Research Progress on the Application of in Vitro Digestion Model in Nutritional Active Substances of Aquatic Products
-
摘要: 食物营养素对人体健康的影响主要取决于胃肠道内的消化过程。体外模拟消化可以综合模拟人体消化过程,具有重现性好、简单灵活、应用广泛等优点,不仅可以预测食物成分、结构和消化特性之间的关系,还可以评估食物成分的生物利用度和消化代谢物对人体健康的影响,是研究食品中营养物质的有效工具。体外模拟消化已经广泛用于水产品营养活性成分的研究,本文综述了体外模拟消化模型的现状,对静态模型和动态模型的优缺点及其应用进行了详细描述,并系统总结了体外模拟消化在研究水产品蛋白质消化率、生物活性肽消化稳定性、多糖消化酵解特性及脂质氧化稳定性等方面的应用。此外,还对体外模拟消化模型的局限和优化提出了建议,以期对其在海洋生物医药、海洋功能食品等领域的应用有所助益。Abstract: The impact of food nutrients on human health depends primarily on the digestion process in the gastrointestinal tract. The in vitro digestion model can simulate the digestive processes in vivo conditions integrally. It has the advantages of reproducibility, simplicity and universality. In vitro digestion can not only forecast the relationship among food composition, structure and digestive characteristics, but also calculate the bioavailability of food components and the impact of digestive metabolites on body health, so it is an important way to research nutrients in food. In vitro digestion has been widely used in the study of nutritional active substances in aquatic products. This article reviews the current situation of the in vitro digestion model and states the advantages and disadvantages of static and dynamic models and their applications in detail. It systematically summarizes the application of in vitro digestion in the study of nutritional active substances in aquatic products, including research on the digestibility of protein, the stability of bioactive peptides, the digestive and fermentation characteristics of polysaccharides, and the oxidation stability of lipid. In addition, suggestions for the limitations and optimization of the in vitro digestion model have been provided. It is expected to be useful in the future for its application in marine biomedicine, marine functional food and other fields.
-
Keywords:
- in vitro digestion /
- aquatic products /
- nutritionally active substances /
- protein /
- bioactive peptides /
- polysaccharides /
- lipid
-
食物在人体内的消化过程是一个复杂的程序,消化系统承担着对摄入的食物进行物理和化学分解以促进其营养成分释放和吸收的功能。因此,了解食物成分的消化吸收过程及潜在机制对人类健康至关重要。但由于体内消化试验存在伦理谴责、费用高、体内消化周期长、结果易受实验体个体差异性影响等问题[1-2],无法广泛进行。动物模型可以辅助学者研究有关食品中化合物的消化和吸收的过程,但由于物种特异性解剖学和生理学差异,无法完全替代对人类的研究[3]。为了更好地了解食物与健康之间的联系和所涉及的机制,在体外模拟人类消化的生理过程就显得尤为必要。
体外模拟消化是基于人体体内消化环境和生理过程而建立的,在体外以相似的条件模拟人体消化过程的方法,可以综合模拟人体口腔、胃、小肠和大肠的消化过程,具有重现性好、简单灵活、应用广泛等优点[4]。体外模拟消化不仅可以预测食物成分、结构和消化特性之间的关系,还可以评估食物成分的生物利用度和消化代谢物对人体健康的影响,是研究食品中营养物质的有效工具。
与陆地来源食物相比,海洋生物由于其生活条件的特殊性而形成了独特功能的营养活性物质,尤其是多糖、多肽和脂质等特定功能分子已被广泛用于食品、药品的开发。这些活性物质在进入人体消化过程中,在胃肠消化酶等作用下会发生多肽(蛋白质)降解、多糖消化酵解、脂质氧化等变化,改变其结构和性质,导致体内外生物活性的差异,并对人体产生利害不一的影响,因此有必要对这些营养活性成分的消化行为开展进一步研究。本文综述了体外模拟消化模型的现状、静态模型和动态模型的优缺点及其应用,系统总结了体外模拟消化在水产品营养活性物质研究中最新进展,以期为体外模拟消化的发展和其在水产品研究中的进一步应用提供参考。
1. 体外模拟消化系统的现状
体外模拟消化模型主要应用于植物、肉类、水产品、奶制品和以乳化液为基础的食品[4],大致可以分为静态模拟体系和动态模拟体系,其主要优缺点如下所述。
1.1 静态模拟体系
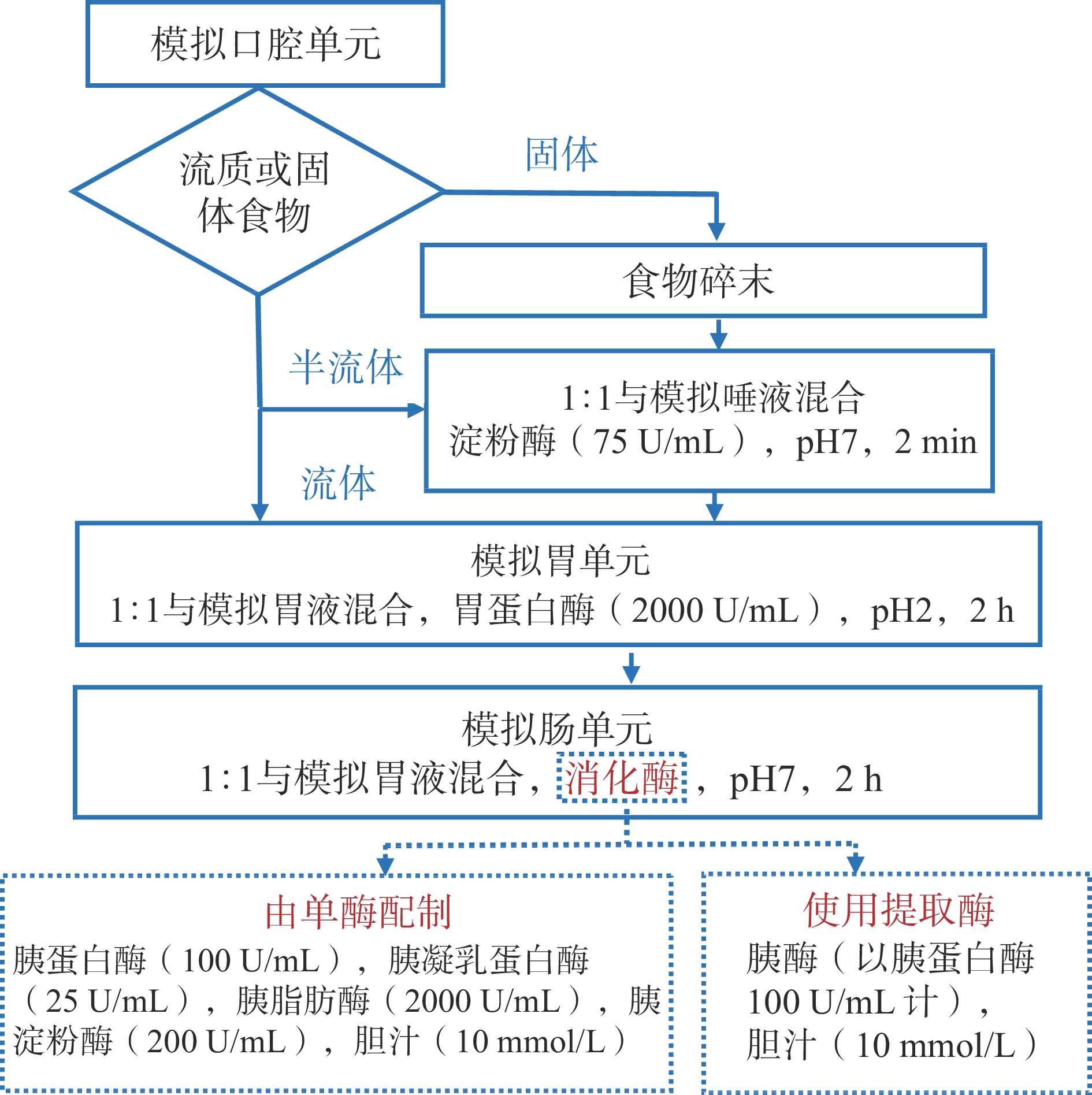
静态模拟体系主要分为口腔单元、胃和小肠单元,有的还包括大肠发酵体系[5]。静态模拟体系操作简单,材料廉价易得,不需要特殊的设备,因此,成为目前使用最为广泛的体外消化模型。随着体外模拟消化的广泛应用,不同研究团队提出了各种静态消化模型。由于体外消化模型受到酶的特性、温度、pH、消化时间等因素的影响[2],导致不同模型的实验数据各不相同,阻碍了研究成果的可比较性。Minekus等[6]提出了一种通用的、标准化的统一静态模拟消化模型(图1),包括口腔、胃和小肠模拟液的配置参数和消化步骤,有助于研究者产生更多的可比数据。
