Multi-model Evaluation of Anti-glycation Effects of Sophora japonica Flowers Aqueous Extract and Its Active Components Analysis
-
摘要: 目的:采用多种模型研究槐花水提物的抗糖化作用,并初步鉴定其有效成分。方法:通过构建牛血清白蛋白(BSA)/还原糖反应、甲基乙二醛(MGO)诱导成纤维细胞糖化以及葡萄糖溶液诱导斑马鱼体内糖基化终末产物(AGEs)增加体系,从生化、细胞及斑马鱼三种不同模型全面评估槐花水提物抗糖化效果。利用超高效液相色谱-飞行时间质谱(UPLC-Triple TOF/MS)联用技术对槐花水提物中的化学成分进行分析鉴定,并进一步测定槐花主要化学成分对生化体系中非酶糖基化的抑制作用。结果:BSA/还原糖体系中,槐花水提物抑制AGEs的IC50值为53.93 μg/mL。细胞模型中,10及40 μg/mL的槐花水提物对人皮肤成纤维细胞羧甲基赖氨酸(CML)表达量分别降低了72.28%和83.85%。斑马鱼模型也同样验证了槐花水提物的抗糖化效果,与模型组相比,2 mg/mL的槐花水提物能使斑马鱼的AGEs生成量降低76.85%。采用液质联用分析,从槐花水提取物中共鉴定了14个化合物,主要为黄酮类成分。对其中7种黄酮类成分进一步进行BSA/还原糖体系分析,发现其均能有效抑制AGEs生成,其中芦丁、槲皮素和山奈酚的IC50值分别为165.5、133.0和42.9 μmol/L,均优于阳性对照药物。结论:槐花水提取物具有显著的抗糖化作用,芦丁、槲皮素和山奈酚等黄酮类化合物是其潜在的主要活性成分。Abstract: Objective: To investigate and analyze anti-glycation effects of the aqueous extract of Sophora japonica flower (SJF) by using different models, as well as its active constitutes identification. Methods: BSA/reducing sugar reaction system, glycosylated fibroblast induced by methylglyoxal and AGEs-increased zebrafish model triggered by glucose solution were simultaneously established to comprehensively evaluate the anti-glycation effects of SJF aqueous extract from biochemical, cellular and zebrafish aspects, respectively. Identification of major components was performed by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry technique (UPLC-Triple TOF/MS). Biochemical system was subsequently adopted to further analyze anti-glycation effects of these primary components. Results: In the BSA/reducing sugar system, IC50 of AGEs inhibition of SJF aqueous extract was 53.93 μg/mL. 10 and 40 μg/mL of SJF aqueous extracts dramatically inhibited CML expressions in fibroblast model (P<0.0001), which decreased by 72.28% and 83.85%, respectively. Then, zebrafish model was also used to verify anti-glycation effects of SJF aqueous extract. When the concentration of SJF aqueous extract reached 2 mg/mL, the glycation inhibitory rate could be as high as 76.85%. Through analysis of UPLC-Triple-TOF/MS, a total of 14 chemical compounds, mainly flavonoids, were preliminarily identified. Seven compounds among them were selected for further anti-glycation evaluation by BSA/reducing sugar system. All of the seven compounds showed variable activities toward anti-AGEs production, notably, rutin, quercetin and kaempferol revealed a remarkable activity with a IC50 of 165.5, 133.0 and 42.9 μmol/L, respectively, which were better than that of positive control drugs. Conclusion: SJF aqueous extract shows remarkable anti-glycation activity. Flavonoids such as rutin, quercetin and kaempferol are its potential active compounds.
-
Keywords:
- Sophora japonica /
- anti-glycation /
- non-enzymatic glycosylation /
- fibroblast /
- zebrafish /
- UPLC-Triple TOF/MS /
- active components
-
糖基化是指蛋白质的氨基和还原糖(如葡萄糖、果糖)的羰基之间发生的缓慢非酶促反应[1]。该反应首先形成不稳定且可逆的schif碱,再经分子重排,最终形成结构多样、不可逆的复杂稳定共价聚合物,称为晚期糖基化终末产物(advanced glycation end products,简称AGEs)[2-3]。目前已经发现的AGEs物质有20多种,其中最具代表性的为羧甲基赖氨酸(Nε-carboxymethyllysine,简称CML)[4],也是人体内糖基化反应的主要生物标志物之一[5]。AGEs分子间可以通过交联形成大分子物质,积聚在包括脑、皮肤在内的各种组织器官中[6-8],研究表明其与多种衰老相关疾病(皮肤褶皱、糖尿病、动脉粥样硬化等)有着密切的关系[9]。
阿司匹林、氨基胍等已被充分证实具有显著的抑制糖基化效果[10-11],但长期服用,对药物安全性的担忧等因素使其依从性不高。研究学者们更多寄希望于从更为安全的植物性食物以及药食同源的中草药中筛选有效的AGEs抑制剂。郑子锋等[12]发现龙眼核多酚能显著抑制蛋白非酶糖基化并对成纤维细胞有明显保护作用。Hyun等[13]发现沙棘提取物能明显抑制非酶糖基化,并且抑制能力与抗氧化性密切相关。Ali等[14]研究人参中22种皂苷类化合物的体外抑制非酶糖基化过程,结果表明人参皂苷Rh1具有较强的抑制作用。
槐花是豆科植物槐(Sophora japonica L.)的花朵,广泛分布在华东华北地区。槐花盛开于四月,很多地方把其当作蔬菜食用。槐花富含黄酮类化合物,其主要成分为芦丁[15]。抗糖化活性筛选和验证实验中,最为广泛应用的是BSA/还原糖体系模型,细胞CML检测模型以及斑马鱼AGEs形成模型鲜有报道。尽管有研究表明,槐花提取物及其主要成分芦丁能抑制生化体系下AGEs的形成[16],但槐花水提物在细胞及斑马鱼模型中的抗糖化效果从未有报道,并且槐花水提物中的其他成分在抗糖化方面的作用也鲜有报道。因此本文采用BSA/还原糖体系、MGO诱导人原代真皮成纤维细胞CML检测模型以及斑马鱼AGEs增加模型,多层面评估槐花水提物的抗糖化活性,并初步探讨槐花主要化学成分在BSA/还原糖体系中抑制AGEs的效果,为槐花抗糖化作用和药效物质基础研究提供一定的参考依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
槐花 产地山东,购自安徽益生源中药饮片科技有限公司,经上海中医药大学附属龙华医院高级实验师刘淑芳博士鉴定为豆科植物槐Sophora japonica L.的干燥花朵;Lifeline Cat#FC-0024原代人皮肤成纤维细胞(HDFs) 上海Lifeline® Cell Technology公司;酪氨酸酶(25 KU,9002-10-2)、二甲基亚砜DMSO(#D4540)、牛血清白蛋白BSA(SRE0098) 美国Sigma公司;甲醇(色谱级) 美国Honeywell公司;芦丁(≥98.0%)、异槲皮苷(≥98.0%)、水仙苷(HPLC≥99.0%)、槲皮苷(≥98.0%)、槲皮素(≥98.0%)、异鼠李素(≥98.0%)、山奈酚(≥98.0%) 上海诗丹德生物技术有限公司;氨基胍、葡萄糖、果糖 上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;DMEM高糖培养基(11965084)、胎牛血清FBS(10099141C)、青霉素-链霉素(10000 U/mL)(10378016)、磷酸缓冲液PBS pH7.4(10010023)、0.025%胰酶(R001100) 美国Gibco公司;Cell Counting Kit-8(CCK-8试剂盒) 上海碧云天;甲基乙二醛MGO、Triton-X-100(88963A) 美国Adamas公司;羧甲基赖氨酸抗体CML一抗(ab125145)、含细胞核荧光染料(DAPI)的抗荧光猝灭封片液(ab104139) 美国Abcam公司;Alexa Fluor®488驴抗小鼠IgG(二抗) 美国Invitrogen公司;96孔板(批号16920006) 美国Corning公司;其他试剂 均购自上海泰坦科技股份有限公司;斑马鱼 均饲养于28 ℃的养鱼用水中(水质:每1 L反渗透水中加入200 mg速溶海盐,电导率为450~550 μS/cm;pH为6.5~8.5;硬度为50~100 mg/L CaCO3),实验动物使用许可证号为:SYXK(浙)2012−0171,饲养管理符合国际AAALAC认证(认证编号:001458)的要求。野生型AB品系斑马鱼,以自然成对交配繁殖方式进行。年龄为受精后5 d(5 dpf)的斑马鱼用于样品抗衰老功效评价。
液质联用系统:Agilent 1290 UPLC超高效液相色谱仪 安捷伦科技有限公司;串联AB Sciex Triple TOF® 4600高分辨质谱 SCIEX公司;Milli-Q超纯水系统 上海技舟化工科技有限公司;XS2051/10万分之一电子天平及MS3002S型电子分析天平 梅特勒-托利多国际贸易有限公司;WF-600EHT型超声波清洗机 宁波海曙五方超声设备有限公司;RWB3220CY-2高速冷冻离心机 德国Eppendorf公司;BB150二氧化碳恒温箱、SH-PG-010恒温水浴锅 美国Thermo公司;FlexStation 3多功能酶标仪 美国Molecular公司;DMi8倒置荧光显微镜 德国Leica公司;Heraeus Fresco17高速冷冻离心机 德国Thermo Fisher公司;JXFSTPRP-24L全自动样品快速研磨仪 上海净信实验设备科技部;HZ-9211K恒温振荡器 太仓市华利达实验设备有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 槐花水提物制备
槐花粉碎,40目过筛,精密称定20.0 g,用12倍体积热水100 ℃回流提取2次,每次1 h。提取液滤过,合并滤液,滤液真空浓缩到小体积,冻干,置于−20 ℃保存备用。
1.2.2 AGEs抑制实验
以Mou等[17]的方法为基础,稍加改进以建立BSA-葡萄糖/D-果糖体系。用磷酸缓冲液(0.2 mol/L,pH7.40)配制4 mg/mL BSA、0.5 mol/L葡萄糖/D-果糖溶液及不同浓度的槐花水提物(31.3~2000.0 µg/mL)。将BSA、葡萄糖/D-果糖和样品溶液过0.45 μm滤膜,并等体积混合,于37 ℃下孵化7 d。测定其经360 nm激发光激发后,在453 nm处的荧光强度,激发和发射狭缝宽度为5 nm。样品对照组:以100 µL PBS替代100 µL BSA。空白组:100 µL样品溶剂替代100 µL样品溶液。空白对照组:100 µL样品溶剂替代100 µL样品溶液,并用100 µL PBS替代100 µL BSA。阳性对照组:氨基胍(AG)用作阳性对照,用水溶解配制成2 mmol/L溶液。芦丁、异槲皮苷、水仙苷、槲皮苷用5% DMSO溶解,配制成2 mmol/L溶液,并用5% DMSO稀释成各浓度梯度。槲皮素、异鼠李素用10% DMSO溶解,配制成1 mmol/L溶液,并用10% DMSO稀释成各浓度梯度。山奈酚用20% DMSO溶解,配制成0.5 mmol/L溶液,并用20% DMSO稀释成各浓度梯度。抑制率计算公式如下:
式中:F1:样品组荧光值;F2:样品对照组荧光值;F3:空白组荧光值;F4:空白对照组荧光值。
1.2.3 细胞抗糖化实验
以Khmaladze等[18]的方法为基础,采用0.5 mmol/L的MGO诱导HDFs细胞建立高CML模型。HDFs细胞培养于含有10% FBS的DMEM高糖培养基中(含100 U/mL青霉素,100 μg/mL链霉素),置CO2孵箱,于37 ℃、5% CO2、饱和湿度环境下用于实验。
1.2.3.1 细胞活力测定
当细胞生长至对数期时,0.25%胰酶消化制成细胞悬液。并以每孔10000个细胞的密度接种到96孔板上。当细胞汇合达到90%时,用不同浓度的样品处理(n=3)。48 h后细胞在PBS中洗涤一次,然后按生产说明书使用CCK-8试剂盒检测细胞活力。酶标仪于450 nm处测定各孔的吸光度(A)值。实验分为空白组:只含培养液;对照组:加培养液正常培养细胞;实验组:不同浓度(1~40 µg/mL)槐花水提物的培养液。按照公式计算细胞活力:
式中:A1:实验组吸光度;A2:对照组吸光度;A3空白组吸光度。
1.2.3.2 槐花水提物对MGO诱导的HDFs细胞中CML表达量的影响
当细胞生长至对数期时,消化制成细胞悬液。以每孔5万个细胞的密度接种到12孔培养皿上。48 h后用0.5 mmol/L MGO处理细胞,继续孵育48 h,空白组不加MGO继续孵育。随后,加入阳性药(0.1 mmol/L氨基胍溶液)或不同浓度的样品溶液(10、40 μg/mL)继续孵育48 h,空白组依旧不做任何处理继续孵育48 h。弃去培养液,PBS洗涤1次后,4 ℃下用多聚甲醛固定细胞一晚。加入0.1%的Triton-X-100室温通透5 min;PBS清洗2次后,加入1% BSA室温封闭1 h。按照1:50稀释CML一抗,4 ℃过夜;次日滴加1:1000荧光标记的二抗在室温下孵育2 h。加入含有DAPI的抗荧光猝灭封片液,室温孵育10 min后在倒置荧光显微镜下观察,显微镜下采集相关荧光图像。用Image J软件量化各组随机选取的不同视觉的CML绿色荧光强度。
1.2.4 斑马鱼体内AGEs抑制实验
槐花水提物用0.4 mol/L葡萄糖溶液配制成20.0 mg/mL母液,现配现用。阳性对照:氨基胍用超纯水配制成20.0 mg/mL母液,−20 ℃储存。
随机选取5 dpf野生型AB品系斑马鱼于1.5 mL离心管中,每管(实验组)均处理10尾斑马鱼。空白组给予水溶液,模型组给予0.4 mol/L葡萄糖溶液建立斑马鱼AGEs增加模型,同时设置阳性对照及样品组,分别用0.4 mol/L葡萄糖溶液给予阳性对照200 μg/mL氨基胍溶液及不同浓度的槐花水提物(500、1000和2000 μg/mL),每管容量为150 μL。设置3个平行实验。60 ℃摇床处理24 h后,离心取上清,测定其经360 nm激发光激发后,在453 nm处的荧光强度,激发和发射狭缝宽度为5 nm,以该指标的统计学分析结果评价样品抗糖化功效。
1.2.5 UPLC-Q-TOF-MS分析槐花化学成分
取槐花水提物适量,加入0.5 mL纯水溶解,超声51 kHz处理5 min,摇匀,离心(转速为12000 r/min)5 min,取上清液进样分析。
超高效液相条件:色谱柱Waters ACQUITY UPLC HSS T3 (2.1 mm×100 mm,1.8 µm),流动相A为0.2%乙酸,流动相B为乙腈,梯度洗脱:0~8 min,15%~50% B;8~10 min,50%~80% B;10~12 min,80% B;12~13 min,80%~15% B,流速为0.2 mL/min,柱温30 ℃,检测波长为340 nm,进样量1 µL。
质谱条件:离子源为ESI源;一级质谱参数为扫描范围:50~1700 m/z;雾化气(psi):50;气帘气(psi):35;离子源电压(V):5000;离子源温度(℃):500;去簇电压(V):100;碰撞能(eV):10。二级质谱参数为扫描范围:50~1250 m/z;去簇电压(V):100;碰撞能(eV):40;碰撞电压摆幅(eV):20。
数据采集软件为MassHunter Workstation Software LC/MS Data Acquisition for 6200 series TOF/6500 series Q-TOF(version B.06.01),数据处理软件为MassHunter Workstation Software Qualitative Analysis(version B.07.00)。鉴定时优先将质谱数据与MassHunter PCDL Manager(version B.07.00)数据库进行匹配,根据各色谱峰得分信息对化合物进行初步筛选,进一步根据各色谱峰一级、二级信息等对化合物进行确认。数据库中未收载的化合物,则根据文献报道、质谱裂解规律等进行鉴定。
1.3 数据处理
采用GraphPad Prism 6.0软件对实验数据进行分析,数据结果以平均值±标准差(
2. 结果与分析
2.1 槐花水提物对AGEs生成的影响
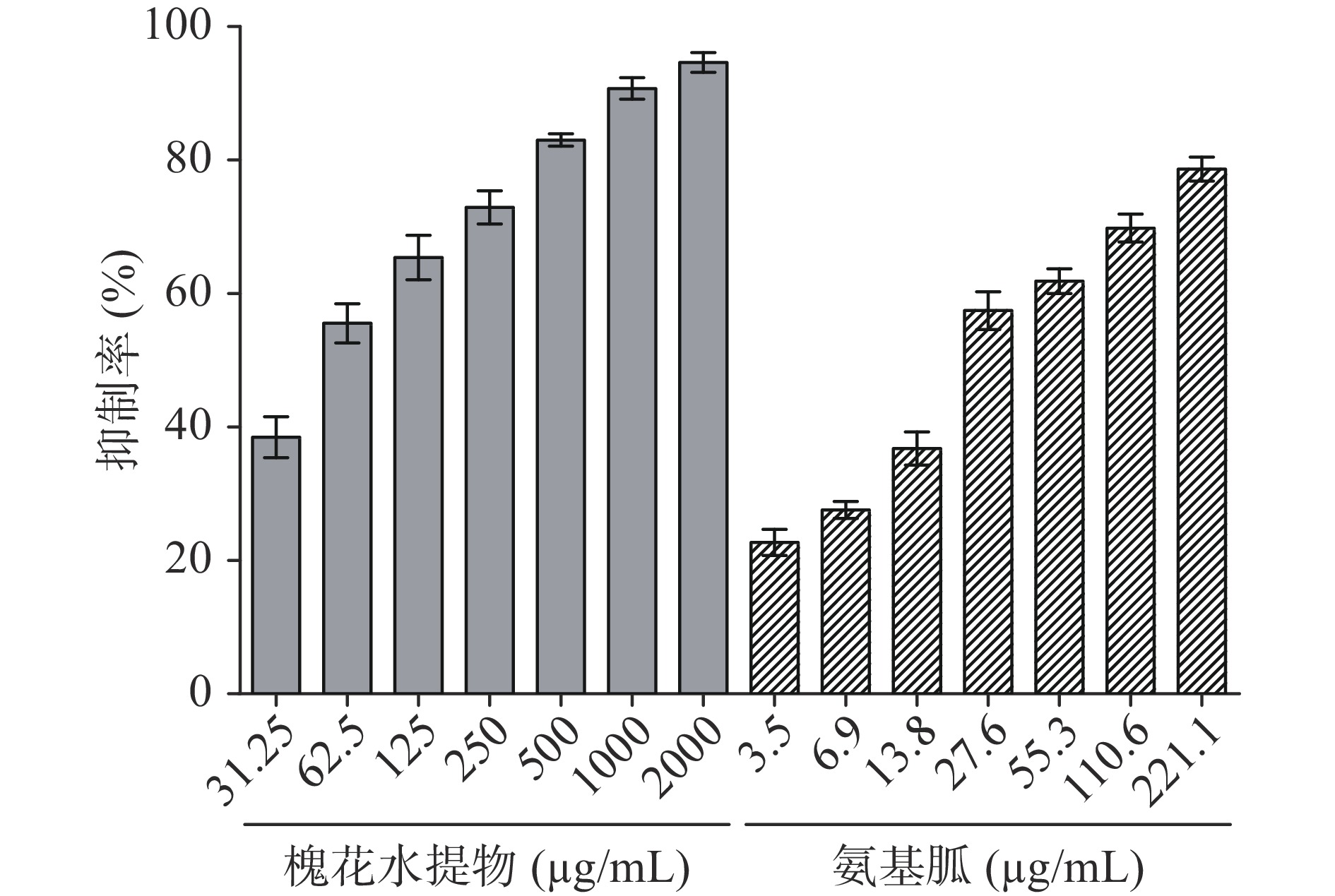
采用体外BSA/还原糖体系作为非酶糖基化反应的模型,考察槐花水提物对AGEs生成的抑制活性。结果如图1所示,不同浓度的槐花水提物(31.25~2000.0 μg/mL)均有一定的体外抑制AGEs生成的活性,抑制率为38.47%±3.05%~94.63%±1.48%,呈明显的剂量依赖关系,IC50为53.93 μg/mL。阳性药氨基胍的IC50为26.03 μg/mL。尽管槐花水提物的IC50略高于阳性对照IC50,其依然显示出较强的AGEs体外生成抑制活性。
2.2 槐花水提物对HDFs细胞活力及CML表达量的影响
在AGEs的形成过程中,MGO是非酶糖基化过程中产生的中间体,是重要的强活性前体[19-20],与赖氨酸侧链反应生成羧甲基赖氨酸(Nε-carboxymethyllysine, CML)[21-23],因此在蛋白质糖基化中起关键作用。随着年龄的增长CML会在人体内不断积聚增多,并与特定的细胞表面受体结合,诱导细胞信号通路的激活,导致细胞功能障碍和细胞死亡,使人表现出衰老现象[24]。由于CML没有荧光性[25],常规的体外荧光分析法无法检测,较为常见的是采用特异性结合的单克隆或多克隆抗体的免疫分析法测定CML含量[26]。因此,本文采用MGO诱导HDFs细胞表达CML进行细胞造模实验,利用单克隆抗体免疫分析法研究槐花在HDFs细胞上的抗糖化效果。
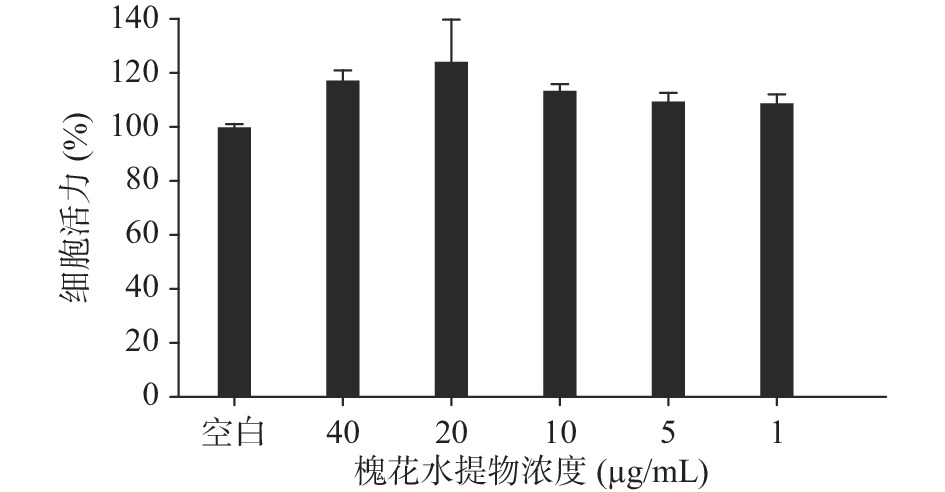
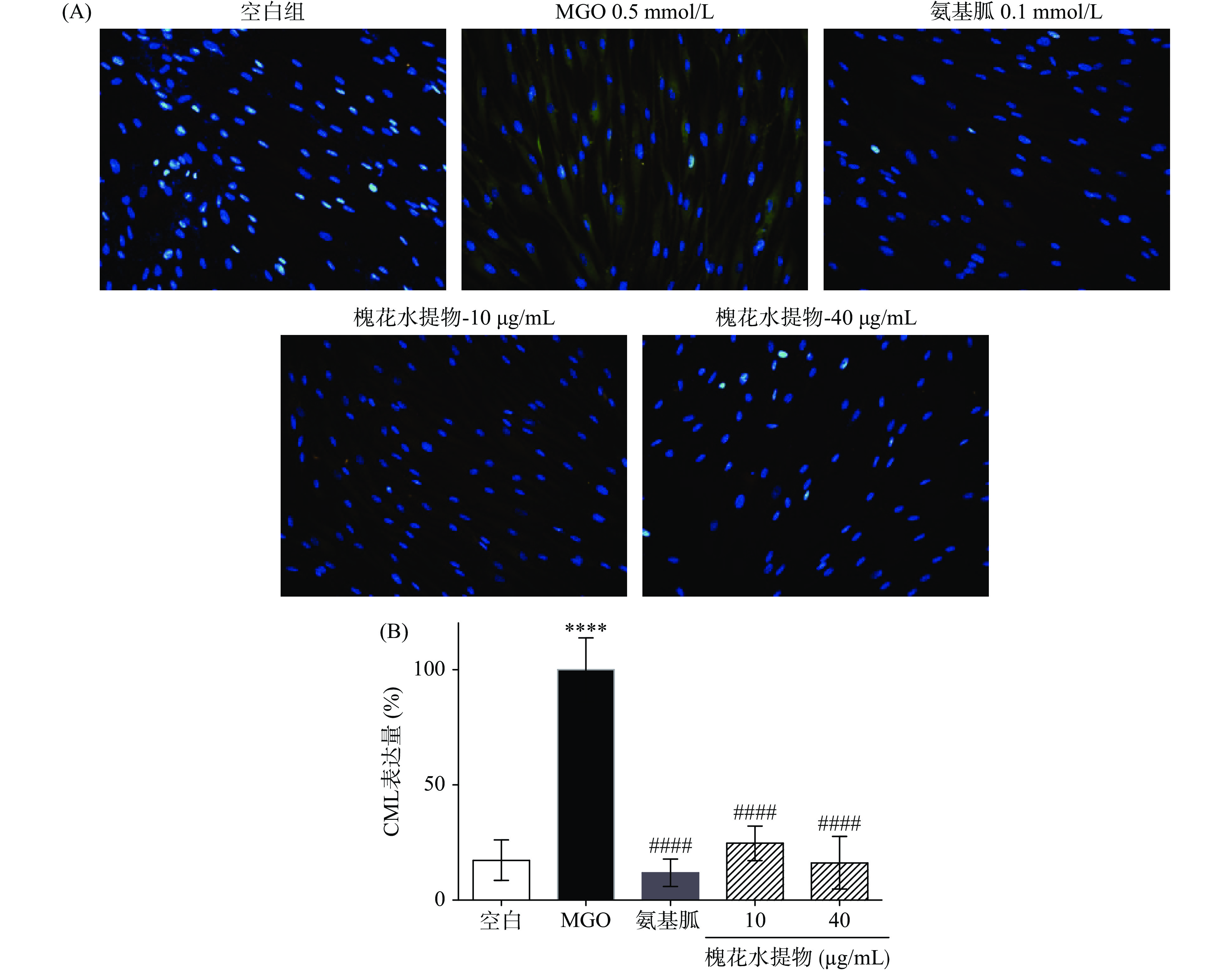
由图2可知,1~40 μg/mL槐花水提物与HDFs共孵育48 h后均未见明显的细胞毒性。因此,选择安全剂量10及40 μg/mL作为低高剂量组继续实验。在HDFs细胞模型中,图3A显示空白组CML绿色荧光响应值很低,说明正常细胞本身几乎不分泌CML。模型组用MGO处理HDFs以诱导糖基化,其CML表达量是空白组的5.8倍,表明MGO可显著诱导CML的表达(P<0.0001)。阳性对照组与模型组相比,CML表达量极显著降低了88.11%(P<0.0001)。实验中分别选用10及40 μg/mL槐花水提物和模型组细胞共孵育,结果由图3B可知,槐花水提物对MGO诱导的糖基化均有极显著的抑制作用(P<0.0001),与模型组相比CML表达量分别降低了72.28%和83.85%,高浓度抑制效果接近于阳性对照药物。
2.3 槐花水提物对斑马鱼体内AGEs生成的影响
斑马鱼(Danio rerio)属于热带鱼类,是一种小型脊椎动物。其基因组与人类基因组有70%的相似性,与已知的人类疾病基因有80%以上同源性[27]。相比于其他动物模型,斑马鱼有其独特优势,例如发育快,成本低,可快速大量繁殖,药物处理方便(可直接从水中吸收药物)、能实时动态观察表型等优点,有研究发现长时间暴露于高浓度葡萄糖溶液中会使斑马鱼体内产生大量AGEs及糖化血红蛋白[28-29],在抗糖化活性评价方面具有广泛的应用前景[30]。因此,本文采用高糖诱导斑马鱼生成AGEs,并研究槐花水提物在斑马鱼模型上的抗糖化效果。
如图4,与空白组比较,用0.4 mol/L葡萄糖溶液处理的斑马鱼作为模型组,其AGEs生成量显著升高(P<0.001),是空白组的1.2倍。与模型组相比,阳性对照组AGEs生成量显著降低13.9%(P<0.001)。而槐花水提物样品组在500、1000及2000 μg/mL浓度时对斑马鱼的糖基化反应均发生了极显著的抑制作用(P<0.0001),分别降低了38.65%,61.94%及76.85%,且呈剂量依赖关系。
2.4 槐花水提物化学成分分析
通过UPLC-Q-TOF-MS对槐花提取液进行分析,结合“Analyst 1.1.7”及“Peakview 1.2.0.3”软件中色谱峰对应的准分子离子信息、二级碎片信息,并参考相关文献(表1),初步鉴定了14个化合物(见图5),均为黄酮类化合物。化合物12的一级质谱准分子离子峰为m/z301.03,UPLC-Q-TOF-MS根据数据处理软件计算其分子式可能为C16H18O9,其二级碎片m/z179、151、121对应的元素依次为C8H3O5、C7H3O4和C7H5O2,与文献报道的槲皮素相一致[31]。化合物1~6、9~11均含有二级离子碎片m/z301,是苷元槲皮素的离子峰,推测均为槲皮素衍生物。化合物5的分子离子峰[M-H]−的m/z值为609.14,丢失末端鼠李糖分子形成碎片m/z463.08,离子丢失芸香糖形成碎片m/z301.03,根据上述信息,并与标准品出峰时间比对,推断化合物5为槲皮素-3-O-葡萄糖-鼠李糖苷(芦丁),与文献[32]报道的相一致,是槐花的主要成分[33]。其他化合物也依据其保留时间、碎片信息、参考文献进行初步推断,结果见表1。
表 1 UPLC–QTOF–MS法鉴定槐花水提物主要成分Table 1. Compounds of Sophora japonica flowers aqueous extract identified by UPLC–QTOF–MS序号 时间(min) 中文名 分子式 分子量 加合离子 MS MS/MS数据 ppm 参考文献 1 3.33 槲皮素-3-O-芸香糖-7-O-葡萄糖苷 C33H40O21 772.21 [M-H]− 771.1965 609.1447;446.0843;301.0341;271.0219 −2.4 [34] 2 3.45 槲皮素3-葡萄糖基-(1→2)-鼠李糖苷-
7-鼠李糖苷C33H40O20 756.21 [M-H]− 755.2022 609.1447;446.0843;301.0843;271.0219 −1.7 [34] 3 3.55 槲皮素7-O-芸香糖苷 C27H30O16 610.15 [M-H]− 609.1448 463.0825;301.0327;300.0264;271.0229 −1.2 [34] 4 4.01 / C32H38O20 742.20 [M-H]− 741.1867 609.1462;463.0875;301.034;178.9979 −1.5 5 4.35 芦丁 C27H30O16 610.15 [M-H]− 609.1483 463.0825;301.0327;300.0264;178.9964 4.5 [35] 6 4.71 异槲皮苷 C21H20O12 464.10 [M-H]− 463.0874 301.0320;300.0269;271.0241;178.9982 −0.5 [34] 7 4.86 山柰酚3-O-芸香糖苷 C27H30O15 594.16 [M-H]− 593.1509 285.0390;284.0322;255.0292;151.0033 0.4 [36] 8 4.96 水仙苷 C28H32O16 624.17 [M-H]− 623.1617 315.0502;300.0265;151.0027 0.8 [37] 9 5.08 槲皮素3-O-鼠李糖苷-7-O-葡萄糖苷 C27H30O16 610.15 [M-H]− 609.1457 301.0344;300.0256;178.9964;151.0031 0.2 [38] 10 5.33 槲皮素3-O-新橙皮糖苷 C27H30O16 610.15 [M-H]− 609.1453 301.0343;300.0263;178.9973;151.0033 −0.4 [39] 11 6.01 槲皮苷 C21H20O11 448.10 [M-H]− 447.0929 301.0339;300.0269;255.0279;151.0030 0.4 [38] 12 7.47 槲皮素 C15H10O7 302.04 [M-H]− 301.0359 178.9971;151.0033;121.0292;107.0137 3.6 [38] 13 8.75 山奈酚 C15H10O6 286.05 [M-H]− 285.0411 255.0268;227.0337;143.0488;117.0337 4.2 [38] 14 8.91 异鼠李素 C16H12O7 316.06 [M-H]− 315.0504 300.0261;271.0241;151.0027;107.0133;63.0235 −0.2 [40] 2.5 槐花水提物中主要化合成分对AGEs生成的抑制活性
选取槐花中主要且市售易得的7个黄酮类化合物(芦丁5、异槲皮苷6、水仙苷8、槲皮苷11、槲皮素12、山奈酚13、异鼠李素14)进行AGEs抑制活性分析,结果如图6所示。7种化合物均能有效地抑制糖基化终末产物AGEs的产生,并且随着化合物浓度的增加活性增强,呈现出浓度依赖关系。化合物5、6、8、11~14的IC50分别为165.5、383.2、244.5、290.3、133.0、42.9 和457.0 μmol/L,山奈酚的活性最高,异鼠李素活性最弱。其中山奈酚、槲皮素和芦丁的IC50低于阳性药氨基胍,IC50排序为:山奈酚<槲皮素<芦丁<阳性对照药物氨基胍(IC50,235.5 μmol/L),显示出非常好的AGEs抑制活性。山奈酚和异鼠李素结构非常相似,异鼠李素仅在5'位多了一个甲氧基,有可能C环4'-OH和5'-OCH3形成分子内氢键,从而影响活性表达。槲皮素为黄酮苷元,当其3-OH变成3-O-糖苷时(芦丁、槲皮苷和异槲皮苷),活性有所下降。因此,推测槐花水提物的抗糖化功效可能与其黄酮类化合物体外抑制非酶糖基化有关。
3. 讨论与结论
人体组织中的糖化过程是非常漫长的过程[41],过多的生成和积累AGEs会对机体造成不可逆的损害,诱导多种糖尿病并发症的产生。皮肤胶原蛋白中存在多种AGEs,包括CML,其含量的积累会损伤皮肤成纤维细胞[42-43],造成皮肤老化和暗斑的形成。本实验通过创建不同抗糖化评价模型,如BSA/还原糖体系评价方法、MGO诱导成纤维(HDFs)细胞损伤模型以及斑马鱼AGEs生成模型,全面评估槐花水提物的抗糖化效果。体外BSA/还原糖体系,发现槐花水提物能明显抑制AGEs生成,IC50为53.93 μg/mL;进而在HDFs细胞模型上发现槐花水提物能抑制细胞糖化过程,极显著降低HDFs细胞的CML表达量(P<0.0001),提示槐花的抑制糖基化作用机制可能就是通过抑制CML的合成路径;最后在斑马鱼体系中进一步验证了槐花水提物的糖基化抑制作用,2 mg/mL浓度时,与模型组相比,糖基化程度降低了76.85%。蒋楠等[16]研究发现,槐花提取物与MGO共孵育后,其主要成分芦丁会发生明显变化,并推测是芦丁与MGO结合,从而阻止糖化反应的进行。但并没有直接研究槐花提取物及其活性成分的抗糖化效果。
为了进一步研究槐花抑制糖基化的主要活性成分,采用UPLC-QTof/MS技术分析并鉴定了槐花水提物中14个化学成分,主要为以芦丁为代表的黄酮类成分。选取其主要成分芦丁、异槲皮苷、水仙苷、槲皮苷、槲皮素、山奈酚、异鼠李素等7种黄酮类化合物进行了生化体系中AGEs抑制实验,结果发现7种黄酮类成分均能显著抑制AGEs的生成,初步认为槐花水提物的抗糖化效果可能是黄酮类化合物共同作用的结果。其中芦丁、槲皮素和山奈酚的糖基化抑制活性高于阳性药物氨基胍,其IC50值山奈酚(42.9 μmol/L)<槲皮素(133.0 μmol/L)<芦丁(165.5 μmol/L)<氨基胍(235.5 μmol/L)。槲皮素和山奈酚作为黄酮苷元,与其他化合物相比,对AGEs生成的抑制效果最佳。韩文凤[44]通过研究三种黄酮单体对CML的抑制作用,也发现对CML的抑制率苷元大于苷同时芦丁作为槐花中含量最高的活性成分,含量在5.94%~9.43%之间[45],同时芦丁在体内也能进一步代谢为槲皮素[46],因此推测槐花抗糖化活性的主要贡献来自于芦丁。国外文献报道,部分黄酮类化合物可通过捕获MGO和GO二羰基化合物形成加合物,从而抑制AGEs的形成[47]。且抑制糖基化能力可能与黄酮类化合物羟基的位置、数量及取代基种类有关[48-49],但具体作用机制目前还不清楚, 值得后续进一步深入研究。
本文分别从体外生化、细胞、斑马鱼体系全面评估了槐花水提物的抗糖化作用,并鉴定了槐花水提物中主要的抗糖化活性成分,为槐花提取物在抗糖化作用方向提供数据参考和依据,也为以后槐花的综合开发应用提供理论支持依据。
-
表 1 UPLC–QTOF–MS法鉴定槐花水提物主要成分
Table 1 Compounds of Sophora japonica flowers aqueous extract identified by UPLC–QTOF–MS
序号 时间(min) 中文名 分子式 分子量 加合离子 MS MS/MS数据 ppm 参考文献 1 3.33 槲皮素-3-O-芸香糖-7-O-葡萄糖苷 C33H40O21 772.21 [M-H]− 771.1965 609.1447;446.0843;301.0341;271.0219 −2.4 [34] 2 3.45 槲皮素3-葡萄糖基-(1→2)-鼠李糖苷-
7-鼠李糖苷C33H40O20 756.21 [M-H]− 755.2022 609.1447;446.0843;301.0843;271.0219 −1.7 [34] 3 3.55 槲皮素7-O-芸香糖苷 C27H30O16 610.15 [M-H]− 609.1448 463.0825;301.0327;300.0264;271.0229 −1.2 [34] 4 4.01 / C32H38O20 742.20 [M-H]− 741.1867 609.1462;463.0875;301.034;178.9979 −1.5 5 4.35 芦丁 C27H30O16 610.15 [M-H]− 609.1483 463.0825;301.0327;300.0264;178.9964 4.5 [35] 6 4.71 异槲皮苷 C21H20O12 464.10 [M-H]− 463.0874 301.0320;300.0269;271.0241;178.9982 −0.5 [34] 7 4.86 山柰酚3-O-芸香糖苷 C27H30O15 594.16 [M-H]− 593.1509 285.0390;284.0322;255.0292;151.0033 0.4 [36] 8 4.96 水仙苷 C28H32O16 624.17 [M-H]− 623.1617 315.0502;300.0265;151.0027 0.8 [37] 9 5.08 槲皮素3-O-鼠李糖苷-7-O-葡萄糖苷 C27H30O16 610.15 [M-H]− 609.1457 301.0344;300.0256;178.9964;151.0031 0.2 [38] 10 5.33 槲皮素3-O-新橙皮糖苷 C27H30O16 610.15 [M-H]− 609.1453 301.0343;300.0263;178.9973;151.0033 −0.4 [39] 11 6.01 槲皮苷 C21H20O11 448.10 [M-H]− 447.0929 301.0339;300.0269;255.0279;151.0030 0.4 [38] 12 7.47 槲皮素 C15H10O7 302.04 [M-H]− 301.0359 178.9971;151.0033;121.0292;107.0137 3.6 [38] 13 8.75 山奈酚 C15H10O6 286.05 [M-H]− 285.0411 255.0268;227.0337;143.0488;117.0337 4.2 [38] 14 8.91 异鼠李素 C16H12O7 316.06 [M-H]− 315.0504 300.0261;271.0241;151.0027;107.0133;63.0235 −0.2 [40] -
[1] ELOSTA A, GHOUS T, AHMED N. Natural products as anti-glycation agents: Possible therapeutic potential for diabetic complications[J]. Current Diabetes Reviews,2012,8(2):92−108. doi: 10.2174/157339912799424528
[2] WEI Q, LIU T, SUN D, et al. Advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) in foods and their detecting techniques and methods: A review[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2018,82:32−45.
[3] DARIVA B, NAGARAJU G. Advanced glycation end products in diabetes, cancer and phytochemical therapy[J]. Drug Discovery Today,2020,25(9):1614−1623. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2020.07.003
[4] BUSER W, ERBERSDOBLER H F, LIARDON R. Identification and determination of Nε-carboxymethyllysine by gas-liquid chromatography[J]. Journal of Chromatography A,1987,387:515−519. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9673(01)94562-5
[5] 韩文凤, 谭兴和, 林晓丽, 等. 食品中羧甲基赖氨酸的形成机理和抑制途径研究进展[J]. 现代食品科技,2018,34(1):251−257. [HAN W F, TAN X H, LIN X L, et al. Research progress on formation mechanism and inhibition pathway of carboxymethyl lysine in food[J]. Modern Food Technology,2018,34(1):251−257. doi: 10.13982/j.mfst.1673-9078.2018.1.038 [6] EMEL V. Glycation, antiglycation, and deglycation: Their role in aging mechanisms and geroprotective effects (literature review)[J]. Advances in Gerontology,2017,7(1):1−9. doi: 10.1134/S2079057017010064
[7] OTT C, JACOBS K, HAUCKE E, et al. Role of advanced glycation end products in cellular signaling[J]. Redox Biology,2014,2:411−429. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2013.12.016
[8] NEDIC O, RATTAN S, GRUNE T, et al. Molecular effects of advanced glycation end products on cell signaling pathways, ageing and pathophysiology[J]. Free Radical Research,2013,47(Suppl 1):28−38.
[9] AHMED N. Advanced glycation end products role in pathology of diabetic complications[J]. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice,2005,67(1):3−21. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2004.09.004
[10] FERREIRA C, PENNACCHI P C, ARAUJO T H, et al. Aminoguanidine treatment increased NOX2 response in diabetic rats: Improved phagocytosis and killing of Candida albicans by neutrophils[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology,2016,772:83−91. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.12.044
[11] RICHARDSON M A, FURLANI R E, PODELL B K, et al. Inhibition and breaking of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) with bis-2-aminoimidazole derivatives[J]. Tetrahedron Letters,2015,56(23):3406−3409. doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2015.01.122
[12] 郑子锋, 孙培冬. 龙眼核多酚对蛋白非酶糖基化的抑制及机制研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(9):25−31. [ZHENG Z F, SUN P D. Inhibition and mechanism of longan nuclear polyphenols on non-enzymatic glycosylation of protein[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2021,47(9):25−31. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.025499 [13] LEE H L, LEE C J, CHOI S Y, et al. Inhibitory effect of sea buckthorn extracts on advanced glycation end product formation[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,373:131364. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131364
[14] ALI M Y, JANNAT S, RAHMAN M M. Ginsenoside derivatives inhibit advanced glycation end-product formation and glucose-fructose mediated protein glycation in vitro via a specific structure-activity relationship[J]. Bioorganic Chemistry,2021,111:104844. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.104844
[15] 刘金亮, 李隆云, 何光华, 等. HPLC 指纹图谱结合化学计量学与抗氧化能力评价不同产地槐米的品质[J]. 中草药,2018,49(19):4644−4652. [LIU J L, LI L Y, HE G H, et al. Evaluation of quality of Sophora japonica from different habitats by HPLC fingerprint combined with stoichiometry and antioxidant capacity[J]. Chinese Herbal Medicine,2018,49(19):4644−4652. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2018.19.027 [16] 蒋楠, 王富静, 封亮, 等. 基于非酶糖基化反应的槐花抑制 AGEs 形成的活性组分筛选[J]. 中国中药杂志,2019,44(14):3100−3106. [JIANG N, WANG F J, FENG L, et al. Screening of active components of Sophora japonica for inhibiting AGEs formation based on non-enzymatic glycosylation[J]. Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2019,44(14):3100−3106. [17] MOU L, HU P, CAO X, et al. Comparison of bovine serum albumin glycation by ribose and fructose in vitro and in vivo[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Basis of Disease,2022,1868(1):166283.
[18] KHMALADZE I, OSTERLUND C, SMILJANICS, et al. A novel multifunctional skin care formulation with a unique blend of antipollution, brightening and antiaging active complexes[J]. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology,2020,19(6):1415−1425. doi: 10.1111/jocd.13176
[19] PARK S H, DO M H, LEE J H, et al. Inhibitory effect of arachis hypogaea (peanut) and its phenolics against methylglyoxal-derived advanced glycation end product toxicity[J]. Nutrients,2017,9(11):12−14.
[20] MARAMALDJ G, TOGNI S, FRANCESCHI F, et al. Anti-inflammation and antiglycation activity of a novel botanical ingredient from African biodiversity (Centevita™)[J]. Clinical Cosmetic & Investigational Dermatology,2013,7:1−9.
[21] ZENG, J, DAVIES, M J. Evidence for the formation of adducts and S-(carboxymethyl) cysteine on reaction of α-Dicarbonyl compounds with thiol groups on amino acids, peptides, and proteins[J]. Chemical Research in Toxicology,2005,18(8):1232−1241. doi: 10.1021/tx050074u
[22] SCHWARZENBOLZ U, HENLE T, HAENER R, et al. On the reaction of glyoxal with proteins[J]. Z Lebensm Unters Forsch,1997,205(2):121−124. doi: 10.1007/s002170050137
[23] ERBERSDOBLER H F, SOMOZA V. Forty years of furosine-forty years of using Maillard reaction products as indicators of the nutritional quality of foods[J]. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research,2007,51(4):423−430.
[24] KASPER M, FUNK H W. Age-related changes in cells and tissues due to advanced glycation end products (AGEs)[J]. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics,2001,32(3):233−243. doi: 10.1016/S0167-4943(01)00103-0
[25] SHARMA C, KAUR A, THIND S S, et al. Advanced glycation end-products (AGEs): An emerging concern for processed food industries[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2015,52(12):7561−7576. doi: 10.1007/s13197-015-1851-y
[26] GARAY M E, LUEVANO C, CHAPMAN K. Nutritional modulation of advanced glycation end products[J]. Molecular Basis of Nutrition & Aging,2016:263−276.
[27] HOWE K, CLARK M D, TORROJA C F, et al. The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome[J]. Nature,2013,496(7446):498−503. doi: 10.1038/nature12111
[28] GUTIERREZ M P, VELAZQUEZ E G. Glucopyranoside flavonoids isolated from leaves of Spinacia oleracea (spinach) inhibit the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and aldose reductase activity (RLAR)[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy,2020,128:110−299.
[29] ALVAREZ Y, CHEN K, REYNOLDS A L, et al. Predominant cone photoreceptor dysfunction in a hyperglycaemic model of non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy[J]. Disease Models & Mechanisms,2010,3(3):236−245.
[30] ADAM M S, MICHAEL N, KEITH W, et al. Developing zebrafish models of autism spectrum disorder (ASD)[J]. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry,2014,50(1):27−36.
[31] 侯晓楠. 槐米中功效成分的分离纯化及其生物活性研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2018 HOU X N. Purification and bioactivity of active components from Sophora japonica[D]. Tianjing: Tianjing University, 2018.
[32] 王翼, 顾苑婷, 丁筑红, 等. 超高效液相色谱-串联高分辨质谱对刺梨槲皮素及其糖苷类化合物的鉴定分析[J]. 分析化学,2020,48(7):955−961. [WANG Y, GU Y T, DING Z H, et al. Identification and analysis of quercetin and its glycosides of Rosa roxburghii Tratt by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem high resolution mass spectrometry[J]. Analytical Chemistry,2020,48(7):955−961. doi: 10.19756/j.issn.0253-3820.191338 [33] 李文杰, 高志慧. 刺槐的槐花与槐米营养成分和芦丁含量的比较[J]. 食品工业,2020,41(3):337−339. [LI W J, GAO Z H. Comparison of nutrient composition and rutin content between flowers and buds of Sophora japonica[J]. Food Industry,2020,41(3):337−339. [34] ABAD B, LOBATO S G, BERRUETA L A, et al. On-line characterization of 58 phenolic compounds in citrus fruit juices from Spanish cultivars by high-performance liquid chromatography with photodiode-array detection coupled to electrospray ionization triple quadrupole mass spectrometry[J]. Talanta,2012,99(15):213−224.
[35] 钟月葵, 蔡庆群, 丘振文. 超高效液相色谱法测定不同产地桑叶中 4 种主要黄酮含量[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2021,12(5):55−60. [ZHONG Y K, CAI Q Q, QIU Z W. Determination of four flavonoids in Folium mori from different habitats by ultra-performance liquid chromatography[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection,2021,12(5):55−60. [36] TANG Y, WANG J H, LI Y F, et al. Flavonols and flavonol glycosides from the pericarp of Sophora japonica[J]. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment,2001,10(2):59−60.
[37] 皮文霞, 赵文望, 蔡宝昌, 等. 槐花对照提取物的制备及槐花中4个黄酮类成分的含量测定[J]. 中国药房,2018,29(19):52−59. [PI W X, ZHAO W W, CAI B C, et al. Extracts preparation and determination of four flavonoids in Sophora japonica[J]. Chinese Pharmacy,2018,29(19):52−59. doi: 10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2018.19.14 [38] YANG Y, TIAN Y P, ZHANG Q H, et al. Comparative effects of flavonoids from fructus sophorae on rat osteoblasts in vitro[J]. Records of Natural Products,2019,14(1):65−76. doi: 10.25135/rnp.138.19.04.1262
[39] DEVKOTA H P, KAWAMURA K, SASANUMA M, et al. Flavonoid glycosides from the leaves of Aphananthe aspera (Thunb.) Planch. (Cannabaceae) and their chemotaxonomic significance[J]. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology,2019,83:112−113. doi: 10.1016/j.bse.2019.01.011
[40] 李娆娆, 原思通. 中药槐花饮片RP-HPLC特征图谱研究[J]. 药物分析杂志,2010,30(11):37−41. [LI R R, YUAN S T. Study on RP-HPLC characteristic chromatogram of Sophora japonica decoction pieces[J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis,2010,30(11):37−41. doi: 10.16155/j.0254-1793.2010.11.009 [41] 杨益宁. 糖基化终产物对人肾系膜细胞胞外基质和mmp-2表达影响及氨基胍干预[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2006 YANG Y N. Effect of glycosylation end products on extracellular matrix and mmp-2 expression in human renal mesangial cells and intervention of aminoguanidine[D]. Nanjing: Dongnan University, 2006.
[42] ALIKHANI Z, ALIKHANI M, BOYD C M, et al. Advanced glycation end products enhance expression of pro-apoptotic genes and stimulate fibroblast apoptosis through cytoplasmic and mitochondrial pathways[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry,2005,280(13):12087−12095. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406313200
[43] 郭昊. 石榴提取物对角质形成细胞抗氧化、抗糖化、抗炎作用和Paget病研究[D]. 沈阳: 中国医科大学, 2020 GUO H. Study on antioxidation, anti-glycosylation, anti-inflammatory effects of pomegranate extract on keratinocytes and Paget's disease[D]. Shengyang: China Medical University, 2020.
[44] 韩文凤. 水果多酚抑制食品中羧甲基赖氨酸形成的作用机理研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2020. HAN W F. Study on the mechanism of fruit polyphenols inhibiting the formation of carboxymethyl lysine in food[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2020.
[45] 唐燕玲, 罗卓卡, 蔡庆群, 等. 超高效液相色谱法测定不同产地槐花中4种黄酮含量[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2020,11(21):8. [TANG Y L, LUO Z K, CAI Q Q, et al. Determination of four flavonoids in Sophora japonica from different producing areas by ultra-performance liquid chromatography[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection,2020,11(21):8. doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2020.21.036 [46] 伍明江, 吴晓磊, 张德芹, 等. UPLC-Q-TOF/MS鉴定芦丁在大鼠体内的代谢产物[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2017,23(17):7. [WU M J, WU X L, ZHANG D Q, et al. Identification of metabolites of rutin in rats by UPLC-Q-TOF/MS[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Formulae,2017,23(17):7. doi: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2017170091 [47] LI L S, SHAO X, CHEN H D, et al. Genistein inhibits advanced glycation end product formation by trapping methylglyoxal[J]. Chemical Research in Toxicology,2011,24(4):579−586. doi: 10.1021/tx100457h
[48] MATSUDA H, WANG T, MANAGI H, et al. Structural requirements of flavonoids for inhibition of protein glycation and radical scavenging activities[J]. Bioorg Med Chem,2003,11(24):5317−5323. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2003.09.045
[49] WU C H, HUANG S M, LIN J A, et al. Inhibition of advanced glycation endproduct formation by foodstuffs[J]. Food & Function,2011,2(5):224.
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 顾宇翔,周羽,刘恕. 护肤类化妆品功效评价理化试验方法的现状和分析. 日用化学工业(中英文). 2024(06): 727-732 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 岳开妍,毛丙永,唐鑫,张秋香,赵建新,崔树茂. 乳酸菌发酵对花生衣抗糖化缓解皮肤衰老功能的影响. 上海理工大学学报. 2024(04): 364-374 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王国凯,龚荣英,杨灵丽,刘文龙,晋海军,田维毅. 槐花水提液发酵工艺优化及其抗氧化活性分析. 食品工业科技. 2024(20): 196-204 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 夏俊英,余海霞,戚仕梅,张富娜,邬婧,肖卫华. 长双歧杆菌胞外多糖对非酶糖基化的抑制作用. 生物学杂志. 2024(05): 6-13+47 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 谢圆芳,袁道欢,张丽山,黄嘉敏,林霁,田佳佳,贺锐,解勇. 黑松露提取物紧致抗皱功效. 香料香精化妆品. 2024(05): 73-77+149 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 曾贝贝,吕静,鲁杏茹,智文博,李带根. 牡丹花酶解肽的理化性质及促进皮肤健康功效. 食品工业科技. 2024(22): 314-321 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)








 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:



