Effects of Ferulic Acid on Oxidation and Gel Properties of Meat Myofibrillar Protein Induced by·OH
-
摘要: 为了探究阿魏酸(FA)对·OH诱导的肌原纤维蛋白(MPs)氧化及凝胶特性的影响,以猪肉肌原纤维蛋白为研究对象,利用Fenton氧化体系模拟实际肉品氧化环境,建立MPs-Fenton氧化体系,研究添加不同浓度水平(0、0.01、0.25、0.50 mg/g蛋白质)阿魏酸对猪肉MPs氧化及其凝胶特性的影响。结果表明:FA可以显著降低MPs羰基含量(P<0.05),且抑制效果具有浓度依赖性,高浓度(0.50 mg/g)FA对羰基含量的抑制率高达38.2%;高浓度FA在氧化的基础上进一步促进MPs巯基损失,经·OH氧化体系氧化12 h后,其总巯基含量极显著降低了4.02%(P<0.01)。MPs氧化后溶解度降低,且随着FA添加浓度的增大,溶解度降低越明显,表明添加FA可以促进蛋白结构进一步展开,对MPs的氧化状态起到介导调控作用。氧化后的MPs凝胶强度显著降低(P<0.05),凝胶弹性增强,当添加0.01 mg/g FA时弹性最强,之后随FA浓度的增加而降低,添加高浓度FA可使凝胶蒸煮损失增大,水分损失越多,保水性变差,氧化会导致MPs结构变化,形成较弱的凝胶网络结构。添加适量FA可以抑制MPs氧化及改善凝胶品质,高浓度的FA会影响蛋白成胶能力和凝胶品质。Abstract: In order to study the effects of ferulic acid (FA) on ·OH-induced oxidation and gel properties of myofibrillar proteins (MPs), porcine MPs was used as the research object and a new system of MPs-Fenton oxidation was established by using Fenton oxidation system to simulate the actual meat oxidation environment. The effects of different concentrations of FA (0, 0.01, 0.25, 0.50 mg/g protein) on the oxidation and gel properties of MPs were studied. The results showed that the contents of carbonyl were reduced significantly (P<0.05) by the addition of FA, and the inhibition effect of FA was concentration-dependent. The inhibitory rate of high concentration of FA (0.50 mg/g) on the content of carbonyl was up to 38.2%. High concentration of FA (0.50 mg/g) further promoted the loss of sulfhydryl group of MPs, and the content of total sulfhydryl group of MPs was significantly reduced by 4.02% (P<0.01) after oxidation for 12 hours by ·OH. The solubility of MPs decreased after oxidation and became more obvious with the increase of FA concentration, indicating that the addition of FA could promote the further unfolding of the protein structure and play a mediating role in regulating the oxidation state of MPs. The gel strength of MPs was significantly reduced after oxidation (P<0.05), and the gel elasticity was enhanced, the elasticity was the strongest with the addition of the 0.01 mg/g FA , and then decreased with the increase of FA concentration. The addition of high concentration FA could increase the cooking loss, water loss and the poor water holding capacity of MPs gel, and the structure of MPs was changed by oxidation, which formed a weakly gel network structure. FA with an appropriate amount could inhibit the oxidation of MPs and improve the gel quality, as well as high concentration of FA could weaken the gelation ability and gel quality of MPs.
-
Keywords:
- ferulic acid (FA) /
- myofibrillary proteins (MPS) /
- oxidation /
- gel properties
-
肌原纤维蛋白(Myofibrillar proteins, MPs)是肌肉中含量最高的蛋白,占肉中总蛋白质含量的55%~60%,是影响肉制品品质的主体蛋白[1]。肉蛋白在加工与储存中难免会发生系列氧化反应,肉类的结构和功能因此受到影响。氧化条件会使蛋白中含有的侧链基团得到修饰,也会使蛋白分子交联聚集,从而影响蛋白质的功能,如凝胶特性等[2],巯基损失以及羰基氧化产物的生成都会影响肉的风味和营养价值。溶解状态下的蛋白分子通过交联聚集能够形成凝胶网络结构,氨基酸残基经自由基修饰可引起蛋白结构发生变化,导致功能特性改变[3- 4]。
如何减缓蛋白氧化速率和降低氧化程度,提高蛋白凝胶等特性已成为肉品科学技术领域的研究热点。添加抗氧化剂是一种简易、有效控制氧化的方法,为了迎合当下国民对“绿色、健康、安全”食品的需求,已有大量研究针对同样具有抗氧化潜力的天然植物多酚取代传统抗氧化剂,用于改善肌肉脂肪及蛋白的氧化。植物多酚具有优良的抗菌、抗炎和抗氧化等生理功效,广泛存在于中草药、香辛料、水果蔬菜、果皮果渣等农产品加工副产物中[5],因而备受关注。Jia等[6]发现儿茶素浓度对MPs的构象及凝胶性质影响较大,低浓度儿茶素有利于蛋白抗氧化且维持较紧密的凝胶网络结构,高浓度儿茶素导致蛋白凝胶严重恶化。有研究发现,高浓度没食子酸会破坏凝胶网络结构,导致凝胶强度变差、保水性减弱,而中、低浓度没食子酸对其影响不大[7];高浓度绿原酸会促进蛋白的交联聚集现象,使蛋白溶解度降低,凝胶结构遭到破坏,低浓度绿原酸会使蛋白结构展开,凝胶特性增强[8]。
阿魏酸(Ferulic acid,FA)是植物多酚中酚酸的一种,是阿魏和当归等部分中药材中的有效成分,在医药、保健品和食品等领域有着广泛的应用[9]。FA分子中的部分活性基团(酚羟基和羧基)能与蛋白侧链反应形成氢键、促进交联,改善凝胶的理化性质,能还原Fe3+,其相对还原力是VC的2倍,能有效清除Fenton氧化体系中生成的羟自由基(·OH),其IC50为1.09 mmol/L[10]。李黎云[11]研究发现日粮中添加阿魏酸和维生素E可显著降低猪肉的剪切力值,改善猪肉嫩度,日粮中单独添加100 mg/kg的阿魏酸可有效增加猪肉冷藏过程中的肉色稳定性,抑制猪肉脂质氧化,降低汁液流失率,有效延长猪肉的冷藏时间。同时FA因副作用小、价格低且容易获得,在食品营养及医药方面的重要性逐渐凸显出来,其生物学作用成为近年来的研究热点之一,其中最受关注的是抗氧化作用。
目前未见有FA诱导调控肉蛋白氧化及其对凝胶特性的影响和相关作用机制研究报道,本研究采用Fenton氧化体系模拟实际肌肉加工过程中存在的·OH,选用FA作为多酚代表用于肌肉蛋白抗氧化,以探讨·OH诱导的氧化对MPs理化特性的影响、多酚类物质与MPs相互作用对MPs凝胶的影响,并阐明相关机理。研究可为富含酚类的天然植提物在肉制品绿色加工中的科学应用提供理论依据和实际参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
猪里脊 重庆市南岸区五公里人人乐超市;FA(纯度99%) 上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;结晶牛血清清蛋白(BSA) 生化试剂,上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;其他化学试剂 均为分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
TA-XT2i质构分析仪 英国Stable Micro Systems公司;CR400色差仪 日本美能达公司;SU1510扫描电镜 日本日立公司;Ultra-Turrax T25 BASIC高速匀浆器 德国Ika-Werke公司;MM12B自动绞肉机 广东省韶关市大金食品机械厂;TGL-20台式高速冷冻离心机 四川蜀科仪器有限公司;TDZ5-WS多管架自动平衡离心机 湖南湘仪离心机仪器有限公司;V2000紫外可见分光光度计、FA2004电子天平 上海舜宇恒平科学仪器有限公司;UV-1900扫描型紫外可见光光度计 翱艺仪器(上海)有限公司;PYX-DHX-400-BS-Ⅱ隔水式电热恒温培养箱 上海龙跃仪器设备有限公司;DGG-9076A电热恒温鼓风干燥箱 上海齐欣科学仪器有限公司;Phs-3C+酸度计 成都世纪方舟科技有限公司;HH-S数显恒温水浴锅 江苏正基仪器有限公司;BCD-215KHN冰箱 青岛海尔股份有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 肌原纤维蛋白的提取
MPs提取参考Cheng等[12]的方法,取50 g猪肉解冻(4 ℃,4 h),切条剁碎后置于绞肉机中于低档位运行30 s,肉泥使用5倍体积的僵直缓冲液(10 mmol/L Na3PO4、0.1 mol/L NaCl、2 mmol/L MgCl2和1 mmol/L EGTA,pH7.0)稀释后使用高速分散器分散1 min。匀浆经冷冻离心(6000 r/min,10 min,4 ℃)后倾去上清液,所得沉淀再次加入5倍体积僵直缓冲液,重复上次步骤共三次。此后所得沉淀加入5倍体积0.1 mol/L NaCl溶液,匀浆后经过滤以除去残余结缔组织等,用0.1 mol/L HCl调pH为7.0后离心,所得白色膏状沉淀即为肌原纤维蛋白,整个提取过程在0~4 ℃条件下进行。用双缩脲法测定MPs浓度,所提取的MPs于冰箱内冷藏保存(4 ℃)并48 h内使用完。
1.2.2 样品处理
如表1,样品共分为5组,第一组为空白组未氧化,不添加任何抗氧化剂,不进行氧化处理,后四组氧化,第二组为对照组,不添加任何抗氧化剂,加入Fenton氧化体系进行强制氧化处理,通过前期的预实验确定另3组分别添加0.01、0.25、0.50 mg/g FA,同时加入Fenton氧化体系强制氧化,MPs样品在4 ℃氧化12 h,加入Trolox溶液1 mL停止氧化。所配制溶液需在4 ℃条件下保存,并在48 h内使用完毕。
表 1 实验样品设置Table 1. Experimental sample组别 处理方法 1 不添加抗氧化剂+PIPES缓冲液+Trolox溶液 2 不添加抗氧化剂+Fenton氧化体系+Trolox溶液 3 添加0.01 mg/g FA+Fenton氧化体系+Trolox溶液 4 添加0.25 mg/g FA+Fenton氧化体系+Trolox溶液 5 添加0.50 mg/g FA+Fenton氧化体系+Trolox溶液 1.2.3 肌原纤维蛋白氧化性能分析
1.2.3.1 羰基含量测定
参照Wang等[13]的研究方法,并作部分修改,采用DNPH法进行测定。吸取4 mL MPs(5 mg/mL)加入5 mL浓度为 10 mmol/L DNPH。设立空白对照组(加入HCl溶液),振荡混匀,37 ℃避光反应1 h,然后添加2 mL 20% TCA溶液充分振荡以沉淀蛋白并终止反应,离心15 min(4 ℃,4500 r/min),离心后的黄色沉淀用乙醇和乙酸乙脂混合物(1:1)洗涤2次。最后一次洗涤后挥干有机溶剂,加入5 mL 盐酸胍(6 mol/L),在37 ℃的水浴锅中温育10 min。之后于25 ℃,4500 r/min离心15 min,于370 nm波长处测定吸光值,用下列公式计算羰基含量:
羰基含量(nmol/mg蛋白质)=(A370−A0)22×d×C×V反总V样×103 式中:A370:样品吸光度;A0:对照组吸光度;d:比色光径=1 cm;C:样品蛋白浓度(mg/mL);V反总:反应体系的总体积(mL);V样:样品加入的体积(mL)。
1.2.3.2 总巯基含量测定
参照熊杰等[14]的测定方法,并作相应的调整,使用DTNB试剂进行测定。取各样品溶液4 mL(MPs浓度5 mg/mL)置于离心管中,加入8 mL Tris-甘氨酸溶液,匀浆后冷冻离心20 min(4 ℃,4000 r/min),取上清液4.5 mL加入0.5 mL的Ellman’s试剂混匀,室温25 ℃避光静置20 min,然后于412 nm波长处测定吸光度,用下列公式计算总巯基含量:
巯基含量(nmol/mg蛋白质)=106×A412×nc×M 式中:A412:样品组在波长为412 nm下的吸光值;c:分子吸光系数,其值为13600 mol/(L·cm);M:MPs浓度(mg/mL),此处为1 mg/mL;n:稀释倍数,此处为1.1。
1.2.3.3 表面疏水性测定
参照Xu等[15]并略做修改,利用溴酚蓝(BPB)结合法测定。取3 mg MPs(浓度为5 mg/mL)溶解于20 mmol/L PBS(pH6.0)中。吸取1 mL MPs加入200 μL BPB(1 mg/mL),25 ℃条件下搅拌混匀10 min,于4000 r/ min离心20 min,用蒸馏水将上清液稀释10倍,于波长595 nm测定吸光度;设立空白对照组。表面疏水性可用以下公式表示:
溴酚蓝结合量(μg/mg蛋白质)=200×(A对照−A样品)A对照 式中:A对照和A样品分别表示不含蛋白的对照组和样品的吸光度。
1.2.3.4 溶解度测定
MPs溶解度的测定参考曹云刚等[16]的方法进行,并做了一些修改。用15 mmol/L PIPES缓冲液(含0.6 mol/L NaCl,pH6.25)将样品稀释为蛋白浓度5 mg/mL,在4 ℃条件下,5000 r/min离心20 min,离心结束后,蛋白的溶解度用上清液蛋白浓度占MPs液总浓度的百分比表示(蛋白浓度采用双缩脲法测定)。
蛋白溶解度(%)=上清液中的蛋白含量原蛋白液中的蛋白含量×100 1.2.4 肌原纤维蛋白凝胶性能分析
1.2.4.1 热诱导凝胶制备
参考Zhang等[17]的实验方法,并做了一些修改。吸取5 g不同处理的MPs放于小玻璃瓶中(16.5 mm×50 mm),放入水浴锅中加热(升温范围:20~75 ℃,升温速率:1 ℃/min)后用冰水冷却30 min,4 ℃保存24 h,所制备凝胶在室温下放置2 h后分析品质。
1.2.4.2 凝胶强度测定
凝胶强度利用质构分析仪进行测定,测试参数:模式distance(10 mm),测前速度1.5 mm/s,测试速度1 mm/s,测后速度1 mm/s,引发力5 g,P/0.5探头。
1.2.4.3 凝胶质构特性测定
参考Zhao等[18]方法利用质构仪进行测定,测试参数如下:测试模式选择压缩比strain,测前速度2 mm/s,测试速度1 mm/s,测后速度1 mm/s,压缩比strain为75%,引发力5 g,P/75探头,触发类型Auto,测试完成后,用仪器自带软件内部宏TPA. MAC对测试结果进行处理。
1.2.4.4 凝胶色差测定
采用色差仪测定凝胶的色差L*(亮度)、a*(红度)和b*(黄度),用下列公式计算白度W。样品测定前仪器需经自检及零点和白板校正,对每种类型至少重复3次测试,取其平均值:
W=100−√(100−L*)2+(a*)2+(b*)2 1.2.4.5 凝胶蒸煮损失测定
凝胶蒸煮损失根据Cao等[19]的方法,并做了一些修改。配制好的蛋白溶液分装为三组平行,分装时称取质量,即为蒸煮前溶胶质量,将凝胶按1.2.4.1方法制作出后,用胶头吸管吸去大部门水分,余下部分同凝胶一起倒出,在2层定性滤纸上滤除水分10 min,称取质量,为蒸煮后溶胶质量,蒸煮损失按下式计算:
蒸煮损失 (%)=M1−M2M1×100 式中:M1为蒸煮前溶胶的重量(g);M2为蒸煮后凝胶的重量(g)。
1.2.4.6 凝胶保水性测定
参照Zhang等[20]的描述,将MPs凝胶样品离心10 min(4 ℃、10000 r/min),并称量离心前后离心管和样品的质量,保水性用下面的公式进行计算:
保水性 (%)= CG −ML CG ×100 式中:ML为离心过程中水分损失重量(g);CG为离心前凝胶的重量(g)。
1.2.4.7 凝胶微观结构观察
参照Zhao等[18]所述方法,将凝胶切成0.5 cm×0.5 cm×0.3 cm的小块,各加入10 mL 2.5%(v/v)戊二醛溶液固定24 h后,用0.1 mol/L PBS清洗3次,每次10 min,洗涤结束后分别用50%、60%、70%、80%、90%、100%乙醇梯度脱水10 min,重复3次,脱水后用100%乙醇和叔丁醇1:1混合液置换15 min,再用叔丁醇置换15 min,置换后冷冻干燥36 h。扫描电镜(SEM)在电压为15.0 kV条件下放大2000倍观察凝胶微观结构变化。
1.3 数据处理
每组样品设置三个平行组,试验测试重复三次,用平均值±标准偏差(
¯X ±SD)来表示结果;差异显著(P<0.05)和极显著(P<0.01)分析采用SPSS 19.0进行ANOVA分析所得。2. 结果与分析
2.1 阿魏酸诱导肌原纤维蛋白氧化性能变化
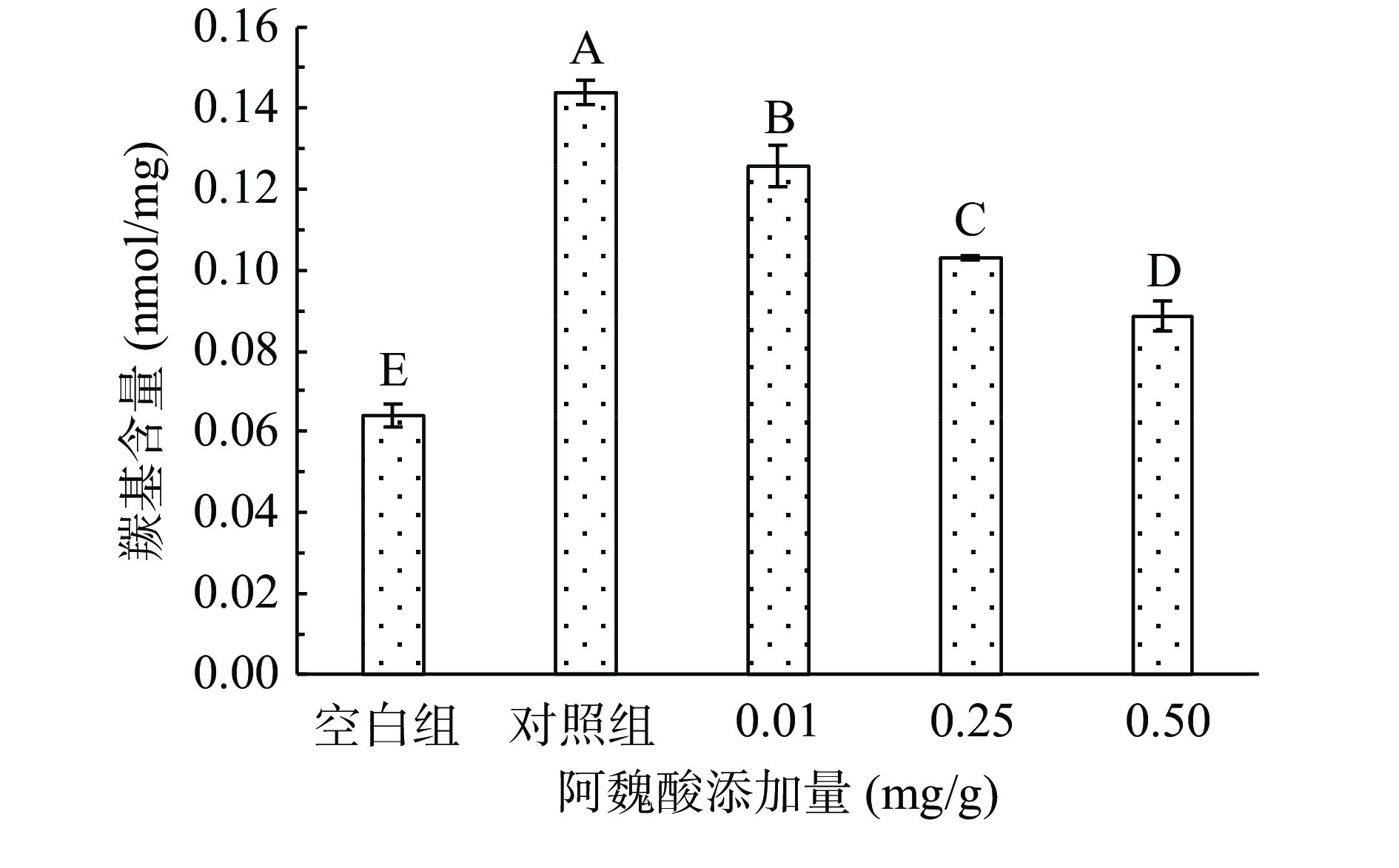
2.1.1 不同浓度阿魏酸对肌原纤维蛋白羰基含量的影响
肌原纤蛋白质中带有NH或NH2的侧链氨基酸官能团遇到ROS极易被氧化生产羰基衍生物,羰基是反应蛋白质变性的重要标志性物质,羰基含量的高低可以间接地反应蛋白质氧化的程度,通常认为羰基含量越高,蛋白氧化越严重[21]。如图1所示,未氧化MPs的羰基含量为0.064 nmol/mg,经·OH氧化体系氧化12 h后,MPs羰基含量极显著升高至0.144 nmol/mg(P<0.01)。在氧化对照基础上,FA的存在极显著降低了MPs羰基含量(P<0.01),尤其在高浓度(0.50 mg/g)条件下,FA对羰基含量的抑制率高达38.20%,由此表明FA能明显抑制蛋白氧化,且抑制效果对其浓度具有依赖性。氧化后羰基浓度变高可能是由于氧化反应发生时,活性氧攻击氨基酸侧链会使肽键断裂,形成羰基衍生物[22],而添加FA后刚开始变化不明显,后总体呈下降趋势,可能是FA中·OH含量略少,溶解度不高,与MPs反应较为困难,而后随浓度增加,越来越多的·OH提升了MPs相互反应的程度。多酚类物质对MPs羰基化的干预效能,课题组前期研究已有类似报道:甘草提取物可有效抑制鸡肉贮藏过程中羰基衍生物的产生[14],鼠曲草提取物可有效抑制猪肉中蛋白羰基的生成[21]。
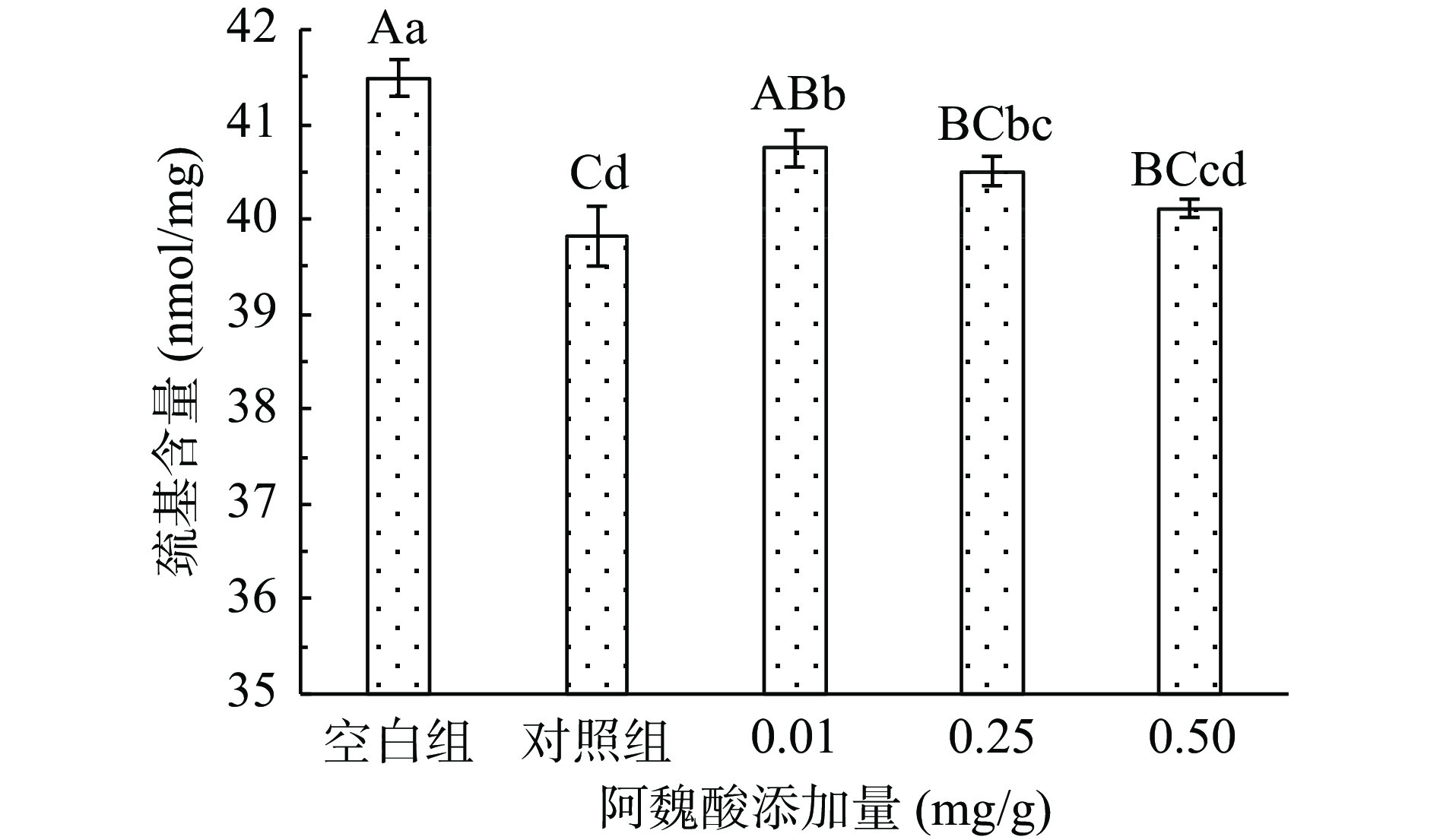
2.1.2 不同浓度阿魏酸对肌原纤维蛋白总巯基含量的影响
蛋白质氧化程度通常用总巯基含量来衡量,MPs中有大量巯基,其中肌球蛋白中巯基含量最多,每个肌球蛋白含有约40个巯基,而巯基容易受到羟自由基的影响转变为分子间或分子内二硫键,含量降低,从而影响蛋白结构,导致功能受到影响[17]。氧化条件下添加不同浓度FA对猪肉MPs总巯基含量的影响如图2所示。
未氧化MPs总巯基含量为41.49 nmol/mg,经·OH氧化体系氧化12 h后,其总巯基含量极显著(P<0.01)降低了4.02%。这是由于蛋白质的结构受氧化作用部分发生展开,使得半胱氨酸中的活性巯基暴露,受·OH攻击后形成二硫键或进一步被氧化为磺酸类或其他氧化产物,从而导致巯基损失[23]。高浓度FA在氧化的基础上进一步促进MPs巯基损失,可能原因是酚类物质与蛋白质相互作用形成“巯基-醌”加合物[24]。实验结果表明,FA造成氧化后蛋白巯基的进一步损失。有研究发现,低浓度的精氨酸(L-Arg)能有效抑制MPs中巯基含量的损失,而高浓度的L-Arg添加量反而会促进巯基含量的损失[25],与本研究总巯基测定结果一致。
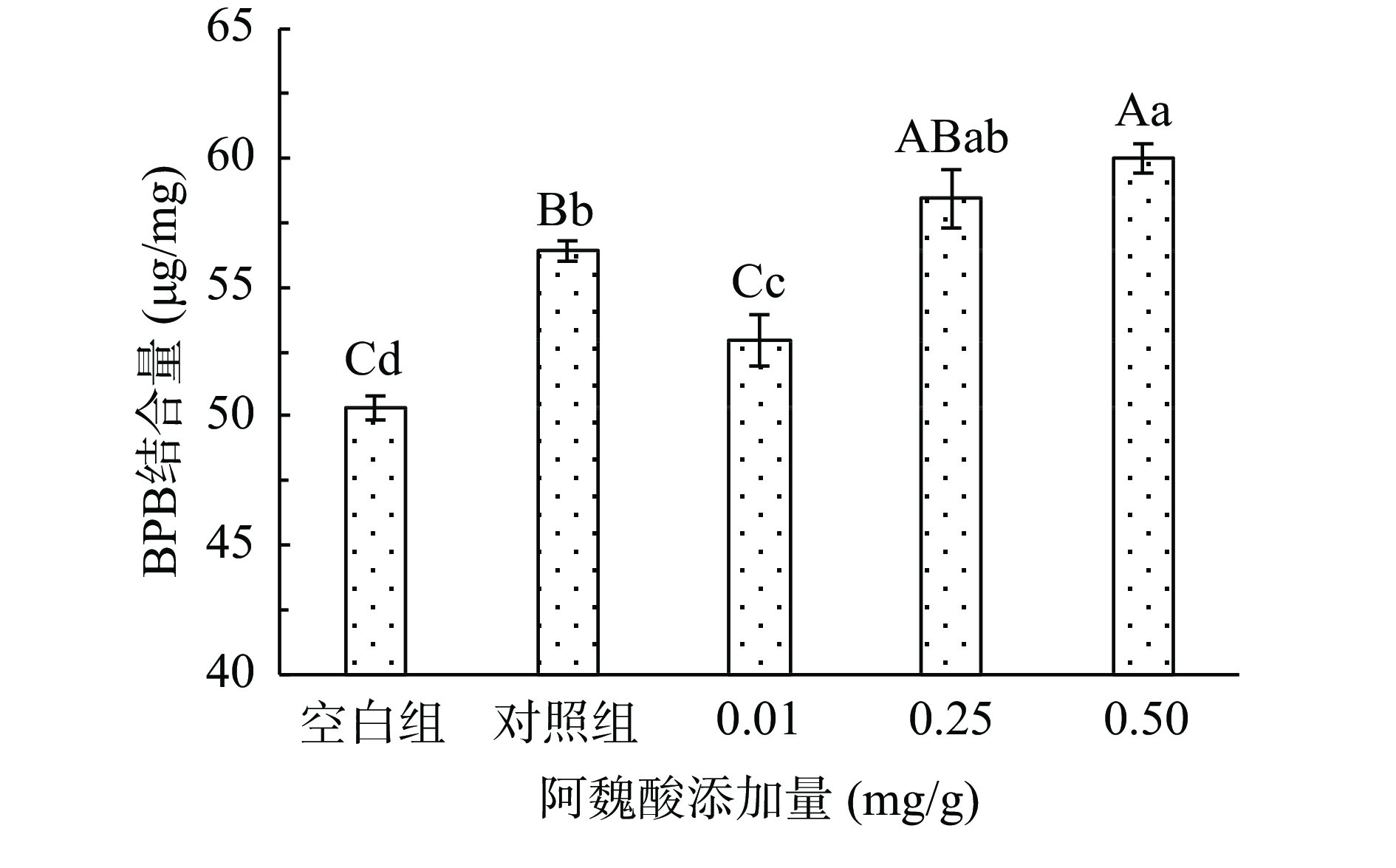
2.1.3 不同浓度阿魏酸对肌原纤维蛋白表面疏水性的影响
表面疏水性反映的是蛋白质表面的疏水性氨基酸残基的数量,蛋白经氧化后,其分子结构往往会发生改变,结构变化越大会使得越多的疏水基团发生暴露,导致表面疏水性增加,根据氨基酸残基与溴酚蓝的结合量来判断蛋白质变性程度[15]。MPs氧化后BPB结合量显著增加(P<0.05),表面疏水性在氧化后显著升高(P<0.05),这是因为蛋白质暴露于氧化环境中导致部分蛋白结构展开,疏水性氨基酸暴露在分子表面,促使BPB与MPs的疏水性氨基酸残基结合量增加明显,与BPB结合使得蛋白质表面疏水性增强。如图3所示,低浓度下FA的添加会缓解由于氧化引起的表面疏水性的增加,可能是因为低浓度的FA缓解了MPs的氧化,减少了氨基酸侧链疏水氨基酸基团的暴露,从而在一定程度上减少了BPB的结合量;但高浓度下会促进蛋白结构的进一步展开,FA的添加会促进蛋白结构的进一步展开,暴露更多的疏水性残基,从而有利于多酚与蛋白质发生疏水相互作用。有研究发现,添加不同浓度没食子酸,表面疏水性逐渐增强,低浓度添加量时表面疏水性略有降低,随后浓度越高表面疏水性越强[26]。
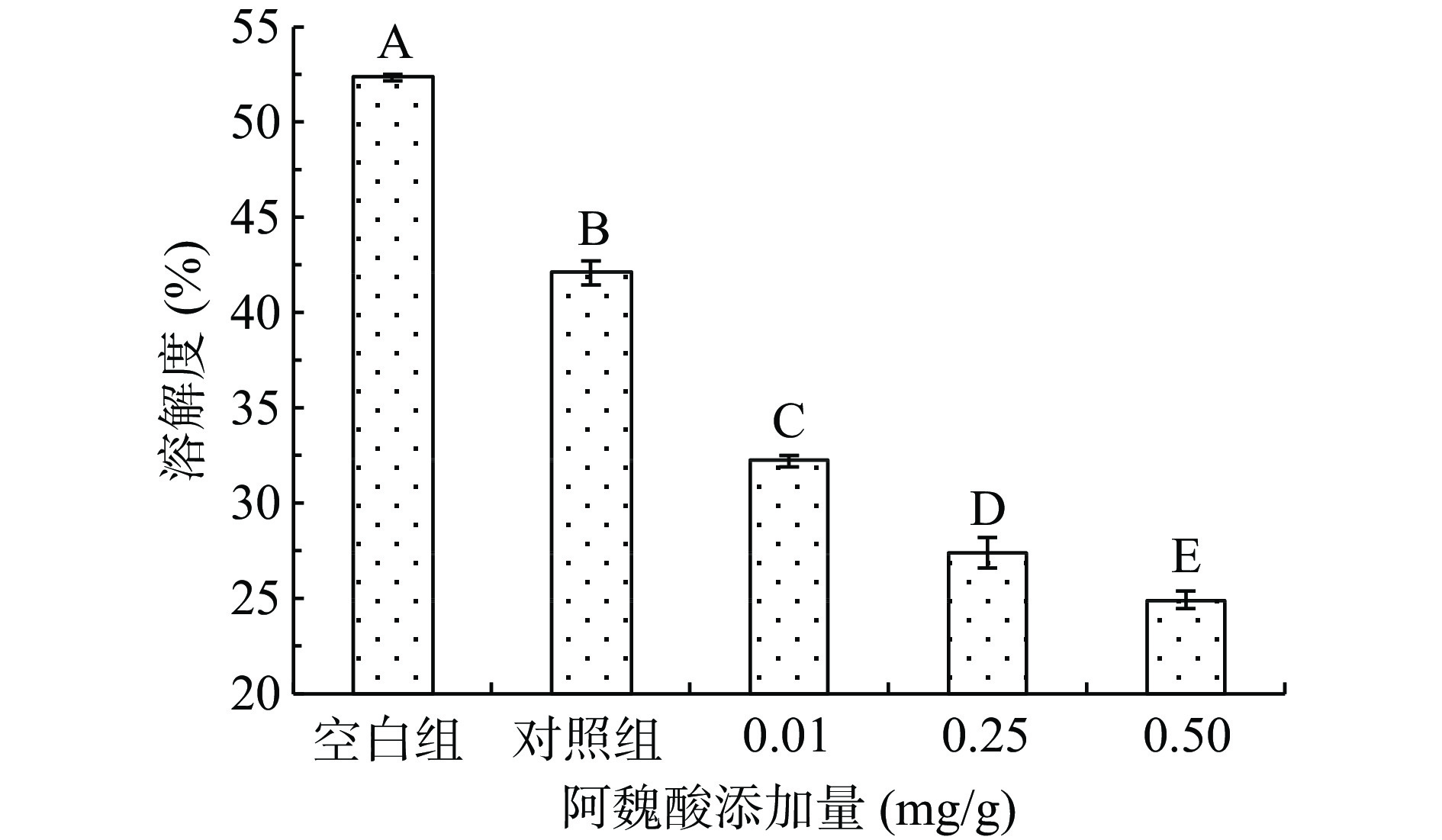
2.1.4 不同浓度阿魏酸对肌原纤维蛋白溶解度的影响
由于蛋白的不溶性会限制部分功能特性,所以蛋白的功能特性通常由蛋白溶解度反映,另外,蛋白质溶解度可从侧面反映其表面疏水情况,通常表面疏水性越大,溶解度便越小[27]。如图4所示,与未经氧化相比,MPs氧化后溶解度降低,且随着FA添加浓度的增大,溶解度降低越明显,其中对照组、0.01、0.25、0.5 mg/g FA添加组的溶解度分别降低了19.04%、38.08%、47.29%、52.04%。蛋白质溶解度下降的原因可能是由于巯基与酚类氧化后形成的醌类物质共价交联,形成的产物会导致溶解度降低,酚类与蛋白反应形成的复合物也会使蛋白溶解度降低,FA添加后表面疏水性加强,形成了疏水结构,蛋白之间存在疏水性聚集,与水的相互作用减弱,也可能与不同FA浓度下蛋白结构不同有关。周扬等[28]研究的酚类物质迷迭香酸的添加同样会导致肌球蛋白表面疏水性升高且溶解度降低。
2.2 肌原纤维蛋白凝胶性能变化
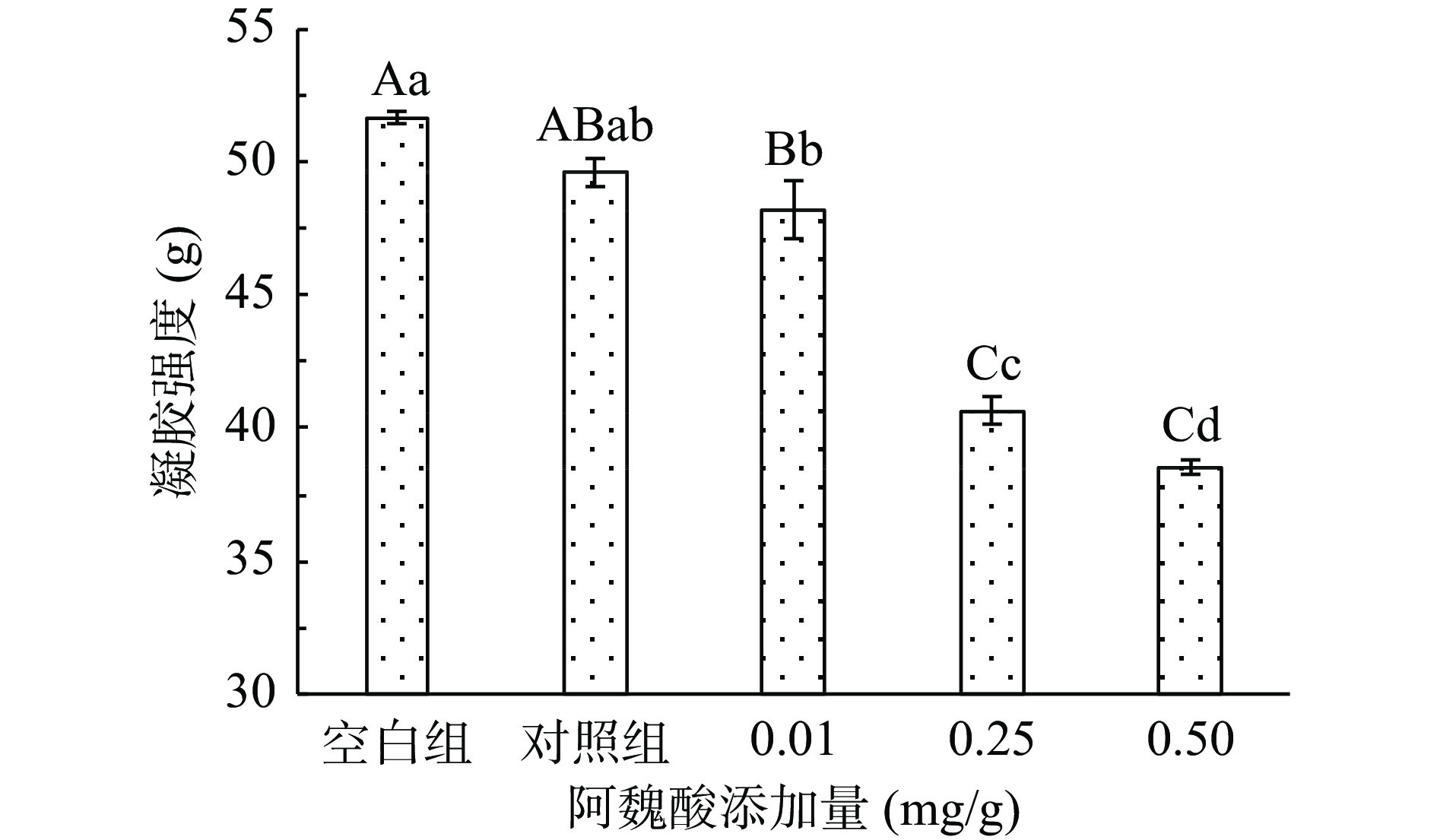
2.2.1 不同浓度阿魏酸对肌原纤维蛋白凝胶强度的影响
蛋白形成凝胶的能力通常由MPs凝胶强度决定,蛋白的氧化导致原有结构变化后,凝胶网络结构会变疏松,强度变弱。氧化条件下添加不同浓度FA对猪肉MPs凝胶强度的影响如图5所示。
MPs凝胶强度的变化趋势与溶解性一致,氧化后的MPs凝胶强度极显著降低(P<0.01),氧化会导致蛋白结构变化,形成较弱的凝胶网络结构,形成能力降低,凝胶强度也随FA添加量的增加而降低,可能原因是添加后因氧化而形成醌类物质,与巯基发生反应产生巯基-醌类加合物,能够有效减少稳定二硫键的生成,使得MPs凝胶网络结构不牢固,强度降低[4],同时,MPs和FA可能形成一种疏水复合物,或者是MPs发生了疏水性聚集、变性等,MPs不能充分溶胀,FA覆盖在MPs表面也可能会阻碍蛋白功能基团中的相互作用,以上都不利于MPs凝胶网络结构形成[8]。有研究发现,不同浓度没食子酸添加后,凝胶强度均有降低,且添加量越多,凝胶强度越弱[29],与本研究结果一致。
2.2.2 不同浓度阿魏酸对肌原纤维蛋白凝胶质构的影响
氧化条件下添加不同浓度FA对猪肉MPs凝胶强度的影响如表2所示。
表 2 氧化及不同浓度阿魏酸对MPs凝胶质构特性的影响Table 2. Effects of oxidation and different concentrations of ferulic acid on the texture properties of MPs gel项目 阿魏酸添加量 (mg/g) 空白组 对照组 0.01 0.25 0.50 硬度(g) 54.599±1.36Aa 41.308±0.06Bb 40.323±1.20Bb 32.642±0.09Cc 31.722±1.97Cc 黏性(g·cm−1) −16.042±0.48ab −14.092±2.32a −13.511±1.75a −15.340±1.06ab −19.953±1.50b 弹性 0.176±0.01 0.192±0.01 0.224±0.01 0.169±0.03 0.181±0.00 胶粘性 7.883±0.69Aa 6.953±0.29ABab 5.648±0.11Bbc 4.227±1.27Bc 5.106±0.22Bc 咀嚼性 1.441±0.10Aa 1.230±0.06ABa 1.167±0.05ABcd 0.956±0.00Bcd 0.936±0.03Bd 内聚性 0.152±0.01 0.140±0.02 0.154±0.02 0.117±0.01 0.125±0.01 回复性 0.051±0.01a 0.044±0.00ab 0.043±0.00ab 0.037±0.01ab 0.034±0.00b 注:同行不同大写字母表示差异极显著(P<0.01),不同小写字母表 示差异显著(P<0.05);表3同。 凝胶质构的重要指标包含凝胶硬度、黏性、弹性、胶粘性、咀嚼性、内聚性、回复性。凝胶硬度表示第一次下压时所受压力达到最大的峰值,氧化后的MPs凝胶硬度显著降低(P<0.05),与MPs凝胶强度的变化趋势一致,说明FA的存在会破坏MPs的凝胶网络结构,会导致凝胶变软。黏性与胶黏性是指食品在一定作用力下的流动性,氧化后MPs的胶黏性与黏性的绝对值显著性下降(P<0.05),并且FA的添加进一步加剧了胶黏性与黏性的减弱,只有在高浓度下有稍有恢复,但效果并不显著(P>0.05)。
凝胶弹性指凝胶在第一次下压变形后回弹的程度,用于反映在凝胶在受力变形和去力后的恢复程度,氧化后MPs凝胶弹性增强,当添加0.01 mg/g FA时弹性最强,随后随FA的增加而降低,可能原因是较高的FA添加量破坏了凝胶结构有关。内聚性是指形成食品所需形态内部的结合力,实验结果表明氧化后MPs的内聚性减弱,FA加入后内聚性进一步减弱,并且0.25 mg/g处理组的内聚性最小,但不同处理组间显著性并不明显(P>0.05)。咀嚼性表示固体食品咀嚼时所需的能量大小,回复性是指食品发生形变后在与导致变形同样的速度、压力条件下回复的程度,MPs凝胶的咀嚼性和回复性都随着FA的添加浓度的升高而降低。质构结果表明,随FA添加量增加,所有性能均有不同程度减弱,可能是过量的FA使得MPs发生聚焦现象,其中的活性基团受到屏蔽,不利于网络结构形成,导致凝胶质构特性变弱[6]。
2.2.3 不同浓度阿魏酸对肌原纤维蛋白凝胶色差的影响
蛋白结构的变化程度通常由凝胶白度值决定,白度值变化越大反映蛋白质的结构变化越大[30]。氧化条件下添加不同浓度FA对猪肉MPs凝胶色差的影响如表3所示。
表 3 氧化及不同浓度阿魏酸对MPs凝胶色差的影响Table 3. Effect of oxidation and different concentrations of ferulic acid on the chromatic aberration of MPs gel项目 阿魏酸添加量 (mg/g) 空白组 对照组 0.01 0.25 0.50 L* 83.43±0.05Bb 84.74±0.02Aa 83.45±0.04Bb 83.14±0.03Cc 83.06±0.03Cc a* −1.87±0.01Cc −1.67±0.00Bb −1.99±0.00Ee −1.90±0.00Dd −1.60±0.01Aa b* −1.72±0.02Dd −0.61±0.01Aa −1.44±0.00Cc −1.06±0.01Bb −1.46±0.01Cc 白度 83.23±0.05Bb 84.64±0.02Aa 83.27±0.04Bb 83.00±0.03Cc 82.92±0.03Cc 和未氧化相比,MPs氧化后凝胶亮度(L*)和白度均显著升高(P<0.05),但添加FA后,随添加浓度的增加,凝胶亮度和白度表现出下降的趋势,可能原因是由于Fe3+的螯合作用以及氧化产生的醌类物质导致凝胶的白度值降低。有研究发现,添加不同浓度的茶多酚后凝胶白度均有降低,茶多酚添加越多,凝胶白度值越低[31],与本研究结果相似。红度(a*:正值偏红、负值偏绿)的变化主要是受肌红蛋白含量的影响,可以用其表征肌红蛋白的氧化程度。与未氧化相比,MPs氧化后,a*显著变小(P<0.05),说明肌红蛋白被氧化形成高铁肌红蛋白,加深了蛋白的颜色,导致a*下降,然而添加FA后,a*先增大再降低,可能是由于在低浓度下FA的存在阻止了肌红蛋白向高铁肌红蛋白的转变,而高浓度下由于FA自身的微黄色导致a*的上升;黄度(b*:正值偏黄、负值偏蓝)变化趋势与a*相同。
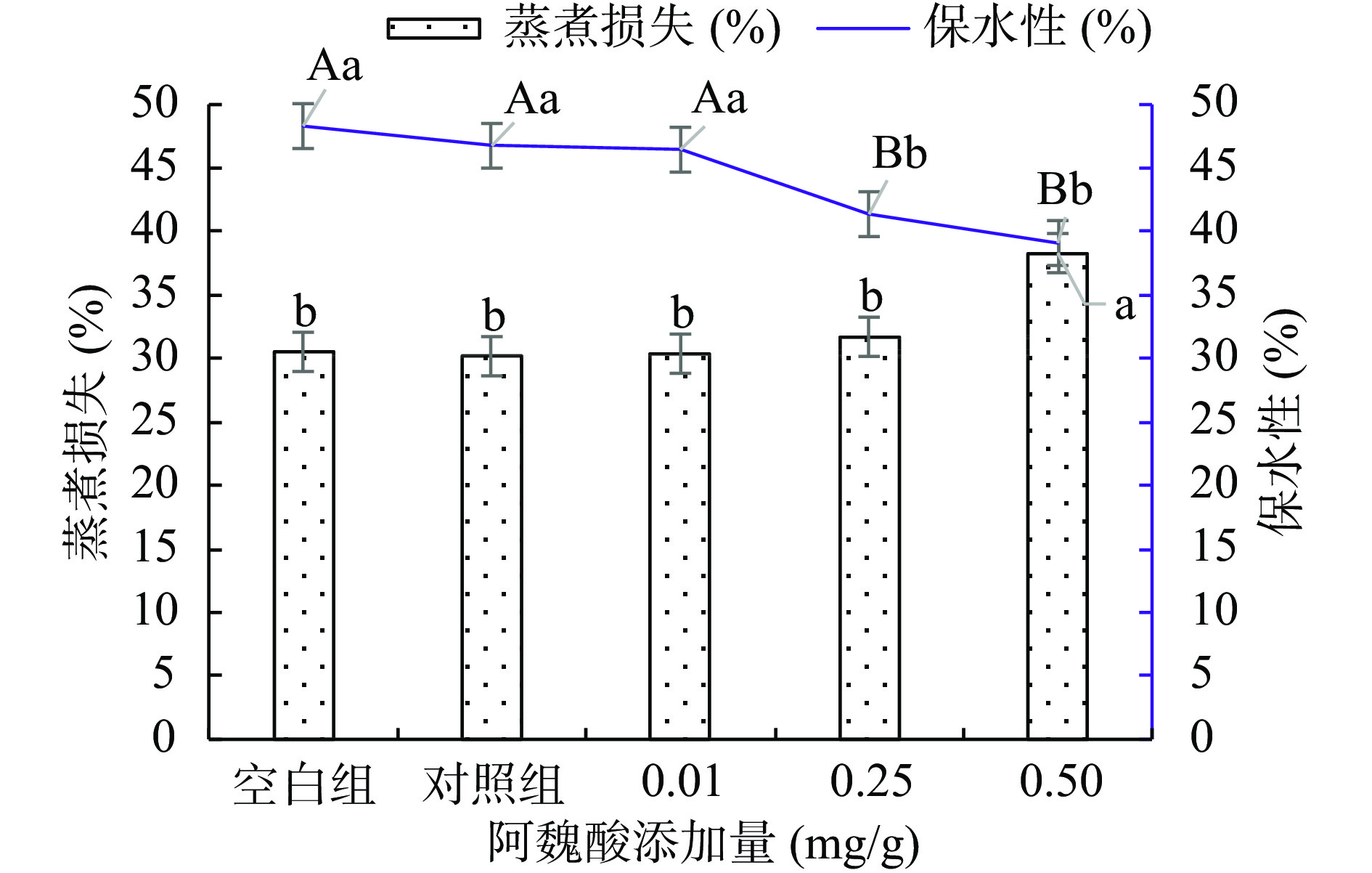
2.2.4 不同浓度阿魏酸对肌原纤维蛋白凝胶蒸煮损失和保水性的影响
由图6可见,未氧化凝胶的蒸煮损失大于氧化后的凝胶,但差异不显著(P>0.05)。添加FA后蒸煮损失增大,添加量越大损失越多,可能是MPs分子间交联聚集加剧,MPs均匀牢固网络结构的形成受到影响,造成蒸煮损失增加[31]。未氧化凝胶的保水性大于氧化后的凝胶,随FA添加量越大,凝胶水分损失越多,这是由于FA导致MPs不能较好的形成三维立体凝胶网络结构,降低了MPs对水分的束缚能力,MPs的侧链氨基酸结构经氧化后受到破坏,蛋白结构发生改变,导致水分析出,同时,由于二硫键发生交联也会降低有序二硫键在热诱导加工中的形成,蛋白官能团间的相互作用降低,质构变差,保水性极显著降低(P<0.01)[4]。保水性作为肉类食用品质评价指标之一,与肉类风味、质构及其凝胶性等属性有密切联系,凝胶的保水性能够直接反映凝胶网络结构的疏密程度,其结构越细密、越均匀,保水性就越好,氧化过程中,氢键、静电作用和疏水作用等会影响凝胶网络结构的形成,MPs和水之间因相互作用而产生的毛细现象也会影响到凝胶的保水性。
2.2.5 不同浓度阿魏酸对肌原纤维蛋白凝胶微观结构的影响
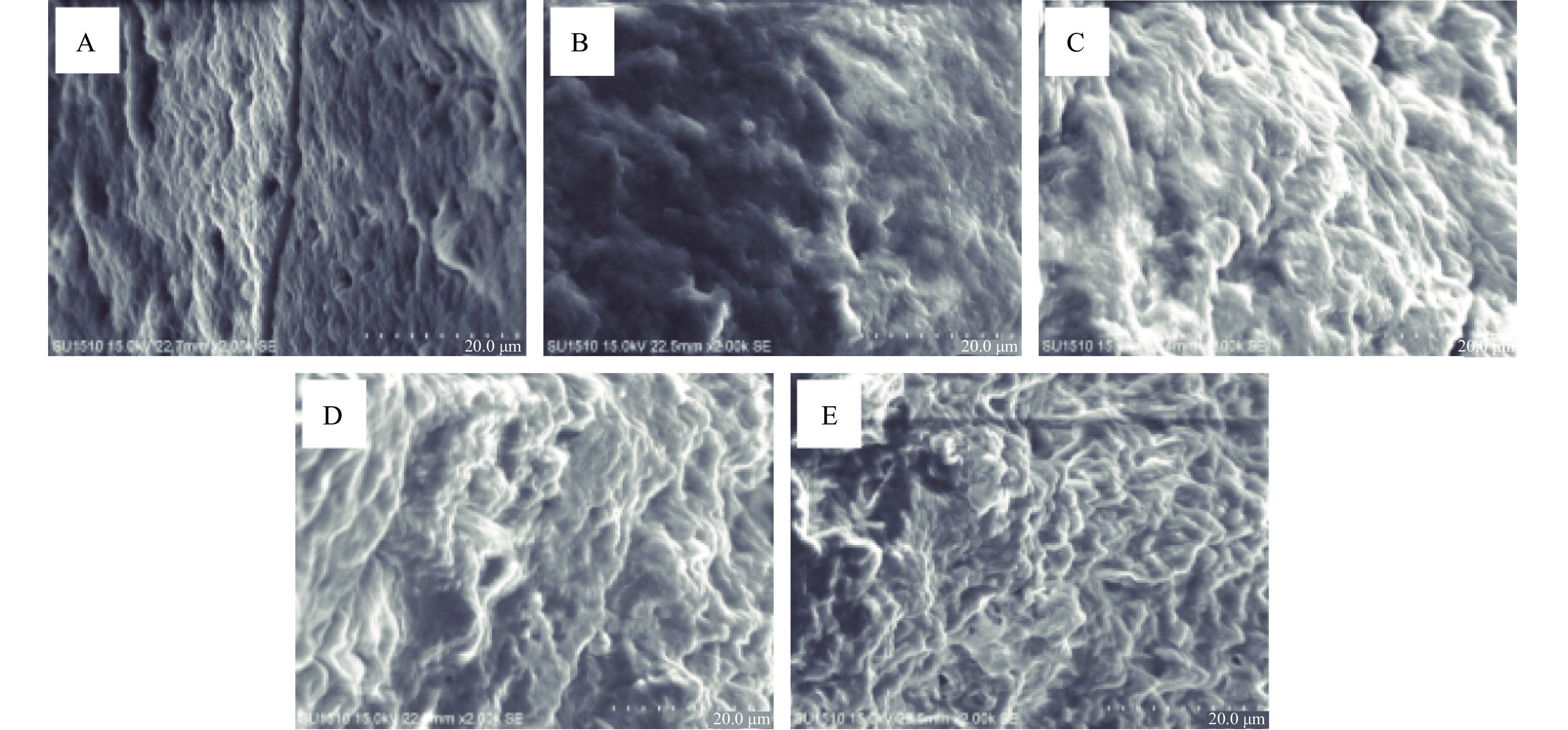
凝胶的网络结构通常是由微观结构直接反映出,其结构变化会影响凝胶的保水性和质构特性等。氧化条件下添加不同浓度FA对猪肉MPs凝胶微观结构的影响如图7所示。
未氧化的MPs凝胶网络结构规则紧密、均匀,而氧化后的MPs结构较为疏松和略显不规则,且有部分较大的孔隙。对照组进行比较,未添加FA的MPs结构相对规则、致密,结构有序,当添加FA后,网络结构凹凸起伏变大,表面不平坦、不规则,变得疏松多孔,尤其是添加量达到0.50 mg/g后,网络结构杂乱,蛋白胶束发生聚集,分布不均匀,凝聚空间呈现不规则,且随FA添加量增大,网络结构越来越松散,MPs凝胶微观结构呈现与保水性结果变化一致。研究表明氧化会导致MPs凝胶结构被破坏,过高浓度的FA会不同程度的破坏凝胶网络结构,添加量越大,破坏程度越高,影响凝胶形成的能力。
3. 结论
研究通过建立MPs-Fenton氧化体系,在氧化条件下探究不同浓度FA对MPs氧化及凝胶特性作用效果,高浓度FA(0.50 mg/g)对羰基含量的抑制率高达38.20%,暴露更多的疏水性残基,从而有利于多酚与蛋白质发生疏水相互作用,进一步促进MPs巯基损失,且随着FA添加浓度的增大,MPs溶解度降低越明显,表明添加FA可有效调控MPs氧化。氧化会导致蛋白结构变化,形成较弱的凝胶网络结构,成胶能力降低,添加适量FA可以改善凝胶品质,当添加0.01 mg/g 时弹性最强,随后随FA的增加而降低,过高浓度的FA会不同程度的破坏凝胶网络结构,添加量越大,破坏程度越高,影响凝胶形成的能力。
-
表 1 实验样品设置
Table 1 Experimental sample
组别 处理方法 1 不添加抗氧化剂+PIPES缓冲液+Trolox溶液 2 不添加抗氧化剂+Fenton氧化体系+Trolox溶液 3 添加0.01 mg/g FA+Fenton氧化体系+Trolox溶液 4 添加0.25 mg/g FA+Fenton氧化体系+Trolox溶液 5 添加0.50 mg/g FA+Fenton氧化体系+Trolox溶液 表 2 氧化及不同浓度阿魏酸对MPs凝胶质构特性的影响
Table 2 Effects of oxidation and different concentrations of ferulic acid on the texture properties of MPs gel
项目 阿魏酸添加量 (mg/g) 空白组 对照组 0.01 0.25 0.50 硬度(g) 54.599±1.36Aa 41.308±0.06Bb 40.323±1.20Bb 32.642±0.09Cc 31.722±1.97Cc 黏性(g·cm−1) −16.042±0.48ab −14.092±2.32a −13.511±1.75a −15.340±1.06ab −19.953±1.50b 弹性 0.176±0.01 0.192±0.01 0.224±0.01 0.169±0.03 0.181±0.00 胶粘性 7.883±0.69Aa 6.953±0.29ABab 5.648±0.11Bbc 4.227±1.27Bc 5.106±0.22Bc 咀嚼性 1.441±0.10Aa 1.230±0.06ABa 1.167±0.05ABcd 0.956±0.00Bcd 0.936±0.03Bd 内聚性 0.152±0.01 0.140±0.02 0.154±0.02 0.117±0.01 0.125±0.01 回复性 0.051±0.01a 0.044±0.00ab 0.043±0.00ab 0.037±0.01ab 0.034±0.00b 注:同行不同大写字母表示差异极显著(P<0.01),不同小写字母表 示差异显著(P<0.05);表3同。 表 3 氧化及不同浓度阿魏酸对MPs凝胶色差的影响
Table 3 Effect of oxidation and different concentrations of ferulic acid on the chromatic aberration of MPs gel
项目 阿魏酸添加量 (mg/g) 空白组 对照组 0.01 0.25 0.50 L* 83.43±0.05Bb 84.74±0.02Aa 83.45±0.04Bb 83.14±0.03Cc 83.06±0.03Cc a* −1.87±0.01Cc −1.67±0.00Bb −1.99±0.00Ee −1.90±0.00Dd −1.60±0.01Aa b* −1.72±0.02Dd −0.61±0.01Aa −1.44±0.00Cc −1.06±0.01Bb −1.46±0.01Cc 白度 83.23±0.05Bb 84.64±0.02Aa 83.27±0.04Bb 83.00±0.03Cc 82.92±0.03Cc -
[1] 常海军, 周文斌. 畜禽肉制品加工工艺与技术[M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学出版社, 2018: 56−59 CHANG H J, ZHOU W B. Processing technology of livestock and poultry meat products [M]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University Press, 2018: 56−59.
[2] SADEGHINEJAD N, SARTESHNIZI R A, GAVLIGHI H A, et al. Pistachio green hull extract as a natural antioxidant in beef patties: Effect on lipid and protein oxidation, color deterioration, and microbial stability during chilled storage[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2019,102:393−402. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2018.12.060
[3] ZHAO X, XU X, ZHOU G. Covalent chemical modification of myofibrillar proteins to improve their gelation properties: A systematic review[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety,2021,20(1):924−959. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12684
[4] LV Y Q, FEN X C, WANG Y J, et al. The gelation properties of myofibrillar proteins prepared with malondialdehyde and (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,340:127817. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127817
[5] LI L, ZHAO J, YANG T, et al. High-speed countercurrent chromatography as an efficient technique for large separation of plant polyphenols: A review[J]. Food Research International,2022,153:110956. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.110956
[6] JIA N, WANG L T, SHAO J H, et al. Changes in the structural and gel properties of pork myofibrillar protein induced by catechin modification[J]. Meat Science,2017,127:45−50. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2017.01.004
[7] CAO Y G, TRUE A D, CHEN J, et al. Dual role (anti-and prooxidant) of gallic acid in mediating myofibrillar protein gelation and gel in vitro digestion[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2016,64(15):54−61.
[8] CAO Y G, XIONG Y L. Chlorogenic acid mediated gel formation of oxidatively stressed myofibrillar protein[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,180(8):235−243.
[9] GU R, LI F, LI D, et al. Effects of ferulic acid on the oxidation stability and nitrozation of myofifibrillar proteins under oxidative stress[J]. Food Chemistry Advances,2022,1:100016. doi: 10.1016/j.focha.2022.100016
[10] LI D, RUI Y, GUO S, et al. Ferulic acid: A review of its pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and derivatives[J]. Life Sciences,2021,284:119921. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119921
[11] 李黎云. 日粮添加阿魏酸与维生素E对育肥猪肉品质和抗氧化性能的影响[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2013 LI L Y. Effects of dietary supplementation of ferulic acid and vitamin E on meat quality and antioxidative capacity of finishing pigs [D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2013.
[12] CHENG J, TANG D, YANG H, et al. The dose-dependent effects of polyphenols and malondialdehyde on the emulsifying and gel properties of myofibrillar protein-mulberry polyphenol complex[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,360:130005. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130005
[13] WANG Z, HE Z, ZHANG D, et al. Antioxidant activity of purslane extract and its inhibitory effect on the lipid and protein oxidation of rabbit meat patties during chilled storage[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2021,101(5):1953−1962. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10811
[14] 熊杰, 伯朝英, 常海军. 甘草提取物对冷藏鸡肉糜脂肪和蛋白质氧化及品质特性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(1):75−81,88. [XIONG J, BO Z Y, CHANG H J. Effects of licorice extract on oxidation and quality characteristics of fat and protein in refrigerated chicken meat batter[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(1):75−81,88. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020030319 [15] XU M, LIAN Z, CHEN X, et al. Effects of resveratrol on lipid and protein co-oxidation in fish oil-enriched whey protein isolate emulsions[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,365:130525. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130525
[16] 曹云刚, 马文慧, 艾娜丝, 等. 氧化强度对肌原纤维蛋白结构及凝胶性能的影响[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(20):21−27. [CAO Y G, MA W H, AI N S, et al. Effects of different oxidation intensities on the structure and gel properties of myofibrillar protein[J]. Food Science,2019,40(20):21−27. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181105-059 [17] ZHANG D, LI H, EMARA A M, et al. Effect of in vitro oxidation on the water retention mechanism of myofibrillar proteins gel from pork muscles[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,315:126226. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126226
[18] ZHAO Y, ZHOU G, ZHANG W. Effects of regenerated cellulose fiber on the characteristics of myofibrillar protein gels[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2019,209:276−281. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.01.042
[19] CAO Y G, MA W H, HUANG J R, et al. Effects of sodium pyrophosphate coupled with catechin on the oxidative stability and gelling properties of myofibrillar protein[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2020,104(7):105722.
[20] ZHANG Z, XIONG Z, LU S, et al. Effects of oxidative modification on the functional, conformational and gelling properties of myofibrillar proteins from Culter alburnus[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,162:1442−1452. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.052
[21] 熊杰, 伯朝英, 常海军, 等. 鼠曲草提取物对·OH 诱导的肌原纤维蛋白氧化及结构的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(3):72−80. [XIONG J, BO Z Y, CHANG H J, et al. Effects of the extract of Gnaphalium affine on the oxidation and structure of myofibrillar protein induced by ·OH[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(3):72−80. [22] HUANG X, SUN L, LIU L, et al. Study on the mechanism of mulberry polyphenols inhibiting oxidation of beef myofibrillar protein[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,372:131241. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131241
[23] CHENG J, XIANG R, TANG D, et al. Regulation of protein oxidation in Cantonese sausages by rutin, quercetin and caffeic acid[J]. Meat Science,2021,175:108422. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2020.108422
[24] TANG C B, ZHANG W G, DAI C, et al. Identification and quantification of adducts between oxidized rosmarinic acid and thiol compounds by UHPLC-LTQ-Orbitrap and MALDI-TOF/TOF tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2015,63(3):902−911. doi: 10.1021/jf5044713
[25] 马文慧, 邝吉卫, 李保玲, 等. 氧化条件下精氨酸对肌原纤维蛋白结构及凝胶性能的调控[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(24):24−31. [MA W H, KUANG J W, LI B L, et al. Effect of L-Arg concentration on structural and gelling properties of myofibrillar protein under oxidative conditions[J]. Food Science,2021,42(24):24−31. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200903-028 [26] 贾娜, 刘丹, 张晓星, 等. 氧化条件下没食子酸对猪肉肌原纤维蛋白结构及凝胶特性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2016,37(23):61−66. [JIA N, LIU D, ZHANG X X, et al. Effect of gallic acid on constructure and gel properties of pork myofibrillar protein under oxidation conditions[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2016,37(23):61−66. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2016.23.003 [27] 伯朝英, 熊杰, 常海军, 等. 马齿苋提取物抑制冷藏猪肉糜脂肪和蛋白氧化及对品质特性的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(22):172−179. [BO Z Y, XIONG J, CHANG H J, et al. Effects of Purslane extract on oxidation and quality of fat and protein in refrigerated minced pork[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022,48(22):172−179. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.029501 [28] 周扬, 陈雪珂, 戴宏杰, 等. 溶液体系中迷迭香酸与肌球蛋白的相互作用及其对蛋白理化特性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(12):14−21. [ZHOU Y, CHEN X K, DAI H J, et al. Interaction of rosmarinic acid with myosin in aqueous buffer solution and its effect on protein physicochemical properties[J]. Food Science,2020,41(12):14−21. [29] 贾娜, 林世文, 王乐田, 等. 没食子酸诱导肌原纤维蛋白巯基含量和表面疏水性变化对蛋白凝胶特性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(22):1−7. [JIA N, LIN S W, WANG L T, et al. Effects of changes in sulfhydryl content and surface hydrophobicity of myofibrillar protein induced by gallic acid on its gel properties[J]. Food Science,2020,41(22):1−7. [30] 陈洪生, 孔保华, 王宇. 蛋清蛋白对猪肉肌原纤维蛋白功能性的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2014,14(5):80−84. [CHEN H S, KONG B H, WANG Y. Effect of egg white protein on functional properties of porcine myofibrillar protein[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2014,14(5):80−84. [31] 李保玲, 李颖, 朱振宝, 等. 氧化亚油酸对肌原纤维蛋白胶凝行为及热诱导凝胶体外消化率的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(19):111−119. [LI B L, LI Y, ZHU Z B, et al. Effect of oxidized linoleic acid on gelling behavior of myofibrillar protein and in vitro digestibility of the heat-induced gel[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(19):111−119. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.026253 -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 陈冠怡,许陈彩,李佳玲,李鑫,张伟坚,陈春蓓,王泽富,刘书成. 亚油酸介导氧化的金鲳鱼肌原纤维蛋白结构和凝胶特性变化. 现代食品科技. 2024(09): 248-256 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:








 下载:
下载:



