Optimization of the Preparation Process of Phosphorylated Soybean Polypeptide Chelated Calcium and Its Effect on the Activity of Osteoblasts
-
摘要: 为了探究磷酸化大豆多肽螯合钙(PSPCC)的生理活性,提高磷酸化大豆多肽螯合钙的钙螯合量,本研究通过单因素实验和响应面试验相结合的方式优化磷酸化大豆多肽螯合钙的制备工艺,并通过体外实验评价了磷酸化大豆多肽螯合钙对成骨细胞的活性影响。结果表明,制备磷酸化大豆多肽螯合钙的最佳工艺条件为:三聚磷酸钠与大豆多肽的质量比1:2,磷酸化反应温度52 ℃,磷酸化反应pH7.0,磷酸化反应时间9.7 h,磷酸化大豆多肽与氯化钙的质量比2:1,螯合反应pH8.0,螯合反应温度50 ℃,螯合反应时间1.5 h,钙螯合量最大为107.25±0.10 mg/g;MTT法结果显示,磷酸化大豆多肽螯合钙组(D组)成骨细胞相对增殖率是大豆多肽组(A组)的1.6倍(第3 d);ALP染色实验表明,D组染色阳性率是空白组的33.6倍。采用ALP试剂盒对各样品第7 d的ALP活性进行检测,结果显示D组ALP活力是空白组的6.2倍。通过茜素红染色实验发现,D组钙结节数量是空白组的94倍。本研究使用响应面法对磷酸化大豆多肽螯合钙的制备工艺优化合理,并初步证明了磷酸化大豆多肽螯合钙对成骨细胞具有显著的促增殖、分化作用(P<0.05),且作用效果高于其它样品,为后续磷酸化大豆多肽螯合钙的进一步开发利用提供了一定的理论基础。Abstract: This study aimed to explore the physiological activity of phosphorylated soybean polypeptide chelated calcium (PSPCC) and improve its calcium chelation capacity. To be specific, the preparation process of PSPCC was optimized by single factor test and response surface methodology. And the effect of phosphorylated soybean peptide chelated calcium on osteoblast activity was evaluated by in vitro experiments. The results showed that, the optimum process of PSPCC was as follows: Mass ratio of sodium tripolyphosphate to soybean polypeptide 1:2, phosphorylation reaction temperature 52 ℃, phosphorylation reaction pH7.0, phosphorylation reaction time 9.7 h, mass ratio of phosphorylated soybean polypeptide to calcium chloride 2:1, chelation reaction pH8.0, chelation reaction temperature 50 °C, and chelation reaction time 1.5 h. The maximum calcium chelation amount of PSPCC was 107.25±0.10 mg/g under the above optimal conditions. The results of MTT assay showed that the relative proliferation rate of osteoblasts in the PSPCC group (group D) was 1.6 times that of the soybean polypeptide group (group A) (the third day). In particular, the ALP staining experiment showed that the positive rate of staining in group D was 33.6 times that of the blank group. In addition, the ALP activity of each sample was detected by the ALP kit on the 7th day, and the results showed that the ALP activity of the group D was 6.2 times that of the blank group. And it was found that the number of calcium nodules in the group D was 94 times higher than that of the blank group through the alizarin red staining experiment. It was reasonable that the preparation process of PSPCC was optimized by response surface methodology, which was preliminarily proved that PSPCC had a significant effect on promoting proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts (P<0.05), and the effect of PSPCC on promoting proliferation and differentiation was higher than that of other samples. This result could provide a theoretical basis for the further exploitation and utilization of PSPCC.
-
Keywords:
- soybean peptides /
- phosphorylation /
- chelated calcium /
- osteoblast /
- functional activity
-
大豆(Glycine max(Linn.)Merr.)是豆科大豆属一年生草本植物,广泛种植于我国的东北、华北等地域[1]。大豆的精深加工过程中会产生大量的大豆分离蛋白粉,由于其具有良好的凝胶性能常被用于提高米面制品的品质[2]。目前,对大豆分离蛋白粉的进一步开发应用主要表现在制备大豆分离蛋白多肽上[3-4]。有研究表明大豆多肽具有较好的降血糖、抗氧化、抗癌、促进骨细胞增殖等作用,具有较高的经济价值[5-6]。
钙是人体必需的常量元素,它参与生物体的神经传递、激素释放和渗透压调节等生命活动[7]。缺钙影响儿童正常的生长发育,还会加大中老年人患骨质软化症、骨质疏松症的风险。我国人民习惯摄入植物性食物,但其中的草酸、植酸会限制钙的吸收[8]。近年来有研究表明,以无机钙和有机钙为原料的第一、第二代补钙制剂具有吸收率差、生物利用率低等缺陷,而将蛋白质酶解成多肽后与钙离子螯合形成的第三代多肽螯合钙制剂具有水溶性好、生物利用率高和钙吸收能力强等特点[9-11]。王思远等[12]以蚕蛹为原料,经过粉碎、脱脂、酶解、螯合以及冷冻干燥等工序制备蚕蛹多肽螯合钙,发现其在胃肠道环境中释放率远远高于碳酸钙和葡萄糖酸钙,具有较高的消化稳定性。Guo等[13]以鱼鳞为原料,经过酸解、超滤、螯合钙等工序制备鱼鳞胶原多肽螯合钙,证明其能显著提高小鼠的股骨骨密度。然而多肽螯合钙负载的钙离子含量较少,人体摄入量较少时不能起到较强的补钙作用[14]。磷酸化修饰改性能引入大量的电负离子,从而增强与钙离子的螯合能力,明显提高补钙制剂中的钙含量[15]。
目前,已有以动物为原料来源制备磷酸化胶原多肽螯合钙的研究报道,但本课题组尚未发现有以大豆分离蛋白粉为原料来源制备磷酸化大豆多肽螯合钙的相关研究,且对其生物活性尚不清楚[16]。本实验以单因素实验筛选出对三聚磷酸钠与大豆多肽磷酸化程度影响较大的因素,再利用Box-Behnken试验对磷酸化大豆多肽的制备工艺进行优化研究,以使大豆多肽获得较为合适的磷酸化程度。最后,制备出磷酸化大豆多肽螯合钙,以验证其生物活性,为大豆延长加工链条和高效应用提供参考依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
大豆分离蛋白粉(纯度≥90%) 深圳乐芙生物科技有限公司;木瓜蛋白酶(批号:9001-73-4,蛋白酶活力≥800 U/mg)、中性蛋白酶(批号:327T011,蛋白酶活力≥50U/mg)、PBS缓冲液 索莱宝科技有限公司;胎牛血清、胰酶、碱性磷酸酶(ALP)检测试剂盒、茜素红染液 Sigma有限公司;人成骨细胞 北京安诺伦生物科技有限公司;碱性磷酸酶(ALP)染色试剂盒 北京伊塔生物科技有限公司;超滤膜 上海善然生物科技有限公司;三聚磷酸钠、葡萄糖酸钙、MTT溶液 阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司。
TU-1901紫外可见分光光度计 北京普析通用有限公司;AB135-S分析天平 梅特勒-托利多公司;RM2016病理切片机 上海徕卡仪器有限公司;Synergy H1多功能酶标仪 美国Biotek公司;Mshot MSX2成像系统 广州市明美光电技术有限公司;ZA3000原子吸收分光光度计 日本日立公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品制备工艺流程
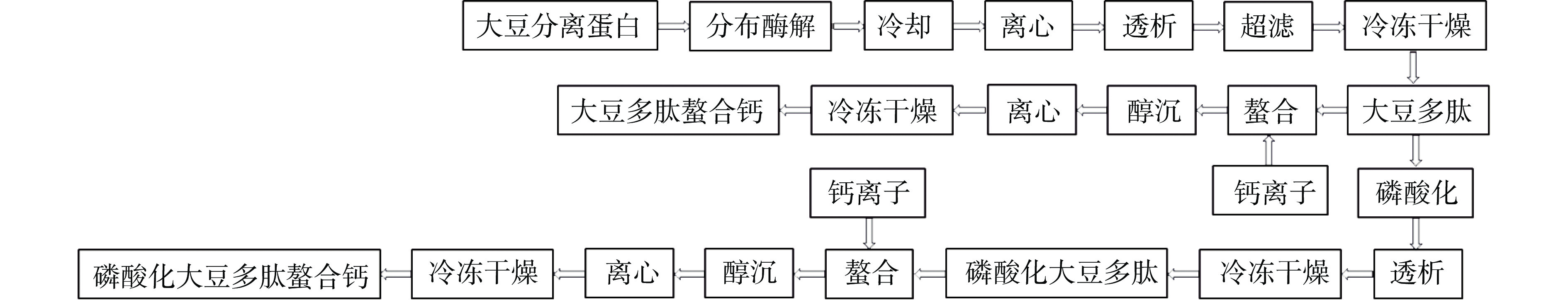
大豆多肽、大豆多肽螯合钙、磷酸化大豆多肽和磷酸化大豆多肽螯合钙的制备工艺流程图如图1所示。
1.2.2 操作要点
1.2.2.1 大豆多肽的制备
参考李宇等[6]的方法制备大豆多肽,首先精确称取35 g大豆分离蛋白粉和0.175 g木瓜蛋白酶,加入到20倍体积的纯净水中,混匀,水浴升温至55 ℃,使用0.1 mol/L的氢氧化钠调节pH至7.0±0.5并保持酶解液pH稳定,酶解3 h,然后将反应体系降温至45 ℃并加入0.35 g的中性蛋白酶,反应2 h,升温至95 ℃灭活蛋白酶20 min,冷却至室温后在8000 r/min的条件下离心15 min,取上清液,透析除盐,并过分子量30 kD的超滤膜,收集透过液,冷冻干燥得到大豆多肽。
1.2.2.2 大豆多肽螯合钙的制备
取1.2.2.1项中的大豆多肽完全溶解于去离子水中,并根据本课题组预实验得到的螯合钙最佳工艺条件进行钙离子螯合,大豆多肽与氯化钙的质量比为2:1,反应pH为8.0,反应温度为50℃,反应时间为1.5 h。最后加入10倍体积的无水乙醇沉淀,在8000 r/min的条件下离心15 min并取出沉淀,冷冻干燥得到大豆多肽螯合钙。
1.2.2.3 磷酸化大豆多肽和磷酸化大豆多肽螯合钙的制备
取1.0 g 1.2.2.1项中的大豆多肽溶解于10 mL去离子水中,加入适量的三聚磷酸钠,调节pH为6.0,50 ℃恒温水浴反应8 h,反应后在4 ℃的纯水中透析24 h以除去游离的磷酸盐,然后冷冻干燥成磷酸化大豆多肽粉,并根据本课题组预实验得到的螯合钙最佳工艺条件进行钙离子螯合,最优螯合条件为磷酸化大豆多肽与氯化钙的质量比为2:1,反应pH为8.0,反应温度为50 ℃,反应时间为1.5 h。最后加入10倍体积的无水乙醇沉淀,离心并取出沉淀,冷冻干燥得到磷酸化大豆多肽螯合钙。
1.2.3 不同磷酸化条件对钙螯合量的影响
1.2.3.1 单因素实验
精确称取1.0 g大豆多肽,设定三聚磷酸钠与大豆多肽的质量比1:2,反应温度50 ℃,反应时间11 h,反应pH7为磷酸化大豆多肽单因素实验过程中的常规变量,以三聚磷酸钠与大豆多肽的质量比(1:3、1:2、1:1、2:1、3:1),反应温度(30、40、50、60、70 ℃),反应时间(5、7、9、11、13 h),反应pH(4、5、6、7、8)四个变量代替单因素实验中的相应常规变量,并将得到的磷酸化大豆多肽与氯化钙在质量比为2:1,反应pH为8.0,反应温度为50 ℃,反应时间为1.5 h条件下反应。反应结束后加入10倍体积的无水乙醇沉淀,离心并取出沉淀,冷冻干燥得到磷酸化大豆多肽螯合钙,测定钙螯合量。
1.2.3.2 响应面试验优化磷酸化大豆多肽的制备工艺
依据单因素实验的结果,选取反应温度(A)、反应时间(B)和反应pH(C)为自变量,设定钙螯合量(Y)为响应值,进行三因素三水平响应面优化试验,实验设计表如表1所示。
表 1 磷酸化大豆多肽的制备工艺响应面试验设计因素与水平Table 1. Design factors and levels of response surface methodology for the preparation of phosphorylated soybean polypeptides水平 A反应温度(℃) B反应时间(h) C反应pH −1 60 11 7 0 50 9 6 1 40 7 5 1.2.4 钙螯合量的测定
使用原子吸收分光光度计测定磷酸化大豆多肽螯合钙中的钙含量,并计算钙螯合量。钙螯合量按公式1计算:
$$ \text{Y}=\frac{\text{A}}{\text{B}} $$ (1) 式中:Y:供试品的钙螯合量(mg/g);A:供试品的含钙量(mg);B:供试品的质量(g)。
1.2.5 细胞活性实验
1.2.5.1 人成骨细胞的培养和传代
参考Brezulier等[17]方法,首先将冻存的人成骨细胞(6×103 cells/cm2)在37 ℃条件下解冻后接种于装有DMEM-F12培养基的离心管中,加入质量分数10%的胎牛血清和1%的抗生素(100 U/mL 青霉素:100 µg/mL 链霉素=1:1),然后以1000 r/min的转速离心2 min,将上清液在无菌条件下弃去后再次加入新鲜的DMEM-F12培养基混悬,最后取适量的细胞悬液转入无菌培养瓶中在37 ℃的细胞培养箱(内含5% CO2)中培养。当细胞融合后,使用乙二胺四乙酸脱落,再次进行离心、混悬和传代,每隔1 d更换培养基,观察培养瓶中成骨细胞的生长状态。
1.2.5.2 MTT比色法检测人成骨细胞相对增殖率
参考Muralidharan等[18]的方法,使用乙二胺四乙酸将传代后的人成骨细胞消化,然后1000 r/min离心5 min,混悬配制成细胞悬液并接种于96孔细胞培养板上(1×104 cells/well)。在细胞培养箱(37 ℃、5% CO2)中培养24 h后,加入浓度为40 µg/mL的大豆多肽(样品A)、磷酸化大豆多肽(样品B)、大豆多肽螯合钙(样品C)、磷酸化大豆多肽螯合钙(样品D)和葡萄糖酸钙(样品E,钙含量10 mg/mL),用不加样品的培养基处理的细胞作为对照组,PBS缓冲液作为空白组。然后继续培养,在样品加入后的5 d内,每隔1 d分别取出细胞培养板,在每孔中加入15 µL的MTT溶液,最后继续培养5 h后取出培养板使用酶标仪在450 nm处测定吸光度。人成骨细胞相对增殖率按式(2)计算:
$$ \text{人成骨细胞相对增殖率}(\text{%})=\frac{{\text{OD}}_{\text{实验组}}-{\text{OD}}_{\text{空白组}}}{{\text{OD}}_{\text{对照组}}-{\text{OD}}_{\text{空白组}}}\text{×100} $$ (2) 1.2.5.3 ALP染色实验
将对数生长期的人成骨细胞接种到无菌细胞培养板上,培养一段时间,待细胞贴壁生长时分别加入样品A、样品B、样品C、样品D和样品E,然后继续在细胞培养箱中培养96 h后使用ALP染色试剂盒进行染色,并观察染色情况。
1.2.5.4 人成骨细胞ALP活性检测
将传代后的人成骨细胞消化、离心、混悬配制成细胞悬液并接种于96孔细胞培养板上(1×104 cells/well)。在细胞培养箱(37 ℃、5% CO2)中培养24 h后,加入浓度为40 µg/mL的大豆多肽(样品A组)、磷酸化大豆多肽(样品B组)、大豆多肽螯合钙(样品C组)、磷酸化大豆多肽螯合钙(样品D组)和葡萄糖酸钙(样品E组,钙含量10 mg/mL),用不加样品的培养基处理的细胞作为对照组,PBS缓冲液作为空白组。当细胞培养第7 d、第14 d时使用ALP活性检测试剂盒检测各样品组细胞的ALP活性。
1.2.5.5 茜素红染色实验
参考郑家强等[19]的方法并根据预实验结果进行茜素红染色实验。首先,在每个样品的平行组中选取细胞相对增殖活性和ALP活性相对较强的组,与空白组一起,将细胞按1×105 cells/well的浓度接种到细胞培养板上,培养24 h后,将培养基换成完全培养基(10%胎牛血清和成骨诱导液)。细胞继续在培养箱中培养14 d后,进行茜素红染色,并使用光学显微镜观察和采集图像。
1.3 数据处理
本实验使用Origin8.6进行图形绘制,Design-Expert V8.0.6软件进行响应面优化试验设计与结果分析,SPASS 22.0软件进行显著性分析和多重比较(t检验),P<0.05说明有显著性差异。所有试验重复3次用平均值±标准偏差
$ \text{(}\overline{\text{x}}\text{±s}\text{)} $ 表示。2. 结果与分析
2.1 磷酸化大豆多肽螯合钙单因素实验结果
2.1.1 三聚磷酸钠与大豆多肽的质量比对钙螯合量的影响
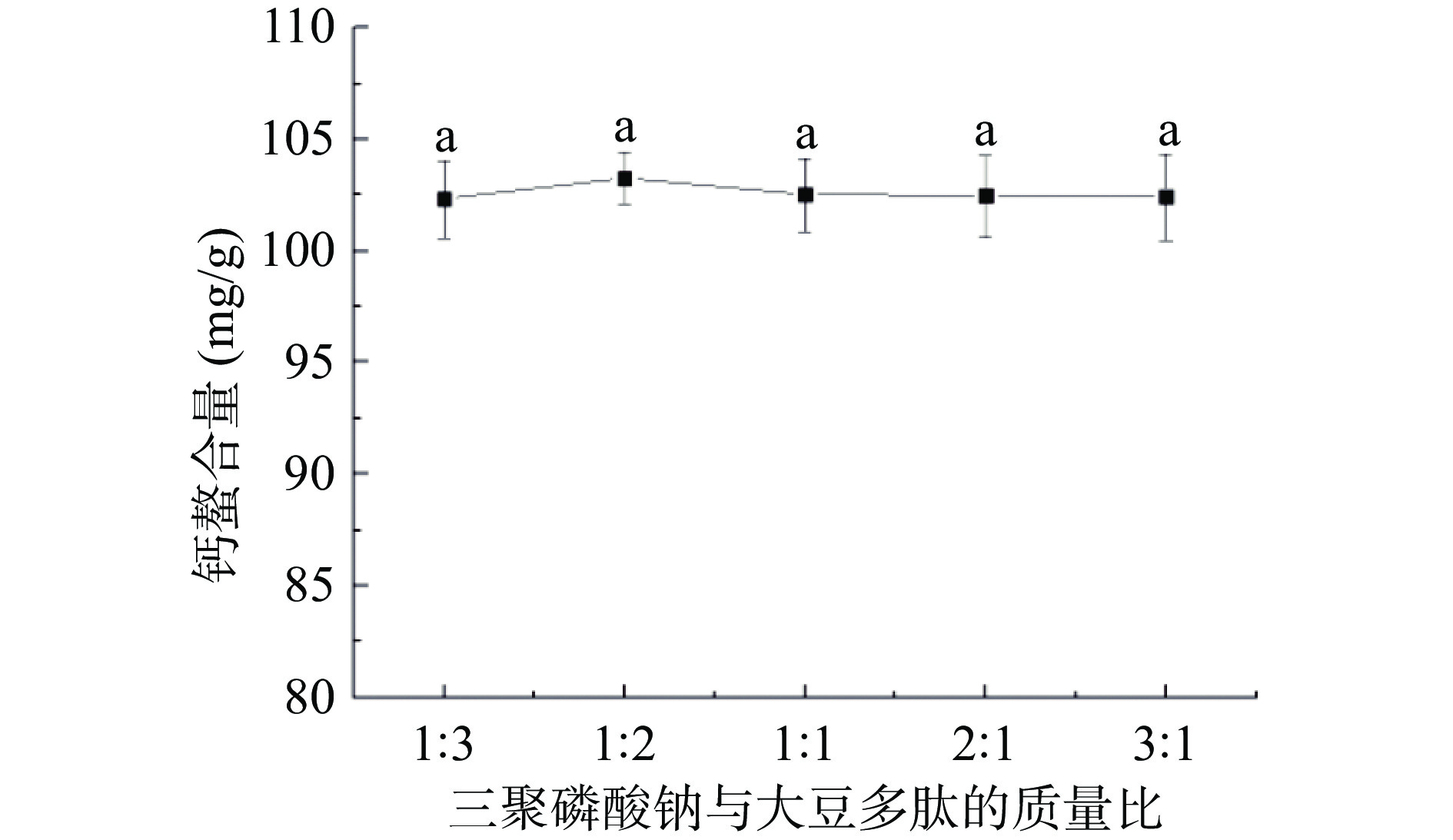
实验结果如图2所示,钙螯合量随着三聚磷酸钠与大豆多肽的质量比的升高,呈现先升高后下降的趋势,但整体效果并不显著(P>0.05)。当三聚磷酸钠与大豆多肽的质量比较小时,磷酸根离子含量过低,大豆多肽未达到最高的钙螯合程度,当三聚磷酸钠与大豆多肽的质量比达到1:2时,磷酸根离子对大豆多肽进行最大程度的改性,螯合到最多的钙离子。当磷酸根离子浓度继续增加时,磷酸根离子在反应体系中处于过饱和状态,使空间位阻强度达到最大,降低了磷酸根离子的改性程度,从而使钙螯合量减小[20]。因此,三聚磷酸钠与大豆多肽的质量比对钙螯合量的影响不显著(P>0.05),考虑到生产成本,选择三聚磷酸钠与大豆多肽的质量比1:2作为反应条件最为合理。
2.1.2 反应温度对钙螯合量的影响
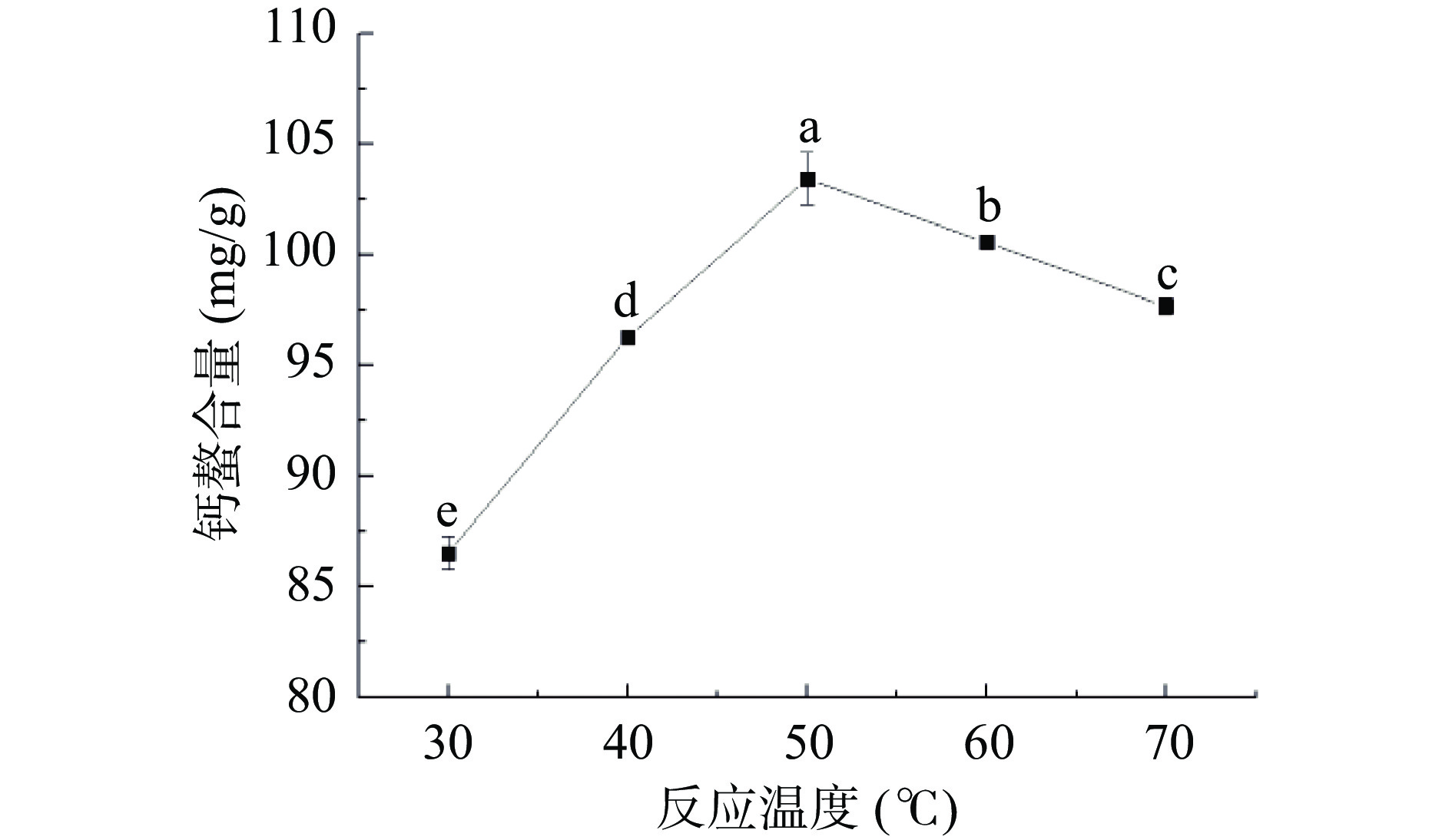
分析图3可知,钙螯合量随着反应温度的提高呈现先升高后降低的趋势,并在50 ℃时达到最高值。温度升高使体系能量变大,提高了大豆多肽、磷酸根离子与钙离子的碰撞机率,增加了单位质量大豆多肽的钙螯合量。当温度高于50 ℃时钙螯合量下降,这可能是因为温度过高使多肽发生了部分变性,从而降低了单位质量大豆多肽的钙螯合量[21]。因此,后续优化试验选择反应温度50 ℃为宜。
2.1.3 反应时间对钙螯合量的影响
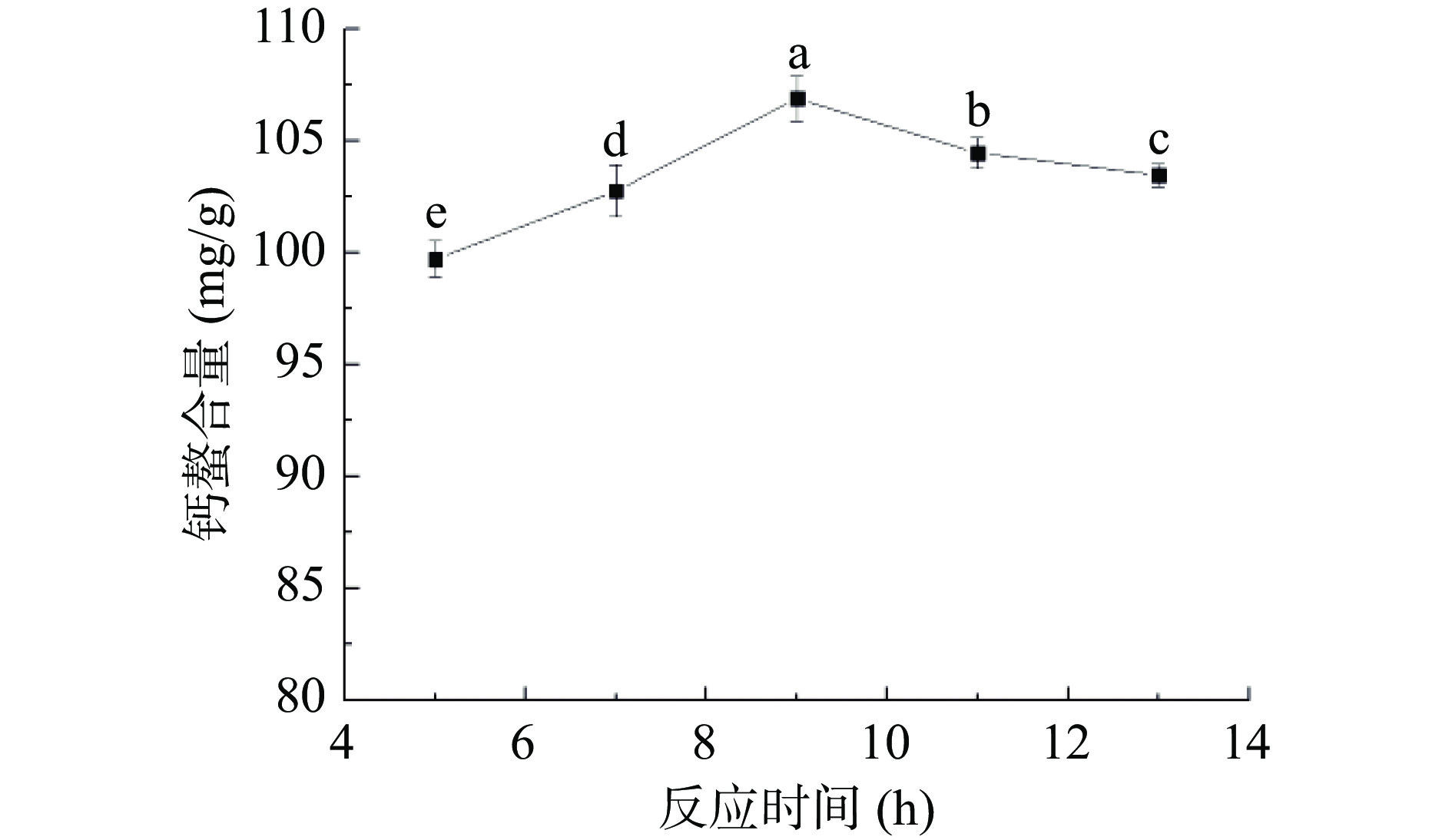
由图4可知,随着反应时间的延长,钙螯合量呈现先升高后降低的现象,在第9 h时钙螯合量达到最大值。随着反应时间的延长,大豆多肽的磷酸化改性程度提高,钙螯合量变大,当反应时间继续延长时,钙螯合量反而下降,这可能是因为磷酸化改性过程伴随着副反应的发生,产生的副产物会阻碍大豆多肽、磷酸根离子和钙离子螯合[22]。因此,选择反应时间9 h最为合适。
2.1.4 反应pH对钙螯合量的影响
由图5可以看出,pH的变化对钙螯合量有显著的影响(P<0.05)。当pH在4~6时,随着pH的增加钙螯合量变大,当pH为6时,钙螯合量最大,当pH继续增加时,钙螯合量逐渐下降。这是因为酸性反应体系,有利于多肽链上氨基酸的羟基易与磷酸根离子形成C-O-P-结构,且pH=6时形成的结构稳定性最强,从而使钙螯合量最高[23]。
2.2 Box-Benhnken试验优化分析
2.2.1 响应面多元回归方程的建立
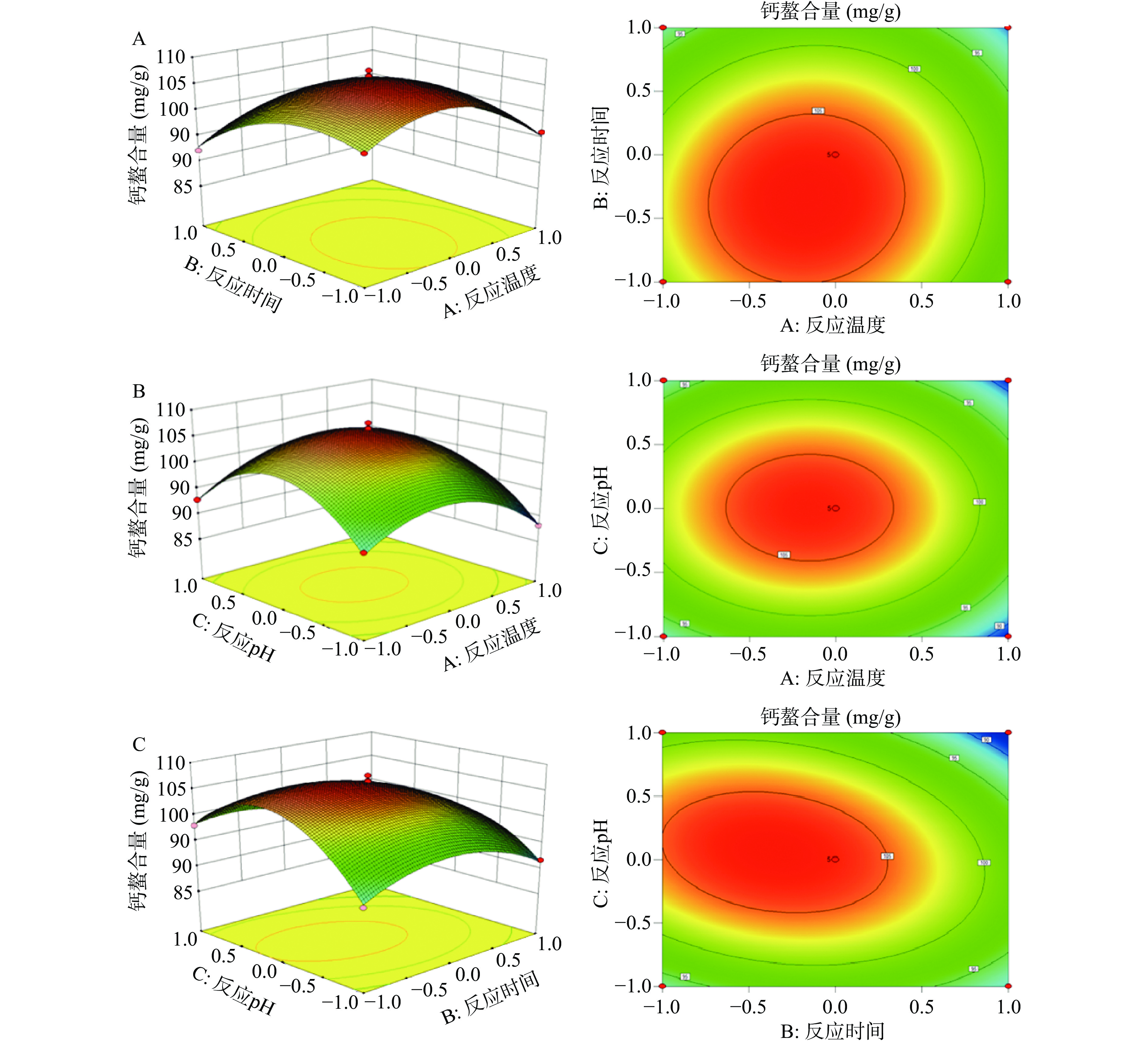
使用Design-Expert V8.0.6软件对表2中的响应面数值与被预测变量之间的相互关系进行多元回归方程拟合分析。获得两个因素之间的交互作用对钙螯合量影响的等高线图和3D立体响应面图(见图3),并获得以钙螯合量为目标的二元多次回归方程模型公式为:Y=106.44800−2.06250A−3.32625B+0.14875C+0.61250AB−(2.50000E−003)AC−2.57000BC−6.78400A2−4.95150B2−9.24650C2。
表 2 磷酸化大豆多肽的制备工艺响应面优化方案及结果Table 2. Optimization scheme and results of response surface methodology for the preparation of phosphorylated soybean polypeptides实验号 A反应温度 B反应时间 C反应pH Y钙螯合量(mg/g) 1 0 0 0 107.72 2 0 0 0 106.22 3 1 0 −1 88.05 4 0 0 0 106.54 5 0 −1 1 98.01 6 −1 −1 0 100.84 7 1 1 0 89.81 8 1 0 1 88.04 9 1 −1 0 96.11 10 0 1 −1 91.63 11 −1 1 0 92.09 12 0 0 0 105.05 13 −1 0 1 92.79 14 0 −1 −1 92.27 15 0 1 1 87.09 16 0 0 0 106.71 17 −1 0 −1 92.79 2.2.2 响应面方差分析
进一步利用响应面软件对模型进行方差分析和显著性检验以验证该模型的有效性,结果如表3所示。
表 3 响应面回归方程模型方差分析Table 3. Analysis of variance of response surface regression equation model来源 偏差平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 878.38 9 97.60 110.62 <0.0001 * A 34.03 1 34.03 38.57 0.0004 * B 88.51 1 88.51 100.32 <0.0001 * C 0.18 1 0.18 0.20 0.6677 AB 1.50 1 1.50 1.70 0.2334 AC 2.500E-005 1 2.500E-005 2.834E-005 0.9959 BC 26.42 1 26.42 29.95 0.0009 * A2 193.78 1 193.78 219.64 <0.0001 * B2 103.23 1 103.23 117.01 <0.0001 * C2 359.99 1 359.99 408.03 <0.0001 * 残差 6.18 7 0.88 失拟项 2.47 3 0.82 0.89 0.5184 纯误差 3.70 4 0.93 总和 884.55 16 注:R2=99.30%,RAdj2=98.40%;*表示有显著性差异(P<0.05)。 从表3可以看出,多元回归方程模型中P<0.05,另外失拟项P=0.5184>0.05,说明得到的多元回归方程模型具有较高的拟合度,可以用来优化磷酸化大豆多肽的制备工艺[24]。另外,该模型的响应值决定系数为R2=0.9930,说明钙螯合量有99.30%的变化可以通过该模型进行解释。该模型的调整系数RAdj2=0.9840,说明该模型的拟合度较好。因此,该模型可以用于优化磷酸化大豆多肽的制备工艺。表3中A与B的P值均小于0.05,而C的P值大于0.05,说明影响钙螯合量的主要因素是反应时间和反应温度,而反应pH对钙螯合量的影响较小[25]。由图6可知,AB、AC各项之间的交互作用等高曲线接近于圆形,而BC各项之间的交互作用等高曲线接近于椭圆形,这说明BC各项的交互作用比AB、AC各项之间的交互作用更加明显[26]。同时,表3中的方差分析结果也表明BC之间的交互作用对响应值的影响显著(P<0.05),AB、AC之间的交互作用对响应值的影响不显著(P>0.05),与等高曲线的分析结果一致。由此模型预测出磷酸化大豆多肽的最佳制备工艺为反应时间9.72 h,反应温度51.68 ℃,反应pH为6.94,在此基础上,预测钙螯合量最高为107.23 mg/g。
结合实际生产情况,并结合反应时间9.7 h,反应温度52 ℃,反应pH为7.0进行三次平行验证实验,得到钙螯合量的平均值为107.25±0.10 mg/g,与多元回归方程模型得到的预测值无明显差异。孙博[27]以玉米黄粉为原料,通过提取、纯化、酶解、超滤以及螯合钙等工艺得到玉米多肽螯合钙,其钙螯合量(77.2 mg/g)低于本实验制得的磷酸化大豆多肽螯合钙,表明磷酸化大豆多肽螯合钙具有较高的钙含量。因此,磷酸化大豆多肽螯合钙具有一定的市场应用价值。
2.3 细胞活性分析
2.3.1 各样品对人成骨细胞相对增殖率的影响
磷酸化对成骨细胞具有调控作用,可调节成骨细胞和破骨细胞之间的平衡,降低成骨细胞凋亡水平[28]。图7是不同样品组对人成骨细胞相对增殖率的影响趋势图。分析图中结果可知,所有样品组均表现出对人成骨细胞具有促增殖的作用。各组样品从第1 d开始,细胞相对增殖率均呈现先升高后减低的趋势,A组、B组、C组和D组均在第3 d出现拐点,E组 在第4 d出现拐点,这是因为随着时间的延长,细胞的代谢能力和样品的作用效果开始减弱,从而导致相对增殖率下降。对各组样品的细胞相对增殖率进行比较,发现第3 d时A组和E组的细胞相对增殖率无显著性差异(P<0.05),B组、C组和D组的细胞相对增殖率是A组和E组1.13~1.67倍。从整体来看,各组样品对人成骨细胞的相对增殖能力强弱顺序为D组>C组>E组>B组>A组,这可能是因为磷酸化降低了成骨细胞凋亡速率,从而导致B组细胞相对增殖率高于A组。同时,多肽螯合钙能刺激细胞,提高细胞增殖能力,且提升程度与钙离子浓度成正相关,磷酸化多肽螯合钙增加了多肽的单位含钙量,所以细胞相对增殖率D组>C组>E组,这与刘闪等[29]的研究结果相似。
2.3.2 ALP染色分析
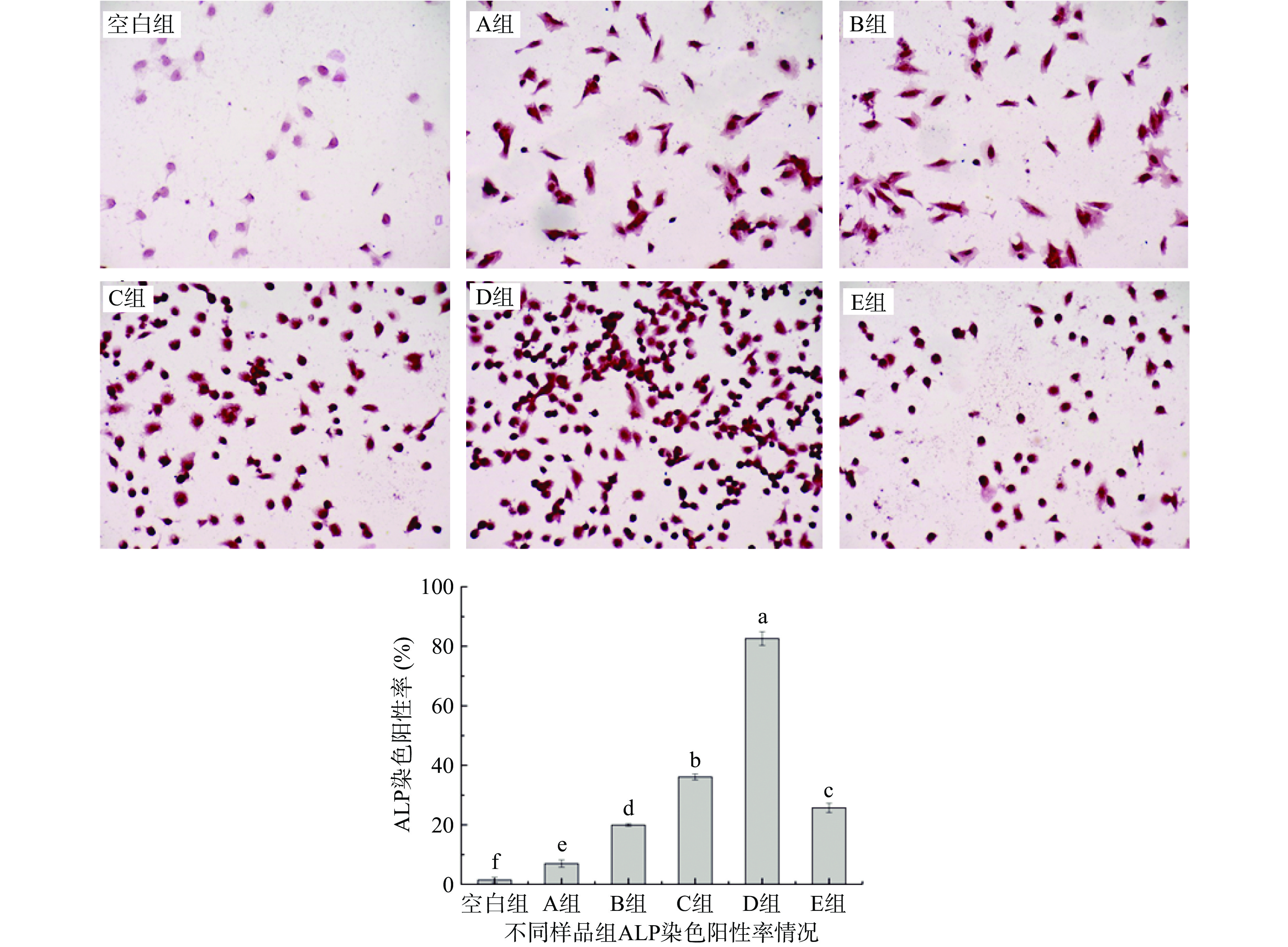
碱性磷酸酶(ALP)是人成骨细胞早期分化过程中产生的标志性产物,它代表着骨钙化的程度[30]。图8反映了在加样96 h后,不同样品组的ALP染色和ALP染色阳性率情况。由图8可知,各样品组与人成骨细胞作用后均呈现阳性反应,但染色阳性率有明显的差异性(P<0.05),空白组的染色程度较低,D组(磷酸化大豆多肽螯合钙)的染色程度最高,这可能是因为成骨细胞的分化程度与其作用的钙浓度有关,磷酸化大豆多肽螯合钙对人成骨细胞具有最强的促分化能力,所以导致各组样品的ALP染色阳性率呈现D组>C组>E组>B组>A组。
![]() 图 8 不同样品组的ALP染色图和ALP染色阳性率图注:不同字母表示组内存在显著性差异(P<0.05);图9同。Figure 8. ALP staining chart and ALP staining positive rate chart of different sample groups
图 8 不同样品组的ALP染色图和ALP染色阳性率图注:不同字母表示组内存在显著性差异(P<0.05);图9同。Figure 8. ALP staining chart and ALP staining positive rate chart of different sample groups2.3.3 ALP活性分析
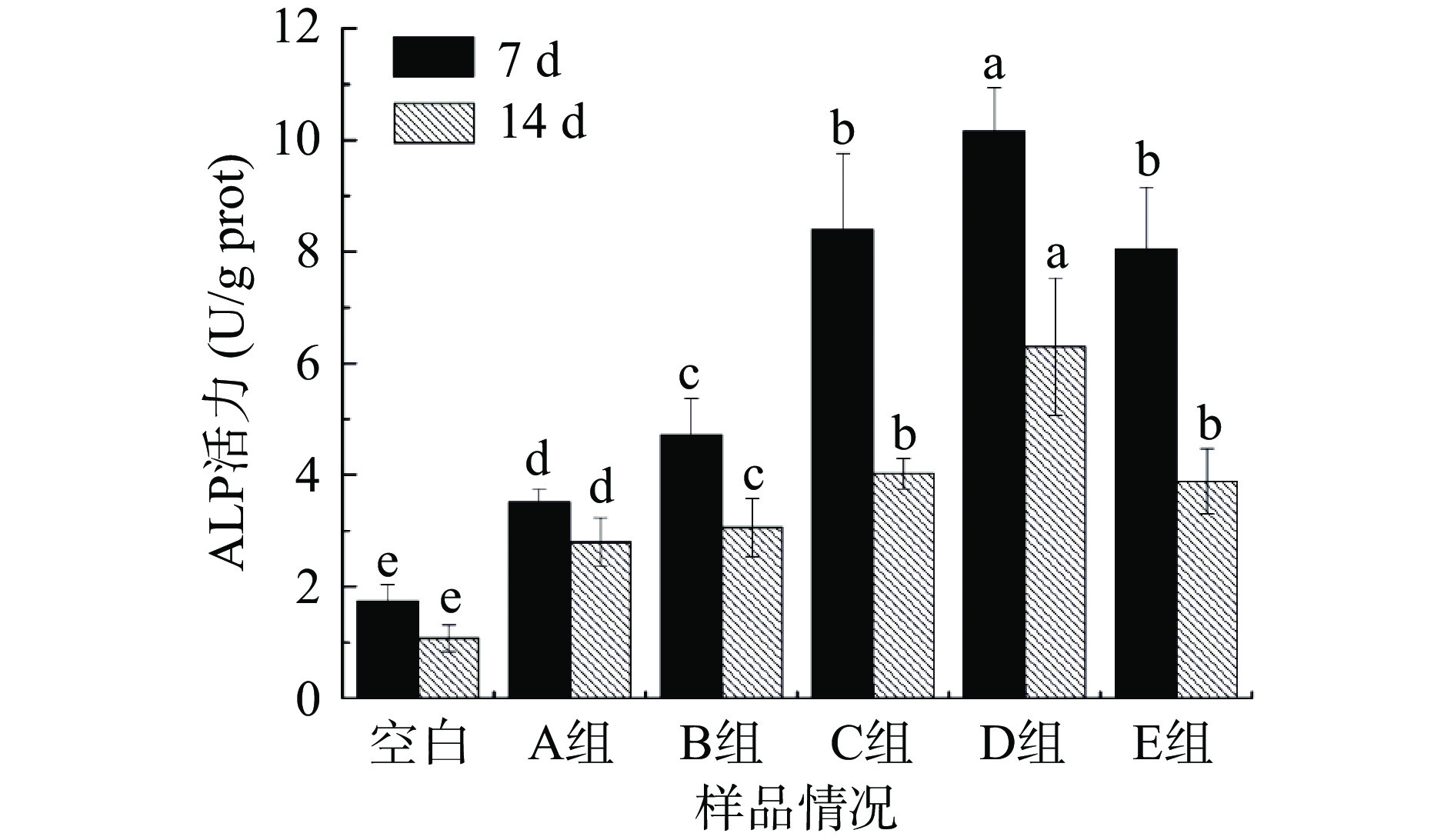
在加入各组样品处理7 d和14 d后人成骨细胞的ALP活性如图9所示。ALP活力值越高,表明人成骨细胞的分化能力越强[31]。从图9中可知,空白组和样品组均表现出一定的ALP活性,且样品组的ALP活力明显高于空白组(P<0.05),其中D组的促分化能力最强,而C组和E组没有显著性差异(P>0.05)。第7 d时,各样品组的ALP活力是空白组的2.2倍以上,这可能是因为磷酸化修饰和钙离子的引入能提高细胞ALP活力,促进成骨细胞分化。在所有组中,第14 d的ALP活力整体低于第7 d,这可能是由于碱性磷酸酶是人成骨细胞分化过程中的早期表型标志物,随着分化时间的延长,碱性磷酸酶可以催化骨磷酸单酯的水解,提供与钙结合的无机磷酸盐来调节骨代谢和分化[30]。
2.3.4 茜素红染色实验分析
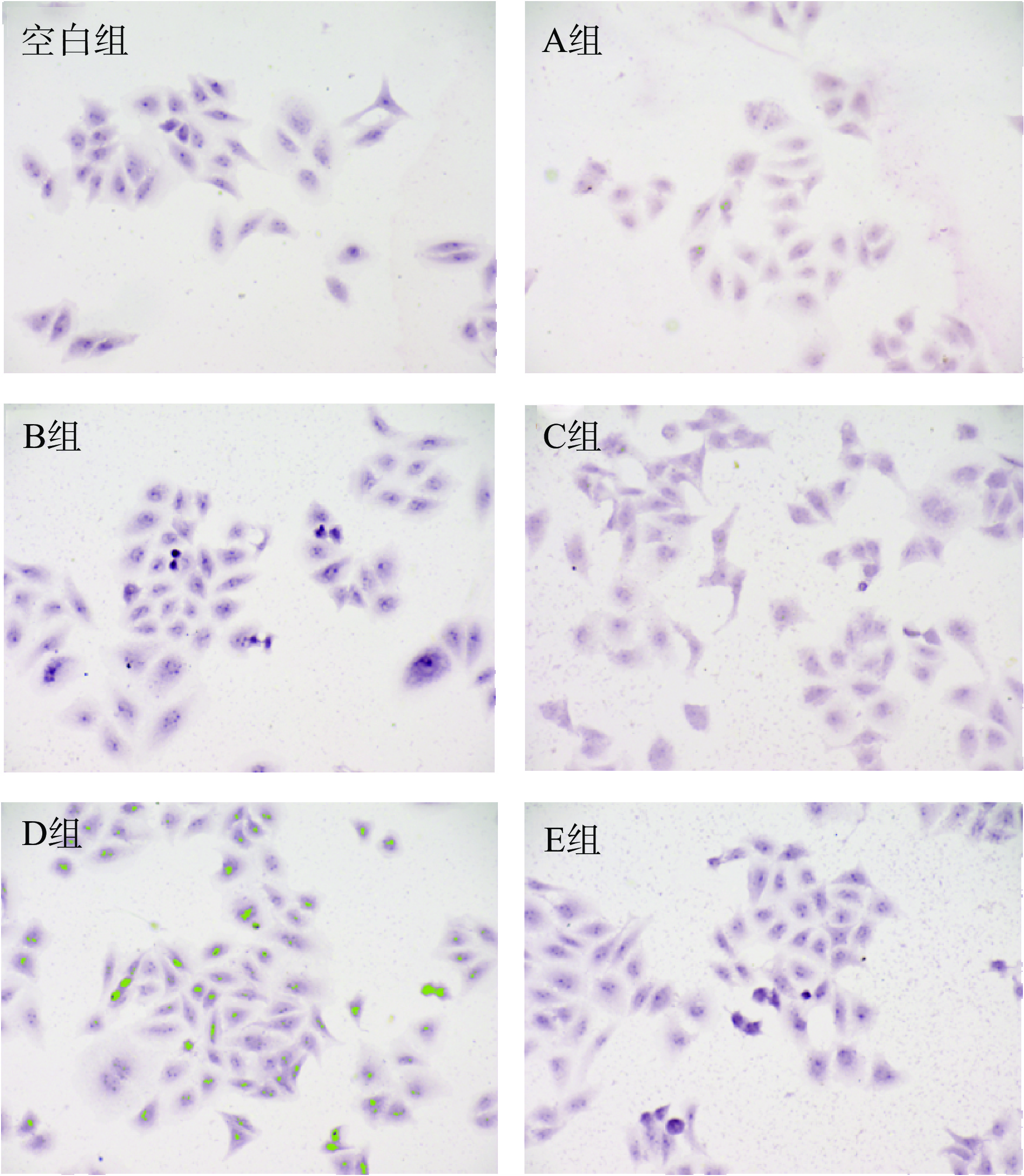
茜素红与钙离子以螯合方式形成复合物,用来识别组织细胞的钙盐成分,通过茜素红染色,产生桔红色沉积(即钙结节),茜素红染色越深表示钙离子沉积越明显,钙结节数量越多,表示向成骨分化能力越高[32]。从表4和图10可以发现,不同样品组中D组钙结节数量最多,C组次之。C组、D组和E组的钙结节数量显著高于A组和B组(P<0.05),这可能是因为样品中的钙离子可以促进钙离子受体和ALP的表达,加速钙结节形成,从而促进人成骨细胞进行增值、分化[31]。因此,钙离子的有效引入,对人成骨细胞的增值、分化具有重要的意义。Wu等[33]将猪骨酶解分别制备猪骨胶原多肽、磷酸化猪骨胶原多肽、猪骨胶原多肽螯合钙以及磷酸化猪骨胶原多肽螯合钙,通过茜素红染色实验分析各样品对成骨细胞MC3T3-E1的增殖、分化作用,证明了各样品中磷酸化猪骨胶原多肽螯合钙具有最高的促增殖、分化作用,这与本实验的研究结果一致。
表 4 不同样品组茜素红染色钙结节计数($\rm \overline{{x}}\pm {s},{n}=3$ )Table 4. Alizarin red staining of calcium nodules in different sample groups ($\rm \overline{{x}}\pm {s},{n}=3$ )组别 钙结节计数(个·孔−1) 空白组 3±1 A组 26±3* B组 77±6* C组 377±30* D组 614±45* E组 282±27* 注:*表示与空白组相比差异显著,P<0.05。 3. 结论
本实验通过单因素实验得到三聚磷酸钠与大豆多肽的质量比、反应温度、反应pH值和反应时间对钙螯合量的影响,并通过Box-Behnken法优化磷酸化大豆多肽螯合钙的制备工艺,得出最佳的制备工艺条件为三聚磷酸钠与大豆多肽的质量比1:2,磷酸化反应温度52 ℃,磷酸化反应pH7.0,磷酸化反应时间9.7 h,磷酸化大豆多肽与氯化钙的质量比2:1,螯合反应pH8.0,螯合反应温度50 ℃,螯合反应时间1.5 h,在此制备工艺条件下钙螯合量最大为107.25±0.10 mg/g。另外,通过检测加样后人成骨细胞的细胞相对增殖率、ALP染色阳性率、ALP活性和钙结节数量,来考察大豆多肽(样品A)、磷酸化大豆多肽(样品B)、大豆多肽螯合钙(样品C)、磷酸化大豆多肽螯合钙(样品D)和葡萄糖酸钙(样品E)对人成骨细胞增殖、分化的影响,结果表明与空白组相比,各样品组对人成骨细胞均有显著促增殖、分化的能力(P<0.05),其中磷酸化大豆多肽螯合钙具有最强的作用效果。这意味着磷酸化大豆多肽螯合钙有望成为一种预防人体骨质疏松的新功能食品原料。本实验为大豆的精深加工和高值化利用指出了一种新方法,提高了大豆原料的附加值。
-
图 8 不同样品组的ALP染色图和ALP染色阳性率图
注:不同字母表示组内存在显著性差异(P<0.05);图9同。
Figure 8. ALP staining chart and ALP staining positive rate chart of different sample groups
表 1 磷酸化大豆多肽的制备工艺响应面试验设计因素与水平
Table 1 Design factors and levels of response surface methodology for the preparation of phosphorylated soybean polypeptides
水平 A反应温度(℃) B反应时间(h) C反应pH −1 60 11 7 0 50 9 6 1 40 7 5 表 2 磷酸化大豆多肽的制备工艺响应面优化方案及结果
Table 2 Optimization scheme and results of response surface methodology for the preparation of phosphorylated soybean polypeptides
实验号 A反应温度 B反应时间 C反应pH Y钙螯合量(mg/g) 1 0 0 0 107.72 2 0 0 0 106.22 3 1 0 −1 88.05 4 0 0 0 106.54 5 0 −1 1 98.01 6 −1 −1 0 100.84 7 1 1 0 89.81 8 1 0 1 88.04 9 1 −1 0 96.11 10 0 1 −1 91.63 11 −1 1 0 92.09 12 0 0 0 105.05 13 −1 0 1 92.79 14 0 −1 −1 92.27 15 0 1 1 87.09 16 0 0 0 106.71 17 −1 0 −1 92.79 表 3 响应面回归方程模型方差分析
Table 3 Analysis of variance of response surface regression equation model
来源 偏差平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 878.38 9 97.60 110.62 <0.0001 * A 34.03 1 34.03 38.57 0.0004 * B 88.51 1 88.51 100.32 <0.0001 * C 0.18 1 0.18 0.20 0.6677 AB 1.50 1 1.50 1.70 0.2334 AC 2.500E-005 1 2.500E-005 2.834E-005 0.9959 BC 26.42 1 26.42 29.95 0.0009 * A2 193.78 1 193.78 219.64 <0.0001 * B2 103.23 1 103.23 117.01 <0.0001 * C2 359.99 1 359.99 408.03 <0.0001 * 残差 6.18 7 0.88 失拟项 2.47 3 0.82 0.89 0.5184 纯误差 3.70 4 0.93 总和 884.55 16 注:R2=99.30%,RAdj2=98.40%;*表示有显著性差异(P<0.05)。 表 4 不同样品组茜素红染色钙结节计数(
¯x±s,n=3 )Table 4 Alizarin red staining of calcium nodules in different sample groups (
¯x±s,n=3 )组别 钙结节计数(个·孔−1) 空白组 3±1 A组 26±3* B组 77±6* C组 377±30* D组 614±45* E组 282±27* 注:*表示与空白组相比差异显著,P<0.05。 -
[1] 刘以晴, 黄亚伟, 王若兰, 等. 大豆储藏过程中浸油赤变的研究进展[J]. 食品科技,2021,46(11):160−165. [LIU Y Q, HUANG Y W, WANG R L, et al. Research progress on red discoloration during storage[J]. Food Science and Technology,2021,46(11):160−165. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2021.11.spkj202111025 [2] 石磊, 王从从, 万守朋, 等. 添加大豆分离蛋白粉新型甜面酱的工艺优化[J]. 食品研究与开发,2018,39(5):126−131. [SHI L, WANG C C, WAN S P, et al. The process optimization of a new type of sweet flour paste with adding soy protein isolate powder[J]. Food Research and Development,2018,39(5):126−131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2018.05.022 [3] YING X, GAO J X, LU J, et al. Preparation and drying of water-in-oil-in-water (W/O/W) double emulsion to encapsulate soy peptides[J]. Food Research International,2021,141:110148. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110148
[4] WEN L R, JIANG Y M, ZHOU X S, et al. Structure identification of soybean peptides and their immunomodulatory activity[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,359:129970. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129970
[5] 王金玲, 王雨淅, 王同, 等. 大豆多肽的制备及功能性研究进展[J]. 中国酿造,2022,41(1):25−31. [WANG J L, WANG Y X, WANG T, et al. Progress on preparation and functionality of soybean polypeptides[J]. China Brewing,2022,41(1):25−31. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2022.01.005 [6] 李宇, 汪芳, 翁泽斌, 等. 酶法制备大豆蛋白成骨活性肽[J]. 中国农业科学,2021,54(13):2885−2894. [LI Y, WANG F, WENG Z B, et al. Preparation of soybean protein-derived pro-osteogenic peptides via enzymatic hydrolysis[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2021,54(13):2885−2894. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2021.13.016 [7] ZHOU J R, GAO G Z, ZHANG S Y, et al. Influences of calcium and magnesium ions on cellular antioxidant activity (CAA) determination[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,320:126625. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126625
[8] HEANEY R P, WEAVER C M, RECKER R R. Calcium absorbability from spinach[J]. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition,1988,47(4):707−709. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/47.4.707
[9] ARICHAYA M, PORNLERT A, SUWIMON K. Chicken foot broth byproduct: A new source for highly effective peptide-calcium chelate[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,345:128713. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128713
[10] ZHANG H R, ZHAO L Y, SHEN Q S, et al. Preparation of cattle bone collagen peptides-calcium chelate and its structural characterization and stability[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2021,144:111264. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111264
[11] 赵梓月, 王思远, 廖森泰, 等. 多肽螯合钙的研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发,2020,41(5):200−206. [ZHAO Z Y, WANG S Y, LIAO S T, et al. Progress in research on peptide chelated calcium[J]. Food Research and Development,2020,41(5):200−206. [12] 王思远, 赵梓月, 穆利霞, 等. 蚕蛹多肽螯合钙的生物可及性研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2019,40(19):47−52. [WANG S Y, ZHAO Z Y, MU L X, et al. Research on the bioaccessibility of silkworm pupa polypeptide chelating calcium[J]. Food Research and Development,2019,40(19):47−52. [13] GUO H H, HONG Z, YI R Z. Core-shell collagen peptide chelated calcium/calcium alginate nanoparticles from fish scales for calcium supplementation[J]. Journal of Food Science,2015,80(7):1595−1601. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.12912
[14] SUN N, JIN Z Q, LI D M. An Exploration of the calcium-binding mode of egg white peptide, Asp-His-Thr-Lys-Glu, and in vitro calcium absorption studies of peptide-calcium complex[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2017,65(44):9782−9789. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b03705
[15] CHOI I, JUNG C, CHOI H, et al. Effectiveness of phosvitin peptides on enhancing bioavailability of calcium and its accumulation in bones[J]. Food Chemistry,2005,93(4):577−583. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.10.028
[16] 王思远, 赵梓月, 穆利霞, 等. 磷酸化处理对蚕蛹多肽结合钙能力的影响[J]. 食品科学技术学报,2021,39(2):103−109. [WANG S Y, ZHAO Z Y, MU L X, et al. Effect of phosphorylation on calcium-binding abilityof silkworm pupa poly-peptide[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2021,39(2):103−109. doi: 10.12301/j.issn.2095-6002.2021.02.013 [17] BREZULIER D, PELLEN M P, TRICOT D S, et al. Development of a 3D human osteoblast cell culture model for studying mechanobiology in orthodontics[J]. European Journal of Orthodontics,2020,42(4):387−395. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjaa017
[18] MURALIDHARAN K, KUMARAVELU P, DAVID D C. Cytotoxic effect of ethanolic extracts of andrographis echioides in human colon cancer cell lines via apoptosis[J]. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology,2020,13(2):871−876. doi: 10.5958/0974-360X.2020.00165.1
[19] 郑家强, 杨建虹. 细胞外钙离子对人成骨样细胞MG-63分化的影响[J]. 中国科学院研究生院学报,2011,28(1):57−64. [ZHENG J Q, YANG J H. Effect of extracellular Ca2+ on osteoblast differentiation in MG-63 cells[J]. Journal of the Graduate School of the Chinese Academy of Sciences,2011,28(1):57−64. [20] 孟陆丽, 程谦伟, 李军生, 等. 丝素蛋白的磷酸化改性研究[J]. 食品科技,2009,34(7):221−224. [MENG L L, CHENG Q W, LI J S, et al. Study on the phosphorylation of fibroin with sodium tripoly phosphate[J]. Food Science and Technology,2009,34(7):221−224. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2009.07.070 [21] 刘长江, 王雪, 曹向宇, 等. 麦麸多肽稳定性的研究[J]. 食品科技,2009,34(5):164−167. [LIU C J, WANG X, CAO X Y, et al. Study on the stability of wheat bran polypeptide[J]. Food Science and Technology,2009,34(5):164−167. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2009.05.042 [22] 陈旸. 超声预处理对磷酸化乳清分离蛋白乳化性的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2016. CHEN Y. The effect of ultrasonic pretreatment on emulsifying property of phosphorylation whey isolate protein[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2016.
[23] 沈宁, 杨光, 孙亦鸣. 花生蛋白磷酸化改性的研究[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2008(1):96−100,136. [SHEN N, YANG G, SUN Y M. The modification of peanut proteins by phosphorylation[J]. China Food Additives,2008(1):96−100,136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2513.2008.01.021 [24] WU J, ZHANG J T, YU X, et al. Extraction optimization by using response surface methodology and purification of yellow pigment fromGardenia jasminoides var. radicans Makikno[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2020,9(2):822−832.
[25] 孙会刚, 陈志轩, 周中驰, 等. 响应面法优化大豆分离蛋白提取及复合酶解制备活性肽[J]. 中国调味品,2022,47(3):82−87. [SUN H G, CHEN Z X, ZHOU Z C, et al. Optimization of soybean protein isolate extraction by response surface method and complex enzymatic hydrolysis for preparing active peptides[J]. China Condiment,2022,47(3):82−87. [26] 傅金凤, 黄美娜, 朱培渤, 等. 响应面法优化发芽糙米酒茶复合饮料制备工艺[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(15):1−9. [FU J F, HUANG M N, ZHU P B, et al. Response surface method optimization study on compound beverage technology ofgerminated brown rice wine tea[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(15):1−9. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021110012 [27] 孙博. 玉米多肽螯合钙的制备及表征[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2019. SUN B. Preparation and characterization of calcium chelated corn polypeptide[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2019.
[28] DENG S, NIE Z G, PENG P J, et al. Decrease of GSK3β Ser-9 phosphorylation induced osteoblast apoptosis in rat osteoarthritis model[J]. Current Medical Science,2019,39(1):75−80. doi: 10.1007/s11596-019-2002-x
[29] 刘闪, 刘良忠, 陈阳明, 等. 白鲢鱼骨胶原低聚肽螯合钙的结构表征及其促细胞增殖作用[J]. 中国食品学报,2016,16(9):185−191. [LIU S, LIU L Z, CHEN Y M, et al. Structural characterization and promoting cell proliferation of collagen oligopeptide chelated calcium from silver carp fish bone[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2016,16(9):185−191. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2016.09.025 [30] BECK G R, SULLIVAN E C, MORAN E, et al. Relationship between alkaline phosphatase levels, osteopontin expression, and mineralization in differentiating MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts[J]. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry,1998,68(2):269−280. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4644(19980201)68:2<269::AID-JCB13>3.0.CO;2-A
[31] 史瑞新, 付喜宏, 庄金良, 等. 低能量激光联合压力对成骨细胞ALP活性和胞内Ca2+浓度的影响[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2016,36(7):2178−2182. [SHI R X, FU X H, ZHUANG J L, et al. Effect of LLLI on secretion of ALP and intracellular calcium concentration in osteoblasts under mechanical stress[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Ajialysis,2016,36(7):2178−2182. [32] 李文, 顾春松, 管连城, 等. 黄芪对D-半乳糖诱导骨髓间充质干细胞钙结节数、骨钙素mRNA 及蛋白表达水平的影响[J]. 时珍国医国药,2020,31(11):2586−2590. [LI W, GU C S, GUAN L C, et al. Effects of Astragalus membranaceus on senescence, calcium nodule number, osteocalcin mRNA and protein expression of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induced by D-galactose[J]. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research,2020,31(11):2586−2590. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2020.11.008 [33] WU W M, HE L C, LI C L, et al. Phosphorylation of porcine bone collagen peptide to improve its calcium chelating capacity and its effect on promoting the proliferation, differentiation and mineralization of osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2020,64(C):103701.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 焦岩,崔璐麟,常影,刘晓兰,赵向宇,张凯策,林巍. 玉米肽螯合钙纳米粒的制备及结构表征分析. 中国粮油学报. 2024(08): 122-130 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:







 下载:
下载:
