Optimization of Alkali Extraction Process of ‘Jinsixiaozao’ Polysaccharide by Response Surface Methodology and Its Antioxidant Activity
-
摘要: 以金丝小枣为原料,通过单因素考察提取温度、时间、料液比和NaOH浓度对多糖得率的影响,在此基础上进行Box-Behnken试验来优化碱提多糖的提取工艺,并对其进行总糖含量、扫描电镜、红外光谱及抗氧化活性测定。结果表明,碱提多糖最佳工艺为:料液比1:35(g/mL),提取温度80 ℃,提取时间120 min,NaOH浓度为0.2 mol/L,在此条件下多糖的得率为11.44%,总糖含量为69.39%。扫描电镜表明其具有不规则块状结构,内部紧实;红外光谱表明枣碱提多糖具有C=O和C-H等酸性多糖的特征吸收峰。抗氧化活性实验表明,碱提多糖具有一定清除自由基的能力,对DPPH和超氧阴离子自由基的IC50分别为1.201 mg/mL和1.176 mg/mL。此研究为进一步开发枣多糖功能性食品及研究碱提多糖的构效关系提供参考。Abstract: In this experiment, ‘Jinsixiaozao’ fruit was used as raw material, the effects of extraction temperature, time, solid-liquid ratio and NaOH concentration on the yield of polysaccharide were investigated by single factor test. On this basis, Box-Behnken experiment was carried out to optimize the extraction process of alkali extracted polysaccharides. Its total sugar content, scanning electron microscopy, infrared spectrum and antioxidant activity were determined. The results showed that the optimal conditions were solid-liquid ratio 1:35 (g/mL), extraction temperature 80 ℃, extraction time 120 min, and NaOH concentration 0.2 mol/L, the polysaccharides yield was 11.44% with total sugar content of 69.39%. Scanning electron microscopic observations showed that it had irregular block structure with compact inside. The infrared spectrum showed that the alkali extracted polysaccharide of jujube had the characteristic absorption peaks of acid polysaccharides such as C=O and C-H. The antioxidant activity experiments showed that the alkali extracted polysaccharide had a certain ability to scavenge free radicals, and the IC50 for DPPH and superoxide anion free radicals were 1.201 mg/mL and 1.176 mg/mL, respectively. This study provides a reference for further developing functional foods of jujube polysaccharides and studying the structure-activity relationship of alkali extracted polysaccharides.
-
Keywords:
- jujube polysaccharide /
- alkali-extraction /
- response surface /
- antioxidant activity
-
枣(Ziziphus jujuba Mill.)是鼠李科枣属植物[1],药食同源。金丝小枣是我国十大主栽品种之一,主要分布在山东省的乐陵、沾化、无棣和河北的沧县、献县等地,其果实核小皮薄,肉质细腻,入口绵甜,因其掰开果实中可清晰看到缕缕金丝而得名。
枣果富含黄酮类[2]、酚类[3]、三萜类[4]、多糖类[5]等生物活性成分,其中多糖是一类高分子聚合物,具有抗氧化[6]、抗肿瘤[7]、免疫调节[8]及降血糖[9]等药理功效。Chang等[10]研究表明,枣果实中酸性多糖对亚铁离子的螯合作用更为明显,具有更强的抗氧化活性;林夕梦[11]研究发现碱提枣渣多糖可以通过阻断自由基链式反应或者激活抗氧化相关酶,有效预防氧化应激。Zhao等[12]研究发现枣多糖中酸性多糖具有更好的免疫促进活性。以上研究都提示枣碱提多糖具有很好的开发潜力。
目前研究的枣多糖提取方法主要有传统水提法、超声助提法、碱液提取法、微波助提法、超临界二氧化碳萃取、酶法等[13-14]。有研究表明通过碱液提取法可以快速稳定地提取植物细胞壁中的多糖,多糖得率较高[15]。而关于金丝小枣多糖碱提工艺及抗氧化活性的研究报道较少,本实验主要采用碱液提取金丝小枣多糖,利用Box-Behnken试验得到最佳工艺参数并对其初级结构及抗氧化活性进行研究,旨在为枣多糖的开发与利用提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
金丝小枣干果 购于河北省沧州市;95%乙醇、氢氧化钠、无水乙醇等均为国产分析纯 天津市华东试剂厂;1,1-二苯基-2-苦基肼基(1,1-dipheny-2-picrylhydrazyl,DPPH)、透析袋 购自北京索莱宝科技有限公司;盐酸及邻苯三酚 天津市科密欧化学试剂有限公司。
TU-1810双光束紫外可见分光光度计 北京普析通用仪器有限公司;SYG-2型数显恒温水浴锅 常州朗越仪器制造有限公司;IKA RV10型旋转蒸发仪 厦门华亿仪器有限公司;CT14RD型高速冷冻离心机 上海天美科学仪器有限公司; DHG-9420A型电热恒温鼓风干燥箱 上海飞越实验仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 碱提多糖的工艺流程
首先把金丝小枣烘干粉碎过60目筛,备用。枣粉用95%乙醇预处理除脂后加入NaOH溶液,水浴加热,离心过滤(8000 r/min,10 min),取上清液后减压浓缩,加入3倍体积的95%乙醇,4 ℃冰箱静置24 h,再次离心弃上清液留多糖沉淀,透析72 h(12000 Da),浓缩后多糖沉淀置于烘箱60 ℃中干燥3 d即为金丝小枣碱提粗多糖。提取工艺主要对提取温度、时间、料液比和NaOH浓度进行考察,在此基础上进行响应面试验进而确定金丝小枣碱提多糖的工艺。
1.2.2 单因素实验
取1 g枣粉,以提取温度70 ℃,提取时间90 min,料液比1:30 g/mL,NaOH浓度0.2 mol/L为基础条件,设计各因素水平分别为提取温度50、60、70、80、90 ℃,料液比为1:10、1:20、1:30、1:40、1:50(g/mL),提取时间30、60、90、120、150 min,NaOH浓度为0.1、0.2、0.3、0.4、0.5 mol/L,重复3次,研究不同因素对金丝小枣碱提多糖得率的影响。
1.2.3 响应面试验设计
在单因素实验的基础上,以NaOH浓度(A)、料液比(B)和提取温度(C)为自变量,金丝小枣多糖得率为响应值,根据Box-Behnken试验设计三因素三水平响应面试验,试验因素与水平设计见表1。
表 1 响应面试验的因素与水平Table 1. Factors and levels of response surface experiment水平值 因素 A-NaOH浓度(mol/L) B-料液比(g/mL) C-提取温度(℃ ) −1 0.2 1:30 70 0 0.3 1:40 80 1 0.4 1:50 90 1.2.4 总糖含量测定及得率的计算
苯酚硫酸法[16]测定样本中的总糖含量,以葡萄糖质量浓度为横坐标,OD490 nm为纵坐标,绘制葡萄糖标准曲线:y=0.0052x+0.010,R2=0.9948,根据回归方程计算出样品中总糖含量为69.39%。
金丝小枣多糖得率计算公式:
多糖得率(%)=M/M0×100 式中:M:干燥后金丝小枣多糖质量(mg);M0:金丝小枣粉末质量(mg)。
1.2.5 扫描电镜(SEM)
取适当多糖使用真空镀金机进行喷金处理后使用扫描电镜对其结构表征进行观察[17]。
1.2.6 傅里叶变换红外光谱分析
取1 mg金丝小枣碱提多糖,与100 mg KBr粉末混合研磨均匀,使用压片机压片,在4000~400 cm−1范围内进行红外光谱扫描[18]。
1.2.7 抗氧化活性的测定
1.2.7.1 DPPH自由基清除率测定
参照张强等[19]的方法稍作修改,取不同浓度金丝小枣多糖溶液(0.1~2 mg/mL)各1 mL,与2 mL 0.2 mmoL/L的DPPH乙醇溶液混合,摇匀,避光反应30 min后,517 nm处测定吸光值,以VC为阳性对照。DPPH自由基清除率计算公式:
DPPH自由基清除率(%)=A0−(A1−A2)A0×100 式中:A0为蒸馏水代替样品的吸光度,A1样品与DPPH溶液的吸光度,A2为蒸馏水代替DPPH溶液的吸光度。
1.2.7.2 超氧阴离子清除率测定
采用邻苯三酚法[20],取不同浓度多糖溶液(0.5~2.5 mg/mL)各1 mL与4.5 mL的Tris-HCl溶液(pH8.2)及25 mmol/L邻苯三酚溶液0.4 mL混合,在25 ℃水浴10 min,加入浓度为8 mol/L盐酸溶液1 mL,在325 nm波长下测定吸光度,以VC为阳性对照。超氧阴离子自由基清除率计算公式:
超氧阴离子自由基清除率(%)=A0−(A1−A2)A0×100 式中:A0为蒸馏水代替样品的吸光度,A1为样品吸光度,A2为蒸馏水替代邻苯三酚的吸光度。
1.3 数据处理
所有实验重复3次,使用SPSS 25.0软件进行方差分析及显著性检验;Design-Expert 11.0对响应面试验结果进行分析;利用GraphPad Prism进行绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素实验结果
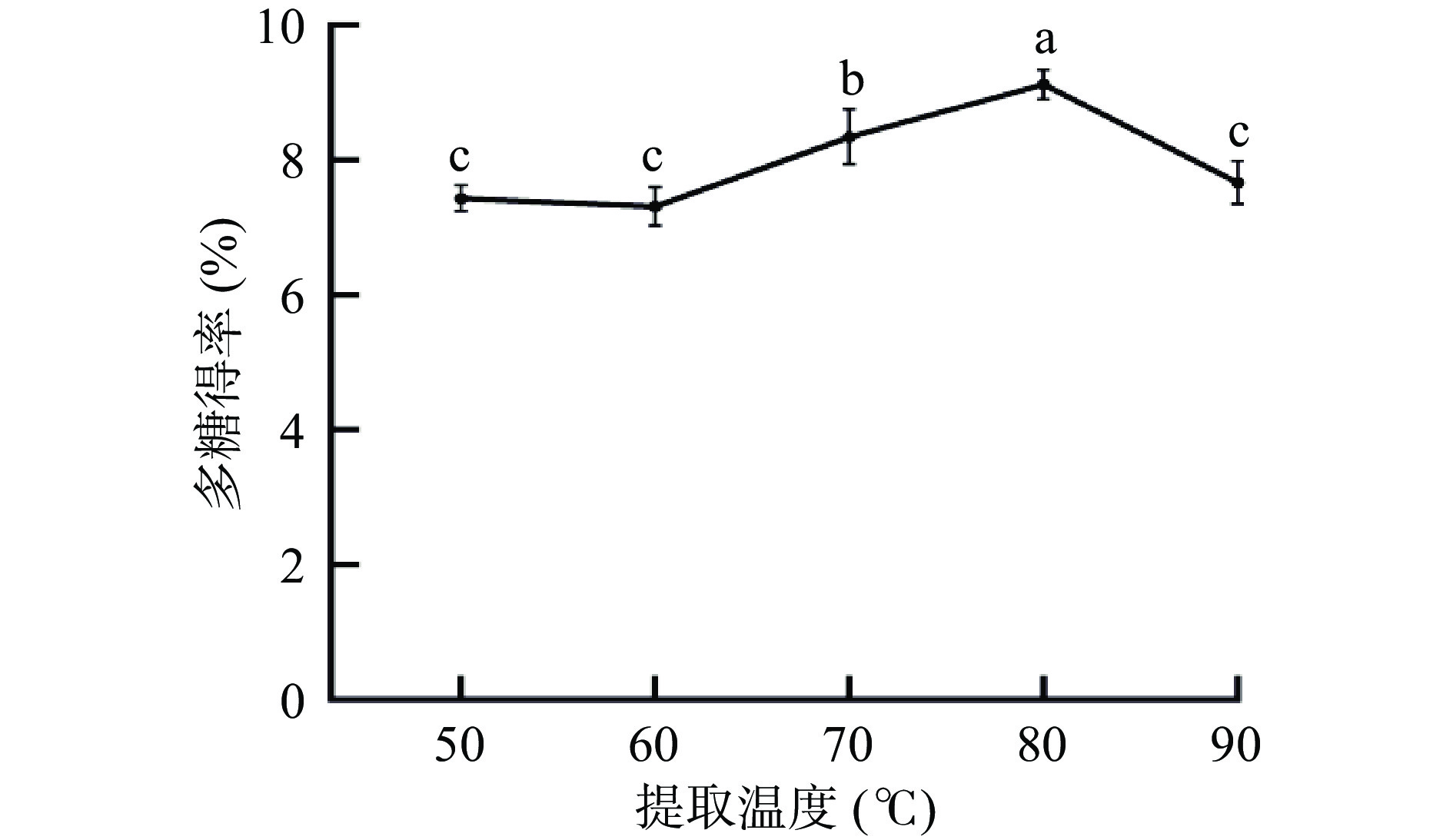
2.1.1 提取温度对多糖得率影响
由图1可知,随着提取温度的升高金丝小枣多糖得率呈先上升后下降的趋势。在提取温度在60~80 ℃之间随着温度的升高多糖溶液黏度减小,多糖得率缓慢上升,当提取温度为80 ℃时,多糖中的分子热运动和扩散加剧,多糖得率达到最大值为9.11%;提取温度为90 ℃多糖得率缓慢下降,这可能与多糖的结构较复杂及稳定性差,遇高温易分解有关[21],因此选择提取温度为70、80、90 ℃进行响应面设计。
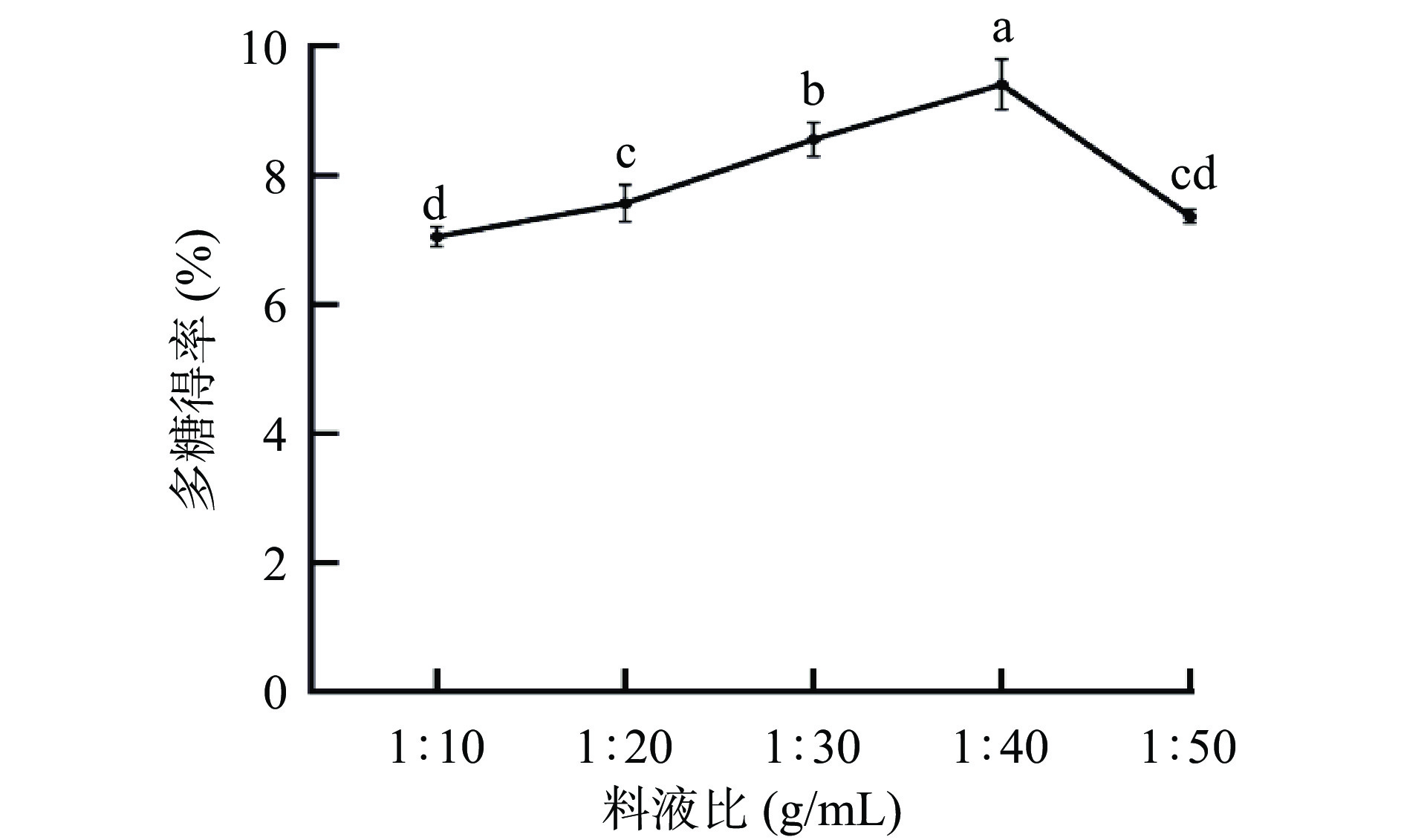
2.1.2 料液比对多糖得率影响
由图2可知,料液比从1:10到1:40(g/mL),金丝小枣多糖得率缓慢上升,当料液比为1:40时,多糖得率为9.55%,提取液的增加可能增大了与枣粉的接触面积,使多糖更易提取出来[22]。随着料液比达到1:50时,其他杂质被提出来占据多糖分子溶出的空间,抑制多糖的溶出,得率出现下降趋势[23]。因此选择料液比为1:30、1:40、1:50 g/mL进行响应面设计。
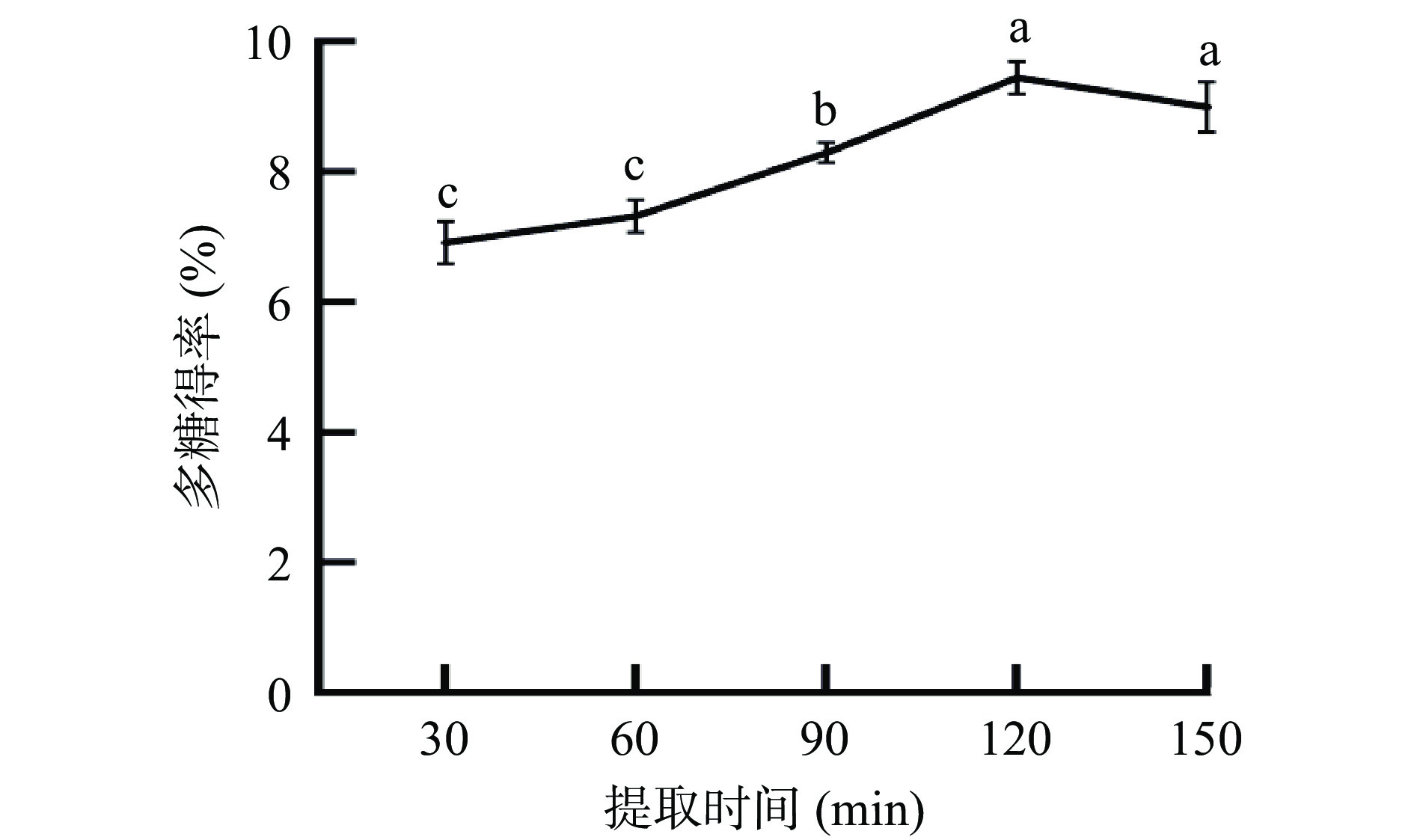
2.1.3 提取时间对多糖得率影响
由图3可知,随着提取时间的增加,多糖从植物细胞中不断地释放出来,其得率不断上升;当提取时间为120 min时多糖得率达到最大值9.5%,再继续延长时间至150 min时多糖得率无显著性变化(P>0.05),呈现饱和的趋势,提取时间过长会造成多糖结构改变,活性降低,因此固定提取时间为120 min,在响应面优化时不再做进一步观察。
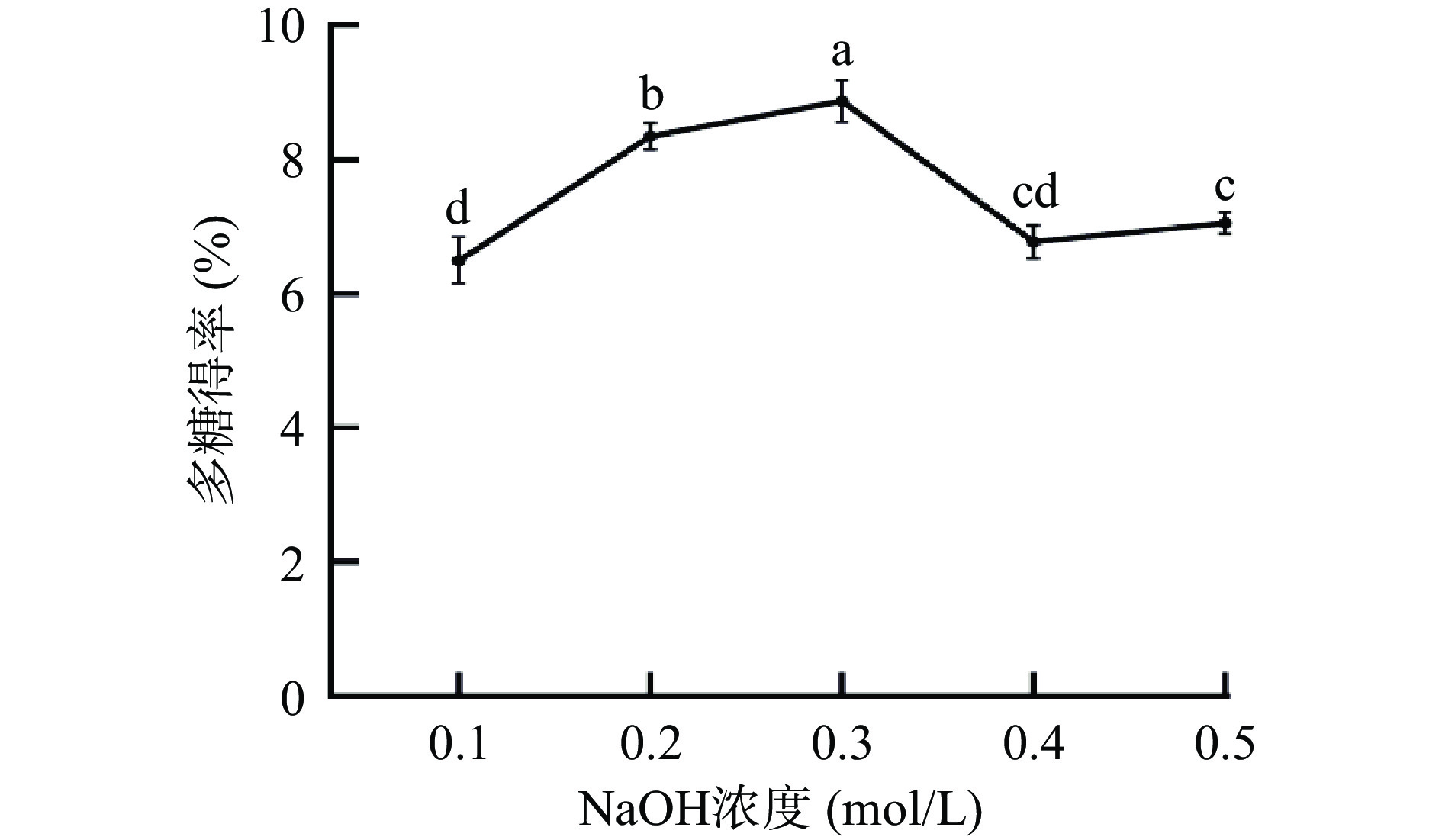
2.1.4 NaOH浓度对多糖得率影响
由图4可知,NaOH提取金丝小枣多糖时碱液浓度在0.1~0.3 mol/L范围内,得率呈现缓慢上升的趋势,碱溶液对细胞壁的破坏,极大地加速多糖从细胞中溢出。NaOH浓度0.3 mol/L时多糖得率为8.75%;随着NaOH浓度的增加,多糖得率出现显著性下降趋势(P<0.05),可能是碱液浓度过高多糖发生脱酯反应[24],破坏其结构引起多糖的降解,因此选择碱液浓度为0.2、0.3、0.4 mol/L进行响应面设计。
2.2 响应面试验结果
在单因素实验结果基础上,固定提取金丝小枣多糖时间为120 min,以NaOH浓度(A)、料液比(B)和提取温度(C)为自变量,金丝小枣多糖得率为响应值,利用Design-Expert 11.0设计三因素三水平Box-Behnken试验,响应面分析结果如表2所示,在此基础上对回归模型进行方差分析结果如表3。
表 2 响应面设计及结果Table 2. Design and results of response surface experiment试验号 A NaOH浓度 B 料液比 C 提取温度 得率(%) 1 −1 −1 0 11.76 2 1 −1 0 10.26 3 −1 1 0 9.71 4 1 1 0 10.19 5 −1 0 −1 10.33 6 1 0 −1 9.28 7 −1 0 1 11.47 8 1 0 1 10.73 9 0 −1 −1 10.18 10 0 1 −1 8.53 11 0 −1 1 10.13 12 0 1 1 11.24 13 0 0 0 11.54 14 0 0 0 11.25 15 0 0 0 11.48 16 0 0 0 11.81 17 0 0 0 11.73 表 3 回归模型方差分析Table 3. Analysis of variance for the regression model变异来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 14.22 9 1.58 19.04 0.0004 ** A-NaOH浓度 0.9870 1 0.9870 11.89 0.0107 * B-料液比 0.8844 1 0.8844 10.66 0.0138 * C-提取温度 3.45 1 3.45 41.51 0.0004 ** AB 0.9801 1 0.9801 11.81 0.0109 * AC 0.0240 1 0.0240 0.2894 0.6073 BC 1.90 1 1.90 22.94 0.0020 ** A² 0.4441 1 0.4441 5.35 0.0540 B² 2.41 1 2.41 29.09 0.0010 ** C² 2.59 1 2.59 31.24 0.0008 ** 残差 0.5811 7 0.0830 失拟项 0.3868 3 0.1289 2.65 0.1845 不显著 纯误差 0.1943 4 0.0486 总和 14.81 16 注:*表示差异显著,P<0.05;**表示差异极显著,P<0.01。 2.2.1 模型的建立及显著性检验
利用统计软件Design-Expert 11.0对表3中实验结果进行多元回归分析,得到二次模型:Y=11.56−0.3513A−0.3325B+0.6563C+0.4950AB+0.0775AC+0.6900BC−0.3248A2−0.7573B2−0.7847C2。
由表3回归模型系数显著性检验结果可看出,该模型P=0.0004<0.01具有极显著性,失拟项的P=0.1845>0.05无显著性,由此可知所建模型适用于金丝小枣多糖的响应面分析。此外模型的一次项A、B,交互项AB显著;一次项C、交互项BC及二次项B2、C2极显著。由回归模型的方差分析结果可知各因素对多糖得率的影响依次为:C>A>B,即提取温度>NaOH浓度>料液比。
2.2.2 响应面分析结果
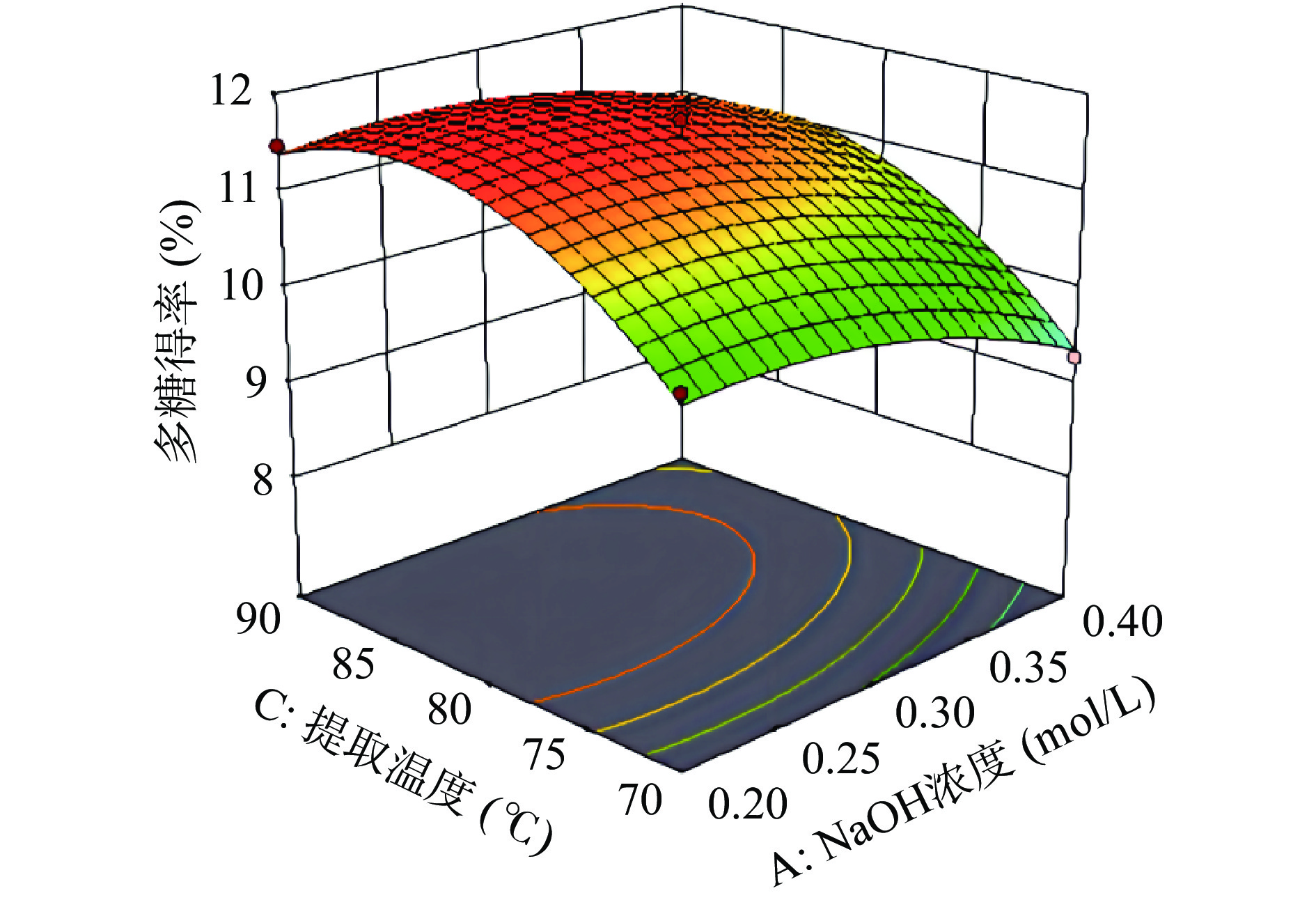
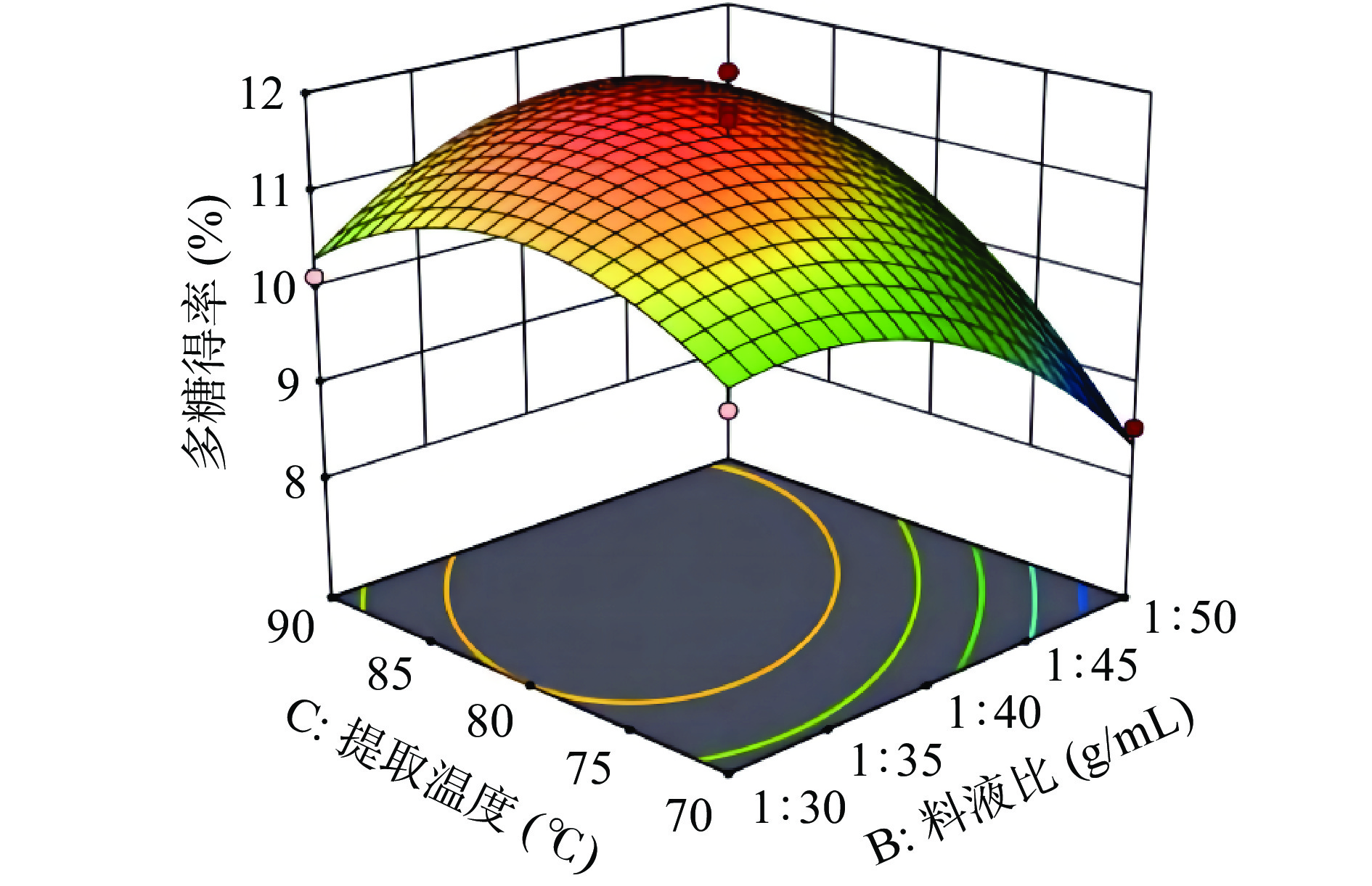
各因素交互作用的响应面图分析,为考察各因素相互作用对金丝小枣碱提多糖得率的影响。通过Design Expert 11.0软件绘制相应的响应面图,结果如图5、图6、图7所示。
从响应面的陡峭程度上可知提取温度与料液比的交互作用接近于椭圆形,表明相互之间作用显著对多糖得率影响较大。提取温度与NaOH浓度的坡度较平缓,表明它的交互作用不显著[25]。通过回归模型的分析,以金丝小枣多糖得率为响应值,使用响应面软件预测金丝小枣碱提多糖的最佳工艺为NaOH浓度0.22 mol/L,料液比1:36.07 g/mL,提取温度为82.05 ℃,预测多糖得率可达11.66%。为实验操作的可行性,确定金丝小枣多糖提取工艺为NaOH浓度0.2 mol/L、料液比为1:35 g/mL、提取温度为80 ℃,在此条件下,重复实验得到金丝小枣多糖的得率为11.44%,理论值与实际得率相差0.22%无显著性差异(P>0.05),结果表明该模型对金丝小枣碱提多糖提取工艺条件参数优化合理。
2.3 扫描电镜(SEM)分析
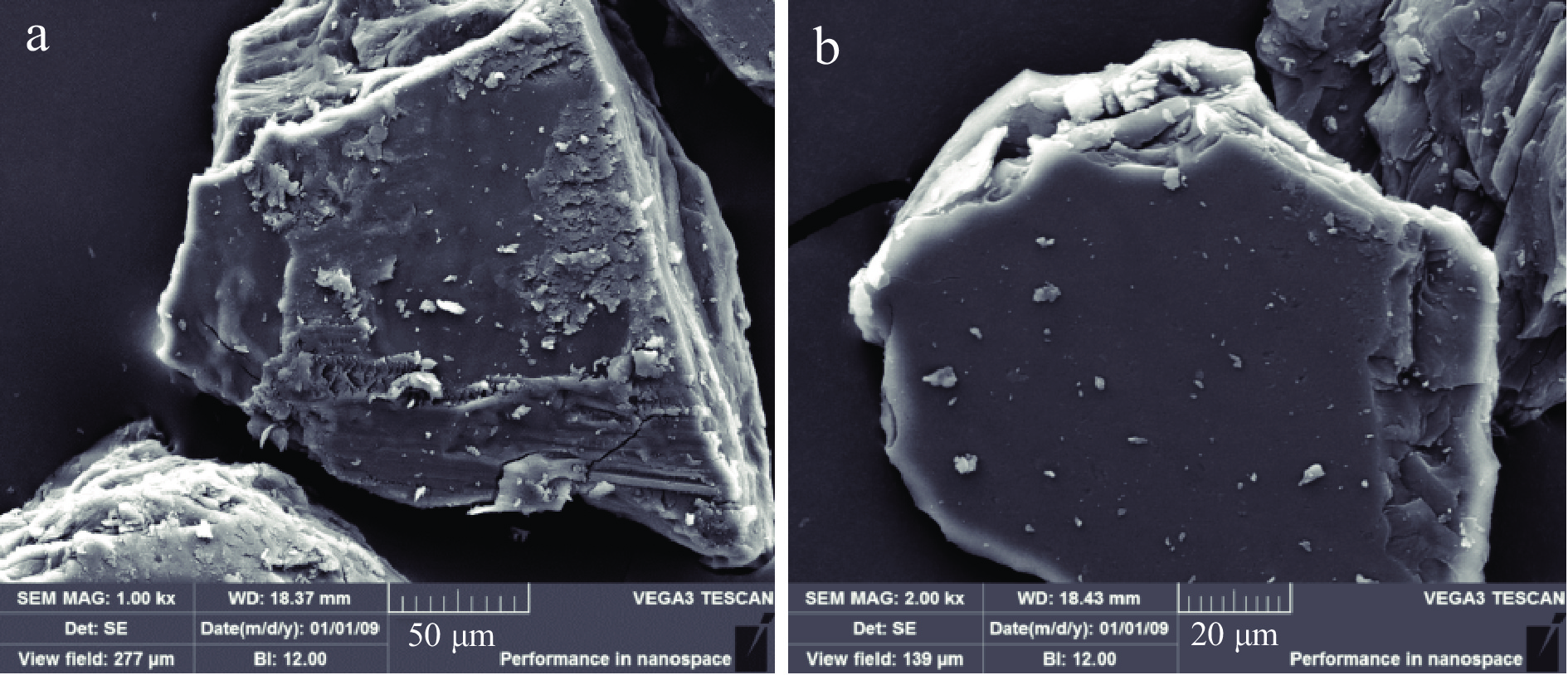
扫描电镜(SEM)主要是观察多糖的表面微观形态特征[26],从图8可知,金丝小枣碱提多糖在扫描电镜中放大1000倍与2000倍观察时,可看出其结构紧密,呈现不规则形状,表面不光滑,为粗糙块状,这可能是碱提的过程中,糖苷键断裂造成多糖表面的形态改变。
2.4 红外光谱扫描
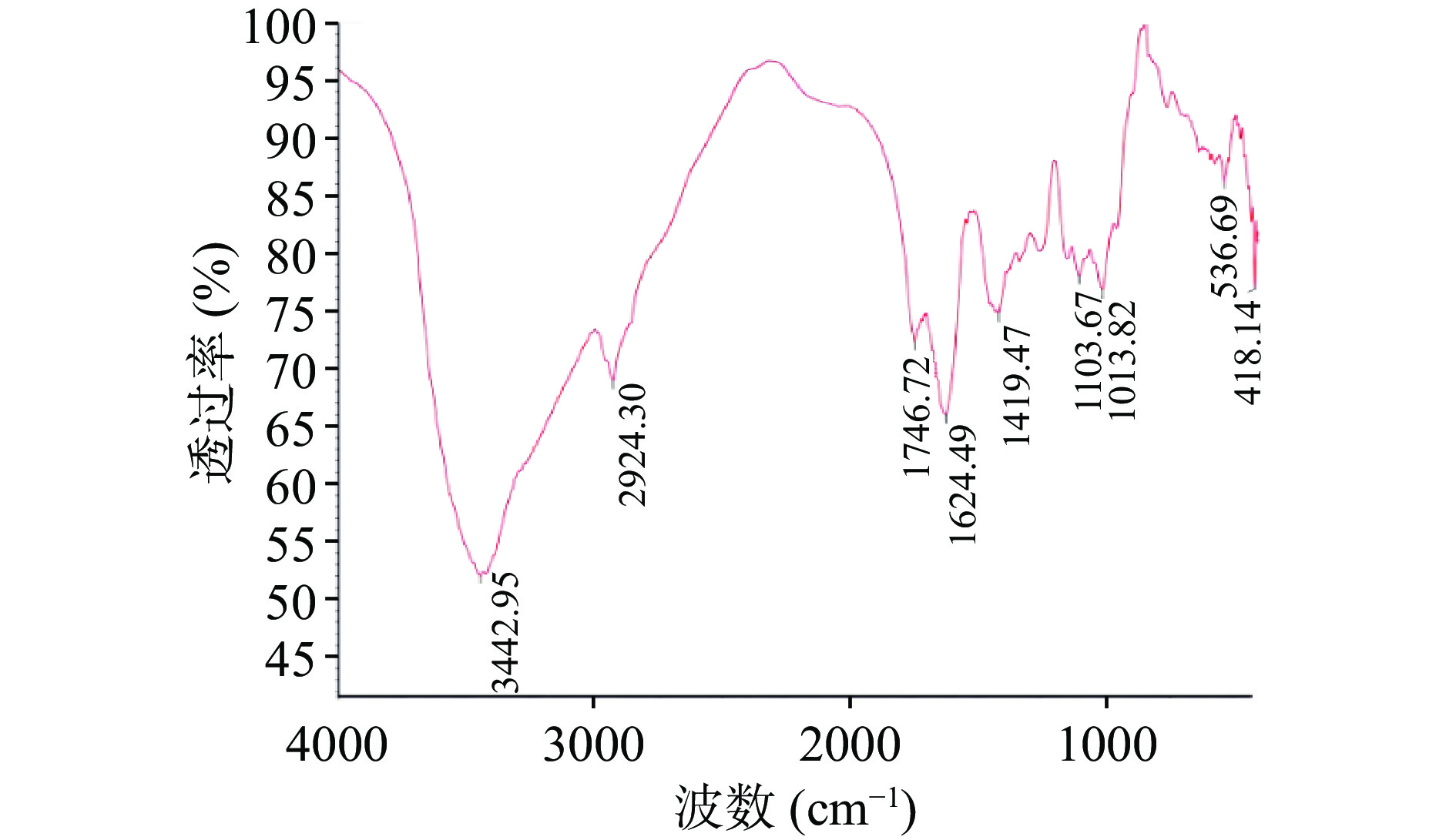
由图9可知,金丝小枣多糖的红外光谱在3442.95 cm−1处有一宽峰,是多糖分子内的氢键中羟基伸缩振动引起的[27];在2924.30 cm−1附近的吸收峰主要是C-H伸缩振动所致[28];在1746.72 cm−1和1624.49 cm−1主要为C=O不对称吸收峰[29],是酸性多糖的特征吸收峰,表明多糖里含有糖醛酸;在1103~1013 cm−1附近的弱吸收峰主要是吡喃环骨架C-O变角振动吸收峰,分子中存在糖环C-O-C及C-O-H结构[30]。根据红外光谱分析结果表明,初步鉴定碱提金丝小枣多糖是含有糖醛酸的吡喃酸性多糖。
2.5 抗氧化活性测定结果
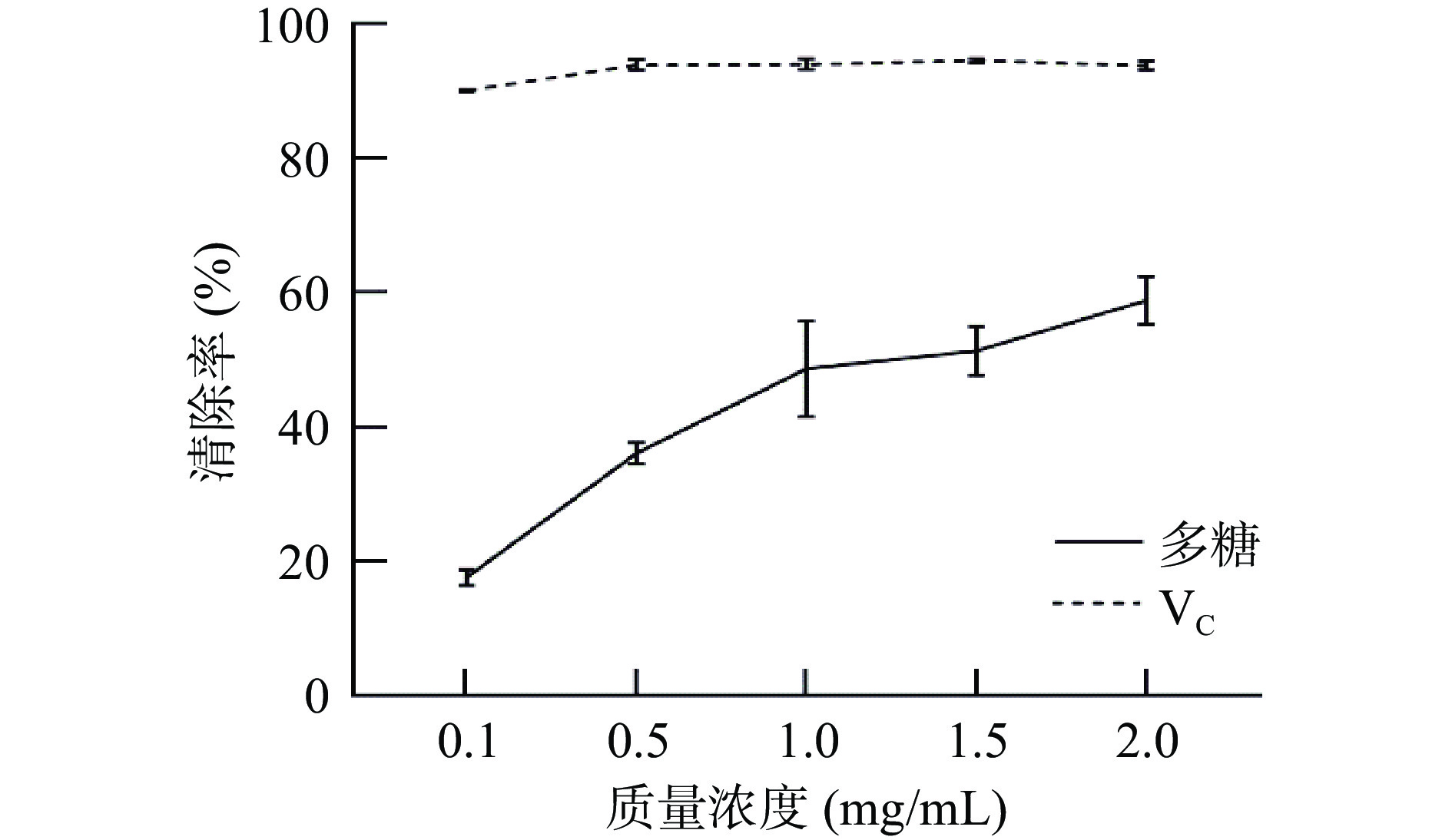
2.5.1 DPPH自由基清除能力
DPPH自由基用于评价短时间内物质的抗氧化活性。由图10可知,金丝小枣多糖对DPPH自由基的清除能力相对VC较弱。当质量浓度为2 mg/mL时,VC的清除率为93.88%;多糖对DPPH自由基的清除率为58.90%,IC50半抑制率为1.201 mg/mL。郭畅等[31]研究发现碱提荔枝草多糖在0.4 mg/mL浓度下,DPPH自由基的清除率为45.02%。表明碱提枣多糖具有一定的清除DPPH自由基活性。
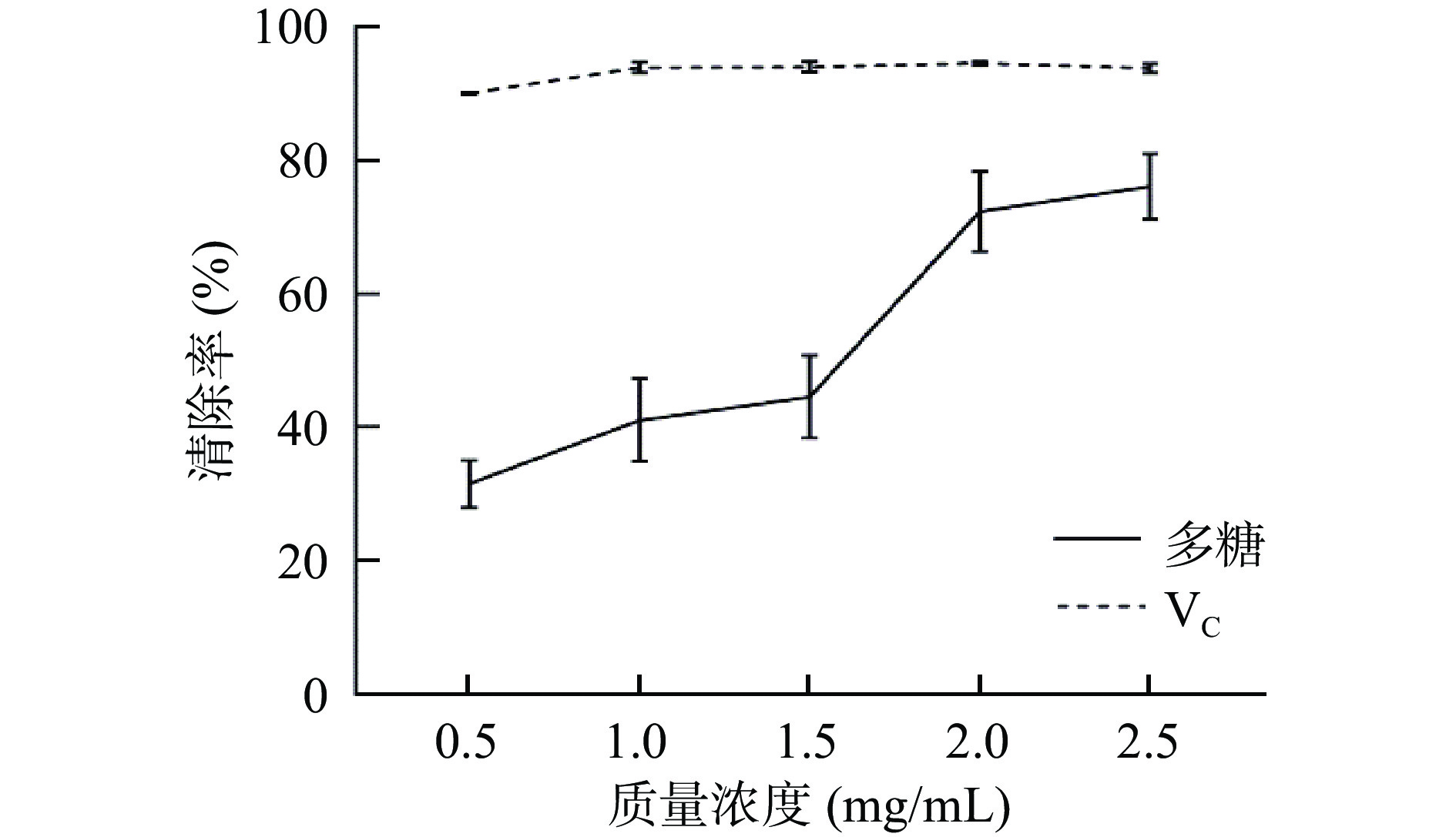
2.5.2 超氧阴离子自由基清除能力
由图11可知,超氧阴离子自由基清除能力与多糖浓度呈正相关,即多糖浓度越高,超氧阴离子自由基清除能力越强。当质量浓度为2.5 mg/mL时,VC对超氧阴离子自由基清除率可达96.84%;多糖对超氧阴离子自由基清除活性为76.13%,IC50值为1.176 mg/mL,研究表明碱提多糖具有较好的抗氧化活性。
3. 结论
本实验采用响应面优化金丝小枣多糖碱提工艺,并对其进行总糖含量、初级结构表征及抗氧化活性研究,在不同因素水平下,金丝小枣多糖得率的影响依次为提取温度>NaOH浓度>料液比,金丝小枣碱提多糖最佳工艺为料液比 1:35(g/mL),提取温度 80 ℃,时间120 min,NaOH浓度为0.2 mol/L,在此条件下多糖的得率为11.44%。红外光谱显示碱提金丝小枣多糖是含有糖醛酸的吡喃酸性多糖。抗氧化实验结果显示,碱提多糖对超氧阴离子及DPPH自由基清除率的IC50为1.176 mg/mL和1.201 mg/mL,表明其具有一定的抗氧化能力,焦中高等[32]研究与传统热水提取法相比,碱提红枣多糖具有较高的抗氧化活性。本研究将为枣多糖在天然抗氧化剂开发利用方面提供理论依据;此外本实验得到的金丝小枣多糖为粗提物,其具体的单一组分、结构与其生理功能之间关系是后续探索及研究的主要方向。
-
表 1 响应面试验的因素与水平
Table 1 Factors and levels of response surface experiment
水平值 因素 A-NaOH浓度(mol/L) B-料液比(g/mL) C-提取温度(℃ ) −1 0.2 1:30 70 0 0.3 1:40 80 1 0.4 1:50 90 表 2 响应面设计及结果
Table 2 Design and results of response surface experiment
试验号 A NaOH浓度 B 料液比 C 提取温度 得率(%) 1 −1 −1 0 11.76 2 1 −1 0 10.26 3 −1 1 0 9.71 4 1 1 0 10.19 5 −1 0 −1 10.33 6 1 0 −1 9.28 7 −1 0 1 11.47 8 1 0 1 10.73 9 0 −1 −1 10.18 10 0 1 −1 8.53 11 0 −1 1 10.13 12 0 1 1 11.24 13 0 0 0 11.54 14 0 0 0 11.25 15 0 0 0 11.48 16 0 0 0 11.81 17 0 0 0 11.73 表 3 回归模型方差分析
Table 3 Analysis of variance for the regression model
变异来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 14.22 9 1.58 19.04 0.0004 ** A-NaOH浓度 0.9870 1 0.9870 11.89 0.0107 * B-料液比 0.8844 1 0.8844 10.66 0.0138 * C-提取温度 3.45 1 3.45 41.51 0.0004 ** AB 0.9801 1 0.9801 11.81 0.0109 * AC 0.0240 1 0.0240 0.2894 0.6073 BC 1.90 1 1.90 22.94 0.0020 ** A² 0.4441 1 0.4441 5.35 0.0540 B² 2.41 1 2.41 29.09 0.0010 ** C² 2.59 1 2.59 31.24 0.0008 ** 残差 0.5811 7 0.0830 失拟项 0.3868 3 0.1289 2.65 0.1845 不显著 纯误差 0.1943 4 0.0486 总和 14.81 16 注:*表示差异显著,P<0.05;**表示差异极显著,P<0.01。 -
[1] 刘孟军, 王玖瑞, 刘平, 等. 中国枣生产与科研成就及前沿进展[J]. 园艺学报,2015,42(9):1683−1698. [LIU M J, WANG J R, LIU P, et al. Historical achievements and frontier advances in the production and research of Chinese jujube (Ziziphus jujuba) in China[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica,2015,42(9):1683−1698. [2] 师仁丽, 翟龙飞, 于文龙, 等. 利用DAD-HPLC和LC-MS法检测金丝小枣中黄酮类化合物[J]. 食品科学,2016,37(16):123−127. [SHI R L, ZHAI L F, YU W L, et al. Determination of flavonoid in Ziziphus jujuba Mill. cv. Jinsixiaozao fruits by DAD-HPLC and LC-MS[J]. Food Science,2016,37(16):123−127. [3] 沈静, 王敏, 苟茜. 不同成熟期灵武长枣酚类组分及抗氧化活性差异分析[J]. 食品科学,2015,36(8):191−195. [SHEN J, WANG M, GOU Q. Changes in phenolic components and antioxidant activity of jujube fruits (Zizyphus jujuba Mill. cv. Lingwuchangzao) during different growth stages[J]. Food Science,2015,36(8):191−195. [4] 胡云峰, 姜晓燕, 崔翰元, 等. 响应面法优化超声波提取灵武长枣中三萜类化合物的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2010,31(5):260−263. [HU Y F, JIANG X Y, CUI H Y, et al. Study on optimization of ultrasonic-extraction conditions of triterpenoids from Lingwu long jujube by RSA[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2010,31(5):260−263. [5] 樊保国. 枣果的功能因子与保健食品的研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2005(9):569−573. [FAN B G. Research status of function factors and health food of Zizyphus jujuba[J]. Food Science,2005(9):569−573. [6] ZHANG Z, ZHANG Y, LIU H, et al. A water-soluble selenium-enriched polysaccharide produced by Pleurotus ostreatus: Purification, characterization, antioxidant and antitumor activities in vitro[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,168:356−370. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.12.070
[7] LI H, FENG Y, SUN W, et al. Antioxidation, anti-inflammation and anti-fibrosis effect of phosphorylated polysaccharides from Pleurotus djamor mycelia on adenine-induced chronic renal failure mice[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,170:652−663. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.12.159
[8] 王晓琴, 冀晓龙, 彭强, 等. 木枣多糖ZJP2的初步结构特征及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 现代食品科技,2016,32(4):100−105. [WANG X Q, JI X L, PENG Q, et al. Primary structural characteristics and antioxidant activity of the polysaccharide ZJP2 from Zizyphus jujuba cv. Muzao[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2016,32(4):100−105. [9] SONG Y, ZHU M, HAO H, et al. Structure characterization of a novel polysaccharide from Chinese wild fruits and its immune-enhancing activity[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,136:324−331. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.06.090
[10] CHANG S C, HSU B Y, CHEN B H. Structural characterization of polysaccharides from Zizyphus jujuba and evaluation of antioxidant activity[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2010,47(4):445−453. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2010.06.010
[11] 林夕梦. 碱提枣渣多糖的结构表征及抗氧化活性研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2020 LIN X M. The structure and antioxidant activity of alkali-extracted jujube pomace from Zizyphus jujuba cv. Muzao[D]. Yangling: Northwest A and F University, 2020.
[12] ZHAO Z, LI J, WU X, et al. Structures and immunological activities of two pectic polysaccharides from the fruits of Ziziphus jujuba Mill. cv. Jinsixiaozao Hort[J]. Food Research International,2006,39(8):917−923. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2006.05.006
[13] HUANG Y Z, CHEN H, ZHANG K F, et al. Extraction, purification, structural characterization, and gut microbiota relationship of polysaccharides: A review[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2022,213:967−986. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.06.049
[14] 李小平, 陈锦屏, 阎雅岚. 红枣多糖提取方法研究进展[J]. 江西农业学报,2007(10):102−104. [LI X P, CHEN J P, YAN Y L. Research progress in extraction method of polysaccharide from jujube date[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi,2007(10):102−104. [15] HUANG S Q, LI J W, WANG Z, et al. Optimization of alkaline extraction of polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidum and their effect on immune function in mice[J]. Molecules,2010,15(5):3694−3708. doi: 10.3390/molecules15053694
[16] YU X H, LIU Z Y YANG J S, et al. Controlling quality of Astragalus polysaccharide meal by combined TLC and phenol-sulfuric acid method[J]. Medicinal Plant,2010(4):58−61.
[17] 张淑杰, 权威, 姜宏伟, 等. 不同纯化程度豌豆水溶性多糖的电镜扫描分析[J]. 农业生物技术学报,2019,27(10):1822−1830. [ZHANG S J, QUAN W, JIANG H W, et al. Analysis of the polysaccharides with different purification levels in pea (Pisum sativum) by scanning electron microscope[J]. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology,2019,27(10):1822−1830. [18] 李健, 张竹青, 陈辉. 气相色谱和红外光谱对金针菇多糖的分析研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2010,31(9):147−149. [LI J, ZHANG Z Q, CHEN H. Analysis of Flammalina velutipes polysaccharide by gas chromatography and infrared spectra[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2010,31(9):147−149. [19] 张强, 韦婉珍, 罗小莉, 等. 响应面优化南酸枣叶多糖的提取工艺及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品研究与开发,2021,42(22):150−156. [ZHANG Q, WEI W Z, LUO X L, et al. Response surface method-assisted extraction and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides from Choerospondias axillaris leaves[J]. Food Research and Evelopment,2021,42(22):150−156. [20] 蔡骏, 李颖, 尹宗宁. 邻苯三酚法测定超氧化物歧化酶缓释片中SOD的活性[J]. 华西药学杂志,2005(1):54−55. [CAI J, LI Y, YIN Z N. Determination of superoxide dismutase activity in its sustained release tablets by pyrograllol autoxidation[J]. West China Medical Journal,2005(1):54−55. [21] 于中玉, 黄佳琪, 宇鹏. 响应曲面法优化超声波辅助提取螺旋藻硒多糖工艺[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2021,32(11):107−112. [YU Z Y, HUANG J Q, YU P. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of selenium polysaccharides from Spirulina using response surface methodology[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Additives,2021,32(11):107−112. [22] 郑植, 庞林江. Box-Behnken响应面法优化超声辅助提取木耳菜果胶及其抗氧化活性分析[J]. 食品科技,2021,46(4):173−179. [ZHENG Z, PANG L J. Optimization of ultrasonic assisted extraction of pectin from Basella rubra by Box-Behnken response surface and the evaluation of antioxidant activity in pectin[J]. Food Science and Technology,2021,46(4):173−179. [23] 章智, 郑娱洁, 季书勤, 等. 响应面法优化栀子花果胶多糖的提取工艺[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2021,32(11):45−52. [ZHANG Z, ZHENG Y J, JI S Q, et al. Optimization of extraction process of gardenia flower pectin polysaccharide by response surface method[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Additives,2021,32(11):45−52. [24] 曾红亮, 张怡, 薛雅茹, 等. 响应面法优化金柑多糖碱提取工艺的研究[J]. 热带作物学报,2015,36(1):179−184. [ZENG H L, ZHANG Y, XUE Y R, et al. Optimization of the alkali extraction technology of Fortunella margarita polysaccharides via response surface methodology[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops,2015,36(1):179−184. [25] 黎云龙, 于震宇, 郜海燕, 等. 骏枣多糖提取工艺优化及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品科学,2015,36(4):45−49. [LI Y L, YU Z Y, GAO H Y, et al. Optimization of extraction process and antioxidant capacity of polysaccharides from Zizyphus jujuba cv. Junzao[J]. Food Science,2015,36(4):45−49. [26] 赵阳, 刘娜, 王园, 等. 蒲公英多糖酶解辅助提取工艺优化及其单糖组成分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(16):199−206. [ZHAO Y, LIU N, WANG Y, et al. Optimization of enzymolysis assisted extraction process of dandelion polysaccharide and its monosaccharide composition analysis[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(16):199−206. [27] ZHANG J Y. Infrared spectrum and gas chromatogram analysis of the polysaccharides separation from mulberry leaves[J]. Science of Sericulture,2007(4):549−552.
[28] HE Y, PENG H, ZHANG H, et al. Structural characteristics and immunopotentiation activity of two polysaccharides from the petal of Crocus sativus[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,180:129−142. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.03.006
[29] YANG W, YING W, LI X, et al. Purification and structural characterization of Chinese yam polysaccharide and its activities[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2015,117(5):1021−1027.
[30] 侯银臣, 叶树才, 梁金明, 等. 长根菇多糖提取工艺及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品科技,2022,47(4):203−208. [HOU Y C, YE S C, LIANG J M, et al. Extraction Technology and in vitro antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Oudemansiella radicata[J]. Food Science and Technology,2022,47(4):203−208. [31] 郭畅, 李超, 侯明明, 等. 荔枝草多糖的提取工艺优化及其体外抗氧化、降血糖活性分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(20):211−219. [GUO C, LI C, HOU M M, et al. Extraction optimization and its inoxidizability and hypoglycemic properties in vitro of polysaccharide from Salvia plebeian R. Br J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(20):211−219.
[32] 焦中高, 张春岭, 刘杰超, 等. 碱提红枣多糖与水提红枣多糖生物活性的比较研究[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2015,6(10):4181−4187. [JIAO Z G, ZHANG C L, LIU J C, et al. Comparison of bioactivities of polysaccharides from Zizyphus jujuba fruit extracted with hot water and alkaline solution[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2015,6(10):4181−4187.





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:



