Effect of Corn By-product Fermented Beverage on Glucolipid Metabolism in Streptozotocin Induced Diabetes Mice
-
摘要: 目的:本实验研究玉米副产物发酵饮料(corn by-product fermented beverage,CPFB)对糖尿病小鼠糖脂代谢的改善作用。方法:采用高脂饲料联合链脲佐菌素(STZ)建立糖尿病小鼠模型,分为正常对照组(NC),模型对照组(MC)、高剂量组(H-CPFB,0.1 mL/10 g·bw)、中剂量组(M-CPFB,0.05 mL/10 g·bw)、低剂量组(L-CPFB,0.025 mL/10 g·bw)、自由饮用组(F-CPFB)和阳性对照组(PC,150 mg/kg盐酸二甲双胍)。实验期间每7 d测定空腹血糖水平(FBG)、体重。连续28 d灌胃不同剂量的发酵饮料后测定口服糖耐量(OGTT)、血清中总胆固醇(TG)、总甘油三酯(TC)、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)、游离脂肪酸(NEFA)、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、丙二醛(MDA)及肝脏中谷丙转氨酶(ALT)、谷草转氨酶(AST)水平。结果:玉米副产物发酵饮料能够极显著降低模型小鼠空腹血糖水平(P<0.01),其中F-CPFB组效果最优,血糖值下降了44.6%;能够减缓糖尿病带来的体重负增长;使口服糖耐量得到缓解(P<0.01);能够极显著降低血清中脂质水平(P<0.01),其中H-CPFB组降低TC水平至6.00±1.13 nmol/L,与NC组无明显差异;极显著降低血清中丙二醛含量并极显著提高超氧化物歧化酶活力(P<0.01);极显著降低肝脏中谷草转氨酶水平(P<0.01),其中H-CPFB组的效果优于其余组,下降了约21.89%,并缓解糖尿病引起的肝损伤。结论:玉米副产物发酵饮料对高脂饲料联合链脲佐菌素建立的糖尿病小鼠模型具有显著降低空腹血糖水平,调节糖脂代谢及缓解肝损伤能力。Abstract: Objective: To study the effect of corn by-product fermented beverage (CPFB) on glucolipid metabolism in diabetes mice. Methods: Diabetes mice model was established by high fat diet combined with streptozocin (STZ). The mice were divided into normal control group (NC), model control group (MC), high dose group (H-CPFB, 0.1 mL/10 g·bw), mid dose group (M-CPFB, 0.05 mL/10 g·bw), low dose group (L-CPFB, 0.025 mL/10 g·bw), free drinking product group (F-CPFB) and positive control group (PC, 150 mg/kg metformin hydrochloride). During the experiment, the fasting blood-glucose level (FBG) and body weight were measured every 7 days. Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), total cholesterol (TG), total triglycerides (TC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), non-esterified fatty acid (NEFA), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and malondialdehyde (MDA) and the levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) in liver were measured after treatment with different doses of fermented beverages for 28 consecutive days. Results: Corn by-product fermented beverage could significantly reduce the fasting blood glucose level of model mice (P<0.01). The effect of F-CPFB group was the best, and the blood glucose value decreased by 44.6%. It could slow down the negative weight gain caused by diabetes. The oral glucose tolerance was relieved (P<0.01). It could significantly reduce the serum lipid level (P<0.01), and the TC level in H-CPFB group was reduced to 6.00±1.13 nmol/L, which was not significantly different from that in NC group. The content of MDA in serum was significantly decreased and the activity of SOD was significantly increased (P<0.01). The level of AST in liver was significantly reduced (P<0.01). The effect of H-CPFB group was better than of other groups, decreased by about 21.89% and relieved the liver injury caused by diabetes. Conclusion: Corn by-product fermented beverage can significantly reduce fasting blood glucose level, regulate glucose and lipid metabolism and alleviate liver injury in diabetes mice model established by high-fat diet combined with streptozotocin.
-
Keywords:
- corn silk /
- corn bract /
- Lactobacillus fementation /
- diabetes /
- glucolipid metabolism
-
糖尿病是常见复杂的代谢疾病,其发病率正在以惊人的速度上升,可导致严重的健康和经济问题[1]。目前,加强对血糖、脂质水平的控制以降低并发症和疾病进展的风险成为现今一大难题[2-3]。而对于当前糖尿病的控制,临床上较多使用西药,主要是服用一些化学合成抗糖尿病药物或人工注射胰岛素治疗[4-5],市面上大多数降糖药都或多或少存在一些可能危害患者健康的副作用[6],如胃肠道不良反应,特别是恶心、呕吐并导致患低血糖风险增加[7]。因此,发现和开发副作用少的替代药物是目前的主要研究领域之一。
乳酸菌是能使糖发酵、并产生大量乳酸的一类有益菌,有合成和提高营养物质的生物利用度的能力,调节免疫系统,潜在降血糖能力以及减少乳糖不耐受症状等益处。有研究表明,补充乳酸菌可显著提升糖尿病患者血清胰岛素含量,并与糖化血红蛋白改善作用有关[8-9]。高伟华[10]基于BSH(胆盐水解酶)活性从胞内提取物筛选出2株具有调节Ⅱ型糖尿病小鼠血糖水平的干酪乳酸菌。Ejtahed等[11]证实乳酸菌发酵酸奶能够改善Ⅱ型糖尿病患者的抗氧化状态。
玉米须和玉米苞叶作为我国传统“药食同源”食材,具有广泛的预防和保健的作用。玉米须不仅有利尿、利胆和止血等保健作用,还对糖尿病患者有一定的作用。玉米苞叶富含多种糖类物质和活性成分,可作为多种产品生产的原料[12]。有研究表明玉米须可以增进机体的胰腺的功能,推动胰岛素分泌,提升耐糖量,降低血糖水平[13-14]。Lee等[15]证实玉米须黄酮类物质能够降低血清胆固醇,预防肥胖。Pan等[16]通过实验证明玉米须多糖(PCS2)能够显著降低链脲佐菌素诱导Ⅱ型糖尿病(T2DM)胰岛素抵抗小鼠血脂及血糖水平。这些具有“药食同源”作用的植物原料结合乳酸菌发酵可使活性成分含量提高从而增强其保健功能性[17]。经乳酸菌发酵产生的酶系作用,将植物基质中多酚等物质转化为更具生物活性的形式或产生新的活性物质,使其功能性增强并丰富食物的营养品质[18-19]。
目前,市场上以玉米副产物为原材料结合乳酸菌发酵的产品较少,而且对于这些产品的功能性及体内活性是否表现良好还未知,无系统的功能性评价而难以被消费者接受。本课题组前期将玉米副产物结合乳酸菌发酵,研制出一款玉米副产物发酵饮料,通过非靶向代谢组技术测定饮料发酵过程中活性物质含量变化,结果表明经乳酸菌发酵产生多种具有调节糖脂代谢功能的活性物质[20]。因此本研究探讨玉米副产物发酵饮料对糖尿病小鼠糖脂代谢的改善作用,为相关降糖降脂产品的功能性研究奠定基础并提供动物实验依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
清洁级雄性KM小鼠 体重18±2 g,90只,生产许可证号为SCXK(辽)2014-0004,锦州医科大学实验动物中心;高脂饲料(主要成分:基础饲料58.8%,猪油20%,胆固醇1%,胆盐0.2%,糖20%) 南京盛民科研动物养殖场;普通饲料(主要成分:蛋白质20%,水分10%,脂肪40%) 沈阳市于洪区前珉饲料有限公司;玉米须、玉米苞叶、桂花、栀子、苦荞 锦州大润发超市;乳酸乳球菌YM313(L. lactisYM313)、干酪乳杆菌YQ336[21](L. casei YQ336) 锦州医科大学食品微生物实验室分离并保存;盐酸二甲双胍 中美上海施贵宝制药有限公司;链脲佐菌素(streptozocin,STZ) 美国Sigma公司;胰岛素(insulin,INS)ELISA分析试剂盒、总胆固醇(total cholesterol,TC)、甘油三酯(triglyceride,TG)、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(high density liptein cholesterol,HDL-C)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(low density lipoprotein cholesterol,LDL-C)、游离脂肪酸(non-esterified fatty acid,NEFA)、丙二醛(malondialdehyde,MDA)、超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD)、谷丙转氨酶(alanine transaminase,ALT)、谷草转氨酶(aspartate transaminase,AST)试剂盒 南京建成生物工程研究所。
百捷血糖测试仪 勤立生物科技股份有限公司;HH-4数显恒温水浴锅 常州恩培仪器有限公司;LD310-2电子秤 沈阳龙腾电子有限公司;RE-501旋转蒸发仪 济南海诺实验仪器有限公司;SW-CJ-1C超净台 苏州净化设备有限公司;YXQ-LS型灭菌锅 上海博讯实业有限公司;MSD550-3显微镜 迈时迪(东莞)科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 玉米副产物发酵饮料的制备
剪碎→水提→过滤→调配→杀菌→接菌→发酵→冷藏
参考张妍等[20]制作方法,按液料比3:1的比例添加主要原料玉米须和玉米苞叶(添加比例为玉米须:玉米苞叶=1:1),随后添加辅料占总体积比例为0.5%桂花、0.2%栀子、5%苦荞进行80 ℃ 1 h水提。使用20目筛子,8层纱布过滤,得到水提液。随后添加7%的乳糖醇进行饮料的调配。将调配后的饮料进行95 ℃ 15 min杀菌。将杀菌好的饮料接种6%的乳酸乳球菌YM313和干酪乳杆菌YQ336(接种比例为1:1)。最后进行37 ℃ 15 h的发酵。即得发酵饮料,再经旋转蒸发仪浓缩10倍,分装至5 mL离心管,4 ℃冰箱保存[22]。
1.2.2 糖尿病小鼠模型建立与分组
实验开始之前,所有雄性KM小鼠在24±3 ℃,55%±5%相对湿度,光照12 h或黑暗12 h/d,提供普通饲料和水,在此条件下,正常喂养一周使小鼠适应环境,开始正式实验。适应性喂养后,取8只小鼠作为NC组,其余82只纳入建模组,在模型建立期间,除NC组外其余小鼠均给予高脂饲料喂养。饲喂两个月后,小鼠禁食12 h不禁水,连续3 d腹腔注射STZ注射液(40 mg/kg)后测定空腹血糖水平,建模成功标准为空腹血糖值≥11.1 mmol/L[23]。对建模成功小鼠进行随机分组(每组8只),分成6组,在28 d实验周期内除NC组外均饲喂高脂饲料,各剂量组每天灌胃发酵饮料1次,具体实验分组及灌胃剂量见表1。所有动物实验均在锦州医科大学伦理委员会的伦理审查和监督下完成。
表 1 动物实验分组及实验方式Table1 Group and method of animal experiment组别 建模期 STZ处理 灌胃期 正常对照组(NC) 普通饲料+蒸馏水 柠檬酸钠缓冲溶液 0.1 mL/(10 g·bw)生理盐水 模型对照组(MC) 高脂饲料+蒸馏水 40 mg/kgSTZ溶液 0.1 mL/(10 g·bw)生理盐水 阳性对照组(PC) 高脂饲料+蒸馏水 40 mg/kgSTZ溶液 150 mg/kg盐酸二甲双胍 高剂量组(H-CPFB) 高脂饲料+蒸馏水 40 mg/kgSTZ溶液 0.1 mL/(10 g·bw) CPFB 中剂量组(M-CPFB) 高脂饲料+蒸馏水 40 mg/kgSTZ溶液 0.05 mL/(10 g·bw) CPFB 低剂量组(L-CPFB) 高脂饲料+蒸馏水 40 mg/kgSTZ溶液 0.025 mL/(10 g·bw) CPFB 自由饮用组(F-CPFB) 高脂饲料+蒸馏水 40 mg/kgSTZ溶液 自由饮用未浓缩饮料 1.2.3 日常生理指标的测定
观察小鼠的日常活动和精神状态,并于每7 d固定时间对小鼠进行称重。
1.2.4 空腹血糖的测定
建模成功后将小鼠禁12 h后用血糖仪记录各组小鼠初始空腹血糖值,实验期间每7 d固定时间对小鼠进行空腹血糖测定一次。
1.2.5 口服糖耐量试验
最后一次灌胃结束后,将小鼠禁食(12 h)后灌胃2 g/kg葡萄糖溶液。分别于0、30、60、120 min测定小鼠空腹血糖值,绘制血糖代谢曲线并计算血糖变化的曲线下面积(Area under the curve,AUC)。
1.2.6 血清生化指标
取小鼠眼眶血3500 r/min离心15 min,分离血清,按照说明书使用试剂盒测定血清中的血脂指标(TG、TC、HDL-C、LDL-C、NEFA),抗氧化指标(SOD、MDA)和血清胰岛素(INS)含量。
1.2.7 肝脏中指标检测
取小鼠肝脏制备匀浆使用试剂盒测定肝脏中的谷草转氨酶(AST)、谷丙转氨酶(ALT)水平。
1.2.8 肝脏病理切片
用H&E染色法,对肝脏的组织病理学变化进行观察。将肝组织于10%甲醛溶液(pH7.4)中固定。固定后,对肝脏组织脱水和包埋。将包埋的肝脏蜡块切成薄片(4 μm厚),苏木精-伊红染色,显微镜观察(200×),拍取组织照片。
1.3 数据处理
采用SPSS 20.0进行数据处理,结果以平均值±标准差(
2. 结果与分析
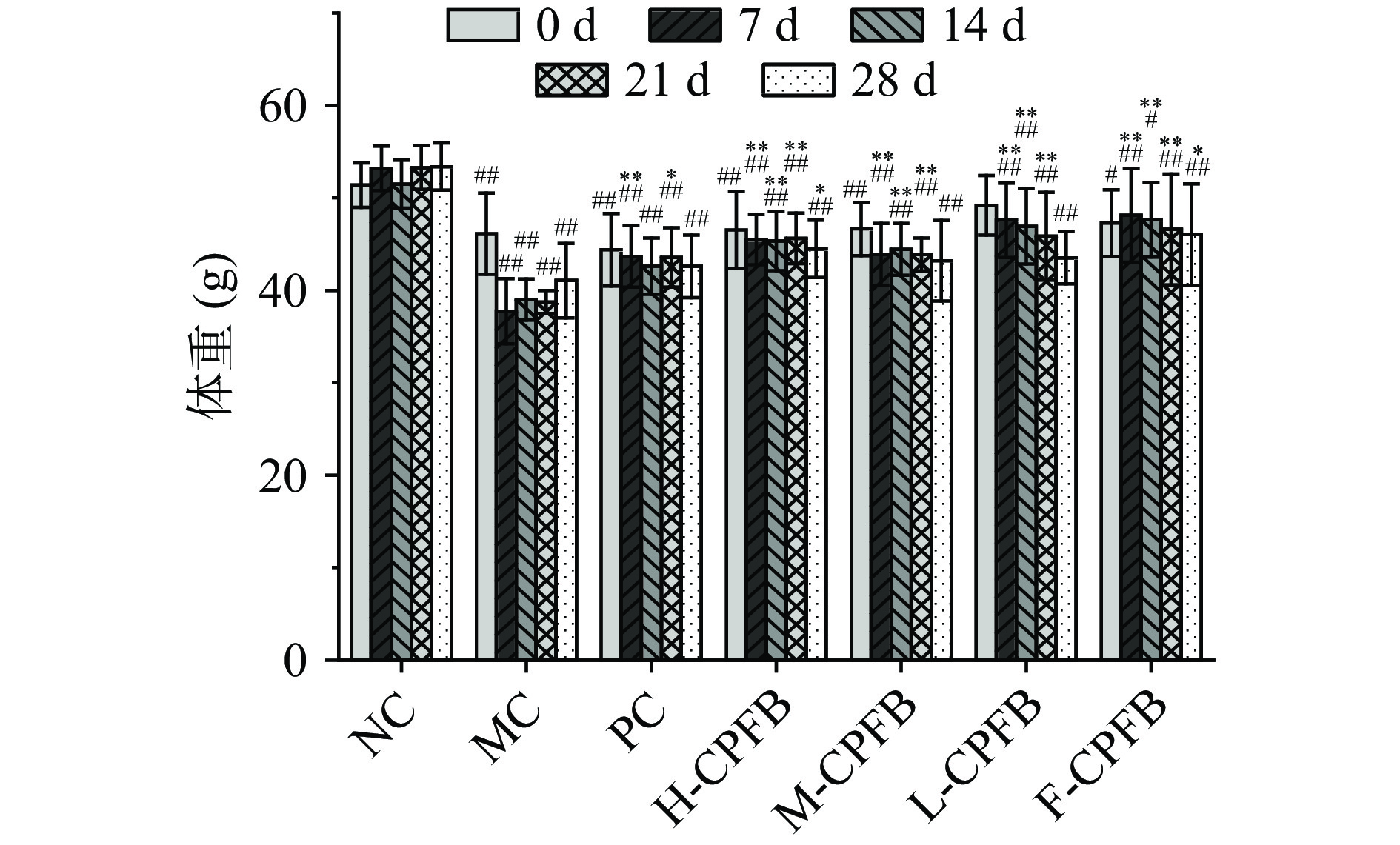
2.1 CPFB对糖尿病小鼠体重的影响
如图1所示,从初始体重来看,MC组小鼠的体重极显著低于NC组小鼠(P<0.01),表明糖尿病模型的建立可能导致小鼠出现典型症状“三多一少”症状。在实验期间,MC组小鼠的体重变化总体呈下降趋势,而NC组小鼠体重变化略有上升总体平稳,二者相比有极显著差异(P<0.01)。经过CPFB干预28 d后,MC组小鼠体重对比第0 d下降了10.26%,而H-CPFB、M-CPFB组、PC组及F-CPFB组的体重分别显著下降了为5.71%、7.21%、3.64%、2.7%。表明经过CPFB干预可缓解小鼠体重的减轻,与MC组相比CPFB减缓了小鼠体重的下降速度,且效果优于PC组。杨紫滟[24]将玉米须黄酮应用于缓解STZ致糖尿病小鼠的体重降低情况,效果显著。Guo等[25]研究结果表明四氧嘧啶诱导的高血糖小鼠给予玉米丝提取物后体重逐渐增加。
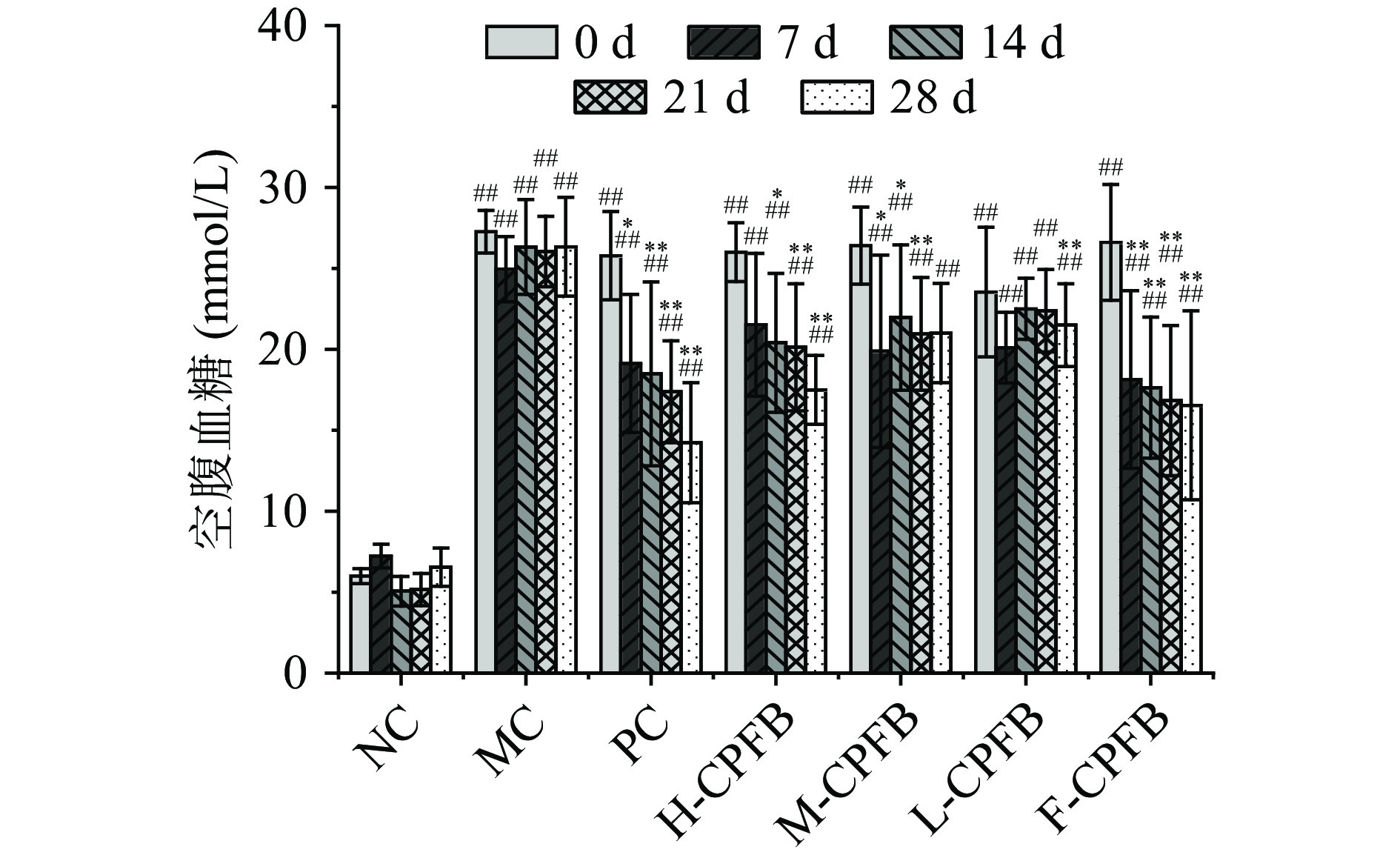
2.2 CPFB对糖尿病小鼠空腹血糖的影响
由图2可知,从初始血糖值来看,MC组小鼠血糖水平极显著高于NC组小鼠(P<0.01),表明糖尿病模型建立成功。经过干预7 d后,各处理组血糖水平均表现不同程度的下降,与MC组相比具有极显著性差异(P<0.01)。在实验期间,MC组小鼠一直处于高血糖水平状态,空腹血糖值一直保持在20 mmol/L以上。经过实验28 d后,各组小鼠血糖值与第0 d相比均下降,H-CPFB、M-CPFB、L-CPFB组、PC组、F-CPFB组分别降低了32.59%、20.53%、7.51%、44.6%、38.73%,各组血糖水平极显著低于MC组小鼠(P<0.01)。其中PC组下降幅度最大,其次为F-CPFB组和H-CPFB组。其中高浓度的CPFB及小鼠自由饮用饮料的降血糖效果最好,表明CPFB干预可减缓空腹血糖水平上升,达到较好的降血糖效果。这与藏传刚等[26]研究玉米须多糖对糖尿病模型大鼠的降血糖作用研究结果一致。
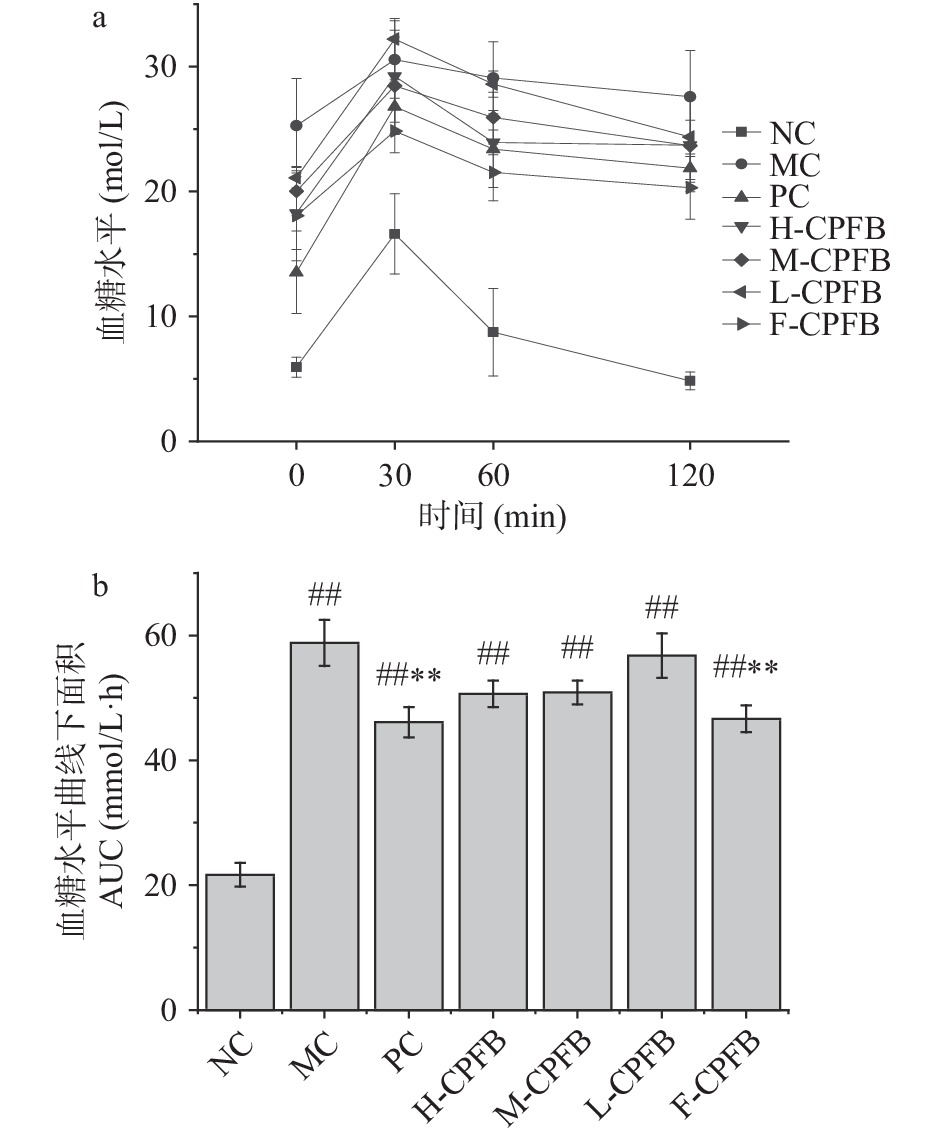
2.3 CPFB对糖尿病小鼠口服糖耐量的影响
如图3a所示,MC组与各给药组小鼠初始空腹血糖值明显高于NC组,并且灌胃葡萄糖溶液后0.5、1、2 h的血糖值也明显较正常组高。各组灌胃葡萄糖溶液后,血糖值随时间呈现先升后降的趋势。如图3b所示,MC组较NC组的AUC值极显著偏大(P<0.01);PC组与F-CPFB组AUC值极显著小于MC组(P<0.01),H-CPFB、M-CPFB、L-CPFB组的AUC值虽有下降趋势不显著。结果表明,糖尿病建模使小鼠出现了糖耐量损伤的情况,而自由饮用CPFB能够改善口服糖耐量异常,且与使用盐酸二甲双胍治疗的PC组效果相当。
2.4 CPFB对糖尿病小鼠血清生化指标的影响
糖尿病通常伴有高血脂症,最明显的表现为血脂指标升高,如表2所示MC组的TC、TG、LDL-C、NEFA等血脂指标与NC组相比极显著升高(P<0.01),通过表中干预28 d后的小鼠血清生化指标的数据分析,各干预组小鼠的TC水平与MC组相比均有极显著降低(P<0.01),其中F-CPFB组效果最好,与NC组已无明显差别。小鼠血清中TG水平除L-CPFB组外其他各组均有显著性降低,其中H-CPFB组与MC组相比降低了38.6%,LDL-C则只有H-CPFB组和F-CPFB组有极显著下降效果(P<0.01)。对比NC组,MC组的NEFA数值提高了1.97倍,而H-CPFB、M-CPFB、PC组和F-CPFB组在降低小鼠血清中的NEFA方面具备更显著的效果(P<0.05或P<0.01),分别降低了49.5%和40.5%、35.64%和25.69%。TC/HDL-C是反应冠心病的重要指标,常被用来表达脂代谢异常的结果。各组通过CPFB处理后TC/HDL-C的比值比MC组降低了37.46%、23%、4.9%、9.81%、35.18%。糖尿病引起的血糖水平升高致使葡萄糖自氧化,增加活性氧的生成,从而导致氧化应激[27]。MC组小鼠SOD活力水平极显著低于NC组小鼠(P<0.01),说明长期高血糖状态导致了一定程度的氧化损伤。通过实验28 d后,H-CPFB、PC、F-CPFB组与MC组的SOD活力相比极显著升高(P<0.01)。MDA是氧化损伤的标志物,在实验初期MC组的MDA含量显著高于NC组,经过CPFB干预后H-CPFB、F-CPFB组MDA含量为7.95±0.64和6.84±0.45 nmol/mL,与MC组相比显著降低了,表明经CPFB处理可以缓解T2DM导致的氧化损伤。综上所述,高剂量的CPFB及小鼠自由饮用饮料表现出色的降低血清脂质水平和抗氧化作用,且效果优于盐酸二甲双胍治疗,证明经过CPFB干预能够调节糖尿病带来的糖脂代谢紊乱和氧化应激。
表 2 小鼠血清中血脂指标及抗氧化指标的变化(组别 TC
(mmol/L)TG
(mmol/L)LDL-C
(mmol/L)HDL-C
(mmol/L)NEFA
(mmol/L)SOD
(U/mL)MDA
(nmol/mL)NC 5.98±0.68 1.162±0.04 0.75±0.33 3.90±0.87 1.45±0.67 84.80±3.32 5.77±0.44 MC 11.59±0.33## 3.53±0.131## 2.27±0.49## 4.87±0.19 4.32±1.23## 69.12±2.05## 9.1±0.38## PC 7.77±0.90##** 2.757±0.22##** 1.50±1.06 3.62±0.38 2.78±0.51##* 83.42±2.4** 8.06±0.58## H-CPFB 7.10±0.66#** 2.167±0.19##** 0.83±0.16** 4.77±0.46 2.18±0.77** 82.92±1.21** 7.95±0.64##** M-CPFB 6.78±0.42##** 2.414±0.27##** 1.79±0.49## 3.7±0.51 2.57±0.73#** 74.79±5.21## 8.93±0.63## L-CPFB 9.80±1.06##** 3.212±0.18## 1.72±0.73## 4.33±1.49 3.34±0.83## 69.9±4.1## 8.54±0.20## F-CPFB 6.00±1.13** 2.232±0.22##** 0.99±0.2** 3.89±1.3 3.21±0.87##* 80.74±2.87** 6.84±0.45##** 注:与MC组相比,“*”表示差异显著,P<0.05;“**”表示差异极显著P<0.01;与NC组相比“#”表示差异显著,P<0.05;“##”表示差异极显著P<0.01;表3同。 2.5 CPFB对糖尿病小鼠胰岛素水平的影响
如表3所示,MC组胰岛素水平为16.15±0.28 mIU/L较NC组10.21±0.94 mIU/L有明显上升(P<0.01),表现出胰岛素分泌过多的问题,造成这一现象的原因可能是高血糖长期刺激产生大量的胰岛素,降低了体内对胰岛素的敏感性,最终导致胰岛素抵抗。而其余几组与MC组相比差异并不显著。表中三种指标[28]代表胰岛β细胞功能、胰岛素抵抗指数(HOMA-IR)与胰岛素敏感指数(ISI),其中MC组的HOMA-β极显著低于NC组(P<0.01),而HOMA-IR极显著高于NC组(P<0.01),这表明糖尿病小鼠的胰岛β细胞功能受损并存在胰岛素抵抗。H-CPFB组、M-CPFB组、L-CPFB组、PC组及F-CPFB组相比MC组,HOMA-β极显著升高(P < 0.01)。H-CPFB组、M-CPFB组、L-CPFB组、PC组及F-CPFB组的HOMA-IR与MC组相比下降了31.33%、19.93%、16.14%、46.14%、33.19%。而对于ISI来说,各组没有显著差异。结果表明经CPFB干预后能够有效改善模型小鼠的HOMA-β及HOMA-IR,缓解胰岛素抵抗。李晓月等[29]研究结果表明玉米皮膳食纤维干预能够降低胰岛素抵抗指数,提高胰岛β细胞功能,与本实验结果基本一致。
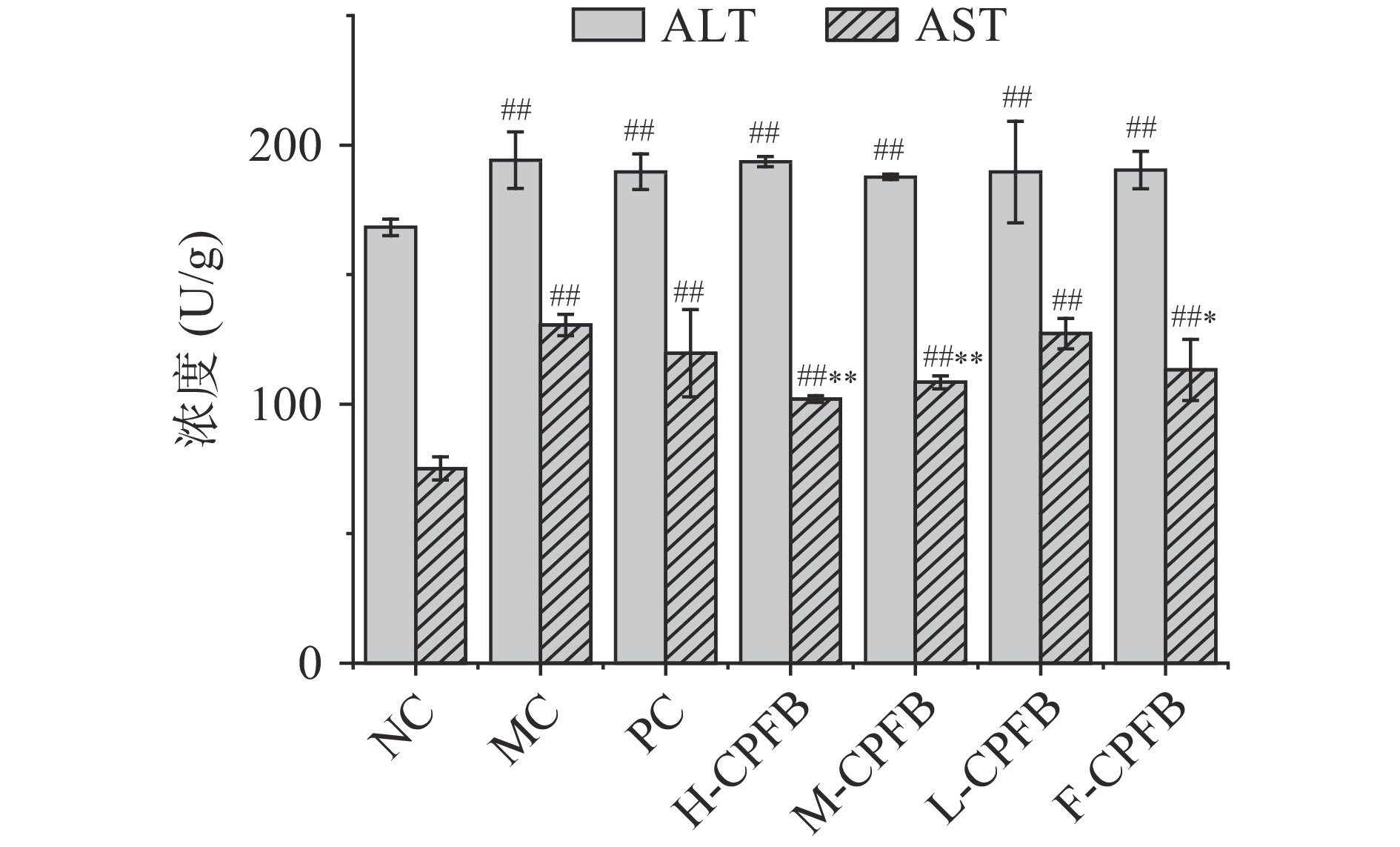
表 3 各组小鼠血清中胰岛素水平及胰岛素相关指标(组别 胰岛素(mIU/ L) HOMA-β HOMA-IR ISI NC 10.26±0.75 67.58±4.97 2.98±0.22 0.016±0.001 MC 16.15±0.28## 15.81±0.63## 18.77±0.75## 0.002±0.001 PC 14.40±0.54## 23.42±0.88##** 10.11±0.38##** 0.004±0.001 H-CPFB 15.35±2.52## 19.28±2.35##** 12.89±2.11##** 0.003±0.002 M-CPFB 17.74±2.04## 22.80±2.62##** 15.03±1.73##** 0.003±0.003 L-CPFB 16.49±0.25## 18.33±0.28##** 15.74±0.24##** 0.003±0.001 F-CPFB 16.94±0.68## 23.12±0.40##** 12.54±0.22##** 0.004±0.003 2.6 CPFB对糖尿病小鼠肝脏中AST与ALT水平的影响
血清中AST和ALT体现了肝损伤的水平,从图4能够看出,由于糖尿病建模导致MC组小鼠ALT、AST水平极显著高于NC组小鼠(P<0.01),说明长期高血糖状态导致模型小鼠出现肝损伤。其余几组经过CPFB干预,相比MC组小鼠,H-CPFB、M-CPFB(P<0.05)和F-CPFB组(P<0.01)的AST水平均显著下降,其中高剂量的CPFB效果最显著,分别降低了21.89%、16.91%、13.24%。盐酸二甲双胍与CPFB处理则对ALT均无明显效果。结果表明通过CPFB干预可以降低小鼠肝脏中的AST水平,进而缓解糖尿病导致的肝损伤。
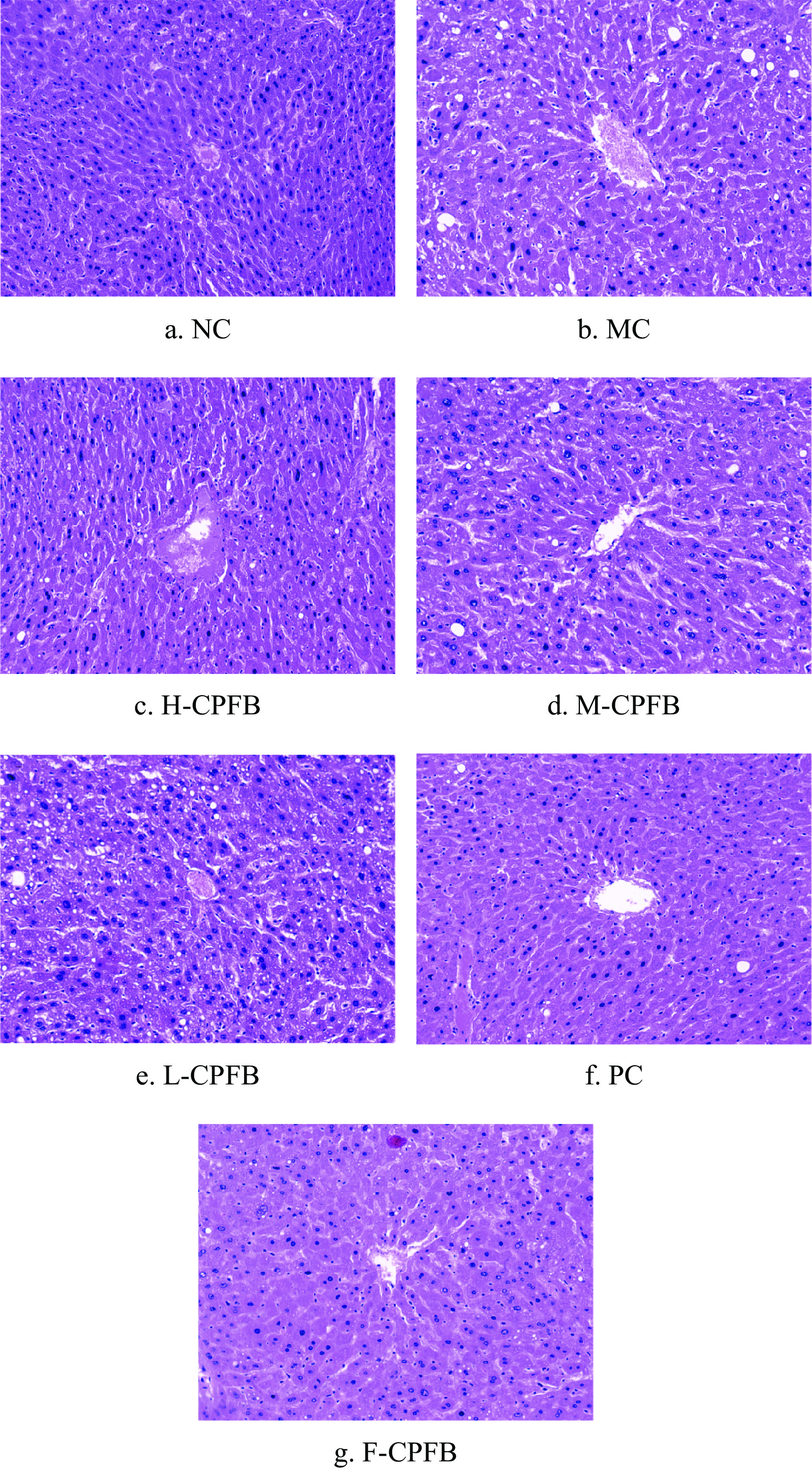
2.7 CPFB对糖尿病小鼠肝脏病理变化的影响
糖尿病会引起广泛的肝脏疾病,从简单的脂肪积累到最后导致非酒精性脂肪性肝炎[30]。从图5得知,NC组肝脏组织细胞形态结构清晰,肝细胞索排列整齐,不存在脂肪性变的情况。MC组小鼠肝组织结构紊乱,细胞肿胀,细胞间隙变大,肝脏出现大小不一的脂肪液滴空泡。L-CPFB组与M-CPFB组小鼠肝脏仍存在不同程度的脂肪液滴空泡和组织结构紊乱,与MC组相比差异不大。F-CPFB组与PC组小鼠肝细胞脂肪性变基本消失,组织结构趋近于正常,且细胞形态与NC组相似。病理切片结果表明小鼠自由饮用CPFB能够缓解长期高血糖带来的脂肪性变及肝损伤,与盐酸二甲双胍治疗效果相当。张众一等[31]研究玉米须多糖确能减轻因糖尿病建模引起的肝损害,与本研究结果一致。
3. 讨论与结论
糖尿病作为代谢性疾病其特征为糖脂代谢调节紊乱[32]。许多科学研究常使用糖尿病小鼠这种动物模型来作为糖尿病机制和药物治疗的研究对象。小鼠采用高脂饮食结合多次注射低剂量STZ诱导建模[33],使模型鼠出现胰岛素分泌功能障碍,血糖水平升高、体重减轻、肝脏脂肪变性和糖耐量损伤等症状[34]。本研究结果表明经过CPFB干预能够显著(P<0.05或P<0.01)降低模型小鼠空腹血糖水平,能够减缓糖尿病引起的体重负增长。口服糖耐量实验结果表明自由饮用CPFB能够达到与抗糖尿病药物相当的效果。未经过干预治疗的糖尿病长期刺激产生大量的胰岛素,使机体对胰岛素不敏感,导致胰岛素抵抗。而经过CPFB处理后,各组小鼠均能显著(P<0.05)降低HOMA-β和HOMA-IR,改善胰岛素抵抗。
血清脂质异常是糖尿病的另一个特点[35],长期被作为心血管疾病的首要风险源。高血糖可增加慢性炎症标志物,促进活性氧的产生,最终导致血管功能障碍。丙二醛作为氧化应激生物标志物,在糖尿病模型小鼠的体内表达显著升高[36-37]。之前也有研究表明玉米须多糖具有一定的降脂效果[38],本实验结果表明COFB能够降低糖尿病小鼠血清中TC、TG、LDL-C、NEFA水平并改善SOD活力和MDA含量,与此研究结果一致。可能是由于CPFB中的玉米须经乳酸菌发酵提高了生物利用率从而达到良好的调节血脂效果和抗氧化作用。
肝损伤通常也为糖尿病的一大表征。胰岛素抵抗导致肝糖异生增强和肝脂代谢受损,血清谷丙转氨酶和谷草转氨酶的含量增加[39],从而导致肝脂肪变性和肝损伤[40]。既往研究表明,玉米须能够改善糖尿病肝脏脂质积聚,防止肝组织形态学改变[41]。而本研究经过高剂量和自由饮用方式CPFB干预可使T2DM小鼠谷草转氨酶水平显著(P<0.05或P<0.01)下降,并通过肝脏病理切片观察CPFB缓解了T2DM小鼠肝脂肪性变及肝损伤。
综上所述,CPFB能显著降低空腹血糖水平并调节糖脂代谢,缓解糖尿病引起的肝损伤及体重降低情况。玉米副产物作为廉价的植物源药用食材,予以乳酸菌发酵提高生物活性,丰富了以天然抗糖尿病植物为原料辅助降糖饮料的种类,为糖尿病人可食用饮料市场提供了一个新产品和新思路。但具体降糖机制尚不明晰,相关研究还待进一步深入。
-
表 1 动物实验分组及实验方式Table1 Group and method of animal experiment
组别 建模期 STZ处理 灌胃期 正常对照组(NC) 普通饲料+蒸馏水 柠檬酸钠缓冲溶液 0.1 mL/(10 g·bw)生理盐水 模型对照组(MC) 高脂饲料+蒸馏水 40 mg/kgSTZ溶液 0.1 mL/(10 g·bw)生理盐水 阳性对照组(PC) 高脂饲料+蒸馏水 40 mg/kgSTZ溶液 150 mg/kg盐酸二甲双胍 高剂量组(H-CPFB) 高脂饲料+蒸馏水 40 mg/kgSTZ溶液 0.1 mL/(10 g·bw) CPFB 中剂量组(M-CPFB) 高脂饲料+蒸馏水 40 mg/kgSTZ溶液 0.05 mL/(10 g·bw) CPFB 低剂量组(L-CPFB) 高脂饲料+蒸馏水 40 mg/kgSTZ溶液 0.025 mL/(10 g·bw) CPFB 自由饮用组(F-CPFB) 高脂饲料+蒸馏水 40 mg/kgSTZ溶液 自由饮用未浓缩饮料 表 2 小鼠血清中血脂指标及抗氧化指标的变化(
Table 2 Changes of lipids and antioxidant indexes in serum of mice (
组别 TC
(mmol/L)TG
(mmol/L)LDL-C
(mmol/L)HDL-C
(mmol/L)NEFA
(mmol/L)SOD
(U/mL)MDA
(nmol/mL)NC 5.98±0.68 1.162±0.04 0.75±0.33 3.90±0.87 1.45±0.67 84.80±3.32 5.77±0.44 MC 11.59±0.33## 3.53±0.131## 2.27±0.49## 4.87±0.19 4.32±1.23## 69.12±2.05## 9.1±0.38## PC 7.77±0.90##** 2.757±0.22##** 1.50±1.06 3.62±0.38 2.78±0.51##* 83.42±2.4** 8.06±0.58## H-CPFB 7.10±0.66#** 2.167±0.19##** 0.83±0.16** 4.77±0.46 2.18±0.77** 82.92±1.21** 7.95±0.64##** M-CPFB 6.78±0.42##** 2.414±0.27##** 1.79±0.49## 3.7±0.51 2.57±0.73#** 74.79±5.21## 8.93±0.63## L-CPFB 9.80±1.06##** 3.212±0.18## 1.72±0.73## 4.33±1.49 3.34±0.83## 69.9±4.1## 8.54±0.20## F-CPFB 6.00±1.13** 2.232±0.22##** 0.99±0.2** 3.89±1.3 3.21±0.87##* 80.74±2.87** 6.84±0.45##** 注:与MC组相比,“*”表示差异显著,P<0.05;“**”表示差异极显著P<0.01;与NC组相比“#”表示差异显著,P<0.05;“##”表示差异极显著P<0.01;表3同。 表 3 各组小鼠血清中胰岛素水平及胰岛素相关指标(
Table 3 Serum insulin levels and insulin-related indexes in different group (
组别 胰岛素(mIU/ L) HOMA-β HOMA-IR ISI NC 10.26±0.75 67.58±4.97 2.98±0.22 0.016±0.001 MC 16.15±0.28## 15.81±0.63## 18.77±0.75## 0.002±0.001 PC 14.40±0.54## 23.42±0.88##** 10.11±0.38##** 0.004±0.001 H-CPFB 15.35±2.52## 19.28±2.35##** 12.89±2.11##** 0.003±0.002 M-CPFB 17.74±2.04## 22.80±2.62##** 15.03±1.73##** 0.003±0.003 L-CPFB 16.49±0.25## 18.33±0.28##** 15.74±0.24##** 0.003±0.001 F-CPFB 16.94±0.68## 23.12±0.40##** 12.54±0.22##** 0.004±0.003 -
[1] RODEN M, SHULMAN G I. The integrative biology of type 2 diabetes[J]. Nature,2019,576(7785):51−60. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1797-8
[2] NDISANG J F, VANNACCI A, RASTOGI S. Insulin resistance, type 1 and type 2 diabetes, and related complications 2017[Z]. Hindawi, 2017.
[3] POUVREAU C, DAYRE A, BUTKOWSKI E G, et al. Inflammation and oxidative stress markers in diabetes and hypertension[J]. Journal of Inflammation Research,2018,11:61. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S148911
[4] ZHENG Y, LEY S H, HU F B. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications[J]. Nature Reviews Endocrinology,2018,14(2):88−98. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2017.151
[5] ESSER N, UTZSCHNEIDER K M, KAHN S E. Early beta cell dysfunction vs insulin hypersecretion as the primary event in the pathogenesis of dysglycaemia[J]. Diabetologia,2020,63(10):2007−21. doi: 10.1007/s00125-020-05245-x
[6] WANG T, LU J, SHI L, et al. Association of insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction with incident diabetes among adults in China: A nationwide, population-based, prospective cohort study[J]. The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology,2020,8(2):115−124.
[7] HE J H, CHEN L X, LI H. Progress in the discovery of naturally occurring anti-diabetic drugs and in the identification of their molecular targets[J]. Fitoterapia,2019,134:270−289. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2019.02.033
[8] DENG J, LIU Y, DUAN Z, et al. Protopanaxadiol and protopanaxatriol-type saponins ameliorate glucose and lipid metabolism in type 2 diabetes mellitus in high-fat diet/streptozocin-induced mice[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology,2017,8:506. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00506
[9] YAO K, ZENG L, HE Q, et al. Effect of probiotics on glucose and lipid metabolism in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of 12 randomized controlled trials[J]. Medical Science Monitor: International Medical Journal of Experimental and Clinical Research,2017,23:3044.
[10] 高伟华. 乳酸菌对高糖高脂2型糖尿病小鼠糖脂代谢及肠道菌群的影响[D]. 临汾: 山西师范大学, 2018 GAO W H. Effects of lactic acid bacteria on glycolipid metabolism and intestinal microflora in type 2 diabetic mice with high glucose and fat[D]. Linfen: Shanxi Normal University, 2018.
[11] EJTAHED H S, MOHTADI-NIA J, HOMAYOUNI-RAD A, et al. Probiotic yogurt improves antioxidant status in type 2 diabetic patients[J]. Nutrition,2012,28(5):539−543. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2011.08.013
[12] GUO Q, MA Q, XUE Z, et al. Studies on the binding characteristics of three polysaccharides with different molecular weight and flavonoids from corn silk (Maydis stigma)[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2018,198:581−588. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.06.120
[13] DA HORA N R, SANTANA L F, DA SILVA V D A, et al. Identification of bioactive metabolites from corn silk extracts by a combination of metabolite profiling, univariate statistical analysis and chemometrics[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,365:130479. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130479
[14] EBRAHIMZADEH M A, POURMORAD F, HAFEZI S. Antioxidant activities of Iranian corn silk[J]. Turkish Journal of Biology,2008,32(1):43−49.
[15] LEE C W, SEO J Y, KIM S L, et al. Corn silk maysin ameliorates obesity in vitro and in vivo via suppression of lipogenesis, differentiation, and function of adipocytes[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy,2017,93:267−275.
[16] PAN Y, WANG C, CHEN Z, et al. Physicochemical properties and antidiabetic effects of a polysaccharide from corn silk in high-fat diet and streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2017,164:370−378. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.01.092
[17] 张庆宏. 药食同源与中药食品化[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报,2009,11(7):54−55. [ZHANG Q H. The homology of medicine and food and the foodization of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Journal of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese,2009,11(7):54−55. [18] GONG X, JI M, XU J, et al. Hypoglycemic effects of bioactive ingredients from medicine food homology and medicinal health food species used in China[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2020,60(14):2303−2326. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2019.1634517
[19] 卢君蓉, 王世宇, 盛菲亚, 等. 中药发酵研究概况[J]. 中药与临床,2012,3(4):47−49. [LU J R, WANG S Y, SHENG F Y, et al. Research overview of Chinese traditional medicine fermentation[J]. Pharmacy and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica,2012,3(4):47−49. [20] 张妍, 赵昕琪, 王天琪, 等. 非靶向代谢组技术研究饮料发酵前后物质变化[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(22):115−120. [ZHANG Y, ZHAO X Q, WANG T Q, et al. Component changes in corn beverage before and after fermentation analyzed by non-targeted metabolomics technique[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(22):115−120. [21] 叶青, 许云贺, 张莉力. 豆腐酸浆中干酪乳杆菌的分离、鉴定及作为豆腐凝固剂的应用[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(18):94−98,104. [YE Q, XU Y H, ZHANG L L. Isolation and identification of Lactobacillus casei from bean curd yogurt and its application as curd coagulant[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(18):94−98,104. [22] 张敏. 荞麦凉茶工艺研究及其对Ⅱ型糖尿病小鼠降血糖作用[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2014 ZHANG M. Study on the technology of buckwheat herbal tea and its hypoglycemic effect on type Ⅱ diabetic mice [D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2014.
[23] 陈小敏, 谭书明, 黄颖, 等. 刺梨汁对Ⅰ型糖尿病小鼠的降糖作用[J]. 现代食品科技,2019,35(8):13−20. [CHEN X M,TAN S M,HUANG Y, et al. Hypoglycemic effect of Rosa roxburghii juice on type I diabetic mice[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2019,35(8):13−20. [24] 杨紫滟. 玉米须黄酮对链脲佐菌素致糖尿病小鼠的影响[J]. 山西农经,2017(22):87−88. [YANG Z Y. Effects of corn silk flavonoids on streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice[J]. Shanxi Agricultural Economy,2017(22):87−88. [25] GUO J, LIU T, HAN L, et al. The effects of corn silk on glycaemic metabolism[J]. Nutrition & Metabolism,2009,6(1):1−6.
[26] 藏传刚, 任珊, 刘宇超, 等. 玉米须多糖与普洱茶多糖降血糖、降血脂作用研究[J]. 中国医学创新,2021,18(16):29−34. [ZANG C G, REN S, LIU Y C, et al. The hypoglycemic and hyperlipidemic effects of stigma-maydis polysaccharides and Pu-erh tea polysaccharides[J]. Medical Innovation of China,2021,18(16):29−34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2021.16.007 [27] WANG X T, GONG Y, ZHOU B, et al. Ursolic acid ameliorates oxidative stress, inflammation and fibrosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy rats[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy,2018,97:1461−1467.
[28] SIAHAAN B S, LINDARTO D. Effect of Puguntano on HOMA-IR in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Majalah Kedokteran Bandung-Mkb-Bandung Medical Journal,2017,49(2):67−72. doi: 10.15395/mkb.v49n2.1051
[29] 李晓月, 楚素平, 张晶晶, 等. 玉米皮膳食纤维对反式脂肪酸致小鼠胰岛素抵抗的影响[J]. 食品科学,2014,35(13):218−222. [LI X Y, CHU S P, ZHANG J J, et al. Effects of dietary fiber from corn husk on trans fatty acids-induced insulin resistance in mice[J]. Food Science,2014,35(13):218−222. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201413042 [30] STEFAN N. Fettleber und diabetes: Pathomechanismen[J]. Der Diabetologe,2020,16(6):560−565. doi: 10.1007/s11428-020-00657-0
[31] 张众一, 张淇, 揭毅, 等. 玉米须多糖对糖尿病小鼠肝损伤及糖代谢的影响[J]. 山东大学学报(医学版),2018,56(5):52−57. [ZHANG Z Y, ZHANG Q, JIE Y, et al. Effects of stigma maydis polysaccharides on liver protection and glycometabolism in diabetic mice[J]. Journal of Shandong University (Health Sciences),2018,56(5):52−57. doi: 10.6040/j.issn.1671-7554.0.2017.1137 [32] HUANG R, WU E, DENG X. Potential of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide for the control of glucose and lipid metabolism disorders: A review[J]. International Journal of Food Properties,2022,25(1):673−680. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2022.2057529
[33] SIM X Y, IBRAHIM B, GAM L H. Urinary metabolites of type 2 diabetes rats fed with palm oil-enriched high fat diet[J]. Heliyon,2021,7(9):e08075. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08075
[34] CLARK A L, YAN Z, CHEN S X, et al. High-fat diet prevents the development of autoimmune diabetes in NOD mice[J]. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism,2021,23(11):2455−2465. doi: 10.1111/dom.14486
[35] LUC K, SCHRAMM-LUC A, GUZIK T J, et al. Oxidative stress and inflammatory markers in prediabetes and diabetes[J]. J Physiol Pharmacol, 2019, 70(6).
[36] BOUHAJJA H, KACEM F H, ABDELHEDI R, et al. Potential predictive role of lipid peroxidation markers for type 2 diabetes in the adult Tunisian population[J]. Canadian Journal of Diabetes,2018,42(3):263−271. doi: 10.1016/j.jcjd.2017.06.006
[37] POBLETE-ARO C, RUSSELL-GUZMÁN J, PARRA P, et al. Efecto del ejercicio físico sobre marcadores de estrés oxidativo en pacientes con diabetes mellitus tipo 2[J]. Revista Médica de Chile,2018,146(3):362−372.
[38] ZHAO W, YIN Y, YU Z, et al. Comparison of anti-diabetic effects of polysaccharides from corn silk on normal and hyperglycemia rats[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2012,50(4):1133−1137. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2012.02.004
[39] SILVA MBDE, TUSTUMI F, DANTAS ACB, et al. Obesity and severe steatosis: The importance of biochemical exams and scores[J]. Arquivos Brasileiros de Cirurgia Digestiva: ABCD = Brazilian Archives of Digestive Surgery, 2022, 34(4): e1626.
[40] LALLUKKA S, YKI-JÄRVINEN H. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and risk of type 2 diabetes[J]. Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism,2016,30(3):385−395.
[41] CHA J H, KIM S R, KANG H J, et al. Corn silk extract improves cholesterol metabolism in C57BL/6J mouse fed high-fat diets[J]. Nutrition Research and Practice,2016,10(5):501−506. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2016.10.5.501
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 李兴凤,杨艳,刘学艳. 云南双江不同季节晒青茶品质对比分析. 热带农业科技. 2025(01): 53-57 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 罗慧,王庆华,施宗运,刘春艳,杨澜,吴华强,关晓阳,周玲. 不同方法渥堆发酵的普洱熟茶品质比较分析. 茶叶通讯. 2024(01): 60-67 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 谢晨昕,赵锋,林雨,蔡良绥,林智,郭丽. 日晒茶风味化学特征研究进展. 茶叶科学. 2024(04): 554-564 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王媛媛,冯勇荣,孙青占,吕兆林. 不同产地沙棘叶茶品质分析及综合评价. 食品与发酵工业. 2024(24): 331-338 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 罗慧,宗加福,刘春艳,王庆华,杨澜,吴华强,关晓阳,周玲. 云南易武和临翔茶区古树晒青茶品质差异分析. 茶叶通讯. 2023(04): 500-508 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:
