Optimization of Enzymatic Oxidation Process and Quality Analysis of High-theaflavins Instant Black Tea
-
摘要: 为实现夏秋绿茶的高值化利用,本研究以夏秋绿茶为原料,开发一款高茶黄素速溶红茶。在单因素实验的基础上,通过响应面法优化酶促氧化工艺条件,最后对产品的感官评价、理化指标及香气组分进行了分析。结果表明,最优工艺为:酶添加量1/1000 (mL/mL),pH4.90,反应温度50 ℃,反应时间44 min。在该工艺条件下,产品清香可口,汤色橙红透亮,茶黄素含量高达2.11%±0.04%,理化指标均达到相关标准要求。采用顶空固相微萃取(headspace solid-phase microextraction,HS-SPME)结合气质联用(gas chromatography-mass spectrometry,GC-MS)法,共检测出70种香气组分,包括醇类16种,酮类15种,醛类6种,酯类9种,酸类5种,酚类4种,碳氢类5种,其他10种。其中醇类相对含量占比最高,高达32.34%±0.14%,整体香气轮廓主要呈现青草香与花香。该研究结果为我国茶叶深加工的发展提供了一定的理论依据。Abstract: In order to realize the high-value utilization of summer-autumn green tea, this study used summer-autumn green tea as the raw material to develop a high-theaflavins instant black tea. Based on single-factor experiments, the enzymatic oxidation process conditions were optimized by response surface methodology. Finally the sensory evaluation, physicochemical index and aroma component of the product were analyzed. The results showed that the optimal process was as follows: Enzyme addition amount of 1/1000 (mL/mL), pH of 4.90, reacted at 50 ℃ for 44 min. Under this process condition, the product obtained, which possessed a sweet fragrance and a bright orange-red liquor color, had theaflavin content as high as 2.11%±0.04%, and physicochemical indicators all met the relevant standard requirements. A total of 70 aroma components, including 16 alcohols, 15 ketones, 6 aldehydes, 9 esters, 5 acids, 4 phenols, 5 hydrocarbons and 10 others were detected by HS-SPME combined with GC-MS. The highest relative content of alcohols was 32.34%±0.14%, and the overall aroma profile was mainly grassy and floral. The results of this study have provided a theoretical basis for the development of deep processing of tea in China.
-
速溶茶是茶叶的一种深加工产品,它是由茶叶中的水溶性物质经浸提、浓缩、干燥等工艺制成的一种能迅速溶解于水的固体茶饮料[1-2]。目前速溶茶的种类主要有速溶红茶和速溶绿茶[3-4]。由于速溶红茶的重要品质成分茶黄素是决定速溶红茶滋味和汤色的主要因素[5],且具有良好的抗氧化、抗突变、清除自由基等药理学功效[6],使得速溶红茶在国际茶业市场上的发展前景广阔,备受青睐[7]。
茶黄素是经儿茶素氧化缩合形成的一类可溶于乙酸乙酯的植物色素的总称[8-10],对红茶的色香味等品质起着重要作用,也是形成红茶“金圈”的主要成分[11-12]。目前,氧化儿茶素制备茶黄素的方法大致可分为自动氧化法、化学氧化法和酶促氧化法[13-14]。例如高学玲等[15]研究了以绿茶为原料,通过氧气氧化并辅以磷酸盐作为稳定剂来制备一种高亮度速溶红茶;萧伟祥等[16]利用化学氧化剂K3Fe(CN)6与NaHCO3氧化儿茶素制备茶色素粉末,该制品中茶黄素与茶红素种类丰富。在酶促氧化法中,大多数学者的研究还是集中在利用茶鲜叶自身的多酚氧化酶进行液态发酵来制备速溶红茶。例如夏涛等[17]研究了茶鲜叶匀浆悬浮发酵体系,发现限制发酵的主要原因是供氧不足,分批补料发酵可以很好地缓解供氧矛盾。然而,通过添加外源多酚氧化酶来提高速溶红茶品质的相关研究报道较少。
五峰县拥有丰富的茶资源,但是夏秋茶的资源浪费一直是制约行业发展的瓶颈[18]。多酚氧化酶能促进儿茶素类物质的氧化,对形成红茶特有的滋味与香气具有积极作用[19]。本研究以五峰当地夏秋绿茶为原料,添加外源多酚氧化酶进行体外酶促液态发酵,探究了将低档绿茶加工为优质速溶红茶的最佳工艺条件。采用感官评价及理化指标对速溶红茶的产品质量进行评估,同时结合HS-SPME-GC-MS对速溶红茶的香气组分进行分析,为推动当地茶叶深加工的发展提供一定的理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
夏秋绿茶 经杀青、揉捻、干燥后的成品眉茶,采购于湖北五峰采花茶业科技园;多酚氧化酶 50000 U/g,河北仟盛生物科技有限公司;硫酸亚铁、酒石酸钾钠、磷酸氢二钠、磷酸二氢钾、甲醇、碳酸氢钠、草酸、乙酸乙酯、95%乙醇、盐酸、硫酸 均为分析纯,西陇科学股份有限公司;碱式乙酸铅 分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司;咖啡碱标准品 色谱纯,上海纯优生物科技有限公司。
5910R台式高速离心机 德国Eppendorf公司;FUS-10全自动高级发酵罐 上海国强生化工程有限公司;XCS-HJSG-3定制型恒温搅拌三联水浴锅 陕西鑫昌实验仪器设备有限公司;FE28 pH计、HE53水分测定仪、ME204电子天平 瑞士梅特勒-托利多公司;754紫外可见分光光度计 上海光谱仪器有限公司;BONA-GM-22陶瓷膜小型实验机 济南博纳生物技术有限公司;R502B旋转蒸发仪 上海申生科技有限公司;ADL311微型喷粉干燥塔 日本雅马拓公司;7890B-5977B气质联用仪 美国安捷伦公司;50/30 μm DVB/CAR/PDMS复合萃取头 美国Supelco公司;MPS Robotic全自动样品前处理平台 德国GERSTEL公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 工艺流程及操作要点
工艺流程:原料→过筛→浸提→过滤→酶促氧化→灭酶→离心→陶瓷膜过滤→浓缩→喷粉
操作要点:将夏秋绿茶粉碎后过80目筛,按照1:25 (g/mL)料液比于恒温水浴锅中90 ℃热水浸提60 min,三层纱布过滤,收集茶汤。待茶汤冷却至室温后将其转入10 L发酵罐并用1 mol/L柠檬酸和碳酸氢钠调节茶汤pH。待温度达到反应温度时加入多酚氧化酶进行体外酶促氧化,反应结束100 ℃灭酶10 min。反应液以3000 r/min离心10 min并将上清液转入陶瓷膜过滤(陶瓷膜孔径0.2 μm,进膜压力0.3 MPa)。透过液以60 ℃,50 r/min旋转蒸发浓缩至干物质40%,最后将浓缩液喷雾干燥(进风温度150 ℃,出风温度100 ℃)得到固体茶粉。
1.2.2 单因素实验
固定酶添加量1/1000 (mL/mL),反应时间60 min,pH4.0,通入足量空气,考察不同反应温度(20、30、40、50、60 ℃)对茶黄素含量的影响。
固定反应温度50 ℃,酶添加量1/1000 (mL/mL),pH4.0,通入足量空气,考察不同反应时间(20、40、60、80、100 min)对茶黄素含量的影响。
固定反应温度50 ℃,反应时间40 min,酶添加量1/1000 (mL/mL),通入足量空气,考察不同pH(4.0、4.5、5.0、5.5、6.0)对茶黄素含量的影响。
固定反应温度50 ℃,反应时间40 min,pH5.0,通入足量空气,考察不同酶添加量(酶液体积/料液体积:1/10000、1/5000、1/1000、1/500、1/100 mL/mL)对茶黄素含量的影响。
1.2.3 响应面试验
在单因素实验的基础上,以反应温度(A)、反应时间(B)、pH(C)、酶添加量(D)为自变量,茶黄素含量(Y)为响应指标进行响应面试验(response surface methodology,RSM)设计,RSM因素与水平见表1。
表 1 Box-Behnken试验设计因素与水平Table 1. Factors and levels of Box-Behnken experiments design水平 A 反应温度
(℃)B 反应时间
(min)C pH D 酶添加量
(mL/mL)−1 40 20 4.5 1:5000 0 50 40 5.0 1:1000 1 60 60 5.5 1:500 1.2.4 速溶红茶感官评价分析
参考国标《GB/T 31740.1-2015 固态速溶茶》及相关文献[20]并稍作修改,对优化后的速溶红茶进行感官评价分析。速溶红茶与水的冲调比例为1:300,水温80 ℃,由10人组成感官评价小组,对速溶红茶的外形、滋味、香气、汤色、组织状态进行评分,每项满分100分,最终得分为加权后10人平均得分。速溶红茶感官评价标准表如表2所示。
表 2 速溶红茶感官评价标准表Table 2. Sensory evaluation standard of instant black tea项目 权重 感官评分(分) 评价标准 80~100 红棕色,色泽均匀明亮,颗粒分明不结块 外形 25% 50~79 红棕色,色泽均匀较明亮,颗粒分明,无明显结块 0~49 红棕色,色泽不均暗淡,颗粒结块明显 80~100 滋味浓厚,鲜爽可口 滋味 25% 50~79 滋味适中,尚可口 0~49 滋味平淡,口感差 80~100 具有红茶原有茶香,茶香浓厚 香气 10% 50~79 具有红茶原有茶香,茶香较淡 0~49 无红茶原有茶香 80~100 红中透亮,色泽均匀 汤色 20% 50~79 汤色适中,色泽均匀 0~49 汤色暗淡无光泽,色泽不均 80~100 溶解均匀,无明显杂质及沉淀 组织状态 20% 50~79 溶解均匀,少量杂质及沉淀 0~49 溶解不均,具有明显杂质及沉淀 1.2.5 速溶红茶理化成分分析
1.2.5.1 茶黄素含量的测定
速溶红茶中茶黄素含量的测定采用系统分析法[21-23]并稍作修改。精密称取0.20 g样品,加入60 ℃温水溶解,再转入100 mL容量瓶定容得到供试液。吸取供试液25 mL于100 mL分液漏斗中,加入25 mL乙酸乙酯,重摇5 min,静置分层,收集酯层I。吸取酯层I 15 mL,加入15 mL 2.5% NaHCO3, 在50 mL分液漏斗中轻摇30 s, 静置分层后,收集酯层II。吸取酯层II萃取液4 mL于25 mL容量瓶中,加入95%乙醇定容得到测试液。用10 mm比色皿,以95%乙醇作空白参比,在波长380 nm处,测定测试液的吸光度A,茶黄素(Theaflavins,TFs)含量的计算公式如下:
TFs(%)=A×5.39m×(1−ω) 式中:A为测试液的吸光度;m为试样质量(g);ω为试样水分含量(%)。
1.2.5.2 水分含量的测定
参考《GB 5009.3-2016 食品中水分的测定》第一法进行测定。
1.2.5.3 茶多酚含量的测定
参考《QB/T 4067-2010食品工业用速溶茶》的附录A进行测定。
1.2.5.4 咖啡因含量的测定
参考《QB/T 4067-2010食品工业用速溶茶》的附录B进行测定。
1.2.5.5 铅含量的测定
参考《GB 5009.12-2017 食品中铅的测定》第一法进行测定。
1.2.5.6 总砷含量的测定
参考《GB 5009.11-2014 食品中总砷及无机砷的测定》第一篇第二法进行测定。
1.2.6 速溶红茶香气组分分析
1.2.6.1 萃取条件
采用顶空固相微萃取法对样品的挥发性香气组分进行提取和富集[24-25]。称取样品1 g,将称取好的样品立即用带有硅橡胶垫的瓶盖密封,放入旋转振荡器中,50 ℃平衡30 min,DVB/CAR/PDMS复合萃取头在50 ℃下萃取30 min,然后进样,250 ℃解析5 min。
1.2.6.2 色谱条件
色谱柱型号:DB-Heavy WAX色谱柱(30 m×0.25 mm×0.25 µm);升温程序:初温40 ℃保持3 min,以5 ℃/min速率升至200 ℃,以10 ℃/min速率升至250 ℃,保持3 min。载气: 高纯氦气;流量及分流比:1.66 mL/min,不分流。
1.2.6.3 质谱条件
离子源:EI;扫描模式:40~500 Da;电离能量:70 eV;传输线温度:250 ℃;离子源温度:230 ℃;四级杆温度:150 ℃。
1.2.6.4 定性分析
通过比对NIST17质谱数据库,导出样品检索报告并保留匹配度大于80的物质。
1.2.6.5 定量分析
采用峰面积归一化法进行相对含量的计算[25],相对含量的计算公式如下:
相对含量(%)=任意挥发性香气组分峰面积总挥发性香气组分峰面积×100 1.3 数据处理
采用Excel 2019软件处理数据,Origin 2018软件绘制单因素实验图,Design-Expert 8.0.6软件进行响应面试验设计及优化分析;所得实验均重复3次,数据以平均值±标准差(
¯X ±SD)表示。2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素实验结果
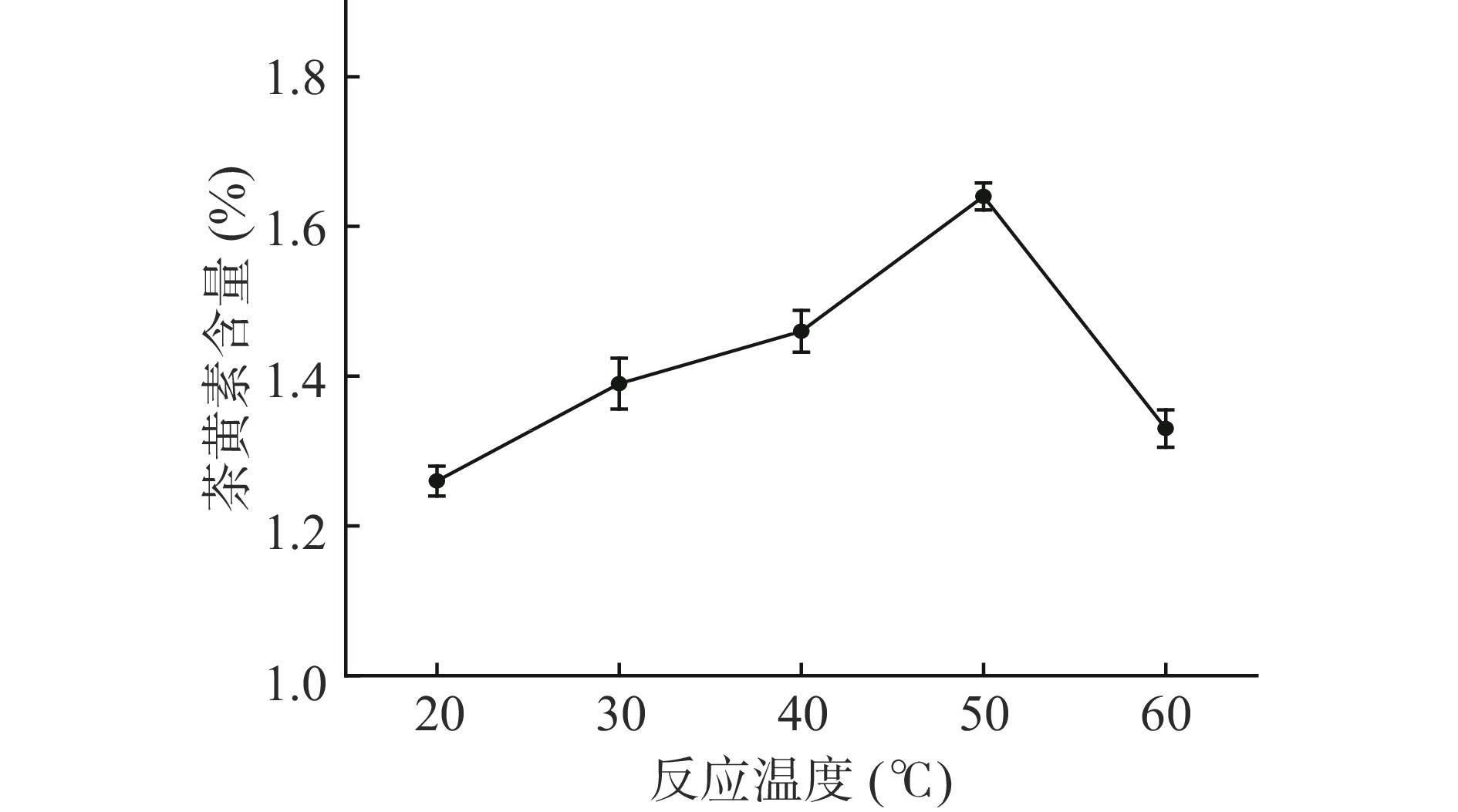
2.1.1 反应温度对茶黄素含量的影响
由图1可知,在20~50 ℃范围内随着温度的升高,茶黄素的含量呈上升趋势,并在50 ℃茶黄素含量达到最大值,温度大于50 ℃时,茶黄素的含量随温度的上升开始下降。前期随着温度的升高,与一般化学反应一样,酶促反应的速率加快[26],茶黄素的合成速率大于分解速率,表现为茶黄素的不断积累。另一方面,随着温度继续升高,酶蛋白逐渐变性失活,茶黄素的合成速率开始逐渐下降。温度过高,茶黄素的分解速率也逐渐加快[27],最终表现为茶黄素含量的下降。故最佳反应温度为50 ℃。
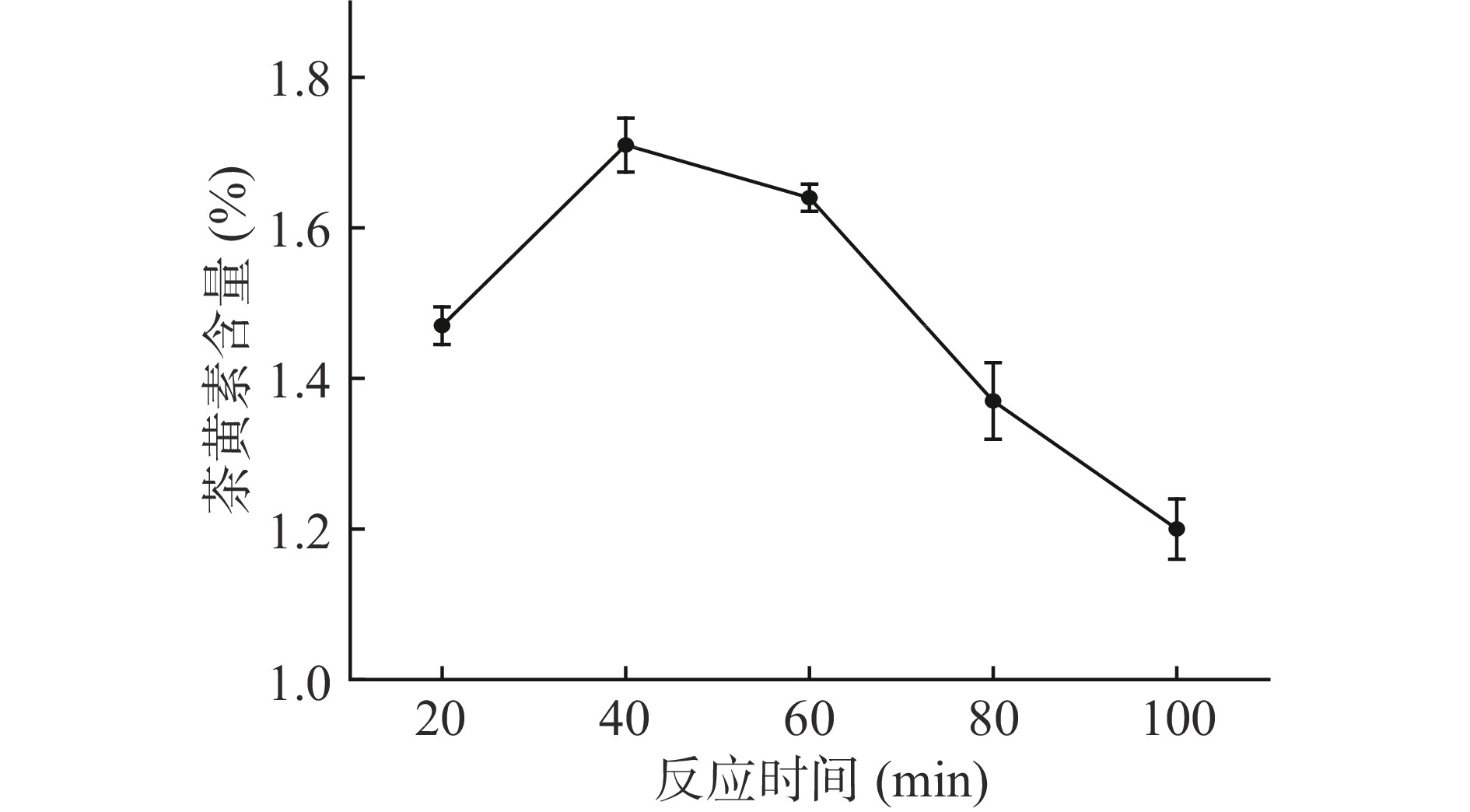
2.1.2 反应时间对茶黄素含量的影响
由图2可知,茶黄素的含量随着反应时间的延长呈现出先增后降的趋势,其中20~40 min内,茶黄素含量迅速升高,并在40 min达到最大值; 40~100 min,茶黄素含量开始急剧下降。这可能是由于随着反应时间的延长,多酚氧化酶的活性逐渐降低所致[28]。在反应前期,大量的儿茶素在多酚氧化酶的作用下参与到了茶黄素的合成当中,主导反应的是茶黄素的合成反应;在40~100 min,多酚氧化酶活性逐渐降低的同时,积累的茶黄素又参与到茶红素和茶褐素的合成[29],因而表现为茶黄素含量的降低。故最佳反应时间为40 min。
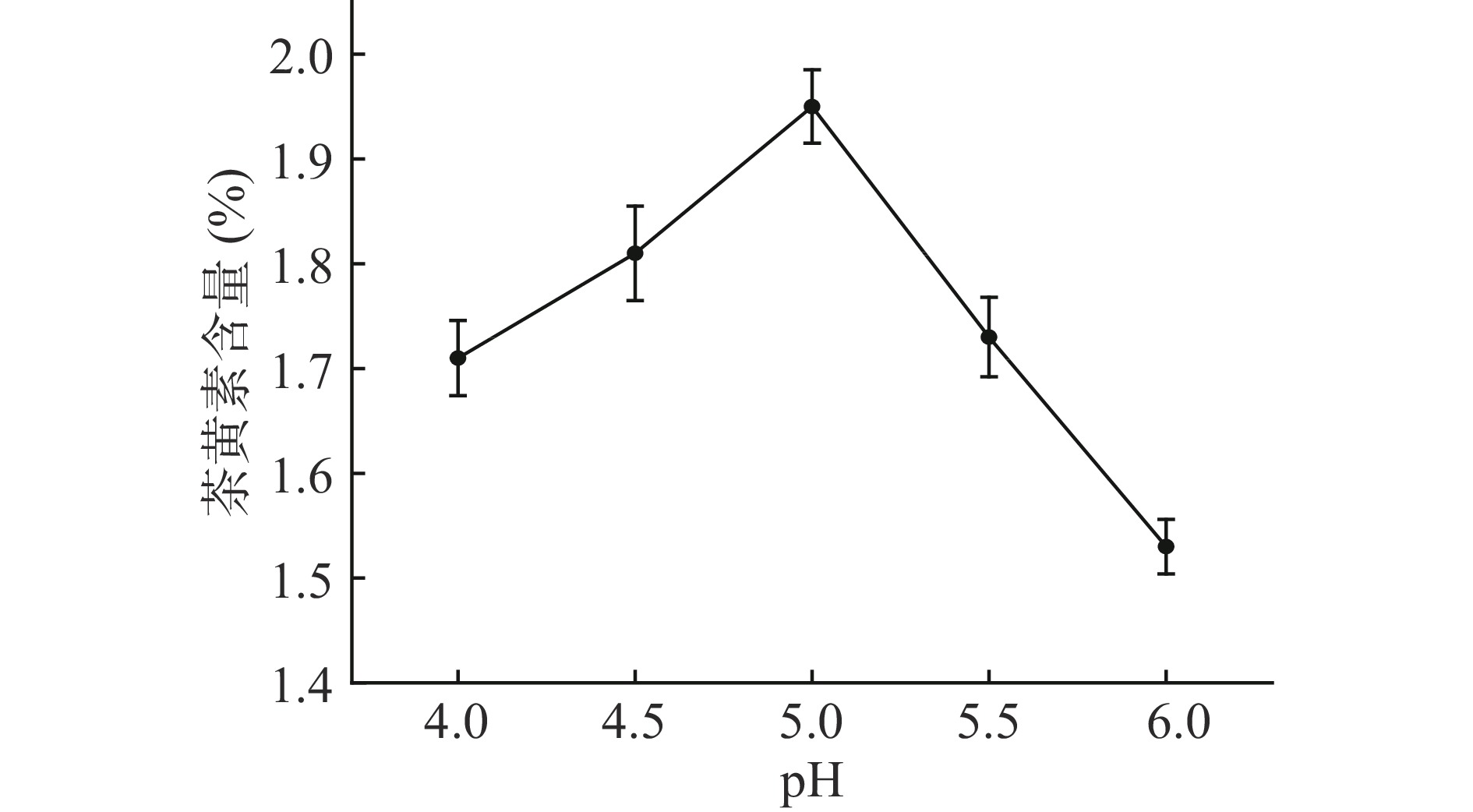
2.1.3 pH对茶黄素含量的影响
由图3可知,该酶的最适pH范围为4.5~5.5,茶黄素的含量在pH为5.0时达到最大值,在此之后随着pH的升高,其含量逐渐降低。虽然茶黄素在酸性条件下较稳定,但过酸条件下反而会抑制茶黄素的合成。毛清黎等[30]通过研究酸处理下红碎茶悬浮发酵模拟实验,发现在偏酸条件下(pH4.5~5.5)有利于茶黄素的合成,而[H+]过高将使三醌的形成受到抑制进而抑制茶黄素的合成。另一方面,pH过高,茶黄素更易氧化分解,参与到其他高聚物的合成当中[29]。当pH大于5.0时,茶黄素的合成速率小于其分解速率,最终表现为茶黄素含量的下降。故最佳反应pH为5.0。
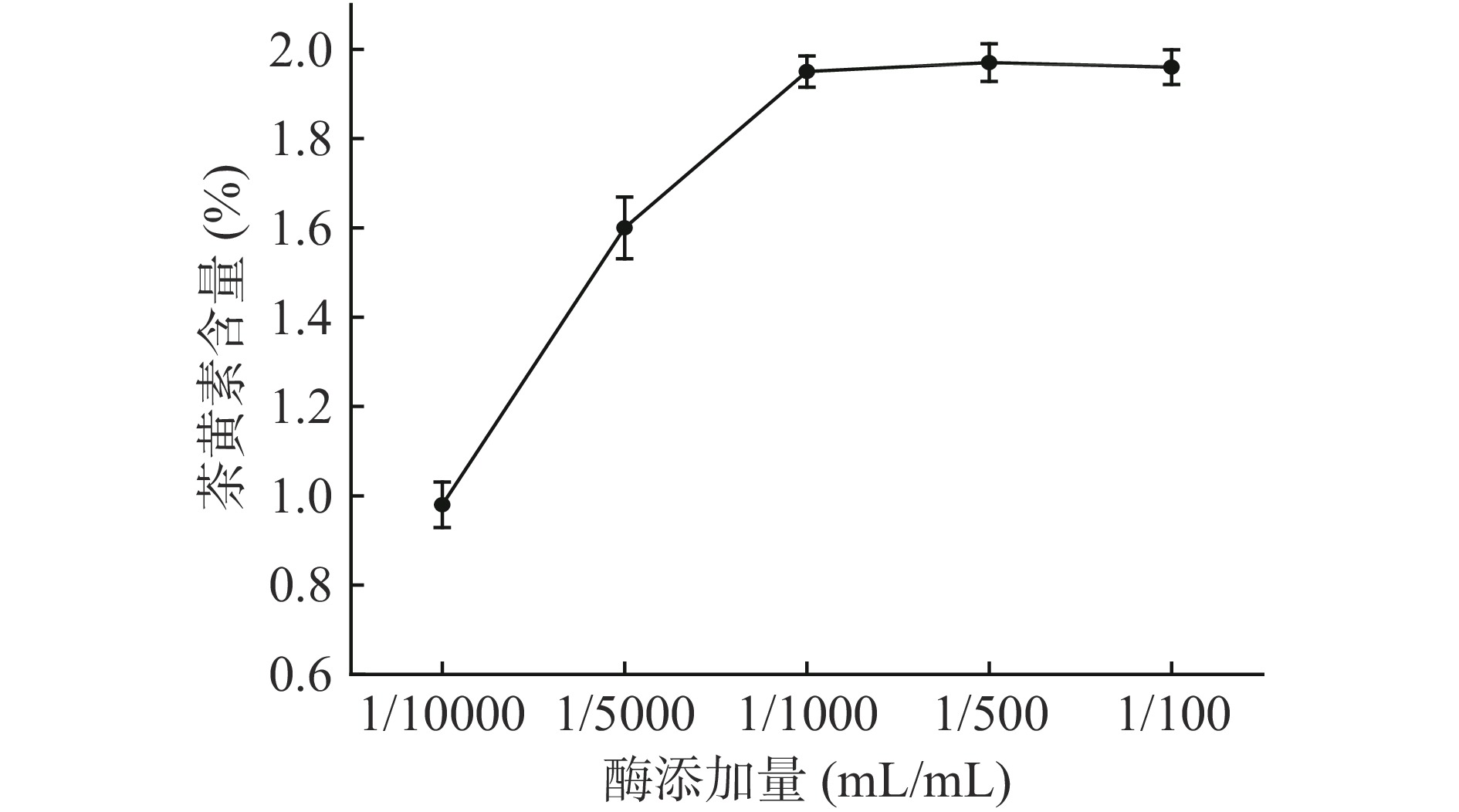
2.1.4 酶添加量对茶黄素含量的影响
由图4可知,茶黄素的含量随着酶添加量的升高而升高,当酶添加量大于1/1000 (mL/mL)时,增长趋于平缓。当过量底物存在时,也就是当底物浓度远远大于酶浓度时,酶促反应速率与酶浓度成正比。随着酶添加量的继续增加,酶分子逐渐趋于饱和,故最佳酶添加量为1/1000 (mL/mL)。
2.2 响应面试验
2.2.1 响应面试验设计及结果
根据上述单因素实验结果,以反应温度(A)、反应时间(B)、pH(C)、酶添加量(D)为自变量,茶黄素含量(Y)为响应值,进行4因素3水平的响应面试验分析。响应面Box-Behnken试验设计及结果与分析见表3。
表 3 响应面试验设计及结果Table 3. Response surface experiment design and results试验号 A 反应温度 B 反应时间 C pH D 酶添加量 Y 茶黄素含量(%) 1 1 1 0 0 1.7 2 0 0 0 0 1.96 3 0 0 −1 1 1.75 4 0 −1 0 −1 1.4 5 −1 0 0 1 1.1 6 0 −1 0 1 1.2 7 1 −1 0 0 1.23 8 −1 0 1 0 1.45 9 0 1 0 1 1.42 10 0 1 1 0 1.52 11 0 0 0 0 2.01 12 0 0 1 1 1.28 13 0 0 0 0 2.05 14 −1 0 0 −1 1.52 15 −1 1 0 0 1.52 16 1 0 0 1 1.28 17 0 0 0 0 1.93 18 0 −1 1 0 1.37 19 0 0 −1 −1 1.53 20 −1 0 −1 0 1.58 21 0 1 0 −1 1.57 22 1 0 −1 0 1.37 23 0 0 1 −1 1.48 24 0 1 −1 0 1.64 25 −1 −1 0 0 1.60 26 1 0 0 −1 1.46 27 1 0 1 0 1.47 28 0 −1 −1 0 1.47 29 0 0 0 0 1.96 2.2.2 模型建立与方差分析
参照表3进行试验,软件分析响应值是茶黄素含量(Y),利用Design-Expert软件对表3进行二次多元回归拟合,得到回归方程:
Y=1.98−0.022A+0.092B−0.064C−0.078D+0.14AB+0.057AC+0.06AD−0.005BC+0.012BD−0.1CD−0.29A2−0.24B2−0.21C2−0.32D2
对模型进行显著性检验,结果如表4所示。由表4可知,此回归方程P<0.01,说明该模型极显著,失拟项P值为0.0501>0.05,不显著,表明该模型可用,试验结果误差小。且该模型决定系数R2=0.9167>0.9,说明该模型拟合效果好,其回归方程可以很好地显现反应时间、反应温度、pH、酶添加量与茶黄素含量之间的真实关系。其中,一次项B、二次项A2、B2、C2、D2对结果影响都是极显著(P<0.01)、一次项C、D、交互项AB对结果影响显著(P<0.05),其他项为不显著(P>0.05);4个因素对茶黄素含量的影响顺序为:B>D>C>A,即反应时间>酶添加量>pH>反应温度。
表 4 回归模型方差分析Table 4. Variance analysis of regression model方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 1.59 14 0.11 11.01 < 0.0001 ** A 5.633E-003 1 5.633E-003 0.55 0.4719 B 0.10 1 0.10 9.79 0.0074 ** C 0.049 1 0.049 4.80 0.0460 * D 0.072 1 0.072 7.00 0.0192 * AB 0.076 1 0.076 7.34 0.0169 * AC 0.013 1 0.013 1.28 0.2763 AD 0.014 1 0.014 1.40 0.2568 BC 1.000E-004 1 1.000E-004 9.706E-003 0.9229 BD 6.250E-004 1 6.250E-004 0.061 0.8090 CD 0.044 1 0.044 4.28 0.0575 A2 0.53 1 0.53 51.35 < 0.0001 ** B2 0.38 1 0.38 36.44 < 0.0001 ** C2 0.28 1 0.28 26.93 0.0001 ** D2 0.67 1 0.67 65.21 < 0.0001 ** 残差 0.14 14 0.010 失拟项 0.14 10 0.014 5.95 0.0501 不显著 纯误差 9.080E-003 4 2.270E-003 总和 1.73 28 R2=0.9167 R²adj=0.8335 注:“*”表示对结果影响差异显著(P<0.05);“**”表示对结果影响差异极显著(P<0.01)。 2.2.3 响应面分析
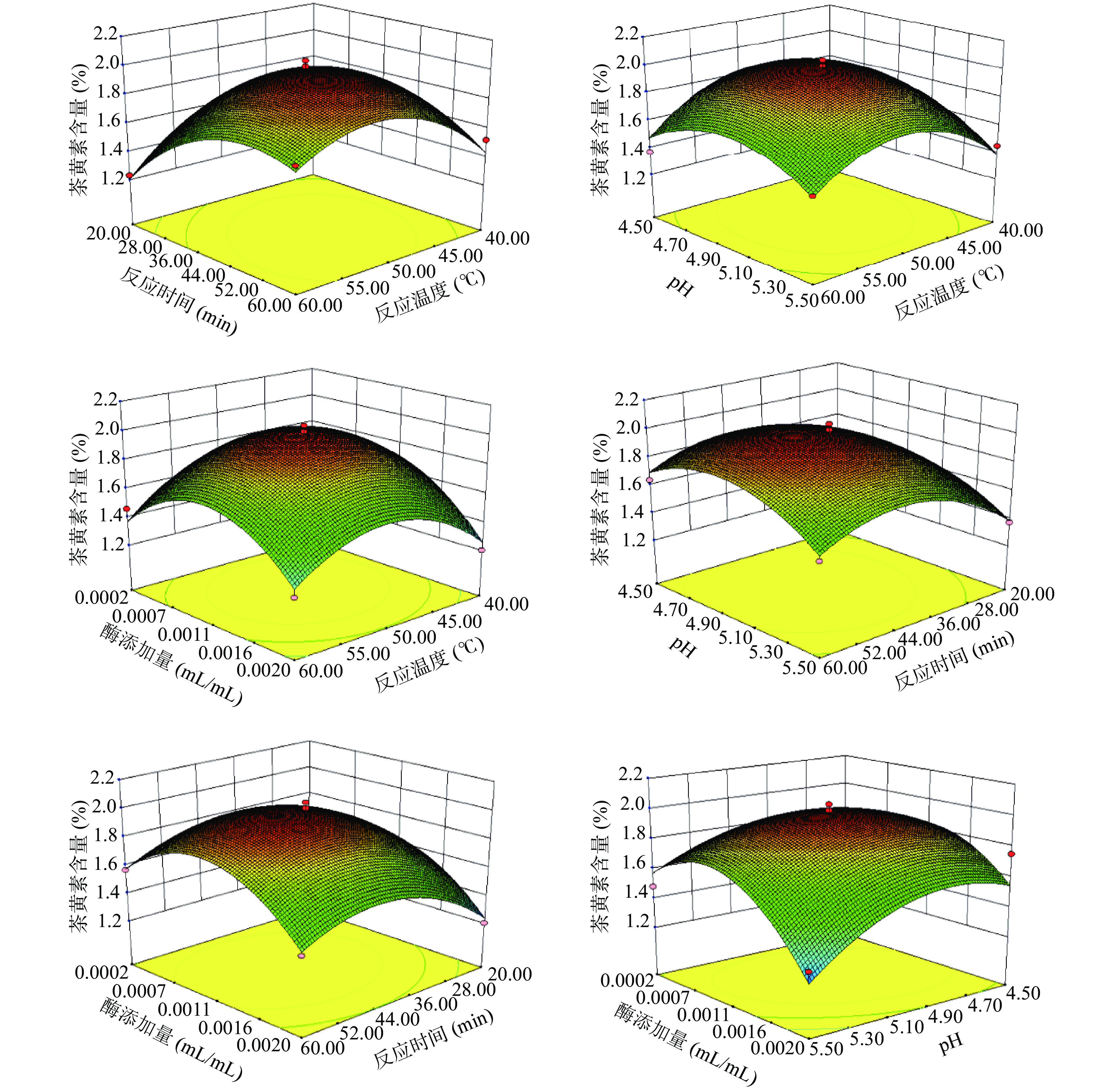
根据回归方程绘制响应面分析图,反应温度、反应时间、pH、酶添加量四个因素之间的交互作用对茶黄素含量影响的响应面及等高线如图5所示。
图5直观地反映了影响茶黄素含量的4个因素两两交互作用,随着反应温度、反应时间、pH和酶添加量的增加,茶黄素的含量呈现先升高后下降的趋势,在所采用的数值间均有极值出现。其中,沿反应时间(B)方向的响应面坡度比酶添加量(D)的响应面坡度更陡,等高线也更密集,说明反应时间对茶黄素含量的影响大于酶添加量;沿酶添加量(D)方向的响应面坡度比pH(C)的响应面坡度更陡,等高线也更密集,说明酶添加量对茶黄素含量的影响大于pH;沿pH(C)方向的响应面坡度比反应温度(A)的响应面坡度更陡,等高线也更密集,说明pH对茶黄素含量的影响大于反应温度,与方差分析结果均一致。三维曲线弯曲程度越大,表明两因素交互作用对茶黄素含量的影响越显著,其中反应温度(A)和反应时间(B)交互作用的三维曲线弯曲程度最大,故两者交互作用最显著,符合方差分析结果。
2.2.4 验证试验结果
由上述响应面分析法求得的最佳条件为反应温度49.84 ℃,反应时间43.69 min,pH4.93, 酶添加量1/1000 (mL/mL),理论最佳的茶黄素含量为2.00%,考虑在实际操作上的方便性,将各因素修正为反应温度50 ℃,反应时间44 min,pH4.90, 酶添加量1/1000 (mL/mL),进行验证试验,通过3次平行试验,发现茶黄素含量可达2.11%±0.04%,与回归方程预测值2.00%基本上吻合。目前我国速溶红茶产品茶黄素含量一般较低,为1%~1.5%。刘紫燕[28]分析了不同产地红茶中茶黄素的比较,95个样品中茶黄素含量最低0.15%,最高1.84%,相较于传统速溶红茶的制备,此方法对高茶黄素速溶红茶的体外氧化制备工艺是具有应用价值的。
2.3 速溶红茶感官评价分析
对优化后的速溶红茶进行感官评价试验,试验结果如表5所示。经优化后速溶红茶茶粉外观呈红棕色,色泽均匀明亮,颗粒分明不结块,平均得分93.8;汤色红亮,具有光泽,平均得分94.5;组织状态上,其热溶性较好,溶解均匀,无明显杂质及沉淀,平均得分96.0;香气方面,具有红茶原有茶香,但茶香较淡,不够浓郁,平均得分72.0;滋味方面,清香可口,但鲜爽度不够,平均得分75.0。李真[31]指出,在速溶茶加工过程中香气组分的种类及含量都有明显下降,其中浸提与浓缩这两步单元操作香气组分损失最大,而过滤与干燥相对较小。另外,本实验所用原料为较低档的夏秋绿茶末,原料本身香气不够丰富,加上逐级单元操作香气的损耗,可能是导致感官评价中香气不够浓郁的原因。滋味方面,也可能与鲜爽度相关的呈味物质因逐级单元操作而大量流失有关,具体原因还需进一步分析。从雷达图6中可以看出产品整体优势突出在外形、汤色与组织状态,经加权后产品总体得分为87.50,感官评价结果整体较好。
表 5 感官评审结果Table 5. Sensory evaluation results外形 滋味 香气 汤色 组织状态 加权后总分 1 96 68 75 98 96 87.30 2 92 75 80 95 93 87.35 3 96 83 71 93 98 90.05 4 93 78 64 95 96 87.35 5 95 71 83 94 97 88.00 6 95 76 69 97 94 87.85 7 95 69 72 91 98 86.00 8 93 68 74 92 96 85.25 9 93 77 60 94 95 86.30 10 90 85 72 96 97 89.55 平均分 93.8 75.0 72.0 94.5 96.0 87.50 2.4 速溶红茶理化成分分析
由检测结果可知,优化后制得的速溶红茶各理化指标均能够达到国标及行业标准中对于速溶红茶的规定。检测结果见表6。
表 6 速溶红茶理化指标Table 6. Physicochemical indexes of instant black tea指标 检测结果 标准要求 评价 参考标准 茶多酚(g/100 g) 27.40±0.66 ≥6.0 合格 QB/T 4067-2010 咖啡因(g/100 g) 4.53±0.04 ≥1.0 合格 水分(%) 2.78±0.35 ≤6.0 合格 铅(mg/kg) 0.038±0.00 <5.0 合格 总砷(mg/kg) 0.044±0.00 <2.0 合格 2.5 速溶红茶香气组分分析
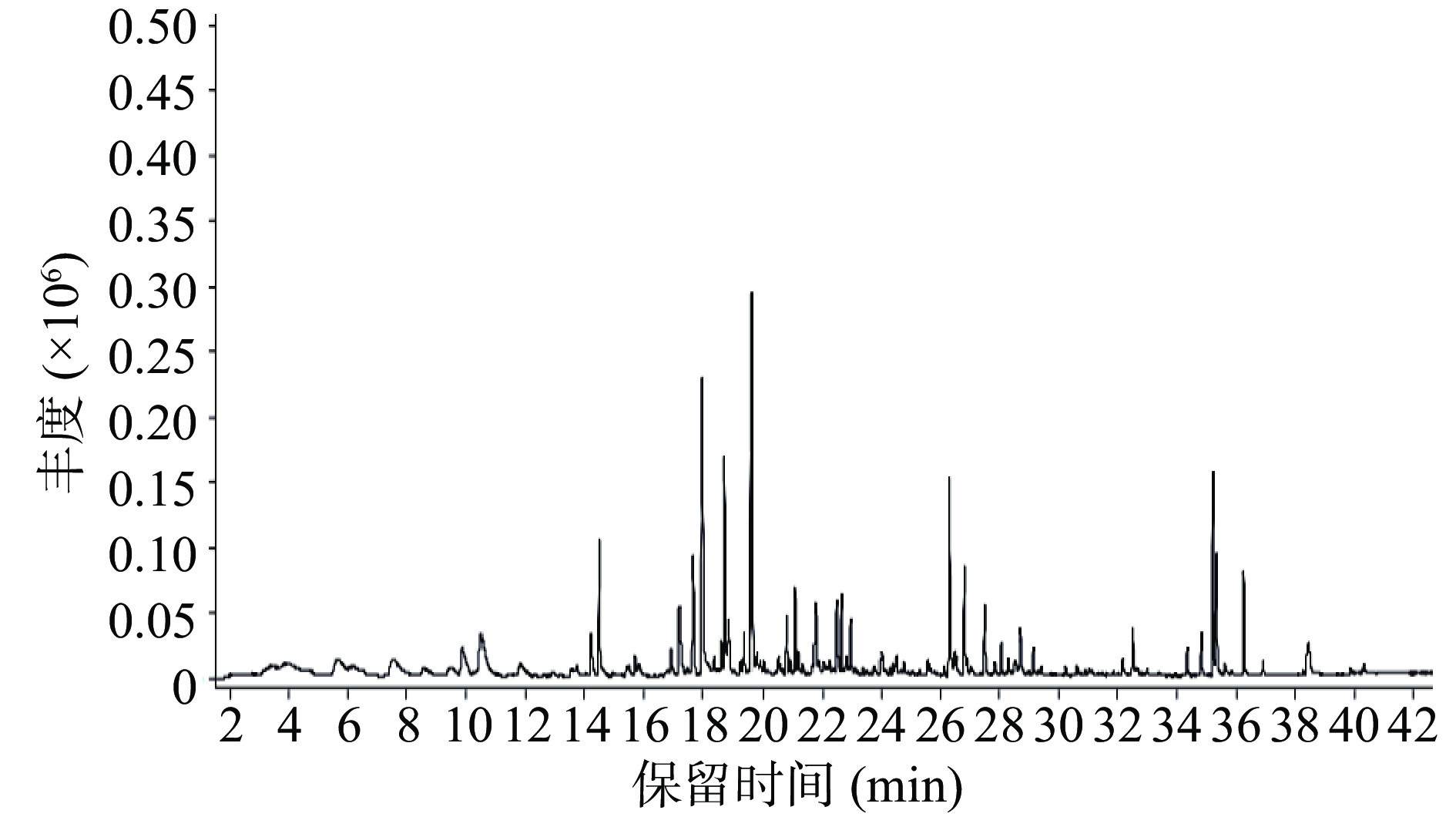
速溶红茶香气组分总离子流图如图7所示。对图7香气组分进行鉴定,结果见表7。由表7可知,速溶红茶共检测出70种香气组分,其中醇类16种,酮类15种,醛类6种,酯类9种,酸类5种,酚类4种,碳氢类5种,其他10种。其中, 醇类相对含量占比最高,达32.34%±0.14%, 其次分别为酸类10.75%±0.21%、酮类9.48%±0.20%、醛类7.87%±0.12%、酯类7.14%±0.15%、酚类7.07%±0.05%、碳氢类4.17%±0.13%。徐玉雪等[32]通过SDE-GC-MS结合GC-O分析了速溶滇红茶的挥发性香气组分,发现样品中主要挥发性香气组分以醇类、酮类以及酯类为主,与本研究结果类似。Wu等[33]通过研究发现红茶香气主要以花果香气为主,其主要香气物质为醇类,如香叶醇、苯甲醇、芳樟醇等。上述醇类香气丰富,推测是形成花果茶树和果实香气的基础。本研究中相对含量占比前10的挥发性成分是:邻二氯苯12.08%±0.23%、芳樟醇10.30%±0.08%、己酸6.62%±0.14%、桉叶油醇5.88%±0.04%、2,4-二叔丁基苯酚5.28%±0.03%、二氢猕猴桃内酯3.78%±0.17%、臧红花醛3.48%±0.12%、十二甲基环六硅氧烷3.46%±0.12%、苯甲醇3.25%±0.06%、2,3-二氢苯并呋喃 2.73%±0.03%。其中芳樟醇与二氢猕猴桃内酯呈现花香,桉叶油醇、2,4-二叔丁基苯酚、藏红花醛呈现青草香,己酸呈现果香,苯甲醇呈现烘烤香[32, 34],整体香气轮廓主要呈现青草香与花香。
表 7 速溶红茶香气组分分析Table 7. Analysis of aroma components of instant black tea类别 序号 挥发性成分 保留时间(min) CAS编号 相对含量(%) 醇类 1 桉叶油醇 10.5097 470-82-6 5.88±0.04 2 顺-2-戊烯醇 13.7399 1576-95-0 0.49±0.00 3 反-Α,Α-5-三甲基-5-乙烯基四氢化-2-呋喃甲醇 16.9436 34995-77-2 1.29±0.04 4 芳樟醇 19.6177 78-70-6 10.30±0.08 5 辛醇 19.7819 111-87-5 1.02±0.00 6 4-松油醇 20.7986 562-74-3 2.03±0.02 7 二氢芳樟醇 21.0845 29957-43-5 2.35±0.04 8 2-甲基-2,4-戊二醇 21.3387 107-41-5 0.38±0.01 9 二甲基硅烷二醇 22.0377 1066-42-8 0.61±0.00 10 糠醇 22.2389 98-00-0 0.40±0.00 11 α-松油醇 22.9644 10482-56-1 1.50±0.03 12 2-苯基-2-丙醇 24.3836 617-94-7 0.21±0.00 13 橙花醇 25.2891 106-25-2 0.15±0.00 14 苯甲醇 26.7983 100-51-6 3.25±0.06 15 苯乙醇 27.4972 60-12-8 2.23±0.02 16 反式-橙花叔醇 30.2297 40716-66-3 0.25±0.00 小计 16 32.34±0.14 酮
类17 异丙叉丙酮 8.5769 141-79-7 0.86±0.03 18 甲基庚烯酮 14.227 110-93-0 2.30±0.08 19 5-乙基-6-甲基庚-3-烯-2-酮 17.4678 57283-79-1 0.20±0.00 20 (3E,5E)-辛-3,5-二烯-2-酮 20.0149 38284-27-4 0.40±0.01 21 6-甲基-3,5-庚二烯-2-酮 20.5126 1604-28-0 0.58±0.03 22 苯乙酮 21.8683 98-86-2 0.33±0.01 23 茶香酮 22.9009 1125-21-9 0.06±0.00 24 大马士酮 25.6915 23726-93-4 0.14±0.00 25 香叶基丙酮 26.4699 689-67-8 0.69±0.05 26 β-紫罗兰酮 28.0638 14901-07-6 0.90±0.03 27 4-[2,2,6-三甲基-7-氧杂二环[4.1.0]庚-1-基]-3-丁烯-2-酮 29.1335 23267-57-4 0.78±0.01 28 3,4-脱氢-β-紫罗兰酮 29.303 1203-08-3 0.14±0.00 29 4'-羟基-2'-甲基苯乙酮 32.978 875-59-2 0.21±0.00 30 3-乙基-4-甲基-吡咯-2,5-二酮 34.3495 20189-42-8 0.84±0.01 31 D-樟脑 18.6381 464-49-3 1.05±0.06 小计 15 9.48±0.20 醛
类32 壬醛 15.715 124-19-6 0.87±0.03 33 苯甲醛 18.8817 100-52-7 2.21±0.07 34 β-环柠檬醛 21.1957 432-25-7 0.93±0.02 35 藏红花醛 21.7676 116-26-7 3.48±0.12 36 桃醛 29.8113 104-67-6 0.06±0.00 37 2,5-二甲基对苯二甲醛 40.3121 7044-92-0 0.32±0.00 小计 6 7.87±0.12 酯
类38 乙酸芳樟酯 19.8984 115-95-7 0.43±0.03 39 水杨酸甲酯 24.7595 119-36-8 0.36±0.01 40 乙酸苯乙酯 25.6333 103-45-7 0.31±0.00 41 2,2,4-三甲基-1,3-戊二醇二异丁酸酯 27.0207 6846-50-0 0.57±0.01 42 三乙酸甘油酯 31.0134 102-76-1 0.22±0.00 43 邻苯二甲酸二甲酯 34.8366 131-11-3 1.25±0.04 44 二氢猕猴桃内酯 35.3238 17092-92-1 3.78±0.17 45 邻苯二甲酸二异丁酯 38.2733 84-69-5 0.09±0.00 46 邻苯二甲酸二丁酯 38.2733 84-74-2 0.13±0.00 小计 9 7.14±0.15 酸
类47 2-甲基己酸 22.4825 4536-23-6 2.36±0.06 48 己酸 26.2899 142-62-1 6.62±0.14 49 反式-3-己烯酸 27.8256 1577-18-0 0.62±0.02 50 庚酸 28.5087 111-14-8 0.78±0.00 51 辛酸 30.6003 124-07-2 0.37±0.00 小计 5 10.75±0.21 酚
类52 4-乙基苯酚 11.0445 123-07-9 0.10±0.00 53 3,5-二甲基苯酚 11.8123 108-68-9 1.44±0.08 54 苯酚 29.4089 108-95-2 0.25±0.00 55 2,4-二叔丁基苯酚 35.2073 96-76-4 5.28±0.03 小计 4 7.07±0.05
碳
氢
类56 十三烷 13.1891 629-50-5 0.11±0.00 57 十二甲基环六硅氧烷 14.5077 540-97-6 3.46±0.12 58 3-甲基十三烷 14.9843 6418-41-3 0.14±0.00 59 正十五烷 18.3945 629-62-9 0.41±0.02 60 对伞花烃 12.3207 99-87-6 0.05±0.00 小计 5 4.17±0.13 其
他61 2-甲基-1-乙烯基咪唑 13.5545 2851-95-8 0.31±0.05 62 2,6-二乙基吡嗪 16.8324 13067-27-1 0.17±0.00 63 邻二氯苯 17.9762 95-50-1 12.08±0.23 64 茶吡咯 20.9204 2167-14-8 0.57±0.02 65 N-乙基琥珀酰亚胺 26.8883 2314-78-5 0.53±0.00 66 2-乙酰基吡咯 28.6887 1072-83-9 1.82±0.03 67 2,3-二氢苯并呋喃 36.2505 496-16-2 2.73±0.03 68 吲哚 36.923 120-72-9 0.41±0.01 69 N-(2-丙炔基)苯胺 37.532 14465-74-8 0.02±0.00 70 咖啡因 38.4587 58-08-2 2.56±0.08 小计 10 21.20±0.41 3. 结论
通过单因素实验和响应面试验考察了反应时间、反应温度、pH、酶添加量对茶黄素含量的影响,确定了最佳工艺条件为反应温度50 ℃,反应时间44 min,pH4.90, 酶添加量1/1000 (mL/mL),在该组合下,茶黄素的平均含量可达2.11%±0.04%。在此工艺条件下制得的速溶红茶,颗粒分明,色泽均匀,汤色橙红透亮,理化指标均达到行业相关要求。同时结合HS-SPME-GC-MS共检测出70种香气组分,包括醇类16种,酮类15种,醛类6种,酯类9种,酸类5种,酚类4种,碳氢类5种,其他10种。其中醇类相对含量占比最高,高达32.34%±0.14%,整体香气轮廓主要呈现青草香与花香。
本研究结果为改善速溶红茶加工工艺和提升产品品质提供一定的理论依据,但是针对于速溶茶加工过程中香气低微等难题依旧难以解决。后续工作,还需进一步针对每级单元操作系统地研究速溶红茶在加工过程中香气损失的情况,开发出更多增香保香的措施,以期解决香气低微这一难题。
-
表 1 Box-Behnken试验设计因素与水平
Table 1 Factors and levels of Box-Behnken experiments design
水平 A 反应温度
(℃)B 反应时间
(min)C pH D 酶添加量
(mL/mL)−1 40 20 4.5 1:5000 0 50 40 5.0 1:1000 1 60 60 5.5 1:500 表 2 速溶红茶感官评价标准表
Table 2 Sensory evaluation standard of instant black tea
项目 权重 感官评分(分) 评价标准 80~100 红棕色,色泽均匀明亮,颗粒分明不结块 外形 25% 50~79 红棕色,色泽均匀较明亮,颗粒分明,无明显结块 0~49 红棕色,色泽不均暗淡,颗粒结块明显 80~100 滋味浓厚,鲜爽可口 滋味 25% 50~79 滋味适中,尚可口 0~49 滋味平淡,口感差 80~100 具有红茶原有茶香,茶香浓厚 香气 10% 50~79 具有红茶原有茶香,茶香较淡 0~49 无红茶原有茶香 80~100 红中透亮,色泽均匀 汤色 20% 50~79 汤色适中,色泽均匀 0~49 汤色暗淡无光泽,色泽不均 80~100 溶解均匀,无明显杂质及沉淀 组织状态 20% 50~79 溶解均匀,少量杂质及沉淀 0~49 溶解不均,具有明显杂质及沉淀 表 3 响应面试验设计及结果
Table 3 Response surface experiment design and results
试验号 A 反应温度 B 反应时间 C pH D 酶添加量 Y 茶黄素含量(%) 1 1 1 0 0 1.7 2 0 0 0 0 1.96 3 0 0 −1 1 1.75 4 0 −1 0 −1 1.4 5 −1 0 0 1 1.1 6 0 −1 0 1 1.2 7 1 −1 0 0 1.23 8 −1 0 1 0 1.45 9 0 1 0 1 1.42 10 0 1 1 0 1.52 11 0 0 0 0 2.01 12 0 0 1 1 1.28 13 0 0 0 0 2.05 14 −1 0 0 −1 1.52 15 −1 1 0 0 1.52 16 1 0 0 1 1.28 17 0 0 0 0 1.93 18 0 −1 1 0 1.37 19 0 0 −1 −1 1.53 20 −1 0 −1 0 1.58 21 0 1 0 −1 1.57 22 1 0 −1 0 1.37 23 0 0 1 −1 1.48 24 0 1 −1 0 1.64 25 −1 −1 0 0 1.60 26 1 0 0 −1 1.46 27 1 0 1 0 1.47 28 0 −1 −1 0 1.47 29 0 0 0 0 1.96 表 4 回归模型方差分析
Table 4 Variance analysis of regression model
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 1.59 14 0.11 11.01 < 0.0001 ** A 5.633E-003 1 5.633E-003 0.55 0.4719 B 0.10 1 0.10 9.79 0.0074 ** C 0.049 1 0.049 4.80 0.0460 * D 0.072 1 0.072 7.00 0.0192 * AB 0.076 1 0.076 7.34 0.0169 * AC 0.013 1 0.013 1.28 0.2763 AD 0.014 1 0.014 1.40 0.2568 BC 1.000E-004 1 1.000E-004 9.706E-003 0.9229 BD 6.250E-004 1 6.250E-004 0.061 0.8090 CD 0.044 1 0.044 4.28 0.0575 A2 0.53 1 0.53 51.35 < 0.0001 ** B2 0.38 1 0.38 36.44 < 0.0001 ** C2 0.28 1 0.28 26.93 0.0001 ** D2 0.67 1 0.67 65.21 < 0.0001 ** 残差 0.14 14 0.010 失拟项 0.14 10 0.014 5.95 0.0501 不显著 纯误差 9.080E-003 4 2.270E-003 总和 1.73 28 R2=0.9167 R²adj=0.8335 注:“*”表示对结果影响差异显著(P<0.05);“**”表示对结果影响差异极显著(P<0.01)。 表 5 感官评审结果
Table 5 Sensory evaluation results
外形 滋味 香气 汤色 组织状态 加权后总分 1 96 68 75 98 96 87.30 2 92 75 80 95 93 87.35 3 96 83 71 93 98 90.05 4 93 78 64 95 96 87.35 5 95 71 83 94 97 88.00 6 95 76 69 97 94 87.85 7 95 69 72 91 98 86.00 8 93 68 74 92 96 85.25 9 93 77 60 94 95 86.30 10 90 85 72 96 97 89.55 平均分 93.8 75.0 72.0 94.5 96.0 87.50 表 6 速溶红茶理化指标
Table 6 Physicochemical indexes of instant black tea
指标 检测结果 标准要求 评价 参考标准 茶多酚(g/100 g) 27.40±0.66 ≥6.0 合格 QB/T 4067-2010 咖啡因(g/100 g) 4.53±0.04 ≥1.0 合格 水分(%) 2.78±0.35 ≤6.0 合格 铅(mg/kg) 0.038±0.00 <5.0 合格 总砷(mg/kg) 0.044±0.00 <2.0 合格 表 7 速溶红茶香气组分分析
Table 7 Analysis of aroma components of instant black tea
类别 序号 挥发性成分 保留时间(min) CAS编号 相对含量(%) 醇类 1 桉叶油醇 10.5097 470-82-6 5.88±0.04 2 顺-2-戊烯醇 13.7399 1576-95-0 0.49±0.00 3 反-Α,Α-5-三甲基-5-乙烯基四氢化-2-呋喃甲醇 16.9436 34995-77-2 1.29±0.04 4 芳樟醇 19.6177 78-70-6 10.30±0.08 5 辛醇 19.7819 111-87-5 1.02±0.00 6 4-松油醇 20.7986 562-74-3 2.03±0.02 7 二氢芳樟醇 21.0845 29957-43-5 2.35±0.04 8 2-甲基-2,4-戊二醇 21.3387 107-41-5 0.38±0.01 9 二甲基硅烷二醇 22.0377 1066-42-8 0.61±0.00 10 糠醇 22.2389 98-00-0 0.40±0.00 11 α-松油醇 22.9644 10482-56-1 1.50±0.03 12 2-苯基-2-丙醇 24.3836 617-94-7 0.21±0.00 13 橙花醇 25.2891 106-25-2 0.15±0.00 14 苯甲醇 26.7983 100-51-6 3.25±0.06 15 苯乙醇 27.4972 60-12-8 2.23±0.02 16 反式-橙花叔醇 30.2297 40716-66-3 0.25±0.00 小计 16 32.34±0.14 酮
类17 异丙叉丙酮 8.5769 141-79-7 0.86±0.03 18 甲基庚烯酮 14.227 110-93-0 2.30±0.08 19 5-乙基-6-甲基庚-3-烯-2-酮 17.4678 57283-79-1 0.20±0.00 20 (3E,5E)-辛-3,5-二烯-2-酮 20.0149 38284-27-4 0.40±0.01 21 6-甲基-3,5-庚二烯-2-酮 20.5126 1604-28-0 0.58±0.03 22 苯乙酮 21.8683 98-86-2 0.33±0.01 23 茶香酮 22.9009 1125-21-9 0.06±0.00 24 大马士酮 25.6915 23726-93-4 0.14±0.00 25 香叶基丙酮 26.4699 689-67-8 0.69±0.05 26 β-紫罗兰酮 28.0638 14901-07-6 0.90±0.03 27 4-[2,2,6-三甲基-7-氧杂二环[4.1.0]庚-1-基]-3-丁烯-2-酮 29.1335 23267-57-4 0.78±0.01 28 3,4-脱氢-β-紫罗兰酮 29.303 1203-08-3 0.14±0.00 29 4'-羟基-2'-甲基苯乙酮 32.978 875-59-2 0.21±0.00 30 3-乙基-4-甲基-吡咯-2,5-二酮 34.3495 20189-42-8 0.84±0.01 31 D-樟脑 18.6381 464-49-3 1.05±0.06 小计 15 9.48±0.20 醛
类32 壬醛 15.715 124-19-6 0.87±0.03 33 苯甲醛 18.8817 100-52-7 2.21±0.07 34 β-环柠檬醛 21.1957 432-25-7 0.93±0.02 35 藏红花醛 21.7676 116-26-7 3.48±0.12 36 桃醛 29.8113 104-67-6 0.06±0.00 37 2,5-二甲基对苯二甲醛 40.3121 7044-92-0 0.32±0.00 小计 6 7.87±0.12 酯
类38 乙酸芳樟酯 19.8984 115-95-7 0.43±0.03 39 水杨酸甲酯 24.7595 119-36-8 0.36±0.01 40 乙酸苯乙酯 25.6333 103-45-7 0.31±0.00 41 2,2,4-三甲基-1,3-戊二醇二异丁酸酯 27.0207 6846-50-0 0.57±0.01 42 三乙酸甘油酯 31.0134 102-76-1 0.22±0.00 43 邻苯二甲酸二甲酯 34.8366 131-11-3 1.25±0.04 44 二氢猕猴桃内酯 35.3238 17092-92-1 3.78±0.17 45 邻苯二甲酸二异丁酯 38.2733 84-69-5 0.09±0.00 46 邻苯二甲酸二丁酯 38.2733 84-74-2 0.13±0.00 小计 9 7.14±0.15 酸
类47 2-甲基己酸 22.4825 4536-23-6 2.36±0.06 48 己酸 26.2899 142-62-1 6.62±0.14 49 反式-3-己烯酸 27.8256 1577-18-0 0.62±0.02 50 庚酸 28.5087 111-14-8 0.78±0.00 51 辛酸 30.6003 124-07-2 0.37±0.00 小计 5 10.75±0.21 酚
类52 4-乙基苯酚 11.0445 123-07-9 0.10±0.00 53 3,5-二甲基苯酚 11.8123 108-68-9 1.44±0.08 54 苯酚 29.4089 108-95-2 0.25±0.00 55 2,4-二叔丁基苯酚 35.2073 96-76-4 5.28±0.03 小计 4 7.07±0.05
碳
氢
类56 十三烷 13.1891 629-50-5 0.11±0.00 57 十二甲基环六硅氧烷 14.5077 540-97-6 3.46±0.12 58 3-甲基十三烷 14.9843 6418-41-3 0.14±0.00 59 正十五烷 18.3945 629-62-9 0.41±0.02 60 对伞花烃 12.3207 99-87-6 0.05±0.00 小计 5 4.17±0.13 其
他61 2-甲基-1-乙烯基咪唑 13.5545 2851-95-8 0.31±0.05 62 2,6-二乙基吡嗪 16.8324 13067-27-1 0.17±0.00 63 邻二氯苯 17.9762 95-50-1 12.08±0.23 64 茶吡咯 20.9204 2167-14-8 0.57±0.02 65 N-乙基琥珀酰亚胺 26.8883 2314-78-5 0.53±0.00 66 2-乙酰基吡咯 28.6887 1072-83-9 1.82±0.03 67 2,3-二氢苯并呋喃 36.2505 496-16-2 2.73±0.03 68 吲哚 36.923 120-72-9 0.41±0.01 69 N-(2-丙炔基)苯胺 37.532 14465-74-8 0.02±0.00 70 咖啡因 38.4587 58-08-2 2.56±0.08 小计 10 21.20±0.41 -
[1] 韩篷慧, 李范洙, 张先, 等. 酶辅助提取法制备寒葱速溶茶的加工工艺[J]. 食品工业,2021,42(10):110−114. [HAN Penghui, LI Fanzhu, ZHANG Xian, et al. The processing technology of enzyme-assisted extraction method to prepare allium victorialis instant tea[J]. The Food Industry,2021,42(10):110−114. [2] SOMESWARARAO C, SRIVASTAV P P. A novel technology for production of instant tea powder from the existing black tea manufacturing process[J]. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies,2012,16:143−147.
[3] SINIJA V R, MISHRA H N, BAL S. Process technology for production of soluble tea powder[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2007,82(3):276−283. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2007.01.024
[4] 涂云飞, 杨秀芳, 孔俊豪, 等. 固态速溶茶贮藏过程中含水率、儿茶素及茶黄素含量变化的研究[J]. 中国茶叶加工,2020(4):76−80. [TU Yunfei, YANG Xiufang, KONG Junhao, et al. Effect on the change of moisture, catechins and theaflavins content of instant tea in solid during storage[J]. China Tea Processing,2020(4):76−80. doi: 10.15905/j.cnki.33-1157/ts.2020.04.013 [5] HUA J, WANG H, JIANG Y, et al. Influence of enzyme source and catechins on theaflavins formation duringin vitro liquid-state fermentation[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2021,139:1−9.
[6] NING Y R, WU Z, LI Z J, et al. Optimization of fermentation process enhancing quality of dandelion black tea on the functional components, activity and sensory quality[J]. Open Access Library Journal,2020,07(5):1−11.
[7] KONG J H, YANG X F, ZUO X B, et al. High-quality instant black tea manufactured using fresh tea leaves by two-stage submerged enzymatic processing[J]. Food Science and Human Wellness,2022,11(3):676−685. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2021.12.025
[8] TANAKA T, MATSUO Y. Production mechanisms of black tea polyphenols[J]. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin,2020,68(12):1131−1142.
[9] 曾俊. 几种植物多酚氧化酶氧化茶多酚生成茶黄素的研究[J]. 茶叶通讯,2020,47(3):443−449. [ZENG Jun. Study on the oxidation of tea polyphenols to theaflavins by several plant polyphenol oxidase[J]. Journal of Tea Communication,2020,47(3):443−449. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-525X.2020.03.012 [10] 王雨鑫, 刘学声, 刘建军, 等. 添加外源儿茶素制备高茶黄素红茶的工艺优化[J]. 贵州农业科学,2020,48(12):114−118. [WANG Yuxin, LIU Xuesheng, LIU Jianjun, et al. Optimization of adding exogenous catechins prepared for high-theaflavins black tea[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences,2020,48(12):114−118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2020.12.024 [11] 李东, 李洁媛, 雷雨, 等. 植物外源多酚氧化酶酶促合成茶黄素的研究进展[J]. 茶叶通讯,2021,48(3):399−404. [LI Dong, LI Jieyuan, LEI Yu, et al. Research progress on the enzymatic synthesis of theaflavins by exogenous polyphenol oxidase from plants[J]. Journal of Tea Communication,2021,48(3):399−404. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-525X.2021.03.003 [12] 徐洪梅. 梨多酚氧化酶生物催化合成茶黄素及其在茶叶深加工中的应用研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江工业大学, 2013 XU Hongmei. Study on the pear polyphenol oxidase biocatalytic synthesis of theaflavins and the application in the tea extraction[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University of Technology, 2013.
[13] 罗学平, 李丽霞, 成洲, 等. 茶多酚氧化产物制备方法研究进展[J]. 南方农业,2017,11(22):96−99. [LUO Xueping, LI Lixia, CHENG Zhou, et al. Research progress on preparation methods of oxidation products of tea polyphenols[J]. South China Agriculture,2017,11(22):96−99. doi: 10.19415/j.cnki.1673-890x.2017.22.030 [14] 张颖. 酶促氧化制备茶黄素及其性质研究[D]. 天津: 天津科技大学, 2010 ZHANG Ying. Studies on prodution theaflavins by using enzymes and it’s characterization[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2010.
[15] 高学玲, 张晶晶, 王玉婉, 等. 高亮度速溶红茶工艺优化[J]. 中国食品学报,2016,16(2):106−114. [GAO Xueling, ZHANG Jingjing, WANG Yuwan, et al. Process optimization of high-polished instant black tea[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2016,16(2):106−114. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2016.02.016 [16] 萧伟祥, 宛晓春, 胡耀武, 等. 茶儿茶素体外氧化产物分析[J]. 茶叶科学,1999,1999(2):145−149. [XIAO Weixiang, WAN Xiaochun, HU Yaowu, et al. Study on the in vitro oxidation product of tea catechines[J]. Journal of Tea Science,1999,1999(2):145−149. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.1999.02.015 [17] 夏涛, 童启庆, 萧伟祥. 茶鲜叶匀浆悬浮发酵工艺学研究[J]. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版),2000(4):22−25. [XIA Tao, TONG Qiqing, XIAO Weixiang. Studies on the technology of suspension fermentation of tea leaf homogenates[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture and Life Sciences),2000(4):22−25. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-9209.2000.04.007 [18] 张宏岐, 柳蔚, 王鑫, 等. 五峰夏秋茶主要呈味成分分析研究[J]. 华中师范大学学报(自然科学版),2017,51(3):335−338. [ZHANG Hongqi, LIU Wei, WANG Xing, et al. Study on the taste components of Wufeng summer-autumn tea[J]. Journal of Central China Normal University (Natural Sciences),2017,51(3):335−338. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1190.2017.03.012 [19] 徐悦, 张阳光, 董若霞, 等. 速溶茶加工中酶技术应用研究进展[J]. 中国茶叶加工,2019(4):50−53. [XU Yue, ZHANG Yangguang, DONG Ruoxia, et al. Research progress of enzyme technology in instant tea processing[J]. China Tea Processing,2019(4):50−53. doi: 10.15905/j.cnki.33-1157/ts.2019.04.012 [20] 刘政权. 多酚氧化酶体外氧化技术优化速溶红茶品质的工艺研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2012 LIU Zhengquan. Studies on the technology to optimize the quality of instant black tea by in vitro oxidation with polyphenol oxidase[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2012.
[21] 程启坤. 红茶色素的系统分析法[J]. 中国茶叶,1981(1):17. [CHENG Qikun. Systematic analysis of black tea pigment[J]. Chinese Teas,1981(1):17. [22] 张正竹. 茶叶生物化学实验教程[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2009: 52−54 ZHANG Zhengzhu. Experimental course of tea biochemistry[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2009: 52−54.
[23] ROBERTS E A H, SMITH R F. Spectrophotometric measurements of theaflavins and thearubigins in black tea liquors in assessments of quality in teas[J]. Analyst,1961,86(1019):94−98. doi: 10.1039/an9618600094
[24] LIU P P, ZHENG P C, FENG L, et al. Dynamic changes in the aroma profile of Qingzhuan tea during its manufacture[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,375:131847. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131847
[25] 黄刚骅, 李沅达, 邓秀娟, 等. 四种干燥方式云南白茶的香气组分分析[J]. 食品工业科技: 1−20 [2022-05-25]. DOI: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021120080. HUANG Ganghua, LI Yuanda, DENG Xiujuan, et al. Analysis of aroma compounds of yunnan white tea by four drying methods[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry: 1−20 [2022-05-25]. DOI: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021120080.
[26] 王镜岩. 生物化学[M]. 第三版. 上册. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2002: 378−379 WANG Jingyan. Biochemistry[M]. The Third Edition. The First Volume. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2002: 378−379.
[27] 陶琳琳, 张娅楠, 闫振, 等. 红茶加工过程中发酵技术研究进展[J]. 广东茶业,2020(1):2−6. [TAO Linlin, ZHANG Yanan, YAN Zhen, et al. Research progress of fermentation technology in black tea processing[J]. Guangdong Tea Industry,2020(1):2−6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7398.2020.01.001 [28] 刘紫燕. 茶黄素在速溶红茶加工中的变化规律及其保护措施研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2015 LIU Ziyan. Variation of theaflavins in the processing of instant black tea and measures of its protective[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2015.
[29] 王领昌. 影响红茶茶红素含量的因素及其成因研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2017 WANG Lingchang. Study on the influence factors and causes on thearubigins quantity of black tea[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2015.
[30] 毛清黎, 朱旗, 刘仲华, 等. 红茶发酵中pH调控对多酚氧化酶活性及茶黄素形成的影响[J]. 湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版),2005(5):66−68. [MAO Qingli, ZHU Qi, LIU Zhonghua, et al. Effects of pH modification on activity of polyphenol oxidases and formatation of theaflavins[J]. Journal of Hunan Agricultural University (Natural Sciences),2005(5):66−68. [31] 李真. 速溶红茶加工过程中香气的变化及保香措施的研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2015 LI Zhen. Changes of aroma constituents of instant black tea during processing and the research of aroma retention measures[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2015.
[32] 徐玉雪, 李婷, 李利君, 等. SDE-GC-MS结合GC-O分析速溶滇红茶的挥发性风味物质[J]. 现代食品科技,2019,35(11):277−284. [XU Yuxue, LI Ting, LI Lijun, et al. Ananlysis of volatile components in the instant Dianhong tea by SDE-GC-MS and GC-O[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2019,35(11):277−284. doi: 10.13982/j.mfst.1673-9078.2019.11.038 [33] WU J X, WU X R, YUAN G A, et al. Comparative analysis of aroma substances of vanilla co-fermented black tea[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science,2021,651(4):42−47.
[34] 李琛, 岳翠男, 杨普香, 等. 功夫红茶特征香气研究进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2021,12(22):8834−8842. [LI Chen, YUE Cuinan, YANG Puxiang, et al. Research progress on characteristic aroma of Congou black tea[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2021,12(22):8834−8842. -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 路晓,李文钊,徐艳朋,李玉爽,王智珍,张亚旭,刘馨阳,阮美娟. 不同预处理对六种药食同源食材加工特性及其饼干品质影响研究. 食品与发酵工业. 2024(12): 258-265 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 邱心茹,张源,蒋远帅,高文慧,刘友雪,衣春颖,李悦,孔峰. 鸡骨粉理化性质及其对全麦饼干品质的影响. 食品科技. 2024(06): 147-152 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 傅新征,林思琦,罗培轩. 响应面法优化超声波辅助酸酶法制备荸荠抗性淀粉工艺. 湖北民族大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(04): 551-558 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
