Effects of Whey Protein and Its Hydrolysates on in Vitro Digestibility and Physicochemical Properties of Potato Starch
-
摘要: 本文通过构建乳清蛋白及乳清蛋白水解物与马铃薯淀粉的共糊化体系来探究乳清蛋白及其水解物对马铃薯淀粉体外消化性和理化性质的影响。结果表明,经过胃蛋白酶和胰酶水解处理的乳清蛋白水解物对淀粉的消化率抑制效果最为明显。其中,天然马铃薯淀粉中快消化淀粉(RDS)含量最高(94.54%),抗性淀粉(RS)含量最低(3.10%)。而经过胃蛋白酶处理后经胰酶处理120 min的样品中的RDS含量最低(67.51%),RS含量最高(12.69%)。乳清蛋白水解物对马铃薯淀粉的溶胀和糊化的抑制作用均强于乳清蛋白。这说明乳清蛋白水解物的分子量对马铃薯淀粉的理化特性和消化性均有较大影响。此外,乳清蛋白及其水解物增强了体系中的氢键作用并提高了淀粉结构的有序程度,表明乳清蛋白及其水解物与马铃薯淀粉之间的相互作用会降低淀粉的消化性。Abstract: The effect of whey protein and its hydrolysates on the in vitro digestibility and physicochemical properties of potato starch (PS) was investigated by constructing the co-gelatinization system between the PS and whey protein or whey protein hydrolysates. The results showed that whey protein hydrolysates hydrolyzed by pepsin-pancreatin (WPP) had the best inhibitory effect on the digestibility of starch. Thereinto, the native PS displayed the highest rapidly digestible starch (RDS) content (94.54%) and lowest resistant starch (RS) content (3.10%). Lower RDS (67.51%) and higher RS (12.69%) contents were found for PS-WPP120 complex. The inhibitory effect of whey protein hydrolysates on the swelling and gelatinization of PS was stronger than that of whey protein. Therefore, the molecular weight of whey protein hydrolysates had a notable influence on both physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility. And whey protein or its hydrolysates strengthened the hydrogen bonding and increased the order degree of PS structure, indicating that the interactions between PS and whey protein or whey protein hydrolysates could reduce in vitro digestibility of PS.
-
Keywords:
- potato starch /
- whey protein /
- protein hydrolysates /
- physicochemical properties /
- digestibility
-
“马铃薯主粮化”与低血糖生成指数(glycemic index,GI)饮食热潮,使得马铃薯淀粉(potato starch,PS)消化性研究受到广泛的关注。此外,与玉米、小麦和大米淀粉相比,马铃薯淀粉可以通过增加胰岛素敏感性而降低体重增加和脂肪积累,减轻餐后葡萄糖峰值,导致其葡萄糖生成率最低[1]。因此,利用马铃薯开发适合糖尿病人食用的慢消化膳食具有重要意义。
目前,对于蛋白及其水解物对淀粉消化性的影响主要集中于外源植物蛋白及其水解物对淀粉消化性的影响研究,如Xu等[2]研究发现面筋或其水解物可以通过抑制α-淀粉酶活性及其与淀粉之间的产生的氢键相互作用来降低小麦淀粉的消化率。Chi等[3]研究发现天然大米蛋白和胃蛋白酶水解的大米蛋白水解物可以通过增强糊化淀粉的有序结构来降低淀粉消化率,而胃蛋白酶-胰酶水解的大米蛋白水解物则通过增强淀粉的V型结构及抑制α-淀粉酶的活性来降低淀粉的消化率。Li等[4]研究发现玉米蛋白质及其酶水解产物对玉米淀粉消化的抑制机制是淀粉有序结构的增强和酶活性的抑制。而关于外源动物蛋白及其水解物对于淀粉消化性的影响缺乏研究。
乳清蛋白饮食作为预防和治疗人类和动物肥胖及2型糖尿病的特殊膳食成分已经广受欢迎。与其他蛋白相比,乳清蛋白中各种必需氨基酸的含量更高[5],短期抑制食欲的效果更强[6],同时乳清蛋白的促胰岛素作用更强[7]。因此,探究马铃薯与乳清蛋白之间的相互作用机制及其对淀粉消化性的影响,不仅可以为开发适合糖尿病人的马铃薯慢消化膳食奠定基础,同时对马铃薯主食深加工产业的发展也具有十分重要的意义。
本研究将不同水解程度的乳清蛋白水解物与马铃薯淀粉复配,研究乳清蛋白及其水解物对马铃薯淀粉糊化特性、结构特性及消化特性的影响,以期为开发马铃薯慢消化型主食产品和马铃薯主食深加工产业提供一定的理论指导。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
马铃薯淀粉(PS) 宁夏华尔晶淀粉有限公司;乳清分离蛋白(whey protein isolate,WPI) 美国Hilmar 公司;胃蛋白酶(≥250 U/mg)、胰酶(8×USP)和淀粉葡萄糖苷酶(≥260 U/mL) 美国Sigma-Aldrich公司;葡萄糖氧化酶-过氧化物酶(GOPOD)试剂盒 北京利德曼生化股份有限公司;其他试剂均为分析纯。
HHS-21-4数显电热恒温水浴锅 上海百典仪器设备有限公司;TGL-18M台式高速冷冻离心机 上海卢湘仪离心机仪器有限公司;RVA 4500快速粘度分析仪 波通澳大利亚公司;SHA-AB恒温培养振荡器 常州市旭日实验仪器厂;SQP型分析天平 赛多利斯科学仪器有限公司;DHG-9123A型电热恒温鼓风干燥箱 上海柏欣仪器设备厂;SCIENTZ-10N冷冻干燥机 宁波新芝生物科技股份有限公司;NEXUS型傅立叶变换红外光谱仪 美国Nicolet 公司;D8型X射线衍射仪 德国布鲁克AXS有限公司;PowerWaveX52型酶标仪 美国Power Wave公司;Waters 1525EF型高效液相色谱仪 美国沃特世公司;X-DSC7000差示扫描量热仪 日本精工电子纳米科技有限公司;DHR-3型旋转流变仪 美国TA公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 乳清蛋白质水解物的制备
参考Chi等[3]的方法将乳清分离蛋白经胃蛋白酶和胰酶水解。先将5 g乳清分离蛋白分散在100 mL胃蛋白酶溶液(4 mg/mL,溶于pH2.0的盐酸中)中,消化60 min后,停止反应(用1 mol/L氢氧化钠溶液将体系pH调至7.0)。部分乳清蛋白水解样品经过冷冻干燥,称为WP60。其余部分样品加入1 g胰酶后,继续水解反应。分别在60 min和120 min酶消化后停止反应,并将水解物立即冷冻在−80 ℃冰箱中,迅速冷冻干燥。以上所有酶消化均在37 ℃水浴中进行。乳清蛋白被胃蛋白酶水解60 min,再被胰酶水解60 min、120 min的乳清蛋白水解样品分别命名为WPP60和WPP120。
1.2.2 马铃薯淀粉和乳清蛋白及其水解物共糊化体系制备
将马铃薯淀粉与乳清分离蛋白或其水解物按质量比为1:0.3的比例混合,在沸水浴中糊化30 min后,放入恒温水浴振荡锅(37 ℃)保温10 min,得到的混合样品分别命名为PS-WPI、PS-WP60、PS-WPP60和PS-WPP120。将糊化样品冷冻干燥后研磨过100目筛。得到的样品分别命名为D-PS-WPI、D-PS-WP60、D-PS-WPP60和D-PS-WPP120。
1.2.3 蛋白质水解物的多肽相对分子量分布
测定方法参照 GB/T 22492-2008 中的附录 A 测定乳清分离蛋白和经胃蛋白酶及胰酶水解后的乳清蛋白水解物中多肽相对分子量分布。使用流动相溶解冷冻干燥后的蛋白质及其水解物至浓度为 0.5%(w/w),使用微孔滤膜(0.45 μm)过滤后进样。进样量为 20 μL。根据保留时间计算相对分子量及百分比。
1.2.4 淀粉体外消化性测定
评估体外淀粉消化率的方法与Englyst等[8]的方法略有不同。向PS-WPI、PS-WP60、PS-WPP60和PS-WPP120糊化样品中添加5 mL的胃蛋白酶溶液(5 mg/L,通过将50 mg胃蛋白酶溶解在10 mL 0.05 mol/L盐酸中制备),并在37 ℃水浴中反应30 min。随后加入2.5 mL混合酶液(用pH5.2的乙酸-乙酸钠缓冲溶液配制的胰酶-淀粉葡萄糖苷酶混合液),充分涡旋后继续在37 ℃下反应。酶解在0、20、60和120 min时,分别取样100 μL,并将其添加到无水乙醇(1 mL)中后,充分涡旋振荡终止酶解。在3500 r/min条件下离心5 min,使用葡萄糖氧化酶过氧化物酶(GOPOD)试剂盒测定上清液中葡萄糖含量。混合体系中快消化淀粉含量(rapidly digestible starch,RDS)、慢消化淀粉含量(slowly digestible starch,SDS)和抗性淀粉含量(resistant starch,RS)分别使用下列公式进行计算:
RDS(%)=(G20−G0)×0.9/TS×100 (1) SDS(%)=(G120−G20)×0.9/TS×100 (2) RS(%)=1−RDS−SDS (3) 式中,G0、G20和G120分别代表混合体系在0、20和120 min时酶解生成的葡萄糖含量,mg,TS代表混合体系中总淀粉质量,mg。
1.2.5 膨胀力测定
膨胀力测定方法如前人所述,并略有修改[9]。将0.5 g淀粉与0.15 g乳清蛋白或其水解物加入到50 mL离心管中,记录混合样品及相对应的空离心管质量。随后加入25 mL去离子水,充分涡旋混合后分别在65、75、85和95 ℃的水浴中糊化30 min,糊化后的样品立即置于冰浴中快速冷却至室温,随后在4000×g的条件下离心20 min。倒出上清液105 ℃下烘干至恒重,称量沉淀质量及烘干后的上清液质量,以下式计算膨胀力(swelling power,SP):
SP(%)=P100(W−A)×100 (4) 式中,P为离心后沉淀物的质量,g;A为105 ℃干燥后上清液的质量,g;W为样品的初始质量,g。
1.2.6 差示扫描量热仪(DSC)
混合样品的热性能采用差示扫描量热仪(DSC)测定,使用空铝制坩埚作为对照。将马铃薯淀粉与乳清分离蛋白及其水解物按质量比为1:0.3的比例混合,取4 mg混合样品及去离子水(8 μL)加到铝制DSC坩埚中,密封后于室温下平衡过夜。然后以10 ℃/min的升温速率将样品从10 ℃加热到120 ℃,以确定参数:起始温度(To)、峰值温度(Tp)、终止温度(Tc)及糊化焓(ΔH)。
1.2.7 糊化特性测定
使用快速粘度分析仪(RVA)测定混合样品的糊化特性。将2 g淀粉与0.6 g乳清蛋白或其水解物分散在25 mL蒸馏水中,充分搅拌均匀。测定条件参照GB/T 24853-2010中的标准程序2,测定样品的糊化特性。
1.2.8 直链淀粉浸出率测定
使用Han等[10]的方法稍加修改。将50 mg淀粉与15 mg乳清蛋白或其水解物分散在10 mL蒸馏水中,涡旋均匀后将样品置于沸水浴中糊化30 min,然后置于冰浴中冷却5 min,将混合样品在室温下以6000×g的离心力下离心20 min。随后取0.5 mL上清液与3 mL 0.1 mol/L氢氧化钠溶液于离心管中涡旋均匀,将离心管置于沸水浴中10 min,放入冰浴中冷却5 min。然后在样品中加入5 mL去离子水稀释,并用0.5%三氯乙酸使混合体系的pH达到4.0。随后将每个样品中分别加入0.5 mL I2-KI(0.01 mol/L)水溶液,使用漩涡振荡器充分混合均匀,最后用去离子水将混合溶液定容到50 mL,并在黑暗中静置20 min。使用蒸馏水作为对照,记录混合溶液在426 nm和634 nm处通过分光光度计读取的吸光度。
1.2.9 X-射线衍射
使用Bruker D8型X射线衍射仪(XRD)测定D-PS-WPI、D-PS-WP60、D-PS-WPP60和D-PS-WPP120的结晶结构。实验条件为陶瓷型X光管,铜靶,电压为40 kV,电流为30 mA,衍射角(2θ)范围5°~30°,扫描速度2.5°/min。
1.2.10 傅立叶红外光谱
使用傅立叶变换红外光谱仪(ATR-FTIR)测定D-PS-WPI、D-PS-WP60、D-PS-WPP60和D-PS-WPP120的短程有序结构并探究混合样品中的相互作用。以空气为参比,在波数为4000~400 cm−1的范围内扫描,扫描64次,分辨率值为4 cm−1。对1100~960 cm−1处的特征峰进行去卷积处理(增强因子为1.9,半峰宽为19 cm−1)比较1047 cm−1和1022 cm−1处的吸光度。
1.3 数据处理
所有实验数据表示为平均值±标准差,同组数值后不同的小写字母表示数据间存在显著性差异(P<0.05),未进行特殊说明均进行三次重复实验。数据通过SPSS 16.0软件进行邓肯检验来评估统计学意义,通过Origin 2017软件绘制图表。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 乳清蛋白水解物相对分子量分布
使用胃蛋白酶和胰酶对乳清蛋白进行不同程度水解。为了了解乳清蛋白的水解程度,将得到的乳清蛋白水解物采用高效液相色谱法测定其中多肽相对分子量的分布,结果如表1所示。
表 1 乳清蛋白水解物相对分子量分布Table 1. Molecular weight of whey protein hydrolysates相对分子质量
(Da)百分含量(%) WPI WP60 WPP60 WPP120 >5000 87.11 74.09 1.51 1.82 5000~3000 5.56 4.54 1.36 0.96 3000~2000 5.52 4.50 2.29 1.45 2000~1000 1.09 6.24 8.95 6.83 1000~500 0.19 5.29 18.00 16.52 <500 0.55 5.34 67.90 72.42 分子量小于500 Da为多肽分子,其中乳清分离蛋白多肽只占0.55%,只经过胃蛋白酶处理的样品多肽分子只占5.34%,表明乳清分离蛋白部分酶解。而经过胃蛋白酶处理后再加入胰酶处理60 min和120 min样品的多肽分子分别占67.90%和72.42%,表明大部分乳清分离蛋白被分解为多肽分子。
2.2 乳清蛋白水解物对糊化马铃薯淀粉体外消化特性的影响
乳清蛋白及乳清蛋白水解物对糊化马铃薯淀粉体外消化特性的影响如表2所示。
表 2 乳清蛋白水解物对糊化马铃薯淀粉体外消化特性的影响Table 2. Effects of whey protein hydrolysates on in vitro digestibility of gelatinized PS蒸煮糊化破坏了马铃薯淀粉的颗粒结构,暴露了淀粉颗粒内部的淀粉酶活性位点,从而提高了淀粉的水解率;使RDS含量提高至94.54%。Mishra等[11]研究发现蒸煮糊化马铃薯淀粉的RDS含量高于90%,与目前的研究结果类似。乳清蛋白及其水解物都可以显著降低马铃薯淀粉的RDS含量,增加SDS及RS含量(P<0.05)。其中RDS含量从94.54%下降到70.95%~67.51%,SDS的含量从2.36%上升到19.04%~19.80%,而RS的含量从3.10%上升到9.96%~12.69%。而与淀粉-蛋白样品相比,糊化后的淀粉-蛋白水解物样品的RDS含量更低,且SDS和RS含量更高,其中只经过胃蛋白酶处理的蛋白质水解物其结构相对完整,导致其淀粉消化率与淀粉-蛋白样品的消化率相似。Lu等[12]探究发现大米蛋白水解物比外源大米蛋白对大米淀粉的消化具有更明显的延缓作用,与本文结果一致。随着蛋白质的水解程度增加,糊化马铃薯淀粉中RDS含量显著降低(P<0.05),SDS及RS含量显著增加(P<0.05),其中胃蛋白酶-胰酶处理120 min的蛋白质样品对马铃薯消化性的影响最大,其中RDS含量为67.51%,RS为12.69%。这可能由于蛋白质水解物对α-淀粉酶或淀粉葡萄糖苷酶具有更强的抑制活性[3]。
2.3 乳清蛋白水解物对马铃薯淀粉膨胀力的影响
膨胀力与淀粉的结构完整性、吸水膨胀能力和分子间氢键的强度有关,与淀粉消化率也有一定的相关性。淀粉的膨胀能力越弱,淀粉消化率就越弱[13]。当温度达到65 ℃时,天然马铃薯大量吸收水分并快速糊化,但当温度达到75 ℃时,天然马铃薯吸水量达到最大(50%)并完全糊化。这与Chen等[14]的研究一致。这可能由于马铃薯淀粉中磷酸单酯基团之间的离子排斥削弱了分子之间的键,从而增加马铃薯淀粉颗粒的水结合能力和膨胀力[15]。
由图1可知,所有样品的膨胀力都随着温度的升高而增加,但在相同温度下,与天然马铃薯淀粉相比,加入乳清蛋白及其水解产物样品中的马铃薯淀粉膨胀力显著降低(P<0.05)。这与Hu等[16]和Sun等[17]的结果相似。这可能是由于蛋白质水解后产生了多肽及氨基酸,加强了与淀粉之间相互作用,从而抑制淀粉的膨胀[18],也可能由于多肽及氨基酸与淀粉颗粒结合,阻断直链淀粉的浸出通道,从而抑制直链淀粉的浸出及水分的进入,抑制淀粉溶胀[19]。此外,在相同的温度下,马铃薯淀粉的膨胀力随着蛋白的水解度增加而显著降低(P<0.05),其中经过双酶水解的蛋白质水解物对淀粉膨胀力的抑制最显著(P<0.05),在95 ℃下,膨胀力分别降低了31.40%和31.23%。这可能由于经过双酶水解的蛋白质产生较多的多肽,增加了大量可电离基团增强了体系中的氢键作用[18]。其中,只经胃蛋白酶水解的乳清蛋白水解物的膨胀力明显低于完整蛋白,但二者对淀粉的消化率没有显著性差异(P>0.05),这可能由于完整蛋白对淀粉的吸附作用强于只经胃蛋白酶水解的乳清蛋白水解物,使完整蛋白对淀粉的屏障作用更强[20]。乳清蛋白及其水解物可以通过降低淀粉膨胀力来降低酶对淀粉的可及性,从而降低淀粉的消化性。
![]() 图 1 乳清蛋白水解物对马铃薯淀粉膨胀力的影响注:不同的小写字母表示差异性显著(P<0.05);图2同。Figure 1. Effect of whey protein hydrolysates on swelling power of PS
图 1 乳清蛋白水解物对马铃薯淀粉膨胀力的影响注:不同的小写字母表示差异性显著(P<0.05);图2同。Figure 1. Effect of whey protein hydrolysates on swelling power of PS2.4 乳清蛋白水解物对马铃薯淀粉热性能的影响
乳清蛋白及其水解产物对马铃薯淀粉热性能的影响如表3所示。马铃薯淀粉的起始温度(To)为60.67 ℃,终止温度(Tc)为72.22 ℃,糊化焓(ΔH)为10.77 J/g,与Liu等[21]的研究一致。添加乳清蛋白及其水解物后,马铃薯淀粉的糊化温度升高,这证明乳清蛋白及其水解产物使淀粉的稳定性增强。且随着蛋白的水解程度增加,糊化温度也显著增加(P<0.05),与López-Barón等[22]的研究一致。这可能由于蛋白质及其水解物中的亲水基团和疏水氨基酸通过氢键或疏水相互作用粘附在淀粉颗粒表面上,从而抑制了淀粉的糊化[18]。
表 3 乳清蛋白及其水解物对马铃薯淀粉热性能的影响Table 3. Effects of whey protein and its hydrolysates on thermal properties of PS样品 To(℃) Tp(℃) Tc(℃) ∆H(J/g) PS 60.67±0.10d 63.73±0.11c 72.22±0.30d 10.77±0.15a PS-WPI 61.72±0.16c 65.48±0.06b 74.19±0.11c 8.86±0.94bc PS-WP60 61.43±0.15c 65.79±0.03b 75.46±0.30b 9.74±0.07b PS-WPP60 63.43±0.19b 68.17±0.04a 76.30±0.47a 8.62±0.07c PS-WPP120 64.27±0.76a 68.21±0.11a 76.22±0.15a 8.60±0.12c 淀粉的焓值(∆H)可以反映淀粉颗粒中双螺旋有序结构的破坏。如表3所示,淀粉和蛋白质及其水解产物混合样品的糊化焓值存在一定差异。加入蛋白质及其水解产物后,糊化焓从10.77 J/g降低到8.60~9.74 J/g,这可能由于蛋白质及其水解产物与淀粉竞争水分,限制了淀粉的水合能力及膨胀能力,抑制了淀粉糊化,从而减少了淀粉有序结构的破坏[23]。
2.5 乳清蛋白水解物对马铃薯淀粉糊化特性的影响
乳清分离蛋白及其水解物对马铃薯淀粉糊化特性影响见表4。
表 4 乳清蛋白及其水解物对马铃薯淀粉糊化特性的影响Table 4. Effects of whey protein and its hydrolysates on pasting properties of PS样品 糊化温度
(℃)峰值黏度
(cP)峰谷黏度
(cP)终止黏度
(cP)崩解值
(cP)回生值
(cP)PS 63.55±0.21c 5488±6a 1517±3a 2130±18a 3971±9a 613±15b PS-WPI 66.95±0.28b 1957±1b 1251±13c 1936±13b 706±14b 685±2a PS-WP60 66.93±0.32b 1550±23c 1071±10d 1642±5d 479±13c 571±5c PS-WPP60 68.33±0.04a 1550±4c 1354±9b 1906±8c 196±13d 552±1c PS-WPP120 68.53±0.32a 1495±5d 1331±3b 1899±4c 164±2e 568±6c 蛋白质及其水解物可能以不同的方式影响糊化过程,这取决于它们的保水能力以及其与淀粉分子的相互作用能力[24]。加入乳清蛋白及其水解产物后,体系的糊化温度显著升高(P<0.05)。这可能由于蛋白质及其水解产物通过氢键或疏水相互作用黏附在淀粉颗粒表面[18]。而经过胰酶水解的样品显示出比完整蛋白及胃蛋白酶水解60 min的样品更高的糊化温度。这可能由于水解后产生大量带有正负电荷的肽,通过静电相互作用抑制了淀粉颗粒的分解[25]。
加入乳清蛋白及其水解产物后,马铃薯淀粉所有黏度参数都降低,包括峰值黏度、峰谷黏度、终止黏度。其中蛋白质水解物对淀粉的峰值黏度影响更大。Kong等[9]研究发现猪血浆蛋白水解物可以显著(P<0.05)降低玉米淀粉的黏度值,与本文研究一致。
崩解值可以反映出淀粉颗粒热稳定性的强弱。天然马铃薯淀粉的热稳定性较差。然而,淀粉在与蛋白质或蛋白质水解物混合糊化后,马铃薯淀粉的崩解值降低,淀粉的热稳定性增强,这表明淀粉分子与蛋白质及其蛋白质水解物之间存在相互作用。其中PS-WPP120样品的崩解值最低,证明蛋白质水解程度越高,蛋白水解物与淀粉的相互作用越强,越能保持淀粉的热稳定性。
回生值通常表明淀粉的短期回生。相比于天然马铃薯淀粉,乳清蛋白水解物和淀粉混合体系的回生值显著降低(P<0.05),这证明乳清蛋白水解物具有抑制马铃薯淀粉短期回生的能力。蛋白质水解物与淀粉分子产生氢键作用,这减弱了淀粉分子间的分子间作用力,从而抑制了淀粉的短期回生[3]。
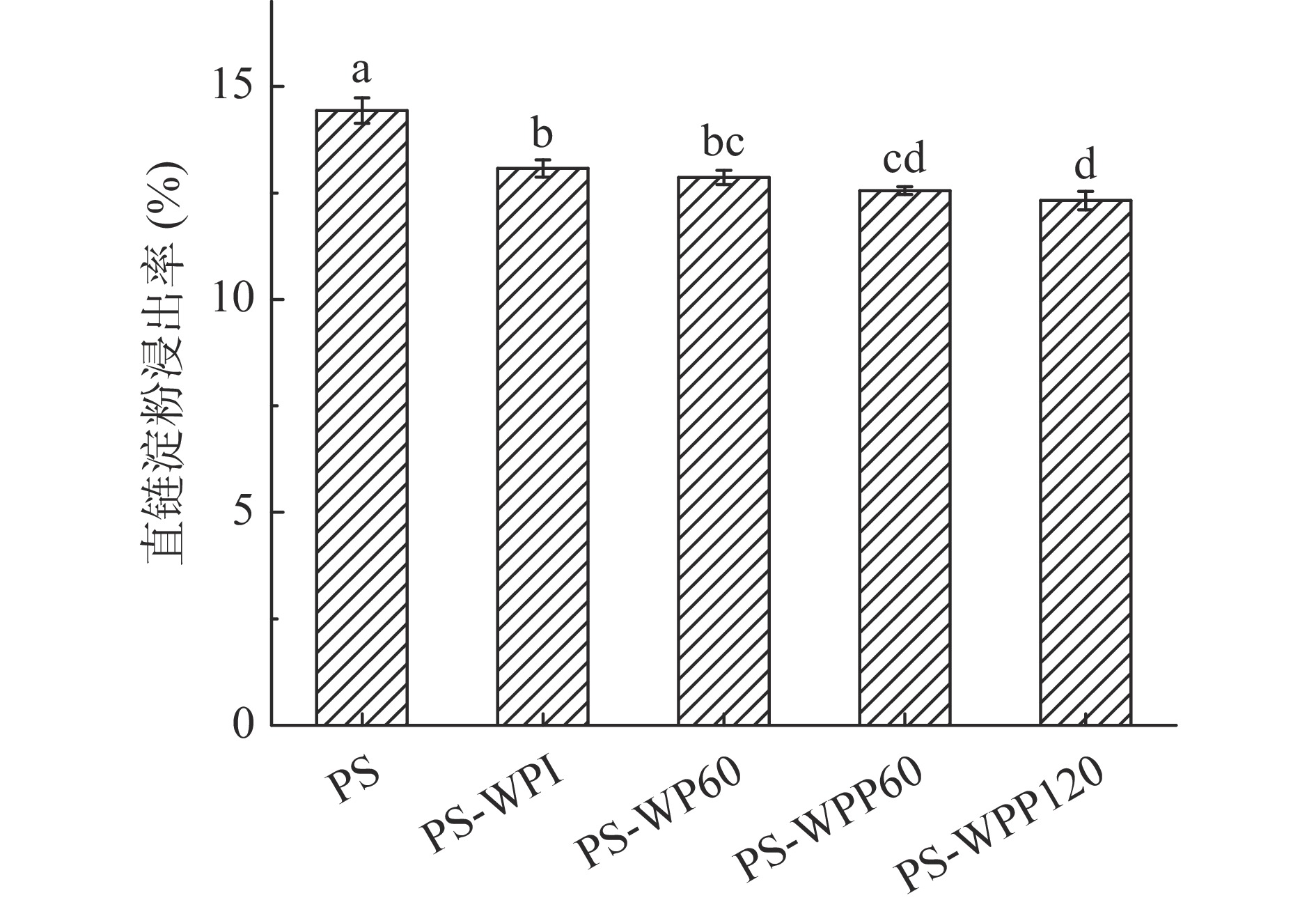
2.6 乳清蛋白水解物对马铃薯淀粉直链淀粉浸出率的影响
直链淀粉浸出率是可以反映出淀粉结构稳定性的指标。淀粉糊化会导致淀粉颗粒破裂,颗粒表面分子间作用力减弱,使直链淀粉从淀粉颗粒中及颗粒表面逸出[3, 26]。不同水解程度的乳清分离蛋白对马铃薯淀粉直链淀粉浸出率的影响如图2所示。
淀粉-蛋白质/蛋白质水解物体系的直链淀粉浸出量显著低于天然马铃薯淀粉(P<0.05),这与Chi等[3]的结果相似。该结果表明蛋白质及其水解物的存在可以有效抑制直链淀粉从淀粉颗粒中逸散。这可能归因于通过分子间氢键或疏水相互作用形成直链淀粉-蛋白质/蛋白质水解物的复合物,从而增强了淀粉热稳定性[3]。因此蛋白质及其水解产物可以抑制直链淀粉浸出,从而抑制淀粉的膨胀,这与2.3的结果一致。
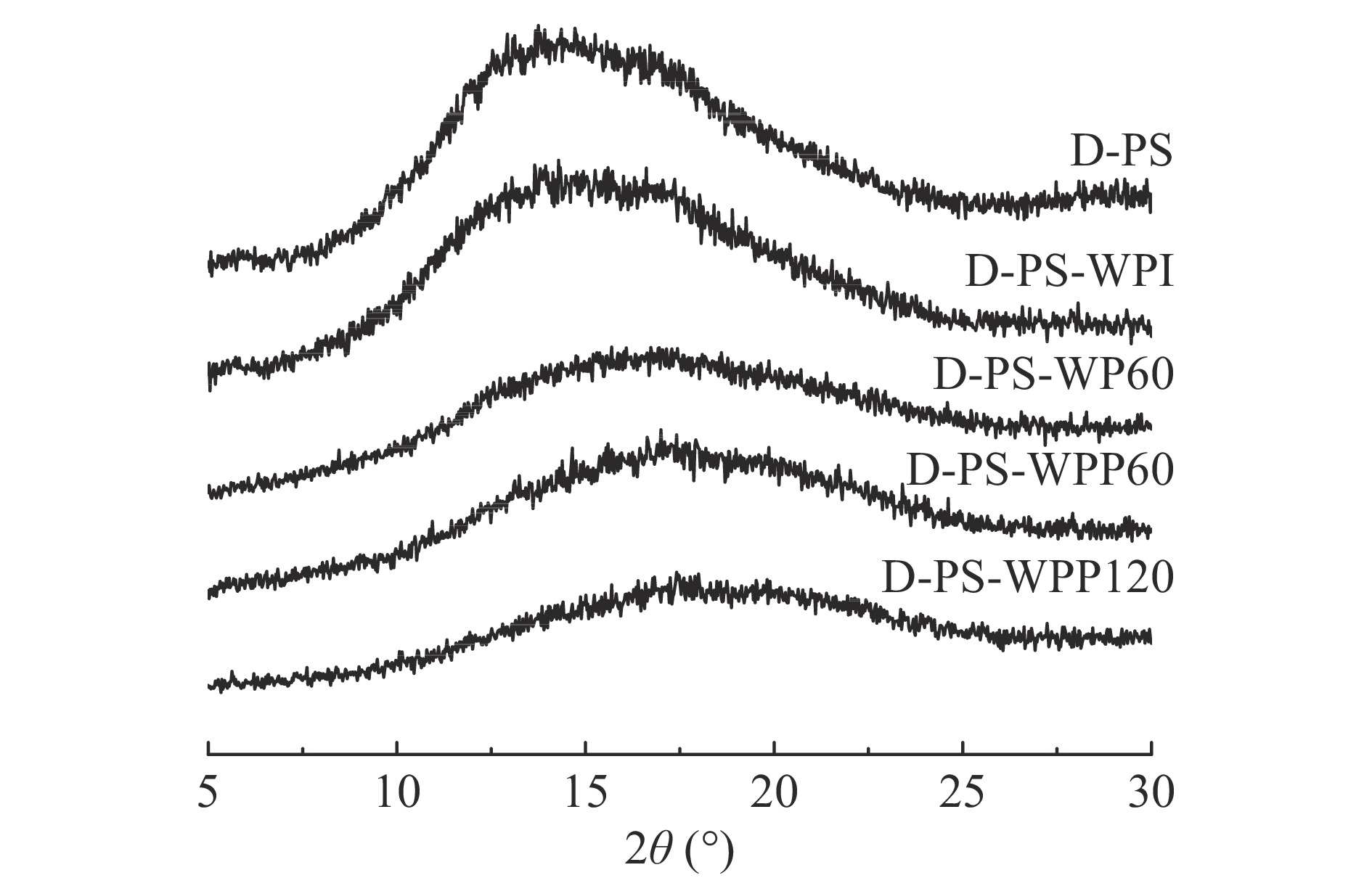
2.7 乳清蛋白水解物对糊化马铃薯淀粉XRD的影响
乳清蛋白及其水解产物对糊化马铃薯淀粉结晶结构影响如图3所示。由于糊化的水热效应完全破坏了淀粉聚合物的有序性,因此糊化后的马铃薯淀粉有一个较宽的峰[27]。乳清分离蛋白的存在对马铃薯淀粉衍射峰的位置没有影响,XRD谱图中没有形成任何与淀粉和蛋白质微晶相关的新峰,与Wang等[27]的研究结果类似。这证明加入乳清蛋白及其水解物不会对马铃薯淀粉的结晶结构产生影响,蛋白质及其水解产物也没有与淀粉形成复合物。但接近无定形峰的2θ随着乳清分离蛋白水解程度的增加逐渐移动到更高的角度。这一现象表明,乳清蛋白水解物可能与直链淀粉产生相互作用并引起晶格畸变[28]。
2.8 傅立叶红外光谱分析
马铃薯淀粉与乳清蛋白及其水解产物的FTIR谱图如图4A。乳清蛋白及其水解物的加入没有使FTIR中产生新的条带,因此乳清蛋白及其水解物与马铃薯淀粉间没有共价作用。
在3000~3600 cm−1范围内的谱带与分子间氢键和O-H的伸缩振动有关[29]。加入乳清蛋白及其水解物后,此处的条带从3297 cm−1移动到3276 cm−1附近,这是由于乳清蛋白和马铃薯淀粉产生了氢键作用[12]。此外,添加了乳清蛋白水解物的样品在3276 cm−1处的峰更平坦,证明蛋白水解物与马铃薯淀粉间形成的氢键更多[30]。这可能是因为蛋白质水解过程中产生了大量的短链多肽可以与淀粉形成氢键,从而提高了淀粉的稳定性,抑制淀粉的消化[18]。
通过对960~1100 cm−1处特征峰进行去卷积处理(如图4B),分析乳清分离蛋白对马铃薯淀粉短程有序结构的影响,如表5所示。淀粉在1047 cm−1和1022 cm−1处的典型淀粉结晶峰与淀粉的短程有序结构有关[31]。其中在1047 cm−1处的谱带与淀粉的结晶度有关,而1022 cm−1处的谱带则与淀粉颗粒无定形域的振动有关[32]。利用1047/1022 cm−1的值可以估计淀粉的短程有序:比率越高,淀粉样品中的短程分子越有序[33]。如表5所示,乳清蛋白及其水解产物的添加显著增加了1047/1022 cm−1的值(P<0.05),证明乳清蛋白及其水解产物增加了马铃薯淀粉的短程有序程度。此外,相较于完整蛋白,水解后的乳清蛋白1047/1022 cm−1的值更高,证明水解后的蛋白与淀粉相互作用,可以形成更加稳定的有序结构,从而降低了淀粉的水解程度。其中经过胃蛋白酶水解的乳清蛋白水解物对淀粉有序程度及氢键强度的影响强于完整蛋白,但二者的对淀粉的消化率没有显著性差异(P>0.05),这可能由于完整蛋白对淀粉的吸附作用强于只经胃蛋白酶水解的乳清蛋白水解物,使完整蛋白对淀粉的屏障作用更强[20]。
表 5 乳清蛋白及其水解物与马铃薯淀粉混合体系的1047/1022 cm−1的值Table 5. 1047/1022 cm−1 of the potato starch mixed system with whey protein and its hydrolysates峰值比 D-PS D-PS-WPI D-PS-WP60 D-PS-WPP60 D-PS-WPP120 1047/1022 cm−1 0.283±0.005d 0.306±0.011c 0.440±0.009a 0.411±0.010b 0.414±0.013b 注:同一行中数字不同的上标字母表示差异性显著(P<0.05)。 3. 结论
乳清蛋白及其水解物的添加显著降低(P<0.05)了糊化后马铃薯淀粉的消化率。其中,经过胃蛋白酶和胰酶共同水解的乳清蛋白水解物对马铃薯淀粉消化性的抑制作用最明显,RDS含量分别降低了24.76%和27.03%,RS分别增加了7.83%和9.59%。与天然乳清蛋白相比,乳清蛋白水解物对淀粉糊化的抑制作用更强,对淀粉结构的有序程度增加显著(P<0.05)。且随着乳清蛋白的水解程度增加,混合体系中氢键作用显著增强(P<0.05)。综上所述,这说明不同分子量的乳清蛋白水解物可以不同程度地影响马铃薯淀粉的理化特性和消化性。此外,乳清蛋白及其水解物与马铃薯淀粉之间的相互作用会降低淀粉的消化性。研究结果可以为开发马铃薯慢消化型主食产品和马铃薯主食深加工产业提供一定的理论指导。
-
图 1 乳清蛋白水解物对马铃薯淀粉膨胀力的影响
注:不同的小写字母表示差异性显著(P<0.05);图2同。
Figure 1. Effect of whey protein hydrolysates on swelling power of PS
表 1 乳清蛋白水解物相对分子量分布
Table 1 Molecular weight of whey protein hydrolysates
相对分子质量
(Da)百分含量(%) WPI WP60 WPP60 WPP120 >5000 87.11 74.09 1.51 1.82 5000~3000 5.56 4.54 1.36 0.96 3000~2000 5.52 4.50 2.29 1.45 2000~1000 1.09 6.24 8.95 6.83 1000~500 0.19 5.29 18.00 16.52 <500 0.55 5.34 67.90 72.42 表 2 乳清蛋白水解物对糊化马铃薯淀粉体外消化特性的影响
Table 2 Effects of whey protein hydrolysates on in vitro digestibility of gelatinized PS
表 3 乳清蛋白及其水解物对马铃薯淀粉热性能的影响
Table 3 Effects of whey protein and its hydrolysates on thermal properties of PS
样品 To(℃) Tp(℃) Tc(℃) ∆H(J/g) PS 60.67±0.10d 63.73±0.11c 72.22±0.30d 10.77±0.15a PS-WPI 61.72±0.16c 65.48±0.06b 74.19±0.11c 8.86±0.94bc PS-WP60 61.43±0.15c 65.79±0.03b 75.46±0.30b 9.74±0.07b PS-WPP60 63.43±0.19b 68.17±0.04a 76.30±0.47a 8.62±0.07c PS-WPP120 64.27±0.76a 68.21±0.11a 76.22±0.15a 8.60±0.12c 表 4 乳清蛋白及其水解物对马铃薯淀粉糊化特性的影响
Table 4 Effects of whey protein and its hydrolysates on pasting properties of PS
样品 糊化温度
(℃)峰值黏度
(cP)峰谷黏度
(cP)终止黏度
(cP)崩解值
(cP)回生值
(cP)PS 63.55±0.21c 5488±6a 1517±3a 2130±18a 3971±9a 613±15b PS-WPI 66.95±0.28b 1957±1b 1251±13c 1936±13b 706±14b 685±2a PS-WP60 66.93±0.32b 1550±23c 1071±10d 1642±5d 479±13c 571±5c PS-WPP60 68.33±0.04a 1550±4c 1354±9b 1906±8c 196±13d 552±1c PS-WPP120 68.53±0.32a 1495±5d 1331±3b 1899±4c 164±2e 568±6c 表 5 乳清蛋白及其水解物与马铃薯淀粉混合体系的1047/1022 cm−1的值
Table 5 1047/1022 cm−1 of the potato starch mixed system with whey protein and its hydrolysates
峰值比 D-PS D-PS-WPI D-PS-WP60 D-PS-WPP60 D-PS-WPP120 1047/1022 cm−1 0.283±0.005d 0.306±0.011c 0.440±0.009a 0.411±0.010b 0.414±0.013b 注:同一行中数字不同的上标字母表示差异性显著(P<0.05)。 -
[1] LEE E S, SHIN H, SEO J M, et al. Effects of raw potato starch on body weight with controlled glucose delivery[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,256:367−372. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.02.150
[2] XU H B, ZHOU J P, YU J L, et al. Mechanisms underlying the effect of gluten and its hydrolysates on in vitro enzymatic digestibility of wheat starch[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,113:106507. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.106507
[3] CHI C D, LI X X, ZHANG Y P, et al. Understanding the mechanism of starch digestion mitigation by rice protein and its enzymatic hydrolysates[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,84:473−480. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.06.040
[4] LI W H, YU Y, GONG S X, et al. Effects of endogenous and exogenous corn protein and its hydrolysates on the structural change and starch digestibility of fried corn starch[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2020,56(6):2732−2741.
[5] JORDAN M J, RYAN P L, JACOB M W, et al. The effects of 8 weeks of whey or rice protein supplementation on body composition and exercise performance[J]. Nutrition Journal,2013,12(1):1−7. doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-12-1
[6] ANDERSON G H, TECIMER S N, SHAH D, et al. Protein source, quantity, and time of consumption determine the effect of proteins on short-term food intake in young men[J]. The Journal of Nutrition,2004,134(11):3011−3015. doi: 10.1093/jn/134.11.3011
[7] PAL S, ELLIS V. The acute effects of four protein meals on insulin, glucose, appetite and energy intake in lean men[J]. British Journal of Nutrition,2010,104(8):1241−1248. doi: 10.1017/S0007114510001911
[8] ENGLYST H N, KINGMAN S M, CUMMINGS J. Classification and measurement of nutritionally important starch fractions[J]. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition,1992,46:S33−50.
[9] KONG B H, NIU H L, SUN F D, et al. Regulatory effect of porcine plasma protein hydrolysates on pasting and gelatinization action of corn starch[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2016,82:637−644. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.10.026
[10] HAN H J, HOU J W, YANG N, et al. Insight on the changes of cassava and potato starch granules during gelatinization[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,126:37−43. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.12.201
[11] MISHRA S, MONRO J, HEDDERLEY D. Effect of processing on slowly digestible starch and resistant starch in potato[J]. Starch-Starke,2008,60(9):500−507. doi: 10.1002/star.200800209
[12] LU X X, MA R R, QIU H W, et al. Mechanism of effect of endogenous/exogenous rice protein and its hydrolysates on rice starch digestibility[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,193:311−318. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.10.140
[13] LIU F Y, YANG Z, GUO X N, et al. Influence of protein type, content and polymerization on in vitro starch digestibility of sorghum noodles[J]. Food Research International,2021,142:110199. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110199
[14] CHEN X, LUO J W, FU L L, et al. Structural, physicochemical, and digestibility properties of starch-soybean peptide complex subjected to heat moisture treatment[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,297:124957. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.124957
[15] 张宏远, 木泰华, 马梦梅. 马铃薯淀粉凝胶形成及其品质影响因素研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(23):450−456. [ZHANG H Y, MU T H, MA M M. Formation of potato starch gel and influencing factors of its quality-A review[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(23):450−456. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2022010181 [16] HU Y, HE C X, ZHANG M Y, et al. Inhibition from whey protein hydrolysate on the retrogradation of gelatinized rice starch[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2020,108:105840. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.105840
[17] SUN Q J, XIONG C X, LIU S. Functional and pasting properties of pea starch and peanut protein isolate blends[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2014,101:1134−1139. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.10.064
[18] LÓPEZ-BARÓN N, SAGNELLI D, BLENNOW A, et al. Hydrolysed pea proteins mitigate in vitro wheat starch digestibility[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,79:117−126. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.12.009
[19] GUAN H N, DIAO X Q, HAN J C, et al. Influence of soy protein isolate hydrolysates obtained under high hydrostatic pressure on pasting and short-term retrogradation behavior of maize starch[J]. Food Biophysics,2021,16(3):395−405. doi: 10.1007/s11483-021-09676-w
[20] RYAN K, BREWER M. In situ examination of starch granule-soy protein and wheat protein interactions[J]. Food Chemistry,2007,104(2):619−629. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.12.037
[21] LIU Q, JIAO A Q, YANG Y Y, et al. The combined effects of extrusion and recrystallization treatments on the structural and physicochemical properties and digestibility of corn and potato starch[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2021,151:112238. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112238
[22] LÓPEZ-BARÓN N, GU Y, VASANTHAN T, et al. Plant proteins mitigate in vitro wheat starch digestibility[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2017,69:19−27. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.01.015
[23] LU Z H, DONNER E, YADA R Y, et al. Physicochemical properties and in vitro starch digestibility of potato starch/protein blends[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2016,154:214−222. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.08.055
[24] RIBOTTA P D, ROSELL C M. Effects of enzymatic modification of soybean protein on the pasting and rheological profile of starch-protein systems[J]. Starch-Starke,2010,62(7):373−383. doi: 10.1002/star.200900259
[25] OOSTEN B. Interactions between starch and electrolytes[J]. Starch-Starke,1990,42(9):327−330. doi: 10.1002/star.19900420902
[26] 叶晓汀. 淀粉颗粒结合蛋白对大米淀粉理化性质的影响[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2018. YE X D. Effects of starch granule-associated proteins on physicochemical properties of rice starch[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2018.
[27] WANG J, ZHAO S M, MIN G, et al. Starch-protein interplay varies the multi-scale structures of starch undergoing thermal processing[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,175:179−187. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.02.020
[28] NIU H, HAN Q, CAO C, et al. Short-term retrogradation behaviour of corn starch is inhibited by the addition of porcine plasma protein hydrolysates[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,115:393−400. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.04.047
[29] LI W, DOBRASZCZYK B, DIAS A, et al. Polymer conformation structure of wheat proteins and gluten subfractions revealed by ATR-FTIR[J]. Cereal Chemistry,2006,83(4):407−410. doi: 10.1094/CC-83-0407
[30] LIAN X J, ZHU W, WEN Y, et al. Effects of soy protein hydrolysates on maize starch retrogradation studied by IR spectra and ESI-MS analysis[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2013,59:143−150. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.03.071
[31] YANG Y Y, JIAO A Q, ZHAO S N, et al. Effect of removal of endogenous non-starch components on the structural, physicochemical properties, and in vitro digestibility of highland barley starch[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,117:106698. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.106698
[32] VAN SOEST J J, TOURNOIS H, DE WIT D, et al. Short-range structure in (partially) crystalline potato starch determined with attenuated total reflectance Fourier-transform IR spectroscopy[J]. Carbohydrate Research,1995,279:201−214. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(95)00270-7
[33] SEVENOU O, HILL S, FARHAT I, et al. Organisation of the external region of the starch granule as determined by infrared spectroscopy[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2002,31(1-3):79−85. doi: 10.1016/S0141-8130(02)00067-3
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 王共明,黄会,丁玉竹,薛敬林,舒志强,井月欣,矫春娜,张健. 海参粉超临界CO_2萃取脱脂工艺优化及对挥发性风味物质的影响. 食品工业科技. 2025(03): 241-248 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 李正阳,刘畅,费靖淳,周浩,韩万鑫,潘一萍,祁艳霞,赵前程. 刺参自溶肽美拉德反应产物表征及抗氧化活性研究. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2025(04): 224-233 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 赵影,田柬昕,钟碧銮,李萌,苏可珍. 海参深加工脱腥技术研究进展. 食品工业. 2024(03): 229-235 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王志龙,王禹,段静瑶,苏岩峰,喻佩. 海参制品腥味化合物形成与脱腥技术研究进展. 中国调味品. 2024(06): 206-212 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 马慧,顾雪敏,李芳,梅洁,王梓棚,孔令明. 菌酶协同处理在食品加工中的研究进展及应用. 中国调味品. 2024(07): 208-213 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)









 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



