Study of the Fumigation Antimicrobial Activity and Mechanism of Essential Oil
-
摘要: 本文采用平板熏蒸法测定六种植物精油在气相状态下对四种常见细菌的最低抑菌浓度(Minimum Inhibitory Concentration,MIC)和最小杀菌浓度(Minimum Bactericidal Concentration,MBC),对效果好的精油进行复配研究并将其应用于小米椒保鲜,通过透射电镜和电导率来阐述肉桂精油熏蒸对大肠杆菌的抗菌机制。结果表明,六种精油中抑菌效果显著的是香茅精油、肉桂精油和罗勒精油,在精油浓度为0.125 μL/mL时可以抑制所有的供试菌,而杀菌效果较好的是香茅精油和肉桂精油,除铜绿假单胞菌外,在精油浓度为0.125 μL/mL时可杀死其余供试菌。将香茅精油、肉桂精油和罗勒精油进行复配,当三者比例为4:1:8时联合熏蒸抗菌效果最好,复配精油对大肠杆菌和沙门氏菌表现出协同增效作用,而对金黄色葡萄球菌则表现为拮抗作用。GC-MS结果表明,香茅精油的熏蒸抗菌能力主要来自香茅醛、香叶醇和香茅醇;肉桂精油主要来自于肉桂醛;罗勒精油则主要来自于草蒿脑、芳樟醇。当复合精油空间浓度为0.125 μL/mL时,对小米椒具有较好的防腐保鲜效果。透镜结果显示经肉桂精油熏蒸后的大肠杆菌形态发生改变、细胞膜皱缩,电导率实验表明熏蒸后的大肠杆菌细胞膜通透性增加,引起电解质的外泄。由此可见,肉桂精油熏蒸大肠杆菌可能的抑菌机理是改变细胞形态和膜通透性。Abstract: In this study, the antibacterial effects of six plant essential oils against four common bacteria in the vapor phase was investigated by plate fumigation method with the measurement of the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC). The combination of essential oils with better bactericidal effect was studied and applied to keep fresh of capsicum frutescens. The antibacterial mechanism of cinnamon essential oil against Escherichia coli (E. coli) was also determined by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and electric conductivity. The results showed that citronella essential oil, cinnamon essential oil and basil essential oil had more significant antibacterial effect, which could inhibit all tested bacteria at the concentration of 0.125 μL/mL. Citronella essential oil and cinnamon essential oil had better bactericidal effect, which could kill all the tested bacteria except Pseudomonas aeruginosa at the concentration of 0.125 μL/mL. Blended essential oils with the ratio of citronella essential oil, cinnamon essential oil and basil essential oil being 4:1:8, demonstrated the best antibacterial activity. The blended essential oils showed synergistic effects on E. coli and Salmonella, but antagonistic effect on Staphylococcus aureues. GC-MS indicated that the antibacterial ability of citronella essential oil mainly came from citronellal, geraniol and citronellol, cinnamon essential oil came from cinnamaldehyde and basil essential oil came from estragole and linalool. The application of blended essential oil in modified atmosphere preservation of capsicum frutescens had a better preservative and fresh-keeping effects when the spatial concentration of blended essential oil was 0.125 μL/mL. TEM showed morphological changes and cell membrane shrinkage of E. coli after fumigation with cinnamon essential oil. The conductivity test showed that the membrane permeability of E. coli increased after fumigation, which resulted in electrolyte leakage. In conclusion, the possible antibacterial mechanism of vapor-phase cinnamon essential oil against E. coli is to change the cell morphology and membrane permeability.
-
植物精油在民间医药、香料工业、食品调味和保鲜等领域一直有着广泛的应用[1],近几十年大量研究表明,精油对多种致病菌具有良好的抗菌作用[2-3],包括金黄色葡萄球菌、蜡状芽孢杆菌、大肠杆菌、单增李斯特菌、鼠伤寒沙门菌、铜绿假单胞菌、黑曲霉和念珠菌等。同时,也有大量文献报道植物精油的液(固)体接触抗菌机理。Cox等[4]研究表明,茶树精油通过改变细胞渗透性,增加细胞内K+的泄漏和扰乱细胞呼吸来抑制金黄色葡萄球菌和大肠杆菌的生长。Lopez-Romero等[5]发现几种精油通过作用于细胞表面并引起膜的破坏来抑制大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的生长。Oussalah等[6]发现牛至精油、肉桂精油和香薄荷精油在它们的最低抑菌浓度下处理会影响大肠杆菌和单增李斯特菌的膜完整性,并诱导细胞内ATP浓度的消耗。这些文献表明植物精油具有良好的液(固)体接触抗菌作用,可以通过作用于菌体细胞膜等来抑制细菌的生长。
虽然精油的抗菌作用都是要与微生物接触才能发挥作用,但是有不少研究证实,与接触抗菌相比,精油的熏蒸抗菌效果要更强[7-8],这可能是因为精油在气相状态下某些成分的相对浓度发生变化[8],还可能是因为水相中的亲脂分子结合形成胶束,从而抑制精油与生物体的附着,而气相状态下则能自由附着在生物体上[7]。Boukhatem等[8]通过抑菌圈实验发现,阿尔及利亚玫瑰天竺葵熏蒸对几种菌的抑菌圈要明显大于液相接触的抑菌圈。刘晓丽等[9]通过滤纸片法、固相扩散法、气相扩散法等体外抗菌实验证明气态抑制效果比固相抑菌效果更强。因此,在相对较低的浓度下,气相精油就可以抑制常见致病菌,从而对食品的感官特性[8,10-11]及环境影响最小,还可以节约成本。因此,可以利用精油的熏蒸抗菌作用将其应用在气调保鲜以及空气消毒剂中。研究也表明,复配精油的综合抑菌性优于单一精油,因为各精油组分间存在协同增效作用,可扩宽抗菌谱,在相互协同抗菌的同时可减少用量[12-13]。
大肠杆菌、铜绿假单胞菌、沙门氏菌、金黄色葡萄球菌在自然界广泛分布,不仅会引起食品污染,还会对人类健康造成威胁,是食品和空气中常见的致病菌[14-17]。前期团队经过抑菌圈实验发现香茅、肉桂、罗勒、茶树、冬青和桉树精油这6种常见的芳香植物精油具有良好的液体接触抑菌活性,其活性也都被报道过[18-22],植物精油的熏蒸抗菌活性使得其在食品气调保鲜、空气消毒等方面具有良好的应用前景,目前关于植物精油的抗菌研究多集中在液(固)体接触抗菌上,而对其熏蒸抗菌活性研究较少。因此,本文研究这6种植物精油对4种常见致病菌的熏蒸抗菌活性,通过复配研究植物精油的联合抗菌效果,并通过在小米椒的熏蒸保鲜中应用,探究复配精油的实际效果,并通过透射电镜和电导率的测定探究肉桂精油熏蒸对大肠杆菌的抗菌机理。本文研究对于植物精油开发成为绿色、高效的食品气相防腐剂和空气抗菌消毒剂具有理论和现实指导意义。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
香茅精油、肉桂精油、罗勒精油、茶树精油、冬青精油、桉树精油 水蒸气蒸馏制备,广州市香思馨情健康科技有限公司提供;营养琼脂 广东环凯微生物科技有限公司;其它试剂均为分析纯。大肠杆菌ATCC8739(Escherichia coli)、铜绿假单胞菌ATCC9027(Pseudomonas aeruginosa)、沙门氏菌ATCC14028(Salmonella)、金黄色葡萄球菌ATCC6538(Staphylococcus aureus) 购于广东省微生物研究所;小米椒 六月份,购于广东广州大学城南亭市场,颜色均匀、无病虫害、无机械伤以及成熟度一致,距离实验时已贮存1 d。
SW-CJ-2F超净工作台 苏州安泰空气技术有限公司;LRH-70F生化培养箱 上海一恒科学仪器有限公司;GZX-9240MBE电热鼓风干燥箱 上海博讯实业有限公司;YXQ-70A高压灭菌锅 上海博迅实业有限公司;TP-114分析天平 赛多利斯仪器有限公司;TU-1950紫外可见分光光度计 北京普析通用仪器公司;5977B气相色谱-质谱联用仪 安捷伦科技有限公司;Talos F200S场发射透射电子显微镜 捷克FEI。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 菌悬液的制备
将菌种于营养肉汤中37 ℃活化24 h,平板划线分离单个菌落,挑取单个菌落用麦氏比浊管配制成0.5麦氏单位(约1.5×108 CFU/mL)的菌悬液,备用。
1.2.2 植物精油熏蒸的最低抑菌浓度测定
参考Lopez等[23]的熏蒸抗菌实验,取0.5麦氏浓度的菌悬液加入已冷却的营养琼脂平板上,涂匀,倒置。取用丙二醇溶解稀释后的不同浓度的肉桂精油0.4 mL滴加在各培养皿盖中央,封口膜密封并置于37 ℃恒温培养箱培养24 h,观察平板上细菌生长情况。以不长菌平板所对应的最低浓度为各精油熏蒸的最低抑菌浓度(Minimum inhibitory concentration, MIC)。每种浓度平行做三个平板。
1.2.3 植物精油熏蒸的最低杀菌浓度测定
采用菌块转移法,用无菌的打孔器在最低抑菌浓度实验中不长菌的平板上打取直径为6 mm菌块转移到新鲜的营养琼脂平板中央,37 ℃生化培养箱中培养24 h,观察菌块的菌落生长情况。菌块仍然不长菌的平板对应的最低浓度为各精油熏蒸的最低杀菌浓度(Minimum bacterial concentration,MBC)。每种浓度平行做三个平板。
1.2.4 气相-质谱联用(GC-MS)分析精油熏蒸抑菌成分
气相色谱条件:采用Agilent 7890B气相色谱仪,HP-5MS色谱柱(60 m×0.25 mm×0.25 μm);初始温度保持在50 ℃ 3 min,并以2 ℃/min的速率逐渐升高到180 ℃。随后,以20 ℃/min的速率将温度升高至300 ℃,并保持10 min;进样量0.2 μL;进样口温度为250 ℃;分流比120:1;载气流速1 mL/min;传输线温度:300 ℃。
质谱条件:采用Agilent 5977B GC/MS,电离方式为EI,atune,离子源温度为230 ℃;四级杆温度为150 ℃;扫描范围29~550 amu。通过结合美国国家标准技术研究院(national institute of standards and technology,NIST)14质谱库和自建香料谱库进行定性检索,参照标准图谱和相关文献确认各组分,并使用峰面积归一化法计算各组分的相对含量。
1.2.5 正交试验设计
为了提高植物精油的杀菌效果和拓宽其杀菌谱,选取综合抗菌性较好的香茅精油、肉桂精油和罗勒精油3种植物精油进行复配。因为精油浓度越大,其抗菌活性越大,为了保证得到最佳配比,采用正交试验优化精油抗菌剂的配比,添加到培养皿中精油的总量控制不变,最终每个培养皿的空间抑菌浓度统一在0.0625 μL/mL,此浓度下致病菌没有完全被抑制,可以区分出不同配比下精油的抑菌能力大小。采用正交表L9(34)优化精油抗菌剂的配比,任选三列来进行正交试验。香茅精油和肉桂精油的总体抗菌性优于罗勒精油,因此选择因素水平表中香茅精油和肉桂精油的最低水平占比1,罗勒精油最低水平占比2,以对各个组合抑菌效果的综合评分为考察指标,抑菌方法按照1.2.2的平板熏蒸法,先按照每一组实验配比对3种精油进行复配,然后对每一组复配植物精油进行稀释,根据最终的精油空间浓度计算出精油添加体积。因素水平表和评分标准[26]见表1和表2,一种精油组合对一种菌的最高得分为10分,对四种菌的抑制结果总分为40分。
表 1 复配精油正交试验因素水平表Table 1. Factor level table of orthogonal test of compound essential oils水平 因素 A 香茅精油占比 B 肉桂精油占比 C 罗勒精油占比 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 4 3 4 4 8 表 2 复配精油实验评分标准Table 2. Scoring standards of compound essential oils平板长菌量(%) 得分 0 10 1~10 9 11~20 8 21~30 7 31~40 6 41~50 5 51~60 4 61~70 3 71~80 2 81~90 1 91~100 0 注:长菌量:菌种在培养皿中生长的相对面积,准备两张直径9 cm的硬透明塑料,其中一张画横线竖线分割成大约185个正方形格子(边长3 mm,边缘面积大于4.5 mm2的格子算一个),将空白与划线塑料重叠在9 cm的长菌玻璃培养皿上,在空白塑料标记长菌正方形个数n,长菌面积约等于n/185×100%。 1.2.6 植物精油熏蒸联合抗菌效果评价
复合植物精油联合熏蒸抑菌效果可用分级抑菌浓度指数(Fractional inhibitory concentration indices,FICI)加以评价[27-28]。指数的计算公式如下式(1):
(1) FICI的判断标准为:FICI≤0.5时为协同作用(S);0.5<FICI≤1为相加作用(A);1<FICI≤4为无关作用(I);FICI>4时为拮抗作用(AN)。
1.2.7 透射电子显微镜进行细菌形态观察
参考文献[29],取正常培养和经肉桂精油熏蒸处理(浓度0.25、1.0 μL/mL,时间24 h)的大肠杆菌,刮菌体于1.50 mL的离心管中,加入200~400 μL的2.5%戊二醛溶液,放在4 ℃的冰箱里冷藏固定4~6 h,再用磷酸缓冲液(pH7.4)洗3次,每次洗完离心(4 ℃,10000 r/min,3 min)再弃掉上清液。依次加入200 μL的30%、50%、70%、95%和100%的乙醇溶液梯度洗脱10 min,离心(4 ℃,10000 r/min,3 min)弃上清液,用无水乙醇重悬菌体使其分散,滴加1~2滴在铜网上,自然干燥,再利用透射电子显微镜观察菌体,并拍摄图像。
1.2.8 肉桂精油熏蒸对大肠杆菌菌液电导率的影响
参考文献方法[30],将大肠杆菌菌悬液涂布在平板37 ℃培养24 h后,在皿盖滴加0.4 mL不同浓度的肉桂精油,使得平板空间内浓度分别达到0.0625、0.125、0.25、0.5和1 μL/mL,同时做空白对照实验。用10 mL无菌去离子水洗脱菌落,制成菌悬液,将各菌液调OD600 nm至1.0±0.01,用电导率仪测其电导率值。每个浓度做三次平行,取其平均值。
将大肠杆菌菌悬液涂布在平板37 ℃培养24 h后,在皿盖滴加肉桂精油,使得平板空间内浓度达到0.5 μL/mL,熏蒸时间分别为0、3、6、9 h,用10 mL无菌去离子水收集菌体,将菌液调OD600 nm至1.0±0.01[31],取10 mL菌悬液测其电导率,进行三次重复实验后取平均值。
1.2.9 复配精油对小米椒的熏蒸保鲜
将小米椒果实随机分成6组,分别进行以下处理。
对照组:直接装入果蔬盒,每盒随机装入15根小米椒。
精油处理组:每个果蔬盒随机装入15根小米椒,将复配精油滴入棉花放置在果蔬盒中,并在每盒棉花滴加相同体积的无菌水增加湿度。假设精油全部挥发使空间浓度分别达到0.0625、0.125、0.25、0.5、1 μL/mL。
所有果蔬盒在40 ℃培养箱中加速腐败,每隔48 h取一盒观察小米椒的霉变个数并对其相关性保鲜指标进行测试。测定指标包括好果率、失重率和果实硬度。好果率参考Zhang等[32]的研究方法,好的小米椒果实不软烂、没有机械损伤、无腐坏迹象,仍具有可食用性和商品性,记录小米椒总数和好果数,按公式(2)计算好果率:
(2) 失重率、果实硬度则参考潘莹等[33]的研究方法。采用称重法计算失重率,按公式(3)计算:
(3) 式中:m0为最初小米椒样品的重量,g;m为样品在储藏期间不同时间测定时的重量,g。
果实硬度采用TA.XTC-18质构仪,条件如下:单次测试;下压距离3 mm,测试前速度为3 mm/s,触发力为N;测试速度为1 mm/s,测试后速度为1 mm/s。
1.3 数据处理
每个样品重复3次实验,使用SPSS 21.0软件(IBM,Armonk,NY,USA)进行统计学分析,并使用单因素方差分析比较平均值之间的差异,包括Waller-Duncan多重范围检验P<0.05显著水平。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同精油熏蒸对四种致病菌的MIC和MBC
根据实验方法,以铜绿假单胞菌、大肠杆菌、沙门氏菌、金黄色葡萄球菌为研究对象,将香茅、肉桂、罗勒、茶树、冬青、桉树精油稀释后加入皿盖,使得培养皿中的空间浓度为1、0.5、0.25、0.125、0.0625 μL/mL,经过精油熏蒸处理,得到不同植物精油对不同细菌熏蒸的最低抑菌浓度,如表3所示。
表 3 不同精油熏蒸的最低抑菌浓度(μL/mL)Table 3. MIC of different essential oils in vapor-phase (μL/mL)致病菌 香茅
精油肉桂
精油罗勒
精油茶树
精油冬青
精油桉树
精油铜绿假单胞菌 0.0625cB 0.125bA 0.125bA 0.5aA 0.5aA 0.5aA 大肠杆菌 0.0625dB 0.125cA 0.125cA 0.5aA 0.25bB 0.5aA 沙门氏菌 0.0625cB 0.125bA 0.125bA 0.5aA 0.5aA 0.5aA 金黄色葡萄球菌 0.125bA 0.0625cB 0.125bA 0.5aA 0.5aA 0.5aA 注:同行不同字母(a~d)表示同一菌株在不同精油中差异显著(P<0.05);同列不同字母(A~B)表示同一精油在不同菌株中差异显著(P<0.05)。 从表3可看出,6种植物精油熏蒸处理对4种常见致病菌都有抑制作用,当精油空间浓度达到0.125 μL/mL时,肉桂精油、香茅精油和罗勒精油均可抑制全部供试菌的生长。其中香茅精油对铜绿假单胞菌、大肠杆菌和沙门氏菌的抑菌作用要优于肉桂精油,抑菌效果最好;肉桂精油与罗勒精油的抑菌效果相当;冬青精油、桉树精油和茶树精油抑制所有供试菌的浓度相当,当空间浓度为0.5 μL/mL时可抑制全部供试菌的生长。其中冬青精油对大肠杆菌的抑菌效果要优于桉树精油和茶树精油。
从表4可看,6种植物精油熏蒸对铜绿假单胞菌的最低杀菌浓度均大于1.0 μL/mL,罗勒、茶树、冬青和桉树精油熏蒸对大肠杆菌的最低杀灭浓度也都高于1.0 μL/mL,而6种植物精油熏蒸对沙门氏菌的最低杀菌浓度均没有超过1.0 μL/mL,说明铜绿假单胞菌对供试的六种精油相对不敏感,大肠杆菌对四种精油相对不敏感,而沙门氏菌对供试的六种精油表现为相对敏感。肉桂精油和香茅精油的杀菌效果最好,当空间浓度达到0.125 μL/mL时,可杀灭除铜绿假单胞菌外的其他三种供试菌,其中肉桂精油对金黄色葡萄球菌的杀灭效果要优于香茅精油。茶树和桉树精油熏蒸对金黄色葡萄球菌的杀灭效果要优于罗勒和冬青精油。
表 4 不同精油熏蒸的最低杀菌浓度(μL/mL)Table 4. MBC of different essential oils in vapor-phase (μL/mL)致病菌 香茅
精油肉桂
精油罗勒
精油茶树
精油冬青
精油桉树
精油铜绿假单胞菌 >1.0 >1.0 >1.0 >1.0 >1.0 >1.0 大肠杆菌 0.125 0.125 >1.0 >1.0 >1.0 1.0 沙门氏菌 0.125 0.125 1.0 0.5 0.5 0.5 金黄色葡萄球菌 0.125 0.0625 1.0 0.5 >1.0 0.5 2.2 植物精油抗菌成分分析
由实验结果可知,肉桂精油、香茅精油和罗勒精油的抑菌效果较好,而香茅精油和肉桂精油的杀菌效果最好,将这三种精油挥发性成分进行GC-MS分析,分析精油熏蒸的主要抗菌成分,三种植物精油的总离子流图见图1,主要化学成分见表5(表中显示相对含量≥0.05%的组分)。
表 5 肉桂精油、香茅精油和罗勒精油主要化学成分Table 5. The main chemical composition of cinnamon essential oil, citronella essential oil and basil essential oil编号 化合物名称 相对含量(%) 编号 化合物名称 相对含量(%) 肉桂精油 香茅精油 罗勒精油 肉桂精油 香茅精油 罗勒精油 1 1,3,5,7-环辛四烯 0.1456 − − 46 萜品油烯 − 0.0605 − 2 α-蒎烯 0.0838 − 0.0574 47 芳樟醇 − 0.9121 14.9571 3 莰烯 0.0584 − − 48 异胡薄荷醇 − 1.1018 − 4 苯甲醛 0.8129 − − 49 香茅醛 − 33.8882 − 5 2-羟基苯甲醛 0.2103 − − 50 α-松油醇 − 0.0575 0.1437 6 苯基乙醇 0.5357 − − 51 癸醛 − 0.0912 − 7 苯丙醛 0.6285 − − 52 橙花醇 − 0.0552 − 8 左旋龙脑 0.1195 − − 53 香茅醇 − 12.0034 − 9 肉桂醛 0.6355 − − 54 (Z)-3,7-二甲基-2,6-辛二烯醛 − 0.2657 − 10 氢化肉桂醇 0.1061 − − 55 香叶醇 − 20.2956 − 11 2-甲氧基苯甲醛 0.6368 − − 56 (E)-3,7-二甲基-2,6-辛二烯醛 − 0.386 − 12 菲斯萘青酯 0.094 − − 57 孟二醇 − 0.2334 − 13 反式肉桂醛 78.967 − − 58 乙酸香茅酯 − 3.2635 − 14 茴香脑 0.0817 − − 59 丁香酚 − 0.875 0.0665 15 反式-肉桂醇 0.1395 − − 60 乙酸香叶酯 − 3.9202 − 16 环苜蓿烯 0.0518 − − 61 β-榄香烯 − 2.3627 − 17 邻甲氧基苯丙酮 0.4609 − − 62 α-石竹烯 − 0.1506 0.274 18 胡椒烯 0.6679 − − 63 D-大根香叶烯 − 2.8593 − 19 石竹烯 0.2263 0.1259 0.503 64 香橙烯 − 0.0726 − 20 反式-α-香柑油烯 0.072 − 0.6387 65 荜澄茄醇 − 0.2031 − 21 香豆素 0.8237 − − 66 α-依兰油烯 − 0.6621 − 22 1-苯基-2-硝基丙烯 0.968 − − 67 α-杜松烯 − 0.1414 − 23 γ-依兰油烯 0.1933 0.2816 − 68 榄香醇 − 3.3795 − 24 α-姜黄烯 0.1535 − − 69 (2E,4S,7E)-4-异丙基-1,7-二甲基环十二烷-2,7-二烯醇 − 0.6484 − 25 (+)-喇叭烯 0.0922 − − 70 金合欢醇 − 0.1735 − 26 α-衣兰油烯 0.1534 − − 71 表荜澄茄油烯醇 − 0.0707 − 27 β-甜没药烯 0.1597 − 0.1036 72 γ-桉叶醇 − 0.3886 − 28 γ-杜松烯 0.1038 0.6534 73 τ-杜松醇 − 0.322 − 29 δ-杜松烯 0.3324 2.4786 0.0548 74 香榧醇 − 0.1111 − 30 邻甲氧基肉桂醛 8.8692 − − 75 β-桉叶醇 − 0.3506 − 31 α-红没药烯 0.063 − − 76 α-桉叶醇 − 0.3425 − 32 橙花叔醇 0.1794 − − 77 合金欢醇 − 0.0724 − 33 桉油烯醇 0.1655 − − 78 桉叶油醇 − − 0.1162 34 石竹素 0.1315 − − 79 β-罗勒烯 − − 0.155 35 肉豆蔻醛 0.0962 − − 80 氧化芳樟醇 − − 0.1063 36 T-依兰油醇 0.068 0.438 − 81 薄荷脑 − − 0.3273 37 α-毕橙茄醇 0.0525 0.8111 − 82 草蒿脑 − − 76.5078 38 α-红没药醇 0.0607 − − 83 Z-柠檬醛 − − 0.3821 39 苯甲酸苄酯 0.0803 − − 84 柠檬醛 − − 0.5954 40 苯甲酸-2-苯乙酯 0.0521 − − 85 甲基丁香酚 − − 0.1055 41 α-布藜烯 0.0689 − − 86 Z-β-金合欢烯 − − 0.289 42 甲基庚烯酮 − 0.0913 0.0957 87 β-荜澄茄油烯 − − 0.3479 43 β-月桂烯 − 0.0739 − 88 E-β-金合欢烯 − − 0.0779 44 柠檬烯 − 3.6393 0.1066 89 对甲氧基肉桂醛 − − 0.3868 45 甜瓜醛 − 0.0503 − 90 氧化石竹烯 − − 0.0728 注:表中仅列出含量大于0.05%的成分;“−”代表不含或含量小于0.05%的成分。 2.2.1 肉桂精油
肉桂精油共鉴定出64种成分,含量最高的为反式肉桂醛,相对含量为78.967%。挥发油中共鉴定出9种醛类化合物,相对含量为90.8976%;鉴定出29种烯烃类化合物,相对含量为4.0705%;鉴定出16种酚醇类化合物,相对含量为1.7798%;其他化合物10种,相对含量为1.6942%。定量结果表明,肉桂精油挥发油富含醛类化合物。
肉桂精油中挥发成分多为15碳以下的小分子化合物,以醛类、酚醇类、烯烃类化合物为主。其中肉桂醛是肉桂精油中的主要活性成分,具有良好的抑菌、抗氧化、抗肿瘤等作用[34]。Vasconcelos等[35]认为反式肉桂醛是肉桂精油的主要活性物质,α, β-不饱和羰基部分是肉桂醛活性部位,其余次要成分在单独使用时可能存在低水平或没有抗菌作用,但它们可能会增加反式肉桂醛的作用或在细菌细胞中有其他作用靶点来提高肉桂精油的抗菌活性。Fraňková等[36]研究了精油蒸汽对克罗诺杆菌的MIC,结果发现最有效的是肉桂和牛至精油及其对应的主要成分为反式肉桂醛和香芹酚。由此可知,肉桂精油熏蒸的主要抗菌成分是反式肉桂醛。
2.2.2 香茅精油
从香茅精油中共分离鉴定出57种挥发性化合物,含量最高的是香茅醛,相对含量为33.8882%,其次为香叶醇(20.2956%)、香茅醇(12.0034%)。挥发油中共鉴定出3种醛类化合物,相对含量为34.0297%;共鉴定出21种烯烃类化合物,相对含量为14.3516%;共鉴定出27种酚醇类化合物,相对含量为43.0448%;其他化合物6种,相对含量为7.3548%。结果表明,香茅精油挥发油富含醛醇类化合物。
蒋小龙等[37]研究发现,香茅精油含31种成分,其中香茅醛含量为35.81%,香叶醇含量为23.4%,香茅醇含量为8.37%,且香茅精油中香茅醛、香茅醇具有良好的抑菌作用。陈晓晶[38]认为香茅精油的抑菌作用与其含有的主要挥发性成分香茅醛、香叶醇以及香茅醇的含量及其与其他微量成分的协同作用有关。由此可推断,香茅精油熏蒸的主要抗菌成分是香茅醛、香叶醇以及香茅醇。
2.2.3 罗勒精油
从罗勒精油中共分离鉴定出48种挥发性化合物,含量最高的是草蒿脑,相对含量为76.5078%,其次为芳樟醇(14.9571%)。挥发油中共鉴定出3种醚类化合物,相对含量为76.565%;鉴定出16种酚醇类化合物,相对含量为16.0826%;共鉴定出19种烯烃类化合物,相对含量为2.8757%;共鉴定出4种醛类化合物,相对含量为1.3936%;其他化合物6种,相对含量为0.2257%。结果表明,罗勒精油挥发油富含醚类和醇类化合物。
通过Koba等[39]的分析,本文的罗勒精油属于甲基黑椒酚-芳樟醇型,此化学类型以草蒿脑和芳樟醇为罗勒精油最主要的成分,Koba等[39]研究发现甲基黑椒酚-芳樟醇型的罗勒精油抑菌效果相比甲基丁香酚型的罗勒精油要差,但相比其主要的单体成分芳樟醇和草蒿脑的抑菌效果要好,芳樟醇对供试的大部分细菌和真菌的抑菌浓度大于500 μL/L,而草蒿脑精油对供试所有真菌和细菌的抑菌浓度均大于500 μL/L;Hussain等[40]研究了不同季节得到的罗勒精油及其主要单体成分芳樟醇的抑菌活性,证明罗勒精油的芳樟醇含量与其抑菌活性紧密相关。由此可以推断,罗勒精油的熏蒸抗菌活性可能与草蒿脑、芳樟醇的抗菌活性以及各微量组分的协同作用相关。
2.3 复配精油正交试验分析
按照方法1.2.5,选取抗菌性较好的香茅精油、肉桂精油和罗勒精油3种植物精油进行复配,正交试验结果见表6。
表 6 复配精油正交试验结果Table 6. Orthogonal test results of compound essential oils试验号 精油占比 平均得分 A 香茅精油 B 肉桂精油 C 罗勒精油 1 1 1 1 29.0 2 1 2 2 25.7 3 1 3 3 31.0 4 2 1 2 26.7 5 2 2 3 35.7 6 2 3 1 32.7 7 3 1 3 38.0 8 3 2 1 27.7 9 3 3 2 33.7 k1 28.6 31.2 29.8 k2 31.7 29.7 28.7 k3 33.1 32.4 34.9 R 4.6 2.8 6.2 由表7各因素的F值与临界值的比较可以看出,F(C)>F0.01,说明罗勒精油对复配精油的熏蒸抑菌效果有极显著影响;F0.01>F(A)>F0.05,说明香茅精油对复配精油的熏蒸抑菌效果有显著影响;F0.05>F(B),说明肉桂精油对复配精油的抑菌效果影响不显著。另外,由各因素F值的大小F(C)>F(A)>F(B)可以看出,影响复配精油的抑菌效果的因素大小为:罗勒精油>香茅精油>肉桂精油。因肉桂精油的影响不显著,选择用量最少的水平1,因此,试验条件下的最佳搭配为A3B1C3,即为香茅精油、肉桂精油、罗勒精油的体积比为4:1:8,此分析结果与实验组最高分对应的比例一致,平均得分为38。
表 7 方差分析表Table 7. The table of variance analysis因素 SS df MS F 显著性 A 32.51851852 2 16.25925926 4.479591837 * B 11.62962963 2 5.814814815 1.602040816 C 66.07407407 2 33.03703704 9.102040816 ** 误差e 32.66666667 9 3.62962963 注:F0.05(2,9)=4.26, F0.01(2,9)=8.02;*表示差异显著(P<0.05),**表示差异极显著(P<0.01)。 2.4 复配精油抗菌效果及其协同效应分析
参考方法1.2.2测定最佳复配精油熏蒸对4种致病菌的最低抑菌浓度,实验结果见表8。为对复配精油的抑菌作用效果进行评价,实验采用1.2.6方法,计算相应的FICI值并进行评价,结果见表9。
表 8 最佳复配精油的最低抑菌浓度(μL/mL)Table 8. MIC of optimal compound essential oil (μL/mL)致病菌 空白 0.00781 0.0156 0.0313 0.0625 0.125 0.25 0.5 1 铜绿假单胞菌 ++ ++ ++ ++ + − − − − 大肠杆菌 ++ ++ + − − − − − − 沙门氏菌 ++ ++ + − − − − − − 金黄色葡萄球菌 ++ ++ ++ ++ + + + − − 注:“++”表示菌种生长良好;“+”表示菌种生长较弱;“−”表示无菌生长。 表 9 复配精油联合抑菌效果评价Table 9. Evaluation of combined antibacterial effect of compound essential oil供试菌种 最低杀菌浓度(μL/mL) FICI 联合效果 香茅精油 肉桂精油 罗勒精油 单用 联合 单用 联合 单用 联合 铜绿假单胞菌 0.0625 0.0385 0.125 0.00962 0.125 0.0769 1.31 无关作用 大肠杆菌 0.0625 0.00963 0.125 0.00241 0.125 0.0193 0.328 协同作用 沙门氏菌 0.0625 0.00963 0.125 0.00241 0.125 0.0193 0.328 协同作用 金黄色葡萄球菌 0.125 0.154 0.0625 0.0385 0.125 0.308 4.31 拮抗作用 由表8可知,复配精油对大肠杆菌和沙门氏菌的抑菌效果最好,MIC值为0.0313 μL/mL;对铜绿假单胞菌的MIC值为0.125 μL/mL;而对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑菌效果相对较差,MIC值达到了0.5 μL/mL。
由表9中计算得到的FICI值可知,复配精油对2种供试菌(大肠杆菌、沙门氏菌)都表现出协同增效作用,对铜绿假单胞菌表现出无关作用,而对金黄色葡萄球菌则表现为拮抗作用。研究表明,很多植物精油联合使用对细菌、霉菌等具有协同增效作用[41-42],这些增效作用可使精油在用量比较少的情况下达到抑菌效果,在实际应用中可节约成本,又能减少精油添加量大带来的负面感官影响。刘晓丽等[9]比较丁香、肉桂精油及其混合精油对11株食品常见污染菌的抑制作用,结果表明,精油联合使用对几种细菌的抑制作用表现为拮抗,本实验中精油联合对金黄色葡萄球菌也表现出拮抗作用,说明这几种精油联合使用削弱了抗菌作用,实际应用中应避免这3种精油联合用于金黄色葡萄球菌的抑菌产品中。
2.5 肉桂精油对大肠杆菌的抗菌机理
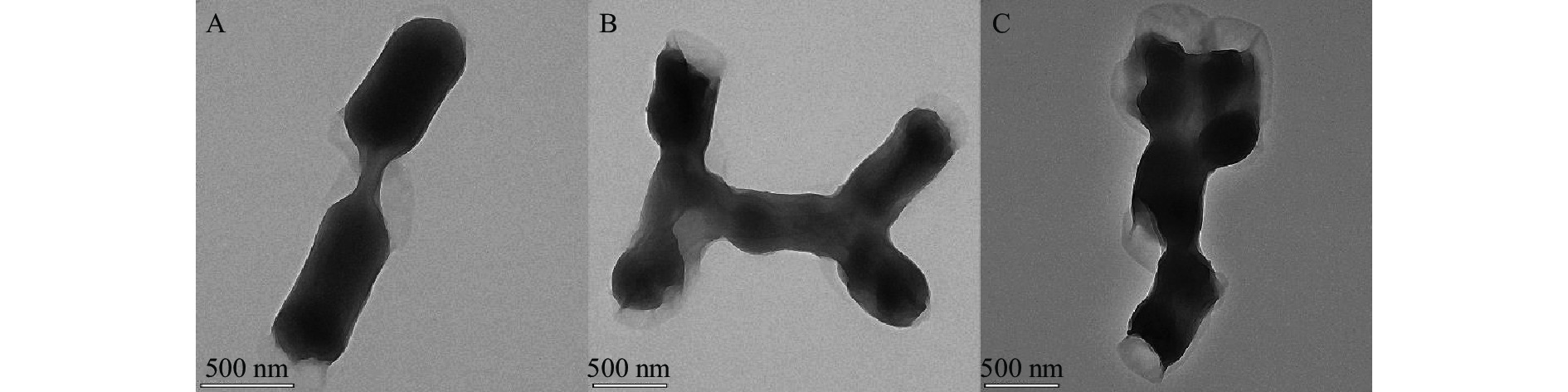
2.5.1 肉桂精油对大肠杆菌显微结构的影响
如图2A所示,正常大肠杆菌表面光滑,圆形边缘整齐,细胞壁与细胞膜结构完整且紧密相黏,细胞内物质均匀分布。经肉桂精油熏蒸的大肠杆菌显微结构如图2B及2C所示,经不同浓度的肉桂精油处理后,大肠杆菌的形态发生不同程度地改变。随肉桂精油浓度增大,大肠杆菌细胞膜与细胞壁的分离程度变大,胞内物质的分布越来越不均匀,形态逐渐凹凸不平,细胞发生皱缩。这种超微结构的变化与肉桂醛处理后的现象一致[43],会导致大肠杆菌细胞质浓缩或泄露,细胞的外膜变形甚至被破坏。由此推断,经过肉桂精油对细胞膜的影响主要是基于肉桂醛的作用,引起细胞表面形态改变,从而可能导致细胞膜发生改变,进而抑制细菌正常生长。
2.5.2 肉桂精油对大肠杆菌电导率的影响
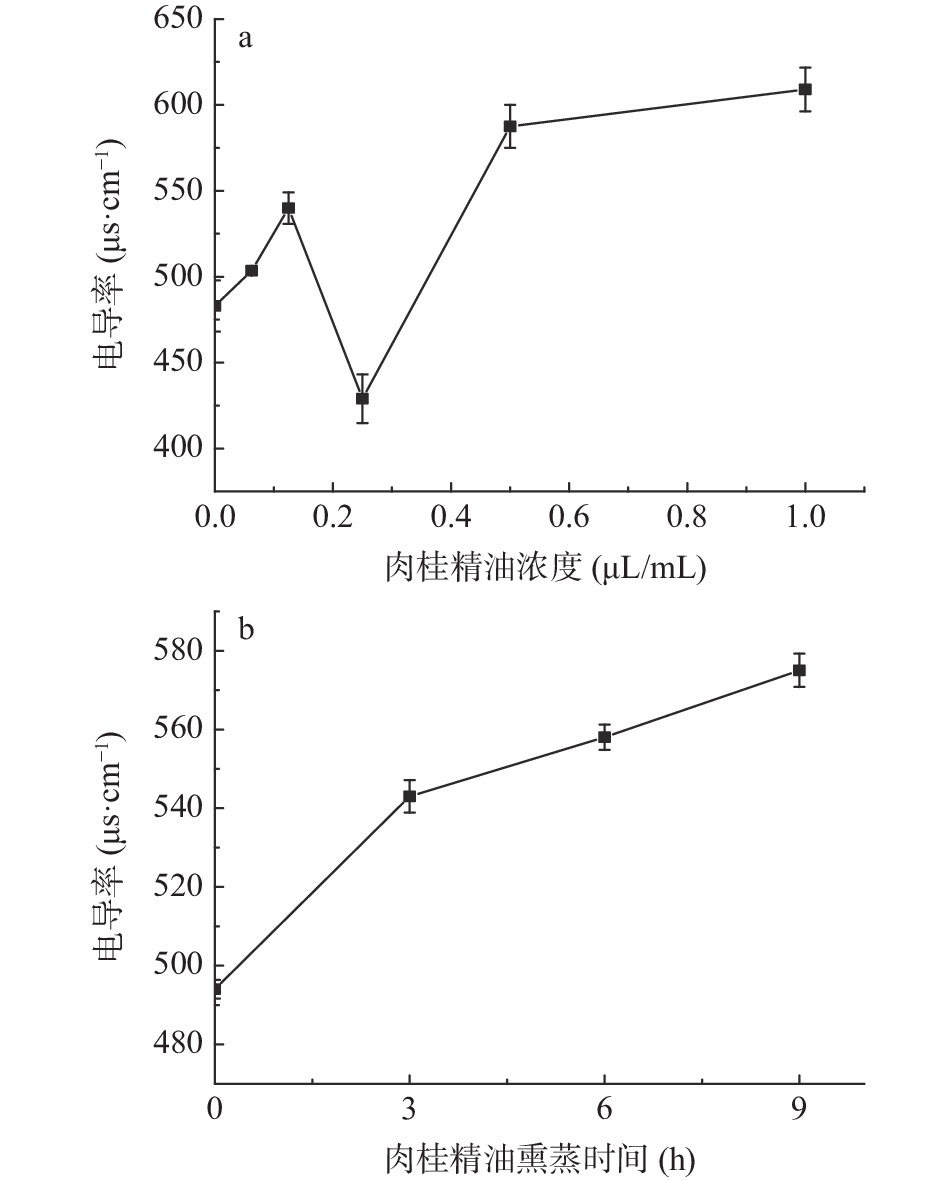
不同浓度肉桂精油和熏蒸时间(肉桂精油浓度0.5 μL/mL)对大肠杆菌菌液电导率的影响如图3所示。
由图3a可知,随着肉桂精油熏蒸浓度的增加,电导率先快速增加后急剧降低再升高随后趋于平缓。电导率总体呈现上升趋势,这可能是因为肉桂精油熏蒸导致大肠杆菌细胞膜的通透性增加,加大了胞内离子流出量[44],期间的上下起伏变化可能与精油影响运输离子的载体蛋白的活性有关[45]。肉桂精油浓度在0~0.125 μL/mL范围内,菌液电导率值升高,说明经过肉桂精油熏蒸后菌体的细胞膜流动性增加[46],通透性提高,此时膜载体蛋白未发生变性,离子从胞内到达菌液环境的速率提高,电导率值升高;在肉桂精油浓度0.125~0.25 μL/mL范围内,菌液电导率值下降到最低,这可能是因为随着肉桂精油浓度的提高,使膜载体蛋白发生变性,限制了协助扩散的进行,因此离子透过细胞膜受到阻碍,电导率值降低;肉桂精油浓度继续升高到一定浓度时,膜流动性降低、硬度增加[20],此时细胞膜可能出现一定程度损伤,胞内离子可能因此而直接流出,电导率再次升高。在肉桂精油0.5 μL/mL及其以上浓度处理后,大肠杆菌菌液电导率值变化不大,说明高浓度的精油可能严重破坏了细胞膜的结构,细胞膜破损严重,导致胞内离子大量外泄,最终维持在一个稳定值。由图3b可看出,随着肉桂精油处理时间的增加,菌液的电导率值增加。其中0~3 h内菌液电导率增加幅度最大,随后增幅减缓。说明在实验时间内,精油熏蒸导致的菌液电导率值与熏蒸时间呈正相关,由此可知,在实际应用中,时间效应也是影响抗菌性能的重要因素。
Kang等[47]研究表明,肉桂精油可通过影响细胞膜通透性导致电解质泄漏,电解质过度丢失会导致大肠杆菌死亡。因此,肉桂精油熏蒸导致的大肠杆菌死亡一方面因为电解质的过度丢失,一方面也可能是因为精油对细胞形态和细胞膜的破坏。
2.6 复配精油对辣椒的保鲜作用
从图4可以看出,小米椒对照组随着贮藏时间的延长失重明显,失重率上升速度快,在贮藏时间第10 d时失重率达到9.46%,而经过复配精油处理后的小米椒失重率变化幅度较低,随着精油空间浓度增大,失重率大体呈上升趋势。随着贮藏时间的延长,对照组的小米椒好果率下降迅速,在第10 d时,对照组好果率仅达到26.67%,而精油处理组好果率从空间浓度由小到大分别为40%、60%、66.67%、66.67%、73.33%,明显高于对照组。在40 ℃的贮藏环境下,在精油浓度为0.0625和0.125 μL/mL处理时,小米椒的硬度明显高于对照组,储存10 d时,空间浓度0.0625、0.125 μL/mL的复配精油处理后的小米椒相对于对照组硬度分别提高37.52%、33.68%。而精油浓度过高,肉眼明显观察到对小米椒的果皮产生很大影响,使其发软。
由此可见,复配精油处理可以降低小米椒的失重率,且对小米椒微生物的生长繁殖具有抑菌作用,起到防腐保鲜的作用。另一方面复配精油中的某些活性成分延缓了果实内部果胶酶的分解作用[48],当其提高到一定浓度后破坏其细胞结构,使得果实组织变软,硬度降低。综合来看,当复合精油空间浓度为0.125 μL/mL时,小米椒的各项指标较好,试验范围内保鲜效果最好。
3. 结论
本文通过平板熏蒸法研究了6种精油对4种致病菌的抗菌活性,香茅精油、肉桂精油和罗勒精油的抑菌效果最好,而肉桂精油和香茅精油的杀菌效果最好。GC-MS分析表明香茅精油的熏蒸抗菌能力主要来自香茅醛、香叶醇和香茅醇;肉桂精油主要来自于肉桂醛;而罗勒精油主要来自于草蒿脑、芳樟醇。将这3种精油复配后得到最佳抗菌组合(香茅精油:肉桂精油:罗勒精油为4:1:8),复配精油对大肠杆菌和沙门氏菌的抑菌效果表现出协同增效作用。植物精油对致病菌的熏蒸抗菌机理几乎很少有报道,本文以食品和空气中最常见的致病菌-大肠杆菌为模式菌,研究肉桂精油的熏蒸抗菌机理。肉桂精油熏蒸大肠杆菌可导致菌体细胞形态发生改变,细胞膜通透性改变,并对细胞膜造成损伤从而抑制细菌生长或导致死亡。将复配精油应用到小米椒的熏蒸保鲜中,可以有效降低小米椒在储存期间的失重率,减缓硬度降低趋势及抑制微生物生长,起到防腐保鲜的作用。植物精油作为绿色、高效、安全抗菌剂的来源之一,联合协同抗菌可减少抗菌剂用量,节约成本,未来在食品气相保鲜、室内空气微生物杀菌、净化室内环境中将会得到更多的应用。
-
表 1 复配精油正交试验因素水平表
Table 1 Factor level table of orthogonal test of compound essential oils
水平 因素 A 香茅精油占比 B 肉桂精油占比 C 罗勒精油占比 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 4 3 4 4 8 表 2 复配精油实验评分标准
Table 2 Scoring standards of compound essential oils
平板长菌量(%) 得分 0 10 1~10 9 11~20 8 21~30 7 31~40 6 41~50 5 51~60 4 61~70 3 71~80 2 81~90 1 91~100 0 注:长菌量:菌种在培养皿中生长的相对面积,准备两张直径9 cm的硬透明塑料,其中一张画横线竖线分割成大约185个正方形格子(边长3 mm,边缘面积大于4.5 mm2的格子算一个),将空白与划线塑料重叠在9 cm的长菌玻璃培养皿上,在空白塑料标记长菌正方形个数n,长菌面积约等于n/185×100%。 表 3 不同精油熏蒸的最低抑菌浓度(μL/mL)
Table 3 MIC of different essential oils in vapor-phase (μL/mL)
致病菌 香茅
精油肉桂
精油罗勒
精油茶树
精油冬青
精油桉树
精油铜绿假单胞菌 0.0625cB 0.125bA 0.125bA 0.5aA 0.5aA 0.5aA 大肠杆菌 0.0625dB 0.125cA 0.125cA 0.5aA 0.25bB 0.5aA 沙门氏菌 0.0625cB 0.125bA 0.125bA 0.5aA 0.5aA 0.5aA 金黄色葡萄球菌 0.125bA 0.0625cB 0.125bA 0.5aA 0.5aA 0.5aA 注:同行不同字母(a~d)表示同一菌株在不同精油中差异显著(P<0.05);同列不同字母(A~B)表示同一精油在不同菌株中差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 4 不同精油熏蒸的最低杀菌浓度(μL/mL)
Table 4 MBC of different essential oils in vapor-phase (μL/mL)
致病菌 香茅
精油肉桂
精油罗勒
精油茶树
精油冬青
精油桉树
精油铜绿假单胞菌 >1.0 >1.0 >1.0 >1.0 >1.0 >1.0 大肠杆菌 0.125 0.125 >1.0 >1.0 >1.0 1.0 沙门氏菌 0.125 0.125 1.0 0.5 0.5 0.5 金黄色葡萄球菌 0.125 0.0625 1.0 0.5 >1.0 0.5 表 5 肉桂精油、香茅精油和罗勒精油主要化学成分
Table 5 The main chemical composition of cinnamon essential oil, citronella essential oil and basil essential oil
编号 化合物名称 相对含量(%) 编号 化合物名称 相对含量(%) 肉桂精油 香茅精油 罗勒精油 肉桂精油 香茅精油 罗勒精油 1 1,3,5,7-环辛四烯 0.1456 − − 46 萜品油烯 − 0.0605 − 2 α-蒎烯 0.0838 − 0.0574 47 芳樟醇 − 0.9121 14.9571 3 莰烯 0.0584 − − 48 异胡薄荷醇 − 1.1018 − 4 苯甲醛 0.8129 − − 49 香茅醛 − 33.8882 − 5 2-羟基苯甲醛 0.2103 − − 50 α-松油醇 − 0.0575 0.1437 6 苯基乙醇 0.5357 − − 51 癸醛 − 0.0912 − 7 苯丙醛 0.6285 − − 52 橙花醇 − 0.0552 − 8 左旋龙脑 0.1195 − − 53 香茅醇 − 12.0034 − 9 肉桂醛 0.6355 − − 54 (Z)-3,7-二甲基-2,6-辛二烯醛 − 0.2657 − 10 氢化肉桂醇 0.1061 − − 55 香叶醇 − 20.2956 − 11 2-甲氧基苯甲醛 0.6368 − − 56 (E)-3,7-二甲基-2,6-辛二烯醛 − 0.386 − 12 菲斯萘青酯 0.094 − − 57 孟二醇 − 0.2334 − 13 反式肉桂醛 78.967 − − 58 乙酸香茅酯 − 3.2635 − 14 茴香脑 0.0817 − − 59 丁香酚 − 0.875 0.0665 15 反式-肉桂醇 0.1395 − − 60 乙酸香叶酯 − 3.9202 − 16 环苜蓿烯 0.0518 − − 61 β-榄香烯 − 2.3627 − 17 邻甲氧基苯丙酮 0.4609 − − 62 α-石竹烯 − 0.1506 0.274 18 胡椒烯 0.6679 − − 63 D-大根香叶烯 − 2.8593 − 19 石竹烯 0.2263 0.1259 0.503 64 香橙烯 − 0.0726 − 20 反式-α-香柑油烯 0.072 − 0.6387 65 荜澄茄醇 − 0.2031 − 21 香豆素 0.8237 − − 66 α-依兰油烯 − 0.6621 − 22 1-苯基-2-硝基丙烯 0.968 − − 67 α-杜松烯 − 0.1414 − 23 γ-依兰油烯 0.1933 0.2816 − 68 榄香醇 − 3.3795 − 24 α-姜黄烯 0.1535 − − 69 (2E,4S,7E)-4-异丙基-1,7-二甲基环十二烷-2,7-二烯醇 − 0.6484 − 25 (+)-喇叭烯 0.0922 − − 70 金合欢醇 − 0.1735 − 26 α-衣兰油烯 0.1534 − − 71 表荜澄茄油烯醇 − 0.0707 − 27 β-甜没药烯 0.1597 − 0.1036 72 γ-桉叶醇 − 0.3886 − 28 γ-杜松烯 0.1038 0.6534 73 τ-杜松醇 − 0.322 − 29 δ-杜松烯 0.3324 2.4786 0.0548 74 香榧醇 − 0.1111 − 30 邻甲氧基肉桂醛 8.8692 − − 75 β-桉叶醇 − 0.3506 − 31 α-红没药烯 0.063 − − 76 α-桉叶醇 − 0.3425 − 32 橙花叔醇 0.1794 − − 77 合金欢醇 − 0.0724 − 33 桉油烯醇 0.1655 − − 78 桉叶油醇 − − 0.1162 34 石竹素 0.1315 − − 79 β-罗勒烯 − − 0.155 35 肉豆蔻醛 0.0962 − − 80 氧化芳樟醇 − − 0.1063 36 T-依兰油醇 0.068 0.438 − 81 薄荷脑 − − 0.3273 37 α-毕橙茄醇 0.0525 0.8111 − 82 草蒿脑 − − 76.5078 38 α-红没药醇 0.0607 − − 83 Z-柠檬醛 − − 0.3821 39 苯甲酸苄酯 0.0803 − − 84 柠檬醛 − − 0.5954 40 苯甲酸-2-苯乙酯 0.0521 − − 85 甲基丁香酚 − − 0.1055 41 α-布藜烯 0.0689 − − 86 Z-β-金合欢烯 − − 0.289 42 甲基庚烯酮 − 0.0913 0.0957 87 β-荜澄茄油烯 − − 0.3479 43 β-月桂烯 − 0.0739 − 88 E-β-金合欢烯 − − 0.0779 44 柠檬烯 − 3.6393 0.1066 89 对甲氧基肉桂醛 − − 0.3868 45 甜瓜醛 − 0.0503 − 90 氧化石竹烯 − − 0.0728 注:表中仅列出含量大于0.05%的成分;“−”代表不含或含量小于0.05%的成分。 表 6 复配精油正交试验结果
Table 6 Orthogonal test results of compound essential oils
试验号 精油占比 平均得分 A 香茅精油 B 肉桂精油 C 罗勒精油 1 1 1 1 29.0 2 1 2 2 25.7 3 1 3 3 31.0 4 2 1 2 26.7 5 2 2 3 35.7 6 2 3 1 32.7 7 3 1 3 38.0 8 3 2 1 27.7 9 3 3 2 33.7 k1 28.6 31.2 29.8 k2 31.7 29.7 28.7 k3 33.1 32.4 34.9 R 4.6 2.8 6.2 表 7 方差分析表
Table 7 The table of variance analysis
因素 SS df MS F 显著性 A 32.51851852 2 16.25925926 4.479591837 * B 11.62962963 2 5.814814815 1.602040816 C 66.07407407 2 33.03703704 9.102040816 ** 误差e 32.66666667 9 3.62962963 注:F0.05(2,9)=4.26, F0.01(2,9)=8.02;*表示差异显著(P<0.05),**表示差异极显著(P<0.01)。 表 8 最佳复配精油的最低抑菌浓度(μL/mL)
Table 8 MIC of optimal compound essential oil (μL/mL)
致病菌 空白 0.00781 0.0156 0.0313 0.0625 0.125 0.25 0.5 1 铜绿假单胞菌 ++ ++ ++ ++ + − − − − 大肠杆菌 ++ ++ + − − − − − − 沙门氏菌 ++ ++ + − − − − − − 金黄色葡萄球菌 ++ ++ ++ ++ + + + − − 注:“++”表示菌种生长良好;“+”表示菌种生长较弱;“−”表示无菌生长。 表 9 复配精油联合抑菌效果评价
Table 9 Evaluation of combined antibacterial effect of compound essential oil
供试菌种 最低杀菌浓度(μL/mL) FICI 联合效果 香茅精油 肉桂精油 罗勒精油 单用 联合 单用 联合 单用 联合 铜绿假单胞菌 0.0625 0.0385 0.125 0.00962 0.125 0.0769 1.31 无关作用 大肠杆菌 0.0625 0.00963 0.125 0.00241 0.125 0.0193 0.328 协同作用 沙门氏菌 0.0625 0.00963 0.125 0.00241 0.125 0.0193 0.328 协同作用 金黄色葡萄球菌 0.125 0.154 0.0625 0.0385 0.125 0.308 4.31 拮抗作用 -
[1] TULLIO V, NOSTRO A, MANDRAS N, et al. Antifungal activity of essential oils against filamentous fungi determined by broth microdilution and vapour contact methods[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology,2007,102(6):1544−1550. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2006.03191.x
[2] PINA-VAZ C, GONCALVES RODRIGUES A, PINTO E, et al. Antifungal activity of thymus oils and their major compounds[J]. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology,2004,18(1):73−78. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2004.00886.x
[3] MUTLU-INGOK A, DEVECIOGLU D, DIKMETAS D N, et al. Antifungal, antimycotoxigenic, and antioxidant activities of essential oils: An updated review[J]. Molecules,2020,25(20):4711. doi: 10.3390/molecules25204711
[4] COX S D, GUSTAFSON J E, MANN C M, et al. Tea tree oil causes K+ leakage and inhibits respiration in Escherichia coli[J]. Letters in Applied Microbiology,1998,26(5):355−358. doi: 10.1046/j.1472-765X.1998.00348.x
[5] LOPEZ-ROMERO J C, GONZALEZ-RIOS H, BORGES A, et al. Antibacterial effects and mode of action of selected essential oils components against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine,2015:795435.
[6] OUSSALAH M, CAILLET S, LACROIX M. Mechanism of action of spanish oregano, Chinese cinnamon, and savory essential oils against cell membranes and walls of Escherichia coli O157: H7 and Listeria monocytogenes[J]. Journal of Food Protection,2006,69(5):1046−1055. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X-69.5.1046
[7] LAIRD K, PHILLIPS C. Vapour phase: A potential future use for essential oils as antimicrobials?[J]. Letters in Applied Microbiology,2012,54(3):169−174. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765X.2011.03190.x
[8] BOUKHATEM M N, KAMELI A, SAIDI F. Essential oil of algerian rose-scented geranium (Pelargonium graveolens): Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity against food spoilage pathogens[J]. Food Control,2013,34(1):208−213. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2013.03.045
[9] 刘晓丽, 钟少枢, 吴克刚, 等. 丁香和肉桂精油气相抑菌活性研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2010,36(1):21−24, 38. [LIU X L, ZHONG S S, WU K G, et al. Antimicrobial activity in the vapour phase of a combination of cinnamon and clove essential oils[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2010,36(1):21−24, 38. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.2010.01.033 [10] TYAGI A K, MALIK A. Antimicrobial action of essential oil vapours and negative air ions against Pseudomonas fluorescens[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2010,143(3):205−210. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2010.08.023
[11] JI H, KIM H, BEUCHAT L R, et al. Synergistic antimicrobial activities of essential oil vapours against Penicillium corylophilum on a laboratory medium and beef jerky[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2019,291:104−110. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2018.11.023
[12] 钟少枢, 吴克刚, 柴向华, 等. 七种单离食用香料对食品腐败菌抑菌活性的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2009,30(5):68−71. [ZHONG S S, WU K G, CHAI X H, et al. Study on bacteriostasis of seven isolate spices to food spoilage organism[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2009,30(5):68−71. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2009.05.014 [13] 田双娥, 赵晶. 7种植物精油对霉菌的抑制作用研究[J]. 中国文物科学研究,2021,3:60−64. [TIAN S E, ZHAO J. Study on the inhibitory effect of seven plant essential oils on fungi[J]. China Cultural Heritage Scientific Research,2021,3:60−64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9677.2021.02.010 [14] 宁亚维, 苏丹, 付浴男, 等. 抗菌肽brevilaterin与柠檬酸联用对大肠杆菌的协同抑菌机理[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(19):31−37. [NING Y W, SU D, FU Y N, et al. Antibacterial mechanism of antimicrobial peptide brevilaterin combined with citric acid against Escherichia coli[J]. Food Science,2020,41(19):31−37. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191008-026 [15] 刘雅夫, 符腾飞, 刘宸成, 等. 低温等离子体对金黄色葡萄球菌和铜绿假单胞菌杀菌效果及动力学特性性[J]. 现代食品科技,2021,37(12):127−135. [LIU Y F, FU T F, LIU C C, et al. Study on bactericidal efficacy and kinetics of cold plasma on Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2021,37(12):127−135. [16] LIU S Q, BRUL S, ZAAT S A J. Bacterial persister-cells and spores in the food chain: Their potential inactivation by antimicrobial peptides (AMPs)[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2020,21(23):8967. doi: 10.3390/ijms21238967
[17] 祁迪亚, 孔佳仪, 钱志浩, 等. 食品中不同环境条件对沙门氏菌持留菌形成的影响[J]. 生物加工过程, 2023, 21(1): 91-97. QI D Y, KONG J Y, QIAN Z H, et al. Influence of different food environmental conditions on the formation of Salmonella persisters[J]. Chinese Journal of Bioprocess Engineering, 2023, 21(1): 91-97.
[18] 翁宗昱, 李紫晗, 孙琴, 等. 肉桂抑菌活性部位提取工艺优化及HPLC定量研究[J]. 亚太传统医药,2020,16(12):59−62. [WENG Z Y, LI Z H, SUN Q, et al. Optimization of extraction process and HPLC quantitative study on the antibacterial active part of Cinnamomi cortex[J]. Asia-Pacific Traditional Medicine,2020,16(12):59−62. [19] 陈悦, 胡璇, 于福来, 等. 18种芳香植物精油抑菌活性的比较研究[J]. 中国调味品,2020,16(12):59−62. [CHEN Y, HU X, YU F L, et al. Comparative study on the antibacterial activity of 18 kinds of aromatic plant essential oils[J]. China Condiment,2020,16(12):59−62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2020.12.013 [20] 董路路, 任春涛, 张新华, 等. 6种植物精油对果蔬灰霉菌和青霉菌的抑菌效果[J]. 食品科技,2019,44(8):211−216. [DONG L L, REN C T, ZHANG X H, et al. Antibacterial effect of six plant essential oil on Botrytis cinerea and Penicillium of fruits and vegetables[J]. Food Science and Technology,2019,44(8):211−216. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2019.08.038 [21] 王昭人, 韩露露, 牛月月, 等. 水包油型茶树油纳米乳的制备及其体外抑菌活性研究(英文)[J]. 河南大学学报(医学版),2022,41(1):22−28. [WANG Z R, HAN L L, NIU Y Y, et al. Studies on O/W tea tree oil nano-emulsions preparation and its bacteriostatic activity in vitro[J]. Journal of Henan University Medical Science,2022,41(1):22−28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7606.2022.1.hndxxb-yxkxb202201004 [22] 柴向华, 董艳, 吴克刚, 等. 植物精油对食品中常见有害微生物的抑菌活性研究[J]. 现代食品科技,2016,32(8):123−127, 114. [CHAI X H, DONG Y, WU K G, et al. Antibacterial activity of plant essential oils against common harmful microorganisms in foods[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2016,32(8):123−127, 114. doi: 10.13982/j.mfst.1673-9078.2016.8.019 [23] LOPEZ P, SANCHEZ C, BATTLE R, et al. Vapor-phase activities of cinnamon, thyme, and oregano essential oils and key constituents against foodborne microorganisms[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2007,55(11):4348−4356. doi: 10.1021/jf063295u
[24] 刘欢, 赵巨堂, 何力, 等. 金盏花精油的微波辅助提取及其成分与抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(10):180−188. [LIU H, ZHAO J T, HE L, et al. Microwave-assisted extraction of essential oil from Calendula officinalis L. and its components and antioxidant activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(10):180−188. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021060062 [25] 石小翠, 曹冬花, 李佳, 等. 三种香茅精油的化学成分及体外抗氧化和抗炎活性评价[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(21):83−90. [SHI X C, CAO D H, LI J, et al. Chemical composition, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of essential oils of three cymbopogon plants[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(21):83−90. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021030051 [26] 段雪娟, 吴克刚, 柴向华. 香辛料精油成分对生鲜食品中有害菌杀灭活性研究[J]. 林产化学与工业,2022,32(3):87−91. [DUAN X J, WU K G, CHAI X H. Bactericidal activities of spicy essential oils on microorganisms in crude foods[J]. Chemistry and Industry of Forest Products,2022,32(3):87−91. [27] LEE S, KIM H, BEUCHAT L R, et al. Synergistic antimicrobial activity of oregano and thyme thymol essential oils against Leuconostoc citreum in a laboratory medium and tomato juice[J]. Food Microbiology,2020,90:103489. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2020.103489
[28] 李南薇, 刘佳, 刘锐, 等. 32种食品添加剂对蜡样芽孢杆菌的协同抑菌作用[J]. 中国食品学报,2015,15(2):138−142. [LI N W, LIU J, LIU R, et al. Synergistic inhibitory effect of food additives against Bacillus cereus[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2015,15(2):138−142. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2015.02.021 [29] 段雪娟, 韩雅莉, 刘泽璇, 等. 肉桂精油气相熏蒸金黄色葡萄球菌的抗菌机理[J]. 现代食品科技,2021,37(9):50−58. [DUAN X J, HAN Y L, LIU Z X, et al. Antibacterial mechanism of cinnamon essential oil vapor fumigation against Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2021,37(9):50−58. doi: 10.13982/j.mfst.1673-9078.2021.9.1210 [30] 吴克刚, 赵欣欣, 段雪娟, 等. 芳樟醇气相抗菌活性与作用机制[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(1):61−67. [WU K G, ZHAO X X, DUAN X J, et al. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of vapor-phase linalool[J]. Food Science,2020,41(1):61−67. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181130-365 [31] 马培培, 苏梦茹, 李鑫鑫, 等. 大肠埃希菌细菌计数分光光度计法的建立及应用[J]. 动物医学进展,2020,41(5):29−33. [MA P P, SU M R, LI X X, et al. Establishment and application of Escherichia coli counting method based on spectrophotometer[J]. Progress in Veterinary Medicine,2020,41(5):29−33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5038.2020.05.006 [32] ZHANG Z, HUBER D, QU H, et al. Enzymatic browning and antioxidant activities in harvested litchi fruit as influenced by apple polyphenols[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,171:191−199. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.09.001
[33] 潘莹, 齐军航, 谭联, 等. 暴马丁香花提取物对辣椒贮藏期间理化指标的影响[J/OL]. 吉林农业大学学报: 1−4 [2023-02-06]. https://doi.org/10.13327/j.jjlau.2020.5544. PAN Y, QI J H, TAN L, et al. Effect of extract from the flowers of Syringa reticulata (Blume) hara var. on physicochemical indexes of hot pepper during storage[J/OL]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University: 1−4 [2023-02-06]. https://doi.org/10.13327/j.jjlau.2020.5544.
[34] KALLEL I, HADRICH B, GARGOURI B, et al. Optimization of cinnamon (Cinnamomum zeylanicum blume) essential oil extraction: Evaluation of antioxidant and antiproliferative effects[J]. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine,2019,2019:6498347.
[35] VASCONCELOS N G, CRODA J, SIMIONATTO S. Antibacterial mechanisms of cinnamon and its constituents: A review[J]. Microbial Pathogenesis,2018,120:198−203. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.04.036
[36] FRAŇKOVÁ A, MAROUNEK M, MOZROVÁ V, et al. Antibacterial activities of plant-derived compounds and essential oils toward Cronobacter sakazakii and Cronobacter malonaticus[J]. Foodborne Pathogens and Disease,2014,11(10):795−797. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2014.1737
[37] 蒋小龙, 寸东义, 杨晶焰. 香茅精油、香茅醛、香茅醇对储粮霉菌和害虫抑制与熏杀效果的试验研究[J]. 郑州粮食学院学报,1994(1):39−47. [JIANG X L, CUN D Y, YANG J Y. Study on the inhibition and fumigation effects of citronella, citronellal and citronellol on stored grain mold and pests[J]. Journal of Henan University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),1994(1):39−47. [38] 陈晓晶. 香茅精油对番木瓜果实采后保鲜及作用机制研究[D]. 海口: 海南大学, 2021. CHEN X J. Study on fresh-keeping and mechanism of citronella essential oil on papaya fruit[D]. Haikou: Hainan University, 2021.
[39] KOBA K, POUTOULI P W, RAYNAUD C, et al. Chemical composition and antimicrobial properties of different basil essential oils chemotypes from Togo[J]. Bangladesh Journal of Pharmacology,2009,4(1):1−8.
[40] HUSSAIN A I, ANWAR F, HUSSAIN SHERAZI S T, et al. Chemical composition, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of basil (Ocimum basilicum) essential oils depends on seasonal variations[J]. Food Chemistry,2008,108(3):986−995. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.12.010
[41] 鞠健. 丁香酚和柠檬醛对娄地青霉和黑曲霉的协同抑菌机理探究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2021. JU J. Study on the synergistic inhibitory mechanism of eugenol and citral against Penicillium roqueforti[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2021.
[42] 郝文凤, 田玉红, 董菲, 等. 植物精油协同抑菌的研究进展[J]. 中国调味品,2020,45(3):172−175. [HAO W F, TIAN Y H, DONG F, et al. Research progress on synergistic bacteriostasis of plant essential oil[J]. China Condiment,2020,45(3):172−175. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2020.03.035 [43] SHEN S, ZHANG T, YUAN Y, et al. Effects of cinnamaldehyde on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus membrane[J]. Food Control,2015,47:196−202. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2014.07.003
[44] 魏彤竹. 三种植物精油对六种食源性致病菌的抑菌活性研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2019. WEI T Z. Study on the antibacterial activities of three plant essential oils against six foodborne pathogens[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2019.
[45] 王媛. 猕猴桃展青霉素产生菌的识别分析及控制机制研究[D]. 西安: 西北农林科技大学, 2017. WANG Y. Identification and analysis of patulin-producing fungi from kiwifruit and the study of their control mechanism[D]. Xi’an: Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University, 2017.
[46] 萨仁高娃, 胡文忠, 冯可, 等. 植物精油及其成分对病原微生物抗菌机理的研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(11):285−294. [SARENGAOWA, HU W Z, FENG K, et al. Antimicrobial mechanisms of essential oils and their components on pathogenic bacteria: A review[J]. Food Science,2020,41(11):285−294. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190603-018 [47] KANG J M, JIN W Y, WANG J F, et al. Antibacterial and anti-biofilm activities of peppermint essential oil against Staphylococcus aureus[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2019,101:639−645. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2018.11.093
[48] 孔繁渊, 段杨峰, 吴新, 等. 草莓果实热空气和茉莉酸甲酯复合处理保鲜条件优化[J]. 食品科学,2011,32(18):323−328. [KONG F Y, DUAN Y F, WU X, et al. Conditions optimization of preservation of strawberry fruits by combinatorial treatment of hot air and methyl jasmonate[J]. Food Science,2011,32(18):323−328.





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:



