Effect of Electron Beam Irradiation Sterilization on Volatile Components of Zhaotong Soybean Paste
-
摘要: 为探究辐照灭菌对昭通酱的可行性,本文考察了不同剂量电子束辐照对昭通酱感官评分、微生物含量及挥发性成分变化的影响。结果表明,当电子束辐照剂量为3.68 kGy时,昭通酱感官综合评价较好,菌落总数、真菌、大肠菌群含量均达到卫生标准,昭通酱辐照前共鉴定出41种挥发性成分,辐照后共检出100种挥发性成分,辐照后挥发性成分主要由32种酯类、4种醛类、26种烯烃类、15种醇类、11种酮类、1种醚类、2种酚类和9种其它类物质组成。其中辐照剂量对醇类、酯类、醛类及其它类挥发性物质影响较大,辐照后酯类物质种类和含量增加明显,醛类和烯烃类物质含量下降。昭通酱辐照前挥发性成分主要有异丁醇、芳樟醇、4,7-二甲基十一烷和亚油酸甲酯,分别占总含量的36.90%、20.29%、11.70%和4.94%。辐照后昭通酱中挥发性成分主要有芳樟醇、亚油酸甲酯、苯甲酸乙酯、川芎嗪。辐照后异丁醇相对含量降低明显,而芳樟醇上升明显。根据结果可以得出3.68 kGy属昭通酱辐照灭菌的可靠剂量,其结果为昭通酱向高原地方特色产品的推广提供了参考信息。Abstract: This paper examined the effects of different doses of electron beam irradiation on the sensory evaluation, microbial content and changes in volatile components of Zhaotong soybean paste, aiming to investigate the feasibility of irradiation sterilization for Zhaotong soybean paste. According to the results, when the electron beam irradiation dose was 3.68 kGy, the comprehensive sensory evaluation of Zhaotong soybean paste was good, and the total number of bacteria, fungi and coliform contents met the health standards. A total of 41 volatile components were identified in Zhaotong soybean paste before irradiation and 100 volatile components were detected after irradiation. The volatile components after irradiation mainly consisted of 32 esters, 4 aldehydes, 26 alkenoids, 15 alcohols, 11 ketones, 1 ether, 2 phenols and 9 other substances. Among them, the irradiation dose had greater effects on alcohols, esters, aldehydes and other types of volatile substances. The types and contents of esters increased significantly after irradiation, while the contents of aldehydes and alkylenes decreased. The volatile components of Zhaotong soybean paste before irradiation were mainly isobutanol, linalool, 4,7-dimethyl undecane and methyl linoleate, accounting for 36.90%, 20.29%, 11.70% and 4.94% of the total content, respectively. On the other hand, the volatile components in irradiated Zhaotong paste were dominantly linalool, methyl linoleate, ethyl benzoate and Ligustrazine. The relative contents of isobutanol decreased significantly after irradiation while linalool remarkably increased. Based on the results, it could be concluded that 3.68 kGy was a reliable dose for the irradiation sterilization of Zhaotong soybean paste, and the results would provide reference information for the promotion of Zhaotong soybean paste to the highland local specialties.
-
昭通大豆酱(以下简称昭通酱)与传统豆酱的区别在于其主料—黄豆是经过高温炒熟制成,辅料主要有辣椒、花椒、香辛料和白酒等。昭通酱需经历两次发酵,第一次发酵主要是用炒熟的黄豆在自然条件下进行发酵,第二次发酵是在一次发酵的基础上经过刷霉、粉碎、加料、晒酱等步骤制得,因工序繁杂,传统上需加工半年才能制成[1]。昭通酱作为昭通当地传统高原特色产品,其成品色泽鲜红,口感协调,料液均匀,体态稀稠,具有豆酱固有香味及滋味[2]。由于昭通酱的制作过程与其它地区豆酱制作相似,是开放式“自然发酵”过程,其菌群复杂,如保藏不当容易污染杂菌[3-5]。
Han等[6]在豆制品加工过程中检出金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌和蜡样芽孢杆菌等致病菌。罗信旭等[7]发现自然发酵的豆豉容易被蜡样芽抱杆菌污染。白凤岚等[8]通过基因测序等技术从多份发酵食品中分离得到16株蜡样芽抱杆菌携带毒力基因,而且这些毒力基因的存在可能会增加蜡样芽抱杆菌的溶血风险。近年来由于豆酱保藏过程中造成中毒事件也越发频繁,因此,对豆酱进行灭菌处理,为消费者提供安全食用保障很有必要。目前大多数豆酱由于其高盐的特性很少进行灭菌处理,但豆酱作为豆制品,含有高蛋白和丰富的不饱和脂肪酸的特点[3],高温强热(蒸煮)会使得蛋白质过度变性,脂肪发生氧化,并且产生不愉快的高温蒸煮味,使产品杀菌后风味品质下降,严重影响消费者的购买欲[9]。
辐照灭菌又叫做“冷杀菌”,是一种高效非热加工技术[10],该技术有杀菌时间短,能耗低,不产生核废料污染环境,以及无需高温处理,最大限度保留了食品原有的风味品质等优点,近年来得到广泛的关注[11-14]。世界卫生组织(WHO)、国际原子能机构(IAEA)和联合国粮农组织(FAO)已经认可辐照技术应用于食品中的安全性[15-16]。辐照灭菌的原理是放射性同位素比如60Co和137Cs,所产生的γ射线或者利用电子加速器产生的超能电子束作用于样品,使得样品中微生物发生几乎不可逆的物理、化学及生物学反应,而导致微生物失去活性甚至死亡的过程[17]。60Co和137Cs因其射线有穿透能力强和可靠性高的优点最先应用于食品加工行业,但也存在核安全问题以及利用率低的缺点[18];而电子加速器灭菌过程不需要辐射源,电子束的产生和消逝可控性强,能量利用率高且成本较低的优势,正好弥补了放射性同位素辐照灭菌的不足,是一种理想辐照灭菌技术[19]。目前暂未发现采用电子束对豆酱进行灭菌的报道,因此本文基于电子束灭菌的优势以及在前期的研究基础上[1-2,20],采用顶空固相微萃取/气相色谱-质谱法(HS-SPME /GC-MS)探究了昭通酱电子束辐照过程中的挥发性物质的变化,以期为昭通酱的发展、创新以及更好地工业化生产提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
昭通酱 实验室自制,原料来自当地沃尔玛超市(具体操作步骤参照作者前期工作[1]执行);重铬酸银和重铬酸钾银剂量计 湖南省核农学与航天育种研究所提供。
6890-MS 5973N型气相色谱-质谱联用仪 美国Agilent公司;固相微萃取装置及50/30 μm Carboxen/SPM萃取头、色谱柱:HP-88石英毛细管柱(100 m×0.25 mm,0.20 μm) J&W Scientific, Incorporated公司(美国)。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 昭通酱辐照处理
昭通酱选用避光纸质材料(内层为锡箔材料)进行密封包装,分装成每袋250 g。样品准备完成后,立即进行辐照处理。
电子束辐照采用清华同方威视IS1020电子加速器在湖南湘华华大生物科技有限公司进行,功率15 kW,电子束能量10 MeV。将样品平铺于托盘上,对电子加速器功率进行设置,使其剂量率约1 kGy/s,样品随着环状传送带进入辐照区,通过辐照区域即为一个周期或者一圈,通过调节传送带的速度控制辐照时间从而控制样品所接收的辐照剂量。每一周期的平均辐照剂量约2.0 kGy,样品每完成1个周期的辐照后即取出相应的样品,并手动将其余样品换面继续辐照(辐照1个周期即2 kGy,辐照2个周期即4 kGy,以此类推)。辐照过程用重铬酸钾银剂量计进行剂量跟踪,重铬酸钾银剂量计经中国计量科学研究院国家剂量保证服务(NDAS)比对标定,样品分别于表面和底面的中心以及4个边角处跟踪剂量计,所有剂量计的平均值为平均剂量。剂量设计参考前期研究内容[20-21],分别为F-1 (0 kGy)、F-2 (2.00 kGy)、F-3 (6.00 kGy)、F-4 (8.00 kGy)、F-5 (10.00 kGy)、F-6 (12.00 kGy) ,电子束辐照实测剂量分别为F-1 (0 kGy)、F-2 (2.01 kGy)、F-3 (3.68 kGy)、F-4 (5.80 kGy)、F-5 (8.15 kGy)、F-6 (9.80 kGy)。以上每个剂量设6个平行。样品辐照后均贮藏于4 ℃冰箱中待检测,所有样品检测重复3次。
1.2.2 感官评定方法
参考黄豆酱(酿造豆酱)的执行标准GB/T 24399-2009《食品安全国家标准 黄豆酱》稍作修改执行[22]:通过选取酱中主要挥发性物质种类和相对含量最多的时期对其色、香、味和体态进行感官评价,选取20名有经验的感官品评人员,对色泽、香气、口感、体态各占25分,满分100分,具体评分标准及分值范围见表1。
表 1 昭通酱感官评分标准Table 1. Sensory evaluation standard of Zhaotong soybean paste感官指标 感官评分(分) 21~25 16~20 10~15 色泽 酱体红棕色,色泽均匀 酱体棕色,色泽不均匀 浅棕色,色泽不协调 香气 酱香或酯香浓郁,留香时间长,无异香 酱香或酯香稍淡,留香时间一般,稍有异味 酱香或酯香很淡,留香时间较差,异香浓 口感 鲜甜味适中,无苦涩味,口感协调 鲜甜味稍弱、略有哈喇味, 轻微不协调 鲜甜味弱,有哈喇味,不协调 体态
稀稠无变化,无结块,无汁液析出稍变稀或变稠,有结块或者有汁
液析出酱呈浅棕色,色泽不均匀,酱香酯香很淡,
变稀或变稠,结块严重或者汁液析出严重1.2.3 微生物测定
菌落总数:参照GB 4789.2-2016 《食品安全国家标准 食品微生物学检验 菌落总数测定》执行[23];霉菌:参照GB 4789.15-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品微生物学检验 霉菌和酵母计数》执行[24];大肠菌群:参照GB 4789.3-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品微生物学检验 大肠菌群计数》执行[25]。
1.2.4 挥发性成分的测定
参考蒋立文等[26]方法稍作修改,采用HS-SPME方法萃取样品中挥发性化学物质,将灰色50/30 μm Carboxen /SPME 萃取头在GC进样口温度为240 ℃的条件下老化1 h,备用;将不同剂量辐照后的昭通酱样品进行研磨,分别取研磨后的酱样约4 g于25 mL顶空进样瓶中,用密封垫和盖帽进行密封;然后在70 ℃条件下平衡30 min,将已活化的萃取头穿过密封垫插入顶空进样瓶内后推出纤维头,露出纤维头距离样品液面约10~15 mm,顶空吸附40 min,插入GC进样口解析5 min。
气相色谱条件:HP-88石英毛细管柱(100 m×0.25 mm,0.20 μm);载气:高纯氦气(99.999%),流速1.0 mL·min−1;进样口温度:250 ℃;不分流进样。升温程序:柱温60 ℃,保持5 min,以3 ℃·min−1升至140 ℃,保持5 min,以5℃·min−1升至210 ℃,保持10 min,以5 ℃·min−1升至240 ℃,保持3 min。
质谱条件:离子源EI,温度200 ℃;发射电流150 μA;倍增器电压1037 V; 萃取头接口温度 220 ℃;电子能量70 eV; 质量扫描范围45~500 amu。
定性分析:采用 NIST2014 s 标准质谱库检索,相似度在80%以上作为有效峰面积进行分析处理,根据保留时间确定不同发酵阶段昭通酱样品挥发性成分,用峰面积归一化法进行相对含量分析。
1.3 数据处理
采用Excel软件、Origin2018、IBM SPSS statistics 26等软件进行数据处理。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 电子束辐照对感官指标的影响
根据电子束辐照剂量不同,对样品进行感官评分见表2,随着辐照剂量的增加,感官评分逐渐降低,其中辐照剂量在9.80 kGy时昭通酱感官综合总分最低,为60分,表明昭通酱在这个辐照剂量下品质不好,不容易被人接受;未辐照时昭通酱感官评分最高,为86分,当辐照剂量为3.68 kGy(F-3)时,昭通酱总体感官评分变化较小,超过该剂量时,酱体颜色开始变暗,并且有哈刺味产生,口感不协调,因此感官开始大幅度降低。辐照对色泽的影响较小,而对香气、口感和体态影响较大,当辐照剂量为3.68 kGy时,昭通酱的香气评分有所上升,随后随辐照剂量的增加而下降,可能因为低辐照剂量增加了香味物质的种类或者加强了香味物质的释放,而高剂量处理后的昭通酱明显有哈刺味产生,有可能由于辐照剂量的增加加速了油脂的氧化和酸败造成的[27-28]。昭通酱主要原料为大豆,而大豆属于高蛋白、油脂的食品,而且豆酱含水量一般较高,在电子束辐照过程中,食品中水会产生羟自由基,促进蛋白质和油脂发生氧化,导致食品产生哈刺味,或者辐照异味[29-31],也可能来源于蛋白质中含硫氨基酸氧化产生的硫化物[32]。根据前期研究数据[20],随着辐照剂量的增加,昭通酱中过氧化值上升明显,还原糖和蛋白质变化不显著,当剂量超过3.68 kGy时脂肪下降显著,因此综合考虑可得知3.68 kGy内辐照的昭通酱基本能够被人们所接受。
表 2 不同辐照剂量对昭通酱感官评分的影响Table 2. Sensory evaluation of Zhaotong soybean paste at different fermentation stages辐照剂量
(kGy)感官指标(分) 总分 色泽 香气 口感 体态 F-1
(0 )酱体红棕色,
色泽均匀(22)豆酱香气浓郁,无异香,
留香时间一般(18)鲜甜味适中,无苦涩味,
口感协调(22)稀稠无变化,无结块,无汁液析出(24) 86 F-2
(2.01)酱体红棕色,颜色较暗,
色泽均匀(21)豆酱香气浓郁,无异香,
留香时间长(19)鲜甜味适中,无苦涩味,
口感协调(22)稀稠无变化,表面局部较干,无汁液析出(23) 85 F-3
(3.68)酱体红棕色,颜色较暗,
色泽均匀(21)豆酱香气浓郁,无异香,
留香时间长(19)鲜甜味适中,无苦涩味,
口感协调一般(21)稀稠无变化,表面局部干,无汁液析出(23) 84 F-4
(5.80)酱体棕色,颜色较暗,
色泽均匀(20)豆酱香气一般,有哈刺味,
留香时间一般(17)鲜甜味适中,无苦涩味,
口感不协调(17)稀稠无变化,表面局部较干,有少许汁液析出(17) 71 F-5
(8.15)酱体棕色,颜色较暗,
色泽均匀(20)豆酱香气一般,哈刺味浓,
留香时间一般(16)鲜甜味一般,无苦涩味,
口感不协调(15)稍变稠,表面干,有少许汁液析出(15) 66 F-6
(9.80)酱体深棕色,颜色暗淡,
表面色泽不均匀(17)豆酱香气一般,哈刺味浓,
留香时间一般(16)鲜甜味一般,无苦涩味,
口感不协调,有异味(14)稍变稠,表面干,有较多汁液析出(13) 60 2.2 电子束辐照剂量对昭通酱微生物的影响
由表3可知,电子束辐照对昭通酱中菌落总数、真菌和大肠菌群负荷量的变化影响显著,随着辐照剂量的增加,样品中菌落总数、真菌含量和大肠杆菌含量下降明显,均呈显著负相关(P<0.05)。当剂量为2.01 kGy时,大肠菌群数量已无法检出;当辐照剂量3.68 kGy时真菌含量已低于最低检出值;而剂量达到8.15 kGy时,菌落负荷量下降至最低检出值以下,说明电子束辐照能有效抑制昭通酱中微生物的含量,延长货架期。根据辐照剂量与菌落总数对数值的线性变化,可得出其回归方程为y=−0.9263 x+6.5698(R²=0.9987),由此可计算出D10值为1.16 kGy,表明1.16 kGy的电子加速器辐照剂量可以使昭通酱中90%的细菌被杀死。当辐照剂量为3.68 kGy时,昭通酱中菌落总数为未辐照时的0.03%,同时真菌数和大肠菌群数已低于最低检测限度。电子束辐照原理是电子通过真空管加速运动变成高能电子束照射在样品上,使得某些物质发生一定的物理、化学和生物学效应[33]。昭通酱又属于高水分食品,水受到高能辐射后会产生水化电子、羟自由基和氢原子自由基,这些物质都是高度活性进一步导致微生物衰亡,加强辐照灭菌的效果[34-35]。因此综合感官评分结果,昭通酱的辐照剂量不宜超过3.68 kGy。
表 3 电子束辐照剂量对昭通酱微生物的影响Table 3. Effect of electron beam irradiation on microbial diversity of Zhaotong soybean paste辐照剂量(kGy) 菌落总数(lg(CFU·g−1)) 真菌(lg(CFU·g−1)) 大肠菌群(lg(MPN·g−1)) F-1(0) 6.561±0.111a 4.715±0.132a 1.282±0.121a F-2(2.01) 4.783±0.115b 1.185±0.171b <1±0.000b F-3(3.68) 3.051±0.109c <1±0.000c <1±0.000b F-4(5.80) 1.241±0.121d <1±0.000c <1±0.000b F-5(8.15) <1±0.000e <1±0.000c <1±0.000b F-6(9.80) <1±0.000e <1±0.000c <1±0.000b 注:同列字母不同表示差异性显著(P<0.05)。 2.3 电子束辐照对昭通酱挥发性成分的影响
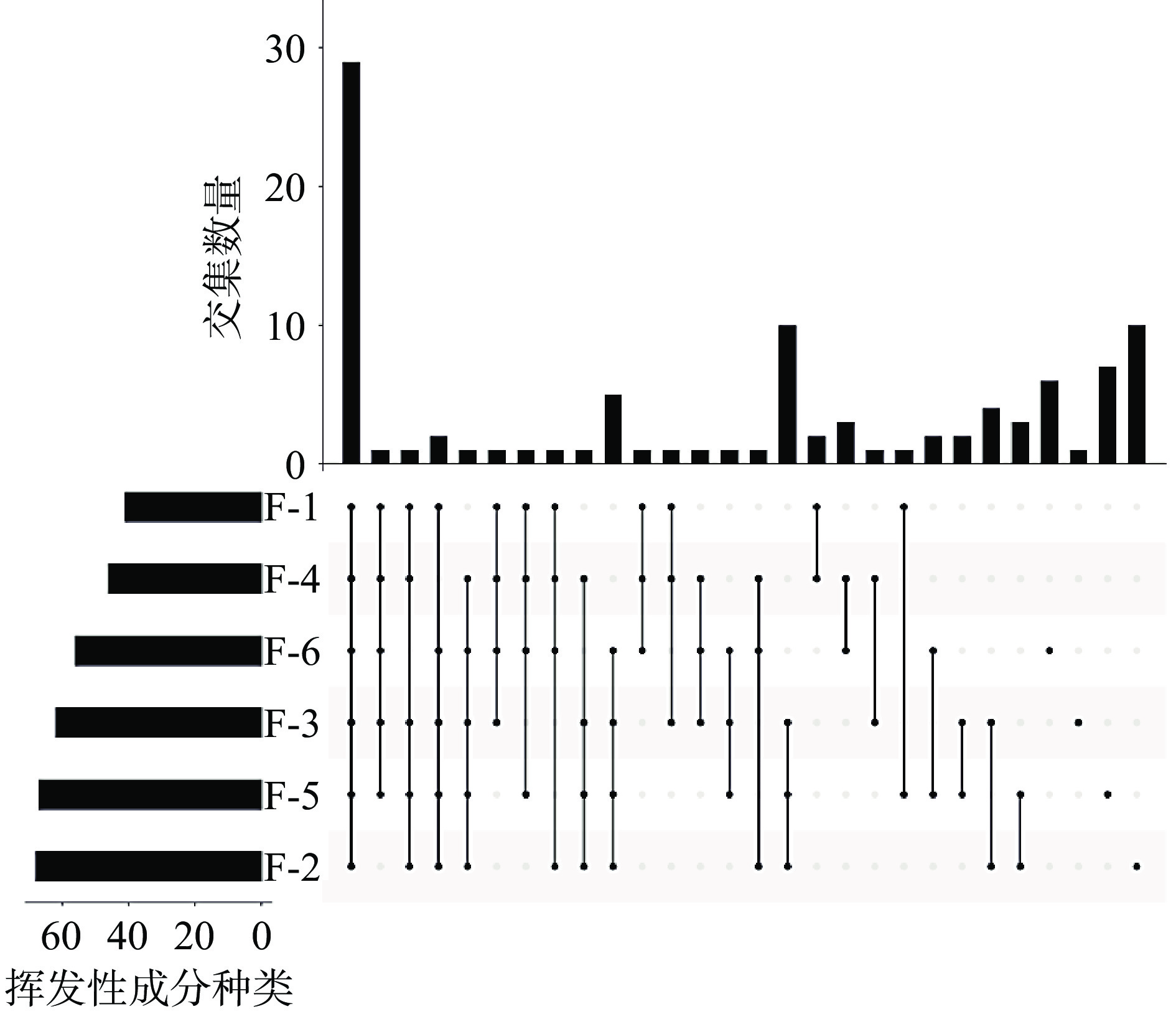
昭通酱经不同剂量电子束辐照处理后共鉴定出的挥发性化合物的种类及相对含量见表4。共检出100种挥发性成分,主要由32种酯类、4种醛类、26种烯烃类、15种醇类、11种酮类、1种醚类、2种酚类和9种其它类物质组成。F-2样品中挥发性物质种类最多有78种,随着辐照剂量的增加,挥发性物质的种类有先增加后减少的趋势。辐照前挥发性成分主要由异丁醇、芳樟醇、α-松油醇、4,7-二甲基十一烷、亚油酸甲酯、棕榈酸甲酯组成,其中,芳樟醇有铃兰花香,α-松油醇呈丁香香味。辐照后主要由芳樟醇、苯甲酸乙酯、棕榈酸乙酯、石竹烯、茴香脑和川芎嗪组成,其中苯甲酸乙酯呈冬青油香气,茴香脑呈甜味和具茴香的香气,石竹烯有淡的丁香似香味,棕榈酸乙酯带有蜡香、果爵奶油香气,这些物质丰富了辐照后昭通酱的风味。从图1可知,左侧柱状图代表各样本挥发性成分种类数,上侧柱状图以及下侧的点线代表各组昭通酱之间挥发性物质的交集情况(即相同的挥发性物质种类数量),下侧实心点的连线表示样品与样品之间共同挥发性物质的种类数,无连线表示该样品独有的挥发性成分种类数,如第一列结果显示,昭通酱辐照组(F-2、F-3、F-4、F-5、F-6)与未辐照组(F-1)相比,经过辐照处理后仍保留有29种相同的挥发性组分,其中不同辐照剂量的样品中挥发性成分种类交集数量较少,说明了昭通酱辐照后挥发性物质变化的无序性。但随着剂量的增加,也有许多挥发性物质的相对含量均有所改变,结合表2感官评分结果,当辐照剂量超过5.80 kGy时,昭通酱整体感官发生了明显的变化,结合F-2至F-6样品中特有的挥发性成分,由表4可知,辛酸乙酯、17-甲基硬脂酸甲酯、正己酸乙酯、油酸甲酯、亚油酸甲酯、乙酸香叶酯、十四酸甲酯、棕榈油酸甲酯、癸酸乙酯、桃金娘烯醛、佛术烯、桧烯、月桂烯、γ-松油烯、十六烷、1-甲基-5-亚甲基-1,6-环癸二烯、十四烷、十二烷、桉树醇、1-辛烯-3-醇、顺式-7-十四烯-1-醇、胡椒酮、环十二酮(6Cl,7Cl,8Cl,9Cl)、β-酯罗酮、3,5-二乙基-2-甲基-吡嗪等物质基本构成了辐照后昭通特殊的气味物质。
表 4 昭通酱电子束辐照灭菌过程中挥发性成分组成及相对含量Table 4. Composition and content of volatile components in the process of electron beam irradiation sterilization of Zhaotong soybean pasteCAS 化合物分子式 中文名称 挥发性成分相对含量(%) 风味特征* F-1 F-2 F-3 F-4 F-5 F-6 酯类 544-35-4 C20H36O2 亚油酸乙酯 0.43 13.40 10.70 3.87 8.99 5.13 DNC 1191-41-9 C20H34O2 亚麻酸乙酯 0.25 1.16 0.94 0.27 0.87 0.32 DNC 6114-18-7 C20H38O2 反油酸乙酯 0.35 2.88 2.25 0.87 1.90 1.32 花香、果香油脂气 93-89-0 C9H10O2 苯甲酸乙酯 0.39 4.05 4.55 4.78 4.90 5.16 冬青油和依兰油气 106-33-2 C14H28O2 月桂酸乙酯 0.25 1.05 0.96 0.76 0.86 0.69 果香气味 119-36-8 C8H8O3 水杨酸甲酯 0.58 0.24 0.31 0.30 0.27 0.36 冬青叶香味 101-97-3 C10H12O2 苯乙酸乙酯 1.13 0.21 0.24 0.31 0.28 0.20 蜂蜜香气 124-06-1 C16H32O2 十四酸乙酯 0.67 1.03 1.01 0.49 0.79 0.67 椰子、鸢尾和蜂蜡似香气 112-39-0 C17H34O2 棕榈酸甲酯 3.38 0.24 0.27 0.15 0.15 0.16 DNC 628-97-7 C18H36O2 棕榈酸乙酯 0.56 5.26 4.38 2.72 3.39 3.35 蜡香、果爵奶油香气 54546-22-4 C18H34O2 9-十六碳烯酸乙酯 0.22 1.13 1.01 0.15 0.78 0.57 DNC 115-95-7 C12H20O2 乙酸芳樟酯 0.25 0.98 0.94 0.38 0.96 0.65 清香带甜香气 93-58-3 C8H8O2 苯甲酸甲酯 0.42 − − 0.93 0.34 0.85 花香和樱桃香味 2462-85-3 C19H34O2 亚油酸甲酯 4.94 − − 0.24 − 0.43 DNC 111-61-5 C20H40O2 硬脂酸乙酯 1.24 − − 0.08 − − 蜡香 106-32-1 C10H20O2 辛酸乙酯 − 0.19 0.05 − 0.15 0.29 菠萝的香味,甜味 55124-97-5 C20H40O2 17-甲基硬脂酸甲酯 − 0.27 0.16 − 0.13 0.11 DNC 123-66-0 C8H16O2 正己酸乙酯 − 0.12 0.10 − 0.19 − 水果香气味 112-62-9 C19H36O2 油酸甲酯 − 0.14 0.2 − 0.09 − DNC 112-63-0 C19H34O2 亚油酸甲酯 − 0.73 0.62 − 0.50 − DNC 105-87-3 C12H20O2 乙酸香叶酯 − 0.21 0.09 − − − 玫瑰油与薰衣草油香气 124-10-7 C15H30O2 十四酸甲酯 − 0.08 0.12 − − − DNC 1120-25-8 C17H32O2 棕榈油酸甲酯 − 0.13 0.12 − − − DNC 105-68-0 C8H16O2 丙酸异戊酯 − 0.54 − − − − 清甜果香气息 111-82-0 C13H26O2 月桂酸甲酯 − 0.06 − − − − 类似酒香及花香 614-18-6 C8H9NO2 烟酸乙酯 − 0.19 − − − − DNC 111-62-6 C20H38O2 油酸乙酯 − 0.18 − − − − 呈鲜花香气 110-38-3 C12H24O2 癸酸乙酯 − − 0.16 − 0.39 0.31 有椰子香味 56219-09-1 C17H32O2 9-十五烯酸乙酯 − − 0.14 − − − DNC 77-83-8 C12H14O3 3-甲基-3-苯基缩水甘油酸乙酯 − − − 0.09 − 0.10 强烈草莓水果香气 1215128-19-0 C16H30O2 6-壬烯酸8-甲基己基酯 − − − − 0.13 − DNC 25265-77-4 C12H24O3 十二碳醇酯 − − − − − 0.06 DNC 酯类合计 15.12 34.44 29.29 16.30 26.03 20.76 醛类 100-52-7 C7H6O 苯甲醛 1.27 0.14 0.17 0.28 0.15 0.37 特殊的杏仁气味 564-94-3 C10H14O (-)-桃金娘烯醛(香桃木醛) 0.66 − 0.16 0.19 − 0.13 DNC 6502-22-3 C10H12O 2-异丙基苯甲醛 0.36 0.17 0.15 − 0.13 0.20 DNC 18486-69-6 C10H14O 桃金娘烯醛 − 0.15 − − 0.17 − DNC 醛类合计 2.29 0.46 0.48 0.47 0.45 0.70 烯烃类 5989-27-5 C10H16 d-柠檬烯 0.34 0.49 0.44 0.33 0.78 0.27 橙子香气,樟脑和萜气 3338-55-4 C10H16 罗勒烯 异构体混合物 0.17 − 0.01 0.30 0.06 0.26 DNC 629-62-9 C15H32 十五烷 0.48 0.59 0.54 0.30 0.61 0.85 DNC 87-44-5 C15H24 石竹烯 0.41 4.16 4.28 1.72 3.34 2.63 淡的丁香似香味 25246-27-9 C15H24 香树烯 1.07 1.09 0.10 − 1.21 0.65 DNC 68832-35-9 C15H24 4,11,11-三甲基-8-亚甲基-,(1R,4E,9R)-
双环十一碳-4-烯,0.69 − 1.07 0.48 − − DNC 17301-32-5 C13H28 4,7-二甲基十一烷 11.7 − − 0.01 − − DNC 6753-98-6 C15H24 α-石竹烯 − 0.91 0.90 0.47 0.80 − DNC 10219-75-7 C15H24 佛术烯 − 0.14 0.64 − 0.70 0.56 DNC 3387-41-5 C10H16 桧烯 − 0.16 0.33 − 0.28 − DNC 123-35-3 C10H16 月桂烯 − 0.16 0.29 − 0.18 − 甜橘味和香脂气 99-85-4 C10H16 γ-松油烯 − 0.12 0.16 − 0.18 − 柑橘和柠檬香气 544-76-3 C16H34 十六烷 − 0.32 0.29 − 0.11 − DNC 23986-74-5 C15H24 1-甲基-5-亚甲基-1,6-环癸二烯 − 1.35 1.33 − 0.85 − DNC 3856-25-5 C15H24 α-蒎烯 − 0.08 − − − − DNC 629-73-2 C16H32 1-十六烯 − 0.10 − − − − DNC 13877-91-3 C10H16 罗勒烯 − 0.10 − − − − DNC 630-02-4 C28H58 正二十八烷 − 0.25 − − − − DNC 629-59-4 C14H30 十四烷 − − 0.17 0.21 − − DNC 112-40-3 C12H26 十二烷 − − − 0.19 − 0.15 DNC 55333-99-8 C26H54 7-己基环烷 − − − − 0.19 0.19 DNC 629-50-5 C13H28 正十三烷 − − − − 0.11 − DNC 35365-59-4 C18H34 9-十八炔 − − − − 0.12 − DNC 34303-81-6 C16H32 (Z) -3-十六烯 − − − − 0.10 − DNC 3779-61-1 C10H16 (E)-Β-罗勒烯 − − − − − 0.27 DNC 2437-56-1 C13H26 1-十三烯 − − − − − 0.10 DNC 烯烃类合计 14.86 10.02 10.55 4.01 9.62 5.93 醇类 123-51-3 C5H12O 异戊醇 0.27 0.41 0.23 0.41 0.24 0.26 苹果白兰地香气和辛辣味 78-83-1 C10H18O2 异丁醇 36.90 0.34 0.73 0.76 0.31 0.53 DNC 78-70-6 C10H18O 芳樟醇 20.29 41.10 46.80 60.60 48.40 54.70 花香,似铃兰香气 98-55-5 C10H18O α-松油醇 4.56 0.60 0.43 0.64 0.56 − 特有的丁香香气 100-51-6 C7H8O 苯甲醇 0.61 0.26 0.20 0.45 0.29 0.36 微弱芳香气味 60-12-8 C8H10O 苯乙醇 0.21 0.34 0.35 0.72 0.39 0.46 玫瑰花样香气 20126-76-5 C10H18O (-)-萜烯-4-醇 0.54 0.92 − 1.29 − 1.24 DNC 470-82-6 C10H18O 桉树醇 − 0.23 0.21 − 0.37 − 樟脑气息和草药味道 3391-86-4 C8H16O 1-辛烯-3-醇 − 0.18 0.22 − − − DNC 68797-95-5 C15H30O 6-戊癸烯-1-醇(6Z) − 0.08 − − − − DNC 40642-43-1 C14H28O 顺式-7-十四烯-1-醇 − − 0.11 0.15 − 0.12 DNC 562-74-3 C10H18O 4-萜烯醇 − − 0.90 − 1.09 − 胡椒香、泥土香和木材气息 106-24-1 C10H18O 香叶醇 − − − − 0.35 0.12 玫瑰花气息,味有苦感 51276-34-7 C10H18O2 2,6-二甲基-3,7-辛二烯-2,6-二醇 − − − − 0.16 − DNC 7785-53-7 C10H18O (R)-α,α-4-三甲基-3-环己烯-1-甲醇 − − − − − 0.70 DNC 醇类合计 63.38 44.46 50.18 65.02 52.16 58.49 醚类 91-16-7 C8H10O2 邻苯二甲醚 0.30 0.37 0.48 0.59 0.40 0.56 DNC 酮类 546-80-5 C10H16O (-)-α-侧柏酮 1.37 0.22 0.38 0.21 0.27 0.13 DNC 1125-21-9 C9H12O2 茶香酮 0.14 0.07 0.11 0.29 0.15 0.12 DNC 89-81-6 C10H16O 胡椒酮 − 0.07 0.09 − 0.25 0.17 DNC 2550-52-9 C16H30O 环十二酮(6Cl,7Cl,8Cl,9Cl) − 0.17 0.18 − 0.18 − DNC 79-77-6 C13H20O β-酯罗酮 − 0.27 − − 0.13 − 紫罗兰香味 4780-14-7 C7H8O3 3-甲氧基-2-甲基-4H-吡喃-4-酮 − 0.16 − − 0.12 − DNC 3796-70-1 C13H22O 香叶基丙酮 − − 0.10 − 0.08 − DNC 471-15-8 C10H16O 側柏酮 − − − 0.35 − 0.23 DNC 590-90-9 C4H8O2 4-烃基-2-丁酮 − − − − 0.33 − DNC 65649-04-9 C10H14O 六氢-,6-甲氨基-3ah-茚-4(1H)-酮 − − − − 0.26 − DNC 689-67-8 C13H22O 香叶基丙酮 − − − − − 0.10 DNC 酮类合计 1.51 0.96 0.86 0.85 1.77 0.75 酚类 90-05-1 C7H8O2 愈创木酚 0.59 0.07 0.09 0.06 0.09 0.15 特殊芳香气味 96-76-4 C14H22O 2,4-二叔丁基苯酚 − 0.11 0.20 0.18 0.36 0.25 DNC 酚类合计 0.59 0.18 0.29 0.24 0.45 0.40 其它类 14667-55-1 C7H10N2 2,3,5-三甲基吡嗪 0.26 0.26 0.17 0.50 0.24 0.40 DNC 104-46-1 C10H12O 茴香脑 0.49 2.02 1.95 1.07 1.88 1.98 甜味,具茴香的香气 634-36-6 C9H12O3 1,2,3-三甲氧基苯 0.18 0.41 0.33 0.22 0.33 0.30 DNC 1124-11-4 C8H12N2 川芎嗪 0.80 5.89 5.12 10.60 6.26 9.11 牛肉、猪脂香气和发酵大豆味 13925-07-0 C8H12N2 2-乙烷基-3,5-二甲基吡嗪 0.22 − − − 0.23 − 威士忌酒和炒花生似香气 473-13-2 C15H24 八氢-4,8-二甲基(1-甲基乙烯基)-萘 − 0.14 0.30 − 0.18 0.20 DNC 17398-16-2 C9H14N2 3,5-二乙基-2-甲基-吡嗪 − 0.12 − 0.13 − 0.13 DNC 39029-41-9 C15H24 八氢-7-甲基-4-亚甲基-1-(1-甲基乙基)-萘 − 0.27 − − − − DNC 13360-65-1 C8H12N2 3-乙基-2,5-甲基吡嗪 − − − − − 0.29 DNC 其它类合计 1.95 9.11 7.87 12.52 9.12 12.41 注:−表示未检出;DNC表示未确定;* 风味特征描述来源于http://www.perflavory.com;https://www.chemicalbook.com。 2.3.1 酯类组分变化
根据表4可知,昭通酱经辐照后酯类物质总含量有所上升。传统发酵的昭通酱,酯类化合物能赋予其悦人的果香、甜香[36-37]。由表4可知,昭通酱主要的挥发性成分是酯类物质,其种类最丰富,有34种,未辐照的昭通酱中检测出14种,通过辐照后酯类的种类增加了20种,在F-2 (2.01 kGy)时酯类总含量最大,达34.44%。亚油酸乙酯、亚麻酸乙酯、反油酸乙酯、月桂酸乙酯、十四酸乙酯、9-十六碳烯酸乙酯和棕榈酸乙酯的相对含量随辐照剂量的增加先增大后减少,苯甲酸乙酯的含量随辐照剂量的增加而增大,从0.39%增大到5.16%,水杨酸乙酯和苯乙酸乙酯随辐照剂量的增加而降低。其中辛酸乙酯、17-甲基硬脂酸甲酯、正己酸乙酯、油酸甲酯、亚油酸甲酯、乙酸香叶酯、十四酸甲酯、棕榈油酸甲酯、丙酸异戊酯、月桂酸甲酯、烟酸乙酯、油酸乙酯在未辐照前均未被检出。据前人报道,酯类的增加说明样品中形成该物质的底物(醇类和有机酸)有所增加,而这些底物的增加除了样品本身所含有之外,还有可能来自蛋白质和脂肪的分解,特别是脂肪氧化后会产生系列的醇类物质和游离的脂肪酸[38]。
2.3.2 醛类组分变化
昭通酱经辐照后醛类物质总含量有所下降。由表4可知,传统发酵的昭通酱,检出了苯甲醛、(-)-桃金娘烯醛(香桃木醛)、2-异丙基苯甲醛,其相对含量相近分别为1.27%、0.66%、0.36%,桃金娘烯醛是经辐照后才被检出,其相对含量在0.15%~0.17%之间。醛类物质辐照前总相对含量为2.29%,经辐照后变化较敏感,最终在0.45%~0.70%之间,此结果与吕梁玉等[39]研究辐照对带鱼鱼糜醛类成分的影响结果基本一致。昭通酱产生醛类物质的途径有很多,如酵母代谢产生饱和醛[40-41],Strecker反应降解产生醛[42]等,比如苯丙氨酸的降解产物就有苯甲醛[43]。出现此结果原因可能有两点,参照前期研究结果[20]发现昭通酱在辐照过程中苯丙氨酸的含量变化并不显著,其次辐照本身就有降解醛类物质的作用[44]。
2.3.3 烯烃类组分变化
根据表4可知,昭通酱经辐照后烯烃类物质总含量下降。昭通酱中被检出的烯烃类化合物含量相对较少,但检出的烯烃类化合物种类相对较多,有26种烯烃类。辐照前烯烃类物质只有7种且含量较低,分别为d-柠檬烯、罗勒烯(异构体混合物)、十五烷、石竹烯、香树烯,4,11,11-三甲基-8-亚甲基-,(1R,4E,9R)-双环十一碳-4-烯、4,7-二甲基十一烷,其中石竹烯含量随着辐照剂量的增加上升明显。经过辐照后产生了15种新的烯烃类,但总含量随着辐照剂量的增加呈下降趋势,说明辐照后随烯烃类种类增多了,但相对含量却呈降低趋势。出现该结果主要原因有可能是脂肪酸烷基自由基的断裂的结果[39]。
2.3.4 醇类组分变化
醇类化合物能赋予大豆酱宜人的特殊香气。由表4可知,醇类物质总含量经辐照后变化不大。辐照前昭通酱中主要醇类物质有异丁醇、芳樟醇和α-松油醇,分别占36.90%、20.29%和4.56%,其中异丁醇经过辐照后其相对含量降低明显,辐照不足1%,说明该物质对电子束辐照极其敏感,无论辐照剂量大小,下降幅度都很大,出现此结果的原因目前尚未清楚。芳樟醇辐照前相对含量为20.29%,经辐照后其相对含量增加至41.10%~60.60%。桉树醇、1-辛烯-3-醇、顺式-7-十四烯-1-醇、4-萜烯醇、香叶醇、2,6-二甲基-3,7-辛二烯-2,6-二醇、(R)-α,α-4-三甲基-3-环己烯-1-甲醇,在辐照前未被检出,辐照后有检出,其中F-4检出量较大。醇类物质种类增多大多数原因可能是由脂质氧化分解[39],也有可能是经辐照后使得某些以糖苷健结合的含羟基类物质释放,以及氨基酸的去氨基和去羧基反应的原因[45]。
2.3.5 醚类组分变化
由表4可知,昭通酱中被检出的醚类化合物含量和种类较少,只有一种邻苯二甲醚,其未辐照前相对含量为0.30%,辐照剂量继续加大,但邻苯二甲醚的含量并未有明显的变化。说明可能邻苯二甲醚对辐照不敏感。
2.3.6 酮类和酚类组分变化
昭通酱中被检出的酚类和酮类化合物种类和含量相对较少。其中,酚类物质共检出2种。具有芳香气味的愈创木酚在辐照前后均被检出,辐照前相对含量为0.59%,但随着辐照剂量的增加,愈创木酚的含量减少;2,4-二叔丁基苯酚只有经辐照后才被检出且受辐照剂量的影响不大。酮类物质共检出10种,其中(-)-α-侧柏酮、茶香酮均被检出,(-)-α-侧柏酮在辐照前相对含量为1.37%,经辐照后该物质的含量大幅度减少,最低时只有0.13%,但在F-2 (2.01 kGy)至F-6 (9.80 kGy)的辐照剂量内对其含量影响不大。由表4可知,酮类物质的总含量在F-5 (8.15 kGy)时其相对含量达到1.51%,与未被辐照前含量一样,但种类却增加了8种,有可能脂类氧化促进了酮类物质的形成[39]。
2.3.7 其它组分变化
由表4可知,昭通酱经辐照后其它类挥发性物质总含量有所下降。在所有的样品中均检测出2,3,5-三甲基吡嗪、茴香脑、1,2,3-三甲氧基苯、川芎嗪,其中川芎嗪受辐照剂量影响最大,在未辐照前相对含量为0.50%,经辐照后含量有所增加,在F-4 (5.80 kGy)的剂量下辐照其相对含量达到最大值为12.52%。其它成分在辐照前未被检出且含量相对较低。吡嗪类一般呈特色类似香料、香精的香味[46],随着辐照剂量的增大,茴香脑和川芎嗪的含量上升明显,茴香脑由辐照前0.49%最高上升至1.98%,川芎嗪由0.80%最高上升到10.60%。辐照前的昭通酱吡嗪类物质的相对含量为0.46%,经辐照后其相对含量为0.69%,总体变化不大。
2.4 辐照后昭通酱挥发性成分的PCA及相关性分析
食品中各类挥发性风味物质有着非常关键的联系[47],Wang等[48]优化增味挥发性成分进行了提取,并对46种挥发性化合物进行了鉴定,结果表明大多数挥发性化合物的强度,特别是醛类和酯类,与增味感官呈正相关。辐照对昭通酱挥发性风味差异和组间样本差异如图2(左)所示,采用PCA多元变量统计分析,可知各组昭通酱的特征变量99.07%的累计差异被描述,包含86.11%的PCA1和12.96%的PCA2。可明显看出辐照与非辐照的差异相当明显,5个辐照组之间的差异较小,说明辐照对昭通酱中挥发性成分的影响比较明显。各挥发性物质种类的相关性聚类情况如图2(右)所示,烯烃类与醚类呈极显著(P<0.01)负相关,醇类与酯类呈极显著(P<0.01)负相关性,另外其它类物质与烯烃类(P<0.01)、醛类(P<0.05)呈负相关性,而与酯类呈正相关性(P<0.05)。此结果与表4中各挥发性物质的变化基本相符。
3. 结论
随着电子束辐照剂量的增加,昭通酱中微生物载荷量呈显著下降趋势,当剂量为3.68 kGy时,细菌、真菌数和大肠菌群数已达到卫生标准。继续增大剂量,昭通酱的色泽、香味和口感均发生了不同程度的变化,甚至还会产生不愉快的气味和滋味,表明3.68 kGy电子束辐照剂量既能杀死昭通酱中大多数微生物,又能使得产品风味变化降到最小。昭通酱经辐照后挥发性成分种类显著增加,主要由酯类、烯烃类和醇类组成,其中酯类物质种类最丰富。研究结果发现辐照剂量对昭通酱中醇类、酯类及其它类挥发性物质影响较大,辐照促进了酯类挥发性物质的增多,但同时也增加了吡嗪类等特殊气味物质的含量。
豆酱在我国历史悠久,市面上不同豆酱都具有地方特色,但很多地方特色豆酱由于保藏期难以控制其品质,限制了销售范围。该研究分析表明辐照是昭通酱的可靠灭菌方法,虽通过PCA结果分析可知经过辐照后的昭通酱与未辐照的昭通酱无论感官、微生物含量以及挥发性成分之间均表现出一定得差异性,但只要控制好剂量,可以最大限度保留昭通酱原有的感官和风味,甚至低剂量辐照还能丰富昭通酱的风味成分。从研究结果中可看出辐照虽能解决昭通酱灭菌的目的,对改进地方豆酱规模化生产以及推广当地高原特色农产品具有重要意义,但辐照也会导致产品中新物质的增加,其安全性尚待评估。
-
表 1 昭通酱感官评分标准
Table 1 Sensory evaluation standard of Zhaotong soybean paste
感官指标 感官评分(分) 21~25 16~20 10~15 色泽 酱体红棕色,色泽均匀 酱体棕色,色泽不均匀 浅棕色,色泽不协调 香气 酱香或酯香浓郁,留香时间长,无异香 酱香或酯香稍淡,留香时间一般,稍有异味 酱香或酯香很淡,留香时间较差,异香浓 口感 鲜甜味适中,无苦涩味,口感协调 鲜甜味稍弱、略有哈喇味, 轻微不协调 鲜甜味弱,有哈喇味,不协调 体态
稀稠无变化,无结块,无汁液析出稍变稀或变稠,有结块或者有汁
液析出酱呈浅棕色,色泽不均匀,酱香酯香很淡,
变稀或变稠,结块严重或者汁液析出严重表 2 不同辐照剂量对昭通酱感官评分的影响
Table 2 Sensory evaluation of Zhaotong soybean paste at different fermentation stages
辐照剂量
(kGy)感官指标(分) 总分 色泽 香气 口感 体态 F-1
(0 )酱体红棕色,
色泽均匀(22)豆酱香气浓郁,无异香,
留香时间一般(18)鲜甜味适中,无苦涩味,
口感协调(22)稀稠无变化,无结块,无汁液析出(24) 86 F-2
(2.01)酱体红棕色,颜色较暗,
色泽均匀(21)豆酱香气浓郁,无异香,
留香时间长(19)鲜甜味适中,无苦涩味,
口感协调(22)稀稠无变化,表面局部较干,无汁液析出(23) 85 F-3
(3.68)酱体红棕色,颜色较暗,
色泽均匀(21)豆酱香气浓郁,无异香,
留香时间长(19)鲜甜味适中,无苦涩味,
口感协调一般(21)稀稠无变化,表面局部干,无汁液析出(23) 84 F-4
(5.80)酱体棕色,颜色较暗,
色泽均匀(20)豆酱香气一般,有哈刺味,
留香时间一般(17)鲜甜味适中,无苦涩味,
口感不协调(17)稀稠无变化,表面局部较干,有少许汁液析出(17) 71 F-5
(8.15)酱体棕色,颜色较暗,
色泽均匀(20)豆酱香气一般,哈刺味浓,
留香时间一般(16)鲜甜味一般,无苦涩味,
口感不协调(15)稍变稠,表面干,有少许汁液析出(15) 66 F-6
(9.80)酱体深棕色,颜色暗淡,
表面色泽不均匀(17)豆酱香气一般,哈刺味浓,
留香时间一般(16)鲜甜味一般,无苦涩味,
口感不协调,有异味(14)稍变稠,表面干,有较多汁液析出(13) 60 表 3 电子束辐照剂量对昭通酱微生物的影响
Table 3 Effect of electron beam irradiation on microbial diversity of Zhaotong soybean paste
辐照剂量(kGy) 菌落总数(lg(CFU·g−1)) 真菌(lg(CFU·g−1)) 大肠菌群(lg(MPN·g−1)) F-1(0) 6.561±0.111a 4.715±0.132a 1.282±0.121a F-2(2.01) 4.783±0.115b 1.185±0.171b <1±0.000b F-3(3.68) 3.051±0.109c <1±0.000c <1±0.000b F-4(5.80) 1.241±0.121d <1±0.000c <1±0.000b F-5(8.15) <1±0.000e <1±0.000c <1±0.000b F-6(9.80) <1±0.000e <1±0.000c <1±0.000b 注:同列字母不同表示差异性显著(P<0.05)。 表 4 昭通酱电子束辐照灭菌过程中挥发性成分组成及相对含量
Table 4 Composition and content of volatile components in the process of electron beam irradiation sterilization of Zhaotong soybean paste
CAS 化合物分子式 中文名称 挥发性成分相对含量(%) 风味特征* F-1 F-2 F-3 F-4 F-5 F-6 酯类 544-35-4 C20H36O2 亚油酸乙酯 0.43 13.40 10.70 3.87 8.99 5.13 DNC 1191-41-9 C20H34O2 亚麻酸乙酯 0.25 1.16 0.94 0.27 0.87 0.32 DNC 6114-18-7 C20H38O2 反油酸乙酯 0.35 2.88 2.25 0.87 1.90 1.32 花香、果香油脂气 93-89-0 C9H10O2 苯甲酸乙酯 0.39 4.05 4.55 4.78 4.90 5.16 冬青油和依兰油气 106-33-2 C14H28O2 月桂酸乙酯 0.25 1.05 0.96 0.76 0.86 0.69 果香气味 119-36-8 C8H8O3 水杨酸甲酯 0.58 0.24 0.31 0.30 0.27 0.36 冬青叶香味 101-97-3 C10H12O2 苯乙酸乙酯 1.13 0.21 0.24 0.31 0.28 0.20 蜂蜜香气 124-06-1 C16H32O2 十四酸乙酯 0.67 1.03 1.01 0.49 0.79 0.67 椰子、鸢尾和蜂蜡似香气 112-39-0 C17H34O2 棕榈酸甲酯 3.38 0.24 0.27 0.15 0.15 0.16 DNC 628-97-7 C18H36O2 棕榈酸乙酯 0.56 5.26 4.38 2.72 3.39 3.35 蜡香、果爵奶油香气 54546-22-4 C18H34O2 9-十六碳烯酸乙酯 0.22 1.13 1.01 0.15 0.78 0.57 DNC 115-95-7 C12H20O2 乙酸芳樟酯 0.25 0.98 0.94 0.38 0.96 0.65 清香带甜香气 93-58-3 C8H8O2 苯甲酸甲酯 0.42 − − 0.93 0.34 0.85 花香和樱桃香味 2462-85-3 C19H34O2 亚油酸甲酯 4.94 − − 0.24 − 0.43 DNC 111-61-5 C20H40O2 硬脂酸乙酯 1.24 − − 0.08 − − 蜡香 106-32-1 C10H20O2 辛酸乙酯 − 0.19 0.05 − 0.15 0.29 菠萝的香味,甜味 55124-97-5 C20H40O2 17-甲基硬脂酸甲酯 − 0.27 0.16 − 0.13 0.11 DNC 123-66-0 C8H16O2 正己酸乙酯 − 0.12 0.10 − 0.19 − 水果香气味 112-62-9 C19H36O2 油酸甲酯 − 0.14 0.2 − 0.09 − DNC 112-63-0 C19H34O2 亚油酸甲酯 − 0.73 0.62 − 0.50 − DNC 105-87-3 C12H20O2 乙酸香叶酯 − 0.21 0.09 − − − 玫瑰油与薰衣草油香气 124-10-7 C15H30O2 十四酸甲酯 − 0.08 0.12 − − − DNC 1120-25-8 C17H32O2 棕榈油酸甲酯 − 0.13 0.12 − − − DNC 105-68-0 C8H16O2 丙酸异戊酯 − 0.54 − − − − 清甜果香气息 111-82-0 C13H26O2 月桂酸甲酯 − 0.06 − − − − 类似酒香及花香 614-18-6 C8H9NO2 烟酸乙酯 − 0.19 − − − − DNC 111-62-6 C20H38O2 油酸乙酯 − 0.18 − − − − 呈鲜花香气 110-38-3 C12H24O2 癸酸乙酯 − − 0.16 − 0.39 0.31 有椰子香味 56219-09-1 C17H32O2 9-十五烯酸乙酯 − − 0.14 − − − DNC 77-83-8 C12H14O3 3-甲基-3-苯基缩水甘油酸乙酯 − − − 0.09 − 0.10 强烈草莓水果香气 1215128-19-0 C16H30O2 6-壬烯酸8-甲基己基酯 − − − − 0.13 − DNC 25265-77-4 C12H24O3 十二碳醇酯 − − − − − 0.06 DNC 酯类合计 15.12 34.44 29.29 16.30 26.03 20.76 醛类 100-52-7 C7H6O 苯甲醛 1.27 0.14 0.17 0.28 0.15 0.37 特殊的杏仁气味 564-94-3 C10H14O (-)-桃金娘烯醛(香桃木醛) 0.66 − 0.16 0.19 − 0.13 DNC 6502-22-3 C10H12O 2-异丙基苯甲醛 0.36 0.17 0.15 − 0.13 0.20 DNC 18486-69-6 C10H14O 桃金娘烯醛 − 0.15 − − 0.17 − DNC 醛类合计 2.29 0.46 0.48 0.47 0.45 0.70 烯烃类 5989-27-5 C10H16 d-柠檬烯 0.34 0.49 0.44 0.33 0.78 0.27 橙子香气,樟脑和萜气 3338-55-4 C10H16 罗勒烯 异构体混合物 0.17 − 0.01 0.30 0.06 0.26 DNC 629-62-9 C15H32 十五烷 0.48 0.59 0.54 0.30 0.61 0.85 DNC 87-44-5 C15H24 石竹烯 0.41 4.16 4.28 1.72 3.34 2.63 淡的丁香似香味 25246-27-9 C15H24 香树烯 1.07 1.09 0.10 − 1.21 0.65 DNC 68832-35-9 C15H24 4,11,11-三甲基-8-亚甲基-,(1R,4E,9R)-
双环十一碳-4-烯,0.69 − 1.07 0.48 − − DNC 17301-32-5 C13H28 4,7-二甲基十一烷 11.7 − − 0.01 − − DNC 6753-98-6 C15H24 α-石竹烯 − 0.91 0.90 0.47 0.80 − DNC 10219-75-7 C15H24 佛术烯 − 0.14 0.64 − 0.70 0.56 DNC 3387-41-5 C10H16 桧烯 − 0.16 0.33 − 0.28 − DNC 123-35-3 C10H16 月桂烯 − 0.16 0.29 − 0.18 − 甜橘味和香脂气 99-85-4 C10H16 γ-松油烯 − 0.12 0.16 − 0.18 − 柑橘和柠檬香气 544-76-3 C16H34 十六烷 − 0.32 0.29 − 0.11 − DNC 23986-74-5 C15H24 1-甲基-5-亚甲基-1,6-环癸二烯 − 1.35 1.33 − 0.85 − DNC 3856-25-5 C15H24 α-蒎烯 − 0.08 − − − − DNC 629-73-2 C16H32 1-十六烯 − 0.10 − − − − DNC 13877-91-3 C10H16 罗勒烯 − 0.10 − − − − DNC 630-02-4 C28H58 正二十八烷 − 0.25 − − − − DNC 629-59-4 C14H30 十四烷 − − 0.17 0.21 − − DNC 112-40-3 C12H26 十二烷 − − − 0.19 − 0.15 DNC 55333-99-8 C26H54 7-己基环烷 − − − − 0.19 0.19 DNC 629-50-5 C13H28 正十三烷 − − − − 0.11 − DNC 35365-59-4 C18H34 9-十八炔 − − − − 0.12 − DNC 34303-81-6 C16H32 (Z) -3-十六烯 − − − − 0.10 − DNC 3779-61-1 C10H16 (E)-Β-罗勒烯 − − − − − 0.27 DNC 2437-56-1 C13H26 1-十三烯 − − − − − 0.10 DNC 烯烃类合计 14.86 10.02 10.55 4.01 9.62 5.93 醇类 123-51-3 C5H12O 异戊醇 0.27 0.41 0.23 0.41 0.24 0.26 苹果白兰地香气和辛辣味 78-83-1 C10H18O2 异丁醇 36.90 0.34 0.73 0.76 0.31 0.53 DNC 78-70-6 C10H18O 芳樟醇 20.29 41.10 46.80 60.60 48.40 54.70 花香,似铃兰香气 98-55-5 C10H18O α-松油醇 4.56 0.60 0.43 0.64 0.56 − 特有的丁香香气 100-51-6 C7H8O 苯甲醇 0.61 0.26 0.20 0.45 0.29 0.36 微弱芳香气味 60-12-8 C8H10O 苯乙醇 0.21 0.34 0.35 0.72 0.39 0.46 玫瑰花样香气 20126-76-5 C10H18O (-)-萜烯-4-醇 0.54 0.92 − 1.29 − 1.24 DNC 470-82-6 C10H18O 桉树醇 − 0.23 0.21 − 0.37 − 樟脑气息和草药味道 3391-86-4 C8H16O 1-辛烯-3-醇 − 0.18 0.22 − − − DNC 68797-95-5 C15H30O 6-戊癸烯-1-醇(6Z) − 0.08 − − − − DNC 40642-43-1 C14H28O 顺式-7-十四烯-1-醇 − − 0.11 0.15 − 0.12 DNC 562-74-3 C10H18O 4-萜烯醇 − − 0.90 − 1.09 − 胡椒香、泥土香和木材气息 106-24-1 C10H18O 香叶醇 − − − − 0.35 0.12 玫瑰花气息,味有苦感 51276-34-7 C10H18O2 2,6-二甲基-3,7-辛二烯-2,6-二醇 − − − − 0.16 − DNC 7785-53-7 C10H18O (R)-α,α-4-三甲基-3-环己烯-1-甲醇 − − − − − 0.70 DNC 醇类合计 63.38 44.46 50.18 65.02 52.16 58.49 醚类 91-16-7 C8H10O2 邻苯二甲醚 0.30 0.37 0.48 0.59 0.40 0.56 DNC 酮类 546-80-5 C10H16O (-)-α-侧柏酮 1.37 0.22 0.38 0.21 0.27 0.13 DNC 1125-21-9 C9H12O2 茶香酮 0.14 0.07 0.11 0.29 0.15 0.12 DNC 89-81-6 C10H16O 胡椒酮 − 0.07 0.09 − 0.25 0.17 DNC 2550-52-9 C16H30O 环十二酮(6Cl,7Cl,8Cl,9Cl) − 0.17 0.18 − 0.18 − DNC 79-77-6 C13H20O β-酯罗酮 − 0.27 − − 0.13 − 紫罗兰香味 4780-14-7 C7H8O3 3-甲氧基-2-甲基-4H-吡喃-4-酮 − 0.16 − − 0.12 − DNC 3796-70-1 C13H22O 香叶基丙酮 − − 0.10 − 0.08 − DNC 471-15-8 C10H16O 側柏酮 − − − 0.35 − 0.23 DNC 590-90-9 C4H8O2 4-烃基-2-丁酮 − − − − 0.33 − DNC 65649-04-9 C10H14O 六氢-,6-甲氨基-3ah-茚-4(1H)-酮 − − − − 0.26 − DNC 689-67-8 C13H22O 香叶基丙酮 − − − − − 0.10 DNC 酮类合计 1.51 0.96 0.86 0.85 1.77 0.75 酚类 90-05-1 C7H8O2 愈创木酚 0.59 0.07 0.09 0.06 0.09 0.15 特殊芳香气味 96-76-4 C14H22O 2,4-二叔丁基苯酚 − 0.11 0.20 0.18 0.36 0.25 DNC 酚类合计 0.59 0.18 0.29 0.24 0.45 0.40 其它类 14667-55-1 C7H10N2 2,3,5-三甲基吡嗪 0.26 0.26 0.17 0.50 0.24 0.40 DNC 104-46-1 C10H12O 茴香脑 0.49 2.02 1.95 1.07 1.88 1.98 甜味,具茴香的香气 634-36-6 C9H12O3 1,2,3-三甲氧基苯 0.18 0.41 0.33 0.22 0.33 0.30 DNC 1124-11-4 C8H12N2 川芎嗪 0.80 5.89 5.12 10.60 6.26 9.11 牛肉、猪脂香气和发酵大豆味 13925-07-0 C8H12N2 2-乙烷基-3,5-二甲基吡嗪 0.22 − − − 0.23 − 威士忌酒和炒花生似香气 473-13-2 C15H24 八氢-4,8-二甲基(1-甲基乙烯基)-萘 − 0.14 0.30 − 0.18 0.20 DNC 17398-16-2 C9H14N2 3,5-二乙基-2-甲基-吡嗪 − 0.12 − 0.13 − 0.13 DNC 39029-41-9 C15H24 八氢-7-甲基-4-亚甲基-1-(1-甲基乙基)-萘 − 0.27 − − − − DNC 13360-65-1 C8H12N2 3-乙基-2,5-甲基吡嗪 − − − − − 0.29 DNC 其它类合计 1.95 9.11 7.87 12.52 9.12 12.41 注:−表示未检出;DNC表示未确定;* 风味特征描述来源于http://www.perflavory.com;https://www.chemicalbook.com。 -
[1] 李俊杰, 李浪, 张正彪, 等. 原料不同预处理对昭通豆酱风味品质影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(4):312−322. [LI J J, LI L, ZHANG Z B, et al. Effect of different pretreatment of raw materials on flavor quality of zhaotong soybean paste[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(4):312−322. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021060112 [2] 李俊杰, 李志鹏, 王磊, 等. 昭通酱发酵过程中理化成分变化研究[J]. 现代食品,2021(11):111−115. [LI J J, LI Z P, WANG L, et al. Study on the changes of physical and chemical components of zhaotong soybean paste during fermentation[J]. Modern Food,2021(11):111−115. doi: 10.16736/j.cnki.cn41-1434/ts.2021.11.032 [3] CAPOZZI V, RUSSO P, MARÍA T D, et al. Lactic acid bacteria producing B-group vitamins: Agreat potential for functional cereals products[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2012,96(6):1383−1394. doi: 10.1007/s00253-012-4440-2
[4] 黄小青, 朱建鸿. 传统豆酱储存过程中品质变化及其防腐体系的抑菌效果[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(14):151−156. [HUANG X Q, ZHU J H. Quality variety of traditional soybean paste and antibacterial effect of its antiseptic system during storage[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(14):151−156. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2019.14.025 [5] JIN, SEOK, MOON, et al. Isolation and characterization of biogenic amine-producing bacteria in fermented soybean pastes[J]. The Journal of Microbiology,2010,48(2):257−261. doi: 10.1007/s12275-010-0040-y
[6] HAN B, KIERS J L, NOUT R M J. Solid-substrate fermentation of soybeans with Rhizopus spp. : Comparison of discontinuous rotation with stationary bed fermentation[J]. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering,1999,88(2):205−209. doi: 10.1016/S1389-1723(99)80203-5
[7] 罗信旭, 袁时洁, 陆敏, 等. 细菌型豆豉蜡样芽孢杆菌的动态变化研究[J]. 中国酿造,2016,35(12):31−34. [LUO X X, YUAN S J, LU M, et al. Dynamic changes of Bacillus cereus in bacteria-fermented douchi[J]. China Brewing,2016,35(12):31−34. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2016.12.006 [8] 白凤岚, 陈松, 罗梦幽, 等. 食品中蜡样芽孢杆菌的分离及携带毒力基因的检测[J]. 现代食品科技,2018,34(10):247−252,204. [BAI F L, CHEN S, LUO M Y, et al. Identification and virulence genes detection of Bacillus cereus food isolates[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2018,34(10):247−252,204. doi: 10.13982/j.mfst.1673-9078.2018.10.033 [9] 何苗, 陈洁, 曾茂茂, 等. 高温杀菌对福建风味鸭风味的影响[J]. 食品与机械,2014,30(3):29−34. [HE M, CHEN J, ZENG M M, et al. Effects of high temperature sterilization on volatiles in Fujian flavor duck[J]. Food & Machinery,2014,30(3):29−34. [10] FARKAS J, C MOHÁCSI. History and future of food irradiation[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2011,22(2-3):121−126. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgs.2010.04.002
[11] SHI F, ZHAO H, SONG H, et al. Effects of electron-beam irradiation on inoculated Listeria innocua, microbiological and physicochemical quality of fresh noodles during refrigerated storage[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2020,8(1):114−123. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.1277
[12] UYGUN S, BAY M, ERGUN E, et al. Effect of gamma irradiation and storage on lutein and zeaxanthin in liquid, frozen and dried egg yolk samples[J]. Journal of Radioanalytical & Nuclear Chemistry,2014,301(2):597−605. doi: 10.1007/s10967-014-3171-5
[13] FENG X, JO C, NAM K C, et al. Impact of electron-beam irradiation on the quality characteristics of raw ground beef[J]. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies,2019,54:87−92.
[14] KONG Q, WU A, QI W, et al. Effects of electron-beam irradiation on blueberries inoculated with Escherichia coli and their nutritional quality and shelf life[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2014,95:28−35. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2014.04.004
[15] ROBERTS, PETER B. Food irradiation is safe: Half a century of studies[J]. Radiation Physics & Chemistry,2014,105:78−82.
[16] 王珊珊, 潘俊, 曹美云, 等. 国内外食品辐照技术标准的应用现状分析[A]. 中国核学会. 中国核科学技术进展报告(第六卷)—中国核学会2019年学术年会论文集第8册(辐射研究与应用分卷、核技术工业应用分卷、辐照效应分卷、核电子学与核探测技术分卷、核医学分卷、放射性药物分卷)[C]// 北京: 中国核学会, 2019: 6. DOI: 10.26914/c.cnkihy.2019.071373. WANG S S, PAN J, CAO M Y, et al. Analysis on the application status of food irradiation technical standards at home and abroad [A]. China Nuclear Society Progress report on China's nuclear science and Technology (6)- Volume 8 of proceedings of 2019 academic annual meeting of China Nuclear Society (radiation research and application, industrial application of nuclear technology, irradiation effect, nuclear electronics and nuclear detection technology, nuclear medicine and radio pharmaceuticals)[C]// Beijing: China Nuclear Society, 2019: 6.
[17] 王梁燕, 洪奇华, 孙志明, 等. 电子束辐照技术在生命科学中的应用[J]. 核农学报,2018,32(2):283−290. [WANG L Y, HONG Q H, SUN Z M, et al. Application of electron beam irradiation in life sciences[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2018,32(2):283−290. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2018.02.0283 [18] 华跃进. 中国核农学通论[M]. 上海: 上海交通大学出版社, 2016. HUA Y J. General theory of nuclear agriculture in China[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University Press, 2016.
[19] 张莹, 朱加进. 电子束辐照技术及其在食品工业中的应用研究[J]. 食品与机械,2013,29(1):236−239. [ZHANG Y, ZHU J J. Review of development of electron accelerators on foods[J]. Food & Machinery,2013,29(1):236−239. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5788.2013.01.061 [20] 李俊杰, 张正彪, 李浪, 等. 电子束辐照灭菌对昭通酱品质影响研究[J]. 中国酿造,2021,40(10):64−69. [LI J J, ZHANG Z B, LI L, et al. Effect of electron beam irradiation sterilization on the quality of Zhaotong soybean paste[J]. China Brewing,2021,40(10):64−69. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2021.10.010 [21] 李俊杰, 杨奎, 亢凯杰, 等. 昭通酱的不同加工工艺对亚硝酸盐含量的影响研究[J]. 食品安全导刊,2021(19):143−145. [LI J J, YANG K, KANG K J, et al. Effects of different processing technologies of Zhaotong soybean paste on nitrite content[J]. China Food Safety Magazine,2021(19):143−145. doi: 10.16043/j.cnki.cfs.2021.19.085 [22] 国家食品药品监督管理总局, 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB/T 24399-2009 食品安全国家标准. 黄豆酱 [S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009. State Food and Drug Administration, State Health and Family Planning Commission. GB/T 24399-2009. National food safety standard soybean paste[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2009.
[23] 国家食品药品监督管理总局, 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 4789.2-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品微生物学检验 菌落总数测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. State Food and Drug Administration, State Health and Family Planning Commission. GB 4789.2-2016 National food safety standard. Microbiological examination of food determination of total bacterial count[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016.
[24] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 4789.15-2016. 食品安全国家标准. 食品微生物学检验. 霉菌和酵母计数[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. State Food and Drug Administration, State Health and Family Planning Commission. GB 4789.15-2016. National food safety standard microbiological examination of food mold and yeast count[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016.
[25] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 4789.3-2016. 食品安全国家标准 食品微生物学检验 大肠菌群计数[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. State Food and Drug Administration, State Health and Family Planning Commission. GB 4789.3-2016. National food safety standard. Microbiological examination of food coliform count[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016.
[26] 蒋立文, 谢艳华, 李跑, 等. HS-SPME/GC-MS和电子感官技术分析毛霉型豆豉发酵过程中风味品质[J]. 核农学报,2020,34(7):1497−1506. [JIANG L W, XIE Y H, LI P, et al. Analysis of the volatile flavor components and quality of mucor-type douchi with HS-SPME/GC-MS method and electric-sense technology[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2020,34(7):1497−1506. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2020.07.1497 [27] 王文亮, 李霞, 王守经, 等. 食品油脂辐照氧化研究进展[J]. 中国食物与营养,2009(2):29−31. [WANG W L, LI X, WANG S J, et al. Research progress of irradiation oxidation of food oil[J]. Food and Nutrition in China,2009(2):29−31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9577.2009.02.008 [28] 哈益明, 王锋. 辐射诱导冷却肉脂肪氧化机理与抑制方法研究[J]. 辐射研究与辐射工艺学报,2006(5):257−261. [HA Y M, WANG F. Mechanisms of lipid oxidation in pork samples irradiated at chilling temperatures and the ways to control the lipid oxidation[J]. Journal of Radiation Research and Radiation Processing,2006(5):257−261. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3436.2006.05.001 [29] 冯敏, 汪敏, 常国斌, 等. 电子鼻检测辐照肉鸭产品的挥发性风味物质[J]. 核农学报,2019,33(6):1116−1121. [FENG M, WANG M, CHANG G B, et al. The detection of volatile flavor substances of irradiated duck products by electronic nose[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2019,33(6):1116−1121. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2019.06.1116 [30] PATEIRO M, VARGAS F C, CHINCHA A, et al. Guarana seed extracts as a useful strategy to extend the shelf life of pork patties: UHPLC-ESI/QTOF phenolic profile and impact on microbial inactivation, lipid and protein oxidation and antioxidant capacity[J]. Food Research International,2018,114(DEC.):55−63. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.07.047
[31] 胡科娜, 谷贵章, 高兴杰, 等. 浒苔多酚协同低剂量电子束辐照对鳗鱼鲞菌落总数和油脂氧化的作用[J]. 食品科学,2021(19):157−163. [HU K N, GU G Z, GAO X J, et al. Effects of enteromorpha prolifera polyphenols combined with low-dose electron beam irradiation on microbial count and lipid oxidation in dried salted eel[J]. Food Science,2021(19):157−163. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200915-193 [32] 乔宇, 廖李, 雷琪, 等. 竹叶黄酮对泡椒鸭掌辐照异味的去除及抗氧化研究[J]. 现代食品科技,2016,32(3):79−85,157. [QIAO Y, LIAO L, LEI Q, et al. Removal of irradiation-derived off-flavor of duck web with pickled pepper by bamboo leaf flavone and its antioxidant activity[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2016,32(3):79−85,157. doi: 10.13982/j.mfst.1673-9078.2016.3.014 [33] 侯铮迟, 孙大宽, 秦宗英, 等. 高剂量辐照猪肉的挥发物、脂氧化和感官特征分析[J]. 辐射研究与辐射工艺学报,2005(1):35−39. [HOU Z C, SUN D K, QIN Z Y, et al. Analysis of volatile organic compounds and sensory characteristics of pork loin samples irradiated to high doses[J]. Journal of Radiation Research and Radiation Processing,2005(1):35−39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3436.2005.01.008 [34] AHN D U, LEE E J. Production of off-odor volatiles from liposome-containing amino acid homopolymers by irradiation[J]. Journal of Food Science,2002,67(7):2659−2665. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2002.tb08795.x
[35] KIM Y H, NAM K C, AHN D U. Volatile profiles, lipid oxidation and sensory characteristics of irradiated meat from different animal species[J]. Meat Science,2002,61(3):257−265. doi: 10.1016/S0309-1740(01)00191-7
[36] 王娴, 陈云堂, 范家霖, 等. 辐照对花生酱理化品质及风味影响的研究[J]. 食品科技,2021,46(2):157−163. [WANG X, CHEN Y T, FAN J L, et al. Effects of irradiation on physicochemical quality and flavor of peanut butter[J]. Food Technology,2021,46(2):157−163. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2021.02.025 [37] 曾剑华, 王冰, 刘琳琳, 等. 中国传统发酵豆制品风味物质的研究进展[J]. 大豆科学,2018,37(6):969−974. [ZENG J H, WANG B, LIU L L, et al. Research progress on flavor compounds of traditional fermented soybean products in China[J]. Soybean Science,2018,37(6):969−974. doi: 10.11861/j.issn.1000-9841.2018.06.0969 [38] 马玲, 郝教敏, 杨华, 等. 辐照对低脂Mozzarella干酪成熟过程中挥发性风味物质的影响[J]. 核农学报,2014,28(1):77−84. [MA L, HAO J M, YANG H, et al. Effects of irradiation on volatile compounds of low fat Mozzarella cheese during ripening[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2014,28(1):77−84. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2014.01.0077 [39] 吕梁玉, 官爱艳, 张单阳, 等. 电子束辐照对带鱼鱼糜及其热诱导凝胶挥发性风味成分的影响[J]. 食品科学,2016,37(18):77−83. [LÜ L Y, GUAN A Y, ZHANG S Y, et al. Effects of electron beam irradiation on the volatile flavor components of hairtail surimi and its thermally inducted Gel[J]. Food Science,2016,37(18):77−83. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201618013 [40] JUN R W, JIA C Z, PU S, et al. Bacterial community involved in traditional fermented soybean paste dajiang made in northeast[J]. China Annals of Microbiology,2013,63(4):1417−1421. doi: 10.1007/s13213-013-0604-2
[41] YI S H, HONG S P. Characteristics of bacterial strains with desirable flavor compounds from korean traditional fermented soybean paste (doenjang)[J]. Molecules,2021,26(16):5067. doi: 10.3390/molecules26165067
[42] 曹蓓. 美味牛肝菌挥发性风味物质的研究[D]. 天津: 天津科技大学, 2013. CAO B. Studies on volatile flavor compounds in boletus edulis[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2013.
[43] SANTOS B M, GOMES A, MONTEIRO M J, et al. Nutritional, textural and sensory properties of Coalho cheese made of goats', cows' milk and their mixture[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2013,50(2):538−544. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2012.08.011
[44] 马晓雁, 倪梦婷, 李军, 等. UV-C辐照降解水中藻源性污染物β-环柠檬醛[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版),2013,41(11):26−31. [MA X Y, NI M T, LI J, et al. Degradation of algae derived pollutants in water by UV-C irradiation β- cyclocitral[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition),2013,41(11):26−31. doi: 10.13245/j.hust.2013.11.022 [45] TUFARIELLO M, CAPONE S, SICILIANO P. Volatile components of Negroamaro red wines produced in Apulian Salento area[J]. Food Chemistry,2012,132(4):2155−2164. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.11.122
[46] 林勇, 鉏晓艳, 陈玉霞, 等. 辐照对桂花酱的灭菌效果及保质期的影响[J]. 湖北农业科学,2019,58(24):197−200. [LIN Y, CHU X Y, CHEN Y X, et al. Effect of irradiation on sterilization effect and shelf life of sweet osmanthus sauce[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences,2019,58(24):197−200. doi: 10.14088/j.cnki.issn0439-8114.2019.24.048 [47] YANG Y, TERM C N, SHAN W, et al. Physicochemical, flavor and microbial dynamic changes during low-salt doubanjiang (broad bean paste) fermentation[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,351(4):128454. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128454
[48] WANG S, LIU X, TAMURA T, et al. Effect of volatile compounds on the quality of miso (traditional Japanese fermented soybean paste)[J]. LWT- Food Science and Technology,2020,139(1):110573. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110573
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 刘冀黔,旦正杰,韩丽娟,桂林生,侯生珍,王志有,杨葆春. 不同月龄黑藏羊肉品质及风味评价分析. 饲料研究. 2024(13): 105-111 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 宁舒娴,曾金秀,沙小梅,丁红秀. 不同生境来源的鳙鱼肉挥发性物质组成比较分析. 食品工业科技. 2024(18): 265-272 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 董平,范文教,朱开宪,吴华昌,邓静. 不同复热方式对咸烧白风味的影响. 食品科技. 2023(02): 122-129 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 陈方雪,邓祎,谌玲薇,李冬生,乔宇,吴文锦,熊光权,汪兰,李新,石柳,丁安子. 预制冷风风干武昌鱼干制过程中的品质变化及香气形成. 现代食品科技. 2023(02): 9-17 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张蓝月,孙万成,罗毅皓. 基于气相色谱-离子迁移谱分析不同地区羊肉的挥发性风味化合物. 食品与发酵工业. 2023(10): 265-272 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 火玉明,柯汉杰,吴晨昕,姜红贺,梁鹏,汪晴,陈小辉. 海鲈鱼鱼松加工工艺研究. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2022(10): 3367-3374 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 戴振庭,周惠敏,殷泽生,周瑜,陈舜胜. 添加植物油对鲣鱼鱼松滋味的影响. 甘肃农业大学学报. 2022(06): 227-234 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