静态模型的参数相对固定,食物成分与酶浓度和比率、pH、电解质等参数在起始阶段设定,且在整个相应阶段保持不变。因此,虽然静态模拟体系能模拟体内生理条件,但不能模拟体内发生的动态物理过程,且缺少胃排空、连续分泌物、pH改变等条件的控制,无法模拟消化过程的机械力、流体动力或与宿主的生理相互作用[7],因此往往导致模拟消化结果并不能真实反映实际情况。目前,静态模型主要用于简单成分和分离纯化的营养物质消化研究。
1.2 动态模拟体系
动态消化模型可模拟人体肠胃的生理环境和胃肠道中发生的动态消化过程(例如消化液的分泌、可变的酶浓度、pH变化、食糜的转运等)[7],相比静态消化模型,更接近真实人体胃肠道,可以同时模拟胃肠道中物理作用、化学作用以及不同消化时间下发生的其他变化[8],逐渐成为国内外研究者们更为倾向的体外消化模型。表1中对应用于食品的静态与动态体外人体模拟消化模型进行了比较。
表 1 应用于食品的静态与动态体外人体模拟消化模型的比较Table 1. Comparison of the characteristics of static and dynamic models主要特征 静态模拟体系 动态模拟体系 研究类型 适用于有限的消化阶段(胃和/或肠道) 适用于研究整个消化过程 研究对象 简单均一的食物;分离/纯化的化合物 复杂的食物 研究目的 改善食品特性;初步验证食物与营养健康的关系 食物成分、结构等对营养物质输送、营养相互作用、益生菌存活等的影响;
为新产品开发提供基础数据优点 快速简单、经济高效;只需根据其预期用途进行验证 更准确地了解肠道的动态环境;可以与体内/临床研究结果直接比较 缺点 无法模拟消化过程的机械力和不断变化的生化环境;
代谢物过度积累会干扰消化操作相对复杂;应验证其重现胃肠道环境的能力 应用 常量营养素的生物利用度研究;生物活性分子研究;
从简单的食品基质中制备营养物质适合消化复杂的食物或药物,例如从复杂物质中
制备营养物质及其生物利用度研究为了克服静态模型在消化中的缺点,国内外研究者已经设计和开发了多种动态模拟消化模型,主要包括:动态胃模型(DGM)[9]、人体胃模拟器(HGS)[10]、TNO胃肠模型(TIM-1)[11]、DIDGI®[12]、体外机械胃系统(IMGS)[13]、胃模拟模型(GSM)[14]、动态体外人胃系统(DIVHS)[15]等。
2. 体外模拟消化在水产品营养活性物质研究的应用
2.1 水产品蛋白质的体外模拟消化研究
水产品可为人体提供高水平的优质蛋白质。蛋白质消化吸收理论认为,蛋白质在消化道内经胃肠蛋白酶的水解后生成小肽和游离氨基酸被人体吸收利用。蛋白质消化率(即吸收的蛋白质占摄入蛋白质总量的百分比)是评价食物中蛋白质营养价值的重要指标[16]。
如表2,国内外主要采用体外模型模拟蛋白质在体内的消化环境和过程,来测定其消化率,以此评价蛋白质的利用情况。不同烹饪和加工工艺会导致食物中蛋白质等营养素发生不同程度的变性、氧化和分解,从而影响食物的消化率。戴泽川等[17]用体外模拟消化法,探究高强度超声对凡纳滨对虾蛋白结构和消化率的影响,结果表明,超声波处理使得蛋白质构象的展开和平均粒径的降低,经过超声15、25 min凡纳滨对虾蛋白消化率分别提高到了78.13%和81.97%。相反,热处理会降低虾肉蛋白质的消化率,于小番[18]探究了蒸制、烤制、微波三种热处理方式对虾肉蛋白质消化率的影响,发现随着中心温度的增加,三种热处理方式下虾肉蛋白质的体外模拟消化率均呈下降趋势。胡吕霖等[19]在对鱼肉蛋白质的体外模拟消化研究也发现了相似的结论,水煮、汽蒸、微波、烤箱烤制、油炸等热处理方式都会不同程度降低鱼肉蛋白的消化率,并且烤制和油炸类样品的消化率最低,可能是由于烤制与油炸等剧烈条件下,蛋白质氧化程度加重,更易于发生分子交联与聚集,形成致密结构,能够抵抗酶的水解。
表 2 水产品蛋白质的体外模拟消化研究报道Table 2. Research on in vitro digestion of protein in aquatic products研究对象 外部条件 模拟消化条件 蛋白质消化率变化 凡纳滨对
虾蛋白[17]高强度超声 胃蛋白酶(100:1),pH2,37 ℃恒温消化3 h,胰蛋白酶(100:1),pH7.6,37 ℃消化2 h。 经过超声15和25 min凡纳滨对虾蛋白消化率分别提高到了78.13%和81.97%。 刀额新对
虾蛋白[18]蒸制、烤制、微波加热 4 mL胃蛋白酶溶液(0.032 g/mL,pH2),4 mL胰蛋白酶溶液(0.024 g/mL,pH7.5),分别37 ℃消化2 h。 蛋白质的消化率随中心温度的升高而降低,消化率的变化主要与蛋白质的氧化与结构的变化有关。 草鱼重组
鱼肉蛋白[20]芬顿氧化体系和谷氨酰胺转氨酶处理 模拟胃液(pH2.0,含胃蛋白酶),37 ℃消化1 h;模拟肠液(pH8.0,含胰蛋白酶),37 ℃消化2 h。 随着氧化时间的延长,干物质消化率、蛋白质消化率和BCA蛋白浓度均先增加后降低。 草鱼重组
鱼肉蛋白[21]水煮、汽蒸、微波、
油炸模拟胃液(pH2.0,含胃蛋白酶),37 ℃消化1 h;模拟肠液(pH8.0,含胰蛋白酶),37 ℃消化2 h。 微波加热和油炸样品消化率较另外两组偏低,整个消化过程中分子质量逐渐变小。 草鱼蛋白[22] 超高压和冻藏 胃蛋白酶(1%,pH1.2),胰蛋白酶(1.25%,pH6.9)和胆汁(1.4%),分别37 ℃消化3 h。 经冷冻处理的草鱼鱼肉消化性较新鲜草鱼有所降低,而超高压处理的草鱼鱼肉更易消化。 鲟鱼蛋白[19] 水煮、汽蒸、微波、烤箱烤制、油炸 在3 mL模拟唾液中37 ℃消化5 min, 5 mL模拟胃液(pH2.0),消化1 h,最后加入5 mL模拟小肠液(pH8.0),消化2 h。 胃消化阶段,烤制与油炸样品降低了蛋白质消化性,胃肠道消化后,各类熟制样品蛋白消化性都降低。 可见,蛋白质消化率是外部和内部因素共同作用的结果,体外模拟消化不仅可以通过评价蛋白质消化率来比较、筛选和评价水产品加工工艺,还可以预测原料成分、结构和消化特性之间的关系。
2.2 水产品生物活性肽的体外模拟消化研究
生物活性肽是一类具有特殊生理作用的蛋白,通常含3~30个氨基酸残基,以不同组成和排列方式构成特殊的活性结构[23]。近年来,针对水产品生物活性肽的生理功能相关研究探索了包括抗菌、抗氧化、抗高血压、抗糖尿病和抗癌活性等[24]多种生物活性。生物活性肽经口服进入人体后,需要穿越人类肠道屏障进入血液循环系统发挥生物效应,而这个过程必须确保活性肽不被降解并以必要的浓度到达靶位点发挥其作用[25]。然而,人体消化系统中的胃酸和各类酶都可破坏活性肽结构,从而影响其生物活性,导致多肽体内外活性的差异。
体外消化模型在一定程度上反映了活性肽在消化道中的变化情况,如表3,相关研究人员对抗氧化活性肽的体外模拟消化研究发现,在胃消化阶段主要以大肽断键为小肽为主,小分子量多肽的释放促进了抗氧化活性提高,1 kDa以下的多肽在胃消化过程中可保持结构完整性并发挥其抗氧化活性;但在肠消化阶段,由于胰蛋白酶的作用,活性肽结构和构象部分发生变化、具备抗氧化活性的疏水性氨基酸从肽链完整结构中释放,导致抗氧化活性下降[26-28]。此外,研究人员在对ACE抑制肽的体外模拟消化中发现,ACE抑制肽的胃肠稳定性相对较弱,消化后活性有所降低[29-30],而另有研究人员却得出了相反的结论,认为胃肠道消化不仅增加了活性肽的ACE抑制活性,还发现了一种新的具有ACE抑制能力的十肽[31]。活性肽在胃肠环境下稳定性的差异可能与其分子量、氨基酸序列和末端残基等因素有关[23]。
表 3 体外模拟消化对水产品生物活性肽稳定性影响Table 3. Effects of in vitro digestion on the stability of bioactive peptides in aquatic products活性肽来源 活性肽功能 模拟消化条件 分子量变化 功能活性变化 暗纹东方鲀鱼皮胶原蛋白肽[26] 抗氧化活性 胃蛋白酶(0.8%,pH2.0),胰酶(0.8%,pH7.0),分别于37 ℃
酶解2 h。胃消化阶段分子量分布无明显变化;肠消化后小于1 kDa比例更多,分子量更小。 胃消化后,抗氧化活性显著提高;胃肠消化后,抗氧化活性出现小幅度下降。 海洋鱼骨胶原
低聚肽[27]抗氧化活性 胃蛋白酶(3%,pH2.0),胰蛋白酶(3%,pH6.8),分别于37 ℃
酶解3 h。大于10000 u的肽相对含量降低,小于1000 u的肽相对含量同时增加。 整体提高了其抗氧化活性,但DPPH自由基清除能力经模拟胰液消化后有一定的降低。 鳕鱼鱼肉蛋白肽[28] 抗氧化活性 胃蛋白酶(2%),胰酶(2%,pH7.0),分别在37 ℃酶解2 h。 分子量大的肽比例减少,低于500 u肽部分的比例增加,但变化程度不大。 鱼肉蛋白肽发生降解,导致对DPPH自由基的清除率降低;TEAC活性保持稳定。 牡蛎低聚肽[32] 抗氧化活性 胃蛋白酶(1%,pH2.0),胰酶(1%,pH7.5),分别在37 ℃酶解2 h。 胃蛋白酶和胰蛋白酶消化后重均分子量下降不超过8.2%。 胃肠消化对牡蛎低聚肽的抗氧化活性评价各指标均无显著性影响。 两种皮氏蛾螺ACE抑制肽[30] ACE抑制
活性胃蛋白酶(1%),胰蛋白酶(0.5%,pH6.8),分别在37 ℃酶解0~6 h。 − 在胃肠液中稳定性相对较弱,其ACE抑制活性有所降低。 军曹鱼皮水解肽[29] ACE抑制
活性胃蛋白酶(4%,pH2.0),胰酶(4%),分别在37 °C酶解4 h。 − 通过模拟的胃肠道消化,PX-5和PN-5的ACE抑制活性显著降低。 鱿鱼皮胶原
蛋白肽[31]ACE抑制
活性胃蛋白酶(4%),胰酶(4%,pH7.5),分别在37 ℃酶解2 h。 胃蛋白酶消化几乎不改变肽的分子量分布;胰酶消化会增加低分子量肽的含量。 ACE抑制活性在胃肠道消化后增加,发现了一种新的ACE抑制肽(430~75 kDa)。 体外消化模型可以筛选出特定的具有消化稳定性的活性肽段,同时也能更为准确和合理地评价其活性,对于探究活性肽的构效关系、作用机制以及海洋生物活性肽功能食品、药品的开发有重要意义。
2.3 水产品多糖的体外模拟消化研究
2.3.1 水产品多糖的模拟消化
如表4,口腔和胃肠道的消化介质可能会改变多糖的物理和化学性质,如分子量、化学成分和生物活性,可通过测定消化前后植物多糖的相对分子质量分布、还原糖、游离单糖组成等来预测多糖的消化特性[33]。研究表明,人体胃肠消化没有显著降低鲍鱼硫酸化多糖的分子量[34],江蓠多糖、海带多糖等藻类多糖在口腔、胃和小肠模拟消化条件下均没有被消化[35-36]。然而在对牡蛎多糖的外模拟消化发现,唾液消化后其分子量略有降低,经胃消化后分子量显著下降,表明牡蛎多糖可被胃液部分降解[37],扇贝多糖在体外模拟消化体系中多糖的糖苷键断裂,形成很多小分子的片段,但不产生游离单糖[38]。多糖的不同消化特性可能与糖苷键的类型、分子量和单糖组成等有关。
表 4 水产品多糖的体外模拟消化和酵解特性研究的文献报道Table 4. Research on in vitro digestion and fermentation characteristics of polysaccharides in aquatic products研究对象 体外模拟消化条件 消化特性 酵解特性 扇贝多糖[38] α-淀粉酶(0.05%),胃蛋白酶(0.08%,pH2.0),胰酶
(7%,pH7.0),37 ℃恒温消化。糖苷键断裂,形成很多小分子的片段,但不产生游离单糖。 − 牡蛎多糖[37] 新鲜唾液,模拟胃液(112.5 mg胃脂肪酶、106.2 mg胃蛋白酶,pH3.0),模拟肠液(13.0 mg胰蛋白酶,pH7.0),
37 ℃恒温消化。牡蛎多糖在体外模拟消化过程中被部分降解。 难消化的牡蛎多糖可以调节肠道微生物群,发酵促进了短链脂肪酸的产生。 小珊瑚藻多糖[41] α-淀粉酶(75 U/mL),模拟胃液(3.6 mg胃蛋白酶、
3.8 mg胃脂肪酶,pH2.0),模拟肠液(1.3 mg胰蛋白酶、10.0 g胰酶溶液,pH7.0)37 °C恒温消化。在体外模拟消化过程中
不被消化。可以促进短链脂肪酸的产生,在体外调节肠道微生物群的结构。 海带多糖[36] 唾液α-淀粉酶溶液(1500 U/mL),37 °C消化5 min,胃蛋白酶溶液(25000 U/mL),胰酶溶液(800 U/mL),分别
37 °C下反应2 h。不能在胃肠道中被
完全消化。酵解后产生大量的短链脂肪酸,并导致肠道菌群结构与功能的改变(血脂异常及代谢综合征相关)。 泡叶藻多糖[42] 新鲜唾液,模拟胃液(112.5 mg胃脂肪酶、106.2 mg胃蛋白酶)pH3.0,模拟肠液(13.0 mg胰蛋白酶)pH7.0,
37 ℃恒温消化。不能在胃肠道中被消化,分子量和还原糖含量显著降低。 可以显著调节肠道微生物群的组成,特别是增加了拟杆菌门和厚壁菌门的相对丰度,此外,总发酵后SCFA含量显著增加。 龙须菜多糖[43] 胃蛋白酶(236 mg/L,pH2.0),胰酶溶液(7%,pH7.5),
37 ℃恒温消化。体外模拟胃肠道消化的过程中仅发生少量降解。 能有效促进肠道内产生短链脂肪酸细菌的生长,并增加粪便中短链脂肪酸含量和
水分含量。江蓠硫酸化多糖[35] 新鲜唾液,模拟胃液(112.5 mg胃脂肪酶、106.2 mg胃蛋白酶,pH3.0),模拟肠液(13.0 mg胰蛋白酶,pH7.0),
37 ℃恒温消化。在模拟口腔、胃、小肠条件下不被消化。 逐渐被肠道微生物群降解和利用,短链脂肪酸浓度增加,尤其是乙酸、丙酸和异丁酸。 鲍鱼硫酸化多糖[34] 2 mL人唾液、模拟胃液、模拟肠液分别和2 mL多糖溶液充分混合,37 °C下恒温消化。 人体胃肠消化没有显著降低鲍鱼硫酸化多糖的分子量。 鲍鱼硫酸化多糖对肠道双歧杆菌和拟杆菌的增殖有促进作用,丙酸盐和丁酸盐的含量显著增加。 2.3.2 水产品多糖的体外酵解
体外模拟消化模型不仅可以模拟口腔和胃肠的消化吸收过程,还可通过利用粪便微生物对整个结肠发酵进行模拟[39]。Ma等[37]探究了牡蛎多糖体外模拟消化发酵特性及其对肠道菌群的影响,研究表明,经过体外消化,牡蛎多糖糖苷键断裂被部分降解,难消化的牡蛎多糖可进一步在结肠中被肠道微生物群降解和利用,产生了短链脂肪酸,也改变了微生物群落的组成,增加了有益细菌的丰度。Vernazza等[40]利用体外肠道发酵模型研究了壳聚糖及其寡糖对肠道菌群的影响,表明壳聚糖可能是一种益生元,能促进肠道双歧杆菌和乳酸杆菌的生长。藻类多糖[35-36,41-43]、海参岩藻糖基化硫酸软骨素[44]的体外酵解也都表明其能被肠道微生物群利用,并调节肠道微生物群落结构。通过多糖体外酵解研究发现,大部分海洋多糖很难在胃肠中被消化吸收,但当其进入大肠后可被肠道菌群降解和利用,通常优先被益生菌利用,改变和重塑肠道菌群的群落结构,促进肠道相关菌群释放短链脂肪酸[45]。
2.3.3 多糖消化吸收和酵解与生物活性的关系
海洋多糖已被证实具有多种生物活性,但由于缺乏对多糖在体内代谢的认识,其确切作用机制仍不明晰。Ai等[34]用体外模拟消化模型研究太平洋鲍鱼硫酸化多糖(AGSP)的作用机制,结果表明,AGSP很难被人体吸收,大部分通过粪便排出体外,研究者认为AGSP的各种生物活性主要归因于肠道微生物菌群的调节,而不是直接作用于身体器官。也有研究者认为肠道菌群消化产生的丙酸可以抑制肝脏中胆固醇的合成,促进胆固醇在血浆和肝脏中的再分布,降低浓度血浆胆固醇,丙酸盐还可抑制脂肪生成酶从而影响血脂水平[44]。可见,海洋多糖在体内的生物活性与其结构有关,亦与其被消化吸收和酵解的过程有关。
2.4 水产品脂质的体外模拟消化研究
2.4.1 水产品脂质消化过程的氧化稳定性
如表5,目前比较常见的海洋脂质主要包括鱼油、鱼肝油、磷虾油以及藻油。海洋脂质中含有大量的ω-3系列多不饱和脂肪酸,对人体具有良好的营养保健生理功效。但是富含不饱和脂肪酸的脂质极易在贮藏和食用过程中发生脂质氧化,其氧化降解产物(如α,β-不饱和醛)可能与DNA和蛋白质相互作用,从而可能导致细胞功能受损[46]。有研究者提出,人体的胃肠道环境会加速脂质的氧化反应,从而诱发胃肠道癌症[47],体外模拟消化可以用来监测脂质在体内的复杂的氧化反应,研究它们被食用后在胃肠道中的后续变化。通过对鱼肝油的体外静态和动态模拟消化研究发现,在模拟消化过程中会生成丙二醛(MDA)、反式-4-羟基-2-己烯醛(HHE)和反式-4-羟基-2-壬烯醛(HNE)等氧化产物[46,48],其生成量随着消化时间的增加而增加,证实了海洋脂质可以在肠道消化过程中被氧化,且脂质的分解程度和氧化程度之间存在正相关关系[49]。另外,不同来源的海洋脂质在消化过程中的氧化程度可能不同,Tullberg等[50]研究发现,与鱼油和鱼肝油相比,磷虾油和藻类油在静态体外模拟消化过程中的氧化程度更低,Lü等[51]在对微藻油的模拟胃肠消化后也发现,微藻油能够表现出一定的抗氧化能力,这可能与其含有的内源性抗氧化成分有关。
表 5 水产品脂质体外模拟消化的氧化稳定性研究报道Table 5. Oxidative stability of lipid in aquatic products after in vitro digestion研究对象 体外模拟消化条件 氧化稳定性 氧化调控及结果 鱼肝油[53] 胃蛋白酶(50000 U/mL,pH3.0),胰酶(800 U/mL,pH7.0),分别于37 ℃恒温消化。 鱼肝油在体外模拟消化过程中发生了脂质氧化反应。 添加迷迭香提取物,经过体外模拟消化后,迷迭香提取物能够显著抑制鱼肝油氧化,且随其浓度的升高抑制效果也增强。 海鲈鱼脂肪[56] α-淀粉酶(150 U/mL);胃蛋白酶(4000 U/mL);
胰蛋白酶(200 U/mL)和胆盐(20 mmol/L)。体外模拟消化会促进脂质的氧化,其中炸制样品的脂肪氧化程度较高。 − 蓝圆鲹鱼油[57] 胃蛋白酶(1%,pH2.0);胰蛋白酶(2%,pH6.8)分别于37 ℃恒温消化。 − 对蓝圆鲹鱼油进行包埋,体外模拟消化结果表明包埋后的鱼油能够有效抵抗口胃液环境的消化,提高鱼油在肠液中的稳定性。 磷虾油、藻油、鱼肝油和
鳀鱼油[50]唾液α-淀粉酶(75 U/mL),37 °C消化2 min;胃蛋白酶(2000 U/mL,pH3.0),37 °C消化2 h;胰蛋白酶
(100 U/mL),脂肪酶(2000 U/mL),pH7.0,
37 °C消化2 h。在静态体外消化过程中的脂质发生氧化氧化,且鱼肝油和鳀鱼油比磷虾油和藻油更容易氧化。 奥利司他是一种脂肪酶抑制剂,在消化过程中减少了醛的形成。生育酚减少了消化过程中脂质的氧化。 鱼肝油[52] 将黑曲霉脂肪酶以100 U/mL添加到胃液中并使用牛胆汁提取物浓度18.75 g/L。口腔、胃和肠道体外消化的时间分别为5 min、2和4 h。 体外胃肠消化过程中的鱼肝油氧化导致ω-3脂肪酸减少。 在鱼肝油中添加20 ppm抗氧化剂2,6-二叔丁基羟基甲苯(BHT)时,观察到轻微的抗氧化作用,800 ppm时几乎完全抑制了脂质氧化。 鱼肝油[46] TNO胃肠动态消化模型(tiny-TIM)。 在模拟消化过程中会生成MDA、HHE 和 HNE等。 − 鱼肝油[48] 胃蛋白酶(0.45 mg /mL,pH3),37 °C消化2 h,胆汁
(20 mg/mL)和胰酶(2.4 mg/mL),pH7,消化1.5 h。生成MDA、HHE 和 HNE等氧化产物,在胃消化过程中较低,在肠消化
过程中升高。− 鳕鱼肝油[55] 胃蛋白酶(1%,pH1.7),胰酶(1%,pH6.8),
37 °C分别消化3 h。鱼油的过氧化值大幅度增加,肠液比胃液消化对鱼油的氧化影响更大。 添加天然抗氧化食品番茄汁、猕猴桃汁能很好的抑制鱼油的氧化。 2.4.2 水产品脂质的抗氧化调控
利用天然或化学合成抗氧化剂可以有效减缓海洋脂质在体外模拟消化过程中的氧化反应,增强其氧化稳定性。在一项研究中,将0.13 mmol/L乙二胺四乙酸(EDTA)添加到乳化鱼肝油中时,体外消化胃相中的醛类含量略有下降[46]。在鱼肝油中添加20 ppm抗氧化剂2,6-二叔丁基羟基甲苯(BHT)时,在体外消化过程中观察到轻微的抗氧化作用,800 ppm时几乎完全抑制了脂质氧化[52]。迷迭香提取物也能够显著抑制鱼肝油在模拟胃肠道消化过程中发生的脂质氧化反应[53]。叔丁基对苯二酚(TBHQ)、茶多酚、维生素E、没食子酸丙醋(PG)等添加到鳕鱼肝油中,均具有良好的抗氧化效果[54]。天然抗氧化食物如番茄汁、猕猴桃汁等也能很好的减少体外消化过程中的脂质氧化[55]。因此,强化海洋脂质食品的配方或和一些天然抗氧化食物一起食用,可以提高海洋脂质食品的营养价值。
3. 展望
体外模拟消化是代替体内研究食物消化过程的一种非常重要且有效的研究手段,然而,尽管在标准化和生理相关性的方法方面取得了进展,但模型仍存在局限性,与体内消化比较的一致性和准确性仍需要广泛的实验验证。人体研究倾向于测量血液中的生物活性浓度,而体外研究通常得到的是营养物质释放到胃肠的数据,这是比较体外模拟消化和体内消化的困难所在。未来通过充分利用迅速发展的人工智能、生物信息学及代谢组学等多组学技术,与体外模型相结合,有望使体外数据越来越多地通过体内数据进行验证,为在某些研究领域取代动物和人类研究提供可能性。随着对模型的不断改进、优化以及新的科学检测技术的发展,模拟消化模型未来将在海洋生物医药、海洋功能食品等科学领域发挥巨大的作用。
-
表 1 应用于食品的静态与动态体外人体模拟消化模型的比较
Table 1 Comparison of the characteristics of static and dynamic models
主要特征 静态模拟体系 动态模拟体系 研究类型 适用于有限的消化阶段(胃和/或肠道) 适用于研究整个消化过程 研究对象 简单均一的食物;分离/纯化的化合物 复杂的食物 研究目的 改善食品特性;初步验证食物与营养健康的关系 食物成分、结构等对营养物质输送、营养相互作用、益生菌存活等的影响;
为新产品开发提供基础数据优点 快速简单、经济高效;只需根据其预期用途进行验证 更准确地了解肠道的动态环境;可以与体内/临床研究结果直接比较 缺点 无法模拟消化过程的机械力和不断变化的生化环境;
代谢物过度积累会干扰消化操作相对复杂;应验证其重现胃肠道环境的能力 应用 常量营养素的生物利用度研究;生物活性分子研究;
从简单的食品基质中制备营养物质适合消化复杂的食物或药物,例如从复杂物质中
制备营养物质及其生物利用度研究表 2 水产品蛋白质的体外模拟消化研究报道
Table 2 Research on in vitro digestion of protein in aquatic products
研究对象 外部条件 模拟消化条件 蛋白质消化率变化 凡纳滨对
虾蛋白[17]高强度超声 胃蛋白酶(100:1),pH2,37 ℃恒温消化3 h,胰蛋白酶(100:1),pH7.6,37 ℃消化2 h。 经过超声15和25 min凡纳滨对虾蛋白消化率分别提高到了78.13%和81.97%。 刀额新对
虾蛋白[18]蒸制、烤制、微波加热 4 mL胃蛋白酶溶液(0.032 g/mL,pH2),4 mL胰蛋白酶溶液(0.024 g/mL,pH7.5),分别37 ℃消化2 h。 蛋白质的消化率随中心温度的升高而降低,消化率的变化主要与蛋白质的氧化与结构的变化有关。 草鱼重组
鱼肉蛋白[20]芬顿氧化体系和谷氨酰胺转氨酶处理 模拟胃液(pH2.0,含胃蛋白酶),37 ℃消化1 h;模拟肠液(pH8.0,含胰蛋白酶),37 ℃消化2 h。 随着氧化时间的延长,干物质消化率、蛋白质消化率和BCA蛋白浓度均先增加后降低。 草鱼重组
鱼肉蛋白[21]水煮、汽蒸、微波、
油炸模拟胃液(pH2.0,含胃蛋白酶),37 ℃消化1 h;模拟肠液(pH8.0,含胰蛋白酶),37 ℃消化2 h。 微波加热和油炸样品消化率较另外两组偏低,整个消化过程中分子质量逐渐变小。 草鱼蛋白[22] 超高压和冻藏 胃蛋白酶(1%,pH1.2),胰蛋白酶(1.25%,pH6.9)和胆汁(1.4%),分别37 ℃消化3 h。 经冷冻处理的草鱼鱼肉消化性较新鲜草鱼有所降低,而超高压处理的草鱼鱼肉更易消化。 鲟鱼蛋白[19] 水煮、汽蒸、微波、烤箱烤制、油炸 在3 mL模拟唾液中37 ℃消化5 min, 5 mL模拟胃液(pH2.0),消化1 h,最后加入5 mL模拟小肠液(pH8.0),消化2 h。 胃消化阶段,烤制与油炸样品降低了蛋白质消化性,胃肠道消化后,各类熟制样品蛋白消化性都降低。 表 3 体外模拟消化对水产品生物活性肽稳定性影响
Table 3 Effects of in vitro digestion on the stability of bioactive peptides in aquatic products
活性肽来源 活性肽功能 模拟消化条件 分子量变化 功能活性变化 暗纹东方鲀鱼皮胶原蛋白肽[26] 抗氧化活性 胃蛋白酶(0.8%,pH2.0),胰酶(0.8%,pH7.0),分别于37 ℃
酶解2 h。胃消化阶段分子量分布无明显变化;肠消化后小于1 kDa比例更多,分子量更小。 胃消化后,抗氧化活性显著提高;胃肠消化后,抗氧化活性出现小幅度下降。 海洋鱼骨胶原
低聚肽[27]抗氧化活性 胃蛋白酶(3%,pH2.0),胰蛋白酶(3%,pH6.8),分别于37 ℃
酶解3 h。大于10000 u的肽相对含量降低,小于1000 u的肽相对含量同时增加。 整体提高了其抗氧化活性,但DPPH自由基清除能力经模拟胰液消化后有一定的降低。 鳕鱼鱼肉蛋白肽[28] 抗氧化活性 胃蛋白酶(2%),胰酶(2%,pH7.0),分别在37 ℃酶解2 h。 分子量大的肽比例减少,低于500 u肽部分的比例增加,但变化程度不大。 鱼肉蛋白肽发生降解,导致对DPPH自由基的清除率降低;TEAC活性保持稳定。 牡蛎低聚肽[32] 抗氧化活性 胃蛋白酶(1%,pH2.0),胰酶(1%,pH7.5),分别在37 ℃酶解2 h。 胃蛋白酶和胰蛋白酶消化后重均分子量下降不超过8.2%。 胃肠消化对牡蛎低聚肽的抗氧化活性评价各指标均无显著性影响。 两种皮氏蛾螺ACE抑制肽[30] ACE抑制
活性胃蛋白酶(1%),胰蛋白酶(0.5%,pH6.8),分别在37 ℃酶解0~6 h。 − 在胃肠液中稳定性相对较弱,其ACE抑制活性有所降低。 军曹鱼皮水解肽[29] ACE抑制
活性胃蛋白酶(4%,pH2.0),胰酶(4%),分别在37 °C酶解4 h。 − 通过模拟的胃肠道消化,PX-5和PN-5的ACE抑制活性显著降低。 鱿鱼皮胶原
蛋白肽[31]ACE抑制
活性胃蛋白酶(4%),胰酶(4%,pH7.5),分别在37 ℃酶解2 h。 胃蛋白酶消化几乎不改变肽的分子量分布;胰酶消化会增加低分子量肽的含量。 ACE抑制活性在胃肠道消化后增加,发现了一种新的ACE抑制肽(430~75 kDa)。 表 4 水产品多糖的体外模拟消化和酵解特性研究的文献报道
Table 4 Research on in vitro digestion and fermentation characteristics of polysaccharides in aquatic products
研究对象 体外模拟消化条件 消化特性 酵解特性 扇贝多糖[38] α-淀粉酶(0.05%),胃蛋白酶(0.08%,pH2.0),胰酶
(7%,pH7.0),37 ℃恒温消化。糖苷键断裂,形成很多小分子的片段,但不产生游离单糖。 − 牡蛎多糖[37] 新鲜唾液,模拟胃液(112.5 mg胃脂肪酶、106.2 mg胃蛋白酶,pH3.0),模拟肠液(13.0 mg胰蛋白酶,pH7.0),
37 ℃恒温消化。牡蛎多糖在体外模拟消化过程中被部分降解。 难消化的牡蛎多糖可以调节肠道微生物群,发酵促进了短链脂肪酸的产生。 小珊瑚藻多糖[41] α-淀粉酶(75 U/mL),模拟胃液(3.6 mg胃蛋白酶、
3.8 mg胃脂肪酶,pH2.0),模拟肠液(1.3 mg胰蛋白酶、10.0 g胰酶溶液,pH7.0)37 °C恒温消化。在体外模拟消化过程中
不被消化。可以促进短链脂肪酸的产生,在体外调节肠道微生物群的结构。 海带多糖[36] 唾液α-淀粉酶溶液(1500 U/mL),37 °C消化5 min,胃蛋白酶溶液(25000 U/mL),胰酶溶液(800 U/mL),分别
37 °C下反应2 h。不能在胃肠道中被
完全消化。酵解后产生大量的短链脂肪酸,并导致肠道菌群结构与功能的改变(血脂异常及代谢综合征相关)。 泡叶藻多糖[42] 新鲜唾液,模拟胃液(112.5 mg胃脂肪酶、106.2 mg胃蛋白酶)pH3.0,模拟肠液(13.0 mg胰蛋白酶)pH7.0,
37 ℃恒温消化。不能在胃肠道中被消化,分子量和还原糖含量显著降低。 可以显著调节肠道微生物群的组成,特别是增加了拟杆菌门和厚壁菌门的相对丰度,此外,总发酵后SCFA含量显著增加。 龙须菜多糖[43] 胃蛋白酶(236 mg/L,pH2.0),胰酶溶液(7%,pH7.5),
37 ℃恒温消化。体外模拟胃肠道消化的过程中仅发生少量降解。 能有效促进肠道内产生短链脂肪酸细菌的生长,并增加粪便中短链脂肪酸含量和
水分含量。江蓠硫酸化多糖[35] 新鲜唾液,模拟胃液(112.5 mg胃脂肪酶、106.2 mg胃蛋白酶,pH3.0),模拟肠液(13.0 mg胰蛋白酶,pH7.0),
37 ℃恒温消化。在模拟口腔、胃、小肠条件下不被消化。 逐渐被肠道微生物群降解和利用,短链脂肪酸浓度增加,尤其是乙酸、丙酸和异丁酸。 鲍鱼硫酸化多糖[34] 2 mL人唾液、模拟胃液、模拟肠液分别和2 mL多糖溶液充分混合,37 °C下恒温消化。 人体胃肠消化没有显著降低鲍鱼硫酸化多糖的分子量。 鲍鱼硫酸化多糖对肠道双歧杆菌和拟杆菌的增殖有促进作用,丙酸盐和丁酸盐的含量显著增加。 表 5 水产品脂质体外模拟消化的氧化稳定性研究报道
Table 5 Oxidative stability of lipid in aquatic products after in vitro digestion
研究对象 体外模拟消化条件 氧化稳定性 氧化调控及结果 鱼肝油[53] 胃蛋白酶(50000 U/mL,pH3.0),胰酶(800 U/mL,pH7.0),分别于37 ℃恒温消化。 鱼肝油在体外模拟消化过程中发生了脂质氧化反应。 添加迷迭香提取物,经过体外模拟消化后,迷迭香提取物能够显著抑制鱼肝油氧化,且随其浓度的升高抑制效果也增强。 海鲈鱼脂肪[56] α-淀粉酶(150 U/mL);胃蛋白酶(4000 U/mL);
胰蛋白酶(200 U/mL)和胆盐(20 mmol/L)。体外模拟消化会促进脂质的氧化,其中炸制样品的脂肪氧化程度较高。 − 蓝圆鲹鱼油[57] 胃蛋白酶(1%,pH2.0);胰蛋白酶(2%,pH6.8)分别于37 ℃恒温消化。 − 对蓝圆鲹鱼油进行包埋,体外模拟消化结果表明包埋后的鱼油能够有效抵抗口胃液环境的消化,提高鱼油在肠液中的稳定性。 磷虾油、藻油、鱼肝油和
鳀鱼油[50]唾液α-淀粉酶(75 U/mL),37 °C消化2 min;胃蛋白酶(2000 U/mL,pH3.0),37 °C消化2 h;胰蛋白酶
(100 U/mL),脂肪酶(2000 U/mL),pH7.0,
37 °C消化2 h。在静态体外消化过程中的脂质发生氧化氧化,且鱼肝油和鳀鱼油比磷虾油和藻油更容易氧化。 奥利司他是一种脂肪酶抑制剂,在消化过程中减少了醛的形成。生育酚减少了消化过程中脂质的氧化。 鱼肝油[52] 将黑曲霉脂肪酶以100 U/mL添加到胃液中并使用牛胆汁提取物浓度18.75 g/L。口腔、胃和肠道体外消化的时间分别为5 min、2和4 h。 体外胃肠消化过程中的鱼肝油氧化导致ω-3脂肪酸减少。 在鱼肝油中添加20 ppm抗氧化剂2,6-二叔丁基羟基甲苯(BHT)时,观察到轻微的抗氧化作用,800 ppm时几乎完全抑制了脂质氧化。 鱼肝油[46] TNO胃肠动态消化模型(tiny-TIM)。 在模拟消化过程中会生成MDA、HHE 和 HNE等。 − 鱼肝油[48] 胃蛋白酶(0.45 mg /mL,pH3),37 °C消化2 h,胆汁
(20 mg/mL)和胰酶(2.4 mg/mL),pH7,消化1.5 h。生成MDA、HHE 和 HNE等氧化产物,在胃消化过程中较低,在肠消化
过程中升高。− 鳕鱼肝油[55] 胃蛋白酶(1%,pH1.7),胰酶(1%,pH6.8),
37 °C分别消化3 h。鱼油的过氧化值大幅度增加,肠液比胃液消化对鱼油的氧化影响更大。 添加天然抗氧化食品番茄汁、猕猴桃汁能很好的抑制鱼油的氧化。 -
[1] GUERRA A, ETIENNE-MESMIN L, LIVRELLI V, et al. Relevance and challenges in modeling human gastric and small intestinal digestion[J]. Trends in Biotechnology,2012,30(11):591−600. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2012.08.001
[2] BOISEN S, EGGUM B O. Critical evaluation of in vitro methods for estimating digestibility in simple-stomach animals[J]. Nutrition Research Reviews,1991,4(1):141−162. doi: 10.1079/NRR19910012
[3] LEE C M, BOILEAU A C, BOILEAU T W, et al. Review of animal models in carotenoid research[J]. Journal of Nutrition,1999,129(12):2271−2277. doi: 10.1093/jn/129.12.2271
[4] SUN J H, LIM B O, DECKER E A, et al. In vitro human digestion models for food applications[J]. Food Chemistry,2011,125(1):1−12. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.08.036
[5] 龚凌霄, 曹文燕, 王静, 等. 动态智能人体消化模拟体系及其在食品研究领域中的应用[J]. 中国食品学报,2018,18(10):258−268. [XIAO G L, YAN C W, JING W, et al. Advances in dynamic, multi-compartmental gastrointestinal tract models and its food applications[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2018,18(10):258−268. [6] MINEKUS M, ALMINGER M, ALVITO P, et al. A standardised static in vitro digestion method suitable for food-an international consensus[J]. Food & Function,2014,5(6):1113−1124.
[7] MACKIE A, MULET-CABERO A I, TORCELLO-GOMEZ A. Simulating human digestion: Developing our knowledge to create healthier and more sustainable foods[J]. Food Funct,2020,11(11):9397−9431. doi: 10.1039/D0FO01981J
[8] 张文龙. 模拟胃肠道反应器的开发及其初步应用[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2019 ZHANG W L. Development of a gastrointestinal simulation reactor and its preliminary application[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2019.
[9] WICKHAM M J S, FAULKS R M, MANN J, et al. The esign, doperation, and application of a dynamic gastric model[J]. Dissolution Technologies,2012,19(3):15−22. doi: 10.14227/DT190312P15
[10] KONG F B, SINGH R P. A human gastric simulator (HGS) to study food digestion in human stomach[J]. Journal of Food Science,2010,75(9):E627−E635. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2010.01856.x
[11] MINEKUS M, MARTEAU P, HAVENAAR R, et al. Multicompartmental dynamic computer-controlled model simulating the stomach and small intestine[J]. Alternatives to Laboratory Animals,1995,23(2):197−209. doi: 10.1177/026119299502300205
[12] MÉNARD O, CATTENOZ T, GUILLEMIN H, et al. Validation of a new in vitro dynamic system to simulate infant digestion[J]. Food Chemistry,2014,145:1039−1045. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.09.036
[13] BARROS L, RETAMAL C, TORRES H, et al. Development of an in vitro mechanical gastric system (IMGS) with realistic peristalsis to assess lipid digestibility[J]. Food Research International,2016,90:216−225. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2016.10.049
[14] LI Y W, FORTNER L, KONG F B. Development of a gastric simulation model (GSM) incorporating gastric geometry and peristalsis for food digestion study[J]. Food Research International,2019,125:108598. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.108598
[15] WANG J J, WU P, LIU M H, et al. An advanced near real dynamic in vitro human stomach system to study gastric digestion and emptying of beef stew and cooked rice[J]. Food Funct,2019,10(5):2914−2925. doi: 10.1039/C8FO02586J
[16] JOYE I. Protein digestibility of cereal products[J]. Foods,2019,8(6):199. doi: 10.3390/foods8060199
[17] 戴泽川, 毛相朝, 郝亚楠, 等. 高强度超声对凡纳滨对虾蛋白结构和功能特性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(19):80−87. [DAI Z C, MAO X Z, HAO Y N, et al. Effects of high intensity ultrasound on protein structural and functional properties of protein of Litopenaeus vannamei[J]. Food Science,2022,43(19):80−87. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20210818-236 [18] 于小番. 不同烹调热处理对刀额新对虾蛋白质结构、氧化特性及消化性的影响[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2021 YU X F. Effects of different cooking heat treatments on protein structure, oxidation characteristics and digestibility of Metapenaeus ensis[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2021.
[19] 胡吕霖, 任思婕, 沈清, 等. 不同烹饪方式及体外模拟消化环境对鲟鱼蛋白质氧化及消化性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(20):63−70. [HU L L, REN S J, SHEN Q, et al. Effect of different cooking treatments and in vitro digestion on protein oxidation and digestibility of sturgeon fillets[J]. Food Science,2018,39(20):63−70. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201820010 [20] 孟粉, 秦求思, 董烨, 等. 蛋白质氧化和酶对草鱼重组鱼肉品质及体外模拟消化的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2021,21(9):288−295. [MENG F, QIN Q S, DONG Y, et al. Effects of protein oxidation and TGase on the quality of restructured minced grass carp and in vitro simulated digestion[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2021,21(9):288−295. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2021.09.032 [21] 孟粉, 秦求思, 董烨, 等. 烹饪方式对重组鱼排质构及体外模拟消化的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2021,21(6):70−80. [MENG F, QIN Q S, DONG Y, et al. Effects of cooking methods on the texture and in vitro simulated digestion of recombinant fish steaks[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2021,21(6):70−80. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2021.06.009 [22] 孙忱, 潘见, 李颖, 等. 超高压和冻藏对草鱼食用品质及可消化性的研究[J]. 食品工业,2018,39(2):218−221. [SUN C, PAN J, LI Y, et al. Study on ultra high pressure and freezing treatment on digestibility and eating quality of grass carp[J]. The Food Industry,2018,39(2):218−221. [23] CUNHA S A, PINTADO M E. Bioactive peptides derived from marine sources: Biological and functional properties[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2022,119:348−370.
[24] SRIDHAR K, INBARAJ B S, CHEN B. Recent developments on production, purification and biological activity of marine peptides[J]. Food Research International,2021,147:110468. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110468
[25] XU Q, HONG H, WU J, et al. Bioavailability of bioactive peptides derived from food proteins across the intestinal epithelial membrane: A review[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2019,86:399−411.
[26] 曹振海, 乐彩虹, 陶宁萍, 等. 体外模拟消化对暗纹东方鲀鱼皮胶原蛋白肽结构特征及抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(23):61−69. [CAO Z H, LE C H, TAO N P, et al. Effects of structural characteristics and antioxidant activity of collagen bioactive peptides from Takifugu obscurus skin during simulated gastrointestinal digestion[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(23):61−69. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.028686 [27] 冯晓文, 赵晓涵, 潘骁琦, 等. 体外模拟消化对海洋鱼骨胶原低聚肽结构和抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(5):173−179. [FENG X W, ZHAO X H, PAN X Q, et al. Simulated digestion in vitro on structure and antioxidant activity of marine fish bone collagen oligopeptides[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022,48(5):173−179. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.025654 [28] 霍艳姣, 王波, 郭珊珊, 等. 鱼肉蛋白肽在模拟胃肠消化吸收过程中的抗氧化活性和生物利用度[J]. 食品工业科技,2016,37(6):174−178. [HUO Y J, WANG B, GUO S S, et al. Antioxidant activity and bioavailability of the Pacific cod meat peptides during simulated gastrointestinal digestion and absorption[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2016,37(6):174−178. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2016.06.027 [29] LIN Y H, CHEN C A, TSAI J S, et al. Preparation and identification of novel antihypertensive peptides from the in vitro gastrointestinal digestion of marine cobia skin hydrolysates[J]. Nutrients,2019,11(6):1351. doi: 10.3390/nu11061351
[30] 刘鑫烔, 宋铖铖, 乔变文, 等. 两种皮氏蛾螺ACE抑制肽的稳定性和抑制活性[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(19):7−12,19. [LIU X T, SONG C C, QIAO B W, et al. Research on the stability and activity of two ACE inhibitory peptides from Volutharpa ampullaceal perryi[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(19):7−12,19. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020.19.002 [31] ALEMÁN A, GÓMEZ-GUILLÉN M C, MONTERO P. Identification of ace-inhibitory peptides from squid skin collagen afterin vitro gastrointestinal digestion[J]. Food Research International,2013,54(1):790−795. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2013.08.027
[32] 马勇, 高丽辉, 冯晓文, 等. 模拟胃肠消化对牡蛎低聚肽抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 食品与机械,2020,36(11):133−137, 176. [MA Y, GAO L H, FENG X W, et al. Effect of simulated gastrointestinal digestion in vitro on the antioxidant activity of oyster oligopeptides[J]. Food & Machinery,2020,36(11):133−137, 176. doi: 10.13652/j.issn.1003-5788.2020.11.026 [33] 陈培琳, 游卿翔, 常青, 等. 植物多糖消化酵解特性的研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(1):299−304. [CHEN P L, YOU Q X, CHANG Q, et al. Research progress of digestive and fermentation characteristics of plant polysaccharides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(1):299−304. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2019.01.053 [34] AI C Q, MA N, SUN X N, et al. Absorption and degradation of sulfated polysaccharide from pacific abalone in in vitro and in vivo models[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2017,35:127−133. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2017.05.022
[35] DI T, CHEN G J, SUN Y, et al. In vitro digestion by saliva, simulated gastric and small intestinal juices and fermentation by human fecal microbiota of sulfated polysaccharides from Gracilaria rubra[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2018,40:18−27. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2017.10.040
[36] 高洁. 海带多糖的结构表征及其对血脂异常相关肠道菌群的影响研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2019 GAO J. Study on structural characterization of Laminaria japonica polysaccharide and its beneficial effects on dyslipidemias-associated intestinal bacteria[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2019.
[37] MA Y Y, JIANG S S, ZENG M Y. In vitro simulated digestion and fermentation characteristics of polysaccharide from oyster (Crassostrea gigas), and its effects on the gut microbiota[J]. Food Research International,2021,149:110646. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110646
[38] 魏婉露. 扇贝废弃液多糖的分离鉴定及消化吸收情况的研究[D]. 大连: 大连海洋大学, 2022 WEI W L. Study on separation, purification, digestion and absorption of polysaccharide from scallop waste liquid[D]. Dalian: Dalian Ocean University, 2022.
[39] PAYNE A N, ZIHLER A, CHASSARD C, et al. Advances and perspectives in in vitro human gut fermentation modeling[J]. Trends in Biotechnology,2012,30(1):17−25. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2011.06.011
[40] VERNAZZA C L, GIBSON G R, RASTALL R A. In vitro fermentation of chitosan derivatives by mixed cultures of human faecal bacteria[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2005,60(4):539−545. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2005.03.008
[41] WANG Y D, CHEN G J, PENG Y J, et al. Simulated digestion and fermentation in vitro with human gut microbiota of polysaccharides from Coralline pilulifera[J]. LWT,2019,100:167−174. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2018.10.028
[42] CHEN L G, XU W, CHEN D, et al. Digestibility of sulfated polysaccharide from the brown seaweed Ascophyllum nodosum and its effect on the human gut microbiota in vitro[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,112:1055−1061. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.01.183
[43] 黄诗铭. 龙须菜多糖调节脂质代谢及肠道菌群功效研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2019 HUANG S M. Regulating lipid metabolism effect and modulation on intestinal microfloras of polysaccharide extracted from Gracilaria lemaneiformis[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2019.
[44] WEI C Y, LIAO N B, ZHANG Y, et al. In vitro fermentation behaviors of fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from Pearsonothuria graeffei by human gut microflora[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2017,102:1195−1201. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.04.036
[45] COCKBURN D W, KOROPATKIN N M. Polysaccharide degradation by the intestinal microbiota and its influence on human health and disease[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology,2016,428(16):3230−3252. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2016.06.021
[46] LARSSON K, TULLBERG C, ALMINGER M, et al. Malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-hexenal are formed during dynamic gastrointestinal in vitro digestion of cod liver oils[J]. Food Funct,2016,7(8):3458−3467. doi: 10.1039/C6FO00635C
[47] KRISTINOVA V, STORRØ I, RUSTAD T. Influence of human gastric juice on oxidation of marine lipids-in vitro study[J]. Food Chemistry,2013,141(4):3859−3871. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.06.011
[48] TULLBERG C, LARSSON K, CARLSSON N G, et al. Formation of reactive aldehydes (MDA, HHE, HNE) during the digestion of cod liver oil: Comparison of human and porcine in vitro digestion models[J]. Food Funct,2016,7(3):1401−1412. doi: 10.1039/C5FO01332A
[49] LARSSON K, CAVONIUS L, ALMINGER M, et al. Oxidation of cod liver oil during gastrointestinal in vitro digestion[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2012,60(30):7556−7564. doi: 10.1021/jf301444x
[50] TULLBERG C, VEGARUD G, UNDELAND I. Oxidation of marine oils during in vitro gastrointestinal digestion with human digestive fluids-role of oil origin, added tocopherols and lipolytic activity[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,270:527−537. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.07.049
[51] LÜ J W, YANG X Q, MA H X, et al. The oxidative stability of microalgae oil (Schizochytrium aggregatum) and its antioxidant activity after simulated gastrointestinal digestion: Relationship with constituents[J]. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology,2015,117(12):1928−1939. doi: 10.1002/ejlt.201400588
[52] NIEVA-ECHEVARRÍA B, GOICOECHEA E, GUILLÉN M D. Polyunsaturated lipids and vitamin A oxidation during cod liver oil in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. Antioxidant effect of added BHT[J]. Food Chemistry,2017,232:733−743. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.04.057
[53] 李云菲, 郭晓莉, 曹腾正, 等. 迷迭香提取物对自由基诱导鱼肝油氧化及模拟消化过程中脂质氧化的抑制作用研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2020,41(21):28−33. [LI Y F, GUO X L, CAO T Z, et al. Inhibitory effects of rosemary extract on oxidation of cod liver oil induced by free radicals or during the simulated digestion[J]. Food Research and Development,2020,41(21):28−33. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2020.21.005 [54] 刘超, 苗钧魁, 刘小芳, 等. 鳕鱼肝油的氧化稳定性及抗氧化性研究[J]. 青岛大学学报(自然科学版),2015,28(1):49−52. [LIU C, MIAO J K, LIU X F, et al. Study on the oxidation stability and oxidation resistance of cod liver oil[J]. Journal of Qingdao University (Natural Science Edition),2015,28(1):49−52. [55] 陈小玲, 李秀丽, 罗红宇. 体外模拟消化环境对鱼油抗氧化品质的影响[J]. 营养学报,2013,35(4):357−360. [CHEN X L, LI X L, LUO H Y. Effects of simulated gastrointestinal environment on the antioxidant quality of fish oil in vitro[J]. Acta Nutrimenta Sinica,2013,35(4):357−360. doi: 10.13325/j.cnki.acta.nutr.sin.2013.04.001 [56] 赵洪雷, 冯媛, 白旭婷, 等. 蒸制和炸制对海鲈鱼肉体外消化特性的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(24):109−114. [ZHAO H L, FENG Y, BAI X T, et al. Effects of steaming and frying on digestive characteristics of Perca fluviatilis muscle in vitro[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(24):109−114. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.024929 [57] 杨小斌, 周爱梅, 王爽, 等. 蓝圆鲹鱼油微胶囊的结构表征与体外消化特性[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(1):117−122. [YANG X B, ZHOU A M, WANG S, et al. Characterization and in vitro digestibility of microencapsulated Decapterus maruadsi fish oil[J]. Food Science,2019,40(1):117−122. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20171205-066 -
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



