Drying Characteristics and Process Optimization by Heat Pump Drying of Green Sichuan Pepper
-
摘要: 为了探究青花椒热泵干燥特性并优化干燥工艺参数以提高干制花椒品质,本文以温度、风速和铺放厚度为试验因子,以有效水分扩散系数、光合色素单位质量含量和色差为评价指标,对青花椒热泵干燥过程进行单因素试验和正交试验,并采用6种常用干燥数学模型分别对正交试验数据进行非线性拟合。结果表明,Page模型对试验数据的拟合度最好,是描述青花椒热泵干燥的最佳模型;在恒温干燥条件下,温度对有效水分扩散系数和色差的影响极显著(P<0.01),温度越高,有效水分扩散系数和色差变化越大;风速对色差的影响显著(P<0.05),风速越大,色差变化越大;铺放厚度对色差的影响极显著(P<0.01),铺放厚度越大,色差变化越小;而光合色素单位质量含量在不同温度条件下均具有先略下降再上升后又迅速下降至稳定的趋势,温度越高,光合色素单位质量含量变化越快,不利于干制青花椒品质的提高。综合考虑温度、风速、铺放厚度对青花椒色差、光合色素单位质量含量和有效水分扩散系数的影响,确定最优干燥工艺参数为温度40 ℃、风速0.3 m/s、铺放厚度11.9 mm,在此条件下,干制青花椒色泽品质最佳,色差为20.01,光合色素单位质量含量为2.9601×10−4 mg/g。研究结果可为青花椒热泵干燥工艺应用提供参考。Abstract: In order to investigate the drying characteristics of green Sichuan pepper by heat pump and optimize the drying process parameters to improve the quality of dried green Sichuan pepper, the single-factor experiments and orthogonal tests on the drying process of green Sichuan pepper were conducted in this study. Temperature, air speed and laying thickness were defined as test factors, and effective moisture diffusion coefficient, photosynthetic pigment unit mass content and color difference were determined as evaluation indexes. Six commonly used drying mathematical models were used to fit the orthogonal test data nonlinearly, respectively. The results showed that the Page model had the best fit to the test data and it was the best model to describe the drying of green Sichuan pepper by heat pump. Under the constant temperature drying condition, the effect of temperature on the effective moisture diffusion coefficient and color difference was highly significant (P<0.01). The higher the temperature, the greater the change of effective moisture diffusion coefficient and color difference. The effect of air speed on color difference was significant (P<0.05). The higher the air speed, the greater the change of color difference. The effect of laying thickness on color difference was highly significant (P<0.01). The higher the laying thickness, the greater the color difference. However, under different temperatures the unit mass content of photosynthetic pigment slightly decreased, and then increased, and then rapidly decreased until it reached stability. The higher the temperature, the faster the change of the unit mass content of photosynthetic pigment, which was not beneficial to the quality improvement of dried green Sichuan pepper. By comprehensively the effects of temperature, air speed and laying thickness on the color difference, unit mass content of photosynthetic pigment and effective moisture diffusion coefficient, the optimal parameters of drying process were determined as temperature of 40 ℃, air speed of 0.3 m/s and laying thickness of 11.9 mm. Under these conditions, the best color quality of dried green Sichuan pepper was achieved, with a color difference of 20.01 and a photosynthetic pigment unit mass content of 2.9601×10−4 mg/g. The results of the study could provide reference for the application of heat pump drying process of green Sichuan pepper.
-
青花椒(Zanthoxylum schinifolium Sieb. et Zucc)是芸香科花椒属的一种,因果实成熟后为青绿色而得名。青花椒是调味品的重要原料,色香味俱佳,经济价值高[1]。青花椒在四川、重庆、云南、贵州等省市广泛种植,青花椒干燥设备具有很大的市场需求[2]。干燥是花椒采后加工中的重要环节,良好的干燥技术和最佳的干燥工艺可以有效提升花椒品质[3]。花椒干燥方法主要包括热风、微波、真空、热泵、远红外等[4-5],其中基于热风的堆积式干燥应用最广,热源常为热风炉和热泵。热泵干燥具有节能、高效、可控等优点,因此在青花椒干燥中得到应用。
色泽是青花椒品质最主要的评价指标,干燥过程中果皮由于光合色素降解而导致色泽变化。果皮光合色素主要包括叶绿素和类胡萝卜素,其中叶绿素使青花椒果皮呈现青绿色。青花椒常在干燥过程中的褐变主要是由叶绿素降解导致。相应地,干燥工艺及工艺参数对青花椒叶绿素降解方面的研究得到较多关注。叶绿素降解方式主要为叶绿素酶降解和叶绿素光降解。汪洋等[6]研究了干燥过程中光对青花椒叶绿素降解的影响及光降解原因,结果表明紫外光对叶绿素光降解影响最大。为了降低光对叶绿素酶降解的影响,一般干燥过程均处于避光环境中进行。叶绿素酶降解受温度、酶浓度和时间的影响较明显。温度越高,酶活性越强;酶浓度越高,酶降解强度越大;干燥时间越长,酶降解越充分。因而,叶绿素酶降解成为青花椒色泽变化的最主要因素[7]。通过对干燥工艺及参数优化,可以调控温度、浓度和时间三者对叶绿素酶降解的进程和影响,以提高干制青花椒品质[8-10]。杨英鹏等[11]通过试验研究表明水分含量变化的快慢也会影响叶绿素的降解速率。类胡萝卜素主要有物理降解、化学降解和生物降解等方式[12-13],但类胡萝卜素降解对青花椒色泽影响有限。
青花椒色泽品质极大地影响椒农收益,因此本文针对青花椒干燥过程中干燥工艺参数对果皮色泽的影响,即果皮光合色素降解影响色泽的问题,采用热泵干燥机对新鲜青花椒进行干燥处理,以温度、风速和铺放厚度为试验因子,研究青花椒热泵干燥特性并建立数学模型,对青花椒光合色素降解和色泽进行分析;通过单因素实验确定因子水平,并进行正交试验和数据分析,探究干燥工艺参数对青花椒果皮光合色素和色泽的影响,为青花椒热泵干燥工艺参数优化和品质提升提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
新鲜青花椒(九叶青) 2021年7月购于重庆市江津区某椒园,4~8 ℃冷藏备用;丙酮 分析纯,重庆川东化工(集团)有限公司;95%乙醇 重庆市普康消毒用品有限公司;30目标准筛网(GB/T 6003.1-2012,以下简称“筛网”) 绍兴市上虞区豪泉筛具厂。
1HGKB-4热泵干燥机(图1) 自制;BSA2245-CW赛多利斯电子天平 赛多利斯科学仪器(北京)有限公司;SUMMIT-565热线式风速仪 韩国SUMMIT有限公司;NR60C色差仪 深圳市三恩时科技有限公司;FBS-760A卤素水分测定仪 厦门市弗布斯检测设备有限公司;721G INESA可见分光光度计 上海仪电科学仪器股份有限公司;S-J220 D&T电子分析天平 天津市德安特传感技术有限公司,用于光合色素测定时的果皮样品称量。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 单因素实验
单因素实验作为预试验,得到青花椒热泵干燥特性,分析温度、风速、铺放厚度对干燥速率及色差的影响,确定正交试验因子水平。热泵干燥机由热泵系统、干燥室和控制系统等组成,如图1所示。干燥室内置15层筛网架,根据风速仪测得第1、8、15层的风速分别为0.3、0.5、0.7 m/s。根据筛网高度确定铺放厚度水平,分别为6.2、11.9、17.6 mm(对应青花椒质量50、100、150 g)。各单因素实验工艺参数见表1。试验时,热泵干燥机设置为恒温模式,每隔0.5 h对样品称取质量、测色差。青花椒湿基含水率降至10%以下且质量稳定时停止干燥[14],每组试验重复3次。
表 1 单因素实验方案Table 1. Scheme of single factor test工艺参数 温度(℃) 风速(m·s−1) 铺放厚度(mm) 温度 35 0.7 11.9 40 45 50 55 60 风速 40 0.3 11.9 0.5 0.7 铺放厚度 40 0.7 6.2 11.9 17.6 1.2.2 正交试验
以温度、风速和铺放厚度为试验因子,以有效水分扩散系数、光合色素单位质量含量、色差为评价指标进行正交试验,选择正交表L9(34)[15],根据单因素实验确定因子水平,因子与水平见表2。
表 2 正交试验因子与水平设计Table 2. Design of orthogonal experimental factors and levels水平 因子 A温度(℃) B风速(m·s−1) C铺放厚度(mm) 1 40 0.3 6.2 2 50 0.5 11.9 3 60 0.7 17.6 1.2.3 指标测定及计算
1.2.3.1 干燥指标测定与计算
使用卤素水分测定仪测量青花椒初始含水率,3次重复。干燥过程中青花椒的含水率按照国家标准GB 5009.3-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品中水分的测定》进行测量,湿基含水率W和干基含水率M分别按公式(1)、(2)计算:
W = mt−m0mt×100 (1) M = mt−m0m0 (2) 式中:W为湿基含水率,%;M为干基含水率,g/g;mt为干燥过程中t时刻青花椒质量,g;m0为青花椒干物质质量,g。
干燥速率DR按公式(3)计算:
DR = M1−M2t2−t1×100 (3) 式中:DR为干燥速率,g/(g·h);M1、M2分别为干燥过程中t1、t2时刻青花椒干基含水率,g/g。
水分比MR按公式(4)计算:
MR = M1−MeM0−Me (4) 式中:Me为青花椒平衡干基含水率,g/g;M0为青花椒初始干基含水率,g/g。
有效水分扩散系数(Effective Moisture Diffusivity,EMD)按公式(5)计算:
lnMR = ln(6π 2)−π 2Deff4r2t (5) 式中:Deff为有效水分扩散系数,m2/s;r为花椒颗粒平均半径,m;r=0.002 m;t为干燥时间,s。
活化能按公式(6)计算[14]:
Deff = D0exp(−EaRTa) (6) 式中:D0为扩散前置因子,m2/s;Ea为活化能,J/mol;R为摩尔气体常数,8.314 J/(mol·K);Ta为干燥温度,K。
1.2.3.2 光合色素测定与计算
选取温度分别为40、50、60 ℃,按干燥速率最快时的风速和铺放厚度条件,即风速0.7 m/s,铺放厚度6.2 mm,进一步研究青花椒光合色素随温度的变化。采用有机溶剂直接浸提法提取光合色素[16]。使用分析纯丙酮混合纯净水制备80%丙酮溶液,按体积比1:1将80%丙酮溶液与95%乙醇溶液混合制备光合色素提取液(以下简称“提取液”)[17]。取干燥过程中不同时刻青花椒果皮0.1~0.2 g放入离心管中,取10 mL提取液加入其中,浸泡果皮,在黑暗环境下静置72 h,至果皮色泽变淡。取2 mL提取液倒入1号比色皿,长时间静置后在离心管内液体充分摇匀后,取2 mL倒入2号比色皿,将两支比色皿分别放入分光光度计槽中,分别在470、645、663 nm波长下测量光吸收值[18-20],结合Arnon公式确定类胡萝卜素、叶绿素a、叶绿素b的含量。叶绿素a含量和叶绿素b含量分别按公式(7)、(8)计算[21-22]:
Ca = 12.71×A663− 2.59×A645 (7) Cb = 22.88×A645− 4.67×A663 (8) 式中:Ca、Cb分别为叶绿素a和叶绿素b含量,mg/L;A663、A645分别为浸泡过青花椒果皮的提取液在663、645 nm下的光吸收值。
类胡萝卜素按公式(9)计算:
Car = 1000×A470− 3.27×Ca− 104×Cb229 (9) 式中:Car为类胡萝卜素含量,mg/L;A470为浸泡过青花椒果皮的提取液在波长470 nm下的光吸收值。
光合色素总量按公式(10)计算:
CT = Ca+Cb+Car (10) 式中:CT为光合色素总量,mg/L。
光合色素单位质量含量按公式(11)计算:
C = CT×VTFW×1000×n (11) 式中:C为光合色素单位质量含量,mg/g;VT为提取液体积,L,VT=0.01 L;FW为提取果皮质量,mg;n为稀释倍数,n=1。
1.2.3.3 色差测定与计算
用标准白色板和黑色板校正色差仪,取外观品质好的新鲜青花椒,用色差仪测量总色差ΔE,作为后续试验色差标样。设置色差仪为平均测量模式,每隔0.5 h随机取样测量青花椒果皮色差。色差ΔE采用国际CIE Lab色度空间表示,按公式(12)[23]计算:
ΔE = √(ΔL*)2+(Δa*)2+(Δb*)2 (12) 式中:L*为明亮度,变化范围为0~100,0为绝对黑色,100为绝对白色;a*为红绿值,变化范围为−100~+100,负值为偏绿,正值为偏红;b*为黄蓝值,变化范围为−100~+100,负值为偏蓝,正值为偏黄。
1.2.3.4 干燥数学模型及评价指标
表3为6种常用干燥数学模型,分别对正交试验的9组试验数据进行非线性拟合。选用决定系数R2、卡方χ2、均方根误差RMSE评价模型拟合的优劣。R2越接近1,χ2越小,模型与试验数据拟合效果越好。均方根误差RMSE表明模型预测值和试验数据的平均偏差程度,越小两者越接近。评价指标分别按公式(13)~(15)计算:
R2 = 1 −N∑1(MRexp,i− MRpre,i)2N∑1(¯MRexp,i− MRpre,i)2 (13) χ2 = N∑1(MRexp,i− MRpre,i)2N −n (14) RMSE = √N∑1(MRexp,i− MRpre,i)2N (15) 式中:MRexp,1,i为第i个数据点测量水分比;MRpre,i为第i个数据点模型预测水分比;
¯MRexp,i 为测量水分比平均值;N为数据点个数;n为模型中参数个数。1.3 数据处理
使用软件Design-Expert 12设计正交试验方案并分析试验结果,使用软件Excel 2016处理数据,使用软件Origin 2019b绘制试验数据变化曲线,使用SPSS Statistics 26拟合干燥数学模型。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素实验
2.1.1 温度
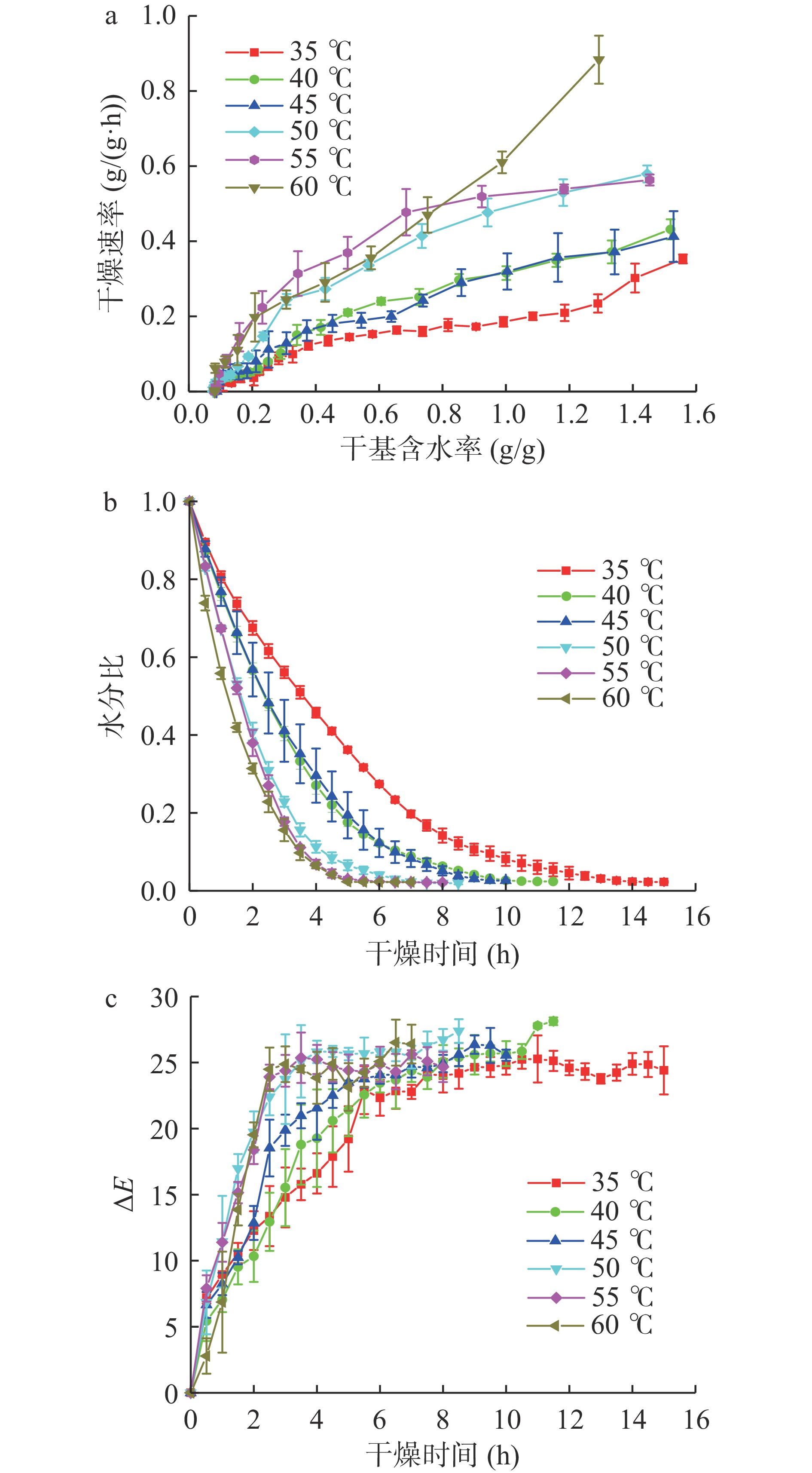
图2表示温度对青花椒干燥速率、水分比及色差的影响。由图2a可知,干燥温度越高,干燥速率越大;由图2b可知,在干燥初始阶段水分比下降较快,随着时间延长,水分比下降趋于平缓。当温度分别为35、40、45、50、55、60 ℃时,湿基含水率降至10%的时间分别为15.0、11.5、10.0、8.5、8.0、7.0 h,即温度越高青花椒完成干燥所需时间越短,干燥速率越快;由图2c可知,青花椒果皮色差在干燥初期变化较大,温度越高青花椒果皮色泽变化越快。
青花椒热泵干燥有效水分扩散系数及其平均活化能通过拟合得出结果,见表4。由表4可知,随着温度升高,有效水分扩散系数增大,青花椒内部水分子扩散速度提高,脱水能力增强,干燥速率相应增大,与图2分析结果一致。干燥时的平均活化能为32153.8 J/mol,表示在给定热泵干燥条件下,蒸发1 mol水所需能量为32153.8 J。综合有效水分扩散系数,选择40~60 ℃进行正交试验。
表 4 不同温度时的有效水分扩散系数及平均活化能Table 4. Deff and average activation energy of green Sichuan pepper at different temperatures温度(℃) 有效水分扩散系数
(10−7 m2·s−1)相关系数 活化能(J·mol−1) 相关系数 35 4.4222 0.9931 32153.8 0.9828 40 5.7654 0.9951 45 6.3414 0.9919 50 8.3972 0.9858 55 10.3484 0.9669 60 11.3942 0.9842 2.1.2 风速
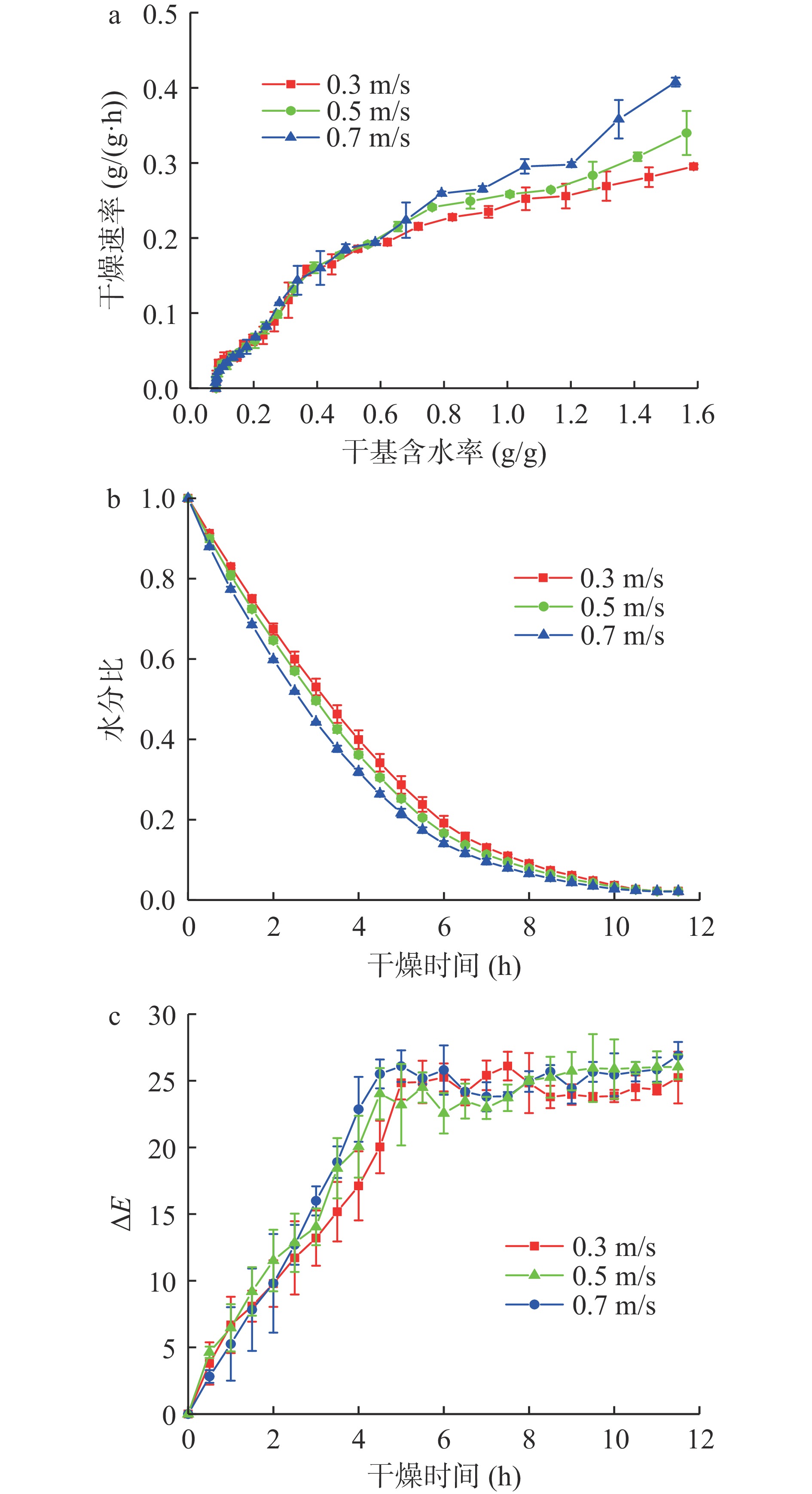
图3表示风速对青花椒干燥速率、水分比及色差的影响。由图3可知,青花椒在干燥初期,干基含水率较高,风速越高干燥速率越快,水分比下降越快,色泽变化也越大。在温度40 ℃、铺放厚度11.9 mm的条件下,风速0.7 m/s时干燥开始时干燥速率可达0.4 g/(g·h)以上。在干燥前期,干燥速率较快,水分比下降较快,随着时间延长,干燥速率降低,水分比下降趋于平缓,与图2所示规律一致。这是由于干燥后期青花椒内存在部分结合水不易流失,且自由水减少后使水分梯度减小,从而表现为降速[26],例如风速0.3 m/s时,干燥开始后干燥速率为0.2953 g/(g·h),之后逐渐降低至接近0。
由于热风干燥中活化能仅与温度相关,故研究不同风速下的有效水分扩散系数及其平均活化能时应改变温度,通过拟合得出结果,结果见表5。由表5可知,随着风速与温度的升高,有效水分扩散系数增大,平均活化能为24137.57 J/mol。
表 5 不同风速时的有效水分扩散系数及平均活化能Table 5. Deff and average activation energy of green Sichuan pepper at different air speed风速(m·s−1) 温度(℃) 有效水分扩散系数(10−7 m2·s−1) 相关系数 活化能(J·mol−1) 相关系数 0.3 40 5.6832 0.9836 24137.57 0.9979 0.5 50 7.7763 0.9946 0.7 60 10.1570 0.9822 2.1.3 铺放厚度
图4表示铺放厚度对青花椒干燥速率、水分比及色差的影响。由图4可知,青花椒在筛网内的铺放厚度越小,干燥速率越快,水分比变化越快,色泽变化越大。当干燥时间达6 h时,总色差ΔE趋于平稳,即不同铺放厚度条件下的青花椒色泽变化保持稳定。干燥后期,青花椒果皮皱缩,导致内部通道堵塞,酶促反应减少,因此色差趋于平稳。
研究不同铺放厚度下的有效水分扩散系数及其平均活化能通过拟合得出结果,结果见表6。由表6可知,随着铺放厚度与温度的升高,有效水分扩散系数增大,平均活化能为25070.33 J/mol。
表 6 不同铺放厚度时的有效水分扩散系数及平均活化能Table 6. Deff and average activation energy of green Sichuan pepper at different laying thickness铺放厚度(mm) 温度(℃) 有效水分扩散系数(10−7·m2·s−1) 相关系数 活化能(J·mol−1) 相关系数 6.2 40 5.5397 0.9932 25070.33 0.9893 11.9 50 7.9069 0.9956 17.6 60 10.1252 0.9693 2.2 数学模型
2.2.1 模型选择
拟合结果见表7,对比6种干燥数学模型的卡方χ2、决定系数R2、均方根误差RMSE可知,模型2~模型6的决定系数平均值达到0.99及以上,其中Page模型和Modified Page模型对试验数据的拟合度最好,此两种模型R2最大,同时χ2和RMSE最小,模型评价指标的平均值均为R2=0.99896,χ2=0.00011,RMSE=0.00907。从简化和实用角度考虑,选择Page模型进行模型验证和数据分析。
表 7 青花椒热泵干燥数学模型拟合结果Table 7. Mathematical model fitting results of heat pump drying of green Sichuan pepper模型 参数及指标 试验参数值及指标值拟合结果 平均值 试验号1 试验号2 试验号3 试验号4 试验号5 试验号6 试验号7 试验号8 试验号9 1 k 0.28212 0.27726 0.2872 0.38352 0.38906 0.40898 0.54678 0.54979 0.52568 / R2 0.97772 0.97900 0.98188 0.99147 0.99325 0.99082 0.99292 0.98800 0.99141 0.98739 χ2 0.00225 0.00211 0.00179 0.00083 0.00065 0.00090 0.00072 0.00127 0.00088 0.00127 RMSE 0.04747 0.04588 0.04236 0.02886 0.02543 0.03002 0.02688 0.03567 0.02959 0.03468 2 k 0.17451 0.17435 0.18866 0.30937 0.32379 0.33044 0.47302 0.45364 0.45191 / n 1.33349 1.32084 1.29755 1.19091 1.16481 1.19946 1.18186 1.23935 1.17860 / R2 0.99863 0.99886 0.99921 0.99974 0.99959 0.99924 0.99938 0.99828 0.99774 0.99896 χ2 0.00014 0.00011 0.00008 0.00003 0.00004 0.00008 0.00006 0.00018 0.00023 0.00011 RMSE 0.01175 0.01069 0.00886 0.00501 0.00004 0.00868 0.00792 0.01348 0.01517 0.00907 3 k 0.27003 0.26649 0.27655 0.37338 0.3798 0.39725 0.53077 0.52844 0.50969 / n 1.33398 1.32106 1.29758 1.19093 1.16484 1.19951 1.18188 1.23961 1.17883 / R2 0.99863 0.99886 0.99921 0.99974 0.99959 0.99924 0.99938 0.99828 0.99774 0.99896 χ2 0.00014 0.00011 0.00008 0.00003 0.00004 0.00008 0.00006 0.00018 0.00023 0.00011 RMSE 0.01175 0.01069 0.00886 0.00501 0.00004 0.00868 0.00792 0.01348 0.01517 0.00907 4 a 1.07868 1.07777 1.07549 1.04778 1.04118 1.04779 1.03770 1.04520 1.03191 / k 0.30252 0.29758 0.30762 0.40121 0.40459 0.42755 0.56600 0.57240 0.54133 / R2 0.98351 0.98480 0.98733 0.99382 0.99499 0.99301 0.99410 0.98947 0.99200 0.99034 χ2 0.00167 0.00152 0.00125 0.00060 0.00048 0.00069 0.00060 0.00112 0.00082 0.00099 RMSE 0.04084 0.03903 0.03541 0.02458 0.02192 0.02620 0.02453 0.03340 0.02855 0.03050 5 a 1.14612 1.14193 1.12455 1.08740 1.07346 1.11468 1.06351 1.08582 1.07029 / k 0.23889 0.23762 0.25549 0.34627 0.35708 0.41458 0.51018 0.49119 0.46783 / c −0.10056 −0.09574 −0.07594 −0.05901 −0.04887 −0.02876 −0.03874 −0.05919 −0.05614 / R2 0.99244 0.99265 0.99309 0.99715 0.99741 0.99624 0.99619 0.99428 0.99589 0.99504 χ2 0.00076 0.00074 0.00068 0.00028 0.00025 0.00027 0.00039 0.00061 0.00042 0.00049 RMSE 0.02766 0.02715 0.02615 0.01669 0.01577 0.01629 0.01973 0.02461 0.02047 0.02161 6 a 1.87501 1.86979 1.85648 1.73628 1.69979 1.75020 1.72022 1.77877 1.70094 / k 0.40828 0.40142 0.41308 0.51817 0.51516 0.55603 0.72954 0.75434 0.69286 / R2 0.99772 0.99831 0.99906 0.99980 0.99969 0.99939 0.99943 0.99793 0.99784 0.99880 χ2 0.00023 0.00017 0.00009 0.00002 0.00003 0.00006 0.00006 0.00022 0.00022 0.00012 RMSE 0.01517 0.01300 0.00966 0.00446 0.00541 0.00776 0.00763 0.01480 0.01486 0.01031 2.2.2 模型验证
正交试验各试验号的干燥数学模型表达式见表8。通过数学模型表达式可计算出试验各条件下干燥至安全含水率(10%w.b.)即水分比约为6%时所需的干燥时间。试验值由表2试验号3的试验条件(温度40 ℃、风速0.7 m/s、铺放厚度17.6 mm)试验得到,预测值由表8试验号3表达式计算,预测值与试验值对比如图5。Page模型预测值与试验值之间的平均相对误差为8.34%,拟合度较高。
表 8 干燥数学模型及干燥时间Table 8. Drying mathematical model and drying time实验号 Page模型 干燥时间(h) 1 MR=exp(−0.17451t1.33349) 6.92146 2 MR=exp(−0.17435t1.32084) 7.05580 3 MR=exp(−0.18866t1.29755) 6.87662 4 MR=exp(−0.30937t1.19091) 5.39502 5 MR=exp(−0.32379t1.16481) 5.38777 6 MR=exp(−0.33044t1.19946) 5.04567 7 MR=exp(−0.47302t1.18186) 3.81568 8 MR=exp(−0.45364t1.23935) 3.70897 9 MR=exp(−0.45191t1.17860) 3.98110 2.3 正交试验
2.3.1 有效水分扩散系数和活化能
正交试验结果、不同干燥条件下的有效水分扩散系数及平均活化能见表9。平均活化能根据公式(6)拟合得到,拟合时有效水分扩散系数为40、50、60 ℃时的平均值。其中,第8组有效水分扩散系数最大,与表6中干燥时间最短的组号一致。不同温度条件下Deff的范围分别为6.0362×10−7~6.1747×10−7、7.5437×10−7~8.0574×10−7、10.6057×10−7~10.8882×10−7 m2/s,Deff随温度升高而升高,与温度单因素实验结论相符。与表5、表6对比,活化能相对误差分别为3.93%、7.94%,可知风速与铺放厚度对Deff影响较小。
表 9 试验结果、有效水分扩散系数及平均活化能Table 9. Results test, Deff and average activation energy实验号 A温度 B风速 C铺放厚度 D误差 色差 光合色素单位质量含量(10−4·mg·g−1) 有效水分扩散系数(10−7·m2·s−1) 决定系数 活化能(J·mol−1) 1 1 1 1 1 20.87 2.04892 6.1747 0.9840 23225.63
(R2=0.9766)2 1 2 2 2 19.64 3.00457 6.0473 0.9892 3 1 3 3 3 21.15 2.56018 6.0362 0.9922 4 2 1 2 3 22.18 1.93573 7.5437 0.9949 5 2 2 3 1 24.27 1.47309 7.6075 0.9971 6 2 3 1 2 25.72 1.17079 8.0574 0.9873 7 3 1 3 2 23.89 1.56878 10.6057 0.9899 8 3 2 1 3 26.38 1.15968 10.8613 0.9639 9 3 3 2 1 24.47 1.40890 10.8882 0.9633 2.3.2 数据分析
通过色差仪测量青花椒果皮色泽变化,发现青花椒干燥初始阶段色泽变化基本呈现偏黑少绿少黄,在一定干燥时间后,青花椒果皮出现偏红,第1~9组开始出现偏红现象的干燥时间分别为2.0、3.0、2.0、1.0、1.5、0.5、0.5、0.5 h。然后以湿基含水率降至10%以下时的色差、光合色素单位质量含量值及有效水分扩散系数作为响应指标,分别进行极差分析和方差分析,结果分别见表10和表11。
表 10 极差分析Table 10. Analysis of range评价指标 A温度 B风速 C铺放厚度 D误差 色差 K1 61.66 66.94 72.97 69.61 K2 72.17 70.29 66.29 69.25 K3 74.74 71.34 69.31 69.71 R1 13.08 4.40 6.68 0.46 因子主次 1 3 2 4 光合色素
单位质量含量K1 7.6137 5.5534 4.3794 4.9309 K2 4.5796 5.6373 6.3492 5.7441 K3 4.1374 5.1399 5.6021 5.6556 R2 3.4763 0.4975 1.9698 0.8132 因子主次 1 4 2 3 有效水分
扩散系数K1 18.2535 24.3194 24.0887 24.6657 K2 23.2086 24.5161 24.4792 24.7104 K3 32.3552 24.9818 24.2494 24.4412 R3 14.097 0.6577 0.844 0.2692 因子主次 1 3 2 4 注:K1、K2、K3为水平数据和;R1、R2、R3为极差。 表 11 方差分析Table 11. Analysis of variance评价指标 方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 显著性 色差 A 32.0168 2 16.0084 820.4767 S** B 3.5206 2 1.7603 90.2192 S* C 7.4598 2 3.7299 191.1686 S** 误差 0.0390 2 0.0195 − − 优组合 A1B1C2 光合色素
单位质量含量A 2.3795 2 1.1897 17.9148 S(*) B 0.0468 2 0.0234 0.3525 C 0.6591 2 0.3295 4.9622 误差 0.1328 2 0.0664 − − 优组合 A1B2C2 有效水分
扩散系数A 34.0991 2 17.0496 2459.1870 S** B 0.0763 2 0.0382 5.5606 C 0.1269 2 0.0636 9.0394 S* 误差 0.0141 2 0.0071 − 优组合 A3B3C1 注:F0.01(2,2)=99.01,F0.05(2,2)=19.00,F0.1(2,2)=9.00,F0.25(2,2)=3.00;S**为极显著,S*为显著,S(*)为较显著。 由表10和表11可知,有99%的概率可认为,在显著性水平α=0.01的条件下,温度和铺放厚度对青花椒果皮色差影响极显著;有95%的概率可认为,在显著性水平α=0.05的条件下,风速对青花椒果皮色差影响显著。较优的干燥工艺参数为温度40 ℃、风速0.3 m/s、铺放厚度11.9 mm。
有90%的概率可认为在显著性水平α=0.1的条件下,温度对青花椒果皮光合色素单位质量含量影响较显著,与单因素实验结果一致,即青花椒果皮内光合色素的分解随温度升高而加快。有75%的概率可认为在显著性水平α=0.25的条件下,铺放厚度对青花椒果皮光合色素单位质量含量有一定影响。风速对光合色素单位质量含量影响最小。较优的干燥工艺参数为温度40 ℃、风速0.5 m/s、铺放厚度11.9 mm。
有99%的概率可认为在显著性水平α=0.01的条件下,温度对青花椒有效水分扩散系数影响极显著,与单因素实验结果一致,即青花椒干燥速度随温度升高而加快。有75%的概率认为在显著性水平α=0.25的条件下,风速对青花椒有效水分扩散系数有一定影响。有90%的概率认为在显著性水平α=0.1的条件下,铺放厚度对青花椒有效水分扩散系数影响显著。有效水分扩散系数最大时的干燥工艺参数为温度60 ℃,风速0.7 m/s,铺放厚度6.2 mm,即温度越高、风速越大、铺放厚度越小时,有效水分扩散系数越大。
综合考虑干燥工艺参数对色差、光合色素单位质量含量和有效水分扩散系数的影响,确定最优工艺参数为:温度40 ℃、风速0.3 m/s、铺放厚度11.9 mm。以此条件试验验证,得色差为20.01,光合色素单位质量含量为2.9601×10−4 mg/g。
2.4 干燥温度对干燥中光合色素含量的影响
根据正交试验,温度对光合色素单位质量含量指标的影响最显著,结果如图6所示。
由图6可知,在干燥初始阶段,温度对青花椒光合色素含量变化有显著影响。随着干燥时间的延长,光合色素单位质量含量会呈现先略下降再上升而后再下降至趋于稳定的变化。首先,“先略下降”是由于高温胁迫使光合色素发生酶促降解,此降解反应在酶完全失活之前持续作用。同时,植物因高温胁迫会激发自我防御机制,酶促防御系统中的保护酶开始时具有较高活性,随着干燥时间延长而迅速下降,光合色素随之受到影响[27]。但高温胁迫时间过长会对叶绿体造成损害,导致叶绿素含量减少[28]。其次,“再上升”是由于干燥使青花椒果皮大量失水,导致光合色素单位质量含量短暂上升,或者由于短期热激诱使青花椒为抵抗高温胁迫而略微提高叶绿素含量[29]。再次,光合色素单位质量含量到达峰值时,由于青花椒果皮失水量减小,失水变缓,单位质量含量开始下降,青花椒果皮几乎不再失水,光合色素单位质量含量趋于平衡。而且高温胁迫对光合色素破坏不可逆[30],因而,应当尽可能保证使干制青花椒果皮光合色素含量保持较高水平。
此外,类胡萝卜素含量随温度变化趋势与叶绿素相似,温度越高,胁迫时间越长,含量下降越明显[31]。因此,光合色素单位质量含量在温度为60 ℃时的稳定值比40和50 ℃时更低。
3. 结论
随着温度和风速的升高、铺放厚度的减小,干燥速率升高,干燥至安全含水率(10%w.b.)所需的时间减少;拟合结果表明Page模型是描述青花椒热泵干燥的最佳模型,且温度越高,有效水分扩散系数越大。温度对青花椒热泵干燥色差和光合色素单位质量含量的影响最显著。青花椒热泵干燥色泽较优条件为温度40 ℃、风速0.3 m/s、铺放厚度11.9 mm,在此温度和铺放厚度条件下的光合色素单位质量含量较优,但风速对其影响较小。青花椒光合色素单位质量含量随干燥的进行呈现出先下降再上升又迅速下降至稳定的趋势。温度越高,光合色素单位质量含量变化越快,不利于干制青花椒品质的提高,干燥工艺设计时应重点关注温度的影响。本研究中未研究光合色素的分解抑制方法,青花椒工艺微观理论研究不足,今后需与控制干燥条件相结合研究青花椒光合色素降解机理,以保证青花椒果皮内的叶绿素含量。
-
表 1 单因素实验方案
Table 1 Scheme of single factor test
工艺参数 温度(℃) 风速(m·s−1) 铺放厚度(mm) 温度 35 0.7 11.9 40 45 50 55 60 风速 40 0.3 11.9 0.5 0.7 铺放厚度 40 0.7 6.2 11.9 17.6 表 2 正交试验因子与水平设计
Table 2 Design of orthogonal experimental factors and levels
水平 因子 A温度(℃) B风速(m·s−1) C铺放厚度(mm) 1 40 0.3 6.2 2 50 0.5 11.9 3 60 0.7 17.6 表 3 干燥数学模型
Table 3 Drying mathematical models
表 4 不同温度时的有效水分扩散系数及平均活化能
Table 4 Deff and average activation energy of green Sichuan pepper at different temperatures
温度(℃) 有效水分扩散系数
(10−7 m2·s−1)相关系数 活化能(J·mol−1) 相关系数 35 4.4222 0.9931 32153.8 0.9828 40 5.7654 0.9951 45 6.3414 0.9919 50 8.3972 0.9858 55 10.3484 0.9669 60 11.3942 0.9842 表 5 不同风速时的有效水分扩散系数及平均活化能
Table 5 Deff and average activation energy of green Sichuan pepper at different air speed
风速(m·s−1) 温度(℃) 有效水分扩散系数(10−7 m2·s−1) 相关系数 活化能(J·mol−1) 相关系数 0.3 40 5.6832 0.9836 24137.57 0.9979 0.5 50 7.7763 0.9946 0.7 60 10.1570 0.9822 表 6 不同铺放厚度时的有效水分扩散系数及平均活化能
Table 6 Deff and average activation energy of green Sichuan pepper at different laying thickness
铺放厚度(mm) 温度(℃) 有效水分扩散系数(10−7·m2·s−1) 相关系数 活化能(J·mol−1) 相关系数 6.2 40 5.5397 0.9932 25070.33 0.9893 11.9 50 7.9069 0.9956 17.6 60 10.1252 0.9693 表 7 青花椒热泵干燥数学模型拟合结果
Table 7 Mathematical model fitting results of heat pump drying of green Sichuan pepper
模型 参数及指标 试验参数值及指标值拟合结果 平均值 试验号1 试验号2 试验号3 试验号4 试验号5 试验号6 试验号7 试验号8 试验号9 1 k 0.28212 0.27726 0.2872 0.38352 0.38906 0.40898 0.54678 0.54979 0.52568 / R2 0.97772 0.97900 0.98188 0.99147 0.99325 0.99082 0.99292 0.98800 0.99141 0.98739 χ2 0.00225 0.00211 0.00179 0.00083 0.00065 0.00090 0.00072 0.00127 0.00088 0.00127 RMSE 0.04747 0.04588 0.04236 0.02886 0.02543 0.03002 0.02688 0.03567 0.02959 0.03468 2 k 0.17451 0.17435 0.18866 0.30937 0.32379 0.33044 0.47302 0.45364 0.45191 / n 1.33349 1.32084 1.29755 1.19091 1.16481 1.19946 1.18186 1.23935 1.17860 / R2 0.99863 0.99886 0.99921 0.99974 0.99959 0.99924 0.99938 0.99828 0.99774 0.99896 χ2 0.00014 0.00011 0.00008 0.00003 0.00004 0.00008 0.00006 0.00018 0.00023 0.00011 RMSE 0.01175 0.01069 0.00886 0.00501 0.00004 0.00868 0.00792 0.01348 0.01517 0.00907 3 k 0.27003 0.26649 0.27655 0.37338 0.3798 0.39725 0.53077 0.52844 0.50969 / n 1.33398 1.32106 1.29758 1.19093 1.16484 1.19951 1.18188 1.23961 1.17883 / R2 0.99863 0.99886 0.99921 0.99974 0.99959 0.99924 0.99938 0.99828 0.99774 0.99896 χ2 0.00014 0.00011 0.00008 0.00003 0.00004 0.00008 0.00006 0.00018 0.00023 0.00011 RMSE 0.01175 0.01069 0.00886 0.00501 0.00004 0.00868 0.00792 0.01348 0.01517 0.00907 4 a 1.07868 1.07777 1.07549 1.04778 1.04118 1.04779 1.03770 1.04520 1.03191 / k 0.30252 0.29758 0.30762 0.40121 0.40459 0.42755 0.56600 0.57240 0.54133 / R2 0.98351 0.98480 0.98733 0.99382 0.99499 0.99301 0.99410 0.98947 0.99200 0.99034 χ2 0.00167 0.00152 0.00125 0.00060 0.00048 0.00069 0.00060 0.00112 0.00082 0.00099 RMSE 0.04084 0.03903 0.03541 0.02458 0.02192 0.02620 0.02453 0.03340 0.02855 0.03050 5 a 1.14612 1.14193 1.12455 1.08740 1.07346 1.11468 1.06351 1.08582 1.07029 / k 0.23889 0.23762 0.25549 0.34627 0.35708 0.41458 0.51018 0.49119 0.46783 / c −0.10056 −0.09574 −0.07594 −0.05901 −0.04887 −0.02876 −0.03874 −0.05919 −0.05614 / R2 0.99244 0.99265 0.99309 0.99715 0.99741 0.99624 0.99619 0.99428 0.99589 0.99504 χ2 0.00076 0.00074 0.00068 0.00028 0.00025 0.00027 0.00039 0.00061 0.00042 0.00049 RMSE 0.02766 0.02715 0.02615 0.01669 0.01577 0.01629 0.01973 0.02461 0.02047 0.02161 6 a 1.87501 1.86979 1.85648 1.73628 1.69979 1.75020 1.72022 1.77877 1.70094 / k 0.40828 0.40142 0.41308 0.51817 0.51516 0.55603 0.72954 0.75434 0.69286 / R2 0.99772 0.99831 0.99906 0.99980 0.99969 0.99939 0.99943 0.99793 0.99784 0.99880 χ2 0.00023 0.00017 0.00009 0.00002 0.00003 0.00006 0.00006 0.00022 0.00022 0.00012 RMSE 0.01517 0.01300 0.00966 0.00446 0.00541 0.00776 0.00763 0.01480 0.01486 0.01031 表 8 干燥数学模型及干燥时间
Table 8 Drying mathematical model and drying time
实验号 Page模型 干燥时间(h) 1 MR=exp(−0.17451t1.33349) 6.92146 2 MR=exp(−0.17435t1.32084) 7.05580 3 MR=exp(−0.18866t1.29755) 6.87662 4 MR=exp(−0.30937t1.19091) 5.39502 5 MR=exp(−0.32379t1.16481) 5.38777 6 MR=exp(−0.33044t1.19946) 5.04567 7 MR=exp(−0.47302t1.18186) 3.81568 8 MR=exp(−0.45364t1.23935) 3.70897 9 MR=exp(−0.45191t1.17860) 3.98110 表 9 试验结果、有效水分扩散系数及平均活化能
Table 9 Results test, Deff and average activation energy
实验号 A温度 B风速 C铺放厚度 D误差 色差 光合色素单位质量含量(10−4·mg·g−1) 有效水分扩散系数(10−7·m2·s−1) 决定系数 活化能(J·mol−1) 1 1 1 1 1 20.87 2.04892 6.1747 0.9840 23225.63
(R2=0.9766)2 1 2 2 2 19.64 3.00457 6.0473 0.9892 3 1 3 3 3 21.15 2.56018 6.0362 0.9922 4 2 1 2 3 22.18 1.93573 7.5437 0.9949 5 2 2 3 1 24.27 1.47309 7.6075 0.9971 6 2 3 1 2 25.72 1.17079 8.0574 0.9873 7 3 1 3 2 23.89 1.56878 10.6057 0.9899 8 3 2 1 3 26.38 1.15968 10.8613 0.9639 9 3 3 2 1 24.47 1.40890 10.8882 0.9633 表 10 极差分析
Table 10 Analysis of range
评价指标 A温度 B风速 C铺放厚度 D误差 色差 K1 61.66 66.94 72.97 69.61 K2 72.17 70.29 66.29 69.25 K3 74.74 71.34 69.31 69.71 R1 13.08 4.40 6.68 0.46 因子主次 1 3 2 4 光合色素
单位质量含量K1 7.6137 5.5534 4.3794 4.9309 K2 4.5796 5.6373 6.3492 5.7441 K3 4.1374 5.1399 5.6021 5.6556 R2 3.4763 0.4975 1.9698 0.8132 因子主次 1 4 2 3 有效水分
扩散系数K1 18.2535 24.3194 24.0887 24.6657 K2 23.2086 24.5161 24.4792 24.7104 K3 32.3552 24.9818 24.2494 24.4412 R3 14.097 0.6577 0.844 0.2692 因子主次 1 3 2 4 注:K1、K2、K3为水平数据和;R1、R2、R3为极差。 表 11 方差分析
Table 11 Analysis of variance
评价指标 方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 显著性 色差 A 32.0168 2 16.0084 820.4767 S** B 3.5206 2 1.7603 90.2192 S* C 7.4598 2 3.7299 191.1686 S** 误差 0.0390 2 0.0195 − − 优组合 A1B1C2 光合色素
单位质量含量A 2.3795 2 1.1897 17.9148 S(*) B 0.0468 2 0.0234 0.3525 C 0.6591 2 0.3295 4.9622 误差 0.1328 2 0.0664 − − 优组合 A1B2C2 有效水分
扩散系数A 34.0991 2 17.0496 2459.1870 S** B 0.0763 2 0.0382 5.5606 C 0.1269 2 0.0636 9.0394 S* 误差 0.0141 2 0.0071 − 优组合 A3B3C1 注:F0.01(2,2)=99.01,F0.05(2,2)=19.00,F0.1(2,2)=9.00,F0.25(2,2)=3.00;S**为极显著,S*为显著,S(*)为较显著。 -
[1] 田冰, 王玲, 彭林, 等. 多指标综合评分法优化青花椒热泵-微波联合干燥工艺[J]. 食品研究与开发,2019,40(19):149−155. [TIAN B, WANG L, PENG L, et al. Optimization of heat pump-microwave combined drying process for Zanthoxylum Schinifolium by multi-index comprehensive scoring method[J]. Food Research and Development,2019,40(19):149−155. [2] 代建武, 付琪其, 黄欢, 等. 青花椒真空脉动干燥特性及干燥品质工艺优化[J]. 农业工程学报,2021,37(8):279−287. [DAI J W, FU Q Q, HUANG H, et al. Drying characteristics and quality optimization of green prickly ashes during vacuum pulsed drying[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2021,37(8):279−287. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.08.032 [3] 杨森, 陈鸿平, 刘友平, 等. 花椒干燥技术研究进展[J]. 中国调味品,2021,46(3):175−178, 184. [YANG S, CHEN H P, LIU Y P, et al. Research progress on the drying technology of Zanthoxylum bungeanum[J]. China Condiment,2021,46(3):175−178, 184. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2021.03.036 [4] 王春霞, 易文裕. 花椒干燥技术研究[J]. 现代农业科技,2020(21):236−237, 242. [WANG C X, YI W Y. Study on drying technology of Zanthoxylum bungeanum[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology,2020(21):236−237, 242. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2020.21.092 [5] JING Nana, WANG Minyan, GAO Menglu, et al. Color sensory characteristics, nutritional components and antioxidant capacity of Zanthoxylum bungeanum Maxim. as affected by different drying methods[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2021,160:113167. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.113167
[6] 汪洋, 阚建全. 光照对鲜青花椒干燥过程中叶绿素降解的影响[J]. 食品科学,2014,35(3):10−15. [WANG Y, KAN J Q. Chlorophyll breakdown in green prickleyash with illumination during drying[J]. Food Science,2014,35(3):10−15. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201403003 [7] 徐毅, 阚建全. 青花椒干燥过程叶绿素光降解原因初探[J]. 中国食品学报,2015,15(11):135−141. [XU Y, KAN J Q. Studies on the photodegradation mechanism of chlorophyll from green prickleyash during drying process[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2015,15(11):135−141. [8] 蒲彪, 姚佳. 鲜食青花椒热处理工艺[J]. 食品科学,2012,33(12):46−51. [PU B, YAO J. Optimization of thermal treatment of fresh chinese prickly ash (Zanthoxylum schinifolium Sieb. et Zucc)[J]. Food Science,2012,33(12):46−51. [9] 杨兵, 梅晓飞, 彭林, 等. 热风干制对青花椒品质的影响及工艺优化[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2018,44(11):251−258. [YANG B, MEI X F, PENG L, et al. Effects of hot air drying on the quality of Zanthoxylum schinifolium and its optimization[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2018,44(11):251−258. [10] 张甫生, 陈科伟, 郑炯, 等. 微波与护色剂结合处理对自然干制青花椒色泽的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2013,34(24):329−333. [ZHANG F S, CHEN K W, ZHENG J, et al. Effect of microwave combined antibrowning reagent treatment on the color of green prickleyashes during natural drying[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2013,34(24):329−333. [11] 杨英鹏, 张德康. 烘烤过程中烟叶水分含量变化和叶绿素降解速率探究[J]. 南方农业,2021,15(24):4−7. [YANG Y P, ZHANG D K. Study on moisture content change and chlorophyll degradation rate of tobacco leaves during curing[J]. South China Agriculture,2021,15(24):4−7. [12] 朱明明, 樊明涛, 何鸿举. 类胡萝卜素降解方式的研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(11):308−317. [ZHU M M, FAN M T, HE H J. Advances in methods for the degradation of carotenoids[J]. Food Science,2017,38(11):308−317. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201711048 [13] 宋朝鹏, 高远, 武圣江, 等. 密集烘烤定色期烟叶类胡萝卜素降解及相关酶活性变化[J]. 中国农业科学,2009,42(8):2875−2881. [SONG Z P, GAO Y, WU S J, et al. The degradation mechanism of carotenoids in flue-cured tobacco and the changes of the related enzymes activities at leaf-drying stage during the bulk curing process[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2009,42(8):2875−2881. [14] 武逸凡, 杨明金, 李瑞, 等. 基于温度-水分-色泽耦合的青花椒变温干燥工艺研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(24):201−208. [WU Y F, YANG M G, LI R, et al. Research on temperature-varying drying technology of green prickleyashes based on temperature-moisture-color coupling[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(24):201−208. [15] 葛宜元. 试验设计方法与Design-Expert软件应用[M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学出版社, 2015 GE Y Y. Experimental design method and application of design-expert software[M]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology Press, 2015.
[16] NKHATA S G. Total color change (ΔE) is a poor estimator of total carotenoids lost during post-harvest storage of biofortified maize grains[J]. Heliyon,2020,6(10):e05173. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05173
[17] 张秀君, 孙钱钱, 乔双, 等. 菠菜叶绿素提取方法的比较研究[J]. 作物杂志,2011(3):57−60. [ZHANG X J, SUN Q Q, QIAO S, et al. A comparative study of chlorophyll extraction methods[J]. Crops,2011(3):57−60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7283.2011.03.014 [18] 胡秉芬, 黄华梨, 季元祖, 等. 分光光度法测定叶绿素含量的提取液的适宜浓度[J]. 草业科学,2018,35(8):1965−1974. [HU B F, HUANG H L, JI Y Z, et al. Evaluation of the optimum concentration of chlorophyll extract for determination of chlorophyll content by spectrophotometry[J]. Pratacultural Science,2018,35(8):1965−1974. doi: 10.11829/j.issn.1001-0629.2017-0418 [19] 刘畅, 王世才, 卢东昱. 利用光学多通道分析仪与分光光度计测定叶绿素的紫外-可见光区吸收光谱[J]. 物理试验,2005(12):38−41. [LIU C, WANG S C, LU D Y. Measurement of UV-Vis absorption spectra of chlorophyll by using oma and spectrophotometer[J]. Physics Experimentation,2005(12):38−41. [20] 张宪政. 植物叶绿素含量测定——丙酮乙醇混合液法[J]. 辽宁农业科学,1986(3):26−28. [ZHANG X Z. Determination of plant chlorophyll content by acetone ethanol mixture method[J]. Liaoning Agricultural Sciences,1986(3):26−28. [21] 徐敏, 刘君, 阿衣古力·阿布都瓦依提. 植物生理试验教学中叶绿素提取方法比较[J]. 试验科学与技术,2018,16(4):129−133. [XU M, LIU J, AYIGULI A B D W Y T. Comparative methods on chlorophyll extraction in plant physiology experiment teaching[J]. Experiment Science and Technology,2018,16(4):129−133. [22] TALAPATRA N, GAUTAM R, MITTAL V, et al. A comparative study of the growth of microalgae-bacteria symbiotic consortium with the axenic culture of microalgae in dairy wastewater through extraction and quantification of chlorophyll[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2021.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.06.227.
[23] GANJE M, JAFARI S M, FARZANEH V, et al. Kinetics modelling of color deterioration during thermal processing of tomato paste with the use of response surface methodology[J]. Heat and Mass Transfer,2018,54(12):3663−3671. doi: 10.1007/s00231-018-2394-3
[24] 尹晓峰, 杨明金, 李光林, 等. 稻谷薄层热风干燥工艺优化及数学模型拟合[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(8):198−205. [YIN X F, YANG M J, LI G L, et al. Optimization and mathematical modeling of thin layer hot-air drying of rough rice[J]. Food Science,2017,38(8):198−205. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201708031 [25] 王立霞, 兰昊, 郑倩雨, 等. 红枣气体射流冲击干燥特性及干燥模型[J]. 食品科学技术学报,2022,40(2):131−140. [WANG L X, LAN H, ZHENG Q Y, et al. Drying characteristics and model of jujube in air jet impingement[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2022,40(2):131−140. [26] 杨森, 冯靖雯, 刘友平, 等. 热风干燥温度对竹叶花椒干燥特性及品质的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(12):203−209. [YANG S, FENG J W, LIU Y P, et al. The effect of hot air drying temperature on the drying characteristics and quality of Zanthoxylum armatum DC J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(12):203−209.
[27] 赵玉国, 王新忠, 吴沿友, 等. 高温胁迫及恢复对水稻叶绿素荧光动力学特性和保护酶活性的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学,2011,39(27):16487−16488, 16625. [ZHAO Y G, WANG X Z, WU Y Y, et al. Effects of high temperature stress and recovery on ps Ⅱ dynamic characteristics and protective enzyme activities of rice (O. sativa L. )[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2011,39(27):16487−16488, 16625. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2011.27.003 [28] 陈文佳. 细叶小羽藓快繁体系及对逆境的生理响应研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江农林大学, 2012 CHEN W J. Study on rapid propagation system and physiological responses of stress of Haplocladium microphyllum[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang A&F University, 2012.
[29] 王曼, 沙伟, 张梅娟, 等. 高温胁迫对毛尖紫萼藓生理生化特性的影响[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学,2015,34(6):1290−1295. [WANG M, SHA W, ZHANG M J, et al. Effects of high temperature stress on the physiological and biochemical characteristics in Grimmia pilifera[J]. Genomics and Applied Biology,2015,34(6):1290−1295. [30] WOJDYŁO A, NOWICKA P, TKACZ K, et al. Fruit tree leaves as unconventional and valuable source of chlorophyll and carotenoid compounds determined by liquid chromatography-photodiode-quadrupole/time of flight-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (LC-PDA-qTof-ESI-MS)[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,349:129156. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129156
[31] 徐超, 王明田, 杨再强, 等. 高温对温室草莓光合生理特性的影响及胁迫等级构建[J]. 应用生态学报,2021,32(1):231−240. [XU C, WANG M T, YANG Z Q, et al. Effects of high temperature on photosynthetic physiological characteristics of strawberry seedlings in greenhouse and construction of stress level[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2021,32(1):231−240. -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 侯丽慧,王乐,张宇,韩文静,李旭辰,司云珊,于秀华. 一测多评法测定冰川滴丸中6个个成成分分含含量. 中国药业. 2024(10): 76-80 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 庞敏. 线叶金雀花茶中矿物质元素含量测定及饮用安全性分析. 食品与发酵科技. 2024(05): 137-142+171 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张毅. 一测多评法测定胃乃安胶囊中4种异黄酮成分含量. 实用中医内科杂志. 2022(07): 42-44 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)






 下载:
下载:



















 下载:
下载:



