Optimization of Extraction Technology of Polysaccharides from Ganoderma lingzhi Mycelium and Its Protective Effect on Alcoholic Liver Injury
-
摘要: 本研究以灵芝菌丝体为材料,采用水提醇沉法提取灵芝菌丝体多糖,在单因素实验基础上,结合响应面分析法优化灵芝菌丝体多糖提取工艺,通过Sevage法及透析法去除蛋白和小分子,获得初步纯化灵芝菌丝体多糖(SGP)。动物模型:将60只小鼠随机分成空白对照组、模型组、阳性对照组和给药低、中、高组(125、250、500 mg/kg·bw),除空白组外,各组按照0.1 mL/10 g·bw剂量灌胃56°北京红星二锅头,建立慢性酒精肝损伤模型。第15 d开始,各给药组造模4 h后,分别灌胃水飞蓟宾(200 mg/kg·bw)和不同剂量的SGP溶液,连续2周后,解剖。采用试剂盒法测定小鼠血清及肝脏组织中谷草转氨酶(AST)、谷丙转氨酶(ALT)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GSH-PX)、丙二醛(MDA)、总胆固醇(TC)、甘油三酯(TG)和白介素-6(IL-6)、白介素-1β(IL-1β)和肿瘤坏死因子α(TNF-α)水平,并观察小鼠的肝脏病理切片。结果表明:灵芝菌丝体多糖最优提取条件为提取温度89 ℃、提取时间2.5 h和液料比85:1(mL/g),在此条件下,多糖得率为3.44%。动物实验结果表明,与模型组相比,SGP中、高剂量组小鼠肝脏指数极显著下降(P<0.01);SGP 中、高剂量组肝脏和血清中的 CAT、SOD和GSH-PX 活力显著上升(P<0.05),SGP高剂量组 ALT、AST 活力及 MDA、TC、TG、IL-6、IL-1β、TNF-α含量极显著下降(P<0.01);病理组织切片结果显示,SGP可明显改善肝脏受损情况。说明,SGP可以通过改善小鼠肝脏氧化应激水平,脂质代谢水平并降低小鼠肝脏细胞炎症因子含量,进而对慢性酒精性肝损伤小鼠发挥保护作用。Abstract: In this study, Ganoderma lingzhi mycelium powder was used as material to extract polysaccharides from Ganoderma lingzhi mycelium by water extraction and alcohol deposition method. On the basis of single factor experiment, response surface methodology was combined to optimize the extraction process of polysaccharides from Ganoderma lingzhi mycelium. Proteins and small molecules were removed by Sevage method and dialysis method, then, the preliminary purification of Ganoderma lingzhi mycelium polysaccharide (SGP) was obtained. Animal model: 60 mice were randomly divided into blank control group, model group, positive control group and low, medium and high administration groups (125, 250 and 500 mg/kg·bw). Except for blank group, each group was given 56° Beijing Red Star Erguotou by gavage at a dose of 0.1 mL/10 g·bw to establish a chronic alcohol liver injury model. Starting from the 15th day, 4 h after modeling, each administration group was given intragastric administration of silybin (200 mg/kg·bw) and different doses of SGP solution, respectively, and dissected after 2 consecutive weeks. The levels of aspartate amino transferase (AST), aspartate transaminase (ALT), catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-PX), malondialdehyde (MDA), total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in serum and liver tissues of mice were determined by kit method, and the liver pathological sections of mice were observed. The results showed that the optimal extraction conditions of polysaccharides from Ganoderma lingzhi mycelium were 89 ℃, 2.5 h and liquid/solid ratio 85:1 mL/g. Under these conditions, the yield of polysaccharides was 3.44%. Animal experiment results showed that the liver index of mice in SGP medium and high dose groups was significantly decreased (P<0.01). The activities of CAT, SOD and GSH-PX in liver and serum of SGP medium and high dose groups were significantly increased (P<0.05), the activities of ALT and AST and the contents of MDA, TC, TG, IL-6, IL-1β and TNF-α were significantly decreased in SGP high-dose group (P<0.01). The results of pathological tissue sections showed that SGP could significantly improve liver damage. These results indicate that SGP can play a protective role in mice with chronic alcoholic liver injury by improving the oxidative stress level, lipid metabolism level and reducing the content of inflammatory factors in mouse liver cells.
-
Keywords:
- mycelium /
- polysaccharide /
- response surface /
- alcoholic liver injury
-
灵芝(Ganoderma lingzhi)俗称赤芝,属于担子菌门(Basidiomycota)、多孔菌目(Polyporales)、灵芝科(Ganodermataceae)、灵芝属(Ganoderma)[1]。在我国, 灵芝作为一种珍贵的中药材使用已有200多年的历史,具有很高的药用价值[2-4]。目前国内大部分灵芝都是种植灵芝,传统种植方法的生产周期长,采收时间受到限制,而灵芝菌丝体具有培养周期短、产量大等优点[5],因此,通过发酵获得灵芝活性成分更加高效。
据统计,酒精性肝病已经成为第二大肝脏疾病,长期饮酒会导致肝脏脂质代谢及乙醇氧化过程受到阻碍造成脂肪肝和氧化应激反应,同时会令肝脏细胞释放大量炎症因子,造成肝脏损伤或肝细胞坏死[6-7]。多糖是灵芝中重要活性成分,灵芝多糖具有降糖降脂[8-9]、免疫调节[10]、抗氧化、抗衰老[11-12]等作用。已有研究表明,灵芝菌丝体多糖可通过降低MDA含量,升高CAT、SOD水平,减轻机体氧化应激反应并提高抗氧化能力来保护肝脏[13],但其是否能通过调节脂质代谢等其他水平对酒精性肝损伤起到保护作用尚不明确。
本研究以灵芝菌丝体多糖为研究对象,在单因素基础上,结合响应面分析方法,获得灵芝菌丝体多糖最佳提取工艺,随后通过Sevage法除蛋白、透析法去除小分子,获得初步纯化的灵芝菌丝体多糖(SGP),并通过建立小鼠体内酒精肝损伤模型,考察灵芝菌丝体多糖对小鼠酒精肝损伤的保护作用,该研究为灵芝菌丝体多糖的深入开发提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
灵芝菌丝体粉末 由内蒙古锦华生物科技有限公司提供;6周龄雄性昆明小鼠SPF级,体重35~45 g,购买于北京华阜康生物科技股份有限公司(SCXK(京)2019-0008),并饲养于吉林农业大学实验动物中心;无水乙醇、三氯甲烷、正丁醇、浓硫酸、三氟乙酸、甲醇、溴化钾等 北京化工厂;岩藻糖、阿拉伯糖、半乳糖、葡萄糖、木糖、甘露糖、果糖、核糖、半乳糖醛酸、葡萄糖醛酸 美国sigma公司;56°北京红星二锅头 北京红星股份有限公司;水飞蓟宾 天津天士力圣特制药有限公司;谷草转氨酶(aspartate amino transferase,AST)、谷丙转氨酶(aspartate transaminase,ALT)、过氧化氢酶(catalase,CAT)、超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD)、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(glutathione peroxidase,GSH-PX)、丙二醛(malondialdehyde,MDA)、总胆固醇(total cholesterol,TC)和甘油三酯(triglyceride,TG)检测试剂盒 南京建成生物工程研究所;白介素-6(interleukin-6,IL-6)、白介素-1β(interleukin-1β,IL-1β)和肿瘤坏死因子α(tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)检测试剂盒 上海酶联生物科技有限公司;HE(苏木精-伊红)染色试剂盒 索莱宝生物科技有限公司。
HH-4数显恒温水浴锅 常州市江南实验仪器厂;离子色谱柱(Ohpak SB-803、804、805 HQ(300 mm×8 mm)) 美国赛默飞世尔科技公司;OPTILAB T-rex示差检测器 美国怀雅特技术公司;DAWN HELEOS-Ⅱ激光光散射检测器 美国怀雅特技术公司;NICOLET iS10傅立叶变换红外光谱仪 美国赛默飞世尔科技公司;Mode 1680多功能酶标仪 美国伯腾仪器有限公司;2235石蜡切片机 莱卡;Image A3显微镜 Zeiss。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 灵芝菌丝体多糖的提取
采用水提醇沉法提取多糖。准确称取干燥灵芝菌丝体粉末5 g置于烧杯中,加入一定比例水后放入水浴锅中,在一定温度下提取一定时间,在7500 r/min下离心10 min,获得提取液,并浓缩至原有体积的1/5,加入3倍体积的无水乙醇溶液,封口室温静置24 h,在7500 r/min下离心10 min,弃去上清液,取沉淀物进行烘干并称重,采用以下公式计算得率。将烘干后的灵芝菌丝体粗多糖用蒸馏水充分溶解,在7500 r/min下离心10 min后取上清,采用Sevage(正丁醇:三氯甲烷=1:4)法除蛋白,重复多次。除蛋白后的粗多糖溶液转入截流量为3500 Da的透析袋,在4 ℃条件下,蒸馏水透析48 h(每4 h换一次蒸馏水),透析结束后用冷冻干燥机冻干,得到灵芝菌丝体多糖(SGP),采用苯酚硫酸法测定多糖含量[14]。
多糖得率(%)=A1/A2×100 式中:A1为干燥灵芝菌丝体粗多糖质量(g);A2为干燥灵芝菌丝体粉末质量(g)。
1.2.2 单因素实验
精确称取5 g干燥灵芝菌丝体粉末置于各烧杯中,固定提取时间为2.5 h,按照液料比60:1(mL/g)加入去离子水,封口,分别在温度为60、70 、80 、90、100 ℃条件下提取多糖;固定提取温度为80 ℃,按照液料比60:1(mL/g)加入去离子水,封口,分别在时间为1.5、2、2.5、3、3.5 h条件下提取多糖;固定提取温度80 ℃、提取时间2.5 h,分别在液料比为30:1、40:1、50:1、60:1、70:1、80:1、90:1(mL/g)条件下加入去离子水,封口,提取多糖,过滤两次后,在65~70 ℃条件下将滤液浓缩至原体积的1/5,浓缩后加入3倍体积的无水乙醇溶液,封口室温静置24 h,在7500 r/min下离心10 min,弃上清液,取沉淀物进行烘干并称重,即为灵芝菌丝体粗多糖。上述实验,每组均3个平行。
1.2.3 响应面优化多糖提取条件
在单因素筛选的基础上,采用响应面分析法[14]进行提取工艺条件的优化。根据Box-Behnken中心组合试验设计原理,综合单因素实验结果,选取提取温度、提取时间、液料比3个因素,分别以A、B、C为代表,每个因素设3个试验水平,分别以−1 、0、1进行编码,试验因素与水平设计见表1。
表 1 Box-Behnken设计因素水平表Table 1. The factors and levels of Box-Behnken design因素 代码 水平 −1 0 1 提取温度(℃) A 70 80 90 提取时间(h) B 2 2.5 3 液料比(mL/g) C 70:1 80:1 90:1 1.2.4 灵芝菌丝体多糖对酒精肝损伤的保护作用研究
1.2.4.1 酒精肝损伤动物模型的建立、分组及给药
将60只小鼠适应性饲养一周后(动物实验伦理号:20210322002),随机分成6组。空白对照组(Control,CN)按照0.1 mL/10 g·bw每天灌胃生理盐水,模型组(Alcohol,AL)、阳性组(Silybinin,SL)和给药治疗各组按照同等量灌胃56°北京红星二锅头,连续两周,观察小鼠有醉酒症状。第15 d开始,空白对照组每天灌胃生理盐水,其他各剂量组分别每天灌胃56°北京红星二锅头,4 h后,分别灌胃生理盐水、200 mg/kg·bw剂量水飞蓟宾和125、250、500 mg/kg·bw剂量SGP溶液,1次/d,连续2周后,末次给药后断食不断水12 h,解剖。麻醉后眼球取血,取肝脏,一部分肝脏用4%多聚甲醛固定,另一部分放入−80 ℃保存。
1.2.4.2 小鼠肝脏指数的测定
小鼠猝死取出肝脏后,迅速称量并记录。根据以下公式计算小鼠脏器指数。
小鼠肝脏指数(%)= A1/A2×100
式中:A1为小鼠肝脏质量(g);A2为小鼠体质量(g)。
1.2.4.3 血清指标测定
小鼠眼球取血,在3500 r/min条件下离心15 min,取上清后,在相同条件下离心10 min,再取上清。按试剂盒中操作指南上的方法测定小鼠血清中的 ALT、AST、CAT、SOD、GSH-Px、 活力和 MDA含量。
1.2.4.4 肝脏组织指标测定
小鼠取肝脏,按照脏器(g):生理盐水(mL)= 1:9,制成10 %的脏器组织匀浆,3500 r/min 条件下离心10 min,取上清。按试剂盒中操作指南上的方法测定小鼠CAT、SOD、GSH-Px活力和 MDA、TC和TG含量。 同时,采用ELISA法检测小鼠肝脏中细胞因子IL-6、IL-1β和TNF-α水平。
1.2.4.5 小鼠肝脏病理学观察
将4%多聚甲醛中固定的肝脏取出,流动水冲洗一段时间,将多聚甲醛除去。经脱水、透明、包埋、切片和HE(苏木精-伊红)染色后,显微镜观察并拍照。
1.3 数据处理
所有实验重复3次,结果取平均值,图表数据以平均值±标准偏差表示,使用Origin 9.0软件作图,Design-Expert 11.0软件对响应面试验进行分析,数据使用SPSS 16.0 软件进行统计学显著性分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素实验结果分析
本研究考察了提取温度、提取时间及液料比三者对灵芝菌丝体多糖提取的影响,结果表明,随着温度的升高,得率逐渐增大,但在80 ℃后,得率逐渐下降,可能是由于长时间高温,会造成多糖的水解或杂质析出时会吸附部分多糖,从而降低多糖得率[15],故80 ℃为提取最佳温度(图1 A)。图1 B结果表明,随着提取时间的增加,多糖得率逐渐增大,但2.5 h后,得率呈下降趋势,这可能是由于其他水溶性杂质溶出原因[16],因此,2.5 h为提取最佳时间。图1 C结果显示,随着液料比的增大,多糖得率逐渐增大,到 80:1 mL/g的比例时,得率最大,这是由于干燥的药材吸水膨胀限制了多糖的溶出,当药材充分溶胀后,料液比的增加使植物细胞内外多糖浓度差增加,加速了多糖的溶出[17],故液料比为80:1 mL/g是最佳比例。因此,单因素实验结果表明,提取温度80 ℃、提取时间2.5 h和液料比80:1 mL/g为最佳提取条件,以此条件进行进一步优化分析。
2.2 响应面优化试验
2.2.1 响应面优化结果和方差分析
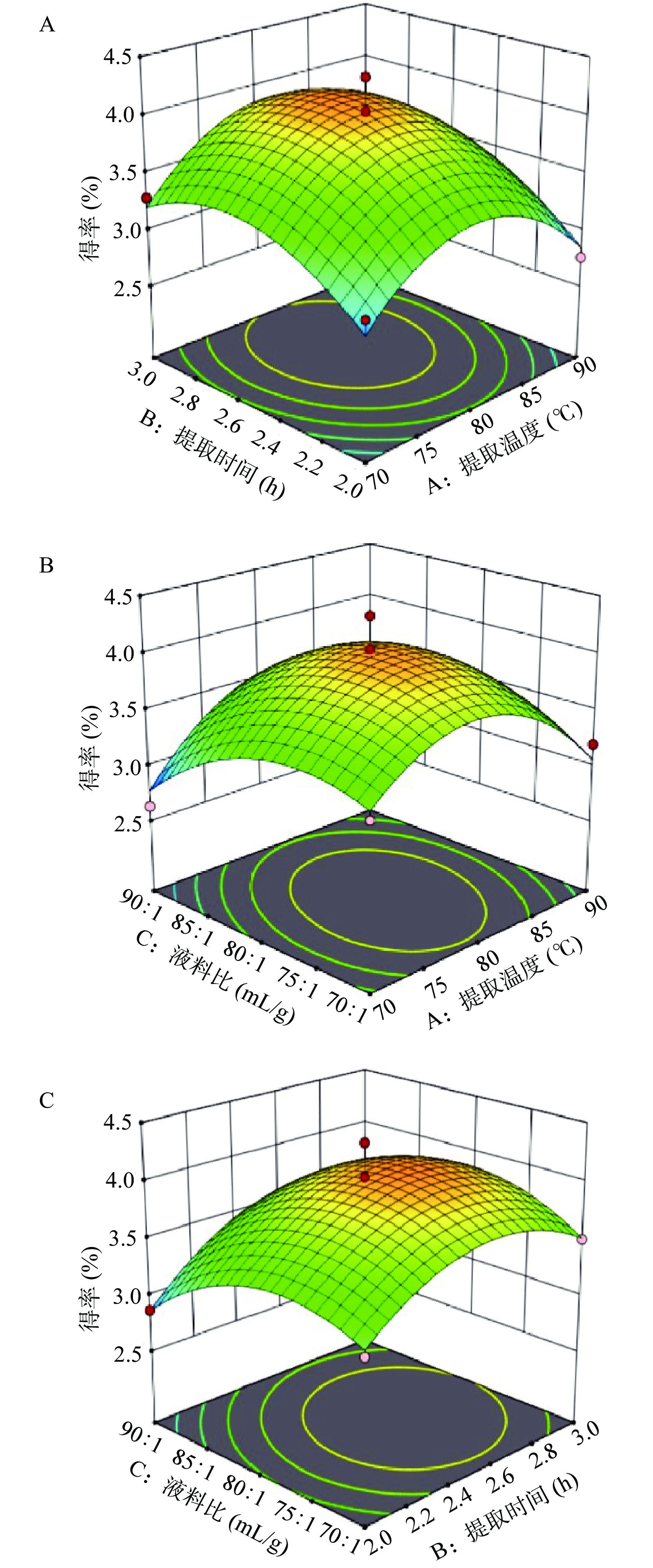
在单因素实验结果的基础上,根据 Box-Behnken 试验设计原理,以提取温度(A)、提取时间(B)和液料比(C)3个因素为变量设计试验,试验设计和结果见表2。分析得到:Y=4.03−0.0375A+0.2175B−0.1075C+0.0550AB+0.1850AC+0.1050BC−0.5680A2−0.3780B2−0.3580C2二元多项式方程,决定系数 R2=0.9367。根据表3回归模型方程进行方差分析,模型 P=0.0020<0.01,说明试验设计可靠。失拟项 P=0.4487>0.05,表明模型计算结果与检验结果无显著性差异,表明该模型可以很好地描述测试结果。
表 2 Box-Behnken试验设计方案及试验结果Table 2. The design scheme and test results of Box-Behnken experiment试验号 A:提取温度 B:提取时间 C:液料比 得率(%) 1 0 0 0 4.33±0.31 2 0 0 0 3.89±0.03 3 0 1 1 3.56±0.04 4 −1 0 1 2.63±0.03 5 0 1 −1 3.50±0.16 6 1 0 −1 3.20±0.05 7 −1 0 −1 3.28±0.04 8 1 0 1 3.29±0.06 9 −1 −1 0 3.01±0.02 10 0 −1 −1 3.23±0.09 11 −1 1 0 3.29±0.08 12 1 1 0 3.26±0.16 13 0 0 0 4.04±0.13 14 0 0 0 3.92±0.1 15 0 −1 1 2.87±0.05 16 1 −1 0 2.76±0.02 17 0 0 0 3.95±0.15 表 3 回归模型方差分析Table 3. Variance analysis of regression model来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 3.45 9 0.3833 11.51 0.0020 ** A 0.0113 1 0.0113 0.3379 0.5793 B 0.3785 1 0.3785 11.37 0.0119 * C 0.0924 1 0.0924 2.78 0.1396 AB 0.0121 1 0.0121 0.3634 0.5656 AC 0.1369 1 0.1369 4.11 0.0822 BC 0.0411 1 0.0411 1.32 0.2876 A2 1.36 1 1.36 40.8 0.0004 ** B2 0.6016 1 0.6016 18.07 0.0038 ** C2 0.5396 1 0.5396 16.21 0.005 ** 失拟项 0.1049 3 0.035 1.09 0.4487 不显著 纯误差 0.1281 4 0.032 总差 3.68 16 R2=0.9367 Adj.R2=0.8554 CV=5.35 注:**P<0.01,差异极显著;*P<0.05,差异显著。 2.2.2 响应面分析
采用Design-Expert 软件分析,得到灵芝菌丝体多糖两因素交互作用响应面图(图2)。如图2B所示,提取温度与液料比两因素间的交互作用相对显著。如图2A和图2C所示,提取温度与提取时间和提取时间与液料比两组因素有交互作用但不显著。三因素对多糖提取率的影响程度由高到低依次为:B(提取时间)>C(液料比)>A(提取温度)。
2.3 提取工艺优化验证分析
本研究通过建立的数学模型进行参数优化分析,获得灵芝菌丝体多糖最优提取条件为提取温度89.08 ℃、提取时间2.54 h和液料比84.58:1 mL/g,在此条件下模型预测多糖得率为3.57%。进一步进行验证实验,考虑实验的可操作性,将最佳工艺条件调整为提取温度89 ℃、提取时间2.5 h和液料比85:1 mL/g,多糖得率为3.44%±0.15%,该结果与模型预测结果数据仅差0.13%,说明优化参数准确可靠,具有实际应用价值。通过苯酚硫酸法测定多糖含量为52.7%。
2.4 灵芝菌丝体多糖对酒精肝损伤小鼠肝脏指数的影响
大量摄入酒精会引起肝损伤,导致肝脏肿大及肝脏质量增加[18]。本研究考察了SGP对小鼠肝脏指数的影响(图3),结果表明:与空白对照组相比,模型组小鼠肝脏指数显著提高(P<0.05),说明肝细胞膨大,肝脏发生损伤。与模型组比,给予250和500 mg/kg·bw剂量SGP小鼠的脏器指数极显著降低(P<0.01),说明肝脏状态得到改善,灵芝菌丝体多糖对酒精造成的肝脏损伤有改善作用。
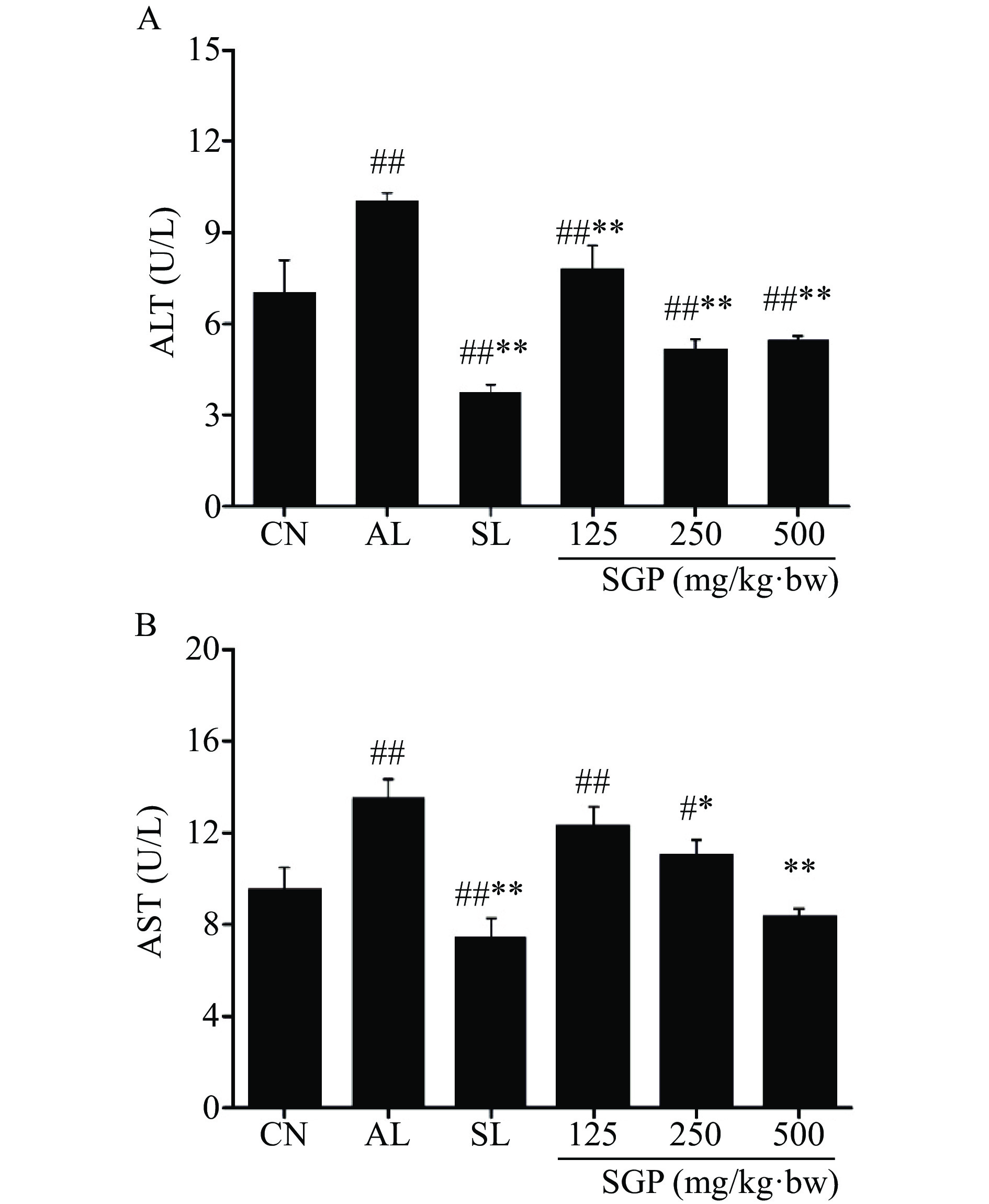
2.5 SGP对酒精肝损伤小鼠血清ALT和AST的影响
采用试剂盒检测SGP灌胃给药后,小鼠血清ALT和AST活性的变化,结果如图4所示,与空白对照组相比,模型组小鼠血清内ALT和AST含量呈极显著上升(P<0.01),说明酒精肝损伤小鼠造模成功。与模型组相比,SGP给药组和SL给药组小鼠血清中ALT含量极显著下降(图4A,P<0.01)。而通过对血清中AST的检测发现,与模型组相比,给药SGP组中250 mg/kg·bw剂量组小鼠血清中AST显著下降(P<0.05),而给药500 mg/kg·bw剂量组小鼠血清中AST含量呈极显著下降(P<0.01)。
2.6 灵芝菌丝体多糖对酒精肝损伤小鼠肝脏组织病理学影响
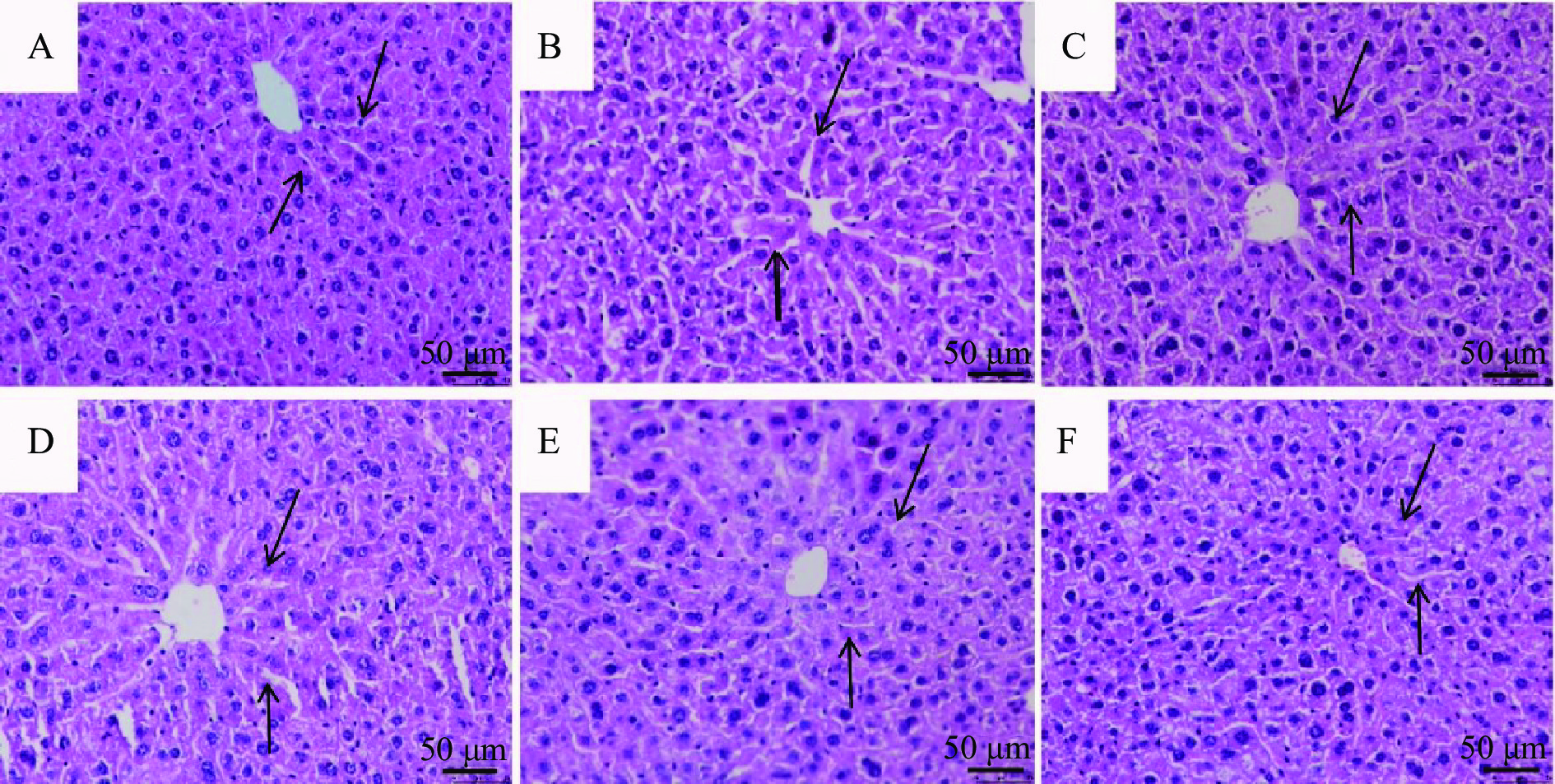
本研究通过HE染色观察给药处理后小鼠肝脏组织的病变状况,结果表明,与空白对照组(图5A)小鼠相比,模型组(图5B)小鼠肝组织细胞排列松散,分布不均,结构紊乱,部分细胞出现坏死现象。与模型组相比,给予低、中、高剂量SGP治疗后,小鼠肝脏细胞排列方式及细胞内部环境都在不同程度上有所改善(图5 D、E 、F),进一步证实SGP对酒精肝损伤小鼠肝脏细胞有明显的改善作用。
2.7 SGP对酒精肝损伤小鼠氧化应激水平的影响
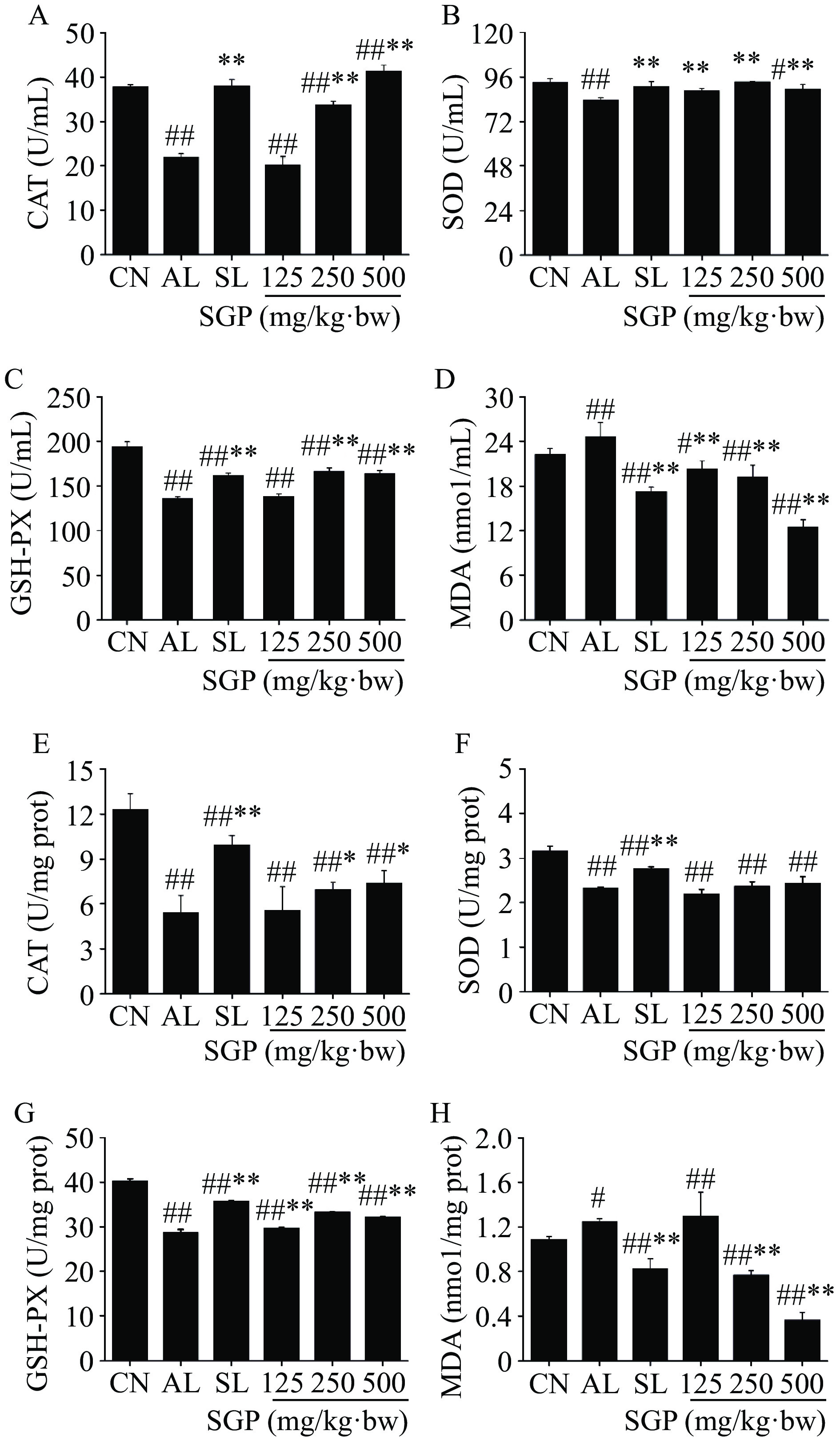
SGP对酒精肝损伤小鼠氧化应激酶和氧化产物的影响如图6所示,与空白对照组相比,模型组小鼠血清和肝脏中MDA水平显著升高(图6D、H,P<0.05),而 CAT 、SOD 和GSH-PX活性极显著降低(图6A、B、C、E、F、G,P<0.01)。给予SGP治疗后发现,与模型组相比,给药SGP后,小鼠血清中各组MDA水平极显著降低,肝脏中SGP 250和500 mg/kg·bw剂量组MDA水平极显著降低(P<0.01),且呈剂量依赖性;血清中SGP 250和500 mg/kg·bw剂量组CAT水平极显著提高(P<0.01),肝脏中CAT水平显著提高(P<0.05);血清中各组SOD水平极显著提升(P<0.01);血清中SGP 250和500 mg/kg·bw剂量组及肝脏中各组GSH-PX水平均极显著提升(P<0.01),说明SGP能有效改善酒精肝损伤小鼠氧化应激水平。
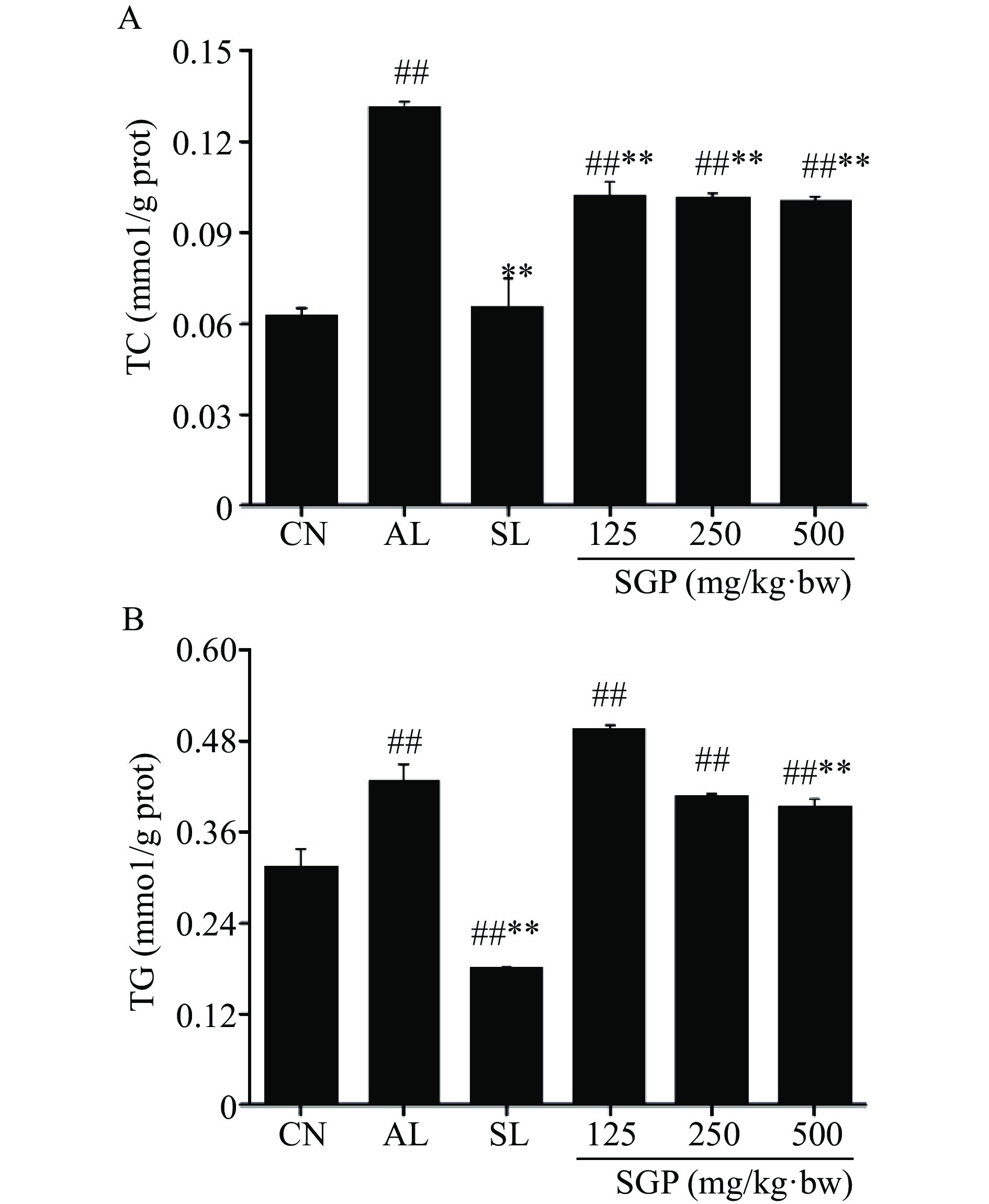
2.8 SGP对酒精肝损伤小鼠肝脏TC和TG水平的影响
肝脏组织中TC 、TG含量是脂质过氧化损伤标志物,可通过降低TC、TG含量实现对酒精损伤肝脏组织的保护作用[19]。本研究进一步考察了SGP对酒精肝损伤小鼠肝脏中脂质代谢的影响,结果如图7所示。由图可知,与空白对照组相比,模型组小鼠肝脏中TC和TG水平皆极显著升高(图7A、B,P<0.01)。与模型组相比,不同剂量的SGP灌胃给药后,各组小鼠的TC含量皆极显著降低(图7A,P<0.01)。而经500 mg/kg·bw SGP给药处理后,该组小鼠的TG含量极显著降低(图7B,P<0.01),以上结果表明,SGP对酒精肝损伤小鼠肝脏脂质代谢有良好的调节作用。
2.9 SGP对酒精肝损伤小鼠肝脏细胞炎症因子水平的影响
通过ELISA法对小鼠肝脏细胞炎症因子表达进行测定,结果如图8所示,与空白对照组小鼠相比,模型组小鼠肝脏IL-6、IL-1β和TNF-α水平皆极显著升高(P<0.01),说明酒精肝损伤会引发小鼠肝脏炎症反应。与模型组相比,250和500 mg/kg·bw剂量SGP组小鼠肝脏中的IL-6和TNF-α含量皆显著降低(图8A、C,P<0.05);500 mg/kg·bw剂量SGP组小鼠肝脏IL-1β水平极显著降低(图8B,P<0.01)。以上结果说明,SGP对酒精肝损伤小鼠肝细胞炎症因子水平具有较好的调节作用。
3. 讨论与结论
响应面优化方法已经在多糖提取工艺中广泛应用。本研究以单因素实验为基础,根据Box-Behnken的中心组合试验设计并结合响应面方法优化灵芝菌丝体多糖提取条件为提取温度89 ℃、提取时间2.5 h和液料比85:1 mL/g,在此条件下多糖得率为3.44%±0.15%。与汪梦雯等[20]通过响应面方法对灵芝子实体多糖的提取条件及得率相比存在一定差异,分析原因可能是灵芝子实体多糖与菌丝体多糖组成存在一定差异[21]。
长期摄入酒精会导致肝脏细胞坏死[22],作为肝脏标志性酶,ALT和AST含量是可用于评判肝功能的指标,当肝脏功能出现问题时,会导致血清中ALT和AST含量升高[23-24]。其次,肝脏损伤时,会使抗氧化物酶CAT和SOD与GSH-PX联合反应,清除机体自由基反应保护细胞膜,从而降低氧化应激终产物MDA含量,减少肝脏损伤[25-26],故可通过CAT、SOD、GSH-PX和MDA含量反映出肝脏的损伤程度。此外,酒精摄入过量会造成肝脏脂质代谢紊乱[27],促进肝脏IL-6、IL-1β、TNF-α等炎症因子的表达,诱发肝脏炎症反应,进而引起肝细胞变性或坏死[28-30]。多糖作为天然产物,具有较高的安全性,可有效保护酒精性肝损伤[31]。
本研究以灵芝菌丝体多糖为实验材料,通过建立小鼠体内酒精肝损伤模型,给予酒精肝损伤小鼠SGP溶液治疗,通过计算小鼠肝脏指数,并对小鼠生化指标检测和肝脏病理学切片观察考察其对慢性酒精性肝损伤的保护作用。首先脏器指数及血清转氨酶检测表明,与正常组相比,模型组小鼠肝脏指数显著提高(P<0.05),血清中ALT和AST含量极显著增加(P<0.01),表明酒精肝损伤模型造模成功。给药治疗后,结果显示给予SGP 250和500 mg/kg·bw剂量组小鼠的脏器指数极显著降低(P<0.01),血清中的AST显著下降(P<0.05),ALT极显著下降(P<0.01)。随后小鼠肝脏病理学切片结果显示,与模型组相比,SGP各剂量组肝脏受损状况皆有明显改善。且与模型组相比,SGP高剂量组小鼠血清和肝脏中氧化产物 MDA的含量明显降低,氧化酶CAT、SOD和GSH-PX含量显著升高,与叶丽云等[13]研究结果一致。此外,本研究进一步对慢性酒精肝损伤小鼠肝脏中脂质代谢产物和炎症因子检测,结果表明,给予高剂量SGP后,能够有效减少酒精肝损伤小鼠肝脏中TC和TG含量,降低炎症因子IL-6、IL-1β和TNF-α水平。上述结果表明,SGP不但能改善酒精性肝损伤小鼠肝脏损伤,通过改善小鼠氧化应激水平起到保肝作用,同时还可以调节肝脏脂质代谢和抑制肝脏炎症因子水平对慢性酒精性肝损伤起到保护作用,这可能与灵芝多糖调控NF-κB等通路或改善肠道菌群组成有关[32],其详细的作用机制有待进一步研究。综上所述,灵芝菌丝体多糖对慢性酒精性肝损伤具有保护作用,且作为天然大分子具有较高的安全性,故,灵芝菌丝体多糖可作为材料应用于功能性食品的开发。
-
表 1 Box-Behnken设计因素水平表
Table 1 The factors and levels of Box-Behnken design
因素 代码 水平 −1 0 1 提取温度(℃) A 70 80 90 提取时间(h) B 2 2.5 3 液料比(mL/g) C 70:1 80:1 90:1 表 2 Box-Behnken试验设计方案及试验结果
Table 2 The design scheme and test results of Box-Behnken experiment
试验号 A:提取温度 B:提取时间 C:液料比 得率(%) 1 0 0 0 4.33±0.31 2 0 0 0 3.89±0.03 3 0 1 1 3.56±0.04 4 −1 0 1 2.63±0.03 5 0 1 −1 3.50±0.16 6 1 0 −1 3.20±0.05 7 −1 0 −1 3.28±0.04 8 1 0 1 3.29±0.06 9 −1 −1 0 3.01±0.02 10 0 −1 −1 3.23±0.09 11 −1 1 0 3.29±0.08 12 1 1 0 3.26±0.16 13 0 0 0 4.04±0.13 14 0 0 0 3.92±0.1 15 0 −1 1 2.87±0.05 16 1 −1 0 2.76±0.02 17 0 0 0 3.95±0.15 表 3 回归模型方差分析
Table 3 Variance analysis of regression model
来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 3.45 9 0.3833 11.51 0.0020 ** A 0.0113 1 0.0113 0.3379 0.5793 B 0.3785 1 0.3785 11.37 0.0119 * C 0.0924 1 0.0924 2.78 0.1396 AB 0.0121 1 0.0121 0.3634 0.5656 AC 0.1369 1 0.1369 4.11 0.0822 BC 0.0411 1 0.0411 1.32 0.2876 A2 1.36 1 1.36 40.8 0.0004 ** B2 0.6016 1 0.6016 18.07 0.0038 ** C2 0.5396 1 0.5396 16.21 0.005 ** 失拟项 0.1049 3 0.035 1.09 0.4487 不显著 纯误差 0.1281 4 0.032 总差 3.68 16 R2=0.9367 Adj.R2=0.8554 CV=5.35 注:**P<0.01,差异极显著;*P<0.05,差异显著。 -
[1] 崔宝凯, 吴声华. 普遍栽培灵芝种类的拉丁学名[J]. 菌物学报,2020,39(1):7−12. [CUI B K, WU S H. Latin scientific names of Ganoderma lucidum species in general cultivation[J]. Acta Bacteriologica Sinica,2020,39(1):7−12. [2] 韩建军, 宁娜. 灵芝的化学成分与药理作用研究进展[J]. 广州化工,2014,42(23):18−19, 29. [HAN J J, NING N. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological action of Ganoderma lucidum[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry,2014,42(23):18−19, 29. [3] 黄晶, 柏青, 华蕾, 等. 富硒灵芝对妊娠期糖尿病大鼠脂代谢的调节作用[J]. 西部医学,2021,33(10):1440−1445. [HUANG J, BAI Q, HUA L, et al. Ganoderma lucidum promotes lipid metabolism in gestational diabetes mellitus rats[J]. Western Medicine,2021,33(10):1440−1445. [4] TANG C C, ZHAO R L, NI H M, et al. Molecule mechanisms of Ganoderma lucidum treated hepatocellular carcinoma based on the transcriptional profiles and miRNA-target network[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy,2020,125:110028.
[5] 李云, 曾东方. 食用菌液体深层发酵的研究热点[J]. 食品工业科技,2006,27(7):198−201. [LI Y, ZENG D F. Research hotspot of submerged fermentation of edible fungi[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2006,27(7):198−201. [6] 许女, 孙建平, 陈旭峰, 等. 山西老陈醋源植物乳杆菌C181对小鼠酒精肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 中国食品学报,2021,21(2):121−127. [XU N, SUN J P, CHEN X F, et al. Protective effects of Lactobacillus plantarum C181 from Shanxi aged vinegar on alcoholic liver injury in mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Science,2021,21(2):121−127. [7] 郭威, 李三强, 宋晓改, 等. L-谷氨酰胺对急性酒精肝损伤小鼠的保护作用机制研究[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志,2020,36(13):1812−1814. [GUO W, LI S Q, SONG X G, et al. Effects of glutamine on liver function in mice with acute alcoholic liver injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology,2020,36(13):1812−1814. [8] XIAO C, WU Q P, ZHANG J M, et al. Antidiabetic activity of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides F31 down-regulated hepatic glucose regulatory enzymes in diabetic mice[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2017,196:47−57. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.11.044
[9] LIANG Z G N, YUAN Z H, LI G Y, et al. Hypolipidemic, antioxidant, and antiapoptotic effects of polysaccharides extracted from Reishi mushroom, Ganoderma lucidum (Leysser: Fr) Karst, in mice fed a high-fat diet[J]. Journal of Medicinal Food,2018,21(12):1218−1227. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2018.4182
[10] 董嘉成, 顾晨曦, 何雨婷, 等. 灵芝多糖对小鼠免疫功能的调节作用[J]. 江苏医药,2021,47(1):10−13. [DONG J C, GU C X, HE Y T, et al. Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides on the regulation of immune function in mice[J]. Jiangsu Pharmaceutical,2021,47(1):10−13. [11] 刘宇琪, 郝利民, 鲁吉珂, 等. 灵芝子实体和孢子粉纯化多糖体外抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(16):27−31. [LIU Y Q, HAO L M, LU J K, et al. Study on the antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidum fruit body and spore powder in vitro[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(16):27−31. [12] WANG J, CAO B, ZHAO H P, et al. Emerging roles of Ganoderma lucidum in anti-aging[J]. Aging and Disease,2017,8(6):691−707. doi: 10.14336/AD.2017.0410
[13] 叶丽云, 程冰, 马水丽, 等. 赤芝多糖对小鼠急性酒精性肝损伤的保护效果和作用机制[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(5):103−110. [YE L Y, CHENG B, MA S L, et al. Effects of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide on liver injury induced by alcohol in mice[J]. Food Science,2022,43(5):103−110. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20210320-254 [14] 杨大俏, 王锦旭, 李来好, 等. 响应面法优化褶牡蛎多糖多肽联产工艺[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(20):269−278. [YANG D Q, WANG J X, LI L H, et al. Optimization of polypeptide co-production process of Crassostrea crassostrea polysaccharides by response surface methodology[J]. Food Science,2019,40(20):269−278. [15] 张颖, 冯晓慧, 丁萌萌, 等. 响应面法优化地衣Umbilicaria muehlenbergii多糖提取工艺及其体外活性研究[J]. 菌物学报,2021,40(1):48−59. [ZAHNG Y, FENG X H, DING M M, et al. Comparison of PBMC parameters with PBMC parameters and PBMC parameters[J]. Chinese Journal of Bacteriology,2021,40(1):48−59. [16] 龚频, 王佩佩, 同美霖, 等. 红枣多糖的提取工艺及药理活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(13):198−207. [GONG P, WANG P P, TONG M L, et al. Study on extraction technology and pharmacological activity of polysaccharides from jujube[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(13):198−207. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021100105 [17] 郭畅, 李超, 侯明明, 等. 荔枝草多糖的提取工艺优化及其体外抗氧化、降血糖活性分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(20):211−219. [GUO C, LI C, HOU M M, et al. The optimization of extraction process of lychee grass polysaccharide and its antioxidant and hypoglycemic activity in vitro[J]. Science and Technology of the Food industry,2022,43(20):211−219. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021120280 [18] 彭国霞, 赵浩安, 刘清清, 等. 茶花粉的抗氧化活性及其对急性酒精肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(17):127−133. [PENG G X, ZAHO H A, LIU Q Q, et al. Effects of different types of tea pollen on liver damage induced by alcohol[J]. Food Science,2018,39(17):127−133. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201817021 [19] 罗慧英, 刘渊, 席国柱, 等. 肉苁蓉总苷对小鼠酒精性肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学,2009,14(11):1225−1228. [LUO H Y, LIU Y, XI G Z, et al. The protective effect of total glycosides of Cistanche on alcoholic liver injury in mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics,2009,14(11):1225−1228. [20] 汪梦雯. 灵芝、香菇和茯茶多糖的提取、结构表征及降糖活性研究[D]. 西安: 陕西科技大学, 2021. WANG M W. The extraction, structural characterization and hypoglycemic activity of polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidum, Lentinus edodes and Fu tea[D]. Xian: Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, 2021.
[21] 于华峥, 刘艳芳, 周帅, 等. 灵芝子实体、菌丝体及孢子粉中多糖成分差异比较研究[J]. 菌物学报,2016,35(2):170−177. [YU H Z, LIU Y F, ZHOU S, et al. Acomparative study of polysaccharide components in fruit body, mycelium and spore powder of Ganoderma lucidum[J]. Chinese Journal of Fungi,2016,35(2):170−177. doi: 10.13346/j.mycosystema.140242 [22] ZHOU Y, WU R M, WANG X Q, et al. Activation of UQCRC2-dependent mitophagy by tetramethylpyrazine inhibits MLKL-mediated hepatocyte necroptosis in alcoholic liver disease[J]. Free Radical Biology and Medicine,2022,179:301−316. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.11.008
[23] CHANG Y N, LI H, REN H, et al. Misclassification of chronic hepatitis B natural history phase: Insight from new ALT, AST, AKP, and GGT reference intervals in Chinese children[J]. Clinica Chimica Acta,2018,489:61−67.
[24] 余佳珍, 邓琳琳. 血清转氨酶与血脂水平检验用于脂肪肝诊断的作用研究[J]. 临床检验杂志(电子版),2019,8(1):15−17. [YU Z Z, DENG L L. Study on the role of serum transaminase and blood lipid level test in the diagnosis of fatty liver[J]. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Science,2019,8(1):15−17. [25] CICHOZ L H, MICHALAK A. Oxidative stress as a crucial factor in liver diseases[J]. World Journal of Gastroenterol,2014,20(25):8082−8091. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i25.8082
[26] 杨牧祥, 田元祥, 姚树坤, 等. 解酒护肝饮对酒精性肝损伤大鼠血清和肝组织MDA、GSH的影响[J]. 河北中医药学报,2000,15(4):1−5,14. [YANG M X, TIAN Y X, YAO S K, et al. Effect of Jijiu Hugan Yin on MDA and GSH in serum and liver tissue of alcoholic liver injury rats[J]. Journal of Hebei Traditional Chinese Medicine,2000,15(4):1−5,14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5615.2000.04.001 [27] LI M R, WU C X, GUO H B, et al. Mangiferin improves hepatic damage-associated molecular patterns, lipid metabolic disorder and mitochondrial dysfunction in alcohol hepatitis rats[J]. Food & Function,2019,10(6):3514−3534.
[28] 李芳芳, 张蕊萌, 丛贺, 等. 榆干离褶伞溶栓酶对酒精诱导大鼠肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(17):121−126. [LI F F, ZHANG R M, CONG H, et al. Effects of lysothrombolytic enzyme from dried elm on liver injury induced by alcohol in rats[J]. Food Science,2021,42(17):121−126. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200821-288 [29] RABIA N, SADIA Z, MUHAMMAD I, et al. HCV-induced regulatory alterations of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and IFN-γ operative, leading liver en-route to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis[J]. Inflammation Research,2017,66(6):477−486. doi: 10.1007/s00011-017-1029-3
[30] 罗怡爽, 郑秀婷, 章浩月, 等. α-荼异硫氰酸酯诱导小鼠胆汁淤积性肝纤维化及其炎症通路[J]. 中国应用生理学杂志,2020,36(2):152−157. [LUO Y S, DENG X T, ZAHNG H Y, et al. Cholestatic liver fibrosis and its inflammatory pathway induced by α -dithiocyanate in mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Physiology,2020,36(2):152−157. doi: 10.12047/j.cjap.5903.2020.034 [31] 王秋艳, 丁慧敏, 朱亚男, 等. 多汁乳菇多糖对小鼠急性酒精性肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(24):313−319. [WANG Q Y, DING H M, ZHU Y N, et al. Protective effects of Lentinan on acute alcoholic liver injury in mice[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(24):313−319. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021010251 [32] 王颖, 魏佳韵, 吴思佳, 等. 灵芝多糖结构特征及药理作用的研究进展[J]. 中成药,2019,41(3):627−635. [WANG Y, WEI J Y, WU S J, et al. Research progress on structural characteristics and pharmacological effects of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides[J]. Chinese Patent Medicine,2019,41(3):627−635. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2019.03.029 -
期刊类型引用(16)
1. 孙细珍,熊亚青,倪兴婷,李强. 吡嗪类化合物对酱香型白酒香气特征的影响分析. 食品与发酵工业. 2025(01): 305-311 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王高伟,曹润洁,陈双,徐岩. 采用顶空固相微萃取结合全二维气相色谱飞行时间质谱解析不同等级中高温大曲的挥发性组分差异特征. 食品与发酵工业. 2025(02): 285-292 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王娜,沈毅,庄园,程伟,罗森,张亚东,刘子轩,刘冰,高红波. 气相色谱-串联质谱同时测定白酒中20种吡嗪类化合物. 食品科学. 2025(05): 30-37 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 蒋倩儿,梁会朋,李琳琳,钟俊辉,刘军峰. 芽孢杆菌在白酒酿造过程中的应用研究进展. 食品工业科技. 2025(08): 391-401 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 杨瑞政. 白酒及原料检验准确性的影响因素及控制策略探讨. 食品安全导刊. 2024(07): 149-151 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 杨沙,罗玉航,张季,侯睿. 高效液相色谱法同时测定不同年份酱香型白酒中12种吡嗪化合物含量. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2024(12): 220-229 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 缪坤辰,张梦梦,赵巧珍,吕志远,吕晓凤,任广花. 两种功能麸曲混合应用对芝麻香型白酒酿造的影响. 酿酒科技. 2024(07): 74-82 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 王宏雨,翁梦婷,孔子浩,张迪. 发酵处理对广叶绣球菌挥发性成分及风味的影响. 菌物学报. 2024(08): 154-170 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 陈艳,王孝彦,刘冲,杨沙,张季. GC-MS/MS法同时测定年份酱香型白酒中19种吡嗪类和呋喃类化合物. 中国酿造. 2024(09): 241-248 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 何艳艳,刘俊男,李瑞杰,丁润月,杨阳,李姝,赵侨,钟小忠,王松涛,周嘉裕. 酱香型白酒风味及其关键物质分析技术研究进展. 中国酿造. 2024(11): 1-7 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 薛锡佳,程伟,陈雪峰,兰伟,李娜,李瑞龙,潘天全,代森. 馥合香型白酒酿造过程中四甲基吡嗪的检测及其溯源分析. 中国酿造. 2024(12): 38-44 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 吕晓凤,孟武,刘玉涛,张梦梦,卢春玲,李强,邱振清,石林,赵巧珍,缪坤辰. 功能菌添加对芝麻香原酒中吡嗪类化合物含量的影响研究. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2023(07): 155-163 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 陈荻,杨康卓,刘志鹏,赵东,郑佳. 包包曲风味萃取方式的对比及GC×GC-TOFMS在其风味化合物鉴定中的应用. 酿酒科技. 2023(06): 71-76 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 苏泽佳,卢斌,李志溥,熊若冰,白卫东,梁景龙,赵文红. 12种市售豉香型白酒挥发性风味物质的分析. 中国酿造. 2023(08): 234-241 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 秦炳伟,吕志远,张梦梦,刘阳晴雪,刘玉涛,王文洁,胥鑫钰,李小杰,崔新莹,商海林,王瑞明,高红波,宋妍妍. 顶空固相微萃取-全二维气相色谱-飞行时间质谱解析泉香型白酒的风味物质. 食品与发酵工业. 2023(18): 289-296 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 陈心雨,刘念,王超凯,张磊,李觅,常少健,蔡海燕,彭奎. 高温大曲中美拉德反应的研究进展. 食品与发酵科技. 2023(06): 109-112 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)






 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:



