Acid-resistant Mechanism of Salmonella Based on iTRAQ Proteomics Technology
-
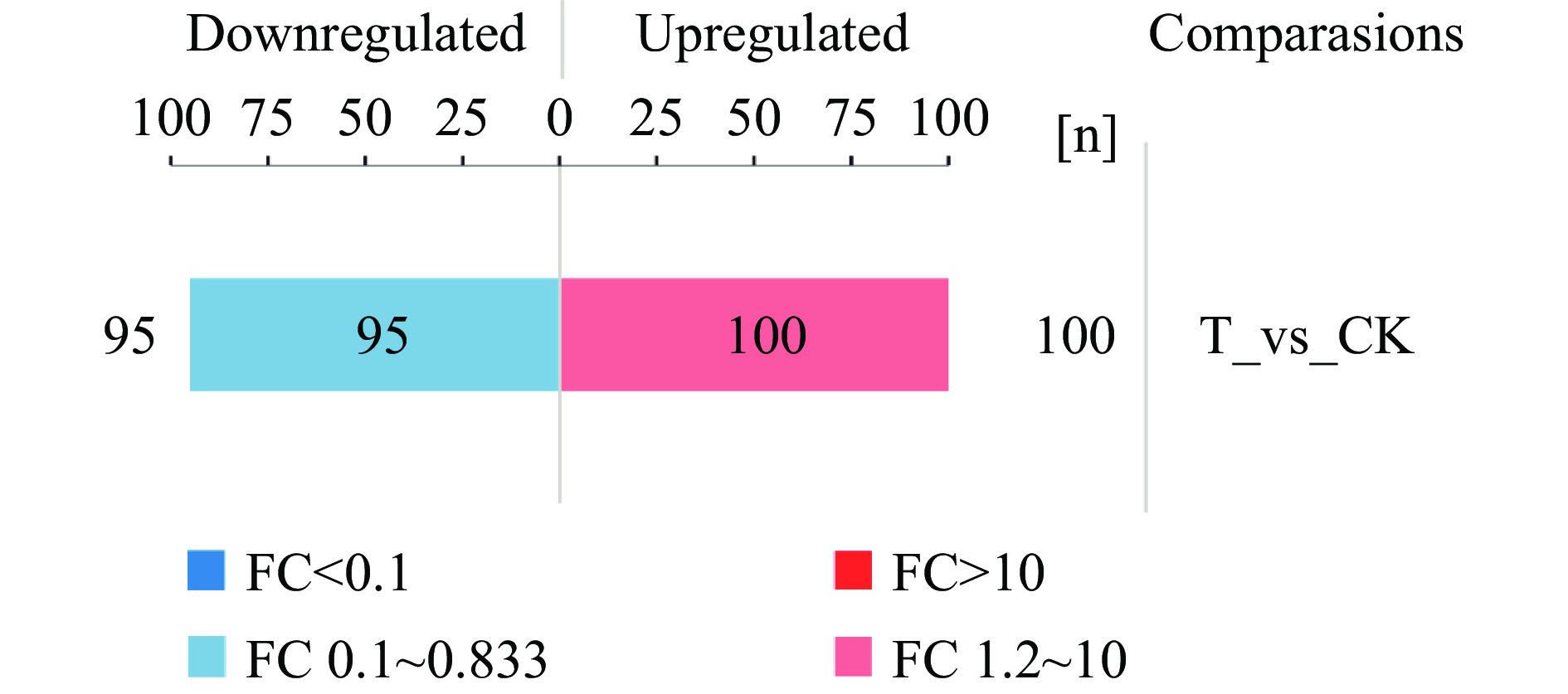
摘要: 目的:以鼠伤寒沙门氏菌CGMCC 1.1190为对象,研究其经柠檬酸反复胁迫处理诱导的抗酸性机理。方法:CGMCC 1.1190在经柠檬酸调节到pH为2.5的TSB培养基中胁迫处理并转接12次培养后,获得的抗酸性菌株。采用iTRAQ技术对CGMCC 1.1190抗酸性菌株的蛋白组进行分析,通过GO功能注释和富集对差异蛋白进行聚类分析,以及KEGG注释和富集对差异蛋白参与的通路进行联合分析。结果:iTRAQ技术结果显示CGMCC 1.1190抗酸性菌株共2373个蛋白,其中195个差异蛋白中,95个显著下调蛋白和100个显著上调蛋白。GO分析和KEGG分析结果显示CGMCC 1.1190抗酸性菌株高表达应激蛋白相关基因;高表达细胞膜相关蛋白可促进CGMCC 1.1190菌体细胞膜的完整性;高表达鞭毛相关蛋白可增强CGMCC 1.1190菌体的运动能力并促进保护性生物被膜的形成;高表达双组分系统相关蛋白来响应酸信号,通过调控酸激蛋白的产生增强CGMCC 1.1190菌体的抗酸性;低表达ABC转运系统相关蛋白来降低细胞膜对H+的通透性,达到保护菌体的作用;高表达能量代谢途径相关蛋白为CGMCC 1.1190菌体应对酸胁迫提供能量。结论:CGMCC 1.1190在经pH为2.5的柠檬酸胁迫后,能通过蛋白水平的表达变化启动一系列应答机制并生存下来,通过合成一些蛋白质来增强CGMCC 1.1190的抗酸性。Abstract: Objective: To investigate the mechanism of acid resistance induced by repeated stress treatment with citric acid for Salmonella typhimurium CGMCC 1.1190. Methods: The acid-resistant strain of CGMCC 1.1190 was obtained after stress treatment in TSB liquid medium adjusted to pH2.5 by citric acid and transferred and incubated 12 times. The proteome of the acid-resistant strain of CGMCC 1.1190 was analyzed based on iTRAQ technology, with clustering analysis of the differential proteins by GO functional annotation and enrichment for biological processes, molecular functions, and cellular components, and KEGG annotation and enrichment for combined analysis of the pathways involved in the differential proteins. Results: The iTRAQ results showed that the CGMCC 1.1190 acid-resistant strain had 2373 proteins, of which 195 differential proteins, including 95 significantly down-regulated proteins and 100 significantly up-regulated proteins. GO analysis and KEGG analysis showed that CGMCC 1.1190 acid-resistant strains highly express stress protein-related genes, which could contribute CGMCC 1.1190 to enhance acid resistance by synthesizing some proteins in response to external stimulation. The high express cell membrane-related proteins could increase the integrity of CGMCC 1.1190 cell membrane, and the high expression of flagellar-related proteins could enhance the motility and increase the formation of protective biofilm of CGMCC 1.1190. The high expression of two-component system-related proteins could enhance acid resistance of CGMCC 1.1190 by regulating the production of acid kinins. The low expression of ABC transport system-related proteins could reduce the permeability of the cell membrane to H+ to protect the bacterium, and the proteins related to the energy metabolism pathway were highly expressed to provide energy and maintain the homeostasis of the CGMCC 1.1190 bacterium in response to acid stress. Conclusion: CGMCC 1.1190 could initiate a series of response mechanisms and survive after citric acid stress at pH2.5 due to some changes in protein expression.
-
Keywords:
- Salmonella typhimurium /
- acid stress /
- iTRAQ /
- differential protein /
- acid-resistant
-
沙门氏菌是一种常见的的食源性致病菌,在自然界中分布较广,在适宜条件下可迅速生长繁殖,引起人类急性、慢性和隐性感染病,如食物中毒和肠胃炎等[1]。在食品的生产、储运和销售过程中,沙门氏菌极易反复受到极端温度、酸、碱、抗生素以及消毒剂等不适生长环境条件的胁迫作用,诱发其产生一系列的适应性变化,达到维持生存的目的[2]。沙门氏菌对食品加工中的消杀措施的适应性变化,潜在地增加了沙门氏菌感染的可能性[3]。已有相关研究表明,大多数微生物在不适生长的环境中会通过特定的抗性蛋白来保证其生存[4]。Chen等[5]研究发现,微生物处于高温、低温和高渗等一系列压力环境下其部分蛋白质的表达会发生变化,来稳定膜结构、维持细胞功能等。
近年来不断完善的蛋白组学技术已用于研究不同环境压力下对微生物产生的影响以及微生物在这些胁迫下的应激机制[6]。蛋白质组学是用于研究单个细胞或一种生物所表达全部蛋白质特征的技术,主要包括蛋白的表达水平、翻译的修饰、蛋白之间的相互作用等[7]。iTRAQ蛋白组技术具有通量高,灵敏度高,可重复性高,定量效果好,结果可靠,适用样品类别广泛等优点,是系统研究生物学规律和相关机制的有效工具[8]。Liu等[9]利用iTRAQ蛋白组技术,探讨沙雷氏菌在铬胁迫下的潜在机制,发现差异蛋白主要集中在碳水化合物代谢、应激反应、氨基酸代谢等方面。张佩佩[10]通过对甲型鼠伤寒沙门氏菌进行热处理,发现其产生抗热性,利用iTRAQ蛋白组技术分析其在热胁迫前后产生的差异蛋白,发现5%的差异蛋白参与热刺激适应,其中DNA连接酶(ligB)、逆境压力反应蛋白(dps)、分子伴侣(HdeB)以及未知蛋白ACN8920515和ynaF均下调,在热胁迫适应中发挥作用,使甲型鼠伤寒沙门氏菌在热胁迫下得以存活。但采用iTRAQ技术从蛋白质组学对鼠伤寒沙门氏菌的抗酸性机制的研究,国内外鲜见相关报道[11]。
本研究以食源致病菌鼠伤寒沙门氏菌为试材,采用iTRAQ技术对鼠伤寒沙门氏菌抗酸性菌株的蛋白组进行了分析,找出酸胁迫处理前后菌体之间的差异表达蛋白,通过GO功能注释和富集对差异蛋白进行生物过程、分子功能和细胞组分的聚类分析,通过KEGG注释和富集对差异蛋白参与的通路进行联合分析,筛选出与菌株抗酸性相关的差异蛋白,并揭示酸胁迫条件下鼠伤寒沙门氏菌在应激反应、双组分系统、ABC转运系统和能量代谢等过程中相关蛋白表达的差异,旨在揭示酸胁迫诱导鼠伤寒沙门氏菌产生抗酸性的机理,对优化食品加工条件和建立食品安全控制体系具有重要意义。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
鼠伤寒沙门氏菌CGMCC 1.1190 中国普通微生物菌种保藏管理中心;异丙醇、磷酸、柠檬酸、氯化钾、磷酸二氢钾、乙腈、甲酸、三氯乙酸、丙酮、溴化四乙铵、十二烷基硫酸钠、二硫苏糖醇、盐酸、三羟甲基氨基甲烷 南京慧杰诚生物科技有限公司;所有试剂 均为分析纯。
SAF-680T型酶标仪、SF-CF-2A型超净工作台 上海三发科学仪器有限公司;AKTA Purifier 100型纯化仪、PHS-3G型pH计 上海仪电科学仪器股份有限公司;Easy nLC 1200型液相色谱仪、Q Exactive型质谱仪 赛默飞世尔科技有限公司;SM-650D型超声波破碎仪 南京舜码仪器设备有限公司;GL-21M型高速冷冻离心机 上海市离心机械研究所有限公司;LDZX-50FBS型立式压力蒸汽灭菌器 上海申安医疗器械厂;GNP-9160型隔水式恒温培养箱 上海三发科学仪器有限公司;ME55型塞多斯精密电子天平 北京塞多斯天平有限公司;SK-1型快速混匀器 金坛市杰瑞尔电器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 菌种活化与预处理
实验菌株CGMCC 1.1190采用胰蛋白胨大豆肉汤(Trypticase Soy Broth,TSB)培养。供试菌经活化后,接入pH7.2的TSB培养基,于37 ℃、150 r/min摇床振荡培养18 h,为后续备用。
1.2.2 鼠伤寒沙门氏菌CGMCC 1.1190抗酸性菌株的获得
pH2.5柠檬酸胁迫处理:将1.2.1中活化的CGMCC 1.1190以体积分数1%转接至100 mL TSB培养基中,37 ℃振荡培养18 h,取10 mL培养液离心(5000 r/min,4 ℃,10 min),弃上清,重悬于柠檬酸调节pH2.5的TSB中进行酸胁迫处理,处理30 min,取体积分数为1%经pH2.5柠檬酸胁迫后的CGMCC 1.1190接种于100 mL TSB培养基中,37 ℃振荡培养18 h,再取10 mL培养液离心(5000 r/min,4 ℃,10 min),取沉淀,重悬于柠檬酸调节pH2.5的TSB中进行酸胁迫处理,处理30 min;以此类推,重复上述摇床振荡培养和酸胁迫处理12次,后续备用[12]。
1.2.3 蛋白组样品的制备
将1.2.1中活化的CGMCC 1.1190原始对照菌株及1.2.2节获得抗pH2.5柠檬酸的菌株分别接种于100 mL TSB中,摇床振荡培养(37 ℃,150 r/min,24 h),离心(5000 r/min,4 ℃,10 min),取沉淀,将菌体沉淀的离心管置于液氮中,速冻10 min,并标记样品号为对照组CK1、对照组CK2、处理组T1和处理组T2,置于−80 ℃冰箱保存,备用。
1.2.4 iTRAQ标记
采用SDT裂解法和TCA丙酮沉淀法提取CGMCC 1.1190菌体蛋白[13],用BCA蛋白浓度测定试剂盒测定蛋白样品浓度。取制备的蛋白样品各100 μg,用FASP法[14]进行酶解,酶解后采用C18 Cartridge对肽段进行脱盐,将上述样品真空冷冻干燥2 h,加入0.1%、40 μL的甲酸溶液复溶肽段。用iTRAQ试剂盒对肽段进行标记,室温静置2 h,标记信息分别为:CK1,113;CK2,114;T1,115;T2,116。等量混合经iTRAQ标记的4组肽段样品,根据强阳离子交换柱法对混合后的肽段进行预分离,之后进行液相分离和质谱分析。
1.2.5 实时荧光定量PCR验证
本研究选取CGMCC 1.1190菌株酸胁迫前后的8个显著差异蛋白的对应表达基因进行实时荧光定量PCR验证和分析。通过在线设计软件Primer 3.0来设计用于荧光定量PCR的引物,引物见表1。用HiScript® II 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit试剂盒进行CGMCC 1.1190菌体第一链cDNA的合成。以cDNA链为模板,16S rRNA基因为内参基因,用ChamQTM SYBR® qPCR Master Mix试剂盒进行实时荧光定量PCR反应,采用ABI 7500 PCR分析荧光定量PCR反应中CGMCC 1.1190菌体对照菌株和抗酸菌株样品中8个待测基因的RNA相对表达含量,对照组为未经过酸处理的CGMCC 1.1190菌体RNA,设其表达水平为1,按照2-△△Ct法计算基因的相对表达量。
表 1 RT-qPCR验证基因及引物设计Table 1. RT-qPCR verification gene and primer design基因 序列(5' to 3') 产物长度(bp) 16S rRNA F: TCGTGTTGTGAAATGTTGGGTTA
R: ACCGCTGGCAACAAAGGAT66 rpoS F: TTGCCCGCCGTTATGG
R: CACGGATAAGCCCCAGGTT75 ompC F: AATGGTGGTAAGGCAGGTCA
R: TGGCACCTTTGTTGAATCCG233 aceA F: CTTTCCGTCGTGCAGATCAG
R: GCCAGCTGATCTTCGAAGTG190 lexA F: TGCTGGCGGTACATAAAACG
R: TAAAGCTTTGTTCGCGCAGA171 phoQ F: CCGTCAGTTCACTTTCACCC
R: ATGGTGCTGGATTTAGGGCT244 phoP F: TCGGCGCTAATGTGGATAGT
R: AGATGTGATCCTCCCCTCCT201 malE F: CGGTCAGCAGGTAGTTTTCG
R: GATTACTCCATCGCCGAAGC235 malK F: GTCGGCGCCAATATGTCTTT
R: TACCAGCACCACGTCATTCT183 1.2.6 生物信息学分析
采用Mascot2.2和Proteome Discover1.4对质谱分析原始数据进行查库鉴定及质量分析[15]。通过对蛋白质相对分子质量、等电点、肽段序列长度、肽段序列覆盖度等方面来对蛋白质鉴定和定量的结果可信度进行评估。以P≤0.05对差异蛋白进行显著性筛选,倍数变化大于1.2或小于0.83的蛋白质被定义为差异蛋白,得到CGMCC 1.1190对照菌株和抗酸菌株之间的上调和下调蛋白的数目。
根据抗酸性CGMCC 1.1190菌株显著差异蛋白的表达特性,采用层次聚类算法对差异表达蛋白质进行分组归类,以热图的形式将表达趋势相同的基因进行聚类[16],同时与抗酸性CGMCC 1.1190菌株的生物学特性建立关联,筛选出符合抗酸性生物学特性的蛋白表进行重点研究。采用Blast2Go软件对CGMCC 1.1190酸胁迫前后筛选出的所有差异表达蛋白质进行GO功能注释[17],向GO数据库中对应功能的term映射,计算每个term中差异蛋白质的数量,然后应用Fisher精确检验CGMCC 1.1190抗酸性菌株与对照菌株差异蛋白的显著性[18],找出差异蛋白显著富集的GO条目,从而对CGMCC 1.1190菌株筛选出的差异蛋白行使的生物学功能进行分析。采用KAAS软件对CGMCC 1.1190菌株酸胁迫前后筛选出的差异表达蛋白质进行KEGG通路注释,通过Fisher精确检验CGMCC 1.1190抗酸性菌株与对照菌株差异蛋白的显著性,找出所有显著差异表达蛋白,并对抗酸性相关代谢的关键蛋白进行分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 鼠伤寒沙门氏菌CGMCC 1.1190蛋白浓度的测定结果
利用BCA法测定所提取总蛋白的浓度,结果见表2。由表2可知,CGMCC 1.1190原始对照菌株(CK1,CK2)提取总蛋白浓度均为2.8 μg/μL,抗pH2.5菌株(T1,T2)提取总蛋白浓度分别为1.7和1.9 μg/μL,提取浓度能满足后续蛋白组测定相关的要求,样品的平行性和评价均较好。
表 2 CGMCC 1.1190对照组和抗酸组菌株蛋白质样品浓度及评价结果Table 2. Concentration and valuation results of protein samples of CGMCC 1.1190 control strain and the acid-resistant strain样品名称 浓度(μg/μL) 体积(μL) 总量(μg) 物种 样品评价 CK1 2.8 200 562.6 鼠伤寒沙门氏菌 a CK2 2.8 200 560.4 鼠伤寒沙门氏菌 a T1 1.7 200 337.5 鼠伤寒沙门氏菌 a T2 1.9 200 378.2 鼠伤寒沙门氏菌 a 2.2 CGMCC 1.1190蛋白表达差异分析
2.2.1 CGMCC 1.1190蛋白表达差异统计
成功鉴定到的蛋白共2373个,已定量的蛋白占99.71%,CGMCC 1.1190对照组和抗酸组的差异蛋白总数为195个,其中包括95个显著下调蛋白和100个显著上调蛋白。蛋白质定量差异结果见图1。
2.2.2 CGMCC 1.1190蛋白表达模式聚类分析
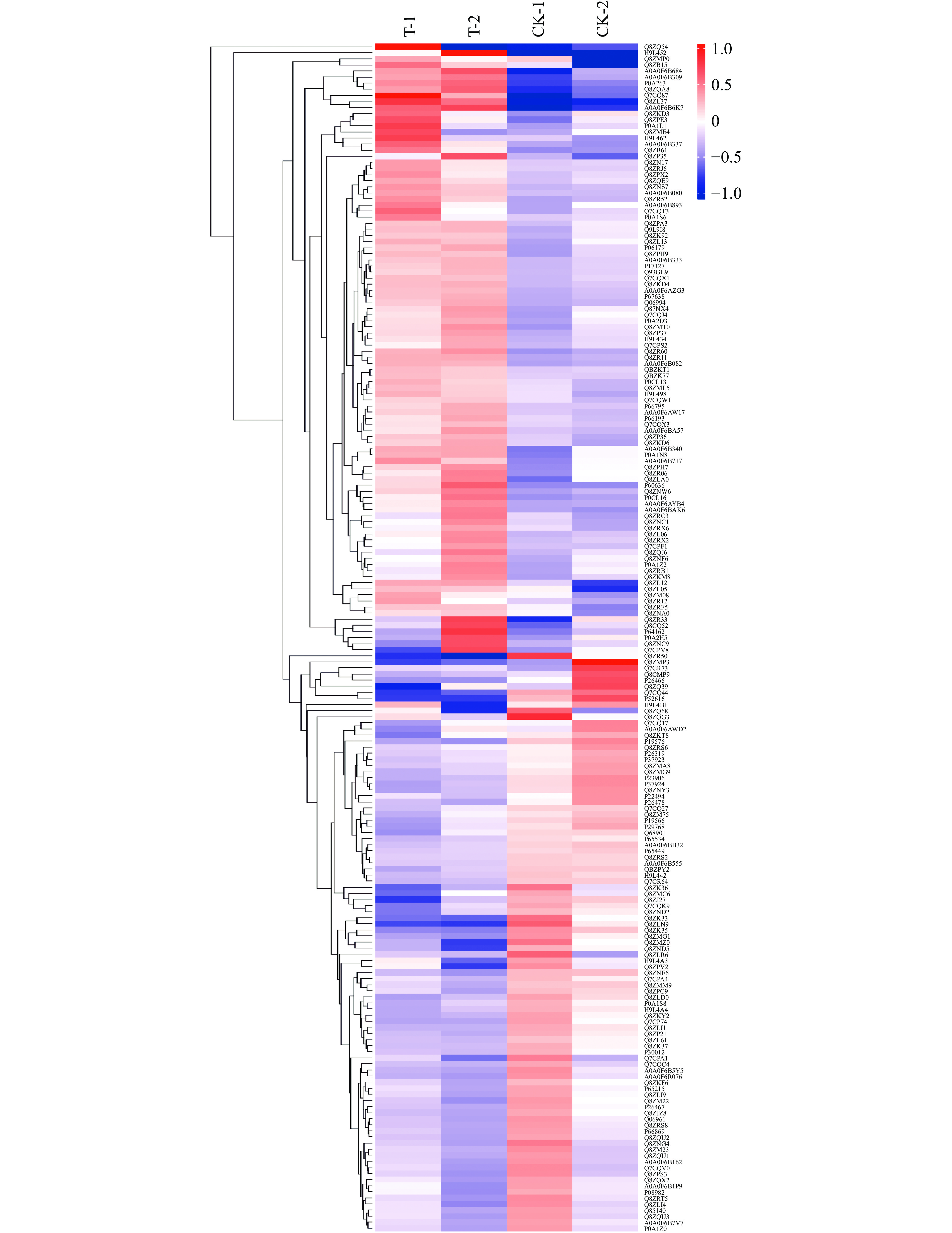
本研究对CGMCC 1.1190对照菌株和抗酸性菌株的差异表达蛋白质进行分析,结果见图2,横坐标对样品进行分析,纵坐标对蛋白质进行分析。从图2中可以看出组内的数据相似性较高,而组间的数据相似性较低,说明对照组和抗酸组的差异蛋白质表达量变化说明酸胁迫处理对样本造成的影响显著,组内平行性较好。100个上调蛋白在CGMCC 1.1190抗酸性菌株中的表达量高于对照菌株,其中,RNA聚合酶σ因子(rpoS)、膜融合蛋白家族蛋白(STM4260)、外膜孔道蛋白(ompC)、鞭毛丝蛋白(fliC)的变化倍数分别为1.83、3.34、2.13、1.88;95个下调蛋白在CGMCC 1.1190抗酸性菌株中的表达量高于对照菌株,其中,LexA阻遏蛋白(lexA)、异柠檬酸脱氢酶(IcdA)、精氨酸脱亚胺酶(arcA)、鸟氨酸氨基甲酰转移酶(arcB)的变化倍数分别为0.75、0.70、0.55、0.57。
2.2.3 CGMCC 1.1190差异表达功能蛋白分类分析
本研究对CGMCC 1.1190对照菌株和抗酸性菌株的蛋白质图谱进行对比分析,得到195个表达差异显著的相关蛋白。在这些差异蛋白中,大多数蛋白质主要参与CGMCC 1.1190内部调节代谢途径的生理功能,包括参与应激反应、细胞膜变化、鞭毛合成、转运系统、双组份系统相关的蛋白等,表明CGMCC 1.1190抗酸性菌株通过上述代谢途径相关的蛋白来调控适应酸胁迫环境。在195个显著差异表达的蛋白中,与应激反应、细胞膜变化、鞭毛合成、转运系统、双组份系统相关的蛋白的信息分别见表3~表8。
表 3 应激相关蛋白信息Table 3. List of protein information related to stress序列号 蛋白质名称 基因名称 变化倍数 P0DM81 RNA聚合酶σ因子 rpoS 1.8342 Q7CQI8 酸胁迫伴侣 hdeB 1.2320 Q7CPF1 小热休克蛋白 ibpA 1.3575 Q93GL9 TraT抗补体蛋白 traT 1.3638 Q7CPS2 抗性蛋白 yqiE 1.3167 Q7CQV9 DNA保护蛋白 dps 1.3061 A0A0F6B082 重组和修复蛋白RecT STM14_1422 1.5535 P0A273 LexA阻遏蛋白 lexA 0.7513 P65977 RecA蛋白 recA 1.1827 表 4 细胞膜相关蛋白信息Table 4. List of protein information associated with membrane序列号 蛋白质名称 基因名称 变化倍数 H9L452 膜融合蛋白家族蛋白 STM4260 3.3396 Q7CQ87 DedA家族膜蛋白 yohD 2.9208 P0A263 外膜孔道蛋白C ompC 2.1344 P60636 UPF0299膜蛋白 yohJ 1.8162 Q8ZPH7 外膜蛋白 STM1530 1.4350 Q8ZPH9 外膜蛋白 STM1528 1.4296 Q8ZQT6 Tol-Pal系统蛋白 tolA 1.2472 Q8ZQT5 Tol-Pal系统蛋白 tolB 1.2997 Q7CQX1 Tol-Pal系统蛋白 tolQ 1.3773 Q7CQX0 Tol-Pal系统蛋白 tolR 1.2260 Q7CQW9 肽多糖相关蛋白 pal 1.2574 P0A1Z2 伴侣蛋白 skp 1.3683 Q7CQI7 外膜脂蛋白 STM1585 0.7387 P37924 外膜传入蛋白 fimD 0.6591 表 5 鞭毛相关蛋白信息Table 5. List of protein information related to flagella序列号 蛋白质名称 基因名称 变化倍数 P06179 鞭毛丝蛋白 fliC 1.8826 P0A1L1 鞭毛蛋白 fliO 1.5576 P0A1N8 鞭毛L环蛋白 flgH 1.4862 P0A1J3 鞭毛基体杆蛋白 flgG 1.3145 P40729 鞭毛生物合成蛋白 flhA 1.3734 表 6 双组分系统相关蛋白信息Table 6. List of protein information related to two-component system序列号 蛋白质名称 基因名称 变化倍数 D0ZV89 病毒性传感器组氨酸激酶 phoQ 1.5249 P0DM78 病毒性转录调节蛋白 phoP 1.4992 P66795 转录调控蛋白 qseB 1.3689 Q8ZLZ9 感应蛋白 qseC 1.1199 P08982 组氨酸激酶传感蛋白 envZ 1.5124 P0AA19 DNA结合双转录调节因子 ompR 1.3231 Q8ZK33 精氨酸脱亚胺酶 arcA 0.5487 Q8ZK35 鸟氨酸氨基甲酰转移酶 arcB 0.5671 P26319 菌毛Z蛋白 fimZ 0.7799 Q8ZNE6 趋化信号转导蛋白 cheV 0.6580 Q8ZP35 感应蛋白 narX 1.7159 表 7 ABC转运系统相关蛋白信息Table 7. List of protein information related to ABC transfer system序列号 蛋白质名称 基因名称 变化倍数 Q8ZRF5 ABC超家族转运蛋白 sbmA 1.3913 P26467 麦芽糖/麦芽糊精运输系统渗透酶蛋白 malF 0.7245 P19566 麦芽糖/麦芽糊精导入ATP结合蛋白 malK 0.7242 Q8ZPY2 ABC转运蛋白 STM1256 0.7165 Q8ZLL2 ABC转运蛋白的ATP酶成分 yheS 0.8449 P19576 麦芽糖/麦芽糊精结合周质蛋白 malE 0.5970 表 8 与能量代谢相关蛋白信息Table 8. List of protein information related to energy metabolism序列号 蛋白质名称 基因名称 变化倍数 Q8ZR15 DASS家族,柠檬酸:琥珀酸反向
运输蛋白CitT 1.8974 A0A0F6AYB4 柠檬酸裂解酶酰基载体蛋白 CitD 1.5281 A0A0F6AWI7 柠檬酸裂合酶 CitG 1.4021 Q8ZR12 柠檬酸裂解酶α链 CitF 1.3776 Q8ZRS8 乌头酸酶 AcnB 0.7323 A0A0F6B076 异柠檬酸脱氢酶 IcdA 1.6976 P51066 异柠檬酸裂解酶 aceA 1.9218 Q8ZME4 焦磷酸酶 MazG 1.3169 P17127 多磷酸转移蛋白 FruB 1.3806 A0A0F6B7V7 磷酸烯醇丙酮酸羧化酶 PckA 0.7609 Q7CQ52 NADH-醌氧化还原酶亚基J nuoJ 1.6067 P67638 富马酸还原酶亚基C frdC 1.4719 A0A0F6BAK6 富马酸还原酶亚基D frdD 1.6074 Q8ZKE6 氨基烷基膦酸酯N-乙酰转移酶 phnO 1.3545 2.2.4 CGMCC 1.1190差异蛋白的GO富集分析
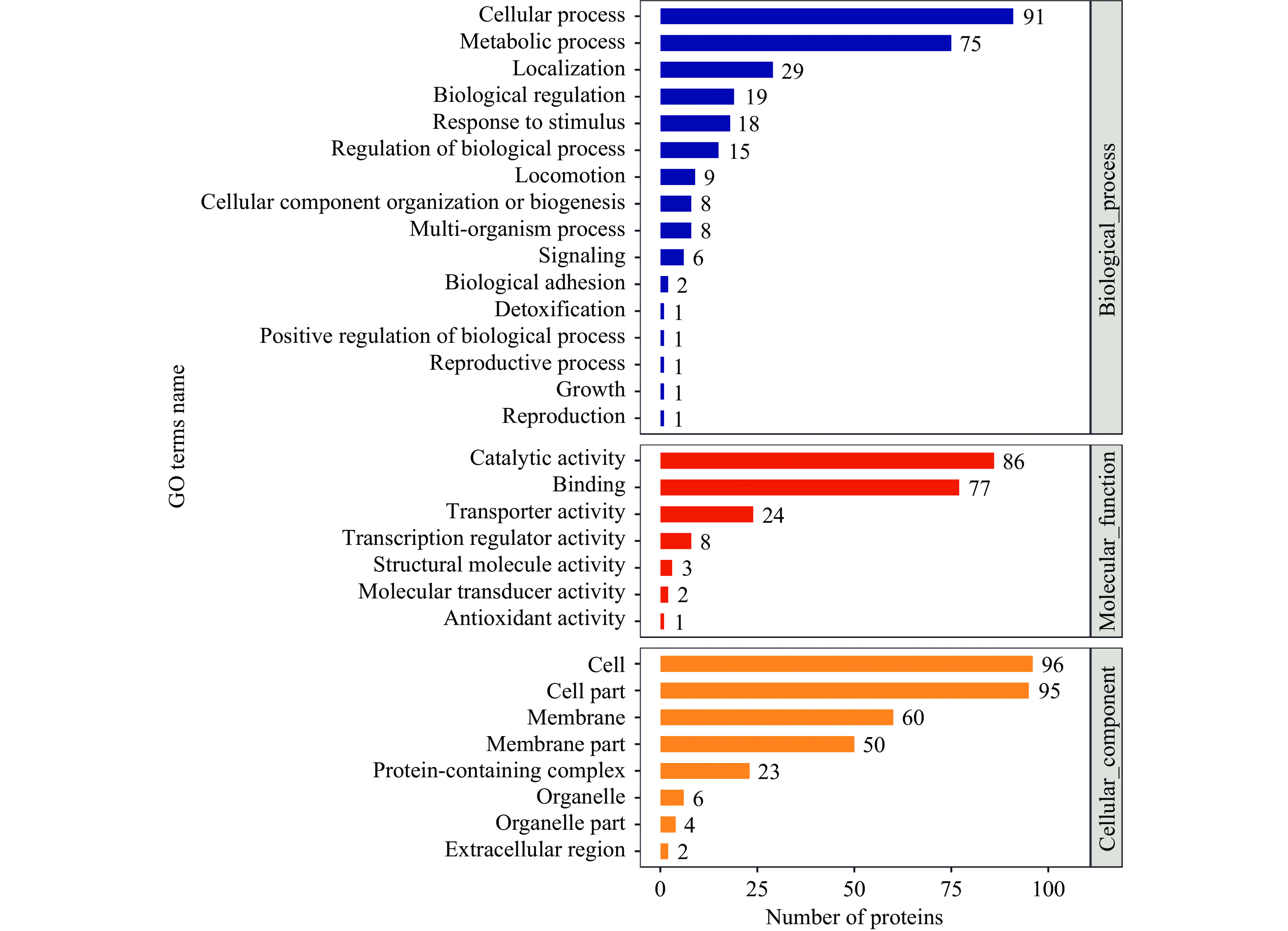
GO分析结果如图3所示,根据生物过程注释,差异蛋白主要与菌体内代谢、应激调节反应有关;根据分子功能注释,差异蛋白主要是各种酶类、修复蛋白以及转运蛋白;根据细胞组分注释,差异蛋白主要涉及细胞膜组成蛋白,得到注释的蛋白中膜蛋白占32.7%。
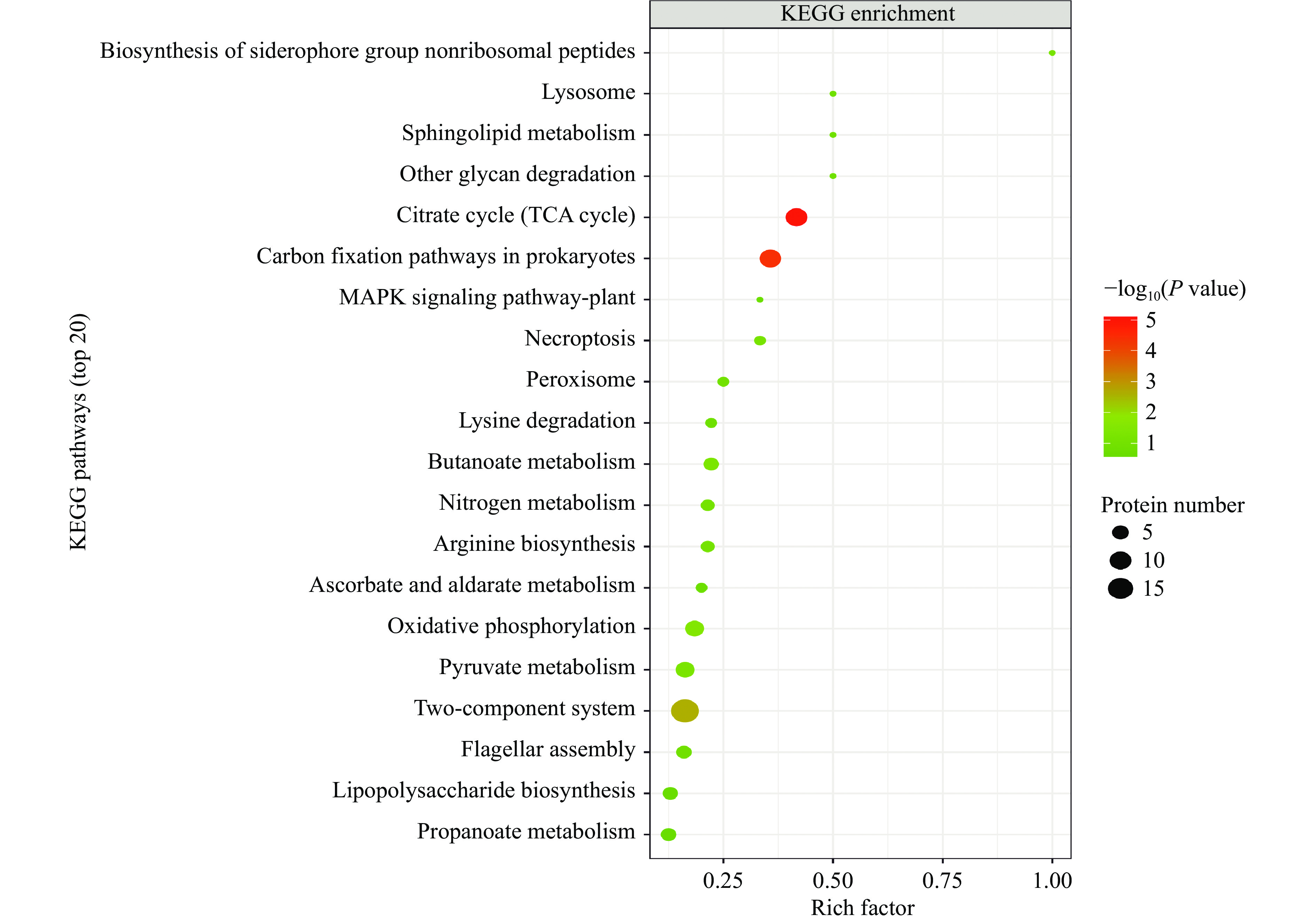
2.2.5 CGMCC 1.1190差异蛋白的KEGG生物通路分析
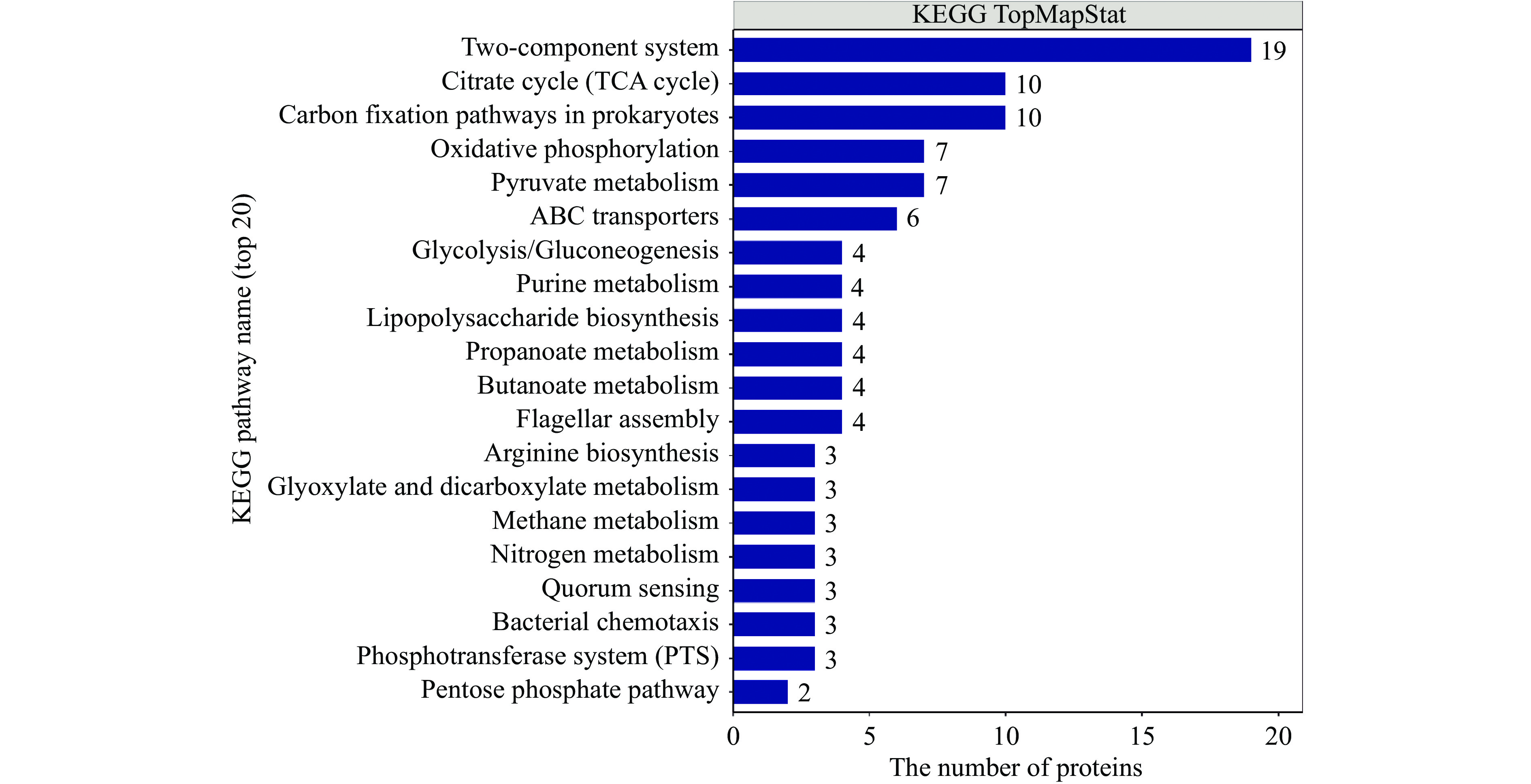
KEGG分析发现CGMCC 1.1190对照菌株和抗酸性菌株的差异蛋白质富集于60条代谢通路上,显著性分析结果见图4~图5。由图4~图5可知,CGMCC 1.1190菌株的差异蛋白质主要影响了6个代谢通路,其中双组分调节系统途径参与的蛋白质有19个,三羧酸循环途径参与的蛋白质有10个,碳固定途径参与的蛋白质有10个,氧化还原途径参与的蛋白质有7个,丙酮酸代谢途径参与的蛋白质有7个,ABC转运系统参与的蛋白质有6个。与CGMCC 1.1190对照菌株相比,抗酸性菌株的蛋白质在双组分调节系统、三羧酸循环、碳固定等通路差异显著。
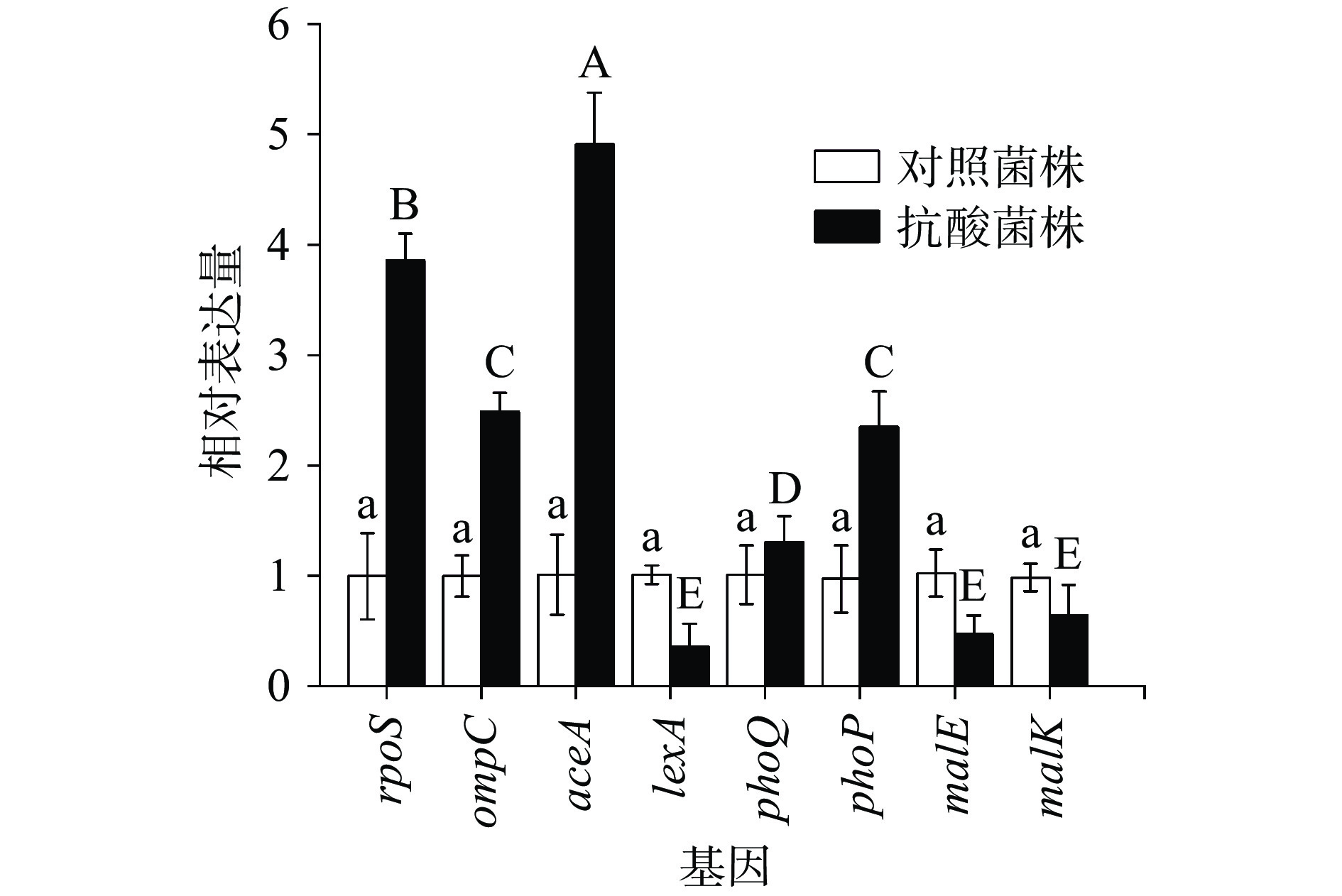
2.2.6 CGMCC 1.1190部分差异表达基因的RT-qPCR验证
为验证本研究中iTRAQ蛋白组数据的准确性,在经柠檬酸调节pH为2.5的TSB培养基反复胁迫后的CGMCC 1.1190中选取8个差异显著蛋白(5个上调蛋白和3个下调蛋白),进行RT-qPCR验证,结果见图6。8个目的基因的RT-qPCR结果与8个差异蛋白的iTRAQ蛋白组测定结果在表达幅度上有一定的差异,但其表达趋势基本一致。
3. 讨论
3.1 抗酸性鼠伤寒沙门氏菌CGMCC 1.1190与应激相关蛋白的分析
微生物常处于不适的环境中,应激蛋白指大多数菌体在遭受外界压力时合成的蛋白,在菌体迅速回应逆境等方面发挥重要作用[19]。对比分析CGMCC 1.1190对照菌株和抗酸性菌株的蛋白组,当菌体经过酸胁迫后,RNA聚合酶σ因子(rpoS)蛋白水平上调约1.8倍,其处于调控较上游的位置并控制休克蛋白表达,保护环境压力下的菌体,对其适应性有调控作用[20]。本研究发现,RNA聚合酶σ因子对CGMCC 1.1190菌体适应酸胁迫环境起到一定的调控作用。热休克蛋白是一种保护性蛋白,通过参与蛋白的正确折叠、维持细胞骨架等来提高细胞的耐热等应激能力,使菌体细胞内的生理过程保持稳定[21]。本研究发现,抗酸性CGMCC 1.1190的小热休克蛋白(ibpA)表达增加,表明其对菌株的耐酸能力也具有一定的调控作用,该调控作用可能与菌株产生耐热性的过程类似。RecA蛋白和LexA阻遏蛋白是与菌体遭受环境胁迫后与修复机制相关的蛋白,当SOS系统被激活,recA和单链DNA会结合生成recA-ssDNA,诱导LexA阻遏蛋白进行自我降解,增加重组酶和聚合酶的表达,修复损伤[22]。本研究发现,抗酸性CGMCC 1.1190的recA蛋白表达增加,lexA阻遏蛋白表达减少,表明在经过酸胁迫后,CGMCC 1.1190抗酸性与菌体内部SOS系统的激活有关,菌体通过相关蛋白的协同作用修复损伤来提高其在酸环境下的生存能力。
3.2 抗酸性CGMCC 1.1190与膜相关蛋白的分析
细菌膜蛋白在其生命活动中起着重要的作用,主要维持细胞膜的完整、流动性、参与菌体内营养物质的运输以及物质代谢[23]。本研究发现,抗酸性CGMCC 1.1190部分膜蛋白的表达量发生改变,其中ompC基因编码的外膜孔道蛋白C表达水平显著上调。戎建荣等[24]发现,在高渗环境中,大肠杆菌通过改变外膜孔道蛋白C的表达水平减少胆盐渗入菌体细胞;受到抗菌药物胁迫的细菌,其外膜孔道蛋白C蛋白表达有助于降低菌体内抗菌药物的浓度、增加耐受力。本研究结果表明外膜孔道蛋白C对CGMCC 1.1190的抗酸性起到一定的调控作用,通过改变细胞膜的通透性,如降低细胞膜对H+的通透性来帮助细菌适应酸胁迫环境。Tol-Pal系统是革兰氏阴性菌高度保守的膜蛋白系统之一,主要由Tol-Pal系统蛋白(tolB)、肽多糖相关蛋白(pal)、Tol-Pal系统蛋白(tolA)、Tol-Pal系统蛋白(tolR)和Tol-Pal系统蛋白(tolQ)组成,其中tolA、tolQ和tolR构成细菌的内膜蛋白,tolB和pal构成细菌外膜复合体,Tol-Pal系统维持革兰氏阴性菌细胞膜的完整性和稳定性。Prouty等[25]研究发现,鼠伤寒沙门氏菌耐受胆盐的能力与Tol-Pal系统的调控有关。本研究CGMCC 1.1190抗酸性菌株Tol-Pal系统蛋白均上调,表明酸胁迫后CGMCC 1.1190产生的抗酸性与其Tol-Pal膜蛋白系统的调控有关,可能通过增加细胞膜的完整性和稳定性来帮助其抵抗并适应极端酸胁迫环境。因此,膜蛋白表达量的变化可能是CGMCC 1.1190酸胁迫菌株比原始菌株更抗酸的原因之一。
3.3 抗酸性CGMCC 1.1190与鞭毛相关蛋白的分析
细菌的鞭毛是一种位于菌体表面的细丝状蛋白质附属物,主要与细菌的运动性和大分子蛋白质的转运有关[26]。Duan等[27]通过对比研究大肠杆菌fliC基因缺失株的运动能力和侵袭能力,发现大肠杆菌fliC缺失株的运动能力和侵袭能力显著低降低。本研究发现,抗酸性CGMCC 1.1190的鞭毛相关差异蛋白均上调,其中鞭毛丝蛋白(fliC)上调约1.9倍,表明抗酸性CGMCC 1.1190的运动能力对其抗酸性有重要影响。细菌鞭毛蛋白调控的运动性也是生物被膜形成初期和成熟期的决定性因素,大肠杆菌运动性的强弱与生物被膜形成能力呈正相关[28]。这与本研究结果一致,表明鞭毛蛋白调控的运动性增强可以促进菌体形成具有抵抗能力的生物被膜。本研究中鞭毛相关蛋白表达的变化表明抗酸性CGMCC 1.1190可能通过调控鞭毛蛋白的表达来增强运动能力,促进生物被膜的形成,使其抗酸性增强。
3.4 抗酸性CGMCC 1.1190与双组分系统相关蛋白的分析
双组分系统(Two-Component System,TCS)是存在于细菌内的一种信号传导系统,与细菌的群体感应、致病性、耐药性、毒力因子表达和生物被膜生成等生物学功能密切相关,是细菌适应环境变化并响应多种刺激的一种调节机制[29]。TCS与细菌的群体感应有关,群体感应是细菌之间信号传递的重要机制,当细胞密度增加达到一定阈值,细菌通过信号传递影响特定基因的表达,来调控微生物群体的生理特征[30]。何绿琴[31]通过构建转录调控蛋白(qseB)/感应蛋白(qseC)缺失株,发现副猪嗜血杆菌生物膜生成能力降低,抵御不良环境能力减弱,毒力下降。双组分系统组氨酸激酶传感蛋白(envZ)/DNA结合双转录调节因子(ompR)主要与细菌的渗透调节相关,通过对膜孔道蛋白进行正向或负向的调控来影响膜内外离子转运、平衡渗透压力[32]。双组分系统精氨酸脱亚胺酶(arcA)/鸟氨酸氨基甲酰转移酶(arcB)对厌氧和需氧生长下细菌的呼吸代谢、生物合成和运动能力有调控作用,主要影响菌体的能量代谢过程。武珊珊[33]研究发现沙门氏菌arcA/arcB缺失株对氨基糖苷类抗生素的抗性有所提高,但其引起的耐药性变化的机理尚未阐明。本研究发现,抗酸性 CGMCC 1.1190双组分系统病毒性传感器组氨酸激酶(phoP)/病毒性转录调节蛋白(phoQ)、qseB/qseC、envZ/ompR的蛋白水平均上调,双组分系统arcA/arcB蛋白水平下调,表明CGMCC 1.1190双组分系统与其抗酸性调控具有密切关系。
3.5 抗酸性CGMCC 1.1190与ABC转运系统相关蛋白的分析
ABC转运系统相关蛋白是指含有ATP结合区域的蛋白,主要功能包括营养物质的转运和排出有害物质等[34]。谢腾飞[35]研究发现,冷胁迫后的副溶血性弧菌通过抑制ABC转运蛋白的量来保护菌体免于低温损伤。MalEFGK是位于菌体内膜上的ABC转运蛋白复合体,麦芽糖/麦芽糊精导入ATP结合蛋白(malK)负责与运输系统的能量偶联;麦芽糖/麦芽糊精运输系统渗透酶蛋白(malF)负责跨膜转运;麦芽糖/麦芽糊精结合周质蛋白(malE)是麦芽糖摄取的关键,参与麦芽糖的ABC运输系统[36]。本研究发现,CGMCC 1.1190抗酸性菌株的菌体中构成MalEFGK复合物的3种蛋白(malK、malF、malE)表达水平均下调,表明CGMCC 1.1190在酸胁迫后可能通过改变细胞膜的通透性和控制转运物质来保护菌体、抵抗不良环境。
3.6 抗酸性CGMCC 1.1190与能量代谢相关蛋白的分析
微生物代谢需要的能量是菌体在酶的作用下通过其细胞内一系列氧化还原反应产生的,微生物提供能量的途径以三羧酸循环和糖酵解为主,能量代谢的正常进行是保证菌体正常生长的必要条件[37]。本研究探讨CGMCC 1.1190抗酸性菌株的蛋白组,发现参与三羧酸循环的蛋白表达多上调,包括异柠檬酸脱氢酶(IcdA)、异柠檬酸裂解酶(aceA)、柠檬酸裂合酶(citG)等,表明CGMCC 1.1190菌体在适应酸胁迫环境时消耗了大量能量来维持自身正常的生理代谢。本研究发现, 抗酸性CGMCC 1.1190丙酮酸分解代谢途径的磷酸烯醇式丙酮酸碳羧化酶(PckA)活跃,说明其分解产生了更多能量以维持酸胁迫下菌体细胞的稳态。此外,本研究还发现,CGMCC 1.1190菌体内氨基烷基膦酸酯N-乙酰转移酶(phnO)上调,该路径可以促进CoA生成。有研究报道,当生物体遭受外界胁迫作用,可以通过CoA激活体内的免疫应答来抵抗外部胁迫[38]。由此推测,酸胁迫下CGMCC 1.1190菌体内的CoA的表达变化激活了菌体内的应激反应,导致抗酸性增加。
4. 结论
本实验通过ITRAQ蛋白组技术对鼠伤寒沙门氏菌CGMCC 1.1190在经柠檬酸调节pH为2.5的TSB基质中进行多次酸胁迫处理后的差异表达蛋白进行研究,共检测到2373个蛋白,其中195个差异蛋白,包括95个显著下调蛋白和100个显著上调蛋白。通过对CGMCC 1.1190菌株的差异蛋白进行GO分析和KEGG分析,发现抗酸性菌株高表达应激蛋白相关基因,可以通过合成一些应答外界刺激的蛋白质来帮助CGMCC 1.1190增强抗酸性;高表达细胞膜相关蛋白来增加CGMCC 1.1190菌体细胞膜的完整性;高表达鞭毛相关蛋白来增强CGMCC 1.1190菌体的运动能力和增加保护性生物被膜的形成;高表达双组分系统相关蛋白来响应酸信号,通过调控酸激蛋白的产生增强CGMCC 1.1190菌体的抗酸性;低表达ABC转运系统相关蛋白来降低细胞膜对H+的通透性,达到保护菌体的作用;高表达能量代谢途径相关蛋白来为CGMCC 1.1190菌体应对酸胁迫提供能量、维持稳态。综上可知,CGMCC 1.1190在经过pH2.5的柠檬酸胁迫,能通过蛋白水平的表达变化启动一系列应答机制并生存下来。
-
表 1 RT-qPCR验证基因及引物设计
Table 1 RT-qPCR verification gene and primer design
基因 序列(5' to 3') 产物长度(bp) 16S rRNA F: TCGTGTTGTGAAATGTTGGGTTA
R: ACCGCTGGCAACAAAGGAT66 rpoS F: TTGCCCGCCGTTATGG
R: CACGGATAAGCCCCAGGTT75 ompC F: AATGGTGGTAAGGCAGGTCA
R: TGGCACCTTTGTTGAATCCG233 aceA F: CTTTCCGTCGTGCAGATCAG
R: GCCAGCTGATCTTCGAAGTG190 lexA F: TGCTGGCGGTACATAAAACG
R: TAAAGCTTTGTTCGCGCAGA171 phoQ F: CCGTCAGTTCACTTTCACCC
R: ATGGTGCTGGATTTAGGGCT244 phoP F: TCGGCGCTAATGTGGATAGT
R: AGATGTGATCCTCCCCTCCT201 malE F: CGGTCAGCAGGTAGTTTTCG
R: GATTACTCCATCGCCGAAGC235 malK F: GTCGGCGCCAATATGTCTTT
R: TACCAGCACCACGTCATTCT183 表 2 CGMCC 1.1190对照组和抗酸组菌株蛋白质样品浓度及评价结果
Table 2 Concentration and valuation results of protein samples of CGMCC 1.1190 control strain and the acid-resistant strain
样品名称 浓度(μg/μL) 体积(μL) 总量(μg) 物种 样品评价 CK1 2.8 200 562.6 鼠伤寒沙门氏菌 a CK2 2.8 200 560.4 鼠伤寒沙门氏菌 a T1 1.7 200 337.5 鼠伤寒沙门氏菌 a T2 1.9 200 378.2 鼠伤寒沙门氏菌 a 表 3 应激相关蛋白信息
Table 3 List of protein information related to stress
序列号 蛋白质名称 基因名称 变化倍数 P0DM81 RNA聚合酶σ因子 rpoS 1.8342 Q7CQI8 酸胁迫伴侣 hdeB 1.2320 Q7CPF1 小热休克蛋白 ibpA 1.3575 Q93GL9 TraT抗补体蛋白 traT 1.3638 Q7CPS2 抗性蛋白 yqiE 1.3167 Q7CQV9 DNA保护蛋白 dps 1.3061 A0A0F6B082 重组和修复蛋白RecT STM14_1422 1.5535 P0A273 LexA阻遏蛋白 lexA 0.7513 P65977 RecA蛋白 recA 1.1827 表 4 细胞膜相关蛋白信息
Table 4 List of protein information associated with membrane
序列号 蛋白质名称 基因名称 变化倍数 H9L452 膜融合蛋白家族蛋白 STM4260 3.3396 Q7CQ87 DedA家族膜蛋白 yohD 2.9208 P0A263 外膜孔道蛋白C ompC 2.1344 P60636 UPF0299膜蛋白 yohJ 1.8162 Q8ZPH7 外膜蛋白 STM1530 1.4350 Q8ZPH9 外膜蛋白 STM1528 1.4296 Q8ZQT6 Tol-Pal系统蛋白 tolA 1.2472 Q8ZQT5 Tol-Pal系统蛋白 tolB 1.2997 Q7CQX1 Tol-Pal系统蛋白 tolQ 1.3773 Q7CQX0 Tol-Pal系统蛋白 tolR 1.2260 Q7CQW9 肽多糖相关蛋白 pal 1.2574 P0A1Z2 伴侣蛋白 skp 1.3683 Q7CQI7 外膜脂蛋白 STM1585 0.7387 P37924 外膜传入蛋白 fimD 0.6591 表 5 鞭毛相关蛋白信息
Table 5 List of protein information related to flagella
序列号 蛋白质名称 基因名称 变化倍数 P06179 鞭毛丝蛋白 fliC 1.8826 P0A1L1 鞭毛蛋白 fliO 1.5576 P0A1N8 鞭毛L环蛋白 flgH 1.4862 P0A1J3 鞭毛基体杆蛋白 flgG 1.3145 P40729 鞭毛生物合成蛋白 flhA 1.3734 表 6 双组分系统相关蛋白信息
Table 6 List of protein information related to two-component system
序列号 蛋白质名称 基因名称 变化倍数 D0ZV89 病毒性传感器组氨酸激酶 phoQ 1.5249 P0DM78 病毒性转录调节蛋白 phoP 1.4992 P66795 转录调控蛋白 qseB 1.3689 Q8ZLZ9 感应蛋白 qseC 1.1199 P08982 组氨酸激酶传感蛋白 envZ 1.5124 P0AA19 DNA结合双转录调节因子 ompR 1.3231 Q8ZK33 精氨酸脱亚胺酶 arcA 0.5487 Q8ZK35 鸟氨酸氨基甲酰转移酶 arcB 0.5671 P26319 菌毛Z蛋白 fimZ 0.7799 Q8ZNE6 趋化信号转导蛋白 cheV 0.6580 Q8ZP35 感应蛋白 narX 1.7159 表 7 ABC转运系统相关蛋白信息
Table 7 List of protein information related to ABC transfer system
序列号 蛋白质名称 基因名称 变化倍数 Q8ZRF5 ABC超家族转运蛋白 sbmA 1.3913 P26467 麦芽糖/麦芽糊精运输系统渗透酶蛋白 malF 0.7245 P19566 麦芽糖/麦芽糊精导入ATP结合蛋白 malK 0.7242 Q8ZPY2 ABC转运蛋白 STM1256 0.7165 Q8ZLL2 ABC转运蛋白的ATP酶成分 yheS 0.8449 P19576 麦芽糖/麦芽糊精结合周质蛋白 malE 0.5970 表 8 与能量代谢相关蛋白信息
Table 8 List of protein information related to energy metabolism
序列号 蛋白质名称 基因名称 变化倍数 Q8ZR15 DASS家族,柠檬酸:琥珀酸反向
运输蛋白CitT 1.8974 A0A0F6AYB4 柠檬酸裂解酶酰基载体蛋白 CitD 1.5281 A0A0F6AWI7 柠檬酸裂合酶 CitG 1.4021 Q8ZR12 柠檬酸裂解酶α链 CitF 1.3776 Q8ZRS8 乌头酸酶 AcnB 0.7323 A0A0F6B076 异柠檬酸脱氢酶 IcdA 1.6976 P51066 异柠檬酸裂解酶 aceA 1.9218 Q8ZME4 焦磷酸酶 MazG 1.3169 P17127 多磷酸转移蛋白 FruB 1.3806 A0A0F6B7V7 磷酸烯醇丙酮酸羧化酶 PckA 0.7609 Q7CQ52 NADH-醌氧化还原酶亚基J nuoJ 1.6067 P67638 富马酸还原酶亚基C frdC 1.4719 A0A0F6BAK6 富马酸还原酶亚基D frdD 1.6074 Q8ZKE6 氨基烷基膦酸酯N-乙酰转移酶 phnO 1.3545 -
[1] XIE S, ZHANG H, MATJEKE R S, et al. Bacillus coagulans protect against Salmonella enteritidis-induced intestinal mucosal damage in young chickens by inducing the differentiation of goblet cells[J]. Poultry Science,2022,101(3):101639. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2021.101639
[2] 翟立公, 李港回, 周紫洁, 等. 高渗适应德尔卑沙门氏菌对交叉环境胁迫抗性分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(15):69−77. [ZHAI L G, LI G H, ZHOU Z J, et al. Tolerance of hypertonic adapted Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica Derby to overlapping various environmental stresses[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022,48(15):69−77. [3] HE S, CUI Y, QIN X, et al. Influence of ethanol adaptation on Salmonella enterica serovar enteritidis survival in acidic environments and expression of acid tolerance-related genes[J]. Food Microbiology,2018,72:193−198. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2017.12.005
[4] ALONSO C C, GUERRERO R E, ALONSO H A, et al. Adaptation and cross-adaptation of Escherichia coli ATCC 12806 to several food-grade biocides[J]. Food Control,2015,56:86−94. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.03.012
[5] CHEN M J, TANG H Y, CHIANG M L. Effects of heat, cold, acid and bile salt adaptations on the stress tolerance and protein expression of kefir-isolated probiotic Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens M1[J]. Food Microbiology,2017,66:20−27. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2017.03.020
[6] 钱静亚, 张咪, 孙文敬, 等. 蛋白质组学在食品非热杀菌中的应用研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(3):288−294. [QIAN Y J, ZHANG M, SUN W J, et al. Advances in the application of proteomics in non-thermal sterilization of foods[J]. Food Science,2020,41(3):288−294. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190120-240 [7] 马骏骏, 王旭初, 聂小军. 生物信息学在蛋白质组学研究中的应用进展[J]. 生物信息学,2021,19(2):85−91. [MA J J, WANG X C, NIE X J. Advances in the application of bioinformatics in proteomics research[J]. Chinese Journal of Bioinformatics,2021,19(2):85−91. doi: 10.12113/202004009 [8] CARVALHAIS V, CERCA N, VILANOVA M, et al. Proteomic profile of dormancy within Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms using iTRAQ and label-free strategies[J]. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, 2015, 99(6): 2751−2762.
[9] LIU Y, QIU Y, YIN Q, et al. iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomic reveals proteomic changes in Serratia sp. CM01 and mechanism of Cr(Ⅵ) resistance[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2021,228:112899. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112899
[10] 张佩佩. 热胁迫下甲型副伤寒沙门氏菌的蛋白质组学研究[D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2016. ZHANG P P. The proteomics of Salmonella paratyphi A under heat stress[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2016.
[11] 何学文. 基于iTRAQ技术探究肉桂醛抑制鼠伤寒沙门氏菌的机制[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2019. HE X W. Investigate the mechanism of cinnamaldehyde inhibiting of Salmonella typhimurium based on iTRAQ technology[D]. Yaan: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2019.
[12] 李琳琼, 洪静, 张丽君, 等. 酸胁迫对鼠伤寒沙门氏菌抗酸性、细胞膜及膜蛋白的影响[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(15):27−36. [LI L Q, HONG J, ZHANG L J, et al. Effect of acid stress on acid resistance, cell membrane and membrane protein of Salmonella typhimurium[J]. Food Science,2021,42(15):27−36. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20201223-261 [13] 王鹏, 王军节, 李贞彪. 适用于蛋白质组分析的粉红单端孢菌蛋白提取方法的建立[J]. 华北农学报,2019,34(3):209−216. [WANG P, WANG J J, LI Z B. Extraction method of total protein from Trichothecium roseum suitable for proteomic analysis[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica,2019,34(3):209−216. doi: 10.7668/hbnxb.201751366 [14] 岳柠柠, 吴真, 张旭敏. 重组LysargiNase蛋白酶的表达纯化及其在蛋白质组学层面的分析[J]. 复旦学报(自然科学版),2022,61(3):284−294. [YUE N N, WU Z, ZHANG X M. Expression purification of recombinant LysargiNase protease and its analysis at the proteomic level[J]. Journal of Fudan University (Natural Science),2022,61(3):284−294. [15] SADEH N M, HILDUM D W, KJENSTAD D, et al. MASCOT: An agent-based architecture for dynamic supply chain creation and coordination in the internet economy[J]. Production Planning & Control,2001,12(3):212−223.
[16] 张彩霞, 袁高鹏, 韩晓蕾, 等. 基于iTRAQ定量蛋白质组技术筛选‘华月’苹果斑点落叶病抗性相关蛋白[J]. 植物病理学报,2018,48(6):787−798. [ZHANG C X, YUAN G P, HAN X L, et al. iTRAQ-based proteomic approach for screening of resistant associated proteins in 'Huayue' apple leaves induced by Alternaria mali[J]. Acta Phytopahologica Sinica,2018,48(6):787−798. [17] STEFAN G, MIGUEL G, JAVIER T, et al. High-throughput functional annotation and data mining with the Blast2GO suite[J]. Nucleic Acids Research,2008,36(10):3420−3435. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn176
[18] M ASHBURNER, C A BALL, J A BLAKE, et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The gene ontology consortium[J]. Nature Genetics,2000,25(1):25−29. doi: 10.1038/75556
[19] JEONGIN S, SAIE M, ADAM G. The ER stress protein IRE1a regulates intracellular calcium, ROS, and the UV damage response through the IP3R inhibitor CIB1[J]. Cancer Research,2021,81(13):2029.
[20] 任洁, 赵明文, 姚玉峰. 沙门菌对酸压力的应答及其与毒力的关系[J]. 微生物学报,2014,54(4):367−375. [REN J, ZHAO M W, YAO Y F. Response of Salmonella to acid pressure and its relationship with virulence[J]. Journal of Microbiology,2014,54(4):367−375. [21] LARISSA S, RACHEL A, CAROLINA B, et al. Phosphatidylinositol monophosphates regulate the membrane localization of HSPA1A, a stress-Inducible 70-kDa heat shock protein[J]. Biomolecules,2022,12(6):856. doi: 10.3390/biom12060856
[22] OJHA D, PATIL K N. p-Coumaric acid inhibits the Listeria monocytogenes RecA protein functions and SOS response: An antimicrobial target[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2019,517(4):655−661. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.07.093
[23] STEPHANIE B, RORY E, LUISA H, et al. Membrane protein comparison between cell membranes and extracellular vesicle membranes of S. pneumoniae provide insights into extracellular vesicle formation and shedding[J]. The FASEB Journal,2022,36:R6072.
[24] 戎建荣, 王淑峰, ALISON, 等. 外膜孔道蛋白ompC, ompF的表达与大肠埃希菌耐药的相关性研究[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志,2009,19(6):621−624. [RONG J R, WANG S F, ALISON, et al. Relationship between porins ompC and ompF and antibiotic resistance in Escherichia coli[J]. Chinese Journal of Nosocomiology,2009,19(6):621−624. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-4529.2009.06.007 [25] PROUTY A M, VELKINBURGH J, GUNN J S. Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium resistance to bile: Identification and characterization of the tolQRA cluster[J]. Journal of Bacteriology,2002,184(5):1270−1276. doi: 10.1128/JB.184.5.1270-1276.2002
[26] 赵卫松, 郭庆港, 董丽红, 等. 枯草芽孢杆菌NCD-2对棉花根系分泌物L-脯氨酸响应的转录-蛋白质组学联合分析[J]. 中国农业科学,2021,54(21):4585−4600. [ZHAO W S, GUO Q G, DONG L H, et al. Transcriptome and proteome analysis of Bacillus subtilis NCD-2 response to L-proline from cotton root exudates[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2021,54(21):4585−4600. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2021.21.009 [27] DUAN Q, ZHOU M, ZHU X, et al. The flagella of F18ab Escherichia coli is a virulence factor that contributes to infection in a IPEC-J2 cell model in vitro[J]. Vet Microbiol,2012,160(1−2):132−140. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2012.05.015
[28] WOOD T K, BA RRIOS A, HERZBERG M, et al. Motility influences biofilm architecture in Escherichia coli[J]. Applied Microbiology Biotechnology,2006,72(2):361−367. doi: 10.1007/s00253-005-0263-8
[29] 武珊珊, 敬文宪, 陈启伟, 等. 鼠伤寒沙门氏菌双组分系统arcB基因缺失株的构建及药物敏感性分析[J]. 中国预防兽医学报,2020,42(9):879−886. [WU S S, JING W X, CHEN Q W, et al. Construction of a two-component system arcB gene deletion strain of Salmonella typhimurium and sensitivity analysis of antimicrobial agents[J]. Chinese Journal of Preventive Veterinary Medicine,2020,42(9):879−886. [30] 胡桂花, 陈彪, 黄运红, 等. 炭样小单孢菌JXNU-1双组分信号转导系统的生物信息学分析[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学,2020,39(11):5106−5114. [HU G H, CHEN B, HUANG Y H, et al. Bioinformatic analysis of two-component signal transduction systems in Micromonospora carbonacea JXNU-1[J]. Genomics and Applied Biology,2020,39(11):5106−5114. doi: 10.13417/j.gab.039.005106 [31] 何绿琴. 副猪嗜血杆菌双组份系统QseB/QseC调控功能研究[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2018. HE L Q. Study on the regulatory function of two-component system QseB/QseC of Haemophilus parasuis[D]. Yaan: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2018.
[32] 关亚楠. 嗜酸性喜温硫杆菌中EnvZ/OmpR双组分调控系统的研究[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2017. GUAN Y N. Functional analysis of two-component system EnvZ/OmpR in Acidithiobacillus caldus[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2017.
[33] 武珊珊. 鼠伤寒沙门氏菌CVCC541耐药性双组分系统的筛选及功能研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2020. WU S S. Screening and function of a two-component system for drug resistance of Salmonella typhimurium CVCC541[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2020.
[34] LAMBERT N, KAISAR A M, XIAOYU W, et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis metC (Rv3340) derived hydrogen sulphide conferring bacteria stress survival[J]. Journal of Drug Targeting,2019,27(9):1004−1016. doi: 10.1080/1061186X.2019.1579820
[35] 谢腾飞. 中国食源性副溶血性弧菌遗传多样性分析与冷胁迫研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2018. XIE T F. Study on genetic diversity and cold stress study of foodborne Vibrio parahaemolyticus in China[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2018.
[36] MÄCHTEL R, NARDUCCI A, GRIFFITH D A, et al. An integrated transport mechanism of the maltose ABC importer[J]. Research in Microbiology,2019,170(8):321−337. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2019.09.004
[37] 玄美娟, 张晓云, 高莹, 等. 大肠杆菌糖酵解途径和三羧酸循环启动子的表征及其应用[J]. 中国生物工程杂志,2020,40(6):20−30. [XUAN M J, ZHANG X Y, GAO Y, et al. Characterization of the glycolytic pathway and tricarboxylic acid cycle promoter in Escherichia coli and its application[J]. China Biotechnology,2020,40(6):20−30. [38] 张闪闪. 嗜盐细菌的分离鉴定与Natranaerobius thermophiles盐适应机制的蛋白质组学分析[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2016. ZHANG S S. The isolation and identification of haiophilic bacteria and the proteomic analysis of the adapation to salinity of Natranaerobius thermophiles[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2016.
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 于有伟,张少颖,徐建国,卫永华,崔美林,张亮亮. “悉学思用”四位一体协同培养食品类专业学位硕士研究生应用创新能力研究. 高教学刊. 2023(26): 43-46 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘摇,张鸿雁,雷兴梦,邓丽莉,姚世响,曾凯芳. 枣果实采后侵染性病害及其化学防治研究进展. 植物生理学报. 2022(02): 237-246 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 温晓丽. 外源磷酸钠对枣果实活性氧和苯丙烷代谢关键酶活性及酚类物质积累的影响. 食品工业科技. 2022(17): 381-386 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 赵梅慧,庞林江,成纪予,陆国权,路兴花,王孙杰. 长喙壳菌侵染对不同抗性甘薯细胞壁的影响. 包装工程. 2022(21): 10-16 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



