Isolation, Identification and Safety Evaluation of Lactobacillus gasseri from Fecal Samples of Healthy Infants
-
摘要: 目的:本研究从125例健康婴儿粪便样本中分离鉴定出加氏乳杆菌(Lactobacillus gasseri)并对其安全性和抑菌性能进行评价。方法:本研究以1月龄健康婴儿粪便样本为对象,经过MRS培养基分离纯化、革兰氏染色、生化鉴定和16S rRNA测序技术进行菌种鉴定;随后,对分离得到的加氏乳杆菌利用血琼脂平板进行溶血性评价;利用微量肉汤稀释法对常见抗生素的药物敏性进行测定,并对加氏乳杆菌的安全性进行评价;最后,采用牛津杯法检测对大肠杆菌ATCC 25922和金黄色葡萄球菌ATCC 25923的抑制作用。结果:从125例健康婴儿粪便样本中成功分离并鉴定出15株加氏乳杆菌。溶血性检测结果显示,14株均无溶血性;待测菌株对四环素、万古霉素、利奈唑胺、利福平敏感性较高,对亚胺培南完全敏感,对甲氧苄啶完全耐药;抑菌实验结果显示,有6株菌同时对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌具有抑菌效果。结论:本研究从健康婴儿粪便样本中成功分离筛选出3株安全性较高且对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌同时具有一定抑制作用的加氏乳杆菌,编号分别为:LGI 6-1、LGI 6-2、LGI 6-3,作为潜在的益生菌资源,为后续深入探究加氏乳杆菌功能提供研究对象。Abstract: Objective: To isolate and identify Lactobacillus gasseri from 125 fecal samples of healthy infants, and to evaluate its safety and antimicrobial activity. Methods: In this study, fecal samples of 1-month-old healthy infants were taken, and the strains were separated by MRS medium, Gram staining, biochemical identification and 16S rRNA sequencing technology were used to strain identification. Subsequently, the hemolysis of the isolated L. gasseri was evaluated by blood agar. The drug sensitivity of antibiotics was determined by micro broth dilution method, and the safety of the isolated strains were evaluated. Finally, the inhibitory effects of the 15 isolated L. gasseri strains on E. coli ATCC 25922 and S. aureus ATCC 25923 were detected by Oxford cup method. Results: Fifteen strains of L. gasseri were successfully isolated from 125 fecal samples of healthy infants. Hemolysis test results showed that 14 strains of them was hemolytic negative. The 15 tested strains were highly sensitive to tetracycline, vancomycin, linezolid and rifampicin, completely sensitive to imipenem and completely resistant to trimethoprim. The results of antibacterial activity test showed that 6 strains could effectively in inhibiting both E. coli and S. aureus. Conclusion: In this study, three strains of L. gasseri were successfully isolated from healthy infant’s fecal samples, which could not only inhibit E. coli and S. aureus, but also passed the safety test (LGI 6-1, LGI 6-2 and LGI 6-3). As potential probiotic resources, they could provide a research target for further research on function exploring.
-
乳酸菌属是一类广泛存在于自然界中的微生物,包括乳杆菌属、双歧杆菌属、链球菌属等;在食品、生物技术以及医疗卫生等领域具有重要价值。尤其是作为益生菌,具有调节肠道微生态平衡、调节免疫反应、缓解肠道疾病等重要生理功能;近年来,益生菌作为潜在的天然抗生素替代物和天然抗氧化物,逐渐被人们接受[1]。其中,加氏乳杆菌(Lactobacillus gasseri)又称为格氏乳杆菌[2],是乳杆菌属中的重要菌种,属于革兰氏阳性、杆状、兼性厌氧细菌,广泛存在于胃肠道、阴道或母乳中。2010年,加氏乳杆菌被我国卫生部列为可以在食品中添加使用的菌种[3]。
作为广泛存在于人类体内的天然菌株,加氏乳杆菌能够通过产生细菌素、有机酸、过氧化氢等方式发挥益生特性,包括抑制病原菌生长,缓解肠道炎症,抗氧化等。Garcia-Gutierrez等[4]从人乳中分离的一株格式乳杆菌LM19能够通过产生多种细菌素拮抗致病菌的生长;Authier等[5]发现格式乳杆菌LA806与瑞氏乳杆菌LA401联用能够缓解由白色念珠菌引起的胃肠道炎症;Oh等[6]从婴儿粪便样本中分离的20多种乳酸菌株进行功能评价后发现格式乳杆菌4M13具有较高的抗炎、抗氧化性;并且,Rastogi等[7]对不同来源的3株加氏乳杆菌的抑菌能力进行评估,选择17种肠道常见病原菌,结果显示,其中1株来自婴儿肠道加氏乳杆菌MVS25的抑菌能力优于其他来源菌株。
抗生素耐药性是全球安全问题之一[8]。因此,寻找效果良好的抗生素替代物成为迫切需求。Gunyakti等[9]从人乳中分离出格氏乳杆菌MA-4,对其进行药敏检测结果显示对青霉素、阿莫西林等5种药物敏感,对卡那霉素、庆大霉素等5种药物表现出耐药;Ahire等[10]对女性生殖道分离出的格式乳杆菌UBLG36进行安全性评价,发现该菌株对甲氧苄啶、利福平在内的11种药物均表现出耐药;周钦育等[11]从婴儿粪便样本中分离的一株格式乳杆菌对四环素、万古霉素等5种药物均表现敏感;从以上报道可以看出,不同菌株之间存在功能特异性;因此,需要不断开发新型菌株,以期找到绿色、安全的抗生素替代物;本团队也推测,来自婴儿肠道的乳酸菌是否可能具有更强的益生性能和更高的安全性。Španová等[12]发现,人源性益生菌菌株更能在人体胃肠道中稳定生存且持续发挥功能。对于新型加氏乳杆菌株的发现,多数是从成人粪便或女性生殖道中分离,但我国对于婴儿肠源优良加氏乳杆菌的筛选还远远不足,因此,本团队希望从婴儿肠道中发掘出能够适应人体肠道环境并对致病菌产生抑制作用的益生菌,为开发抗生素替代物、益生菌制剂等奠定基础。
本研究从健康婴儿粪便样本中分离加氏乳杆菌,在体外对其安全性进行评价,并筛选出对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌均有抑制功能的菌株。旨在发掘筛选出安全性能较高并具有潜在拮抗致病菌生长的新型加氏乳杆菌菌株,为抗生素替代制剂提供更有前景的菌种资源。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
125份健康婴儿新鲜粪便样本 来自某月子中心,该研究通过空军军医大学唐都医院医学伦理委员会许可(伦理编号:201903-29),并获得被试者知情同意;质控菌:大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli ATCC 25922)、金黄色葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923)、粪肠球菌(Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212) 均购自北京保藏生物科技有限公司;MRS肉汤培养基:牛肉粉0.5%、酵母粉0.4%(北京奥博星生物技术公司);蛋白胨1%(牛津有限责任公司);葡萄糖2%、结晶乙酸钠0.5%、吐温80 0.1%、无水磷酸氢二钾0.2%、柠檬酸铵0.2%、无水硫酸镁0.02%、四水硫酸锰0.005% 天津市科密欧化学试剂有限公司;哥伦比亚血平皿 芜湖欧克生物技术有限公司;无菌无酶水、50×TAE缓冲液(pH8.0) 陕西中晖赫彩生物医药科技有限公司;引物27F、引物1492R 生工生物工程股份有限公司;2×pro Taq Master mix(dye plus)、GL DNA Marker 2000、琼脂糖凝胶 艾科瑞生物工程有限公司;抗生素类药物(四环素、利福平、万古霉素、亚胺培南、甲氧苄啶和利奈唑胺) 上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;一次性无菌拭子 扬州市创新医疗器械厂;生化鉴定试剂盒 环凯微生物科技有限公司;Muller-Hinton(M-H)培养基 青岛海波生物技术有限公司;LB肉汤培养基:酵母粉0.5%(北京奥博星生物技术公司)、蛋白胨1%(牛津有限责任公司)、氯化钠1%(天津市天力化学试剂有限公司);革兰氏染色试剂 南京建成科技有限公司;琼脂糖凝胶 湖南艾科瑞生物工程有限公司。
SW-CJ-2FD洁净工作台 苏州安泰空气技术有限公司;DHG-303-4B电热恒温培养箱 浙江力辰仪器科技有限公司;YDS-10-80液氮生物容器 乐山市东亚机电工贸有限公司;TC1000-G PCR梯度基因扩增仪 大龙兴创实验仪器股份公司;TGL-16M台氏高速冷冻离心机 湖南湘仪实验室仪器开发有限公司;BM2000生物显微镜 南京麦迪森仪器有限公司;DW-YL270医用低温箱 中科美菱低温科技股份有限公司;721型分光光度计 上海菁华科技仪器有限公司;YP6002B型电子天平 上海衡际科学仪器有限公司;WGZ-XT细菌浊度仪 杭州齐威仪器有限公司;XFH-40CA电热式压力蒸汽灭菌锅 浙江新丰医疗器械有限公司;JY-SPFT电泳仪 北京君意东方电泳设备。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样本的采集和处理
样本采集:使用一次性无菌拭子采集婴儿新鲜粪便样本,放入培养基中,4 ℃暂存,送至实验室于48 h内进行分离(伦理委员会许可号:201903-29,且获得被试对象知情同意)。
样本处理:将带有新鲜粪便样品的拭子放入1 mL灭菌生理盐水中涡旋振荡2800 r/min 30 s,制成样本悬液并进行10倍系列稀释。
1.2.2 菌株的分离纯化
取不同稀释度200 μL均匀涂布在MRS琼脂培养基上,37 ℃ 湿度80% RH厌氧培养48 h,从每个平板上随机挑取乳白色,圆形有光泽的3个可疑单菌落,在新鲜MRS平板上重新划线继续分离培养48 h,连续划线分离3次后,进行后续鉴定。
1.2.3 形态及生理生化鉴定
将分离出的菌株划线接种在MRS琼脂平板上,37 ℃培养24 h,观察菌落的形态特征;并对菌株进行革兰氏染色,显微镜下观察;同时,进行生理生化鉴定:过氧化氢酶(接触酶)试验、明胶液化实验、葡萄糖产酸产气实验、碳水化合物发酵实验;实验方法参照《乳酸细菌分类鉴定及实验方法》[13]和《常见细菌系统鉴定手册》[14];其中,碳水化合物发酵实验使用上海麦克林生化科技有限公司的生化鉴定试剂盒。
1.2.4 16S rRNA的扩增和序列分析
根据参考文献[15],进行PCR扩增前处理和扩增程序建立。
16S rRNA测序及BLAST对比:本研究委托生工生物工程股份有限公司对PCR样本进行测序。对测序得到的序列结果进行BLAST分析,将序列相似度>99%的配对结果作为菌株的初步鉴定结果。再利用MEGA 7.0软件,构建系统发育树,进一步确定其具体种属。
1.2.5 溶血性评价
采用血平板划线法[16];具体方法为:从MRS平板上挑取单菌落接种于6 mL MRS肉汤培养基中,37 ℃、24 h,之后在哥伦比亚血平板上划线,37 ℃、24 h后观察;阴性对照组为显示γ-溶血的粪肠球菌ATCC 25922,阳性对照组为显示β-溶血的金黄色葡萄球菌ATCC 25923。
1.2.6 抗生素敏感性实验
采用微量肉汤稀释法[17]对菌株的药敏性进行评价;从MRS平板上取单菌落接种于6 mL M-H培养基中37 ℃、24 h后,调整菌液浓度为0.5麦氏浊度,再用M-H培养基稀释200倍备用;用96孔板进行药敏试验,具体方法为:首先在96孔板上分装好M-H改良肉汤培养基,设置抗生素母液浓度并在孔内倍比系列稀释成梯度浓度(四环素64~0.125 μg/mL、万古霉素8~0.5 μg/mL、亚胺培南16~1 μg/mL、利奈唑胺4~0.25 μg/mL、甲氧苄啶4~0.25 μg/mL、利福平8~0.5 μg/mL),按照1:1的体积比加入菌液,并设置溶剂对照(加入等体积抗生素溶剂)和阳性对照(不加抗生素)之后在37 ℃培养24 h后,肉眼观察孔板中菌种抑制情况,确定MIC值。
1.2.7 抑菌能力测定
采用牛津杯法[18]进行抑菌试验,具体方法如下:首先制备大肠杆菌菌液,挑取大肠杆菌ATCC 25922单菌落,接种到10 mL LB肉汤培养基中,设置摇床转速160 r/min,37 ℃培养16~18 h。测量菌液在600 nm处吸光度,并调整吸光度至OD600 nm=1备用;
双层琼脂培养基的制备:先配制琼脂含量1.5%的LB琼脂培养基,121 ℃高压灭菌20 min后,每个平皿倒15 mL,4 ℃凝固备用;再配制琼脂含量1%的LB琼脂培养基,121 ℃高压灭菌20 min后,降温至40 ℃左右,按照1:10的体积比加入调整浓度后的大肠杆菌ATCC 25922菌液,涡旋30 s充分混匀后,倒入已凝固的1.5%的琼脂LB平板上,倒入前放上灭菌牛津杯(每个平皿放3个),每个平皿倒15 mL,等待凝固;取待测加氏乳杆菌单菌落接种于4 mL MRS肉汤培养基中,37 ℃培养24 h后取菌液200 μL加入牛津杯内,4 ℃下吸收15 h[19],再放入培养箱37 ℃培养24 h,观察并测量抑菌圈直径。
1.3 数据处理
实验均为三次生物学重复,数据采用均值±标准差表示,多组间均数的比较采用方差分析(One-way ANOVA)利用GraphPad 7对数据进行统计分析绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 菌株分离与初步鉴定
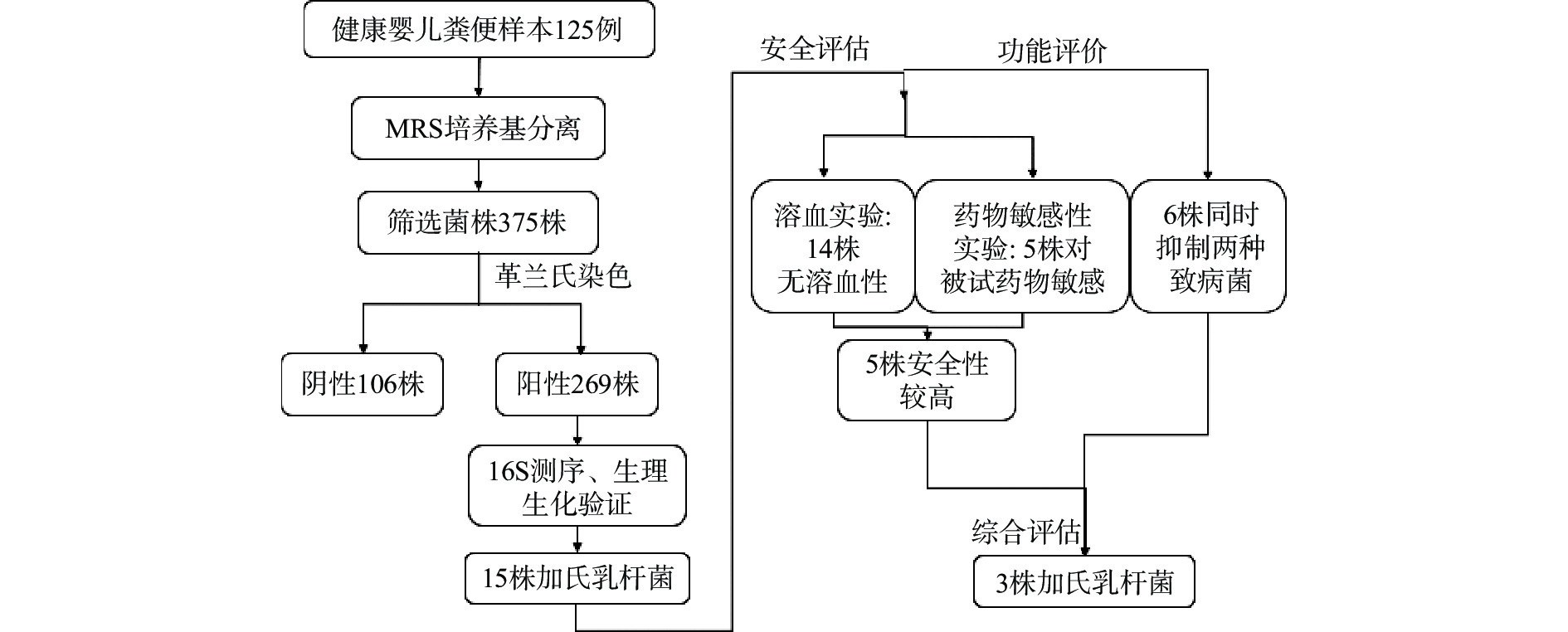
鉴定流程参见图1;本研究对125例健康婴儿粪便样本,利用MRS培养基进行厌氧分离培养,并对可疑单菌落连续三次划线分离,共得到375株乳酸菌可疑菌株。通过革兰氏染色镜检、琼脂糖凝胶电泳等手段,发现革兰氏阴性菌106株、革兰氏阳性菌269株。
接着,本研究还利用27F(5′-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3′)和1492R(5′-GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3′)通用引物对上述革兰氏阳性菌株的16S rRNA基因进行PCR扩增,扩增产物进行Sanger测序,将序列进行BLAST比对。结果初步鉴定出,粪肠球菌68株,植物乳杆菌58株,嗜酸乳杆菌32株,加氏乳杆菌15株,霍氏肠杆菌16株,副干酪乳杆菌24株,鼠李糖乳杆菌10株。
2.2 形态及生理生化鉴定验证结果
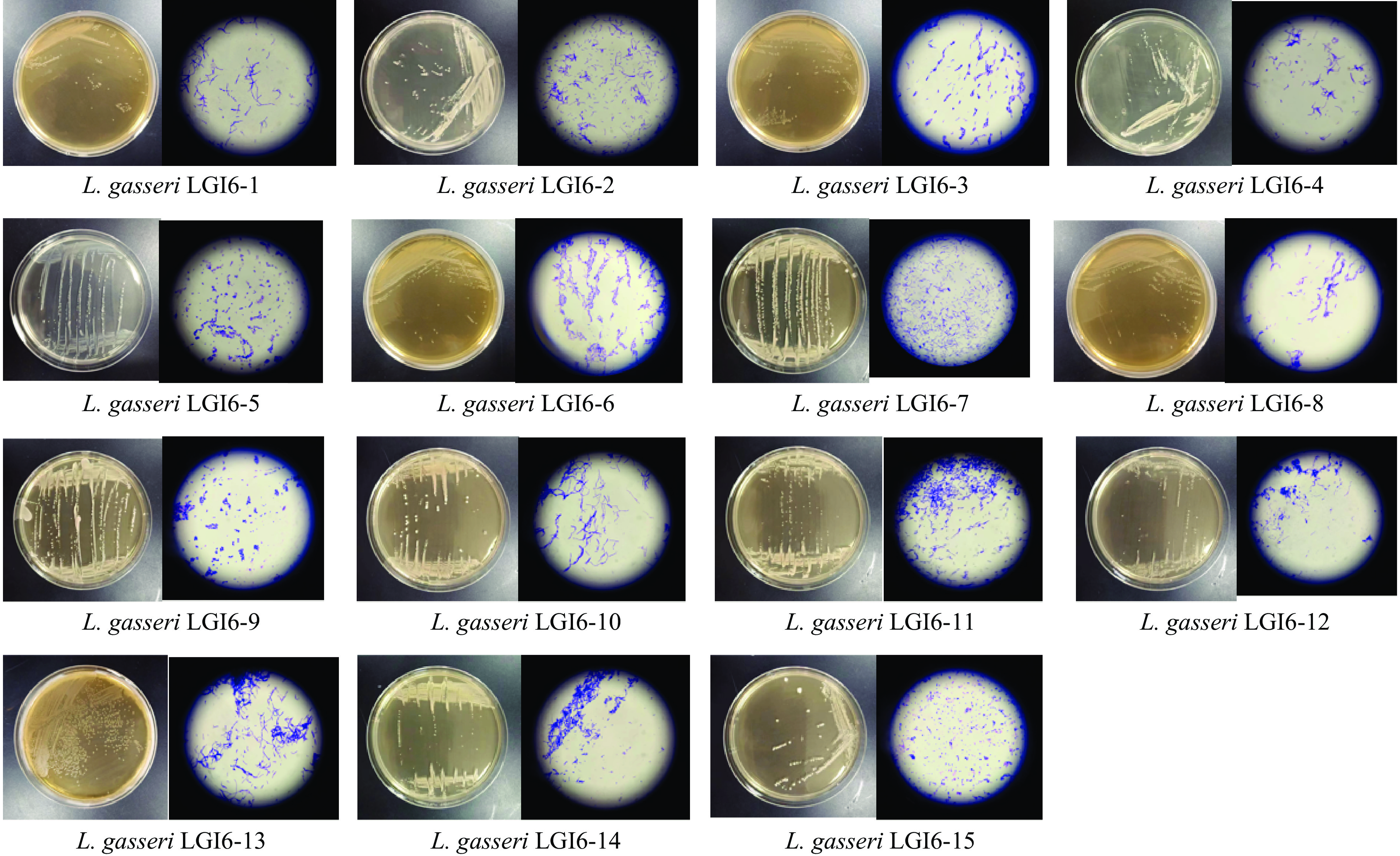
本研究使用了形态学鉴定和生理生化鉴定方法对上述15株加氏乳杆菌菌株的初步鉴定结果进行进一步验证。上述15株初步鉴定的加氏乳杆菌在MRS培养基上生长良好,结果见图2。菌落形态表现为乳白色,圆形,表面光滑,湿润有光泽;革兰氏染色结果显示,15株菌株均为革兰氏阳性,其中LGI 6-5、LGI 6-9、LGI 6-15为接近球状的短杆菌,其他均为长杆菌。
糖发酵试验结果及其他生化特性实验结果见表1。结果显示,15株初步鉴定的加氏乳杆菌均能发酵七叶苷、蔗糖、水杨苷、麦芽糖和纤维二糖;其中LGI 6-1、LGI 6-2、LGI 6-9、LGI 6-12、LGI 6-13、LGI 6-14可发酵棉子糖;并且接触酶试验、明胶液化试验均为阴性;均能发酵葡萄糖产酸,但不产气;以上生化结果符合乳杆菌属的生化特性。
表 1 15株加氏乳杆菌生物学特性结果Table 1. Biological characteristics of 15 strains of Lactobacillus gasseri菌种编号 形状 颜色 革兰氏染色 七叶苷 棉子糖 蔗糖 麦芽糖 纤维二糖 水杨苷 接触酶 明胶液化 葡萄糖产酸 葡萄糖产气 L. gasseri LGI6-1 杆菌 乳白 G+ + + + + + + − − + − L. gasseri LGI6-2 杆菌 乳白 G+ + + + + + + − − + − L. gasseri LGI6-3 杆菌 半透 G+ + − + + + + − − + − L. gasseri LGI6-4 杆菌 乳白 G+ + − + + + + − − + − L. gasseri LGI6-5 短杆菌 乳白 G+ + − + + + + − − + − L. gasseri LGI6-6 杆菌 乳白 G+ + − + + + + − − + − L. gasseri LGI6-7 杆菌 乳白 G+ + − + + + + − − + − L. gasseri LGI6-8 杆菌 乳白 G+ + − + + + + − − + − L. gasseri LGI6-9 短杆菌 乳白 G+ + + + + + + − − + − L. gasseri LGI6-10 杆菌 乳白 G+ + − + + + + − − + − L. gasseri LGI6-11 杆菌 乳白 G+ + − + + + + − − + − L. gasseri LGI6-12 杆菌 乳白 G+ + + + + + + − − + − L. gasseri LGI6-13 杆菌 乳白 G+ + + + + + + − − + − L. gasseri LGI6-14 杆菌 乳白 G+ + + + + + + − − + − L. gasseri LGI6-15 短杆菌 乳白 G+ + − + + + + − − + − 注:“+”表示阳性;“−”表示阴性;“G+”表示革兰氏染色呈阳性。 2.3 系统发育树的构建
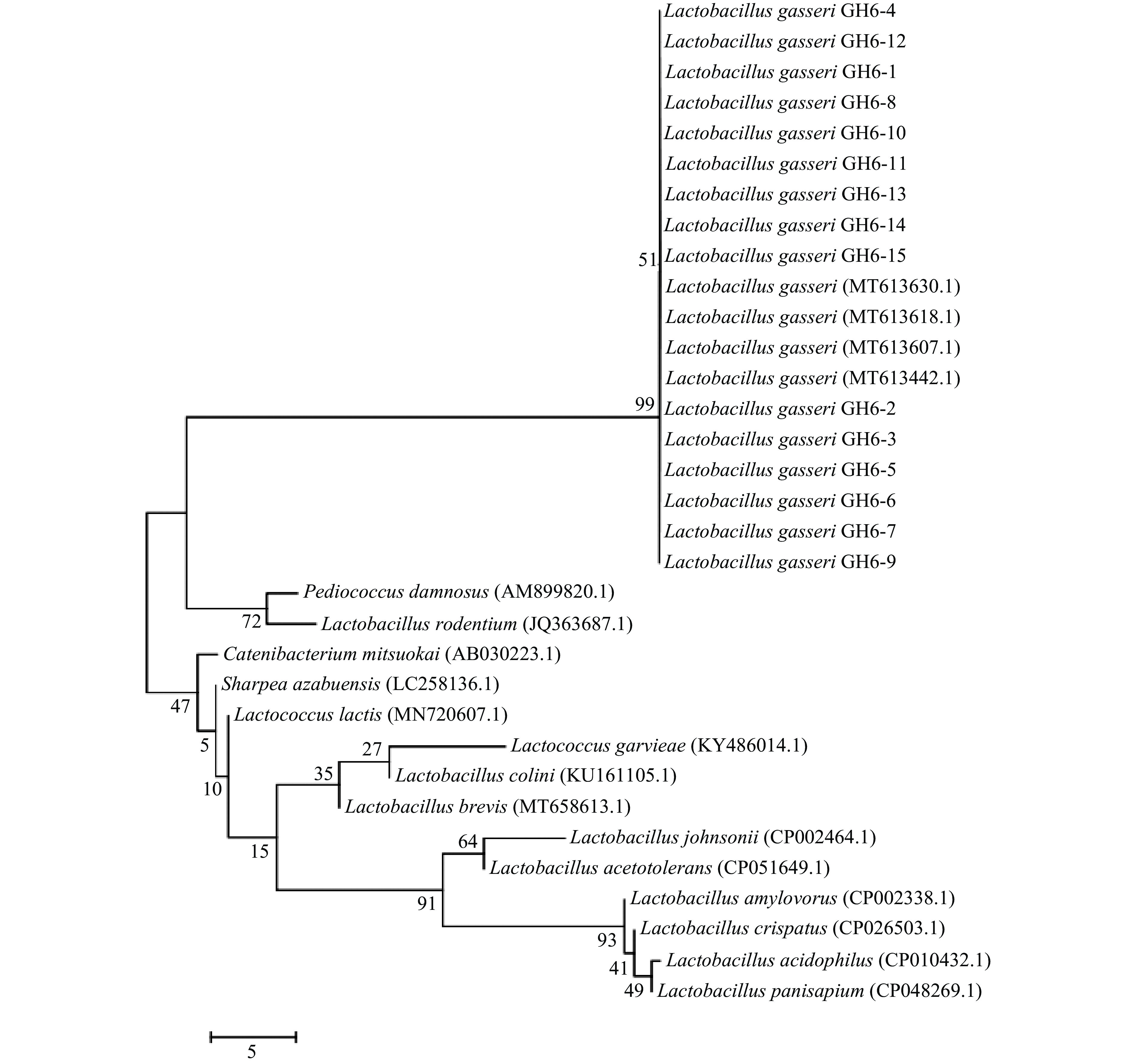
本研究将15株初步鉴定为加氏乳杆菌的菌株,经PCR扩增后的16S rRNA基因序列与GeneBank数据库中部分序列,利用MEGA 7构建系统发育树。图3可以看出,15株菌株与L. gasseri (MT613630.1)、L. gasseri (MT613618.1)、L. gasseri (MT613607.1)和L. gasseri (MT613442.1)亲缘关系达到99%,其中,LGI 6-15与MT613630.1亲缘关系最近,LGI 6-2与MT613442.1亲缘关系最近。系统发育树的结果显示15株菌株均为加氏乳杆菌。
2.4 溶血实验结果
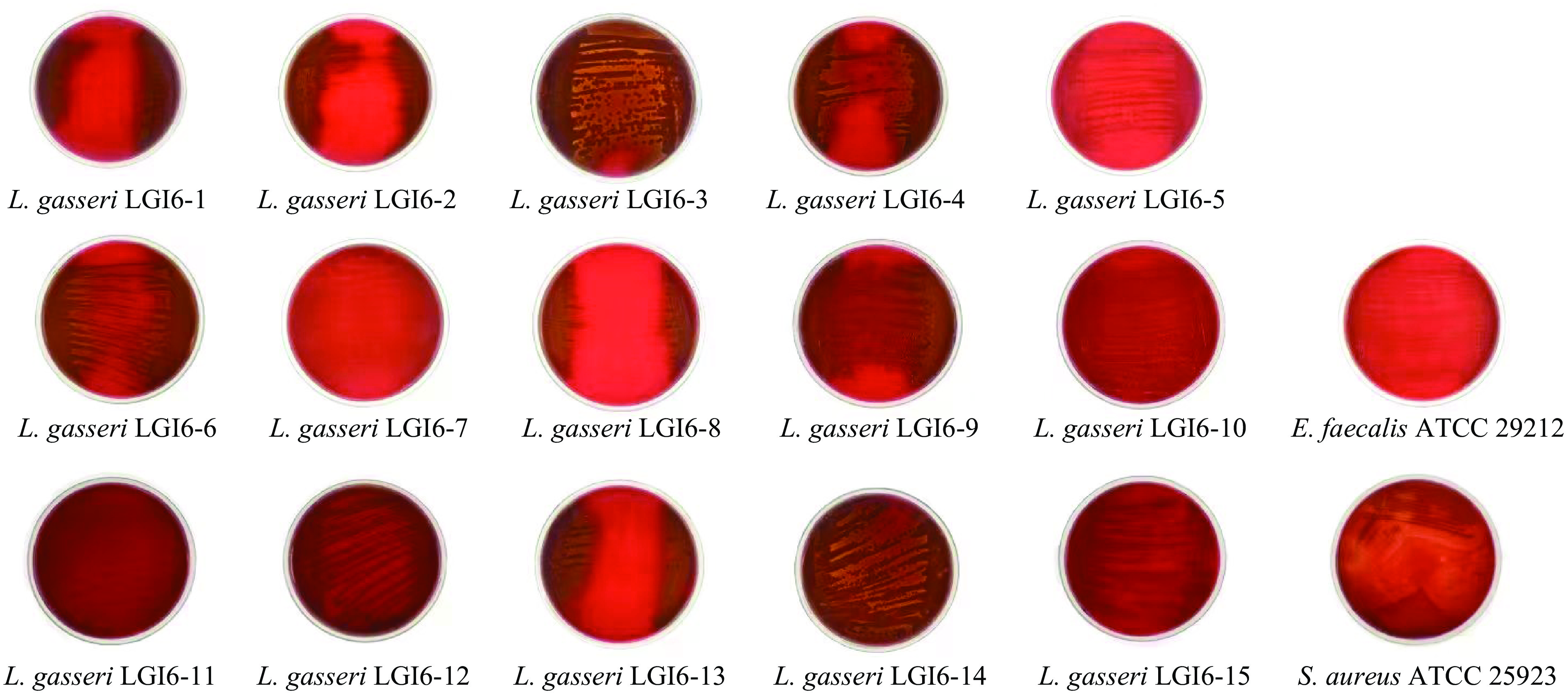
加氏乳杆菌被认为是普遍安全的菌种,但是受外界环境影响,有转变为低毒性条件致病菌的可能性[20],根据世界卫生组织规定,任何可能发生溶血的新型菌株都应进行溶血评估[21],且溶血能力是乳酸菌属安全性评价的重要筛选标准之一[22];微生物的溶血类型[23]包括三种:α-溶血(菌落周围出现草绿色)、β-溶血(菌落周围出现透明圈)、γ-溶血(菌落周围无草绿色无透明圈),其中,α-溶血和γ-溶血均无致病性,仅有β-溶血与致病性有关,可能会引起宿主出现不良反应,比如水肿、贫血等[24-25]。15株加氏乳杆菌的溶血实验结果见图4;选择具有β-溶血和γ-溶血特性的金黄色葡萄球菌ATCC 25923和粪肠球菌ATCC 29212作为对照。
15株加氏乳杆菌的溶血情况见表2,结果显示,LGI 6-1、LGI 6-2、LGI 6-3、LGI 6-4、LGI 6-6、LGI 6-13、LGI 6-14表现为α-溶血;LGI 6-5、LGI 6-7、LGI 6-8、LGI 6-10、LGI 6-11、LGI 6-12、LGI 6-15表现为γ-溶血;仅有LGI6-9表现为β-溶血。张晓伶[26]对从女性生殖道分泌物分离的加氏乳杆菌HMV18的溶血活性进行评估,结果显示为α-溶血。与本研究结果相似。在本研究中,15株加氏乳杆菌在溶血性检测中,仅有1株显示为β-溶血。以上结果提示:在溶血方面,健康人体环境来源尤其是婴儿肠道来源的加氏乳杆菌可能具有较高的安全性。
表 2 15株加氏乳杆菌的溶血情况表Table 2. Hemolysis of 15 strains of Lactobacillus gasseri菌种名称 溶血类型(α、β、γ) L. gasseri LGI 6-1 α L. gasseri LGI 6-2 α L. gasseri LGI 6-3 α L. gasseri LGI 6-4 α L. gasseri LGI 6-5 γ L. gasseri LGI 6-6 α L. gasseri LGI 6-7 γ L. gasseri LGI 6-8 γ L. gasseri LGI 6-9 β L. gasseri LGI 6-10 γ L. gasseri LGI 6-11 γ L. gasseri LGI 6-12 γ L. gasseri LGI 6-13 α L. gasseri LGI 6-14 α L. gasseri LGI 6-15 γ E. faecalis ATCC 29212 γ S. aureus ATCC 25923 β 2.5 抗生素敏感实验结果
有研究结果表明,抗生素的耐药基因会通过食物链传播[27],而由于耐药基因的可转移性,使益生菌可能成为耐药基因传播载体对人类的安全造成威胁;因此,药物敏感性是益生菌安全性评价的重要标准之一[28]。对本研究分离并鉴定的15株加氏乳杆菌药敏检测结果及耐药情况见表3、表4;根据抗菌药物敏感性试验的技术要求(WS/T 639-2018)选取抗生素的种类,其中包括四环素、利福平、万古霉素、亚胺培南、甲氧苄啶和利奈唑胺;质控菌为粪肠球菌ATCC 29212,质控菌的实验结果均在允许范围之内。药敏结果判断依据参考CLSI M100《抗微生物药物敏感性试验执行标准》[29]第30版。
表 4 15株加氏乳杆菌的MIC值及耐药性Table 4. MIC value and drug resistance of 15 strains of Lactobacillus gasseri抗生素类别
(μg/mL)LGI6-1 LGI 6-2 LGI6-3 LGI6-4 LGI6-5 LGI6-6 LGI6-7 LGI6-8 LGI6-9 LGI6-10 LGI6-11 LGI6-12 LGI6-13 LGI6-14 LGI6-15 四环素 0.5(S) <0.125(S) 1(S) <0.125(S) 1(S) 0.5(S) 2(S) <0.125(S) 0.125(S) 32(R) 8(R) 0.125(S) 0.125(S) 0.125(S) 0.5(S) 万古霉素 2(S) 2(S) 2(S) 2(S) 4(R) 4(R) 2(S) 2(S) 2(S) 2(S) 2(S) 2(S) 2(S) 4(R) 2(S) 利福平 2(I) 2(I) 2(I) 2(I) 4(R) 4(R) 2(I) 2(I) 2(I) 2(I) 2(I) 2(I) 4(R) 2(I) 4(R) 利奈唑胺 2(S) 2(S) 2(S) 4(R) 2(S) 1(S) 4(R) 1(S) 4(R) 1(S) 1(S) 1(S) 1(S) 1(S) 1(S) 亚胺培南 2(S) 2(S) 2(S) 1(S) 2(S) 2(S) 1(S) 2(S) 1(S) 2(S) 2(S) 2(S) 2(S) 2(S) 4(S) 甲氧苄啶 >4(R) >4(R) >4(R) >4(R) >4(R) >4(R) >4(R) >4(R) >4(R) >4(R) >4(R) >4(R) >4(R) >4(R) >4(R) 注:S表示敏感;I表示中敏;R表示耐药。 根据测定的MIC值显示,本研究分离得到的15株测试菌株对四环素、万古霉素、利奈唑胺、利福平和亚胺培南的耐药率分别为13.3%、13.3%、20%、20%和0%,对甲氧苄啶表现出完全耐药,其中对甲氧苄啶为乳酸菌的固有耐药[31]。排除固有耐药的抗生素类型,共筛选出5株对以上药物均表现敏感的菌株:L. gasseri LGI 6-1、LGI 6-2、LGI 6-3、LGI 6-8和LGI 6-12。根据前人报道,苏炳森等[32]从健康女性生殖道中分离的一株格式乳杆菌LGV03在药敏性测试中发现对万古霉素、利奈唑胺等均不具有抗性;周兴雅[33]对成人粪便样本中分离的20株格式乳杆菌进行抗生素敏感性实验,结果显示对甲氧苄啶表现出完全耐药,对利福平表现出完全敏感,对四环素、万古霉素等表现为部分耐药;以上研究结果与供试菌结果部分相似。产生不同结果的原因可能与样本来源不同有关,即同菌种不同菌株之间在功能特性方面可能存在巨大差异;并且也有报道称,由于畜牧业以及传染病的防治对抗生素的依赖,使得近年来,发掘出安全的有潜力的新型益生菌变得比较困难,即使通过药物敏感性测试,依然需要在基因水平对其是否携带耐药基因进行进一步探究。
2.6 抑菌实验结果
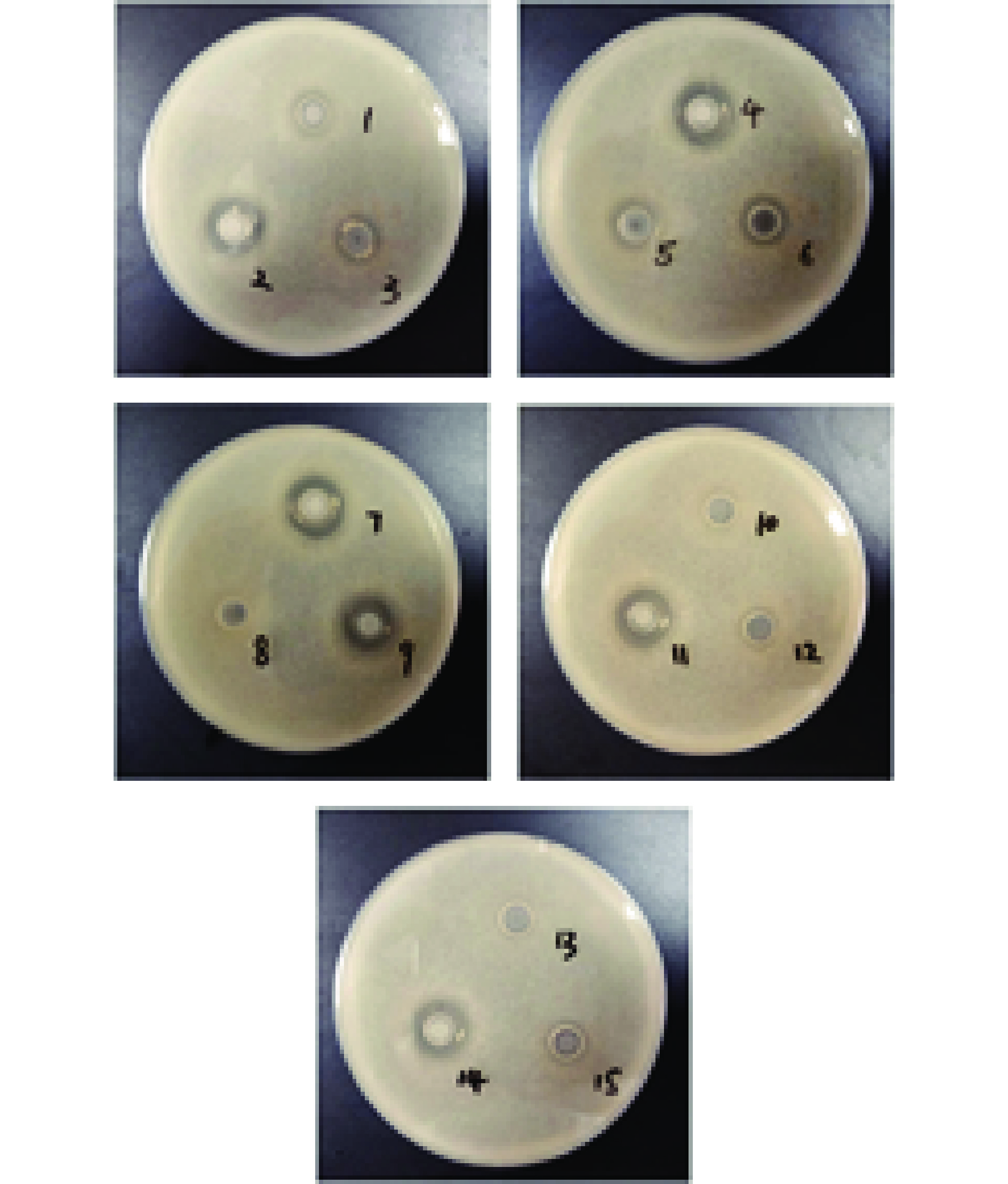
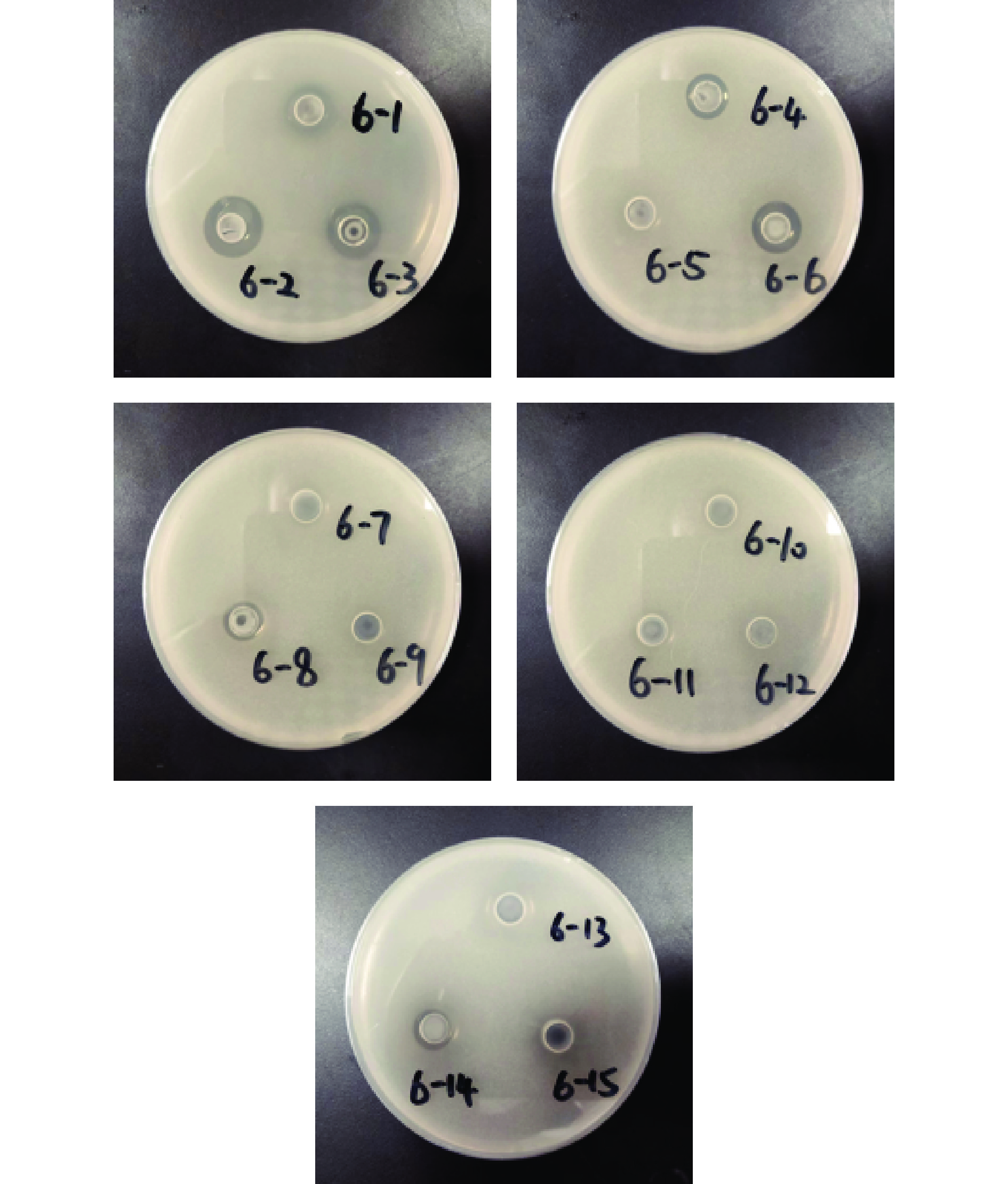
本研究利用牛津杯法测试了15株加氏乳杆菌对大肠杆菌ATCC 25922和金黄色葡萄球菌ATCC 25923的抑菌效果;结果如图5、图6和表5所示,对大肠杆菌具有抑制功能的菌株有:L. gasseri LGI 6-1、LGI 6-2、LGI 6-3、LGI 6-4、LGI 6-5、LGI 6-6、LGI 6-7、LGI 6-9、LGI 6-11、LGI 6-14和LGI 6-15;对金黄色葡萄球菌具有抑制功能的菌株有:L. gasseri LGI 6-1、LGI 6-2、LGI 6-3、LGI 6-4、LGI 6-6、LGI 6-8和LGI 6-14。在这15株加氏乳杆菌中有6株对两种致病菌同时具有不同程度抑制效果,包括:L. gasseri LGI 6-1、LGI 6-2、LGI 6-3、LGI 6-4、LGI 6-6和LGI 6-14号菌。提示这6株菌可能在对致病微生物的抑制方面具有一定应用潜力。以上结果与很多研究报道具有相似之处,桑佳特等[30]对女性阴道分泌物中分离得14株乳酸菌进行抑菌活性测定,其中分离的加氏乳杆菌HMV18对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌同时具有抑制作用;Rodrigues等[34]对分离自婴儿粪便样本的30株加氏乳杆菌的抑菌能力进行评估后,发现对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌均具有拮抗作用;大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌作为典型的革兰氏阴性菌和革兰氏阳性菌[35],对其具有抑制作用的结果提示,供试菌可能对胃肠道和食物中的致病菌具有广谱抑菌作用,本团队将做进一步探索;除此之外,对于具体的抑菌物质也需要深入研究,这对于食品保存和药物制剂方面具有重要意义。
表 5 15株加氏乳杆菌抑菌圈直径结果(mm)Table 5. Results of bacteriostatic circle diameter of 15 strains of Lactobacillus gasseri (mm)菌种名称 大肠杆菌
ATCC 25922金黄色葡萄球菌
ATCC 25923L. gasseri LGI 6-1 10.00±0.10 14.20±0.10 L. gasseri LGI 6-2 16.15±0.05 16.25±0.05 L. gasseri LGI 6-3 10.55±0.50 14.25±0.05 L. gasseri LGI 6-4 15.65±0.15 11.70±0.10 L. gasseri LGI 6-5 10.07±0.70 − L. gasseri LGI 6-6 11.55±0.45 13.80±0.10 L. gasseri LGI 6-7 16.10±0.60 − L. gasseri LGI 6-8 − 10.65±0.05 L. gasseri LGI 6-9 10.85±1.95 − L. gasseri LGI 6-10 − − L. gasseri LGI 6-11 15.16±0.30 − L. gasseri LGI 6-12 − − L. gasseri LGI 6-13 − − L. gasseri LGI 6-14 14.60±0.50 10.60±0.10 L. gasseri LGI 6-15 10.25±0.15 − 注:“−”表示无抑菌圈。 3. 结论
本研究对125例健康婴儿粪便样本中的益生菌进行分离鉴定,共分离出乳酸菌223株,其中包括嗜酸乳杆菌、加氏乳杆菌、鼠李糖乳杆菌等。之后对分离得到的15株加氏乳杆菌的安全性和抑菌能力进行进一步评价;其中有14株加氏乳杆菌无溶血性,有5株加氏乳杆菌药物敏感性评价结果较好,有6株表现出对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌均有抑制作用,最终共得到3株安全性较高且具有一定抑菌能力的加氏乳杆菌。本研究提示,来自于健康婴儿样本的加氏乳杆菌,凭借其安全性和功能性或可作为益生菌资源开发和利用的重要资源。近年来,益生菌制剂的研究成为抗生素替代物领域的研究热点[36];有研究将不同优良益生菌进行复合,制成益生菌制剂,部分或全部替代猪饲料中的抗生素[37];这也为本团队提供思路。在下一步的工作中,本团队将对潜力菌株进行基因水平的检测,在功能上进行深入探究,发掘出益生功能出色的优良菌种资源。
-
表 1 15株加氏乳杆菌生物学特性结果
Table 1 Biological characteristics of 15 strains of Lactobacillus gasseri
菌种编号 形状 颜色 革兰氏染色 七叶苷 棉子糖 蔗糖 麦芽糖 纤维二糖 水杨苷 接触酶 明胶液化 葡萄糖产酸 葡萄糖产气 L. gasseri LGI6-1 杆菌 乳白 G+ + + + + + + − − + − L. gasseri LGI6-2 杆菌 乳白 G+ + + + + + + − − + − L. gasseri LGI6-3 杆菌 半透 G+ + − + + + + − − + − L. gasseri LGI6-4 杆菌 乳白 G+ + − + + + + − − + − L. gasseri LGI6-5 短杆菌 乳白 G+ + − + + + + − − + − L. gasseri LGI6-6 杆菌 乳白 G+ + − + + + + − − + − L. gasseri LGI6-7 杆菌 乳白 G+ + − + + + + − − + − L. gasseri LGI6-8 杆菌 乳白 G+ + − + + + + − − + − L. gasseri LGI6-9 短杆菌 乳白 G+ + + + + + + − − + − L. gasseri LGI6-10 杆菌 乳白 G+ + − + + + + − − + − L. gasseri LGI6-11 杆菌 乳白 G+ + − + + + + − − + − L. gasseri LGI6-12 杆菌 乳白 G+ + + + + + + − − + − L. gasseri LGI6-13 杆菌 乳白 G+ + + + + + + − − + − L. gasseri LGI6-14 杆菌 乳白 G+ + + + + + + − − + − L. gasseri LGI6-15 短杆菌 乳白 G+ + − + + + + − − + − 注:“+”表示阳性;“−”表示阴性;“G+”表示革兰氏染色呈阳性。 表 2 15株加氏乳杆菌的溶血情况表
Table 2 Hemolysis of 15 strains of Lactobacillus gasseri
菌种名称 溶血类型(α、β、γ) L. gasseri LGI 6-1 α L. gasseri LGI 6-2 α L. gasseri LGI 6-3 α L. gasseri LGI 6-4 α L. gasseri LGI 6-5 γ L. gasseri LGI 6-6 α L. gasseri LGI 6-7 γ L. gasseri LGI 6-8 γ L. gasseri LGI 6-9 β L. gasseri LGI 6-10 γ L. gasseri LGI 6-11 γ L. gasseri LGI 6-12 γ L. gasseri LGI 6-13 α L. gasseri LGI 6-14 α L. gasseri LGI 6-15 γ E. faecalis ATCC 29212 γ S. aureus ATCC 25923 β 抗菌药物类别 药物名称 MIC值判定标准(μg/mL) 质控菌株允许范围
(E. faecalis ATCC 29212)S I R 四环素类 四环素 ≤4 8 ≥16 8~32 碳青霉烯类 亚胺培南 ≤4 8 ≥16 0.5~2.0 恶唑烷酮类 利奈唑胺 ≤2 − − 1~4 安沙霉素 利福平 ≤1 2 ≥4 0.5~4.0 糖肽类 万古霉素 ≤2 − − 1~4 叶酸代谢途
径抑制剂甲氧苄啶 ≤2 − ≥4 0.12~0.5 表 4 15株加氏乳杆菌的MIC值及耐药性
Table 4 MIC value and drug resistance of 15 strains of Lactobacillus gasseri
抗生素类别
(μg/mL)LGI6-1 LGI 6-2 LGI6-3 LGI6-4 LGI6-5 LGI6-6 LGI6-7 LGI6-8 LGI6-9 LGI6-10 LGI6-11 LGI6-12 LGI6-13 LGI6-14 LGI6-15 四环素 0.5(S) <0.125(S) 1(S) <0.125(S) 1(S) 0.5(S) 2(S) <0.125(S) 0.125(S) 32(R) 8(R) 0.125(S) 0.125(S) 0.125(S) 0.5(S) 万古霉素 2(S) 2(S) 2(S) 2(S) 4(R) 4(R) 2(S) 2(S) 2(S) 2(S) 2(S) 2(S) 2(S) 4(R) 2(S) 利福平 2(I) 2(I) 2(I) 2(I) 4(R) 4(R) 2(I) 2(I) 2(I) 2(I) 2(I) 2(I) 4(R) 2(I) 4(R) 利奈唑胺 2(S) 2(S) 2(S) 4(R) 2(S) 1(S) 4(R) 1(S) 4(R) 1(S) 1(S) 1(S) 1(S) 1(S) 1(S) 亚胺培南 2(S) 2(S) 2(S) 1(S) 2(S) 2(S) 1(S) 2(S) 1(S) 2(S) 2(S) 2(S) 2(S) 2(S) 4(S) 甲氧苄啶 >4(R) >4(R) >4(R) >4(R) >4(R) >4(R) >4(R) >4(R) >4(R) >4(R) >4(R) >4(R) >4(R) >4(R) >4(R) 注:S表示敏感;I表示中敏;R表示耐药。 表 5 15株加氏乳杆菌抑菌圈直径结果(mm)
Table 5 Results of bacteriostatic circle diameter of 15 strains of Lactobacillus gasseri (mm)
菌种名称 大肠杆菌
ATCC 25922金黄色葡萄球菌
ATCC 25923L. gasseri LGI 6-1 10.00±0.10 14.20±0.10 L. gasseri LGI 6-2 16.15±0.05 16.25±0.05 L. gasseri LGI 6-3 10.55±0.50 14.25±0.05 L. gasseri LGI 6-4 15.65±0.15 11.70±0.10 L. gasseri LGI 6-5 10.07±0.70 − L. gasseri LGI 6-6 11.55±0.45 13.80±0.10 L. gasseri LGI 6-7 16.10±0.60 − L. gasseri LGI 6-8 − 10.65±0.05 L. gasseri LGI 6-9 10.85±1.95 − L. gasseri LGI 6-10 − − L. gasseri LGI 6-11 15.16±0.30 − L. gasseri LGI 6-12 − − L. gasseri LGI 6-13 − − L. gasseri LGI 6-14 14.60±0.50 10.60±0.10 L. gasseri LGI 6-15 10.25±0.15 − 注:“−”表示无抑菌圈。 -
[1] VIECO-SAIZ N, BELGUESMIA Y, RASPOET R, et al. Benefits and Inputs from lactic acid bacteria and their bacteriocins as alternatives to antibiotic growth promoters during food-animal production[J]. Front Microbiol,2019,10:57. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00057
[2] FRANCL A L, THONGARAM T, MILLER M J. The PTS transporters of Lactobacillus gasseri ATCC 33323[J]. BMC Microbiology,2010,10(1):77. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-10-77
[3] 闫文杰,段昊,吕燕妮.益生菌在我国保健食品中的应用进展[J].食品工业科技:1−14[2022-06-07]. YAN Wenjie, DUAN Hao, LÜ Yanni. Application progress of probiotics in health food in China[J]. Food Industry Technology: 1−14[2022-06-07]
[4] GARCIA-GUTIERREZ E, O’CONNOR P M, COLQUHOUN I J, et al. Production of multiple bacteriocins, including the novel bacteriocin gassericin M, by Lactobacillus gasseri LM19, a strain isolated from human milk[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 104, 3869-3884.
[5] AUTHIER H, SALÓN M L, RAHABI M, et al. Oral administration of Lactobacillus helveticus LA401 and Lactobacillus gasseri LA806 combination attenuates oesophageal and gastrointestinal candidiasis and consequent gut inflammation in mice[J]. Fungi,2021,7:57. doi: 10.3390/jof7010057
[6] OH N S, JOUNG J Y, LEE J Y, KIM Y. Probiotic and anti-inflammatory potential of Lactobacillus rhamnosus 4B15 and Lactobacillus gasseri 4M13 isolated from infant feces[J]. PLoS One,2018,13(2):e0192021. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192021
[7] RASTOGI S, MITTAL V, SINGH A. In vitro assessment of antioxidant and antimicrobial potential of Lactobacillus gasseri strains isolated from human milk and infant faeces[J]. Pure Appl Microbiol,2020,14(2):1305−1315. doi: 10.22207/JPAM.14.2.26
[8] ASLAM B, WANG W, ARSHAD M I, et al. Antibiotic resistance: A rundown of a global crisis[J]. Infection and Drug Resistance,2018,11:1645−1658. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S173867
[9] GUNYAKTI A, ASAN-OZUSAGLAM M. Lactobacillus gasseri from human milk with probiotic potential and some technological properties[J]. LWT, 2019, 109: 261-269.
[10] AHIRE J J, SAHOO S, KASHIKAR M S, et al. In vitro assessment of Lactobacillus crispatus UBLCp01, Lactobacillus gasseri UBLG36, and Lactobacillus johnsonii UBLJ01 as a potential vaginal probiotic candidate[J]. Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins,2021:1−12.
[11] 周钦育,许喜林,赵珊,等. 婴儿肠道源格氏乳杆菌的安全性评价及益生特性[J]. 食品科学, 2021, 42(16):61−68. ZHOU Qinyu, XU Xilin, ZHAO Shan, et al Safety evaluation and prebiotic characteristics of Lactobacillus Griffiths from infant intestine[J]. Food Science, 2021,42 (16): 61−68.
[12] ŠPANOVÁ A, DRÁB V, TURKOVÁ K, et al. Selection of potential probiotic Lactobacillus strains of human origin for use in dairy industry[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2015,241(6):861−869. doi: 10.1007/s00217-015-2511-1
[13] 凌代文. 乳酸细菌分类鉴定及实验方法[M]. 北京: 中国轻工业出版社, 1999: 23 LING Daiwen. Classification, identification and experimental methods of lactic acid bacteria[M]. Beijing: China Light Industry Press, 1999: 23
[14] 东秀珠, 蔡妙英. 常见细菌系统鉴定手册[M]. 北京: 北京科学出版社, 2001 DONG Xiuzhu, CAI Miaoying. Manual for system identification of common bacteria[M]. Beijing: Beijing Science Press, 2001
[15] 鲁曦, 马雨哲, 李国花, 等. 健康婴儿粪便样本中罗伊氏乳杆菌的分离鉴定与体外益生特性初步研究[J]. 陕西科技大学学报,2022,40(3):59−65. [LU Xi, MA Yuzhe, LI Guohua, et al. Isolation and identification of Lactobacillus reuteri from fecal samples of healthy infants and preliminary study on its prebiotic properties in vitro[J]. Journal of Shaanxi University of Science and Technology,2022,40(3):59−65. doi: 10.19481/j.cnki.issn2096-398x.2022.03.027 [16] 玛丽娜·库尔曼. 降胆固醇益生菌的筛选鉴定及降血脂功能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2020. MARINA kurman. Screening and identification of cholesterol lowering probiotics and Study on their lipid lowering function[D]. Harerbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2020.
[17] 尚红, 王毓三, 申子瑜, 等. 全国临床检验操作规程[M]. 人民卫生出版社, 2015 SHANG Hong, WANG Yusan, SHEN Ziyu, et al. National clinical laboratory operating procedures[M]. People's Health Publishing House, 2015
[18] 王志新, 韩烁培, 王雨, 等. 植物乳杆菌的筛选、鉴定及其抑菌物质研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(9):133−139,146. [WANG Zhixin, HAN Shuopei, WANG Yu, et al. Screening and identification of Lactobacillus plantarum and study on its antibacterial substances[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2019,40(9):133−139,146. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2019.09.024 [19] 李宏伟, 慈百全, 侯明磊, 等. 鸡源乳酸菌的分离鉴定及其生物学特性分析[J]. 江苏农业科学,2020,48(13):188−192. [LI Hongwei, CI Baiquan, HOU Minglei, et al. Isolation, identification and biological characteristics of lactic acid bacteria from chicken[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Science,2020,48(13):188−192. doi: 10.15889/j.issn.1002-1302.2020.13.038 [20] KLINGBERG T D, LESNIK U, ARNEBORG N, et al. Comparison of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains of clinical and nonclinical origin by molecular typing and determination of putative virulence traits[J]. Fems Yeast Res,2008,8:631−640. doi: 10.1111/j.1567-1364.2008.00365.x
[21] JOINT F A O. WHO working group report on drafting guidelines for the evaluation of probiotics in food[J]. London, Ontario, Canada,2002:30.
[22] SHARMA P, TOMAR S K, SANGWAN V, et al. Antibiotic resistance of Lactobacillus sp. isolated from commercial probiotic preparations[J]. Journal of Food Safety,2016,36:38−51. doi: 10.1111/jfs.12211
[23] KIM M J, KU S, KIM S Y, et al. Safety evaluations of Bifidobacterium bifidum BGN4 and Bifidobacterium longum BORI[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2018,19:1422. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051422
[24] BEECHER D J, SCHOENI J L, WONG A. Enterotoxic activity of hemolysin BL from Bacillus cereus[J]. Infect Immun,1995,63:4423−4428. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.11.4423-4428.1995
[25] 叶露. 加氏乳杆菌JDM511安全性分析[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2014 YE Lu. Safety analysis of Lactobacillus gasseri JDM511[D]. Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2014
[26] 张晓伶. 一株对致病菌有拮抗作用的格氏乳杆菌HMV18的分离鉴定及安全性评价[D]. 石家庄: 河北医科大学, 2020 ZHANG Xiaoling. Isolation, identification and safety evaluation of a Lactobacillus gasseri HMV18 with antagonistic effect on pathogenic bacteria[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei Medical University, 2020.
[27] TEUBER M, MEILE L, SCHWARZ F. Acquired antibiotic resistance in lactic acid bacteria from food[J]. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek,1999,76(1-4):115−137.
[28] 董沛晶. 微生态制剂的应用研究进展[J]. 现代临床医学, 2017, 43(2): 91−93 DONG Peijing. Research progress in the application of microecological agents[J]. Modern Clinical Medicine, 2017, 43(2): 91−93
[29] CLSI. 抗菌药物敏感性实验执行标准M100(第30版)[S]. 2020 CLSI. Antimicrobial susceptibility test executive standard M100 (30th Edition)[S]. 2020
[30] 桑佳特, 张瑞, 肖冰冰, 等. 健康女性阴道乳杆菌抑菌功能的初步研究[J]. 现代妇产科进展,2013,22(4):292−296, 301. [SANG Jiate, ZHANG Rui, XIAO Bingbing, et al. A preliminary study on the antibacterial function of Lactobacillus vaginalis in healthy women[J]. Progress in Modern Obstetrics and Gynecology,2013,22(4):292−296, 301. doi: 10.13283/j.cnki.xdfckjz.2013.04.014 [31] 于涛, 姜晓冰, 李磊, 等. 市售酸奶中乳酸菌耐药性及耐药基因的检测[J]. 食品科学, 2016, 37(11):131−136 YU Tao, JIANG Xiaobing, LI Lei, et al. Detection of drug resistance and drug resistance genes of lactic acid bacteria in commercial yoghurt[J]. Food Science, 2016, 37(11): 131−136.
[32] 苏炳森, 操龙斌, 郑介婷, 等. 健康妇女生殖道内格氏乳杆菌的分离鉴定与安全性评价[J]. 南方医科大学报,2021,41(12):1809−1815. [SU Bingsen, CAO Longbin, ZHENG Jieting, et al. Isolation, identification and safety evaluation of Lactobacillus grignai in reproductive tract of healthy women[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University,2021,41(12):1809−1815. [33] 周兴雅. 格氏乳杆菌与副格氏乳杆菌的筛选、基因组比较及安全性评价[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2019 ZHOU Xingya. Screening, genome comparison and safety evaluation of Lactobacillus gasseri and Lactobacillus paragasseri[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2019.
[34] RODRIGUES D A, CUNHA L, FERREIRA C L, et al. Characterization of Lactobacillus gasseri isolates from a breast-fed infant[J]. Gut Microbes,2012,3:15−24. doi: 10.4161/gmic.19489
[35] 刘彩琴, 陆胤, 王石磊, 等. 黄酒米浆水中抗菌乳酸菌的筛选及特性分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(9):114−118. [LIU Caiqin, LU Yin, WANG Shilei, et al. Screening and characteristic analysis of antibacterial lactic acid bacteria in rice wine and rice slurry[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2020,41(9):114−118. doi: 10.13386/jissn1002-0306.2020.09.018 [36] SHANAHAN F, MCCARTHY J. Functional foods and probiotics time for gastroenterologists to embrace the concept[J]. Cur Gastroenterol Rep,2000,2(5):345−346. doi: 10.1007/s11894-000-0030-z
[37] 肖宏德. 用益生菌制剂代替断奶仔猪日粮中抗生素的实验研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2013 XIAO Hongde. Experimental study on the replacement of antibiotics in the diet of weaned piglets with probiotics[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2013
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 王园园,万金庆,杜欣雨,王友君,孙晓琳,童年. 冰温脱水对草鱼鱼糜凝胶品质的影响. 食品与发酵工业. 2024(01): 225-231 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 郑赵敏,徐巧玲,郑洪梨,刘俊辰,施咏淇,姚春霞,肖春元,汪兰. 枸杞粉对白鲢鱼糜凝胶品质的影响. 食品与发酵工业. 2024(02): 168-176 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 陈训俭,陈泽宇,丁婷,胡婷,王蔚新,占剑峰. 豌豆全粉对鱼糜凝胶品质的影响. 食品科技. 2024(06): 142-146 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 黄楚雄,李洁,刘纪红,严守雷,王茜. 不同品种莲藕加工藕圆子适应性评价. 食品工业科技. 2023(06): 283-291 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 施咏淇,王攀,周思瑞,郑赵敏,邹航,赵尚龙,张恩来,姚春霞,谭志国. 芋头粉对白鲢鱼糜制品品质的影响. 食品工业科技. 2023(24): 63-71 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(5)





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



