Effects of Temperature and Time of Waterless Transportation on Muscle Quality and Physiological Stress of Litopenaeus vannamei
-
摘要: 为探讨南美白对虾无水保活运输的适宜温度和时间,本文研究了对虾低温休眠温度,测定了4、10 ℃条件下模拟运输不同时间段的存活率,分析了对照组、休眠组、运输组和运输后复水唤醒30 min ,4种状态下对虾肌肉品质以及生理应激指标。结果表明,南美白对虾的休眠温度为(10.0±0.2)℃;模拟运输12 h内,两温度组存活率均为100%,36 h后两组存活率均低于30%。不同运输温度对肉质指标影响不显著(P>0.05);除蒸煮损失率,相同温度下运输应激对水分、粗蛋白、粗脂肪含量影响均不显著(P>0.05)。生理应激指标中,两种温度下模拟运输24 h后,肌糖原、琥珀酸脱氢酶(succinate dehydrogenase,SDH)、乳酸脱氢酶(lactate dehydrogenase,LDH)和丙二醛(malondialdehyde,MDA)含量与对照组相比均发生显著变化(P<0.05),且复水后也均不能恢复到对照组水平。南美白对虾可以通过低温诱导休眠的方式进行无水保活运输,10 ℃适于18 h内短途运输,长途运输则可选用4 ℃。Abstract: In order to explore the suitable temperature and time for waterless live transportation of Litopenaeus vannamei, this paper investigated the low dormancy temperature and determined the survival rate at different time periods of simulated transportation under 4 and 10 ℃. The muscle quality and physiological stress indexes were analyzed in four states: Control group, dormant group, transport group and recovered for 30 min group. The results indicated that the dormancy temperature of Litopenaeus vannamei was (10.0±0.2) ℃. The survival rates of two temperature groups were both 100% within 12 h of simulated transportation and lower than 30% after 36 h. The effects of different transport temperatures on muscle quality indexes were not significant (P>0.05). Except for the cooking loss rate, the effects of transport stress on moisture, crude protein and crude fat content at the same temperature were not significant (P>0.05). Compared with the control, the contents of muscle glycogen, succinate dehydrogenase (SDH), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and malondialdehyde (MDA) were significantly (P<0.05) changed after 24 h of simulated transportation at both temperature groups, and none of them could be restored to the control level after recovery. Litopenaeus vannamei can be transported without water by means of low temperature-induced dormancy, and 10 ℃ is suitable for short-distance transportation within 18 h, while 4 ℃ can be selected for long-distance transportation.
-
南美白对虾(Litopenaeus vannamei)属对虾科、滨对虾属,是我国主要水产养殖品种,2019年产量达到181万吨[1]。对虾体内酶活强,死亡后易变质;且受我国饮食观念影响,即便活虾价格高于冷冻虾两倍,消费者仍更青睐鲜活产品[2],因此针对南美白对虾的保活运输研究具有重要意义。
水产品活体运输方法主要有带水和无水两种形式[3],与带水运输相比,无水运输操作简便、运载量大、成本低、物理损伤小、废水污染少,有利于远距离运输[4-6]。无水运输前需借助低温或麻醉剂使其进入休眠状态以减少运输应激,而实际流通中麻醉剂存在过量使用等安全问题[7],与之相较,低温法则具有更广泛的应用价值。低温无水运输可以减缓呼吸频率、降低新陈代谢,减少应激反应引起的物理损伤,同时增加了呈鲜味物质的含量、提高鱼肉风味[5, 8-9]。此外,低温可以减弱血液中氧化反应[10],也可抑制有害微生物生长及酶的活性,4 ℃条件下活运牡蛎,6 d后菌落总数仍符合微生物限量标准[11]。可见,低温无水运输是一种较为安全的活运方法,并且对水产动物的存活率、肌肉品质及生理活性都具有较好的保持作用。
目前对甲壳类保活运输的研究主要集中在不同降温速度或麻醉剂对其影响上,不同运输温度下指标变化、运输不同时间后立刻复水能否恢复则鲜见报道,本文探究了南美白对虾在生态冰温10 ℃和冷藏运输车温度4 ℃下模拟运输不同时间、复水30 min后肌肉品质及生理应激指标的变化规律,为南美白对虾保活运输的实际应用提供理论参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
南美白对虾 购于山东省烟台市芳华园农贸市场,随机挑选有活力且个体规格相近的对虾,平均质量(23.81±1.78)g,体长(14.2±1.8)cm,于水箱中空气曝气暂养4 h,该环境平均水温(17.8±0.6)℃,盐度35‰,pH为8.1,溶氧含量6~7 mg/L;氧气 工业纯,烟台牟平区儒林气体有限公司;所用化学试剂均为分析纯 国药集团化学试剂有限公司;肌糖原、丙二醛、琥珀酸脱氢酶、乳酸脱氢酶试剂盒 南京建成生物工程研究所。
ACO-003型电磁式空气泵 广东日生集团有限公司;DHG-9070A型电热鼓风干燥箱和HWS-28型电热恒温水浴锅 上海一横科学仪器有限公司;K1100全自动凯氏定氮仪、SH420F石墨消解仪、SOX406脂肪测定仪 海能未来技术集团股份有限公司;TX-100高速冷冻离心机 赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司;Epoch全波长酶标仪 美国伯腾仪器有限公司;UV-2450紫外可见分光光度计 岛津公司;Q22型小型数控冰箱 深圳亚松科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 南美白对虾休眠温度的确定
将暂养4 h后的对虾放入盛有洁净海水(初始水温(17.8±0.6)℃,溶氧含量6~7 mg/L,盐度35‰,pH8.1)的透明塑料箱(40 cm×28 cm×23 cm)中,虾水比为10尾虾:4.5 L水,通过向水中加生物冰袋、以15 ℃/h的速率缓慢降温的方式诱导其休眠,观察到对虾侧翻无法自主立起且刺激后基本不动或行动非常迟缓、虾脚偶有轻微摆动等现象,即进入休眠状态[12]。
1.2.2 南美白对虾无水保活存活率的测定
将海绵于洁净海水中浸泡10 s,控水备用。待对虾进入休眠状态后,用海绵包裹虾体,放入塑料自封袋(14 cm×36 cm)中,冲入纯氧放置于冰箱内进行保活实验。以只做暂养处理且在有水条件下(水温(17.8±0.6)℃,溶氧含量6~7 mg/L,盐度35‰,pH8.1)养殖的南美白对虾作为对照,测定在4、10 ℃下保活12~36 h对虾的存活率,每组10尾虾,三组重复,该过程进行摇晃模拟运输颠簸。实验结束后,将各组对虾分别放入当季常温水(与有水对照组各项指标相同)中复水唤醒30 min,计算存活率。预实验发现在18 h时两组均出现死亡情况,为进一步确定每个温度下具体死亡时间,在12~18 h之间,以2 h为间隔,再次重复上述实验。
1.2.3 南美白对虾无水保活肌肉及应激指标的测定
运输前处理同1.2.2。以未做处理暂养4 h后的南美白对虾为对照组;仅诱导休眠而未进行保活运输的为休眠组;在4、10 ℃下以6 h为一间隔保活18~36 h,设定为运输组,每组10尾虾,三组重复,该过程进行摇晃模拟运输颠簸。模拟运输结束后,将各运输组对虾分别放入当季常温水(各项指标与暂养海水相同)中复水唤醒30 min,记为复水组。每组选取运输后、复水后各3只有生命迹象的虾取样并检测肌肉品质及生理应激指标。
1.2.4 取样方法
肌肉:去除非肌肉部分,用手术剪剪取部分组织块测量蒸煮损失率;剩余部分用绞肉机搅碎,用冷的生理盐水漂洗肌肉样本后,滤纸吸干表面水分,用于水分含量、粗蛋白、粗脂肪及肌糖原水平的测定。虾鳃:参考梁敏等[2]的方法,用吸水纸吸干体表水分,在冰盘上迅速解剖,取鳃,装入1.5 mL离心管中,迅速放入−80 ℃冰箱保存待测。拭干漂洗后的虾鳃组织块,取0.2~0.5 g组织,剪碎研磨,加入9倍的4 ℃生理盐水(0.86%),制成10%组织匀浆液,恒温4 ℃下,2000 r/min离心15 min,取上清液分装,用于测定琥珀酸脱氢酶(succinate dehydrogenase,SDH)和乳酸脱氢酶(lactate dehydrogenase,LDH)活力。肝胰腺:采用张玉晗等[13]的方法,将对虾置于冰盘上解剖出肝脏,置于密封袋中、存放于−80 ℃冰箱。取0.3~0.7 g对虾肝脏组织,制成10%组织匀浆液,恒温4 ℃下,2000 r/min离心15 min,取上清液测定丙二醛(malondialdehyde,MDA)含量。
1.2.5 指标测定
1.2.5.1 存活率的测定
存活率(%)=当季水温下恢复30min后存活数每组总只数×100 1.2.5.2 肌肉品质的测定
蒸煮损失率:精确称量1~2 g样品置于离心管中,放入沸水中蒸煮10 min后取出,室温冷却后吸干表面水分,称重,计算公式如下;肌肉水分含量参照 GB/T 5009.3-2016[14]的直接干燥法进行测定;粗蛋白参照 GB/T 5009.5-2016[15]的凯氏定氮法进行测定;粗脂肪参照 GB/T 5009.6-2016[16]中的索氏抽提法进行测定。
蒸煮损失率(%)=W1−W2W1×100 式中:W1为蒸煮前样品质量(g),W2为蒸煮后质量(g)。
1.2.5.3 生理应激指标的测定
肌糖原含量、呼吸代谢指标(SDH采用比色法、LDH 采用微板法)、肝胰腺中MDA含量测定均依据南京建成生物工程研究所检测试剂盒说明书进行操作。
1.3 数据处理
每组对应各指标均做三次平行实验。分别使用Microsoft Excel 2019和SPSS 26.0软件绘制相关图表、对实验结果进行统计分析。显著性分析采用 Duncan 多重比较法,结果用平均值±标准差(SD)表示,P<0.05表示显著性差异。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 南美白对虾低温休眠温度的确定
水生生物在低温和空气暴露条件下容易发生急性应激反应[17]。而在低温无水活运中,水产品一直处于暴露空气和低温状态,容易导致持续的生理应激反应和严重的质量损失,甚至死亡[18-19],运输前休眠是减少装载和运输应激的关键。本实验确定了南美白对虾适宜休眠温度为(10.0±0.2)℃。表1为从暂养水温降到休眠水温过程中南美白对虾的行为变化。排除特殊个体,可认为水温在(10.0±0.2)℃时,南美白对虾即进入休眠状态(图1)。徐德峰等[20]发现,5~10 ℃是南美白对虾的生态冰温;将中国对虾放入8 ℃的水中,虾的游动速度减慢,逐渐进入休眠状态且应激反应不强烈[12];齐静涛[21]建议,在运输包装前2 h将水温降至12 ℃有助于提高日本对虾存活率,都与本实验发现的温度区间一致。
表 1 暂养水温降至休眠水温过程中南美白对虾行为变化Table 1. Behavioral changes of Litopenaeus vannamei from active state to dormancy state during water temperature drop温度区间 14~18 ℃ 10~14 ℃ 10 ℃以下 南美白对虾
行为变化对虾在中下层水体正常游动,
对刺激反应明显,未进入休眠
状态;因冷刺激个别跃出
水面大部分对虾游动缓慢,静卧水底,甚至失去平衡侧翻,对刺激无明显反应,开始进入休眠状态 个别活力较强对虾仍可直立,但无明显活动;大部分个体在水底侧翻,受刺激后不动或只有虾脚轻微摆动,完全进入休眠状态 2.2 运输温度对南美白对虾存活率的影响
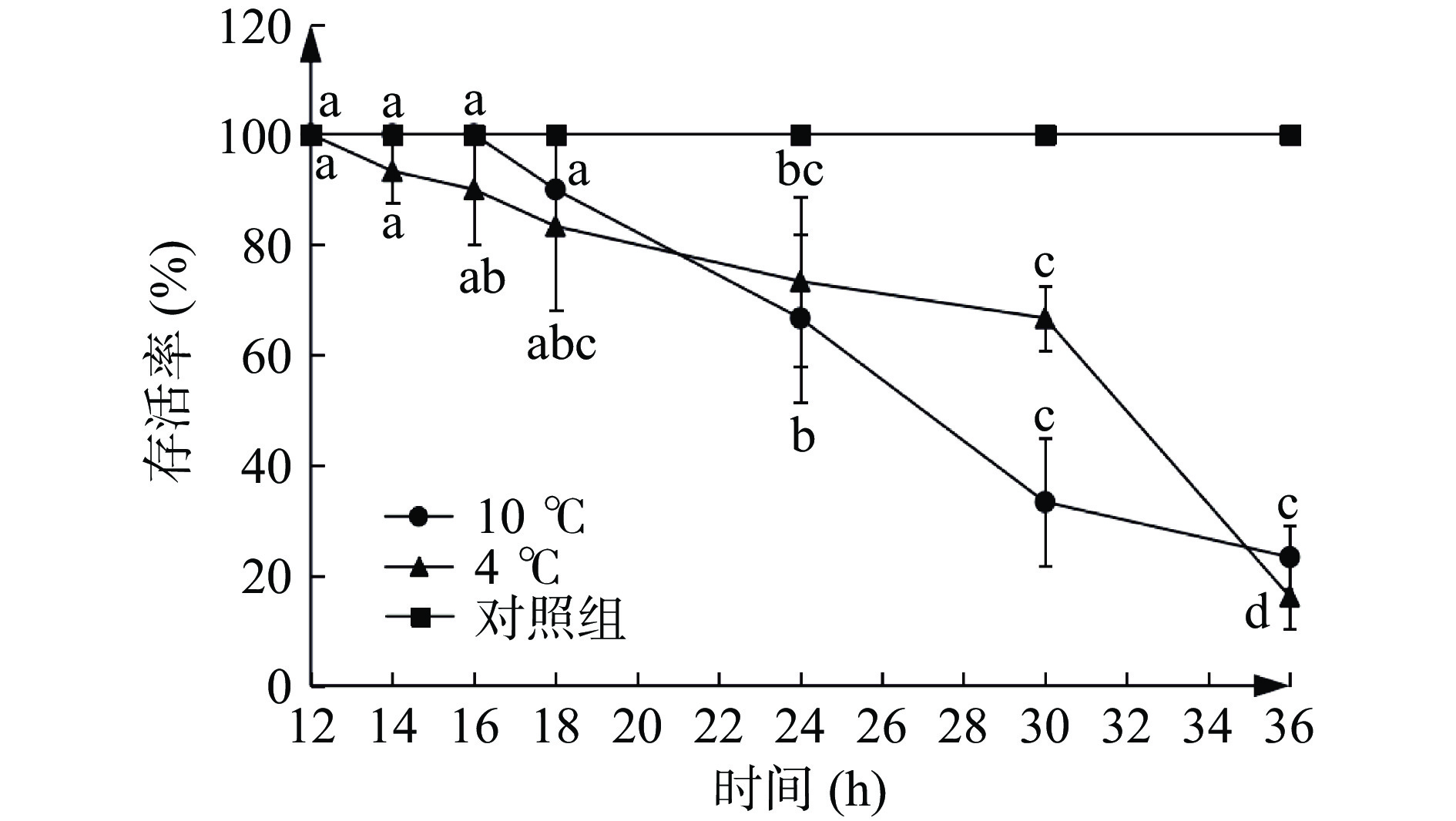
高死亡率是虾类在保活运输过程中经常发生的现象[22]。存活率是表明保活运输效果的关键指标,其高低直接说明方法是否可行[23]。由图2可知,4 ℃组和10 ℃组分别在运输14 h和18 h后首次出现对虾死亡现象。18 h内,4 ℃组存活率下降较快,推测4 ℃与当季水温((17.8±0.6)℃)温差更大,应激反应更强烈导致死亡率增大;随着保活时间的延长,10 ℃组比4 ℃组下降更快,因为适应低温后4 ℃下对虾处于更深休眠状态,代谢活动微弱,可以较长时间保持生命活力;运输36 h后存活均不到30%。结合实际考虑,10 ℃的生态冰温运输条件可以满足18 h内的省内、邻省运输,且节约制冷所需成本;若距离较长则4 ℃冷藏车温度运输存活率更高,但不宜超过30 h。
2.3 运输温度和时间对南美白对虾肌肉品质的影响
肌肉品质是反映无水运输技术能否应用于实践的决定性指标之一。蒸煮损失率是指肌肉在蒸煮过程中水分和可溶性物质的流失率,该数值越高表示营养物质流失越严重、肌肉品质越差。如表2,与其他肉质品质指标相比,低温运输对南美白对虾肌肉蒸煮损失率影响较大;同时与对照组相比,在4 ℃条件下运输36 h后蒸煮损失率升高了152%,而10 ℃升高了176%,即使复水30 min后仍极显著高于对照组(P<0.05)。这是因为肉中肌原纤维蛋白通过毛细作用保持水分,环境应激改变其网络结构和变性降解程度,运输时间越久蛋白锁水能力越弱,加热变性时汁液损失增多、口感也会相应变差。总体来看,4 ℃组可溶性物质流失比10 ℃组更严重,这可能是由于温度越低蛋白结构降解越严重。
表 2 10 ℃和4 ℃下保活时间对南美白对虾肌肉品质的影响(%)Table 2. Effect of transportation time on muscle quality of Litopenaeus vannamei at 10 ℃ and 4 ℃ (%)10 ℃下 对照组 休眠组 18 h 24 h 30 h 36 h 运输后 复水后 运输后 复水后 运输后 复水后 运输后 复水后 蒸煮损失率 13.39±4.01c 13.88±5.17c 19.36±2.68c 17.80±1.58c 20.40±8.88c 20.15±4.29c 25.33±2.81a 23.03±1.41b 36.91±5.33a 34.50±1.22a 水分含量 71.77±0.31b 68.10±0.49c 71.51±0.91b 72.20±0.16b 71.59±0.58b 74.64±0.22a 72.27±0.61b 75.55±0.31a 72.40±0.31b 72.67±1.62b 粗蛋白(干基) 90.95±0.02a 84.37±0.01ab 85.49±0.02ab 85.69±0.03ab 89.64±0.01ab 82.45±0.04b 84.42±0.04ab 84.85±0.10ab 84.68±0.04ab 83.11±0.03ab 粗脂肪(干基) 1.25±0.18 1.23±0.24 1.20±0.55 1.18±0.43 1.16±0.14 0.99±0.49 1.10±0.39 1.06±0.16 0.68±0.29 0.65±0.39 4 ℃下 对照组 休眠组 18 h 24 h 30 h 36 h 运输后 复水后 运输后 复水后 运输后 复水后 运输后 复水后 蒸煮损失率 13.39±4.01c 13.88±5.17c 24.20±2.38a 19.14±1.94c 24.03±2.73a 21.98±3.12b 27.09±4.81a 22.28±3.54b 33.79±7.77a 28.66±3.34a 水分含量 71.77±0.31b 68.10±0.49c 71.36±0.13b 71.20±0.74b 71.99±1.02b 70.44±1.45b 74.81±0.52ab 75.24±0.01a 71.59±1.02b 72.81±1.35b 粗蛋白(干基) 90.95±0.02a 84.37±0.01ab 86.09±0.01ab 85.70±0.02ab 84.38±0.06ab 76.28±0.01c 89.32±0.03a 88.39±0.03a 84.74±0.02ab 82.85±0.02b 粗脂肪(干基) 1.25±0.16 1.23±0.24 1.20±0.46 1.27±0.32 0.84±0.17 0.88±0.29 0.80±0.17 0.66±0.06 0.68±0.39 0.59±0.24 注:表格中同行肩标相同小写字母或无字母表示差异不显著(P>0.05),不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),n=3。 将休眠操作后的各项指标与对照组相比,虾体水分含量显著降低(P<0.05),下降了3.67%,其余肉质指标均变化不显著(P>0.05)。根据何菊登等[24]对鲟鱼的研究发现,受冷应激的个体肌肉的含水量显著降低,这也是本实验休眠过程中虾体肌肉水分下降的原因。但休眠后的虾体内水分可维持相对稳定,两种温度下36 h后肌肉水分含量仍高于71%,这可能是因为虾的甲壳可保持水分,减少蒸发;也可能是因为加盖湿润海绵保持了相对恒定的湿度、温度,使其代谢稳定且维持在较低水平,降低自身代谢对水分的消耗。
在两温度下所有运输组中,南美白对虾肌肉中粗蛋白、粗脂肪含量均无显著性变化(P>0.05)。这是因为运输时间不长且低温导致基础代谢减缓,使其对高分子储能物质利用率不高。各复水组与其运输组相比,除4 ℃下运输24 h后显著下降(P<0.05),其他组的含量下降均不显著。复水后粗蛋白含量下降可能是因为进入常温环境后代谢逐渐恢复,使得大分子物质分解为小分子物质供能而减少。模拟运输36 h后,肌肉中脂肪下降含量约占其原有含量的46%,而蛋白质下降含量约占原有含量的7%,所以脂肪下降比例远高于蛋白质的消耗。这是因为不同物种对贮存能量物质的利用情况也不同,除少数种类消耗蛋白质外[25],大部分水产品消耗脂肪[26-27]。由此推测,对于南美白对虾,脂肪为其首要供能物质。南美白对虾饥饿试验也证实了该结论[28]。
2.4 运输温度和时间对南美白对虾生理应激的影响
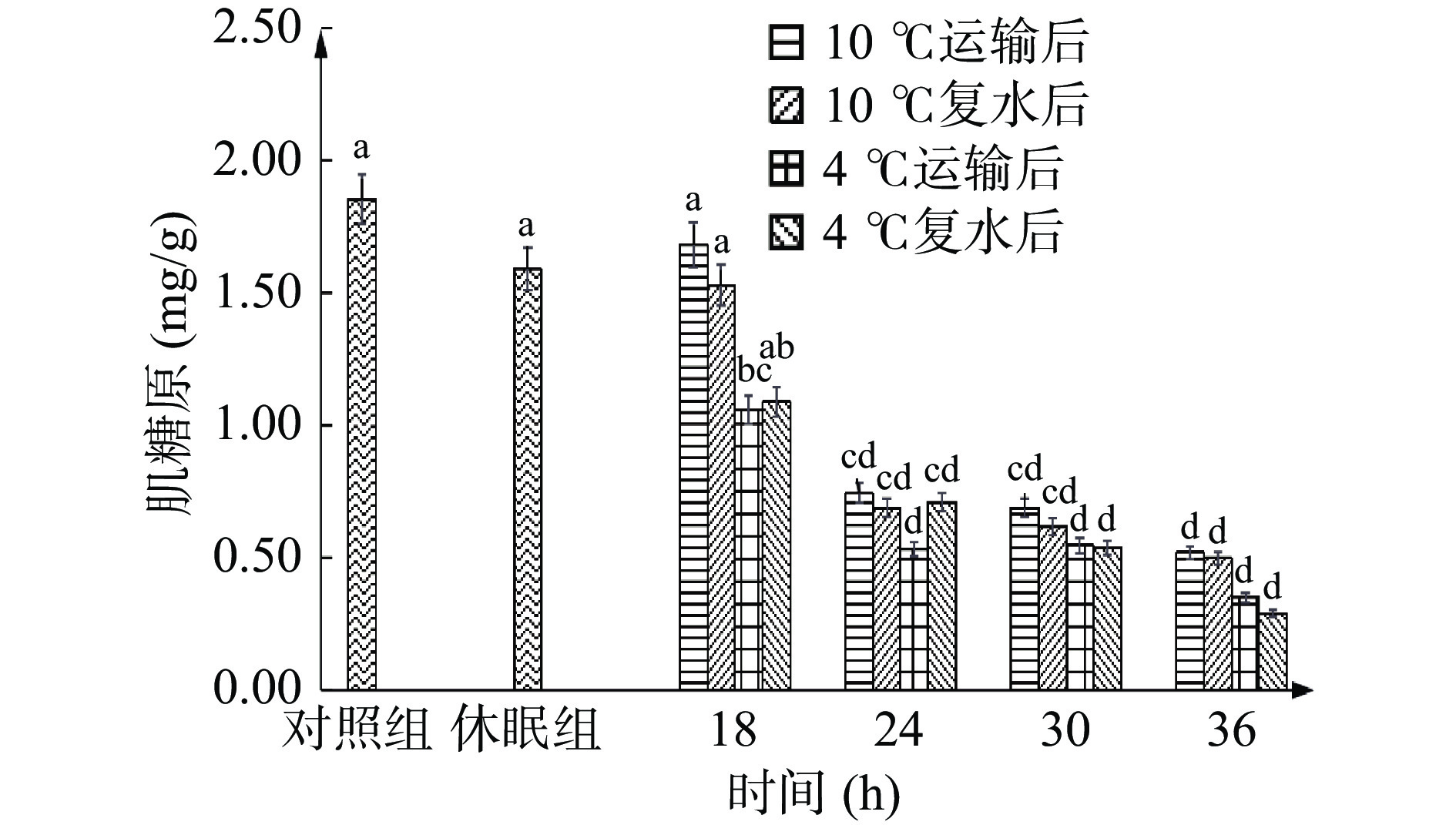
肌糖原的变化能够清晰地反映机体对环境的适应情况[29],是机体应激反应的重要指标之一。由图3可见,休眠处理未使肌糖原含量发生显著变化(P>0.05)。随着保活时间的延长,糖原含量呈下降趋势。这是因为运输过程中,生物体将肌糖原分解为葡萄糖来供能,使肌糖原含量下降,并且因为氧气不足,有氧呼吸转变为无氧,导致肌糖原大量转化为乳酸而减少。当糖原含量的消耗超过耐受程度时就会出现大量死亡,这一实验结果也与前文24 h后死亡率增大的实验现象相印证。其中:10 ℃条件下,保活18~24 h时肌糖原含量从1.68 mg/g骤降至0.74 mg/g,后又趋于平缓;4 ℃条件下18 h肌糖原即显著(P<0.05)下降至1.06 mg/g,但18 h后下降速率明显慢于10 ℃。因为18 h内4 ℃下应激反应更强烈,更强的运输压力导致新陈代谢加快,因此肌糖原耗损更多,但运输后期因低温抑制了代谢活力,其下降速率明显减缓。复水后数值与运输组相比不显著(P>0.05),只是略有下降,推测因进入有水、相较高氧环境,刺激代谢恢复而导致肌糖原的进一步利用。
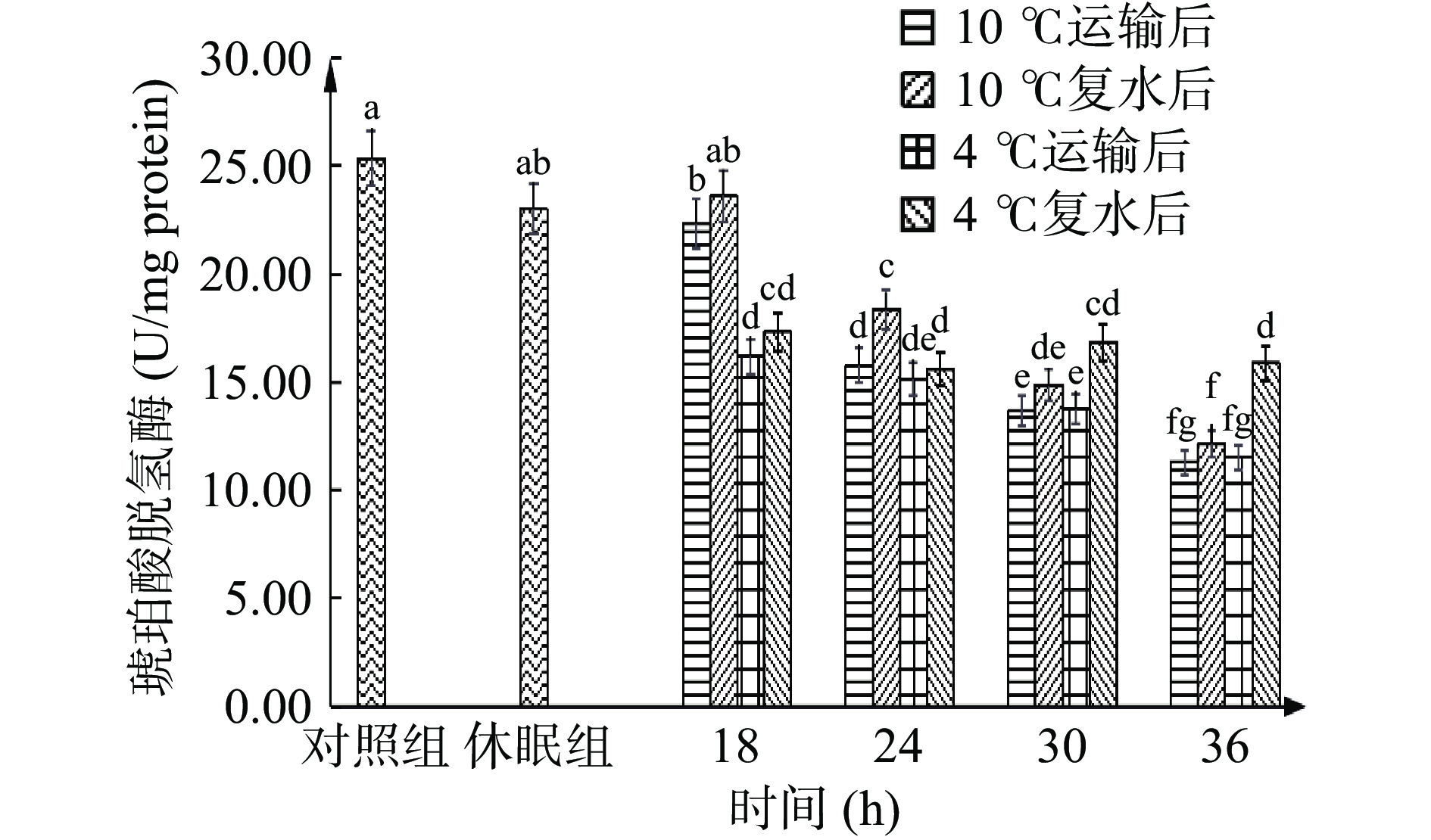
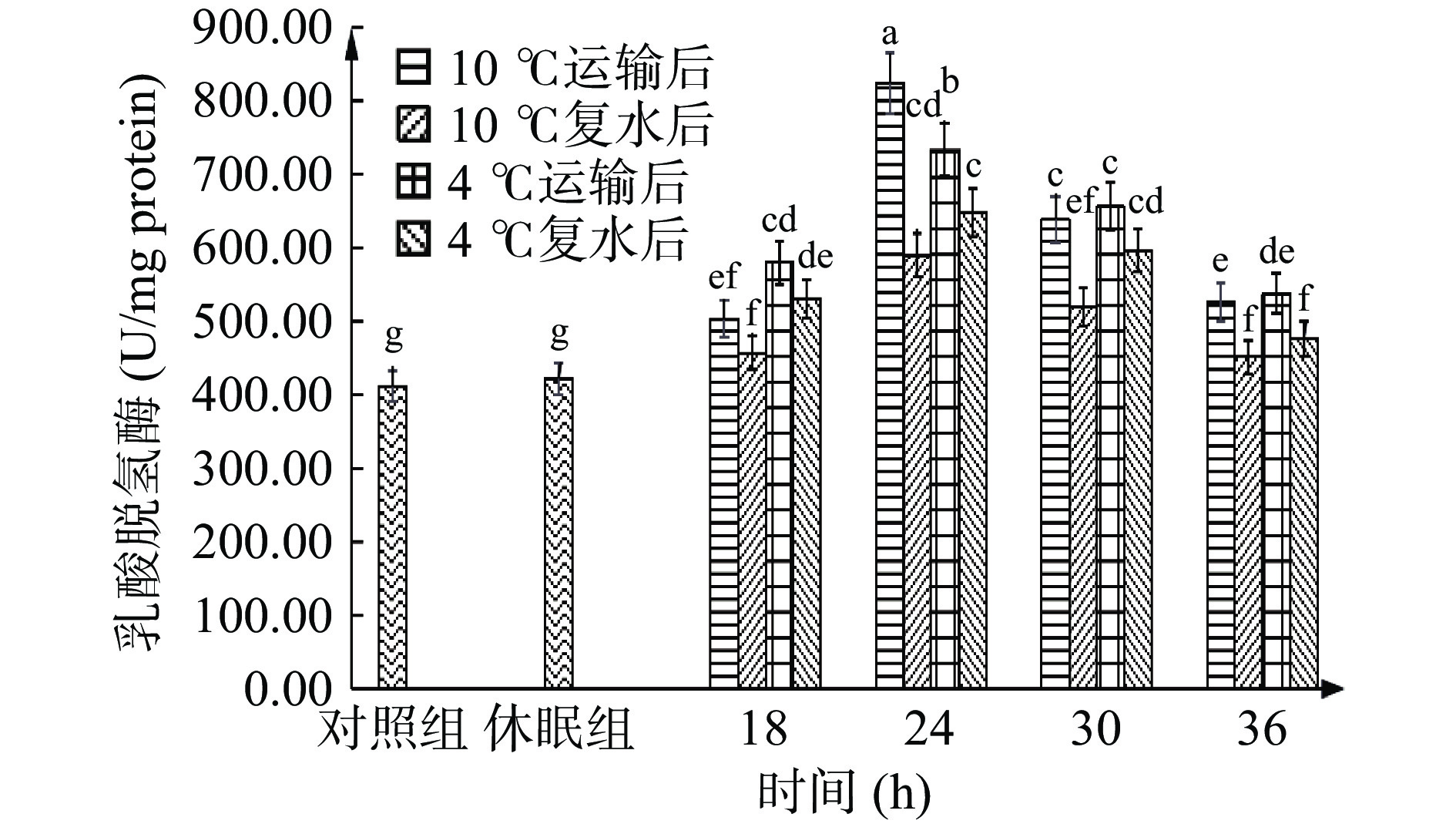
SDH和LDH酶活变化可以反应南美白对虾对包装袋中氧气的利用情况。SDH活性可反映对虾有氧代谢的水平,外源性应激例如氧气不足等不良因素,都会导致SDH 活力的下降[30]。图4显示,SDH酶活在休眠后未发生显著变化(P>0.05),但在运输过程中酶活显著降低(P<0.05),10 ℃组18~24 h下降最快,减少了29.38%,4 ℃运输18 h后酶活急速下降了33.56%,后趋于平缓。运输前期由于有湿润海绵包裹,对虾仍可借助鳃部及虾血中贮藏的氧气维持一定程度的有氧呼吸,18~24 h后氧气急速耗尽,导致SDH活力大幅下降。在运输18~36 h过程中,对虾在4 ℃条件下有氧呼吸酶的酶活较相同运输时间下10 ℃下降更缓慢。这是由于低温对代谢的抑制作用,使得相同运输时间下对虾在4 ℃条件下氧气利用率更稳定。与此相对,LDH酶活可反应对虾的无氧代谢水平。如图5示,LDH酶活在休眠后也未发生显著变化(P>0.05),但运输中的LDH酶活在18 h后显著上升(P<0.05),24 h达到最高水平824.41 U/mg protein(10 ℃)、733.34 U/mg protein(4 ℃),后开始下降,24~36 h内下降最剧烈,分别减少了36.36%和26.72%。这是由于虾体受到低氧应激时,LDH 同工酶转录上调[31],且长期的无水低温胁迫影响虾的代谢系统,从而导致LDH活性在后期有所减弱。
复水后,有水环境大大提高了氧气利用效率,SDH酶活呈现升高趋势而LDH酶活下降,但除10 ℃ 18 h组SDH酶活复水后可恢复至对照水平,其他实验组均无法恢复,且在10 ℃ 24 h和4 ℃ 30、36 h复水后SDH酶活虽比其运输组酶活显著增加(P<0.05),尤其是4 ℃ 36 h增加至15.87 U/mg protein,却仍和对照组呈现显著差异(P<0.05);LDH酶活无法恢复至对照组水平,这可能与恢复时间较短或两种酶的调控机制有关,说明长时间缺氧会导致呼吸代谢紊乱,甚至对呼吸系统造成不可逆的损伤。
因低温运输导致生物体发生氧化应激反应,过量的氧自由基引起脂质过氧化,产生MDA等破坏生物体细胞结构和功能,MDA水平的升高通常被认为是一种脂类过氧化的指标[32]。有研究表明[13],肝胰腺作为虾体抗氧化反应的主要器官,其组织内MDA含量与肝实质细胞凋亡数量有显著的正相关关系,以此间接测定肝脏系统受损程度。如图6示,低温休眠处理后对虾体内MDA含量增加不显著(P>0.05);不同运输温度均会导致活运过程中对虾肝组织产生脂质过氧化,呈现先升后降的总趋势。对照组MDA含量为122.15 nmol/mg protein,4 ℃、10 ℃模拟运输24 h和30 h后分别达到峰值,为未处理组的254.06%和273.69%。运输18~30 h MDA含量成倍增加导致肝脏系统受损,这可能是南美白对虾无法长时间活运的原因之一。当机体发生氧化应激反应时,体内抗氧化防御系统被激活以保护细胞免受氧化应激侵害,但是因抗氧化物的产生及作用过程具有滞后性[7, 22],使其清除氧自由基的作用在运输后期才显现,从而导致MDA含量呈现先升后降的趋势。运输30~36 h后,4 ℃组MDA含量均显著低于10 ℃组(P<0.05),下降趋势也更剧烈,说明运输前期(24 h前)4 ℃氧化应激反应较10 ℃更强烈,体内产生更多抗氧化物质,后期下降也就更为迅速。曾鹏等[33]发现鲫鱼脑丙二醛水平在低温诱导休眠后受储藏温度影响显著(P<0.05),与0 ℃、4 ℃相比,8 ℃储藏条件下MDA含量较高,且呈先升后降趋势,与本实验结果一致。各运输组复水后均无法恢复至对照组水平,且除了10 ℃ 30 h组MDA含量与其运输组相比发生显著下降,其他处理均无显著性变化(P<0.05)。复水操作导致的MDA含量变化与对虾从低温进入常温后的二次应激对肝胰腺的损伤作用以及进入常温后部分恢复的代谢水平等因素密切相关。
3. 结论
本文研究了4 ℃、10 ℃两个温度下南美白对虾无水保活运输过程中存活率、肉质指标与生理应激的变化。结果表明,南美白对虾较佳休眠水温为10.0 ℃,运输18 h后存活率显著下降(P<0.05),且运输温度越高总体下降速度越快。低温休眠处理不会对肌肉品质与生理生化代谢造成显著影响(P>0.05)。随着运输时间延长,除蒸煮损失率大幅增加,肌肉指标变化均不显著(P>0.05),且运输温度差异对肉质指标影响不大;但不管什么运输条件,都会对水产品造成严重生理应激,且几乎无法在复水30 min内恢复。建议南美白对虾无水活运温度为10 ℃,当运输时间超过18 h,采用4 ℃运输;为提高存活率,休眠降温以及复水升温应缓慢进行,尽量减少升降温过程对南美白对虾的应激损伤。本文可为南美白对虾无水活体运输的应用实践提供参考。
-
表 1 暂养水温降至休眠水温过程中南美白对虾行为变化
Table 1 Behavioral changes of Litopenaeus vannamei from active state to dormancy state during water temperature drop
温度区间 14~18 ℃ 10~14 ℃ 10 ℃以下 南美白对虾
行为变化对虾在中下层水体正常游动,
对刺激反应明显,未进入休眠
状态;因冷刺激个别跃出
水面大部分对虾游动缓慢,静卧水底,甚至失去平衡侧翻,对刺激无明显反应,开始进入休眠状态 个别活力较强对虾仍可直立,但无明显活动;大部分个体在水底侧翻,受刺激后不动或只有虾脚轻微摆动,完全进入休眠状态 表 2 10 ℃和4 ℃下保活时间对南美白对虾肌肉品质的影响(%)
Table 2 Effect of transportation time on muscle quality of Litopenaeus vannamei at 10 ℃ and 4 ℃ (%)
10 ℃下 对照组 休眠组 18 h 24 h 30 h 36 h 运输后 复水后 运输后 复水后 运输后 复水后 运输后 复水后 蒸煮损失率 13.39±4.01c 13.88±5.17c 19.36±2.68c 17.80±1.58c 20.40±8.88c 20.15±4.29c 25.33±2.81a 23.03±1.41b 36.91±5.33a 34.50±1.22a 水分含量 71.77±0.31b 68.10±0.49c 71.51±0.91b 72.20±0.16b 71.59±0.58b 74.64±0.22a 72.27±0.61b 75.55±0.31a 72.40±0.31b 72.67±1.62b 粗蛋白(干基) 90.95±0.02a 84.37±0.01ab 85.49±0.02ab 85.69±0.03ab 89.64±0.01ab 82.45±0.04b 84.42±0.04ab 84.85±0.10ab 84.68±0.04ab 83.11±0.03ab 粗脂肪(干基) 1.25±0.18 1.23±0.24 1.20±0.55 1.18±0.43 1.16±0.14 0.99±0.49 1.10±0.39 1.06±0.16 0.68±0.29 0.65±0.39 4 ℃下 对照组 休眠组 18 h 24 h 30 h 36 h 运输后 复水后 运输后 复水后 运输后 复水后 运输后 复水后 蒸煮损失率 13.39±4.01c 13.88±5.17c 24.20±2.38a 19.14±1.94c 24.03±2.73a 21.98±3.12b 27.09±4.81a 22.28±3.54b 33.79±7.77a 28.66±3.34a 水分含量 71.77±0.31b 68.10±0.49c 71.36±0.13b 71.20±0.74b 71.99±1.02b 70.44±1.45b 74.81±0.52ab 75.24±0.01a 71.59±1.02b 72.81±1.35b 粗蛋白(干基) 90.95±0.02a 84.37±0.01ab 86.09±0.01ab 85.70±0.02ab 84.38±0.06ab 76.28±0.01c 89.32±0.03a 88.39±0.03a 84.74±0.02ab 82.85±0.02b 粗脂肪(干基) 1.25±0.16 1.23±0.24 1.20±0.46 1.27±0.32 0.84±0.17 0.88±0.29 0.80±0.17 0.66±0.06 0.68±0.39 0.59±0.24 注:表格中同行肩标相同小写字母或无字母表示差异不显著(P>0.05),不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),n=3。 -
[1] 农业农村部渔业渔政管理局, 全国水产技术推广总站, 中国水产学会. 中国渔业统计年鉴-2019[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2019. Fisheries and Fisheries Administration Bureau of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Areas, National Aquatic Technology Promotion Station, China Society of Fisheries. China fishery statistical yearbook-2019[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2019.
[2] 梁敏, 吉宏武, 郝记明, 等. 凡纳滨对虾在二氧化碳麻醉无水保活过程中呼吸代谢及免疫的变化[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(4):280−284, 295. [LIANG M, JI H W, HAO J M, et al. Respiratory metabolism and immune response of CO2-anesthetized white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei during waterless transportaton[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(4):280−284, 295. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2018.04.051 [3] 徐子涵, 茅林春. 虾保活运输的关键技术及装备研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(9):306−310, 324. [XU Z H, MAO L C. Research progress on key technologies and equipment for live transportation of shrimp[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(9):306−310, 324. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2018.09.054 [4] REFAEY M M, LI D P, TIAN X, et al. High stocking density alters growth performance, blood biochemistry, intestinal histology, and muscle quality of channel catfish Ictalurus punctatus[J]. Aquaculture,2018,492(4):73−81.
[5] WANG W S, ZHANG Y J, LIU Y, et al. Effects of waterless live transportation on survivability, physiological responses and flesh quality in Chinese farmed sturgeon (Acipenser schrenckii)[J]. Aquaculture,2020,518:734834. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734834
[6] ZHANG Y J, NING Y F, ZHANG X S, et al. Multi-sensors-based physiological stress monitoring and online survival prediction system for live fish waterless transportation[J]. IEEE Access,2020,8:40955−40965. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2976509
[7] 徐子涵. 南美白对虾的无水低温胁迫响应和无水保活运输装置[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018. XU Z H. The response of Penaeus vannamei to waterless and low temperature stress and equipment for waterless transportation[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2018.
[8] 何蓉, 谢晶, 苏辉, 等. 不同温度对无水保活条件下的中华鳖肌肉营养成分及血液生化指标影响[J]. 食品科学,2014,35(6):194−199. [HE R, XIE J, SU H, et al. Effect of temperature on muscle nutritional components and blood biochemical parameters of Pelodiscus sinensis alive without water[J]. Food Science,2014,35(6):194−199. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201406042 [9] 曹杰, 王琪, 梅俊, 等. 有水与无水保活运输对大菱鲆生理应激及鱼肉品质的影响[J]. 水产学报,2021,45(7):1034−1042. [CAO J, WANG Q, MEI J, et al. Effects of transport in water and waterless transport on physiological stress and flesh quality of turbot (Scophthalmus maximus)[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China,2021,45(7):1034−1042. [10] ZENG P, CHEN T J, SHEN J. Effects of cold acclimation and storage temperature on crucian carp (Carassius auratus gibelio) in a waterless preservation[J]. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry,2014,40(3):73−82.
[11] 高加龙, 章超桦, 秦小明, 等. 不同温度无水保活对香港牡蛎微生物和基本营养成分的影响[J]. 广东海洋大学学报,2020,40(5):90−96. [GAO J L, ZHANG C H, QIN X M, et al. Effects of different temperatures waterless keep alive on total number of bacteria and coliform group, and basic nutritional compositions in Crassostrea hongkongensis[J]. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University,2020,40(5):90−96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9159.2020.05.011 [12] 米红波. 鲫鱼和中国对虾的无水保活及冰温保鲜技术研究[D]. 浙江: 浙江大学, 2014. MI H B. Study on waterless preservation and controlled freezing-point storage of crucian crap and Chinese white shrimp (Fenneropenaeus chinensis)[D]. Zhejiang: Zhejiang University, 2014.
[13] 张玉晗, 谢晶. 低温休眠预处理对花鲈无水保活效果的影响[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(23):221−226. [ZHANG Y H, XIE J. Effect of precooling treatment on survival of Lateolabrax maculatus during live transportation without using water[J]. Food Science,2018,39(23):221−226. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201823033 [14] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 5009.3-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品中水分的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017. National Health and Family Planning Commission of China, China Food and Drug Administration. National Food Safety Standard GB 5009.3-2016 Determination of moisture in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2017.
[15] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.5-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品中蛋白质的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017. National Health and Family Planning Commission of China, China Food and Drug Administration. National Food Safety Standard GB 5009.5-2016 Determination of protein in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2017.
[16] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.6-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品中脂肪的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017. National Health and Family Planning Commission of China, China Food and Drug Administration. National Food Safety Standard GB 5009.6-2016 Determination of fat in food[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2017.
[17] FAN X P, QIN X M, ZHANG C H, et al. Metabolic and anti-oxidative stress responses to low temperatures during the waterless preservation of the hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscogutatus ♀×Epinephelus lanceolatus ♂)[J]. Aquaculture,2019,508(4):10−18.
[18] WANG W S, XU J C, ZHANG W F, et al. Optimization and validation of the knowledge-based traceability system for quality control in fish waterless live transportation[J]. Food Control,2020,122:107809.
[19] HUR J W, KANG K H, KANG Y J. Effects of acute air exposure on the hematological characteristics and physiological stress response of olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) and Japanese croaker (Nibea japonica)[J]. Aquaculture,2019,502(12):142−147.
[20] 徐德峰, 王雅玲, 孙力军, 等. 降温及生态冰温条件对凡纳滨对虾无水存活时间的影响[J]. 广东海洋大学学报,2019,39(6):101−107. [XU D F, WANG Y L, SUN L J, et al. Effect of temperature-descending procedures and storing parameters on the preservation time of pacific white shrimp under waterless environment[J]. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University,2019,39(6):101−107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9159.2019.06.013 [21] 齐静涛. 日本对虾活体干法运输技术研究[J]. 齐鲁渔业,1996,13(5):47−48. [QI J T. On technique for transporting live kuruma shrimp with dry-package[J]. Shandong Fisheries,1996,13(5):47−48. [22] XU D F, WU J X, SUN L J, et al. Combined stress of acute cold exposure and waterless duration at low temperature induces mortality of shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei through injuring antioxidative and immunological response in hepatopancreas tissue[J]. Journal of Thermal Biology,2021,100:103080. doi: 10.1016/j.jtherbio.2021.103080
[23] 吴胜泽, 熊波, 黄钟标, 等. 无水保活下鲫鱼生理生化指标的变化[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2018,9(15):3992−3998. [WU S Z, XIONG B, HUANG Z B, et al. Changes of physiological and biochemical properties of Crucianauratus waterless keep-alive during the transportation[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2018,9(15):3992−3998. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2018.15.019 [24] 何登菊, 杨兴, 姚俊杰, 等. 低温保活运输对鲟鱼肌肉主要营养成分的影响[J]. 贵州农业科学,2010,38(6):157−158. [HE D J, YANG X, YAO J J, et al. Effect of low temperature transport on major nutritional components in muscle of Acipenser sturio[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences,2010,38(6):157−158. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2010.06.047 [25] MADDOCK D M, BURTON M P M. Some effects of starva-tion on the lipid and skeletal muscle layers of the winter flounder, Pleuronectes americanus[J]. NRC Research Press Ottawa, Canada,1994,72(9):1672−1679.
[26] BARCLAY M C, DALL W, SMITH D M. Changes in lipid and protein during starvation and the moulting cycle in the tiger prawn, Penaeus esculentus Haswell[J]. Elsevier,1983,68(3):229−244.
[27] KIM M K, LOVELL R T. Effect of restricted feeding regi-mens on compensatory weight gain and body tissue changes in chan-nel catfish Ictalurus punctatus in ponds[J]. Aquaculture,1995,135(4):285−293.
[28] 林小涛, 周小壮, 于赫男, 等. 饥饿对南美白对虾生化组成及补偿生长的影响[J]. 水产学报,2004,28(1):47−53. [LIN X T, ZHOU X Z, YU H N, et al. The effects of starvation on biochemical composition and compensatory growth in Penaeus vannamei[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China,2004,28(1):47−53. [29] BAI C, XIONG G Q, XU P, et al. Effect of cold-anesthetization rate on blood biochemical parameters and muscle composition during live channel catfish Ictalurus punctatus waterless preservation.[J]. Fisheries Science,2020,86:1043−1053. doi: 10.1007/s12562-020-01474-6
[30] ZENTENO-SAVIN T, SALDIERNA R, AHUEJOTE-SAN-DOVAL M. Superoxide radical production in response to environ-mental hypoxia in cultured shrimp[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology. Toxicology and Pharmacology: CBP,2006,142(3−4):301−308.
[31] SONANEZ-ORGANIS J G, RODRIGUEZ-ARMENTA M, LEAL-RUBIO B, et al. Alternative splicing generates two lactate dehydrogenase subunits differentially expressed during hypoxia via HIF-1 in the shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei[J]. Biochimie, 2012, 94(5): 1250−1260.
[32] GARCIA D, LIMA D, DA SILVA D G H, et al. Decreased malondialdehyde levels in fish (Astyanax altiparanae) exposed to diesel: Evidence of metabolism by aldehyde dehydrogenase in the liver and excretion in water[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2020,190:110107. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.110107
[33] 曾鹏, 申江, 陈天及. 休眠方式、温度和时间对离水储藏鲫鱼生理指标的影响[J]. 水产科学,2019,38(4):492−497. [ZENG P, SHEN J, CHEN T J. Effects of resting mode, temperature and time on physiological indices in crucian carp stored in air[J]. Fisheries Science,2019,38(4):492−497. doi: 10.16378/j.cnki.1003-1111.2019.04.008 -
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 马凯华,梁丽雅. 不同原料肉配比对风干肠理化特性及品质的影响. 天津农学院学报. 2023(02): 42-48 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈援援,刘文秀,马凯华,杨华,马俪珍. 接种乳酸菌发酵剂对风干肠成熟过程中微生物群落动态变化及感官品质的影响. 肉类研究. 2022(02): 1-8 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 陈援援,牛文秀,马凯华,梁丽雅,马俪珍. 接种乳酸菌发酵剂对风干肠加工过程中理化性质及安全品质的影响. 食品工业科技. 2022(08): 148-156 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 陈援援,马凯华,牛文秀,孙慧娟,任小青,马俪珍. 微生物发酵剂对风干肠风味形成及变化的影响. 食品科学. 2022(14): 125-135 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)







 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



