Screening of Fermentation Strains of Trachinotus ovatus and Biological Characteristic and Flavor Formation Evaluation
-
摘要: 为了有效控制发酵鱼的品质及其保质期,从传统发酵金锠鱼中筛选适合作发酵剂的菌株。以过氧化氢酶阳性、耐盐性、抗菌性及不产生组胺为筛选指标,采用稀释分离法分离目标菌株,并对其生物学特性、发酵风味与口感进行评价。结果显示,从发酵金锠鱼中分离到的38株菌株中,筛选出的两株潜在发酵菌株(zh-b和zh-f)经形态鉴定与16S rRNA分析鉴定为戊糖片球菌(Pediococcus pentosaceus)和植物乳杆菌(Lactobacillus planta-ruma),其最适温度分别为20与30 ℃,最适pH为5、6。两株菌对金黄色葡萄球菌与大肠标杆菌均具有抗菌活性,但植物乳杆菌抗菌活性更好,且产酸能力明显高于戊糖片球菌。电子鼻对发酵产物进行测定,发现戊糖片球菌产生的甲基类、硫化物、氮氧化合物、醇类或醛酮类和有机芳香硫化物响应值(64.10、57.98、44.75、40.22和19.93)高于植物乳杆菌(5.50、34.11、10.68、0和8.95),是香气成分的主要贡献者。电子舌测定发现,两株菌均具有产生鲜味、鲜回味的能力,且戊糖片球菌的味值分别为14.32、6.64,明显高于植物乳杆菌产生鲜味、鲜回味(3.20、2.90),但只有植物乳杆菌产生酸味。另外,两株菌也产生非常少量的苦味。研究为两株菌作为发酵剂用于规模化生产发酵金鲳鱼提供依据。Abstract: To effectively control quality and shelf life of fermented fish, strains, which can be used as starter culture, were separated and screened from traditional fermented Trachinotus ovatus. Using catalase positive, salt tolerance, antibacterial properties and histamine-free as the valuation indexes, the target strains were isolated by dilution separation method, and strains biological characteristics, flavor and tastes of metabolites were evaluated. The experimental results showed that two potential fermented strains (zh-b and zh-f) were screened from 38 strains, which were isolated from the fermented Trachinotus ovatus. According to molecular biological identification, two strains were Pediococcus pentosaceus and Lactobacillus plantaruma, and their most appropriate temperatures were 20 and 30 ℃, the optimal pH was 5 and 6, respectively. Both strains had antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli, but the Lactobacillus plantarum showed the better antibacterial activity, and the acid production capacity was far higher than that of Pediococcus pentosaceus. Fermentation products were determined by electronic nose, it was and found that methyl groups, sulfides, nitrogen oxides, alcohols or aldehydes and ketones and organic aromatic sulfides produced by Pediococcus pentosaceus (64.10, 57.98, 44.75, 40.22 and 19.93) were higher than those of Lactobacillus plantarum (5.50, 34.11, 10.68, 0.00 and 8.95), which was a major contributor to aroma components. The electronic tongue test showed that both strains had the ability to produce umami and fresh aftertaste, and the taste values of Pediococcus pentosaceus were 14.32 and 6.64, which were significantly higher than those of Lactobacillus plantarum, which produced umami and fresh aftertaste (3.20 and 2.90), but only Lactobacillus plantarum produced a sour taste. In addition, both strains also produced a very small amount of bitterness. The research would provide a basis for the large-scale production of fermented Trachinotus ovatus using the two strains as a mixed starter.
-
金鲳鱼(Trachinotus ovatus)学名卵形鲳鯵,常生活于热带及温带海洋中,其肉质细腻、鲜甜、口感绵延,是一种深受消费者喜爱的海洋鱼类。近年来,随着深海网箱、海洋牧场等技术的不断推广与应用,金鲳鱼养殖产量逐年快速增加,成为南方沿海规模化生产的鱼类之一[1]。但同时由于过快地扩张,导致金鲳鱼市场供过于求,而且目前的市场销售以活鲜、冰鲜和冷冻鱼等产品为主[2],行业存在产品种类单一,高附加值深加工产品缺乏等问题,造成利润严重下滑,制约了金鲳鱼产业发展的空间。湛江乌石镇地处雷州半岛西南部,是广东省主要渔港之一,全镇以渔业为主,其中当地居民用传统盐制的发酵的方式,形成具有独特湛江风味的发酵金锠鱼,受到消费者喜爱。
发酵是一种经济而古老的食品加工与保存方法[3],通过微生物与食物成分的相互作用及微生物酶的降解作用,产生乳酸、酮类、醛类、醇、烯烃类等物质,赋予发酵产品独特的风味、口感与色泽[4-6],Narzary等[7]对18种发酵鱼产品的营养成分、风味、滋味、益生性及微生物的组成进行了报道,发现发酵鱼中微生物对其营养、风味有重要的影响,同时产生的抑菌物质又延长了产品的保质期。因此,开发以发酵金鲳鱼为代表的深加工产品有望成为解决滞销、行业低迷等问题的有效途径。但是,利用盐制或风干方法制备的传统发酵鱼中的微生物是来自于自然富集的,由于受到不同年份、不同季节温度与湿度的影响,参与发酵的微生物种群不确定,影响其产品质量的稳定性、保质期以及安全食用性[8]。因此,筛选具有良好特性的微生物进行人工接种,对提高与稳定产品质量,缩短发酵时间尤为重要。而用于接种发酵的微生物通常是从传统发酵产品中分离优质微生物这一策略获得[9],Shubham等[10]利用此策略从印度的发酵鱼中分离筛选到40株乳酸菌,并发现其中两株菌具有较好的应用特性。近年来,研究发现植物乳杆菌属、片球菌属、乳杆菌属等乳酸菌在鱼的发酵过程中起到了关键的作用[11-12]。另外,田国军等[13]成功地从自然发酵的腊鱼中分离到1株优质乳酸菌,并接种到新鲜的腊鱼中进行发酵,其产品的风味和质量均得到了明显的改善。Barbara等[14]发现,乳杆菌属用于鱼发酵香肠生产中,有效减少了发酵时间。总之,随着人工接种发酵技术的不断成熟,在食品发酵中使用发酵剂进行定向接种已成为提高加工速度和产品质量的重要手段[15]。
针对传统方法制备的发酵鱼微生物种群结构的不确定性,导致产品质量不稳定这一问题,本研究以广东湛江乌石镇传统方法制备的优质发酵金鲳鱼为材料,从中分离筛选出适合作为发酵剂的微生物菌种,并对分离菌株的生物学特性及其形成的风味进行评价,以期为实现定向接种,人工控制发酵生产提供依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
传统发酵金鲳鱼 新鲜优质,来自于广东湛江乌石镇,每条400 g左右;金黄色葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus aureus ATCC29213)、大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli ATCC35218) 均购自广东省微生物研究所;MRS肉汤、MRS培养基、营养肉汤(NB)、营养琼脂(NA) 青岛海博生物技术公司;Mighty Amp DNA Polymerase Ver.2 宝生物工程有限公司;16S rRNA细菌通用引物27F:5'-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3',1492R:5'-GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3' 上海生工生物技术有限公司合成。
CFX96 Touch型实时荧光定量PCR仪、Gel Doc XR+型凝胶成像仪 美国BIO-RAD公司;PEN3型电子鼻 德国AIRSENSE公司;SA402B型电子舌 日本INSENT公司;Varioskan Flash型酶标仪 美国热电公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 发酵菌株的筛选
用无菌水冲洗掉发酵金锠鱼表面的杂质,沥干水之后,用灭菌剪子剪碎,称取25 g加到无菌均质袋中,再加入pH7.2灭菌的PBS 225 mL,均质30 s后,吸取0.1 mL均匀涂布于MRS培养基中,30 ℃培养48~72 h。挑取不同形态特征的菌落,反复纯化,直至获得纯的分离株。
参照文献[16],筛选具备过氧化氢酶实验呈阳性、发酵葡萄糖产酸,但不产生生物胺、不产气,具有一定的耐盐性,并有良好的抗菌活性菌株作为潜在发酵菌株。抗菌活性测定采用牛津杯法[17],其它指标测定采用《常见细菌系统鉴定手册》描述方法[18]。
1.2.2 发酵菌株的16S rRNA鉴定
分别以27F、1492R为正、反向引物,使用MightyAmp DNA聚合酶对发酵菌株进行菌落PCR,PCR体系与反应条件按照Lu等[19]的方法。再将目的PCR产物寄送生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司进行测序。根据测得的16S rRNA基因序列,从EzBioCloud数据库进行同源性搜索,下载相似性高的模式菌株的相应基因序列[20],并用MEGA5.1建立系统发育树。
1.2.3 温度对发酵菌株生长的影响
挑取两环发酵菌株,接种于50 mL MRS液体中,30 ℃静置培养18 h,作为发酵菌株的种子液,再将种子液按3%接至MRS液体中,混匀后分别置于20、25、30 ℃培养28 h,且每间隔2 h测定发酵液的OD600 nm[21],绘制生长曲线,评价温度对两株发酵菌的影响。
1.2.4 pH对发酵菌株生长的影响
将1.2.3中的发酵菌株的种子液按3%的接种量分别接种于pH为3.0、4.0、5.0、6.0和7.0的MRS液体中,30 ℃静置培养24 h后,测定发酵液OD600 nm值[22],绘制生长曲线,评价pH对两株发酵菌的影响。
1.2.5 发酵菌株产酸能力测定
按3%接种量将种子液接种于100 mL的MRS液体中,30 ℃静置培养24 h,每间隔4 h取样,测定发酵液的pH[23]。
1.2.6 发酵菌株抗菌活性的测定
挑取两环S. aureus与E. coli分别接种于NB中,37 ℃摇床中培养16~20 h,然后将两种指示菌的菌液浓度稀释至106 CFU/mL,再将指示菌的稀释液按1:100的比例加到55 ℃的NB中,混匀后趁未凝固前快速倒入摆放有灭过菌的牛津杯培养皿中,待凝固后拔出牛津杯。接着吸取200 μL发酵菌上清液加到杯孔中,37 ℃静止培养18 h,观察是否出现抑菌圈,并测量抑菌圈的直径[24]。同时,以生理盐水代替发酵上清液做空白对照。
1.2.7 发酵菌株发酵液的电子鼻测定
将1.2.3中发酵菌的种子液按3%的接种量接于MRS液体中,30 ℃静止培养24 h,再量取发酵液20 mL于顶空瓶中,静置30 min后进行电子鼻检测,测定条件为:顶空时间20 min,样品及载气流速均为300 mL/min,传感器自清洗时间60 s,样品测试时间60 s,数据采集间隔为1 s,PEN3电子鼻传感器对不同成份敏感性能描述见表1。
表 1 PEN3型电子鼻传感器描述Table 1. Description of PEN3 electronic nose sensor performance阵列序号 传感器名称 敏感性能描述 1号 W1C 芳香成分与苯类 2号 W5S 氮氧化合物 3号 W3C 芳香成分与氨类 4号 W6S 对氢化物有选择性 5号 W5C 短链烷烃芳香成分 6号 W1S 甲基类 7号 W1W 硫化物 8号 W2S 醇类、醛酮类 9号 W2W 芳香成分与有机硫化物 10号 W3S 长链烷烃类 1.2.8 发酵菌株发酵液的电子舌测定
将1.2.7中得到的菌株发酵液稀释5倍,在4 ℃下,以3000 r/min离心20 min,收集上清液过滤,吸收100 mL上清滤液装入专用烧杯中,进行电子舌的检测。电子舌AAE、CT0、CA0、C00和AE1传感器的响应特性分别为鲜味、咸味、酸味、苦味和涩味。在测定前,所有传感器先放在参比溶液(0.30 mmol/L酒石酸和30.00 mmol/L氯化钾混合溶液)中活化24 h,再装机进行自检至信号稳定,每个样品做4次循环,取后3次结果,并对味觉特征进行分析。
1.3 数据处理
实验重复3次,采用平均值±标准差(
2. 结果与分析
2.1 发酵菌株的确定
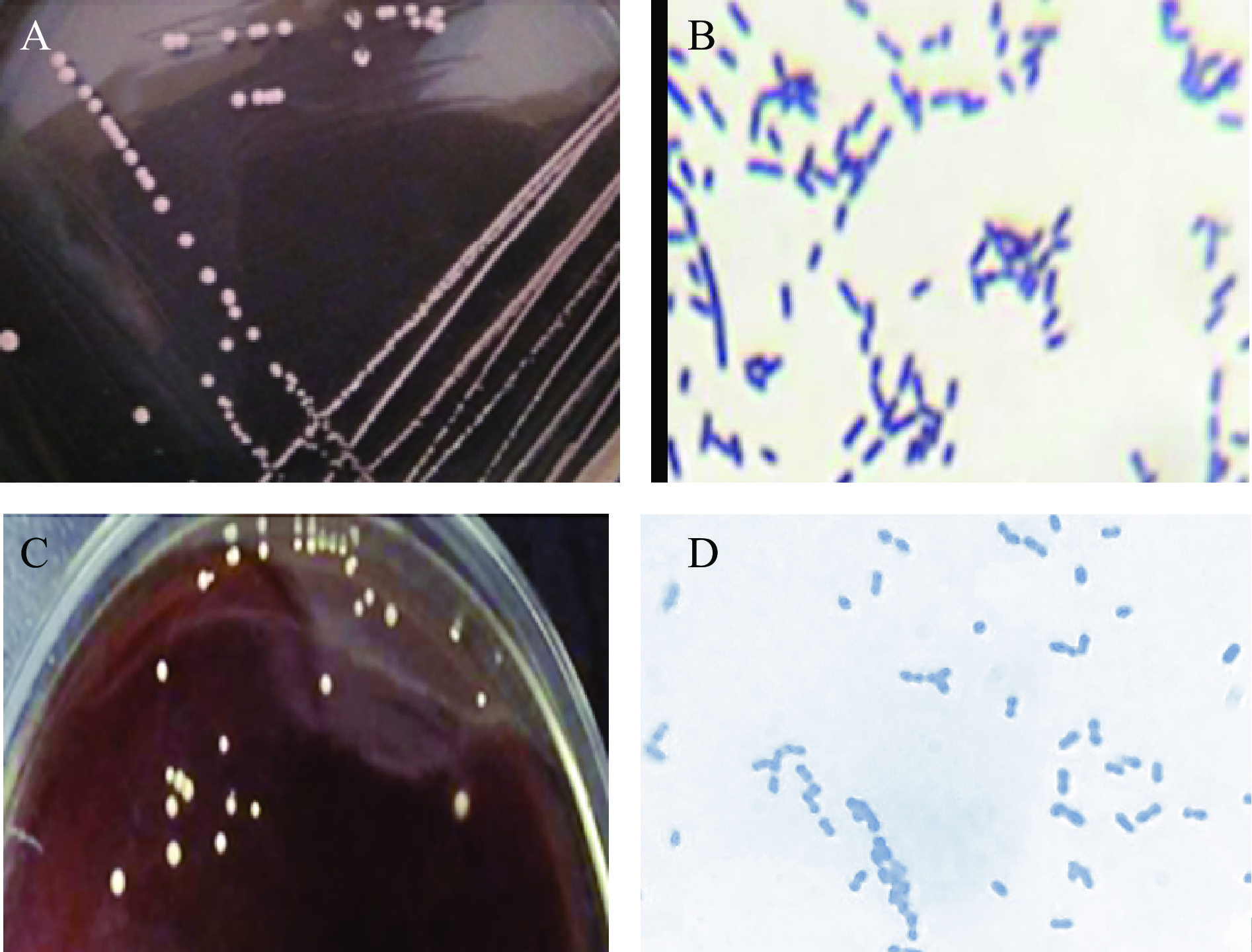
从传统发酵金鲳鱼中分离纯化到38株菌,通过发酵菌株筛选实验,菌株zh-b与菌株zh-f符合发酵菌株筛选标准[16],确定为潜在发酵菌。在MRS培养基上,菌株zh-f菌落呈圆形,色白,细密,显微形态为杆状(图1A、图1B);菌株zh-b在MRS培养基的菌落呈圆形,乳白色,凸起,边缘整齐,不透明,显微形态为球状(图1C、图1D)。Samarjit等[12]也从印度曼尼普人制备的传统发酵鱼中分离到46株形态不同的菌株,传统发酵鱼已成为分离用于发酵微生物的重要来源。
2.2 发酵菌株的16S rDNA鉴定
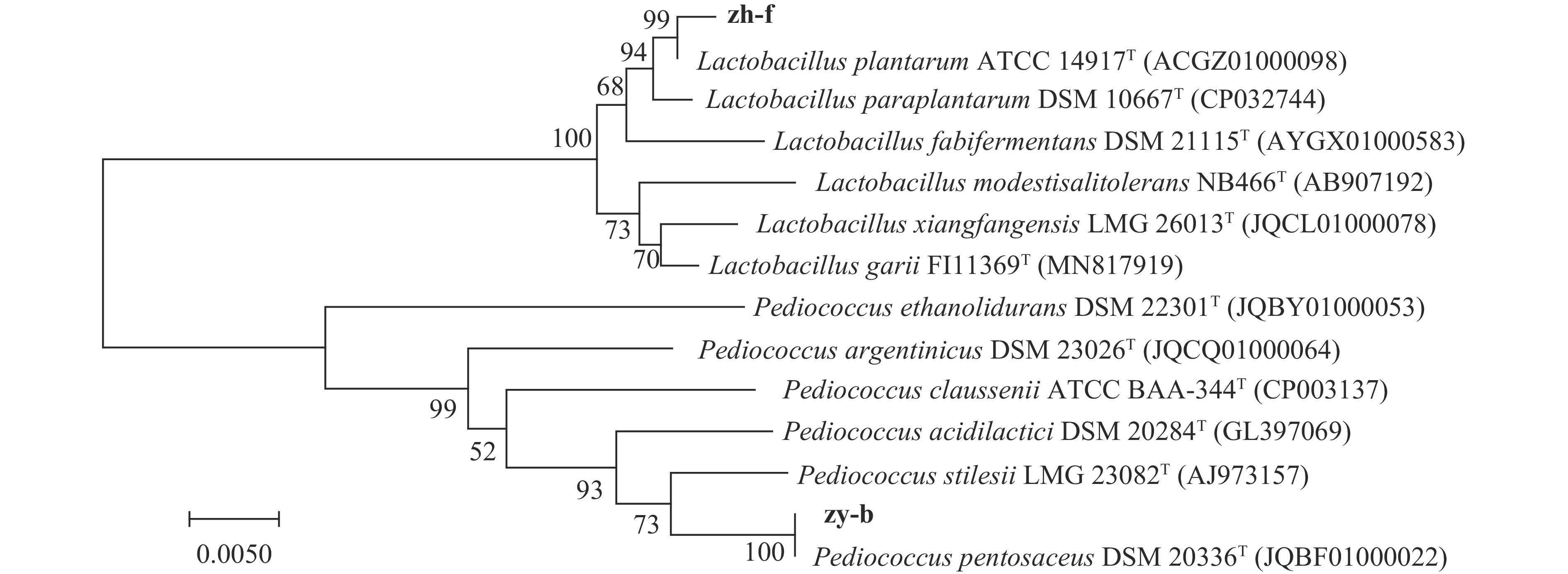
将菌株zh-b与菌株zh-f的16S rRNA序列与标准菌株进行比对分析,发现菌株zh-b与模式菌株Pediococcus pentosaceus DSM 20336相似性最高,相似率为99.26%,而菌株zh-f与模式菌株Lactobacillus plantaruma ATCC 14917相似性最高,相似率为99.11%,并用MEGA 5.1软件构建系统发育树(图2)。结合形态鉴定及16S rRNA序列分析,菌株zh-b与zh-f分别鉴定为戊糖片球菌(Pediococcus pentosaceus)与植物乳杆菌(Lactobacillus plantarum)。从印尼的发酵鱼中也分离到了L. plantaruma与P. pentosaceus[25],而谭汝城等[21]不仅从自然发酵鱼鲊中分离到L. plantaruma与P. pentosaceus,而且又将其接种于新鲜鱼中进行发酵,并与自然发酵鱼的化学指标和感官品质进行比较,结果表明,接种发酵可以改善鱼鲊游离氨基酸的组成,并有效提高了鱼鲊的感官品质。
2.3 温度对发酵菌株生长的影响
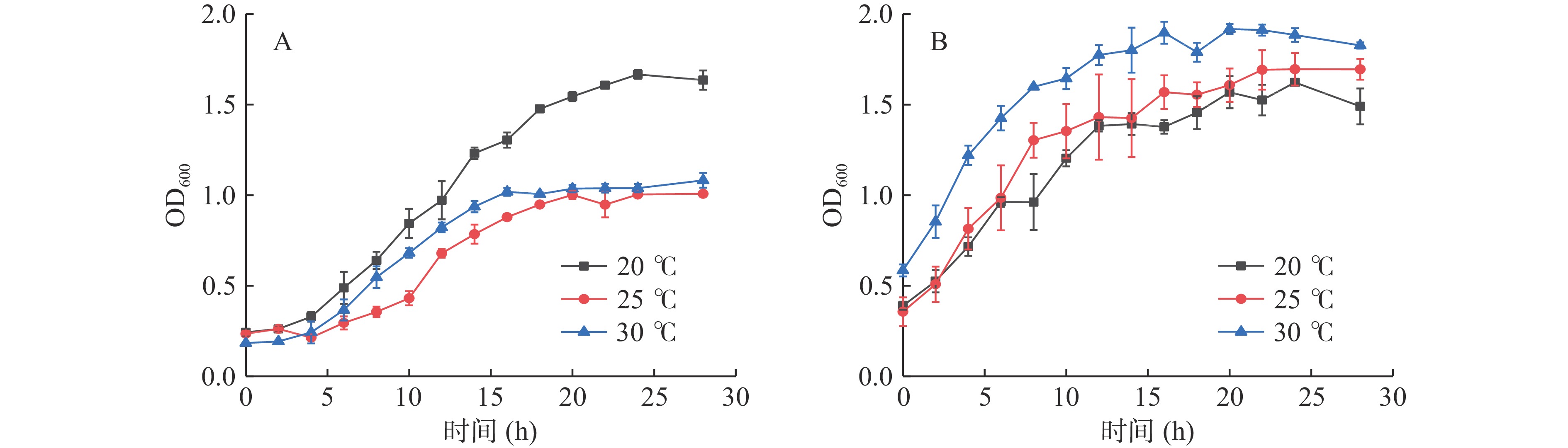
图3为两株发酵菌株在20、25和30 ℃的生长曲线,从图中可以看出,在30 h内两株菌的OD600随着培养时间的延长而不断升高,并逐渐趋于平稳,说明菌数随着培养时间的延长而不断提高,并达到稳定期。其中,菌株戊糖片球菌zh-b(图3A)菌液浓度在同一培养时间20 ℃生长最好,其次是30与25 ℃。而植物乳杆菌zh-f(图3B)是30 ℃菌液浓度最高,其次是25与20 ℃。
通过比较分析,两株菌混合发酵液的最适发酵温度确定为30 ℃,从生长曲线出现平稳时间分析,确定两株最适发酵时间为16 h。
2.4 pH对发酵菌株的生长影响
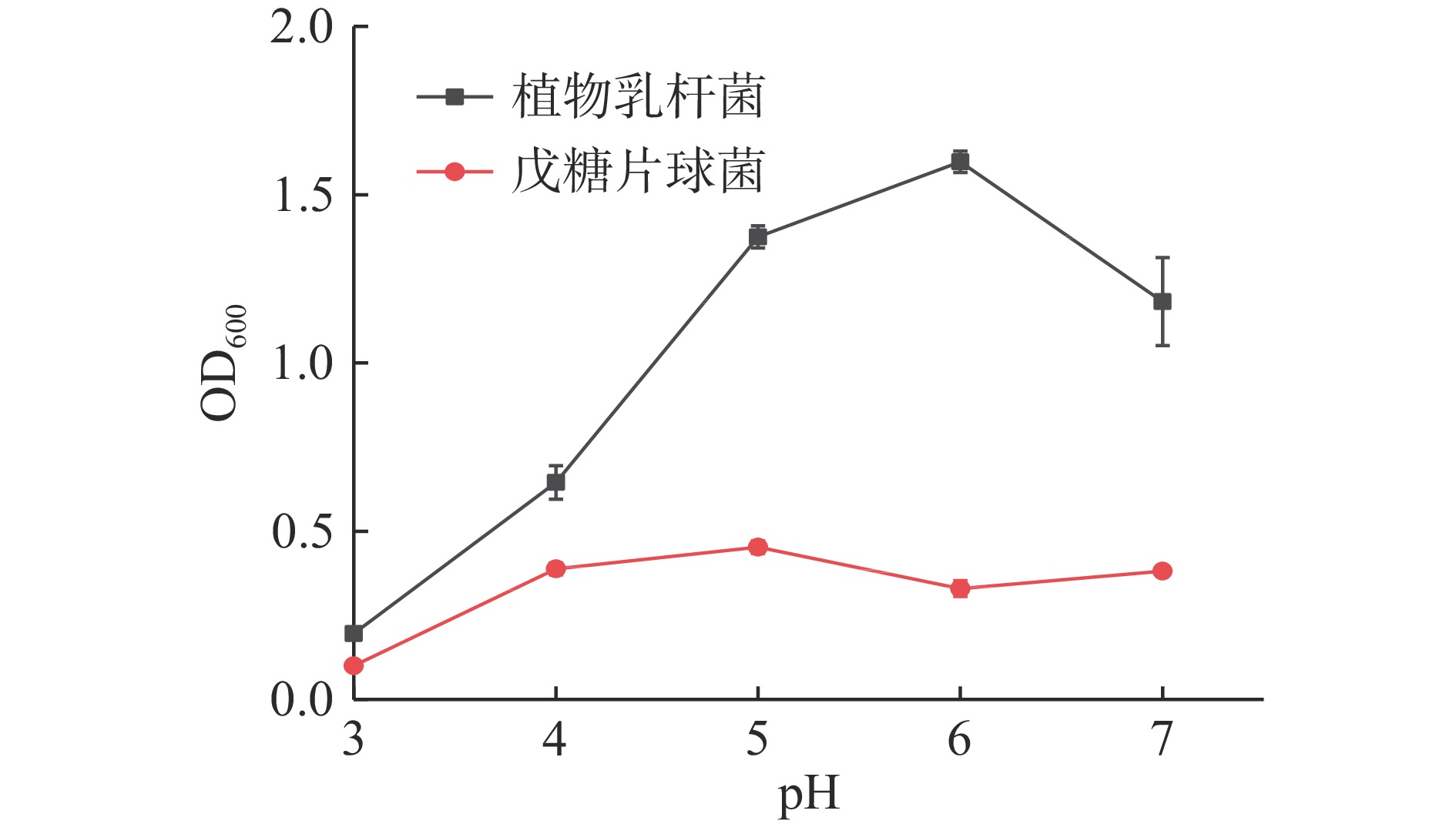
图4为两株菌在不同pH培养条件下的生长曲线,其中戊糖片球菌的OD600曲线在pH3~5区间的OD600值呈上升趋势,并在pH5时达到最大值0.45,但在pH6时,OD600出现微小低谷。OD600值总体变化幅度小于0.4,即戊糖片球菌zh-b的生长受pH影响不大。而植物乳杆菌zh-f的生长随着pH的增高,出现了先增大再减小的现象,pH在3~6区间其OD600值随着pH的增大而增大,且增幅明显,并在pH6时,OD600达到最大值1.60后,接着OD600开始下降。
2.5 发酵菌株产酸能力测定
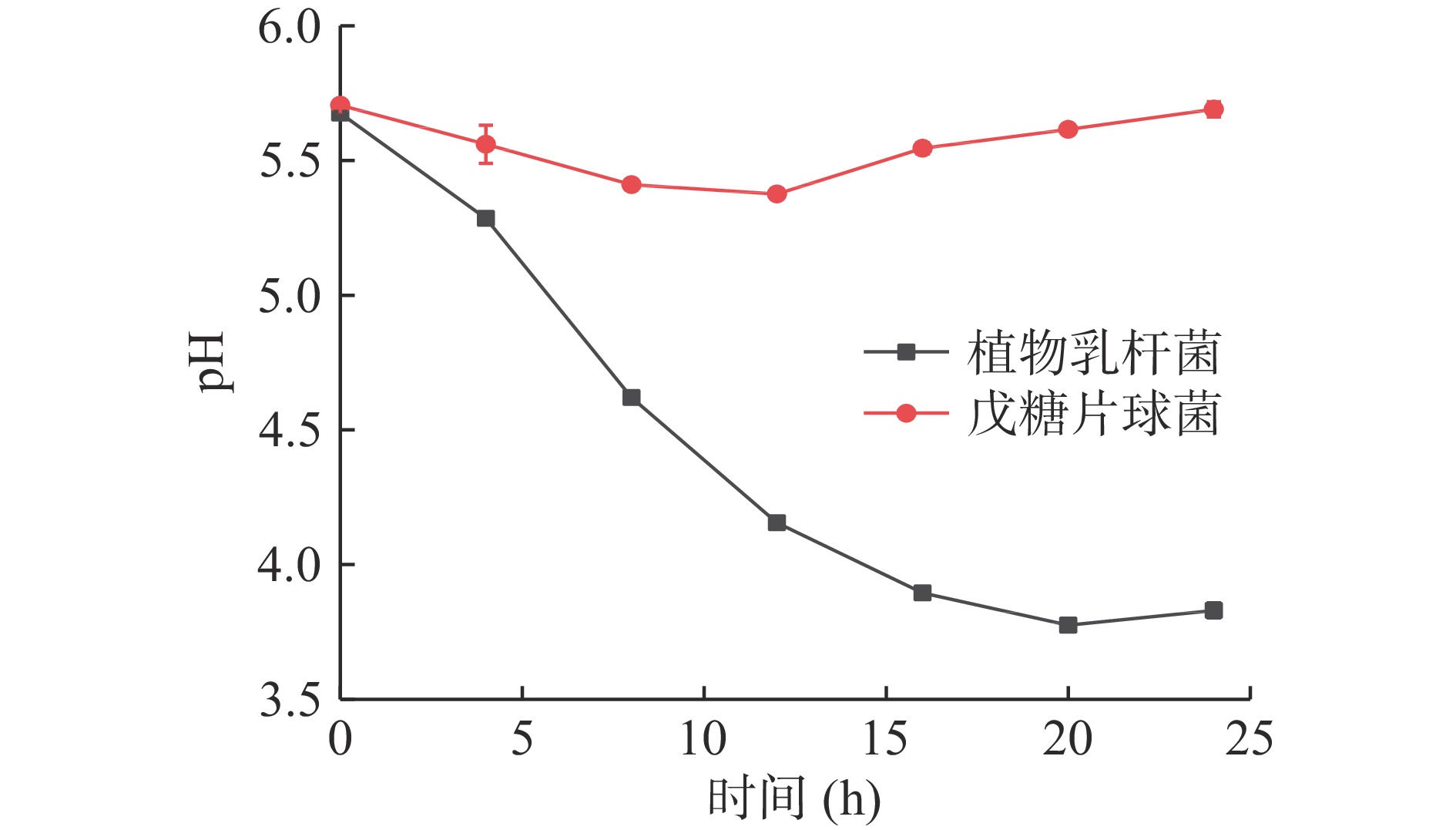
不同乳酸菌产酸能力存在一定的差异,由图5可知,zh-b在24 h内产酸能力较弱,仅在前13 h pH有微小的降低后又开始上升。而zh-f在24 h内一直在产酸,尤其在4~13 h pH下降较快,产酸速率最大,说明该阶段产酸能力最强,20 h后pH达到3.775趋于平缓,说明植物乳杆菌zh-f将是发酵金鲳鱼中产酸的主要贡献者。
2.6 两株发酵菌的抗菌活性
由表2可知,两株发酵菌对E. coli和S. aureus均有抗菌活性,其中植物乳杆菌zh-f对两种指标菌表现出较强的抗菌活性;而戊糖片球菌zh-b对E. coli和S. aureus虽然也对两株菌有抑菌效果,但不及zh-f的抗菌效果,这可能与植物乳杆菌产酸能力或产生其它抗菌物质有关。
表 2 两株发酵菌株抗菌活性Table 2. Antibacterial activity of fermentation strains菌种名称 E. coli S. aureus 戊糖片球菌zh-b ++ + 植物乳杆菌zh-f +++ +++ 注:抑制效果:≤8 mm,-(没有抑菌效果);8~10 mm,+;10~15 mm ,++;15~20 mm,+++。 2.7 发酵菌株的电子鼻测定
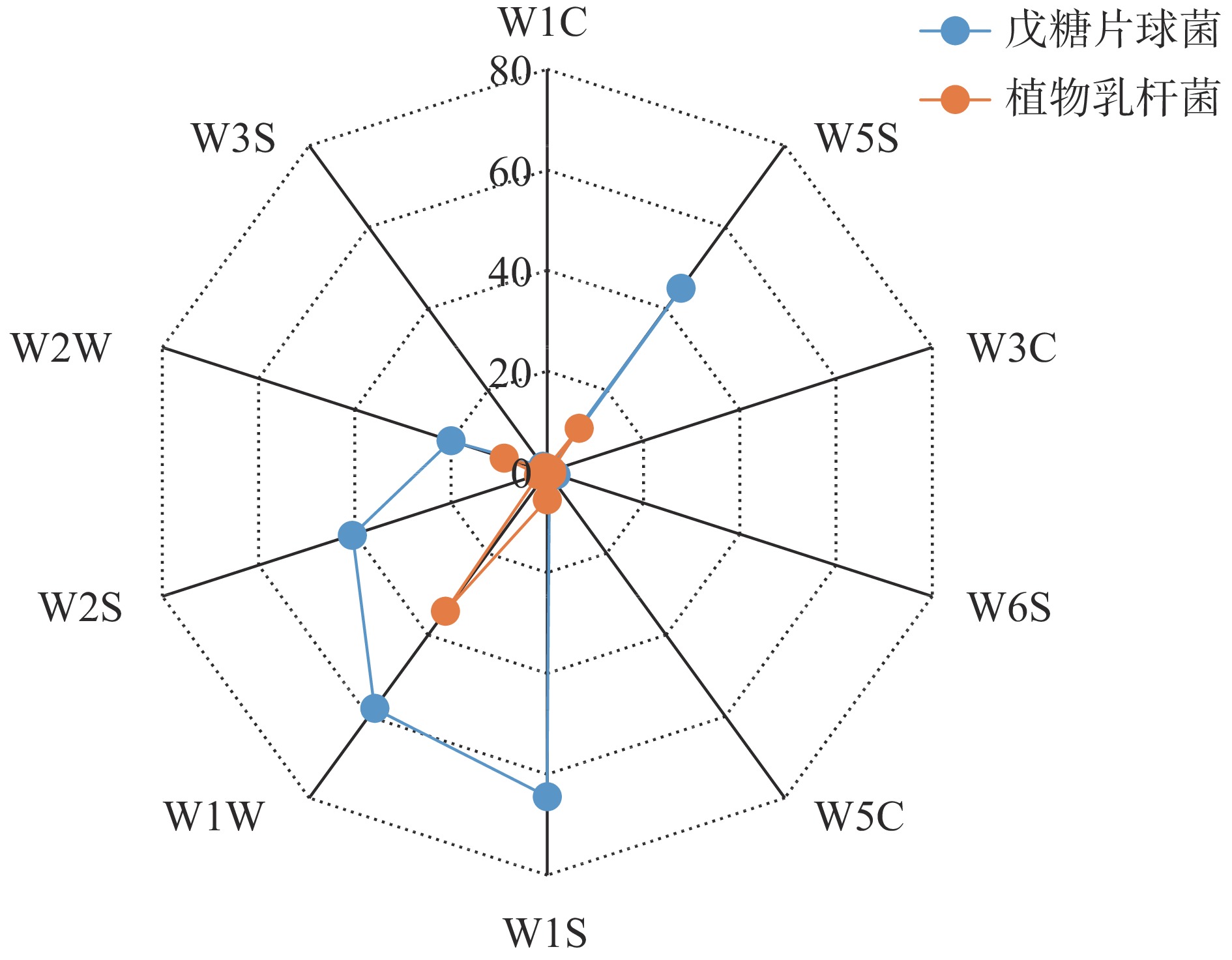
用AIRSENSE PEN3型电子鼻对两株菌发酵液的气味成分进行测定,根据响应值绘制雷达图(图6)。通过比较发现,戊糖片球菌zh-b和植物乳杆菌zh-f菌株发酵液均含有甲基类(W1S)、硫化物(W1W)、氮氧化合物(W5S)和有机芳香硫化物(W2W)4种相同的香气成分,但zh-b的响应值明显高于zh-f,另外还产生了醇类或醛酮类(W2S)成分。其中,戊糖片球菌发酵液中的主要香气成分W1S、W1W、W5S、W2S、W2W的响应值依次是64.10、57.98、44.75、40.22和19.93,其他传感器测得的响应值均低于2,香气成分不明显。而zh-f发酵液中主要香气成分硫化物(W1W)、氮氧化合物(W5S)、有机芳香硫化物(W2W)、甲基类(W1S)的响应值分别为34.11、10.68、8.96和5.50,其他传感器W2S、W3S、W6S、W5S、W3C和W1C,响应值均低于2,香气成分不明显。分析表明,戊糖片球菌zh-b是发酵金鲳鱼香气成分的主要贡献者。Shen等[26]采用相关网络模型预测了关键微生物与风味形成存在明显的关系,采用美国Isenso公司的iNose电子鼻检测植物乳杆菌、干酪乳杆菌及戊糖片球菌混合菌制备的发酵带鱼,发现发酵过程中形成了氮氧化合物、有机硫化物,萜类、酯类、甲基类以及无机硫化物风味物质 [27]。
2.8 发酵菌株的电子舌测定
SA402B电子舌传感器酸味和咸味对应传感器的无味点下限分别为-13和-6,其他味觉指标对应传感器的无味点下限均为0,按该电子舌的规定大于无味点的味觉指标,即可作为评价对象。根据电子舌对两株菌味觉响应值的测定,绘制滋味雷达图(图7)。从图中可以看出,两株菌的咸味、涩味、苦回味及涩回味的测定值均不大于无味点下限值,表明两株不产生对应的味道。对于酸味,戊糖片球菌酸味值为-29.5,小于-13,说明该菌不产生酸味,而植物乳酸菌的酸味值为-3.58,明显大于-13,说明该菌具有较强的产酸能力,这与2.5的结果一致。对于鲜味、鲜回味,两株菌的响应值均大于无味点下限,具有产生鲜味、鲜回味的能力,其中,戊糖片球菌的味值分别为14.32、6.64,高于植物乳杆菌产生鲜味、鲜回味(3.20、2.90)。另外,两株菌也产生非常少量的苦味(4.74与1.58)。不同的微生物发酵产品的味觉也存在差异,将清酒乳杆菌接种到鳓鱼中进行固态发酵,采用法国阿尔法莫斯公司的ASTREE II电子舌对味道进行测定,检测到发酵鳓鱼中的酸味、复合味1、复合味2及鲜味比未接种的对照组显著[28],说明微生物在发酵过程中对味觉的形成影响较大。
3. 结论
本研究以过氧化氢酶呈阳性、耐盐性、抗菌性及不产生组胺为评价指标,从湛江传统发酵金鲳鱼中分离筛选出两株潜在发酵菌株(zh-b和zh-f),经分子生物学鉴定为戊糖片球菌(Pediococcus pentosaceus)和植物乳杆菌(Lactobacillus plantaruma),且最适温度分别为20、30 ℃,最适pH为5、6。两株菌均具有抗菌活性,但植物乳杆菌zh-f的抗菌活性更好,且产酸能力明显高于戊糖片球菌zh-b。但zh-b产生的甲基类、硫化物、氮氧化合物、醇类或醛酮类和有机芳香硫化物高于zh-f,而且zh-b产生的鲜味、鲜回味也高于zh-f。本研究从传统发酵鱼中筛选到的两株发酵菌株,由于具有良好的特性,且风味与滋味有较好的互补性,因此,两株菌在发酵鱼应用中的潜力不容忽视。
-
表 1 PEN3型电子鼻传感器描述
Table 1 Description of PEN3 electronic nose sensor performance
阵列序号 传感器名称 敏感性能描述 1号 W1C 芳香成分与苯类 2号 W5S 氮氧化合物 3号 W3C 芳香成分与氨类 4号 W6S 对氢化物有选择性 5号 W5C 短链烷烃芳香成分 6号 W1S 甲基类 7号 W1W 硫化物 8号 W2S 醇类、醛酮类 9号 W2W 芳香成分与有机硫化物 10号 W3S 长链烷烃类 表 2 两株发酵菌株抗菌活性
Table 2 Antibacterial activity of fermentation strains
菌种名称 E. coli S. aureus 戊糖片球菌zh-b ++ + 植物乳杆菌zh-f +++ +++ 注:抑制效果:≤8 mm,-(没有抑菌效果);8~10 mm,+;10~15 mm ,++;15~20 mm,+++。 -
[1] 张大为, 张洁, 田永航. 发酵金锠鱼糜制品工艺条件的优化及发酵过程中品质变化分析[J]. 现代食品科技,2020,36(9):211−218. [ZHANG D W, ZHANG J, TIAN Y H. Optimization of process conditions of fermented golden pomfret surimi production and analysis of quality changes in fermentation in process[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2020,36(9):211−218. [2] 王琦, 岳大鹏, 王然然, 等. 风干金锠鱼制品加工过程中脂质氧化和挥发性成分的变化[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(1):54−60. [WANG Q, YUE D P, WANG R R, et al. Changes of lipid-oxidation and volatile compounds of air-dried golden pomfret during processing[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(1):54−60. [3] TAMANG J P, WATANABE K, HOLZAPFEL W H. Review: Diversity of microorganisms in global fermented foods and beverages[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2016,7(5):1−28.
[4] DOMINGUEZ R, AGREGAN R, LORENZO J M. Role of commercial starter cultures on microbiological, physicochemical characteristics, volatile compounds and sensory properties of dry-cured foal sausage[J]. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Disease,2016,6(5):396−403.
[5] DZIKUNOO J, LETSYO E, ADAMS Z, et al. Ghana’s indigenous food technology: A review of the processing, safety, packaging techniques and advances in food science and technology[J]. Food Control,2021,127:108116.
[6] XU Y, ZANG J, REGENSTEIN J M, et al. Technological roles of microorganisms in fish fermentation: A review[J]. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr,2021,61:1000−1012.
[7] NARZARY Y, DAS S, GOYAL A K, et al. Fermented fish products in South and Southeast Asian cuisine: Indigenous technology processes, nutrient composition, and cultural significance[J]. Journal of Ethnic Foods,2021,8:1−9. doi: 10.1186/s42779-021-00077-5
[8] HUA Q, GAO P, XU Y S, et al. Effect of commercial starter cultures on the quality characteristics of fermented fish-chili paste[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2020,122(1):109016.
[9] 张巧云. 豆酱中微生物多样性及人工接种多菌种发酵豆酱的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2013. ZHANG Q Y. Microbial diversity analysis on soybean paste and research on fermentation using multi-strains via artificial inoculation[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2013.
[10] SHUBHAM G, UPASANA M, RANENDRA K, et al. Isolation and characterization of lactic acid bacteria from traditional fermented fish product Shidal of India with reference to their probiotic potential[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2021,146:111641. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111641
[11] 林城杏, 黄瑶, 周迎春, 等. 传统淡水鱼发酵制品中乳酸菌的分离筛选及发酵特性[J]. 肉类研究,2019,33(5):13−18. [LIN C X, HUANG Y, ZHOU Y C, et al. Isolation and fermentation characteristics of lactic acid bacteria from traditional fermented freshwater fish in China[J]. Meat Research,2019,33(5):13−18. doi: 10.7506/rlyj1001-8123-20190307-049 [12] SAMAJIT S, SURAIJIT D M, ESTHER L, et al. Antimicrobial, antioxidant and probiotics characterization of dominant bacterial isolates from traditional fermented fish of Manipur, North-East India[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2018,55(5):1870−1879. doi: 10.1007/s13197-018-3103-4
[13] 田国军, 尚艳艳, 黄泽元. 腊鱼中优势乳酸菌的分离, 纯化及性质鉴定[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2011,37(6):78−81. [TIAN G J, SHANG Y Y, HUANG Z Y. Isolation, purification and identification of dominant lactic acid bacteria from cured fish[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2011,37(6):78−81. [14] BARBARA S, ANGELA R, LUCIANO B, et al. Autochthonous lactic acid bacteria with probiotic aptitudes as starter cultures for fish-based products[J]. Food Microbiology,2017,65(8):244−253.
[15] 康慎敏, 徐睿, 武瑞赟. 乳酸菌在发酵鱼制品中的应用[J]. 中国水产,2021(7):84−87. [KANG S M, XU R, WU R Y. Application of lactic acid bacteria in fermented fish products[J]. Chinese Journal of Fisheries,2021(7):84−87. [16] 朱雯娟, 安俊莹, 张雪梅, 等. 梅香鱼发酵菌株的筛选及对品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2015,36(23):165−169. [ZHU W J, AN J Y, ZHANG X M, et al. Selection of starter culture from traditional fermented Meixiang fish and its effect on quality[J]. Food Science,2015,36(23):165−169. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201523030 [17] 罗怡, 张瀛, 刘颖, 等. 华贵栉孔扇贝肠道产细菌素乳酸菌的分离筛选[J]. 食品科技,2019,44(2):27−32. [LUO Y, ZHANG Y, LIU Y, et al. Isolation and screening of bacteriocin Lactobacillus from the intestinal tract of Chlamys nobilis[J]. Food Science and Technology,2019,44(2):27−32. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2019.02.005 [18] 东秀珠, 蔡妙英. 常见细菌系统鉴定手册[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001. DONG X Z, CAI M Y. Handbook of systematic identification of common bacteria[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2001.
[19] LU Q F, HU H Q, MO J J, et al. Enhanced amplifification of bacterial and fungal DNA using a new type of DNA polymerase[J]. Australasian Plant Pathology,2012,41(6):661−663. doi: 10.1007/s13313-012-0144-4
[20] ZHANG W, SUN Z R. Random local neighbor joining: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees[J]. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution,2008,47(1):117−128.
[21] 谭汝城, 欧阳加敏, 卢晓莉, 等. 接种植物乳杆菌和戊糖片球菌发酵对鱼鲊品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2007,28(12):268−272. [TAN R C, OUYANG J M, LU X L, et al. Fermentation conditions of Yuzha by inoculated Lactobacillus plantarum and Pediococcus pertosaceus[J]. Food Science,2007,28(12):268−272. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2007.12.062 [22] 韩庆功, 崔艳红, 王元元, 等. 植物乳杆菌的生理特性及体外益生效果研究[J]. 粮食与饲料工业,2018(3):42−46. [HAN Q G, CUI Y H, WANG Y Y, et al. Physiological characteristics of Lactobacillus plantarum and its beneficial effects in vitro[J]. Cereal & Feed Industry,2018(3):42−46. [23] 汤水平, 朱泽瑞, 谢伟岸, 等. 腌制藠头发酵过程中乳酸菌的鉴定及生物学特性比较研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2008,29(5):128−130. [TANG S P, ZHU Z R, XIE W A, et al. Identification and biological characteristics of lactic acid bacteria from the natural fermentation of Allium bakei[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2008,29(5):128−130. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2008.05.031 [24] ZHANG Y, YANG J M, LIU Y, et al. A novel bacteriocin PE-ZYB1 produced by Pediococcus pentosaceus zy-B isolated from intestine of Mimachlamys nobilis: Purification, identification and its anti-listerial action[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2020,118(1):108760.
[25] KARYANTINA M, ANGGRAHINI S, UTAMI T, et al. Moderate halophilic lactic acid bacteria from Jambal roti: A traditional fermented fish of central Java, Indonesia[J]. Journal of Aquatic Food Product Technology,2020,29(1):1−11.
[26] SHEN Y, WU Y, WANG Y, et al. Contribution of autochthonous microbiota succession to flavor formation during Chinese fermented mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi)[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,348(2):129107.
[27] 吴燕燕, 王悦齐, 李来好, 等. 基于电子鼻与HS-SPME-GC-MS技术分析不同处理方式腌干带鱼挥发性风味成分[J]. 水产学报,2016,40(12):1931−1940. [WU Y Y, WANG Y Q, LI L H, et al. Analysis of volatile components in various cured hairtail by electronic nose and HS-SPME-GC-MS[J]. Journal of Fisheries of China,2016,40(12):1931−1940. [28] 庞一扬, 余远江, 袁桃静, 等. 腌鱼腌制过程中挥发性成分的变化分析[J]. 现代食品科技,2020,36(8):281−289. [PANG Y Y, YU Y J, YUAN T J, et al. Analysis of volatile compounds changes of cured fish during the curing process[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2020,36(8):281−289. doi: 10.13982/j.mfst.1673-9078.2020.8.0119





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



