywords:
- response surface /
- optimization /
- the senses /
- enzyme /
- relaxing bowel
-
便秘是日常生活中出现较为频繁的胃肠道综合征之一,其特点是大便干结、排便伴有刺痛、排便艰难且排便次数少[1]。便秘在人群中的患病率高达27%,其中女性多于男性,老年多于青、壮年,不仅给患者带来痛苦,还会造成相当大的社会和经济负担[2]。药物和饮食是治疗便秘的主要两种方式,长期服用药物具有依赖性和副作用,因此便秘患者对药物的治疗方法心存担忧[3]。研发出具有润肠通便功能的饮食,已成为主流趋势。
近年来,用于润肠通道的益生元产品广受便秘患者关注。研究证实,功能性产品如发酵果汁、酵素等具有明显的润肠通便作用[4]。酵素是指以动物、植物、菌类为原料,添加或不添加辅料,经过微生物发酵制得的含有特定生物活性的产品[5],具有抗氧化、改善肠道环境、润肠通便、抗炎等功效。索婧怡等[6]发现果蔬发酵汁中富含膳食纤维等有益物质,可促进肠道蠕动。蒋欣荣等[7]发现经过乳酸菌发酵的果蔬饮品有改善小鼠便秘的功效,尤其是以鼠李糖乳杆菌和植物乳杆菌等多种复合菌发酵的果蔬饮料,在促进小鼠排便方面更为显著。朱艳等[8]通过研究发现果蔬酵素可以有效提升益生菌的利用率,从而改善肠道菌群紊乱。目前既保留原料营养成分,又具有润肠通便功效的酵素少见研究,因此明确酵素的生产配方,生产富含多种营养成分且具有润肠通便功效的酵素成为市场需求。
本文探究不同因素对于综合果蔬酵素感官的影响,优化综合果蔬酵素工艺配方,分析饮用综合果蔬酵素后盐酸洛哌丁胺便秘小鼠的便秘改善情况,旨在研发一款安全性较高,能够缓解便秘的综合果蔬酵素。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
低聚异麦芽糖 保龄宝生物股份有限公司;燕麦麸皮 张家口新素燕麦食品科技有限公司;山楂、大枣、沙棘 樟树市仁德中药饮片有限公司;雄性ICR小鼠(18~22 g) 辽宁长生生物技术有限公司(SCXK(辽)2020-0001);盐酸洛哌丁胺胶囊(盐酸洛哌丁胺含量为2 mg/粒) 西安杨森制药有限公司;阿拉伯树胶粉(分析纯) 上海源叶生物有限公司;活性炭粉 浙江兴达活性炭有限公司。
LDZX-50KBS高压蒸汽灭菌锅 上海申安医疗器械厂;50L浓缩罐、NSQ-0.05浓缩器 华强中天流体设备(北京)有限公司;FBR-GDM30-500L(30 L)发酵罐 镇江福倍尔生物工程有限公司;ZQA-380-18电加热蒸汽发生器 东莞市蒸启安环保科技有限公司;GQLY-125N管式分离机 辽阳中联制药机械有限公司;101A-3电热恒温干燥箱 上海康路仪器设备有限公司;DHP-360电热恒温培养箱 北京市永久光明医疗器械有限公司;PHS-25B酸度计 上海大普仪器有限公司;SW-CJ-2D超净工作台 沈阳鑫科之杰仪器化玻有限公司;H1650医用离心机 长沙湘仪离心机仪器有限公司;TG1650-WS台式高速离心机 上海卢湘仪离心机仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 工艺流程
1.2.2 操作要点
1.2.2.1 原料预处理
将燕麦麸皮用水全部浸透,加水量为发酵重量的3/10,搅拌均匀不结块,蒸煮30 min,冷却后细纱布过滤;再将麦芽、山楂、大枣、橘皮、沙棘直接投入多功能提取罐中,加水蒸煮60 min过滤。
1.2.2.2 发酵培养基配制将
将过滤后的料液打入二级发酵罐,滤液量为发酵重量的98%(误差为±1%);将浓缩复合果蔬汁、低聚异麦芽糖按比例投入滤液中,和料液混合均匀(所有原料均溶解)。
1.2.2.3 发酵
无菌接种:接种量为3%~5%。搅动培养,装液量:50%~75%;搅动培养,搅拌速度:30~50 r/min;通气量为0;初始气压0.02~0.03 MPa;培养时间68±4 h;发酵液状态:黄色液体,口感酸,发酵香,淡淡的麦芽味道及果蔬味。
1.2.2.4 离心、浓缩
离心液状态:浅黄色液体,溶液均一,无杂质。浓缩至1.5倍,浓缩参数:温度60~70 ℃,一级浓缩器压力−0.090±0.005 MPa,二级浓缩器压力−0.080±0.005 MPa。
1.2.2.5 灭菌
在85~95 ℃条件下灭菌20~30 min;灭菌后料液取样检测无杂菌。
1.2.3 单因素实验
按照1.2.1中工艺流程,选取发酵时间(h)、发酵温度(℃)、低聚异麦芽糖添加量(%)、燕麦麸皮添加量(%)4个因素作为单因素考察指标,研究不同条件下综合果蔬酵素的感官评分。
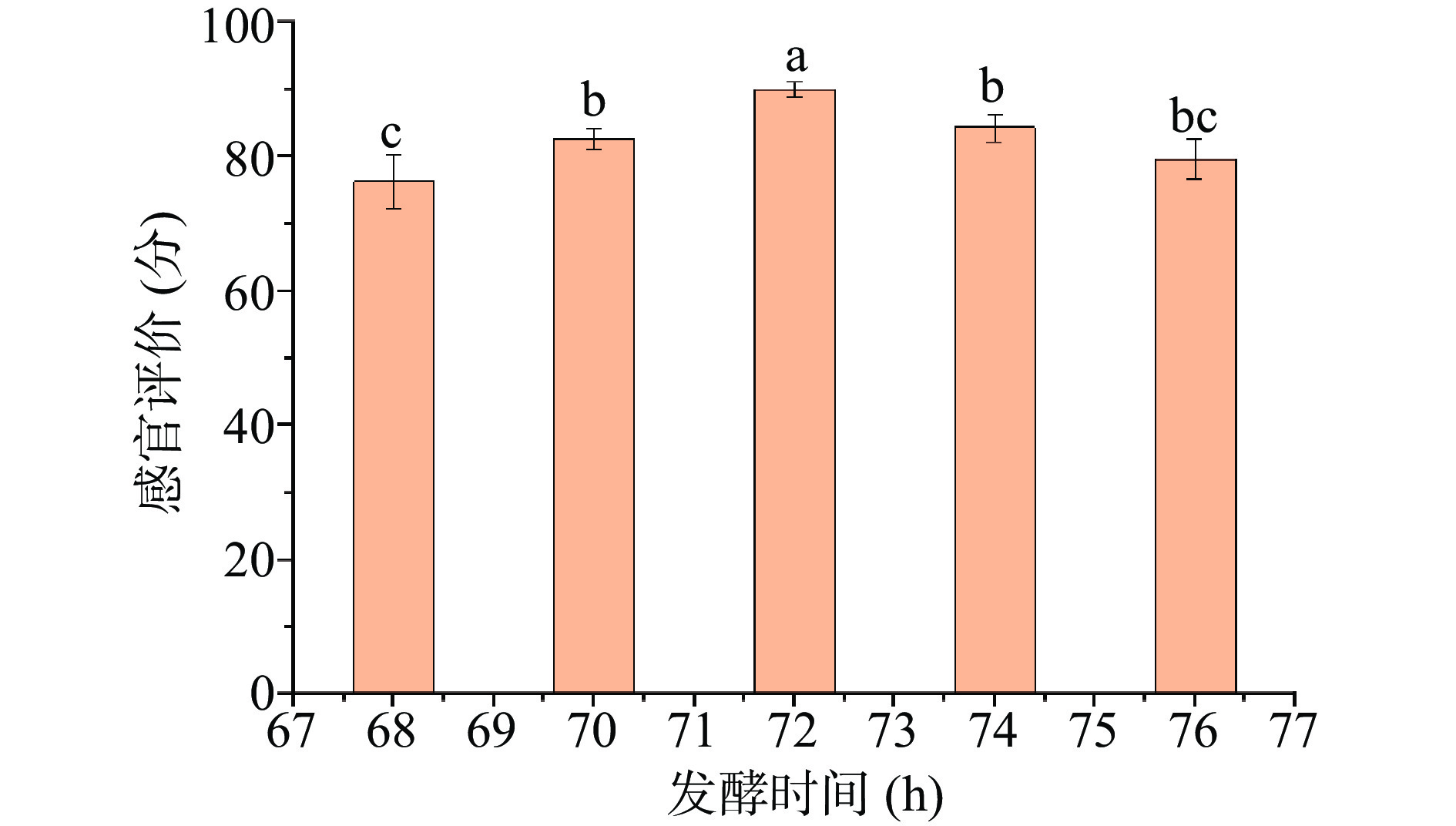
1.2.3.1 发酵时间对综合果蔬酵素感官品质的影响
以燕麦麸皮、麦芽、山楂、大枣、橘皮、沙棘、浓缩复合果蔬汁和低聚异麦芽糖为原料,选用植物乳杆菌、罗伊乳杆菌、鼠李糖乳杆菌为发酵菌株,确定低聚果糖添加量为3%、燕麦麸皮添加量为3%,发酵温度为37 ℃,发酵时间分别为68、70、72、74和76 h,以感官评价为质量检测指标,根据综合果蔬酵素的感官评分,研究发酵时间对感官品质的影响。
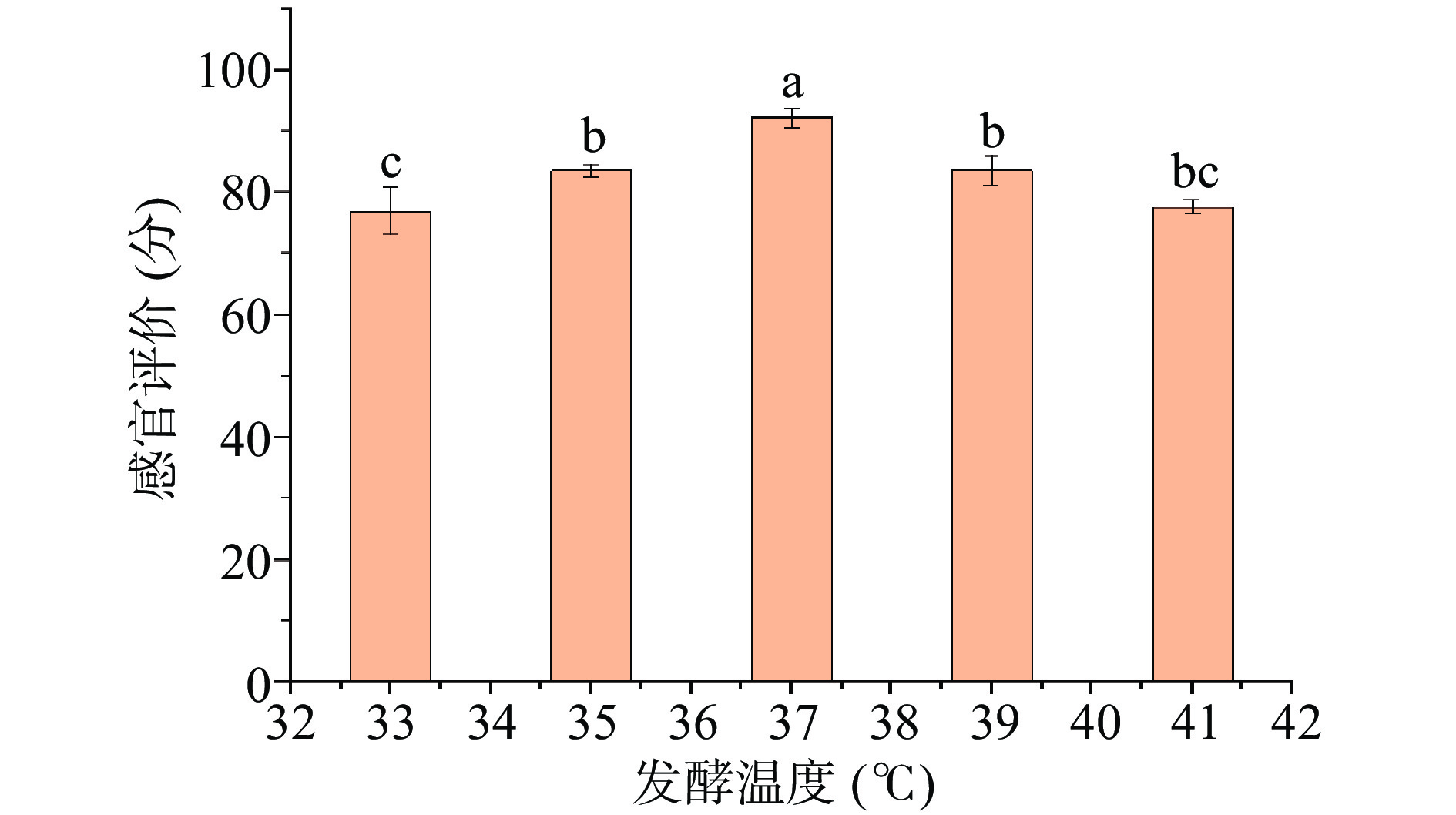
1.2.3.2 发酵温度对综合果蔬酵素感官品质的影响
以燕麦麸皮、麦芽、山楂、大枣、橘皮、沙棘、浓缩复合果蔬汁和低聚异麦芽糖为原料,选用植物乳杆菌、罗伊乳杆菌、鼠李糖乳杆菌为发酵菌株,确定发酵时间为72 h,低聚异麦芽糖添加量为3%,燕麦麸皮添加量为3%,发酵时间分别为33、35、37、39和41 ℃,以感官评价为质量检测指标,根据综合果蔬酵素的感官评分,研究发酵时间对感官品质的影响。
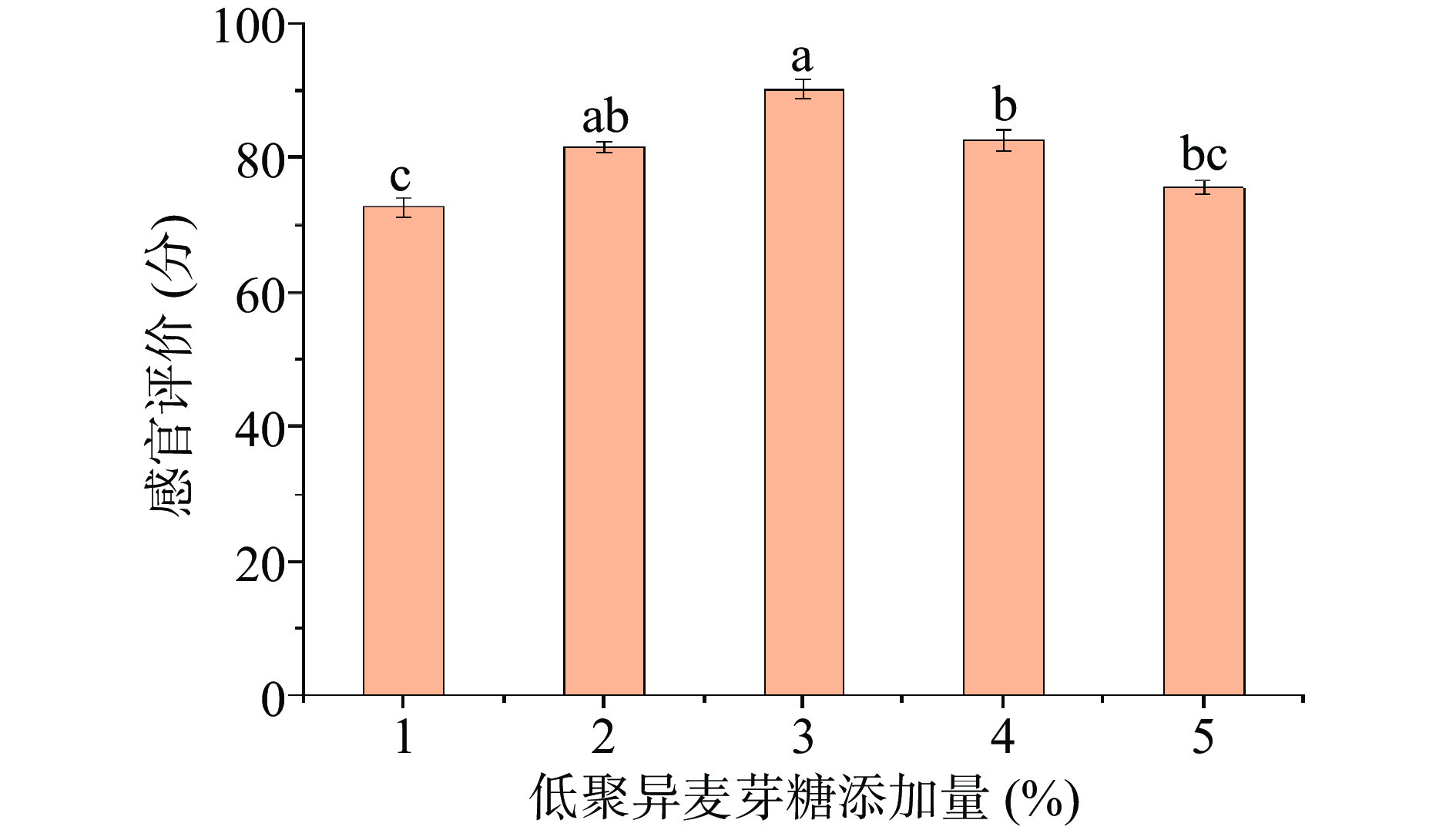
1.2.3.3 低聚异麦芽糖添加量对综合果蔬酵素感官品质的影响
以燕麦麸皮、麦芽、山楂、大枣、橘皮、沙棘、浓缩复合果蔬汁和低聚异麦芽糖为原料,选用植物乳杆菌、罗伊乳杆菌、鼠李糖乳杆菌为发酵菌株,确定发酵时间为72 h,发酵温度为37 ℃,燕麦麸皮添加量为3%,低聚异麦芽糖添加量为分别为1%、2%、3%、4%和5%,以感官评价为质量检测指标,根据综合果蔬酵素的感官评分,研究发酵时间对感官品质的影响。
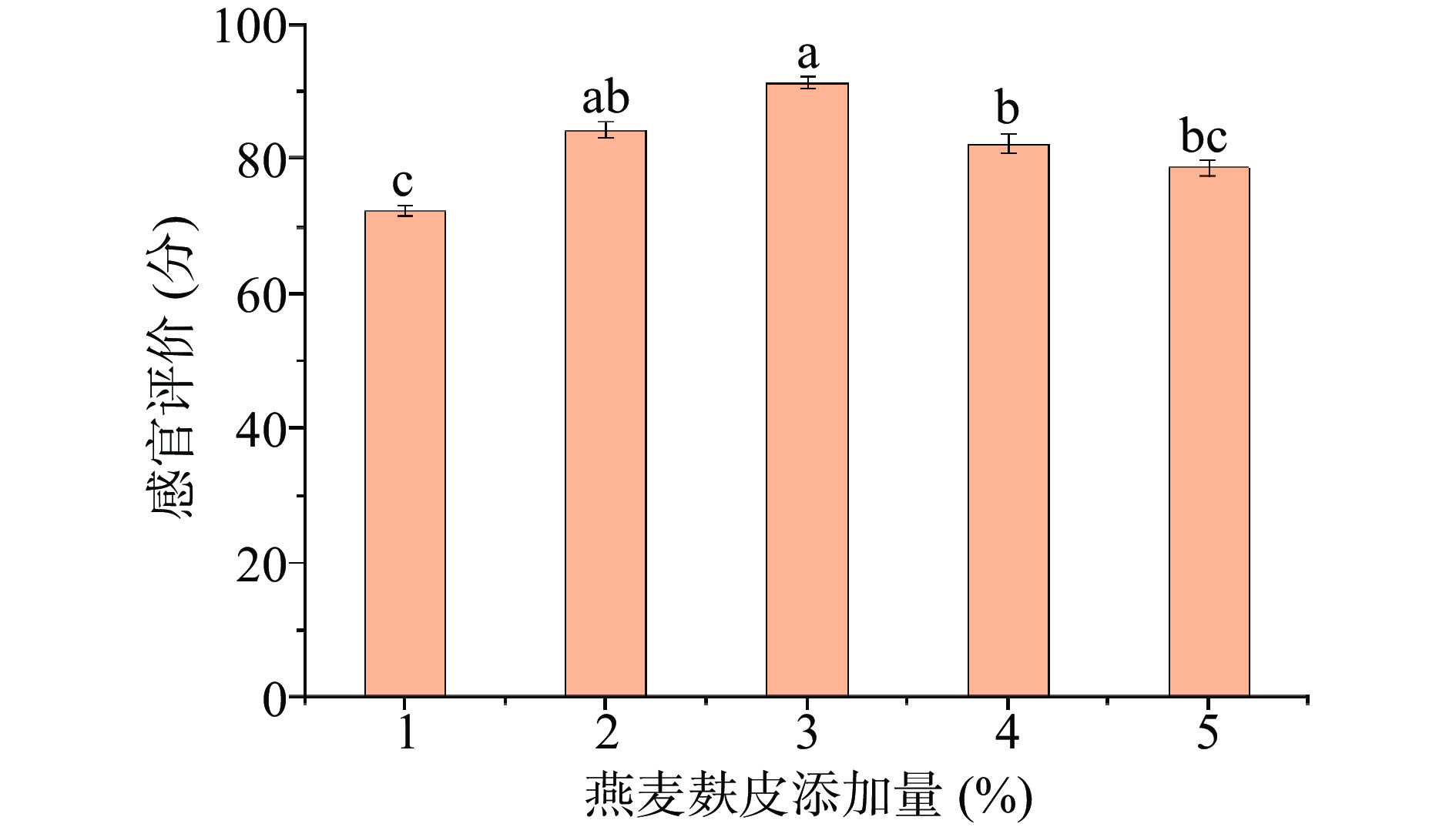
1.2.3.4 燕麦麸皮添加量对综合果蔬酵素感官品质的影响
以燕麦麸皮、麦芽、山楂、大枣、橘皮、沙棘、浓缩复合果蔬汁和低聚异麦芽糖为原料,选用植物乳杆菌、罗伊乳杆菌、鼠李糖乳杆菌为发酵菌株,确定发酵时间为72 h,发酵温度为37 ℃,低聚异麦芽糖添加量为3%,燕麦麸皮添加量为分别为1%、2%、3%、4%和5%,以感官评价为质量检测指标,根据综合果蔬酵素的感官评分,研究发酵时间对感官品质的影响。
1.2.4 感官评价
选取经过专业受训的50人对对综合果蔬酵素进行感官测评[9],男女各25人,年龄为25~50岁不等,分别从色泽、香气、口感、状态对酵素产品进行感官评价,具体感官评分标准见表1。
表 1 感官评分标准Table 1. Sensory scoring criteria项目 指标 得分 色泽(20分) 金黄色,清澈透亮且光泽协调 15~20 黄色,清澈透亮,无光泽 10~14 淡黄色,澄清度低,无光泽 <10 香气(30分) 香气醇厚,果味浓郁,香味协调 25~30 香气醇厚,果味寡淡,香味不突出 20~24 无明显香气,无其他异味 <20 口感(40分) 口感纯正,柔和协调,回味甘甜 35~40 口感柔和,不够醇厚 30~34 口感缺少柔和性,无回味 <30 状态(10分) 状态均匀,无沉淀物 8~10 状态不稳定,出现少许沉淀物 5~7 状态浑浊,出现沉淀物 <5 1.2.5 响应面试验设计
采用四因素三水平响应面试验,以感官评分为指标,对发酵时间(h)、发酵温度(℃)、低聚异麦芽糖添加量(%)、燕麦麸皮添加量(%)4个工艺参数进行优化,确定最优综合果蔬酵素的加工工艺[10],试验设计见表2。
表 2 响应面试验因素水平设计Table 2. Response surface coding table因素 水平 −1 0 1 A发酵时间(h) 70 72 74 B发酵温度(℃) 35 37 39 C低聚异麦芽糖添加量(%) 2 3 4 D燕麦麸皮添加量(%) 2 3 4 1.2.6 综合果蔬酵素特征性指标测定
综合果蔬酵素的特征性成分游离氨基酸、乳酸及γ-氨基丁酸含量的测定委托谱尼测试集团股份有限公司完成。
1.2.7 综合果蔬酵素营养成分测定
综合果蔬酵素的营养成分水分、灰分、能量、蛋白质、脂肪、碳水化合物、钠含量的测定委托广电计量检测(沈阳)有限公司完成测定,总膳食纤维的测定委托河南广电计量检测有限公司完成测定。
1.2.8 动物饲养与分组
试验动物福利伦理审查批文号为HZYX2207153750。将试验雄性ICR小鼠饲养在安静、清洁、通风和温暖的环境中,环境温度在(22±1) ℃,湿度在45%~65%,保证小鼠自由饮食。将小鼠按体质量(bw),随机分为10组,每组10只。前5组用于小肠运动试验,后5组用于小鼠排便试验。设计小鼠便秘模型组(服用盐酸洛哌丁胺组),对照组(不服用盐酸洛哌丁胺)和便秘组灌胃等体积蒸馏水(10 mL/(kg·d)),剂量组分为低剂量组、中剂量组和高剂量组,综合果蔬酵素每天按5 、10和15 mL/kg,各实验组连续灌胃14 d,期间自由饮水、自由进食标准饲料。10组小鼠灌胃前和灌胃14 d后测定小鼠体重[11]。
1.2.9 小鼠小肠推进试验
配制墨汁:将5 g阿拉伯胶与40 mL蒸馏水混合均匀后蒸煮,直至煮沸,加入2.5 g活性炭粉搅拌均匀后煮沸,反复沸腾3次后进行冷却,容量瓶定容至50 mL,冷藏备用。
小鼠经过按不同剂量(按1.2.7处理)连续灌胃14 d后,将小鼠禁食不限制水饲喂16 h,各组经口灌胃5 mg/kg·bw盐酸洛哌丁胺,对照组除外,构建小鼠便秘模型。当便秘组小肠推进率低于对照组时,小鼠便秘模型构建成功。建模0.5 h后将5组试验小鼠分别灌胃墨汁(10 mg/kg·bw),30 min后脱颈椎处死小鼠,测量小肠全长和小肠自幽门处到墨汁前进的距离,计算墨汁推进率。
墨汁推进率(%)=墨汁移动距离/小肠全长×100 1.2.10 小鼠排便试验
同1.2.8中构建小鼠便秘模型、同等灌胃剂量。5组小鼠经墨汁灌胃后,正常饮水,记录每只小鼠首次排出黑便时间和每组小鼠在6 h内黑便排出粒数[12]。
1.3 数据处理
数据以
¯x ±SD表示,应用SPSS19.0软件进行差异显著性分析,P<0.05或P<0.01具有统计学意义,Origin 8.5软件作图。2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素实验结果
2.1.1 发酵时间对综合果蔬酵素感官的影响
由图1可知,不同发酵时间对于感官评分的影响显著(P<0.05),随着发酵时间延长,感官评分随之上升,发酵72 h感官评分达到最高90.00分。发酵时间超过72 h,感官评分逐渐下降,分析原因可能是发酵时间过长,导致酵素中乳酸菌活性下降,进而分解酵素产品中的酚类物质,产酸较多使综合果蔬酵素感官评分下降[13]。
2.1.2 发酵温度对综合果蔬酵素感官的影响
结果如图2所示,发酵温度在37 ℃时感官评分最高在92.33分,发酵温度超过37 ℃后感官评分显著(P<0.05)下降趋势。分析原因可能是过高的温度不适宜微生物代谢,益生菌不能发挥作用,酵素内存在较少益生菌代谢产物,导致综合果蔬酵素感官评分降低[14]。
2.1.3 低聚异麦芽糖添加量对综合果蔬酵素感官的影响
低聚异麦芽糖不同添加量对综合果蔬酵素感官评分的影响结果如图3所示。随着低聚异麦芽糖添加量增加,感官评分逐渐升高,在添加量为3%时感官评分达到最高90.33分,低聚异麦芽糖添加量超过3%时感官评分显著(P<0.05)下降。郭留城等[15]研究发现低聚异麦芽糖的过度添加,影响其他成分的风味,使得甜味浓郁导致感官评分下降。刘重慧等[16]研究发现低聚异麦芽糖可促进益生菌产生短链脂肪酸和短链有机酸,短链脂肪酸对于维持大肠的正常功能和结肠上皮细胞的形态和功能具有重要作用。酵素的感官评分显著(P<0.05)降低,分析原因可能是低聚异麦芽糖在促进益生菌发挥作用后,剩余过多的低聚异麦芽糖无法发挥作用,导致甜度增加影响综合果蔬酵素整体口感,酵素液的流动性等感官因素受到影响,因此选择合适添加量为3%。
2.1.4 燕麦麸皮添加量对综合果蔬酵素感官的影响
燕麦麸皮不同添加量对综合果蔬酵素感官评分的影响,结果如图4所示。随着麦芽麸皮添加量增多,由于燕麦麸皮原料自身口感使得感官评分逐渐升高,添加量在3%时感官评分最高为91.33分,超过3%添加量时感官评分显著(P<0.05)下降,燕麦麸皮中富含膳食纤维,过多的燕麦麸皮导致酵素口感粗糙颜色加深,影响酵素整体的感官评分,因此最优添加量为3%。
2.2 响应面试验结果
2.2.1 综合果蔬酵素的响应面设计
对发酵时间(A)、发酵温度(B)、低聚异麦芽糖添加量(C)、燕麦麸皮添加量(C)进行四因素三水平响应面试验,试验设计及结果见表3。
表 3 响应面设计方案及结果Table 3. Response surface design scheme and results实验号 因素 Y:感官评分(分) A B C D 1 0 0 0 0 95.45 2 1 0 0 1 75.16 3 0 0 −1 1 86.49 4 0 −1 1 0 87.13 5 −1 0 −1 0 79.46 6 1 −1 0 0 75.43 7 −1 0 0 1 78.53 8 1 0 0 −1 77.36 9 0 −1 0 −1 87.13 10 0 0 0 0 94.13 11 0 1 0 1 89.16 12 0 0 0 0 97.16 13 −1 0 0 −1 79.13 14 0 1 −1 0 89.17 15 −1 0 1 0 79.63 16 0 1 0 −1 86.67 17 0 0 1 −1 89.14 18 1 0 1 0 75.39 19 0 0 0 0 93.46 20 0 1 1 0 87.19 21 −1 −1 0 0 79.03 22 0 −1 −1 0 87.11 23 0 0 −1 −1 90.13 24 0 0 0 0 94.16 25 −1 1 0 0 79.01 26 1 0 −1 0 80.37 27 0 −1 0 1 85.39 28 1 1 0 0 79.93 29 0 0 1 1 89.17 2.2.2 综合果蔬酵素响应面试验结果分析
应用Design-Expert V 8.0.6软件对表4的试验数据进行多元回归拟合,得回归方程:
表 4 回归模型方差分析Table 4. Regression model variance analysis项目 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P 模型 1186.63 14 84.76 54.33 <0.0001 A 10.36 1 10.36 6.64 0.0219 B 8.18 1 8.18 5.25 0.0380 C 2.15 1 2.15 1.38 0.2600 D 2.67 1 2.67 1.71 0.2119 AB 5.11 1 5.11 3.27 0.0919 AC 6.63 1 6.63 4.25 0.0583 AD 0.64 1 0.64 0.41 0.5322 BC 1.00 1 1.00 0.64 0.4367 BD 4.47 1 4.47 2.87 0.1125 CD 3.37 1 3.37 2.16 0.1639 A2 1 120.84 1 1120.84 718.43 <0.0001 B2 98.92 1 98.92 63.41 <0.0001 C2 54.60 1 54.60 35.00 <0.0001 D2 92.02 1 92.02 58.98 <0.0001 残差 21.84 14 1.56 失拟项 13.22 10 1.32 0.61 0.7583 纯误差 8.62 4 2.16 总离差 1208.47 28 注:P<0.01表示极显著;0.01<P<0.05表示显著。 Y=94.87−0.93A+0.83B−0.42C−0.47D+1.13AB−1.29AC−0.4AD−0.5BC+1.06BD+0.92CD−13.15A2−3.91B2−2.9C2−3.77D2
对模型方程进行方差分析见表4。由表4可知,影响综合果蔬酵素感官评分的顺序为:发酵时间>发酵温度>燕麦麸皮添加量>低聚异麦芽糖添加量。回归方程模型P<0.0001,说明该方程模型极显著,失拟项P=0.7583不显著,说明该回归方程是可行的。模型的决定系数R2为0.9819,
R2adj 为0.9639,可以准确预测实际试验结果。由此得出,各试验因素对响应值的影响不是简单的线性关系[17]。2.2.3 响应面两两因素交互作用
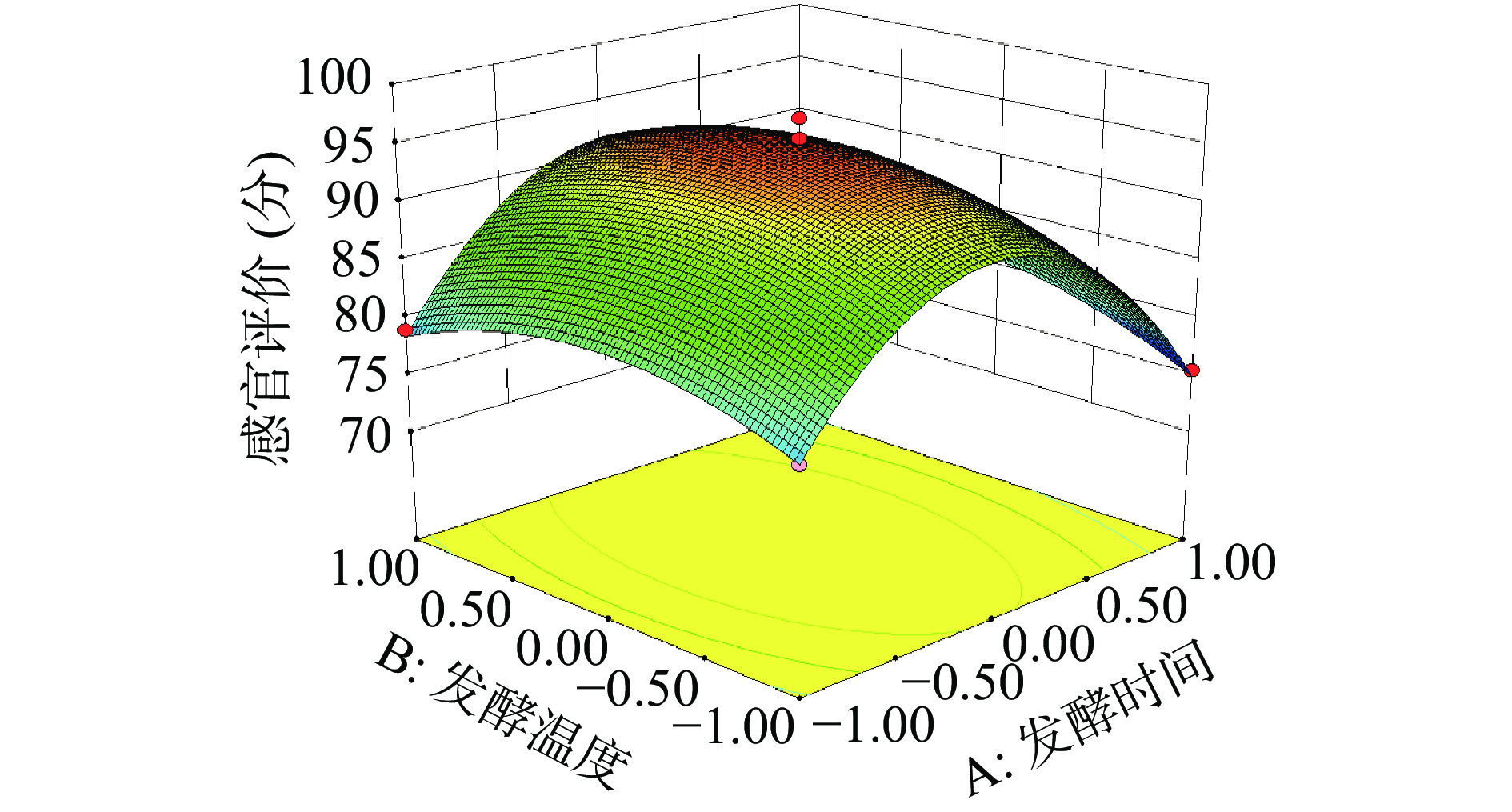
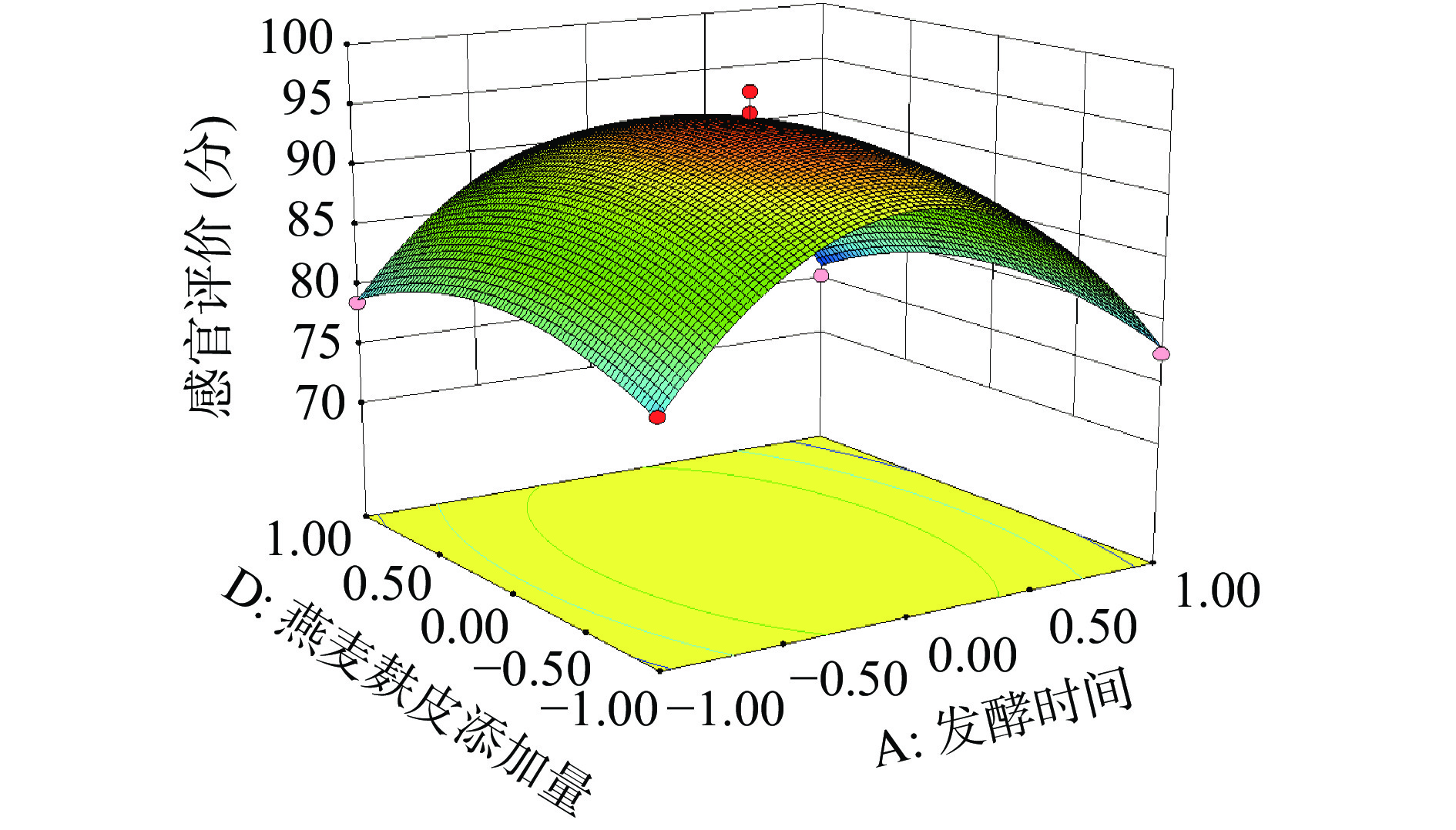
发酵时间(A)P值=0.0219<0.05,表明发酵时间对综合果蔬酵素感官评分起到显著影响作用,发酵温度(B)P值=0.0380<0.05,表明发酵温度对综合果蔬酵素感官评分起到显著影响作用。由图5可以看出当低聚异麦芽糖添加量和燕麦麸皮添加量确定时,发酵时间和发酵温度的坡度凸起越明显,表明AB交互作用越明显。BC、BD、CD交互作用响应面三维图坡度平缓,表明两两因素交互作用不明显,对综合果蔬酵素感官评分影响较小,由BC的P值=0.4367>0.5,BD的P值=0.1125>0.5,CD P值=0.1639>0.5均可证明立体图结果[18]。
2.2.4 最优工艺配方验证试验
采用上述响应面法制备综合果蔬酵素,根据分析计算,得出响应面优化综合果蔬酵素最优工艺条件为发酵时间为71.6 h,发酵温度为37.5 ℃,低聚异麦芽糖添加量为2.9%,燕麦麸皮添加量为2.9%,预测感官评分94.96分。验证试验中选取发酵时间为72 h,发酵温度为37 ℃,低聚异麦芽糖添加量为3%,麦芽麸皮添加量为3%,在此条件下进行3次平行试验,其感官评分分别为95、96、95,均值为95.33分,与预测值较为接近,表明预测模型具有良好的可靠性。
2.3 综合果蔬酵素成分测定结果
2.3.1 综合果蔬酵素特征性成分测定
应用优化后的配方制备综合果蔬酵素,测定特征性成分指标结果如表5所示。
表 5 综合果蔬酵素特征性成分测定结果Table 5. Determination results of characteristic components of dietary fiber enzymes in fruits and vegetables检验项目 限值 检验结果 检验标准 乳酸(mg·kg−1) ≥550 1.1×103 GB 5009.157-2016 γ-氨基丁酸(mg·kg−1) ≥0.03 100 QB/T 4587-2013附录A 游离氨基酸(mg·100 g−1) ≥33 1.2×102 GB 5009.124-2016 乳酸有很强的防腐保鲜功效,具有调节pH、抑菌、延长保质期、调味、保持食品色泽、提高产品质量等作用,由于乳酸的酸味温和适中,还可作为软饮料和果汁的首选酸味剂,综合果蔬酵素中富含1100 mg/kg乳酸,有效成分含量较高[19-20]。γ-氨基丁酸具有多种功能,包括镇静神经、抗焦虑、降低血压、提高脑活力,促进乙醇代谢、防止皮肤老化、消除体臭、改善脂质代谢,防止动脉硬化高效减肥等[21];果蔬膳食纤维中富含γ-氨基丁酸100 mg/kg,可镇静安神,有效改善代谢[22]。综合果蔬酵素中含有120 mg/100 g的游离氨基酸,可消除疲劳,改善睡眠质量,提高免疫力等功效[23]。
2.3.2 综合果蔬酵素营养成分
测定综合果蔬酵素产品中营养成分结果如表6所示,酵素中含有的基本营养成分,另含有膳食纤维,其在消化系统中有吸收水份的作用,可增加肠道及胃内的食物体积,可增加饱足感,又能促进肠胃蠕动,可舒解便秘。同时膳食纤维也能吸附肠道中的有害物质以便排出,改善肠道菌群,为益生菌的增殖提供能量和营养[24-25]。
表 6 综合果蔬酵素营养成分测定结果Table 6. Determination results of integrated fruit and vegetable enzymenutrients in fruits and vegetables检测项目 单位 检测依据 检测结果 水分 g/100 mL GB 5009.3-2016 第一法 67.9 灰分 g/100 mL GB 5009.4-2016 第一法 0.67 能量 kJ/100 mL GB 28050-2011 719 蛋白质 g/100 mL GB 5009.5-2016 第一法 0.074 脂肪 g/100 mL GB 5009.6-2016 第二法 0.2 碳水化合物 g/100 mL GB 28050-2011 41.8 钠 mg/100 mL GB 5009.91-2017 第一法 17.7 总膳食纤维 g/100 mL GB 5009.88-2014 0.249 2.4 小鼠试验结果
2.4.1 小鼠墨汁推进率试验中体重的变化
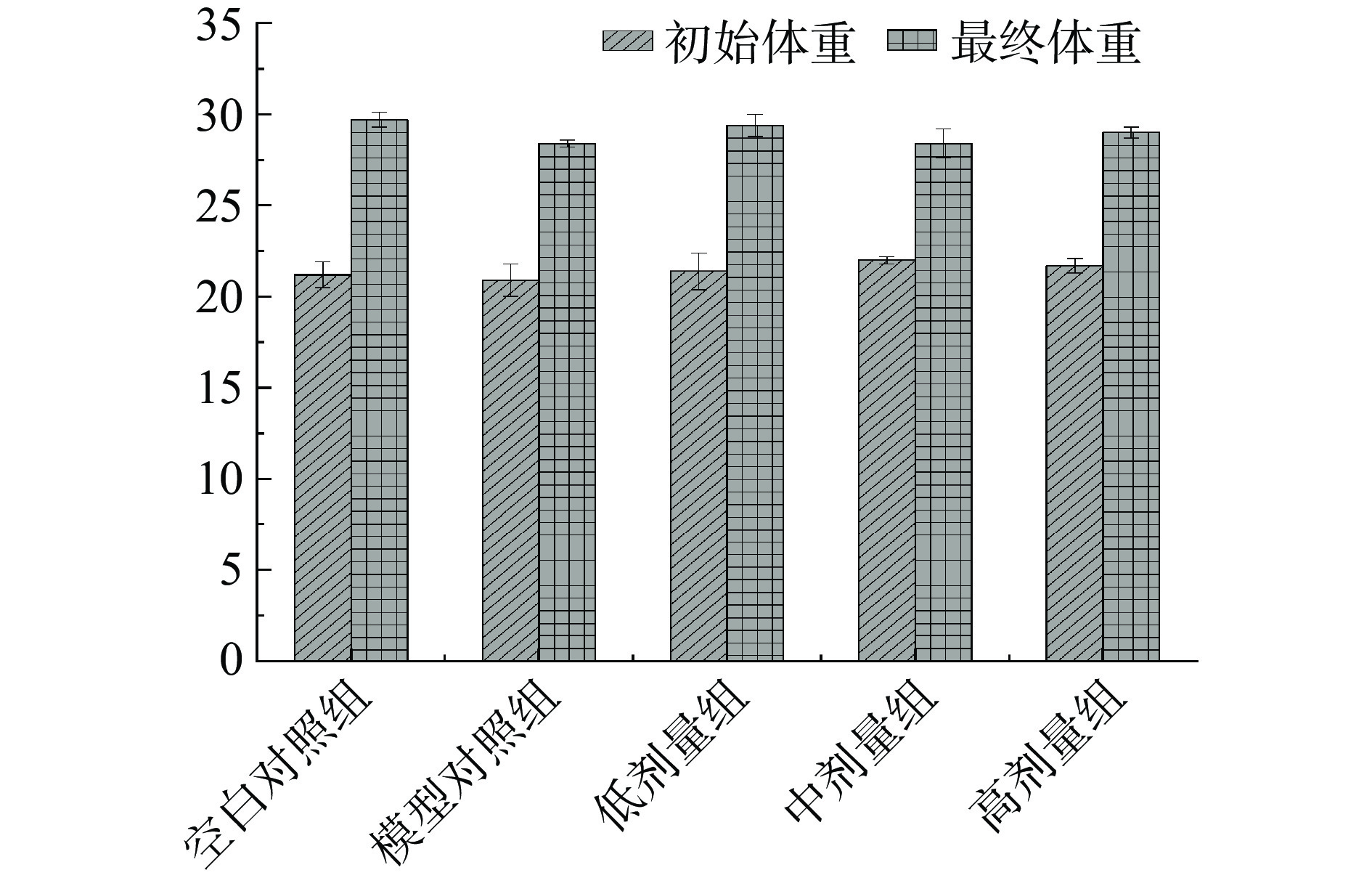
为探究综合果蔬酵素服用安全性,测定小鼠服用不同剂量酵素对小鼠体重的影响。小鼠小肠墨汁推进率试验如图8所示,组间小鼠体重无显著差异(P>0.05),试验过程中小鼠生命特征正常,饮食饮水良好,无呕吐腹泻等不良反应,体重出现逐渐上升趋势,说明综合果蔬酵素不同级联对小鼠体重无明显影响。
![]() 图 8 小鼠小肠运动中体重变化注:表中各组间比较均无显著性差异(P>0.05);图9同。Figure 8. Changes in body weight during small intestine movement in mice
图 8 小鼠小肠运动中体重变化注:表中各组间比较均无显著性差异(P>0.05);图9同。Figure 8. Changes in body weight during small intestine movement in mice2.4.2 小鼠排便试验中小鼠体重变化
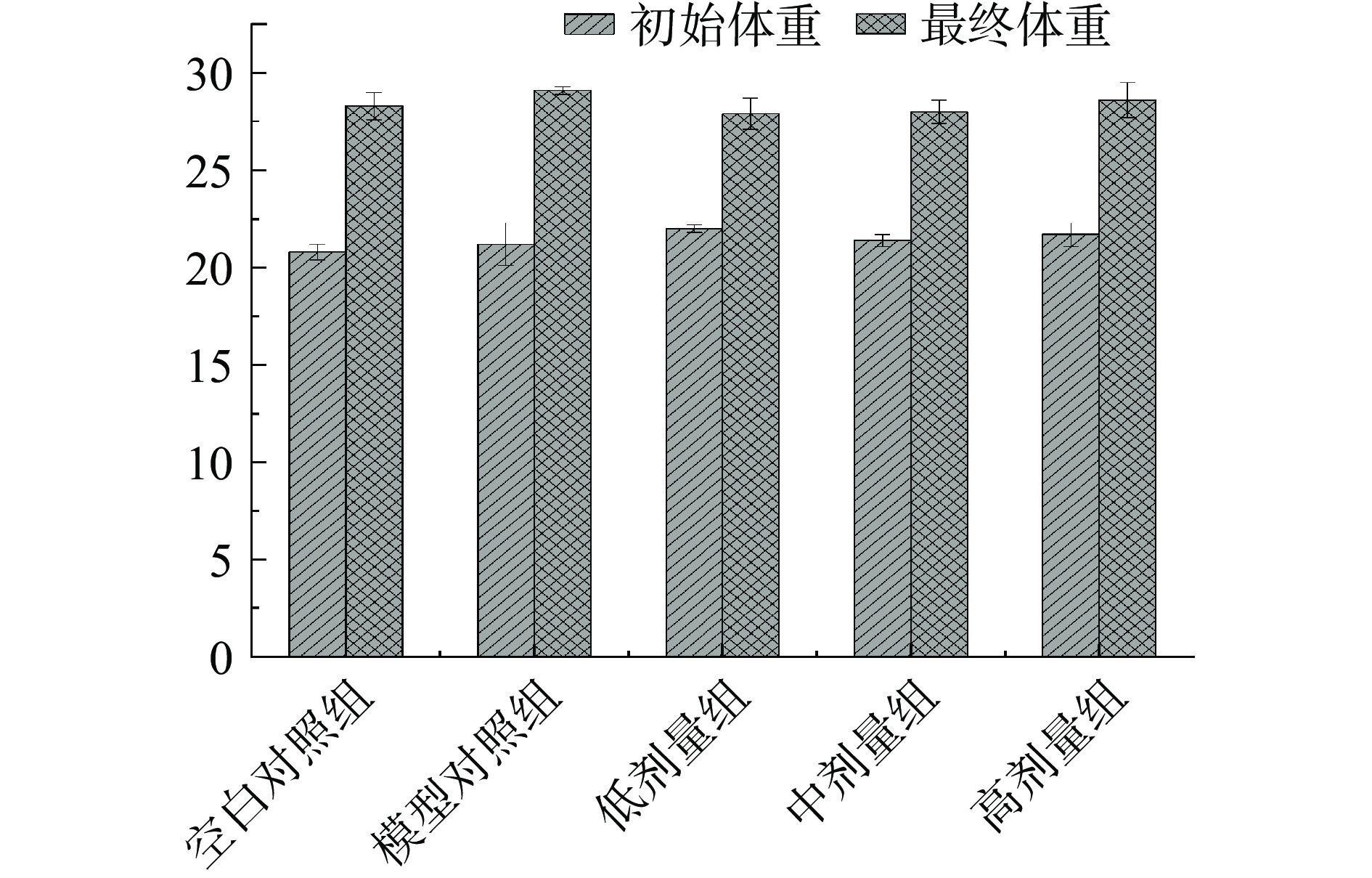
探究综合果蔬酵素服用安全性,测定小鼠服用不同剂量酵素对小鼠体重的影响。小鼠粪便试验中体重变化如图9所示,组间小鼠体重无显著差异(P>0.05),试验过程中小鼠生命体征健康,饮食饮水良好,无呕吐腹泻等不良反应,体重出现逐渐上升趋势,说明综合果蔬酵素不同级联对小鼠体重无明显影响。
2.4.3 小鼠墨汁推进率试验结果
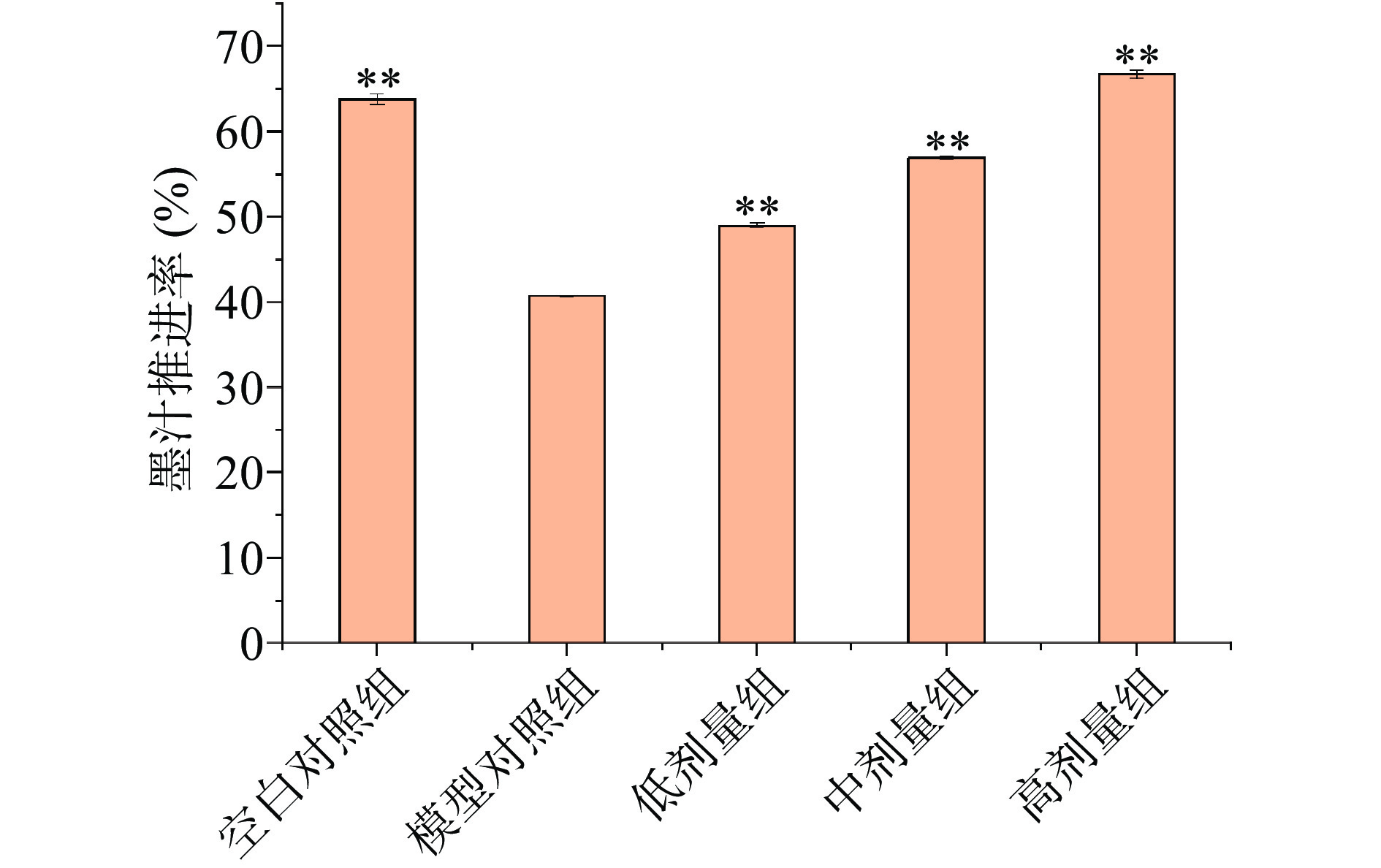
为验证综合果蔬酵素润肠通便功效,测定小鼠服用不同剂量酵素后,小肠内墨汁推进率,结果如图10所示。模型对照组的墨汁推进率为40.8%,极显著低于空白对照组(P<0.01),说明构建小鼠便秘模型成功[26]。
![]() 图 10 小鼠墨汁推进率试验结果注:与模型对照组比较,**为差异极显著 P<0.01;图11同。Figure 10. Experimental results of mouse ink propulsion rate
图 10 小鼠墨汁推进率试验结果注:与模型对照组比较,**为差异极显著 P<0.01;图11同。Figure 10. Experimental results of mouse ink propulsion rate小鼠服用不同剂量的综合果蔬酵素墨汁推进率不同,低剂量组、中剂量组和高剂量对比模型对照组,墨汁推进率均有所提升。服用高剂量的小鼠墨汁推进率高达66.7%,极显著(P<0.01)缩短了粪便在肠道内滞留时间。试验表明当综合果蔬酵素每天服用量达到5 mL/kg以上可发挥润肠通便作用。分析原因产品中适量添加低聚异麦芽糖,促进益生菌发挥作用,且成品中含有膳食纤维,可有效促进肠道蠕动,有效缩短粪便停留时间[27-28]。
2.4.4 小鼠排便试验结果
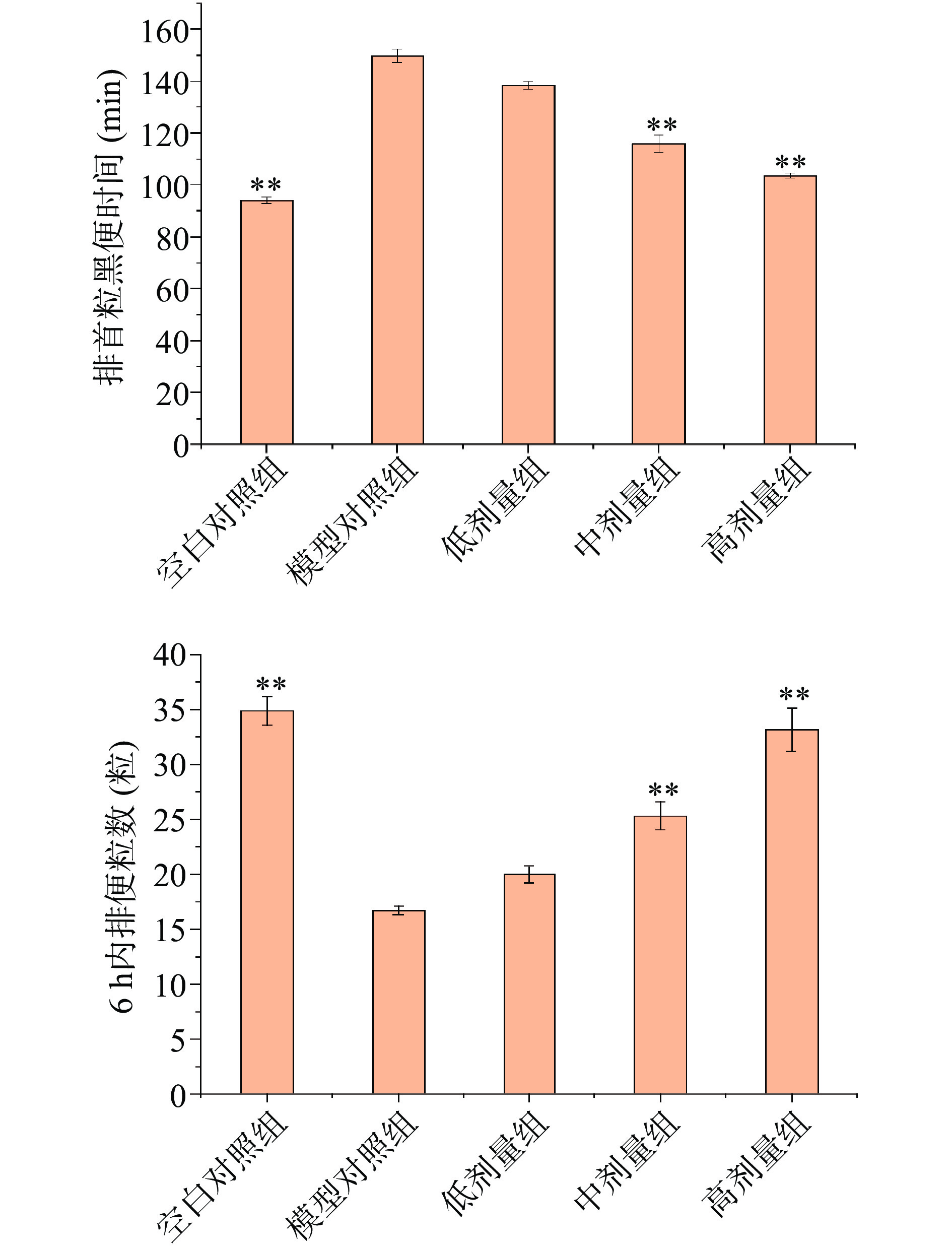
小鼠经过墨汁灌胃后,首粒黑便排出时间和6 h内排便粒数反映出小鼠排便效果,验证小鼠服用综合果蔬酵素的润肠通便作用。试验结果如图11所示,小鼠首粒黑便排出时间和6 h内排便粒数的空白对照组和模型对照组存在极显著差异(P<0.01),小鼠便秘试验模型构建成功。
与模型组对比,小鼠首粒黑便排出时间不同剂量组均有所减少,服用高剂量组小鼠排便时间为103.72 min,中剂量组和高剂量组均极显著缩短排便时间( P<0.01),分别缩短33.92和46.71 min。6 h内排便粒数高剂量组达到33.16粒,极显著(P<0.01)高于模型对照组16.74粒。试验结果说明综合果蔬酵素有较好的润肠通便功效,其中高剂量组的综合果蔬酵素效果更为显著[29-30]。
3. 结论
本试验应用单因素和响应面法优化综合果蔬酵素感官评分,得出最优添加配方为:发酵时间为72 h,发酵温度为37 ℃,低聚异麦芽糖添加量为3%,麦芽麸皮添加量为3%,在此条件下感官评分为95.33分,与预测值基本一致。测定综合果蔬酵素的营养成分和特征性指标,结果显示酵素产品内含有膳食纤维、γ-氨基丁酸等有效成分。对综合果蔬酵素的润肠通便功效进行探究,通过小鼠墨汁推进率和排便试验可以得出,不同剂量的综合果蔬酵素对小鼠体质量无显著影响,高剂量的小鼠墨汁推进率高达66.7%,6 h内排便粒数高剂量组达到33.16粒。综上所述根据最优工艺添加量制备的果蔬膳食纤维,具有较好的感官评分,小鼠试验中,可明显缩短粪便在小肠内的停留时间,具有较好的润肠通便功效。与以往研究相比应用不同的原料,根据原料特性优化其最佳加工工艺,开发效果更好的适用于便秘人群的一款酵素产品,为生产缓解便秘的产品提供研究基础,同时满足便秘人群的需要。
酵素是由水果、蔬菜等物质经过益生菌发酵而成的一种食品,发挥润肠通便的主要功效物质为膳食纤维、低聚糖、有机酸,可刺激肠胃蠕动,改善肠道菌群,利于润肠通便。研究在今后的研究中会作出人体体外试验方向的拓展,以期提供更为高效的缓解便秘的酵素。
-
图 8 小鼠小肠运动中体重变化
注:表中各组间比较均无显著性差异(P>0.05);图9同。
Figure 8. Changes in body weight during small intestine movement in mice
图 10 小鼠墨汁推进率试验结果
注:与模型对照组比较,**为差异极显著 P<0.01;图11同。
Figure 10. Experimental results of mouse ink propulsion rate
表 1 感官评分标准
Table 1 Sensory scoring criteria
项目 指标 得分 色泽(20分) 金黄色,清澈透亮且光泽协调 15~20 黄色,清澈透亮,无光泽 10~14 淡黄色,澄清度低,无光泽 <10 香气(30分) 香气醇厚,果味浓郁,香味协调 25~30 香气醇厚,果味寡淡,香味不突出 20~24 无明显香气,无其他异味 <20 口感(40分) 口感纯正,柔和协调,回味甘甜 35~40 口感柔和,不够醇厚 30~34 口感缺少柔和性,无回味 <30 状态(10分) 状态均匀,无沉淀物 8~10 状态不稳定,出现少许沉淀物 5~7 状态浑浊,出现沉淀物 <5 表 2 响应面试验因素水平设计
Table 2 Response surface coding table
因素 水平 −1 0 1 A发酵时间(h) 70 72 74 B发酵温度(℃) 35 37 39 C低聚异麦芽糖添加量(%) 2 3 4 D燕麦麸皮添加量(%) 2 3 4 表 3 响应面设计方案及结果
Table 3 Response surface design scheme and results
实验号 因素 Y:感官评分(分) A B C D 1 0 0 0 0 95.45 2 1 0 0 1 75.16 3 0 0 −1 1 86.49 4 0 −1 1 0 87.13 5 −1 0 −1 0 79.46 6 1 −1 0 0 75.43 7 −1 0 0 1 78.53 8 1 0 0 −1 77.36 9 0 −1 0 −1 87.13 10 0 0 0 0 94.13 11 0 1 0 1 89.16 12 0 0 0 0 97.16 13 −1 0 0 −1 79.13 14 0 1 −1 0 89.17 15 −1 0 1 0 79.63 16 0 1 0 −1 86.67 17 0 0 1 −1 89.14 18 1 0 1 0 75.39 19 0 0 0 0 93.46 20 0 1 1 0 87.19 21 −1 −1 0 0 79.03 22 0 −1 −1 0 87.11 23 0 0 −1 −1 90.13 24 0 0 0 0 94.16 25 −1 1 0 0 79.01 26 1 0 −1 0 80.37 27 0 −1 0 1 85.39 28 1 1 0 0 79.93 29 0 0 1 1 89.17 表 4 回归模型方差分析
Table 4 Regression model variance analysis
项目 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P 模型 1186.63 14 84.76 54.33 <0.0001 A 10.36 1 10.36 6.64 0.0219 B 8.18 1 8.18 5.25 0.0380 C 2.15 1 2.15 1.38 0.2600 D 2.67 1 2.67 1.71 0.2119 AB 5.11 1 5.11 3.27 0.0919 AC 6.63 1 6.63 4.25 0.0583 AD 0.64 1 0.64 0.41 0.5322 BC 1.00 1 1.00 0.64 0.4367 BD 4.47 1 4.47 2.87 0.1125 CD 3.37 1 3.37 2.16 0.1639 A2 1 120.84 1 1120.84 718.43 <0.0001 B2 98.92 1 98.92 63.41 <0.0001 C2 54.60 1 54.60 35.00 <0.0001 D2 92.02 1 92.02 58.98 <0.0001 残差 21.84 14 1.56 失拟项 13.22 10 1.32 0.61 0.7583 纯误差 8.62 4 2.16 总离差 1208.47 28 注:P<0.01表示极显著;0.01<P<0.05表示显著。 表 5 综合果蔬酵素特征性成分测定结果
Table 5 Determination results of characteristic components of dietary fiber enzymes in fruits and vegetables
检验项目 限值 检验结果 检验标准 乳酸(mg·kg−1) ≥550 1.1×103 GB 5009.157-2016 γ-氨基丁酸(mg·kg−1) ≥0.03 100 QB/T 4587-2013附录A 游离氨基酸(mg·100 g−1) ≥33 1.2×102 GB 5009.124-2016 表 6 综合果蔬酵素营养成分测定结果
Table 6 Determination results of integrated fruit and vegetable enzymenutrients in fruits and vegetables
检测项目 单位 检测依据 检测结果 水分 g/100 mL GB 5009.3-2016 第一法 67.9 灰分 g/100 mL GB 5009.4-2016 第一法 0.67 能量 kJ/100 mL GB 28050-2011 719 蛋白质 g/100 mL GB 5009.5-2016 第一法 0.074 脂肪 g/100 mL GB 5009.6-2016 第二法 0.2 碳水化合物 g/100 mL GB 28050-2011 41.8 钠 mg/100 mL GB 5009.91-2017 第一法 17.7 总膳食纤维 g/100 mL GB 5009.88-2014 0.249 -
[1] CHEN X, QIU T T, WANG Y, et al. A shigella sp. variant is causally linked to intractable functional constipation[J]. The Journal of Clinical Investigation,2022,132(14):e150097. doi: 10.1172/JCI150097
[2] HE Y H, LIU, XIA C, et al. Laxative effect of mulberry ferment on two models of constipated mice[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2022,90:104971. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2022.104971
[3] TANG R Y, ZHANG J J, NAN H P, et al. Exploring Molecular mechanisms of aloe barbadmsis miller on diphenoxylate-Induced constipation in mice[J]. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine,2022:6225758.
[4] 赵金凤, 曲佳乐, 皮子凤, 等. 植物酵素润肠通便保健功能研究[J]. 食品与发酵科技,2012,48(3):54−56. [ZHAO J F, QU J L, PI Z F, et al. Study on the health care function of relieving constipation of plant enzyme[J]. Food and Fermentation Science & Technology,2012,48(3):54−56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-506X.2012.02-014 [5] 杨彬彦, 党娅, 尤丽. 蓝莓酵素功能特性研究进展[J/OL]. 食品与发酵工业, 2022, 6(6): 1−10. YANG B Y, DANG Y, YOU L. Research progress on functional characteristics of blueberry Jiaosu[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2022, 6(6): 1−10.
[6] 索婧怡, 朱雨婕, 陈磊, 等. 食用酵素的研究及发展前景分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(19):271−283. [SUO J Y, ZHU Y J, CHEN L, et al. The research and development prospect of edible Jiaosu[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(19):271−283. [7] 蒋欣容. 单一及混合乳酸菌发酵果蔬乳饮料对小鼠润肠通便作用的影响[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2017. JIANG X R. Effects of single and mixed lactic acid bacteria fermented fruit and vegetable milk drink on moistening bowel and purging effect in mice[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2017.
[8] 朱艳, 尹曼, 魏颖. 果蔬发酵汁对肠道益生菌及大肠杆菌黏附能力的影响[J]. 食品科技,2019,44(11):9−15. [ZHU Y, YIN M, WEI Y. Effect of fermented juices of fruits and vegetables on the adhesion of intestinal probiotics and Escherichia coli[J]. Food Science and Technology,2019,44(11):9−15. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2019.11.003 [9] 张巧, 柯博芳, 唐小闲, 等. 不同发酵菌种对大果山楂酵素品质的影响[J]. 食品工业,2020,285(6):162−166. [ZHANG Q, KE B F, TANG X X, et al. Effect of different fermentation strains on the quality of malus domeri (Bois) Chev. enzyme drink[J]. The Food Industry,2020,285(6):162−166. [10] ANA E C F, ANA P R F, et al. Sequential optimization approach for prebiotic galactooligosaccharides synthesis by Pseudozyma tsukubaensis and Pichia kluyveri[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2015,63(2):1214−1219. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2015.04.064
[11] WANG Y, YU M, SHI Y W, et al. Effects of a fermented beverage of Changbai Mountain fruit and vegetables on the composition of gut microbiota in mice[J]. Plant Foods for Human Nutrition,2019,74(4):468−473. doi: 10.1007/s11130-019-00761-7
[12] 樊莹润, 郑婷婷, 刘琨毅, 等. 黄皮疣柄牛肝菌多糖对小鼠通便作用及血清指标的影响[J]. 食品研究与开发,2022,43(4):48−56. [FAN Y R, ZHENG T T, LIU K Y, et al. Effect of polysaccharides from Leccinellum crocipodium (Letellier.) watliag on laxative and serum indexes of mice[J]. Food Research and Development,2022,43(4):48−56. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2022.04.008 [13] 宁楚洁, 赵倩, 谢春阳, 等. 玉米须果蔬复合酵素饮料的研制及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品研究与开发,2019,40(20):116−122. [NING C J, ZHAO Q, XIE C Y, et al. Extraction of functional components from corn stigma and preparation of corn stigma, fruit and vegetable complex enzyme beverage[J]. Food Research and Development,2019,40(20):116−122. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2019.20.021 [14] 韦璐, 孙钦菊, 黄杰, 等. 发酵型香蕉复合果汁饮料的研制及营养成分研究[J]. 中国酿造,2020,39(10):210−215. [WEI L, SUN Q J, HUANG J, et al. Development of fermented banana compound juice beverage and its nutritioal active components[J]. China Brewing,2020,39(10):210−215. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2020.10.039 [15] 郭留城, 杜利月, 王飞. 香菇风味奶片的制备及品质分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(16):185−191. [GUO L C, DU L Y, WANG F. Preparation and quality analysis of lentinula edodes flavored milk tablets[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(16):185−191. [16] 刘重慧, 张静, 范誉川, 等. 低聚异麦芽糖调节肠道菌群及润肠通便作用的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(7):298−302. [LIU C H, ZHANG J, FAN Y C, et al. Studies on the effects of isomaltooligosaccharides regulating intestinal microbial flora proliferation and relieving constipated function[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(7):298−302. [17] MARTINGARCIA B, AZNARROMS M J, VERARDO V, et al. The establishment of ultrasonic-assisted extraction for the recovery of phenolic compounds and evaluation of their antioxidant activity from morus alba leaves[J]. Foods,2022,11(3):314. doi: 10.3390/foods11030314
[18] BASHIR M M, RASTOGI S, HARIPRYA S. Optimization of process variables for the preparation of almond gum incorporated set-yogurt using Box-Behnken response surface model[J]. Applied Food Research,2021,1(2):100016. doi: 10.1016/j.afres.2021.100016
[19] 高庆超. 黑果枸杞酵素发酵过程中微生物及物质变化规律的研究[D]. 西宁: 青海大学, 2020. GAO Q C. Study on change law of microorganisms and metabolites during fermentation progress of Lycium ruthenium Murr. Jiaosu[D]. Xining: Qinghai University, 2020.
[20] 杨钰昆, 宋佳, 乔沈, 等. 高效液相色谱法同时测定酵素原液中的乳酸和醋酸[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(10):246−250. [YANG Y K, SONG J, QIAO S, et al. Simultaneous determination of lactic acid and acetic acid in enzyme solution by high performance liquid chromatography[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(10):246−250. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2018.10.045 [21] 寇德麟, 杨丰伟, 吴征宇, 等. 富含γ-氨基丁酸的青花菜芽菜酸奶的研制[J]. 保鲜与加工,2022,22(3):35−42. [KOU D L, YANG F W, WU Z Y, et al. Development of broccoli sprout yogurt rich in γ-aminobutyric acid[J]. Storage and Process,2022,22(3):35−42. [22] 高熳熳, 张旭普, 白俊岩, 等. 不同发酵工艺糙米酵素中游离氨基酸、γ-氨基丁酸及挥发性香气成分分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(23):36−41. [GAO M M, ZHANG X P, BAI J Y, et al. Component analysis of Free amino acids, GABA and volatile aroma in brown rice enzymes with different fermentation processes[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(23):36−41. [23] 金哲宁, 方晟, 沙如意, 等. 沙棘酵素功能成分及其体外抗氧化性能研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2020,41(17):20−28. [JIN Z N, FANG S, SHA R Y, et al. Study on the functional components and in vitro antioxidant activity of sea-buckthorn Jiaosu[J]. Food Research and Development,2020,41(17):20−28. [24] BISHEHSARI F, ENGEN P A, PREITE N Z, et al. Dietary fiber treatment corrects the composition of gut microbiota, promotes SCFA production, and suppresses colon carcinogenesis[J]. Genes,2018,9(2):102. doi: 10.3390/genes9020102
[25] LIU H B, LIAO C, WU L, et al. Ecological dynamics of the gut microbiome in response to dietary fiber[J]. The ISME Journal,2022,16(8):2040−2055. doi: 10.1038/s41396-022-01253-4
[26] 李国坤, 董嘉华, 肖健海, 等. 复合代糖的通便功效及其对肠道菌群的调节作用[J]. 现代食品科技,2021,37(7):14−22. [LI G K, DONG J H, XIAO J H, et al. The purgative effect of complex sugar substitute and its regulation effect on intestinal flora[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2021,37(7):14−22. [27] HAYEEAWAEMA F, WICHIENCHOT S, KHHUITUAN P. Amelioration of gut dysbiosis and gastrointestinal motility by konjac oligo-glucomannan on loperamide-induced constipation in mice[J]. Nutrition,2019,73:110715.
[28] REN X, LIU L, GAMALLAT Y, et al. Enteromorpha and polysaccharides from Enteromorpha ameliorate loperamide-induced constipation in mice[J]. Biomed Pharmacother,2017,96:1075−1081. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.11.119
[29] 陈叙汐, 李娜, 岳午阳, 等. 芦荟、西洋参、番泻叶联用对便秘小鼠肠道菌群的影响[J]. 现代预防医学,2020,47(24):4497−4502,4506. [CHEN X X, LI N, YUE W Y, et al. Effect of aloe, American ginseng and sensa combination on intestinal flora in mice with constipation[J]. Modern Preventive Medicine,2020,47(24):4497−4502,4506. [30] 李日许, 黄暨生, 郭秋平. 圆苞车前子壳复配粉剂的通便功能研究[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2020,11(22):8593−8597. [LI R X, HUANG J S, GUO Q P. Research on the defecation function of hypocotyls of Plantago rotundus compound power[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2020,11(22):8593−8597. -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 蒋美君,张启元,蒙扬辉,白科,张兴志,农珍珍,钟方杰,朱鹏,彭金霞,官俊良,严雪瑜. 香港牡蛎BMP7基因克隆与表达. 广东海洋大学学报. 2023(04): 129-136 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 周晖,汤保贵,伍栩民,彭梓峰,钟培贵,于鸽,孔繁森. 香港牡蛎在综合养殖池塘育肥期间不同组织的碳、氮稳定同位素周转. 热带海洋学报. 2023(04): 125-132 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 汤保贵,周晖,赵力强,伍栩民,彭梓峰,钟培贵,于鸽. 香港牡蛎在异地基围育肥时的生长、形态及体成分变化. 水生生物学报. 2023(11): 1762-1768 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)






 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:



