Effects of Plasma-activated Water and Annealing on Structure and Properties of Waxy Maize Starch and Maize Starch
-
摘要: 本文研究了等离子体活化水(plasma-activated water,PAW)协同韧化处理对蜡质玉米淀粉(waxy maize starch,WMS)和玉米淀粉(maize starch,MS)结构及性能的影响。结果表明,与常规韧化处理相比,PAW韧化没有改变WMS和MS的结晶类型,但降低了相对结晶度。WMS的相对结晶度从37.1%降低到25.9%,MS的相对结晶度从30.3%降低到27.7%。PAW韧化没有使淀粉分子产生新的官能团,但导致WMS和MS的短程有序性降低。PAW韧化降低了WMS和MS的糊化焓(WMS:13.33~12.10 J/g、MS:10.76~10.26 J/g)、峰值黏度和黏弹性,提高了淀粉糊的凝胶强度。PAW协同韧化处理提供了一种淀粉双重物理改性的新方法,在淀粉基凝胶领域具有潜在的应用。Abstract: In this study, the effect of annealing (ANN) with plasma-activated water (PAW) on the structure and properties of waxy maize starch (WMS) and maize starch (MS) was investigated. The results showed that PAW-ANN did not change the crystallinity type of WMS and MS, but decreased the relative crystallinity compared with the conventional ANN. The relative crystallinity of WMS decreased from 37.1% to 25.9%, and the relative crystallinity of MS decreased from 30.3% to 27.7%. PAW-ANN did not induce starch molecules to generate new functional groups, but resulted in a reduction in the short-range order of WMS and MS. PAW-ANN decreased the gelatinization enthalpy (WMS: 13.33~12.10 J/g, MS: 10.76~10.26 J/g), peak viscosity, and viscoelasticity of WMS and MS, and improved the gel strength of starch pastes. PAW combined with annealing provides a novel dual physical modification method of starch, which has potential applications in the field of starch-based hydrogels.
-
Keywords:
- plasma-activated water /
- annealing /
- structure /
- properties /
- waxy maize starch /
- maize starch
-
淀粉是人类营养最重要的碳水化合物来源,在食品工业中具有广泛应用。淀粉由两类大分子组成:直链淀粉,其通过α-1,4糖苷键线性连接;支链淀粉,其主要通过α-1,4糖苷键连接,在分支位点由α-1,6糖苷键连接[1]。天然淀粉具有水合性能差、热稳定性低、抗剪切性低和易回生等缺点[2],而改性淀粉在糊透明度、凝胶性、成膜性和黏合性等方面具有显著优势[3]。淀粉通常通过物理、化学和酶法进行改性,以获得特定的功能特性[4]。物理改性因其安全性高、成本低且废弃物少,受到大家越来越多的重视[5]。
韧化处理是一种在高水分含量(超过40%,w/w)和高于玻璃化转变温度但低于糊化温度的温度下(低于60 ℃)对淀粉进行物理改性的方法,因其仅涉及水和热,近年来已经受到了广泛的关注[6]。为了提高韧化改性的效果,韧化与其他技术联合的多重改性方法已逐渐受到大家的青睐,例如柠檬酸-韧化[7]、赖氨酸-韧化[8]、超声-酶-韧化[9]等。
等离子体活化水(PAW)是一种对水进行等离子体处理后得到的水,其具有和普通水一样的流动性和均一性。等离子体处理水后会产生酸性环境,并生成过氧化氢、硝酸和过氧亚硝酸等活性物质,从而导致PAW的pH、氧化还原电位和电导率发生变化。目前,PAW已被广泛应用于植物生长促进[10]、农产品保鲜[11]、广谱杀菌[12]等领域,具有潜在的应用前景。然而,PAW在淀粉改性领域研究较少。本课题组前期已经研究了单独PAW处理对淀粉结构及性能的影响,然而其改性作用不明显,可能是因为室温下PAW中活性成分未能和淀粉分子发生相互作用。因此,PAW协同韧化处理可能是一种有效的解决方法。
本文将PAW与韧化结合用于玉米淀粉改性,研究了其对蜡质玉米淀粉(WMS)和玉米淀粉(MS)的结构和性能的影响。该双重物理改性方法避免了改性中化学物质或生物酶的使用,简单方便、绿色安全且效果优于常规韧化处理,为淀粉韧化改性提出了一种新思路,同时也为PAW韧化改性方法的应用奠定了理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
蜡质玉米淀粉(直链淀粉含量为4.5%,水分含量10.8%) 河南恒瑞淀粉科技股份有限公司;玉米淀粉(直链淀粉含量为23.2%,水分含量11.3%) 秦皇岛骊骅淀粉有限公司;无水乙醇(分析纯) 天津富宇精细化工有限公司。
TS-PL200空气常压等离子体射流装置 深圳市东信高科自动化设备有限公司;JSM-6490LV型扫描电子显微镜 日本电子株式会社;BX53M偏光显微镜 日本奥林巴斯公司;Bruker D8型X-射线衍射仪、Vertex70型傅里叶变换红外光谱仪 德国布鲁克公司;Atlas型手动压片机 英国斯贝凯公司;Invia Qontor型激光共聚焦显微拉曼光谱仪 英国Renishaw公司;Q20差示扫描量热仪、Discovery HR-1旋转流变仪 美国TA公司;RVA4500快速粘度分析仪 瑞典波通公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 等离子体活化水制备
蒸馏水(DW,100 mL)经空气常压等离子体射流装置处理2 min后得到PAW。PAW的pH为2.72,氧化还原电位值为569.67 mV,电导率值为764.67 µS/cm。电源频率约为25 kHz,输入功率为750 W,等离子体探头在水面正上方2 cm左右。
1.2.2 DW与PAW韧化处理淀粉
将WMS和MS(30 g,干基)在45 ℃烘箱中干燥,使其水分含量降至约5%。然后分别用DW或PAW调节淀粉水分含量至60%,充分搅拌下置于反应釜中,于50 ℃烘箱中加热12 h。冷却、洗涤、烘干后,研磨过筛得改性淀粉。DW、PAW韧化处理淀粉样品分别用DW-WMS、PAW-WMS、DW-MS和PAW-MS表示。其中,WMS和DW-WMS为一组对照,MS和DW-MS为另一组对照。
1.2.3 颗粒形态观察
a. 扫描电子显微镜(SEM):根据课题组以前的方法[13]进行测试,用导电胶粘取适量WMS、DW-WMS、PAW-WMS、MS、DW-MS和PAW-MS样品均匀地贴在样品台上,进行镀金处理以增加电导率。测试所用电压为20 kV,然后采用扫描电子显微镜对样品进行观察,并以1500的放大倍数拍摄图片。
b. 偏光显微镜(PLM):用丙三醇和水的混合液(1:1,v/v)将WMS、DW-WMS、PAW-WMS、MS、DW-MS和PAW-MS样品分别配成1%的淀粉乳液,加一滴于载玻片上,盖上盖玻片,然后采用偏光显微镜观察,并以200的放大倍数拍摄淀粉的偏光十字图片[14]。
1.2.4 X-射线衍射(XRD)
测试前,WMS、DW-WMS、PAW-WMS、MS、DW-MS和PAW-MS样品需在室温下用饱和NaCl溶液平衡一周[13]。用光滑的载玻片将几个样品(0.5 g)弄平并放在模具的圆形螺纹处。用Burker D8型X-射线衍射仪测定,采用波长为0.1542 nm的单色Cu-Kα射线,管压为40 kV,管流为30 mA,扫描速度为2°/min,扫描区域为5°~35°,采样步宽为0.02°,扫描方式为连续,重复次数为1。用Jade 6.0软件计算样品的相对结晶度(relative crystallinity,RC)。
1.2.5 傅里叶变换红外光谱(FTIR)
将溴化钾置于105 ℃烘干后,取一定量的WMS、DW-WMS、PAW-WMS、MS、DW-MS和PAW-MS样品和溴化钾(质量比:1:100)置于研钵中,混合并研磨1 min左右以使样品和溴化钾充分混匀。混合样采用压片机压片,其中,压力保持在10 MPa范围内1 min左右后取出,进行测试。测试条件:扫描波数为4000~400 cm−1,分辨率为4 cm−1,扫描时间为64 s[13]。使用OMNIC 8.2软件分析所得数据,在1200~800 cm−1的范围内进行去卷积并归一化,峰宽为38 cm−1,增强因子为1.9。
1.2.6 拉曼光谱(Raman)
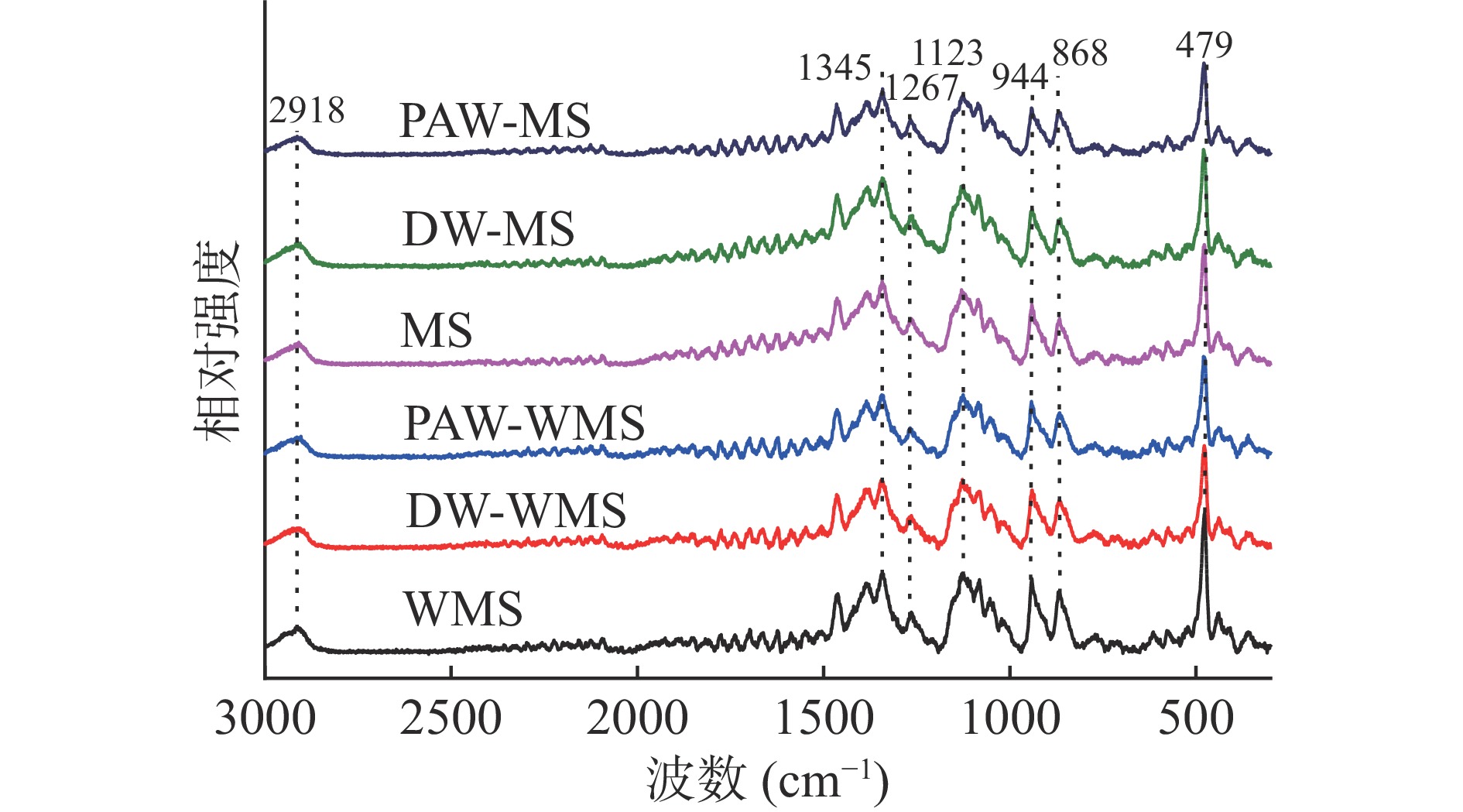
用载玻片将WMS、DW-WMS、PAW-WMS、MS、DW-MS和PAW-MS样品压至平整,在显微镜下将激光聚焦到清晰的淀粉颗粒表面。采用激光共聚焦显微拉曼光谱仪测定,激光波长为785 nm,输出功率为150 W,扫描次数为1次,曝光时间为10000 ms,光谱扫描范围为3000~300 cm−1。使用Wire 5.4软件计算479 cm−1处特征峰的半峰宽(full width at half maxima, FWHM),以表征淀粉的短程有序结构[13]。
1.2.7 差示扫描量热(DSC)
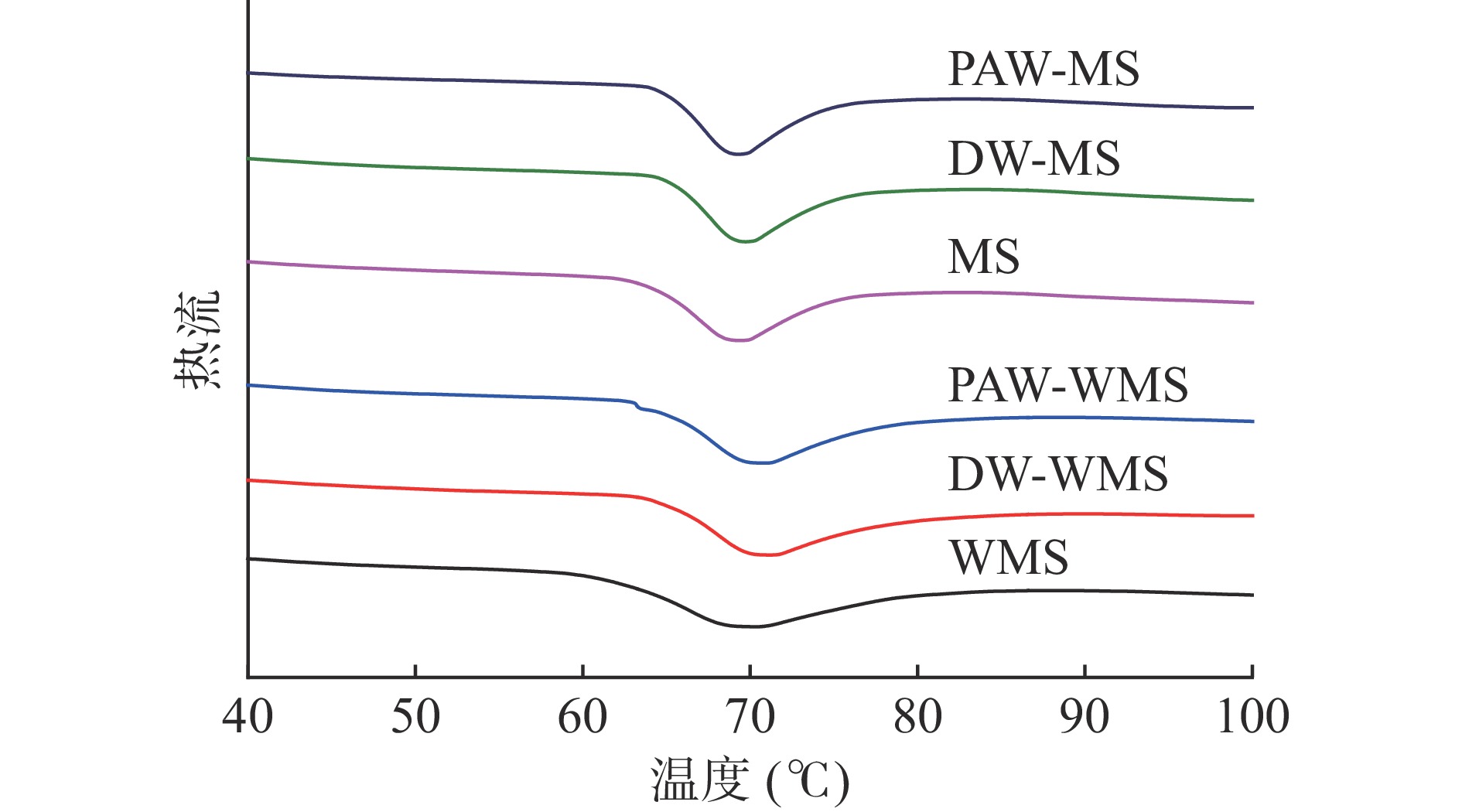
分别称取WMS、DW-WMS、PAW-WMS、MS、DW-MS和PAW-MS样品(3 mg,干基)于铝盘中,加入蒸馏水至12 mg后密封,室温下平衡24 h。测试时,用一个空的铝盘作为参考,在30~120 ℃范围内,以10 ℃/min的速度进行扫描[13]。记录样品的起始温度(To)、峰值温度(Tp)、终止温度(Tc)和糊化焓(ΔH),并用TA2000软件进行分析。
1.2.8 糊化特性(RVA)
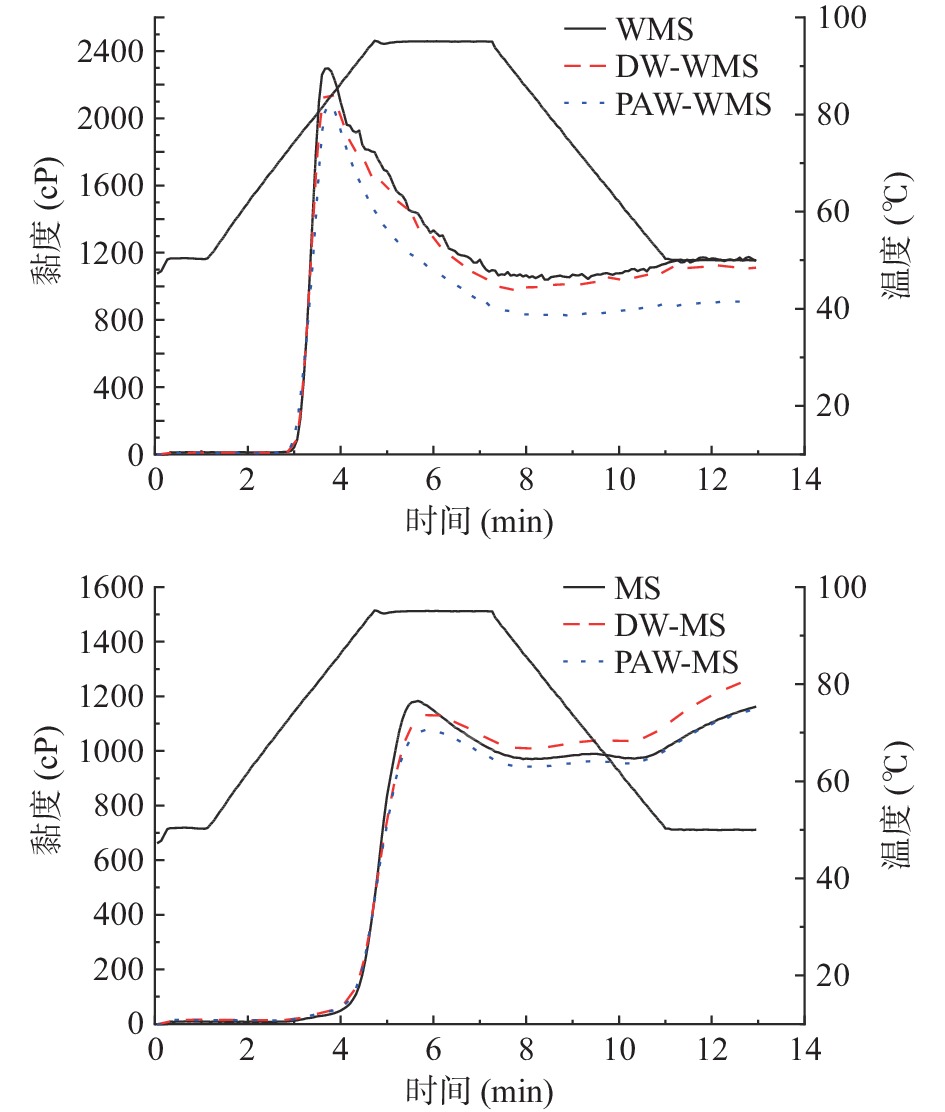
分别称取WMS、DW-WMS、PAW-WMS、MS、DW-MS和PAW-MS样品于铝罐中,加去离子水,使其总重量为28 g(质量分数8%,干基)。使用RVA标准程序1进行测试,将天然和改性淀粉浆液在50 ℃下平衡1 min,在222 s内加热至95 ℃,然后在95 ℃下保持150 s,在228 s内冷却至50 ℃,然后在50 ℃下平衡2 min。在此过程中,桨叶的速度在前10 s保持在960 r/min,随后保持在160 r/min[14]。糊化曲线和参数通过RVA系统软件获得。
1.2.9 流变特性
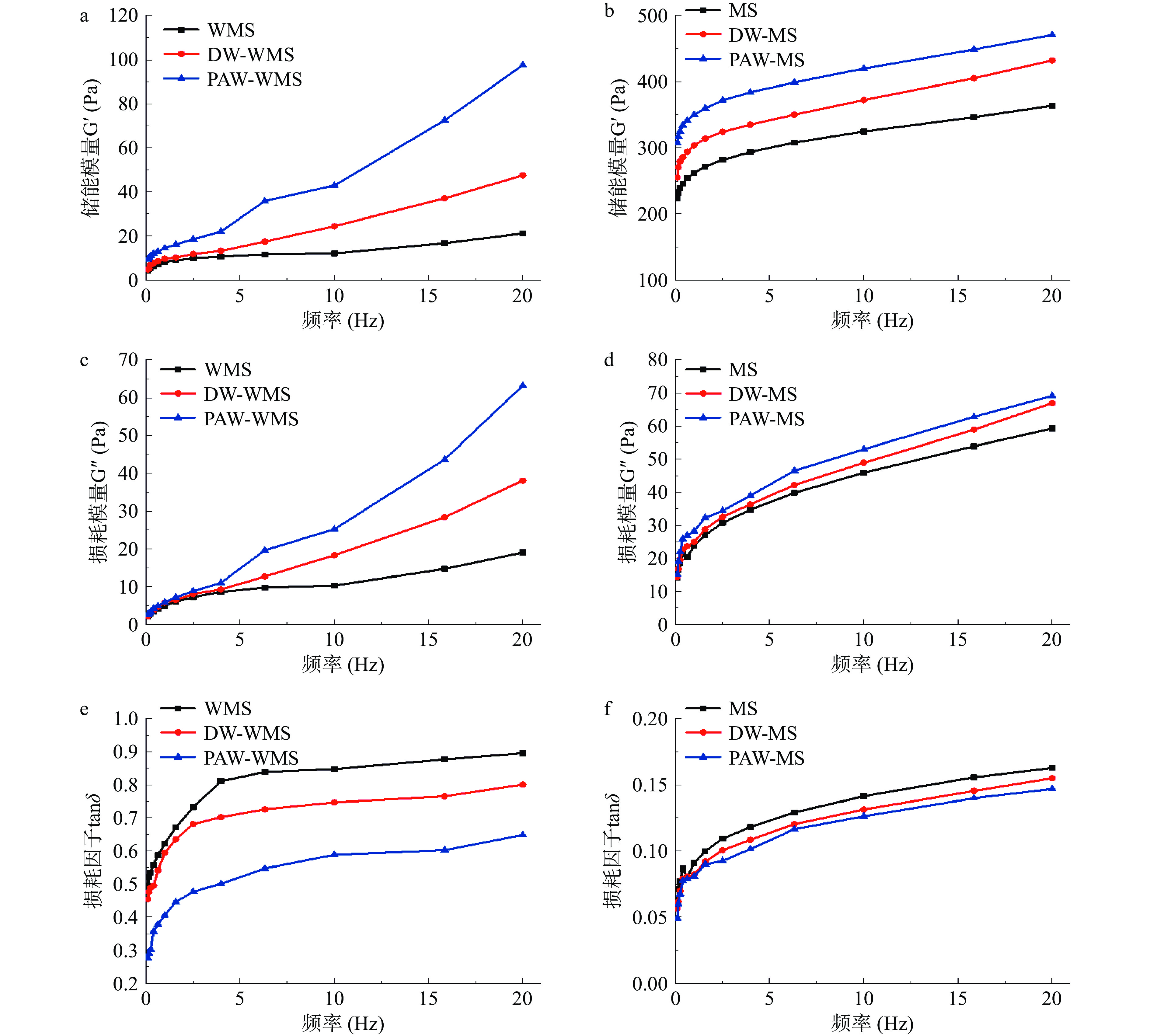
根据课题组以前的方法[14],通过旋转流变仪获得样品的动态流变性质。将通过RVA获得的样品转移到流变仪板(直径40 mm,间隙1000 μm)上,在样品边缘涂抹硅油以防水分蒸发,平衡5 min后,在25 ℃下进行流变测试。在质量分数1%应变下进行0.1~20 Hz的频率范围扫描,并记录得到的储能模量(G′),损耗模量(Gʺ)和损耗因子(tanδ:Gʺ/G′)。
1.3 数据处理
所有试验数据重复三次,使用IBM SPSS Statistics 26.0软件程序Duncan检验法进行显著性分析(P<0.05),所得结果用平均值±标准差表示。本研究均采用Origin 9.0软件作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 PAW韧化处理对WMS和MS颗粒形貌的影响
2.1.1 SEM分析
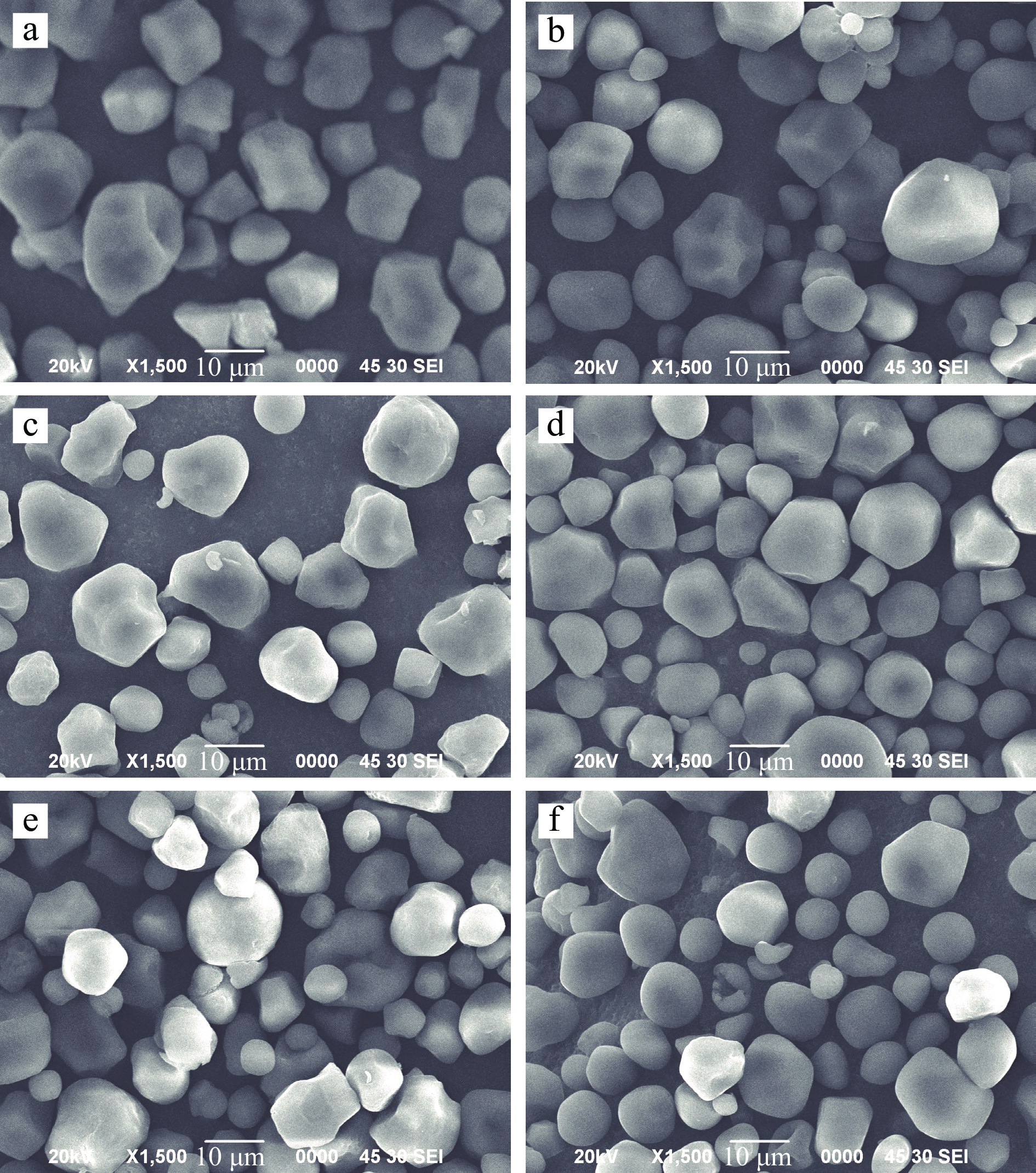
天然淀粉和韧化处理淀粉的扫描电镜图片如图1所示。WMS颗粒大多是有棱角的不规则多面体,MS颗粒则呈现出球形或不规则的多面体,且颗粒体积偏小;两种淀粉表面光滑,大颗粒表面存在少许凹陷。经DW韧化处理后,WMS和MS颗粒表面没有明显改变。而经PAW韧化处理后,WMS和MS颗粒出现了少许破裂,形状变得更不规则,这可能是因为PAW中活性成分对淀粉颗粒表面的蚀刻作用[15]。
![]() 图 1 PAW韧化处理WMS和MS的扫描电子显微镜图(1500×)注:a:WMS;b:MS;c:DW-WMS;d:DW-MS;e:PAW-WMS;f:PAW-MS;图2同。Figure 1. SEM images of WMS and MS treated by PAW and annealing (1500×)
图 1 PAW韧化处理WMS和MS的扫描电子显微镜图(1500×)注:a:WMS;b:MS;c:DW-WMS;d:DW-MS;e:PAW-WMS;f:PAW-MS;图2同。Figure 1. SEM images of WMS and MS treated by PAW and annealing (1500×)2.1.2 PLM分析
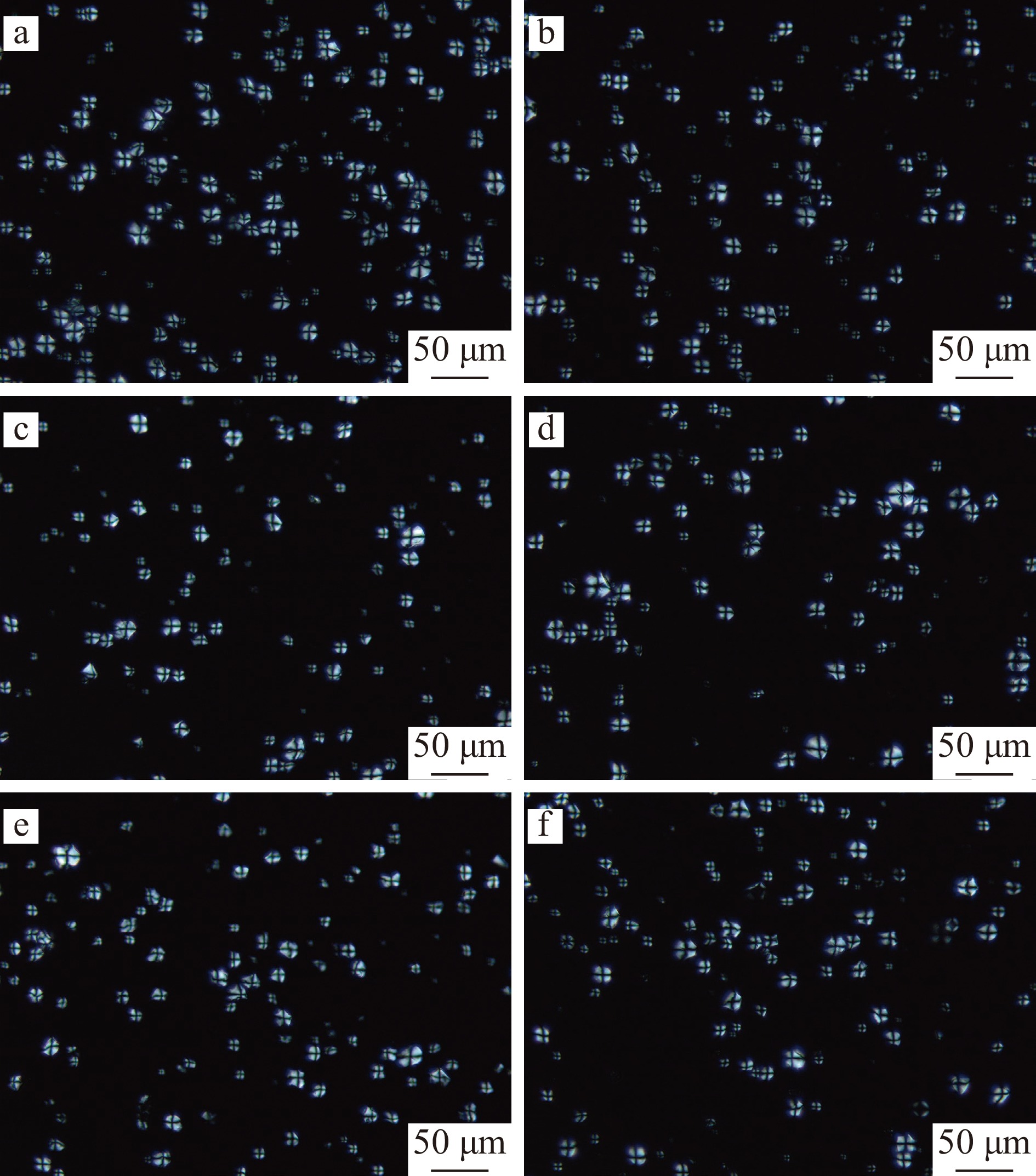
天然淀粉和韧化处理淀粉的偏光显微镜图如图2所示。淀粉颗粒显示特征性的双折射模式(“马耳他十字”),双折射的强度取决于相对结晶度颗粒的总体尺寸和微晶取向[16]。从图2可以看出,经DW韧化和PAW韧化处理后,WMS和MS呈现的偏光十字没有明显变化。
2.2 PAW韧化处理对WMS和MS结晶结构的影响
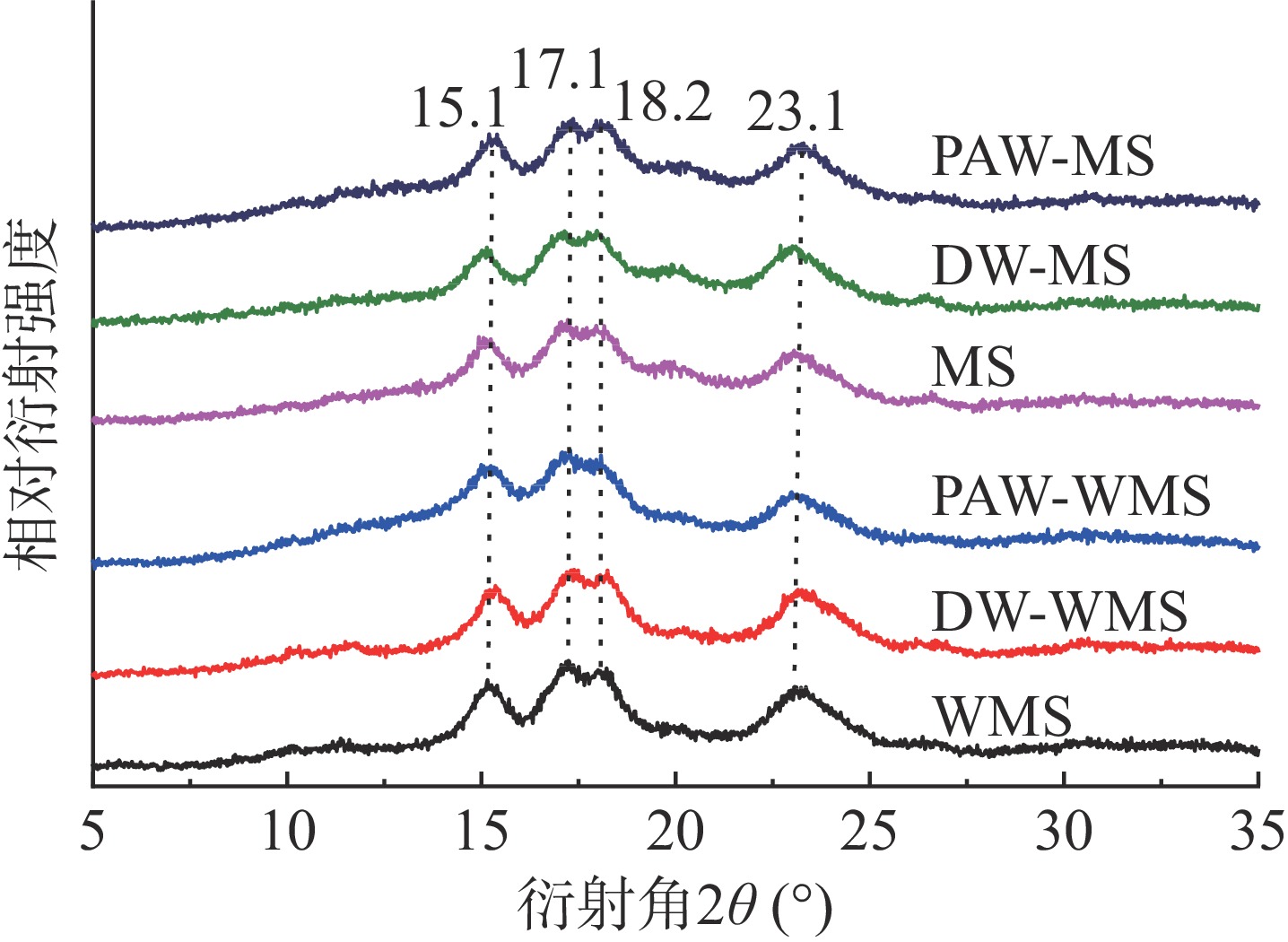
天然淀粉和韧化处理淀粉的X射线衍射图如图3所示。WMS和MS经韧化处理前后衍射图在15.1°、17.1°、18.2°和23.1°处出现衍射峰,属于A型淀粉结构[17],说明韧化并没有改变WMS和MS的结晶结构类型。从表1看出,对于WMS和MS而言,韧化处理淀粉的RC都低于天然淀粉,这可能是由于韧化破坏了淀粉颗粒中的结晶结构或使其发生了重新取向[18]。此外,相比天然和DW韧化处理淀粉,PAW韧化处理淀粉的RC最低,这可能是因为韧化处理后,淀粉对酸水解的敏感性增强,从而导致其结晶区更易被PAW中的酸性成分水解[19]。值得注意的是,PAW韧化导致WMS的RC从37.1%降低到25.9%,变化明显大于MS。
表 1 PAW韧化处理WMS和MS的RC、R1047/1022和FWHMTable 1. RC, R1047/1022 and FWHM of WMS and MS by PAW and annealing样品 RC(%) R1047/1022 FWHM(cm−1) WMS 37.1±0.25a 0.9164±0.002a 14.95±0.014c DW-WMS 33.2±0.30b 0.8844±0.007a 15.84±0.021b PAW-WMS 25.9±0.31c 0.8472±0.032b 16.49±0.205a MS 30.3±0.21a 0.8938±0.004a 15.36±0.035c DW-MS 28.9±0.35b 0.8268±0.005b 16.26±0.071b PAW-MS 27.7±0.33c 0.8124±0.011b 16.85±0.014a 注:数值为平均值±标准差,同列同类淀粉不同字母表示显著性差异(P<0.05);表2同。 2.3 PAW韧化处理对WMS和MS分子结构及短程有序性的影响
2.3.1 FTIR分析
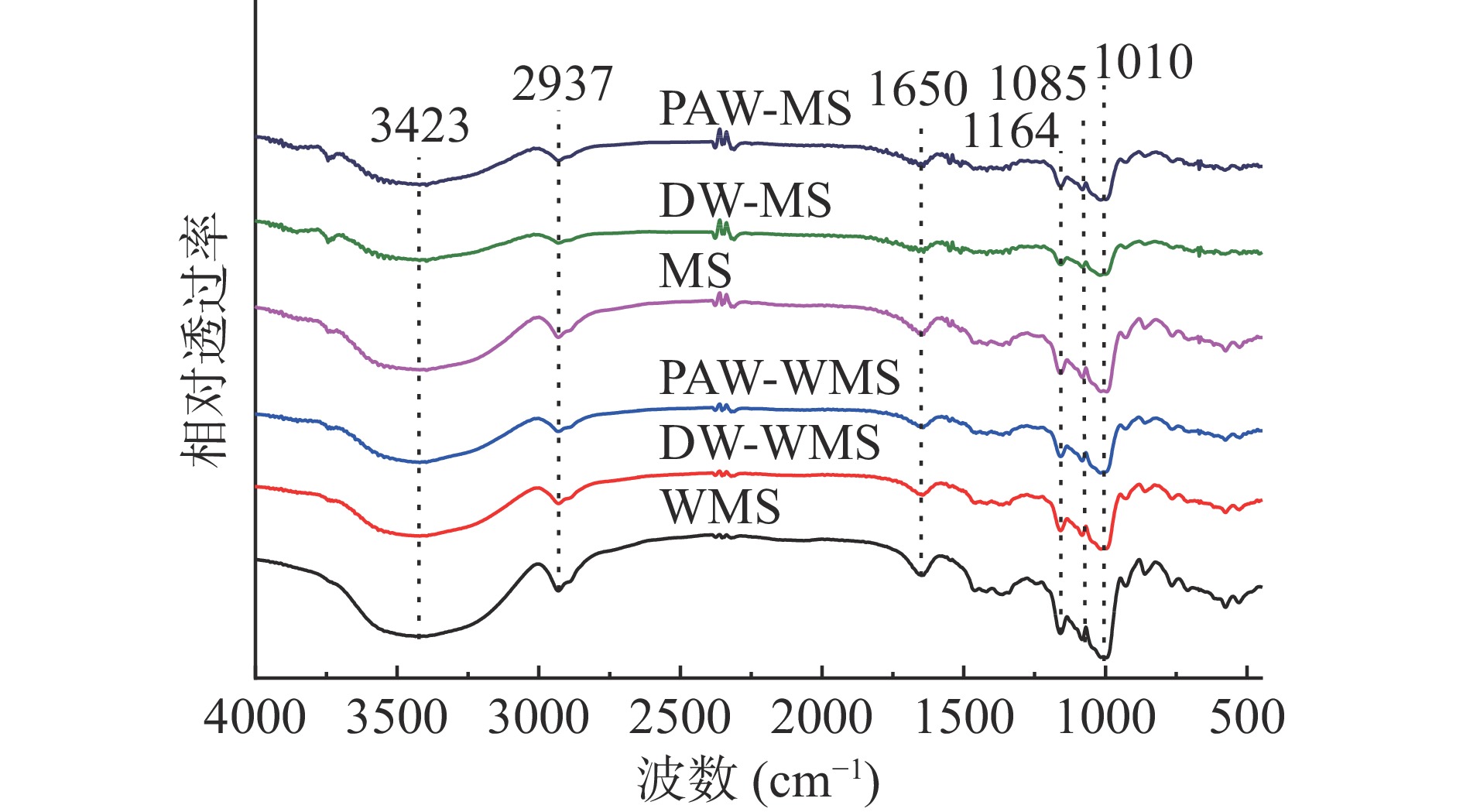
天然淀粉和韧化处理淀粉的红外光谱如图4所示。所有淀粉样品的红外光谱显示出相同的特征峰,表明韧化过程中没有新的官能团形成。3700~3100 cm−1处的谱带是羟基伸缩振动的特征峰[20],2937 cm−1处的特征峰归因于C-H的伸缩振动[21],1650 cm−1处的特征峰归因于淀粉无定形区域中水分子-OH的剪切振动[22],1164、1085和1010 cm−1处的特征峰分别对应于不对称的C-O-C、C-O和C-C骨架伸缩振动[23]。
1047和1022 cm−1处的红外特征峰分别表示淀粉的结晶结构和无定形结构,两者的吸光度比值R1047/1022可以反映淀粉分子的短程有序性[24]。从表1得出,对于WMS和MS而言,PAW韧化处理淀粉的R1047/1022低于天然淀粉和DW韧化处理淀粉,这可能是因为韧化使淀粉颗粒内部的有序结构受到破坏,而且PAW中的酸性成分和活性物质与淀粉链之间的相互作用加剧了这种破坏[25]。R1047/1022结果与XRD相对结晶度结果基本一致。
2.3.2 Raman光谱分析
天然淀粉和韧化处理淀粉的拉曼光谱如图5所示。所有淀粉样品的拉曼光谱显示出相同的特征峰,表明没有新的官能团形成。2800~3000 cm−1谱带归因于C-H的伸缩振动[26],800~1500 cm−1谱带属于淀粉的指纹区,1345、1267、1123、944和868 cm−1分别为C-OH弯曲振动、CH2变形振动、C-O伸缩振动、C1-O-C4'对称伸缩振动和C-H变形振动[27],479 cm−1处的强谱带为淀粉的吡喃环骨架振动区域[28]。
在479 cm−1处吸收峰的FWHM可用来表征淀粉的短程有序性,FWHM越低,淀粉短程有序性越高[29]。从表1中可以得出,对于WMS和MS而言,韧化处理淀粉的FWHM均高于天然淀粉,其中PAW韧化处理淀粉的FWHM最高。这是因为韧化可能导致淀粉双螺旋结构减少,短程有序性下降;而PAW中活性成分能够使淀粉分子链发生断裂,从而进一步降低淀粉的短程有序性。Raman结果与FTIR和XRD结果基本一致。
2.4 PAW韧化处理对WMS和MS热力学性质的影响
天然淀粉和韧化处理淀粉的DSC曲线如图6所示。所有淀粉样品都呈现出一个相似的吸热峰,这是典型的淀粉糊化峰,具体的糊化参数见表2。从表2可以明显看出,韧化增加了WMS和MS的峰值糊化温度(Tp)。这是因为韧化增强了直链淀粉与直链淀粉或支链淀粉之间的相互作用[30]。ΔH的变化反映了淀粉内部双螺旋含量的变化[31]。表2中韧化处理淀粉ΔH均低于天然淀粉,其中,PAW韧化处理淀粉的ΔH最小。这是因为韧化导致了淀粉颗粒内部双螺旋结构含量的下降[32],而PAW导致淀粉分子链发生断裂,从而使淀粉的双螺旋结构进一步减少。ΔH结果与XRD、FTIR和Raman结果基本一致。
表 2 PAW韧化处理WMS和MS的热力学参数Table 2. Thermal parameters of WMS and MS treated by PAW and annealing样品 To(℃) Tp(℃) Tc(℃) ΔH(J/g) WMS 62.20±0.148c 69.09±0.162b 83.31±0.692a 13.33±0.491a DW-WMS 65.24±0.007a 70.51±0.035a 82.65±1.270a 12.28±0.122b PAW-WMS 64.91±0.071b 69.92±0.662a 80.95±0.629a 12.10±0.035b MS 64.30±0.141b 68.97±0.212b 80.67±0.021a 10.76±0.056a DW-MS 65.54±0.073a 69.57±0.042a 78.82±0.246b 10.45±0.021b PAW-MS 65.26±0.145a 69.33±0.197ab 77.81±0.318c 10.26±0.007c 2.5 PAW韧化处理对WMS和MS糊化特性的影响
天然淀粉和韧化处理淀粉的糊化特性曲线如图7所示。韧化处理后WMS和MS的峰值黏度均降低。这可能是由于韧化增强了淀粉分子链间的相互作用,使其结合水的能力降低,抑制了颗粒膨胀和淀粉的溶出[33]。PAW韧化处理淀粉的峰值黏度最低,可能是因为酸水解导致淀粉链发生断裂,产生短链淀粉分子[34]。
2.6 PAW韧化处理对WMS和MS动态流变特性的影响
天然和韧化处理淀粉的动态流变特性如图8所示。储能模量G′和损耗模量Gʺ分别代表淀粉凝胶的弹性和黏性[35],损耗因子tanδ表示黏性和弹性组分对淀粉糊黏弹性的相对贡献[36]。从图中可以看出,所有淀粉糊的G′和Gʺ都随频率的增加而增加,这表明淀粉糊具有典型的弱凝胶结构[37]。与天然淀粉相比,改性淀粉显示出更高的G′、Gʺ和更低的tanδ值,该结果表明经过韧化处理后淀粉的固体特性和凝胶强度增强。这可能是因为在改性过程中,通过淀粉颗粒表面上形成的孔和裂缝流出的直链淀粉单元的重新排列增加了淀粉凝胶的硬度[38]。特别地,PAW韧化处理淀粉表现出最低的tanδ,具有较低的黏弹性和最高的凝胶强度,将可能成为软糖、冰淇淋和肉类食品的潜在胶凝剂[14]。相比MS,PAW韧化处理对WMS的tanδ影响更为显著。
3. 结论
本文研究表明,PAW协同韧化处理对WMS和MS的结构和性能具有明显影响。XRD、FTIR和拉曼结果表明,与常规DW韧化处理相比,PAW韧化处理中PAW中的活性成分会破坏淀粉颗粒内部支链淀粉的双螺旋结构,导致其含量下降,进而导致WMS和MS长程有序性和短程有序性降低。DSC、糊化特性和流变特性分析表明,PAW韧化处理导致WMS和MS的糊化焓、峰值黏度和黏弹性均下降,而淀粉糊的凝胶强度增加。PAW韧化处理对WMS的改性作用略大于MS。该研究为PAW在淀粉改性中的应用提供了新思路,在淀粉基凝胶领域具有潜在的应用。
-
图 1 PAW韧化处理WMS和MS的扫描电子显微镜图(1500×)
注:a:WMS;b:MS;c:DW-WMS;d:DW-MS;e:PAW-WMS;f:PAW-MS;图2同。
Figure 1. SEM images of WMS and MS treated by PAW and annealing (1500×)
表 1 PAW韧化处理WMS和MS的RC、R1047/1022和FWHM
Table 1 RC, R1047/1022 and FWHM of WMS and MS by PAW and annealing
样品 RC(%) R1047/1022 FWHM(cm−1) WMS 37.1±0.25a 0.9164±0.002a 14.95±0.014c DW-WMS 33.2±0.30b 0.8844±0.007a 15.84±0.021b PAW-WMS 25.9±0.31c 0.8472±0.032b 16.49±0.205a MS 30.3±0.21a 0.8938±0.004a 15.36±0.035c DW-MS 28.9±0.35b 0.8268±0.005b 16.26±0.071b PAW-MS 27.7±0.33c 0.8124±0.011b 16.85±0.014a 注:数值为平均值±标准差,同列同类淀粉不同字母表示显著性差异(P<0.05);表2同。 表 2 PAW韧化处理WMS和MS的热力学参数
Table 2 Thermal parameters of WMS and MS treated by PAW and annealing
样品 To(℃) Tp(℃) Tc(℃) ΔH(J/g) WMS 62.20±0.148c 69.09±0.162b 83.31±0.692a 13.33±0.491a DW-WMS 65.24±0.007a 70.51±0.035a 82.65±1.270a 12.28±0.122b PAW-WMS 64.91±0.071b 69.92±0.662a 80.95±0.629a 12.10±0.035b MS 64.30±0.141b 68.97±0.212b 80.67±0.021a 10.76±0.056a DW-MS 65.54±0.073a 69.57±0.042a 78.82±0.246b 10.45±0.021b PAW-MS 65.26±0.145a 69.33±0.197ab 77.81±0.318c 10.26±0.007c -
[1] FUJITA N. Starch[J]. Encyclopedia of Applied Plant Sciences,2017,2:106−111.
[2] KAUR M, SINGH S. Influence of heat-moisture treatment (HMT) on physicochemical and functional properties of starches from different Indian oat (Avena sativa L.) cultivars[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,122:312−319. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.10.197
[3] PUNIA S. Barley starch modifications: Physical, chemical and enzymatic-A review[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,144:578−585. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.12.088
[4] YADAV B S, GULERIA P, YADAV R B. Hydrothermal modification of Indian water chestnut starch: Influence of heat-moisture treatment and annealing on the physicochemical, gelatinization and pasting characteristics[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2013,53(1):211−217. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2013.02.007
[5] ZHANG F, ZHANG Y Y, THAKUR K, et al. Structural and physicochemical characteristics of lycoris starch treated with different physical methods[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,275:8−14. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.09.079
[6] GUO B Z, WANG Y T, PANG M, et al. Annealing treatment of amylose and amylopectin extracted from rice starch[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,164:3496−3500. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.245
[7] TTMDA B, NTMHC D, NTLPB D, et al. Physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility of mung-bean starches varying amylose contents under citric acid and hydrothermal treatments[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,164:651−658. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.187
[8] SUDHEESH C, SUNOOJ K V, ANJALI K U, et al. Effect of lysine incorporation, annealing and heat moisture treatment alone and in combination on the physico-chemical, retrogradation, rheological properties and in vitro digestibility of kithul (Caryota urens L.) starch[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2020,55(6):2391−2398.
[9] WANG X Y, HU A J, ZHENG J, et al. Physicochemical properties and structure of annealed sweet potato starch: Effects of enzyme and ultrasound[J]. Starch-Stärke,2020,72(11-12):1900247.
[10] THIRUMDAS R, KOTHAKOTA A, ANNAPURE U, et al. Plasma activated water (PAW): Chemistry, physico-chemical properties, applications in food and agriculture[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2018,77:21−31.
[11] LIAO X Y, SU Y, LIU D D, et al. Application of atmospheric cold plasma-activated water (PAW) ice for preservation of shrimps (Metapenaeus ensis)[J]. Food Control,2018,94:307−314. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2018.07.026
[12] ZHOU R W, ZHOU R S, PRASAD K, et al. Cold atmospheric plasma activated water as a prospective disinfectant: The crucial role of peroxynitrite[J]. Green Chemistry,2018,20(23):5276−5284. doi: 10.1039/C8GC02800A
[13] YAN Y Z, FENG L L, SHI M M, et al. Effect of plasma-activated water on the structure and in vitro digestibility of waxy and normal maize starches during heat-moisture treatment[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,306:125589. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125589
[14] YAN Y Z, PENG B X, NIU B, et al. Understanding the structure, thermal, pasting, and rheological properties of potato and pea starches affected by annealing using plasma-activated water[J]. Frontiers in Nutrition,2022,9:842662. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.842662
[15] ZHOU Y P, YAN Y Z, SHI M M, et al. Effect of an atmospheric pressure plasma jet on the structure and physicochemical properties of waxy and normal maize starch[J]. Polymers,2019,11(1):8.
[16] ZHANG B J, LI X X, LIU J, et al. Supramolecular structure of A- and B-type granules of wheat starch[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2013,31(1):68−73. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2012.10.006
[17] SHI M M, LU W Q, YU S J, et al. Effect of acid-ethanol treatment on physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility of maize starches varying in AM content[J]. Starch-Stärke,2014,66(5-6):429−435.
[18] WANG S J, WANG J R, YU J L, et al. A comparative study of annealing of waxy, normal and high-amylose maize starches: The role of amylose molecules[J]. Food Chemistry,2014,164:332−338. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.05.055
[19] NAKAZAWA Y, WANG Y J. Acid hydrolysis of native and annealed starches and branch-structure of their Naegeli dextrins[J]. Carbohydrate Research,2003,338(24):2871−2882. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2003.09.005
[20] JI N, LI X J, QIU C, et al. Effects of heat moisture treatment on the physicochemical properties of starch nanoparticles[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2015,117:605−609. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.10.005
[21] LIU Q, LI F, LU H, et al. Enhanced dispersion stability and heavy metal ion adsorption capability of oxidized starch nanoparticles[J]. Food Chemistry,2017,242:256−263.
[22] PASCOAL A M, DI-MEDEIROS M C, BATISTA K A, et al. Extraction and chemical characterization of starch from S. lycocarpum fruits[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2013,98(2):1304−1310. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.08.009
[23] KIZIL R, IRUDAYARAJ J, SEETHARAMAN K. Characterization of irradiated starches by using FT-Raman and FTIR spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2002,50(14):3912−3918. doi: 10.1021/jf011652p
[24] CAPRON I, ROBERT P, COLONNA P, et al. Starch in rubbery and glassy states by FTIR spectroscopy[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2007,68(2):249−259. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2006.12.015
[25] BANURA S, THIRUMDAS R, KAUR A, et al. Modification of starch using low pressure radio frequency air plasma[J]. LWT-Food Sciences and Technology,2018,89:719−724. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2017.11.056
[26] KIZIL R, IRUDAYARAJ J. Discrimination of irradiated starch gels using FT-Raman spectroscopy and chemometrics[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2006,54(1):13−18. doi: 10.1021/jf051491f
[27] 杨雪凡, 张维, 顾欣哲, 等. 拉曼光谱在食品加工及品质控制中的应用[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(19):361−368. [YANG X F, ZHANG W, GU X Z, et al. The application of Raman spectroscopy in quality control and food processing[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(19):361−368. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020.19.056 [28] SUN Z H, CHEN Z W, XU B, et al. Distribution of octenylsuccinate substituents within a single granule of modified waxy maize starch determined by Raman microspectroscopy[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2019,216:282−286. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.04.034
[29] WANG S J, WANG J R, ZHANG W, et al. Molecular order and functional properties of starches from three waxy wheat varieties grown in China[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,181:43−50. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.02.065
[30] ZHANG B, WU C S, LI H Y, et al. Long-term annealing of C-type kudzu starch: Effect on crystalline type and other physicochemical properties[J]. Starch-Stärke,2015,67(7-8):577−584.
[31] LIU H, LIANG R, ANTONIOU J, et al. The effect of high moisture heat-acid treatment on the structure and digestion property of normal maize starch[J]. Food Chemistry,2014,159:222−229. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.02.162
[32] QI X, TESTER R F, SNAPE C E, et al. Molecular basis of the gelatinisation and swelling characteristics of waxy barley starches grown in the same location during the same season. Part II. Crystallinity and gelatinisation characteristics[J]. Journal of Cereal Science,2004,39(1):57−66. doi: 10.1016/S0733-5210(03)00066-3
[33] LAN H, HOOVER R, JAYAKODY L, et al. Impact of annealing on the molecular structure and physicochemical properties of normal, waxy and high amylose bread wheat starches[J]. Food Chemistry,2009,111(3):663−675.
[34] ZAMBELLI R A, MARIA M T G A, DE MENDONCA L G, et al. Effect of different levels of acetic, citric and lactic acid in the cassava starch modification on physical, rheological, thermal and microstructural properties[J]. Food Science and Technology Research,2018,24(4):747−754. doi: 10.3136/fstr.24.747
[35] SUDHEESH C, SUNOOJ K V, SINHA S K, et al. Impact of energetic neutral nitrogen atoms created by glow discharge air plasma on the physicochemical and rheological properties of kithul starch[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,294:194−202. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.05.067
[36] CHEN L, TIAN Y Q, BAI Y X, et al. Effect of frying on the pasting and rheological properties of normal maize starch[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2017,77:85−95.
[37] YANG C H, ZHONG F, GOFF H D, et al. Study on starch-protein interactions and their effects on physicochemical and digestible properties of the blends[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,280:51−58. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.12.028
[38] SUDHEESH C, SUNOOJ K V, NAVAF M, et al. Hydrothermal modifications of nonconventional kithul (Caryota urens) starch: Physico-chemical, rheological properties and in vitro digestibility[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2020,57(8):2916−2925. doi: 10.1007/s13197-020-04323-7
-
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 苏敏,李红丽,白亚敏,黄大亮,刘元,吴彦蕾. 基于液相色谱-串联高分辨质谱技术的食品中污染物检测技术研究进展. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2025(04): 44-52 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张君. 我国南方部分地区蓝莓种植过程中农药残留检测结果分析. 河北农机. 2024(03): 136-138 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张申平,秦宇,顾颖娟. QuEChERS-超高效液相色谱-四极杆/静电场轨道阱质谱法测定牛羊乳及其乳粉中21种兽药. 乳业科学与技术. 2024(02): 24-29 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李红洲,国果,李博岩,梁桂娟,李志远. 超高效液相色谱-四极杆-飞行时间-高分辨质谱法分析6种李果实中的代谢物差异性. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2024(11): 63-73 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 刘宇航,于寒冰,杨红菊,马啸,温雅君,孙志伟,习佳林,熊慧勤,肖志勇. 高效液相色谱-四极杆-飞行时间质谱法快速筛查蔬菜中124种药物与个人护理品残留量. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2024(16): 175-184 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 朱春雨,吴移山,郑景娇. 高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定鸡蛋中地克珠利、妥曲珠利及其代谢物残留量. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2024(16): 211-218 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 肖泳,曾小明,李政,袁列江,邓航,王淑霞,潘照. 超高效液相色谱-四极杆/静电场轨道阱高分辨质谱法测定鸡蛋中94种农药残留. 食品与发酵工业. 2024(21): 333-340 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 王颖怡,吴玉田,孟春杨,周贻兵,刘利亚. HPLC-MS/MS技术同时测定鸡蛋中5种抗球虫药. 食品工业. 2023(06): 291-294 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 李晓慧,李建洪,王洪萍,金芬. 植物源性食品中化学性危害物质的色谱-质谱检测技术研究进展. 分析测试学报. 2023(10): 1357-1369 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 周雪莼,胡婷婷,王佳慧,白静,杨颖,侯宇,张哲,张勋. 高效液相色谱-高分辨质谱法快速筛查动物源性药食同源产品中32种抗生素兽药残留. 吉林中医药. 2023(12): 1469-1474 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 范轶欧,迟英欣,杨路平,焦燕妮. 高分辨质谱技术在环境和食品风险物质非靶向筛查检测中应用的研究进展. 预防医学论坛. 2023(12): 955-960 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



