Effect of Freezing-Thawing Times on Collagen Properties and Quality of Yak Meat
-
摘要: 为探究冻融次数对牦牛肉胶原蛋白特性和品质的影响。以牦牛肉为研究对象,分析不同冻融次数下牦牛肉剪切力、pH、解冻损失、蒸煮损失、色差、质构、胶原蛋白含量及溶解性、酶活性及微观结构的变化规律。结果表明,随着冻融次数的增加,牦牛肉剪切力下降了59.72%,牦牛肉胶原蛋白溶解性、β-半乳糖苷酶和β-半乳糖醛酶活力、解冻损失、蒸煮损失和b*值显著上升(P<0.05),胶原蛋白含量、剪切力、pH、L*值、a*值以及质构显著下降(P<0.05)。相关性分析表明:剪切力与L*值、a*值、pH、胶原蛋白含量和溶解性、质构指标呈显著正相关(P<0.01),与解冻损失、蒸煮损失、b*值、β-半乳糖苷酶活性和β-葡糖醛酸酶活性呈极显著负相关(P<0.001);pH与胶原蛋白特性呈极显著正相关(P<0.001);胶原蛋白特性与质构指标呈极显著正相关(P<0.001)。牦牛肉组织结构随冻融次数增加表现为破坏严重,肌纤维边界模糊。综上,冻融次数增加,牦牛肉的胶原蛋白含量降低,溶解性增高,剪切力降低,质构特性变差,胶原蛋白特性对牦牛肉的品质具有一定影响,不超过3次是保持牦牛肉加工品质的适宜冻融次数。研究结果为牦牛肉的产品开发和品质控制提供理论依据和数据支持。Abstract: To investigate the effects of freezing-thawing times on the collagen properties and the yak meat quality. The changes of shear force, pH, thawing loss, cooking loss, color difference, texture, collagen content and solubility, enzyme activity and microstructure of yak meat were analyzed on different freezing-thawing times. The results showed that with the increase of freezing-thawing times, the shear force of yak meat decreased by 59.72%, moreover, the collagen solubility, β-galactosidase and β-galacturonase activity, thawing loss, cooking loss and b* value of yak meat increased significantly (P<0.05). Furthermore, the collagen content, shear force, pH, L* value, a* value and texture decreased significantly (P<0.05). The correlation results showed that shear force was significantly and positively correlated with L*, a*, pH, collagen content and solubility, and texture index (P<0.01). The shear force had a significantly negative correlation with thawing loss, cooking loss, b*, β-galactosidase activity and β-glucuronidase activity (P<0.001). A significantly positive correlation with the pH and collagen properties (P<0.001). There were significantly positive correlation between collagen properties and texture (P<0.001). With the increase of freezing-thawing times, the tissue structure of yak meat showed severe damage, with blurred borders of muscle fibers. In conclusion, with the increase of freezing-thawing times, the collagen content of yak meat decreased, the solubility increased, the shear force decreased, and the texture worse, and the collagen characteristics had influenced the quality of yak meat, no more than 3 times of freezing-thawing was the suitable times to keep the processing quality of yak meat. The results provide theoretical basis and data support for the product development and quality control of yak meat.
-
Keywords:
- yak meat /
- freezing-thawing /
- collagen /
- enzyme activity /
- quality
-
牦牛是主要生存于青藏高原的物种,牦牛肉是牦牛的主要畜产品资源。当前,冷冻仍是牦牛肉的主要保藏方式。冻藏牦牛肉因其具有较长的保存时间[1],深受广大生产者和消费者欢迎。然而,由于冷链的条件不完善和技术缺陷,冻藏牦牛肉在贮藏、运输以及消费过程中会发生冻融循环[2-3],进而对肉品品质产生显著影响。
目前已有研究发现冻融会影响肉品品质,冻融过程中的冰晶反复形成和溶解,会造成肌肉中的水分含量逐渐下降,进而影响肉品的营养价值。李婉竹[4]表明多次冻融循环引起牦牛肉蛋白质氧化程度加剧,同时造成保水性降低。曹银娟等[5]发现经反复冻融处理后的牛瘤胃的胶原蛋白功能降低,结构遭到破坏,胶原蛋白降解、交联、聚集等变性程度增大。戚军[6]证明了冻融次数显著影响羊肉品质,其多不饱和脂肪酸含量随冻融次数的增加逐渐增加。李贞子等[7]报道随着冻融次数的增加,早胜牛肉的干物质比重不断增加,蛋白质比重不断下降,其理化品质和营养成分均遭到破坏。李金平等[8]的研究结果证明反复冻融使牛外脊肉的解冻时间缩短,影响其蛋白质降解。相关研究表明,冻融会造成肉品质劣变。然而,对于牦牛肉而言,冻融次数对其品质和胶原蛋白特性的影响如何,在冻融过程中胶原蛋白特性变化对牦牛肉品质的影响规律尚不清楚。
为此,以牦牛肉为研究对象,研究了冻融处理对牦牛肉剪切力、pH、保水性、色差和质构等品质指标和胶原蛋白特性的影响,分析了冻融过程中牦牛肉微观结构的变化,并进行相关性分析。旨在明确冻融处理对牦牛肉胶原蛋白特性及其品质的影响,探究冻融过程中牦牛肉胶原蛋白特性变化对牦牛肉品质的影响规律,以期为牦牛肉的保藏、加工和品控提供理论依据和数据支持。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
牦牛肉 购自于青海夏华清真肉食品有限公司,选取生长发育正常、健康无病、体况相近的3~4岁牦牛,取其里脊,真空包装后在4 ℃下冷却24 h;4-羟基-α-吡咯甲酸(羟脯氨酸) 无锡必康生物工程有限公司;β-半乳糖苷酶、β-葡糖醛酸酶酶联免疫检测试剂盒 上海远慕生物科技有限公司;4%多聚甲醛组织固定液 北京兰杰柯科技有限公司;9 cm×13 cm蒸煮袋 雄县旭日纸塑包装有限公司。
722S 可见分光光度计 上海菁华仪器有限公司;YP-402N电子天平 上海菁华仪器有限公司;ADCI-60-C色差计 北京辰泰克仪器技术有限公司;848 pH测定仪 东莞市希玛仪表有限公司;HHS-4S电子恒温不锈钢水浴锅 绍兴宝加仪器有限公司;CT3质构分析仪 美国Brookfield公司;IX70荧光显微镜 日本Olympus株式会社;H/T16MM台式高速离心机 湖南赫西离心机仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品采集和制备
将肉样切成质量200 g左右的块状,用聚乙烯食品保鲜袋包装,将样品随机分为6 组,每组至少5 份平行,设定−18 ℃冷冻12 h后4 ℃解冻12 h为1次冻融循环,分别在冻融0、1、2、3、4、5和6 次测定相应的指标[5]。
1.2.2 剪切力的测定
将肉样顺着肌纤维的方向切成30 mm×10 mm×10 mm的长条状,将探头沿着垂直于肌纤维方向切割,测定其剪切力,单位为kg。探头型号为TA3/100,夹具为TA-DEC,测试速度为1.50 mm/s,每个肉样平行测定5次,实验结果取其平均值[6]。
1.2.3 pH的测定
将pH测定仪插入肉样的新鲜切面中,待读数稳定后记录数据,每个肉样平行测定5次,取平均值作为该肉样的pH[6]。
1.2.4 保水性的测定
1.2.4.1 蒸煮损失率的测定
取150 g的肉样蒸煮前称重(W1),在85 ℃水浴中加热至中心温度70 ℃,后冷却至4 ℃,用吸水纸吸干水分,然后再次称重(W2),蒸煮损失率按(1)计算。每个样品测定5个平行,取平均值[6]。
蒸煮损失率(%)=W1−W2W1×100 (1) 1.2.4.2 解冻损失率的测定
样品分别在解冻前后,用吸水纸擦去表面渗出水分后准确称量其重量分别为W3和W4,解冻损失率按式(2)计算。每个样品测定5个平行,取平均值[6]。
解冻损失率(%)=W3−W4W3×100 (2) 1.2.5 色差的测定
利用色差仪测定。测定前要对仪器进行校正,剔除肉样上的可见筋膜及结缔组织,将处理好的肉样的鲜切面放置于光线充足的实验台上30 min后,垂直将色差仪镜头置于肌肉横断面上,镜口紧扣肌肉横断面,随机在每个样品的5个不同位置各测定1次,测定位置均匀分布于肌肉横切面。记录所测的亮度(L*)值、红度(a*)值、黄度(b*)值,计算平均值作为色差值[6]。
1.2.6 质构的测定
将肉样用刀顺着肌纤维的方向切成10 mm×10 mm×10 mm的立方体状,使用质构仪将探头沿着垂直于肌纤维方向进行压缩,测定其质构。探头型号为TA3/100,夹具为TA-SBA,设定参数为:目标值为98 mm,测试速度为1.00 mm/s,测试目标为距离。每个肉样平行测定5次,实验结果取其平均值[6]。
1.2.7 微观结构的观察
从样品上切取10 mm×10 mm的块状,于4%多聚甲醛组织固定溶液中固定过夜,随后用30%~100%乙醇进行梯度洗脱,然后用二甲苯洗脱2次,组织切片,切片厚度5 μm,经苏木精-伊红染色液染色后制成切片标本,用显微镜观察不同冻融次数牦牛肉的微观结构变化[4]。
1.2.8 胶原蛋白含量及溶解性的测定
参考曹银娟等[5]的方法,测定样品中羟脯氨酸浓度的标准曲线为:y=0.0031x+0.0102,R2=0.9981(其中y为羟脯氨酸质量浓度(μg/mL);x为吸光度)。羟脯氨酸的含量乘以系数7.25换算为胶原蛋白含量。采用曹银娟等[5]的方法分离可溶性胶原蛋白与不可溶性胶原蛋白,其中上清液中的蛋白含量为可溶性胶原蛋白含量;沉淀中的蛋白含量为不溶性蛋白含量。胶原蛋白溶解性通过式(3)进行计算。
胶原蛋白溶解性(%)=可溶性胶原蛋白含量(mg/g)总胶原蛋白含量(mg/g)×100 (3) 1.2.9 β-半乳糖苷酶和β-葡糖醛酸酶活力的测定
β-半乳糖苷酶和β-葡醛糖酸酶活力均采用试剂盒进行测定,具体操作和计算方法参照试剂盒说明书进行,具体操作步骤为[5]:称取1 g经冻融处理后的样品,加入9 mL的PBS,pH7.4,匀浆,4000~5000 r/min离心20 min,酶标板分别设置空白孔和待测样品孔,每孔按操作步骤分别加入试剂充分混匀,于37 ℃在暗处反应15 min,于波长450 nm下测定样品吸光值。
1.3 数据处理
采用SPSS26.0对数据进行统计分析,相关性采用Pearson相关系数分析法,各处理间平均数差异显著性分析采用Duncan多重比较法,P<0.05表示差异显著,P<0.01表示极显著性差异。
2. 结果与分析
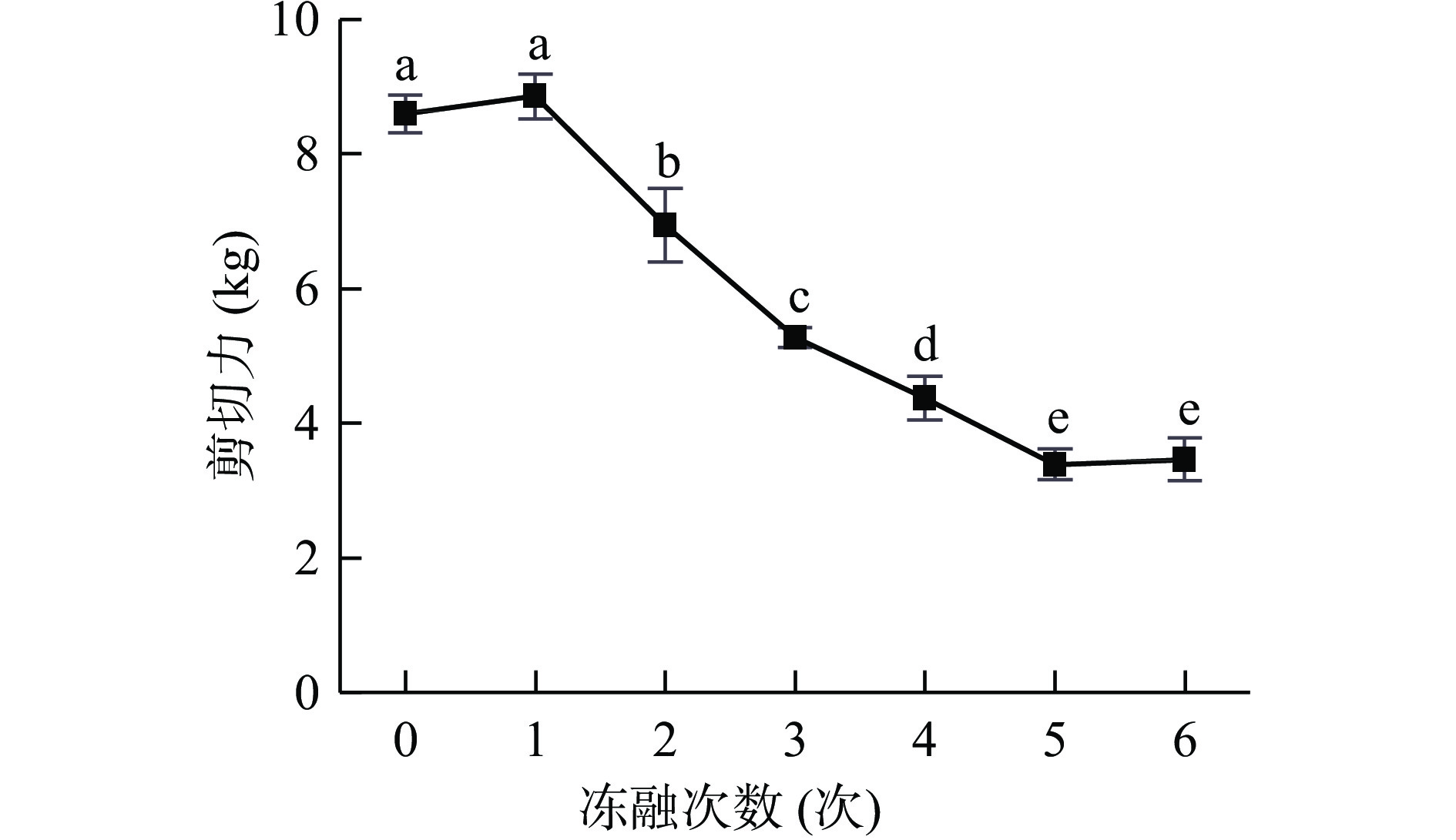
2.1 冻融对牦牛肉剪切力的影响
嫩度是牦牛肉的主要食用品质之一[9],是影响消费者选择购买与否的主要衡量指标和其市场接受性的关键因素[10-11]。剪切力作为一种嫩度的客观评定指标,直接反映肉的质地,是肌肉中结缔组织含量与性质、肌原纤维蛋白的化学结构状态的总体反映,剪切力越小代表肉品的嫩度越高。冻融对牦牛肉剪切力的影响如图1所示,随着冻融次数的增加,牦牛肉剪切力总体呈下降的趋势,冻融6次时的剪切力较新鲜牦牛肉下降了59.72% (P<0.05),其趋势与曹银娟等[5]的研究结果基本一致。随着冻融次数的增加,牦牛肉剪切力的降低一方面是因为肌纤维受到冰晶的机械损伤发生断裂、降解,使得牦牛肉的剪切力下降;另一方面的原因可能是牦牛肉的胶原蛋白降解,促进牦牛肉结缔组织的弱化,使牦牛肉的剪切力下降[12-14]。本研究表明经过3 次冻融循环后的牦牛肉剪切力下降速率变缓。
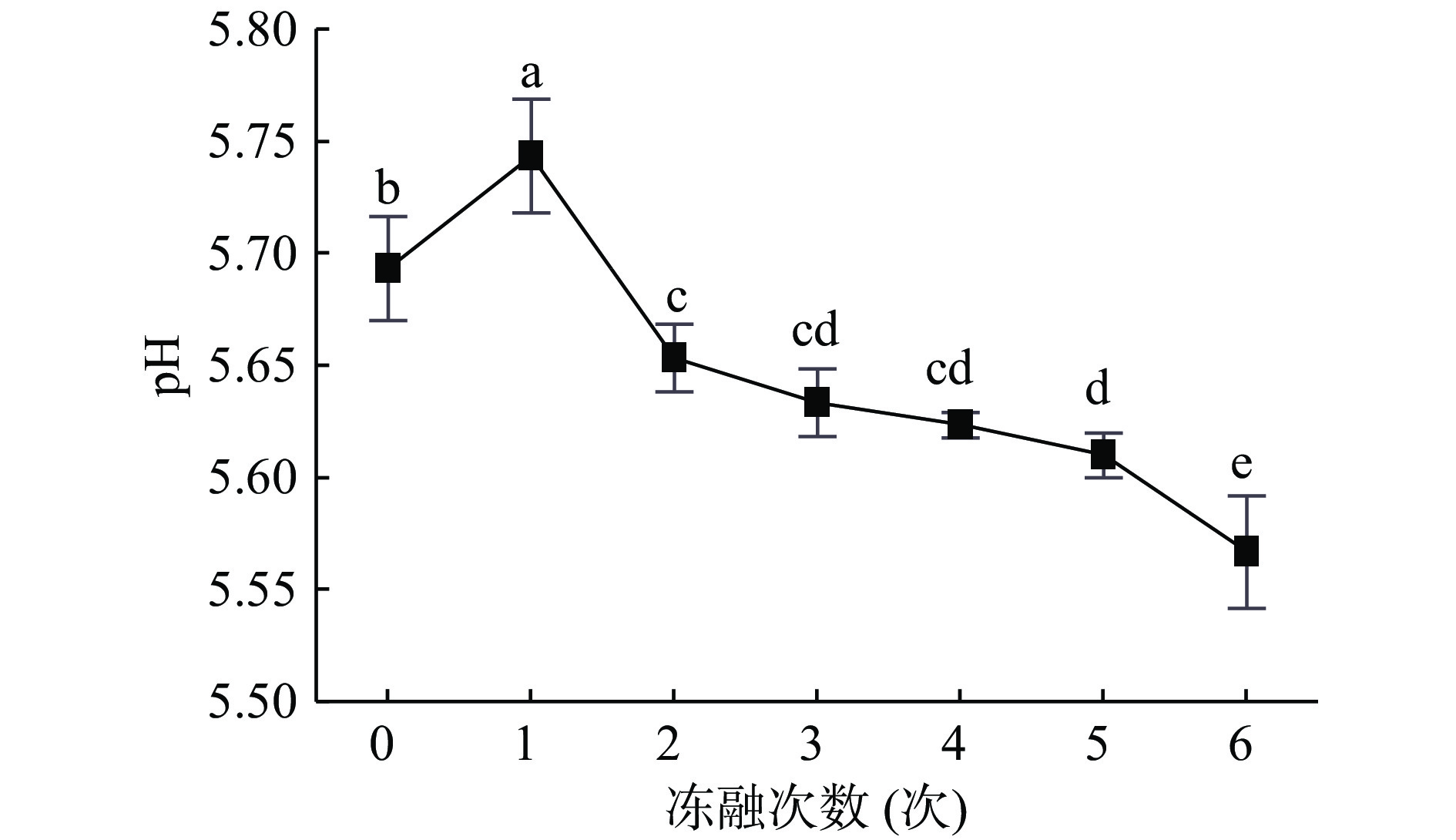
2.2 冻融对牦牛肉pH的影响
pH是评定肉质的重要指标之一,主要受肌肉中糖酵解产生乳酸含量的影响,与牦牛肉的嫩度和保水性密切相关[15-17]。冻融次数对牦牛肉pH的影响如图2所示,随着冻融次数的增加,牦牛肉pH呈先上升后下降(P<0.05)的趋势,冻融1次时,pH达到最大,冻融6次时从新鲜肉样的5.69±0.02下降至5.57±0.03。在第1次冻融时pH上升可能是因为在冻融过程中牦牛肉的蛋白质发生降解,产生的碱性自由氨基酸的含量高于酸性自由氨基酸[18],或者是冻融过程使肌肉中含氮物质分解。pH的下降可能是由于冻融使牦牛肉中的糖酵解过程加剧和磷酸化酶的激活而导致,生成的游离脂肪酸等酸性物质累积导致的[19]。
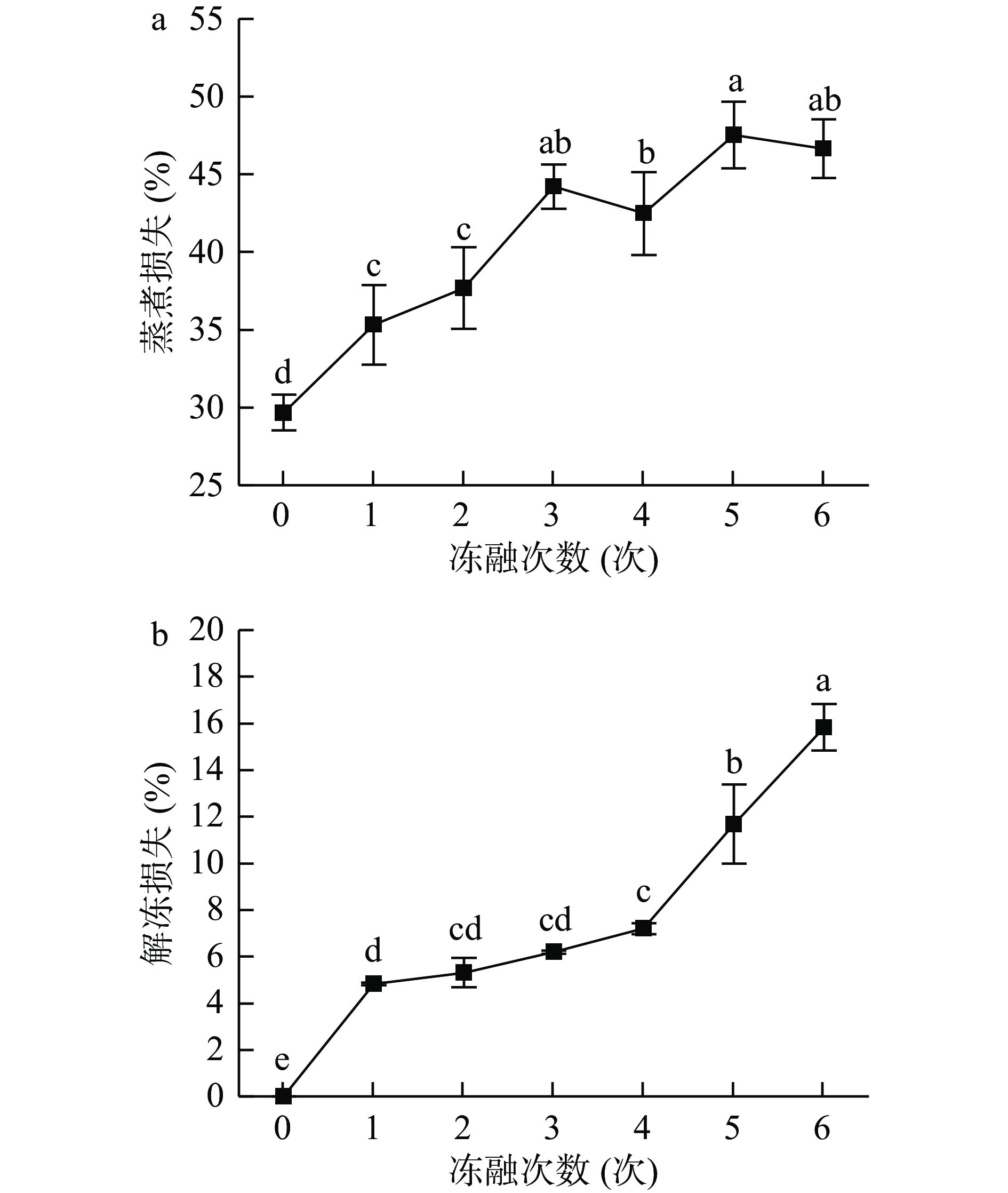
2.3 冻融对牦牛肉保水性的影响
保水性是指肉在贮藏和蒸煮过程中保持其原有水分的能力,蒸煮损失率和解冻损失率的高低直接反映原料肉保水性的大小[20]。由图3可知,随着冻融次数的增加,牦牛肉的蒸煮损失率和解冻损失率均呈增加趋势 (P<0.05),分别由新鲜牦牛肉的29.67%±1.16%、0%增加到46.65%±1.88%、15.83%±0.99%,与李金平等[8]的研究结果一致。原因可能是反复冻融使冰晶处于溶解-形成的循环状态,其所占的水分比例较大,在细胞中的汁液流失增大[11, 21]。也可能是由于蛋白质的结构发生一定程度的改变,蛋白质发生变性,导致牦牛肉在解冻和蒸煮过程中损失大量水分,表现为保水性变差,从而造成了牦牛肉胶原蛋白含量降低的情况。同时在本研究发现经过3次冻融循环后,牦牛肉的解冻损失率上升速率加剧。
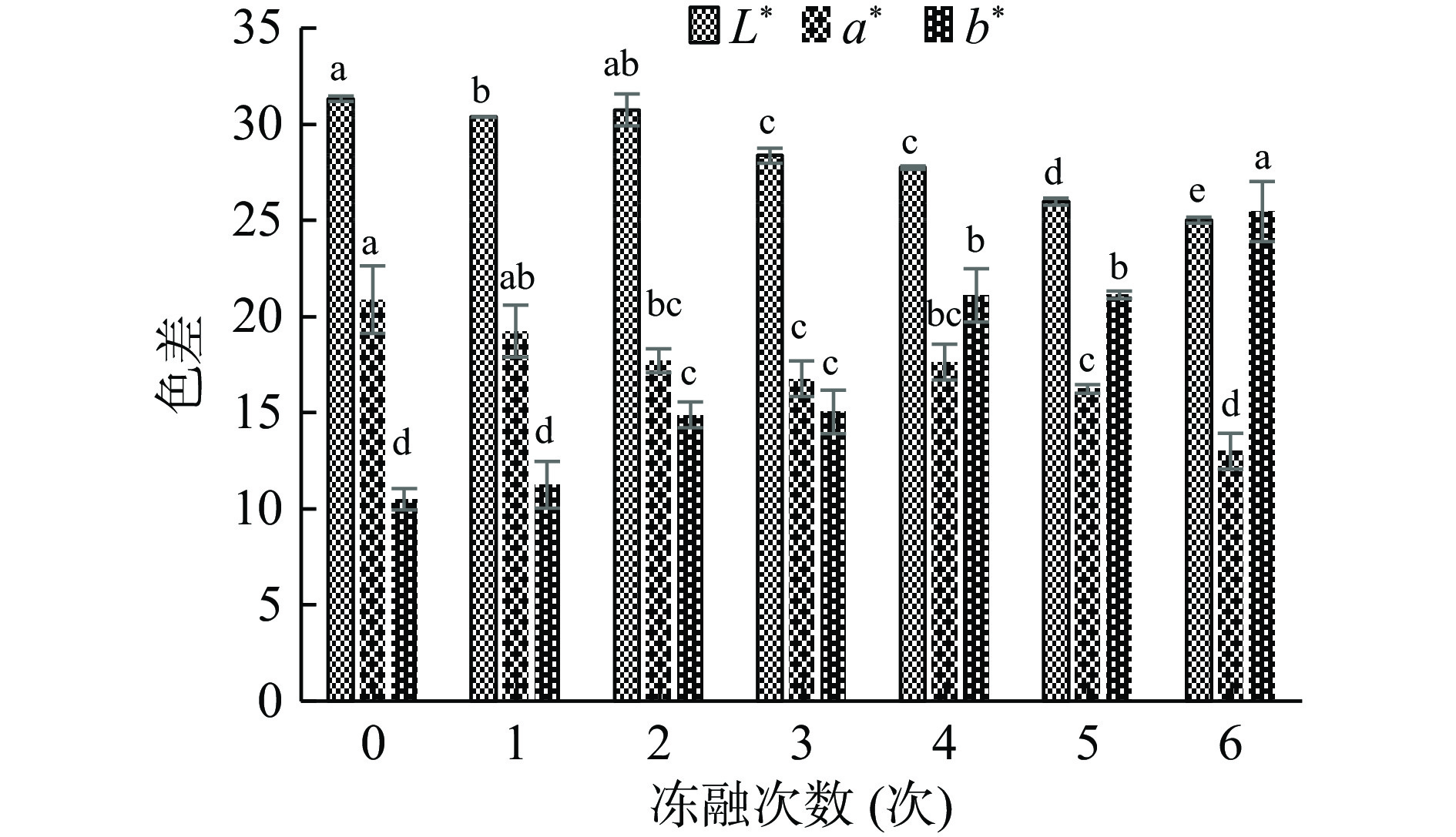
2.4 冻融对牦牛肉色差的影响
肌肉的颜色是影响消费者选购的主要因素[19]。肌肉中肌红蛋白的含量和状态决定肌肉的颜色[4]。肌肉中的L* 值的变化与肌肉中水分含量相关,a* 值和 b* 值的变化受到冻融过程中冰晶形成时细胞内氧气浓度的影响。由图4可知,新鲜牦牛肉的 L* 值、a* 值和 b* 值分别为 31.33±0.14、20.88±1.75和10.50±0.55,随着冻融次数的增加,L* 值和 a* 值均呈下降的趋势(P<0.05),b* 值呈现上升的趋势(P<0.05),冻融6次时,L* 值和 a* 值下降了 20.15% 和37.74%,b* 值增加了 142.48%。本研究中与李金平等[8]在研究反复冻融对牛外脊肉品质影响中发现 L* 值增大的趋势不一致,可能是因为肌肉中的 L* 值的变化与肌肉中蛋白质的种类和变性降解程度有关。而本研究中 a* 值与 b* 值的变化趋势与 PIETRASIK 等 [22]的研究结果一致。
2.5 冻融对牦牛肉质构特性的影响
牦牛肉在冻融过程中的质构特性的变化如表1所示,与新鲜牦牛肉相比,硬度、内聚性、弹性、胶着性和咀嚼性均呈下降的趋势 (P<0.05),其下降幅度分别为58.43%、22.22%、38.87%、39.57%和45.01%。说明随着冻融次数的增加,牦牛肉的质构特性发生了明显变化,表现为牦牛肉的食用品质下降。分析认为冻融处理通过影响牦牛肉中胶原蛋白的特性和肌纤维的完整性,进而影响牦牛肉的质构品质[23]。
表 1 冻融次数对牦牛肉质构特性的影响Table 1. Effect of freeze-thaw times on the structural properties of yak meat冻融次数(次) 硬度(kg·cm−1) 内聚性 弹性 胶着性 咀嚼性(mJ) 0 6948.33±70.47a 0.54±0.02a 5.48±0.84a 4232.67±360.01a 3529.40±618.08a 1 5351.33±422.51b 0.53±0.03ab 4.55±0.61ab 3638.00±266.32ab 3036.77±671.30ab 2 5537.67±463.11b 0.49±0.02bc 4.06±0.13ab 3419.33±147.14abc 2922.07±557.82ab 3 4685.67±877.05bc 0.46±0cde 4.05±0.31ab 3367±1186.26abc 2468.45±523.90 ab 4 4364.67±1165.20bc 0.47±0.04cd 3.91±0.28ab 3196±288.36abc 2247.20±765.34b 5 3735±810.49cd 0.43±0.03cde 3.88±0.83ab 2992.00±288.36bc 2191.53±85.80b 6 2888.67±469.26d 0.42±0.01e 3.35±0.29b 2558.00±352.88c 1940.83±394.49b 注:表中同列小写字母不同表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 2.6 冻融对牦牛肉微观结构的影响
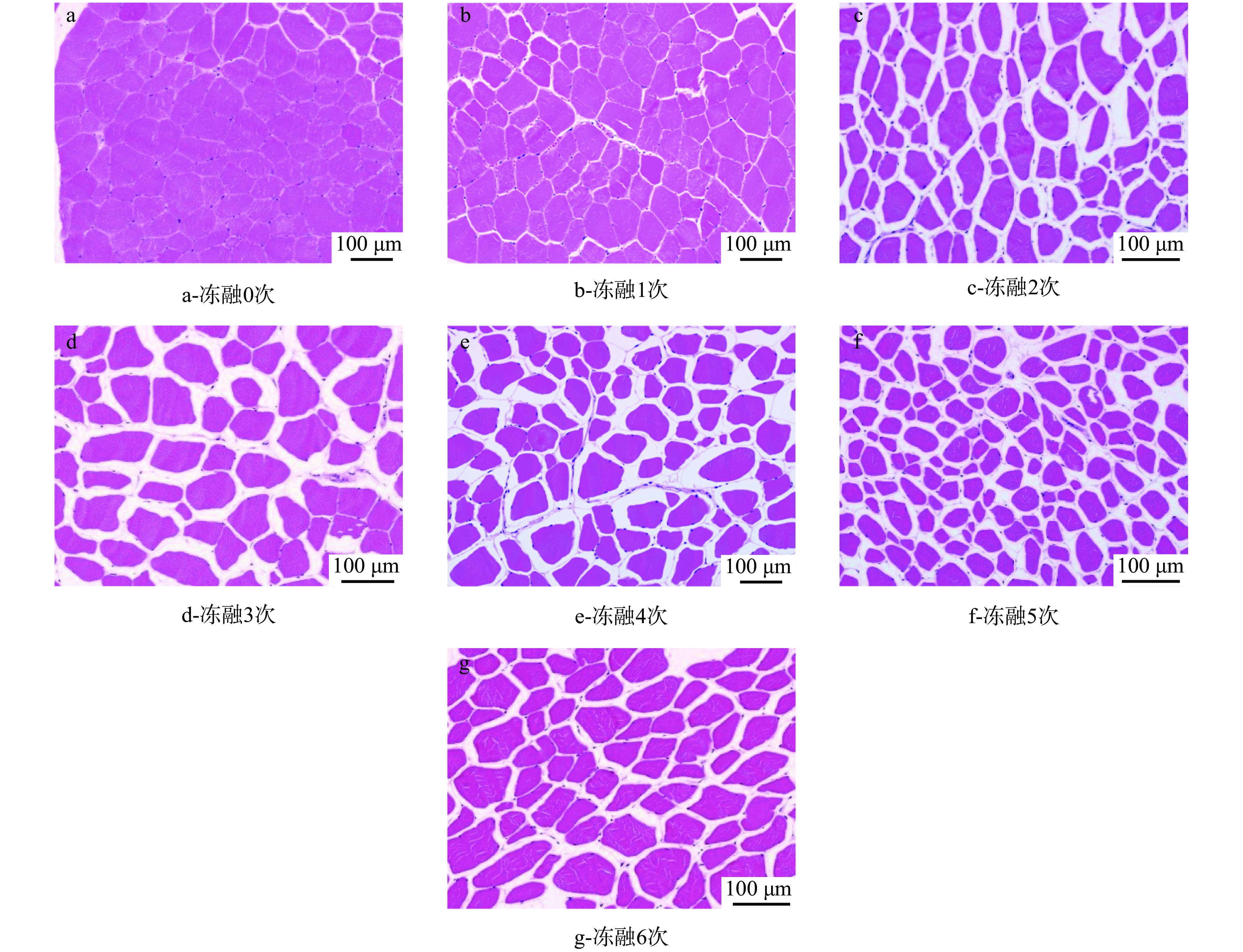
图5显示了经过6次冻融循环的牦牛肉和新鲜牦牛肉在显微镜下的微观结构图。新鲜牦牛肉的肌纤维排列密致且均匀,肌纤维之间间隙小,其切面多呈圆形或多边形;肌肉在冻融1 次时,肌纤维排列混乱,发生破裂,肌束膜收缩导致肌纤维之间的间隙增大,其切面形状发生扭曲;冻融4 次时,肌束膜发生破裂,肌纤维排列混乱、结构疏松。冻融6 次时,肌肉组织肌肉破坏更加明显,肌纤维边界模糊,排列紊乱,出现溃散、断开的情况,肌肉组织中出现大小不一的空泡。随着冻融次数的增加,冰晶的机械破坏作用使结缔组织丧失完整性,使肌纤维受到损害。另一方面,在冻融过程中,肌肉的保水性下降,造成大量汁液流失,使得肌纤维收缩,最终导致细胞内的水分损失,肌纤维之间产生间隙。常海军等[21]研究中发现随着冷冻-解冻次数的增加,猪肉肌纤维明显发生断裂、结缔组织膜严重受损,使肌肉失去原有的完整性。
2.7 冻融对牦牛肉胶原蛋白含量及溶解性的影响
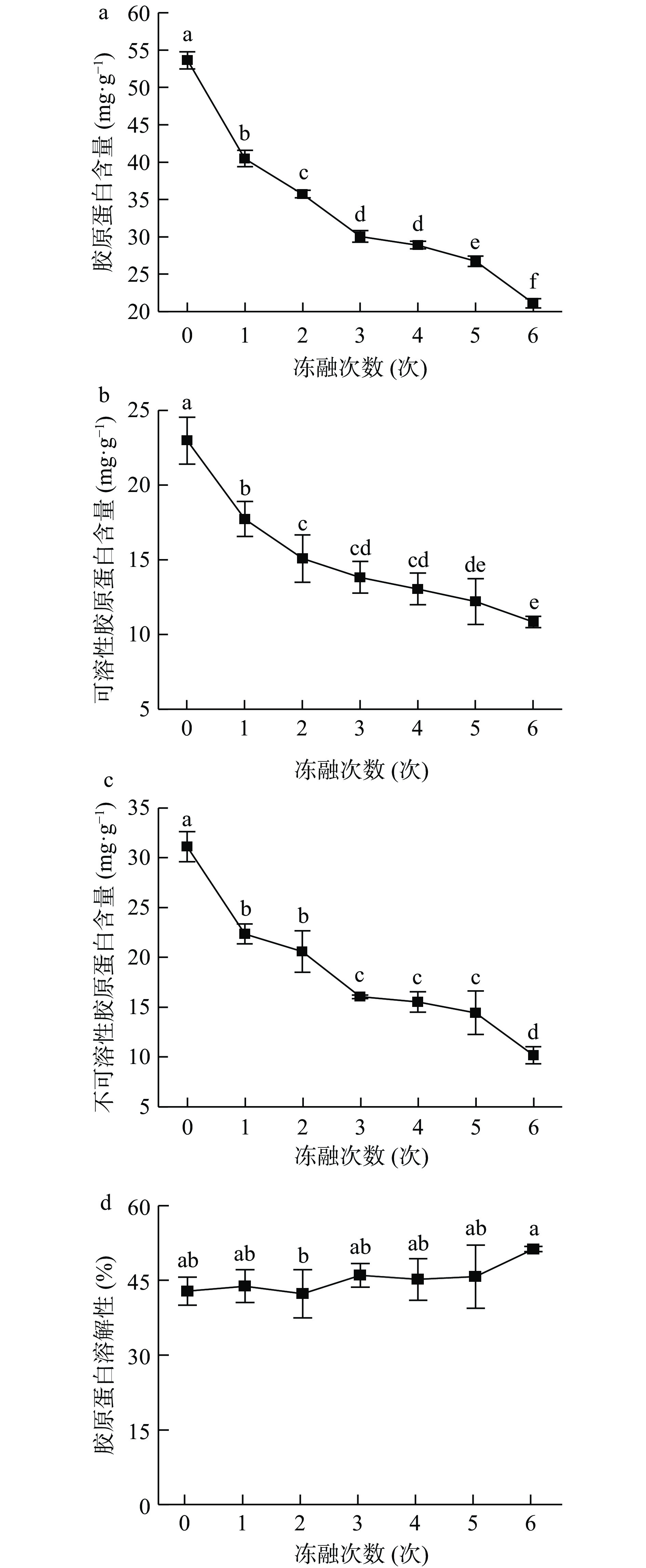
胶原蛋白作为肌肉中结缔组织的主要成分,其含量及溶解性影响肉品的食用特性[24]。冻融过程中总胶原蛋白含量、不溶性胶原蛋白含量、可溶性胶原蛋白含量、胶原蛋白溶解性分别如图6所示,总胶原蛋白含量在冻融过程中由新鲜牦牛肉的(53.64±0.15) mg·g−1降低到冻融6次时的(21.11±0.62) mg·g−1 (P<0.05),降低了60.65%;可溶性胶原蛋白含量由新鲜牦牛肉的(22.97±1.56) mg·g−1降低到冻融6次时的(10.82±0.38) mg·g−1 (P<0.05),降低了52.90%;不可溶性胶原蛋白含量由新鲜牦牛肉的(31.11±1.51) mg·g−1降低到冻融6次时的(10.17±0.86) mg·g−1 (P<0.05),降低了67.31%。胶原蛋白含量降低一方面可能是因为在冻融过程中冰晶的反复形成导致牦牛肉中水分的流失,胶原蛋白作为营养成分存在流失[25],其含量降低。另一个原因可能是在冻融过程中可溶性胶原蛋白溶于冰晶融化的汁液中,而不可溶性胶原蛋白的三螺旋结构逐渐松散[26-27],导致一部分胶原蛋白明胶化,最终表现出胶原蛋白含量下降的情况。而胶原蛋白溶解性随冻融次数的增加呈上升趋势,由新鲜牦牛肉的(42.83±2.83)%增加到冻融6次时的(51.26±0.56)% (P<0.05),增加了19.68%,原因可能是冻融过程中细胞膜被破坏,蛋白酶被释放,增加了胶原蛋白的溶解性[28]。张诚[28]研究反复冻融对鸡肉的品质影响中发现鸡肉胶原蛋白含量在冻融过程中呈显著下降的趋势,从而影响鸡肉的嫩度。由此可知,肌肉结缔组织在冻融过程中随着冰晶的不断重新形成和分布,肌肉结缔组织结构受到机械破坏,胶原蛋白及核心蛋白多糖发生降解,进而影响胶原蛋白特性的变化。
2.8 冻融对牦牛肉β-半乳糖苷酶和β-葡糖醛酸酶酶活性的影响
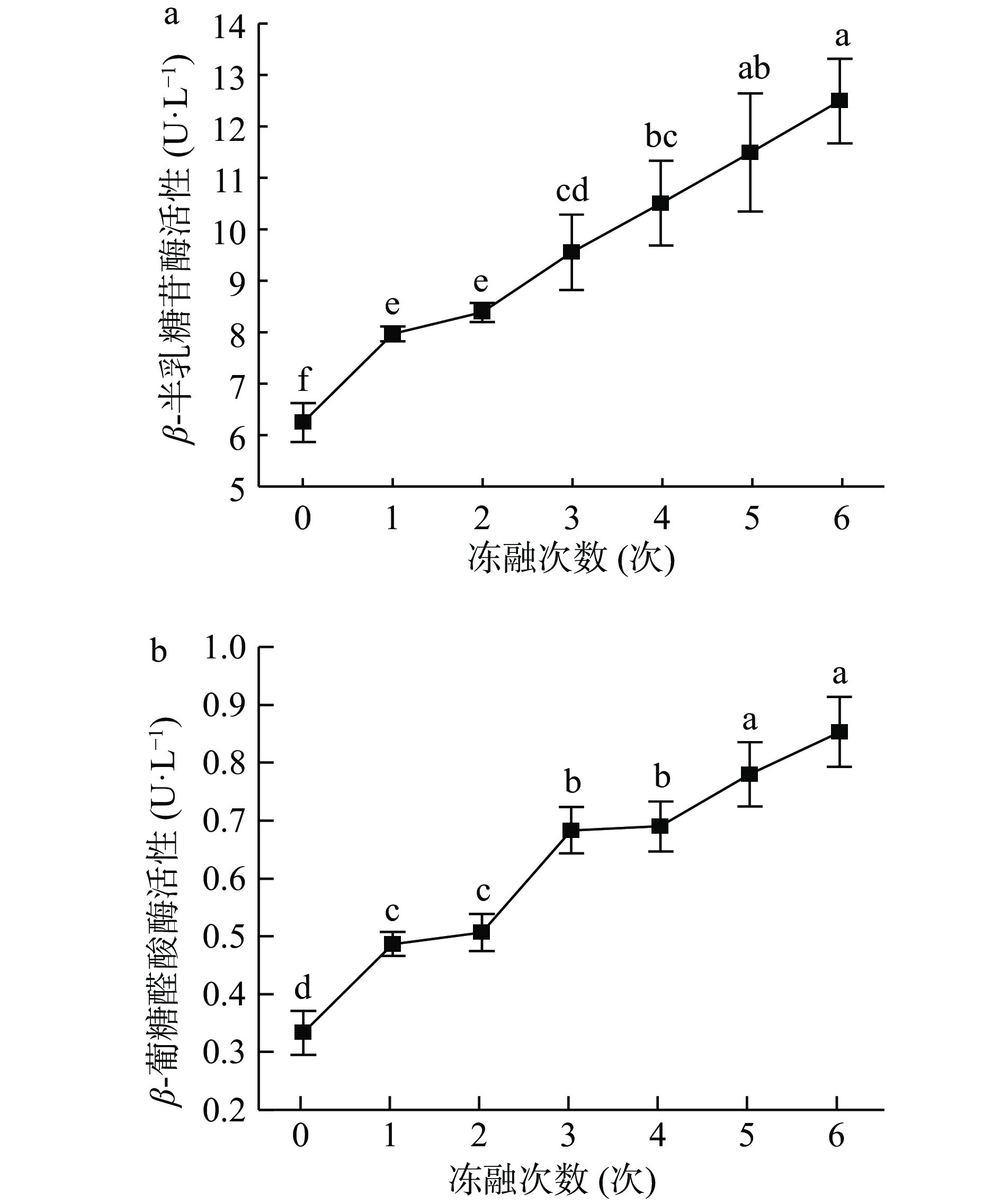
β-半乳糖苷酶和β-葡糖醛酸酶可降解肌内胶原蛋白基质多糖(蛋白多糖)[29],而基质蛋白多糖是维持结缔组织机械强度的主要成分[30],其降解可以改善肌肉的嫩度。由图7可知,β-半乳糖苷酶的活力随着冻融次数的增加而提高,在冻融6次时增加到(12.50±0.83)U·L−1,显著高于新鲜牦牛肉的(6.25±0.38) U·L−1 (P<0.05)。而β-葡糖醛酸酶的活力呈波动式上升(P<0.05),由新鲜牦牛肉时的(0.33±0.04) U·L−1增加到冻融6次时的(0.85±0.06) U·L−1。β-半乳糖苷酶和β-葡糖醛酸酶活力随冻融次数增加而提高的原因可能是冻融过程中,细胞膜结构被削弱,溶酶体被破坏,促进β-半乳糖苷酶和β-葡糖醛酸酶的释放,验证了胶原蛋白含量随冻融次数增加而下降[5]。
2.9 相关性分析
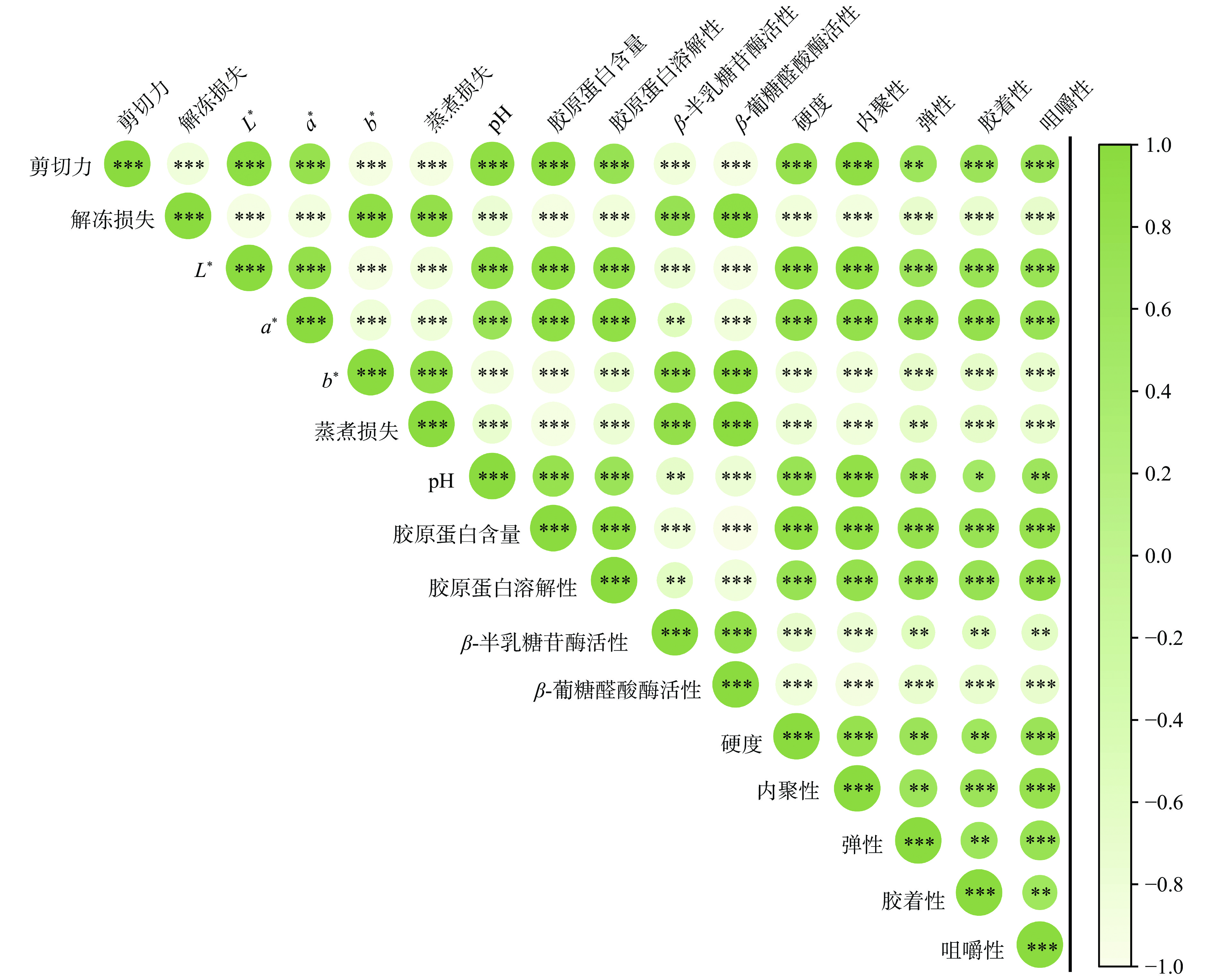
由图8可知,剪切力与L*、a*、pH、胶原蛋白含量和溶解性、硬度、内聚性、胶着性和咀嚼性呈极显著正相关(P<0.001),与弹性呈显著正相关(P<0.01),与解冻损失、蒸煮损失、b*、β-半乳糖苷酶活性和β-葡糖醛酸酶活性呈极显著负相关(P<0.001)。说明随着冻融次数的增加,胶原蛋白降解变性情况明显,无法维持结缔组织结构,导致肌肉内结缔组织的破坏愈发严重。
pH与保水性指标呈极显著负相关(P<0.001),与胶原蛋白含量和溶解性呈极显著正相关 (P<0.001),说明随着冻融次数的增加,冰晶的机械破坏作用增大,造成肌肉内汁液流失,pH下降,使胶原蛋白溶解性增大。郝婉名等[15]认为牛肉pH的改变会影响胶原蛋白的热溶解性,使胶原蛋白变性降解,影响胶原蛋白水合能力的变化,从而影响牛肉的嫩度。
胶原蛋白含量和溶解性与剪切力和质构指标呈极显著正相关(P<0.001)。β-半乳糖苷酶活性与硬度和内聚性呈极显著负相关(P<0.001),与弹性、胶着性和咀嚼性呈显著负相关(P<0.01),β-葡糖醛酸酶活性与质构指标呈极显著负相关(P<0.001),说明肌肉的质构特性在一定程度上与胶原蛋白特性有关。随着冻融次数的增加,肌肉内β-半乳糖苷酶活性和被β-葡糖醛酸酶活性增加,蛋白多糖发生降解[31],质构指标下降,从而改善牦牛肉的嫩度[32]。
本研究结果表明随着冻融次数的增加,胶原蛋白含量下降,溶解性增大,剪切力下降,pH下降,保水性变差,质构指标下降,此外,从肉品加工和食品的角度考虑,选用不同冻融次数的原料肉是牦牛肉加工的关键因素。在冻融3次时,剪切力下降速率变缓,保水性变差速率升高,可见冻融3次后牦牛肉在改善嫩度的基础上增加了损失。
3. 结论
随着冻融次数的增加,牦牛肉胶原蛋白降解程度增大,胶原蛋白溶解性增大,结缔组织破坏严重,剪切力下降,肌肉嫩度得到改善;pH下降,解冻损失率和蒸煮损失率增大,使牦牛肉保水性下降,牦牛肉组织结构破坏。然而在冻融3次后,剪切力下降速率变慢,保水性变差速率加快。因此,从食用品质和商业价值综合考虑,冻融次数应控制在3次以内。
-
表 1 冻融次数对牦牛肉质构特性的影响
Table 1 Effect of freeze-thaw times on the structural properties of yak meat
冻融次数(次) 硬度(kg·cm−1) 内聚性 弹性 胶着性 咀嚼性(mJ) 0 6948.33±70.47a 0.54±0.02a 5.48±0.84a 4232.67±360.01a 3529.40±618.08a 1 5351.33±422.51b 0.53±0.03ab 4.55±0.61ab 3638.00±266.32ab 3036.77±671.30ab 2 5537.67±463.11b 0.49±0.02bc 4.06±0.13ab 3419.33±147.14abc 2922.07±557.82ab 3 4685.67±877.05bc 0.46±0cde 4.05±0.31ab 3367±1186.26abc 2468.45±523.90 ab 4 4364.67±1165.20bc 0.47±0.04cd 3.91±0.28ab 3196±288.36abc 2247.20±765.34b 5 3735±810.49cd 0.43±0.03cde 3.88±0.83ab 2992.00±288.36bc 2191.53±85.80b 6 2888.67±469.26d 0.42±0.01e 3.35±0.29b 2558.00±352.88c 1940.83±394.49b 注:表中同列小写字母不同表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 -
[1] 黄彩霞. 牦牛肉商品质量特征及评定技术方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2014. HUANG C X. Research on commercial quality and assessment technology of yak meat[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2014.
[2] JEONG J Y, KIM G D, YANG H S, et al. Effect of freeze-thaw cycles on physicochemical properties and color stability of beef semimembranosus muscle[J]. Food Research International,2011,44(10):3222−3228. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2011.08.023
[3] 游辉煌. 冻藏温度及冻融循环对猪蹄贮藏品质的影响研究[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2016. YOU H H. The effect of freezing storage temperature and freeze-thaw cycles on the storage quality of pig trotter[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2016.
[4] 李婉竹. 多次冻融对牦牛肉品质及其蛋白质氧化的影响[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2017. LI W Z. Effects of multiple freezing and thawing on quality and protein oxidation of yak meat[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2017.
[5] 曹银娟, 韩玲, 余群力, 等. 冻融对牛瘤胃平滑肌胶原蛋白降解、交联及品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(3):221−226. [CAO Y J, HAN L, YU Q L, et al. Effect of freeze-thaw cycles on the degradation, cross-linking and quality of bovine rumen smooth muscle collagen[J]. Food Science,2022,43(3):221−226. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20201025-251 [6] 戚军. 反复冻融对羊肉品质的影响研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2009. QI J. Effect of repeated freeze-thaw cycles on goal quality[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2009.
[7] 李贞子, 阿依木古丽, 蔡勇, 等. 反复冻融对早胜牛肉理化品质和营养成分的影响[J]. 西北民族大学学报(自然科学版),2010,31(3):71−75. [LI Z Z, AYI M G L, CAI Y, et al. Physicochemical properties and nutrients changes in Zaosheng cattle muscle as influenced by different freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Journal of Northwest University Nationalities (Natural science),2010,31(3):71−75. [8] 李金平, 李春保, 徐幸莲, 等. 反复冻融对牛外脊肉品质的影响[J]. 江苏农业学报,2010,26(2):406−410. [LI J P, LI C B, XV X L, et al. Effect of freeze-thaw cycle on meat quality of beef striploin[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences,2010,26(2):406−410. [9] 李升升, 张燕, 赵立柱. 不同杂交牛肉加工特性研究[J/OL]. 甘肃农业大学学报, 1−9[2022-08-15]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/62.1055.s.20220602.1859.013.html. LI S S, ZHANG Y, ZHAO L Z. Study on the processing characteristics of different hybrid beef[J/OL]. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University, 1−9[2022-08-15]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/62.1055.s.20220602.1859.013.html.
[10] LI R, GUO M, LIAO E, et al. Effects of repeated freezing and thawing on myofibrillar protein and quality characteristics of marinated Enshi black pork[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,378:131994. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131994
[11] 王可. 不同部位青海高原型牦牛肉加工特性与加工适宜性研究[D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2020. WANG K. Study on processing characteristics and suitability of Qinghai plateau yak meat from different parts[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2021.
[12] 李升升, 张燕, 赵立柱, 等. 牦牛、犏牛和黄牛乳的营养及加工特性[J]. 食品工业,2022,43(4):343−346. [LI S S, ZHANG Y, ZHAO L Z, et al. Nutrition and processing properties of yak milk, cattle-yak milk and cattle milk[J]. Food Industry,2022,43(4):343−346. [13] 周昱宇, 毛云, 王立娜, 等. 冻融次数对藏羊肉品质特性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(11):342−349. [ZHOU X Y, MAO Y, WANG L N, et al. Effect of freezing-thawing times on quality characteristics of Tibetan mutton[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(11):342−349. [14] YANG X, ZHANG Y, LUO X, et al. Influence of oxygen concentration on the fresh and internal cooked color of modified atmosphere packaged dark-cutting beef stored under chilled and superchilled conditions[J]. Meat Science,2022,188:108773. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2022.108773
[15] 郝婉名, 祝超智, 赵改名, 等. 肌肉嫩度的影响因素及pH调节牛肉嫩化技术研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(24):349−354. [HAO W M, ZHU C Z, ZHAO G M, et al. Research progress on the influence factors of the tenderness of the muscle and the technology of adjusting the tenderization of the beef[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(24):349−354. [16] 吴斌, 孙宝忠, 孙晓明, 等. 牛肉嫩度的色差值预测模型研究[J]. 食品科技,2011,36(1):76−79. [WU B, SUN B Z, SUN X M, et al. Research of forecasting models of beef tenderness established by the L*, a*, b* color space[J]. Food Science and Technology,2011,36(1):76−79. [17] HE L, ZOU L K, YANG Q R, et al. Antimicrobial activities of nisin, tea polyphenols, and chitosan and their combinations in chilled mutton[J]. Journal of Food Science,2016,81(6):M1466−M1471. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.13312
[18] LEYGONIE C, BRITZ T J, HOFFMAN L C. Oxidative stability of previously frozen ostrich Muscularis iliofibularis packaged under different modified atmospheric conditions[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2011,46(6):1171−1178.
[19] SHEN Y Q, GUO X X, LI X P, et al. Effect of cooking temperatures on meat quality, protein carbonylation and protein cross-linking of beef packed in high oxygen atmosphere[J]. LWT,2022,154:112633. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112633
[20] 王钰. 不同品种及不同贮藏方式冷鲜鸡肉品质比较研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2020. WANG Y. A comparative study on the chilled chicken meat quality of different varieties and under different storage conditions[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2020.
[21] 常海军, 牛晓影, 周文斌. 不同冻融次数对猪肉品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2014,35(15):43−48. [CHANG H J, NIU X Y, ZHOU W B. Effects of different freezing and thawing cycles on pork quality[J]. Food Science,2014,35(15):43−48. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201415009 [22] PIETRASIK Z, JANZ J A M. Influence of freezing and thawing on the hydration characteristics, quality, and consumer acceptance of whole muscle beef injected with solutions of salt and phosphate[J]. Meat Science,2009,81(3):523−532. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2008.10.006
[23] 张帆. 反复冻融、解冻方法及加热方式对鸭肉品质影响的研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2016. ZHANG F. The study on the effects of freeze-thaw cycles, thawing methods and heating methods on the quality of duck meat[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2016.
[24] 常海军, 徐幸莲, 周光宏. 肌内结缔组织与肉嫩度关系研究[J]. 肉类研究,2009(7):9−14. [CHANG H J, XU X L, ZHOU G H. Research on relationship between intramuscular connective tissue and meat tenderness[J]. Meat Research,2009(7):9−14. [25] 董轶群, 牛素敏, 罗鑫, 等. 武昌鱼宰后4 ℃冷藏条件下品质变化规律[J]. 肉类研究,2022,36(3):32−37. [DONG Y Q, NIU S M, LUO X, et al. Quality changes of Megalobrama amblycephalala during postmortem storage at 4 ℃[J]. Meat Research,2022,36(3):32−37. [26] GAO Y L, QIU Y, NAN H L, et al. Ultra-high pressure-assisted preparation of cowhide gelatin as a promising fat substitute: Improve the nutrition ratio and antioxidant capacity of beef patties[J]. Food Research International,2022,157:111260. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111260
[27] TANG C, ZHOU K, ZHU Y, et al. Collagen and its derivatives: From structure and properties to their applications in food industry[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,131:107748. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2022.107748
[28] 张诚. 冻藏及反复冻融对文昌鸡肉品质的影响[D]. 海口: 海南大学, 2014. ZHANG C. Influence of frozen storage and freeze-thawing cycles on the quality of Wenchang chicken[D]. Haikou: Hainan University, 2014.
[29] BARBUT S, SOSNICKI A A, LONERGAN S M, et al. Progress in reducing the pale, soft and exudative (PSE) problem in pork and poultry meat[J]. Meat Science,2008,79(1):46−63. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2007.07.031
[30] 曹银娟. 反复冻融对牛瘤胃平滑肌胶原蛋白特性及品质的影响[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2021. CAO Y J. Effect of repeated freeze-thaw on the collagen properties and quality of bovine rumen smooth muscle[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2021.
[31] WANG Y, TIAN X J, LIU X Z, et al. Focusing on intramuscular connective tissue: Effect of cooking time and temperature on physical, textual, and structural properties of yak meat[J]. Meat Science,2022,184:108690. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2021.108690
[32] 乔鑫, 潘丽, 刘莹, 等. 反复冻融对羊肉蛋白质氧化及其品质影响的研究[J]. 食品科技,2021,46(9):109−115. [QIAO X, PAN L, LIU Y, et al. Effect of repeated freezing and thawing on protein oxidation and quality of mutton[J]. Food Science and Technology,2021,46(9):109−115. -
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 谭德馨,唐小闲,张奕涛,李官丽,黎小椿,罗杨合,伍淑婕. 马蹄脆片微波真空干燥工艺优化及其水分变化. 食品研究与开发. 2024(03): 107-115 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 黄楚雄,李洁,刘纪红,严守雷,王茜. 不同品种莲藕加工藕圆子适应性评价. 食品工业科技. 2023(06): 283-291 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 黎小椿,罗杨合,梁宁,伍淑婕,李官丽. 不同蒸制时间下红芽芋的风味品质评价. 现代食品科技. 2023(06): 230-239 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 孟令晗,雷思佳,吴迪,汤晓智. 全麦速冻油条复热加工中风味与抗氧化特性. 食品科学. 2022(04): 167-174 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 刘盼盼,任广跃,段续,李琳琳,赵路洁,任星,苗峻伟. 基于变异系数法对不同干燥方式白萝卜品质及风味的评价. 食品与发酵工业. 2022(13): 218-226 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 李官丽,聂辉,黎小椿,伍淑婕,罗杨合. 四种典型蒸煮加工方式荸荠挥发性风味物质研究. 食品工业. 2022(09): 110-114 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 刘盼盼,任广跃,赵路洁,段续,李琳琳,王兆凯. 白萝卜饱和蒸汽-热泵组合干燥过程中生物活性和挥发性成分分析. 中国食品学报. 2022(10): 325-339 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 罗丽,王顺民,徐为雯,潘文洁. 超声-热处理鲜切莲藕贮藏期间品质变化的研究. 食品与发酵工业. 2022(24): 203-210 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)








 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



