Cold Plasma Treatment Accelerated the Oxidation and Structural Changes of Myofibrillar in Tilapia
-
摘要: 以新鲜罗非鱼为研究对象,采用不同时间(0、1、2、3、4、5 min)和电压(40、50、60、70、80 kV)进行处理,分析处理后鱼肉的羰基含量、巯基含量、疏水性、Zeta电位、SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳、紫外光谱、荧光光谱和拉曼光谱,探究低温等离子体处理对罗非鱼肌原纤维蛋白氧化及结构的影响。结果表明:随着低温等离子体处理时间延长及电压升高,鱼肉中羰基含量和疏水性逐渐增加,总巯基和活性巯基含量减少;当处理时间延长至5 min时,总巯基和活性巯基分别减少至66.91 和52.76 μmol/g;处理电压升高至80 kV时,羰基含量从1.23 nmol/mg上升至2.16 nmol/mg;处理低温等离子体处理使肌原纤维蛋白Zeta电位绝对值降低;SDS-PAGE表明,低温等离子体处理使肌原纤维蛋白的肌球蛋白重链条带加重;随着低温等离子体处理时间的延长及电压的升高,紫外吸收光谱蓝移并且吸收强度增强,荧光吸收强度减弱;鱼肉经高电压、长时间等离子体处理后,α-螺旋增加,β-转角和β-折叠减少,无规卷曲无明显变化。综上,低温等离子体处理能够加速肌原纤维蛋白氧化,导致蛋白质的二级结构和构象发生改变。Abstract: To investigate the effects of cold plasma treatment on the oxidation and structure changes of myofibrillar proteins tilapia, the fish was treated by cold plasma with different time (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 min) and different voltage (40, 50, 60, 70, 80 kV), respectively, the carbonyl content, sulfhydryl content, hydrophobicity, Zeta potential, SDS-PAGE, UV spectra, fluorescence spectra and Raman spectrometer of myofibrillar protein were measured after treatment. The results showed that the carbonyl content and surface hydrophobicity of myofibrillar protein were increased gradually, as the treatment time extending or voltage increased, while the total sulfhydryl and the active sulfhydryl content were decreased. When the treatment time was extending to 5 min, the total sulfhydryl and the active sulfhydryl content were decreased to 66.91 and 52.76 μmol/g, respectively. The carbonyl content increased from 1.23 to 2.16 nmol/mg, if the treatment voltage was increased to 80 kV. Cold plasma treatment decreased the absolute value of Zeta potential of myofibrillar protein. The myosin heavy chain band of myofibrillar protein was increased based on SDS-PAGE results. As treatment time extending and voltage increasing, the UV spectrum of myofibrillar protein was blue-shifted with an increased UV absorption intensity, and the fluorescence absorption intensity of protein was weakened. Based on the Raman spectrometer determination, the content of α-helix was increased, the contents of β-sheet and β-turn were reduced, and the random coils had no obvious changes in myofibrillar protein of tilapia after cold plasma treatment. In conclusion, extending the treatment time or increasing treatment voltage of cold plasma can accelerate the oxidation of myofibrillar protein to result in the changes of their second-order structure and conformation.
-
Keywords:
- cold plasma /
- myofibrillar protein /
- tilapia /
- protein oxidation
-
罗非鱼繁殖快,抗病性强,营养价值高,是日常生活中优质价廉的蛋白质来源,深受消费者喜爱,罗非鱼养殖业发展迅速,占据国内渔业养殖产业的主体[1]。罗非鱼自身水分含量高,营养丰富,易受微生物污染导致腐败,目前罗非鱼保鲜技术有低温保鲜、气调保鲜、低温等离子体保鲜、辐照保鲜、化学保鲜等[2]。
低温等离子体是新兴的非热食品加工技术,对食品微生物具有显著的杀菌保鲜效果,能有效提高食品的安全性,延长保质期[3]。目前低温等离子体保鲜技术已广泛应用于水产品中,Albertos等[4]研究表明,低温等离子体处理能显著减少鲭鱼片中好氧嗜冷菌、假单胞菌和乳酸菌总数,延长其货架期。低温等离子体能有效灭活食品微生物,是由于在低温等离子体处理过程中产生的活性氧、活性氮、过氧化氢等活性物质遏制了微生物的生长繁殖[5],但这些活性物质会与鱼肉中的脂质、蛋白质相互作用,发生氧化反应,导致蛋白质等营养成分结构发生变化[6]。Huang等[7]研究表明,低温等离子体处理鲑鱼鱼糜后,微生物显著减少的同时伴随着脂质的氧化,硫代巴比妥酸(thiobarbituric acid reactive substances, TBARS)值略微升高。姜竹茂等[8]研究表明,低温等离子体处理鲅鱼鱼肉,加速蛋白质氧化,羰基含量、疏水性增加,巯基含量减少。杜曼婷等[9]研究表明随着低温等离子体处理时间的延长,羊肉肌原纤维蛋白羰基含量显著增加,低温等离子体加速了蛋白质氧化。
Wang等[10]对罗非鱼、金鲳鱼和鲣鱼肌原纤维蛋白表征的比较研究表明,罗非鱼肌原纤维蛋白溶解度最高,蛋白结构更稳定,其具有稳定乳化剂的潜力。虽然已有很多研究表明,低温等离子体处理会加速水产品蛋白质氧化,但不同来源的肌原纤维蛋白结构特性存在差异。关于低温等离子体处理条件对罗非鱼的肌原纤维蛋白特性变化以及乳化性质的影响研究相对较少。罗非鱼作为我国主要经济鱼类之一,研究低温等离子体处理对罗非鱼肌原纤维蛋白氧化及结构的影响尤为重要,也为低温等离子体应用于不同鱼类及水产品保鲜提供必要信息。
本研究以罗非鱼为研究对象,采用不同低温等离子体处理时间及电压处理鱼肉,分析其对罗非鱼蛋白氧化的影响,并进一步测定Zeta电位、紫外光谱、荧光光谱、拉曼光谱分析处理对蛋白质结构变化影响,为低温等离子体保鲜技术应用于罗非鱼保鲜提供理论指导。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
新鲜罗非鱼(Oreochromis mossambicus) 每条重(750±200)g,购自海口市沿江三农贸市场;尿素 西陇科学股份有限公司;氯化钠、SDS、溴酚蓝 广东广试试剂科技有限公司;DNPH、DTNB 国药集团化学试剂有限公司;总蛋白定量测试盒 南京建成生物工程研究所。
MAP-H360型复合气调包装机 苏州森瑞保鲜设备有限公司;BK130/36高压电转换器 美国Phoenix公司;Zetasizer Nano ZS90激光粒度分析仪 英国Malvern Instrument公司;UV-1800紫外可见分光光度计 日本岛津有限公司;F-7000荧光分光光度计 日本日立公司;Reflex in Via拉曼光谱仪 英国Renishaw plc公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品处理
将新鲜罗非鱼宰杀,除去头、尾、表皮及内脏,称取鱼肉块(50±2 g)放入塑料包装盒中,用包装机进行空气密封包装后,将包装盒放置于低温等离子体装置两电极之间,低温等离子体进行如下处理:A处理时间:在70 kV电压条件下分别处理0、1、2、3、4、5 min;B 处理电压:在40、50、60、70、80 kV电压条件下处理3 min;未经低温等离子体处理的样品作为对照组,对照组包装后在4 ℃条件下放置相同时间取样。
1.2.2 肌原纤维蛋白提取
参考Han等[11]的方法略作修改。称取5 g鱼肉糜于25 mL PBS缓冲液中,在冰浴条件下均质1 min(10000 r/min),均质后离心(10000 r/min,4 ℃,10 min),弃上清液,沉淀用PBS缓冲液洗3次后加入20 mL PBS(0.6 mol/L NaCl)缓冲液,冰浴下均质15 s(10000 r/min),4 ℃下提取2 h后4层纱布过滤,所得滤液为罗非鱼肌原纤维蛋白,蛋白浓度用试剂盒进行测定。
1.2.3 羰基含量的测定
参考Mesquita等[12]的方法略作修改。用PBS(0.6 mol/L NaCl)缓冲液将蛋白浓度调整为2 mg/mL,将0.4 mL稀释后的蛋白溶液与0.4 mL 10 mmol/L DNPH溶液(含0.5 mol/L H3PO4)混合,与等量0.5 mol/L H3PO4溶液混合作为对照组,将混合溶液于25 ℃下暗处反应10 min,反应完成后,向混合溶液中加入0.2 mL 6 mol/L NaOH溶液,并在25 ℃继续反应10 min,在450 nm波长处测定混合溶液吸光度。计算公式如下:
羰基含量(nmol/mg)=A×n×106ε×ρ (1) 式中:A为450 nm波长处的吸光值;n为稀释倍数;ε为摩尔吸光系数22000(L/(mol·cm));ρ为蛋白质量浓度(mg/mL)。
1.2.4 巯基含量的测定
参考徐红艳等[13]的方法略作修改。总巯基测定:用PBS(0.6 mol/L NaCl)缓冲液将蛋白浓度调整为2 mg/mL,取0.5 mL稀释后的蛋白溶液依次加入2 mL尿素-十二烷基硫酸钠溶液(含8.0 mol/L尿素,30 g/L SDS,0.1 mol/L磷酸钠缓冲液,pH7.4)和0.5 mL 10 mmol/L DTNB试剂(溶解在0.1 mol/L 磷酸钠缓冲液中,pH7.4),在室温下反应15 min,取上清液在412 nm下测定吸光值,用PBS(0.6 mol/L NaCl)缓冲液代替蛋白液用于空白对照。
活性巯基测定:用PBS(0.6 mol/L NaCl)缓冲液将蛋白浓度调整为2 mg/mL,取0.5 mL稀释后的蛋白溶液依次加入2 mL十二烷基硫酸钠溶液(含30 g/L SDS,0.1 mol/L 磷酸钠缓冲液,pH7.4)和0.5 mL 10 mmol/L DTNB 试剂(溶解在0.1 mol/L 磷酸钠缓冲液中,pH7.4),在室温下反应15 min,取上清液在412 nm下测定吸光值,用PBS(0.6 mol/L NaCl)缓冲液代替蛋白液用于空白对照。计算公式如下:
巯基含量(µmol/g)=A×n×106ε×ρ (2) 式中:A为412 nm波长处的吸光值;n为稀释倍数;ε为摩尔吸光系数13600(L/(mol·cm));ρ为蛋白质质量浓度(mg/mL)。
1.2.5 表面疏水性的测定
参考黄倩等[14]的方法略作修改。用PBS(0.6 mol/L NaCl)缓冲液将蛋白浓度调整为2 mg/mL,取1 mL稀释后的蛋白溶液,加入200 μL 1 mg/mL溴酚蓝溶液后离心(6000 r/min,15 min),并对上清液进行10倍稀释,以PBS(0.6 mol/L NaCl)缓冲液为空白对照,在595 nm下测定吸光度值,以溴酚蓝结合量来表示表面疏水性。计算公式如下:
溴酚蓝结合量(µg)=(A1−A2)A1×200 (3) 式中:A1为空白对照组溴酚蓝吸光值;A2为样品吸光值。
1.2.6 Zeta电位测定
参考李子晗等[15]的方法略作修改。采用粒度仪进行测定,用PBS(0.6 mol/L NaCl)缓冲液将蛋白浓度调整为1 mg/mL,在25 ℃下测定,蒸馏水作为溶剂。
1.2.7 SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳
参考石钢鹏等[16]的方法略作修改。用PBS(0.6 mol/L NaCl)缓冲液将蛋白浓度调整为1 mg/mL,取10 μL SDS-PAGE蛋白上样缓冲液(5×)与40 μL样品混匀后沸水浴加热5 min,为电泳样品,上样量为15 μL。采用质量分数为10%的分离胶,质量分数为4%的浓缩胶,样品在浓缩胶时电压为80 V,进入分离胶时电压改为120 V。电泳结束后,使用染色液染色20 min后脱色至条带清晰。
1.2.8 紫外吸收光谱测定
参考张海璐等[17]的方法略作修改。用PBS(0.6 mol/L NaCl)缓冲液将蛋白浓度调整为1 mg/mL,置于紫外分光光度计中测定紫外吸收光谱,扫描波长范围为240~340 nm,扫描速率为2 nm/min。
1.2.9 内源荧光光谱测定
参考张海璐等[17]的方法略作修改。用PBS(0.6 mol/L NaCl)缓冲液将蛋白浓度调整为2 mg/mL,置于荧光分光光度计中测定内源荧光光谱,设置激发波长280 nm,发射波长290~500 nm,电压700 V,狭缝宽度2.5 nm,扫描速度2400 nm/min。
