Characteristics of Mineral Elements Contents and Discriminant Analysis of Foxtail Millet from Different Producing Areas in Gansu Province Based on ICP-MS
-
摘要: 通过分析不同主产区小米矿物元素含量特征,结合化学统计学建立小米产地判别模型。该研究以甘肃省陇中地区、陇东地区和河西地区的主栽小米品种为研究对象,采用电感耦合等离子体质谱(ICP-MS)法测定了小米中18种矿物元素含量,利用方差分析、主成分分析(PCA)、正交偏最小二乘判别分析(OPLS-DA)、线性判别分析(LDA)和聚类分析(HCA)对数据进行统计分析。结果表明:小米样品18种矿物元素中有13种元素含量在3个主产区间存在显著差异(P<0.05),不同主产区小米矿物元素含量具有独特的地域分布特征;18种矿物元素之间存在较强的相关性;PCA分析共提取4个主成分,累计方差贡献率为75.82%;基于LDA和OPLS-DA的判别模型对小米产地判别正确率均为100%,基本可以实现甘肃省不同区域小米产地的精准判别,通过OPLS-DA模型确定了小米产地判别的特征元素(V、Fe、Cu、Cd、Se、Pb);基于特征元素的HCA分析可以成功地对小米产地进行判别。研究证明基于小米矿物元素含量构建的判别模型可以有效区分甘肃省不同产区的小米,为小米产地溯源和质量控制提供了科学依据。
-
关键词:
- 小米 /
- 电感耦合等离子体质谱法 /
- 矿物元素 /
- 含量特征 /
- 产地判别
Abstract: Based on the analysis of characteristics of mineral elements contents of foxtail millet from different producing areas, the geographical origin discrimination models were established in combination with chemometrics. In this study, major cultivars of foxtail millet from Longzhong area, Longdong area and Hexi area of Gansu Province were regarded as main research objects. The contents of 18 mineral elements in foxtail millet were determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS), the data was analyzed by one way ANOVA, principal component analysis (PCA), orthogonal partial least squares-discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA), linear discriminant analysis (LDA) and hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA). The results showed that there was a significant difference for 13 mineral elements out 18 in foxtail millet from three producing areas (P<0.05), and mineral elements contents of foxtail millet showed distinct regional distribution characteristic. Correlation analysis showed there were significant relationships between 18 mineral elements. Four principal components were extracted after PCA, and the cumulative contribution ratio of the four components was 75.82%. Correct discrimination rates of LDA and OPLS-DA models were both 100%, which could be used for the geographical origin discriminantion of foxtail millet in different producing areas of Gansu Province, and six characteristic elements (V、Fe、Cu、Cd、Se、Pb) of foxtail millet from different producing areas were screened by OPLS-DA models. HCA regarding the characteristic elements as variables could classify the foxtail millet into different categories, which was consistent with their geographical origins. The research suggests that the discrimination model based on mineral element contents can effectively identify foxtail millet from different producing areas, which provides a scientific basis for origin traceability discrimination and quality control of foxtail millet. -
谷子(Setaria italica(L.)P. Beauv.)是中国北方的传统杂粮作物,具有抗干旱、耐贫瘠和耐储藏的特性,在我国西北、华北和东北等干旱丘陵地区有大面积的种植[1-2]。谷子脱壳后称为小米,是一种高营养的暖性食物,富含维生素、氨基酸、脂肪、蛋白质和矿物元素等人体所需的基本营养物质,营养素配比合理,有抗氧化、健脾胃等功效,是改善民众膳食结构和增进人体身体健康不可或缺的食物[3-4]。目前对小米的研究主要集中在栽培育种、食味蒸煮品质和营养品质等方面[5-8],关于小米矿物元素的研究较少。甘肃省作为全国谷子主栽培区之一,产业规模和品牌影响在全国范围内都具有一定竞争力,庆阳小米获得了国家农产品地理标志认证,张掖市甘州区的金花寨小米获国家有机食品认证,有“功能营养小米”的称号,现为甘肃省名牌产品,为防止外源劣质小米伪冒优质小米、破坏地区特色小米品牌价值,保护和发展地理标志农产品,亟需研发一种有效的产地溯源鉴别技术。
目前,农产品产地溯源技术主要包括矿物元素指纹技术[9]、稳定同位素技术[10]、近红外光谱分析技术[11]和分子生物学技术[12]等。在上述新兴技术中,矿物元素指纹技术被认为是判别植物源性农产品产地最简便最有效的手段之一[13-14]。矿物元素是农产品的基本组成要素,不能在植物体内自身合成,必须从其生长环境中获取,所以农产品的矿物元素含量与其产地环境的元素组成密切相关,因而带有其产地特有的元素指纹信息,从而使矿物元素成为农产品产地判别的有效指标[15-17]。矿物元素指纹技术通过分析不同产地农产品中各元素组成与含量特征,利用主成分分析法、判别分析法、聚类分析法等统计学方法,筛选有效判别指标并构建产地判别模型[18],从而实现农产品产地溯源与确证。目前,矿物元素指纹分析技术已经被广泛应用于茶叶[19-21]、中药材[22-23]、果蔬[24-25]、粮谷[26-28]等农产品的产地溯源。随着科学技术的快速发展,电感耦合等离子体质谱(inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry,ICP-MS)被广泛应用于矿物元素含量的测定。由于ICP-MS拥有检出限低、灵敏度高、检测速度快、可同时检测多种元素等优势[29-30],使矿物元素作为农产品地理来源的判别指标显示出了较大的优势。开建荣等[31]利用矿物元素产地溯源技术对宁夏中宁县5个小产区的枸杞样品进行分析,采用线性判别分析和正交偏最小二乘法建立了枸杞产地溯源模型,两种判别模型的整体正确判别率分别为82.0%和91.89%,基本实现了小尺度区域内枸杞的原产地判别。甘肃省小米主要种植在陇东地区、中部地区和河西地区,地域跨度极大,因此各小米主产区的地理环境条件呈现出了巨大差异,导致不同产区小米具有明显不同的矿物营养特性,为小米产地精准判别提供了极大的可能性。
因此,本研究以甘肃省陇中地区(会宁)、陇东地区(庆阳)和河西地区(张掖)的主栽小米品种为研究对象,利用ICP-MS测定了小米中18种矿物元素含量,比较分析不同主产区小米矿物元素含量特征,结合主成分分析(principal component analysis,PCA)、正交偏最小二乘判别分析(orthogonal partial least squares-discriminant analysis,OPLS-DA)、线性判别分析(linear discriminant analysis,LDA)和聚类分析(hierarchical cluster analysis,HCA)建立小米产地判别模型,以期为甘肃小米产地溯源、质量安全控制和推动小米产业健康持续发展提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
小米样品 于2020年10月收获季采集于甘肃省三个谷子核心主产区,共采集30份不同地理来源的小米样品,其中陇中地区(白银市会宁县)12份,陇东地区9份(庆阳市镇原县6份,环县、庆城县和西峰区各1份),河西地区9份(张掖市6份,酒泉市2份,武威市1份);Mg、K、Ca、Na、Mn、Fe、Cu、Zn、Mo、Se、V、Co、Ni、Ba、Sr、Pb、As、Cd单元素标准溶液(1000 ng/mL) 中国计量科学研究院;含有Ce、Co、Li、Mg、Tl、Y的调谐液(1 μg/L)、含有7Li、45Sc、72Ge、103Rh、115In、159Tb、175Lu、208Bi的内标溶液(100 μg/mL) 美国安捷伦科技有限公司;硝酸、高氯酸 优级纯,天津市科密欧化学试剂有限公司;所有试验用水均为一级水。
Agilent 7900电感耦合等离子体质谱仪 美国安捷伦科技有限公司;EG37C型微控电热板 北京莱伯泰科仪器股份有限公司;SQP224型万分之一电子天平 北京赛多利斯科学仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 标准工作曲线的建立与检出限
根据前期预测试验结果得到小米矿物元素含量,确定标准工作曲线的浓度范围。准确量取各单元素标准溶液,用3%硝酸溶液逐级稀释,配制成混合标准工作溶液,具体质量浓度见表1。利用ICP-MS对混合标准溶液矿物元素含量进行测定,Na23、Mg24、K39、Ca43、V51、Mn55、Co59、Fe56、Ni60、Cu63、Zn66、As75、Se78元素选择Ge72为内标,Mo95、Sr88、Cd111、Ba137元素选择Rh103为内标,Pb208元素选用Bi209为内标。将混合内标标准溶液用3%硝酸溶液稀释至1 μg/mL,通过T型三通在线引入。以标准工作液质量浓度(μg·L−1)为横坐标,以各元素响应值(CPS)与相应内标元素响应值(CPS)的比值为纵坐标,建立标准工作曲线。连续测定11次样品空白溶液的响应值(CPS),计算标准偏差(σ),分别以3σ、10σ对应的质量浓度为检出限(limit of detection,LOD)和定量限(limit of quantitation,LOQ)。
表 1 18种矿物元素标准系列浓度Table 1. Standard series concentrations of 18 mineral elements元 素 标准系列浓度(μg·L−1) Na 0、200、400、800、1600、3200、4000 Mg、K、Ca 0、100、200、400、800、1600、2000 Fe、Zn 0、50、100、200、400、800、1000 Mn 0、25、50、100、200、400、500 Cu、Ni、Sr、Ba 0、5、10、20、40、80、100 Mo 0、1、2、4、8、16、20 V、Co、Se、Cd、Pb、As 0.00、0.10、0.20、0.40、0.80、1.60、3.20 1.2.2 方法验证
取混合标准工作溶液(第四个点)连续测定6次,计算各元素质量浓度的RSD值,以验证方法的精密度;称取同一份小米样品6份,按“1.2.3.1”项下方法制备供试液,上机测定各元素的含量,计算各元素含量的RSD值,以验证方法的重复性;称取已测定小米样品,分别添加高、中、低三个浓度水平的混合标准溶液,每个水平做3份平行,制备供试液并上机测定矿物元素含量,计算加标回收率,以验证方法的准确度。
1.2.3 矿物元素含量测定
1.2.3.1 供试品溶液制备
将谷子晾晒干脱壳后得到小米,去除杂质和碎米,用磨粉机将小米磨成粉,过100目筛后备用[32],所有样品采用统一处理方式。小米样品消解采用湿法消解[33],精密称取0.2500 g小米粉置于250 mL锥形瓶内,加入10.00 mL混合酸(硝酸:高氯酸=7:1),盖上漏斗,在常温下放置过夜。次日将锥形瓶放置在控温电热板上加热,采用升温方式消解,升温条件为:150 ℃(60 min)、升至200 ℃(60 min)、最后升至250 ℃,直至消化液呈无色透明状,继续赶酸至1 mL左右,取下锥形瓶,稍微冷却后,加入少量一级水和0.75 mL硝酸,加热至有蒸汽冒出时,取下锥形瓶冷却至室温,转移到25.00 mL塑料比色管中,用一级水定容,摇匀备用,随同做空白对照样。每个小米样品制备三个平行样。按照下述ICP-MS仪器工作条件,同位素和内标元素的选择同“1.2.1”项,上机定量测定小米样品中Mg、K、Ca、Na、Mn、Fe、Cu、Zn、Mo、Se、V、Co、Ni、Ba、Sr、Pb、As、Cd 18种矿物元素含量,供试液稀释25倍后上机测定K和Mg元素的含量,稀释5倍后上机测定Ca元素的含量。当内标元素的RSD>5%时,需要对样品进行重新测定。
1.2.3.2 仪器工作条件
仪器开机预热至稳定后,用调谐液进行仪器调谐优化参数,获得最佳工作条件。ICP-MS工作参数如下:射频功率:1550 W;等离子体气体流量15.0 L·min−1;辅助气体流量1.0 L·min−1;雾化气流量1.0 L·min−1;雾化室温度 2 ℃;采样深度:10 mm;样品引入速度0.30 r/s;样品引入时间30 s;重复次数:3次;氧化物(156/140)≤2%;双电荷(70/140)≤3%。在He模式下进行样品测定,并在线引入1 μg/mL的内标溶液。
1.3 数据处理
采用R软件进行各元素相关性分析并绘制热图;利用SPSS 26.0分析软件进行单因素方差分析(One Way ANOVA)、主成分分析(PCA)、线性判别分析(LDA)和聚类分析(HCA),利用Sicma 14.0分析软件进行正交偏最小二乘判别分析(OPLS-DA);采用Origin 2019b软件绘制元素含量热图和主成分向量雷达图。由于小米样品各矿物元素含量在量纲和数量级存在较大差异,因此在PCA、LDA、OPLS-DA和HCA分析之间,对试验数据进行标准化预处理,绘制元素含量热图之前对试验数据进行归一化预处理,以平衡各元素的含量差异。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 标准曲线与检出限
18种矿物元素的标准曲线、检出限及定量限如表2所示,各元素线性决定系数数值在0.9990~1.0000之间,表明各元素线性关系良好,满足分析要求。检出限是方法灵敏度和精密度的综合指标,也是评价仪器性能及分析方法的主要技术指标[34],本试验中各元素的检出限和定量限分别在0.0033~27.2 μg·L−1、0.011~90.7 μg·L−1之间,说明该方法可以对小米样品各矿物元素含量进行测定。
表 2 18种元素的线性回归方程、检出限及定量限Table 2. Linear regression equation, limit of detection and limit of quantitation of 18 elements元 素 内标物 线性回归方程 决定系数(R2) 检出限 (μg·L−1) 定量限 (μg·L−1) Na23 Ge72 y=4.003×10−2x+1.187 0.9992 27.2 90.7 Mg24 Ge72 y=2.865×10−3x+2.488×10−2 0.9997 0.65 2.17 K39 Ge72 y=2.021×10−3x+3.562×10−1 0.9993 8.04 26.8 Ca43 Ge72 y=5.846×10−6x+3.926×10−4 0.9996 24.61 82.0 V51 Ge72 y=4.680×10−2x +4.119×10−3 0.9998 0.096 0.32 Mn55 Ge72 y=2.440×10−2x+5.155×10−3 0.9999 0.18 0.60 Fe56 Ge72 y=4.844×10−2x+1.859×10−1 0.9994 6.11 20.4 Co59 Ge72 y=1.269×10−1x +1.100×10−3 0.9999 0.0064 0.021 Ni60 Ge72 y=4.178×10−2x +1.222×10−1 0.9999 0.33 1.10 Cu63 Ge72 y=1.253×10−1x+1.997×10−2 0.9999 0.15 0.50 Zn66 Ge72 y=1.377×10−2x+3.018×10−1 0.9999 2.63 8.77 As75 Ge72 y=6.954×10−3x +7.681×10−3 0.9992 0.056 0.19 Se78 Ge72 y=4.013×10−4x+8.835×10−5 0.9996 0.030 0.100 Mo95 Rh103 y=1.715×10−3x+2.266×10−5 0.9999 0.018 0.060 Sr88 Rh103 y=2.571×10−2x +6.326×10−3 0.9999 0.11 0.37 Cd111 Rh103 y=5.549×10−4x+2.974×10−6 0.9993 0.0033 0.011 Ba137 Rh103 y=4.333×10−4x+1.857×10−4 1.0000 0.10 0.33 Pb208 Bi209 y=1.508×10−2x+3.842×10−3 0.9990 0.081 0.27 2.2 方法学验证
为了进一步验证分析实际样品时所建方法的准确性,对该方法的精密度、重复性和加标回收率进行考察。在精密度试验中,连续6次测定的各元素质量浓度的RSD值为0.33%~4.49%,说明仪器的精密度良好;重复性试验中,由于样品中Cd含量较低,导致其RSD稍高(6.69%),其余元素RSD在1.74%~4.81%之间,说明实验的重复性良好;表3列出了所有元素高、中、低三个浓度水平的加标回收率,各矿物元素的平均加标回收率在90.35%~106.24%,说明该方法准确度良好。
表 3 18种元素加标回收率Table 3. Recovery rate of 18 elements元素 本底值(μg·L−1) 加标浓度(μg·L−1) 回收率(%) 平均回收率(%) 元素 本底值(μg·L−1) 加标浓度(μg·L−1) 回收率(%) 平均回收率(%) Na 235.78 64 88.19 Cu 151.43 64 93.75 120 105.99 101.11 120 102.64 100.98 176 109.16 176 106.53 Mg 13008.68 10000 96.23 Zn 305.78 64 91.53 20000 93.78 93.72 120 98.98 96.87 30000 91.14 176 100.11 K 28159.24 10000 101.81 As 0.3132 0.20 104.80 20000 97.46 98.98 0.40 105.95 106.24 30000 97.67 0.60 107.98 Ca 1726.94 800 104.21 Se 0.1902 0.20 106.50 1600 105.76 106.21 0.40 100.93 103.89 2400 108.66 0.60 104.23 V 0.5695 0.20 95.30 Mo 2.91 1.20 96.67 0.40 99.13 97.94 2.40 106.25 100.70 0.60 99.40 3.60 99.17 Mn 130.99 64 102.09 Sr 17.53 16 98.44 120 98.08 100.94 24 98.88 97.86 176 102.64 32 96.25 Fe 385.6 64 89.38 Cd 0.03568 0.20 95.46 120 93.28 93.36 0.40 100.43 99.69 176 97.43 0.60 103.17 Co 0.4858 0.20 104.70 Ba 14.48 16 94.69 0.40 100.68 101.80 24 95.13 93.90 0.60 100.03 32 91.88 Ni 25.39 16 92.38 Pb 1.052 0.20 89.00 24 97.50 94.61 0.40 90.98 90.35 32 93.94 0.60 91.07 2.3 矿物元素差异特征
2.3.1 小米矿物元素含量特征
为了比较小米中矿物元素含量的大小,对甘肃省陇中地区、陇东地区和河西地区3个主产区30份小米样品中矿物元素含量的平均值、变幅范围和变异系数进行分析,结果见表4。小米中K、Mg、Ca、Na四种常量元素的含量大小依次为K>Mg>Ca>Na,平均含量分别为3071.03、1401.40、169.23、33.22 mg/kg,K是所有小米样品中含量高的元素,这与之前的研究一致[33, 35]。小米的平均钾钠比是92.45,属于高钾低钠食品,利于预防或减缓高血压症状。Zn、Mn、Cu、Fe、Mo、Se、V、Co、Ni、Sr、Ba、As、Pb、Cd 14种微量元素中,Fe元素的含量明显高于其它微量元素,平均含量为52.66 mg/kg,其次为Zn和Mn元素,含量均超过10 mg/kg,Cu、Ni、Sr、Ba含量平均值在1.0~10.0 mg/kg,Mo、Se、V、Co、As、Cd、Pb平均含量均小于1.0 mg/kg。Pb、Cd、As属于有害微量元素,具有潜在的毒性,GB 2762-2017《食品安全国家标准 食品中污染物限量》对去壳谷物中Pb、Cd、As限量要求分别是0.2、0.1、0.5 mg/kg。本研究中小米Pb、Cd、As的最高检出值分别是0.15、0.021、0.061 mg/kg,说明以上3种有害元素含量均低于As、Cd、Pb的限量指标。
表 4 小米中矿物元素含量Table 4. Mineral elements contents in foxtail millet元素分类 元 素 平均值 最小值 最大值 变异系数(%) 常量元素 Na(mg/kg) 33.22 19.93 44.33 20.22 Mg(mg/kg) 1401.40 1047.04 1857.14 13.50 K(mg/kg) 3071.03 1742.11 4203.06 30.79 Ca(mg/kg) 169.23 120.02 221.07 15.84 微量元素 Mn(mg/kg) 14.17 9.24 20.13 17.76 Fe(mg/kg) 52.66 26.41 74.57 24.81 Ni(mg/kg) 2.23 0.70 3.68 31.89 Cu(mg/kg) 8.01 5.01 18.93 40.87 Zn(mg/kg) 26.76 17.42 35.60 15.86 Sr(mg/kg) 1.90 1.00 3.24 32.31 Ba(mg/kg) 1.76 0.85 3.05 32.31 V(μg/kg) 62.51 34.40 120.34 36.64 Co(μg/kg) 58.88 26.53 106.31 34.70 Se(μg/kg) 29.76 10.30 91.60 68.96 Mo(μg/kg) 328.87 150.20 537.05 32.06 重金属元素 As(μg/kg) 37.68 21.80 61.20 29.68 Cd(μg/kg) 8.60 3.90 20.80 43.14 Pb(μg/kg) 106.60 64.04 147.10 24.03 小米中18种矿物元素含量的变异系数值分布在13.50%~68.96%之间,属中等变异强度。其中Se元素含量的变幅范围最大(0.010~0.092 mg/kg),变异系数值为68.96%,表明不同主产区小米中Se元素含量差异较大;Cd和Cu元素含量的变幅范围次之,变异系数值分别为43.14%和40.87%;Mg、Ca、Zn、Mn元素含量的变幅范围较小,变异系数值在13.50%~17.76%。
2.3.2 不同主产区小米矿物元素含量差异
为了研究会宁、庆阳、张掖三个主产区小米中18种矿物元素含量的差异性,对各元素含量进行单因素方差分析,如表5所示。结果表明,Mg、K、Zn、Mn、Cu、Fe、Se、Mo、Ba、Co、V、Cd、Pb 13种矿物元素的含量在3个主产区间差异显著(P<0.05),Na、Ca、Ni、Sr、As 5种矿物元素的含量在不同产区间差异性不显著(P>0.05)。会宁小米中Cu含量显著高于庆阳小米和张掖小米(P<0.05),平均含量为10.33 mg/kg,K、Fe、Zn、Co、Mo和Pb含量显著高于张掖小米(P<0.05),平均含量分别为3252.83、49.13、27.48、0.063、0.39、0.12 mg/kg;庆阳小米中Fe、V含量显著高于会宁小米和张掖小米(P<0.05),平均含量分别是68.32、0.089 mg/kg,Mg、K、Zn、Mn、Ba、Co、Pb的含量显著高于张掖小米(P<0.05),含量分别是1485.11、3317.22、29.54、15.23、2.13、0.070、0.12 mg/kg,Cd含量显著高于会宁小米(P<0.05),含量为0.0084 mg/kg;张掖小米中Se和Cd显著高于庆阳小米和会宁小米(P<0.05),平均含量分别是0.056和0.012 mg/kg。张掖小米Se含量最高值为0.10 mg/kg,平均含量分别是会宁小米和庆阳小米Se含量的2.76倍和3.43倍,因此张掖小米在富硒小米产业发展方面具有很大优势[36]。从上述分析可以看出,由于植物体内的矿物元素含量与其产地环境密切相关,因此不同产地来源的小米样品,其矿物元素含量有明显的地域差异。
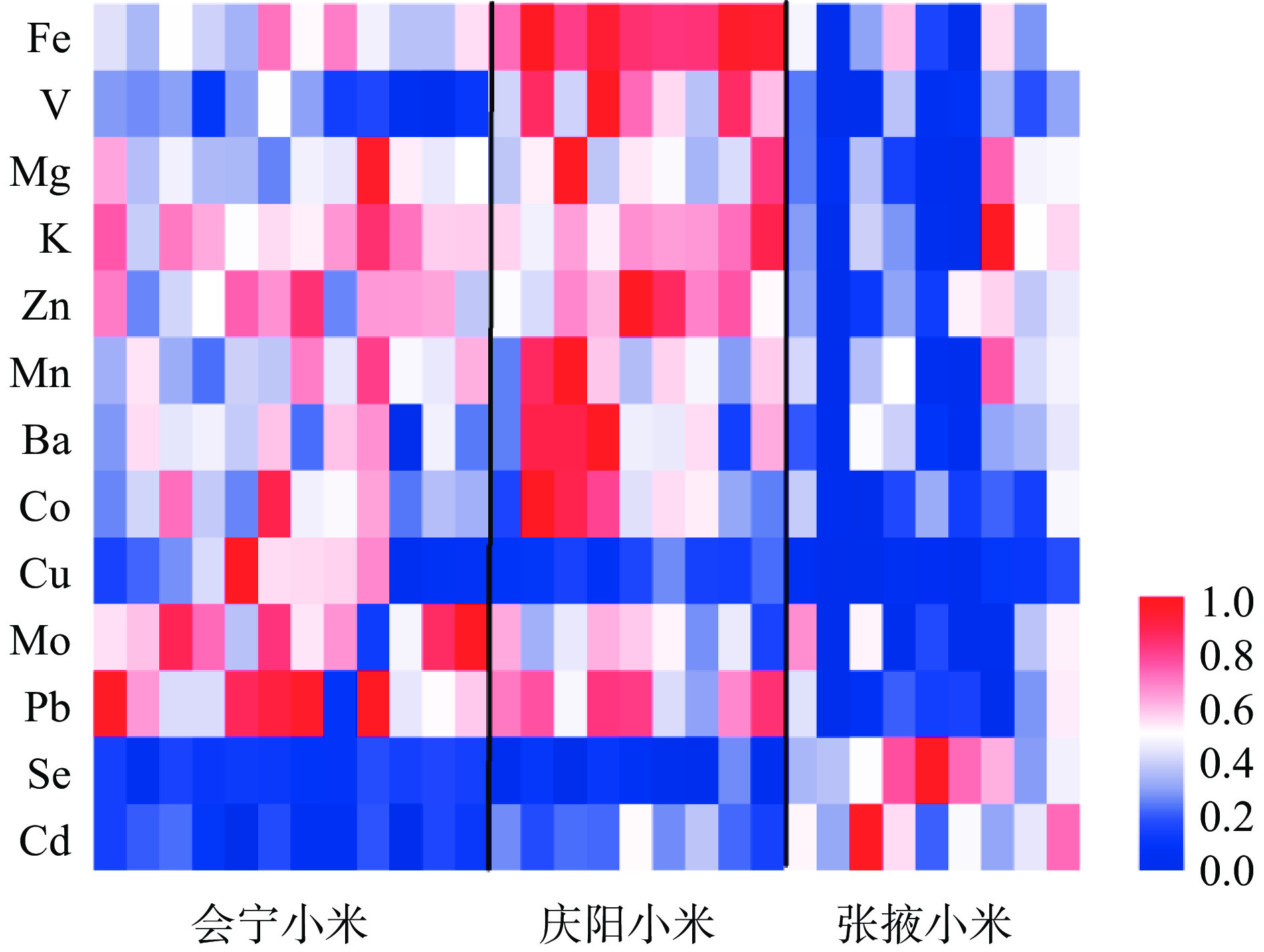
表 5 不同主产区小米矿物元素含量Table 5. Mineral elements contents in foxtail millet from different producing regions元素分类 元 素 会宁小米(n=12) 庆阳小米(n=9) 张掖小米(n=9) 常量元素 Na(mg/kg) 32.35±6.97a 31.12±5.31a 36.46±7.11a Mg(mg/kg) 1434.17±144.41ab 1485.11±181.21a 1274.04±201.08b K(mg/kg) 3252.83±302.35a 3317.22±297.24a 2582.44±795.22b Ca(mg/kg) 165.67±22.38a 180.78±28.76a 162.44±29.47a 微量元素 Mn(mg/kg) 14.38±1.80ab 15.23±2.74a 12.83±2.77b Fe(mg/kg) 49.13±6.08b 68.32±4.29a 41.72±10.97c Ni(mg/kg) 2.12±0.63a 2.39±0.69a 2.22±0.88a Cu(mg/kg) 10.33±4.12a 7.04±0.88b 5.89±0.78b Zn(mg/kg) 27.48±3.44a 29.54±3.38a 23.03±3.52b Sr(mg/kg) 2.04±0.27a 1.81±0.82a 1.79±0.73a Ba(mg/kg) 1.75±0.42ab 2.13±0.66a 1.41±0.40b V(μg/kg) 52.40±11.91b 89.29±19.81a 49.21±12.46b Co(μg/kg) 62.53±16.1a 69.91±23.46a 42.99±12.88b Se(μg/kg) 20.23±2.94b 16.29±6.53b 55.93±18.99a Mo(μg/kg) 394.17±94.91a 321.11±63.29ab 249.56±101.87b 重金属元素 As(μg/kg) 35.4±10.73a 43.79±10.24a 34.61±11.39a Cd(μg/kg) 5.89±1.27c 8.39±1.90b 12.43±4.06a Pb(μ/kg) 118.02±24.03a 117.44±16.15a 80.56±15.31b 注:同行不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 将不同产区间存在显著差异的13种元素含量归一化处理后,绘制矿物元素含量热图(见图1),可以看出不同主产区小米矿物元素含量明显不同,具有其独特的区域分布特征,因此可以利用矿物元素指纹图谱对小米产地进行判别分析。
2.4 矿物元素相关性分析
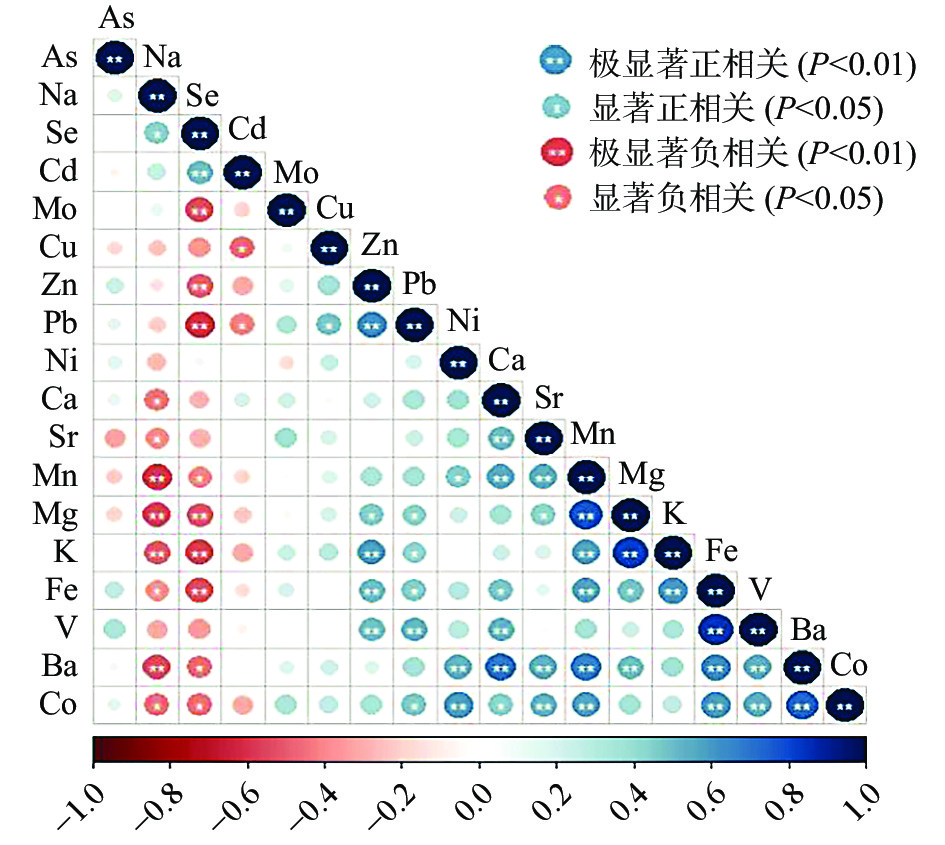
植物的生长是多种营养元素相互作用的结果,各类矿物元素也会在植物体内相互协同与制约帮助植物健康生长[37],为了探究小米中各种矿物元素之间的相互关系,对小米样品中18种矿物元素含量进行皮尔逊相关性分析(见图2)。统计结果表明,小米中有29对元素间存在极显著正相关(P<0.01),12对元素之间存在显著正相关(P<0.05),如Mn与Mg、K、Fe、Ba、Co、Ca、Sr呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),Fe与Pb、Ca、Mg呈显著正相关(P<0.05),表明小米在富集以上元素时呈现相互促进或协同吸收的作用。有10对元素之间存在极显著负相关(P<0.01),9对元素之间存在显著负相关(P<0.05),如Se与Mo、Zn、Pb、Mg、K、Fe呈极显著负相关(P<0.01),Na与Ca、Sr、Fe、Co呈显著负相关(P<0.05),揭示这些矿物元素间存在拮抗抑制吸收作用。其余各矿物元素之间多呈现正相关,但是未达到显著性水平。小米对各矿物元素的吸收富集不仅与品种有关,还有其产地环境有关,小米生长过程中这些矿物元素是如何相互影响的还需进一步研究。相关性分析表明,小米各元素之间相关性较强,可以通过降维简化产地判别指标,为后续产地判别分析提供了依据[38]。
2.5 基于矿物元素的小米产地判别分析
植物源性农产品中矿物元素含量通常取决于其生长环境,因此不同地理来源同一农产品之间在矿物元素含量方面存在着一定差异[39]。矿物元素含量的差异表明了不同主产区的小米确实存在差异,但不足以对小米源产地进行准确判别,为了实现对不同主产区小米的产地判别,分别采用主成分分析(PCA)、正交偏最小二乘法判别分析(OPLS-DA)、线性判别分析(LDA)和聚类分析(HCA)对3个不同产区的小米样品进行判别分析。
2.5.1 主成分分析
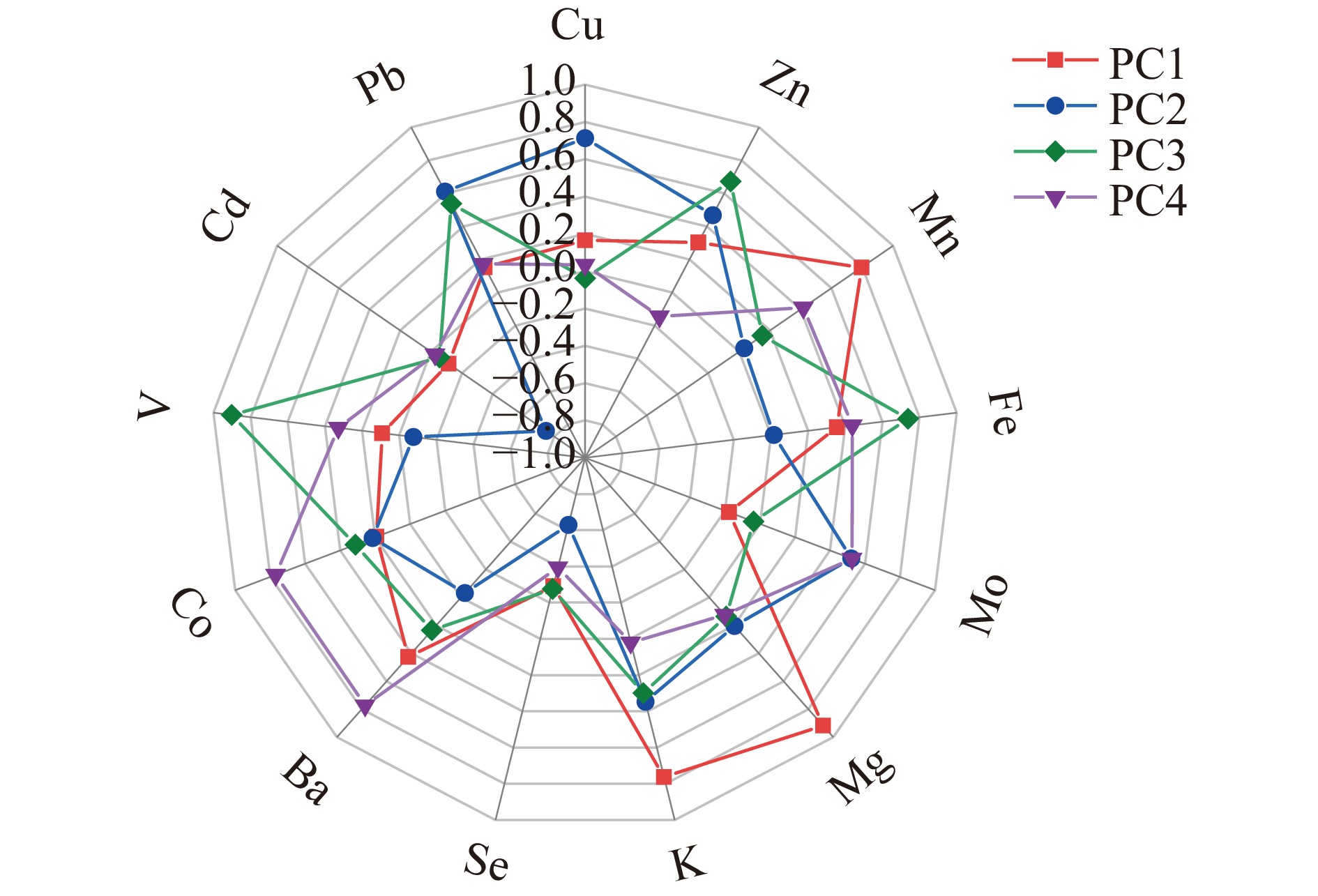
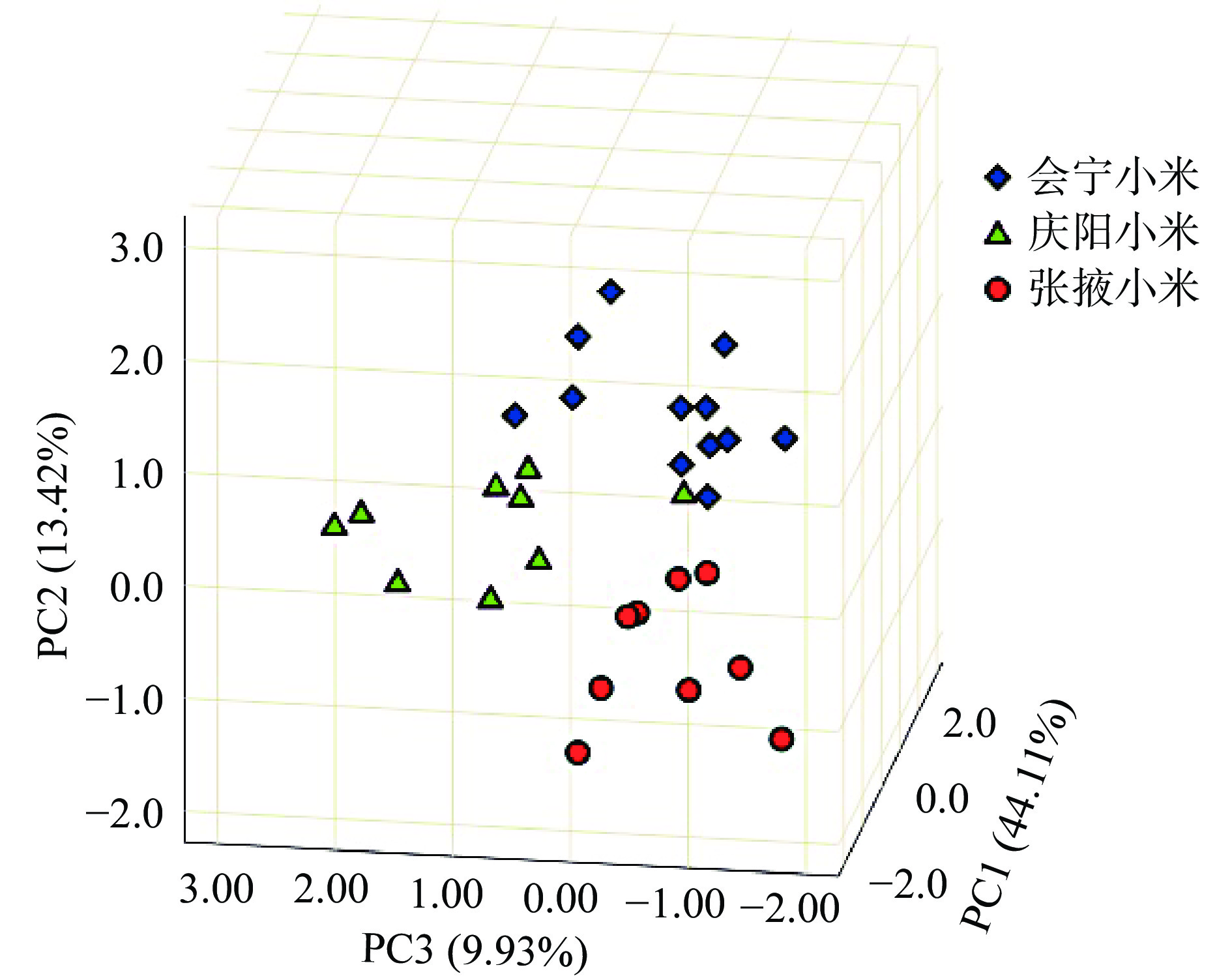
主成分分析(PCA)是一种无监督分析方法,可以将原有的多个指标浓缩成少数几个代表性好的综合指标,这些综合指标彼此之间互不相关,可以集中典型地表征原始变量的数据特征,从而充分反映数据总体信息[40-41]。对三个不同主产区小米中具有显著差异(P<0.05)的Mg、K、Mn、Fe、Zn、Cu、Se、Mo、Ba、Co、V、Cd、Pb 13种矿物元素含量进行PCA分析(KMO为0.684>0.5,表明小米各矿物元素指标间信息重叠度高,可以进行PCA分析),13种元素变量降至4个主成分(特征值>1),第1主成分的方差贡献率是44.11%,其它三个主成分的方差贡献率分别是13.42%、9.93%、8.36%,累计方差贡献率为75.82%,表明前4个主成分代表了原始指标大部分的信息。如图3所示,第1主成分主要综合了小米样品中Mn、K、Mg的信息,第二主成分主要综合了Cu、Cd、Se的信息,第三主成分主要综合了Fe、V、Zn的信息,第四主成分主要综合Ba与Co的信息。为了便于直观分析,以前三个主成分得分做3D散点图,如图4所示,每个主产区的小米均有聚类趋势,来自同一产区间的小米矿物元素变异小于不同产地间的变异程度,但是庆阳小米和会宁小米仍有少部分样品重叠,这可能是由于庆阳和会宁地理距离相对较近,具有相似的地理环境。不同产区小米聚集空间距离较近。虽然主成分分析未能将三个产区小米进行完全区分,但是利用特征矿物元素对小米产地判别是有效的。
2.5.2 线性判别分析
线性判别分析(LDA)是一种有监督的判别分析方法,以投影后类内方差最小,类间方差最大的原则对数据进行降维,实现样品的分类[42]。为了进一步考察各矿物元素含量对小米产地归属的判别情况,采用LDA法对3个产区小米矿物元素含量进行多变量判别分析,以13种存在显著差异(P<0.05)的矿物元素含量作为判别分析的自变量,建立产地判别模型。对小米样品进行逐步判别分析,Cu、Fe、Mo、Se、Cd 5种对小米产地判别显著的元素被引入到判别模型,构建了两个典型判别函数。Willks' Lambda的检验结果进一步证实,在α=0.05的显著性水平下,2个判别函数对分类效果均为显著。判别函数F1和F2解释了100%变异(F1和F2分别解释了变异的67.1%和32.9%),典型相关系数分别为0.934和0.878,判别函数如下所示:
F1=−0.145Cu−0.405Fe−0.301Mo+0.718Se+0.752Cd
F2=0.705Cu−0.847Fe+0.873Mo+0.251Se−0.376Cd
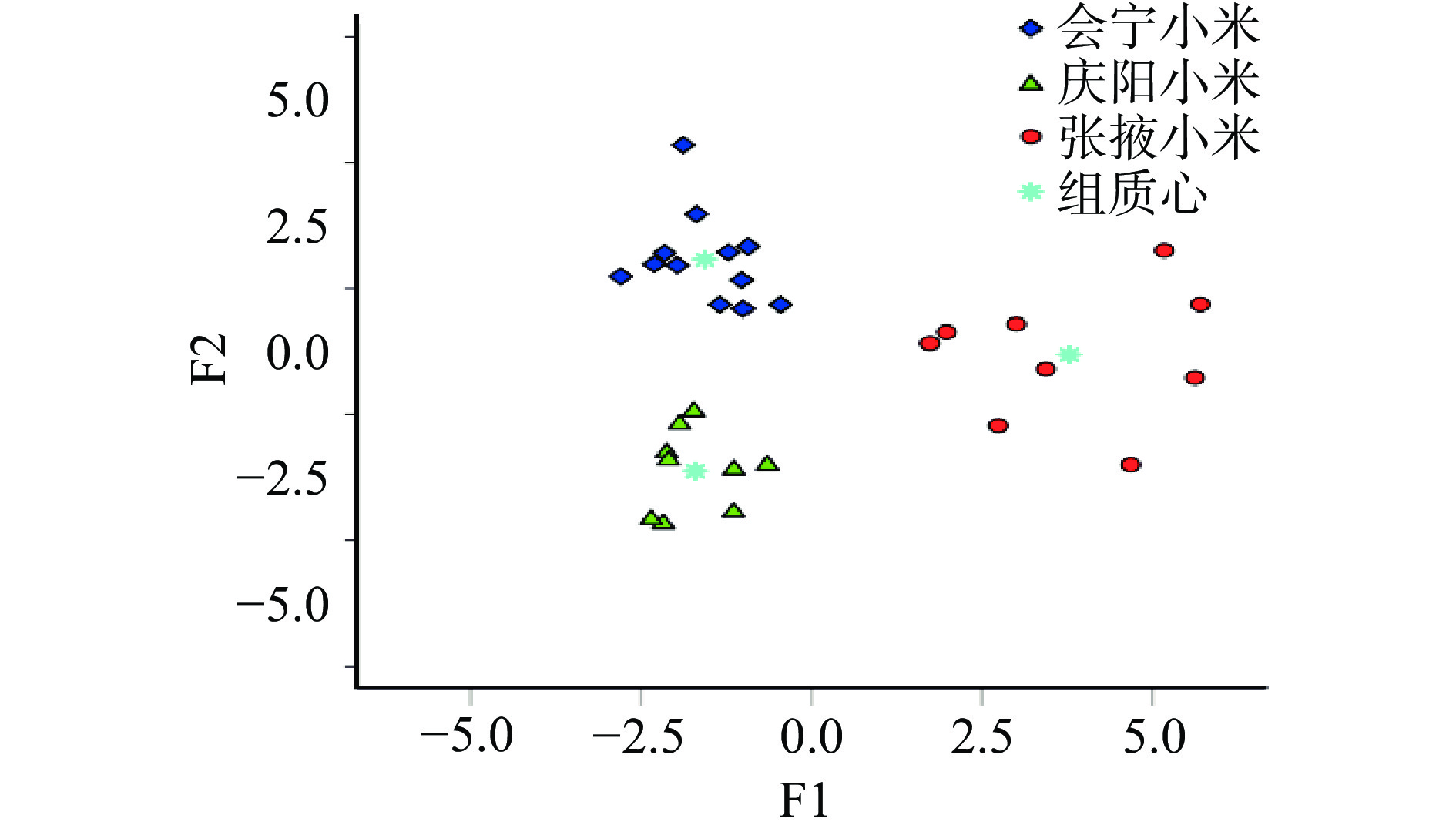
利用F1和F2的得分值绘制散点图(见图5),不同主产区小米样品具有特有的空间分布,3个主产区小米被有效识别。利用回代检验和留一交叉验证两种方法对LDA判别模型进行验证,结果见表6,会宁、庆阳和张掖三个产区小米样品回代检验和留一法交叉检验的总体判别正确率均是100%,说明以Cu、Fe、Mo、Se、Cd构建的判别模型可以有效地鉴别小米产地。3个主产区小米的Fisher线性判别函数如下:
表 6 不同主产区小米判别分析分类结果Table 6. Classification result of discriminant analysis of foxtail millet from different producing regions方法 原属产地 最后判属类别 正确
判断率
(%)总体正确
判断率(%)会宁
小米庆阳
小米张掖
小米回代检验 会宁小米(n=12) 12 0 0 100 100 庆阳小米(n=9) 0 9 0 100 张掖小米(n=9) 0 0 9 100 交叉验证 会宁小米(n=12) 12 0 0 100 100 庆阳小米(n=9) 0 9 0 100 张掖小米(n=9) 0 0 9 100 Y(会宁小米)=1.831Cu−1.588Fe+2.443Mo−1.231 Se−2.686Cd−3.802
Y(庆阳小米)=−1.725Cu+4.704Fe−1.843Mo+3.359Se−0.563Cd−5.463
Y(张掖小米)=−0.717Cu−2.586Fe−1.414Mo+5.00Se+4.144Cd−8.379
2.5.3 正交偏最小二乘判别分析
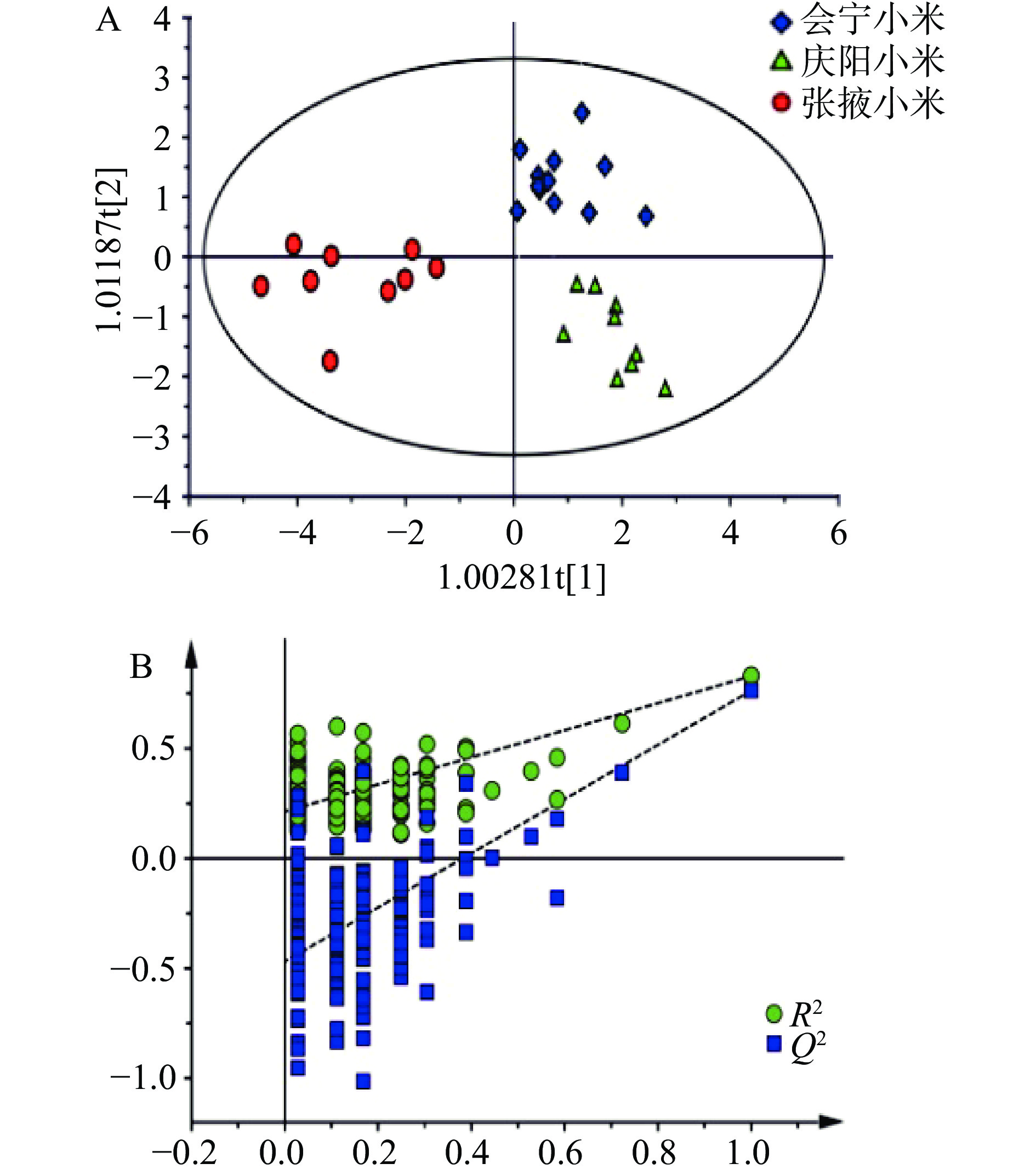
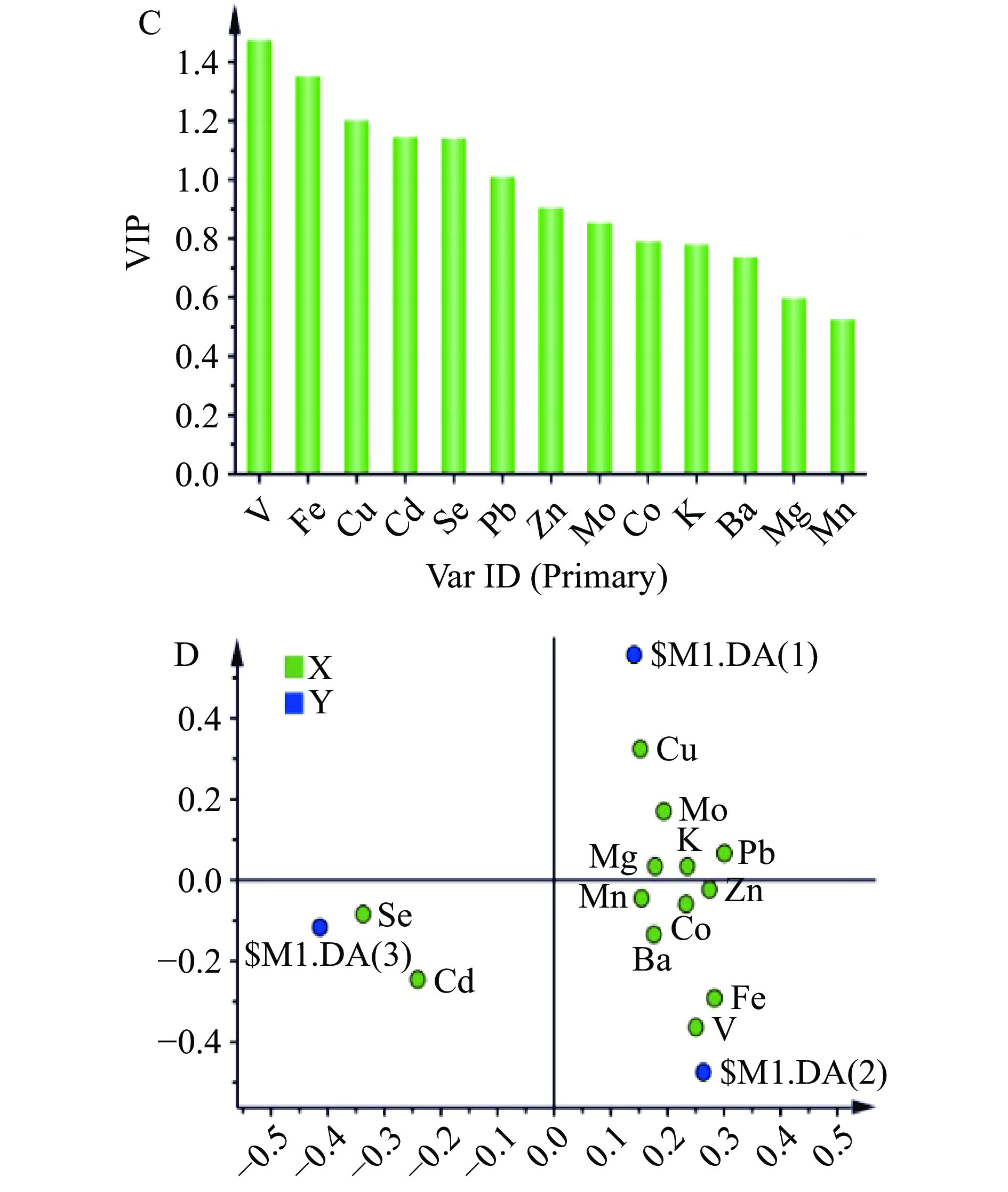
对于样本量小及自变量较少的数据,利用有监督的正交偏最小二乘判别分析(OPLS-DA)具有一定优势。为了排除干扰信息,以13种存在显著差异(P<0.05)的元素含量作为变量,进行OPLS-DA分析,构建不同产地小米的区分模型。利用交叉验证法共拟合出了2个主成分,其中R2X=0.653,R2Y=0.839,Q2=0.744,表明该模型中两个主成分可以有效解释3个主产区间的差异,且该模型具有较好的预测能力(R2>0.5,Q2>0.5)。为了进一步验证该判别模型的可预测性,进行了200次模型置换交叉检验(图6(B))。置换检验的R2=0.214,Q2=−0.458,表明该模型没有过拟合现象(R2<0.5,Q2<0),具有统计学意义。以OPLS-DA模型的第1、2主成分得分绘制散点图,如图6(A)所示,30份小米聚为三簇,会宁小米处于第一象限,庆阳小米处于第四象限,张掖小米处于第二、三象限,不同产地的小米呈现出明显的聚集趋势,各聚集空间相互分离,能够完全区分不同产地小米样品。各元素VIP分值和荷载图如图6(C)和图6(D),VIP值越大,对小米产地判别的差异性越显著,荷载图中距离原点越远的点权重值越大,决定样本差异的作用越大[22]。以VIP>1为标准,得到V、Fe、Cu、Cd、Se、Pb 6种元素在三个产区小米中具有显著差异,由荷载图可知,上述6种元素均离原点距离较远,表明这6种元素可以作为会宁小米、庆阳小米和张掖小米产地判别的特征元素。
2.5.4 聚类分析
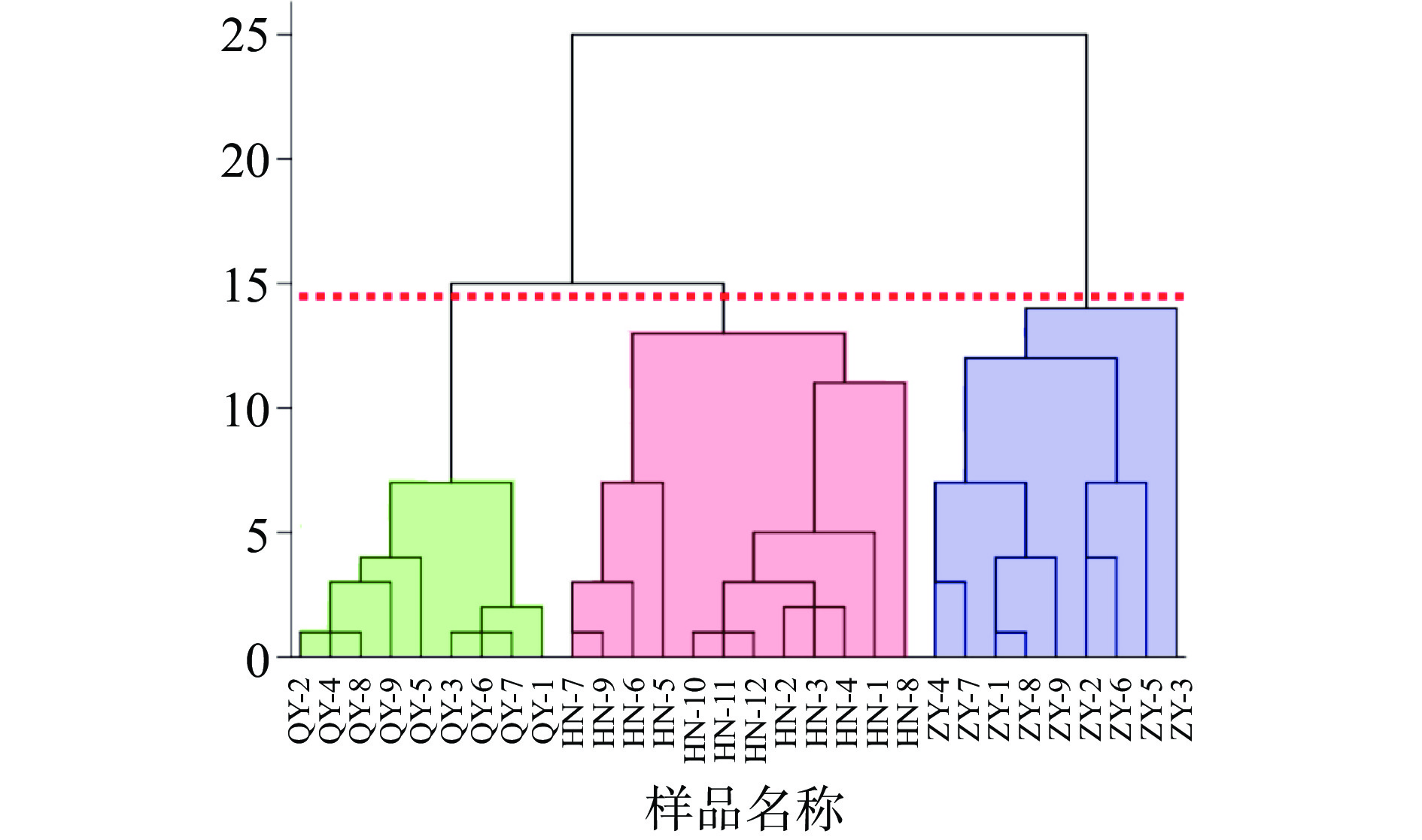
为了验证V、Fe、Cu、Cd、Se、Pb 6种特征元素对小米产地判别的效果和进一步可视化各样品经判别后的所属分类,以6种特征元素含量为自变量,对小米样品进行无监督的聚类分析(HCA)。以欧式距离平方为准则采用组间连接聚类,聚类树状图见图7,当聚类距离为14时,所有小米样品聚为3类,与按地理来源分类结果一致,表明特征元素结合聚类分析可以有效实现对小米产地的鉴别。
3. 结论
通过分析小米中18种矿物元素含量特征,明确了小米中13种矿物元素含量存在的地域差异,其中会宁小米Cu、Mo和Pb元素含量最高,庆阳小米Fe、V、Mg、K、Zn、Mn、Ba、Co元素含量最高,张掖小米Cd和Se元素含量高,不同产区小米中矿物元素的含量明显不同,具有各自的产地特征。采用PCA、LDA、OPLS-DA和HCA对3个主产区小米进行产地判别分析。无监督的PCA分析无法完全区分3个主产区的小米,但是表明了利用矿物元素指纹图谱技术对小米产地判别是有效的;基于Cu、Fe、Mo、Se、Cd的LDA判别模型可以有效鉴别小米的产地,回代检验和留一叉法交叉检验的整体正确判别率均为100%;OPLS-DA模型可以将3个主产区的小米样品100%准确识别,通过VIP值和元素荷载图确定了V、Fe、Cu、Cd、Se、Pb 6种矿物元素为小米产地判别的特征元素;以6种特征元素为变量的HCA分析也可以准确识别小米的产地归属,因此,利用矿物元素指纹图谱技术对小米的产地判别有效可行,为甘肃省内小米的产地溯源和质量控制提供了基础依据。本研究虽建立了一种以矿物元素为对象的小米产地判别方法,但仅对甘肃省会宁、庆阳和张掖三地小米进行了初步研究,生产实际中的普适性还需以多个地区及大量的样本为支撑,以建立更为高效、稳定、精准、实用的小米产地判别模型,为小米产地判别提供理论依据和技术手段。
-
表 1 18种矿物元素标准系列浓度
Table 1 Standard series concentrations of 18 mineral elements
元 素 标准系列浓度(μg·L−1) Na 0、200、400、800、1600、3200、4000 Mg、K、Ca 0、100、200、400、800、1600、2000 Fe、Zn 0、50、100、200、400、800、1000 Mn 0、25、50、100、200、400、500 Cu、Ni、Sr、Ba 0、5、10、20、40、80、100 Mo 0、1、2、4、8、16、20 V、Co、Se、Cd、Pb、As 0.00、0.10、0.20、0.40、0.80、1.60、3.20 表 2 18种元素的线性回归方程、检出限及定量限
Table 2 Linear regression equation, limit of detection and limit of quantitation of 18 elements
元 素 内标物 线性回归方程 决定系数(R2) 检出限 (μg·L−1) 定量限 (μg·L−1) Na23 Ge72 y=4.003×10−2x+1.187 0.9992 27.2 90.7 Mg24 Ge72 y=2.865×10−3x+2.488×10−2 0.9997 0.65 2.17 K39 Ge72 y=2.021×10−3x+3.562×10−1 0.9993 8.04 26.8 Ca43 Ge72 y=5.846×10−6x+3.926×10−4 0.9996 24.61 82.0 V51 Ge72 y=4.680×10−2x +4.119×10−3 0.9998 0.096 0.32 Mn55 Ge72 y=2.440×10−2x+5.155×10−3 0.9999 0.18 0.60 Fe56 Ge72 y=4.844×10−2x+1.859×10−1 0.9994 6.11 20.4 Co59 Ge72 y=1.269×10−1x +1.100×10−3 0.9999 0.0064 0.021 Ni60 Ge72 y=4.178×10−2x +1.222×10−1 0.9999 0.33 1.10 Cu63 Ge72 y=1.253×10−1x+1.997×10−2 0.9999 0.15 0.50 Zn66 Ge72 y=1.377×10−2x+3.018×10−1 0.9999 2.63 8.77 As75 Ge72 y=6.954×10−3x +7.681×10−3 0.9992 0.056 0.19 Se78 Ge72 y=4.013×10−4x+8.835×10−5 0.9996 0.030 0.100 Mo95 Rh103 y=1.715×10−3x+2.266×10−5 0.9999 0.018 0.060 Sr88 Rh103 y=2.571×10−2x +6.326×10−3 0.9999 0.11 0.37 Cd111 Rh103 y=5.549×10−4x+2.974×10−6 0.9993 0.0033 0.011 Ba137 Rh103 y=4.333×10−4x+1.857×10−4 1.0000 0.10 0.33 Pb208 Bi209 y=1.508×10−2x+3.842×10−3 0.9990 0.081 0.27 表 3 18种元素加标回收率
Table 3 Recovery rate of 18 elements
元素 本底值(μg·L−1) 加标浓度(μg·L−1) 回收率(%) 平均回收率(%) 元素 本底值(μg·L−1) 加标浓度(μg·L−1) 回收率(%) 平均回收率(%) Na 235.78 64 88.19 Cu 151.43 64 93.75 120 105.99 101.11 120 102.64 100.98 176 109.16 176 106.53 Mg 13008.68 10000 96.23 Zn 305.78 64 91.53 20000 93.78 93.72 120 98.98 96.87 30000 91.14 176 100.11 K 28159.24 10000 101.81 As 0.3132 0.20 104.80 20000 97.46 98.98 0.40 105.95 106.24 30000 97.67 0.60 107.98 Ca 1726.94 800 104.21 Se 0.1902 0.20 106.50 1600 105.76 106.21 0.40 100.93 103.89 2400 108.66 0.60 104.23 V 0.5695 0.20 95.30 Mo 2.91 1.20 96.67 0.40 99.13 97.94 2.40 106.25 100.70 0.60 99.40 3.60 99.17 Mn 130.99 64 102.09 Sr 17.53 16 98.44 120 98.08 100.94 24 98.88 97.86 176 102.64 32 96.25 Fe 385.6 64 89.38 Cd 0.03568 0.20 95.46 120 93.28 93.36 0.40 100.43 99.69 176 97.43 0.60 103.17 Co 0.4858 0.20 104.70 Ba 14.48 16 94.69 0.40 100.68 101.80 24 95.13 93.90 0.60 100.03 32 91.88 Ni 25.39 16 92.38 Pb 1.052 0.20 89.00 24 97.50 94.61 0.40 90.98 90.35 32 93.94 0.60 91.07 表 4 小米中矿物元素含量
Table 4 Mineral elements contents in foxtail millet
元素分类 元 素 平均值 最小值 最大值 变异系数(%) 常量元素 Na(mg/kg) 33.22 19.93 44.33 20.22 Mg(mg/kg) 1401.40 1047.04 1857.14 13.50 K(mg/kg) 3071.03 1742.11 4203.06 30.79 Ca(mg/kg) 169.23 120.02 221.07 15.84 微量元素 Mn(mg/kg) 14.17 9.24 20.13 17.76 Fe(mg/kg) 52.66 26.41 74.57 24.81 Ni(mg/kg) 2.23 0.70 3.68 31.89 Cu(mg/kg) 8.01 5.01 18.93 40.87 Zn(mg/kg) 26.76 17.42 35.60 15.86 Sr(mg/kg) 1.90 1.00 3.24 32.31 Ba(mg/kg) 1.76 0.85 3.05 32.31 V(μg/kg) 62.51 34.40 120.34 36.64 Co(μg/kg) 58.88 26.53 106.31 34.70 Se(μg/kg) 29.76 10.30 91.60 68.96 Mo(μg/kg) 328.87 150.20 537.05 32.06 重金属元素 As(μg/kg) 37.68 21.80 61.20 29.68 Cd(μg/kg) 8.60 3.90 20.80 43.14 Pb(μg/kg) 106.60 64.04 147.10 24.03 表 5 不同主产区小米矿物元素含量
Table 5 Mineral elements contents in foxtail millet from different producing regions
元素分类 元 素 会宁小米(n=12) 庆阳小米(n=9) 张掖小米(n=9) 常量元素 Na(mg/kg) 32.35±6.97a 31.12±5.31a 36.46±7.11a Mg(mg/kg) 1434.17±144.41ab 1485.11±181.21a 1274.04±201.08b K(mg/kg) 3252.83±302.35a 3317.22±297.24a 2582.44±795.22b Ca(mg/kg) 165.67±22.38a 180.78±28.76a 162.44±29.47a 微量元素 Mn(mg/kg) 14.38±1.80ab 15.23±2.74a 12.83±2.77b Fe(mg/kg) 49.13±6.08b 68.32±4.29a 41.72±10.97c Ni(mg/kg) 2.12±0.63a 2.39±0.69a 2.22±0.88a Cu(mg/kg) 10.33±4.12a 7.04±0.88b 5.89±0.78b Zn(mg/kg) 27.48±3.44a 29.54±3.38a 23.03±3.52b Sr(mg/kg) 2.04±0.27a 1.81±0.82a 1.79±0.73a Ba(mg/kg) 1.75±0.42ab 2.13±0.66a 1.41±0.40b V(μg/kg) 52.40±11.91b 89.29±19.81a 49.21±12.46b Co(μg/kg) 62.53±16.1a 69.91±23.46a 42.99±12.88b Se(μg/kg) 20.23±2.94b 16.29±6.53b 55.93±18.99a Mo(μg/kg) 394.17±94.91a 321.11±63.29ab 249.56±101.87b 重金属元素 As(μg/kg) 35.4±10.73a 43.79±10.24a 34.61±11.39a Cd(μg/kg) 5.89±1.27c 8.39±1.90b 12.43±4.06a Pb(μ/kg) 118.02±24.03a 117.44±16.15a 80.56±15.31b 注:同行不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 6 不同主产区小米判别分析分类结果
Table 6 Classification result of discriminant analysis of foxtail millet from different producing regions
方法 原属产地 最后判属类别 正确
判断率
(%)总体正确
判断率(%)会宁
小米庆阳
小米张掖
小米回代检验 会宁小米(n=12) 12 0 0 100 100 庆阳小米(n=9) 0 9 0 100 张掖小米(n=9) 0 0 9 100 交叉验证 会宁小米(n=12) 12 0 0 100 100 庆阳小米(n=9) 0 9 0 100 张掖小米(n=9) 0 0 9 100 -
[1] 吴立根, 屈凌波. 谷子的营养功能特性与加工研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发,2018,39(15):191−196. [WU L G, QU L B. A review on the resource and processing of the millet[J]. Food Research and Development,2018,39(15):191−196. [2] 冯耐红, 侯东辉, 杨成元, 等. 不同品种小米主要营养成分及氨基酸组分评价[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(8):224−229. [FENG N H, HOU D H, YANG C Y, et al. Evaluation of main nutrients and amino acid components of different varieties of foxtail millet[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(8):224−229. [3] SALEH A S M, ZHANG Q, CHEN J, et al. Millet grains: Nutritional quality processing and potential health benefits[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety,2013,12(3):281−295. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12012
[4] 刘建垒, 常柳, 段晓亮, 等. 谷子的生产概况及其保健功能与机理研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(5):389−395. [LIU J L, CHANG L, DUAN X L, et al. Foxtail millet: Production status, advances in health benefits and its mechanism[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(5):389−395. [5] 郑楠楠, 綦文涛, 王春玲, 等. 不同品种谷子营养成分及功能活性成分差异化分析[J]. 粮油食品科技,2018,26(2):34−39. [ZHENG N N, QI W T, WANG C L, et al. Comparative analysis of nutritional and functional components in different kinds of millet[J]. Science and Technology of Cereals, Oils and Foods,2018,26(2):34−39. [6] YANG Q H, ZHANG P P, QU Y, et al. Comparison of physicochemical properties and cooking edibility of waxy and non-waxy proso millet (Panicum miliaceum L.)[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,257:271−278. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.03.009
[7] 韦露露, 秦礼康, 文安燕, 等. 基于主成分分析的不同品种小米品质评价[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(9):49−56. [WEI L L, QIN L K, WEN A Y, et al. Quality evaluation of different varieties millet based on principal components analysis[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(9):49−56. [8] 杨延兵, 张会笛, 秦岭, 等. 种植地点和加工精度对小米营养与安全品质的影响[J]. 中国粮油学报,2021,36(9):54−59. [YANG Y B, ZHANG H D, QIN L, et al. Effect of planting location and processing fineness on nutrition and safety quality of millet[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2021,36(9):54−59. [9] KUANG L X, NIE J Y, ZHANG J Y, et al. Discrimination of geographical origin of blueberries from three major producing areas of China using mineral element analyses[J]. Atomic Spectroscopy,2021,42(2):91−98.
[10] 于海跃, 续文婕, 周旸, 等. 稳定同位素指纹分析在蚕茧产地溯源中的应用研究[J]. 核农学报,2022,36(3):621−627. [YU H Y, XU W J, ZHOU Y, et al. Application of stable isotope fingerprint analysis in the origin traceability of silkworm cocoons[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2022,36(3):621−627. [11] 刘庭恺, 胡子康, 龙婉君, 等. 基于近红外和中红外光谱的杜仲产地溯源[J]. 化学试剂,2022,44(7):952−959. [LIU T K, HU Z K, LONG W J, et al. Origin tracing of Eucommia ulmoides by near mid infrared spectroscopy combined with chemometrics[J]. Chemical Reagents,2022,44(7):952−959. doi: 10.13822/j.cnki.hxsj.2022.0085 [12] TIAN X R, LÜ S X, TIAN H L, et al. Development of an accurate and reliable DNA method for botanical origin authentication of ginseng food products[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2020,87:103419. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2020.103419
[13] GONZÁLVEZ A, LLORENS A, CERVERA M L, et al. Elemental fingerprint of wines from the protected designation of origin Valencia[J]. Food Chemistry,2009,112(1):26−34. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.05.043
[14] 钱丽丽, 邱彦超, 李殿威, 等. 基于产地、品种和年份影响矿物元素含量的大米判别[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(16):322−327. [QIAN L L, QIU Y C, LI D W, et al. Influence of geographical origin, variety and crop year on mineral element contents of rice and geographical origin discrimination based on mineral elements[J]. Food Science,2021,42(16):322−327. [15] CUI D S, LIU Y, YU H S, et al. Geographical traceability of soybean based on elemental fingerprinting and multivariate analysis[J]. Journal of Consumer Protection and Food Safety,2021,16(4):323−331. doi: 10.1007/s00003-021-01340-2
[16] 邓诗意, 殷萍, 张强, 等. 食药同源产品产地溯源技术研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(14):328−335. [DENG S Y, YIN P, ZHANG Q, et al. Research progress of origin traceability technology for food and drug homologous products[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022,48(14):328−335. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.028740 [17] 刘雯雯, 陈岩, 杨慧, 等. 稳定同位素及矿物元素分析在谷物产地溯源中应用的研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(13):340−348. [LIU W W, CHEN Y, YANG H, et al. Recent advances in the application of stable isotope and mineral element analysis in tracing the geographical origin of cereal grains[J]. Food Science,2019,40(13):340−348. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20180813-125 [18] 卢丽, 刘青, 丁博, 等. 元素含量分析应用于樱桃产地溯源[J]. 分析测试学报,2020,39(2):219−226. [LU L, LIU Q, DING B, et al. Origin traceability of cherries by mineral element analysis[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis,2020,39(2):219−226. [19] 张明露, 黄聪薇, 黎礼科, 等. 贵州铜仁梵净山地区绿茶的产地溯源[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(8):299−304. [ZHANG M L, HUANG C W, LI L K, et al. Geographical origin traceability of green tea from Fanjing mountain area, Tongren, Guizhou[J]. Food Science,2021,42(8):299−304. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200401-003 [20] ZHANG J, YANG R D, LI Y C, et al. Use of mineral multi-elemental analysis to authenticate geographical origin of different cultivars of tea in Guizhou, China[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2020,100(7):3046−3055. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10335
[21] NI K, WANG J, ZHANG Q F, et al. Multi-element composition and isotopic signatures for the geographical origin discrimination of green tea in China: A case study of Xihu Longjing[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2018,67:104−109. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2018.01.005
[22] 王小芝, 陈瑶, 吴海龙, 等. 基于元素指纹的白术产地溯源及其与土壤的相关性研究[J]. 化学学报,2022,80(2):159−167. [WANGx Z, CHEN Y, WU H L, et al. Study on the origin traceability of Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz. and its correlation with soil based on mineral elements[J]. Acta Chimica Sinica,2022,80(2):159−167. doi: 10.6023/A21090441 [23] 贺媛媛, 孙倩倩, 郭波莉, 等. 基于矿质元素指纹的粉葛产地溯源研究[J]. 核农学报,2021,35(7):1565−1573. [HE Y Y, SUN Q Q, GUO B L, et al. Traceability of Puerariae thomsonii Radix (Fenge) geographical origin based on mineral element fingerprint[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2021,35(7):1565−1573. [24] KURAS M J, ZIELINSKA P M, DUSZYNSKA J, et al. Determination of the elemental composition and antioxidant properties of dates (Phoenix dactyliferia) originated from different regions[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2020,57(8):2828−2839. doi: 10.1007/s13197-020-04314-8
[25] ROSARIA F, ANTONIO T, ADA N, et al. Italian tomato-based products authentication by multi-element approach: A mineral elements database to distinguish the domestic provenance[J]. Food Control,2018,93:211−218. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2018.06.002
[26] 张高强, 袁建, 鞠兴荣, 等. 不同产地稻米中元素含量特征及其产地判别研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(14):61−70. [ZHANG G Q, YUAN J, JU X R, et al. Study on the characteristics of elements content and the discrimination of the origin of rice in different producing areas[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(14):61−70. [27] WANG F, ZHAO H Y, YU C D, et al. Determination of the geographical origin of maize (Zea mays L.) using mineral element fingerprints[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2020,100(3):1294−1300. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10144
[28] LIU H Y, WEI Y M, ZHANG Y Q, et al. The effectiveness of multi-element fingerprints for identifying the geographical origin of wheat[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2017,52(4):1018−1025.
[29] 周秀雯, 吴浩, 陈海泉, 等. 基于矿物元素指纹差异的榴莲产地甄别[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(14):255−262. [ZHOU X W, WU H, CHEN H Q, et al. Discrimination of durian from different geographical origins based on mineral element fingerprint characteristics[J]. Food Science,2021,42(14):255−262. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200716-218 [30] WU F H, ZHAO H A, SUN J, et al. ICP-MS-based ionomics method for discriminating the geographical origin of honey of Apis cerana Fabricius[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,354:129568−129568. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129568
[31] 开建荣, 石欣, 李彩虹, 等. 基于矿物元素技术的中宁不同产区枸杞的判别分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(9):253−260. [KAI J R, SHI X, LI C H, et al. Discriminant analysis of Lycium barbarum from different areas in Zhongning based on mineral element technique[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022,48(9):253−260. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.027625 [32] 崔纪菡, 赵宇, 刘猛, 等. 不同品种小米矿质元素含量差异分析[J]. 中国农业科技导报,2017,19(8):84−91. [CUI J H, ZHAO Y, LIU M, et al. Mineral chemical analysis of different foxtail millet (Setaria italic L. Beauv) cultivars[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology,2017,19(8):84−91. doi: 10.13304/j.nykjdb.2017.0070 [33] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.14-2017 食品安全国家标准 食品中锌的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017: 2 National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People 's Republic of China, China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.14-2017 National food safety standard the measurement of iron in food[S]. Beijing: China Standard Publishing House, 2017: 2
[34] 刘丽南, 吴春敏, 高镯, 等. 基于ICP-MS/MS技术测定大米中30种微量元素[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(23):259−265. [LIU L N, WU C M, GAO Z, et al. Determination of 30 trace elements in rice based on ICP-MS/MS[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(23):259−265. [35] 潘少香, 孟晓萌, 刘雪梅, 等. 基于电感耦合等离子体质谱法对不同产地小米矿物元素的差异性分析[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(1):72−79. [PAN S X, MENG X M, LIU X M, et al. Analysis of the difference of mineral elements of millet from different regions based on inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2022,13(1):72−79. [36] 汤超华, 青余, 张凯, 等. 富硒农产品研究开发助力我国营养型农业发展[J]. 中国农业科学,2019,52(18):3122−3133. [TANG C H, ZHAO Q Y, ZHANG K, et al. Promoting the development of nutritionally-guided agriculture in research and development of selenium-enriched agri-products in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2019,52(18):3122−3133. [37] 赵霞, 司晶晶, 赵鲲鹏, 等. 不同生长期黄芪无机元素动态特征分析[J]. 食品工业科技, 2022, 43(18): 293-299. ZHAO X, SI J J, ZHAO K P, et al. Dynamic characteristics of inorganic elements in astragalus membranaceus at different growth stages[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(18): 293-299.
[38] 石春红, 曹美萍, 胡桂霞. 基于矿物元素指纹图谱技术的松江大米产地溯源[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(16):300−306. [SHI C H, CAO M P, HU G X. Geographical origin traceability of Songjiang rice based on mineral elements fingerprints[J]. Food Science,2020,41(16):300−306. [39] ZHANG T W, WANG Q, LI J R, et al. Study on the origin traceability of Tibet highland barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) based on its nutrients and mineral elements[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,346:128928. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128928
[40] LIU W W, CHEN Y, LIAO R X, et al. Authentication of the geographical origin of Guizhou green tea using stable isotope andmineral element signatures combined with chemometric analysis[J]. Food Control,2021,125:107954. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.107954
[41] 李雪婷, 伊雄海, 樊祥, 等. 基于多元素含量分析结合化学计量学技术的橄榄油等级鉴别方法[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(8):317−323. [LI X T, YI X H, FAN X, et al. Grade identification of olive oil based on multi-element analysis and chemometrics[J]. Food Science,2022,43(8):317−323. [42] 姜浩琛, 王世成, 李波, 等. 基于碳、氮同位素和矿物元素的青萝卜产地判别研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(10):234−239. [JIANG H C, WANG S C, LI B, et al. Origin discrimination study of the green turnip based on carbon and nitrogen isotopes and mineral elements[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022,48(10):234−239. -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. Dai Zhaoyang,Hu Liyun,Li Fuyan,Ai Yong,Zhang Wenyun,Zhang Bing. Study on Antibacterial Efficacy of Plant-Derived Compound Preservative and Its Product Application. China Detergent & Cosmetics. 2023(01): 52-59 .  必应学术
必应学术
2. 赵海桃,吴小杰,钟明旭,邱隽蒙,石统帅,符群. 细叶小檗不同生长部位生物碱抑菌活性研究. 北京林业大学学报. 2022(07): 126-134 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 戴朝阳,胡丽云,李福艳,艾勇,张文云,张兵. 植物源复配防腐剂抑菌效能及其产品应用研究. 日用化学品科学. 2022(10): 11-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



