Advance on Inflammation-mediated Relationship between Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Developments in Corresponding Treatment of Dietary Intervention
-
摘要: 肥胖引起的2型糖尿病是我们目前面临的最严重的非传染性疾病之一,脂肪组织中的慢性炎症是导致肥胖人群患2型糖尿病的关键。本文首先从细胞水平和分子水平综述了由炎症介导的肥胖与2型糖尿病关系的研究进展,聚焦免疫细胞和信号通路,其次总结了以免疫细胞与信号通路为靶点的膳食干预治疗研究成果,包括调整巨噬细胞极化状态、T细胞功能以及信号通路活性,以期寻求安全、健康、高效的降血糖膳食原料和有关的特殊医学用途配方食品原料,从而为2型糖尿病的膳食干预疗法提供思路和方案。Abstract: Type 2 diabetes mellitus arising from obesity is one of the most serious noncommunicable diseases which currently have serious impacts on human health. Chronic inflammation in adipose tissue is the key to developing type 2 diabetes mellitus in obese people. This paper firstly reviews the progress in the relationship between obesity mediated by inflammation and type 2 diabetes mellitus from the cellular and molecular levels, focusing on immune cells and signaling pathways. Secondly, it summarizes the results of dietary intervention in targeting immunocytes and signaling pathways, which can adjust the polarization of macrophages, the function of T cells and the activities of various signaling pathways in order to seek the special medical purposes with safe, healthy and efficient lowering blood glucose, so as to provide ideas and programs for the dietary intervention of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
-
Keywords:
- type 2 diabetes mellitus /
- obesity /
- inflammation /
- immunocytes /
- dietary intervention
-
肥胖是指机体总脂肪或局部脂肪含量过多。肥胖与血糖、血脂、血压异常以及胰岛素抵抗(Insulin Resistance,IR)等有关,这些指标异常被称为“代谢综合征”。从20世纪末到21世纪初期,由于人们生活方式和饮食习惯的改变,这一时期肥胖率快速上升。据世界卫生组织的相关报道,相较于1975年的世界肥胖人口数量,现阶段大约增长了三倍;根据2017年全球疾病负担统计,每年有400万以上人口死于超重或肥胖[1]。糖尿病属于患病率极高的非传染性疾病,根据第九版的世界糖尿病地图,2019年全球糖尿病患者数量约4.63亿[2]。糖尿病分为1型糖尿病、2型糖尿病(type 2 diabetes mellitus,T2DM)、妊娠期糖尿病和其他特殊类型糖尿病,T2DM患者数量占90%以上[3],主要特征之一就是会出现IR。
肥胖与T2DM之间存在密切联系。早在1956年Vague等[4]就发现了肥胖会引起代谢紊乱并与糖尿病有关;1982年Kissebah等[5]发现腹型肥胖妇女的腹部脂肪细胞大小与餐后血糖及胰岛素水平呈现出显著的相关性。2002年Ross等[6]对腹型肥胖的绝经前妇女的脂肪组织与胰岛素敏感性之间的关系进行研究,发现腹部肥胖可以作为引起IR的独立因素。随着人们对糖尿病与肥胖关系的研究不断深入,发现糖尿病发病率随成人平均体质量指数(Body mass index,BMI)的升高而升高[7],由此推测肥胖是引起糖尿病的关键因素,并且肥胖引起糖尿病的机制也逐渐得到认识。Nemes等[8]通过对雄性C57Bl/6 J小鼠进行高脂饮食饲喂,发现6周后小鼠体重显著增加并伴随促炎性细胞因子的表达升高及IR,由此证明炎症在肥胖及IR的过程中起到关键性作用。随着科学家对肥胖、炎症和T2DM三者之间关系研究的深入,T2DM治疗的新靶点也得以揭示。本文主要从细胞和分子水平介绍肥胖引起T2DM的机制,并在此基础上以调节脂肪组织免疫细胞和胰岛素的信号通路为靶点,总结食品或药食同源原料中具有降血糖活性成分的研究成果,以期为2型糖尿病的膳食干预治疗提供方案。
1. 炎症介导的肥胖与T2DM的关系
1.1 细胞水平的变化
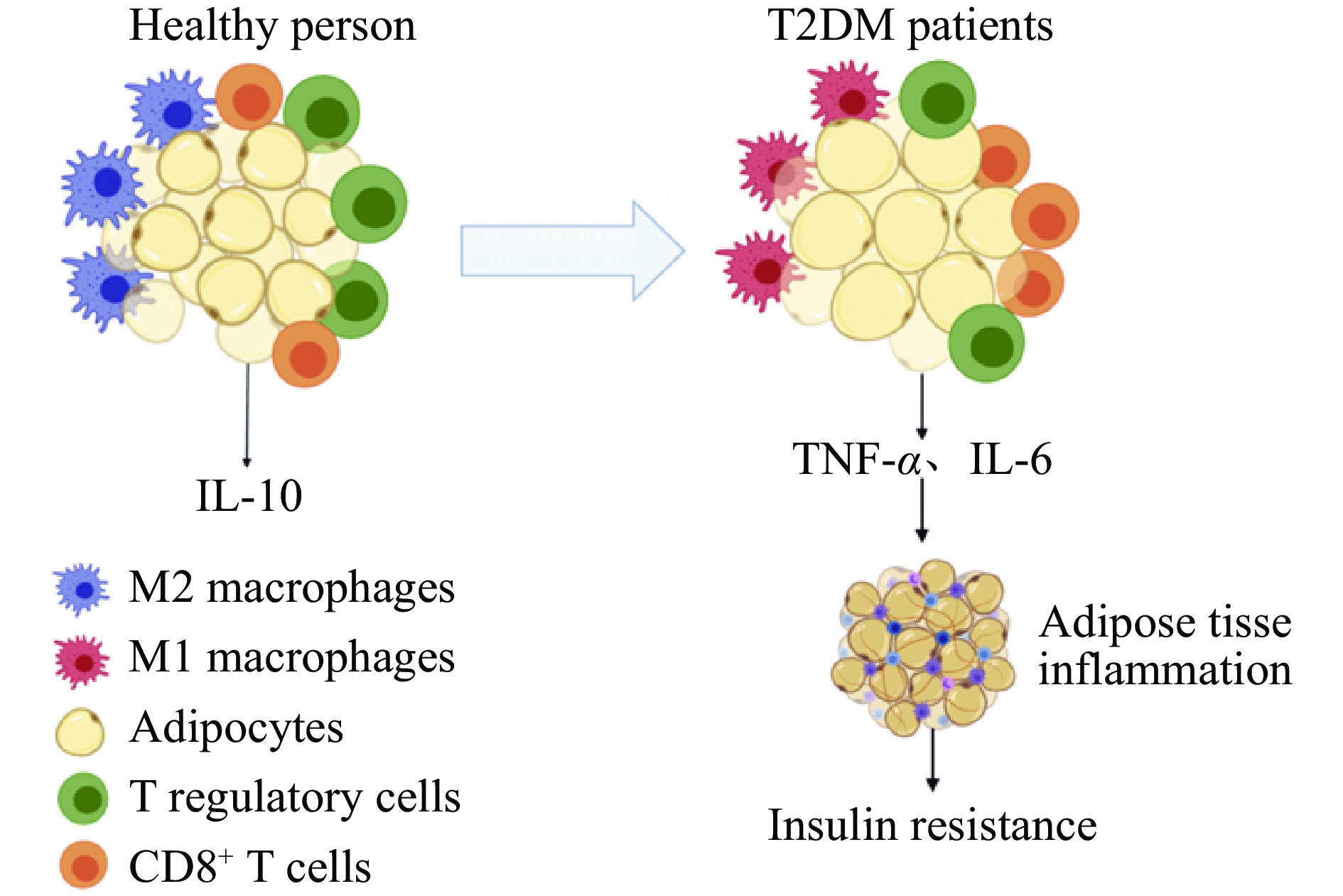
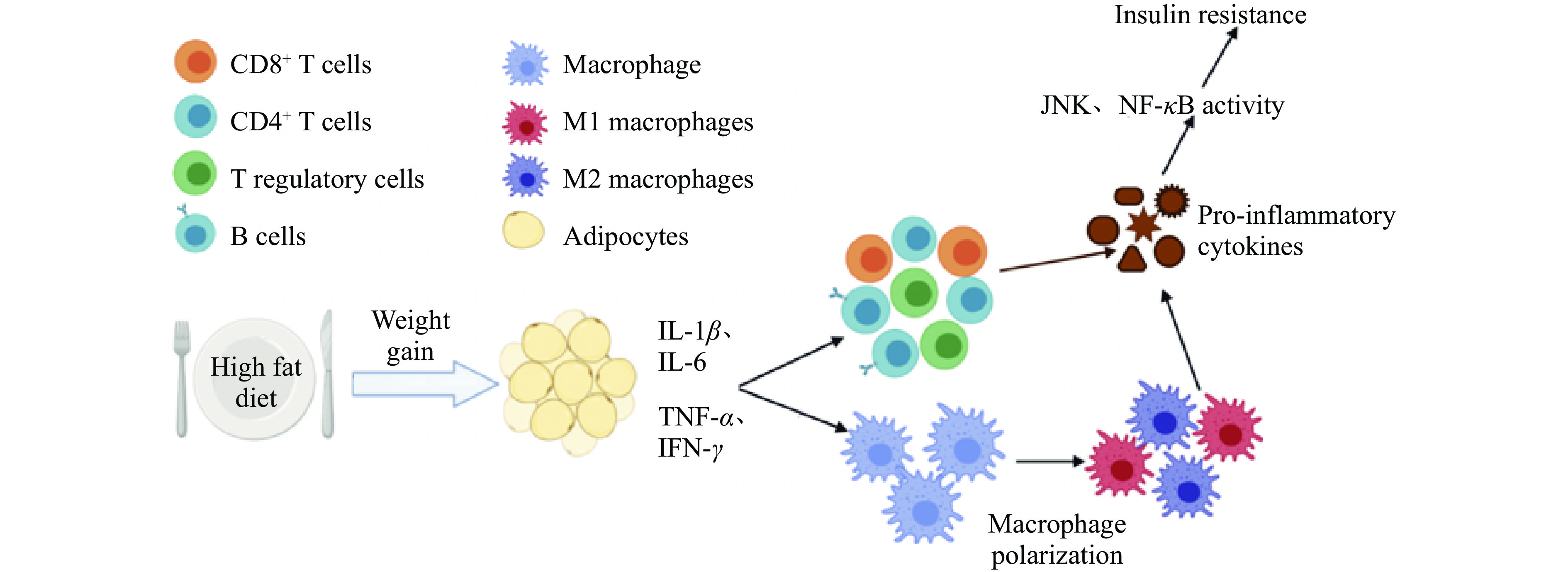
肥胖在炎症的刺激下引发T2DM的过程,在细胞水平上主要体现为免疫细胞发生的变化。肥胖会对脂肪的免疫系统产生重大影响,加速肥胖和相关代谢性疾病的发展。脂肪细胞不仅会分泌特异性细胞因子,还会分泌作用于免疫反应中的促炎或抗炎性细胞因子[9]。肥胖时脂肪组织中肿瘤坏死因子(Tumor necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)、C-C基序趋化因子配体2、白细胞介素-1β(Interleukin-1β,IL-1β)、白细胞介素-6(Interleukin-6,IL-6)等促炎因子水平升高,通过形成脂肪组织的炎性环境来应对营养过剩的问题,形成的炎性环境会吸引更多的免疫细胞浸润,多以巨噬细胞和T淋巴细胞的浸润为主,会进一步加剧炎症反应并抑制细胞代谢功能[10]。健康人群与T2DM患者的免疫细胞差异如图1所示。
脂肪组织巨噬细胞(Adipose tissue macrophages,ATMs)是肥胖引起炎症过程中必不可少的细胞,它的浸润会促进脂肪组织产生炎症。巨噬细胞具有两种表型即M1型与M2型,M2表型稳定存在于健康人群的脂肪组织中。肥胖刚开始时巨噬细胞的初始浸润是一种保护作用,脂肪免疫细胞通过吞噬破裂细胞产生的游离脂肪酸来保护组织免受毒性[11]。随着肥胖的继续发展,促炎信号的增加,M2型巨噬细胞会转变为M1型的促炎表型。C-C基序趋化因子受体2呈阳性的单核细胞的持续聚集以及IV型补体受体呈阳性的ATMs的积累都会促使M1型巨噬细胞压倒M2型巨噬细胞的保护作用[12],诱导脂肪细胞分泌TNF-α等促炎细胞因子,促进炎症反应和IR。
T淋巴细胞根据表面不同的白细胞分化抗原(Cluster of differentiation,CD)可分为两个亚群,即CD4+T细胞和CD8+T细胞。CD4+T细胞促进B淋巴细胞分泌抗体,并能够促进抗体类型的转变,提高与抗原结合的能力,改善机体的特异性免疫功能[13];CD8+T淋巴细胞在健康人群的脂肪组织中占比很小,但在肥胖状态下,它们会在脂肪组织中大量浸润并且和BMI呈正相关,同时肥胖状态下的大规模浸润会刺激M1型ATMs的极化及炎症[14]。研究发现对CD8+T细胞缺陷的小鼠饲喂高脂饲料,促炎因子TNF-α和IL-6的水平没有升高;将CD8+T细胞转移给CD8+T细胞缺陷小鼠则加重了脂肪组织的炎症[15],说明CD8+T淋巴细胞浸润是肥胖引起炎症的关键。正常情况下,CD4+T细胞和CD8+T细胞之间互相拮抗,使机体达到平衡状态,共同参与调节免疫反应;一旦二者数量出现明显的变化,就会引起免疫功能的衰退或者紊乱。由于CD4+ T细胞和CD8+ T细胞具有共同的细胞表面受体分子即CD3,因此,CD3+T细胞代表全部成熟的T淋巴细胞,其数量能够直接反映机体免疫功能的状态[16]。在糖尿病患者中往往会出现CD3+T细胞、CD4+T细胞数量显著减少,以及CD8+T细胞数量不变或增多的情况[17]。
调节性T细胞(Regulatory cells,Treg)主要通过分泌抗炎细胞因子如IL-10抑制自身免疫[18]。在肥胖过程中,脂肪组织中巨噬细胞的炎性浸润以及促炎性细胞因子的水平提高,会导致环境的变化,不利于Treg细胞的进入、扩增和存活,使其数量减少,进而导致炎症并产生IR。此外,肥胖患者会由于机体出现的IR,激活Treg细胞中的蛋白激酶B(Protein kinase B,PKB/Akt),再进一步刺激Akt下游底物的磷酸化,减少IL-10的分泌[19],从而影响到Treg细胞在自身免疫过程中对机体的保护作用,及其缓解炎症的功能。
1.2 分子水平的变化
由肥胖引起的炎症不仅会使免疫细胞的正常代谢功能受到影响,产生的促炎因子还会通过细胞内的信号通路如核转录因子κB(Nuclear factor-kappa B,NF-κB)、c-Jun氨基末端激酶(c-Jun NH2-teminal Kinase,JNK)、磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase,PI3K)/Akt、腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶(AMP-activated protein kinase,AMPK)一系列经典信号通路引发IR(如图2所示),并与炎症相互作用加速T2DM进程。
生理状态下,NF-κB与核因子κB抑制蛋白α(NF-κB Inhibitor protein α,IκBα)在髓样细胞和胰岛素靶向细胞的细胞质中发生结合[20]。当细胞受到生长因子、细胞因子、外来病原体等刺激时,NF-κB抑制蛋白激酶(Inhibitory of kappa B kinase,IKK)诱导IκBα的32和36位点丝氨酸(Serine,Ser)的磷酸化,随后NF-κB与IκBα发生解离,暴露NF-κB核定位序列,向细胞核发生移位,于其中开启促炎因子的转录[21]。NF-κB信号通路的激活提高了促炎因子、内皮粘附分子和化学介质的表达水平,引起单核巨噬细胞向促炎表型M1型巨噬细胞的分化及其在脂肪组织中的炎性浸润[22],导致局部和全身的促炎状态,并在胰岛素靶细胞中形成IR。NF-κB的激活在导致IR的同时,还会诱导NF-κB靶基因的表达增加,这些靶基因表达的产物例如IL-6、TNF-α、IL-1β和抵抗素,会通过正反馈机制进一步激活NF-κB,不断发生恶性循环,最终的结果是胰岛素敏感性的不断降低,导致IR的加剧[23]。
JNK属于丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)家族,具有进化保守性。受到促炎因子等刺激后,c-Jun氨基末端发生磷酸化,参与细胞的免疫反应、IR等过程。JNK途径是目前IR模型中研究最多的信号转导途径。JNK信号通路被激活后,会启动促炎基因的转录,促进胰岛素受体底物1(Insulin receptor substrate 1,IRS1)的磷酸化,使胰岛素信号传导受阻并引发IR[24]。研究表明肥胖小鼠的JNK活性是高于正常小鼠的,并且用JNK1缺陷的小鼠进行高脂饲料喂养后,这些小鼠没有出现IR[25-26]。所以,JNK在肥胖导致IR的过程中是不可缺少的酶。糖尿病患者胰腺中的p-JNK大量升高,会导致胰岛β细胞凋亡及IR[27]。
PI3K属于脂质激酶,根据其序列同源性和底物差异分为I型、II型和III型[28]。细胞受到促炎因子等刺激时,首先激活受体酪氨酸激酶(Receptor tyrosine kinase,RTKs)和G蛋白偶联受体(G protein-coupled receptors,GPCRs),接着通过激活三磷酸鸟苷结合蛋白;或招募I型PI3Ks到质膜;或直接使GPCRs与PI3K相互作用等方式来激活PI3K[29]。激活的PI3K会在质膜上形成磷脂酰肌醇-3,4,5-三磷酸,招募具有同源结构域的Akt转移至细胞膜上[28],在激酶的作用下使Akt蛋白Thr308位和Ser 473位点磷酸化,激活Akt[30]。PI3K/Akt信号通路能够促进脂肪组织内脂质合成并增强胰岛敏感性,促进脂肪和葡萄糖代谢,但肥胖患者升高的促炎因子和肥大的脂肪细胞会通过阻断PI3K/Akt信号通路,使患者机体内发生糖、脂代谢紊乱,进一步引起IR[30]。
AMPK是激活的一磷酸腺苷(Adenosine monophosphate,AMP)依赖的蛋白激酶,是高度保守的Ser/苏氨酸(Threonine,Thr)激酶,它包含催化亚基α1和α2[31]。AMPK可以通过促进α亚基上Thr 172位点的磷酸化,或提升AMP与三磷酸腺苷的比值来激活AMPK信号通路,从而提高机体的葡萄糖利用率,防止脂质的异常沉积,改善T2DM引起的糖、脂代谢紊乱[32]。对于肥胖患者而言,肝细胞内会分泌胎球蛋白B(Fetuin B),并由促炎因子激活NF-κB使脂肪组织特异性分泌抵抗素,抵抗素和Fetuin B会通过降低AMPK活性,抑制AMPK信号通路从而形成IR[33-34]。
2. 对2型糖尿病的膳食干预治疗
针对糖尿病的治疗药物如双胍类、磺脲类等虽然疗效较好,但对人体肝肾功能有损伤;若直接注射胰岛素及其类似物,不仅成本高,也存在容易感染的问题[35]。因此找到既有良好的降糖效果,又能减轻对患者损伤的治疗方案是学者们关注的研究方向。根据在肥胖、炎症和T2DM之间关系的研究中所发现的靶点——免疫细胞和信号通路,许多学者也在探究食物和药食同源的原料中是否存在降血糖的有效成分,寻求安全、健康、高效的降血糖膳食干预疗法和膳食原料及特殊医学用途配方食品(Food for special medical purpose,FSMP)。
2.1 基于免疫功能的膳食干预治疗
T2DM患者的显著特征之一就是免疫力低下,并且高血糖与免疫功能之间的联系一直备受关注。有学者认为,淋巴细胞的分裂会受到高血糖的影响[36],T2DM会引起免疫功能的下降。对于T2DM患者,需要进行针对增强免疫功能的治疗。
山楂、枸杞、银杏叶提取物及芝麻酚都能以巨噬细胞为靶点改善T2DM患者非特异性免疫功能低下的问题。以山楂枸杞为原料制作的保健酸奶可以显著提高腹腔巨噬细胞吞噬率和吞噬指数,改善T2DM患者巨噬细胞的功能[37];银杏叶提取物与芝麻酚可以减少T2DM小鼠ATMs浸润,调控巨噬细胞由M2型向M1促炎表型分化的失衡状态,从而减轻脂肪组织炎症、IR以及脂质代谢紊乱的情况[38-39]。
枸杞、鸡内金、绿茶、红茶以及功能性酸乳均能以T淋巴细胞为靶点改善T2DM。枸杞多糖能提高脂肪组织内CD4+T细胞数量,并显著降低CD8+T细胞的表达水平,提高CD4+/CD8+的比例,刺激淋巴细胞成熟及抗体分泌,进而强化机体的免疫功能[40];鸡内金多糖可提高脾脏及胸腺指数,促进淋巴细胞的成熟分化[41],改善T2DM患者的特异性免疫功能;绿茶中表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(Epigallocatechin gallate,>EGCG)和红茶中的茶黄素是具有抗炎、降血糖、降血脂等功效的活性成分,能够增强Treg细胞的功能,减轻自身免疫损伤并缓解T2DM[42-43];乳酸菌不仅具有调节肠道菌群、抗氧化的能力,同时还具有调节机体特异性和非特异性免疫的功能,其中乳杆菌和双歧杆菌能够提高T淋巴细胞活性并产生抗炎因子[44],缓解T2DM引起的免疫功能衰退和炎症。
除了上述用作药食同源的膳食材料外,以肠内营养制剂(enteral nutrition,EN)形式存在的糖尿病特医食品,在广泛的临床环境中发挥积极作用,可以作为膳食替代品,为糖尿病的预防和治疗做出贡献。糖尿病EN制剂也具有能够明显改善糖尿病患者体内免疫功能衰退的情况。牡蛎肽具有强化免疫功能的特点,采用以牡蛎肽作为蛋白源,以麦芽糊精为主要碳水化合物来源,并添加螺旋藻等成分制成的牡蛎肽EN制剂,可以提高巨噬细胞的吞噬指数,增强巨噬颗粒异物的能力,从而增强非特异性免疫功能[45]。膳食纤维通过降低促炎因子水平达到抗炎作用,并且可以保护肠粘膜上皮细胞,起到提高免疫的作用,含有大豆多糖等多种膳食纤维的康全力以及添加可溶性膳食纤维的EN制剂,可以提高糖尿病患者CD4+T细胞表达和CD4+/CD8+的比例[46],从而促进抗体分泌,改善免疫功能。精氨酸具有刺激淋巴细胞增殖分化和成熟的功能,添加精氨酸的EN制剂可以提高CD3+T细胞、CD4+T细胞数量及CD4+/CD8+的比例,促进淋巴细胞的成熟以及抗体的分泌,强化糖尿病患者的免疫功能[47]。
2.2 基于信号通路的膳食干预治疗
肥胖患者的脂肪组织会分泌大量的促炎因子,它们会通过炎症信号通路使机体产生炎症反应和IR,加速T2DM进程。随着网络药理学研究领域的逐渐成熟,寻找以信号通路作为靶点的膳食干预疗法已经受到重视[48]。
荞麦、金钗石斛、薏苡仁、桑叶、绿茶、亚麻籽、嘉宝果以及米糠都可以通过抑制NF-κB通路改善T2DM。荞麦中富含的荞麦花叶黄酮和金钗石斛都可以下调T2DM大鼠的NF-κB及其磷酸化水平,促进胰岛素受体底物2(Insulin receptor substrate-2,IRS2)的表达,通过干预NF-κB/IRS2信号通路,减少肝脏组织中炎性细胞浸润、细胞肿胀坏死[49-50]。薏苡仁和桑叶提取物中的黄酮、多糖、生物碱等物质可以下调IκB激酶β(Inhibitory of kappa B kinase β,IKKβ)、IκBα、NF-κB P65等基因的mRNA和蛋白水平,抑制NF-κB活性达到缓解IR和炎症的目的[51-52]。绿茶中的EGCG对T淋巴细胞的调节作用也是通过干预NF-κB信号通路实现的[42]。亚麻籽中含有丰富的木脂素,木脂素会被代谢生成肠内素,调节促炎因子水平并干扰IκB的降解,影响NF-κB的激活,从而导致脂多糖刺激的TNF-α分泌减少[53]。嘉宝果是一种来自巴西的水果,富含花青素、矿物质、纤维等成分,嘉宝果中的提取物能和来自米糠中的δ-生育三烯酚能够降低IL-1β、IL-6和TNF-α等促炎因子水平,并抑制NF-κB的活性,减少由于T2DM引起的组织和细胞中脂质的异常沉积并减轻炎症[54-55]。
苦瓜、柠檬、菊花、金银花、紫苏、桑叶以及米糠均可通过调节JNK通路改善T2DM。苦瓜中含有的苦瓜皂苷和柠檬中的苷类活性物质如橙皮苷可以降低Caspase-6抗体、JNK、p-JNK的mRNA和蛋白质表达量,并且随着剂量的增多,对JNK信号通路的调节作用更明显;同时苦瓜皂苷和橙皮苷都具有能够降低甘油三酯和胆固醇水平的能力,可以改善由于T2DM引起的脂代谢紊乱[56-57]。来自菊花、金银花、紫苏中的木犀草素属于黄酮类化合物,可以降低胰腺中Toll样受体4(Toll-like receptor 4,TLR4)和JNK的表达水平,通过调节TLR4/JNK信号通路起到抗炎、降血糖和改善IR的效果[58]。桑叶和米糠除了可以通过阻止NF-κB信号通路被过度激活导致的IR以外,还可通过下调JNK和IRS1及其磷酸化,抑制JNK通路,改善由肥胖引起的炎症并延缓T2DM进程[55,59]。
铁皮石斛、黄芪、芦荟和海参都能以调节PI3K/Akt通路为靶点,改善糖尿病患者的病理情况。铁皮石斛多糖是具有降血糖、降血脂、保护肝等功能的重要活性成分,可以改善肝脏组织中由于T2DM引起的脂代谢紊乱,并改善肝脏组织功能;同时还能够提高细胞中p-IRS2、p-PI3K、p-Akt的表达水平,通过促进PI3K/Akt信号通路的激活,使脂代谢和T2DM得到改善[60]。黄芪甲苷是黄芪的主要有效成分,与芦荟中的大黄素都具有提高PI3K、Akt表达水平的能力,促进肝功能恢复,改善T2DM[61-62]。海参可以显著提高肝脏和骨骼肌组织中p-Akt及磷酸化的糖原合成酶激酶-3(Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3β,GSK-3)的水平,通过激活PI3K/Akt/GSK-3通路,促进糖原合成,在达到降血糖效果的同时还能够改善由于肥胖引起的IR与慢性炎症[63]。
人参、姜黄、桑叶、葛根和燕麦可以通过上调AMPK通路中个各节点的磷酸化强度,加速肝细胞摄取利用葡萄糖,延缓T2DM进程。人参皂苷(Compound K,CK)能提高p-AMPK水平以及p-AMPK/总AMPK比值,激活AMPK活性[64]。姜黄素可以促进细胞摄取葡萄糖,并且用AMPK或p38MAPK抑制剂均可阻断姜黄素诱导的葡萄糖摄取过程,表明姜黄素诱导葡萄糖摄取与AMPK和p38MAPK通路有关[65]。桑叶黄酮可以促进T2DM肝脏细胞中AMPK磷酸化,提高AMPK表达水平;桑叶水提物能明显提高IR状态下人肝癌细胞(Human hepatocellular carcinomas,HepG2)的AMPK磷酸化水平,通过激活AMPK途径促进肝细胞对葡萄糖的吸收[66],改善IR。葛根素通过降低Fetuin B、乙酰辅酶A羧化酶的mRNA及其蛋白的表达水平,激活AMPK信号通路[34],改善糖、脂代谢并缓解IR。燕麦因其含有大量的β-葡聚糖,可以激活肝脏和脂肪组织中AMPK通路,防止脂质在肝脏及脂肪组织中的异常沉积,能够改善糖尿病患者的脂代谢异常并缓解T2DM进程[67]。
3. 总结与展望
全球肥胖症的流行导致代谢紊乱的发病率越来越高,从而产生代谢性疾病的风险也越来越高。随着对T2DM发病机制研究的深入,人们对肥胖与T2DM之间的关系逐渐有所认识,其中由炎症介导肥胖引起IR和T2DM是其中之一。肥胖过程中会使免疫细胞的数量及其活性发生变化而导致细胞的结构和功能紊乱,局部活化的免疫细胞对应激环境的反应会产生促炎性细胞因子,如TNF-α、IL-6、IL-1β和抵抗素等,通过各种信号通路,逐渐演变成慢性炎症和IR;二者又会反作用于细胞,影响到细胞水平的变化。因此,糖尿病患者在细胞水平与分子水平上发生的变化不是独立存在,而是会相互影响的。这就导致由细胞水平变化引起的炎症与分子水平上信号通路变化引起的IR相伴相生,共同导致T2DM的加剧。
肥胖患者的免疫细胞和信号通路为其相关代谢并发症的治疗策略开辟了新的前景。近年来人们已经发现来自于食物、药食同源原料及特医食品中的某些营养成分对于糖尿病患者的干预不是简单地针对某一单个靶点进行干预治疗,可能是通过对多种信号通路进行调节并以各个信号通路之间的相互影响以及信号通路与细胞之间的关系作为靶点进行干预。膳食治疗已经被证明在改善肥胖诱导的IR方面是有效的,并且相较于药物其副作用小。因此,更好地了解脂肪组织的常驻免疫群体、肥胖期间免疫系统的失衡、各个信号通路之间及其与细胞的相互影响,将有助于我们找到治疗脂肪组织炎症和IR的新靶点,并最终找到通过合理地调整膳食以及运用特医食品改善T2DM的方案。
-
-
[1] LANCET T. Obesity and diabetes in 2017: A new year [J]. The Lancet, 2017, 389(10064).
[2] SAEEDI P, PETERSOHN I, SALPEA P, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the international diabetes federation diabetes atlas[J]. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice,2019,157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843
[3] 中国2型糖尿病防治指南 ( 2020年版 ) ( 上 ) [J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2021, 41(8): 668−695 Guidelines for T2DM in China (2020 Edition) (Volume 1)[J]. The Chinese Journal of Practical Internal Medicine, 2021, 41 ( 8 ) : 668−695
[4] VAGUE J. The degree of masculine differentiation of obesities: A factor determining predisposition to diabetes, atherosclerosis, gout, and uric calculous disease[J]. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition,1956,4(1):20−34. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/4.1.20
[5] KISSEBAH A H, VYDELINGUM N, MURRAY R, et al. Relation of body fat distribution to metabolic complications of obesity[J]. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism,1982,54(2):254−260.
[6] ROSS R, FREEMAN J, HUDSON R, et al. Abdominal obesity, muscle composition, and insulin resistance in premenopausal women[J]. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism,2002,87(11):5044−5051.
[7] 王超. 中国成人超重和肥胖及主要危险因素对糖尿病发病的影响[D]. 北京: 北京协和医学院, 2014 WANG C. Effect of overweight and obesity and major risk factors on the onset of diabetes in Chinese adults[D]. Beijing: Peking Xiehe Medical College, 2014.
[8] NEMES, HOMOKI, KISS, et al. Effect of anthocyanin-rich tart cherry extract on inflammatory mediators and adipokines involved in type 2 diabetes in a high fat diet induced obesity mouse model[J]. Nutrients,2019,11(9):1966. doi: 10.3390/nu11091966
[9] 尤玉青, 王妍之, 李伟. 2 型糖尿病的代谢免疫[J]. 现代免疫学,2021,41(2):157−160. [YOU Y Q, WANG Y Z, LI W. Metabolic immunity in T2DM[J]. Modern Immunology,2021,41(2):157−160. [10] WANG T, HE C. Pro-inflammatory cytokines: The link between obesity and osteoarthritis[J]. Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews,2018,44:38−50.
[11] RUSSO L, LUMENG C N. Properties and functions of adipose tissue macrophages in obesity[J]. Immunology,2018,155(4):407−417. doi: 10.1111/imm.13002
[12] PAN Y, HUI X, HOO R L C, et al. Adipocyte-secreted exosomal microRNA-34a inhibits M2 macrophage polarization to promote obesity-induced adipose inflammation[J]. The Journal of Clinical Investigation,2019,129(2):834−849. doi: 10.1172/JCI123069
[13] RUTERBUSCH M, PRUNER K B, SHEHATA L, et al. In vivo CD4+ T cell differentiation and function: Revisiting the Th1/Th2 paradigm[J]. Annual Review of Immunology,2020,38:705−725. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-103019-085803
[14] WANG L, SUN P, WU Y, et al. Metabolic tissue-resident CD8+T cells: A key player in obesity-related diseases[J]. Obesity Reviews,2021,22(3):e13133.
[15] NISHIMURA S, MANABE I, NAGASAKI M, et al. CD8+ effector T cells contribute to macrophage recruitment and adipose tissue inflammation in obesity[J]. Nature Medicine,2009,15(8):914−920. doi: 10.1038/nm.1964
[16] BO X U, FAN C, WANG A, et al. Suppressed T cell-mediated immunity in patients with COVID-19: A clinical retrospective study in Wuhan, China[J]. Journal of Infection,2020,81(1):e51−e60. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.012
[17] CHIU Y L, TSAI W C, HUNG R W, et al. Emergence of T cell immunosenescence in diabetic chronic kidney disease[J]. Immunity & Ageing,2020,17(1):1−10.
[18] DOMINGUEZ-VILLAR M, HAFLER D A. Regulatory T cells in autoimmune disease[J]. Nature Immunology,2018,19(7):665−673. doi: 10.1038/s41590-018-0120-4
[19] WEN J, LIU Q, LIU M, et al. Increasing imbalance of Treg/Th17 indicates more severe glucose metabolism dysfunction in overweight/obese patients[J]. Archives of Medical Research,2021,52(3):339−347. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.11.012
[20] MCLAUGHLIN T, ACKERMAN S E, SHEN L, et al. Role of innate and adaptive immunity in obesity-associated metabolic disease[J]. The Journal of Clinical Investigation,2017,127(1):5−13. doi: 10.1172/JCI88876
[21] ZATTERALE F, LONGO M, NADERI J, et al. Chronic adipose tissue inflammation linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes[J]. Frontiers in Physiology,2020,10:1607. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01607
[22] LI Y, FENG L, LI G, et al. Resveratrol prevents ISO-induced myocardial remodeling associated with regulating polarization of macrophages through VEGF-B/AMPK/NF-κB pathway[J]. International Immunopharmacology,2020,84:106508. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106508
[23] PANAHI G, PASALAR P, ZARE M, et al. High glucose induces inflammatory responses in HepG2 cells via the oxidative stress-mediated activation of NF-κB, and MAPK pathways in HepG2 cells[J]. Archives of Physiology and Biochemistry,2018,124(5):468−474. doi: 10.1080/13813455.2018.1427764
[24] YUNG J H M, GIACCA A. Role of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) in obesity and type 2 diabetes[J]. Cells,2020,9(3):706. doi: 10.3390/cells9030706
[25] HIROSUMI J, TUNCMAN G, CHANG L, et al. A central role for JNK in obesity and insulin resistance[J]. Nature,2002,420(6913):333−336. doi: 10.1038/nature01137
[26] SABIO G, DAS M, MORA A, et al. A stress signaling pathway in adipose tissue regulates hepatic insulin resistance[J]. Science,2008,322(5907):1539−1543. doi: 10.1126/science.1160794
[27] LIU J, LI X, WANG X, et al. Angiotensin (1–7) improves islet function in diabetes through reducing JNK/caspase-3 signaling[J]. Hormone and Metabolic Research,2022,54(4):250−258. doi: 10.1055/a-1796-9286
[28] HUANG X, LIU G, GUO J, et al. The PI3K/Akt pathway in obesity and type 2 diabetes[J]. International Journal of Biological Sciences,2018,14(11):1483. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.27173
[29] VERY N, VERCOUTTER-EDOUART A S, LEFEBVRE T, et al. Cross-dysregulation of O-GlcNAcylation and PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis in human chronic diseases[J]. Frontiers in Endocrinology,2018,9:602. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00602
[30] GAO J R, QIN X J, FANG Z H, et al. To explore the pathogenesis of vascular lesion of type 2 diabetes mellitus based on the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Diabetes Research,2019:2019.
[31] WU S, ZOU M-H. AMPK, mitochondrial function, and cardiovascular disease[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2020,21(14):4987. doi: 10.3390/ijms21144987
[32] CHEN M, HUANG N, LIU J, et al. AMPK: A bridge between diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer's disease[J]. Behavioural Brain Research,2021,400:113043. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2020.113043
[33] 罗招凡, 李芳萍, 程桦. 抵抗素介导AMPK信号通路对HepG2细胞脂质代谢的影响[J]. 实用医学杂志,2017,33(11):1743−1747. [LUO Z F, LI F P, CHENG H. Effect of resistin-mediated AMPK signaling on lipid metabolism in HepG2 cells[J]. Journal of Practical Medicine,2017,33(11):1743−1747. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2017.11.007 [34] GAO J, LIU M, GUO Z, et al. Puerarin alleviates insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic mice by modulating fetuin B-AMPK/ACC signaling pathway in the liver[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University,2021,41(6):839−846.
[35] 李锋, 刘中国. 降糖药不良反应425例分析报告[J]. 山西医药杂志,2018,47(14):1715−1717. [LI F, LIU Z G. Analysis report of 425 cases of adverse reactions of hypoglycemic drugs[J]. Shanxi Medical Journal,2018,47(14):1715−1717. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9926.2018.14.037 [36] 张峰, 高永峰, 张继国. 四叶参多糖对糖尿病大鼠血糖及免疫功能的影响[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2012,18(2):184−186. [ZHANG F, GAO Y F, ZHANG J G. Effects of four-leaf ginseng polysaccharide on blood glucose and immune function in diabetic rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Formulology,2012,18(2):184−186. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9903.2012.02.054 [37] 栾金水. 山楂枸杞保健酸奶的功能性研究[J]. 食品科学,2006(4):233−236. [LUAN J S. Functional study of hawthorn wolfberry health yogurt[J]. Food Science,2006(4):233−236. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2006.04.058 [38] PAN L, LU Y, LI Z, et al. Ginkgo biloba extract EGb761 attenuates bleomycin-induced experimental pulmonary fibrosis in mice by regulating the balance of M1/M2 macrophages and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB)-mediated cellular apoptosis[J]. Medical Science Monitor:International Medical Journal of Experimental and Clinical Research,2020,26:e922634.
[39] 孔祥, 华强, 姚新明, 等. 芝麻酚调控巨噬细胞极化改善肥胖小鼠脂肪组织炎症及胰岛素抵抗[J]. 中国临床药理学与治疗学,2020,25(7):728−733. [KONG X, HUA Q, YAO X M, et al. Sesame phenol regulates macrophage polarization to improve adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance in obese mice[J]. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics in China,2020,25(7):728−733. doi: 10.12092/j.issn.1009-2501.2020.07.002 [40] 曾丽容. 枸杞多糖对老年2型糖尿病免疫功能及抗氧化功能的影响[J]. 中国民间疗法,2022,30(3):72−74. [ZWNG L R. Effects of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on immune and antioxidant function of aged type 2 diabetes[J]. Chinese Folk Therapy,2022,30(3):72−74. doi: 10.19621/j.cnki.11-3555/r.2022.0325 [41] 蒋长兴, 蒋顶云, 熊清平, 等. 鸡内金多糖对糖尿病高脂血症大鼠血脂、血糖及细胞免疫功能的影响[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2012,18(20):255−258. [JIANG C X, JIANG D Y, XIONG Q P, et al. Effects of chicken gpolysaccharide on blood lipid, glucose and cellular immune function in diabetic hyperlipidemia rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Formulology,2012,18(20):255−258. doi: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2012.20.074 [42] YUN J-M, JIALAL I, DEVARAJ S. Effects of epigallocatechin gallate on regulatory T cell number and function in obese v. lean volunteers[J]. British Journal of Nutrition,2010,103(12):1771−1777. doi: 10.1017/S000711451000005X
[43] MAHMOUD F, HAINES D, AL-OZAIRI E, et al. Effect of black tea consumption on intracellular cytokines, regulatory T cells and metabolic biomarkers in type 2 diabetes patients[J]. Phytotherapy Research,2016,30(3):454−462. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5548
[44] 刘恋, 罗育才, 肖莲荣. 降血糖酸乳的研究进展[J]. 食品科技,2020,45(10):71−75. [LIU L, LUO Y C, XIAO L R. Progress in hypoglycemic milk[J]. Food Technology,2020,45(10):71−75. [45] 蔡冰娜, 吴园涛, 孙恢礼. 牡蛎肽肠内营养制剂对小鼠免疫功能的影响[J]. 时珍国医国药,2010,21(11):2816−2818. [CAI B N, WU Y T, SUN H L. Effect of enteral nutrition preparations of oyster peptide on immune function in mice[J]. Shizhen National Chinese Medicine,2010,21(11):2816−2818. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2010.11.043 [46] 李知翰, 王勇. 添加可溶性膳食纤维的肠内营养制剂对炎症性肠病患者肠道免疫平衡和肠道菌群的影响[J]. 黑龙江中医药,2021,50(1):106−108. [LI Z H, WANG Y. Effect of enteral nutrition preparations supplemented with soluble dietary fiber on the intestinal immune balance and intestinal microflora in patients with inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Heilongjiang Traditional Chinese Medicine,2021,50(1):106−108. [47] 曾兢. 谷氨酰胺和精氨酸强化的肠内营养对大鼠重型颅脑损伤后免疫功能及蛋白代谢影响的实验研究[D].重庆: 第三军医大学, 2006 ZENG J. Experimental study on the effects of glutamine and arginine-fortified enteral nutrition on immune function and protein metabolism after severe rat brain injury [D]. Chongqing: Third Military Medical University, 2006.
[48] NOOR F, REHMAN A, ASHFAQ U A, et al. Integrating network pharmacology and molecular docking approaches to decipher the multi-target pharmacological mechanism of Abrus precatorius L. acting on diabetes[J]. Pharmaceuticals,2022,15(4):414. doi: 10.3390/ph15040414
[49] 高媛, 林琳, 满玉洁. 荞麦花叶黄酮干预自发肥胖型2型糖尿病大鼠NF-κB/IRS2信号通路的实验研究[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志,2020,19(1):30−34. [GAO Y, LIN L, MAN Y J. Study of buckwheat leaf flavonoids intervention in NF-κB/IRS2 signaling in spontaneously obese T2DM rats[J]. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine,2020,19(1):30−34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2020.01.009 [50] 刘庆春. 金钗石斛对糖尿病大鼠肝组织 NF-κB 表达的影响[J]. 中医临床研究,2017,9(11):23−24. [[LIU Q C. Effect of Dendrobium stem on NF-κB expression in liver tissues of diabetic rats[J]. Clinical Research of TCM,2017,9(11):23−24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7860.2017.11.008 [51] HU Y, ZHOU Q, LIU T, et al. Coixol suppresses NF-κB, MAPK pathways and NLRP3 inflammasome activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 cells[J]. Molecules,2020,25(4):894. doi: 10.3390/molecules25040894
[52] 常化静. 桑叶提取物通过NF-κB信号通路改善KKAy小鼠胰岛素抵抗的机制研究[D]. 广州: 南方医科大学, 2015 CHANG H J. Mechanism of mulberry leaf extracts to improve insulin resistance in KKAy mice by NF-κB signal pathway [D]. Guangzhou: Southern Medical University, 2015.
[53] LI D, LUO F, GUO T, et al. Targeting NF-κB pathway by dietary lignans in inflammation: Expanding roles of gut microbiota and metabolites[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2022:1−17.
[54] HSU J D, WU C C, HUNG C N, et al. Myrciaria cauliflora extract improves diabetic nephropathy via suppression of oxidative stress and inflammation in streptozotocin-nicotinamide mice[J]. Journal of Food and Drug Analysis,2016,24(4):730−737. doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2016.03.009
[55] SHEN J, YANG T, XU Y, et al. δ-Tocotrienol, isolated from rice bran, exerts an anti-inflammatory effect via MAPKs and PPARs signaling pathways in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2018,19(10):3022. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103022
[56] 马春宇, 王慧娇, 于洪宇, 等. 苦瓜总皂苷对2型糖尿病大鼠胰岛素信号转导通路的影响[J]. 中药新药与临床药理,2015,26(3):289−294. [MA C Y, WANG H J, YU H Y, et al. Effect of total saponin on insulin signaling transduction pathway in T2DM rats[J]. New Medicine and Clinical pharmacology of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2015,26(3):289−294. [57] 殷章红, 罗鹏程, 王才英. 橙皮苷抑制JNK信号通路辅助治疗2型糖尿病大鼠[J]. 长春中医药大学学报,2015,31(3):460−462. [YIN H Z, LUO P C, WANG C Y. Hesperidine inhibition of JNK signaling in the adjuvant treatment of T2DM[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2015,31(3):460−462. doi: 10.13463/j.cnki.cczyy.2015.03.008 [58] SATO S, MUKAI Y. Modulation of chronic inflammation by quercetin: The beneficial effects on obesity[J]. Journal of Inflammation Research,2020,13:421. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S228361
[59] 罗明琍. 桑叶有效部位降血糖作用与JNK信号通路的关系[D]. 广州: 广州中医药大学, 2013 LUO M L. Relationship between hypoglycemic effect and JNK signaling pathway in effective sites of mulberry leaves [D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, 2013.
[60] WANG K, WANG H, LIU Y, et al. Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide attenuates T2DM via the regulation of PI3K/Akt-mediated glycogen synthesis and glucose metabolism[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2018,40:261−271. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2017.11.004
[61] 季天娇. 黄芪甲苷调节PI3K/Akt通路来改善2型糖尿病大鼠肝糖代谢异常的分子机制[D]. 合肥: 安徽医科大学, 2020 JI T J. The PI3K / Akt pathway to improve the molecular mechanism of abnormal hepatic glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetic rats [D]. Hefei: Anhui Medical University, 2020.
[62] XIAN M, CAI J, ZHENG K, et al. Aloe-emodin prevents nerve injury and neuroinflammation caused by ischemic stroke via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR and NF-κB pathway[J]. Food & Function,2021,12(17):8056−8067.
[63] WANG T, ZHENG L, ZHAO T, et al. Anti-diabetic effects of sea cucumber (Holothuria nobilis) hydrolysates in streptozotocin and high-fat-diet induced diabetic rats via activating the PI3K/Akt pathway[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2020,75:104224. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2020.104224
[64] BAI L, GAO J, WEI F, et al. Therapeutic potential of ginsenosides as an adjuvant treatment for diabetes[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology,2018,9:423. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00423
[65] KIM J H, PARK J M, KIM E K, et al. Curcumin stimulates glucose uptake through AMPK‐p38 MAPK pathways in L6 myotube cells[J]. Journal of Cellular Physiology,2010,223(3):771−778.
[66] MENG Q, QI X, FU Y, et al. Flavonoids extracted from mulberry (Morus alba L. ) leaf improve skeletal muscle mitochondrial function by activating AMPK in T2DM[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2020,248:112326. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112326
[67] LIU B, YANG T, LUO Y, et al. Oat β-glucan inhibits adipogenesis and hepatic steatosis in high fat diet-induced hyperlipidemic mice via AMPK signaling[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2018,41:72−82. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2017.12.045
-
期刊类型引用(9)
1. 陈屹轩,布冠好,杨趁仙,辛颖,段晓杰,李梦瑶. 枯草芽孢杆菌发酵对花生蛋白抗原性的影响. 河南工业大学学报(自然科学版). 2025(01): 19-25+32 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 任圆圆,何俊叶,刘成,王思瑶,孙朋朋. 低酯果胶和玉米淀粉对泥鳅肌原纤维蛋白凝胶特性的影响. 中国调味品. 2024(04): 60-65 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王欢,贾强,江津津,欧爱芬. 超声辅助磷酸化对大豆分离蛋白分子及凝胶特性的影响. 中国食品添加剂. 2023(01): 233-238 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 郑辉,张鉴达,宫若楠. 不同蛋白酶对碧根果蛋白肽制备的影响及抗氧化活性研究. 中国食品添加剂. 2023(04): 235-241 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 高越,杨雪飞,郑志,麻志刚,季一顺. 不同凝固方式制备豆腐的特性分析. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2023(10): 118-126 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 姜彩霞,郑喜群,刘晓兰,王俊彤,赵婉宏,曾祥瑞. 体外模拟胃部消化对白芸豆α-淀粉酶抑制剂活性及结构的影响. 中国粮油学报. 2023(06): 46-51 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 张俊杰,郑嘉琛,谢宜桐,罗文江,张媛,何熙,刘丹怡,韩建春. 高水分挤压温度对绿豆蛋白结构的影响. 食品工业科技. 2022(20): 130-136 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 母梦羽,张霞,贾峰,王琦,梁赢,王金水. 微波功率对面筋蛋白-淀粉复合体系功能特性的影响. 河南工业大学学报(自然科学版). 2021(04): 16-21 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 陈兵兵,叶仁伟,付晴雨,荐佳琳,高振华. 金属离子对大豆基木材胶黏剂胶合性能的影响. 林产工业. 2021(10): 54-59+64 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(13)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
