Research Progress on Regulation of Bacterial Exopolysaccharide Biosynthesis by Cyclic Diguanylate
-
摘要: 细菌胞外多糖(Exopolysaccharide,EPS)是细菌生长代谢过程中自身合成并分泌到细胞壁外的一种次级代谢产物,可以调节细胞对不同基质的初始附着,保护细胞抗环境胁迫和脱水。作为潜在的益生元,EPS具有安全,无毒和特殊的理化性质,广泛应用在食品、医药、生物和工业等领域。然而,细菌代谢系统复杂,EPS的生物合成机制仍未得到全面解析。环二鸟苷酸(Cyclic diguanylate,c-di-GMP)作为一类重要的第二信使,在细菌的生物被膜形成、运动性、黏附、毒力以及EPS合成等众多生理活动上发挥重要的调控作用。c-di-GMP转录调控机制的解析,为探明细菌EPS的生物合成机理提供了全新的思路。本文详细总结了c-di-GMP的特性及合成降解途径,重点综述c-di-GMP在介导细菌EPS生物合成过程中的调控机理。本篇综述为揭示细菌EPS生物合成机理和构效关系的研究提供理论基础。Abstract: Bacterial exopolysaccharide (EPS) is a secondary metabolite that is synthesized and secreted outside the cell wall during bacterial growth and metabolism. It can regulate the initial attachment of cells to different substrates and protect cells against environmental stress and dehydration. As a potential prebiotic, EPS has the characteristics of safety, non-toxicity and unique physical and chemical properties, and is widely used in the fields of food, medicine, biology and industry. However, the bacterial metabolic system is complex, and the biosynthetic mechanism of EPS has not been fully elucidated. Cyclic diguanylate (c-di-GMP) is an important second messenger, and it plays an important role in the regulation of many physiological activities such as biofilm formation, motility, adhesion, virulence and EPS synthesis. The analysis of the transcriptional regulation mechanism of c-di-GMP provides a new idea for exploring the biosynthesis mechanism of bacterial EPS. This paper summarizes the characteristics and synthetic degradation pathways of c-di-GMP in detail, and focuses on the regulatory mechanism of c-di-GMP in the process of bacterial EPS biosynthesis. This paper provides a theoretical basis for revealing the mechanism of bacterial EPS biosynthesis and the structure-activity relationship.
-
Keywords:
- bacteria /
- exopolysaccharide /
- biosynthesis /
- cyclic diguanylate
-
细菌在不同的培养条件下可以产生具有多种化学结构和组成的生物聚合物,其中一些生物聚合物是分泌到周围环境中的多糖,即胞外多糖(Exopolysaccharide,EPS)[1]。EPS根据单糖组成可分为同型多糖和异型多糖。产EPS的细菌主要包括根瘤菌(Rhizobium)、假单胞菌(Pseudomonas adaceae)、土壤杆菌(Alcaligenes faecalis)、葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus)、霍乱弧菌(Vibrio cholerae)、短乳杆菌(Lactobacillus brevis)、肠膜明串珠菌(Leuconostoc mesenteroides)、融合魏斯氏菌(Weissella cibaria)和罗伊氏乳杆菌(Lactobacillus reuteri)等[1-3]。EPS作为细胞外基质的主要成分,不仅参与生物膜的形成,还可以促进细胞间粘附、表面附着,作为物理屏障保护封闭的细菌群落免受环境压力[3],并通过保护细胞免受包括宿主防御因素在内的非生物和生物胁迫而提供生存优势[4-5]。EPS具有抗炎、抗氧化、抑制肿瘤、抗病毒、抗辐射、自身免疫调节、土壤重金属吸附等功能特性,广泛应用在生物、化学、医药和环境等领域[6]。此外,EPS作为增稠剂、稳定剂、乳化剂以及潜在的益生元,添加到食品和饲料中,可以改善产品的质量和品质[7]。与植物、动物和藻类等其他来源的多糖相比,细菌EPS分离纯化方法简单、易于提纯,在一定条件下可稳定生产。目前已经被商业化生产的EPS主要包括斯宾根、黄原胶、葡聚糖、海藻酸盐和纤维素等[7]。
EPS具有多种优良的特点是因为其本身独特的结构,除少量EPS外,大多数EPS拥有大量的羟基、羧基,因此其本身易溶于水,易发挥生物活性。要探明EPS的结构性质,首先要解析细菌EPS的生物合成机制,然而细菌代谢通路复杂,EPS合成由多个调控路径共同作用。近年来,多种产EPS的菌株被分离鉴定,EPS的结构和性质探究逐步成为研究热点,然而细菌EPS生物合成的细胞和环境信号具有很大的变异性,调控机制及构效关系仍未得到解析。因此,探究细菌EPS的生物合成机制对其应用具有重要的作用,但调节细菌EPS产生的细胞和环境信号以及信号网络很复杂,影响因素多,研究难度大,这些因素限制了EPS的开发及应用。EPS合成主要涉及三种经典代谢调控路径,包括群体感应系统[8]、双组分调控系统[9]和第二信使调控系统[8]。第二信使是近年来逐渐兴起的能够影响EPS生物合成的重要调控因子,但第二信使对细菌EPS合成的调控机制并未完全解析。因此,探究第二信使的理化性质以及对EPS的调控作用,将有助于揭示细菌EPS的生物合成途径,为EPS的合成机理研究提供新的思路,促进糖生物学的进一步发展。
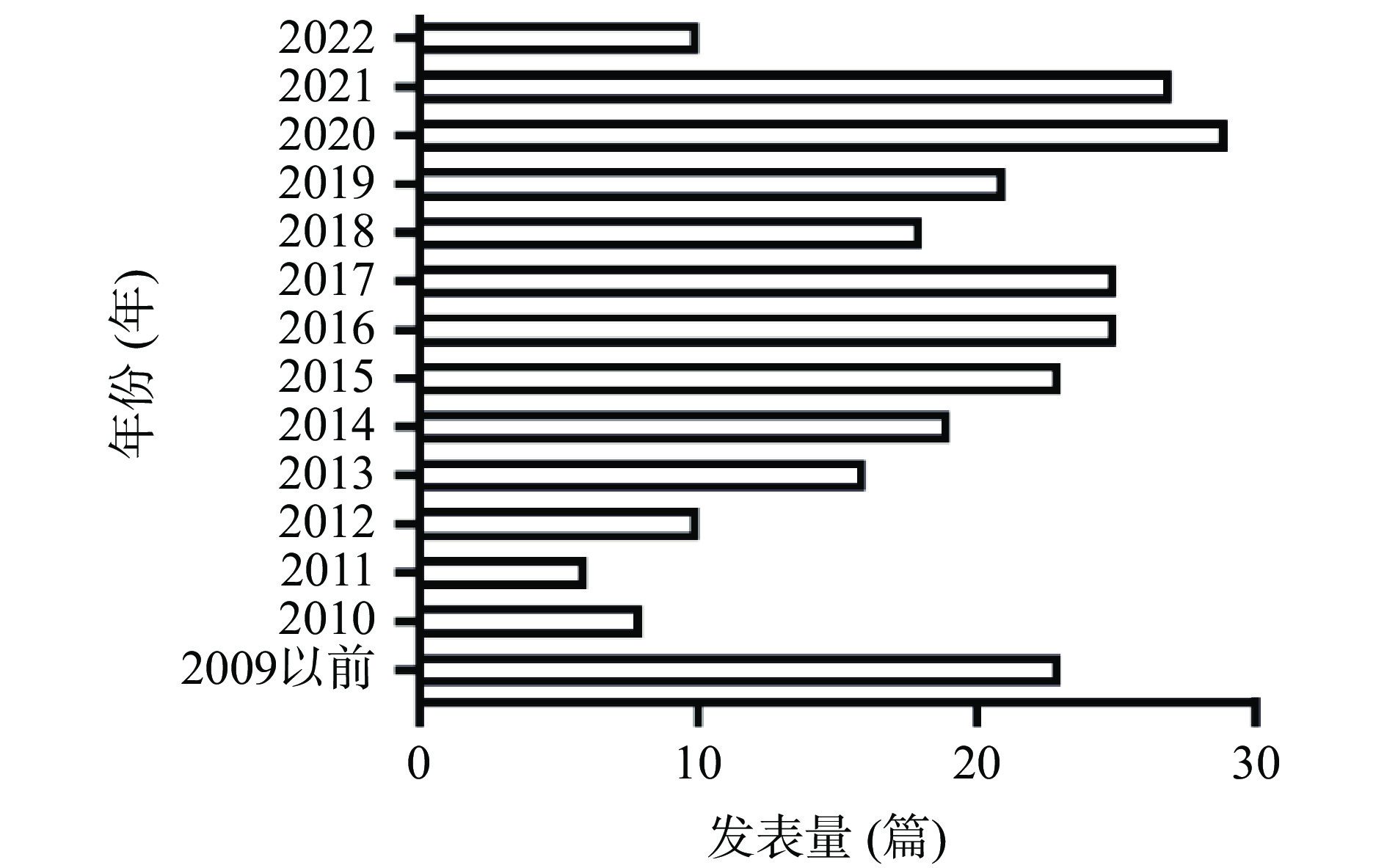
第二信使主要包括环腺苷酸(cAMP)、环鸟苷酸(cGMP)、环二鸟苷酸(Cyclic diguanylate)、环二腺苷酸(Cyclic diadenylate,c-di-GMP)、肌醇三磷酸(IP3)、甘油二酯(DAG)、钙离子(Ca2+)等[10]。第二信使分子与细胞表面的受体结合后,通过受体信号转导来调控细菌EPS的生物合成,其中c-di-GMP是目前广泛研究的第二信使分子[4]。c-di-GMP是一种鸟苷酰寡核苷酸类物质,对纤维素合成酶有变构激活作用,最初由Benziman在1987年发现[11]。c-di-GMP可以参与调节细胞周期进程,包括细胞分化、细菌运动的形成、致病因子的产生以及生物膜的形成等[12]。c-di-GMP与多种效应物相互作用,通过c-di-GMP的结合进行变构调节活性,并由几个蛋白质和RNA受体家族执行信号转导[13]。c-di-GMP能介导多种细胞功能,特别参与细菌运动和固着方式的转变[11]。c-di-GMP通过调节细菌EPS操纵子的转录水平,以及EPS生物合成和分泌机制的翻译后调节,来介导细菌EPS的生物合成[14]。通过PubMed数据库平台搜索关键词“c-di-GMP和EPS”分析近年公开发表的论文数量,可以看出c-di-GMP介导细菌EPS的研究正逐渐成为微生物领域的研究热点(图1)。本文从第二信使的角度综述了c-di-GMP的代谢途径,重点阐述c-di-GMP对几种重要细菌EPS生物合成的操纵机制。
1. c-di-GMP代谢途径
c-di-GMP的合成代谢受二鸟苷酸环化酶(Diguanylate cyclase,DGC)和磷酸二酯酶(Phosphodiesterase,PDE)调控[14]。细菌通过DGC与PDE的联合调控,使细胞内c-di-GMP的浓度维持在相对稳定的水平,进而使细胞行使正常功能。DGC与PDE能够催化合成c-di-GMP的关键在于其含有GGDEF结构域和EAL结构域[10]。GGDEF和EAL结构域分布非常广泛,存在于微生物系统发育树的各个分支,但在古生菌和真核生物中不含有类似结构域。DGC通过羧基末端的GGDEF结构域将两分子的GTP催化缩合成为c-di-GMP。GGDEF结构域的氨基酸基序为Gly-Gly-Asp-Glu-Phe,长度约为180个氨基酸左右。DGC含有能够与底物结合的催化位点A,以及能够与其发生竞争并抑制c-di-GMP合成的含有RXXD基序的I位点[15]。Ramírez-mata等[16]通过构建巴西偶氮螺菌(Spirophyllum brassica)cdg-A缺失菌株,结合CA染色分析表明野生型与突变株之间EPS的产量存在显著差异,c-di-GMP浓度下降会抑制EPS的生物合成,证明含有GGDEF结构域的cdg-A参与调控EPS的生物合成。对于不具备I位点的DGC,则需要PDE来进行联合调控。
PDE含有EAL或HD-GYP蛋白结构域,可以将c-di-GMP降解为线性5′-O-膦酰基胍基-(3′->5′)-鸟苷三钠盐(5′-pGpG)或2分子GMP。EAL结构域含有Glu2-Ala-Leu基序,长度约为240个氨基酸。含有EAL的PDE对其底物具有高度特异性,但需要Mg2+或Mn2+作用下才能发挥功能。EAL结构域通过酯键的水解催化c-di-GMP的不对称开放,生成5′-pGpG。EAL型PDE的高级结构在脱氮硫杆菌(Thiobacillus denitrificans)和肺炎克雷伯菌(Klebsiella pneumonia)等菌株中被测定[17]。
1.1 c-di-GMP效应分子
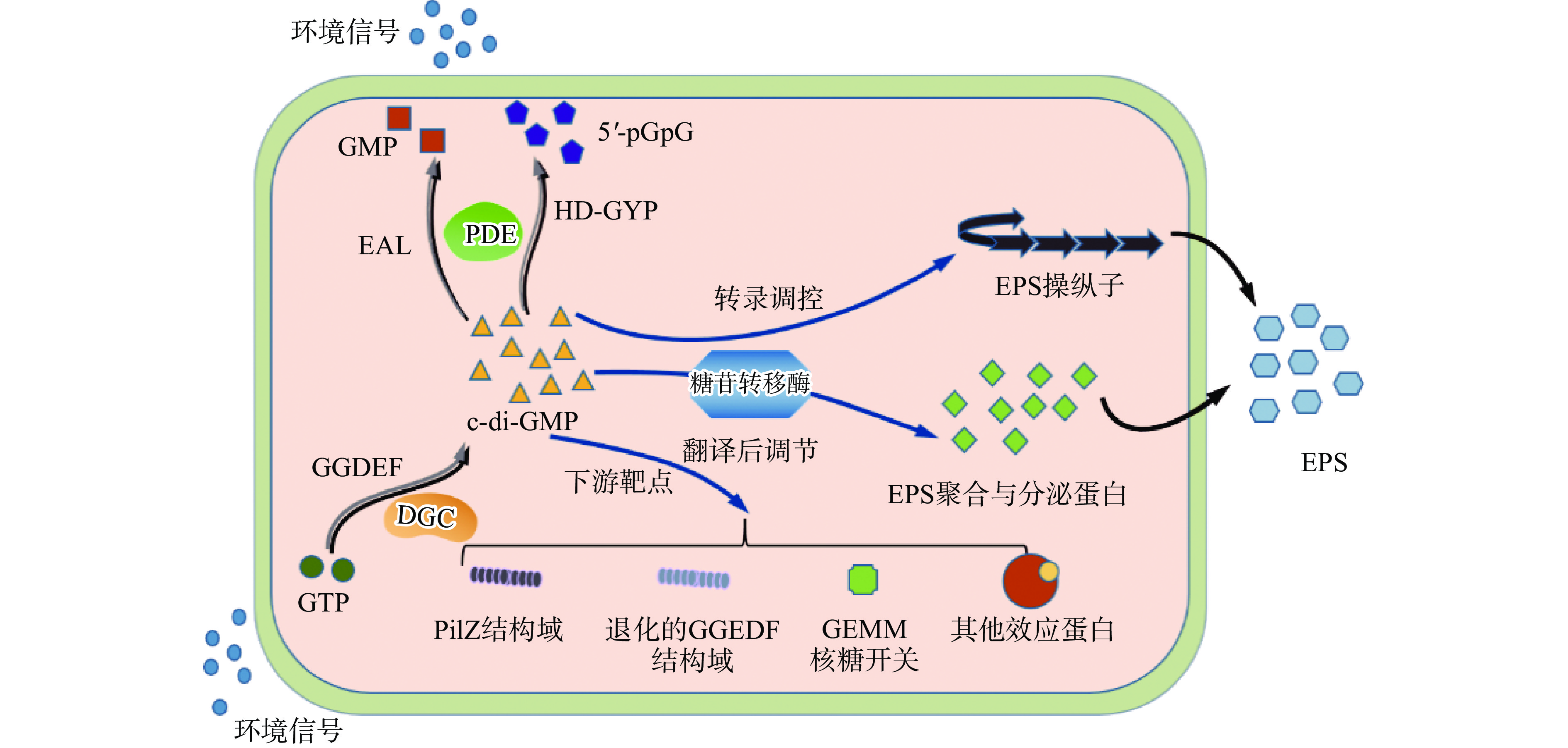
c-di-GMP能在多个水平上干扰细胞信号,包括转录[13]、翻译[17]、蛋白质活性[18]、蛋白质分泌和蛋白质稳定性[19]等。这种分子机制的多样性使c-di-GMP存在多种特异性效应器,主要包括PilZ结构域效应蛋白、核糖开关、退化的GGDEF结构域(图2)[15]。
1.1.1 PilZ结构域
PilZ结构域是第一个被确定的c-di-GMP受体。比较序列分析发现,PilZ结构域是一种广泛存在的蛋白质模块,系统发育分布模式类似于含有GGDEF和EAL结构域的蛋白质,通常与调节、催化(GGDEF、EAL和HD-GYP)、转运结构域相关[20]。PilZ结构域具有几个特征,使其在c-di-GMP结合蛋白中具有独特的特性。首先,它包含两个独立的序列基序,围绕一个c-di-GMP鸟嘌呤碱基的保守精氨酸残基的RXXXR基序,另一个DXSXXG基序围绕另一个鸟嘌呤碱基。其次,PilZ结构域不需要进行太多的构象调整就能够与c-di-GMP分子结合[21-22]。Amikam 等[23]发现 BcsA 的 C 末端是 c-di-GMP 的结合部位,该部位与PilZ结构域具有高度同源性,这是第一个被证明受c-di-GMP调节的酶。在众多菌群中含有PilZ结构域的效应蛋白大都能与c-di-GMP结合,例如在V. cholerae PlzD蛋白的复合物中,只有一个c-di-GMP效应分子被检测到[24],而与恶臭假单胞菌(Pseudomonas putida)密切相关的YcgR蛋白能与c-di-GMP结合,纤维素合成酶亚基Plg44蛋白中的PilZ结构域也是如此[25]。在铜绿假单胞菌(Pseudomonas aeruginosa)和棕色固氮菌(Azotobacter vinelandii)中,PilZ结构域与海藻酸盐合成结构域耦连,调控海藻酸盐的生物合成[26]。此外,在多种蛋白质的功能分析中已经阐明了PilZ结构域在细胞中的特定作用,能够调控动植物病原体毒力[27]、运动性和EPS合成等[28]。
1.1.2 核糖开关
核糖开关是一类通过结合小分子代谢物来调控基因表达以响应其目标配体浓度变化的mRNA结构域,由约100个核苷酸组成,参与c-di-GMP信号传导[29],最早由Tamayo等[30]提出。如今被发现的核糖开关有20多种,与其响应的配体种类繁多。第一个c-di-GMP核糖开关由Breaker团队于2008年发现,并根据其作用方式分为Ⅰ类核糖开关与Ⅱ类核糖开关[31]。核糖开关控制着细胞周期进程的基因表达,包括毒力基因的表达、菌毛形成和鞭毛的生物合成。c-di-GMP作为小分子配体与核开关结合以后,引起核开关的构象发生改变,阻止mRNA的转录或者抑制翻译的起始,从而调节与c-di-GMP相关的基因活动[32]。核糖开关是第一个发现的能结合第二信使的基因调控RNA(gene-regulatory RNA)[31]。目前,在V. cholerae、P. aeruginosa、交替单胞菌(Alteromonas)中均发现了核糖开关。苏云金芽孢杆菌(Bacillus thuringiensis)CT-43中的Bc3、Bc4、Bc5以Ⅰ型核糖开关的形式与c-di-GMP结合,促进下游基因的表达[33]。然而,在一些细菌中,c-di-GMP与核糖开关的结合也会抑制下游基因的表达。在V. cholerae中,c-di-GMP与核糖开关通过隔离SD序列与抑制翻译来下调tfoY基因的表达,从而响应配体的结合[34]。
1.1.3 退化的GGDEF结构域
退化GGDEF结构域是另一类功能重要的c-di-GMP受体,它能够通过保守I位点(RXXD)进行c-di-GMP传感和信号传递 [35]。GGDEF结构域具有一个退化的活性位点,在新月柄杆菌(Caulobacter crescentus)PleD的晶体结构中观察到c-di-GMP与这些蛋白的结合会诱导GGDEF结构域在亚基内或亚基间的交联[36-37],或将该结构域连接在它们的目标蛋白上,从而导致c-di-GMP结合在效应因子时产生很大的构象变化。P. aeruginosa的PelD,V. cholerae的CdgG都含有类似的功能[35]。
2. c-di-GMP调控细菌EPS的生物合成
细菌的生存需要感知外界信号以此来适应复杂的外界环境,c-di-GMP通过与细胞表面受体结合,形成信号通路来影响EPS生物合成操纵子的转录水平,介导EPS的生物合成,以及通过糖基转移酶在EPS生物合成和分泌机制的翻译后调节(图2)[38]。许多EPS在一定程度上受到c-di-GMP的调控,包括广泛分布的细菌纤维素和聚-β(1-6)-N-乙酰-D-葡萄糖胺(PNAG)、海藻酸盐、β-葡聚糖(β-MLG)、植物伴生细菌产生的凝胶多糖、黄原胶、Pel多糖、Psl多糖等[15]。
2.1 c-di-GMP调控纤维素的合成
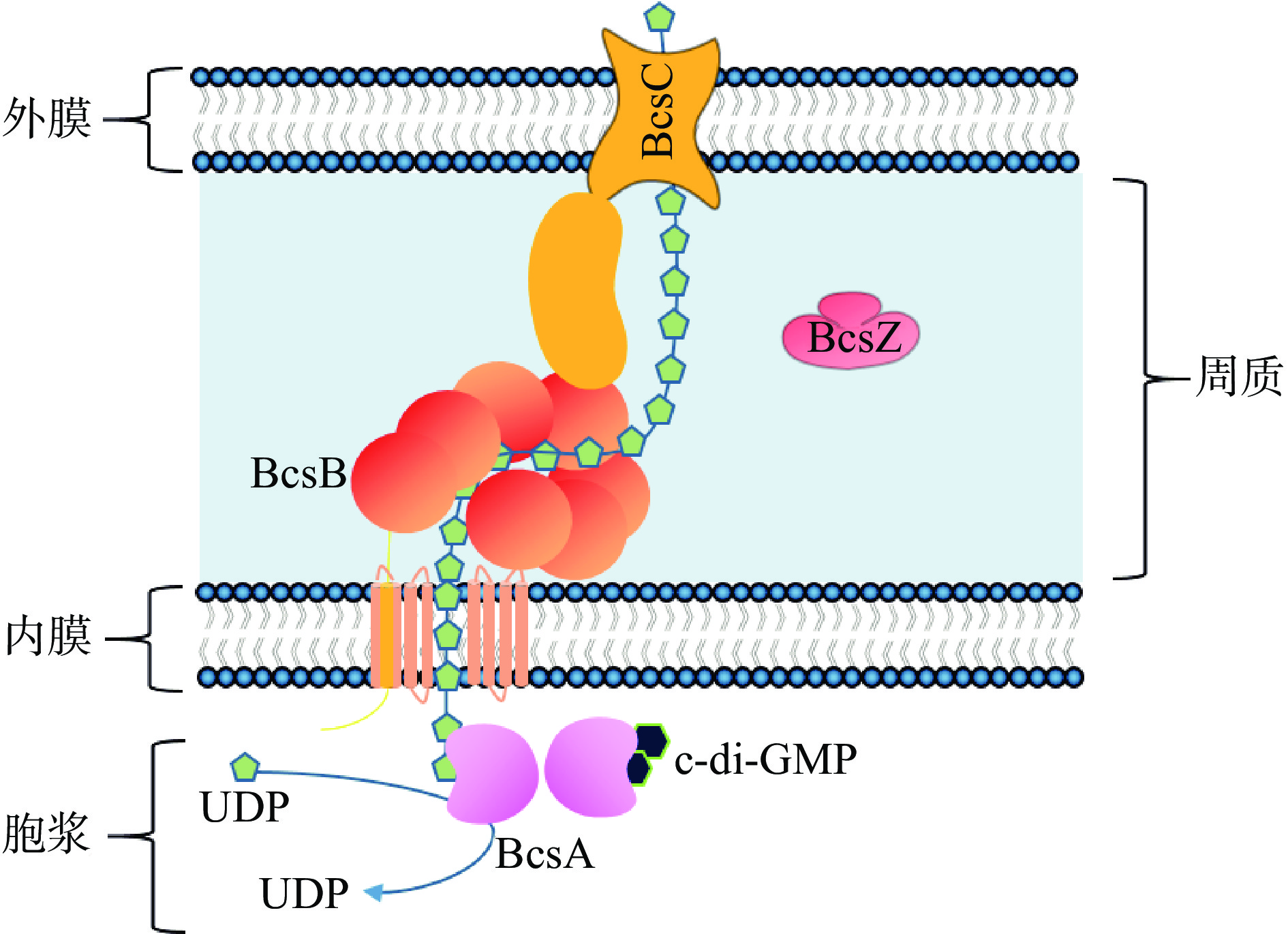
纤维素是自然界中分布最广、含量最多的一种多糖,主要由葡萄糖组成。在革兰氏阳性菌和革兰氏阴性菌中都观察到纤维素的产生[39]。醋酸菌属(Acetobacter)、土壤杆菌属(Agrobacterium)、根瘤菌属(Rhizobium)和八叠球菌属(Sarcina)是纤维素的主要来源菌[39-40]。细菌生物膜中存在的纤维素也经常被其他物质修饰,例如O-醋酸盐和O-磷脂酰乙醇胺(pEtN)基团。细菌纤维素的生物合成依赖于细胞c-di-GMP浓度。在体外,c-di-GMP的存在可以使木霉的纤维素生物合成量增加50到200倍,c-di-GMP可以通过结合和激活纤维素合成酶(Bcs)启动子在转录水平上影响纤维素的生物合成[41],但木霉中主要的激活机制是通过纤维素合成酶复合物Bcs本身的直接变构激活(图3)[42]。
1990年发现了第一个细菌纤维素合成酶操纵子,并发现该操纵子编码四种核心蛋白质(BcsA、BcsB、BcsC和BcsD),这四种蛋白质是革兰氏阴性细菌中纤维素生物合成所需的[43]。除此之外,还包括能够水解纤维素为还原性寡糖的内切葡聚糖酶(BcsZ)。此后,在其他革兰氏阴性和革兰氏阳性细菌中也发现了该操纵子的变体,包括驯化的大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli)K12菌株[13]。c-di-GMP调节纤维素生物合成的主要机制也是通过细菌纤维素合成酶催化亚基(BcsA)蛋白的变构激活[13]。c-di-GMP与纤维素合成酶中C-末端PilZ结构域的保守RXXD基序结合来激活纤维素产生[27]。通过这种机制,c-di-GMP结合释放出一种蛋白质的自抑制状态,称为“门控环”,它与PilZ结构域相互作用,并控制底物与活性位点的结合。c-di-GMP与PilZ结构域的结合将“门控环”从活性部位移开,并允许底物扩散[42]。在这些条件下,c-di-GMP不会影响底物的米氏常数(Km),但会增加具有催化活性的酶的比例[44]。在没有c-di-GMP结合的情况下,BcsA采用自动抑制构象,阻止底物结合。相应地,细胞内较高的c-di-GMP浓度与BcsA活性增加相关,从而诱导更多的纤维素及更长的纤维素聚合物的产生[13]。
c-di-GMP可以与多种调控蛋白结合,促进纤维素的合成。BcsE蛋白存在于编码pEtN纤维素生产的操纵子中,它与c-di-GMP进行结合,有助于纤维素合成酶内膜复合物的形成和稳定[45]。与木霉EPS合成机制不同,E. coli通过bcsRQABZC操纵子以及位于它的相反链的bcsEFG操纵子来编码合成更大的纤维素复合物。其中BcsE蛋白是一种59 kDa的可溶性蛋白,它的C端含有一个类似的GGDEF结构域,与c-di-GMP的结合需要通过保守I位点来完成并引起构象变化,使C端结构域更靠近N端结构域。BcsE蛋白与BcsQ和BcsR形成一个2:2:2的复合物,进而通过与BcsA的PilZ结构域的相互作用来合成纤维素合酶复合物,从而大量合成纤维素[45-46]。除此之外,c-di-GMP还可以通过提高糖基转移酶活性来提高纤维素的合成。例如在根癌农杆菌(Agrobacterium tumefaciens)胞内c-di-GMP浓度提高刺激含PilZ结构域的CelA糖基转移酶亚基活性,进而提高纤维素的合成与分泌[4]。
纤维素合酶的激活机制已经取得了重大的进展,但鉴于纤维素生物合成机制的复杂性,仍然需要更多的试验来探索不同菌株中EPS的生物合成机制。基于基因相似性,研究者们认为c-di-GMP与BcsE结合可能通过形成BcsEFG复合物来调节BcsG的pEtN转移酶活性[47],这意味着c-di-GMP在激活纤维素合成和调节pEtN修饰方面发挥着双重作用。但c-di-GMP是否在E. coli和其他革兰氏阴性菌中调控pEtN对纤维素的修饰,以及这种调控机制的主要分子细节的阐述,这些问题仍有待研究。
2.2 c-di-GMP调控海藻酸盐的生物合成
藻酸盐又称海藻酸盐、海藻酸胶、褐藻酸盐,主要存在于褐藻的细胞壁和细胞间黏胶质中,也存在于一些产黏质荚膜的假单胞菌(Pseudomonas adaceae)和固氮菌等细菌中[48],主要由β-D-甘露糖醛酸(β-D-mannuronic acid,ManA)和α-L-古洛糖醛酸(α-l-guluronic acid,GluA)通过β-(1→4)糖苷键连接组成的线性EPS。藻酸盐的生物合成调控网络具有高度复杂性,包括转录、转录后和翻译后调控,需要13种蛋白质的配合,其中有12种蛋白质由藻酸盐合成的膜蛋白糖基转移酶(Alg)基因(alg)操纵子编码,而algC编码GDP ManA糖核苷酸生物合成所需的磷酸甘露糖突变酶。
Alg 44是海藻酸盐生物合成中的重要组件,编码含有PilZ结构域的蛋白质[25]。Whitney等[25]确定了与c-di-GMP结合的Alg 44 PilZ结构域的晶体结构,该模型显示Alg 44 PilZ结构域以同型二聚体存在,每个PilZ结构域通过RXXXR基序与二聚体c-di-GMP结合。Alg 44的N端PilZ结构域通过单程跨膜螺旋连接到周质C端膜融合结构域[25]。Alg 8是海藻酸生物合成的聚合酶,是一种内膜蛋白。在P. aeruginosa中,MucR已被证实是Alg 44的c-di-GMP依赖性调节的来源[49]。Alg 44与Alg 8相互作用,形成海藻酸-聚合酶复合物[50],并形成由AlgK、AlgE、AlgG和AlgX组成的周质支架[26],促进聚ManA链在细胞质上的易位,进而调控海藻酸盐的生物合成,证明c-di-GMP能够在翻译后调节P. aeruginosa海藻酸盐的产生,具体代谢路径见图4[42]。不同菌种负责c-di-GMP依赖性调节的来源也不相同,Carlos发现与P. aeruginosa中控制c-di-GMP合成的MucR不同,在藤兰偶氮杆菌(Azotobacter vinelandii)中MucR作为PDE来限制c-di-GMP的合成,而AvGReg主要负责c-di-GMP的合成,并与氧转移速率(OTR)来共同调节海藻酸盐的合成与分子量[49]。对海藻酸盐合成途径的探索证明其代谢通路并不同于纤维素的“门控环”调节,也不涉及聚合酶复合物的稳定,而是通过Alg 44与Alg 8的激活机制控制海藻酸盐的合成。对海藻酸盐代谢途径的阐明加速了相关领域的发展,但是不同水平的c-di-GMP对海藻酸盐分子量的影响有待进一步研究。
2.3 c-di-GMP调控多聚氮乙酰葡萄糖胺(PNAG)的生物合成
PNAG是细菌细胞壁基质和生物膜广泛存在的一种线性多糖,在革兰氏阳性菌葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus)中也称为多糖细胞间粘附素(PIA),是迄今为止报道的最常见的生物膜相关EPS之一,由革兰氏阳性菌和革兰氏阴性菌产生。其中革兰氏阴性菌中PNAG的产生主要由c-di-GMP调控,且这种调节大都发生在翻译后。PNAG的合成涉及到四种蛋白质之间的互作,它们由pgaABCD操纵子编码合成,统称为PNAG合酶[51]。PgaA和PgaB负责PNAG胞外运输,PgaC和PgaD是多糖聚合与延伸所必需的[52]。c-di-GMP可以调控E. coli的生物膜和PNAG产生,其中PgaD蛋白的浓度依赖于DGC的活性,并且这种调控发生在翻译后[52]。c-di-GMP可以直接与PgaC和PgaD结合,在内膜中形成稳定的复合物,变构激活PgaC的糖基转移酶活性,缺少c-di-GMP,则PgaD不稳定,并迅速降解[53]。此外,c-di-GMP与PgaCD复合物的结合被证明可以变构激活PgaC的糖基转移酶活性[53]。但PgaCD和c-di-GMP之间复合物的性质及其变构激活PgaC的确切机制尚未确定。
革兰氏阳性菌PNAG的产生独立于c-di-GMP的调控。例如表皮葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus epidermidis)中去N-N-乙酰化PNAG的合成依赖于含GGDEF结构域的蛋白GdpS,但GdpS作为一种DGC是不活跃的。S. epidermidis的gdpS基因似乎通过一种独立于其蛋白编码功能的机制来调节icaABCD操纵子的转录和胞外多糖的合成[54]。
2.4 c-di-GMP调控Pel的生物合成
Pel是P. aeruginosa生物膜细胞外基质的结构成分,在生物膜周围、茎区的细胞粘附和细胞外DNA中发挥作用[51]。Pel由部分去乙酰化的1,4-N-乙酰葡萄糖胺(GlcNAc)和N-乙酰半乳糖胺(GalNAc)组成,生物合成需要pelABCDEFG操纵子的蛋白产物[55-56],并依赖合酶多糖分泌途径进行。在革兰氏阴性菌中,该途径是由外膜蛋白、含有周质四肽重复序列的支架蛋白和内膜嵌入的合酶组成的。这些系统的合酶组分由糖基转移酶结构域催化聚合,该结构域由c-di-GMP变构调控。
与海藻酸盐和纤维素一样,Pel合成主要是由c-di-GMP翻译后调控,然而不同的是,参与Pel合成的蛋白质都不包含PilZ结构域。筛选pel操纵子中编码的c-di-GMP结合蛋白发现,PelD的细胞质结构域是c-di-GMP的结合蛋白。PelD包含四个N端跨膜螺旋、C端GAF结构域和一个GGDEF结构域。Whitney等[57]发现了PelD的C末端结构域的结构,并揭示了c-di-GMP与PelD的RXXD基序结合。除了RXXD基序的R367和D370之外,来自GGDEF结构域的R402是c-di-GMP结合所必需的,而GAF结构域的R161与结合的c-di-GMP相互作用,但不是结合所必需的[57]。此外,PelD的N端跨膜结构域和C端GAF/GGDEF结构域的区域形成卷曲螺旋二聚化结构域[25],影响Pel的生物合成。但目前尚不清楚c-di-GMP与PelD的结合是如何在翻译后调节Pel的产生,推测PelD与PelE和PelG形成了一个内膜复合物,共同将糖基转移酶PelF招募到细胞膜上并调节EPS的合成[56],具体的作用机制需要对PelDEFG复合物进行进一步的结构分析。
除了上述调控路径,c-di-GMP也可以在转录水平调控EPS的合成。FleQ是P. aeruginosa中的增强子结合蛋白,通过结合pel和psl操纵子的启动子发挥转录抑制作用,这种抑制作用通过c-di-GMP与FleQ的直接结合而解除。与c-di-GMP结合后,FleQ占据不同的启动子区域,因此激活pel操纵子转录合成Pel[58]。
2.5 c-di-GMP调控葡聚糖的生物合成
葡聚糖是指以葡萄糖为单糖组成的同型线性多糖,葡萄糖单元之间以糖苷键连接。其中根据糖苷键的类型又可分为α-葡聚糖和β-葡聚糖,是一种重要的EPS。苜蓿中华根瘤菌(Sinorhizobium meliloti)、白色念球菌(Candida albicans)以及部分乳酸菌(Lactic acid bacteria)是葡聚糖的主要来源菌[59]。在S. meliloti中,BgsA作为一种糖基转移酶,可以催化形成由(1→3)(1→4)糖苷键连接而成新型线性β-D-葡聚糖[60]。c-di-GMP对不含有PilZ结构域的BgsA的细胞质C端结构域(C-BgsA)具有高亲和力和特异性,在转录水平以及翻译后调节葡聚糖的生物合成[60]。此外,S. meliloti中的AraC家族的转录调控因子CuxR的二聚体也可以在c-di-GMP的作用下调控细菌EPS的生物合成[61]。
乳酸菌作为益生菌,产生的EPS主要为葡聚糖,是目前细菌EPS的主要来源。作为潜在的益生元,乳酸菌EPS分离纯化方法简单,易于大量生产,广泛应用在食品、医药和化工等领域[62]。然而乳酸菌基因组较大,代谢系统复杂,EPS的合成受到多种调控因子的作用,其生物合成机理及构效关系仍未得到解析。随着在厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)中发现了c-di-GMP,促使研究者开始关注c-di-GMP在乳酸菌中的作用。研究发现,在植物乳杆菌(Lactobacillus plantarum)和嗜酸乳杆菌(Lactobacillus species)等一些乳酸菌中发现了含有EAL结构域蛋白,但c-di-GMP合成酶和分解酶的特性尚不清楚,推测该蛋白是一种参与调节EPS合成的跨膜蛋白[63]。随后He等[64]发现在Lb. species EPS生物合成过程中,c-di-GMP可以调控EPS的生成,糖苷转移酶基因的表达影响dgc基因转录调控,证明二鸟苷酸环化酶和磷酸二酯酶和糖苷转移酶可能共同调节EPS产生。在先前的研究中,课题组从Ln. mesenteroides、假肠膜明串珠菌(Leuconostoc pseudomensenteroides)和乳酸片球菌(Pediococcus acidilactici)的基因组中均筛选挖掘得到c-di-GMP合成代谢基因dgc和pde,并证实EPS含量和糖苷转移酶的活性与c-di-GMP含量和dgc表达量呈正相关,其具体的调控机制有待进一步探究。
3. 总结与展望
c-di-GMP能够在翻译后调节EPS生物合成,包括细菌纤维素、聚乙酰葡糖胺、凝胶多糖、黄原胶、单极性多糖、Psl和Pel等。尽管这些多糖的生物合成都受到c-di-GMP的直接调控,但它们通过不同的c-di-GMP受体和激活机制来完成这一调控。c-di-GMP的效应蛋白和受体靶标的研究比较成熟,但是新受体靶标的鉴定,多种效应蛋白的不同调节模式有待进一步研究。对c-di-GMP信号转导机制的了解主要局限于遗传研究、推断的蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用、序列比对或分离的GGDEF结构域的同源性建模。随着糖生物学基础研究的发展,研究者们力求从新的视角和思路去探究细菌EPS生物合成的新方法和新理论,然而由于细菌代谢系统复杂,EPS的生物合成受到多种转录调控因子的精密调控。此外,不同菌株遗传特性和代谢途径具有复杂性,调控机理不具普遍适用性。有关c-di-GMP对EPS合成调控的研究起步较晚,其代谢通路和信号机制有待完善。虽然大量研究已经报道了c-di-GMP在P. aeruginosa、V. cholerae、Sionrhizobium、念球菌(Albicans)等细菌中的调控作用,但是在乳酸菌等益生菌EPS生物合成的研究较少,且具体的调控机制仍不清楚。乳酸菌代谢受多种调控网络共同作用,使得所产生的EPS结构和性质差异较大。在乳酸菌EPS生物合成过程中,c-di-GMP的信号通路也不是孤立的,可能与多种信号分子组成了复杂的信号传递网络。因此,探究乳酸菌及益生菌EPS的生物合成机制将对其在食品、化工、医药等领域的应用起到积极的推动作用,而这一机制的解析有望通过第二信使调控机制的探明得以解决。在未来研究中,应进一步探究c-di-GMP在乳酸菌等益生菌EPS生物合成中的作用,综合利用多种研究手段,开拓新的研究方法加速第二信使以及糖生物学的进一步发展。
-
-
[1] SCHMID J. Recent insights in microbial exopolysaccharide biosynthesis and engineering strategies[J]. Current Opinion in Biotechnology,2018,53:130−136. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2018.01.005
[2] 姜静, 郭尚旭, 张鑫, 等. 融合魏斯氏菌(Weissella confusa)XG-3的分离鉴定及其胞外多糖性质初步研究[J]. 黑龙江大学自然科学学报,2020,37(1):71−80. [JIANG J, GUO S X, ZHANG X, et al. Isolation and identification of exopolysaccharide-producing Weissella confusa XG-3 and primary characterization of its exopolysaccharide[J]. Journal of Natural Science of Heilongjiang University,2020,37(1):71−80. [3] YAN J, BASSLER B L. Surviving as a community: Antibiotic tolerance and persistence in bacterial biofilms[J]. Cell Host & Microbe,2019,26(1):15−21.
[4] 艾连中, 范艺周, 熊智强. 第二信使分子调控细菌胞外多糖生物合成研究进展[J]. 中国食品学报,2021,21(4):1−8. [AI L Z, FAN Y Z, XIONG Z Q. Advances in bacterial exopolysaccharide biosynthesis regulated by the second messenger molecule[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2021,21(4):1−8. [5] KUNZ S, TRIBENSKY A, STEINCHEN W, et al. Cyclic di-GMP signaling in Bacillus subtilis is governed by direct interactions of diguanylate cyclases and cognate receptors[J]. Mbio,2020,11(2):e03122−19.
[6] RANA S, UPADHYAY L S B. Microbial exopolysaccharides: Synthesis pathways, types and their commercial applications[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,157:577−583. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.04.084
[7] ZHANG H, REN W, GUO Q, et al. Characterization of a yogurt-quality improving exopolysaccharide from Streptococcus thermophilus AR333[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,81:220−228. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.12.017
[8] DAS S. Genetic regulation, biosynthesis and applications of extracellular polysaccharides of the biofilm matrix of bacteria[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2022,9(291):119536.
[9] CAI L, MA W, ZOU L, et al. Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola response regulator vemr is co-opted by the sensor kinase Chea for phosphorylation of multiple pathogenicity-related targets[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2022,13:928551. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.928551
[10] HOMMA M, KOJIMA S. Roles of the second messenger c-di-GMP in bacteria: Focusing on the topics of flagellar regulation and Vibrio spp[J]. Genes to Cells,2022,27(3):157−172. doi: 10.1111/gtc.12921
[11] AMIKAM D, BENZIMAN M. Cyclic diguanylic acid and cellulose synthesis in Agrobacterium tumefaciens[J]. Journal of Bacteriology,1989,171(12):6649−6655. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6649-6655.1989
[12] 路新枝, 刘湛军, 于文功. 环二鸟苷酸——新型的细菌第二信使[J]. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2009,25(5):400−406. [LU X Z, LIU Z J, YU W G. Cyclic diguanylate-new second messenger in bacteria[J]. Chinese Journal of Biochemistry Molecular Biology,2009,25(5):400−406. [13] RICHTER A M, POSSLING A, MALYSHEVA N, et al. Local c-di-GMP signaling in the control of synthesis of the E. coli biofilm exopolysaccharide pEtN-cellulose[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology,2020,432(16):4576−4595. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.06.006
[14] RöMLING U, GALPERIN M Y, GOMELSKY M. Cyclic di-GMP: The first 25 years of a universal bacterial second messenger[J]. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews,2013,77(1):1−52. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00043-12
[15] PÉREZ-MENDOZA D, SANJUÁN J. Exploiting the commons: Cyclic diguanylate regulation of bacterial exopolysaccharide production[J]. Current Opinion in Microbiology,2016,4(30):3036−3043.
[16] RAMÍREZ-MATA A, LÓPEZ-LARA L I, XIQUI-VÁZQUEZ M L, et al. The cyclic-di-GMP diguanylate cyclase CdgA has a role in biofilm formation and exopolysaccharide production in Azospirillum brasilense[J]. Research in Microbiology,2016,167(3):190−201. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2015.12.004
[17] HENGGE R. High-specificity local and global c-di-GMP signaling[J]. Trends in Microbiology,2021,29(11):993−1003. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2021.02.003
[18] ORR M W, WEISS C A, SEVERIN G B, et al. A subset of exoribonucleases serve as degradative enzymes for pGpG in c-di-GMP signaling[J]. Journal of Bacteriology,2018,200(24):e00300−18.
[19] MONDS R D, NEWELL P D, GROSS R H, et al. Phosphate-dependent modulation of c-di-GMP levels regulates Pseudomonas fluorescens Pf0-1 biofilm formation by controlling secretion of the adhesin LapA[J]. Molecular Microbiology,2007,63(3):656−679.
[20] GALPERIN M Y, CHOU S H. Structural conservation and diversity of PilZ-related domains[J]. Journal of Bacteriology,2020,202(4):e00664−19.
[21] DUERIG A, ABEL S, FOLCHER M, et al. Second messenger-mediated spatiotemporal control of protein degradation regulates bacterial cell cycle progression[J]. Genes & Development,2009,23(1):93−104.
[22] VALENTINI M, FILLOUX A. Multiple roles of c-di-GMP signaling in bacterial pathogenesis[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology,2019,73(1):387−406. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-020518-115555
[23] AMIKAM D, GALPERIN M Y. PilZ domain is part of the bacterial c-di-GMP binding protein[J]. Bioinformatics,2006,22(1):3−6. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti739
[24] CHOU S-H, GALPERIN M Y. Diversity of cyclic di-GMP-binding proteins and mechanisms[J]. Journal of Bacteriology,2016,198(1):32−46. doi: 10.1128/JB.00333-15
[25] WHITNEY J C, WHITFIELD G B, MARMONT L S, et al. Dimeric c-di-GMP is required for post-translational regulation of alginate production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry,2015,290(20):12451−12462. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.645051
[26] KRASTEVA P V, BERNAL-BAYARD J, TRAVIER L, et al. Insights into the structure and assembly of a bacterial cellulose secretion system[J]. Nature Communications,2017,8(1):1−10. doi: 10.1038/s41467-016-0009-6
[27] CHEANG Q W, XIN L, CHEA R Y F, et al. Emerging paradigms for PilZ domain-mediated c-di-GMP signaling[J]. Biochemical Society Transactions,2019,47(1):381−388. doi: 10.1042/BST20180543
[28] CONNER J G, ZAMORANO-SÁNCHEZ D, PARK J H, et al. The ins and outs of cyclic di-GMP signaling in Vibrio cholerae[J]. Current Opinion in Microbiology,2017,36:20−29. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2017.01.002
[29] ARIZA-MATEOS A, NUTHANAKANTI A, SERGANOV A. Riboswitch mechanisms: New tricks for an old dog[J]. Biochemistry,2021,86(8):962−975.
[30] TAMAYO R, PRATT J T, CAMILLI A. Roles of cyclic diguanylate in the regulation of bacterial pathogenesis[J]. Annual Review of Microbiology,2007,61(1):131−148.
[31] SUDARSAN N, LEE E, WEINBERG Z, et al. Riboswitches in eubacteria sense the second messenger cyclic di-GMP[J]. Science,2008,321(5887):411−413. doi: 10.1126/science.1159519
[32] MCNERNEY M P, STYCZYNSKI M P. Small molecule signaling, regulation, and potential applications in cellular therapeutics[J]. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Systems Biology and Medicine,2018,10(2):e1405.
[33] ZHOU H, ZHENG C, SU J, et al. Characterization of a natural triple-tandem c-di-GMP riboswitch and application of the riboswitch-based dual-fluorescence reporter[J]. Scientific Reports,2016,6(1):1−13. doi: 10.1038/s41598-016-0001-8
[34] PURSLEY B R, MAIDEN M M, HSIEH M-L, et al. Cyclic di-GMP regulates TfoY in Vibrio cholerae to control motility by both transcriptional and posttranscriptional mechanisms[J]. Journal of Bacteriology,2018,200(7):e00578−17.
[35] PURIFICAÇÃO A D D, AZEVEDO N M D, ARAUJO G G D, et al. The world of cyclic dinucleotides in bacterial behavior[J]. Molecules,2020,25(10):2462−2503. doi: 10.3390/molecules25102462
[36] CHAN C, PAUL R, SAMORAY D, et al. Structural basis of activity and allosteric control of diguanylate cyclase[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,2004,101(49):17084−17089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0406134101
[37] CHRISTEN B, CHRISTEN M, PAUL R, et al. Allosteric control of cyclic di-GMP signaling[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry,2006,281(42):32015−32024. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(19)84115-7
[38] KRASTEVA P V, GIGLIO K M, SONDERMANN H. Sensing the messenger: The diverse ways that bacteria signal through c-di-GMP[J]. Protein Science: A Publication of the Protein Society,2012,21(7):929−948. doi: 10.1002/pro.2093
[39] LIU Y, LEE C, LI F, et al. A cyclic di-GMP network is present in Gram-positive Streptococcus and Gram-negative Proteus species[J]. ACS Infectious Diseases,2020,6(10):2672−2687. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00314
[40] ABIDI W, TORRES-SÁNCHEZ L, SIROY A, et al. Weaving of bacterial cellulose by the Bcs secretion systems[J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews,2022,46(2):fuab051. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuab051
[41] ZOUHIR S, ABIDI W, CALEECHURN M, et al. Structure and multitasking of the c-di-GMP-sensing cellu secretion regulator BcsE[J]. Mbio,2020,11(4):e01303−20.
[42] POULIN M B, KUPERMAN L L. Regulation of biofilm exopolysaccharide production by cyclic di-guanosine monophosphate[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2021,12:730980. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.730980
[43] ROSS P, MAYER R, WEINHOUSE H, et al. The cyclic diguanylic acid regulatory system of cellulose synthesis in Acetobacter xylinum. chemical synthesis and biological activity of cyclic nucleotide dimer, trimer, and phosphothioate derivatives[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry,1990,265(31):18933−18943. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(17)30606-3
[44] MORGAN J L, MCNAMARA J T, ZIMMER J. Mechanism of activation of bacterial cellulose synthase by cyclic di-GMP[J]. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology,2014,21(5):489−496.
[45] ZOUHIR S, ABIDI W, CALEECHURN M, et al. Structure and multitasking of the c-di-GMP-sensing cellulose secretion regulator BcsE[J]. MBio,2020,11(4):e01303−20.
[46] ABIDI W, ZOUHIR S, CALEECHURN M, et al. Architecture and regulation of an enterobacterial cellulose secretion system[J]. Science Advances,2021,7(5):eabd8049. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abd8049
[47] ANDERSON A C, BURNETT A J, HISCOCK L, et al. The Escherichia coli cellulose synthase subunit G (BcsG) is a Zn2+-dependent phosphoethanolamine transferase[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry,2020,295(18):6225−6235. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.011668
[48] AHUMADA-MANUEL C L, MARTíNEZ-ORTIZ I C, HSUEH B Y, et al. Increased c-di-GMP levels lead to the production of alginates of high molecular mass in Azotobacter vinelandii[J]. Journal of Bacteriology,2020,202(24):e00134−20.
[49] MARTíNEZ-ORTIZ I C, AHUMADA-MANUEL C L, HSUEH B Y, et al. Cyclic di-GMP-mediated regulation of extracellular mannuronan C-5 epimerases is essential for cyst formation in Azotobacter vinelandii[J]. Journal of Bacteriology,2020,202(24):e00135−20.
[50] MORADALI M F, DONATI I, SIMS I M, et al. Alginate polymerization and modification are linked in Pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. MBio,2015,6(3):e00453−15.
[51] BUNDALOVIC-TORMA C, WHITFIELD G B, MARMONT L S, et al. A systematic pipeline for classifying bacterial operons reveals the evolutionary landscape of biofilm machineries[J]. PLoS Computational Biology,2020,16(4):e1007721. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007721
[52] 赵腊梅, 孙惠芳, 刘正杰, 等. c-di-GMP对细菌胞外多糖合成与运输的调控[J]. 微生物学通报,2017,44(5):1196−1205. [ZHAO L M, SUN H F, LIU Z J, et al. Regulation in EPS biosynthesis and transportation by cyclic diguanylate[J]. Microbiology China,2017,44(5):1196−1205. [53] VÁRALLYAY É, VÁLÓCZI A, ÁGYI Á, et al. Plant virus-mediated induction of miR168 is associated with repression of ARGONAUTE1 accumulation[J]. The EMBO Journal,2010,29(20):3507−3519. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.215
[54] ZHOU E, SEMINARA A B, KIM S-K, et al. Thiol-benzo-triazolo-quinazolinone inhibits Alg44 binding to c-di-GMP and reduces alginate production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. ACS Chemical Biology,2017,12(12):3076−3085. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.7b00826
[55] WHITFIELD G B, MARMONT L S, BUNDALOVIC-TORMA C, et al. Discovery and characterization of a Gram-positive Pel polysaccharide biosynthetic gene cluster[J]. PLoS Pathogens,2020,16(4):e1008281. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008281
[56] WHITFIELD G B, MARMONT L S, OSTASZEWSKI A, et al. Pel polysaccharide biosynthesis requires an inner membrane complex comprised of PelD, PelE, PelF, and PelG[J]. Journal of Bacteriology,2020,202(8):e00684−19.
[57] WHITNEY J C, COLVIN K M, MARMONT L S, et al. Structure of the cytoplasmic region of PelD, a degenerate diguanylate cyclase receptor that regulates exopolysaccharide production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry,2012,287(28):23582−23593. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.375378
[58] BARAQUET C, MURAKAMI K, PARSEK M R, et al. The FleQ protein from Pseudomonas aeruginosa functions as both a repressor and an activator to control gene expression from the pel operon promoter in response to c-di-GMP[J]. Nucleic Acids Research,2012,40(15):7207−7218. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks384
[59] PÉREZ-MENDOZA D, BERTINETTI D, LORENZ R, et al. A novel c-di-GMP binding domain in glycosyltransferase BgsA is responsible for the synthesis of a mixed-linkage β-glucan[J]. Scientific Reports,2017,7(1):1−11. doi: 10.1038/s41598-016-0028-x
[60] BAENA I, PÉREZ-MENDOZA D, SAUVIAC L, et al. A partner-switching system controls activation of mixed-linkage β-glucan synthesis by c-di-GMP in Sinorhizobium meliloti[J]. Environmental Microbiology,2019,21(9):3379−3391. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.14624
[61] 杜心恬, 宋馨, 刘欣欣, 等. 细菌胞外多糖生物合成转录调控因子研究进展[J]. 微生物学通报,2021,48(2):573−581. [DU X Y, SONG X, LIU X X, et al. Advances in transcription regulators of bacterial exopolysaccharides biosynthesis[J]. Microbiology China,2021,48(2):573−581. [62] 赵丹, 曹慧莹, 孙梦, 等. 假肠膜明串珠菌HDL-3胞外多糖的分离纯化及结构性质分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(21):115−122. [ZHAO D, CAO H Y, SUN M, et al. Isolation, purification and structural properties analysis of exopolysaccharide from Leuconostoc pseudointestinalis HDL-3[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(21):115−122. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2022020092 [63] BROWN R, MARCHESI J R, MORBY A P. Functional characterisation of Lp_2714, an EAL-domain protein from Lactobacillus plantarum[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2011,411(1):132−136. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.06.112
[64] HE J, RUAN W, SUN J, et al. Functional characterization of c-di-GMP signaling-related genes in the probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2018,29(9):1935.





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



