Comparison and Correlation Analysis of Nutrient Composition and Bacterial Diversity of Holstein and Jersey Milk under High-altitude Feeding
-
摘要: 为了分析高原饲养的荷斯坦和娟姗牛乳营养成分及其与细菌多样性间的相关性,本研究测定了两种牛乳的营养成分和细菌多样性并进行了相关性分析。结果表明,两种牛乳基本成分(脂肪、蛋白质、干物质和非脂固体)、14种氨基酸和矿物质钙、磷含量存在显著差异(P<0.05)。两种乳中细菌群落组成结构相似、丰度不同,鲸杆菌属(Cetobacterium)、气单胞菌属(Aeromonas)、拟杆菌属(Bacteroides)、阿克曼氏菌属(Akkermansia)、假单胞菌属(Pseudomonas)和乳杆菌属(Lactobacillus)为共同优势菌属。Spearman相关热图分析显示细菌群落与乳成分之间存在一定的相关性。综合分析表明,高原饲养环境下娟姗牛乳品质优于荷斯坦牛乳,乳细菌群落可能受到乳成分影响。Abstract: In order to analyze the nutrient composition of Holstein milk and Jersey milk under high-altitude feeding and its correlation with bacterial diversity, the nutrient components and bacterial diversity of the two types of milk were determined and correlation analysis was carried out in this study. The results showed that there were significant differences in the contents of basic components (fat, protein, dry matter and non-fat solids) and 14 amino acids, as well as in mineral contents of calcium and phosphorus, in the two types of milk (P<0.05). Their bacterial communities were similar in structure but different in abundance, with Cetobacterium, Aeromonas, Bacteroides, Akkermansia, Pseudomonas and Lactobacillus being their common dominant genera. Heatmap of Spearman correlation analysis showed a correlation between bacterial community and milk composition. To sum up, the quality of Jersey milk was better than that of Holstein milk under high-altitude feeding, and the bacterial community may be affected by milk components.
-
牛乳是一种营养丰富且易于被消化吸收的天然产品,含有丰富的氨基酸、生物活性肽和蛋白质;不同品种牛乳中营养成分种类和组成基本相同,但含量存在一定差异[1]。荷斯坦牛是我国饲养最多的奶牛品种之一,其特点是生产性能好、产奶量高;娟姗牛耐热性强、采食性好、耐粗饲抵抗力强,近年来我国引入较多[2]。生牛乳作为乳品加工企业的主要原料,其营养成分水平和特性与乳制品的质量直接相关[3]。奶牛的品种、饲养地域和饲养条件等差异对牛乳营养成分有较大的影响,有研究表明娟姗牛乳的乳脂率和乳蛋白率高于荷斯坦牛乳[4-5],但高原环境下饲养对娟姗和荷斯坦牛乳营养成分的影响研究较为缺乏。鹤庆牧场位于云南大理,地处云贵高原,海拔2200 m,冬无酷暑夏无严寒,境内光热条件充足,水源充沛,土地宽广,具有奶牛养殖的优越气候和饲料资源条件,为本研究的开展提供了乳样。
牛乳中丰富的营养成分是微生物的天然培养基,能为微生物的生长代谢提供良好环境[3],牛乳中营养成分的差异会导致牛乳优势微生物群结构和组成的不同[6-7]。马静等[8]研究证明牦牛乳与犏牛乳的基本营养成分(脂肪、乳糖、蛋白质、总固形物和非脂固形物)与乳微生物多样性存在相关性。牛乳样品中优势微生物群也受奶牛品种、饲养地域、采样月份、加工阶段和储存温度等条件的影响[9]。关于牛乳中微生物多样性的研究较多,但相同高原环境饲养条件下的荷斯坦牛与娟姗牛生乳中微生物群落结构尚不清楚,其与营养成分的相关性也尚待深入研究。
本研究通过测定鹤庆牧场相同饲养条件下荷斯坦和娟姗牛生乳中的营养成分和细菌群落分布情况,分析乳营养成分与细菌多样性之间的相关性,为高原饲养条件下两种牛乳的加工、安全品质评估等提供依据,为不同乳环境与微生物多样性的研究提供了数据参考。
1. 材料方法
1.1 材料与仪器
牛乳 采样时间:2021年11月;采样地点:云南大理白族自治州鹤庆牧场;随机选取健康状况、年龄、胎次和泌乳期基本一致且在相同饲养环境中的荷斯坦奶牛和娟姗奶牛各4头,每头各采3份混合,共8组;采集的样品用干冰运输回实验室,−80 ℃保存用于营养成分分析和细菌多样性测定。盐酸(浓度≥36%)、硝酸、氢氧化钠、柠檬酸钠、苯酚 天津市致远化学试剂有限公司;ExKubit dsDNA HS Assay Kit 上海吉泰依科赛生物科技有限公司;Monarch DNA Gel Extractionn 北京鸿跃创新科技有限公司;VAHTSTM DNA Clean Beads 南京诺唯赞生物科技有限公司;SMRTbell Template Prep Kit、PacBio Binding kit、Primer、Polymerase、AMpure PB Beads 美国PacBio公司;所有试剂均为国产优级纯。
DW-86L500超低温冰箱(−80 ℃) 山东澳柯玛有限公司;CJ-2S超净工作台 天津市泰斯特仪器有限公司产品;Foss FT120乳成分分析仪 上海展仪仪器设备有限公司;DCC体细胞检测仪 哈罗德(北京)科技有限公司;L-8900氨基酸自动分析仪 日本日立高新技公司;ICP-MS电感耦合等离子体质谱仪 美国赛默飞世尔科技公司;UV-7504C紫外可见光分光光度计 上海沪粤明科学仪器有限公司;veriti96well9902梯度基因扩增仪 Appliedbiosystems;synergy HTX酶标仪 GeneCompang Limited;电泳仪 北京博美富鑫科技有限公司;Sequel II测序仪 美国PacBio公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 牛乳常规成分分析
采用乳成分分析仪测定脂肪、乳糖、蛋白质、干物质和非脂固体含量;体细胞检测仪测定体细胞数量。
1.2.2 牛乳氨基酸含量测定
按照GB 5009.124-2016《食品中氨基酸的测定》进行测定。
1.2.3 牛乳矿物质含量测定
按照GB 5009.92-2016《食品中钙的测定》,GB 5009.14-2017《食品中锌的测定》,GB 5009.87-2016《食品中磷的测定》,GB 5009.91-2017《食品中钾、钠的测定》,GB 5009.90-2016《食品中铁的测定》,GB 5009.13-2017《食品中铜的测定》,GB 5009.241-2017《食品中镁的测定》,GB 5009.242-2017《食品中锰的测定》进行测定。
1.2.4 DNA提取及PCR扩增、测序
使用TGuide S96磁珠法DNA提取试剂盒提取各样品的总DNA,检测DNA浓度、纯度和提取质量。所用细菌16S rRNA引物为通用引物27F(5'-AGRGTTTGATYNTGGCTCAG-3')和1492R(5'-TASGGHTACCTTGTTASGACTT-3')。PCR扩增程序为:95 ℃预变性2 min,98 ℃变性10 s,55 ℃退火30 s,72 ℃延伸90 s,共30个循环,72 ℃延伸7 min。PCR产物使用1.8%琼脂糖凝胶回收,用Agencourt AMPure XP Beads进行回收产物纯化,并使用Qubit dsDNA HS Assay Kit进行定量。单个量化后将等量产物合并,通过SMRTbell Express Template Prep Kit 2.0制备SMRTbell文库并进行测序。PCR扩增、PCR产物混合、纯化,文库构建及上机测序流程均由北京百迈客生物科技有限公司完成。
1.3 数据处理
1.3.1 测序数据处理
原始数据质量过滤使用Trimmomatic(version 0.33),引物序列的识别与去除使用Cutadapt(version 1.9.1),其后使用USEARCH(version 10)对双端reads进行拼接并去除嵌合体(UCHIME, version 8.1)。原始下机subreads 进行校正得到CCS(Circular Consensus Sequencing)序列(SMRT Link , version8.0),然后使用lima(v1.7.0)软件对CCS序列进行Barcode识别,长度过滤,去除嵌合体,得到Effective CCS序列。
1.3.2 菌群多样性分析
使用USEARCH(version 10.0)在相似性97%(默认)的水平上对序列进行聚类,默认以测序所有序列数的0.005%作为阈值过滤OTUs。
通过QIIME2(https://qiime2.org/)计算ACE、Chao1、Shannon、Simpson指数和Unifrac,使用R软件分析样品稀释曲线、Alpha多样性指数差异。多级物种差异判别分析(LEfSe)分析菌群组成,LDA Score筛选值为3.5,R软件分析组间差异显著物种。以上分析内容和Spearman相关热图分析均在 BMKCloud(www.biocloud.net)上完成。
1.3.3 统计分析
显著性检验均用IBM SPSS Statistics 26进行,结果以平均值(means)±标准差(SD)表示。P<0.01为极显著差异,P<0.05为显著差异。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 荷斯坦牛乳与娟姗牛乳营养成分对比
2.1.1 荷斯坦牛乳与娟姗牛乳基本成分比较分析
荷斯坦牛乳与娟姗牛乳基本成分如表1所示,荷斯坦牛乳体细胞数为8.46万个/mL,娟姗牛乳为9.24万个/mL,两种牛乳的体细胞数差异显著(P<0.05),但均低于25万个/mL,所测奶牛均为未患乳房炎的健康牛[10]。娟姗牛乳脂肪含量为4.38 g/100 g,比荷斯坦牛乳高10.61%;蛋白质含量为3.78 g/100 g,比荷斯坦牛乳高12.17%,且差异显著(P<0.05)。娟姗牛乳干物质含量(13.96 g/100 g)与荷斯坦牛乳干物质含量(13.28 g/100 g)呈显著差异(P<0.05);娟姗牛乳中非脂固体占比(9.33%)也显著高于荷斯坦牛乳(9.14%)(P<0.05)。
表 1 荷斯坦与娟姗牛乳成分比较Table 1. Composition comparison of Holstein and Jersey milk2.1.2 荷斯坦牛乳与娟姗牛乳氨基酸含量比较分析
荷斯坦牛乳与娟姗牛乳中氨基酸的含量如表2所示,通常检测食品中蛋白质氨基酸为18种,两种牛乳中均检测出16种氨基酸,色氨酸和胱氨酸未检出;谷氨酸在两种牛乳中含量均最高,在荷斯坦牛乳中达到0.98 g/100 g,在娟姗牛乳中达到1.23 g/100 g。荷斯坦与娟姗牛乳中氨基酸总量分别为4.44 g/100 g、5.82 g/100 g,必需氨基酸含量分别为1.79 g/100 g、2.36 g/100 g,娟姗牛乳中的氨基酸总量和必需氨基酸含量均显著高于荷斯坦牛乳(P<0.05)。Lim等[4]的研究证明韩国饲养的娟姗牛乳中氨基酸含量也高于荷斯坦牛乳。必需氨基酸分别占氨基酸含量的40.32%和40.55%,必需氨基酸与非必需氨基酸的比值分别为0.675和0.682,接近FAO/WHO标准规定的必需氨基酸含量(40%)和TEAA/TNEAA值(0.6)[11]。两种牛乳中脯氨酸和赖氨酸含量差异极显著(P<0.01),丝氨酸和精氨酸无显著差异(P>0.05),其余的12种氨基酸均存在显著差异(P<0.05)。
表 2 荷斯坦与娟姗牛乳氨基酸含量比较(g/100 g)Table 2. Comparison of amino acid contents in Holstein and Jersey milk (g/100 g)氨基酸种类 荷斯坦牛乳 娟姗牛乳 赖氨酸(Lys) a 0.36±0.03 0.48±0.03** 脯氨酸(Pro) 0.38±0.04 0.57±0.04** 谷氨酸(Glu) 0.98±0.09 1.23±0.09* 天冬氨酸(Asp) 0.32±0.04 0.43±0.03* 酪氨酸(Tyr) 0.24±0.02 0.30±0.02* 丙氨酸(Ala) 0.14±0.02 0.19±0.02* 甘氨酸(Gly) 0.08±0.01 0.11±0.01* 亮氨酸(Leu) a 0.42±0.04 0.54±0.03* 缬氨酸(Val) a 0.28±0.03 0.37±0.02* 苯丙氨酸(Phe) a 0.22±0.03 0.28±0.03* 异亮氨酸(Ile) a 0.23±0.03 0.30±0.02* 苏氨酸(Thr) a 0.19±0.02 0.25±0.02* 甲硫氨酸(Met) a 0.09±0.00 0.13±0.02* 组氨酸(His) 0.12±0.02 0.16±0.01* 丝氨酸(Ser) 0.24±0.03 0.29±0.02 精氨酸(Arg) 0.14±0.01 0.19±0.02 TEAA 1.79±0.18 2.36±0.17* TAA 4.44±0.44 5.82±0.41* TEAA/TAA(%) 40.32 40.55 TEAA/TNEAA 0.675 0.682 注:a 必需氨基酸,TAA-氨基酸,TEAA-必需氨基酸,TNEAA-非必需氨基酸。 2.1.3 荷斯坦牛乳与娟姗牛乳矿物质含量比较分析
荷斯坦牛乳与娟姗牛乳中矿物质含量如表3所示,所测8种矿物质中锰在两种牛乳中含量均最低(<10 μg/100 g);荷斯坦牛乳中钾含量最高,为124.67 mg/100 g;娟姗牛乳中钙含量最高,137.00 mg/100 g,且与荷斯坦牛乳中的钙含量差异极显著(P<0.01);娟姗牛乳中的磷含量(116.33 mg/100 g)显著高于荷斯坦牛乳(97.63 mg/100 g)(P<0.05);娟姗牛乳的钙磷比(1.18)也极显著高于荷斯坦牛乳(1.06)(P<0.01)。
表 3 荷斯坦与娟姗牛乳矿物质含量比较Table 3. Comparison of mineral contents in Holstein and Jersey milk矿物质种类 荷斯坦牛乳 娟姗牛乳 钙(mg/100 g) 103.00±1.00 137.00±10.54** 磷(mg/100 g) 97.63±7.27 116.33±4.93* 钾(mg/100 g) 124.67±18.50 80.63±28.5 镁(mg/100 g) 11.01±1.10 11.80±0.46 锌(mg/100 g) 0.43±0.07 0.46±0.15 铁(mg/100 g) 0.09±0.00 0.10±0.02 铜(μg/100 g) 198.33±51.40 136.27±79.69 锰(μg/100 g) <10 <10 钙磷比 1.06 1.18** 2.2 细菌多样性分析
2.2.1 细菌群落多样性分析
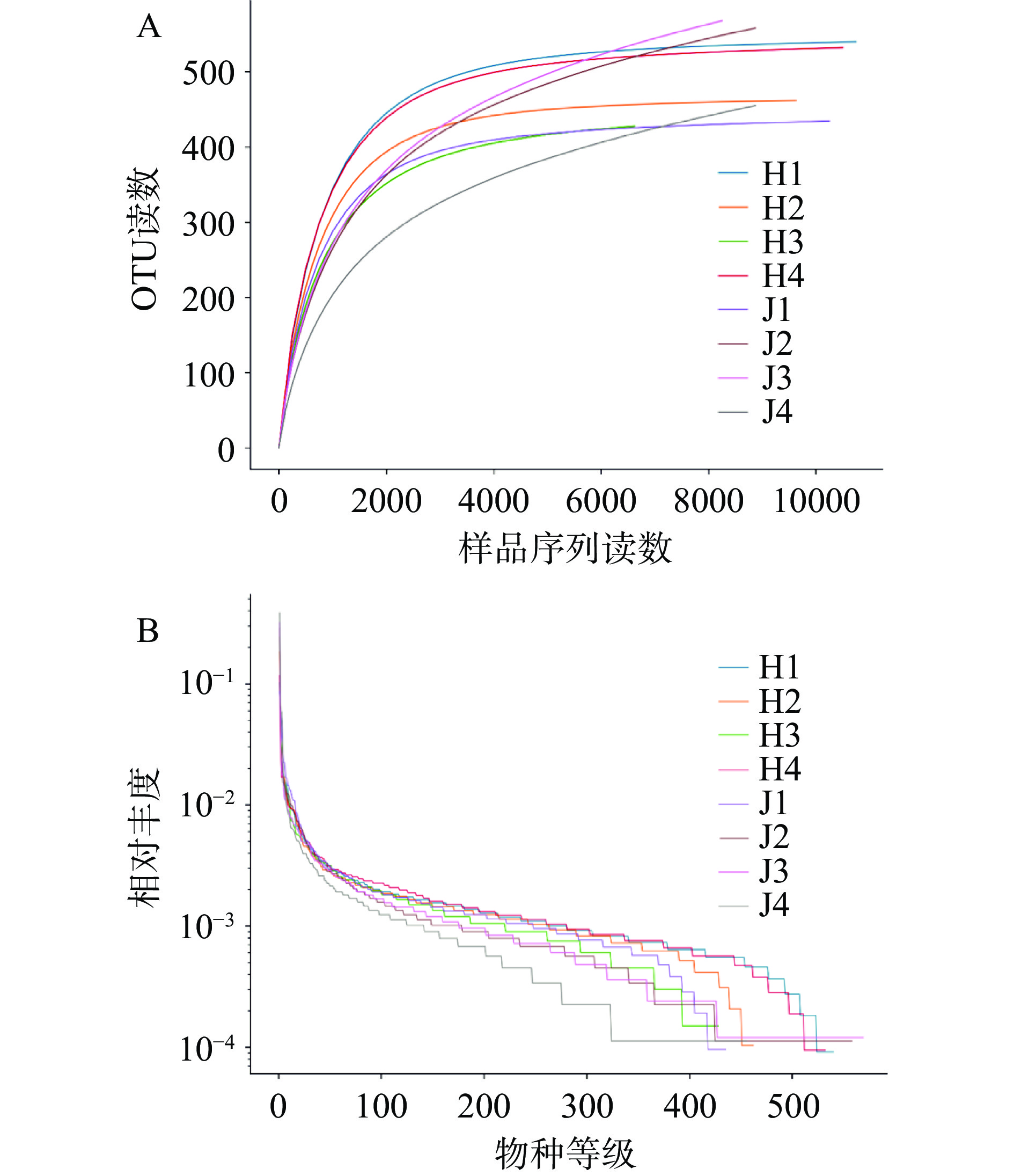
通过Barcode识别后共获得100180条CCS序列,每个样品至少产生10900条CCS序列,平均产生12523条CCS序列。经质控过滤平均得到99917条有效数据,质控有效数据量达98063,质控有效率达97.28%。样品稀释曲线(图1A)趋于平缓,样品序列充分,样品中已包含绝大多数细菌物种信息。等级丰度曲线(图1B)在横轴上的范围较大,在垂直方向渐进平缓,表明所测样品中物种丰富度较高且分布均匀。根据Shannon、Simpson、ACE和Chao1指数(表4),荷斯坦牛乳和娟姗牛乳样品中细菌群落多样性和种群丰富度均无显著差异(P>0.05)。
![]() 图 1 Alpha多样性分析注:A:样品稀释曲线;B:等级丰度曲线。H1、H2、H3、H4表示荷斯坦牛乳样品;J1、J2、J3、J4表示娟姗牛乳样品,图3同。Figure 1. Alpha diversity analysis表 4 Alpha 多样性指数Table 4. Alpha diversity indexes
图 1 Alpha多样性分析注:A:样品稀释曲线;B:等级丰度曲线。H1、H2、H3、H4表示荷斯坦牛乳样品;J1、J2、J3、J4表示娟姗牛乳样品,图3同。Figure 1. Alpha diversity analysis表 4 Alpha 多样性指数Table 4. Alpha diversity indexes分组 Shannon Simpson ACE Chao1 荷斯坦牛乳 7.39±0.58 0.96±0.02 495.86±51.89 502.68±25.57 娟姗牛乳 6.32±0.86 0.91±0.06 587.52±108.45 625.00±125.25 P 0.085 0.112 0.178 0.121 2.2.2 细菌群落组成分析
将有效测序列在97.0%的相似度水平下进行聚类,共获得1712个OTUs,两种牛乳中共有的OTUs为626个,荷斯坦牛乳特有549个OTUs,娟姗牛乳特有537个OTUs,娟姗牛乳特有的OTUs略低于荷斯坦牛乳。
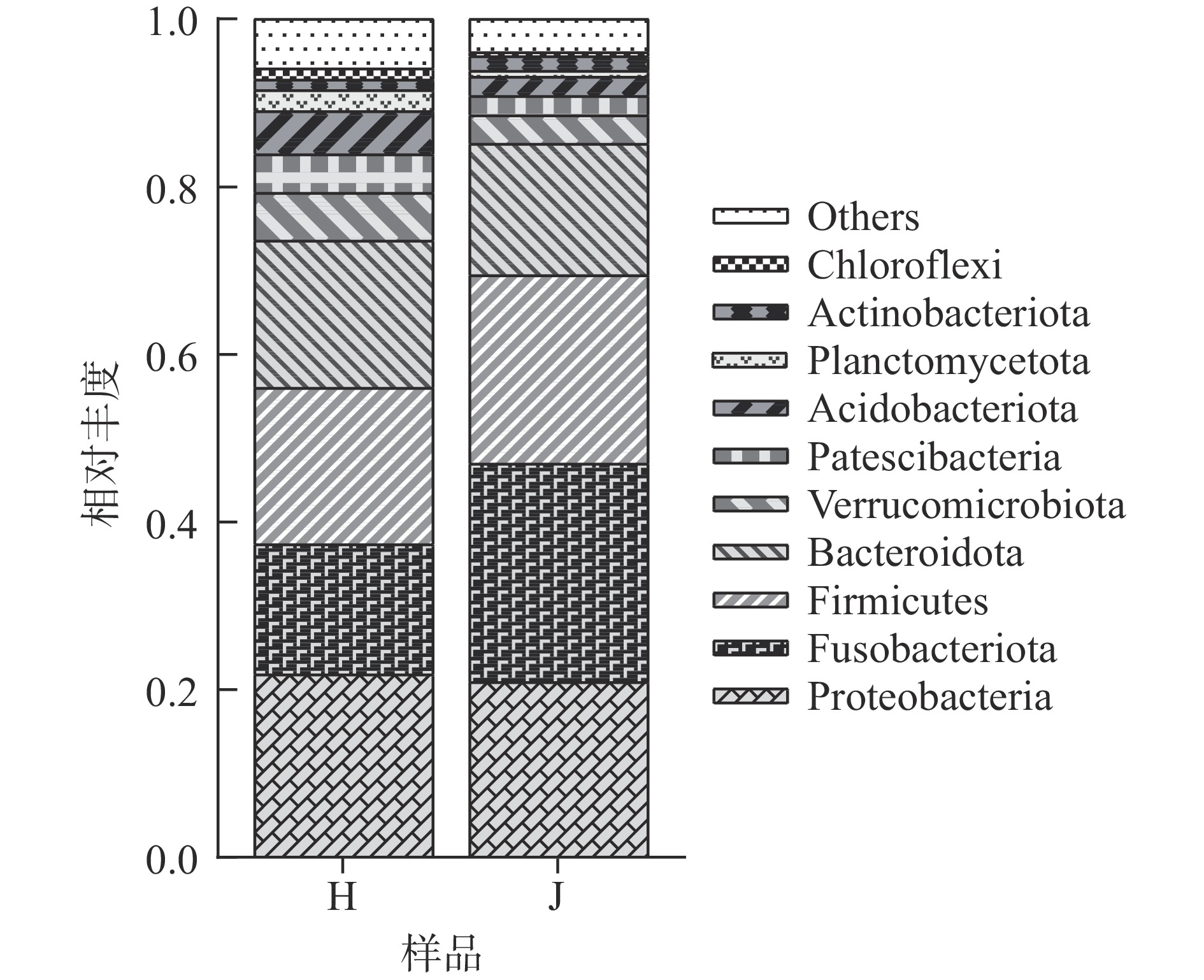
荷斯坦牛乳和娟姗牛乳中细菌门水平上前10种菌落的相对丰度如图2所示,变形菌门(Proteobacteria)、梭杆菌门(Fusobacteriota)、厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)和拟杆菌门(Bacteroidota)在两种牛乳中均占优势,与Breitenwieser等 [12]的研究结果相似。荷斯坦牛乳和娟姗牛乳中的变形菌门相对丰度分别为21.86%和20.95%,梭杆菌门相对丰度分别为15.48%和26.03%,厚壁菌门相对丰度分别为18.66%和22.51%,拟杆菌门相对丰度分别为17.58%和15.66%。其次疣微菌门(Verrucomicrobiota)、酸杆菌门(Acidobacteriota)、髌骨细菌门(Patescibacteria)、浮霉菌门(Planctomycetota)、放线菌门(Actinobacteriota)和绿弯菌门(Chloroflexi)也占一定比例。
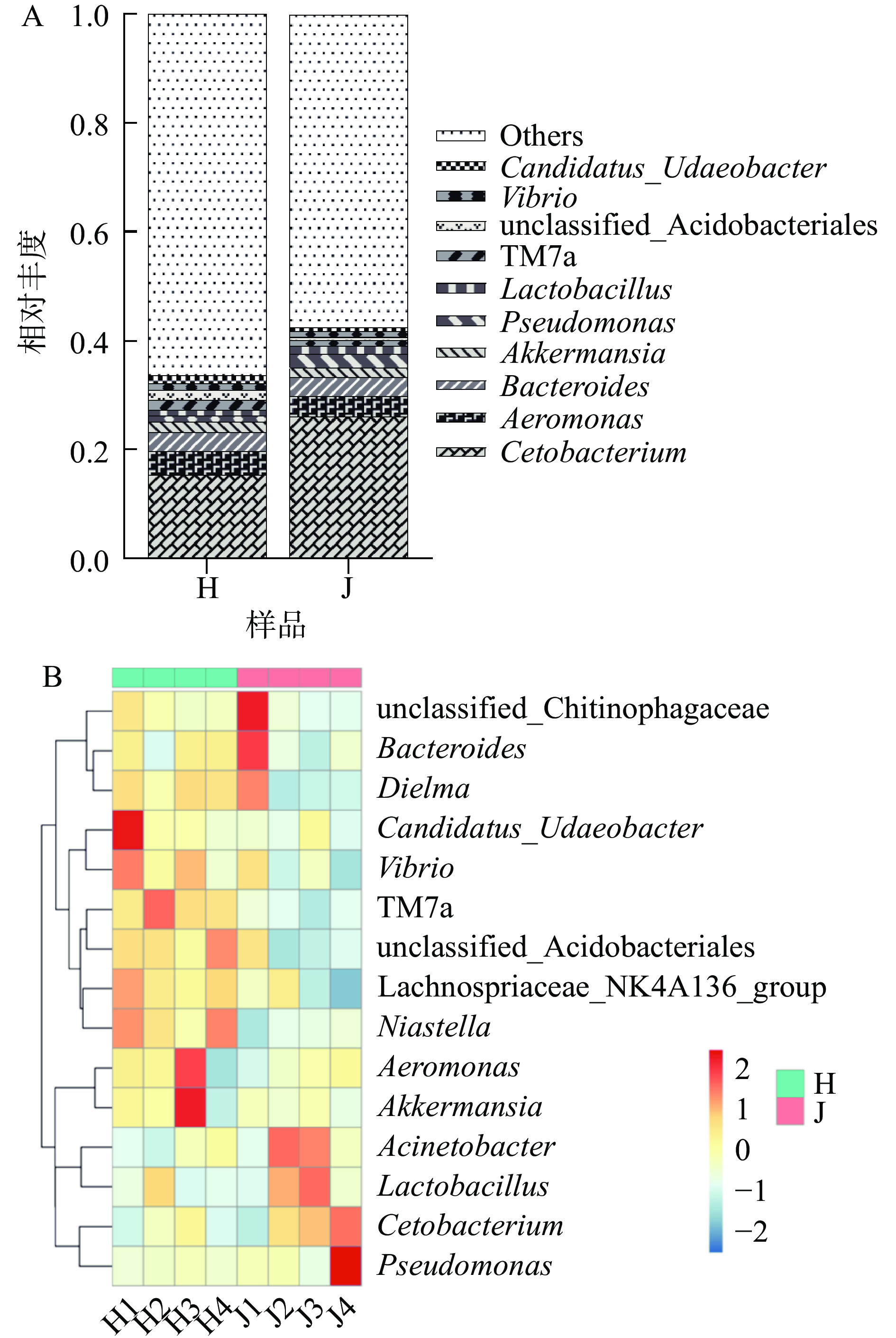
荷斯坦牛乳和娟姗牛乳中细菌属水平的比较如图3A所示,两种牛乳中所含优势菌属种类差异较小,鲸杆菌属(Cetobacterium)、气单胞菌属(Aeromonas)、拟杆菌属(Bacteroides)、阿克曼氏菌属(Akkermansia)、假单胞菌属(Pseudomonas)和乳杆菌属(Lactobacillus)为两种牛乳中的共同优势菌属。娟姗牛乳中的鲸杆菌属、乳杆菌属和假单胞菌属相对丰度高于荷斯坦牛乳,气单胞菌属和阿克曼氏菌属相对丰度低于荷斯坦牛乳,拟杆菌属丰富度基本相同。假单胞菌属(Pseudomonas)、气单胞菌属(Aeromonas)、拟杆菌属(Bacteroides)和乳杆菌属(Lactobacillus)在生牛乳中占优势较为常见[6, 13],但鲸杆菌属(Cetobacterium)和阿克曼氏菌属(Akkermansia)在其他地区牛乳中未见报道。鲸杆菌属(Cetobacterium)在反刍动物黑山羊肠道中被检测出[14];阿克曼氏菌属(Akkermansia)则被证明在高海拔藏羚羊肠道中占优势[15]。由属水平下的细菌多样性热图(图3B)可知,荷斯坦牛乳中以气单胞菌属(Aeromonas)、Candidatus_Udaeobacter和阿克曼氏菌属(Akkermansia)为主;娟姗牛乳中假单胞菌属(Pseudomonas)、拟杆菌属(Bacteroides)和噬几丁质杆菌科未分类的细菌属(unclassified_Chitinophagaceae)较为常见。
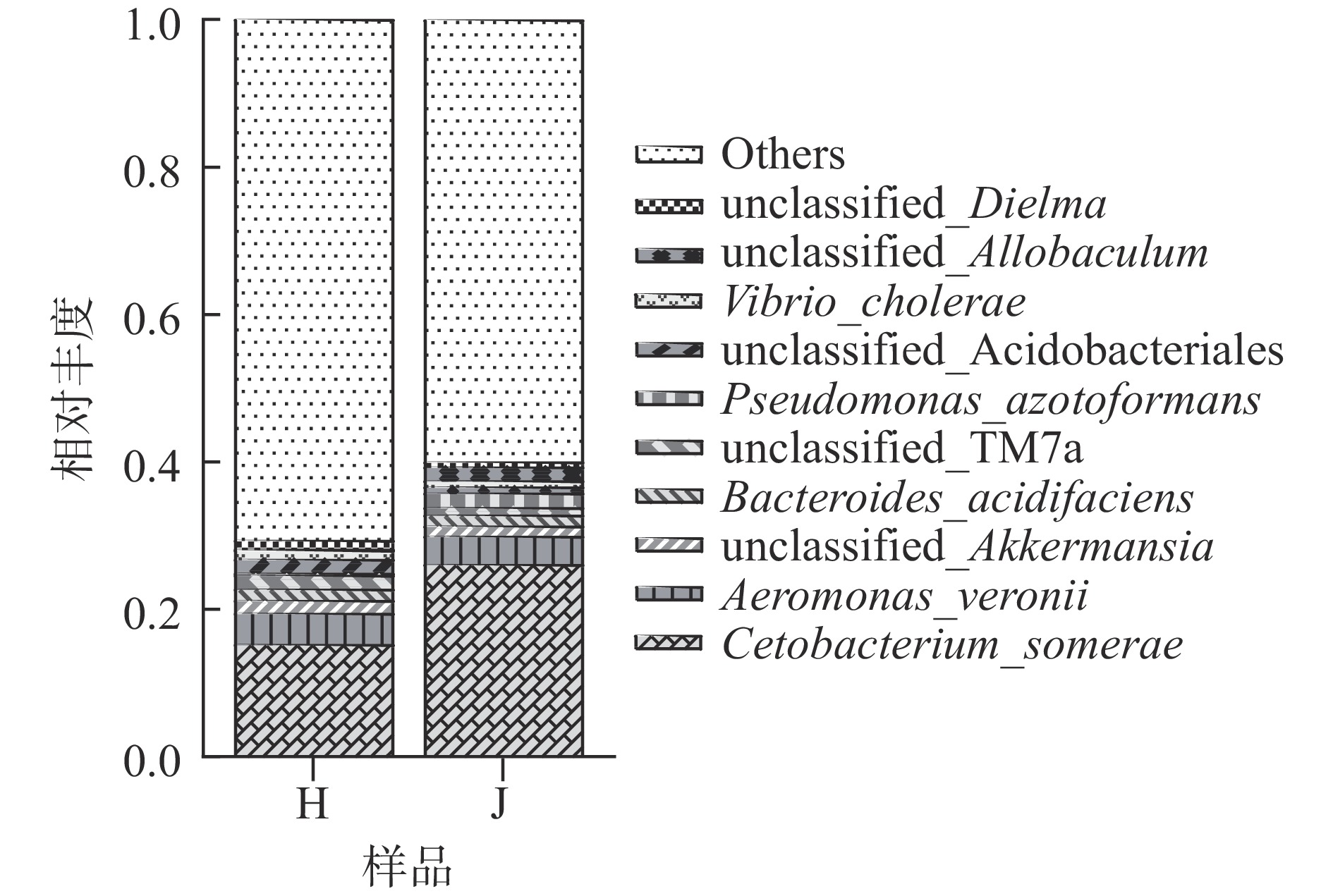
荷斯坦牛乳和娟姗牛乳中细菌种水平的比较如图4所示,索氏鲸杆菌(Cetobacterium_somerae)和维氏气单胞菌(Aeromonas_veronii)为两种牛乳中的共同优势菌种,其中索氏鲸杆菌(Cetobacterium_somerae)在娟姗牛乳中的相对丰度达到26.01%,明显高于荷斯坦牛乳(15.42%),未分类的阿克曼氏菌(unclassified_Akkermansia)和产酸拟杆菌(Bacteroides_acidifaciens)在两种牛乳中也占较大比例。荷斯坦牛乳中unclassified_TM7a和酸杆菌目未分类的细菌属(unclassified_Acidobacteriales)相对丰度高于娟姗牛乳,产氮假单胞菌(Pseudomonas_azotoformans)和别样棒菌属未分类的细菌(unclassified_Allobaculum)相对丰度低于娟姗牛乳。
2.2.3 组间差异分析
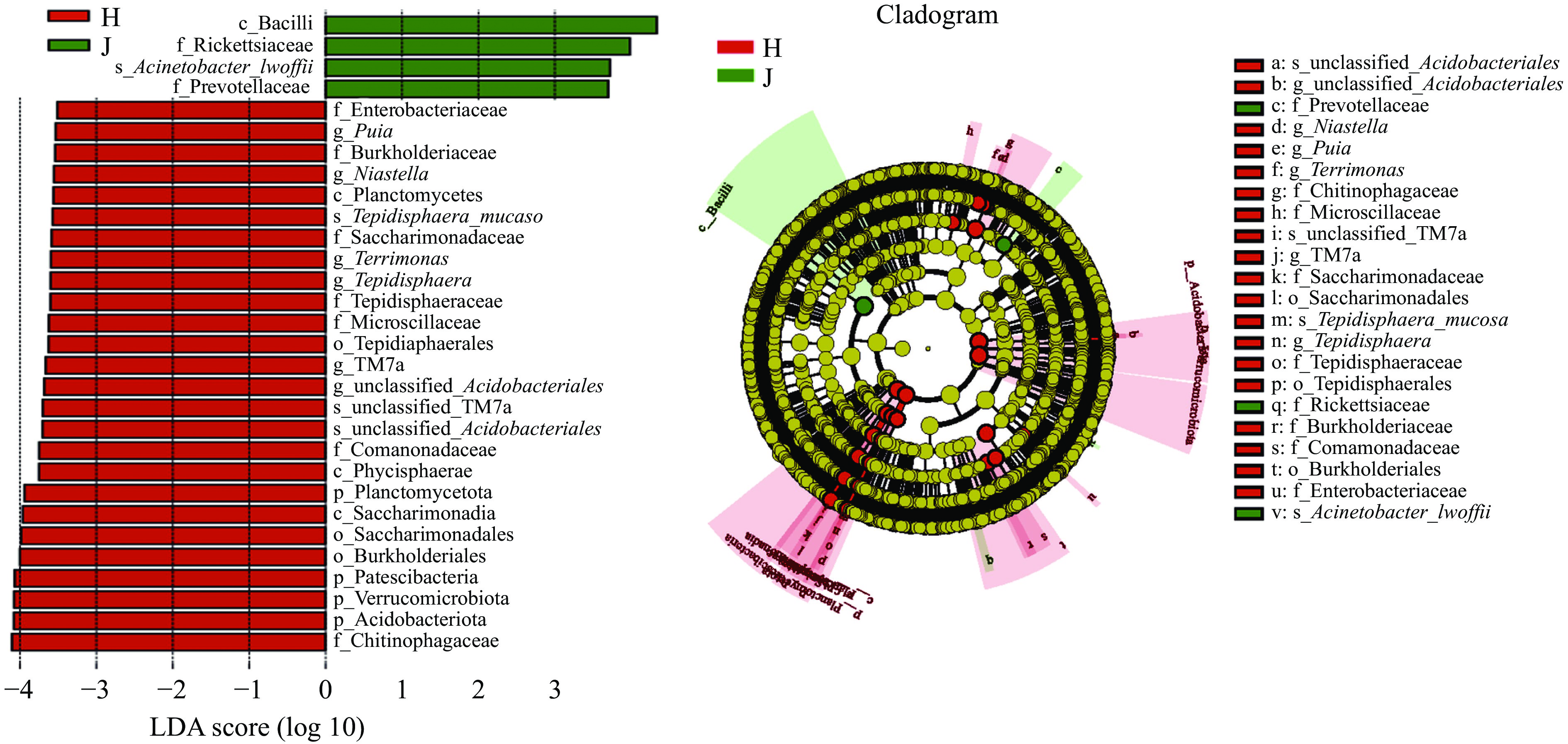
为了确定最有可能导致荷斯坦牛乳和娟姗牛乳样本之间细菌群落组成差异的细菌分类群,使用线性判别分析(LDA)效应大小(LEfSe)方法进行分析,结果如图5所示,共有30个(LDA score>3.5)物种对于区分两组奶样的贡献最大。娟姗牛乳中的杆菌纲(Bacilli),洛菲不动杆菌(Acinetobacter_lwoffii)和普雷沃氏菌科(Prevotellaceae)等与娟姗乳样细菌群落联系紧密,是造成娟姗牛乳与荷斯坦牛乳细菌群落差异的关键类群;荷斯坦牛乳中造成与娟姗牛乳细菌群落差异的关键菌有26种,门水平至种水平均有分布,其中造成与娟姗牛乳细菌群落差异的最关键类群为酸杆菌门(Acidobacteriota)、疣微菌门(Verrucomicrobiota)、骨细菌门(Patescibacteria)、伯克氏菌目(Burkholderiales)和几丁质科(Chitinophagaceae)(LDA score>4.0)。
2.3 营养成分与细菌多样性的相关性分析
2.3.1 乳基本成分与细菌相关性分析
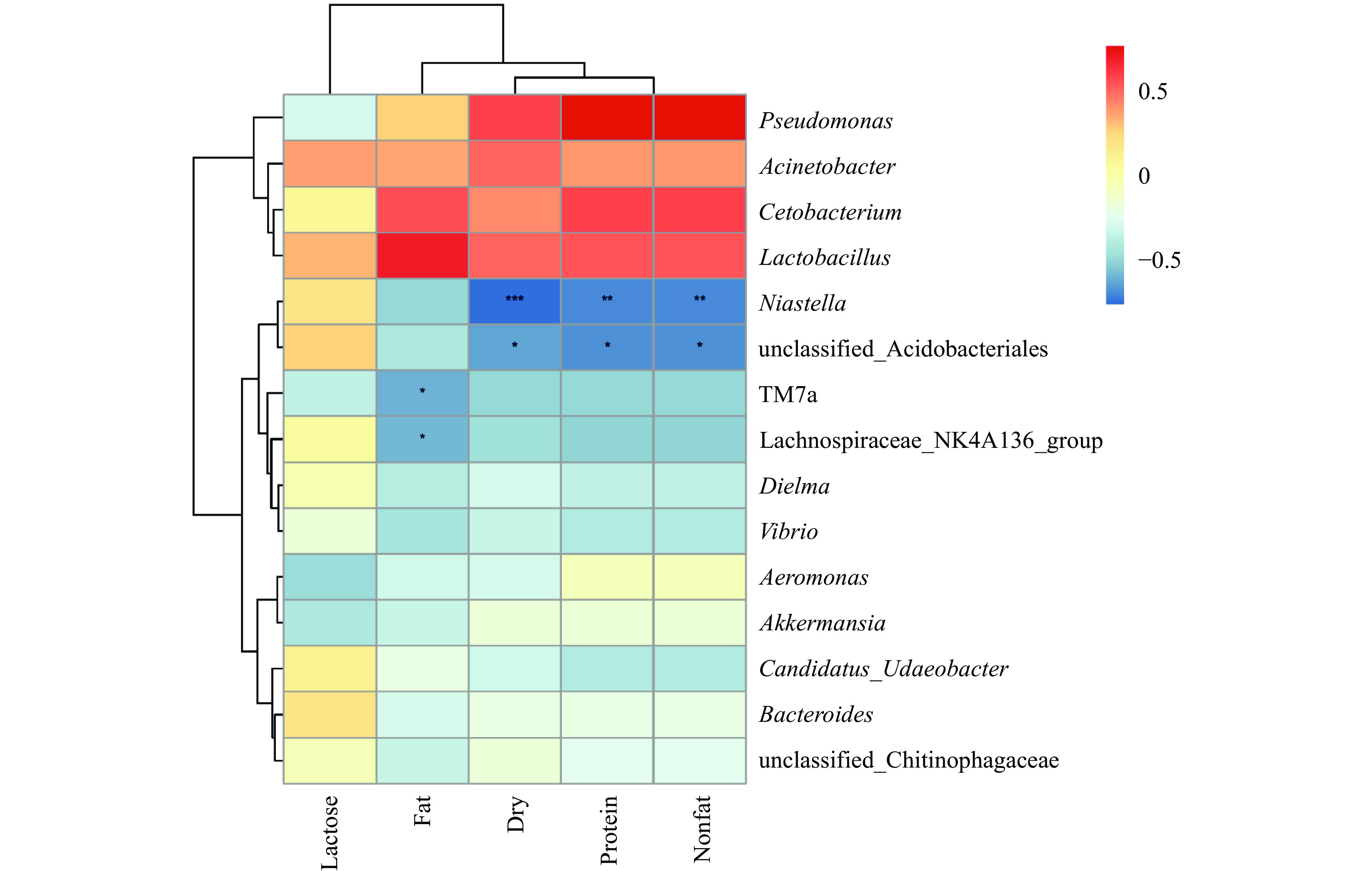
细菌群落与乳基本成分相关性如图6所示,蛋白质、干物质、非脂固体和脂肪与假单胞菌属(Pseudomonas)、不动杆菌属(Acinetobacter)、鲸杆菌属(Cetobacterium)和乳杆菌属(Lactobacillus)呈正相关,与其它菌属基本呈负相关。干物质、蛋白质和非脂固体对农研丝杆菌属(Niastella)影响极显著(P<0.01),对酸杆菌目未分类的细菌属(unclassified_Acidobacteriales)影响显著(P<0.05);脂肪对TM7a和毛螺菌科NK4A136群(Lachnospiraceae_NK4A136_group)具有显著影响(P<0.05);其他菌属受乳基本成分影响不显著(P>0.05)。
2.3.2 氨基酸与细菌相关性分析
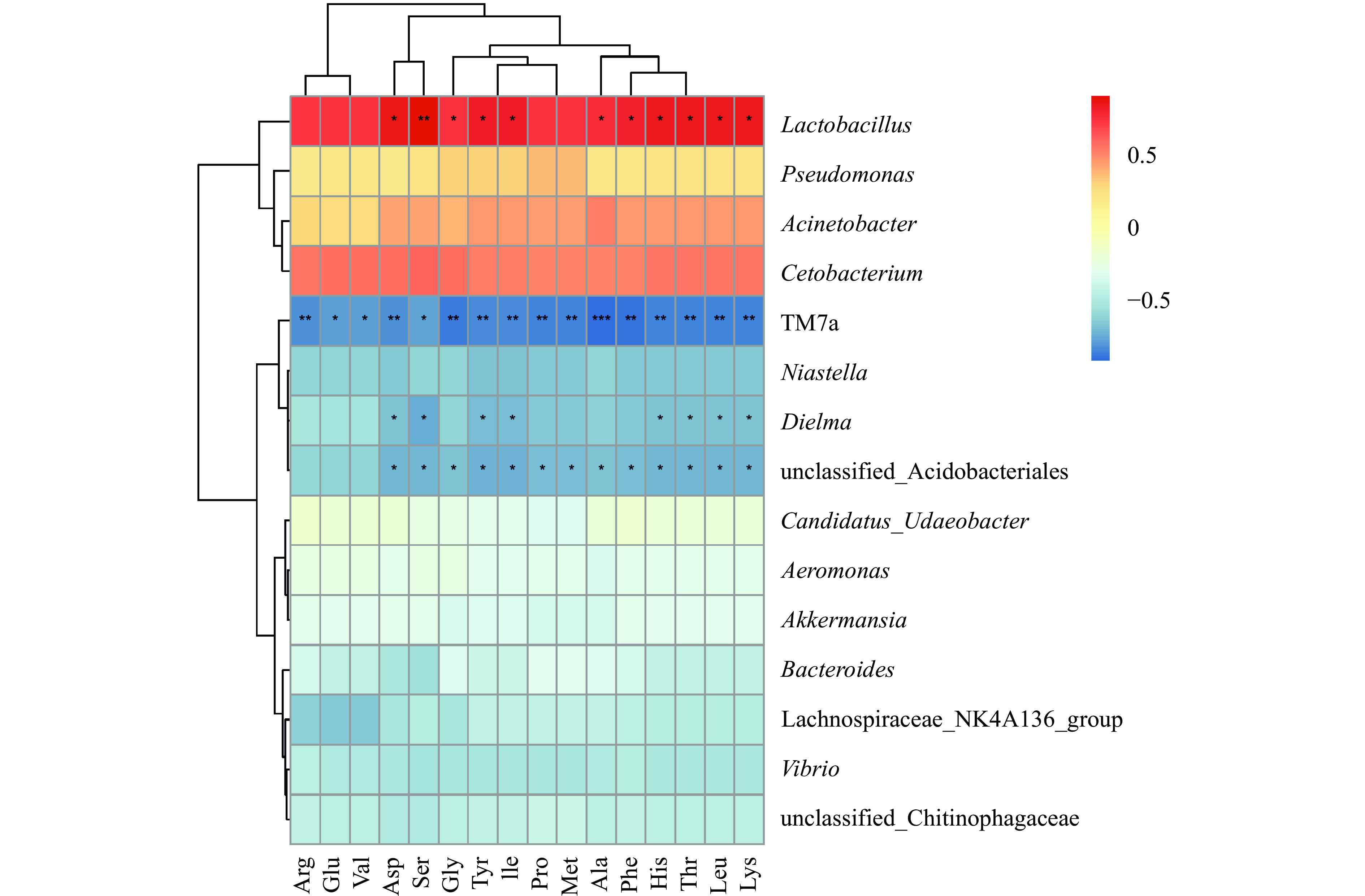
细菌群落与乳中氨基酸含量相关性如图7所示,所测16种氨基酸主要与乳杆菌属(Lactobacillus)呈正相关,与酸杆菌目未分类的细菌属(unclassified_Acidobacteriales)、TM7a和Dielma呈负相关,与其他菌属相关性较弱。丝氨酸对乳杆菌属(Lactobacillus)影响极显著(P<0.01),天冬氨酸、甘氨酸、酪氨酸、异亮氨酸、丙氨酸、苯丙氨酸、组氨酸、苏氨酸、亮氨酸和赖氨酸对乳杆菌属(Lactobacillus)影响显著(P<0.05);所测16种氨基酸均对TM7a有影响,其中谷氨酸、缬氨酸和丝氨酸对TM7a影响显著(P<0.05),其余13种氨基酸对TM7a影响极显著(P<0.01);天冬氨酸、丝氨酸、酪氨酸、异亮氨酸、组氨酸、苏氨酸、亮氨酸和赖氨酸对Dielma影响显著(P<0.05);除精氨酸、谷氨酸和缬氨酸之外的13种氨基酸均对酸杆菌目未分类的细菌属(unclassified_Acidobacteriales)具有显著影响(P<0.05)。
2.3.3 矿物质与细菌相关性分析
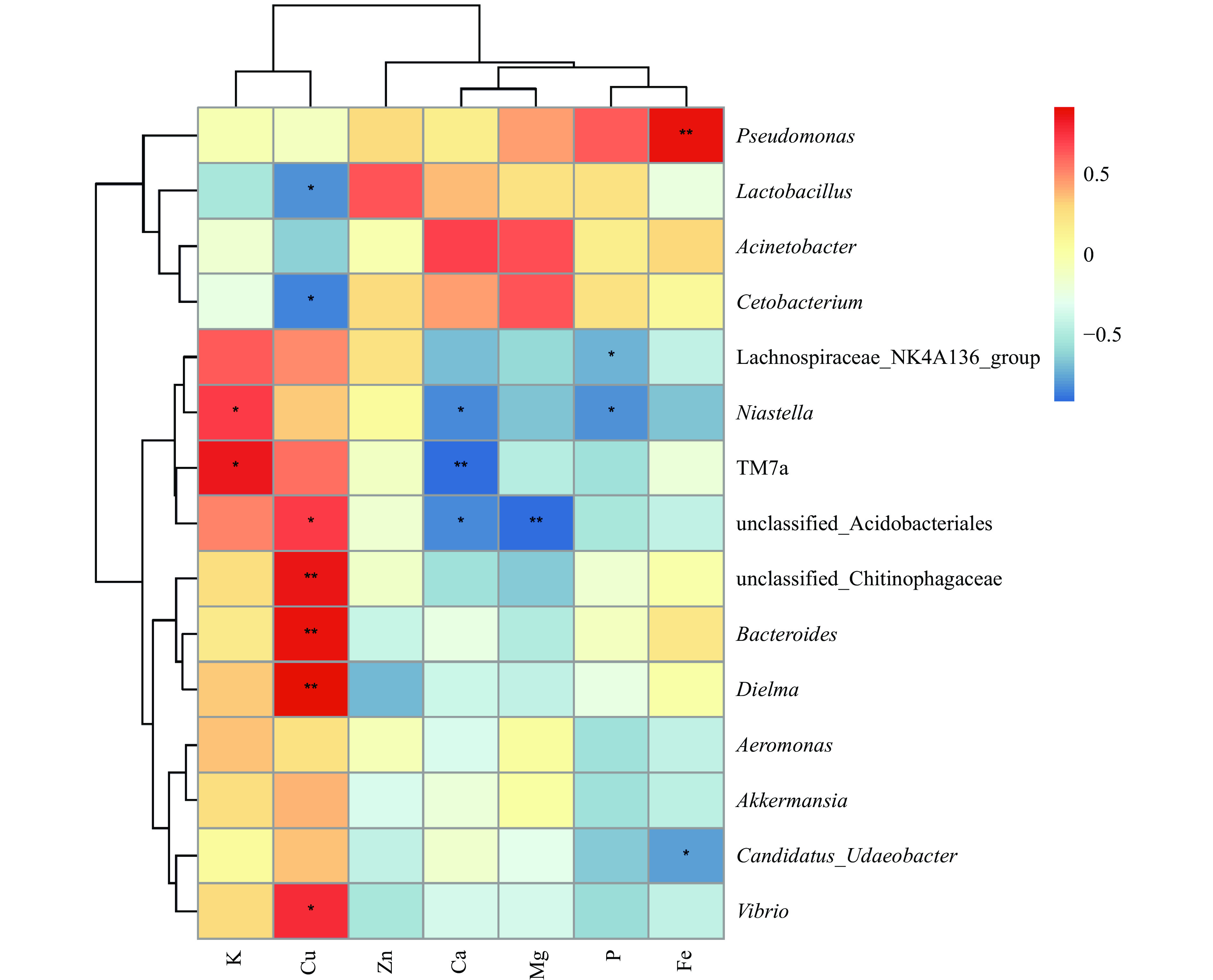
细菌群落与乳矿物质含量相关性如图8所示,所测矿物质中钾对TM7a和农研丝杆菌属(Niastella)影响显著(P<0.05);铜对Dielma、拟杆菌属(Bacteroides)和噬几丁质杆菌科未分类的细菌属(unclassified_Chitinophagaceae)影响极显著(P<0.01),对弧菌属(Vibrio)、酸杆菌目未分类的细菌属(unclassified_Acidobacteriales)、鲸杆菌属(Cetobacterium)和乳杆菌属(Lactobacillus)影响显著(P<0.05);钙对TM7a影响极显著(P<0.01),对酸杆菌目未分类的细菌属(unclassified_Acidobacteriales)和农研丝杆菌属(Niastella)影响显著(P<0.05);镁对酸杆菌目未分类的细菌属(unclassified_Acidobacteriales)影响极显著(P<0.01);磷对农研丝杆菌属(Niastella)和毛螺菌科NK4A136群(Lachnospiraceae_NK4A136_group)影响显著(P<0.05);铁对假单胞菌属(Pseudomonas)影响极显著(P<0.01),对Candidatus_Udaeobacter影响显著(P<0.05)。
3. 讨论
牛乳能为人类提供关键营养元素和生物活性物质,作为乳品供应链上游的原料乳,生乳的品质较为关键[16]。乳营养成分含量的差异受地域、采样时间、泌乳期、胎次等多种因素的影响[17-19],本研究两种奶牛均饲养于相同的高原环境下,且年龄、胎次、泌乳期、健康状况基本相同,所以奶牛品种的不同可能是导致娟姗牛乳的乳脂率、乳蛋白率、氨基酸含量和钙和磷含量显著高于荷斯坦牛乳的主要原因(P<0.05),娟姗牛乳的品质总体优于荷斯坦牛乳,能为生产高质量乳制品提供更优质的乳源。本研究荷斯坦牛乳营养成分优于多数已报道的低海拔地区同种牛乳,娟姗牛乳营养成分与其他地区差别较小[5, 20-23]。可能是因为荷斯坦牛耐寒不耐热[24],高原饲养对乳营养成分分泌更有利;而娟姗牛耐热性较好[25],所以高原饲养环境对其乳营养成分影响较小。
生乳中微生物的具体组成会对牛乳质量和保质期产生影响,直接关系到乳制品的后续加工[26]。本研究荷斯坦牛乳与娟姗牛乳中的细菌组成相似,丰度不同;优势菌门与其他研究基本一致,而种属水平的差异较明显[12-13, 27]。同一环境不同品种生牛乳中的细菌种属水平组成相似,但不同地区间细菌种属水平组成差异较大,表明牛品种和宿主遗传对牛乳微生物群落组成影响较小,地域和饲养环境等因素对牛乳微生物群落组成影响较大[28]。乳微生物来源较广,有研究推测母体肠道中的细菌可以转移到乳腺[29]。本研究牛乳中首次报道的鲸杆菌属(Cetobacterium)和阿克曼氏菌属(Akkermansia)也存在于反刍动物肠道中,其与肠道微生物间的关系需要进一步分析[14-15]。微生物生长代谢利用营养物质的途径不同,与代谢相关的营养物质影响物种的适应性[30]。本研究两种牛乳中的细菌组成一致,说明细菌的来源相同,但在乳中的生长代谢依赖于乳中的营养成分,乳营养成分的差异可能会导致细菌丰度的不同[31]。环境因子对微生物生态具有关键作用,乳营养成分对微生物群落结构的具体影响及其影响机制还需进一步研究。
4. 结论
本研究对高原饲养条件下的荷斯坦牛乳与娟姗牛乳营养成分及细菌多样性进行了测定,并对两者间的相关性进行了分析。结果显示高原环境相同饲养条件下娟姗牛乳脂肪含量比荷斯坦牛乳高10.61%,蛋白质含量比荷斯坦牛乳高12.17%;娟姗牛乳中的氨基酸总量和必需氨基酸含量均显著高于荷斯坦牛乳(P<0.05);娟姗牛乳中钙含量、磷含量及钙磷比均显著高于荷斯坦牛乳(P<0.05)。两种牛乳中的细菌群落组成基本一致,所占比例不同。属水平上娟姗牛乳中的鲸杆菌属、乳杆菌属和假单胞菌属相对丰度高于荷斯坦牛乳,气单胞菌属和阿克曼氏菌属相对丰度低于荷斯坦牛乳;种水平上索氏鲸杆菌在娟姗牛乳中的相对丰度达到26.01%,明显高于荷斯坦牛乳(15.42%)。通过Spearman相关性分析得出乳基本成分、氨基酸和矿物质均与细菌群落呈现一定相关性。本研究为高原环境下两种牛乳营养成分和细菌多样性异同以及牛乳细菌与营养成分相关性提供了数据参考。
-
图 1 Alpha多样性分析
注:A:样品稀释曲线;B:等级丰度曲线。H1、H2、H3、H4表示荷斯坦牛乳样品;J1、J2、J3、J4表示娟姗牛乳样品,图3同。
Figure 1. Alpha diversity analysis
表 1 荷斯坦与娟姗牛乳成分比较
Table 1 Composition comparison of Holstein and Jersey milk
表 2 荷斯坦与娟姗牛乳氨基酸含量比较(g/100 g)
Table 2 Comparison of amino acid contents in Holstein and Jersey milk (g/100 g)
氨基酸种类 荷斯坦牛乳 娟姗牛乳 赖氨酸(Lys) a 0.36±0.03 0.48±0.03** 脯氨酸(Pro) 0.38±0.04 0.57±0.04** 谷氨酸(Glu) 0.98±0.09 1.23±0.09* 天冬氨酸(Asp) 0.32±0.04 0.43±0.03* 酪氨酸(Tyr) 0.24±0.02 0.30±0.02* 丙氨酸(Ala) 0.14±0.02 0.19±0.02* 甘氨酸(Gly) 0.08±0.01 0.11±0.01* 亮氨酸(Leu) a 0.42±0.04 0.54±0.03* 缬氨酸(Val) a 0.28±0.03 0.37±0.02* 苯丙氨酸(Phe) a 0.22±0.03 0.28±0.03* 异亮氨酸(Ile) a 0.23±0.03 0.30±0.02* 苏氨酸(Thr) a 0.19±0.02 0.25±0.02* 甲硫氨酸(Met) a 0.09±0.00 0.13±0.02* 组氨酸(His) 0.12±0.02 0.16±0.01* 丝氨酸(Ser) 0.24±0.03 0.29±0.02 精氨酸(Arg) 0.14±0.01 0.19±0.02 TEAA 1.79±0.18 2.36±0.17* TAA 4.44±0.44 5.82±0.41* TEAA/TAA(%) 40.32 40.55 TEAA/TNEAA 0.675 0.682 注:a 必需氨基酸,TAA-氨基酸,TEAA-必需氨基酸,TNEAA-非必需氨基酸。 表 3 荷斯坦与娟姗牛乳矿物质含量比较
Table 3 Comparison of mineral contents in Holstein and Jersey milk
矿物质种类 荷斯坦牛乳 娟姗牛乳 钙(mg/100 g) 103.00±1.00 137.00±10.54** 磷(mg/100 g) 97.63±7.27 116.33±4.93* 钾(mg/100 g) 124.67±18.50 80.63±28.5 镁(mg/100 g) 11.01±1.10 11.80±0.46 锌(mg/100 g) 0.43±0.07 0.46±0.15 铁(mg/100 g) 0.09±0.00 0.10±0.02 铜(μg/100 g) 198.33±51.40 136.27±79.69 锰(μg/100 g) <10 <10 钙磷比 1.06 1.18** 表 4 Alpha 多样性指数
Table 4 Alpha diversity indexes
分组 Shannon Simpson ACE Chao1 荷斯坦牛乳 7.39±0.58 0.96±0.02 495.86±51.89 502.68±25.57 娟姗牛乳 6.32±0.86 0.91±0.06 587.52±108.45 625.00±125.25 P 0.085 0.112 0.178 0.121 -
[1] PEREIRA, PAULA C. Milk nutritional composition and its role in human health[J]. Nutrition,2014,30(6):619−627. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2013.10.011
[2] 郭梦玲, 王海洋, 梁艳, 等. 江苏某奶牛场荷斯坦牛和娟姗牛泌乳性能的比较分析[J]. 中国牛业科学,2021,47(2):29−33. [GUO M L, WANG H Y, LIANG Y, et al. Comparative analysis of lactation performance between Holstein and Jersey cows in a dairy farm in Jiangsu[J]. Chinese Cattle Science,2021,47(2):29−33. [3] 王宇. 生牛奶中的主要微生物、检测方法及其控制[J]. 现代畜牧科技,2019(5):6−7. [WANG Y. Main microorganisms in raw milk, detection methods and their control[J]. Modern Animal Husbandry Technology,2019(5):6−7. [4] LIM D H, MAYAKRISHNAN V, LEE H J, et al. A comparative study on milk composition of Jersey and Holstein dairy cows during the early lactation[J]. Journal of Animal Science and Technology,2020,62(4):565−576. doi: 10.5187/jast.2020.62.4.565
[5] TACOMA R, FIELDS J, EBENSTEIN D B, et al. Characterization of the bovine milk proteome in early-lactation Holstein and Jersey breeds of dairy cows[J]. J Proteomics,2016,130:200−210. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2015.09.024
[6] QUIGLEY L, O'SULLIVAN O, STANTON C, et al. The complex microbiota of raw milk[J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews,2013,37(5):664−698. doi: 10.1111/1574-6976.12030
[7] 谢芳, 谢华德, 李孟伟, 等. 冬夏两季水牛乳中细菌多样性的比较分析[J]. 中国乳品工业,2021,49(7):8−12, 17. [XIE F, XIE H D, LI M W, et al. Analysis of bacterial diversity in colostrum and normal milk of buffalo based on 16S rDNA high-throughput sequencing[J]. Chinese Dairy Industry,2021,49(7):8−12, 17. [8] 马静, 张琳琳, 柴沙驼, 等. 基于高通量测序技术分析青藏高原牦牛和犏牛乳中微生物多样性的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(9):122−128. [MA J, ZHANG L L, CHAI S T, et al. Study on microbial diversity in milk of yak and cattle-yak in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau based on high-throughput sequencing technology[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(9):122−128. [9] PORCELLATO D, ASPHOLM M, SKEIE S B, et al. Microbial diversity of consumption milk during processing and storage[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2017,266:21−30.
[10] DOHOO I R, MEEK A H. Somatic cell counts in Bovine milk[J]. The Canadian Veterinary Journal. La Revue Veterinaire Canadienne,1982,23(4):119−125.
[11] FAO/WHO. Energy and protein requirements[R]. Geneva: World Health Organization, 1973.
[12] BREITENWIESER F, DOLL E V, CLAVEL T, et al. Complementary use of cultivation and high-throughput amplicon sequencing reveals high biodiversity within raw milk microbiota[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2020,11:1557. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01557
[13] NAN L, WANG Y, YOU C, et al. Variation in raw milk microbiota throughout 12 months and the impact of weather conditions[J]. Scientific Reports,2018,8(1):2371. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20862-8
[14] LI A, YANG Y, QIN S, et al. Microbiome analysis reveals gut microbiota alteration of early-weaned Yimeng black goats with the effect of milk replacer and age[J]. Microbial Cell Factories,2021,20(1):78. doi: 10.1186/s12934-021-01568-5
[15] BAI X, LU S, YANG J, et al. Precise fecal microbiome of the herbivorous Tibetan antelope inhabiting high-altitude alpine plateau[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2018,28:2321.
[16] MURPHY S C, MARTIN N H, BARBANO D M, et al. Influence of raw milk quality on processed dairy products: How do raw milk quality test results relate to product quality and yield?[J]. Journal of Dairy Science,2016,99(12):10128−10149. doi: 10.3168/jds.2016-11172
[17] MORTON J M, AULDIST M J, DOUGLAS M L, et al. Milk protein concentration, estimated breeding value for fertility, and reproductive performance in lactating dairy cows[J]. Journal of Dairy Science,2017,100(7):5850−5862. doi: 10.3168/jds.2016-11273
[18] GUSTAVSSON F, BUITENHUIS A J, JOHANSSON M, et al. Effects of breed and casein genetic variants on protein profile in milk from Swedish Red, Danish Holstein, and Danish Jersey cows[J]. Journal of Dairy Science,2014,97(6):3866−3877. doi: 10.3168/jds.2013-7312
[19] WELTER K C, MARTINS C, PALMA A, et al. Canola oil in lactating dairy cow diets reduces milk saturated fatty acids and improves its omega-3 and oleic fatty acid content[J]. Plos One,2016,11(3):e0151876. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151876
[20] 吴欣悦, 卢徐斌, 徐天乐, 等. 苏北地区中国荷斯坦牛体型性状遗传参数及其与产奶性状关系的分析[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医,2022(7):65−70. [WU X Y, LU X B, XU T L, et al. Analysis of genetic parameters of body shape traits and their relationship with milk production traits in Chinese Holstein cattle in northern Jiangsu[J]. Heilongjiang Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine,2022(7):65−70. [21] LIM D H, MAYAKRISHNAN V, KI K S, et al. The effect of seasonal thermal stress on milk production and milk compositions of Korean Holstein and Jersey cows[J]. Animal Bioscience,2021,34(4):567−574. doi: 10.5713/ajas.19.0926
[22] 李欣, 周靖航, 温万, 等. 宁夏地区荷斯坦奶牛遗传参数估计[J]. 中国畜牧兽医,2017,44(6):1754−1761. [LI X, ZHOU J H, WEN W, et al. Estimation of genetic parameters of Holstein dairy cows in Ningxia[J]. China Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine,2017,44(6):1754−1761. [23] MANUELIAN C L, PENASA M, VISENTIN G, et al. Mineral composition of cow milk from multibreed herds[J]. Animal Science Journal,2018,89(11):1622−1627. doi: 10.1111/asj.13095
[24] 王泽栋, 张林, 李烨青, 等. 持续热应激对荷斯坦牛和西荷杂交牛生理指标和机体代谢的影响[J]. 中国奶牛,2019(8):9−15. [WANG Z D, ZHANG L, LI Y Q, et al. Effects of sustained heat stress on physiological indexes and body metabolism of Holstein and Western Dutch hybrid cattle[J]. China Dairy Cattle,2019(8):9−15. [25] 王洋, 于静, 王巍, 等. 娟姗牛品种特性及适应性饲养研究[J]. 中国奶牛,2011(11):47−48. [WANG Y, YU J, WANG W, et al. Study on breed characteristics and adaptive feeding of Jersey cattle[J]. China Dairy Cattle,2011(11):47−48. [26] FUSCO V, CHIEFFI D, FANELLI F, et al. Microbial quality and safety of milk and milk products in the 21st century[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety,2020,19(4):2013−2049. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12568
[27] 周杏荣, 周辉, 罗洁, 等. 南山牧场生鲜牛乳理化指标与微生物多样性对比分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(3):101−107. [ZHOU X R, ZHOU H, LUO J, et al. Comparative analysis of physical and chemical indexes and microbial diversity of fresh cow milk in Nanshan Pasture[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(3):101−107. [28] OIKONOMOU G, ADDIS M F, CHASSARD C, et al. Milk microbiota: What are we exactly talking about?[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2020,11:60. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00060
[29] BOUCHARD D S, SERIDAN B, SARAOUI T, et al. Lactic acid bacteria isolated from bovine mammary microbiota: Potential allies against bovine mastitis[J]. PloS One,2015,10(12):e0144831. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144831
[30] WASCHINA S, D'SOUZA G, KOST C, et al. Metabolic network architecture and carbon source determine metabolite production costs[J]. The FEBS Journal,2016,283(11):2149−2163. doi: 10.1111/febs.13727
[31] VERDIER-METZ I, GAGNE G, BORNES S, et al. Cow teat skin, a potential source of diverse microbial populations for cheese production[J]. Applied Environmental Microbiology,2012,78:326−333. doi: 10.1128/AEM.06229-11
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 祁联星,胡玉辉,姜骥文,张凯,张欣悦,张子涵,于海明. 水稻秸秆营养穴盘热风辅助微波干燥工艺参数优化. 农机化研究. 2025(01): 210-217 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 马爱芳,张嘉伦,王小军,毛润科,胡勐鸿. 山野菜乌龙头加工技术探讨. 中国林副特产. 2025(02): 88-89 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张海燕,康三江,曾朝珍,袁晶. 碱性钙对‘秦冠’苹果块贮藏品质及生理特性的影响. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2023(04): 41-49 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 宁静红,贾永勤,王润霞,杨挺然,张子扬,尤利超. 基于液态空气喷雾速冻鲜枣片的数值分析. 中国食品学报. 2023(06): 258-266 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 吴海燕,施晓玲,袁秋梅. 荠菜过氧化物酶热失活动力学的研究. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2022(18): 5933-5938 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 周湘,李思敏. 甜豆护色保脆条件优化及冻藏品质研究. 广东轻工职业技术学院学报. 2022(05): 25-30 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 周瑜,唱惠宇,陈舜胜. 盐酸提取大眼金枪鱼骨中可溶性钙工艺优化. 甘肃农业大学学报. 2022(06): 218-226 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



