Comparative Study on Hepatoprotective Effects of Alcohol Extract and Total Flavonoids of Penthorum chinense Pursh against Alcohol-induced Subacute Liver Injury in Mice
-
摘要: 目的:比较赶黄草醇提物和赶黄草总黄酮对小鼠亚急性酒精性肝损伤的保护作用。方法:将昆明小鼠随机分为正常组、模型组、阳性组(联苯双酯,150 mg/kg)、赶黄草醇提物3个不同剂量处理组(400、800和1600 mg/kg)及赶黄草总黄酮3个不同剂量处理组(100、200和400 mg/kg);应用酒精灌胃方法建立亚急性酒精性肝损伤小鼠模型,检测各组小鼠肝脏系数、肝组织病理变化和血清生化指标。结果:与模型组比较,赶黄草醇提物和赶黄草总黄酮高、中剂量组小鼠肝脏系数均显著降低(P<0.05),肝组织损伤和脂肪变性明显减轻,小鼠血清谷丙转氨酶(alanine transaminase,ALT)、谷草转氨酶(aspartate transaminase,AST)、碱性磷酸酶(alkaline phospha-tase,ALP)、乳酸脱氢酶(lactic dehydrogenase,LDH)活性及总胆红素(total bilirubin,TBIL)、总胆固醇(total cholesterol,TC)、甘油三酯(triglycerides,TG)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(low density lipoprotein cholesterol,LDL-C)含量均显著降低(P<0.05,P<0.01)。与等生药剂量的赶黄草醇提物组比较,赶黄草总黄酮组小鼠血清ALT、AST、ALP、LDH活性及TBIL、TC、TG和LDL-C含量均显著降低(P<0.05,P<0.01)。结论:赶黄草醇提物和赶黄草总黄酮对亚急性酒精性肝损伤均具有保护作用,赶黄草总黄酮优于赶黄草醇提物,赶黄草总黄酮是赶黄草抗酒精性肝损伤的主要功效成分。Abstract: Object: To compare the hepatoprotective effects of alcohol extract and total flavonoids of Penthorum chinense Pursh on alcohol-induced subacute liver injury in mice. Methods: The mice were randomized into the normal group, model group, positive group (bifendate, 150 mg/kg), ethanol extract of Penthorum chinense Pursh with three different dose treatment groups (400, 800 and 1600 mg/kg), and total flavonoids of Penthorum chinense Pursh with three different dose treatment groups (100, 200 and 400 mg/kg). The model of subacute alcoholic liver injury in mouse was set up by intragastric administration of alcohol. The liver index, pathological changes of liver tissue and serum biochemical indexes were measured in each group. Results: Compared with mice in the model group, the hepatic index was decreased significantly (P<0.05), the liver injury pathological state was ameliorated, the activities of serum alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) and the content of total bilirubin (TBIL), total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) were decreased significantly (P<0.05, P<0.01) in the high and medium treatment groups of alcohol extract and total flavonoids of Penthorum chinense Pursh. The activities of serum ALT, AST, ALP, LDH as well as the content of TBIL, TC, TG and LDL-C in the total flavonoids group were significantly lower than those in the alcohol extract group with the same crude drug dose (P<0.05, P<0.01). Conclusion: Both alcohol extract and total flavonoids of Penthorum chinense Pursh can protect subacute alcoholic liver injury, but total flavonoids does better than alcohol extract. The total flavonoids is a main functional component of Penthorum chinese Pursh to protect alcoholic liver injury.
-
酒精性肝损伤是由于长期大量饮酒而导致的肝脏损害,严重时可导致肝细胞坏死,甚至引发肝功能衰竭[1-3]。近年来,酒精消耗量逐年攀升,酒精仅次于肝炎病毒,已成为肝损伤的第二大诱因;酒精性肝损伤的发病率逐年上升,目前尚无特异性药物治疗[4-8];现今市售保肝药物,如糖皮质类固醇、己酮可可碱和多烯磷脂酰胆碱等,绝大多数治疗效果不明显,而且大多对人体具有毒副作用[9-10]。从药食同源植物中寻找有效预防酒精性肝损伤的功效成分,并将其开发为抗酒精性肝损伤的保健食品,是有效预防酒精性肝损伤的重要途径[11-12]。
赶黄草(Penthorum chinense Pursh)是虎耳草科扯根菜属植物扯根菜的干燥地上部分,是四川古蔺道地药材。2020年6月被国家卫健委正式批准为新食品原料,赶黄草为药食同原植物。赶黄草性平、无毒、归肝经,治疗肝病,疗效独特[13]。现代临床及实验表明赶黄草对酒精性肝损伤具有较好的保护作用[14],但其主要功效成分尚未明确。目前从赶黄草中分离得到约120个化合物,其中黄酮类化合物占到1/3以上[14-17],黄酮类化合物是赶黄草的主要化学成分。项目组前期测得赶黄草中总黄酮的含量为4.92%(以乔松素计),制备了总黄酮含量超过50%的赶黄草总黄酮[18]。赶黄草总黄酮主要由异槲皮苷、乔松素、槲皮素、山奈酚和芹菜素等对化学性肝损伤具有保护作用的黄酮类化合物组成[19],前期实验表明赶黄草总黄酮对四氯化碳所致小鼠急性化学性肝损伤具有保护作用[19],但尚不清楚赶黄草总黄酮是否对酒精所致肝损伤具有保护作用。
基于我国酒精性肝损伤危害者大多具有长期饮用低度酒(25~40% Vol)的习惯,本试验以浓度30%的乙醇(10 mL/kg)灌胃小鼠15 d,建立小鼠亚急性酒精肝损伤模型,通过比较赶黄草醇提物和赶黄草总黄酮对亚急性酒精性肝损伤小鼠肝脏系数、肝组织病理学、血清生化指标的影响,旨在阐明赶黄草总黄酮是赶黄草抗酒精性肝损伤的主要功效成分,为开发安全有效的抗酒精性肝损伤的保健食品提供依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
赶黄草 采自四川古蔺县,经西南医科大学税丕先教授鉴定为虎耳草科植物扯根菜(Penthorum chinese Pursh)的干燥全草;SPF级昆明小鼠 雄性,体重(20±2 g),西南医科大学实验动物中心,实验动物许可证号:SCXK(川)2018-17,实验动物福利伦理审查批准号:西南医科大学实验动物伦理委员会20210819-16;联苯双酯 万邦德制药有限公司;谷丙转氨酶(alanine aminotransferase,ALT)试剂盒、谷草转氨酶(aspartate transaminase,AST)试剂盒、碱性磷酸酶(alkaline phosphatase,ALP)试剂盒、乳酸脱氢酶(lactic dehydrogenase,LDH)试剂盒、甘油三酯(triglycerides,TG)试剂盒、总胆固醇(total cholesterol,TC)试剂盒、小鼠总胆红素(total bilirubin,TBIL)试剂盒、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(low density lipoprotein cholesterol,LDL-C)试剂盒 迈克生物股份有限公司;4%多聚甲醛 广州赛国生物科技有限公司;苏木素-伊红染液 湖北百奥斯生物科技有限公司。
5804高速离心机 上海艾本德中国有限公司;EYELAN-1300D旋转蒸发仪 日本东京理化公司;Milli-Q超纯水系统 密理博(中国)有限公司;AU480全自动生化测定仪 美国贝克曼库尔特有限公司;JJ-12J脱水机、JB-P5包埋机 武汉俊杰电子有限公司;RM2016病理切片机 上海徕卡仪器有限公司;Nikon Eclipse CI正置光学显微镜、Nikon DS-U3成像系统 日本Nikon公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 赶黄草醇提物及赶黄草总黄酮的制备
称取250 g赶黄草粗粉,以55%乙醇加热回流提取三次,合并提取液,减压浓缩,回收溶剂,60 ℃真空干燥,得赶黄草醇提物40.05 g,提取率为16.02%,醇提物中总黄酮含量为16.50%(以乔松素计)[18] 。称取20 g赶黄草醇提物,以聚酰胺柱色谱纯化,以含水乙醇洗脱,收集70%乙醇洗脱部位,减压浓缩,回收溶剂,60 ℃真空干燥,得赶黄草总黄酮产品4.916 g,得率为24.58%,赶黄草总黄酮产品中总黄酮含量为50.34%(以乔松素计)。赶黄草醇提物和赶黄草总黄酮临用前用蒸馏水配至所需浓度。1 g赶黄草醇提物相当于6.25 g赶黄草生药;1 g赶黄草总黄酮相当于4 g赶黄草醇提物,相当于25 g赶黄草生药。
1.2.2 动物模型建立及剂量设计
90只小鼠适应性喂养1周后,将小鼠随机分为正常组(N)、模型组(M)、联苯双酯阳性对照组(Bif,150 mg/kg)、赶黄草醇提物高剂量组(GCG,1600 mg/kg)、中剂量组(GCZ,800 mg/kg)、低剂量组(GCD,400 mg/kg),以及赶黄草总黄酮高剂量组(GZG,400 mg/kg)、中剂量组(GZZ,200 mg/kg)、低剂量组(GZD,100 mg/kg),共9组,每组10只。联苯双酯组、赶黄草醇提物各剂量组和赶黄草总黄酮各剂量组小鼠,每天均按照相应剂量灌胃给药1次,灌胃量为10 mL/kg;正常组和模型组给予等体积蒸馏水,连续15 d。从第16 d起,模型组和各给药组灌胃给药4 h后,再给予30%乙醇(10 mL/kg);正常组给予等体积蒸馏水,连续15 d。小鼠每3 d称重1次,根据体重调整给药量。
1.2.3 样品的采集与处理
末次给药后,小鼠禁食4 h,称重。小鼠眼球取血,3000 r/min离心10 min,分离得到血清;解剖取肝,称重,生理盐水冲洗,肝脏左叶以4%多聚甲醛固定。
1.2.4 指标检测与方法
1.2.4.1 小鼠肝脏系数
根据1.2.3方法记录小鼠体重和肝脏重量,按下述公式计算小鼠肝脏系数:
肝脏系数(%)=肝脏质量(g)体重(g)×100 1.2.4.2 小鼠肝组织病理学检查
取出固定于4%多聚甲醛的肝脏左叶,常规方法制作石蜡切片、HE染色。光镜下观察肝细胞变性(脂肪变性、水样变性、胞浆凝聚、气球样变)、肝细胞坏死和炎症改变等,并进行计分。计分方法:将每只动物肝细胞各种病理变化得分相加计分,每只动物肝脏细胞病变总分=肝细胞变性得分×1+肝细胞炎症改变得分×1+肝细胞坏死得分×2。其中肝细胞变性得分=气球样变得分+脂肪变性得分+胞浆凝聚得分+水样变性得分[20]。以总分进行统计分析。
1.2.4.3 小鼠血清生化指标检测
小鼠血清ALT、AST、ALP、LDH活性和TBIL、TC、TG、LDL-C含量均按照相应试剂盒说明书方法进行检测。
1.3 数据处理
用SPSS 17.0软件进行统计学处理,数据以均数±标准差(
¯X ±SD)表示,用单因素方差分析(ANOVA)进行差异性检验,采用LSD法进行多重比较分析,P<0.05表示有显著性差异,P<0.01表示有极显著性差异。2. 结果与分析
2.1 小鼠亚急性酒精性肝损伤模型的建立
为明确是否成功建立小鼠亚急性酒精性肝损伤模型,根据国家食品药品监督管理局2011年发布的《对化学性肝损伤有辅助保护功能评价方法(修订稿)》(方案三)判定标准,对正常组和模型组小鼠血清TC、LDL-C、TBIL含量和肝组织病变分数进行分析[20-21]。由表1可知,连续15 d灌胃30%乙醇(10 mL/kg)后,模型组小鼠血清TC、LDL-C、TBIL含量和肝细胞病变总分均高于正常组,有极显著统计学差异(P<0.01),表明小鼠亚急性酒精性肝损伤模型成功建立。
表 1 亚急性酒精性肝损伤小鼠模型成模的判定(¯x ±s,n=10)Table 1. Judgment of the successful model of subacute alcoholic live injury in mice (¯x ±s, n=10)组别 TC
(mmol/L)LDL-C
(mmol/L)TBIL
(mmol/L)肝组织病变总分
(分)正常组(N) 2.67±0.48 0.323±0.03 1.705±0.325 0.68±0.19 模型组(M) 4.68±0.91## 0.615±0.15## 2.803±0.502## 2.71±1.01## 注:与正常组(N)比较,##:差异极显著,P<0.01。 2.2 赶黄草醇提物和赶黄草总黄酮对亚急性酒精性肝损伤小鼠体重的影响
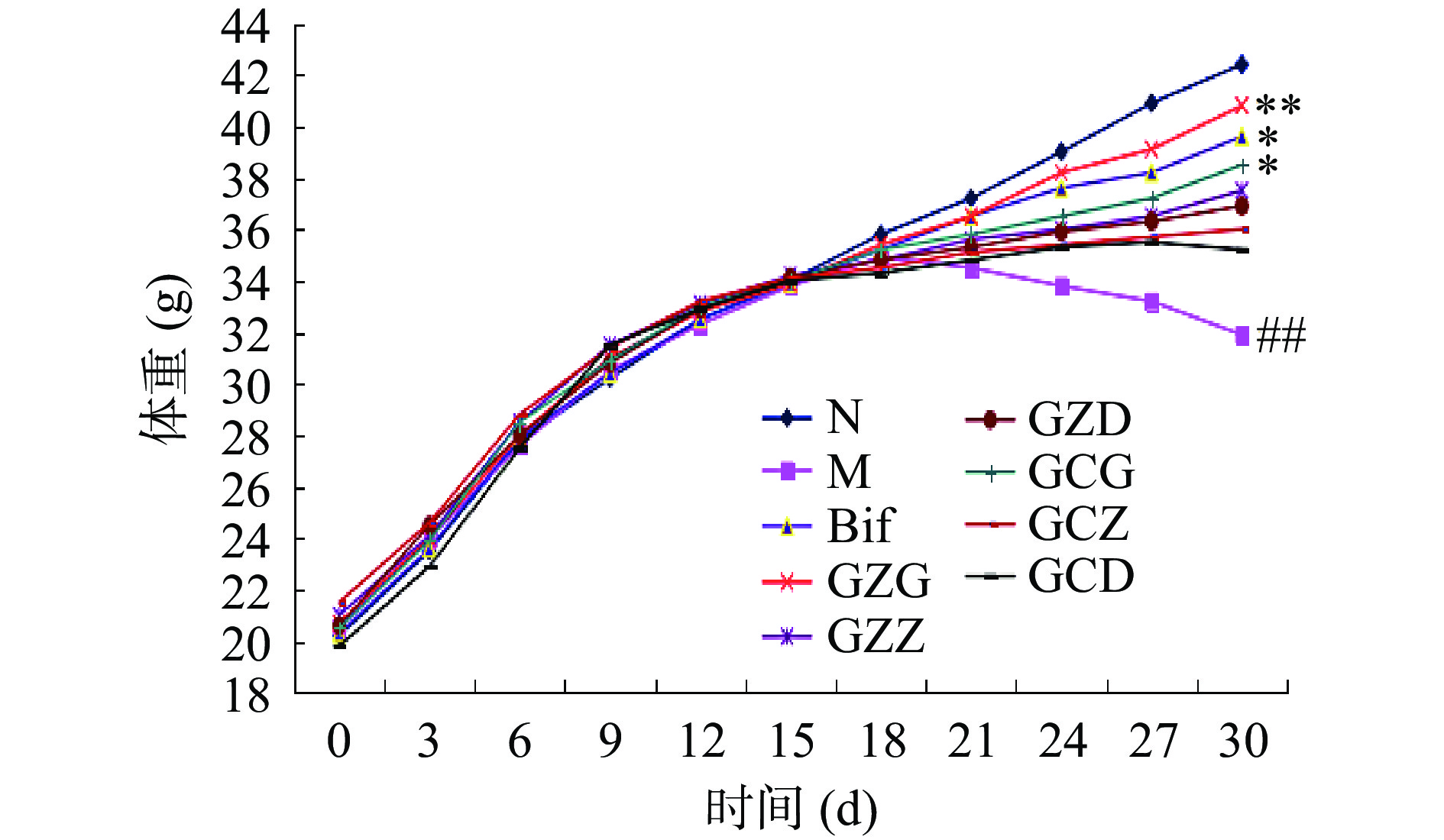
小鼠体重变化如图1所示。从实验开始到第15 d,各组小鼠由20 g左右增长到34 g左右,体重增长较快,但各组并无显著差异(P>0.05),表明赶黄草醇提物和赶黄草总黄酮对小鼠体重影响无明显差异。模型组小鼠在第16~21 d乙醇灌胃期间,体重缓慢增长;在第22~30 d乙醇灌胃期间,体重下降。各给药组小鼠在第16~30 d,体重增长缓慢。在第30 d实验结束时,与正常组(N)比较,模型组(M)小鼠体重极显著降低(P<0.01);与模型组(M)比较,赶黄草总黄酮高剂量组(GZG)小鼠体重极显著增加(P<0.01);联苯双酯组(Bif)和赶黄草醇提物高剂量组(GCG)小鼠体重显著增加(P<0.05);其它各给药组小鼠体重也不同程度地增加,表明赶黄草总黄酮和赶黄草醇提物对酒精所致小鼠体重减轻具有改善作用。
2.3 赶黄草醇提物和赶黄草总黄酮对亚急性酒精性肝损伤小鼠肝脏系数的影响
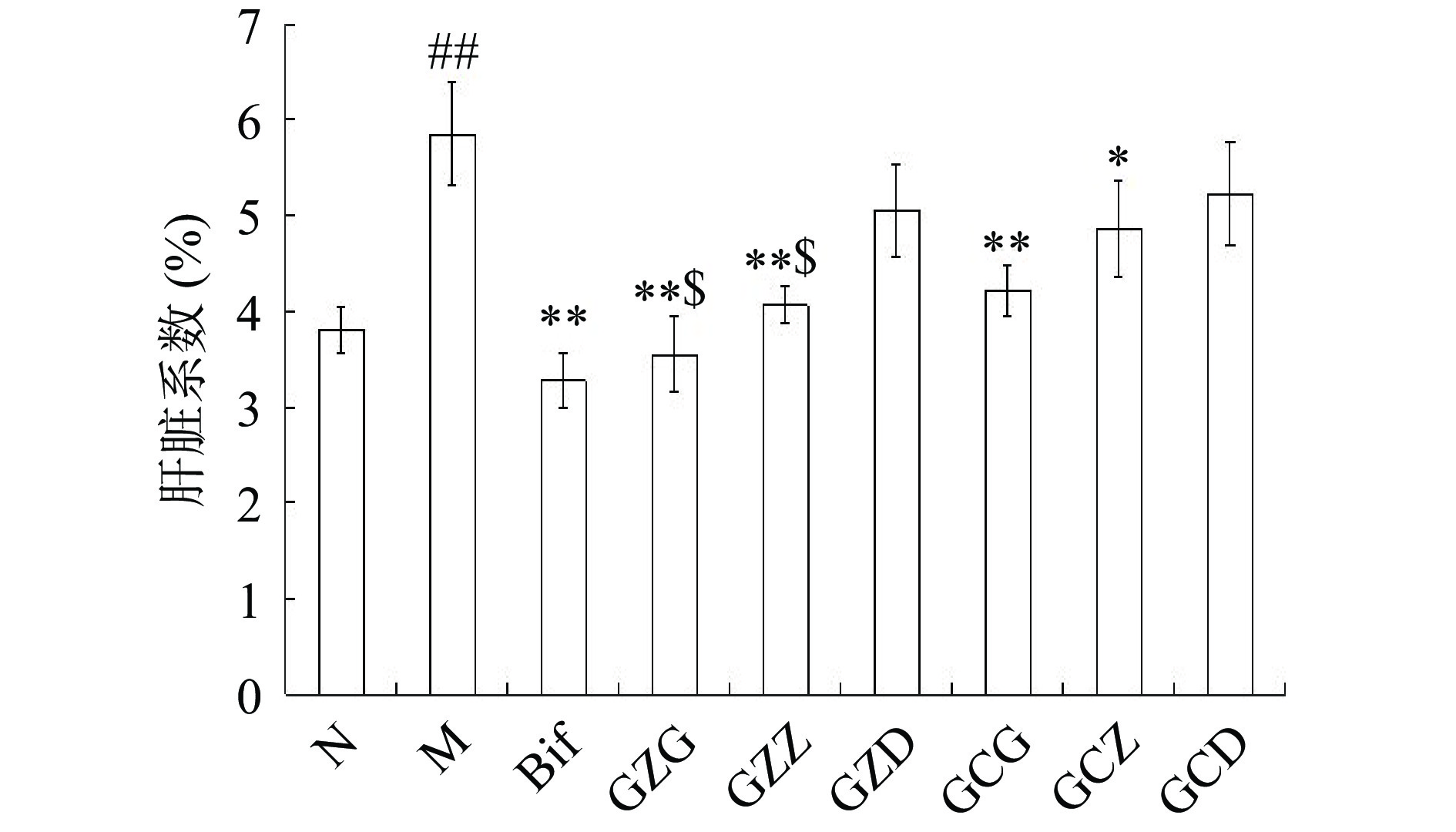
肝脏系数可反映肝脏受损程度。小鼠肝脏系数变化如图2所示。实验结束时,与正常组(N)比较,模型组(M)小鼠肝脏系数极显著升高(P<0.01)。与模型组(M)比较,联苯双酯组(Bif)组、赶黄草总黄酮高剂量组(GZG)、赶黄草总黄酮中剂量组(GZZ)和赶黄草醇提物高剂量组(GCG)肝脏系数均极显著降低(P<0.01),赶黄草醇提物中剂量组肝脏系数显著降低(P<0.05),提示赶黄草总黄酮和赶黄草醇提物可有效降低酒精导致的小鼠肝脏系数升高。赶黄草总黄酮高、中剂量组小鼠肝脏系数分别显著低于等生药剂量的赶黄草醇提物高、中剂量组小鼠肝脏系数(P<0.05),表明赶黄草总黄酮降低酒精导致的小鼠肝脏指数升高,其作用优于赶黄草醇提物。
![]() 图 2 赶黄草醇提物和赶黄草总黄酮对亚急性酒精性肝损伤肝脏系数的影响(
图 2 赶黄草醇提物和赶黄草总黄酮对亚急性酒精性肝损伤肝脏系数的影响(¯x ±s,n=10)注:与正常组(N)比较,##:差异极显著,P<0.01;与模型组(M)比较,*:差异显著,P<0.05,**:差异极显著,P<0.01;与等生药剂量赶黄草醇提物比较,$:差异显著,P<0.05。Figure 2. Effects of alcohol extract and total flavonoids of Penthorum chinense Pursh on liver indexes of mice with subacute alcoholic live injury (¯x ±s, n=10)2.4 赶黄草醇提物和赶黄草总黄酮对小鼠肝组织病理变化的影响
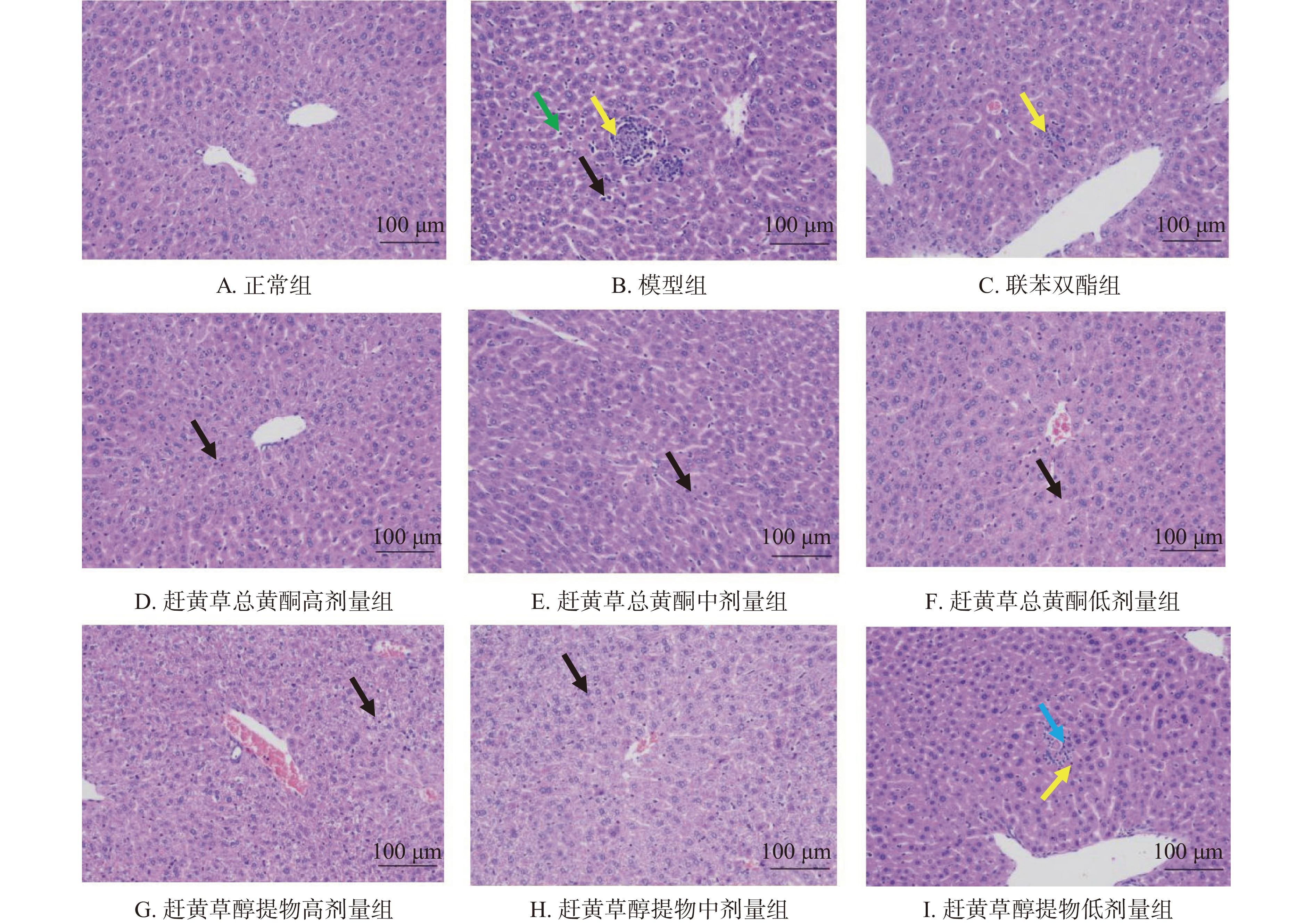
各组小鼠肝组织病理检测结果如图3所示。正常组小鼠肝小叶结构完整清晰,以中央静脉为中心呈放射状排布,肝细胞索排列整齐,肝细胞形态正常,无炎性细胞浸润、细胞坏死等病变;模型组小鼠肝小叶结构模糊,肝细胞出现颗粒变性(黑色箭头),胞质疏松,胞质中有少量空泡,广泛肝窦轻微扩张,肝窦中白细胞数量变多(绿色箭头),组织可见轻度的炎性反应,局部汇管区、局部静脉周围和局部肝小叶可见炎性细胞浸润小灶(黄色箭头),表明酒精导致了肝损伤。联苯双酯组肝小叶结构清晰,肝细胞索排列整齐,未见明显的肝细胞变性,肝小叶中可见个别炎性细胞浸润小灶(黄色箭头)。赶黄草总黄酮高、中、低剂量组,以及赶黄草醇提物高、中剂量组,肝小叶结构清晰,肝细胞索排列整齐,汇管区周围可见较多肝细胞轻度颗粒变性(黑色箭头),胞质疏松淡染,未见明显炎性细胞浸润。赶黄草醇提物低剂量组肝小叶结构清晰,肝细胞索排列整齐,未见明显肝细胞变性,肝小叶中可见个别炎性细胞浸润小灶(黄色箭头),个别肝细胞点状坏死(蓝色箭头)。
小鼠肝组织病变积分如表2所示,与正常组比较,模型组小鼠肝脏细胞病变总分极显著升高(P<0.01)。与模型组比较,联苯双酯组、赶黄草总黄酮高剂量组和赶黄草醇提物高剂量组小鼠肝脏细胞病变总分降低,有极显著性统计学差异(P<0.01);赶黄草总黄酮中剂量组和赶黄草醇提物中剂量组小鼠肝脏细胞病变总分降低,有显著性统计学差异(P<0.05)。赶黄草总黄酮高、中剂量组小鼠肝脏细胞病变总分分别低于等生药剂量的赶黄草醇提物高、中剂量组,有显著性统计学差异(P<0.05),提示赶黄草总黄酮改善酒精导致的肝细胞病变优于赶黄草醇提物。
表 2 赶黄草醇提物和赶黄草总黄酮对小鼠肝细胞病变分数的影响(¯x ±s,n=10)Table 2. Effects of the alcohol extract and total flavonoids of Penthorum chinense Pursh on pathologic score in the liver cell of mice (¯x ±s, n=10)组别 肝细胞变性 炎性改变 细胞坏死 病变总分(分) 水样变性 气球变性 脂肪变性 胞浆凝聚 N 0.25±0.06 0.12±0.04 0±0 0.22±0.07 0.09±0.03 0±0 0.68±0.19 M 0.41±0.12 0.42±0.11 0.53±0.11 0.33±0.12 0.42±0.14 0.30±0.10 2.71±1.01## Bif 0.21±0.07 0.23±0.08 0.21±0.08 0.30±0.13 0.15±0.03 0.15±0.04 1.40±0.35** GZG 0.23±0.07 0.12±0.07 0.31±0.10 0.28±0.08 0.17±0.04 0.16±0.05 1.33±0.40**$ GZZ 0.25±0.08 0.19±0.08 0.40±0.13 0.30±0.11 0.22±0.06 0.18±0.06 1.72±0.51*$ GZD 0.34±0.09 0.25±0.07 0.48±0.11 0.33±0.13 0.33±0.13 0.25±0.05 2.23±0.65 GCG 0.24±0.08 0.15±0.04 0.36±0.07 0.25±0.08 0.25±0.08 0.22±0.07 1.69±0.48** GCZ 0.31±0.10 0.28±0.10 0.39±0.12 0.31±0.12 0.35±0.13 0.25±0.06 2.14±0.62* GCD 0.36±0.09 0.37±0.11 0.45±0.14 0.31±0.15 0.41±0.15 0.25±0.07 2.40±0.61 注:与正常组(N)比较,##:差异极显著,P<0.01;与模型组(M)比较,*:差异显著,P<0.05,**:差异极显著,P<0.01;与等生药剂量赶黄草醇提物组比较,$:差异显著,P<0.05;表3~表4同。 小鼠肝组织病理及肝细胞病变积分结果表明赶黄草总黄酮及赶黄草醇提物均能减轻酒精所致小鼠肝细胞肿胀、变性和炎性细胞浸润,降低肝细胞病变总分,有效改善酒精性肝损伤的肝脏组织病理学改变。赶黄草总黄酮改善酒精导致的肝细胞病变优于赶黄草醇提物。
2.5 赶黄草醇提物和赶黄草总黄酮对小鼠血清肝功能的影响
肝细胞受到损伤时,肝细胞膜通透性增加,从而导致肝功能指标发生变化[22]。ALT和AST活性是评价肝损伤程度的公认生化指标[23-25],ALP、LDH活性以及TBIL含量是肝功能的重要指标[26-27],ALT、AST、ALP、LDH活性和TBIL含量反映肝细胞的损伤程度。小鼠血清肝功能指标如表3所示,与正常组比较,模型组小鼠血清ALT、AST、ALP和LDH活性极显著增强(P<0.01),TBIL含量极显著升高(P<0.01),表明长期摄入酒精可导致肝损伤。与模型组比较,赶黄草总黄酮高、中剂量组小鼠血清ALT、AST、ALP和LDH活性极显著减弱(P<0.01),TBIL含量极显著降低(P<0.01);赶黄草总黄酮低剂量组小鼠血清AST活性显著降低(P<0.05)。与模型组比较,赶黄草醇提物高剂量组小鼠血清ALT、AST活性显著减弱(P<0.05),TBIL含量显著降低(P<0.05),ALP和LDH活性极显著减弱(P<0.01);赶黄草醇提物中剂量组小鼠血清ALT、ALP和LDH活性显著减弱(P<0.05),TBIL含量显著降低(P<0.05)。上述表明赶黄草总黄酮和赶黄草醇提物均能改善亚急性酒精性肝损伤小鼠血清肝功能指标。赶黄草总黄酮高、中剂量组小鼠血清ALT、AST、ALP、LDH活性和TBIL含量分别显著低于等生药剂量的赶黄草醇提物高、中剂量组(P<0.05);赶黄草总黄酮低剂量组的AST活性显著低于等生药剂量的赶黄草醇提物低剂量组(P<0.05),提示赶黄草总黄酮改善血清肝功能指标优于赶黄草醇提物。
表 3 赶黄草醇提物和赶黄草总黄酮对小鼠血清肝功能指标的影响(¯x ±s,n=10)Table 3. Effects of alcohol extract and total flavonoids of Penthorum chinense Pursh on serum liver function levels in mice (¯x ±s, n=10)组别 ALT(U/L) AST(U/L) ALP(U/L) LDH(U/L) TBIL(mmol/L) N 36.30±4.03 107.90±12.76 102.00±25.96 1101.50±107.86 1.705±0.325 M 69.60±8.45## 199.10±29.36## 193.00±29.29## 1977.81±247.15## 2.803±0.502## Bif 39.90±3.54** 114.70±17.41** 148.30±43.91** 1175.00±428.66** 1.885±0.411** GZG 40.60±6.79**$ 114.70±19.75**$ 124.50±34.77**$ 1095.90±172.70**$ 1.903±0.398**$ GZZ 45.70±7.67**$ 123.00±25.30**$ 136.40±39.96**$ 1138.40±149.59**$ 2.108±0.401**$ GZD 58.70±6.85 157.50±22.60*$ 170.25±42.56 1592.35±198.62 2.689±0.689 GCG 46.00±5.41* 158.60±29.16* 141.00±43.83** 1495.70±315.23** 2.401±0.326* GCZ 52.00±4.27* 165.00±37.46 157.77±34.68* 1540.30±255.73* 2.501±0.502* GCD 60.61±5.15 190.00±27.25 180.05±38.55 1782.00±302.73 2.702±0.702 2.6 赶黄草醇提物和赶黄草总黄酮对亚急性酒精性肝损伤小鼠血脂的影响
当肝功能受损时脂类代谢常发生紊乱,从而导致血脂浓度发生改变[28-30]。小鼠血脂如表4所示,与正常组比较,模型组的TG、TC和LDL-C含量均极显著升高(P<0.01),表明长期摄入酒精可引起脂质代谢紊乱。与模型组比较,赶黄草总黄酮高剂量组TG、TC和LDL-C均极显著降低(P<0.01);赶黄草总黄酮中剂量组TG、TC和LDL-C均显著降低(P<0.05);赶黄草醇提物的高、中剂量组小鼠血清中TG、TC和LDL-C均显著降低(P<0.05),表明赶黄草总黄酮和赶黄草醇提物均能够调节酒精性肝损伤小鼠血脂代谢,减轻小鼠肝脏脂肪变性,这与病理检测结果一致,提示赶黄草总黄酮和赶黄草醇提物均可改善酒精诱导的脂质代谢紊乱。赶黄草总黄酮高剂量组的TG、TC和LDL-C均显著低于等生药剂量的赶黄草醇提物高剂量组(P<0.05),表明赶黄草总黄酮对脂质代谢的调节作用优于赶黄草醇提物。
表 4 赶黄草醇提物和赶黄草总黄酮对亚急性酒精性肝损伤小鼠血脂的影响(¯x ±s,n=10)Table 4. Effects of alcohol extract and total flavonoids of Penthorum chinense Pursh on serum lipid levels of mice (¯x ±s, n=10)组别 TG(mmol/L) TC(mmol/L) LDL-C(mmol/L) N 1.23±0.24 2.67±0.48 0.323±0.03 M 3.22±1.33## 4.68±0.91## 0.615±0.15## Bif 1.27±0.58** 2.85±0.91** 0.401±0.09** GZG 1.54±0.32**$ 2.91±0.60**$ 0.405±0.12**$ GZZ 1.89±0.38* 3.55±0.88* 0.485±0.18* GZD 2.58±1.38 4.20±0.85 0.543±0.20 GCG 1.91±0.42* 3.32±0.54* 0.491±0.19* GCZ 2.21±0.71* 3.85±0.96* 0.521±0.13* GCD 2.92±0.82 4.51±0.96 0.585±0.21 3. 结论
本研究以浓度30%的乙醇(10 mL/kg)对小鼠连续灌胃15 d,成功建立了小鼠亚急性酒精肝损伤模型。研究结果表明赶黄草总黄酮和赶黄草醇提物均可降低亚急性酒精性肝损伤小鼠肝脏系数,减轻小鼠肝组织损伤和脂肪变性,改善小鼠肝功能和调节小鼠血脂;赶黄草总黄酮和赶黄草醇提物对亚急性酒精性肝损伤小鼠均具有保护作用,赶黄草总黄酮对亚急性酒精性肝损伤小鼠的保护作用优于等生药剂量的赶黄草醇提物。本研究阐明了赶黄草总黄酮是赶黄草抗酒精性肝损伤的主要功效成分,为把其开发为安全有效的抗酒精性肝损伤的保健食品提供了依据。但赶黄草总黄酮抗酒精性肝损伤的具体活性成分和作用机制还有待进一步研究。
-
图 2 赶黄草醇提物和赶黄草总黄酮对亚急性酒精性肝损伤肝脏系数的影响(
¯x ±s,n=10)注:与正常组(N)比较,##:差异极显著,P<0.01;与模型组(M)比较,*:差异显著,P<0.05,**:差异极显著,P<0.01;与等生药剂量赶黄草醇提物比较,$:差异显著,P<0.05。
Figure 2. Effects of alcohol extract and total flavonoids of Penthorum chinense Pursh on liver indexes of mice with subacute alcoholic live injury (
¯x ±s, n=10)表 1 亚急性酒精性肝损伤小鼠模型成模的判定(
¯x ±s,n=10)Table 1 Judgment of the successful model of subacute alcoholic live injury in mice (
¯x ±s, n=10)组别 TC
(mmol/L)LDL-C
(mmol/L)TBIL
(mmol/L)肝组织病变总分
(分)正常组(N) 2.67±0.48 0.323±0.03 1.705±0.325 0.68±0.19 模型组(M) 4.68±0.91## 0.615±0.15## 2.803±0.502## 2.71±1.01## 注:与正常组(N)比较,##:差异极显著,P<0.01。 表 2 赶黄草醇提物和赶黄草总黄酮对小鼠肝细胞病变分数的影响(
¯x ±s,n=10)Table 2 Effects of the alcohol extract and total flavonoids of Penthorum chinense Pursh on pathologic score in the liver cell of mice (
¯x ±s, n=10)组别 肝细胞变性 炎性改变 细胞坏死 病变总分(分) 水样变性 气球变性 脂肪变性 胞浆凝聚 N 0.25±0.06 0.12±0.04 0±0 0.22±0.07 0.09±0.03 0±0 0.68±0.19 M 0.41±0.12 0.42±0.11 0.53±0.11 0.33±0.12 0.42±0.14 0.30±0.10 2.71±1.01## Bif 0.21±0.07 0.23±0.08 0.21±0.08 0.30±0.13 0.15±0.03 0.15±0.04 1.40±0.35** GZG 0.23±0.07 0.12±0.07 0.31±0.10 0.28±0.08 0.17±0.04 0.16±0.05 1.33±0.40**$ GZZ 0.25±0.08 0.19±0.08 0.40±0.13 0.30±0.11 0.22±0.06 0.18±0.06 1.72±0.51*$ GZD 0.34±0.09 0.25±0.07 0.48±0.11 0.33±0.13 0.33±0.13 0.25±0.05 2.23±0.65 GCG 0.24±0.08 0.15±0.04 0.36±0.07 0.25±0.08 0.25±0.08 0.22±0.07 1.69±0.48** GCZ 0.31±0.10 0.28±0.10 0.39±0.12 0.31±0.12 0.35±0.13 0.25±0.06 2.14±0.62* GCD 0.36±0.09 0.37±0.11 0.45±0.14 0.31±0.15 0.41±0.15 0.25±0.07 2.40±0.61 注:与正常组(N)比较,##:差异极显著,P<0.01;与模型组(M)比较,*:差异显著,P<0.05,**:差异极显著,P<0.01;与等生药剂量赶黄草醇提物组比较,$:差异显著,P<0.05;表3~表4同。 表 3 赶黄草醇提物和赶黄草总黄酮对小鼠血清肝功能指标的影响(
¯x ±s,n=10)Table 3 Effects of alcohol extract and total flavonoids of Penthorum chinense Pursh on serum liver function levels in mice (
¯x ±s, n=10)组别 ALT(U/L) AST(U/L) ALP(U/L) LDH(U/L) TBIL(mmol/L) N 36.30±4.03 107.90±12.76 102.00±25.96 1101.50±107.86 1.705±0.325 M 69.60±8.45## 199.10±29.36## 193.00±29.29## 1977.81±247.15## 2.803±0.502## Bif 39.90±3.54** 114.70±17.41** 148.30±43.91** 1175.00±428.66** 1.885±0.411** GZG 40.60±6.79**$ 114.70±19.75**$ 124.50±34.77**$ 1095.90±172.70**$ 1.903±0.398**$ GZZ 45.70±7.67**$ 123.00±25.30**$ 136.40±39.96**$ 1138.40±149.59**$ 2.108±0.401**$ GZD 58.70±6.85 157.50±22.60*$ 170.25±42.56 1592.35±198.62 2.689±0.689 GCG 46.00±5.41* 158.60±29.16* 141.00±43.83** 1495.70±315.23** 2.401±0.326* GCZ 52.00±4.27* 165.00±37.46 157.77±34.68* 1540.30±255.73* 2.501±0.502* GCD 60.61±5.15 190.00±27.25 180.05±38.55 1782.00±302.73 2.702±0.702 表 4 赶黄草醇提物和赶黄草总黄酮对亚急性酒精性肝损伤小鼠血脂的影响(
¯x ±s,n=10)Table 4 Effects of alcohol extract and total flavonoids of Penthorum chinense Pursh on serum lipid levels of mice (
¯x ±s, n=10)组别 TG(mmol/L) TC(mmol/L) LDL-C(mmol/L) N 1.23±0.24 2.67±0.48 0.323±0.03 M 3.22±1.33## 4.68±0.91## 0.615±0.15## Bif 1.27±0.58** 2.85±0.91** 0.401±0.09** GZG 1.54±0.32**$ 2.91±0.60**$ 0.405±0.12**$ GZZ 1.89±0.38* 3.55±0.88* 0.485±0.18* GZD 2.58±1.38 4.20±0.85 0.543±0.20 GCG 1.91±0.42* 3.32±0.54* 0.491±0.19* GCZ 2.21±0.71* 3.85±0.96* 0.521±0.13* GCD 2.92±0.82 4.51±0.96 0.585±0.21 -
[1] 付双楠, 朱平生, 高达. 中医药防治化学性肝损伤的研究进展[J]. 中医学报,2017,32(3):449−454. [FU S N, ZHU P S, GAO D. Progress of TCM studies in TCM treatment of liver injury due to chemical factors[J]. Acta Chinese Medicine,2017,32(3):449−454. doi: 10.16368/j.issn.1674-8999.2017.03.116 [2] 刘袆帆, 朱珍, 苏敏璇, 等. 多糖对酒精性肝损伤干预作用的研究进展[J]. 现代食品科技,2020,36(8):379−393. [LIU H F, ZHU Z, SU M X, et al. Efficacy of polysaccharides as alcoholic liver disease therapeutics: A review[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2020,36(8):379−393. doi: 10.13982/j.mfst.1673-9078.2020.8.0185 [3] SALEEM T S M, CHETTY C M, RAMKANTH S, et al. Hepatoprotective herbs-A review[J]. International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences,2010,1(5):1−5.
[4] 唐川, 李志, 王升贵, 等. 霍山石斛多糖的制备、功能和产品开发的研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(3):313−320. [TANG C, LI Z, WANG S G, et al. Research progress on preparation, function and product development of polysaccharide of Dendrobium huoshanense[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(3):313−320. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2019.03.050 [5] 李志满, 邵紫君, 李珊珊, 等. 人参枳子提取物对小鼠酒精性肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(14):302−306, 313. [LI Z M, SHAO Z J, LI S S, et al. Protective effect of extract from Panax ginsen and Hovenia dulcis Thunb against alcohol-induced liver injury in mice[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(14):302−306, 313. [6] 孟海涛, 汪鹤, 查学强, 等. 霍山石斛不同提取物抗小鼠亚急性酒精性肝损伤活性的比较研究[J]. 食品科学,2015,36(13):229−234. [MENG H T, WANG H, ZHA X Q, et al. Comparison of hepatoprotective effects of different extracts from Dendrobium huoshanense against alcohol-induced subacute liver injury in mice[J]. Food Science,2015,36(13):229−234. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201513042 [7] LOGGE W B, MORLEY K C, HABER P S, et al. Executive function moderates responses to appetitive cues: A study in severe alcohol use disorder and alcoholic liver disease[J]. Alcohol and Alcoholism,2019,54(1):38−46. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agy083
[8] 刘畅, 成玉梁, 郭亚辉, 等. 芦荟多糖联合茶多酚对小鼠酒精性肝损伤的预防作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(22):300−305. [LIU C, CHENG Y L, GUO Y H, et al. Preventive effect of aloe polysaccharide combined with tea polyphenol on alcoholic liver injury in mice[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(22):300−305. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2019.22.052 [9] 牛佳卉, 袁静, 张慧芳, 等. 王浆酸对小鼠酒精性肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(3):291−296. [LIU J H, YUAN J, ZHANG H F, et al. Protective effect of royal jelly acid on the alcoholliver injury in mice[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(3):291−296. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020.03.048 [10] SHEN T, LIU Y, SHANG J, et al. Incidence and etiology of drug-induced liver injury in mainland China[J]. Gastroenterology,2019,156(8):1−12. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.01.006
[11] 白路平, 乔向宇, 吉日木图, 等. 骆驼乳对小鼠酒精性肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 中国食品学报,2022,22(2):140−149. [BAI L P, QIAO X Y, JIRIMUTU, et al. Protective effect of camel milk on alcoholic liver injury in mice[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2022,22(2):140−149. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2022.02.016 [12] LIU Y S, YUAN M H, ZHANG C Y, et al. Puerariae lobatae radix flavonoids and puerarin alleviatealcoholic liver injury in zebrafish by regulating alcohol and lipid metabolism[J]. BiomedicineI & Pharmcotherapy,2021,134:111121−111128.
[13] DING Q C, JIN Z, DONG J H, et al. Bioactivity evaluation of pinocembrin derivatives from Penthorum chinense Pursh stems[J]. Natural Product Communications,2019,14(9):1−9.
[14] WANG A Q, LI M X, HUANG M, et al. A review of Penthorum chinense Pursh for hepatoprotection: Traditional use, phytochemistry, pharmacology, toxicology and clinical trials[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacol,2020,251(6):26−32.
[15] HUANG D D, JIANG Y, CHEN W S, et al. Polyphenols with anti-proliferative activities from Penthorum chinense Pursh[J]. Molecules,2014,19(8):11045−11055. doi: 10.3390/molecules190811045
[16] 张剑, 伍淑明, 杨肖, 等. 赶黄草中化学成分研究进展[J]. 中草药,2017,48(21):4571−4577. [ZHANG J, WU S M, YANG X, et al. Advances in chemical constituents of Penthorum chinense Pursh[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2017,48(21):4571−4577. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2017.21.033 [17] SUN X L, WU A G, BETTY Y K L, et al. The active components derived from Penthorum chinense Pursh protect against oxidative-stress-induced vascular injury via autophagy induction[J]. Free Radical Biology and Medicine,2020,146:160−180. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.10.417
[18] 袁叶飞, 白雪. 赶黄草总黄酮制备方法: 中国, 201811373488.7[P]. 2019-01-25 YUAN Y F, BAI X. Preparation method of total flavone of Penthorum chinense Pursh: China, 201811373488.7[P]. 2019-01-25.
[19] 付满玲, 九红, 袁叶飞. 赶黄草总黄酮对四氯化碳所致小鼠急性化学性肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 现代食品科技,2021,37(6):50−56. [FU M L, JIU H, YUAN Y F. Protective effect of total flavonoids of Penthorum chinense Pursh on acute chemical liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride in mice[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2021,37(6):50−56. doi: 10.13982/j.mfst.1673-9078.2021.6.1054 [20] 王爽, 徐清华, 史保银, 等. 葛白复配颗粒对大鼠亚急性酒精性肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 毒理学杂志,2019,33(1):48−50. [WANG S, XU Q H, SHI B Y, et al. Protective effects of Gebai formulation granule on alcohol-induced hepatic injury in rats[J]. Journal of Toxicology,2019,33(1):48−50. doi: 10.16421/j.cnki.1002-3127.2019.01.008 [21] 苏林梁, 黄业宇, 冯丁山, 等. 槟榔花茶对大鼠亚急性酒精性肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 现代食品科技,2017,33(6):15−19. [SU L L, HUANG Y Y, FENG D S, et al. Protective effects of areca inflorescence tea on alcohol-induced hepatic injury in rats[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2017,33(6):15−19. doi: 10.13982/j.mfst.1673-9078.2017.6.003 [22] QIAO J Y, LI H W, LIU F G, et al. Effects of Portulaca oleracea extract on acute alcoholic liver injury of rats[J]. Molecules,2019,24(16):2887−2910. doi: 10.3390/molecules24162887
[23] 叶文斌, 樊亮, 王昱, 等. 黄果槲寄生果实多糖对急性酒精肝损伤小鼠的保护作用[J]. 安徽农业大学学报,2017,44(2):218−223. [YE W B, FAN L WANG Y, et al. The protectionmechanism of Viscum coloratum (Kom.) Nakai f. lutescens Kitag fruit polysaccharides on acute alcoholic liver injury in mice[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University,2017,44(2):218−223. doi: 10.13610/j.cnki.1672-352x.20170419.021 [24] 易宏伟, 朱笑笑, 黄小莉, 等. 富硒长双歧杆菌抑制乙醇诱导的小鼠肝损伤[J]. 中国药学杂志,2019,54(22):1859−1864. [YI H W, ZHU X X, HUANG X L, et al. Inhibition effect of selenium enriched Bifidobacterium longum on alcohol induced liver damage in mice[J]. Journal of Chinese Pharmaceutical Sciences,2019,54(22):1859−1864. [25] JIANG Z, CHEN C, WANG J, et al. Purple potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) anthocyaanins attenuate alcohol-induced hepatic injury by enhancing antioxidant defense[J]. Journal of Natural Medicines,2016,70(1):45−53. doi: 10.1007/s11418-015-0935-3
[26] NIE G, ZHANG Y, ZHOU Z H, et al. Dynamic evaluation of the protective effect of Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide on acute alcoholic liver injury mice in vitro and in vivo by NIR fluorescence imaging[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry,2021,413(23):5715−5724. doi: 10.1007/s00216-021-03546-7
[27] GOVINDAN S H, JAYABAL A G, SHANMUGAM J K, et al. Antioxidant and hepatoprotective effectsof Hypsizygus ulmarius polysaccharide on alcoholic liver injury in rats[J]. Food Science and Human Wellness,2021,10(4):523−535. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2021.04.015
[28] GAO B, XU M J, BERTOLA A, et al. Animal models of alcoholic liver disease: Pathogenesis and clinical relevance[J]. Gene Express,2017,17(3):173−186. doi: 10.3727/105221617X695519
[29] JAYARAMAN J, NAMASIVAYAM N. Naringenin modulates circulatory lipid peroxidation, antioxidant status and hepatic alcohol metabolizing enzymes in rats with ethanol induced liver injury[J]. Fundamental and Clinical Pharmacology,2011,25(6):682−689. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.2010.00899.x
[30] FANG C, ZHOU Q W, LIU Q Y, et al. Crosstalk between gut microbiota and host lipid metabolism in a mouse model of alcoholic liver injury by chronic Baijiu or ethanol feeding[J]. Food & Function,2022,13(2):596−608.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 常逍柯,田潇凌,林顺顺,李梦琴,田争争,高恩红. 不同制粉方式对黑小麦全麦粉及饼干品质影响. 食品与发酵工业. 2024(21): 266-272 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王冬,任健,王志鹏,宋春丽. 酶预处理对黑珍珠糯玉米粉分散性的影响研究. 齐齐哈尔大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(05): 69-75 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)









 下载:
下载:










 下载:
下载:



