Effect of Sulfation Modification on Antioxidation and Antitumor Activity of Intracellular Polysaccharide from Chlorella vulgaris
-
摘要: 为探究小球藻多糖硫酸化修饰对生物活性影响,本研究采用小球藻(Chlorella sp.22)为实验材料,提取胞内多糖经DEAE-52纤维素阴离子交换柱分离纯化得到纯化多糖HDB-1,对纯化多糖HDB-1进行硫酸化修饰得SHDB-1,对硫酸化修饰前后多糖进行抗氧化活性和抗肿瘤活性研究。结果表明,纯化组分HDB-1以α-呋喃糖为主。用三氧化硫-吡啶法对HDB-1进行硫酸化修饰得到SHDB-1,其取代度为1.046。抗氧化活性结果表明, HDB-1与SHDB-1的DPPH自由基清除率IC50(半抑制浓度)值分别为29.28 mg/mL和14.49 mg/mL,羟自由基清除率IC50值分别为36.75 mg/mL和28.59 mg/mL,可知SHDB-1抗氧化效果优于HDB-1。抗肿瘤结果表明,HDB-1及SHDB-1在1 mg/mL浓度下对细胞无毒性,HDB-1与SHDB-1的IC50值分别为960.16 μg/mL及658.19 μg/mL,可知SHDB-1抑制宫颈癌细胞Hela增殖效果优于HDB-1。以上结果表明,硫酸化修饰的小球藻胞内多糖SHDB-1与HDB-1相比抗氧化活性及体外抑制癌细胞增殖率都有明显提高。Abstract: In order to explore the effect of Chlorella polysaccharide sulfation modification on biological activity, Chlorella sp.22 was used as experimental material in this study. The purified polysaccharide HDB-1 was obtained by extracting intracellular polysaccharides and separated and purified by DEAE-52 cellulose anion exchange column. The purified polysaccharide HDB-1 was sulfated to obtain SHDB-1. The antioxidant activity and antitumor activity of polysaccharides before and after sulfation modification were studied. The results showed that the purified component HDB-1 was mainly α-furanose. SHDB-1 was obtained by sulfation modification of HDB-1 by sulfur trioxide-pyridine method. Its degree of substitution was 1.046. The antioxidant activity results showed that the IC50 (semi-inhibitory concentration) values of HDB-1 and SHDB-1 DPPH radical clearance were 29.28 mg/mL and 14.49 mg/mL, respectively. The IC50 values of hydroxyl radical scavenging were 36.75 mg/mL and 28.59 mg/mL, respectively, indicating that the antioxidant effect of SHDB-1 was better than that of HDB-1. The antitumor results showed that HDB-1 and SHDB-1 were not toxic to cells at 1 mg/mL concentrations. The IC50 values of HDB-1 and SHDB-1 were 960.16 μg/mL and 658.19 μg/mL, respectively, indicating that SHDB-1 inhibited the proliferation of Hela in cervical cancer cells better than HDB-1. The above results show that compared with HDB-1, the antioxidant activity and in vitro inhibition of cancer cell proliferation of the sulfation-modified Chlorella intracellular polysaccharides SHDB-1 are significantly improved.
-
小球藻(Chlorella)属于色球藻目中的一种单细胞绿藻,类型多样,分布范围广泛,在海水和淡水中均有分布。小球藻细胞内的营养物质含量很高,多糖是小球藻营养物质的重要组成部分之一。小球藻多糖已被报道具有多种生物活性,如抑制病毒、抗肿瘤、免疫调节、降血糖、抗炎和抗氧化等[1-2],被广泛应用于食品、工业、医药等领域,有重要经济和科研价值[3]。多糖作为一种天然抗肿瘤药物,有着副作用小、耐药性低等优点,可作为新型的抗肿瘤药物或与化疗药物联用的辅助药物[4-7]。
多糖是由大量单糖分子通过糖苷键聚合而成的大分子碳水化合物[4]。多糖的硫酸化修饰是一种通过在糖环上用硫酸基团取代其他基团,进而修饰多糖生物活性。多糖的化学基团修饰可以使其内在的生物活性得到改变,继而产生新的功能性质[8]。硫酸化修饰后的多糖在多种生物活性方面具有积极作用[9-11]。张子木等[12]对壶瓶碎米荠多糖进行硫酸化修饰,硫酸化的壶瓶碎米荠多糖的抗氧化能力显著提高。李梦圆等[13]对黄山花菇多糖进行硫酸化修饰,证明了硫酸化修饰可以提高多糖的抑制癌细胞增殖效果。目前鲜有小球藻多糖改性的相关研究,因此本实验对小球藻多糖进行硫酸化修饰,以期改善其生物学活性,为深入研究硫酸化小球藻多糖的分子结构和抗肿瘤活性以及为相关药物的开发提供参考。
本工作拟将小球藻胞内多糖经过DEAE-52纤维素阴离子交换柱进行分离纯化,对多糖纯化组分HDB-1进行结构分析和硫酸化修饰,比较多糖硫酸化改性前后的抗氧化活性和抑癌活性变化规律,以期通过硫酸化修饰来提高多糖的生物活性,为小球藻多糖的进一步开发利用提供实验基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
小球藻Chlorella sp.22 经本实验室分离筛选的藻种[3];1,1-二苯基-2-苦基肼(DPPH) 北京博奥拓达科技有限公司;羟自由基清除能力检测试剂盒 索莱宝生物科技有限公司;DEAE-52 纤维素 上海瑞永生物科技有限公司;胰蛋白酶消化液(0.25%)、Cell Counting Kit-8(CCK-8)试剂盒 苏州新赛美生物科技有限公司。
60 L封闭式光生物反应器 上海光语生物科技有限公司;UV-1800紫外可见分光光度计 上海美谱达仪器有限公司;LGJ-10真空冷冻干燥机 北京松源华兴科技发展有限公司;JY92-Ⅱ超声波细胞粉碎机 宁波新芝生物科技股份有限公司;LC-10A高效液相色谱仪 日本Shimadzu 公司;Nicolet IS10傅里叶变换红外光谱仪 美国ThermoFisher公司;Epoch酶标仪 美国伯腾公司;TG1850-WS台式高速离心机 上海卢湘仪离心机仪器有限公司;HH-4数显恒温水浴锅 常州国华电器有限公司;C184322闪式层析柱、C195324球磨口闪式层析柱 重庆欣维尔玻璃有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 小球藻胞内多糖的提取
小球藻按照10%的接种量接种于f/2培养基,置于25±1 ℃,光照强度4000 Lux条件下进行培养,光暗周期为12 h:12 h,取培养至稳定期的小球藻藻液于8000 r/min条件下离心10 min,弃掉上清液,用蒸馏水反复清洗两遍,离心弃上清,沉淀置于−80 ℃低温冰箱冷冻2 h,真空冷冻干燥得小球藻藻细胞粉末,按照料液比1:25 g/mL的比例加入2%氢氧化钠,设置功率100 W,超声时间4 s,间隔时间4 s条件下进行超声提取20 min,离心取沉淀藻细胞并用细胞破碎仪破碎,80 ℃水浴2 h,之后8000 r/min离心10 min取上清,蒸馏水反复清洗2次,合并上清液。将上清液用旋转蒸发仪浓缩,再用Sevage试剂除蛋白,四倍体积乙醇醇沉,8000 r/min离心10 min取沉淀,真空干燥得到胞内粗多糖。
1.2.2 粗多糖紫外光谱表征
将粗多糖溶液配制成0.1%浓度的溶液,紫外分光光度计扫描200~400 nm的吸光值,以蒸馏水作为对照。
1.2.3 粗多糖分离纯化
采用闪式层析柱以DEAE-52纤维素为填料进行装柱,对小球藻胞内粗多糖通过阴离子交换柱进行分离纯化[14]。取1 g多糖溶于5 mL的超纯水中,用0.22 μm的微孔滤膜过滤除菌。从闪式层析柱上端上样,依次使用纯水、0.2、0.5、0.75、1、2 mol/L的NaCl进行梯度洗脱,控制流速为3 mL/min,并对洗脱液进行收集,每管收集9 mL。采用蒽酮硫酸法检测洗脱液中多糖含量,将不同洗脱液组分收集,再通过3500 Da的透析袋透析除盐48 h,蒸馏浓缩,4倍体积无水乙醇醇沉过夜,冷冻干燥得到6个组分的纯化多糖。
1.2.4 HDB-1硫酸化修饰
1.2.4.1 三氧化硫-吡啶法
量取15 mL吡啶(纯度≥99.5%)加入烧杯中进行冰水浴,冰水浴中边搅拌边加入三氧化硫-吡啶1.5 g,烧杯放于热水浴中常温加热,水浴温度达到90 ℃取出,加入0.25 g HDB-1,55 ℃恒温搅拌3 h,冰水浴冷却至室温,配制2 mol/L的NaOH溶液,使反应液pH至7,通过3500 Da的透析袋透析除盐72 h,醇沉,析出沉淀,4 ℃静置过夜后离心,收集沉淀,冷冻干燥,得到硫酸化修饰多糖SHDB-1[15]。
1.2.4.2 SHDB-1硫酸化取代度测定
采用氯化钡明胶法[16]对SHDB-1取代度进行测定,具体步骤如下:取12支试管分为两组,每一组6支试管分别加入0.6 mg/mL 标准硫酸钾溶液0、40、80、120、160、200 μL,用1 mol/L HCl溶液补齐至200 μL,加0.3%三氯乙酸溶液3.8 mL,第一组试管加入1 mL氯化钡-明胶溶液记为A1,第二组试管加1 mL明胶溶液记为A2,完成后在室温下静置20 min,酶标仪检测360 nm处吸光值。以(A1-A2)绘制硫酸根质量浓度标准曲线,所得标准曲线为Y=6.92X−0.0642,R2=0.9914。
取2 mg硫酸化多糖SHDB-1溶解于1 mL 1 mol/L HCl,沸水浴5 h,于360 nm波长处测定吸光度,根据公式计算取代度(DS)。
DS=1.62×S32−1.02×S 式中:S:样品中硫酸基含量(%);DS:硫酸基取代度。
1.2.5 HDB-1及SHDB-1红外光谱表征
采用KBr压片法进行多糖的红外光谱分析,取HDB-1及SHDB-1各1 mg,加入100 mg干燥的KBr,在玛瑙研钵中研磨,使多糖与KBr充分混匀,经压片机压成透明的薄片[17],用红外光谱仪进行扫描,扫描范围400~4000 cm−1。
1.2.6 HDB-1及SHDB-1抗氧化活性研究
1.2.6.1 DPPH自由基清除能力检测
配制多糖样品质量浓度5、10、20、30、40、45、50 mg/mL,以VC作为阳性对照,取2 mL各浓度样品溶液加入2 mL质量浓度为0.04 mg/mL DPPH溶液,摇匀黑暗条件放置30 min,517 nm下测定吸光值[18]。按照公式计算DPPH清除率。
DPPH自由基清除率(%)=(1−As−AcA0)×100 式中:A0:蒸馏水+DPPH溶液;As:样品待测液+DPPH溶液;Ac:样品待测液+甲醇溶液。
1.2.6.2 羟自由基清除能力检测
配制质量浓度为5、10、20、30、40、45、50 mg/mL的多糖样品溶液,以VC作为阳性对照。根据羟自由基清除能力检测试剂盒说明书测定各浓度样品的羟自由基清除能力[19]。按公式计算羟自由基清除率。
羟自由基清除率(%)=A测−A对A空−A对×100 式中:A测:待测样品吸光值;A对:对照管吸光值;A空:空白管吸光值
1.2.7 细胞毒性试验
取保存于液氮罐中普通Vero细胞,静置于37 ℃的恒温水浴锅中解冻1 min,将解冻后的细胞移入培养瓶内,添加DMEM培养液,置于CO2培养箱中,于37 ℃、5% CO2条件下培养2~3 d[20]。
取Vero细胞培养至对数期,培养瓶加入1 mL 0.25%胰蛋白酶消化液消化30 s,显微镜下观察细胞形态,细胞收缩,立即加入DMEM培养基终止消化。转移到新的离心管中,离心去除培养液后用PBS悬浮计数[21]。配制多糖培养液:用DMEM培养液将小球藻胞内多糖配制成0.1、0.2、0.5、1.0、2.5、10 mg/mL的细胞培养液,以正常的细胞培养液为阴性对照。以每孔200 μL的量加入到96 孔板当中,每孔细胞数约为1.0×105 个。再放置到细胞培养箱中,在浓度为5% CO2、温度37 ℃的条件下培养24 h。采用CCK-8(Cell Counting Kit-8)试剂盒检测细胞增殖抑制率。弃掉96孔原有细胞培养基,用PBS缓冲液清洗96孔板1~2次,每孔加入100 μL细胞培养基和10 μL CCK-8溶液,细胞培养箱孵育1 h。酶联免疫检测仪在450 nm下测定吸光值,计算Vero细胞的相对存活率。
1.2.8 多糖抑制宫颈癌细胞Hela增殖活性试验
取保存于液氮罐中宫颈癌细胞Hela,活化方式同1.2.7。
取宫颈癌细胞Hela,加1 mL胰酶细胞消化液消化20 s,显微镜下观察至细胞收缩时停止消化,加入DMEM培养基吹打均匀,每孔200 μL接种于96板,使每孔细胞数为1.0×105 个。细胞培养箱培养24 h。配制多糖培养液:用DMEM培养基将小球藻多糖HDB-1及SHDB-1配制成低浓度(100 μg/mL)、中浓度(500 μg/mL)、高浓度(1000 μg/mL)三种浓度的多糖细胞培养基。采用CCK-8(Cell Counting Kit-8)试剂盒检测细胞增殖抑制率。弃掉96孔原有细胞培养基,用PBS缓冲液清洗96孔板1~2次,每孔加入100 μL细胞培养基和10 μL CCK-8溶液,细胞培养箱孵育1 h。酶联免疫检测仪在450 nm下测定吸光值,按公式计算抑制率。
抑制率(%)=Ac−AsAc−Ab×100 式中:Ab:空白组,含DMEM培养基、CCK-8,不含细胞;Ac:对照组,含细胞、DMEM培养基、CCK-8溶液;As:试验组;含多糖细胞培养基、细胞、DMEM培养基、CCK-8溶液。
1.3 数据处理
IC50预测采用IBM SPSS Statistics 25软件。本试验所作图谱均采用OriginPro 9.1软件作图,且每个试验均做3个重复。
2. 结果与分析
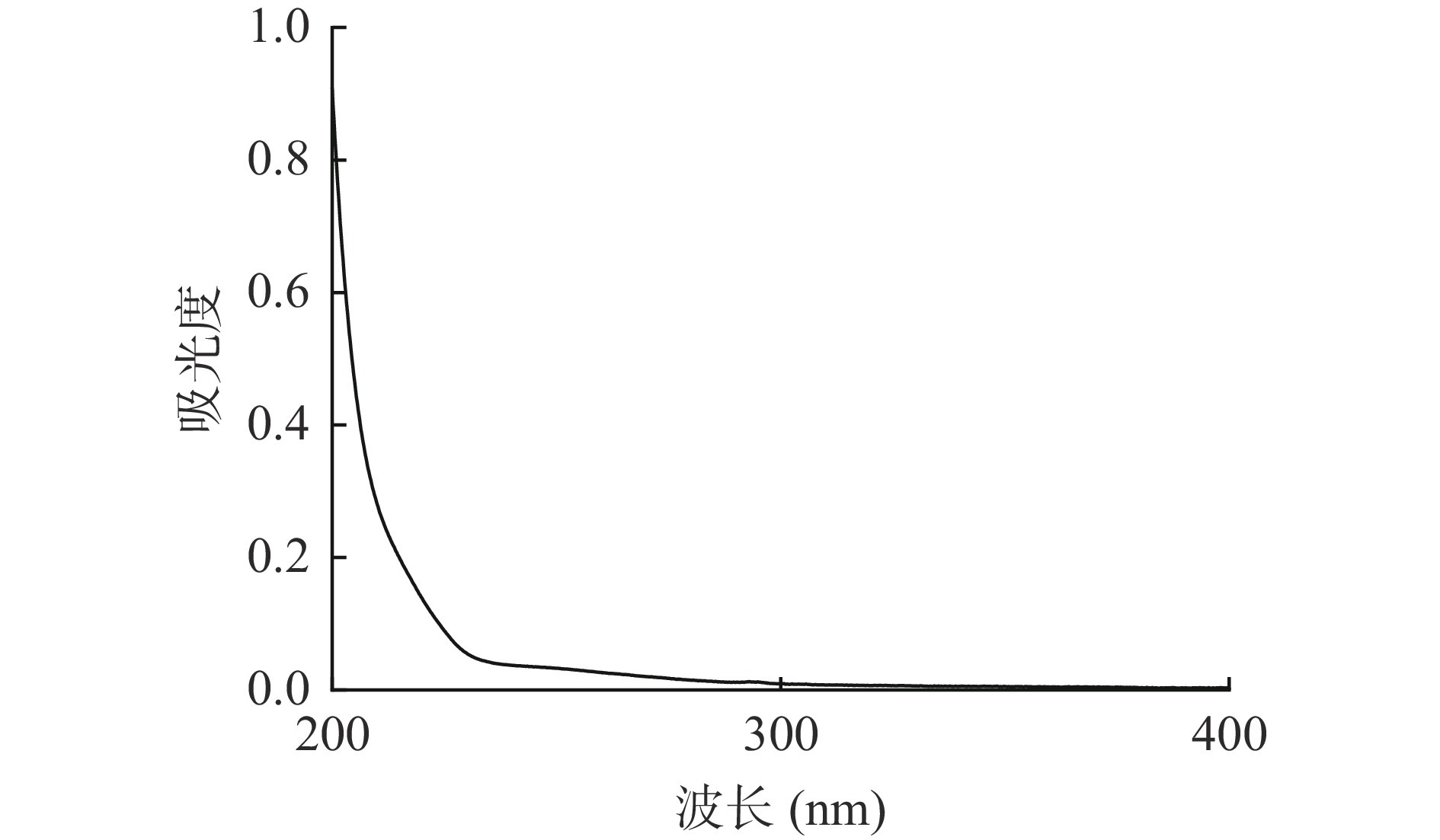
2.1 粗多糖紫外光谱分析
紫外光谱结果如图1所示,多糖溶液在260~280 nm处并无蛋白质及核酸特征峰,说明除去了多糖中的蛋白质和核酸[22]。
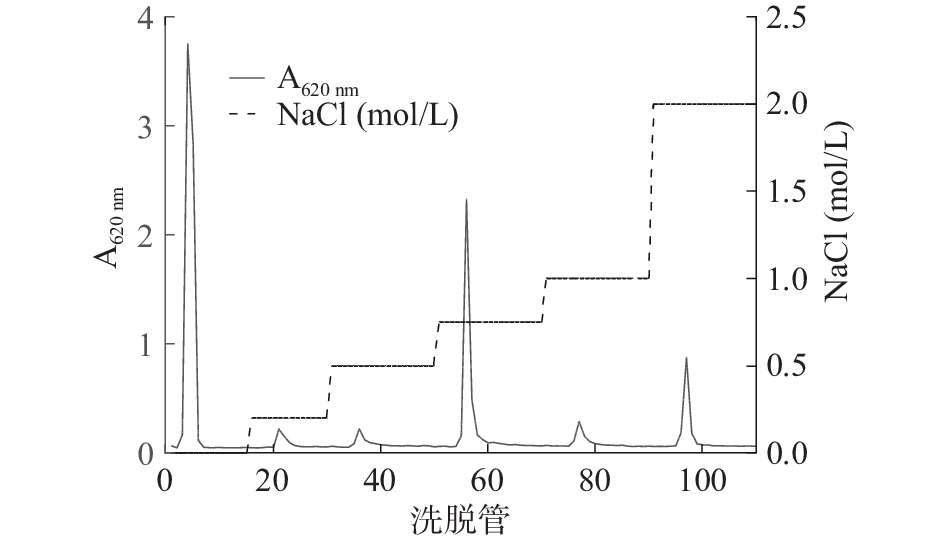
2.2 粗多糖分离纯化
提取的小球藻胞内多糖经Sevage试剂除蛋白、透析袋透析除盐、真空冷冻干燥后,上样于DEAE-52阴离子交换柱,用不同浓度的NaCl洗脱得到的洗脱曲线如图2,分离纯化共得到六个不同的洗脱峰,按出峰时间分别命名为HDB-1、HDB-2、HDB-3、HDB-4、HDB-5、HDB-6。从结果可以看出,不同的NaCl浓度均有洗脱峰出现,其中HDB-1是用超纯水洗脱的组分,是不带电荷的中性多糖组分,其中HDB-1、HDB-4、HDB-5、HDB-6洗脱峰对称,无拖尾现象,说明分离结果理想[23];HDB-2、HDB-3洗脱峰不对称,有拖尾现象,说明分离不理想,多糖成分不够均一。DEAE-52阴离子交换柱分离原理是根据样品负电荷量的数量进行分离,本次分离的六个组分中,HDB-1为中性多糖,HDB-2、HDB-3、HDB-4、HDB-5、HDB-6都是带有不同程度负电荷的多糖,根据负电荷数量大小排序为HDB-6、HDB-5、HDB-4、HDB-3、HDB-2,回收6个纯化组分,冷冻干燥后,HDB-1回收率最高,因此本研究用多糖含量最多的HDB-1组分进行深入研究。
2.3 SHDB-1硫酸化取代度测定
三氧化硫-吡啶法硫酸化修饰得多糖SHDB-1,多糖取代度为1.046,以其进行红外光谱分析及生物活性研究。
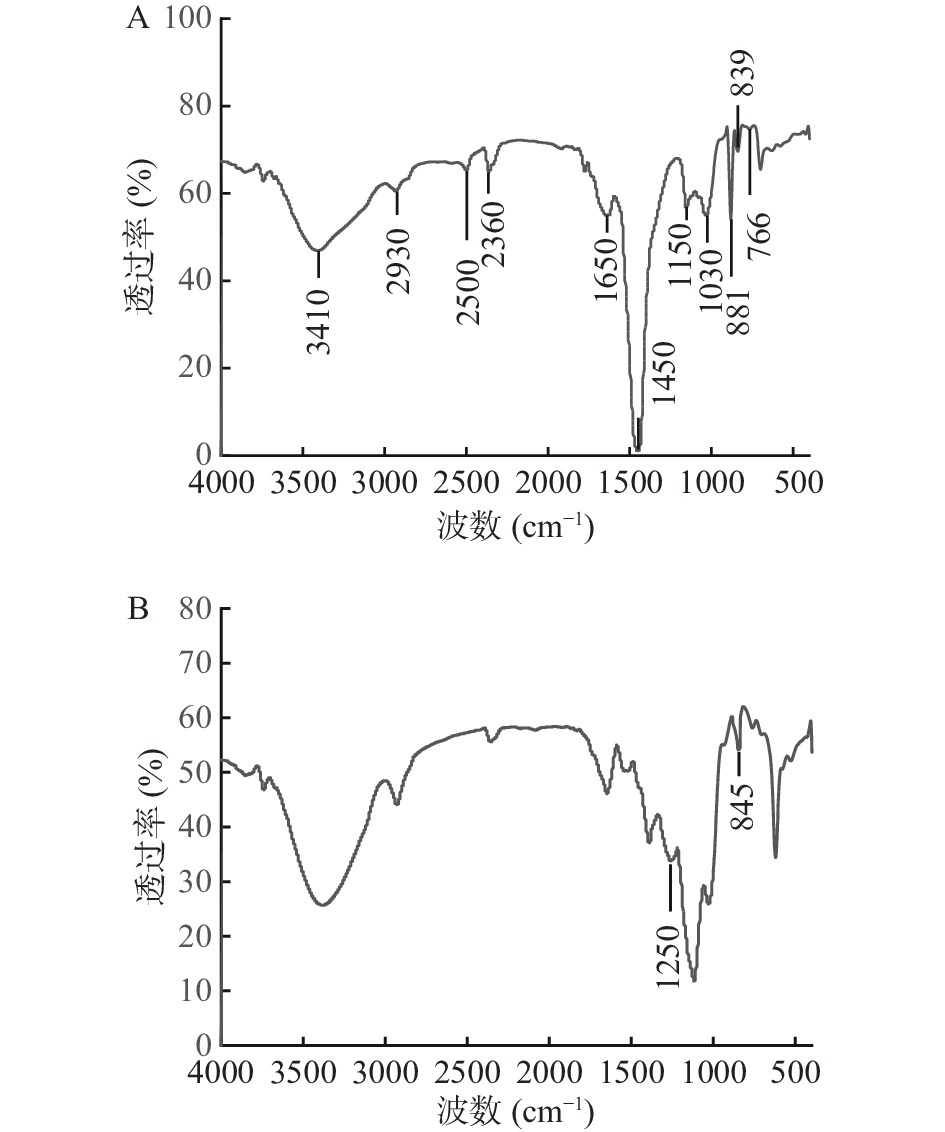
2.4 HDB-1及SHDB-1红外光谱分析
HDB-1的红外光谱图如图3A所示,在3410 cm−1和2930 cm−1附近的峰分别是由-OH拉伸振动和C-H拉伸振动引起的[3]。在1650 cm−1处有C=O伸缩振动吸收峰,在1450 cm−1处存在C-H弯曲振动吸收峰[24]。在1200~1000 cm−1区域内,出现两个呋喃糖吸收峰,1150 cm−1附近是呋喃糖的呼吸振动特征峰[25],HDB-1红外光谱在1150 cm−1和1030 cm−1处有两个特征吸收峰,因此HDB-1为呋喃糖,在红外光谱分析(IR)中,在844±8 cm−1处为α-糖苷键的特征吸收峰,在891±7 cm−1为β-糖苷键的特征吸收峰[26],HDB-1在839 cm−1处有吸收峰,表明有α-糖苷键存在。推测HDB-1是以α-呋喃糖为主的多糖。
小球藻硫酸化修饰多糖(SHDB-1)的红外光谱如图3B所示。相对于小球藻胞内多糖HDB-1的红外光谱来看,在SHDB-1的1250和845 cm−1处出现的新吸收峰,可能是由于在糖环上S=O伸缩振动及C-O-S的拉伸振动引起的[13],说明小球藻多糖SHDB-1实现硫酸化修饰。
2.5 HDB-1及SHDB-1抗氧化活性分析
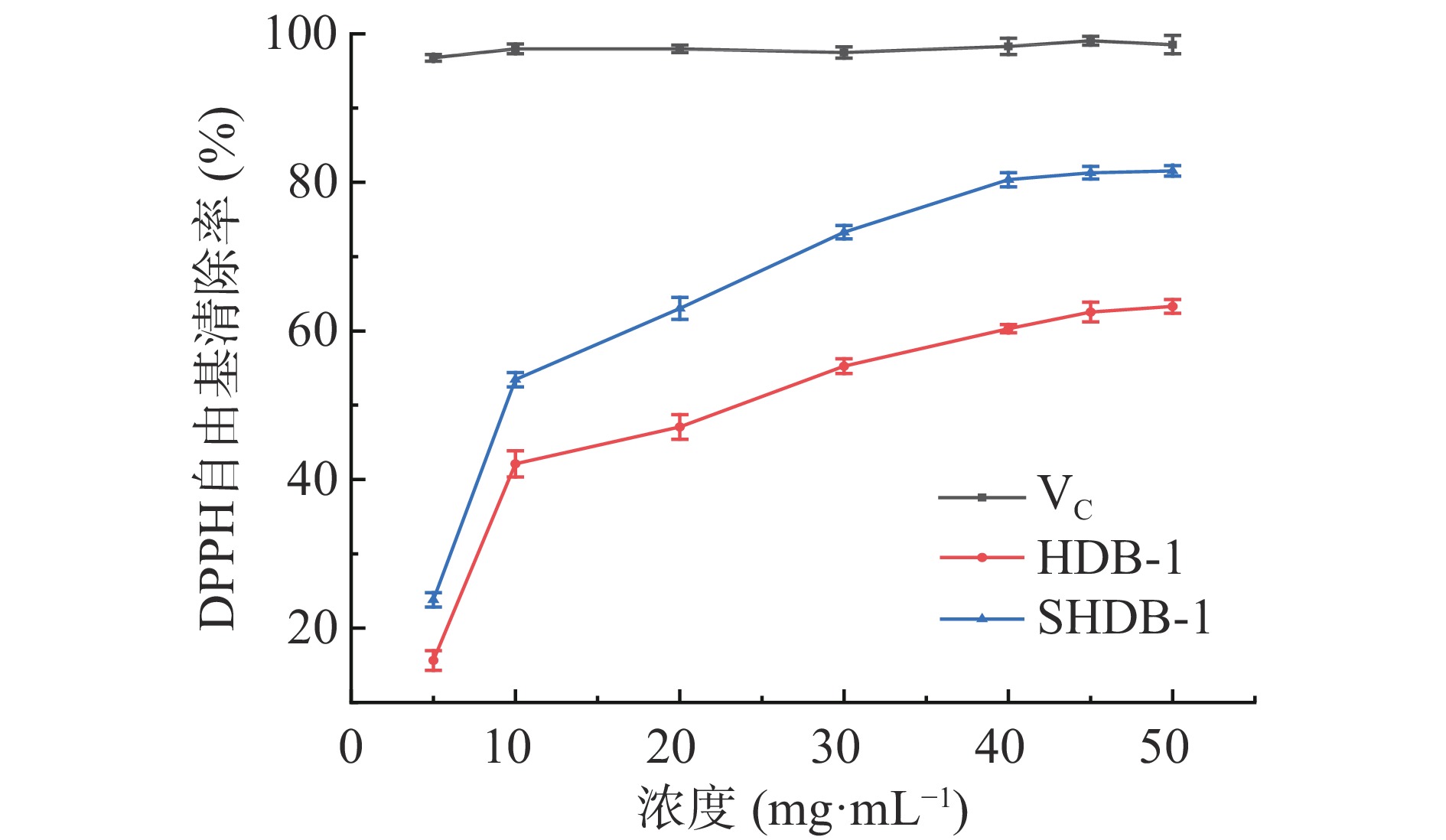
2.5.1 DPPH自由基清除能力
DPPH是一种紫色的稳定自由基[27],可以与氧化剂发生还原反应,导致褪色变为浅黄色,自由基清除率越高,表明物质的抗氧化活性越强[28]。由图4可见,HDB-1的最大清除率为63.3%±0.92%,IC50=29.28 mg/mL;SHDB-1最大清除率为81.53%±0.71%,IC50=14.49 mg/mL,但清除能力始终小于VC。相较于未改性的HDB-1,经过硫酸化修饰后的SHDB-1对DPPH自由基的清除能力有所提高,这说明进行硫酸化修饰过的多糖对DPPH自由基清除率有明显的提高作用。
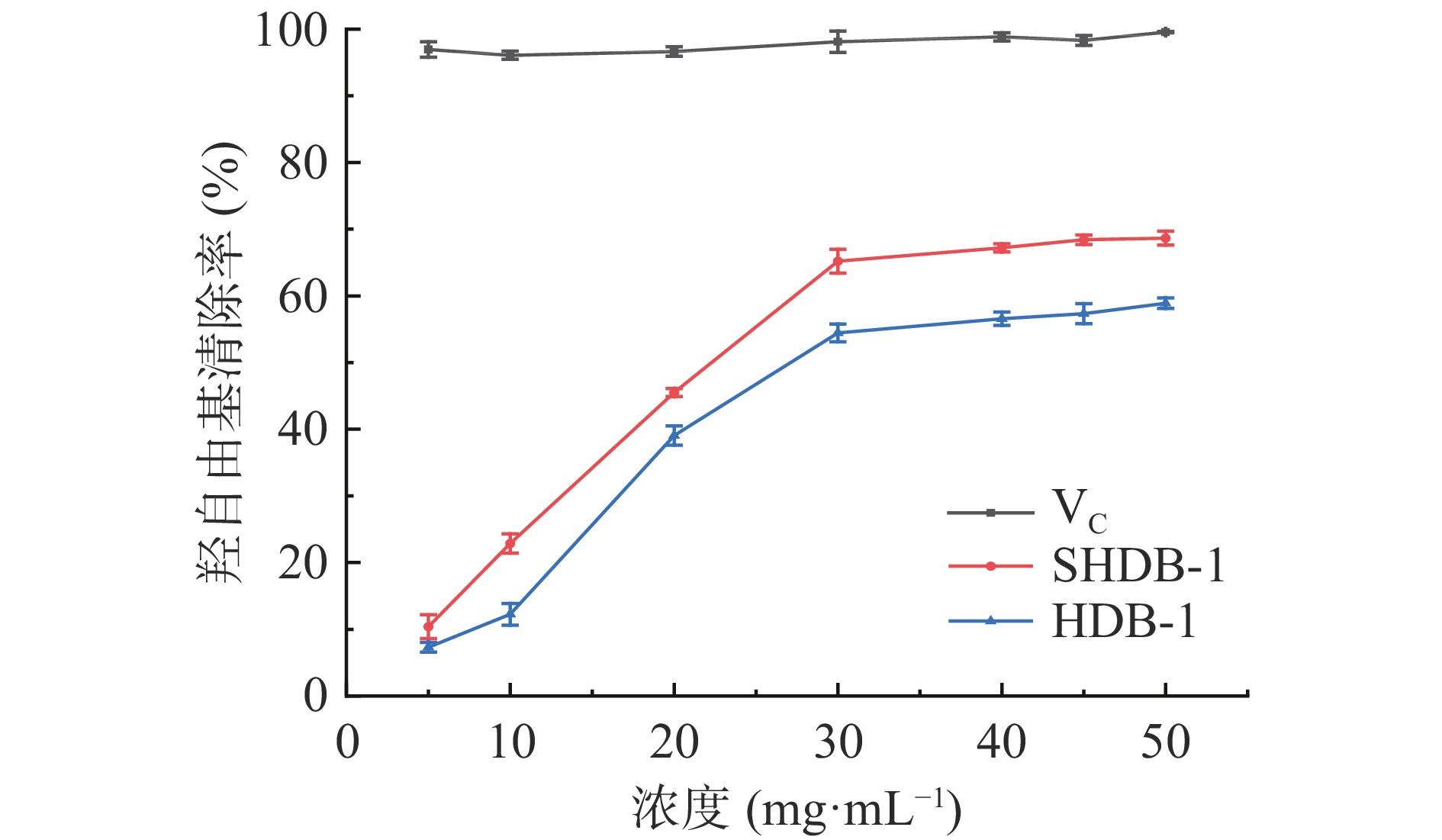
2.5.2 羟自由基清除能力
羟自由基能作用于体内蛋白、核酸等生物分子[29],造成细胞结构功能的损伤,导致突变、致癌,从而使得人体产生疾病,羟自由基的清除率是抗氧化能力的一项重要指标[24]。由图5可知,HDB-1最大清除率达为58.89%±0.78%,IC50=36.75 mg/mL,SHDB-1最大清除率为68.65%±1.05%,IC50=28.59 mg/mL,在设置的浓度范围内,羟自由基的清除能力随着浓度的增加而增加,但清除能力始终小于VC,其中相较于未改性的HDB-1,经过硫酸化修饰后的SHDB-1在羟自由基清除能力上都有所提高,这说明进行硫酸化修饰过的多糖对羟自由基清除率有明显的提高作用。
2.6 细胞毒性试验
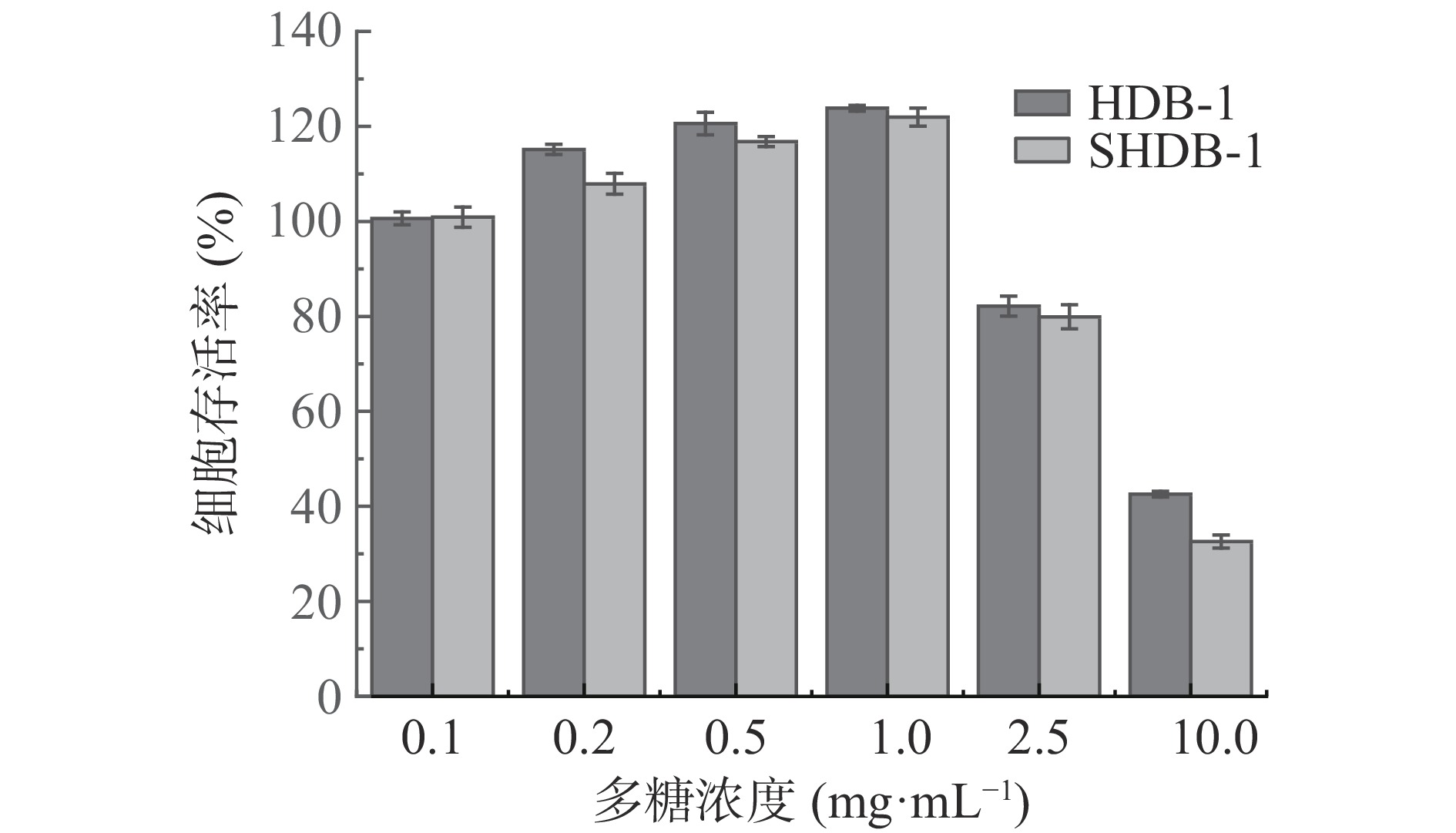
由图6可知,在设置的低浓度组别下(0.1、0.2、0.5、1.0 mg/mL),小球藻多糖(HDB-1)和硫酸化修饰多糖(SHDB-1)对Vero细胞均无毒性,且稍微对Vero细胞有促进作用,HDB-1的促进作用相对较高,但效果均不显著(P>0.05)。当多糖浓度相对较高(2.5、10.0 mg/mL)时,对Vero细胞生长已经有了较大影响,在10.0 mg/mL时对Vero细胞的存活率已经低于50%。
2.7 抗肿瘤活性
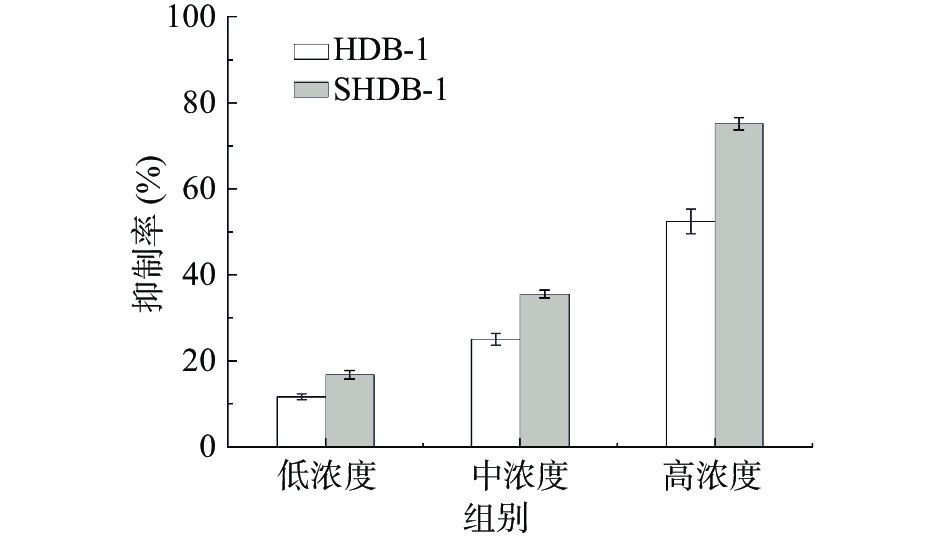
细胞毒性试验结果(图7)表明,HDB-1及SHDB-1在1 mg/mL浓度下,对细胞无毒性作用,并设置三个浓度组别。抗肿瘤活性结果分析可得,HDB-1的IC50(半抑制浓度)值为960.16 μg/mL, SHDB-1的IC50值为658.19 μg/mL,可知SHDB-1抑制宫颈癌细胞Hela增殖效果优于HDB-1。
3. 结论
小球藻胞内多糖经DEAE-52纤维素阴离子交换柱分离纯化得到六个纯化多糖组分。用三氧化硫-吡啶法对小球藻胞内多糖纯化组分HDB-1进行硫酸化修饰得SHDB-1,红外光谱结果显示硫酸化修饰成功。硫酸化修饰取代度为1.046。
对SHDB-1和HDB-1抗氧化活性初步研究,结果表明,HDB-1和SHDB-1均具有一定的抗氧化活性,且多糖经硫酸化修饰后抗氧化能力有所提高。体外抑制宫颈癌细胞增殖试验表明,三种浓度下,SHDB-1及HDB-1都有明显的抑制细胞增殖效果,硫酸化修饰多糖SHDB-1在三种浓度下的抑制宫颈癌细胞增殖率均高于小球藻多糖HDB-1。
本试验通过对小球藻多糖进行硫酸化修饰,证明小球藻多糖糖环上硫酸基团对抗氧化活性和抑制宫颈癌细胞增殖有着重要作用。本试验为进一步加强小球藻多糖抗氧化活性提供有益的参考,为天然抗癌药物的研发提供试验基础。
-
[1] KUSAIKIN M I, ERMAKOVA S P, SHEVCHENKO N M, et al. Structural characteristics and antitumor activity of a new chrysolaminaran from the diatom alga Synedra acus[J]. Chemistry of Natural Compounds,2010,46:1−4. doi: 10.1007/s10600-010-9510-z
[2] SONG L, CHEN X, LIU X, et al. Characterization and comparison of the structural features, immune-modulatory and anti-avian influenza virus activities conferred by three algal sulfated polysaccharides[J]. Marine Drugs,2016,14(1):4.
[3] 吴思伟, 李思雨, 孙寒, 等. 一株产胞外多糖微藻的分离鉴定及其多糖抗氧化活性的研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(24):193−200. [WU S W, LI S Y, SUN H, et al. Isolation and identification of an exopolysaccharide-producing microalgae strain and its antioxidant activity[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(24):193−200. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.027350 [4] 王文丽, 张金玲, 魏亚宁, 等. 天然多糖提取、纯化及生物活性研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(22):470−480. [WANG W L, ZHANG J L, WEI Y N, et al. Extraction, purification, and bioactivity of natural polysaccharides: A review[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(22):470−480. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021120256 [5] 刘思扬, 陆雅琦, 海日汉, 等. 功能性植物多糖及其应用研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(21):444−453. [LIU S Y, LU Y Q, HAI R H, et al. Research progress on plant functional polysaccharides and its application[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(21):444−453. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021110234 [6] YUE Y U, SHEN M, SONG Q, et al. Biological activities and pharmaceutical applications of polysaccharide from natural resources: A review[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2018,18:91−101.
[7] 王祺瑶, 卢畅, 彭婵妮, 等. 海藻岩藻多糖抗肿瘤活性研究新进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(7):2043−2050. [WANG Q Y, LU C, PENG C N, et al. Recent progress on the antitumor activity of fucoidan[J]. Food Safety and Quality Detection Technology,2022,13(7):2043−2050. [8] DENG C, FU H, XU J, et al. Physiochemical and biological properties of phosphorylated polysaccharides from Dictyophora indusiata[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2015,72:894−899. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.09.053
[9] LH A, MS A, GAM B, et al. Sulfated polysaccharides: Mmunomodulation and signaling mechanisms[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2019,92:1−11.
[10] WANG Z, XIE J, SHEN M, et al. Sulfated modification of polysaccharides: Synthesis, characterization and bioactivities[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2018,74:147−157.
[11] HUO Y F, WANG H L, WEI E H, et al. Two new compounds from the roots of Scrophularia ningpoensis and their anti-inflammatory activities[J]. Journal of Asian Natural Products Research,2019,21(11):1083−1089.
[12] 张子木, 黄秀芳, 张琴, 等. 壶瓶碎米荠多糖硫酸化结构修饰及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中国粮油学报,2021,36(12):28−33. [ZHANG Z M, HUANG X F, ZHANG Q, et al. Sulfated structure modification and antioxidant activity of Cardamine hupingshanensis polysaccharide[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2021,36(12):28−33. [13] 李梦圆, 徐金龙, 刘咏, 等. 黄山花菇多糖硫酸化修饰条件的优化及修饰产物抗肿瘤活性研究[J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版),2020,43(7):992−995, 1008. [LI M Y, XU J L, LIU Y, et al. Optimization of sulfated modification condition of polysaccharides from Huangshan floral mushroom and determination of antitumor activity of modified products[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2020,43(7):992−995, 1008. [14] 张霞, 白月明, 谢雪勤, 等. 铁皮石斛多糖分离纯化及其药理活性研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(24):412−422. [ZHANG X, BAI Y M, XIE X Q, et al. Research progress on isolation, purification and pharmacological activities of Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(24):412−422. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021110318 [15] 刘燕琼, 黄雪松. 硫酸化大蒜多糖的制备及其鉴定[J]. 食品科学,2007(2):91−94. [LIU Y Q, HUANG X S. Preparation of sulfated garlic polysaccharide and identification by spectrum[J]. Food Science,2007(2):91−94. [16] 程浩. 大蒜多糖衍生物的制备及抗氧化活性研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆师范大学, 2020. CHENG H. Preparation and antioxidant activity of garlic polysaccharide derivatives[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Normal University, 2020.
[17] 陈晓清, 郑怡, 苏育才. 海水小球藻抗菌多糖的分离纯化[J]. 食品科技,2012,37(4):168−170. [CHEN X Q, ZHENG Y, SU Y C. Isolation and purication of antimicrobial polysaccharides from Chlorella pacifica[J]. Food Science and Technology,2012,37(4):168−170. [18] 杨海燕, 李洁琼, 刘红全, 等. 小球藻 EC04 产胞内多糖条件优化及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 热带海洋学报,2019,38(6):98−104. [YANG H Y, LI J Q, LIU H Q, et al. Study on the optimum conditions for polysaccharide production of Chlorella EC04 and its antioxidant activity analysis[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography,2019,38(6):98−104. [19] WANG L, LI X Y, WANG B B, et al. Synthesis, characterization and antioxidant activity of selenium modified polysaccharides from Hohenbuehelia serotina[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,120:1362−1368.
[20] 钟闰, 吴思伟, 何秀苗, 等. 杜氏盐藻胞外多糖抗肿瘤活性及其机制研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(22):126−133. [ZHONG R, WU S W, HE X M, et al. Antitumor activity and mechanism of exopolysaccharide from Dunaliella salina[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(22):126−133. [21] ZHONG R, LI J Q, WU S W, et al. Transcriptome analysis reveals possible antitumor mechanism of Chlorella exopolysaccharide[J]. Gene,2021,779(Suppl 4):145494.
[22] 贾红倩, 刘嵬, 颜军, 等. 杏鲍菇多糖的分离纯化、乙酰化修饰及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(3):39−44. [JIA H Q, LIU W, YAN J, et al. Isolation and purification, acetylation modification and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides of Pleurotus eryngii Quel[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(3):39−44. [23] LIU D, SUN Q, XU J, et al. Purification, characterization, and bioactivities of a polysaccharide from mycelial fermentation of Bjerkandera fumosa[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2017,167:115−122. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.03.029
[24] 孙延芳, 李子昂, 梁宗锁, 等. 食用菌多糖及其红外光谱分析[J]. 黑龙江农业科学,2011(10):99−100. [SUN Y F, LI Z A, LIANG Z S, et al. Polysaccharides and infrared spectral analysis of edible fungus[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences,2011(10):99−100. [25] 张晨. 杏鲍菇菌丝体多糖的分离纯化及抗衰老、抗糖尿病活性分析[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2018. ZHANG C. Purification, antrti-aging and anti-diabetic effects of mycelia polysaccharides from Pleurotus eryngii[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2018.
[26] 郭丹. 当归多糖在合成当归多糖铁复合物前后的结构比较[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2009. GUO D. The structural comparison of Angelica Sinensis polysaccharide before and after the synthesis of APLC[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2009.
[27] 陈晴晴, 杨金凤, 刘红. 新疆沙枣多糖的提取分离及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2016,37(12):37−40. [CHEN Q Q, YANG J F, LIU H. Purification and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from Elaeagnus angustifolia in Xinjiang[J]. Food Research and Development,2016,37(12):37−40. [28] JIN Y, YANG N, TONG Q, et al. Rotary magnetic field combined with pipe fluid technique for efficient extraction of pumpkin polysaccharides[J]. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies,2016,35:103−110.
[29] 刘玉婷, 李井雷. 多糖体外抗氧化活性研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发,2019,40(6):214−219. [LIU Y T, LI J L. Advances in research on antioxidant activity of polysaccharides in vitro[J]. Food Research and Development,2019,40(6):214−219. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2019.06.037 -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 郜浩帆,王宝亮,关运祥,钱百成. 酸枣仁-茯苓药对及其活性成分治疗失眠作用机制研究进展. 中药新药与临床药理. 2025(01): 152-160 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈旭. 酸枣仁治疗失眠症的研究进展. 基层中医药. 2024(08): 99-103 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)









 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