1.2.10 拉曼光谱测定
参考Zou等[18]的方法略作修改。将提取的蛋白溶液进行冷冻干燥,取冻干后的粉末置于载玻片上,使用50倍长焦镜头进行聚焦,514 nm氩离子激光器,扫描范围为400~2100 cm−1,扫描时间为60 s。
1.3 数据处理
每组实验重复3次,采用Excel 2016进行处理,结果用平均值±标准差表示。采用Origin 2019软件作图,通过SPSS 17.0进行显著性分析,以P<0.05表示差异显著。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 低温等离子体处理对罗非鱼肌原纤维蛋白羰基含量的影响
通过自由基直接修饰氨基酸侧链、肽键断裂或非蛋白羰基单元内收形成羰基,蛋白质氧化往往伴随着羰基的生成[19]。如图1a所示,相比未处理,处理时间对羰基含量有显著影响(P<0.05),随着处理时间的延长,羰基含量逐渐增加,在处理5 min后羰基含量增加至1.95 nmol/mg。随着低温等离子体处理时间的延长,产生的活性氧等活性物质增加,活性自由基攻击氨基酸侧链,使得氨基酸残基、肽链发生改变,形成更多的羰基及羰基衍生物,肌原纤维蛋白的氧化程度也随之增加。Panpipat等[20]的研究中发现,随着低温等离子体处理时间的延长,金线鱼肌球蛋白羰基含量显著增加,这与本研究结论一致。如图1b所示羰基含量随着处理电压的升高呈上升趋势(P<0.05),在电压达到80 kV时羰基含量显著增加至2.16 nmol/mg(P<0.05),低温等离子体处理电压升高,产生的活性物质增加,加速蛋白质氧化。
2.2 低温等离子体处理对罗非鱼肌原纤维蛋白巯基含量的影响
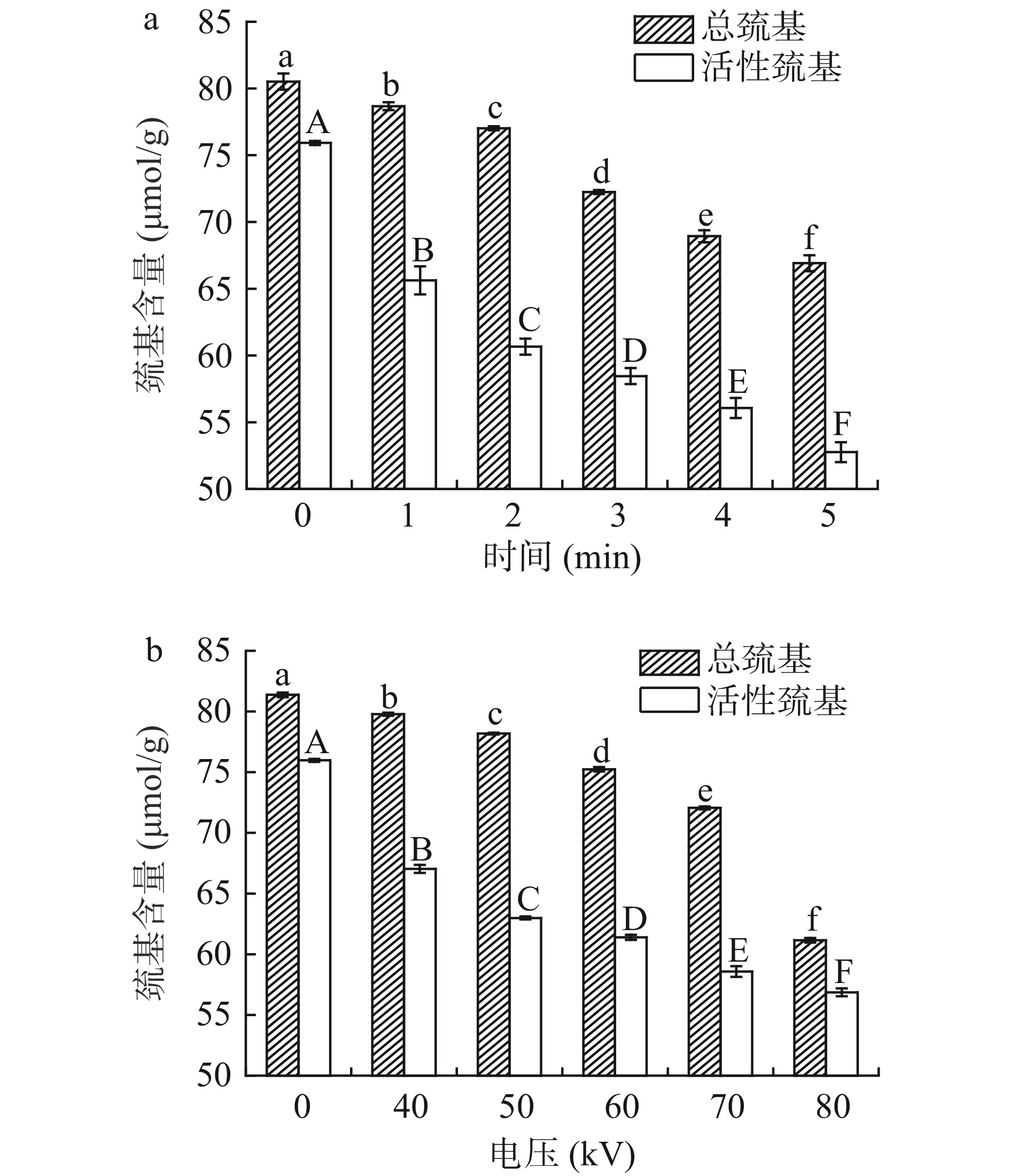
蛋白质氧化会引起巯基含量减少。由图2a可以看出,随着处理时间的延长,总巯基以及活性巯基含量均显著下降(P<0.05),在处理5 min时分别下降至66.91和52.76 μmol/g,说明罗非鱼肌原纤维蛋白的氧化程度随着处理时间的延长而增加。如图2b所示,总巯基和活性巯基含量随着处理电压的升高而减少(P<0.05),在80 kV时分别减少至61.15和56.86 μmol/g。随着等离子体处理电压的升高,产生的过氧化氢、活性氧、活性氮等或活性物质也随之增加,巯基被过氧化氢等自由基氧化为二硫键或生成磺酸衍生物,所以含量减少[21]。唐玲玲等[22]研究表明,随着低温等离子体处理时间延长和电压升高,南美白对虾肌原纤维蛋白总巯基含量显著下降。
2.3 低温等离子体处理对罗非鱼肌原纤维蛋白疏水性的影响
蛋白质表面疏水性与蛋白质的折叠、交联、聚合有关,是评估蛋白质变性的重要指标之一[23]。由图3a可知,与对照组相比,经低温等离子体70 kV处理1 min后,溴酚蓝结合量显著增加了13.07 μg(P<0.05),并且随着处理时间的延长,溴酚蓝结合量逐渐增加。如图3b所示,与对照组相比,经低温等离子体处理40 kV处理3 min后,溴酚蓝结合量显著增加了14.66 μg(P<0.05),溴酚蓝结合量随着处理电压的升高而增加。Miao等[24]研究表明,低温等离子体处理阿拉斯加狭鳕肌原纤维蛋白,随着处理电压从10 kV升高至60 kV,疏水性显著增加。在低温等离子体处理下,ROS、过氧化氢等自由基攻击疏水性氨基酸,蛋白质分子伸展,疏水基团逐渐暴露,使得肌原纤维蛋白疏水性增加[25]。
2.4 低温等离子体处理对罗非鱼肌原纤维蛋白Zeta电位的变化
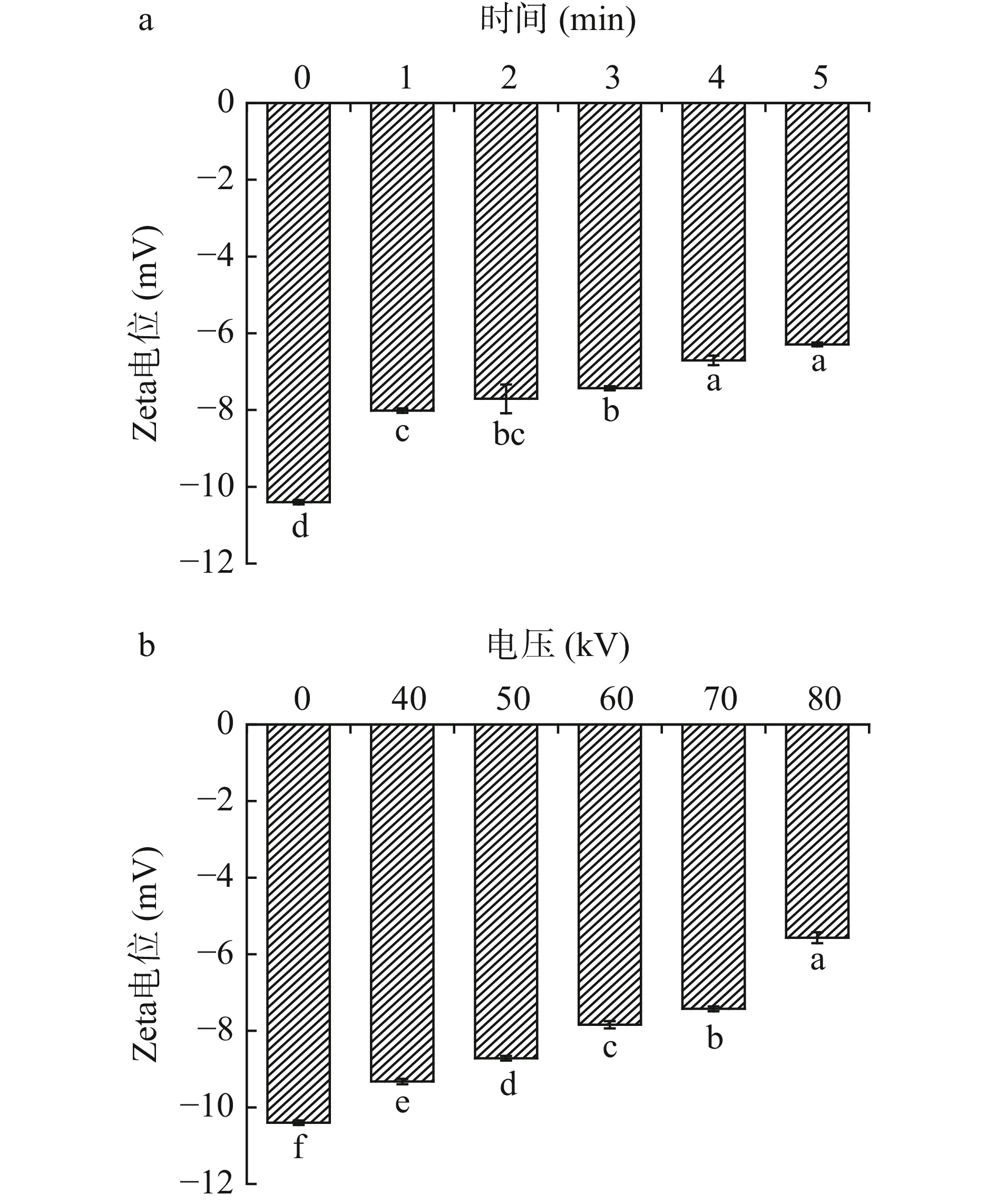
Zeta电位表明分散体中相邻带电粒子之间的静电相互作用程度,电位绝对值越高,说明蛋白质溶液体系越稳定,电位绝对值越低,蛋白质颗粒凝结聚集程度越高[26]。等离子体处理时间对罗非鱼肌原纤维蛋白Zeta电位的影响如图4a所示随着时间延长,肌原纤维蛋白的Zeta电位绝对值显著降低,从对照组的10.4降低至6.29(P<0.05)。如图4b可知随着处理电压升高,肌原纤维蛋白的电位绝对值显著减少,在80 kV时减少至5.57(P<0.05)。Du等[27]研究表明反复冻融处理加速镜鲤肌原纤维蛋白氧化,Zeta电位绝对值从26.87减少至16.50,蛋白质分子之间的排斥减弱,蛋白质之间的聚集增加。等离子体处理产生的自由基促进蛋白质氧化,改变了蛋白表面电荷,破坏了蛋白质之间的氢键、疏水相互作用,使得蛋白质分子发生聚集,Zeta电位绝对值减少[28]。
2.5 低温等离子体处理对罗非鱼肌原纤维蛋白SDS-PAGE的影响
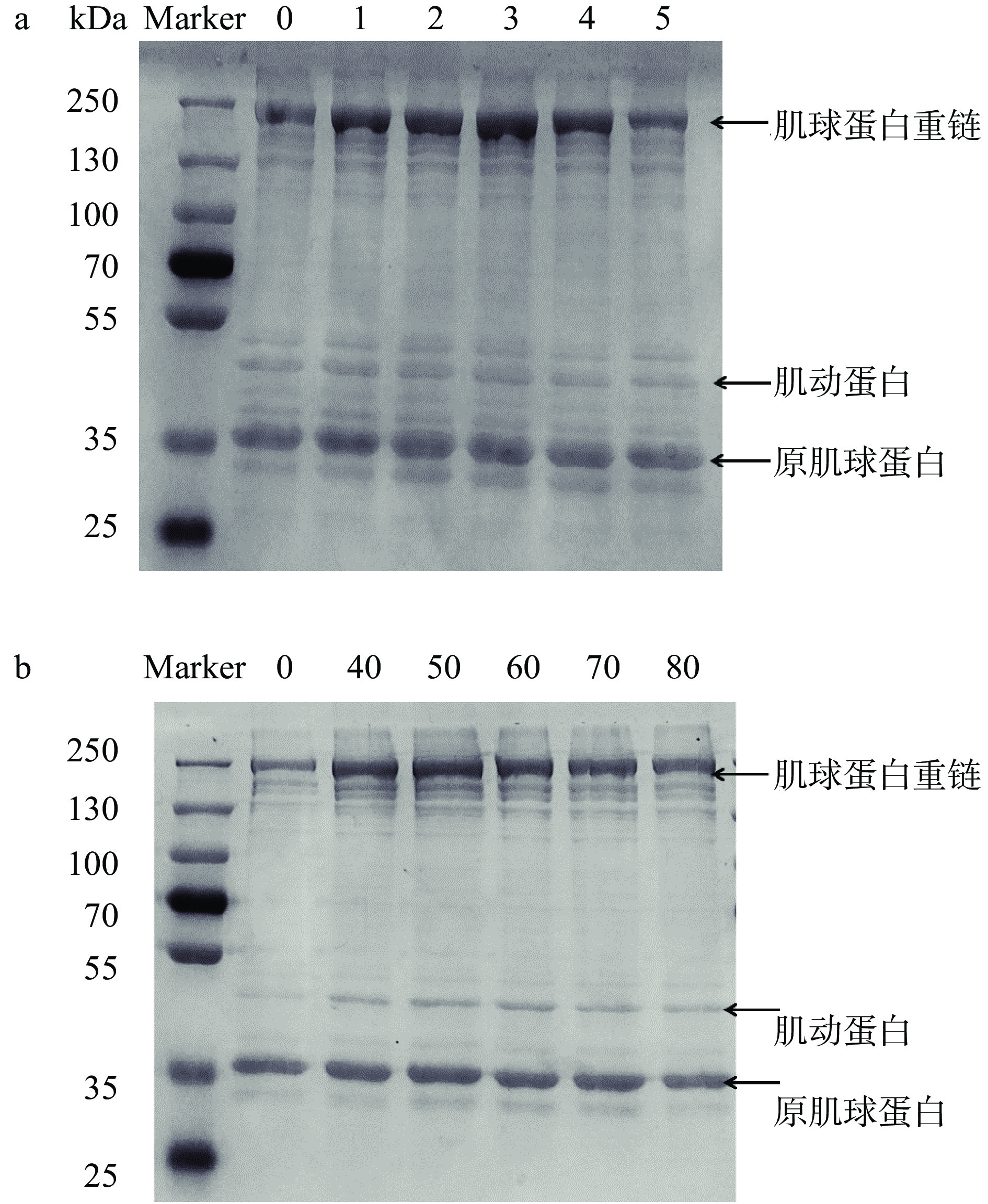
肌球蛋白重链(MHC)和肌动蛋白是肌原纤维蛋白的主要成分,蛋白质氧化涉及蛋白质中共价键链接的变化,导致条带出现模糊、弱化,出现新的低分子量条带[29]。由图5a所示,随着处理时间延长,肌球蛋白重链条带颜色加重。随着低温等离子体处理时间延长,蛋白质分子发生聚集,使得肌球蛋白重链条带加深,但长时间处理会促进大分子蛋白降解为小分子蛋白,肌球蛋白重链条带减弱。如图5b所示,随着处理电压升高,肌球蛋白重链出现扩展现象,肌球蛋白重链条带加深,肌动蛋白条带加深。随着处理时间的延长和电压的增加,自由基使得蛋白质结构发生改变,蛋白质分子交联聚集,导致肌原纤维蛋白出现聚集体,条带发生变化[30]。
2.6 低温等离子体处理对罗非鱼肌原纤维蛋白紫外光谱的影响
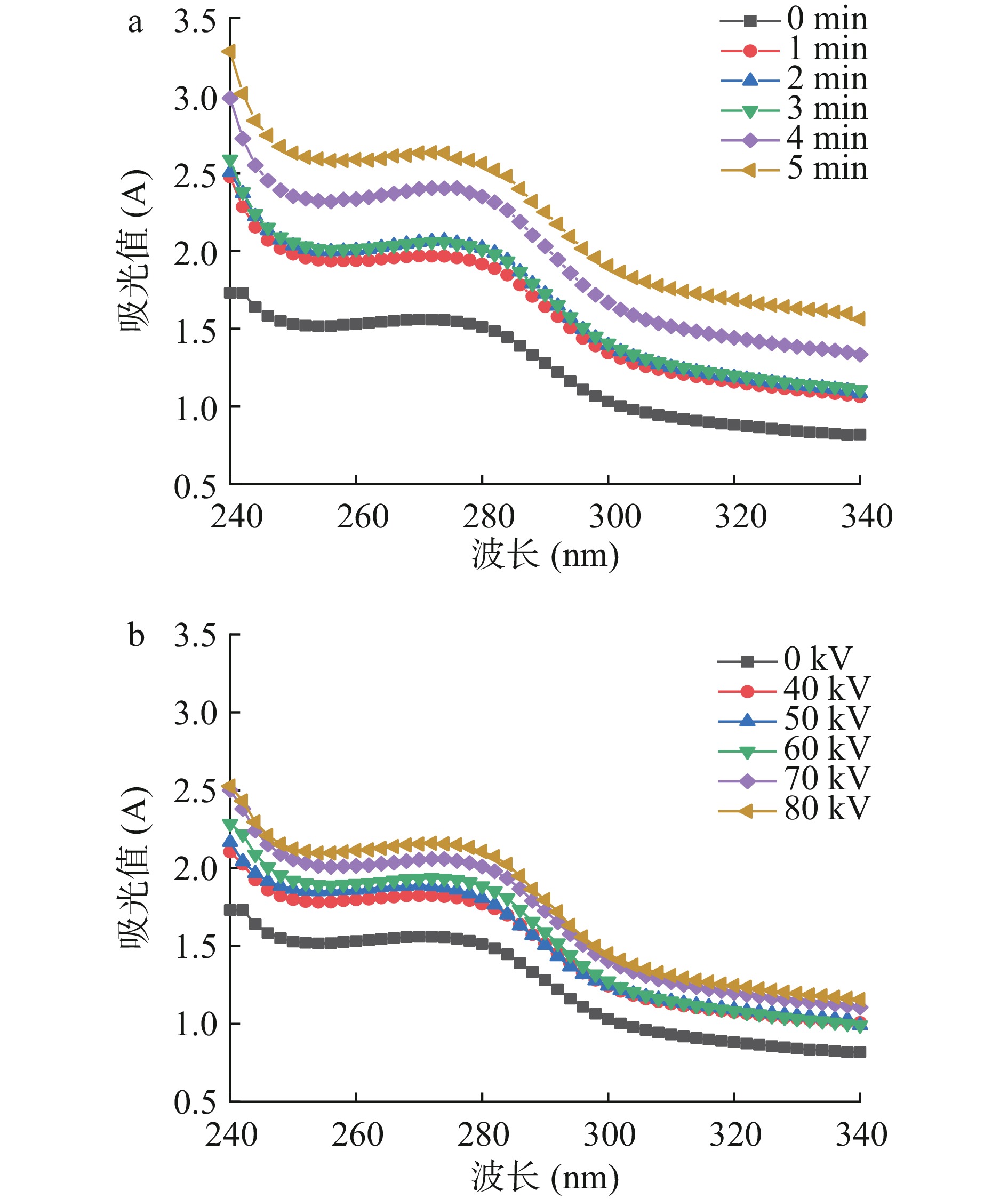
蛋白质中的芳香氨基酸在紫外光下有较强的吸收区域,紫外光谱能反映蛋白质构象变化[31]。由图6可知,经不同时间、不同电压等离子体处理后的肌原纤维蛋白的紫外吸收光谱相似,均在280 nm波长左右出现峰的拐点,说明等离子体处理后的氧化不会改变肌原纤维蛋白整体图谱趋势,但随着处理时间的延长以及处理电压的升高,最大吸收峰出现轻微蓝移,紫外吸收强度增强,表明在低温等离子体处理后,在自由基的攻击下,肌原纤维蛋白质中的芳香族氨基酸基团暴露于表面,结构发生不同程度改变,从而使紫外吸收光谱产生略微差异[32]。
2.7 低温等离子体处理对罗非鱼肌原纤维蛋白内源荧光光谱的影响
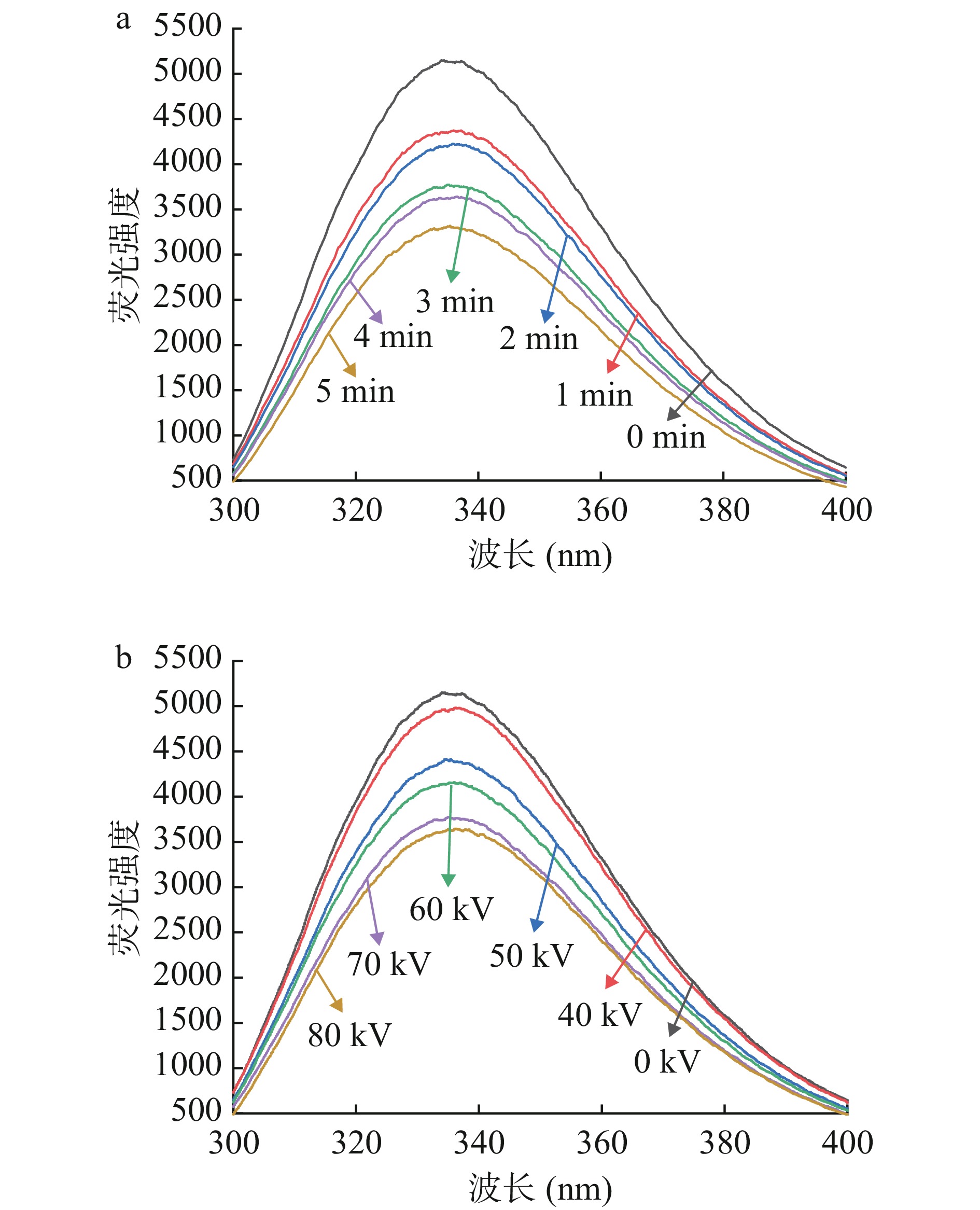
色氨酸的固有荧光性,对微环境及其敏感,用于检测蛋白质三级结构的变化,荧光强度降低,荧光光谱的红移意味着蛋白质氧化程度增加[33]。如图7所示,随着处理时间的延长以及处理电压的升高,肌原纤维蛋白的荧光强度呈现降低趋势,对照组荧光强度最高,低温等离子体70 kV处理5 min和80 kV处理3 min时荧光强度明显降低,随着蛋白质氧化程度的加深,色氨酸荧光吸收强度降低。汪经邦等[34]研究表明,新鲜鱼肉荧光强度最高,随着贮藏天数的增加,鱼肉蛋白氧化程度逐渐增加,荧光强度也随之减弱。低温等离子体处理产生的自由基与蛋白质相互作用形成聚集体,维系三级结构的次级键断裂,使得色氨酸荧光基团被暴露在极性环境中,进而荧光强度减弱[35]。
2.8 低温等离子体处理对罗非鱼肌原纤维蛋白拉曼光谱变化的影响
拉曼光谱是研究二级结构的方法之一,光谱中酰胺I带在1600~1700 cm−1处由蛋白质二级结构成分叠加形成的,1658 cm−1处为α-螺旋形成的吸收峰,其中1670和1665 cm−1处分别为β-转角和β-折叠形成的吸收峰,1685 cm−1处为无规卷曲形成的吸收峰[36]。如图8a所示,在70 kV处理5 min时二级结构中α-螺旋占比从27.32%升至31.78%,β-转角和β-折叠占比减少,无规卷曲无明显变化。如图8b所示,α-螺旋占比先减少后增加,60 kV处理3 min时最低,β-转角占比先增加后减少,β-折叠占比在50 kV处理3 min时占比最高达到36.32%,但在60 kV处理3 min时开始下降,无规卷曲无明显变化。在低电压等离子体处理下,自由基使得羰基和氨基之间的氢键被破坏,α-螺旋结构逐渐解旋,可能转变成β-折叠,而在高电压长时间等离子体处理下,由于鱼肉表面温度略微升高,更多的疏水性基团暴露等原因使得蛋白质分子再次聚集,蛋白质结构更紧密,使得α-螺旋增加。低温等离子体处理过程中肌原纤维蛋白的二级结构处于不断变化中, 可能是在熵的驱动下导致α-螺旋、β-转角、β-折叠和无规卷曲之间的相互转化[37]。
3. 结论
罗非鱼经低温等离子体处理后肌原纤维蛋白结构发生明显变化,低温等离子体处理产生的自由基等活性物质促进鱼肉蛋白氧化。处理电压固定随着处理时间延长,鱼肉中羰基含量和疏水性增加,总巯基、活性巯基含量和Zeta电位绝对值减少,当处理时间延长至5 min时,鱼肉中羰基含量增加至1.95 nmol/mg,溴酚蓝结合量增加至55.05 μg。当处理时间固定处理电压逐渐升高至80 kV时,鱼肉中总巯基、活性巯基含量减少至61.15和56.86 μmol/g,Zeta电位绝对值减少至5.57,同时羰基含量和疏水性增加。低温等离子体处理使得蛋白质分子发生交联聚合,结构发生改变,色氨酸荧光基团暴露于极性环境中,三级结构发生改变,蛋白质二级结构α-螺旋、β-转角、β-折叠和无规卷曲占比不断发生改变。低温等离子体处理产生的自由基导致加速蛋白质氧化,因此通过控制低温等离子体处理条件减少蛋白质氧化程度,为今后低温等离子体处理技术在罗非鱼以及其他水产品冷藏保鲜中的应用提供技术支撑。
-
-
[1] 程琳丽, 李来好, 马海霞. 罗非鱼的保鲜研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技, 2013, 34(11): 372−375 CHENG L L, LI L H, MA H X. Research progress in preservation of tilapia[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2013, 34(11): 372−375.
[2] 李娜, 孙敏, 王春华, 等. 水产品保鲜贮藏期间品质评价方式的研究进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2022, 13(4): 1099−1105 LI N, SUN M, WANG C H, et al. Research progress on quality evaluation indexes of aquatic products during fresh-keeping and storage[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality, 2022, 13(4): 1099−1105.
[3] FEIZOLLAHI E, MISRA N N, ROOPESH M S. Factors influencing the antimicrobial efficacy of dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) atmospheric cold plasma (ACP) in food processing applications[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 2021, 61(4): 666-689.
[4] ALBERTOS I, MARTÍN-DIANA A B, CULLEN P J, et al. Effects of dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) generated plasma on microbial reduction and quality parameters of fresh mackerel (Scomber scombrus) fillets[J]. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies, 2017, 44: 117-122.
[5] 周结倩, 张坤, 徐杰, 等. 低温等离子体在水产品保鲜中的应用研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(22):328−337. [ZHOU J Q, ZHANG K, XU J, et al. Research progress on application of low temperature plasma in aquatic products preservation[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022,48(22):328−337. [6] PÉREZ-ANDRÉS J M, DE ALBA M, HARRISON S M, et al. Effects of cold atmospheric plasma on mackerel lipid and protein oxidation during storage[J]. LWT, 2020, 118: 108697.
[7] HUANG Y M, CHANG W C, HSU C L. Inactivation of norovirus by atmospheric pressure plasma jet on salmon sashimi[J]. Food Research International, 2021, 141: 110108.
[8] 姜竹茂, 桑晓涵, 潘芸芸, 等. 低温等离子体对鲅鱼脂质与蛋白质氧化的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(23):217−224. [JIANG Z M, SANG X H, PAN Y Y, et al. Effects of cold plasma treatment on oxidation of lipids and protein of Spanish mackerel[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022,48(23):217−224. [9] 杜曼婷, 黄俐, 高梦丽, 等. 介质阻挡放电低温等离子体处理对宰后羊肉品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(21):87−92. [DU M T, HUANG L, GAO M L, et al. Effect of dielectric barrier discharge low temperature plasma treatment on mutton quality[J]. Food Science,2022,43(21):87−92. [10] WANG H, PEI Z, XUE C, et al. Comparative study on the characterization of myofibrillar proteins from tilapia, golden pompano and skipjack tuna[J]. Foods, 2022, 11(12): 1705.
[11] HAN Z, CAI M, CHENG J, et al. Effects of microwave and water bath heating on the interactions between myofibrillar protein from beef and ketone flavour compounds[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 2019, 54(5): 1787−1793.
[12] MESQUITA C S, OLIVEIRA R, BENTO F, et al. Simplified 2, 4-dinitrophenylhydrazine spectrophotometric assay for quantification of carbonyls in oxidized proteins[J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 2014, 458: 69-71.
[13] 徐红艳, 张珍, 陈雪琴, 等. 复配香辛料精油处理对冷藏藏羊肉氧化特性的影响[J]. 食品科学技术学报,2020,38(2):90−98. [XU H Y, ZHANG Z, CHEN X Q, et al. Effect of compound spice essential oil on oxidation characteristics of Tibetan mutton during refrigeration[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2020,38(2):90−98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-6002.2020.02.012 [14] 黄倩, 黄兰兰, 陈炼红, 等. 冻融对冷藏藏羊肉保水性及蛋白氧化和溶解特性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技, 2021, 42(19): 21−28 HUANG Q, HUANG L L, CHEN L H, et al. Effects of repeated freezing-thawing on water holding capacity, myofibrillar protein oxidation and dissolution characteristics of Tibetan mutton during chilled storage[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(19): 21−28.
[15] 李子晗, 费子璇, 张瑞丽, 等. 低钠条件下pH值对肌原纤维蛋白乳化性能的影响[J]. 包装工程, 2022, 43(1): 89−97 LI Z H, FEI Z X, ZHANG R L, et al. Effects of pH on the emulsifying properties of lamb myofibrillar protein under low sodium concentration[J]. Packaging Engineering, 2022, 43(1): 89−97.
[16] 石钢鹏, 阙凤, 高天麒, 等. 速冻方式对冷冻贮藏中大口黑鲈鱼肉蛋白质特性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技, 2021, 42(20): 309−319 SHI G P, QUE F, GAO T Q, et al. Effects of different quick-freezing methods on protein properties of largemouth bass (Lateolabrax japonicus)[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(20): 309−319.
[17] 张海璐, 黄翔, 杨燃, 等. 氧化对羊肉肌原纤维蛋白分子与理化特性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(23):8−14. [ZHANG H L, HUANG X, YANG R, et al. Effect of oxidation on molecular and physicochemical properties of mutton myofibrillar protein[J]. Food Science,2020,41(23):8−14. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200615-197 [18] ZOU X, HE J, ZHAO D, et al. Structural changes and evolution of peptides during chill storage of pork[J]. Frontiers in Nutrition, 2020, 7: 151.
[19] XIONG Y L, GUO A. Animal and plant protein oxidation: Chemical and functional property significance[J]. Foods, 2020, 10(1): 40.
[20] PANPIPAT W, CHAIJAN M. Effect of atmospheric pressure cold plasma on biophysical properties and aggregation of natural actomyosin from threadfin bream (Nemipterus bleekeri)[J]. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 2020, 13(5): 851−859.
[21] LUND M N, HEINONEN M, BARON C P, et al. Protein oxidation in muscle foods: A review[J]. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 2011, 55(1): 83−95.
[22] 唐玲玲, 严金红, 徐慧倩, 等. 低温等离子体对南美白对虾肌肉蛋白质性质和结构的影响[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2022, 13(10): 3083−3089 TANG L L, YAN J H, XU H Q, et al. Effects of cold atmospheric plasma on protein properties and structure of Penaeus vannamei[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality, 2022, 13(10): 3083−3089.
[23] CHELH I, GATELLIER P, SANTÉ-LHOUTELLIER V. Technical note: A simplified procedure for myofibril hydrophobicity determination[J]. Meat Science, 2006, 74(4): 681−683.
[24] MIAO W, NYAISABA B M, KODDY J K, et al. Effect of cold atmospheric plasma on the physicochemical and functional properties of myofibrillar protein from Alaska pollock (Theragra chalcogramma)[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 2020, 55(2): 517−525.
[25] 孙克奎, 金声琅, 潘雅燕, 等. 等离子体活性水腌制对猪肉肌原纤维蛋白氧化及结构的影响[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(14):36−41. [SUN K K, JIN S L, PAN Y Y, et al. Effects of plasma-activated water curing on oxidation and structure of pork myofibrillar protein[J]. Food Science,2020,41(14):36−41. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191029-319 [26] ZHANG Z, YANG Y, TANG X, et al. Chemical forces and water holding capacity study of heat-induced myofibrillar protein gel as affected by high pressure[J]. Food Chemistry, 2015, 188: 111−118.
[27] DU X, LI H, NUERJIANG M, et al. Influence of repeated freeze–thaw treatments on the functional and structural properties of myofibrillar protein from mirror carp (Cyprinus carpio L.)[J]. Food Biophysics, 2021, 16(4): 492−501.
[28] 张潮, 吴宇桐, 孔保华. 超声辅助冷冻对鸡胸肉肌原纤维蛋白乳化稳定性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(17):104−110. [ZHANG C, WU Y T, KONG B H. Effect of ultrasound-assisted freezing on emulsifying stability of myofibrillar protein from chicken breast[J]. Food Science,2020,41(17):104−110. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190817-189 [29] OLATUNDE O O, SINGH A, SHIEKH K A, et al. Effect of high voltage cold plasma on oxidation, physiochemical, and gelling properties of myofibrillar protein isolate from asian sea bass (Lates calcarifer)[J]. Foods,2021,10(2):326.
[30] KODDY J K. Understanding the role of atmospheric cold plasma (ACP) in maintaining the quality of hairtail (Trichiurus lepturus)[J]. Food Chemistry,2021:8.
[31] LANGE R, BALNY C. UV-visible derivative spectroscopy under high pressure[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Protein Structure and Molecular Enzymology,2002,1595(1−2):80−93.
[32] 康怀彬, 邹良亮, 张慧芸, 等. 高温处理对牛肉蛋白质化学作用力及肌原纤维蛋白结构的影响[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(23):80−86. [KANG H B, ZOU L L, ZHANG H Y, et al. Effect of high temperature treatment on chemical forces of beef proteins and structure of myofibrillar protein[J]. Food Science,2018,39(23):80−86. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201823013 [33] CAO Y, TRUE A D, CHEN J, et al. Dual role (anti- and pro-oxidant) of gallic acid in mediating myofibrillar protein gelation and gel in vitro digestion[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2016, 64(15): 3054−3061.
[34] 汪经邦, 谢晶, 刘大勇. 暗纹东方鲀低温贮藏期间水分、质地和蛋白质的变化规律[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(21):213−221. [WANG J B, XIE J, LIU D Y. Changes in water mobility, texture and protein structure in Takifugu obscurus during low temperature storage[J]. Food Science,2020,41(21):213−221. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191008-036 [35] 李学鹏, 蔺博燕, 王金厢, 等. 羟自由基氧化对草鱼肌原纤维蛋白热聚集行为的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2020, 46(10): 27−34 LI X P, LIN B Y, WANG J X, et al. Effect of hydroxyl radical oxidation on the thermal aggregation behavior of myofibrillar protein from grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus)[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(10): 27−34.
[36] WANG J Y, YANG Y L, TANG X Z, et al. Effects of pulsed ultrasound on rheological and structural properties of chicken myofibrillar protein[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2017, 38: 225−233.
[37] 吕彤, 林俊杰, 周昌瑜, 等. 热处理强度对猪肉肌球蛋白结构及风味成分吸附特性的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(8):285−291. [LÜ T, LIN J J, ZHOU C Y, et al. Effect of heat treatment intensity on structure and binding capacity of volatile compounds of myosin[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2016,32(8):285−291. -
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 刘璐,李晶峰,兰梦,李冬冰,张凯月,王跃龙,申嘉明,李春楠,张辉,孙佳明. 牡蛎蛋白酶解肽制备工艺优化及其对小鼠睾丸间质细胞睾酮分泌和氧化应激的影响. 食品工业科技. 2024(09): 168-176 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 李冬冰,兰梦,王跃龙,刘璐,申嘉明,李晶峰,张辉,孙佳明. 珍珠母肽酶解工艺的优化及对人肝癌细胞HepG2能量代谢的影响. 现代食品科技. 2024(05): 92-101 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 陈灼娟,柯秀贤,黄霄. 姬松茸抗氧化酶解液的制备. 食品与机械. 2023(03): 183-187+232 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张书会,罗璐,孙雪言,马爱民. 虎奶菇菌丝体抗菌肽提取工艺优化及活性研究. 食品与机械. 2022(08): 158-165 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)









 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



