Preparation and Structure Characterization of Iron(II)-Chelating Corn Oligopeptides
-
摘要: 以玉米低聚肽和氯化亚铁为原料制备玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II),以得率和螯合率评价螯合效果,通过单因素实验、响应面中心组合设计和验证实验确定最佳工艺。通过高效液相色谱仪(HPLC)测定玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的氨基酸组成,并通过傅里叶变换红外光谱(FTIR)和扫描电镜(SEM)对玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的结构进行表征。结果表明,玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的最佳制备工艺为肽盐比5:1,pH7.0,螯合时间35 min,螯合温度65 ℃。此条件下,玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的得率为46.59%±1.69%,铁(II)的螯合率为51.75%±2.10%。玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)中必需氨基酸含量占比25.58%,相对分子质量小于1000 u的组分占比高达89.77%。FTIR结果表明,铁(II)与玉米低聚肽末端羧基或氨基中的氮原子、氧原子形成配位键,从而形成螯合物;SEM结果显示,螯合后分子发生聚集,圆球状结构消失,说明成功生成了一种新型玉米低聚肽铁螯合物。Abstract: Corn oligopeptides and ferrous chloride were used as raw materials to prepare iron (II)-chelating wheat oligopeptides. The chelating effect was evaluated by yield and chelating rate, and the best process was studied by single-factor, response surface centered design and verification experiments. The amino acid composition of iron(II)-chelating corn oligopeptides was determined by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), the structural characteristics of corn oligopeptides before and after chelating were analyzed by Fourier transform infrared radiation (FT-IR) and scanning electron microscope (SEM). The results showed that the optimum preparation conditions of iron (II)-chelating corn oligopeptides were as follows: Mass ratio between corn oligopeptides and ferrous chloride 5:1, pH7.0, chelating time 35 min, and chelating temperature 65 ℃. Under the conditions, the yield was 46.59%±1.69% and the iron (II) chelating rate was 51.75%±2.10%. The content of essential amino acids in iron(II)-chelating corn oligopeptides accounted for 25.58%, and the components with relative molecular weight less than 1000 u accounted for as high as 89.77%. FTIR analysis results showed that iron (II) formed coordination bonds with nitrogen and oxygen atoms in the terminal carboxyl or amino group of the corn oligopeptides to form iron (II)-chelating corn oligopeptides. SEM results showed that after chelating the molecules aggregated and the spherical structure disappeared, indicating that a new type of iron(II)-chelating corn oligopeptides was successfully formed.
-
植物基食品原料绿色、环保、健康理念深入人心,以植物为基础的食品开发将成为食品行业的主流趋势[1]。玉米为我国主要的农作物,以其为原料的加工利用多针对玉米淀粉,玉米蛋白研究较少。研究发现,玉米蛋白含有较高比例的支链氨基酸,且玉米蛋白链的功能区可通过酶解技术被释放[2],具有较高的利用价值。玉米低聚肽是以玉米蛋白粉为原料,通过现代生物酶解技术制备的小分子短肽混合物[2],具有抗氧化[3]、降血压[4]、护肝[5]、解酒[5-7]等多种功能。相比于大分子蛋白,小分子肽类物质具有良好的体外消化稳定性。Wei等[8]、王憬等[9]以大豆肽、卵白肽、玉米肽、乳清肽、海洋骨原肽、海洋胶原肽、海洋蛋白肽7种食源性低聚肽为原料,通过体外模拟消化实验发现,95%以上的低聚肽未被胃蛋白酶消化,90%以上的低聚肽未被胰蛋白酶消化,因此低聚肽更容易被人体吸收和发挥其生理功能。
铁是人体必需的微量元素,作为血红蛋白的重要部分,影响人体生长发育和新陈代谢[10],铁缺乏会导致人体贫血,抵抗力下降,容易疲劳[11]。目前,铁补充剂主要通过无机铁盐(如FeSO4),但长期服用会引起肠胃不适,且稳定性差,生物利用率低[12]。有研究指出,以海洋鱼皮低聚肽、酪蛋白肽以及乳清蛋白肽为主要原料制备铁螯合物,具有作为新型食源性铁补充剂的潜力[13],但目前以玉米低聚肽为原料进行铁螯合物制备的研究较少。
本研究以玉米低聚肽和氯化亚铁为原料制备玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II),评价其氨基酸组成和相对分子质量,以得率和螯合率评价螯合效果,通过单因素实验、响应面中心组合设计和验证实验确定最佳工艺,通过液相-质谱联用仪(LC-MS)测定玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的氨基酸组成,并通过傅里叶变换红外光谱(FTIR)和扫描电镜(SEM)对玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的结构进行表征,以期为食源性肽铁补充剂的开发提供基础技术支持,为玉米低聚肽的高值化利用及植物基食品品质提升提供理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
玉米低聚肽 北京中食海氏生物技术有限公司提供;氯化亚铁、硫酸亚铁铵、邻二氮菲、抗坏血酸、无水乙醇、盐酸、氨水等化学试剂 均为分析纯,北京化学试剂公司;溴化钾(分析纯) 国药集团化学试剂有限公司;乙腈(色谱纯) 美国Fisher公司。
HH型数显恒温水浴锅 金坛区富华仪器有限公司;LRH-99-250型恒温箱 上海一恒科技有限公司;CD 4-2型离心机 北京医用离心机厂;SJ-3 F型pH计 上海精密仪器有限公司;SHZ-3型循环水多用真空泵 郑州朋来仪器有限公司;Pl403型天平 梅特勒-托利多仪器公司;Nicolet 6700型傅立叶变换红外光谱仪 赛默飞世尔科技公司;LC-20A高效液相色谱仪 日本SHI-MADZU公司;A300全自动氨基酸分析仪 德国曼默博尔公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的制备
准确称取一定量的玉米低聚肽粉,用蒸馏水溶解,制备成一定浓度的玉米低聚肽溶液,并加入抗氧化剂。根据后续不同实验参数条件,调节pH,按照一定的肽盐比(w/w)加入FeCl2,在恒温水浴振荡器中恒温螯合,反应结束后蒸发浓缩,醇沉(乙醇)得到粗螯合物。对粗螯合物进行抽滤、洗涤、干燥,制备得到玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)。
1.2.2 玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)螯合效果评价
采用宋莎莎等[14]的方法,利用分光光度法测定螯合前反应体系中铁的含量以及反应生成的玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)中铁的含量。通过公式(1)和公式(2)测定铁的螯合率和玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的得率,以评价玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的螯合效果。
铁螯合率(%)=m1m0×100 (1) 式中:m1为螯合物中铁的量,mg;m0为加入反应体系中铁的总量,mg。
玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)得率(%)=W1W0×100 (2) 式中:W1为玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的总质量(II),mg;W0为玉米低聚肽与铁盐的总质量,mg。
1.2.3 玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)制备工艺单因素实验
采用单因素实验设计肽盐比、pH、螯合温度、螯合时间探究制备玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的最佳工艺,具体实验参数如下:
选用pH6.0,螯合温度为65 ℃,螯合时间为45 min,肽盐比为2:1、4:1、6:1、8:1和10:1,探究肽盐比对玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)螯合效果的影响;
选用螯合温度为65 ℃,螯合时间为45 min,肽盐比为8:1,pH为4.0、5.0、6.0、7.0、8.0,探究pH对玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)螯合效果的影响;
选用pH6.0,螯合时间为45 min,肽盐比为8:1,螯合温度为35、45、55、65、75 ℃,探究螯合温度对玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)螯合效果的影响;
选用pH6.0,螯合温度为65 ℃,肽盐比为8:1,螯合时间为15、30、45、60 min,探究螯合时间对玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)螯合效果的影响。
1.2.4 玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)制备工艺响应面试验
在单因素实验的基础上,以肽盐比、pH、螯合时间、螯合温度和为考察因素,采用Box-Benhnken中心组合设计4因素3水的响应面试验,以玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的得率和铁的螯合率为响应值,分析影响螯合效果各因素的交互作用,确定最佳工艺条件。中心组合实验水平如表1所示。
表 1 中心组合实验水平表Table 1. Center combination experiment level水平 因素 A 肽盐比 B pH C 螯合温度(℃) D螯合时间(min) −1 4:1 6 60 25 0 5:1 7 65 35 1 6:1 8 70 45 1.2.5 玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的氨基酸组成分析
利用全自动氨基酸分析仪,参考GB 5009.124-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品中氨基酸的测定》方法,对玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的水解氨基酸和游离氨基酸组成进行分析[15]。
1.2.6 玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)相对分子质量分布测定
配制玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)溶液的质量浓度为1 mg/mL,经过0.2 μm聚四氟乙烯膜过滤,使用高效液相色谱仪测定样品分子量。同时,分别配制0.1%乙氨酸-乙氨酸-乙氨酸(分子质量189 u)、乙氨酸-乙氨酸-酪氨酸-精氨酸(分子质量451 u)、杆菌酶(分子质量1450 u)、细胞色素C(分子质量12500 u)4种肽标准品溶液,经过0.2 μm聚四氟乙烯膜过滤后进样,制作校正曲线。色谱条件:色谱柱:TSKgel G2000 SWXL 300 mm×7.8 mm;流动相:V乙腈:V水:V三氟乙酸=45:55:0.1;流速:0.5 mL/min;检测波长:220 nm;柱温:30 ℃[16]。
1.2.7 玉米低聚肽及玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的FTIR表征
利用傅里叶变换红外光谱对玉米低聚肽及玉米低聚肽铁(II)进行结构表征。具体为:准确称取5 mg玉米低聚肽螯合铁于玛瑙研钵中,在其中加入500 mg KBr。打开红外灯,在干燥环境下研磨并混合均匀,将均匀粉末置于模具中压片处理,获得均匀透明样品后采用傅里叶变换红外光谱仪扫描,扫描范围为4000~500 cm−1,分辨率为4 cm−1,扫描次数为32次。
1.2.8 玉米低聚肽及玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的微观形貌表征
采用SEM对玉米低聚肽及玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的微观形貌进行表征。具体为:取适量玉米低聚肽和玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)分别均匀涂抹于样盘,喷金镀膜处理,加压3 kV,于电镜下捕捉500×倍的均匀清晰图像。
1.3 数据处理
采用Design Expert 12进行响应面分析,采用SPSS 18.0统计分析软件进行方差分析,采用Origin 2019软件绘制图像。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)制备工艺单因素实验结果
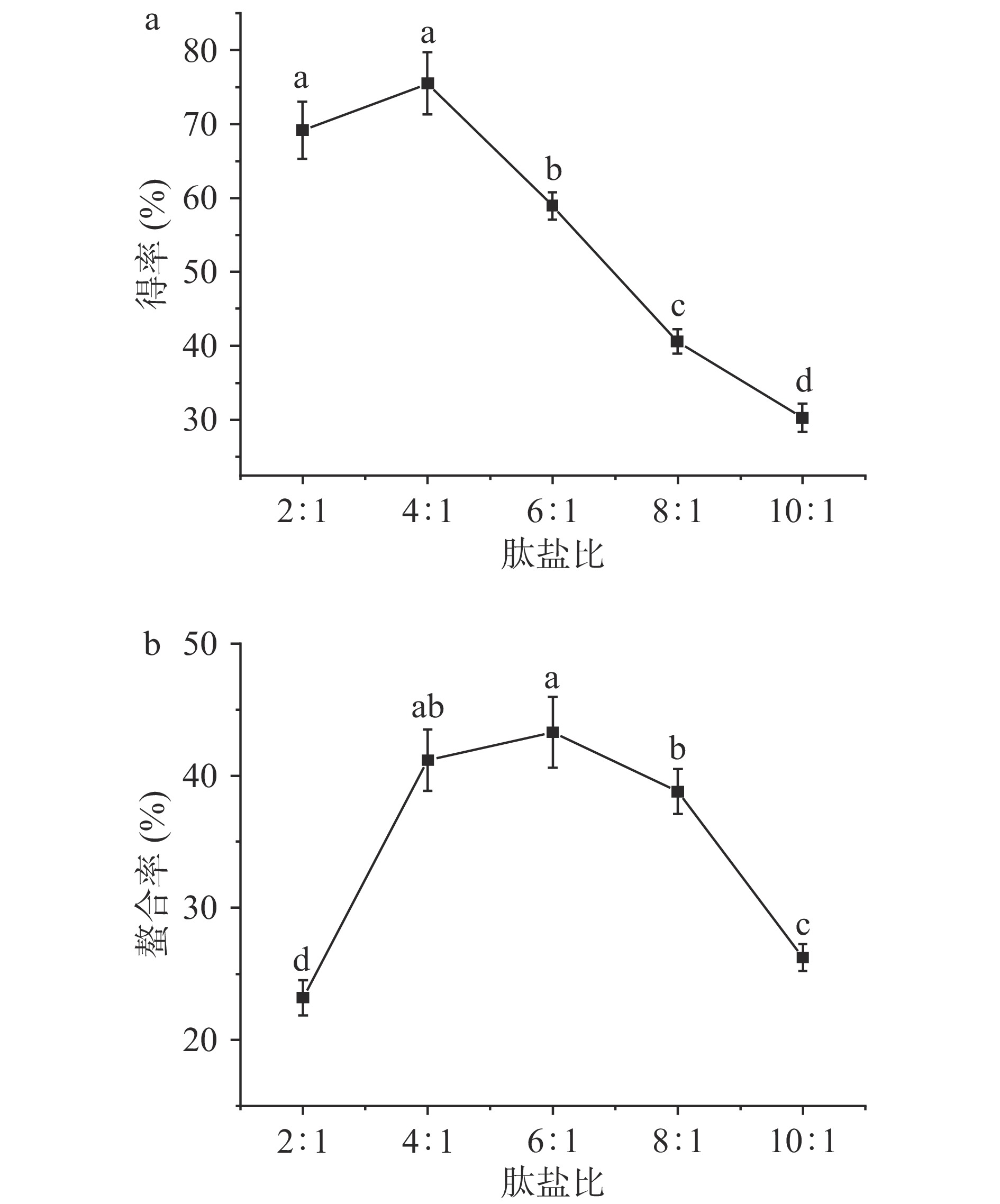
2.1.1 肽盐比对螯合效果的影响
玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的制备是以玉米低聚肽和FeCl2的螯合反应为基础,因此反应底物的相对含量是影响螯合效果的重要因素。选用5组不同肽盐质量比研究螯合效果,结果如图1所示。由图1a可知,随着肽盐质量比的增加,玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的得率呈现先增长后下降的趋势,在肽盐质量比为4:1时得率呈现最大值,为45.30%。铁的螯合率取决于反应体系中肽反应基团的含量以及FeCl2和肽的反应程度。当肽盐质量比较低时,过量的FeCl2无法充分与玉米低聚肽螯合,螯合率均较低,螯合效果差且所得螯合物不稳定。随着玉米低聚肽含量的增加,FeCl2和肽的反应更充分,螯合率上升。但玉米低聚肽含量继续增加,肽与肽之间会发生相互反应,从而影响肽与FeCl2的反应,又会导致螯合率的下降,同时造成得率降低,大量玉米低聚肽的浪费,成本提高[17];由图1b可知,铁的螯合率最高时肽盐质量比为4:1和6:1。综合得率和螯合率结果,后续优化试验中选择肽盐质量比为4:1~6:1,这与宋莎莎等[14]结果相似。
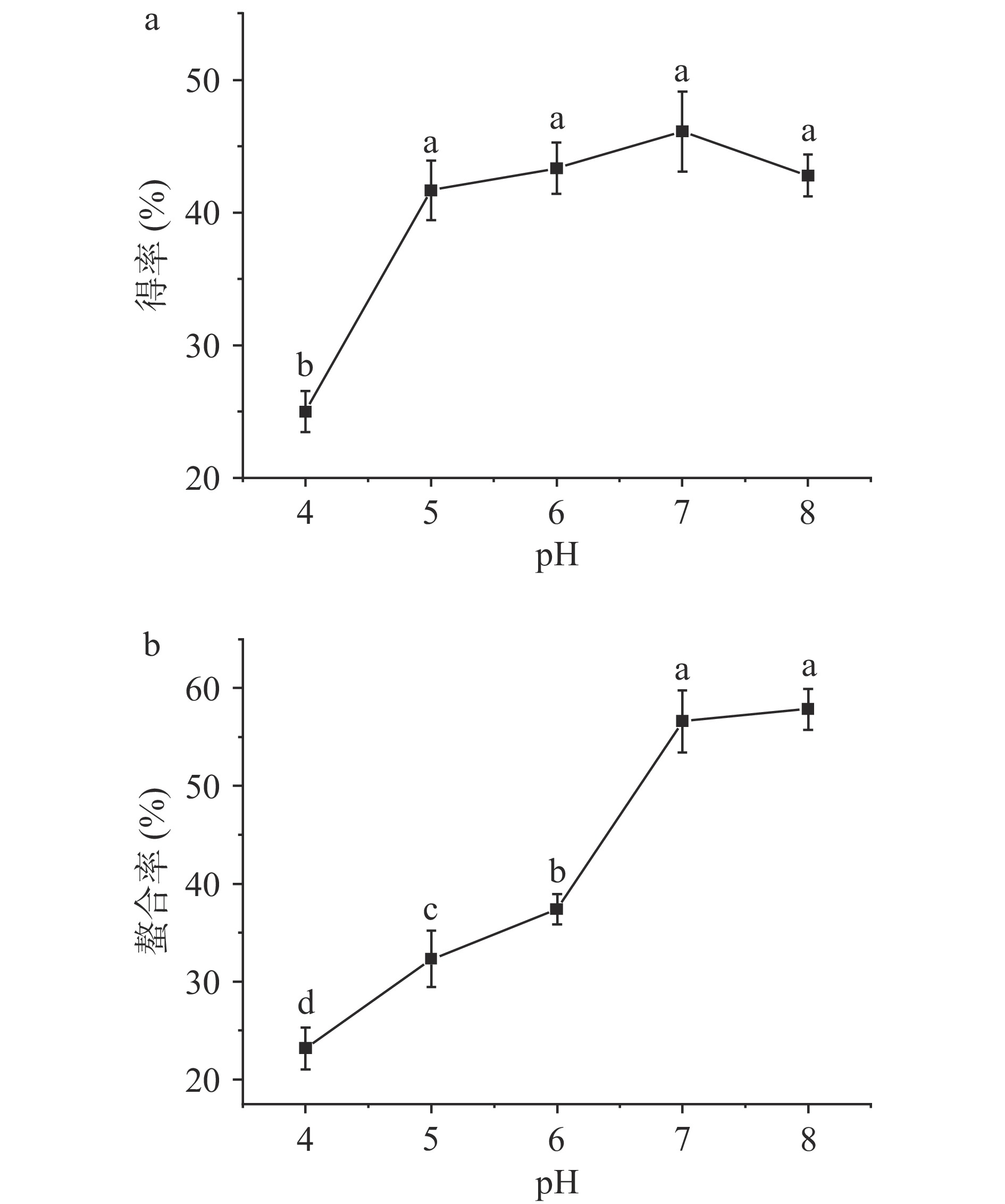
2.1.2 pH对螯合效果的影响
选用pH4.0~8.0来探究其对螯合效果的影响,结果如图2所示。随着pH的提高,玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的得率呈现先上升后下降的趋势,当pH为7.0时,得率最大为46.11%;而铁的螯合率呈现逐渐上升趋势,当pH为8.0时,螯合率最大为57.82%,但此时的螯合率和pH为7.0时(56.58%)的螯合率无显著差异(P>0.05)。研究发现,在酸性环境中,过量的H+会与Fe2+争夺电子基团;而在碱性环境中,OH−会与Fe2+生成氢氧化物沉淀,影响螯合效果。因此,一般中性环境中螯合效果最优。但当大量多肽处于等电点附近时,其螯合效果受H+和OH-影响较小,供电子基团可以充分与金属离子通过配位键形成螯合物[18-19]。这与宋莎莎等[14]制备乌鸡肽铁(II)螯合物所选择的pH6结果不同,说明在玉米低聚肽螯合铁的制备工艺在中性环境螯合效果更好。
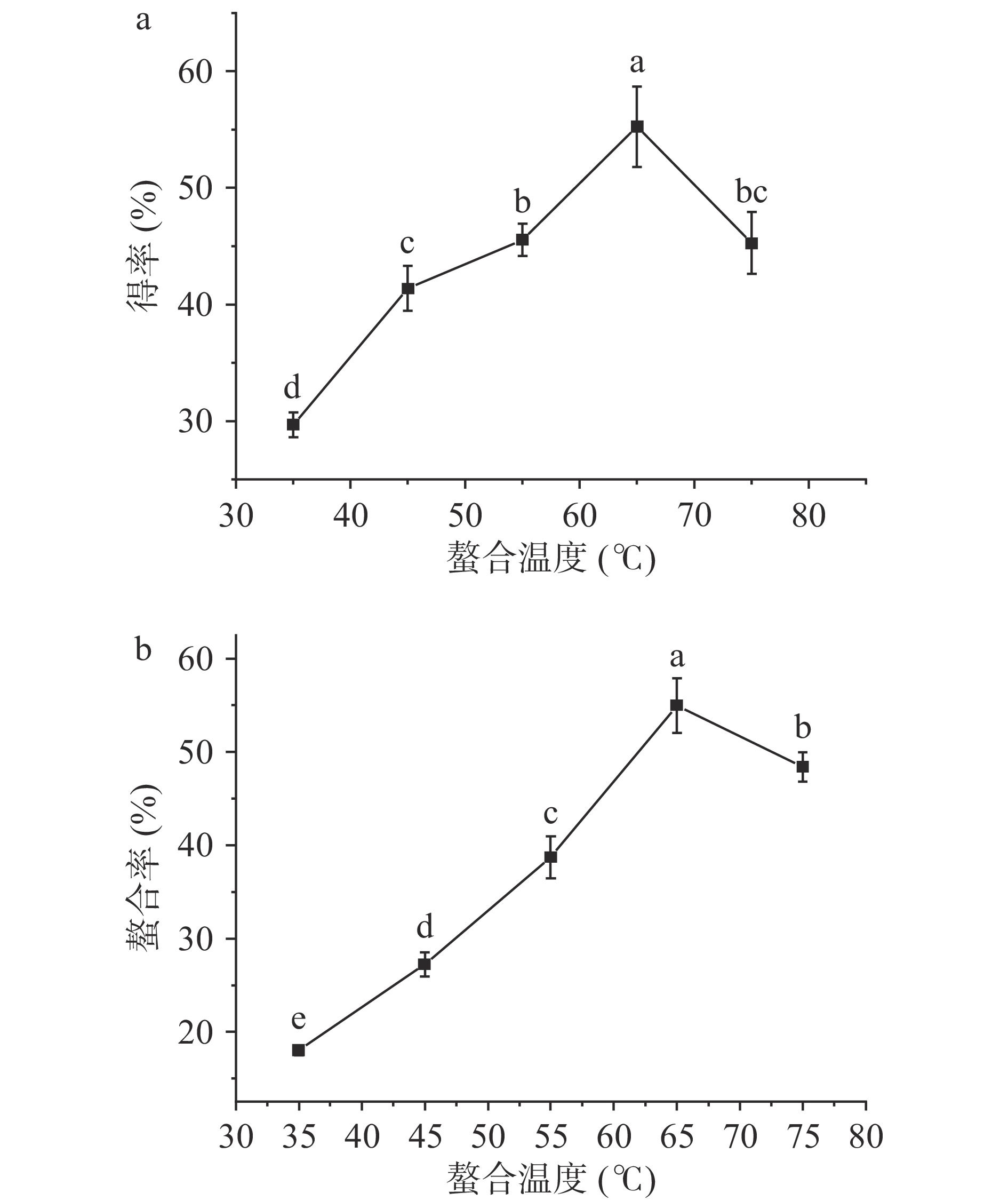
2.1.3 螯合温度对螯合效果的影响
螯合温度不仅影响反应速率,也是影响螯合效果的重要因素之一。如图3所示,随着螯合温度的提升,得率和螯合率均整体上呈现先上升后下降的趋势,当螯合时间为65 ℃时,得率和螯合率取得最大值,为55.28%和54.98%。玉米低聚肽与FeCl2的螯合反应是吸热反应,随着温度的提高,玉米低聚肽的溶解度逐渐增强,Fe2+与肽基团的接触面积增大,螯合反应更彻底,得率和螯合率提高。但是,温度继续升高,会导致玉米低聚肽之间发生副反应,与Fe2+形成竞争,且螯合物在高温下不稳定,极易分解,影响螯合效果,导致得率和螯合率下降[20]。
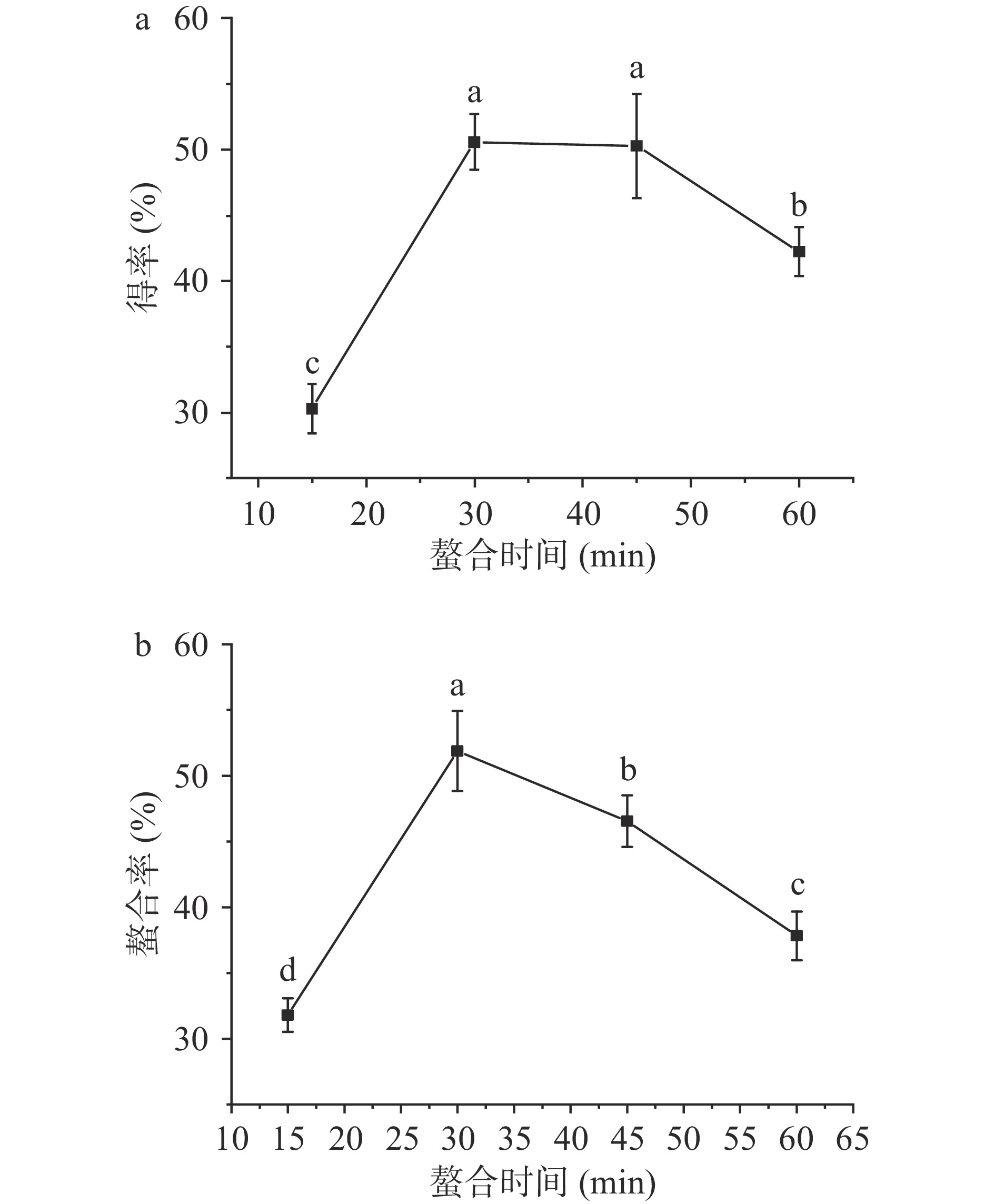
2.1.4 螯合时间对螯合效果的影响
螯合时间是影响螯合反应的重要因素之一,选择螯合时间为15~60 min,探究其对螯合效果的影响,结果如图4所示。结果显示,螯合时间为15~30 min时,得率呈现上升趋势。螯合反应达到30、45 min时,得率均达到50%,螯合时间为60 min时,螯合率略有下降。而铁的螯合率整体呈现先上升后下降的趋势,当反应时间为30 min时,螯合率达到最大值51.88%。这是因为当反应时间过短时,螯合反应不彻底,反应体系中存在大量游离的Fe2+和玉米低聚肽配体,原料利用率低下;反应时间过长,螯合反应发生解离作用,且可能产生副产物,得率和螯合率过低,螯合效果差。综合考虑得率和螯合率结果,选择25~45 min进行后续优化试验。
2.2 响应面设计试验结果及分析
根据单因素实验的结果,设计肽盐比、pH、螯合温度和螯合时间4因素3水平响应面试验探究各影响因素对螯合效果的交互影响,所得结果如表2所示。采用Design Expert 8.0.6软件拟合回归多项参数,得到玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)得率(f(x))及螯合率(g(x))对肽盐比(A)、pH(B)、螯合温度(C)、螯合时间(D)的二次多项回归模型方程分别为:
表 2 响应面试验设计及结果Table 2. Response surface experimental design and results实验号 A肽盐比 B pH C螯合温度(℃) D螯合时间(min) 得率
(%)螯合率(%) 1 −1 −1 0 0 24.60 14.02 2 1 −1 0 0 33.71 15.57 3 −1 1 0 0 19.60 27.81 4 1 1 0 0 39.71 18.14 5 0 0 −1 −1 48.50 26.98 6 0 0 −1 1 11.75 17.73 7 0 0 1 −1 12.25 22.75 8 0 0 1 1 12.80 25.57 9 −1 0 −1 0 11.14 19.83 10 1 0 −1 0 14.60 13.50 11 −1 0 1 0 12.80 16.48 12 1 0 1 0 11.14 15.13 13 0 −1 0 −1 24.50 15.08 14 0 1 0 −1 14.00 15.08 15 0 −1 0 1 15.00 18.84 16 0 1 0 1 12.00 16.07 17 −1 0 0 −1 18.20 23.33 18 1 0 0 −1 11.20 15.08 19 −1 0 0 1 17.20 34.67 20 1 0 0 1 13.57 34.33 21 0 −1 −1 0 17.00 17.15 22 0 1 −1 0 10.00 15.57 23 0 −1 1 0 12.00 27.45 24 0 1 1 0 18.50 45.75 25 0 0 0 0 55.00 58.99 26 0 0 0 0 42.00 48.49 27 0 0 0 0 58.00 58.74 28 0 0 0 0 44.50 49.68 29 0 0 0 0 44.50 48.24 f(x)=48.80+1.7A−1.08B−3.86C−2.79D+2.75AB+0.84AC−1.28AD+1.88BC+3.38BD+9.33CD−14.12A2−12.48B2−16.19C2−18.50D2
g(x)=52.83−2.03A+2.53B+2.41C+3.53D−2.81AB+1.98AC+1.24AD−0.69BC+4.97BD+3.02CD−16.76A2−16.93B2−14.55C2−14.76D2
对回归模型进行方差分析,结果如表3和表4所示。结果表明,两个模型的回归项显著(P<0.05),且失拟项均为不显著(P>0.05),说明模型拟合程度较好,可用于对响应值的预测和分析。表3中结果显示,二次项A2、C2、D2均对玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)得率有极显著性影响(P<0.01),而二次项B2对玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)得率有显著影响(P<0.05),其他项对得率无显著影响。综合F值结果,可得各因素对玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)得率影响主次顺序为:C(螯合温度)>D(螯合时间)>A(肽盐比)>B(pH)。表4结果显示,二次项A2、B2、C2、D2均对铁螯合率有极显著性影响(P<0.01),综合F值结果,可得各因素对铁螯合率的影响主次顺序为:D(螯合时间)>B(pH)>C(螯合温度)>A(肽盐比)。
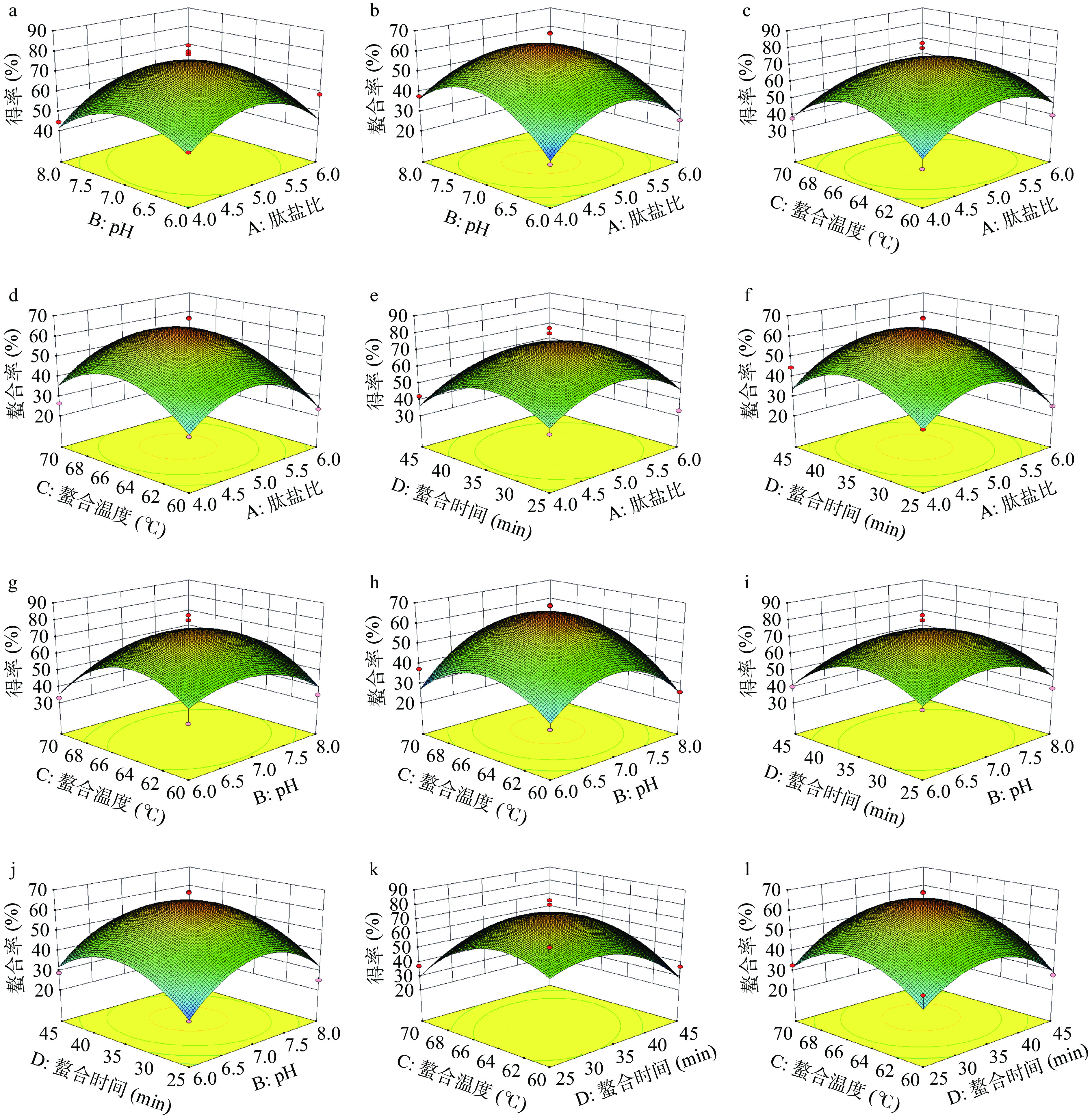
表 3 以玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)得率为响应指标的回归模型方差分析Table 3. Variance analysis of the regression model with the yield of corn oligopeptide chelated iron (II) as the response index方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 5076.10 14 362.58 3.1265 0.0205 * A 25.23 1 25.23 0.2175 0.6481 B 6.75 1 6.75 0.0582 0.8129 C 156.46 1 156.46 1.3491 0.2649 D 117.19 1 117.19 1.0105 0.3318 AB 30.25 1 30.25 0.2608 0.6175 AC 10.14 1 10.14 0.0875 0.7718 AD 43.00 1 43.00 0.3708 0.5523 BC 14.06 1 14.06 0.1213 0.7329 BD 76.56 1 76.56 0.6602 0.4301 CD 347.82 1 347.82 2.9993 0.1053 A2 1434.68 1 1434.68 12.3713 0.0034 ** B2 989.99 1 989.99 8.5368 0.0112 * C2 1647.37 1 1647.37 14.2053 0.0021 ** D2 2434.20 1 2434.20 20.9902 0.0004 ** 残差 1623.56 14 115.97 失拟项 1417.26 10 141.73 2.7480 0.1711 纯误差 206.30 4 51.57 总离差 6699.66 28 注:**表示差异极显著(P<0.01);*表示差异显著(P<0.05);表4同。 表 4 以铁螯合率为响应指标的回归模型方差分析Table 4. Analysis of variance of the regression model with iron chelation as the response index方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 4679.59 14 334.26 4.3980 0.0045 * A 49.54 1 49.54 0.6518 0.4330 B 76.57 1 76.57 1.0074 0.3326 C 69.65 1 69.65 0.9164 0.3547 D 149.64 1 149.64 1.9689 0.1824 AB 31.47 1 31.47 0.4141 0.5303 AC 15.67 1 15.67 0.2062 0.6567 AD 6.20 1 6.20 0.0816 0.7794 BC 1.92 1 1.92 0.0252 0.8760 BD 98.82 1 98.82 1.3002 0.2733 CD 36.42 1 36.42 0.4792 0.5001 A2 1821.43 1 1821.43 23.9657 0.0002 ** B2 1858.40 1 1858.40 24.4521 0.0002 ** C2 1374.10 1 1374.10 18.0798 0.0008 ** D2 1412.45 1 1412.45 18.5844 0.0007 ** 残差 1064.03 14 76.00 失拟项 941.39 10 94.14 3.0706 0.1455 纯误差 122.63 4 30.66 总离差 5743.62 28 根据实验结果和回归模型,利用Design Expert 8.0.6软件绘制肽盐比、pH、螯合温度和螯合时间4因素对螯合效果影响的响应面图,结果如图5所示,响应面坡度和颜色的变化能反映各因素交互作用对结果影响的显著性。结果表明,肽盐比和pH、肽盐比和螯合温度、肽盐比和螯合时间、螯合温度和螯合时间的交互作用对玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的得率影响较小,而对铁螯合率影响较大。在肽盐比相同的情况下,pH是玉米低聚肽螯合铁得率最主要的影响因素,这说明螯合反应过程中,螯合体系中的H+、OH−以及等电点的因素会较大程度上影响Fe2+与肽的螯合反应[16-17];在肽盐比相同的情况下,螯合温度是铁(II)螯合率最主要的影响因素,这说明对于螯合反应(吸热)而言,高温下存在的副反应,且螯合物不稳定,极易分解[20]。
综上分析,利用Design Expert 8.0.6软件得出玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)得率(48.80%)最高的工艺参数为:肽盐比为5.05:1,pH6.93,螯合时间为33.77 min,螯合温度为64.21 ℃;铁螯合率最高(52.86%)的工艺参数为肽盐比为4.99:1,pH7.02,螯合时间为35.10 min,螯合温度为64.89 ℃。根据螯合效果的最优参数和实际制备的可操作性,确定玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的制备工艺为肽盐比5.0:1,pH7.0,螯合时间35 min,螯合温度65 ℃。
2.3 工艺验证
通过响应面的回归模型得到玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的最佳工艺条件为为肽盐比5.0:1,pH7.0,螯合时间35 min,螯合温度65 ℃。此条件下模型理论值得率为48.64%,螯合率为52.16%,通过验证试验,可知在此条件下玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的得率为46.59%±1.69%,铁的螯合率为51.75%±2.10%,与理论值差异较小,该模型得到的优化参数准确性较高。
2.4 玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)氨基酸组成
对以上最优工艺下制备的玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)进行氨基酸组成分析,结果如表5所示。玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)中谷氨酸(Glu)、天冬氨酸(Asp)、脯氨酸(Pro)、丙氨酸(Ala)含量较高,总量达到了14.86 g/100 g,甲硫氨酸(Met)和缬氨酸(Val)含量最低,含量分别是0.530和0.673 g/100 g。在这些氨基酸中,必需氨基酸含量占氨基酸总和的25.58%,说明玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)必需氨基酸含量较为丰富,营养价值较高。此外,谷氨酸(Glu)和天冬氨酸(Asp)含量较高,这有助于玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)呈现良好风味,在食品工业广泛应用[21]。
表 5 玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)氨基酸组成Table 5. Amino acid composition of iron (II)-chelating corn oligopeptides氨基酸名称 含量(g/100 g) 氨基酸名称 含量(g/100 g) 天冬氨酸(Asp) 3.118 赖氨酸(Lys) 1.178 亮氨酸(Leu) 1.682 丙氨酸(Ala) 2.095 丝氨酸(Ser) 1.493 甲硫氨酸(Met) 0.530 缬氨酸(Val) 0.673 组氨酸(His) 1.203 谷氨酸(Glu) 7.619 半胱氨酸(Cys) 0.970 甘氨酸(Gly) 1.468 酪氨酸(Tyr) 0.750 苏氨酸(Thr) 0.944 精氨酸(Arg) 1.236 脯氨酸(Pro) 2.027 苯丙氨酸(Phe) 0.754 异亮氨酸(Ile) 0.716 氨(NH3) 0.865 总和 29.321 2.5 玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)相对分子质量分布
采用HPLC对玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)相对分子质量分布进行了测定,结果如表6所示。在R2为0.9979,标准曲线方程为lg MW=−0.2142t+6.8866(MW为相对分子量,t为时间)的条件下,玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)中多为小分子肽混合物,且相对分子质量小于1000 u的水解物占比高达89.77%。相对分子质量分布于1000~2000 u和2000~3000 u的水解物占比分别为8.22%和1.09%,而相对分子质量高于3000 u的水解物占比为0.93%。研究发现,玉米低聚肽的相对分子质量分布在150~1000的比例达到90%以上,其水解物多为小分子肽混合物[22]。这说明玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)相对分子质量分布和玉米低聚肽相似。
表 6 玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)相对分子量分布Table 6. Molecular weight distribution of iron (II)-chelating corn oligopeptides相对分子量范围 开始时间(min) 结束时间(min) 重均分子量(u) 峰面积百分比(%) >10000 8.947 13.631 13819 0.1881 5000~10000 13.631 15.041 7006 0.2988 3000~5000 15.041 16.080 3773 0.4432 2000~3000 16.080 16.904 2376 1.0868 1000~2000 16.904 18.314 1320 8.2171 150~1000 18.314 22.173 420 74.8800 150以下 22.173 32.365 74 14.8861 重均分子量 523.4 相对分子质量小于1000 u的水解物
所占比例(%)89.77 2.6 玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)结构表征
2.6.1 玉米低聚肽及玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的FTIR结果分析
采用FTIR对玉米低聚肽及玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的结构进行表征,结果如图6所示。由结果可知,玉米低聚肽螯合前后的FTIR图发生了明显变化,尤其在1000~1650 cm−1波段。在玉米低聚肽的FTIR图中,3276 cm−1处(酰胺A带)出现了N—H伸缩振动引起的宽吸收峰[23],1640 cm−1处(酰胺I带)出现了C=O伸缩振动引起的吸收峰[24-25],1529 cm−1处(酰胺II带)出现了N—H弯曲振动和C-N伸缩振动引起的吸收峰[26],1394 cm−1处出现了氨基酸残基侧链基团—COO—伸缩振动引起的吸收峰,1246 cm−1处出现了C—O单键伸缩振动引起的吸收峰,表明玉米低聚肽中含有—COOH结构[27],1044 cm−1处出现了NH2吸收峰[28]。而在玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的FTIR图中,也在3276 cm−1处(酰胺A带)出现了N—H伸缩振动的吸收峰,1608 cm−1处出现了C=O伸缩振动引起的吸收峰,但相比螯合前发生了蓝移,且未出现玉米低聚肽在1529 cm−1处出现的N—H弯曲振动和C—N伸缩振动引起的吸收峰,这说明肽中的N原子是铁螯合反应的配位原子[28];1394、1044 cm−1处的吸收峰发生了蓝移,且1246 cm−1处吸收峰的强度明显减弱,这说明肽中的—COOH也是发生螯合反应的主要部位[29]。周名洋等[30]通过钙螯合鹅骨胶原蛋白制备鹅骨胶原蛋白钙螯合肽,探究螯合机理发现螯合反应主要发生在氨基酸的羧基和氨基上,王孟丽等[31]总结了肽金属离子螯合物的螯合机理指出,肽与金属离子的螯合位点是肽的羧基、氨基和肽键,这与本实验研究结果一致,说明铁主要通过与玉米低聚肽末端羧基或氨基中的氮原子、氧原子形成配位键,从而形成螯合物。
2.6.2 玉米低聚肽及玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的SEM结果分析
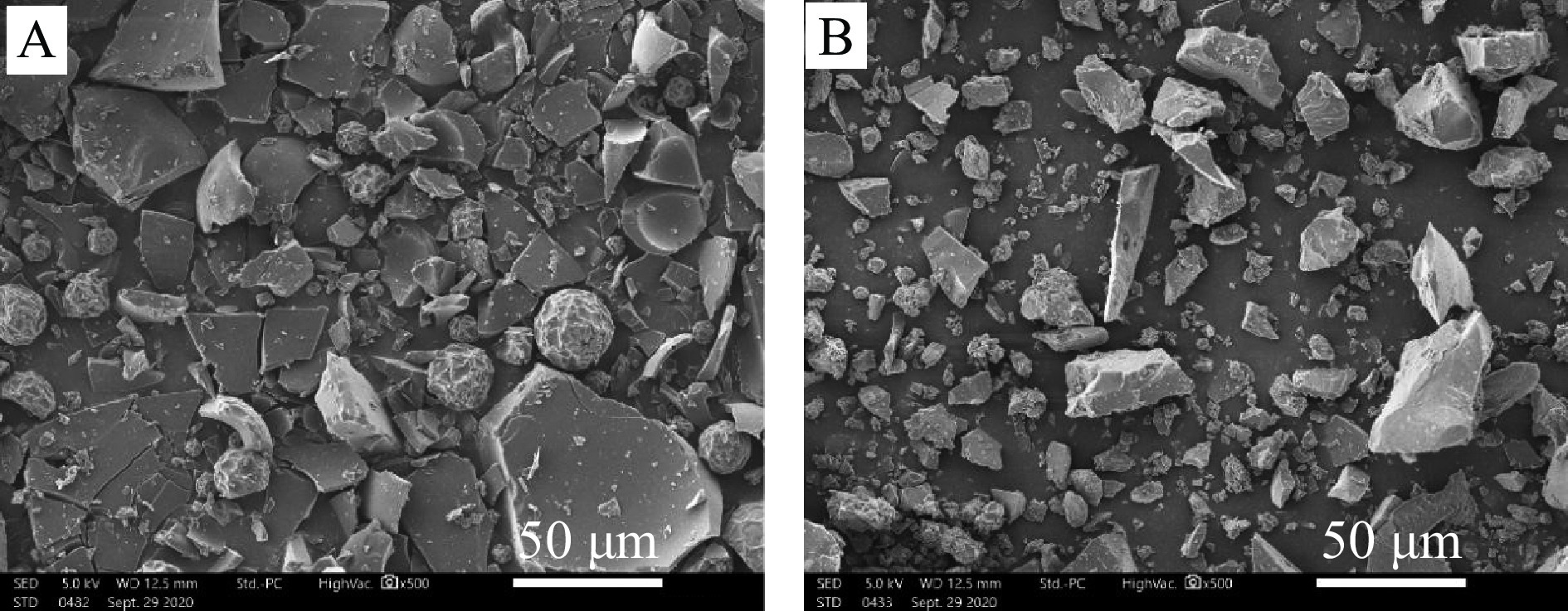
采用SEM对玉米低聚肽及玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的微观形貌进行表征,结果如图7所示。玉米低聚肽表面粗糙,存在明显的圆球状和球状破裂体的形貌,圆球形物体表面凹凸不平,可能与真空干燥过程中的失水有关[20],球状破裂体的表面光滑。而玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的形貌与螯合前相差较大,其结构中无圆球状结构存在,微观形貌更为疏松。通过铁螯合后,玉米低聚肽螯合铁的微观形貌中存在聚集体,这可能是由于铁在螯合过程中破坏了玉米低聚肽的微观结构,通过离子键和配位键生成了玉米低聚肽螯合铁小颗粒[32-33],且玉米低聚肽螯合铁的SEM图中可发现冰晶状物质存在,这可能是吸附在玉米低聚肽上的铁晶体[20]。
3. 结论
本研究利用玉米低聚肽与氯化亚铁螯合制备玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II),综合考虑得率和螯合率确定最佳制备工艺为:肽盐比5:1,pH7.0,螯合时间35 min,螯合温度65 ℃,得到的玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)得率为46.59%±1.69%,铁(II)的螯合率为51.75%±2.10%。玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)中必需氨基酸含量占氨基酸总和的25.58%,富含谷氨酸(7.619 g/100 g)和天冬氨酸(3.118 g/100 g)。且其相对分子质量小于1000 u的水解物占比高达89.77%。进一步,对玉米低聚肽及玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)进行傅里叶变换红外光谱扫描和扫描电镜表征,结果表明玉米低聚肽与铁主要通过肽末端羧基或氨基中的氮原子、氧原子形成配位键,进而形成稳定的环状结构,两者微观形貌存在明显差异,属于不同的物质,证明玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)的成功制备。关于肽螯合铁的研究可进一步探究其安全性,为金属离子螯合肽的制备和表征提供技术支持,拓展铁补充剂的来源,为其在食品、医药行业的应用奠定基础。
-
表 1 中心组合实验水平表
Table 1 Center combination experiment level
水平 因素 A 肽盐比 B pH C 螯合温度(℃) D螯合时间(min) −1 4:1 6 60 25 0 5:1 7 65 35 1 6:1 8 70 45 表 2 响应面试验设计及结果
Table 2 Response surface experimental design and results
实验号 A肽盐比 B pH C螯合温度(℃) D螯合时间(min) 得率
(%)螯合率(%) 1 −1 −1 0 0 24.60 14.02 2 1 −1 0 0 33.71 15.57 3 −1 1 0 0 19.60 27.81 4 1 1 0 0 39.71 18.14 5 0 0 −1 −1 48.50 26.98 6 0 0 −1 1 11.75 17.73 7 0 0 1 −1 12.25 22.75 8 0 0 1 1 12.80 25.57 9 −1 0 −1 0 11.14 19.83 10 1 0 −1 0 14.60 13.50 11 −1 0 1 0 12.80 16.48 12 1 0 1 0 11.14 15.13 13 0 −1 0 −1 24.50 15.08 14 0 1 0 −1 14.00 15.08 15 0 −1 0 1 15.00 18.84 16 0 1 0 1 12.00 16.07 17 −1 0 0 −1 18.20 23.33 18 1 0 0 −1 11.20 15.08 19 −1 0 0 1 17.20 34.67 20 1 0 0 1 13.57 34.33 21 0 −1 −1 0 17.00 17.15 22 0 1 −1 0 10.00 15.57 23 0 −1 1 0 12.00 27.45 24 0 1 1 0 18.50 45.75 25 0 0 0 0 55.00 58.99 26 0 0 0 0 42.00 48.49 27 0 0 0 0 58.00 58.74 28 0 0 0 0 44.50 49.68 29 0 0 0 0 44.50 48.24 表 3 以玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)得率为响应指标的回归模型方差分析
Table 3 Variance analysis of the regression model with the yield of corn oligopeptide chelated iron (II) as the response index
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 5076.10 14 362.58 3.1265 0.0205 * A 25.23 1 25.23 0.2175 0.6481 B 6.75 1 6.75 0.0582 0.8129 C 156.46 1 156.46 1.3491 0.2649 D 117.19 1 117.19 1.0105 0.3318 AB 30.25 1 30.25 0.2608 0.6175 AC 10.14 1 10.14 0.0875 0.7718 AD 43.00 1 43.00 0.3708 0.5523 BC 14.06 1 14.06 0.1213 0.7329 BD 76.56 1 76.56 0.6602 0.4301 CD 347.82 1 347.82 2.9993 0.1053 A2 1434.68 1 1434.68 12.3713 0.0034 ** B2 989.99 1 989.99 8.5368 0.0112 * C2 1647.37 1 1647.37 14.2053 0.0021 ** D2 2434.20 1 2434.20 20.9902 0.0004 ** 残差 1623.56 14 115.97 失拟项 1417.26 10 141.73 2.7480 0.1711 纯误差 206.30 4 51.57 总离差 6699.66 28 注:**表示差异极显著(P<0.01);*表示差异显著(P<0.05);表4同。 表 4 以铁螯合率为响应指标的回归模型方差分析
Table 4 Analysis of variance of the regression model with iron chelation as the response index
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 4679.59 14 334.26 4.3980 0.0045 * A 49.54 1 49.54 0.6518 0.4330 B 76.57 1 76.57 1.0074 0.3326 C 69.65 1 69.65 0.9164 0.3547 D 149.64 1 149.64 1.9689 0.1824 AB 31.47 1 31.47 0.4141 0.5303 AC 15.67 1 15.67 0.2062 0.6567 AD 6.20 1 6.20 0.0816 0.7794 BC 1.92 1 1.92 0.0252 0.8760 BD 98.82 1 98.82 1.3002 0.2733 CD 36.42 1 36.42 0.4792 0.5001 A2 1821.43 1 1821.43 23.9657 0.0002 ** B2 1858.40 1 1858.40 24.4521 0.0002 ** C2 1374.10 1 1374.10 18.0798 0.0008 ** D2 1412.45 1 1412.45 18.5844 0.0007 ** 残差 1064.03 14 76.00 失拟项 941.39 10 94.14 3.0706 0.1455 纯误差 122.63 4 30.66 总离差 5743.62 28 表 5 玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)氨基酸组成
Table 5 Amino acid composition of iron (II)-chelating corn oligopeptides
氨基酸名称 含量(g/100 g) 氨基酸名称 含量(g/100 g) 天冬氨酸(Asp) 3.118 赖氨酸(Lys) 1.178 亮氨酸(Leu) 1.682 丙氨酸(Ala) 2.095 丝氨酸(Ser) 1.493 甲硫氨酸(Met) 0.530 缬氨酸(Val) 0.673 组氨酸(His) 1.203 谷氨酸(Glu) 7.619 半胱氨酸(Cys) 0.970 甘氨酸(Gly) 1.468 酪氨酸(Tyr) 0.750 苏氨酸(Thr) 0.944 精氨酸(Arg) 1.236 脯氨酸(Pro) 2.027 苯丙氨酸(Phe) 0.754 异亮氨酸(Ile) 0.716 氨(NH3) 0.865 总和 29.321 表 6 玉米低聚肽螯合铁(II)相对分子量分布
Table 6 Molecular weight distribution of iron (II)-chelating corn oligopeptides
相对分子量范围 开始时间(min) 结束时间(min) 重均分子量(u) 峰面积百分比(%) >10000 8.947 13.631 13819 0.1881 5000~10000 13.631 15.041 7006 0.2988 3000~5000 15.041 16.080 3773 0.4432 2000~3000 16.080 16.904 2376 1.0868 1000~2000 16.904 18.314 1320 8.2171 150~1000 18.314 22.173 420 74.8800 150以下 22.173 32.365 74 14.8861 重均分子量 523.4 相对分子质量小于1000 u的水解物
所占比例(%)89.77 -
[1] 范兴亮. 浅谈植物基食品创新与挑战[C]//第三届国际食品安全与营养健康高峰论坛论文集, 2021: 78−83. FAN X L. Talking about the innovation and challenges of plant-based food[C]//Proceedings of the third International Food Safety and Nutrition and Health Summit Forum, 2021: 78−83.
[2] 陈亮, 王雨晴, 冀峰, 等. 玉米低聚肽中焦谷氨酰亮氨酸(pEL)二肽的研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(3):49−52. [CHEN L, WANG Y Q, JI F, et al. Study on pEL dipeptide in corn oligopeptides[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(3):49−52. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.024969 [3] QIN X Y, ZHANG J T, LI G M, et al. Selenium-chelating corn oligopeptide as a potential antioxidant supplement: Investigation of the protein conformational changes and identification of the antioxidant fragment composition[J]. International Journal of Food Engineering,2020,16(4):629−656.
[4] 林峰, 梁锐, 王军波, 等. 玉米低聚肽降血压作用的实验研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2009,35(8):1−4. [LIN F, LIANG R, WANG J B, et al. Experimental study on the effect of corn oligopeptides on lowering blood pressure[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2009,35(8):1−4. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.2009.08.041 [5] LI T T, TIAN Y P, SUN F B, et al. Preparation of high Fischer's ratio corn oligopeptides using directed enzymatic hydrolysis combined with adsorption of aromatic amino acids for efficient liver injury repair[J]. Process Biochemistry,2019,84:60−72. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2019.06.002
[6] WANG Y, SONG X, FENG Y, et al. Changes in peptidomes and Fischer ratios of corn-derived oligopeptides depending on enzyme hydrolysis approaches[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,297(1):1−10.
[7] FENG Z, ZHANG J, YONG L. Corn oligopeptides protect against early alcoholic liver injury in rats[J]. Food & Chemical Toxicology,2012,50(6):2149−2154.
[8] WEI Y, ZANG R X, FANG L, et al. Hypoglycemic effects and biochemical mechanisms of pea oligopeptide on high-fat diet and streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice[J]. Journal of Food Biochemistry,2019,43(2):13055−13065.
[9] 王憬, 刘丹, 冯晓文, 等. 食源性低聚肽的体外消化稳定性研究[J]. 食品科技,2020,45(9):238−247. [WANG J, LIU D, FENG X W, et al. Study on the in vitro digestion stability of food-derived oligopeptides[J]. Food Science and Technology,2020,45(9):238−247. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2020.09.037 [10] ZHANG X G, WANG N, MA G D, et al. Preparation of S-iron-enriched yeast using siderophores and its effect on iron deficiency anemia in rats[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,365:130508. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130508
[11] GUO LD, HARNEDY PA, ZHANG L, et al. In vitro assessment of the multifunctional bioactive potential of Alaska pollock skin collagen following simulated gastrointestinal digestion[J]. J Sci Food Agric,2015,95(7):1514−1520. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.6854
[12] QIAN Y, QI J X, ZHENG Y Y, et al. Synthesis, anticancer activity and mechanism of iron chelator derived from 2,6-diacetylpyridine bis(acylhydrazones)[J]. Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry,2019,193:1−8. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2019.01.003
[13] 王梦莹. 食源性低聚肽铁改善大鼠缺铁性贫血的效果研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2019. WANG M Y. Effect of food-derived oligopeptide iron chelates supplementation on iron deficiencv anemic rats[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2019.
[14] 宋莎莎, 高菲, 任迪峰, 等. 乌鸡肽铁(Ⅱ)螯合物的制备及红外光谱鉴定[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2013,39(6):13−17. [SONG S S, GAO F, REN D F, et al. Preparation and infrared spectroscopy identification of black chicken peptide iron (Ⅱ) chelate[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2013,39(6):13−17. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.2013.06.021 [15] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.124-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品中氨基酸的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.124-2016 National food safety standard. Determination of amino acids in food[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2016.
[16] LIU W Y, LU J, GAO F, et al. Preparation, characterization and identification of calcium-chelating Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) ossein oligopeptides[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2015,241(6):851−860. doi: 10.1007/s00217-015-2510-2
[17] 郭芮, 申亮, 毕诗杰, 等. 红鳍东方鲀鱼皮胶原低聚肽螯合钙工艺优化[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(3):147−152. [GUO R, SHEN L, BI S J, et al. Optimization of process of collagen oligopeptide calcium-chelating of Takifugu rubripes skin[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(3):147−152. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2019.03.024 [18] 丁媛媛, 王莉, 张新霞, 等. 麦胚多肽-钙螯合物制备工艺优化及其结构表征[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(10):215−221. [DING Y Y, WANG L, ZHANG X X, et al. Optimized preparation and structural characterization of calciumchelating polypeptides from wheat germ protein hydrolysate[J]. Food Science,2017,38(10):215−221. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201710036 [19] 胡荣, 郭守立, 马宇熙, 等. 鸡蛋壳超微粉粉体性质及其对谷氨酸螯合钙制备的影响[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(10):251−257. [HU R, GUO S L, MA Y X, et al. Properties of ultra-fine eggshell powder and optimization of preparation of calciumchelating glutamate from it[J]. Food Science,2017,38(10):251−257. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201710041 [20] 原洪, 柴丽琴, 王立霞, 等. 花椒籽肽-铁螯合物的制备及其理化性质[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2018,44(6):164−171. [YUAN H, CHAI L Q, WANG L X, et al. Preparation of iron-chelating peptides of Zanthoxylum bungeanum seed and its physicochemical properties[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2018,44(6):164−171. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.015864 [21] 刘文颖, 冯晓文, 李国明, 等. 牡蛎低聚肽的结构表征及体外抗氧化作用[J]. 中国食品学报,2021,21(12):261−269. [LIU W Y, FENG X W, LI G M, et al. Structure characterization and antioxidant effects in vitro of oyster oligopeptides[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Science,2021,21(12):261−269. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2021.12.028 [22] 张江涛, 张铭皓, 高丽辉, 等. 模拟胃肠道消化对玉米低聚肽抗氧化作用的影响[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2021,40(11):54−61. [ZHANG J T, ZHANG M H, GAO L H, et al. Effects of simulated gastrointestinal digestion on antioxidant activity of corn oligopeptides[J]. Journal of Food and Biotechnology,2021,40(11):54−61. [23] WU W F, LI B F, HOU H, et al. Identification of iron-chelating peptides from pacific cod skin gelatin and the possible binding mode[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2017,35:418−427.
[24] HUANG S L, ZHAO L N, CAI X X, et al. Purification and characterisation of a glutamic acid-containing peptide with calcium binding capacity from whey protein hydrolysate[J]. Journal of Dairy Research,2015,82(1):29−35. doi: 10.1017/S0022029914000715
[25] WANG Y, CUI F Z, ZHAI Y, et al. Investigations of the initial stage of recombinant human-like collagen mineralization[J]. Materials Science & Engineering C-Materials for Biological Applications,2006,26(4):635−638.
[26] CURLEY D M, KUMOSINSKI T F, UNRUH J J, et al. Changes in the Secondary structure of bovine casein by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy: Effects of calcium and temperature[J]. Journal of Dairy Science,1998,81(12):3154−3162.
[27] LIU F R, WANG L, WANG R, et al. Calcium-binding capacity of wheat germ protein hydrolysate and characterization of peptide calcium complex[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2013,61(31):7537−7544. doi: 10.1021/jf401868z
[28] 高敏, 汪建明, 甄灵慧, 等. 牛骨多肽螯合物的制备及结构表征[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(8):256−261. [GAO M, WANG J M, ZHEN L H, et al. Preparation and structural characterization of bovine bone polypeptidecalcium chelate[J]. Food Science,2020,41(8):256−261. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181217-183 [29] 杨玉蓉, 李安平, 钟政昌, 等. 桃仁多肽螯合亚铁的抑菌活性及结构表征[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(5):57−62. [YANG Y R, LI A P, ZHONG Z C, et al. Antibacterial activity and structural characterization of peach kernel peptide-ferrous chelate[J]. Food Science,2019,40(5):57−62. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20180201-006 [30] 周名洋, 何雨欣, 孙杨赢, 等. 鹅骨胶原蛋白钙螯合肽的分离纯化及结构鉴定[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(22):8−14. [ZHOU M Y, HE Y X, SUN Y Y, et al. Isolation, purifification and structural identifification of calcium-chelating peptides from goose bone collagen hydrolysate[J]. Food Science,2020,41(22):8−14. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200201-004 [31] 王孟丽, 布冠好. 肽与金属离子螯合物的研究进展[J]. 食品工业,2021,42(5):323−326. [WANG M L, BU G H. The research progress of peptide and metal ion chelate[J]. Food Industry,2021,42(5):323−326. [32] WANG X, GAO A, CHEN Y, et al. Preparation of cucumber seed peptide-calcium chelate by liquid state fermentation and its characterization[J]. Food Chemistry,2017,229:487−494. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.02.121
[33] ZHU C, SUN Y, WANG Y, et al. The preparation and characterization of novel human-like collagen metal chelates[J]. Materials Science & Engineering C,2013,33(5):2611−2619.
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(2)







 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



