Effects of Chlorogenic Acid Combined with Salicylic Acid Treatments on Postharvest Asparagus during Cold Storage
-
摘要: 以新鲜绿芦笋为试材,研究0.3 mmol/L绿原酸(CA)和0.3 mmol/L绿原酸复配0.1 mmol/L水杨酸(CA+SA)处理,以腐烂率、呼吸强度、叶绿素、纤维素、VC、总酚、超氧阴离子(O2−·)、多酚氧化酶(PPO)、过氧化物酶(POD)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)和总超氧化物歧化酶(T-SOD)活性为指标进行测定,探究其对冷藏(4±2 ℃)保鲜效果的影响。结果表明:冷藏中CA和CA+SA处理能显著降低芦笋的呼吸峰(P<0.05),比对照(CK)分别降低了7.21%和6.22%,减缓叶绿素和VC的降解速度,提升总酚、CAT、POD和T-SOD酶活性,抑制腐烂率、超氧阴离子(O2−·)和PPO酶活性,使过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性高峰提前4 d,CA+SA处理效果优于CA处理。CA+SA处理显著抑制了贮藏8 d后芦笋纤维素的增加(P<0.05),其CAT酶活性峰值是CK的1.92倍,而CA处理对芦笋纤维素和CAT峰值没有影响。绿原酸复配水杨酸能较好地保持芦笋的贮藏品质,为芦笋采后贮藏保鲜技术的应用研究提供理论依据。Abstract: The objective of this work was to investigated the influence of chlorogenic acid (CA, 0.3 mmol/L) and CA (0.3 mmol/L) complex salicylic acid (SA, 0.1 mmol/L) on green asparagus postharvest quality during cold storage (4±2 ℃). The rot rate, respiration rate, chlorophyll content, cellulose content, VC content, total phenol content, superoxide anion radical content, the key enzymes of the enzymatic system catalase (CAT), polyphenol oxidase (PPO), peroxidase (POD) and total superoxide dismutase(T-SOD) enzyme activities were measured as indicators. The results showed that CA and CA+SA treatments reduced respiratory peaks of asparagus significantly, which was 7.21% and 6.22% lower than that of CK respectively (P<0.05). The two treatments could maintain higher level of chlorophyll and VC content, increased total phenol content and the activities of CAT, POD and T-SOD, inhibited the decay rate, superoxide anion and PPO activities, the CAT activity peaks were appeared in advance by 4 days. CA+SA treatment was better than CA treatment. CA+SA reduced the cellulose content after 8 d storage significantly (P<0.05), the CAT activitie peak was 1.92 times comparing with CK, but CA had no effect on the CAT activity peaks and cellulose content. These results indicated that CA+SA could maintain the storage quality of green asparagus well, and provide some theoretical basis for the application of the postharvest storage and preservation technology of green asparagus.
-
Keywords:
- asparagus /
- chlorogenic acid /
- salicylic acid /
- preservation
-
芦笋(Asparagus officinalis L.)又叫石刁柏、龙须菜、青芦笋,富含蛋白质、氨基酸、维生素及矿物质等,尤其富含天门冬酰胺和硒、钼、铬等微量元素,被世界卫生组织列为“十大健康蔬菜之首”[1]。我国是世界第一芦笋生产大国,出口量占全世界的25%,在全球芦笋贸易中具有举足轻重的地位。绿芦笋以鲜食为主,但因呼吸旺盛易失水,且采摘机械伤加速其品质变劣和衰老的速度,贮藏期较短,这是限制芦笋产业发展的主要因素之一。目前芦笋贮藏保鲜方法主要有低温贮藏、冰温贮藏、气调包装、化学保鲜剂和生物保鲜等技术[2],相比其他技术,化学保鲜操作简便,结合低温保鲜效果更佳,因此在实践生产中应用较为广泛,但存在一定的安全隐患,开发安全、便捷和高效的天然复合保鲜剂逐渐成为芦笋保鲜领域研究的一大热点。
绿原酸(chlorogenic acid,CA)又称咖啡单宁酸,化学名为3-O-咖啡酰奎尼酸,是一种在有氧呼吸过程中由肉桂酸和奎宁酸经莽草酸途径形成的苯丙素类物质[3],在抵御非生物胁迫中发挥着重要作用[4-5]。绿原酸是一种酚类物质,通过调节参与乙烯生物合成的酶降低乙烯的合成速率[6],诱导防御相关酶活性,抑制果实的后熟进程,保持果蔬感官和营养品质[7-8],目前研究发现CA对苹果[9]、梨[10]、番茄[11]、黄瓜、草莓[12]、葡萄[13]和猕猴桃[14]等果蔬具有良好的保鲜效果。水杨酸(salicylic acid,SA)也是一种酚类化合物,被认为是植物激素,对植物的生长发育、成熟衰老等都有调控作用[15-17],能够延长果蔬保鲜贮藏期。前期研究发现低浓度SA对芦笋具有良好保鲜效果,而高浓度SA造成芦笋失绿。水杨酸结合绿原酸对芦笋保鲜的研究尚未有报道,本研究拟通过以绿芦笋为试材,研究绿原酸及其复配水杨酸对冷藏条件下芦笋呼吸速率、叶绿素、纤维素、VC、总酚、CAT、超氧阴离子等品质指标的影响,确定绿原酸和水杨酸对芦笋贮藏保鲜的可行性,为芦笋采后贮藏保鲜提供理论和科学依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
芦笋 浙江省杭州市农副产品物流蔬菜批发市场,选择色泽鲜亮,笋尖闭合,茎部笔直鲜嫩,基部无木质化,无机械擦伤,无病虫害,长度28~30 cm,直径1.10~1.50 cm的芦笋备用;绿原酸、水杨酸、十六烷基三甲基溴化铵、盐酸羟胺、草酸、没食子酸、福林酚、对氨基苯磺酸 上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;丙酮 杭州双林化工试剂厂;α-萘胺 浙江卡尔生物技术有限公司;可溶性淀粉 国药集团化学试剂有限公司;冰乙酸 天津市永大化学试剂有限公司;乙醇 安徽安特食品股份有限公司;乙酰溴 阿拉丁试剂有限公司;磷酸氢二钠 天津市恒兴试剂有限公司;无水碳酸钠 太仓美试剂有限公司;过氧化氢 上海凌峰化学试剂有限公司;氢氧化钠 西陇科学股份有限公司;磷酸二氢钾 无锡市展望化工试剂有限公司;所用试剂除特殊说明外均为分析纯;总超氧化物歧化酶(T-SOD)测试盒 南京建成生物工程研究所。
Biofuge Primo R台式高速冷冻离心机 赛默飞世尔科技有限公司;UV-2450 PC紫外可见分光光度 日本岛津有限公司;LHS-150 HC-I恒温恒湿箱 上海一恒科学仪器有限公司;DW-88 L102低温冰箱 澳柯玛股份有限公司;DGG-9140 A电热恒温鼓风干燥箱 上海森信实验仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 原料处理
将芦笋分别放入对照组(蒸馏水)、0.30 mmol/L CA、0.30 mmol/L CA+0.10 mmol/L SA溶液中浸泡10 min,取出自然晾干4 h,装入0.025 mm×30 cm×39 cm的聚乙烯袋(PE)包装,每袋500±20 g,每个处理12袋,共36袋。然后放进恒温恒湿箱(温度4±2 ℃、湿度90%)贮藏。
采购当天记为0 d,每4 d取一样测定呼吸强度,并取中部(距顶部10~24 cm)切成1 cm小块放入液氮冷冻,保存于−60 ℃冰箱备用,用以测定叶绿素、维生素C、纤维素、总酚、过氧化氢酶(CAT)、超氧阴离子指标进行测定。
1.2.2 测定指标和方法
1.2.2.1 腐烂率测定
采用观察法对腐烂个数进行统计[18]。按照下面公式计算:
腐烂率(%)=腐烂个数/样品贮前个数×100
1.2.2.2 呼吸强度测定
采用静置法进行测定[19]。芦笋样品500±20 g芦笋放入密闭干燥空间内25 ℃密闭1 h,以每千克芦笋每小时增加CO2量进行表示。
1.2.2.3 叶绿素测定
参考陈贝莉[20]的方法。称取2 g样品,加入30 mL 80%丙酮溶液研磨,10000 r/min高速离心5 min,上清液在波长663 nm和645 nm下测定吸光度。
1.2.2.4 纤维素测定
参考杜甫佑等[21]的方法。取样品3 g加入100 mL酸性洗涤剂(20 g十六烷基三甲基溴化铵溶解于1 L 0.50 mol/L H2SO4),100 ℃加热2 h后抽滤,依次用热蒸馏水和乙醇重复洗涤3次,抽干后105 ℃烘干1 h,称重记录数据。
1.2.2.5 维生素C测定
参考李野等[22]的碘量法。4 g样品加入50 mL 1%草酸溶液研磨,8500 r/min离心5 min提取上清液,用0.001 mol/L的碘液进行滴定,记录消耗碘液的毫升数。
1.2.2.6 总酚测定
参考Liu等[23]的方法并略作改进。称取3 g芦笋,加入10 mL 80%乙醇研磨,4 ℃ 10000 r/min离心20 min,吸取1 mL提取液,加入1 mL 0.5 mol/L福林酚试剂,3 min后加入5 mL 2% Na2CO3,25 ℃避光2 h,定容至25 mL,750 nm测定吸光度。没食子酸(x)与吸光度(y)之间的直线方程y=10.721x−0.1987,决定系数R2=0.9972,线性范围为0.01~0.12 μg·mL−1。
1.2.2.7 CAT酶活性测定
参照胡会刚等[24]的方法。取冷冻芦笋5 g,加入预冷0.05 mol/L 50 mL的磷酸缓冲液(内含1% 交联聚乙烯吡咯烷酮PVPP,pH7.8),4 ℃ 10000 r/min离心20 min,上清液即粗酶液。CAT活性测定采用紫外分光光度法[25]。3 mL 0.015 mol/L H2O2加入0.5mL酶液,测定3 min内OD240 nm的变化,以每分钟下降0.01为一酶活单位U。
1.2.2.8 超氧阴离子(O2−·)产生速率的测定
参考王爱国等[26]的方法。2 mL样品提取液加入3 mL 1 mmo1/L盐酸羟胺25 ℃反应60 min,依次加入2 mL 17 mmo1/L对氨基苯磺酸和2 mL 7 mmo1/L α-萘胺,混匀后25 ℃放置20 min,测定530 nm吸光值[27]。以亚硝酸盐做标准曲线计算样品中O2−·的产生速率,亚硝酸根含量(x)与吸光度(y)之间的直线方程y=0.0076x+0.0151,决定系数R2=0.9998,线性范围为0.01~12.00 μg/mL。
1.2.2.9 POD酶活性测定
参考Ali等[28]的方法,略作修改。粗酶液制备同CAT测定中粗酶液制备方法,反应体系包括2 mL 0.02 mmol/L愈创木酚、0.5 mL酶提取物和1 mL 0.04 mol/L过氧化氢,470 nm波长下测3 min内吸光值,每30 s读数一次,以每分钟吸光度值变化表示酶活性大小,以U/(g·min) Fw表示。
1.2.2.10 多酚氧化酶(PPO)活性测定
参考张芳等[29]的方法,略有改动。粗酶液制备同CAT测定中粗酶液制备方法。将0.1 mol/L的邻苯二酚溶液在30 ℃保温,取该溶液3 mL,迅速加入粗酶提取液0.8 mL,保证反应温度为30 ℃,5 s后扫描398 nm处吸光值变化,以1 min内ΔOD398 nm上升0.01为1个酶活单位,以U/(g·min) Fw表示PPO活性的单位。
1.2.2.11 总超氧化物歧化物酶(T-SOD)活性测定
参考张佳楠等[30]的方法,总T-SOD酶活测定使用T-SOD试剂盒测定。置于450 nm处,测定吸光度测定样品的T-SOD活性。一个T-SOD酶活力单位定义为T-SOD抑制率达50%时所对应的酶量,单位以U/g FW(每克鲜样中T-SOD活力)计。
1.3 数据处理
数据指标采用Excel软件绘图,应用SPSS Statistics 23进行LSD方差显著性分析(P<0.05差异显著,P<0.01差异极显著)。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 绿原酸复配水杨酸对芦笋腐烂率的影响
腐烂更直观反映果蔬采后品质。由图1可以得出:随着贮藏时间的延长,芦笋腐烂率均呈上升趋势,CA对梨黑斑病、水蜜桃青霉病、油桃绿霉病、樱桃以及番茄灰霉病等果实真菌也表现出良好的抑菌效果,能破坏病原菌细胞膜结构发挥抗菌活性[31],课题组前期研究发现适量水杨酸对芦笋菌落总数有抑制作用,CA和CA+SA处理作为保鲜剂应用于芦笋保鲜能使贮藏初期(4 d)腐烂率均为0%,在不同贮藏阶段,CA及其复配SA两处理组腐烂率显著低于CK组(P<0.05),表明CA及其复配SA能有效抑制芦笋腐烂,其中CA+SA组效果更佳。
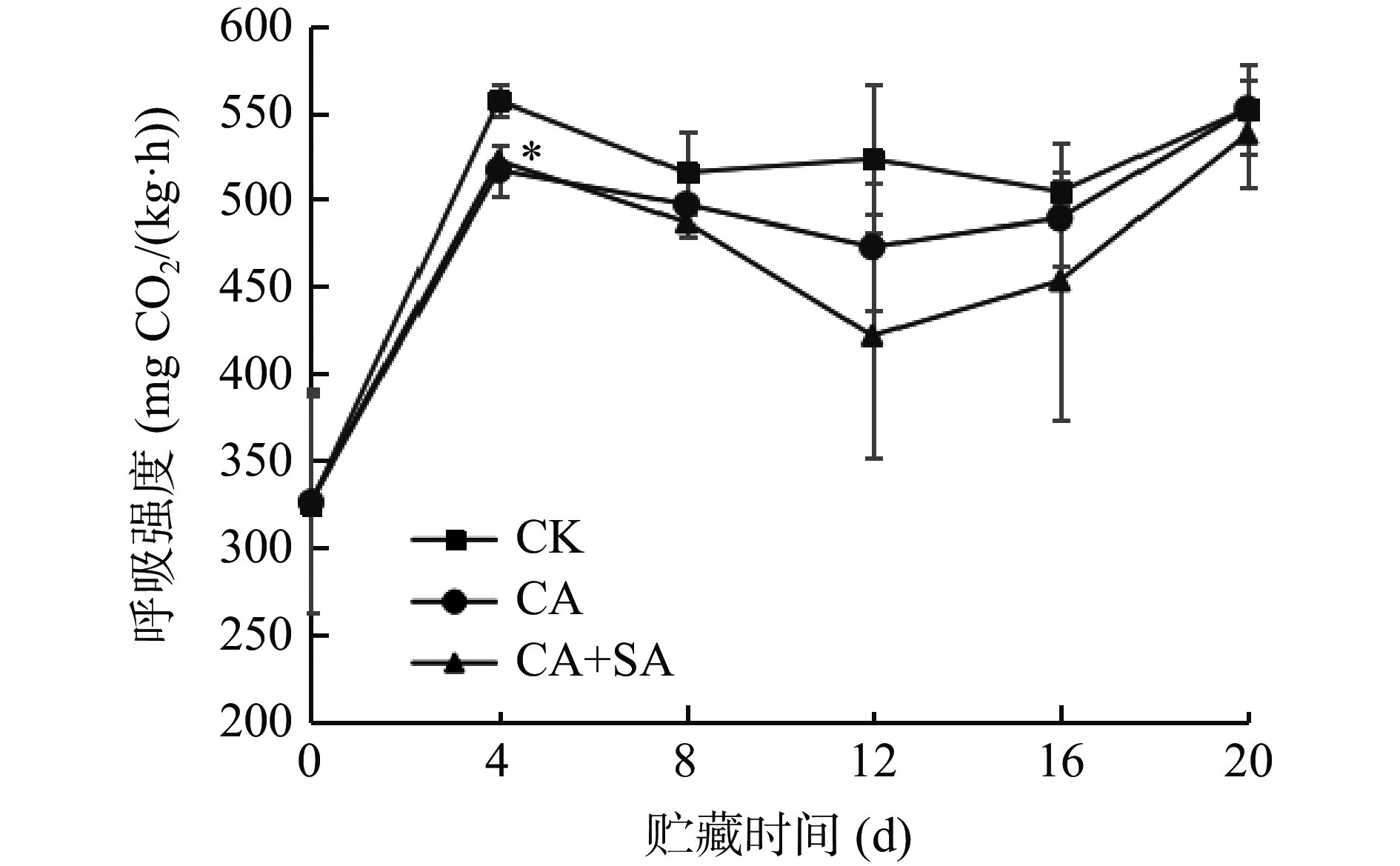
2.2 绿原酸复配水杨酸对芦笋呼吸强度的影响
降低果蔬呼吸强度是延长果蔬采后贮藏期的有效手段之一。如图2所示,芦笋是呼吸跃变型蔬菜,冷藏4 d发生呼吸小跃变,这与陈立才等[32]的研究较为一致。CK组呼吸强度最大峰值达557.03±9.33 mg CO2/(kg·h),CA和CA+SA处理能显著抑制芦笋呼吸峰(P<0.05),分别比CK降低7.21%和6.22%,但两个酸处理间差异不显著(P>0.05)。贮藏4 d后,芦笋呼吸速率下降,两个酸处理能降低呼吸强度,但抑制能力与CK组差异不显著(P>0.05)。贮藏16~20 d,芦笋呼吸强度上升,推测可能是贮藏后期芦笋老化腐烂的微生物所引起[33]。CA和CA+SA能降低芦笋呼吸强度,抑制呼吸峰,但贮藏中后期影响效果较小。
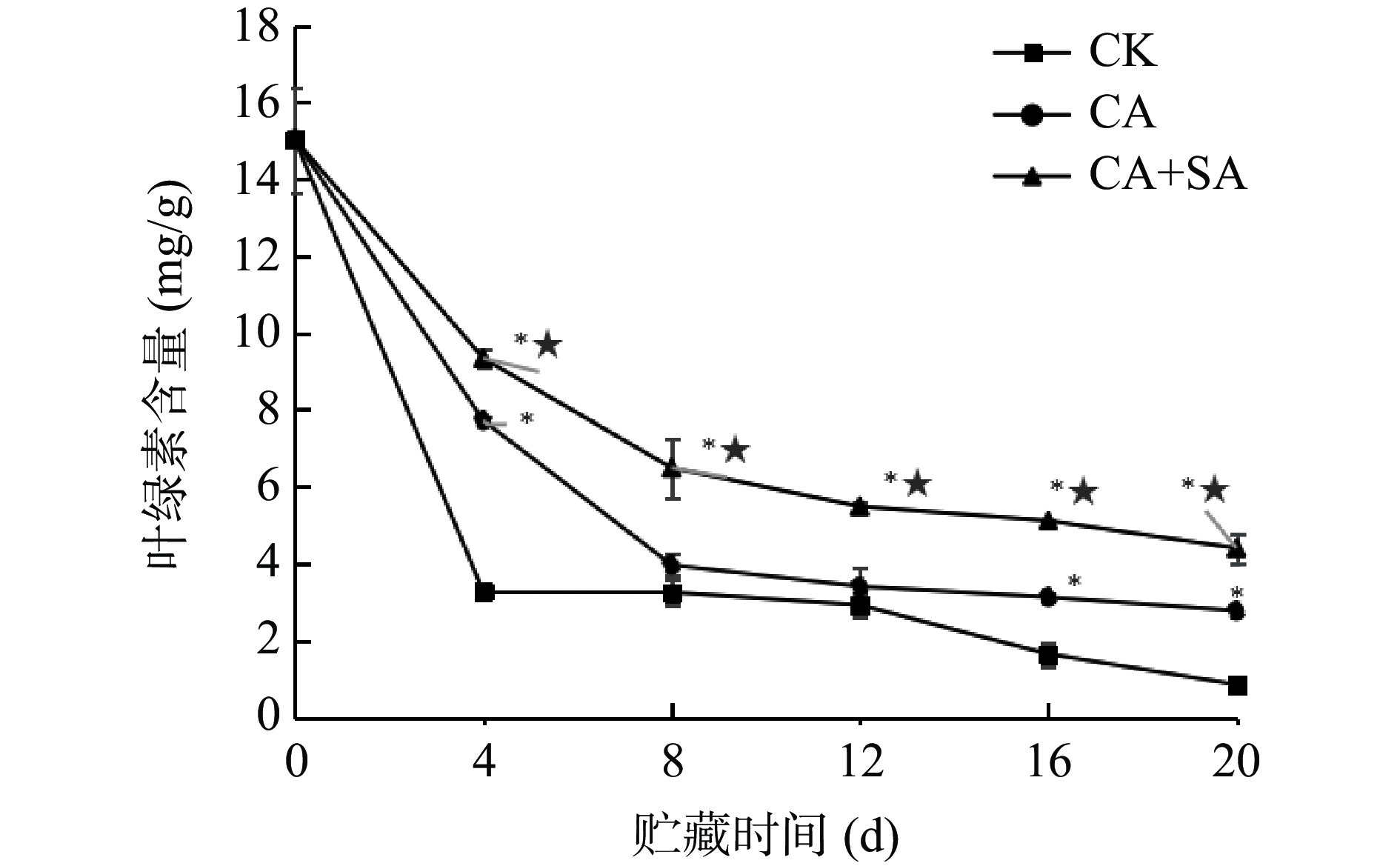
2.3 绿原酸复配水杨酸对芦笋叶绿素的影响
在绿芦笋采后贮藏过程中,叶绿素含量的下降是绿芦笋衰老的重要标志之一。绿芦笋叶绿素变化如图3所示,叶绿素易受光照、温度等环境因素的影响而降解,贮藏4 d前CK处理叶绿素急剧下降,CA、CA+SA两个处理组能显著延缓叶绿素降解速度,CA+SA效果显著优于CA处理(P<0.05)。绿原酸具有一定程度的抗氧化能力,可能是抑制芦笋叶绿素下降的原因所在,这与付远洪[34]的研究结果较为一致。CA对芦笋叶绿素含量下降起减缓作用,其与SA复配效果更加,这对芦笋感官具有积极作用。
2.4 绿原酸复配水杨酸对芦笋纤维素的影响
纤维素含量是反映绿芦笋老化程度的重要指标。在冷藏过程中,绿芦笋嫩茎粗纤维含量随贮藏期的延长而增加(图4)。贮藏8 d后,CA+SA处理抑制了纤维素上升的趋势,其含量显著低于其他两个处理(P<0.05),而CA处理对纤维素无明显效果,复配可抑制芦笋贮藏中后期的纤维素增加。绿原酸是苯丙烷代谢产物,与植物木质素合成有关[35-36],绿原酸能显著减少‘金冠'苹果幼果期果皮木质素含量[10]。本研究认为绿原酸对芦笋纤维素没有抑制效果,复配处理对贮藏后期纤维素增加的抑制可能是水杨酸作用的结果。
2.5 绿原酸复配水杨酸对芦笋VC含量的影响
维生素C(VC)是蔬菜重要的营养物质之一,也是判断新鲜品质的重要指标[25]。绿芦笋体内富含VC,芦笋嫩茎VC含量随着贮藏时间延长呈下降趋势(图5),CA、CA+SA两处理都能显著保持VC含量水平(P<0.05)。贮藏8 d前,两个酸处理之间对芦笋VC抑制水平差异不显著(P>0.05),贮藏12 d后差异显著(P<0.05)。绿原酸及复配水杨酸都能有效控制VC下降速度,复配酸处理对芦笋贮藏后期VC保持效果更优异。绿原酸在中性和碱性环境极不不稳定,易降解[37],绿原酸能抑制芦笋VC产量下降速度,这与何念武等[11]对圣女果和黄瓜保鲜研究结论相一致。绿原酸复配水杨酸后更有利于绿原酸稳定性,有助于发挥其抗氧化功效,进而有效延缓绿芦笋VC含量下降。总之,CA能减缓芦笋VC下降趋势,但CA+SA处理效果更佳。
2.6 绿原酸复配水杨酸对芦笋总酚的影响
酚类物质是果蔬组织重要的次生代谢产物,能作为抗氧化物质为细胞提供保护,也与成熟衰老过程密切相关[38-39]。芦笋木质素生成的前体物质是酚类,采后绿芦笋总酚含量呈现上升趋势(图6),CA和CA+SA两处理总酚含量显著高于CK组(P<0.05),贮藏期内总体平均高出44.22%和71.09%,其中复配CA+SA组显著高于CA组(P<0.05)。外源酚酸能促进芦笋苯丙烷代谢[40-41],促进酚类物质的积累,绿原酸及复配水杨酸都能促进芦笋总酚的积累。
2.7 绿原酸复配水杨酸对芦笋CAT酶的影响
CAT是一种植物体内重要的保护酶,能减少氧活性自由基对细胞膜损伤,维持细胞稳定内环境。由图7可知,在贮藏期内芦笋CAT酶活性呈现先升后降的趋势。贮藏初期,CA和CA+SA两处理CAT酶活性急剧上升,8 d达到最高峰,CAT酶活性分别为445.21±33.55 U/(g·min) FW和865.7±117.2 U/(g·min) FW,都显著高于CK,其中CA+SA处理显著高于CA(P<0.05)。贮藏12 d,CK处理CAT酶活性达到最大,约为449.95±77.65 U/(g·min) FW。贮藏16 d,CA+SA处理CAT酶活性再次升高,但与其他两个处理无显著差异(P>0.05)。研究已证明SA能保持提高梨[40]、莲子[42]、西葫芦[43]过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性,本研究认为CA和CA+SA处理都能促使CAT酶活性峰值提前4 d,CA+SA能增加CAT活性,而CA对CAT活性峰值无明显影响。
2.8 绿原酸复配水杨酸对芦笋超氧阴离子(O2−·)的影响
果蔬体内不断地产生O2−·,也会不断地将其清除,使其浓度处于平衡状态。通过测定芦笋中超氧阴离子的产生速率,能间接地了解到组织细胞的受损状况、抗逆性及老化程度[28]。如图8所示,贮藏期间,芦笋体内O2−·含量急剧增加,可能是由于低温造成体内产生抗逆性所致[44]。绿原酸和水杨酸都能抑制超氧阴离子含量[7,40],本研究中CA和CA+SA两处理都能显著抑制O2−·生成速度(P<0.05),贮藏期内总体平均抑制率分别比CK组高13.05%和25.88%。CA对芦笋O2−·含量的增加具有有效的抑制作用,更有助于保护绿芦笋细胞不受损坏,CA+SA处理效果显著优于CA处理(P<0.05)。
2.9 绿原酸复配水杨酸对芦笋POD活性的影响
POD是植物组织中一种氧化还原酶,能有效清除生物体内过氧化自由基,维护膜脂结构,对减缓果蔬衰老有重要作用[45]。绿原酸复配水杨酸处理对冷藏芦笋POD活性的具体影响见图9。贮藏期内,芦笋POD活性呈现先上升后下降趋势,这与刘红艳等[46]的研究有所差异。贮藏4 d,CK组芦笋POD酶活性达到最高峰,约为735.23 U/(g·min)FW,而CA和CA+SA处理组POD上升幅度更大,分别比CK组高17.3%和59.8%,差异达显著水平(P<0.05)。贮藏20 d后,CA和CA+SA处理组POD酶分别比CK组高26.9%和58.0%,这说明CA、CA+SA处理组能相对更快激发芦笋POD的活性,对细胞膜具有保护性作用。
2.10 绿原酸复配水杨酸对芦笋PPO酶活性的影响
在贮藏过程中,PPO能将果蔬组织内酚类物质氧化为不稳定的醌,进一步聚合引起褐变[28]。贮藏过程中,芦笋PPO酶活性呈现先升后降的趋势,具体如图10所示,这与刘红艳等[46]的研究结果有所差异。CA和CA+SA两个处理显著抑制PPO活性,贮藏期间其PPO活性平均比CK分别低55.50%和81.10%。绿原酸可使多酚氧化酶三级结构发生改变[47],部分研究发现水杨酸对PPO活性的抑制可达1.5%~25.7%[48],本研究表明CA、CA+SA处理能相对抑制芦笋PPO的活性,其中CA复配SA抑制效果更佳,这可能是芦笋总酚含量增加的主要原因。
2.11 绿原酸复配水杨酸对芦笋T-SOD酶活性的影响
SOD是一种保护酶,作用类似于POD,能清除组织中的活性氧,稳定膜结构,维持植物体内正常生理代谢[49]。如图11所示,冷藏条件下采后芦笋T-SOD酶活性呈现先升后降的趋势,贮藏8 d芦笋T-SOD活性达到最高,这与董欢欢[50]对采后芦笋T-SOD的研究较为一致。整个贮藏期内CA+SA组芦笋T-SOD活性一直显著高于CK组(P<0.05),而CA处理T-SOD酶活性仅在贮藏4、12 d显著高于CK组(P<0.05)。总之,CA和CA+SA能提升采后芦笋T-SOD活性,CA+SA处理组对T-SOD效果最好,CA效果有限。
3. 结论
本研究采用0.3 mmol/L CA、0.3 mmol/L CA+0.1 mmol/L SA应用于芦笋保鲜。实验结果表明,绿原酸及其复配水杨酸有助于降低芦笋呼吸强度,延缓叶绿素和VC降解速度,提升总酚、CAT、POD酶和T-SOD酶活性,抑制腐烂率和超氧阴离子含量的累积及PPO酶活性,CA+SA复配处理效果优于CA,但CA处理对纤维素、CAT和T-SOD峰值没有显著性影响,CA+SA仅对贮藏中后期纤维素有抑制上升的作用。综上所述,芦笋在绿原酸复配水杨酸保鲜技术处理下,更有助于品质保持,延长贮藏寿命,比绿原酸单一效果好。该研究成果对芦笋保鲜技术的发展有着积极意义,但多种酚酸类物质复配对蔬菜保鲜效果仍需进一步研究和探索。
-
-
[1] 王晓, 张国强, 刘晨霞, 等. 臭氧结合气调保鲜鲜切绿芦笋的研究[J]. 上海农业学报,2021,37(1):118−122. [WANG X, ZHANG G Q, LIU C X, et al. Ozone combined with modified atmosphere packaging on fresh-keeping effects of fresh-cut green asparagus[J]. Actor Agriculturae Shanghai,2021,37(1):118−122. [2] 王剑功, 褚伟雄, 吴玲妹, 等. 采后芦笋贮藏保鲜技术的研究现状[J]. 食品工业,2019,40(11):266−271. [WANG J G, CHU W X, WU L M, et al. Research status of postharvest asparagus storage and fresh-keeping technology[J]. The Food Industry,2019,40(11):266−271. [3] 何柳, 陈士林. 植物中绿原酸合成途径研究进展[J]. 药物生物技术,2013,20(5):463−466. [HE L, CHEN S L. Research progresses on synthesis of chlorogenic acid in plants[J]. Pharmaceutical Biotechnology,2013,20(5):463−466. [4] NAIKOO M I, DAR M I, RAGHIB F, et al. Role and regulation of plants phenolics in abiotic stress tolerance[J]. Plant Signaling Molecules,2019,9:157−168.
[5] WANG L, LI J, GAO J, et al. Inhibitory effect of chlorogenic acid on fruit russeting in ‘Golden Delicious’ apple[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2014,178:14−22. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2014.07.038
[6] SHU C, ZHANG W L, ZHAO H D, et al. Chlorogenic acid treatment alleviates the adverse physiological responses of vibration injury in apple fruit through the regulation of energy metabolism[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2020,159:110997. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2019.110997
[7] ZHANG D F, BI W L, KAI K, et al. Effect of chlorogenic acid on controlling kiwifruit postharvest decay caused by Diaporthe sp.[J]. Food Science and Technology,2020,132:109805.
[8] 奚宇. 绿原酸对油桃和苹果果实采后成熟衰老的调控作用[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2017. XI Y. Effects of chlorogenic acid on postharvest ripening and senescence of nectarine and apple fruits[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2017.
[9] 王大将, 张梦宇, 岳正洋, 等. 绿原酸对苹果采后灰霉病抗性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(9):177−183. [WANG D J, ZHANG M Y, YUE Z Y, et al. Chlorogenic acid treatment induced resistance to postharvest gray mold on apples[J]. Food Science,2021,42(9):177−183. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200514-156 [10] 关哗晴, 秦晓丽, 裴颖锋, 等. 外源绿原酸对’雪花’梨果点形成和相关基因表达的影响[J]. 农业生物技术学报,2021,29(2):258−267. [GUAN Y Q, QIN X L, PEI Y F, et al. Effect of exogenous chlorogenic acid on fruit dot formation and expression of related genes in 'Xuehua' pear (Pyrus bretschneideri)[J]. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology,2021,29(2):258−267. [11] 何念武, 杨超. 杜仲叶中绿原酸的提取及其在果蔬保鲜中的应用[J]. 江西农业学报,2015,27(7):107−110. [HE N W, YANG C. Extraction of chlorogenic acid from leaves of Eucommia ulmoides and its application in preservation of fruits and vegetables[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi,2015,27(7):107−110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8581.2015.07.029 [12] 杨超, 何念武. 杜仲叶绿原酸对果蔬保鲜作用的试验研究[J]. 江西农业学报,2018,30(11):71−75. [YANG C, HE N W. Experimental study on fresh-keeping effect of chlorogenic acid in Eucommia ulmoides leaves on fruits and vegetables[J]. Acta Agric Ulturae Jiangxi,2018,30(11):71−75. [13] 焦泽铃, 余义和, 郭大龙, 等. 绿原酸处理对‘巨峰’葡萄采后品质的影响[J]. 北方园艺,2021(19):114−120. [JIAO Z L, YU Y H, GUO D L, et al. Effects of chlorogenic acid immersion on postharvest quality of ‘Kyoho’ grapea[J]. Northern Horticulture,2021(19):114−120. [14] 开凯. 绿原酸对猕猴桃和樱桃番茄采后病原菌抑制作用及机理研究[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2021. KAI K. Inhibition and mechanism of chlorogenic acid on postharvest pathogens of kiwifruits and cherry Tomatoes[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2021.
[15] YAN S, DONG X. Perception of the plant immune signal salicylic acid[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology,2014,20:64−68. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2014.04.006
[16] KHAN M I R, ATMA M, PER T S, et al. Salicylic acid-induced abiotic stress tolerance and underlying mechanisms in plants[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science,2015,6:462.
[17] KLSSING D F, CHOI H W, DEMPSEY D M A. Systemic acquired resistance and salicylic acid: Past, present, and future[J]. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions,2018,31:871−888. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-03-18-0067-CR
[18] 唐仁勇, 刘孙鹏, 彭家宣, 等. 不同柑橘精油对低温贮藏芦笋的保鲜效果[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2021(9):1−6. [TANG R Y, LIU S P, PENG J X, et al. Effect of different citrus essential oils on asparagus storage at low temperature[J]. China Food Additives,2021(9):1−6. [19] 邓淑芳, 王鹏, 张怀予, 等. 褪黑素处理对枸杞果实采后生理及贮藏品质的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(2):198−204. [DENG S F, WANG P, ZHANG H Y, et al. Effects of melatonin treatment on postharvest physiology and storage quality of goji berry[J]. Food and Fermentation Industrie,2022,48(2):198−204. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.027111 [20] 陈贝莉. 绿芦笋保鲜及胆固醇护绿机理研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江工商大学, 2015. CHEN B L. Study on prsevation of postharvest green asparugus and green-maitaining mechanism of cheolesterol treatment[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Gongshang University, 2015.
[21] 杜甫佑, 张晓昱, 王宏勋. 木质纤维素的定量测定及降解规律的初步研究[J]. 生物技术,2004,14(5):46−48. [DU F Y, ZHANG X Y, WANG H X. Studies on quantitative assay and degradation law of lignocellulose[J]. Biotechology,2004,14(5):46−48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-311X.2004.05.024 [22] 李野, 尹利辉, 高尚, 等. 食品和药品中维生素C含量测定方法的研究进展[J]. 药物分析杂志, 2016, 36(5): 756. LI Y, YIN L H, GAO S, et al. Research progress of vitamin C content determination in food and drug[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 2016, 36(5): 756.
[23] LIU X, YANG Q, LU Y Z, et al. Effect of purslane (Portulaca oleracea L.) extract on anti-browning of fresh-cut potato slices during storage[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,283:445−453. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.01.058
[24] 胡会刚, 莫亿伟, 谢江辉, 等. 水杨酸提高香蕉采后果实抗氧化能力和保鲜效果研究[J]. 食品科学,2009,30(2):254−259. [HU H G, MO Y W, XIE J H, et al. Effect of Salicylic acid on antioxidation capacity and preservation of post-harvested banana fruits[J]. Food Science,2009,30(2):254−259. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2009.02.058 [25] ZHANG H Y, LIU F R, WANG J J, et al. Salicylic acid inhibits the postharvest decay of goji berry (Lycium barbarum L.) by modulating the antioxidant system and phenylpropanoid metabolites[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2021,178:111558. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2021.111558
[26] 王爱国, 罗广华. 植物的超氧物自由基与羟胺反应的定量关系[J]. 植物生理学通讯,1990(6):55−57. [WANG A G, LUO G H. Quantitative relation between the reaction of hydroxylamine and sugeroxide anion radicals in plants[J]. Plant Physiology Communications,1990(6):55−57. [27] 曾智驰, 章司晨, 石小翠, 等. 野生稻近等基因系应答低温胁迫的生理生化指标分析[J]. 广西植物,2021,41(5):813−822. [ZENG Z C, ZHANG S C, SHI X C, et al. Physiological and biochemical indexes of response to low temperature stress in near isogenic lines of wild rice[J]. Guihaia,2021,41(5):813−822. doi: 10.11931/guihaia.gxzw201905040 [28] ALI S, KHAN A S, MALIK A U, et al. Effect of controlled atmosphere storage on pericarp browning, bioactive compounds and antioxidant enzymes of litchi fruits[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,206:18−29. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.03.021
[29] 张芳, 王梦茹, 贾玉, 等. 曲酸真空浸渍处理对鲜切马铃薯冷藏期褐变及相关生理代谢的影响[J]. 保鲜与加工,2021,21(1):12−18. [ZHANG F, WANG M R, JIA Y, et al. Effect of vacuum impregnation with Kojic acid addition on browning and the related physiological metabolism of fresh-cut potato during cold storage[J]. Storage and Process,2021,21(1):12−18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6221.2021.01.003 [30] 张佳楠, 董成虎, 王志伟, 等. 被动气调包装对采后甜樱桃活性氧清除的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(18):181−186. [ZHANG J N, DONG C H, WANG Z W, et al. Effect of passive modified atmosphere packaging on the removal of active oxygen in sweet cherry[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(18):181−186. [31] ZHANG Y D, XU Z C, LI J L, et al. Research progress on extraction and antibacterial effects of chlorogenic acid[J]. Storage and Process,2022,22(2):113−120.
[32] 陈立才, 陈庆, 黄芳, 等. 匀强高压静电场对采后绿芦笋嫩茎贮藏品质的影响研究[J]. 江西农业大学学报,2018,40(5):949−955. [CHEN L C, CHEN Q, HUANG F, et al. A study on the storage quality of post-harvest green asparagus under uniform high voltage electrostatic field (UHVEF)[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis,2018,40(5):949−955. doi: 10.13836/j.jjau.2018119 [33] 郭一丹, 李奎, 蔚江涛, 等. 电子束和60 Co γ-射线辐照对冬枣的保鲜效果[J]. 食品工业科技,2021(6):276−280, 286. [GUO Y D, LI K, YU J T, et al. Effects of electron beam and 60 Co γ-ray Irradiations on the fresh-keeping of winter jujube[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021(6):276−280, 286. [34] 付远洪. 酚酸类化感物质对马缨杜鹃生长及生理的影响[D]. 贵阳: 贵州师范大学, 2018. FU Y H. Effects of phenolic acids Allelochemicals on growth and physiology in rhododendron delavayi franch[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou Normal University, 2018.
[35] TOMAS B F A, ESPIN J C. Phenolic compounds and related enzymes as determinants of quality in fruits and vegetables[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2001,81(9):853−876. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.885
[36] CAIY P, LI G Q, NIE J Q, et al. Study of the structure and biosynthetic pathway of lignin in stone cells of pear[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2010,125(3):374−379. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2010.04.029
[37] ZHU P, MIAO X L, CHEN Y. Degradation kinetics of chlorogenic acid, cryptochlorogcnic acid, and ncochlogenic, acid at neutral and alkaline pH values[J]. Yaoxue Xuebao,2016,51(1):122−126.
[38] SANCHEN C. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant properties from mushrooms[J]. Synthetic and Systems Biotechnology,2017,2(1):13−22. doi: 10.1016/j.synbio.2016.12.001
[39] HAMINIUK C W I, MACIEL G M, PLATA-OVIE DO M S V, et al. Phenolic compounds in fruits-an overview[J]. International Journal of Food Science and Technology,2012,47(10):2023−2044. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2012.03067.x
[40] 董柏余, 汤洪敏, 姚秋萍, 等. 采后水杨酸处理对金刺梨果实活性氧和苯丙烷代谢的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(17):308−315. [DONG B Y, TANG H M, YAO Q P, et al. Effects of salicylic acid treatment on reactive oxygen species metabolism and phenylpropanoid pathway in rosa sterilis[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(17):308−315. [41] 姜丹, 胡文忠, 陈晨, 等. 水杨酸、硫化氢对鲜切南瓜苯丙烷代谢的调控作用[J]. 食品科技,2016,41(10):42−46. [JIANG D, HU W Z, CHEN C, et al. Regulation of salicylic acid and hydrogen sulfide on the metabolism of fresh-cut pumpkin[J]. Food Science and Technolgy,2016,41(10):42−46. [42] 严锐, 韩延超, 吴伟杰, 等. 水杨酸处理对鲜莲采后品质及抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2022,22(3):235−245. [YAN R, HAN Y C, WU W J, et al. Effect of salicylic acid treatment on the postharvest quality and antioxidant enzyme activity of fresh lotus[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2022,22(3):235−245. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2022.03.026 [43] 王云香, 顾思彤, 左进华, 等. 水杨酸处理对西葫芦采后品质和抗氧化能力的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(19):286−290, 308. [WANG Y X, GU S T, ZUO J H, et al. Effect of salicylic acid treatment on postharvest quality and antioxidant capacity of summer squash[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(19):286−290, 308. [44] 田景花, 王红霞, 张志华, 等. 低温逆境对不同核桃品种抗氧化系统及超微结构的影响[J]. 应用生态学报,2015,26(5):1320−1326. [TIAN J H, WANG H X, ZHANG Z H, et al. Effects of chilling stress on antioxidant system and ultrastructure of walnut cultivar[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2015,26(5):1320−1326. [45] 贾茹羽. 氯化钠结合包装材料对鲜切生姜保鲜效果的研究[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2019. JIA R Y. Study on the fresh-keeping effect of T-SODium chloride combined with packaging material in fresh-cut ginger[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2019.
[46] 刘红艳, 张雷刚, 胡花丽, 等. 气调处理对绿芦笋抗氧化及抗病酶活性的影响[J]. 核农学报,2017,31(6):1119−1127. [LIU H Y, ZHANG L G, HU H L, et al. Effects of controlled atmosphere treatment on the activities of antioxidant and disease resistance-related enzymes in green asparagus[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Scierrces,2017,31(6):1119−1127. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2017.06.1119 [47] 唐金蕾. 外源绿原酸处理对鲜切马铃薯褐变抑制作用研究[D]. 天津: 天津科技大学, 2020. TANG J L. Study on the inhibitory effect of exogenous chlorogenic acid treatment on browning of fresh-cut potato[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin Unversity of Science and Technology, 2020.
[48] 廖滔. 果胶复合体系和水杨酸对多酚氧化酶的活性影响机制[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2021. LIAO T. Impact mechanism of pectin complex system and salicylic acid on the activity of polyphenol oxidase[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2021.
[49] LIN Y F, LIN Y X, LIN H T, et al. lnhibitory effects of propylgallate on browning and its relationship to active oxygen metabolism in pericarp of harvested longan fruit[J]. Food Science and Technology,2015,60(2):1122−1128.
[50] 董欢欢. 豆甾醇对绿芦笋保鲜效果和生理生化影响的研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江工商大学, 2017. DONG H H. Study on effects of stigmasterol on preservation and physiology and biochemistry of of postharvest green asparagus[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Gongshang University, 2017.






 下载:
下载:








 下载:
下载:



