Optimization of Extraction Process and Analysis of Physicochemical Properties of Wild Rice Protein
-
摘要: 以菰米为原料,采用碱提酸沉法提取蛋白质。在单因素实验基础上,以菰米蛋白质提取率为指标,结合响应面法优化,获得菰米蛋白的最佳提取工艺。并通过等电点沉淀后冻干获得菰米蛋白粉,以相同条件下提取获得的淮稻蛋白为对照,对菰米蛋白的分子组成、热稳定性及消化特性进行比较分析。结果表明:不同提取条件对碱提酸沉法提取菰米蛋白的影响为:料液比>温度>提取时间;最佳提取条件为:提取温度为58 ℃、料液比1:25 g/mL、提取时间为3.5 h,此提取条件下菰米蛋白提取率可达45.97%;菰米蛋白等电点pH为3.5;与淮稻蛋白相比,菰米蛋白变性峰值温度为108.4 ℃,ΔH=164.4 J/g,菰米高分子质量蛋白含量较少,消化特性基本相同,但游离氨基酸含量始终较高。综上表明菰米蛋白是人体补充蛋白质的优质来源。Abstract: Wild rice was used as raw material to extract protein by alkali extraction and acid precipitation. Based on the single-factor test, the best extraction process of wild rice protein was obtained by using the index of extraction rate of rice protein and the optimization of the response surface method. The wild rice protein powder was obtained by isoelectric point precipitation and freeze-drying. Compared with the Huai rice protein extracted under the same conditions, wild rice protein's molecular composition, thermal stability, and digestion characteristics were compared and analyzed. The results showed that the effects of different extraction conditions on the extraction of wild rice protein by alkali extraction and acid precipitation were as follows: Ratio of material to liquid>temperature>time, and the optimum extraction conditions were as follows: Extraction temperature 58 ℃, the ratio of material to liquid 1:25 g/mL, extraction time 3.5 h. Under these conditions, the wild rice protein extraction rate was 45.97%, and the isoelectric point (pH) of wild rice protein was 3.5. Compared with Huai rice protein, the denaturation peak temperature of wild rice protein was 108.4 ℃, ΔH=164.4 J/g, the high molecular weight protein content was less, and the digestibility was the same, however, the content of free amino acids was always higher, which was more beneficial to human digestion and absorption. In conclusion, wild rice protein is a high quality source of supplemental protein for human body.
-
Keywords:
- wild rice protein /
- extraction process /
- response surface /
- physicochemical properties /
- digestion
-
菰米为古老的多年水生植物菰[Zinania latifolia (Griseb) Turcz]的颖果,在世界上分布广泛。中国菰作为世界四大菰品种之一,具有3500多年的食用历史。《周礼》中记载“凡王之馈,食用六榖”,菰米是我国古代帝王将相食用的珍稀食品;明代《本草纲目》中将菰米作为中药材使用,具有生津止渴、解烦闷,调肠胃等功效[1]。1989年我国原卫生部批准将菰米作为新的食品资源。研究表明,菰米富含优质蛋白质、膳食纤维、硫胺素及生育酚等,具有降血脂、降血糖及抑制脂质过氧化损伤 [2-4]等功能,可作为肥胖、动脉粥样硬化、糖尿病等人群的良好膳食来源。目前,美国、加拿大等国家已将北美菰米作为高植物蛋白食物广泛开发利用,基本占据了世界全部的菰米市场[5]。我国对菰米的理论研究和开发利用均尚处于起步阶段。
在我国居民膳食中,50%~60%的能量和50%~55%的蛋白质是由谷类食品提供[6],谷物中的蛋白质含量及构成是影响谷类食物营养价值和加工品质的重要影响因素之一。刘传光等[7]报道我国65%以上人口以水稻为主粮,故本研究以淮稻作为对照;本课题组根据GB 5009.5-2016《食品中蛋白质的测定》,采用凯氏定氮法测定出菰米的蛋白质含量为11.05%,远高于淮稻(9.41%)。目前,关于菰米蛋白质的研究仅集中于其氨基酸组成及营养功效,如翟成凯等[8]研究表明中国菰米蛋白质的必需氨基酸含量显著高于大米,氨基酸评分84,接近奶粉。张永青等[9]通过动物实验发现菰米蛋白质易被消化吸收,可有效促进内脏的生长发育。对于菰米蛋白的提取方法、理化特性等方面研究尚未见报道。谷类蛋白的提取方法主要有碱提酸沉法、酶法、盐析法、水提法、反束胶萃取、膜分离法及复合提取法等[10],其中,碱提酸沉法因其操作便利、经济实惠且提取率高的优点,成为目前使用最多的谷类蛋白质提取方法。本试验采用响应面法优化获得碱提酸沉法提取菰米蛋白的最佳工艺,确定提取菰米蛋白等电点后冻干获取蛋白冻干粉,并以淮稻蛋白为对照对菰米蛋白分子组成、热稳定性及消化特性进行对比分析,旨在为我国菰米蛋白的研究和菰米资源的开发利用提供理论支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
菰米、淮稻 2021年采摘于江苏扬州里下河地区;石油醚(30~60 ℃)、氢氧化钠、盐酸、甲基红、亚甲基蓝、硼酸、硫酸铜、甲醇、冰醋酸、96孔板、胃蛋白酶(1200 U/g)、胰蛋白酶(50000 U/g) 国药集团化学试剂有限公司;Bradford蛋白浓度测定试剂盒、SDS-PAGE凝胶配制试剂盒、5X上样缓冲液、10X电泳液、考马斯亮蓝R-250、蛋白分子质量标准(10~180 kDa) 上海碧云天生物技术有限公司;茚三酮、谷氨酸 上海麦克林生化科技有限公司。
DK-8D型电热恒温水槽 上海精宏实验设备有限公司;LGJ-50A型冷冻干燥机 上海贺帆仪器有限公司;1510型酶标仪 赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司;KDN-1000型凯氏定氮仪 上海昕瑞仪器仪表有限公司;H2050R型台式高速冷冻离心机 湖南湘仪实验室仪器开发有限公司;722N型可见分光光度计 上海菁华科技仪器有限公司;WIX-EP300型基础电泳仪 韦克斯科技(北京)有限公司;200F3型差示扫描量热仪 德国NETZSCH公司;BS210S型分析天平 北京赛多利斯天平有限公司;雷磁pH计 上海仪电科学仪器股份有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 蛋白提取工艺流程
根据高柳[11]的方法并加以修改,首先对原料进行预处理:菰米、淮稻各粉碎后过80目筛,以料液比1:10 g/mL加入石油醚,浸泡30 min,用慢速滤纸过滤后室温放置24 h至石油醚完全挥发,4 ℃保存备用。
将预处理好的脱脂菰米、淮稻以料液比1:25 g/mL加纯水后,用1 mol/L NaOH调节pH至9,再4000 r/min离心20 min,取上清液用1 mol/L HCL调节pH至3.5后静置30 min,再4000 r/min离心20 min后取沉淀,将沉淀以料液比1:25 g/mL加入纯水清洗两次以4000 r/min离心20 min离心后,将沉淀调节pH为7再冻干48 h,4 ℃保存备用。
1.2.2 单因素实验
准确称取预处理的菰米粉0.3 g,在料液比1:10 g/mL、pH10、温度45 ℃水浴搅拌条件下,观察不同提取时间(0.5、1、1.5、2、2.5、3、3.5、4 h)对菰米蛋白提取率的影响;在料液比1:10 g/mL、pH10、提取时间1.5 h条件下,观察不同提取温度(35、40、45、50、55、60、65 ℃)对菰米蛋白提取率的影响;在pH10、温度45 ℃、提取时间1.5 h条件下,观察不同料液比(1:5、1:10、1:15、1:20、1:25、1:30 g/mL)对菰米蛋白提取率的影响。
1.2.3 响应面试验设计
根据单因素实验,选取时间、温度、料液比三个因素为响应因子,菰米蛋白提取率为响应值进行响应面设计,优化菰米蛋白的提取条件,实验因素水平设计见表1。
表 1 提取菰米蛋白质响应面试验因素与水平Table 1. Factors and levels of response surface test of protein extraction from wild rice水平 因素 A 提取时间(h) B 温度(℃) C 料液比(g/mL) −1 2.5 50 1:15 0 3.0 55 1:20 1 3.5 60 1:25 1.2.4 菰米蛋白质提取率的测定
根据高柳[11]的方法并加以修改,取菰米蛋白提取液,4000 r/min离心20 min后取上清液,用Bradford蛋白浓度测定试剂盒测定提取菰米蛋白含量:取5 μL上清液加入250 μL考马斯亮蓝蛋白测定试剂,室温反应10 min,用酶标仪在595 nm处测量样品的吸光度。使用不同浓度的牛血清白蛋白(BSA)作为外标进行计算,以BSA浓度C(mg/mL)为横坐标,吸光度A为纵坐标,得到线性回归方程:A=0.6987C+0.6256,R2=0.9952,在BSA质量浓度范围0~1.6 mg/mL内,线性关系良好。蛋白质提取率由溶解在碱提取上清液中的菰米蛋白占菰米中总蛋白的百分比计算,菰米中总蛋白含量的测定参考GB 5009.5-2016《食品中蛋白质的测定》进行测定。
1.2.5 菰米蛋白等电点的确定
根据张兆云[12]的方法并修改,将提取的上清液分为7份,用1 mol/L HCl调节pH分别为2.5、3、3.5、4、4.5、5、5.5,静置30 min后4000 r/min,20 min离心,取上清液于595 nm处测吸光度值,吸光度最小的即为等电点。
1.2.6 SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳
根据郭莲东等[13]的方法并修改,用SDS-PAGE凝胶配制试剂盒配制12%的分离胶、5%的浓缩胶;取5 mg菰米及淮稻蛋白质冻干粉加入250 μL纯水溶解,将溶解液与5X上样缓冲液以1:4混合,在沸水浴中煮沸10 min使蛋白充分变性。在电泳槽位依次加入3 μL Marker、10 μL样品;浓缩胶电压80 V,分离胶电压120 V,条带距底部1 cm处停止电泳;染色2 h后脱色。
1.2.7 DSC分析
参考彭菁[14]的方法并修改,分别称取2 mg菰米及淮稻蛋白冻干粉于坩埚中,加入10 μL纯水,4 ℃平衡24 h,再室温平衡1 h。在30~150 ℃的条件下,N2流量为40 mL/min,扫描速度为10 ℃/min,以空坩埚做参比。用软件 Universal Analysis 2000分析了热力学参数:峰值温度和变性焓值(ΔH,J/g)。
1.2.8 蛋白消化性分析
参考王丽丽等[15]的方法并修改,准确称取5 g菰米及淮稻蛋白冻干样品,加入0.1 mol/L HCl溶液均质并定容到50 mL,于37 ℃气浴振荡箱中振荡5 min,加入1.25 g胃蛋白酶后恒温振荡2 h,调pH为7后加入1 mg/mL的胰蛋白酶溶液1 mL,继续恒温振荡2 h,分别在0、0.5、1、1.5、2、2.5、3、3.5、4 h时取样5 mL,在沸水浴中煮沸5 min灭酶,4000 r/min离心15 min,取上清液用茚三酮法测定游离氨基酸含量,以不同浓度的谷氨酸作为外标进行计算:以谷氨酸含量X为横坐标,吸光度Y为纵坐标,得到线性方程为Y=2.744X+0.1944,R2=0.9959,在谷氨酸质量浓范围0~0.35 mg/g内,线性关系良好。
1.3 数据处理
实验数据以平均值±标准差表示,使用Origin2018、GraphPad Prism8和SPSS 26对数据进行处理,每个实验均进行三组平行实验。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素实验
2.1.1 提取时间对菰米蛋白质提取率的影响
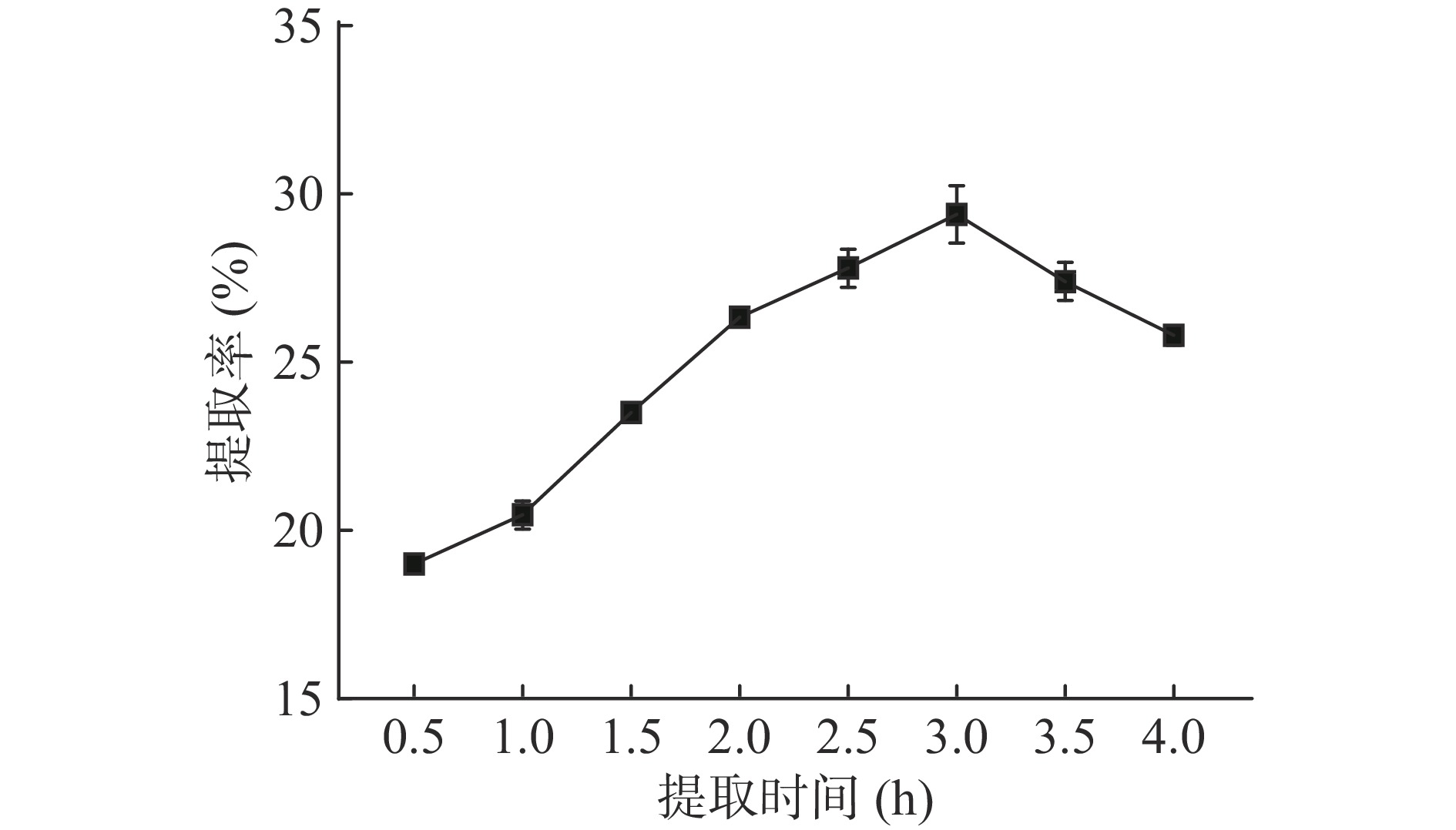
如图1所示,菰米蛋白提取率随提取时间的增加呈先上升后下降的趋势,在3 h前从19%增加至29.4%,增长趋势十分稳定,提取率与时间接近正比,这与Fick扩散定律的可溶性物溶解理论相一致[16]。3 h后继续增加提取时间,菰米蛋白提取率开始下降,这可能是因为提取时间过长使菰米分离蛋白活性开始下降,可溶性蛋白含量减少[17],因此提取菰米蛋白最佳提取时间为3 h。
2.1.2 提取温度对菰米蛋白质提取率的影响
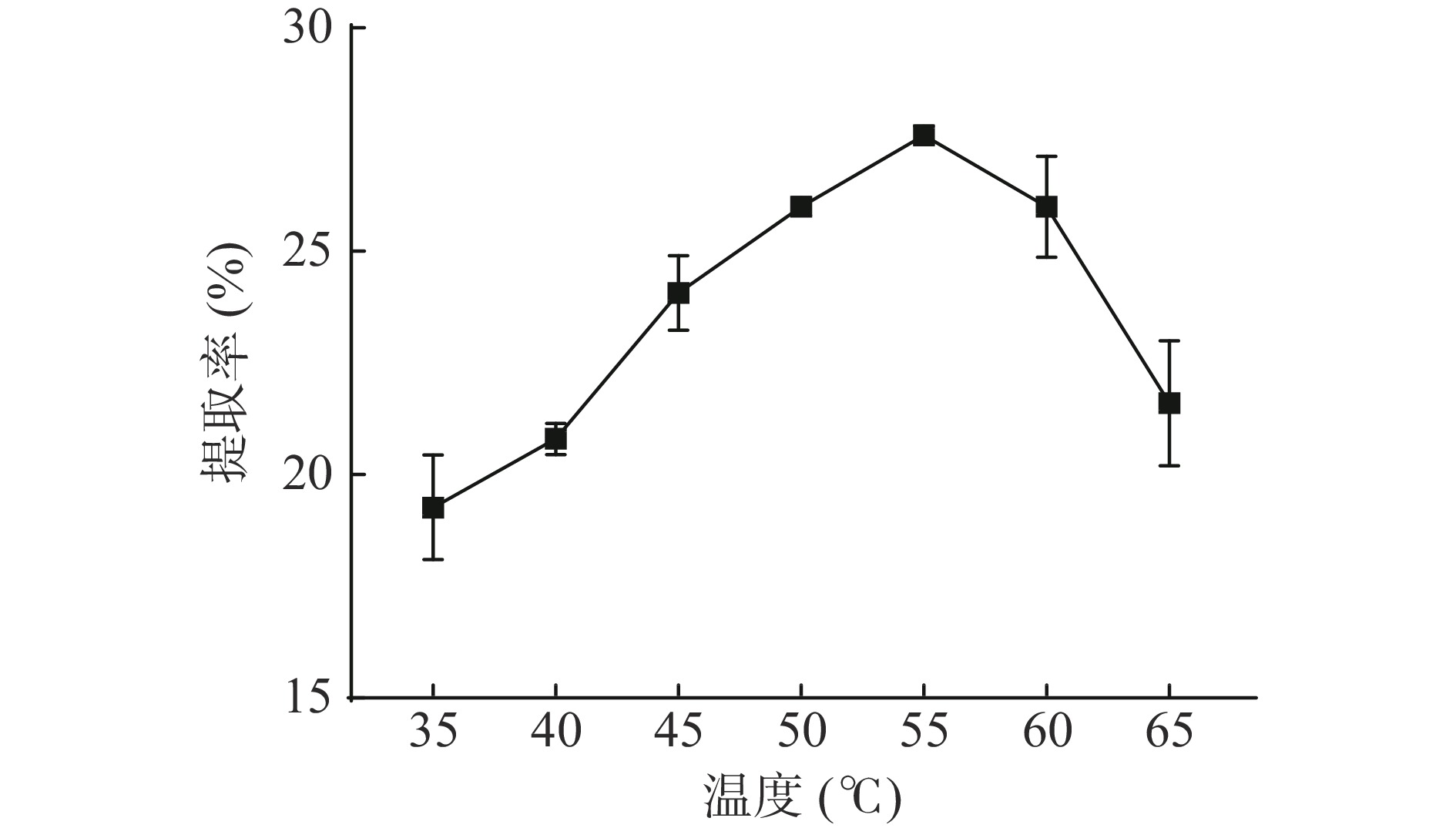
如图2所示,菰米蛋白提取率随温度的升高呈先上升后下降的趋势,当温度为55 ℃时,提取率最高(27.6%),超过55 ℃之后菰米蛋白提取率下降,一方面归因于菰米淀粉对蛋白质提取产生了影响,随着温度升高,菰米淀粉溶解率会增高且使淀粉糊化,会使溶液逐渐黏稠阻碍蛋白质析出[18];另一方面归因于温度升高使部分蛋白变性,而变性可能会展开或暴露蛋白质结构的内部疏水区域,从而降低溶解度[19]。因此提取菰米蛋白最佳温度为55 ℃。
2.1.3 料液比对菰米蛋白质提取率的影响
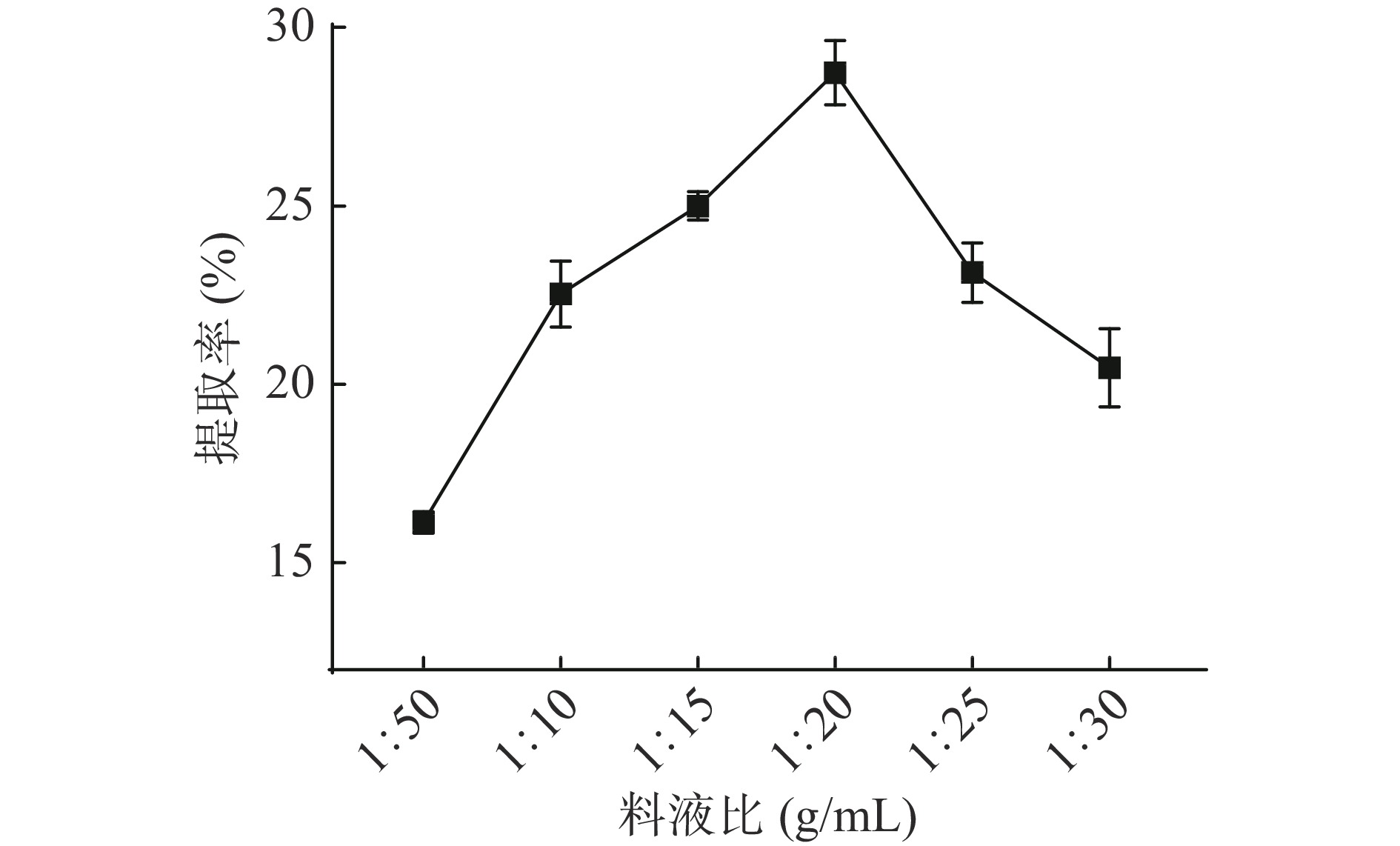
如图3所示,随着溶液的增加,菰米蛋白提取率先呈上升趋势,这是因为溶液太少时菰米蛋白处于过饱和状态。菰米蛋白在液料比1:20时达到饱和,提取率为28.7%。继续增加溶液,菰米蛋白提取率开始下降,一方面归因于溶液过多使菰米蛋白被稀释,使溶质损耗[20];另一方面归因于在碱性环境下,溶液增加使得其他混合物如多糖溶出,使粘度升高阻碍了蛋白质提取过程中的适当混合,降低了菰米蛋白对溶剂的亲和力[21]。因此提取菰米蛋白的最佳料液比为1:20 g/mL。
2.2 响应面法优化结果分析
2.2.1 响应面试验设计及结果
根据Box-Behnken设计原理,以提取时间(A)、温度(B)、料液比(C)为自变量,菰米分离蛋白提取率(Y)为响应值,利用Design Expert 8.0.6.1 软件设计3因素3水平的响应面分析试验,在17个实验组合条件下,设计方案和结果见表2。
表 2 Box-Behnken设计方案及试验结果Table 2. Box-Behnken design and test results序号 A 提取时间 B 温度 C 料液比 Y 蛋白质提取率(%) 1 1 0 −1 39.2 2 −1 0 1 44.3 3 0 0 0 48.0 4 −1 0 −1 38.0 5 1 −1 0 44.1 6 0 0 0 45.8 7 0 1 1 45.5 8 1 1 0 42.2 9 0 0 0 46.7 10 0 1 −1 46.2 11 −1 1 0 45.4 12 0 0 0 47.2 13 0 0 0 46.3 14 0 −1 1 44.2 15 0 −1 −1 37.6 16 1 0 1 46.4 17 −1 −1 0 37.2 2.2.2 回归模型的建立及方程方差分析
根据相应的试验表进行分析,得到料液比、提取温度及提取时间的二次多项回归方程:菰米分离蛋白质提取率Y=46.80+0.88A+2.03B+2.42C−2.53AB+0.22AC−1.83BC−2.99A2−1.59B2−1.84C2。从表3可以看出,模型的P<0.001,模型差异极显著;失拟项P=0.1021,大于0.05表明失拟项不显著。说明未知因素对结果干扰很小;R2为0.9563、R2adj为0.9002,说明自变量与响应值之间线性关系显著,信噪比为11.586远大于4,说明该模型能够准确分析预测最优提取方法[22]。由P值可以看出一次项B、C,交互项AB,二次项A2极显著(P<0.01);交互项BC和二次项B2、C2显著(P<0.05)。说明各因素影响结果的主次顺序为:C(料液比)>B(温度)>A(提取时间)。
表 3 回归方差分析Table 3. Regression analysis of variance来源 总和 自由度 均方 F P 显著性 模型 193.96 9 21.55 12.87 0.0014 ** A 6.13 1 6.13 3.66 0.0974 B 32.81 1 32.81 19.59 0.0031 ** C 51.01 1 47.04 28.10 0.0011 ** AB 25.50 1 25.50 15.23 0.0059 ** AC 0.20 1 0.20 0.12 0.7382 BC 13.32 1 13.32 7.96 0.0257 * A2 37.58 1 37.58 22.45 0.0021 ** B2 10.61 1 10.61 6.34 0.0400 * C2 14.22 1 14.22 8.49 0.0225 * 残差 11.72 7 1.67 失拟项 8.86 3 2.95 4.13 0.1021 不显著 纯误差 0 4 0 总和 202.82 16 R2 0.9563 R2adj 0.9002 注:* 为差异显著(P<0.05);** 为差异极显著(P<0.01)。 2.2.3 响应面交互作用分析
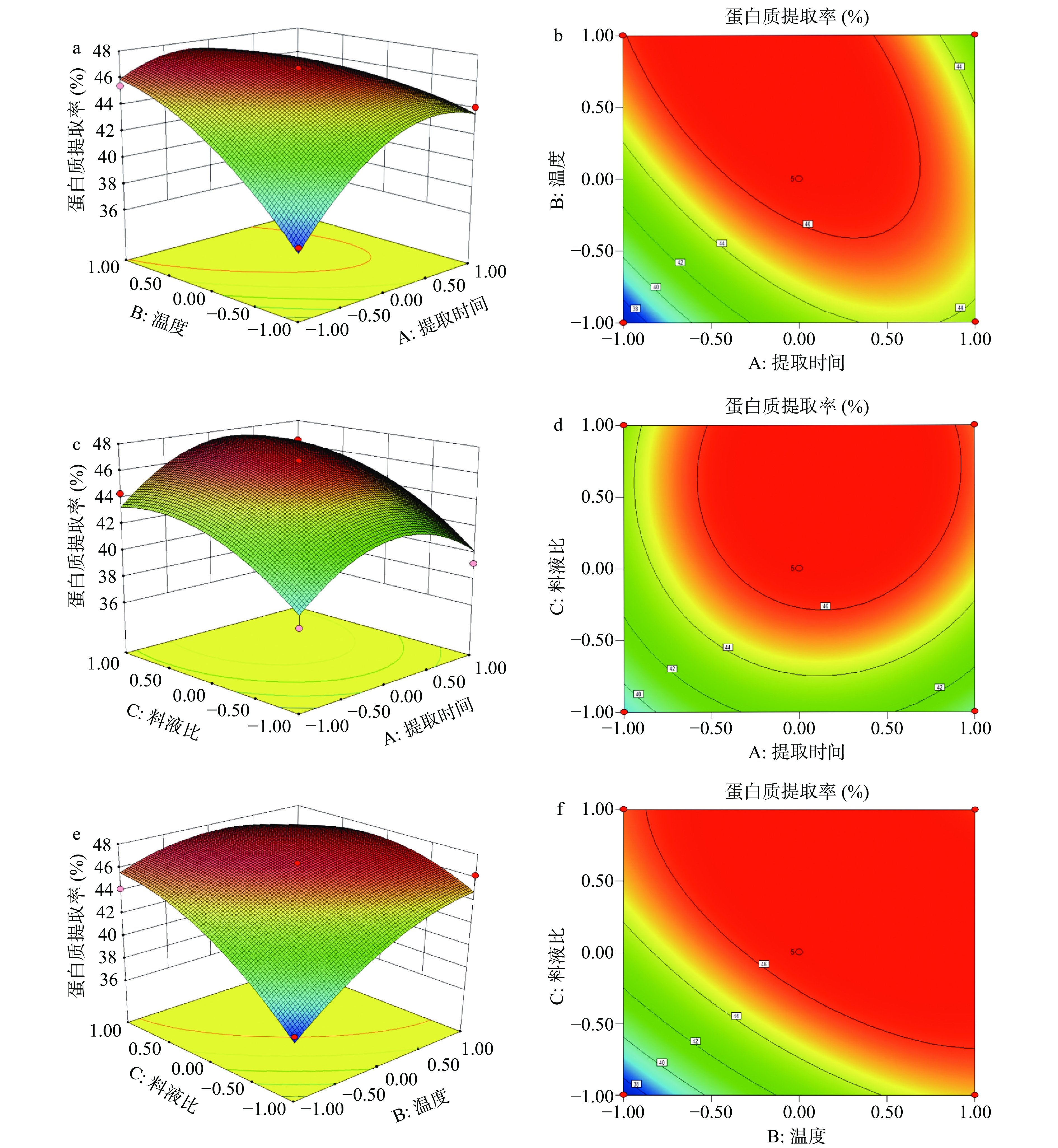
通过响应曲面图的坡度可以直观地看出两因素对因变量的影响程度,若坡度较陡则说明影响较大,若弧度交平缓说明对因变量影响较小。等高线则说明两因素交互作用对因变量的影响,如等高线为椭圆则说明两因素交互作用显著,若为圆形则说明两者交互作用不显著[23]。由图4(a)可知,温度的坡度比时间的坡度陡,说明温度对菰米蛋白提取率的影响比时间显著;图4(b)温度与时间交互作用的等高线为椭圆说明二者交互作用显著;图4(c)中,当时间一定时,可以看到蛋白质提取率随料液比的增加先升高后下降,同理,当料液比一定时,蛋白质提取率随时间的增加先升高后下降,这也与上述单因素分析结果一致;图4(d)时间与液料比的等高线接近圆,说明二者交互作用对菰米蛋白得率的影响并不显著,这也与上述方差分析结果相互印证;图4(e)液料比的坡度比温度陡,说明料液比对蛋白提取率的影响比温度高,图4(f)等高线为椭圆说明料液比与温度的交互作用显著。
2.2.4 验证实验
通过优化得到提取菰米蛋白质的最佳条件为:提取时间3.5 h、提取温度为58.65 ℃、料液比为1:25 g/mL,菰米蛋白预测提取率为46.4%。结合实验条件,在pH为10、提取温度为58 ℃、料液比1: 25 g/mL的条件下对菰米蛋白提取3.5 h,实验重复3次,所得的菰米蛋白提取率平均值为45.97%,与理论得率46.4%无显著性差异,相对误差仅为0.93%,说明模型预测菰米蛋白提取工艺参数准确可靠。
2.3 菰米蛋白质的等电点
等电沉淀是从植物来源中提取蛋白质的传统且最常用的方法。从脱脂种子粉中提取蛋白质的过程主要包括蛋白质在稀碱(pH范围从8到11)中的溶解,然后在稀酸中等电沉淀[24]。从图5可知,在pH2.5至pH5.5之间吸光度呈现先下降后上升的趋势,在pH3.5时吸光度最小,说明此时菰米蛋白所含正负电荷相等,静电斥力减小,蛋白质相互聚集形成沉淀;在pH<3.5和pH>3.5时,由于蛋白-水之间及蛋白-蛋白之间的静电斥力增大,且强酸条件下肽键会被分解,使菰米蛋白沉淀减少[25]。因此在pH3.5时上清液吸光度最小,蛋白沉淀值最大,故菰米蛋白质等电点为 3.5。
2.4 SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳
从图6可知,菰米蛋白的组成较淮稻蛋白复杂,菰米蛋白有17个条带,淮稻有10个。其中菰米有5条明显的特征亚基条带,其分子质量分别为19、20、29、34、52 kDa;淮稻有4条明显的特征亚基条带,分子质量分别为17、24、51、55 kDa;表明菰米蛋白所含小分子质量蛋白较多。在17~24 kDa和33~42 kDa蛋白亚基条带分布与Nieto-Nieto等[26]报道的燕麦蛋白12S球蛋白的酸性肽链(α-亚基)和碱性肽链(β-亚基)大致相同,且Nieto-Nieto指出此部分酸性和碱性多肽在胃消化阶段能迅速水解。菰米蛋白所含17~24 kDa和33~42 kDa分子质量的蛋白较多,因此在消化过程中更易消化,这与下文的消化规律一致。
2.5 DSC分析
图7为蛋白DSC分析,图7(a)为菰米DSC分析图,图7(b)为淮稻DSC分析图。由图可知,菰米蛋白的变性温度峰值为108.4 ℃,与燕麦分离蛋白相似(109.9 ℃)[27],远大于淮稻(96.1 ℃);菰米蛋白ΔH为164.4 J/g,远高于淮稻(ΔH=99.02 J/g)。Deng等[28]报道具有高变性温度的蛋白质在加热过程中失去的天然生物活性较少,因此菰米蛋白在食品加工中较淮稻营养损失少。ΔH是变性所需的能量,通常用来反映未变性蛋白质的比例和有序结构的延伸[29];由王文高等[30]研究可知,DSC中热焓值的变化只与氢键有关与二硫键无关,菰米分离蛋白的热焓值较高,这表明菰米蛋白中有序结构及氢键可能比淮稻分离蛋白含量高,且在蛋白提取和冷冻干燥过程中蛋白发生的变性较少。
2.6 蛋白消化分析
蛋白质经胃蛋白酶、胰蛋白酶水解生成氨基酸及寡肽后才能被人体吸收,因此常用氨基酸含量来反映蛋白质的水解程度,值越高表示蛋白质的消化程度越高[31]。菰米及淮稻的蛋白消化水解曲线如图8所示,在模拟胃消化阶段,氨基酸含量随时间的增加呈先上升后变得较为平缓的趋势,这归因于消化后期胃蛋白酶与蛋白上的作用位点已充分接触[32];在模拟肠消化阶段,氨基酸含量随着时间的延长一直呈上升趋势。总体而言,随着消化时间的延长,两者的游离氨基酸含量不断增加,但菰米中的游离氨基酸含量始终高于淮稻。
3. 结论
本研究利用响应面法建立了菰米蛋白提取的二次项数学模型,通过方差分析得到影响菰米蛋白提取的因素依次为料液比>温度>提取时间,最佳提取工艺为:提取时间3.5 h、提取温度为58 ℃、料液比为1:25 g/mL,在此条件下菰米蛋白提取率为45.97%与理论预测值46.4%无显著性差异。说明响应面法得到的回归模型预测菰米蛋白提取工艺参数准确可靠。将菰米蛋白溶液通过等电点沉淀冻干后与淮稻蛋白进行对比发现:菰米蛋白含有较多小分子质量蛋白,蛋白结构稳定,有着较高的蛋白变性温度峰值及热焓值;且在消化过程中能产生较高的游离氨基酸,是人体补充蛋白质的优质来源。本实验为菰米蛋白的提取及理论研究提供了理论基础,对菰米未来开发利用具有一定的指导意义。
-
表 1 提取菰米蛋白质响应面试验因素与水平
Table 1 Factors and levels of response surface test of protein extraction from wild rice
水平 因素 A 提取时间(h) B 温度(℃) C 料液比(g/mL) −1 2.5 50 1:15 0 3.0 55 1:20 1 3.5 60 1:25 表 2 Box-Behnken设计方案及试验结果
Table 2 Box-Behnken design and test results
序号 A 提取时间 B 温度 C 料液比 Y 蛋白质提取率(%) 1 1 0 −1 39.2 2 −1 0 1 44.3 3 0 0 0 48.0 4 −1 0 −1 38.0 5 1 −1 0 44.1 6 0 0 0 45.8 7 0 1 1 45.5 8 1 1 0 42.2 9 0 0 0 46.7 10 0 1 −1 46.2 11 −1 1 0 45.4 12 0 0 0 47.2 13 0 0 0 46.3 14 0 −1 1 44.2 15 0 −1 −1 37.6 16 1 0 1 46.4 17 −1 −1 0 37.2 表 3 回归方差分析
Table 3 Regression analysis of variance
来源 总和 自由度 均方 F P 显著性 模型 193.96 9 21.55 12.87 0.0014 ** A 6.13 1 6.13 3.66 0.0974 B 32.81 1 32.81 19.59 0.0031 ** C 51.01 1 47.04 28.10 0.0011 ** AB 25.50 1 25.50 15.23 0.0059 ** AC 0.20 1 0.20 0.12 0.7382 BC 13.32 1 13.32 7.96 0.0257 * A2 37.58 1 37.58 22.45 0.0021 ** B2 10.61 1 10.61 6.34 0.0400 * C2 14.22 1 14.22 8.49 0.0225 * 残差 11.72 7 1.67 失拟项 8.86 3 2.95 4.13 0.1021 不显著 纯误差 0 4 0 总和 202.82 16 R2 0.9563 R2adj 0.9002 注:* 为差异显著(P<0.05);** 为差异极显著(P<0.01)。 -
[1] 邢花. 我国菰米中膳食纤维、类黄酮的分析及其对非酒精性肝脂肪变性HepG2细胞作用的研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2012: 10. XING Hua. Analysis of dietary fiber and flavonoids in Chinese millet and their effects on HepG2 cells of non-alcoholic hepatic steatosis[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2012: 10.
[2] ZHAI C K, LU C M, ZHANG X Q, et al. Comparative study on nutritional value of chinese and north American wild rice[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2001,14(4):371−382. doi: 10.1006/jfca.2000.0979
[3] 张红, 曹佩, 翟成凯, 等. 我国菰米对高脂膳食大鼠血脂及炎性因子的影响[J]. 营养学报,2009,31(3):222−225. [ZHANG Hong, CAO Pei, ZHAI Chengkai, et al. Effects of Chinese wild rice on blood lipids and inflammatory factors in rats with high-fat diet[J]. Journal of Nutrition,2009,31(3):222−225. doi: 10.13325/j.cnki.acta.nutr.sin.2009.03.013 [4] 张红, 刘洋, 赵军红, 等. 菰米血糖生成指数的测定及其改善大鼠胰岛素抵抗的作用[J]. 卫生研究,2015,44(2):173−178,184. [ZHANG Hong, LIU Yang, ZHAO Junhong, et al. Determination of glycemic index of wild rice and its effect on insulin resistance in rats[J]. Health Research,2015,44(2):173−178,184. [5] 翟成凯, 殷泰安, 姚修仁, 等. 菰米的营养成分分析[J]. 营养学报,1992(2):210−214. [ZHAI Chengkai, YIN Taian, YAO Xiuren, et al. Analysis of nutritional components of wild rice[J]. Journal of Nutrition,1992(2):210−214. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0512-7955.1992.02.001 [6] 孙长颢. 营养与食品卫生学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2007: 131. SUN Changhao. Nutrition and food hygiene[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2007: 131.
[7] 刘传光, 周新桥, 陈达刚, 等. 功能性水稻研究进展及前景展望[J]. 广东农业科学,2021,48(10):87−99. [LIU Chuanguang, ZHOU Xinqiao, CHEN Dagang, et al. Research progress and prospect of functional rice[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences,2021,48(10):87−99. doi: 10.16768/j.issn.1004-874X.2021.10.010 [8] 翟成凯, 张小强, 孙桂菊, 等. 中国菰米的营养成分及其蛋白质特性的研究[J]. 卫生研究,2000(6):375−378. [ZHAI Chengkai, ZHANG Xiaoqiang, SUN Guiju, et al. Studies on the nutritional components and protein characteristics of Chinese wild rice[J]. Health Research,2000(6):375−378. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8020.2000.06.020 [9] 张永青, 孙慧丽, 何春玲, 等. 野生菰米的蛋白质营养价值评价[J]. 预防医学文献信息,2001(6):618−619. [ZHANG Yongqing, SUN Huili, HE Chunling, et al. Evaluation of protein nutritional value of wild rice[J]. Preventive Medicine Literature and Information,2001(6):618−619. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9153.2001.06.003 [10] 马洪鑫, 袁治浩, 刘洪海, 等. 比较不同方法提取藜麦蛋白[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2021,12(5):1890−1898. [MA Hongxin, YUAN Zhihao, LIU Honghai, et al. Compare different methods of extracting quinoa protein[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection,2021,12(5):1890−1898. doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2021.05.044 [11] 高柳. 黑米蛋白的提取及谷蛋白功能性质和改性研究[D]. 成都: 西华大学, 2019: 9. GAI Liu. Extraction of black rice protein and study on functional properties and modification of glutenin [D]. Chengdu: Xihua University, 2019: 9.
[12] 张兆云. “陇藜1号”藜麦清蛋白分离提取及性质研究[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2021: 25. ZHANG Zhaoyun. Study on isolation, extraction and properties of Chenopodium albumin from "Longli No. 1"[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2021, 25.
[13] 郭莲东, 徐丽, 欧才智, 等. 小米蛋白的分子组成及结构特性[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(24):201−206. [GUO Liandong, XU Li, OU Caizhi, et al. Molecular composition and structural properties of millet protein[J]. Food Science,2019,40(24):201−206. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181225-293 [14] 彭菁. 沙米蛋白和淀粉的理化性质研究及应用[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2017: 20. PENG Jing. Study on physical and chemical properties and application of sand rice protein and starch [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2017: 20.
[15] 王丽丽, 曹珍珍, 李楠楠, 等. 烹制强度对米饭热力学及消化特性的影响[J]. 中国粮油学报,2020,35(8):8−14. [WANG Lili, CAO Zhenzhen, LI Nannan, et al. Effect of cooking intensity on thermodynamics and digestibility of rice[J]. Chinese Journal of Cereals and Oils,2020,35(8):8−14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2020.08.003 [16] 朱亚飞. 粘性液体互扩散的可视化分析及应用[D]. 唐山: 华北理工大学, 2021: 18. ZHU Yafei. Visual analysis and application of viscous liquid interdiffusion[D]. Tangshan: North China University of Technology, 2021: 18.
[17] 林莉, 董玮, 林彩霞, 等. 脱脂油茶饼中蛋白质提取工艺[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2021,32(11):59−66. [LIN Li, DONG Wei, LIN Caixia, et al. Protein extraction technology from defatted camellia cake[J]. China Food Additives,2021,32(11):59−66. doi: 10.19804/j.issn1006-2513.2021.11.009 [18] LI G, WANG S, ZHU F J. Physicochemical properties of quinoa starch[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2016,137:328−338. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.10.064
[19] 周浩纯, 李赫, 赵迪, 等. 亚麻籽饼粕蛋白提取工艺优化及其水解物抑制α-淀粉酶活性研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2020,4(21):61−68. [ZHOU Haochun, LI He, ZHAO Di, et al. Optimization of protein extraction from flaxseed meal and study on α-amylase inhibitory activity of hydrolysate[J]. Food Research and Development,2020,4(21):61−68. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2020.21.011 [20] 胡祥, 刘云, 徐涵, 等. ‘龙佳’核桃品质分析及蛋白质提取工艺优化[J]. 食品科技,2021,46(2):225−231. [HU Xiang, LIU Yun, XU Han, et al. Quality analysis and protein extraction process optimization of 'Longjia' walnut[J]. Food Science and Technology,2021,46(2):225−231. [21] FETZER A, HERFELLNER T, STABLER A, et al. Influence of process conditions during aqueous protein extraction upon yield from pre-pressed and cold-pressed rapeseed press cake[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2018,112:236−246. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.12.011
[22] CUI H, PAN H W, WANG P H, et al. Essential oils from Carex meyeriana Kunth: Optimization of hydrodistillation extraction by response surface methodology and evaluation of its antioxidant and antimicrobial activities[J]. Industrial Crops and Product,2018,124:669−679. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.08.041
[23] 张颖, 赵姗, 王晨熙, 等. 盐地碱蓬粗蛋白的提取工艺优化及特性研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2021,42(16):107−115. [ZHANG Ying, ZHAO Shan, WANG Chenxi, et al. Optimization of extraction process and characteristics of crude protein from Suaeda salsa[J]. Food Research and Development,2021,42(16):107−115. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2021.16.016 [24] DEBORA N L, ROMINA I, PABLO B, et al. “Structural characterization of protein isolates obtained from chia (Salvia hispanica L.) seeds”[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2018,90:396−402. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2017.12.060
[25] 安兆祥, 蔡志鹏, 黄占旺, 等. 黑木耳蛋白提取工艺优化及其功能特性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(18):157−166. [AN Zhaoxiang, CAI Zhipeng, HUANG Zhanwang, et al. Optimization of extraction process and functional properties of Auricularia auricula protein[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2021,42(18):157−166. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020120003 [26] NIETO-NIETO T V, YI X W, OZIMEK L, et al. Effects of partial hydrolysis on structure and gelling properties of oat globular proteins[J]. Food Research International,2014,55(jan.):418−425.
[27] 王美玉. 燕麦蛋白热聚集及对胃蛋白酶消化影响的研究[D]. 晋中: 山西农业大学, 2020: 19. . WANG Meiyu. Study on thermal aggregation of oat protein and its effect on pepsin digestion[D]. Jinzhong: Shanxi Agricultural University, 2020: 19.
[28] DENG Y J, HUANG L X, ZHANG C H, et al. Physicochemical and functional properties of Chinese quince seed protein isolate[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,283:539−548. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.01.083
[29] ZHAO Q, XIONG H, SELOMULYA C, et al. Effects of spray drying and freeze drying on the properties of protein isolate from rice dreg protein[J]. Food and Bioprocess Technology,2013,6(7):1756−1769.
[30] 王文高, 陈正行, 姚惠源. 不同干燥方法对大米蛋白质功能性质的影响[J]. 粮食与饲料工业,2002(5):44−45. [WANG Wengao, CHEN Zhengxing, YAO Huiyuan. Effects of different drying methods on functional properties of rice protein[J]. Grain and Feed Industry,2002(5):44−45. [31] 苏钰亭, 尹涛, 赵思明, 等. 蒸煮模式和大米品种对米饭蛋白质消化特性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2014,35(3):100−105. [SU Yuting, YIN Tao, ZHAO Siming, et al. Effects of cooking patterns and rice varieties on protein digestibility of rice[J]. Food Science,2014,35(3):100−105. [32] 赵城彬, 尹欢欢, 鄢健楠, 等. 不同热处理条件下大豆蛋白体外模拟消化产物结构和分子质量分布[J]. 中国食品学报,2020,20(5):59−65. [ZHAO Chengbin, YIN Huanhuan, YAN JIAN Nan, et al. The structure and molecular weight distribution of soybean protein digestedin vitro were simulated under different heat treatment conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Food,2020,20(5):59−65. -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 郜浩帆,王宝亮,关运祥,钱百成. 酸枣仁-茯苓药对及其活性成分治疗失眠作用机制研究进展. 中药新药与临床药理. 2025(01): 152-160 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈旭. 酸枣仁治疗失眠症的研究进展. 基层中医药. 2024(08): 99-103 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:



