Determination of 16 Phenolic Compounds in Prunella vulgaris and Analysis Their Correlation with Antioxidant Activity
-
摘要: 目的:采用液相色谱-串联质谱法(LC-MS/MS)测定24批夏枯草中16种酚类化合物的含量,并采用灰色关联分析和偏最小二乘回归分析方法探讨酚类化合物与抗氧化能力的相关性。方法:夏枯草样品用80%甲醇超声提取,并基于LC-MS/MS建立夏枯草中16种酚类化合物的含量测定方法,以Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18(2.1 mm×100 mm,1.7 μm)色谱柱为固定相,以0.1%甲酸-乙腈为流动相在体积流量为0.4 mL/min条件下进行梯度洗脱,负离子多反应监测模式检测。以DPPH自由基清除能力、ABTS自由基清除能力和铁离子还原能力评价夏枯草的抗氧化活性。结果:16种酚类化合物在各自浓度范围内线性关系良好,相关系数r均大于0.99,精密度、重复性、稳定性和回收率良好。体外抗氧化实验证明夏枯草具有较强的清除ABTS、DPPH自由基和铁离子还原能力,灰色关联分析和偏最小二乘回归分析结果表明迷迭香酸、咖啡酸、芦丁、金丝桃苷、异槲皮苷对于抗氧化的贡献较大。结论:本研究建立了同时测定夏枯草中16种酚类化合物的LC-MS/MS方法,进一步通过相关性分析确定了夏枯草抗氧化的主要活性成分,从而为夏枯草产品的质量控制与开发利用提供科学依据。Abstract: Objective: To determine the content of 16 phenolic compounds in 24 batches of Prunella vulgaris by liquid chromatography- tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and to investigate the correlation between phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity by grey relational analysis (GRA) and partial least squares regression (PLSR) analysis. Methods: The sample was extracted with 80% methanol by the ultrasonic extraction. A method for the determination of 16 phenolic compounds in Prunella vulgaris was established by LC-MS/MS. The Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 column (2.1 mm×100 mm, 1.7 μm) was selected as the stationary phase. The gradient elution was performed with the mobile phase of 0.1% formic acid-acetonitrile at the flow rate of 0.4 mL/min. The eluted compounds were detected in the negative ion mode with multiple reaction monitoring technology. The antioxidant activities were evaluated by DPPH free radical scavenging capacity, ABTS free radical scavenging capacity and ferric reducing antioxidant power. Results: There were significant linear relationship of 16 phenolic compounds in the range of their concentration with the correlation coefficient (r) greater than 0.99. The precision, repeatability, stability and recovery were good. In vitro antioxidant experiments showed that Prunella vulgaris had strong ability to scavenge ABTS, DPPH free radicals and ferric reduction. The results of GRA and PLSR indicated that rosmarinic acid, caffeic acid, rutin, hyperoside and isoquercitrin were the primary compounds contributing to the antioxidant capacity. Conclusion: A LC-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of 16 phenolic compounds in Prunella vulgaris was established and the primary antioxidant active components were further investigated by correlation analysis, so as to provide scientific basis for quality control, development and utilization of Prunella vulgaris.
-
夏枯草(Prunella vulgaris L.)是唇形科夏枯草属多年生草本植物,广泛分布于东亚和欧洲,在我国有悠久的食用和药用历史[1-2]。夏枯草的主要药用和食用部位为其干燥果穗,具有抗氧化、增强免疫、抗病毒、抗炎、降血压和抗肿瘤等作用[3-4],可作为糖尿病的保健食品和药品[5],也可用作汤料和凉茶[6],其花蜜经充分酿造后具有很好的抗结肠炎和调节肠道菌群的作用[7]。夏枯草含有丰富的酚酸、黄酮、三萜酸等化学成分[2, 8],其中酚类化合物是夏枯草重要的活性成分[9]。酚类化合物可抵御紫外线或病原菌的侵袭,具有很好的抗氧化活性,可清除自由基对人体生命造成的损伤[10],目前已经作为天然的抗氧化剂被广泛应用于食品方面[11]。夏枯草中的酚类化合物主要有迷迭香酸、丹参素、咖啡酸等,在《中国药典》2020年版中,迷迭香酸就被作为夏枯草含量测定的质量评价指标[12]。近年的研究也多采用高效液相色谱法测定酚类物质的含量,但是所能测定的指标多集中于迷迭香酸、丹参素、咖啡酸等少数几种化合物[13-14]。
相对传统的液相色谱-紫外检测法,液相色谱-串联质谱法(liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, LC-MS/MS)具有分析速度快、分离效能高、灵敏度高等优点,现被广泛应用于各种复杂化合物的分析,且测定低限可达纳克级[15-17]。如Ozdal等[18]采用LC-MS/MS法研究了土耳其蜂胶提取物中的多酚组成,并鉴定出32种酚类化合物;Schulz等[19]采用LC-MS/MS法定量了黄色番石榴果实酸水解后的23种酚类物质,不仅具有极高的灵敏度,而且还可提供常规方法难以获取的结构信息;罗弘杉等[20]采用液相色谱-高分辨质谱鉴定夏枯草中的酚类化合物,具有较高的分辨率,但未对多组分进行定量分析。
在色谱分离的基础上,将化学成分和生物活性成分相结合进行相关性分析,可明确不同成分对于生物活性的贡献。灰色关联分析(grey correlation analysis, GRA)和偏最小二乘回归(partial least squares regression, PLSR)分析是较常用的多因素统计方法,GRA将因素间发展的相似性程度作为衡量系统中各因素间的关联程度,即灰色关联度(gray relational degree, GRD),现已被广泛用于解决多因素、多变量之间复杂相互关系的问题;PLSR是一种对主成分分析和多元回归的特征进行泛化和组合的方法,能有效地解决变量间的多重共线性问题[17, 21]。目前对于各种食品的品质调控多采用PLSR或GRA进行评价,并以此计算食品品质的影响程度,进而分析影响因素与综合评分的相关性[22-23]。
因此,本研究采用LC-MS/MS对夏枯草中16种酚类化合物进行定量分析,采用DPPH、ABTS自由基清除能力和铁离子还原能力(ferric reducing antioxidant power, FRAP)对夏枯草的抗氧化活性进行评价,并进一步采用GRA、PLSR法对24批夏枯草中16种酚类化合物的相关性进行分析,以此探讨夏枯草抗氧化的物质基础,为全面提高夏枯草的质量控制水平及其产品开发和应用提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
夏枯草样本分别采自广东、河南等9个省份,其详细信息见表1。样本经遵义医科大学顾丁副教授鉴定为唇形科植物夏枯草(Prunella vulgaris L)的干燥果穗。
表 1 24批夏枯草样品信息Table 1. Information of 24 batches of Prunella vulgaris样品编号 产地 样品编号 产地 样品编号 产地 S1 广东深圳 S9 江苏常州 S17 湖北襄阳 S2 安徽亳州 S10 河南周口 S18 浙江嘉兴 S3 河南郑州 S11 安徽安庆 S19 湖北咸宁 S4 湖北荆州 S12 河南漯河 S20 河北沧州 S5 安徽合肥 S13 安徽黄山 S21 安徽宣城 S6 内蒙包头 S14 广东湛江 S22 河北承德 S7 河南新乡 S15 广东佛山 S23 广东广州 S8 河北石家庄 S16 河北保定 S24 安徽池州 对羟基苯甲酸、异槲皮苷、七叶内酯 Ark Pharm公司;对羟基肉桂酸、2,5-二羟基苯甲酸 Adamas-beta公司;迷迭香酸、绿原酸、咖啡酸、3,4-二羟基苯甲酸、金丝桃苷、阿魏酸、水杨酸、芦丁 上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;异迷迭香酸苷 成都麦德生科技有限公司;丹参素 辰光生物有限公司;3,4-二羟基苯甲醛 北京伊诺凯科技有限公司;所有对照品的纯度≥97%;乙腈 质谱纯,霍尼韦尔贸易有限公司;室验用水 屈臣氏;其余试剂为分析纯。
I-class+XevoTQ-S超高效液相色谱-三重四极杆质谱仪(配MassLynx V.4.1软件) 美国Waters;SB-5200DT型超声波清洗机 宁波新芝生物科技;ME104E电子天平 美国梅特勒-托利多。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品制备
将夏枯草粉碎,过60目筛。准确称取1 g样品粉末,加40 mL 80%的甲醇在室温条件下超声提取30 min,提取完成后将提取液置于−20 ℃条件下静置1 h,吸取上清液,用0.22 μm微孔滤膜过滤后进行色谱分析和抗氧化能力测定。
1.2.2 对照品配制
精密称取16种夏枯草对照品,分别加入甲醇溶解定容至10 mL,配制成浓度为1 mg/mL的标准品溶液,−20 ℃保存备用。使用时用80%甲醇将其稀释成所需的混合对照品工作溶液。
1.2.3 LC-MS/MS法测定16种酚类化合物
1.2.3.1 液相色谱条件
采用Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18(2.1 mm×100 mm,1.7 μm)色谱柱,采用0.1%甲酸(A)-乙腈(B)作为流动相在体积流量为0.4 mL/min下进行梯度洗脱,洗脱程序为0~15 min,95%~70% A;15~19.5 min,70%~50% A;19.5~20.5 min,50%~5% A;20.5~21.5 min,5% A;21.5~22 min,5%~95% A;22~25 min,95% A。柱温为45 ℃;进样器温度为12 ℃;进样量为1 μL。
1.2.3.2 质谱条件
采用电喷雾离子源在负离子及多反应监测(multiple reaction monitoring, MRM)模式下检测16种酚类化合物,并采用两组离子对分别对16种酚类化合物进行定量和定性分析,采用外标法进行定量。毛细管电压为3 kV,蒸发温度为500 ℃、气流量为750 L/Hr。
1.2.4 抗氧化活性
1.2.4.1 铁离子还原能力
取醋酸盐缓冲溶液(pH3.6)、10 mmol/L TPTZ溶液、20 mmol/L FeCl3溶液加入到600 μL稀释后的样品溶液中混匀,暗反应30 min后于593 nm波长处测定样品吸光度。空白组中样品溶液的吸光度测定采用80%的甲醇代替。以Trolox为标准品绘制标准曲线,线性回归方程和相关系数分别为Y=0.0258X+0.0645和r=0.9997,其中,Y为吸光度(Au),X为Trolox浓度(mg/L)。所有样品测量结果均以Trolox当量表示(mg TE/g DW)。
1.2.4.2 ABTS自由基清除能力
ABTS工作液的配制:准确称取ABTS试剂0.0282 g,用蒸馏水溶解定容至7.5 mL,再加入7.5 mL 2.45 mmol/L过硫酸钾水溶液,在室温下避光放置8~12 h后用纯水稀释20倍后备用。取200 μL稀释100倍后的样品溶液加入到0.4 mL ABTS工作液中,暗反应30 min后于734 nm波长处测定样品吸光度。空白组中样品溶液的吸光度测定以80%甲醇代替,以Trolox为标准品绘制标准曲线,线性回归方程和相关系数分别为Y=−0.00901X+0.5311和r=0.9998,其中Y为吸光度(Au),X为Trolox浓度(mg/L)。所有样品测量结果的表示同“1.2.4.1”项。
1.2.4.3 DPPH自由基清除能力
取200 μL稀释30倍后的样品溶液加入到400 μL 0.14 mol/L的DPPH溶液中,混匀,暗反应30 min后于517 nm波长处测定样品吸光度。空白组中样品溶液的吸光度测定以及所有样品测量结果的表示同“1.2.4.1”项。以Trolox为标准品绘制标准曲线,线性回归方程和相关系数分别为Y=−0.0155X+0.8361和r=0.9993。其中Y为吸光度(Au),X为Trolox浓度(mg/L)。
1.2.5 相关性分析
1.2.5.1 GRA
以16种酚类化合物含量和DPPH、ABTS自由基清除能力和FRAP效应值分别作为自变量和因变量。在判别系数设为0.5的情况下,计算GRD值,GRD越高,相应的酚类化合物抗氧化活性越大。
1.2.5.2 PLSR
采用16种酚类化合物的含量作为自变量,DPPH、ABTS和FRAP值作为因变量。将数据导入软件SIMCA 14.1中进行PLSR分析,得出各自的CoeffCS值和VIP值,以分析自变量与因变量的关系。
1.3 数据处理
采用Waters公司的MassLynx V4.1软件进行数据采集;采用Excel进行数据分析;采用Origin 2018版以及SIMCA 14.1版软件进行绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 夏枯草中16种酚类成分质谱条件优化及LC-MS/MS色谱图
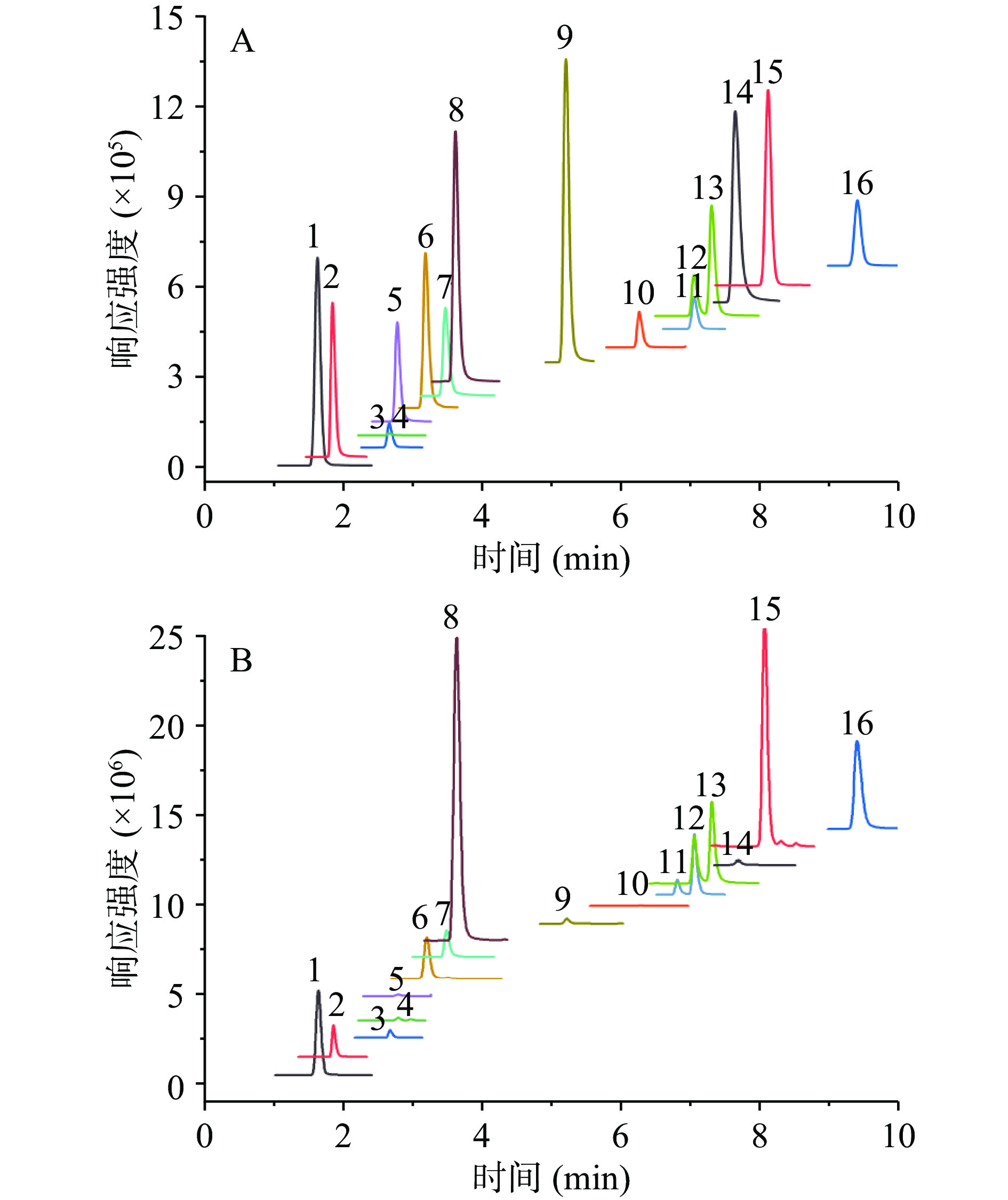
对16种化合物的标准品进行锥孔电压、碰撞能量等条件的优化,优化结果见表2。标准品图见图1A,除丹参素、迷迭香酸和异迷迭香酸苷浓度为5 mg/L外,其余化合物浓度均为0.5 mg/L。夏枯草样品图见图1B。
表 2 16种主要成分的保留时间和质谱参数Table 2. Retention time and mass parameters of the 16 components序号 化合物 保留时间
(min)母离子
(m/z)子离子
(m/z)锥孔电压
(V)碰撞能量
(eV)1 丹参素 1.61 197.2 135.1*/179.1 20 20 2 3,4-二羟基苯甲酸 1.83 153.1 109.1*/— 30 12 3 3,4-二羟基苯甲醛 2.67 137.1 108.1*/90.0 15 20 4 对羟基苯甲酸 2.68 137.1 93.1*/ — 45 12 5 2,5-二羟基苯甲酸 2.78 153.1 109.1*/ — 30 12 6 绿原酸 3.19 353.1 191.1*/179.1 12 15 7 七叶内酯 3.47 177.1 133.1*/149.1 35 18 8 咖啡酸 3.62 178.1 135.1*/117.1 38 16 9 对羟基肉桂酸 5.2 163.1 119.1*/115.1 12 15 10 阿魏酸 6.26 193.1 134.1*/178.1 15 15 11 芦丁 7.04 609.6 301.3*/271.2 30 35 12 金丝桃苷 7.05 463.4 301.3*/300.3 40 20 13 异槲皮苷 7.29 463.4 301.3*/271.2 40 20 14 水杨酸 7.64 137.1 93.1*/ — 20 15 15 异迷迭香酸苷 8.08 521.5 359.3*/179.1 20 20 16 迷迭香酸 9.42 359.3 197.1*/179.1 18 8 注:*代表定量离子对;—代表未检测到离子信息。 2.2 方法学验证
2.2.1 线性关系
分别精密吸取“1.2.2”项下的对照品溶液配制成不同浓度的混标,按“1.2.3”项下的色谱条件进样分析,记录测定后16种酚类化合物的峰面积。以对照品的浓度(mg/L)为横坐标,各待测成分色谱峰峰面积为纵坐标绘制标准曲线,计算回归方程。结果显示,16种酚类成分在各自的线性范围内,线性关系良好(r>0.99)。检出限(S/N=3)在2.80~9.47 ng/mL之间,其回归方程以及相关系数见表3。
表 3 方法学考察Table 3. Method validation of the proposed method序号 组分 线性范围
(mg/L)线性方程 相关系数
(r)LOD
(ng/mL)平均加标回收率
(%)RSD(%) 精密度 稳定性 重复性 回收率 1 咖啡酸 0.2~10 Y=281949.37X+5281.059 0.9964 4.42 99.40 1.03 1.24 1.31 1.56 2 对羟基苯甲酸 0.05~2 Y=3177.54X+81.273 0.9982 6.36 99.65 0.83 4.48 4.40 5.50 3 3,4-二羟基苯甲酸 0.05~2 Y=125185.86X+3446.998 0.9980 9.15 98.50 0.43 0.69 0.76 1.70 4 3,4-二羟基苯甲醛 0.05~2 Y=40216.21X+448.46 0.9988 9.15 98.65 0.50 0.91 0.34 2.76 5 2,5-二羟基苯甲酸 0.005~0.2 Y=73228.37X+140.97 0.9989 4.81 95.31 2.24 5.06 5.46 5.13 6 水杨酸 0.01~0.5 Y=317026.83X+1976.85 0.9987 7.79 96.98 1.31 4.90 5.36 4.72 7 芦丁 0.2~40 Y=20705.10X+1078.38 0.9966 9.26 99.10 1.56 3.76 3.73 2.61 8 对羟基肉桂酸 0.01~0.5 Y=500113.23X+1136.14 0.9990 2.80 97.81 1.63 4.50 4.73 5.02 9 七叶内酯 0.01~2 Y=213825.34X+2134.23 0.9993 7.31 96.71 1.46 2.32 1.98 2.64 10 阿魏酸 0.01~0.5 Y=23305.22X+41.59 0.9998 8.88 96.76 1.49 4.70 5.71 6.24 11 丹参素 2~50 Y=17645.89X+4551.48 0.9954 7.43 102.34 0.64 3.39 2.61 3.21 12 金丝桃苷 0.01~10 Y=38262.69X+1803.65 0.9993 7.91 98.01 1.03 3.74 3.15 3.45 13 迷迭香酸 5~500 Y=4924.67X−5552.72 0.9989 9.47 103.74 0.4 1.05 0.93 1.76 14 绿原酸 0.02~5 Y=170804.82X+1108.71 0.9921 3.98 98.49 1.00 2.34 1.69 1.54 15 异槲皮苷 0.01~10 Y=101301.31X+4147.82 0.9964 8.08 98.89 1.01 3.49 3.20 5.02 16 异迷迭香酸苷 0.5~50 Y=13823.36X+6247.78 0.9996 6.89 98.92 1.12 1.77 1.48 2.28 2.2.2 重复性
称取编号为S14的夏枯草粉末约1 g,按“1.2.1 样品制备”方法平行制备6份供试品溶液,按上述色谱和质谱条件,测定并记录夏枯草中16种化合物的峰面积,计算RSD值,结果显示RSD值≤5.71%。
2.2.3 精密度
精密量取标准品储备溶液并将其配制成0.5 mg/L的工作液(其中,异迷迭香酸苷、丹参素和迷迭香酸浓度为5 mg/L),按上述质谱和色谱条件,连续进样6次,进样量1 μL,测定并记录16种化合物的峰面积,计算RSD值,结果显示RSD值≤2.24%。
2.2.4 稳定性
称取编号为S14的夏枯草粉末约1 g,按“1.2.1 样品制备”方法制备供试品溶液,按上述测试条件在24 h(0、4、8 、12、16、24 h)内测定16种化合物的稳定性,记录夏枯草中16种化合物的峰面积变化并计算RSD值。结果显示24 h内RSD值≤5.06%。
2.2.5 加样回收实验
取同一批含量已知的夏枯草(S6)粉末3份,每份约1 g,按照含量1:1准确加入16种化合物,按“1.2.1 样品制备”方法制备供试品溶液,按上述测试条件进行测定,考察回收率,平均加标回收率在95.31%~103.74%之间,其RSD值≤6.24%。方法学考察结果见表3。
2.3 样品含量测定
分别称取夏枯草样品粉末,按“1.2.1 样品制备”方法制备供试品溶液,进样,按上述测试条件测定夏枯草中16种酚类化合物并记录各种化合物的峰面积,计算其含量,结果见表4。
表 4 24批夏枯草样品中16种酚类化合物含量测定结果(mg/100 g)Table 4. The contents of 16 phenolic compounds in 24 batches of Prunella vulgaris (mg/100 g)编号 七叶
内酯对羟基苯甲酸 3,4-二羟基苯甲醛 2,5-二羟基苯甲酸 丹参素 水杨酸 迷迭
香酸咖啡酸 阿魏酸 异迷迭香酸苷 绿原酸 3,4-二羟基苯甲酸 金丝
桃苷异槲
皮苷芦丁 对羟基肉桂酸 S1 0.93 1.87 1.66 0.15 55.02 0.14 515.61 11.09 0.35 65.80 1.54 1.23 6.32 2.88 19.46 0.20 S2 1.16 1.44 1.67 0.19 38.79 0.23 769.05 15.32 0.36 80.42 0.69 2.38 21.10 12.29 31.72 0.25 S3 1.03 1.54 1.71 0.13 30.36 0.21 745.21 13.18 0.32 84.74 0.52 2.36 17.22 10.49 26.48 0.24 S4 0.82 2.03 1.77 0.12 59.24 0.14 543.46 10.52 0.23 84.16 1.16 1.18 2.65 1.24 14.24 0.19 S5 1.37 1.99 1.97 0.10 26.44 0.28 912.29 14.50 0.29 48.95 0.52 1.70 13.60 9.35 35.89 0.18 S6 2.57 2.54 2.95 0.19 35.99 0.30 1036.73 23.56 0.50 82.29 0.69 3.46 22.54 15.73 50.48 0.35 S7 0.22 0.74 0.67 0.03 18.58 0.07 317.07 4.67 0.15 93.63 0.41 0.70 0.43 0.27 2.76 0.13 S8 1.11 1.31 1.71 0.15 30.08 0.21 712.56 12.84 0.32 76.12 0.50 1.96 8.71 6.01 25.97 0.26 S9 1.63 2.10 2.43 0.20 34.74 0.27 893.35 20.24 0.55 115.78 1.12 2.63 10.03 6.62 38.28 0.35 S10 1.28 1.31 1.82 0.15 28.88 0.23 624.54 12.62 0.30 82.80 0.40 1.96 6.15 4.39 22.20 0.26 S11 0.93 2.02 2.34 0.15 31.13 0.22 683.88 14.91 0.41 57.28 0.64 2.42 3.08 2.08 20.54 0.28 S12 0.15 0.87 0.60 0.03 17.49 0.07 281.28 4.21 0.07 78.28 0.12 0.60 0.26 0.15 2.57 0.11 S13 1.79 2.40 2.65 0.23 37.58 0.30 935.52 22.47 0.64 120.67 1.13 2.86 11.29 6.98 34.27 0.39 S14 0.93 1.56 1.61 0.12 24.35 0.20 662.22 10.63 0.21 48.82 0.42 1.68 9.77 6.08 22.36 0.19 S15 1.32 1.74 1.88 0.16 35.85 0.22 674.66 13.98 0.44 92.14 0.82 2.20 2.97 1.91 23.42 0.31 S16 1.06 2.12 2.07 0.12 49.25 0.14 477.75 8.90 0.36 76.78 1.30 1.16 1.95 0.76 12.92 0.19 S17 0.97 1.45 1.47 0.09 18.78 0.14 332.78 7.71 0.28 70.79 0.33 1.51 0.40 0.28 6.50 0.23 S18 1.65 1.98 2.31 0.24 45.92 0.28 883.23 23.84 0.42 92.11 1.39 2.69 9.41 5.52 38.64 0.36 S19 1.48 2.09 2.24 0.17 34.01 0.25 683.06 15.09 0.33 92.71 0.89 2.43 7.12 4.27 28.25 0.33 S20 0.97 1.33 1.47 0.11 16.83 0.13 230.31 7.45 0.24 44.73 0.36 1.42 0.06 0.05 3.82 0.20 S21 1.09 2.14 2.51 0.14 34.70 0.28 522.35 13.60 0.55 62.55 0.81 2.48 1.78 0.60 10.67 0.33 S22 1.36 2.69 2.36 0.14 18.80 0.21 417.90 10.18 0.42 101.07 0.47 2.50 0.52 0.35 9.30 0.35 S23 1.02 1.40 1.53 0.12 24.55 0.17 600.62 10.97 0.30 69.28 0.48 1.65 2.57 1.68 18.52 0.22 S24 0.20 1.22 0.73 0.02 16.24 0.05 205.97 3.30 0.09 64.30 0.13 0.59 0.27 0.17 2.92 0.07 24批样品中化合物的含量差异很大。其中,迷迭香酸、异迷迭香酸苷含量最高,丹参素次之,其含量分别为205.97~1036.73 mg/100 g、44.73~120.67 mg/100 g和16.24~59.24 mg/100 g。刘月新等[24]的研究表明,夏枯草在不同生长阶段其化学成分含量不同,迷迭香酸和异迷迭香酸苷在枯萎期含量明显增加。刘光敏等[25]的研究指出同一品种夏枯草药材因产地不同其酚类成分含量也有较大差异。因此,样品间的差异不仅与产地有关,而且受采收时间影响。
2.4 抗氧化活性研究
DPPH、ABTS自由基清除能力和铁离子还原能力结果见表5。在24批夏枯草样品中,DPPH、ABTS自由基清除能力和铁离子还原能力的范围分别为7.53~43.83 mg TE/g DW、10.75~34.93 mg TE/g DW和8.53~47.76 mg TE/g DW。其中,抗氧化能力最好的夏枯草样品为S6,较差的样品为S7和S24。
表 5 24批夏枯草抗氧化能力结果Table 5. The antioxidant capacity in 24 batches of Prunella vulgaris样品
编号DPPH
(mg TE/g DW)ABTS
(mg TE/g DW)铁离子还原能力
(mg TE/g DW)S1 28.06 24.49 24.92 S2 33.18 31.31 34.99 S3 32.01 28.48 33.09 S4 14.27 24.65 25.47 S5 36.38 31.40 39.19 S6 43.83 34.93 47.76 S7 12.63 10.75 8.53 S8 31.63 26.92 29.17 S9 36.84 31.87 41.48 S10 27.46 22.76 24.89 S11 32.62 25.52 29.56 S12 13.17 12.30 9.13 S13 37.01 32.90 44.44 S14 34.04 30.14 35.44 S15 30.35 27.46 32.73 S16 17.68 22.28 24.57 S17 9.22 15.47 14.45 S18 35.42 32.39 45.39 S19 20.86 27.17 33.53 S20 7.87 14.93 13.81 S21 15.15 22.20 23.71 S22 12.67 16.69 16.43 S23 18.07 24.22 29.03 S24 7.53 12.30 9.43 2.5 夏枯草中16种酚类化合物与抗氧化能力的关联性分析
2.5.1 GRA分析
利用GRA分析夏枯草中16种酚类化合物含量与抗氧化活性之间的相关性,以评价这些成分的活性贡献。GRD值用来描述成分与抗氧化活性之间的关系,GRD大于0.6说明化合物与抗氧化活性之间具有相关性,GRD大于等于0.8说明相关性较强[26-27]。16种酚类化合物与抗氧化活性相关性的GRD值如表6所示,16种化合物的GRD值均大于0.6,可见这些化合物均和抗氧化活性相关。其中,迷迭香酸与DPPH、ABTS、FRAP的关联度均大于0.8,芦丁和DPPH的关联度大于0.8,咖啡酸、芦丁和FRAP的关联度大于0.8,它们具有相对较高的GRD值可以认为是夏枯草中关键的抗氧化成分。
表 6 GRA结果Table 6. The results of GRADPPH GRD ABTS GRD FRAP GRD 迷迭香酸 0.849 迷迭香酸 0.833 迷迭香酸 0.885 芦丁 0.814 2,5-二羟基苯甲酸 0.797 咖啡酸 0.836 水杨酸 0.767 水杨酸 0.792 芦丁 0.800 咖啡酸 0.764 咖啡酸 0.783 水杨酸 0.799 3,4-二羟基苯甲酸 0.762 3,4-二羟基苯甲醛 0.744 2,5-二羟基苯甲酸 0.794 2,5-二羟基苯甲酸 0.736 3,4-二羟基苯甲酸 0.727 3,4-二羟基苯甲酸 0.772 3,4-二羟基苯甲醛 0.721 对羟基肉桂酸 0.726 3,4-二羟基苯甲醛 0.763 金丝桃苷 0.718 芦丁 0.712 七叶内酯 0.749 对羟基肉桂酸 0.715 对羟基苯甲酸 0.712 对羟基肉桂酸 0.744 异槲皮苷 0.713 阿魏酸 0.711 阿魏酸 0.739 阿魏酸 0.711 七叶内酯 0.690 对羟基苯甲酸 0.698 七叶内酯 0.706 绿原酸 0.674 绿原酸 0.688 对羟基苯甲酸 0.678 异迷迭香酸苷 0.643 异迷迭香酸苷 0.675 丹参素 0.673 金丝桃苷 0.633 金丝桃苷 0.669 异迷迭香酸苷 0.661 异槲皮苷 0.619 异槲皮苷 0.667 绿原酸 0.657 丹参素 0.614 丹参素 0.650 2.5.2 PLSR分析
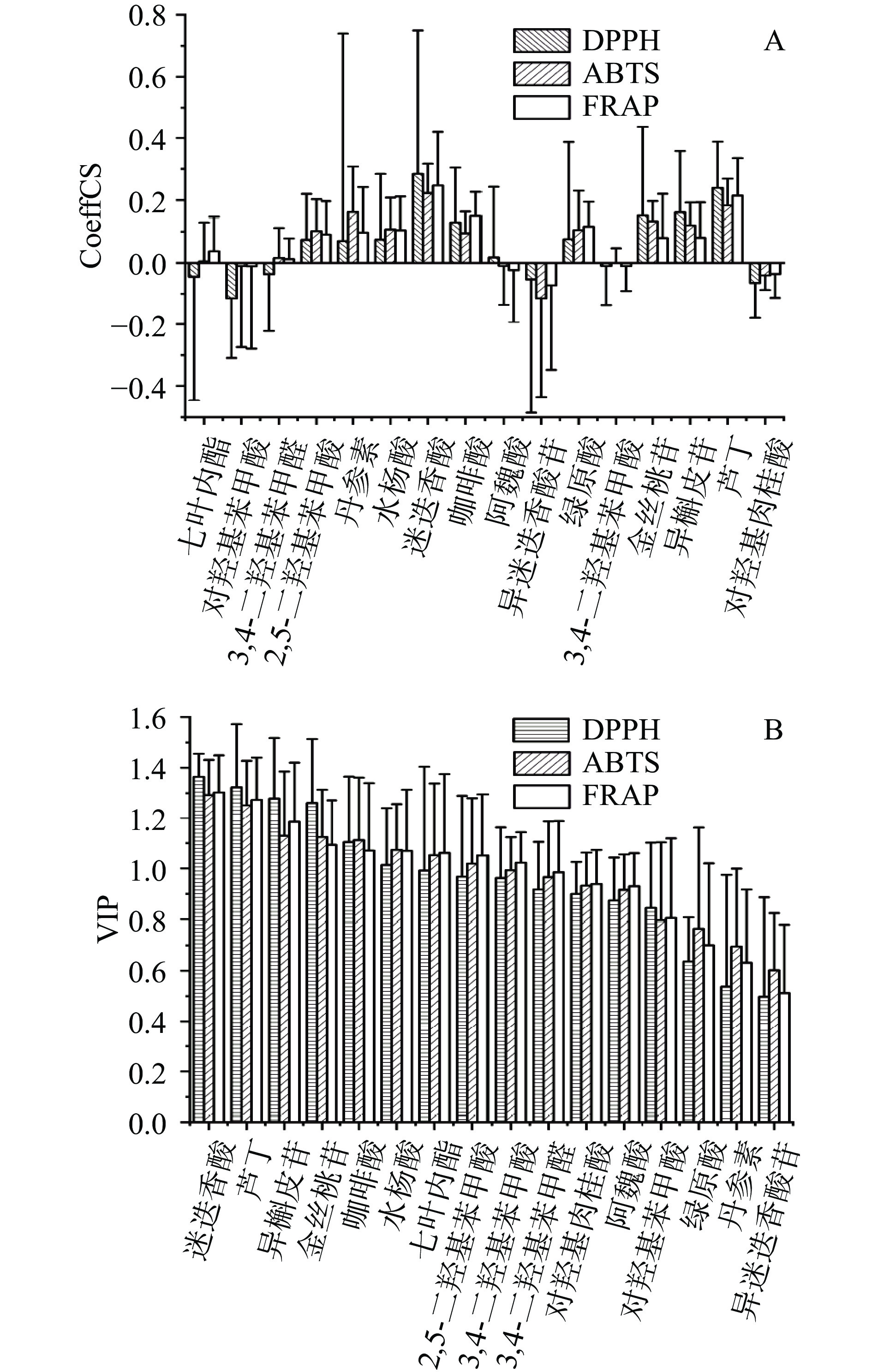
采用PLSR分析DPPH、ABTS、FRAP法与夏枯草中16种酚类化合物的相关性,以16种酚类化合物含量为X变量,以DPPH、ABTS、FRAP值为Y变量进行相关性分析,结果见图2。CoeffCS系数的正负表示不同化合物同抗氧化活性正相关或负相关,VIP值代表相关性强弱。从结果可以看出,对3种抗氧化活性均呈正相关且VIP值大于1.0的化合物有迷迭香酸、芦丁、金丝桃苷、异槲皮苷、咖啡酸、水杨酸、2,5-二羟基苯甲酸。
大量研究表明,酚类化合物是食用/药用植物抗氧化的主要来源[28-29]。本研究结合GRA与PLSR相关性分析可知,夏枯草中16种酚类化合物均具有抗氧化活性,GRD值均大于0.6,且GRA与PLSR相关性分析均表明迷迭香酸抗氧化能力最好。
3. 结论
综上所述,本研究成功运用LC-MS/MS法同时测定夏枯草中16种酚类化合物的含量,该方法线性关系良好(r>0.99),灵敏度较高。24批夏枯草中不同酚类化合物含量在0.02~1036.73 mg/100 g之间,其中,迷迭香酸含量最高,为205.97~1036.73 mg/100 g。进一步采用GRA和PLSR分析了化学成分与DPPH、ABTS自由基清除能力和铁离子还原能力的相关性。GRA结果表明16种酚类化合物与抗氧化活性的关联系数均大于0.6,均与抗氧化活性相关。PLSR的结果表明迷迭香酸、芦丁、金丝桃苷、异槲皮苷、咖啡酸等化合物对抗氧化活性的贡献较大。本研究不仅测定了夏枯草中主要化合物的含量,而且明确了主要化学成分对抗氧化的贡献,可为夏枯草质量控制与开发利用提供参考。
-
表 1 24批夏枯草样品信息
Table 1 Information of 24 batches of Prunella vulgaris
样品编号 产地 样品编号 产地 样品编号 产地 S1 广东深圳 S9 江苏常州 S17 湖北襄阳 S2 安徽亳州 S10 河南周口 S18 浙江嘉兴 S3 河南郑州 S11 安徽安庆 S19 湖北咸宁 S4 湖北荆州 S12 河南漯河 S20 河北沧州 S5 安徽合肥 S13 安徽黄山 S21 安徽宣城 S6 内蒙包头 S14 广东湛江 S22 河北承德 S7 河南新乡 S15 广东佛山 S23 广东广州 S8 河北石家庄 S16 河北保定 S24 安徽池州 表 2 16种主要成分的保留时间和质谱参数
Table 2 Retention time and mass parameters of the 16 components
序号 化合物 保留时间
(min)母离子
(m/z)子离子
(m/z)锥孔电压
(V)碰撞能量
(eV)1 丹参素 1.61 197.2 135.1*/179.1 20 20 2 3,4-二羟基苯甲酸 1.83 153.1 109.1*/— 30 12 3 3,4-二羟基苯甲醛 2.67 137.1 108.1*/90.0 15 20 4 对羟基苯甲酸 2.68 137.1 93.1*/ — 45 12 5 2,5-二羟基苯甲酸 2.78 153.1 109.1*/ — 30 12 6 绿原酸 3.19 353.1 191.1*/179.1 12 15 7 七叶内酯 3.47 177.1 133.1*/149.1 35 18 8 咖啡酸 3.62 178.1 135.1*/117.1 38 16 9 对羟基肉桂酸 5.2 163.1 119.1*/115.1 12 15 10 阿魏酸 6.26 193.1 134.1*/178.1 15 15 11 芦丁 7.04 609.6 301.3*/271.2 30 35 12 金丝桃苷 7.05 463.4 301.3*/300.3 40 20 13 异槲皮苷 7.29 463.4 301.3*/271.2 40 20 14 水杨酸 7.64 137.1 93.1*/ — 20 15 15 异迷迭香酸苷 8.08 521.5 359.3*/179.1 20 20 16 迷迭香酸 9.42 359.3 197.1*/179.1 18 8 注:*代表定量离子对;—代表未检测到离子信息。 表 3 方法学考察
Table 3 Method validation of the proposed method
序号 组分 线性范围
(mg/L)线性方程 相关系数
(r)LOD
(ng/mL)平均加标回收率
(%)RSD(%) 精密度 稳定性 重复性 回收率 1 咖啡酸 0.2~10 Y=281949.37X+5281.059 0.9964 4.42 99.40 1.03 1.24 1.31 1.56 2 对羟基苯甲酸 0.05~2 Y=3177.54X+81.273 0.9982 6.36 99.65 0.83 4.48 4.40 5.50 3 3,4-二羟基苯甲酸 0.05~2 Y=125185.86X+3446.998 0.9980 9.15 98.50 0.43 0.69 0.76 1.70 4 3,4-二羟基苯甲醛 0.05~2 Y=40216.21X+448.46 0.9988 9.15 98.65 0.50 0.91 0.34 2.76 5 2,5-二羟基苯甲酸 0.005~0.2 Y=73228.37X+140.97 0.9989 4.81 95.31 2.24 5.06 5.46 5.13 6 水杨酸 0.01~0.5 Y=317026.83X+1976.85 0.9987 7.79 96.98 1.31 4.90 5.36 4.72 7 芦丁 0.2~40 Y=20705.10X+1078.38 0.9966 9.26 99.10 1.56 3.76 3.73 2.61 8 对羟基肉桂酸 0.01~0.5 Y=500113.23X+1136.14 0.9990 2.80 97.81 1.63 4.50 4.73 5.02 9 七叶内酯 0.01~2 Y=213825.34X+2134.23 0.9993 7.31 96.71 1.46 2.32 1.98 2.64 10 阿魏酸 0.01~0.5 Y=23305.22X+41.59 0.9998 8.88 96.76 1.49 4.70 5.71 6.24 11 丹参素 2~50 Y=17645.89X+4551.48 0.9954 7.43 102.34 0.64 3.39 2.61 3.21 12 金丝桃苷 0.01~10 Y=38262.69X+1803.65 0.9993 7.91 98.01 1.03 3.74 3.15 3.45 13 迷迭香酸 5~500 Y=4924.67X−5552.72 0.9989 9.47 103.74 0.4 1.05 0.93 1.76 14 绿原酸 0.02~5 Y=170804.82X+1108.71 0.9921 3.98 98.49 1.00 2.34 1.69 1.54 15 异槲皮苷 0.01~10 Y=101301.31X+4147.82 0.9964 8.08 98.89 1.01 3.49 3.20 5.02 16 异迷迭香酸苷 0.5~50 Y=13823.36X+6247.78 0.9996 6.89 98.92 1.12 1.77 1.48 2.28 表 4 24批夏枯草样品中16种酚类化合物含量测定结果(mg/100 g)
Table 4 The contents of 16 phenolic compounds in 24 batches of Prunella vulgaris (mg/100 g)
编号 七叶
内酯对羟基苯甲酸 3,4-二羟基苯甲醛 2,5-二羟基苯甲酸 丹参素 水杨酸 迷迭
香酸咖啡酸 阿魏酸 异迷迭香酸苷 绿原酸 3,4-二羟基苯甲酸 金丝
桃苷异槲
皮苷芦丁 对羟基肉桂酸 S1 0.93 1.87 1.66 0.15 55.02 0.14 515.61 11.09 0.35 65.80 1.54 1.23 6.32 2.88 19.46 0.20 S2 1.16 1.44 1.67 0.19 38.79 0.23 769.05 15.32 0.36 80.42 0.69 2.38 21.10 12.29 31.72 0.25 S3 1.03 1.54 1.71 0.13 30.36 0.21 745.21 13.18 0.32 84.74 0.52 2.36 17.22 10.49 26.48 0.24 S4 0.82 2.03 1.77 0.12 59.24 0.14 543.46 10.52 0.23 84.16 1.16 1.18 2.65 1.24 14.24 0.19 S5 1.37 1.99 1.97 0.10 26.44 0.28 912.29 14.50 0.29 48.95 0.52 1.70 13.60 9.35 35.89 0.18 S6 2.57 2.54 2.95 0.19 35.99 0.30 1036.73 23.56 0.50 82.29 0.69 3.46 22.54 15.73 50.48 0.35 S7 0.22 0.74 0.67 0.03 18.58 0.07 317.07 4.67 0.15 93.63 0.41 0.70 0.43 0.27 2.76 0.13 S8 1.11 1.31 1.71 0.15 30.08 0.21 712.56 12.84 0.32 76.12 0.50 1.96 8.71 6.01 25.97 0.26 S9 1.63 2.10 2.43 0.20 34.74 0.27 893.35 20.24 0.55 115.78 1.12 2.63 10.03 6.62 38.28 0.35 S10 1.28 1.31 1.82 0.15 28.88 0.23 624.54 12.62 0.30 82.80 0.40 1.96 6.15 4.39 22.20 0.26 S11 0.93 2.02 2.34 0.15 31.13 0.22 683.88 14.91 0.41 57.28 0.64 2.42 3.08 2.08 20.54 0.28 S12 0.15 0.87 0.60 0.03 17.49 0.07 281.28 4.21 0.07 78.28 0.12 0.60 0.26 0.15 2.57 0.11 S13 1.79 2.40 2.65 0.23 37.58 0.30 935.52 22.47 0.64 120.67 1.13 2.86 11.29 6.98 34.27 0.39 S14 0.93 1.56 1.61 0.12 24.35 0.20 662.22 10.63 0.21 48.82 0.42 1.68 9.77 6.08 22.36 0.19 S15 1.32 1.74 1.88 0.16 35.85 0.22 674.66 13.98 0.44 92.14 0.82 2.20 2.97 1.91 23.42 0.31 S16 1.06 2.12 2.07 0.12 49.25 0.14 477.75 8.90 0.36 76.78 1.30 1.16 1.95 0.76 12.92 0.19 S17 0.97 1.45 1.47 0.09 18.78 0.14 332.78 7.71 0.28 70.79 0.33 1.51 0.40 0.28 6.50 0.23 S18 1.65 1.98 2.31 0.24 45.92 0.28 883.23 23.84 0.42 92.11 1.39 2.69 9.41 5.52 38.64 0.36 S19 1.48 2.09 2.24 0.17 34.01 0.25 683.06 15.09 0.33 92.71 0.89 2.43 7.12 4.27 28.25 0.33 S20 0.97 1.33 1.47 0.11 16.83 0.13 230.31 7.45 0.24 44.73 0.36 1.42 0.06 0.05 3.82 0.20 S21 1.09 2.14 2.51 0.14 34.70 0.28 522.35 13.60 0.55 62.55 0.81 2.48 1.78 0.60 10.67 0.33 S22 1.36 2.69 2.36 0.14 18.80 0.21 417.90 10.18 0.42 101.07 0.47 2.50 0.52 0.35 9.30 0.35 S23 1.02 1.40 1.53 0.12 24.55 0.17 600.62 10.97 0.30 69.28 0.48 1.65 2.57 1.68 18.52 0.22 S24 0.20 1.22 0.73 0.02 16.24 0.05 205.97 3.30 0.09 64.30 0.13 0.59 0.27 0.17 2.92 0.07 表 5 24批夏枯草抗氧化能力结果
Table 5 The antioxidant capacity in 24 batches of Prunella vulgaris
样品
编号DPPH
(mg TE/g DW)ABTS
(mg TE/g DW)铁离子还原能力
(mg TE/g DW)S1 28.06 24.49 24.92 S2 33.18 31.31 34.99 S3 32.01 28.48 33.09 S4 14.27 24.65 25.47 S5 36.38 31.40 39.19 S6 43.83 34.93 47.76 S7 12.63 10.75 8.53 S8 31.63 26.92 29.17 S9 36.84 31.87 41.48 S10 27.46 22.76 24.89 S11 32.62 25.52 29.56 S12 13.17 12.30 9.13 S13 37.01 32.90 44.44 S14 34.04 30.14 35.44 S15 30.35 27.46 32.73 S16 17.68 22.28 24.57 S17 9.22 15.47 14.45 S18 35.42 32.39 45.39 S19 20.86 27.17 33.53 S20 7.87 14.93 13.81 S21 15.15 22.20 23.71 S22 12.67 16.69 16.43 S23 18.07 24.22 29.03 S24 7.53 12.30 9.43 表 6 GRA结果
Table 6 The results of GRA
DPPH GRD ABTS GRD FRAP GRD 迷迭香酸 0.849 迷迭香酸 0.833 迷迭香酸 0.885 芦丁 0.814 2,5-二羟基苯甲酸 0.797 咖啡酸 0.836 水杨酸 0.767 水杨酸 0.792 芦丁 0.800 咖啡酸 0.764 咖啡酸 0.783 水杨酸 0.799 3,4-二羟基苯甲酸 0.762 3,4-二羟基苯甲醛 0.744 2,5-二羟基苯甲酸 0.794 2,5-二羟基苯甲酸 0.736 3,4-二羟基苯甲酸 0.727 3,4-二羟基苯甲酸 0.772 3,4-二羟基苯甲醛 0.721 对羟基肉桂酸 0.726 3,4-二羟基苯甲醛 0.763 金丝桃苷 0.718 芦丁 0.712 七叶内酯 0.749 对羟基肉桂酸 0.715 对羟基苯甲酸 0.712 对羟基肉桂酸 0.744 异槲皮苷 0.713 阿魏酸 0.711 阿魏酸 0.739 阿魏酸 0.711 七叶内酯 0.690 对羟基苯甲酸 0.698 七叶内酯 0.706 绿原酸 0.674 绿原酸 0.688 对羟基苯甲酸 0.678 异迷迭香酸苷 0.643 异迷迭香酸苷 0.675 丹参素 0.673 金丝桃苷 0.633 金丝桃苷 0.669 异迷迭香酸苷 0.661 异槲皮苷 0.619 异槲皮苷 0.667 绿原酸 0.657 丹参素 0.614 丹参素 0.650 -
[1] 宋莉, 倪世峰, 李亚君, 等. 夏枯草不同溶剂提取物抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2016,37(17):32−35. [SONG L, NI S F, LI Y J, et al. Study on antioxidant activity of different solvents extracts of Prunella vulgaris Linn[J]. Food Research and Development,2016,37(17):32−35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2016.17.008 [2] LI C, HUANG Q, FU X, et al. Characterization, antioxidant and immunomodulatory activities of polysaccharides from Prunella vulgaris Linn[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2015,75:298−305. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.01.010
[3] ZHANG X, SHEN T, ZHOU X, et al. Network pharmacology based virtual screening of active constituents of Prunella vulgaris L. and the molecular mechanism against breast cancer[J]. Scientific Reports,2020,10(1):15730. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-72797-8
[4] SHEN J, LIANG B. Sex specific effects of Prunella vulgaris on longevity regulation[J]. Plant Foods for Human Nutrition (Dordrecht, Netherlands),2022:1−2.
[5] CHENG Q, ZHANG X, WANG O, et al. Anti-diabetic effects of the ethanol extract of a functional formula diet in mice fed with a fructose/fat-rich combination diet[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2015,95(2):401−408. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.6737
[6] 万红霞, 杨绍艳, 欧爱芬, 等. 20种凉茶原料水提物的抗氧化和抗MC-38细胞增殖活性评价[J]. 食品科技,2020,45(6):290−296. [WAN H X, YANG S Y, OU A F, et al. Evaluation of antioxidant and antiproliferation activity on MC-38 cell of 20 kinds of herbal tea extracts[J]. Food Science and Technology,2020,45(6):290−296. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2020.06.051 [7] 万正瑞, 李强强, 王凯, 等. 夏枯草蜂蜜提取物对硫酸葡聚糖诱导肠上皮细胞损伤的保护作用及其机制[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(19):161−169. [WAN Z R, LI Q Q, WANG K, et al. Protective effect and mechanism of Prunella vulgaris honey extract on dextran sulfate sodium-induced injury in caco-2 cells[J]. Food Science,2020,41(19):161−169. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190926-321 [8] HWANG Y J, LEE E J, KIM H R, et al. In vitro antioxidant and anticancer effects of solvent fractions from Prunella vulgaris var. lilacina[J]. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine,2013,13(310):2−9.
[9] 李诗卉, 梁诗瑶, 伊美瑾, 等. 夏枯草茎叶复合菌发酵工艺、成分及活性变化研究[J]. 时珍国医国药,2020,31(11):2629−2633. [LI S H, LIANG S Y, YI M J, et al. Study on fermentation technology, composition and activity changes of stem and leaf compound bacteria of Prunella vulgaris[J]. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research,2020,31(11):2629−2633. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2020.11.020 [10] 杨巍巍, 邓航, 李娇, 等. 植物多酚化合物抗氧化损伤研究进展[J]. 现代食品,2020(16):74−78. [YANG W W, DENG H, LI J, et al. Research progress on antioxidant damage of plant polyphenols[J]. Modern Food,2020(16):74−78. doi: 10.16736/j.cnki.cn41-1434/ts.2020.16.022 [11] 王娜, 韩海霞, 钟志明, 等. 红树莓冻干粉中酚类化合物含量测定及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中国调味品,2022,47(4):1−6. [WANG N, HAN H X, ZHONG Z M, et al. Determination of phenolic compounds and antioxidant activity of Rubus idaeus L. lyophilized powder[J]. China Condiment,2022,47(4):1−6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2022.04.001 [12] 《中国药典》2020年版, 一部[S]. 2020: 292 Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2020 edition)[S]. 2020: 292.
[13] 冯伟红, 李春, 信伟梅, 等. 生物测定法用于中药质量评价的探索研究—以夏枯草抗氧化活性与总酚酸含量相关性的研究为例[J]. 中国中药杂志,2016,41(14):2660−2668. [FENG W H, LI C, XIN W M, et al. Exploration on feasibility of introducing bioassay method into quality evaluation of Chinese herbal medicines by studying on the correlation between antioxidant activity of Prunella vulgaris and its total phenolic acids content for example[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2016,41(14):2660−2668. [14] 蔡艳芳, 戴晖, 张丽芬, 等. 高效液相色谱法测定野生夏枯草中5种活性有效成分的含量[J]. 临床合理用药杂志,2020,13(11):136−138. [CAI Y F, DAI H, ZHANG L F, et al. Determination of five active components in wild Prunella vulgaris by HPLC[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Rational Drug Use,2020,13(11):136−138. doi: 10.15887/j.cnki.13-1389/r.2020.31.065 [15] 张萍, 何婷, 王颖, 等. 加速溶剂萃取-超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定大枣中3种五环三萜酸[J]. 食品与药品,2021,23(1):17−21. [ZHANG P, HE T, WANG Y, et al. Simultaneous determination of three pentacyclic triterpenic acids in Jujubae Fructus by accelerated solvent extraction-UPLC-MS/MS[J]. Food and Drug,2021,23(1):17−21. [16] 柏玉冰, 李洪权, 包敏, 等. 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定夏枯草中4种酚酸含量[J]. 中国药业,2020,29(23):24−27. [BAI Y B, LI H Q, BAO M, et al. Simultaneous determination of four phenolic acids in Prunella vulgaris by UPLC-MS/MS[J]. China Pharmaceuticals,2020,29(23):24−27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4931.2020.23.006 [17] XIA J X, ZHAO B B, ZAN J F, et al. Simultaneous determination of phenolic acids and flavonoids in Artemisiae Argyi Folium by HPLC-MS/MS and discovery of antioxidant ingredients based on relevance analysis[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis,2019,175:112734. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2019.06.031
[18] OZDAL T, CEYLAN F D, EROGLU N, et al. Investigation of antioxidant capacity, bioaccessibility and LC-MS/MS phenolic profile of Turkish propolis[J]. Food Research International,2019,122:528−536. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.05.028
[19] SCHULZ M, SERAGLIO S K T, DELLA BETTA F, et al. Determination of phenolic compounds in three edible ripening stages of yellow guava (Psidium cattleianum Sabine) after acidic hydrolysis by LC-MS/MS[J]. Plant Foods for Human Nutrition,2020,75(1):110−115. doi: 10.1007/s11130-019-00792-0
[20] 罗弘杉, 谭知浩, 徐春芳, 等. 夏枯草茎叶总酚酸提取工艺优化及其化学成分研究[J]. 中药新药与临床药理,2022,33(5):700−706. [LUO H S, TAN Z H, XU C F, et al. Optimization of extraction technology and composition analysis of total phenolic acids from stems and leaves of Prunella vulgaris L J]. Traditional Chinese Drug Research and Clinical Pharmacology,2022,33(5):700−706.
[21] ZHU C S, LIN Z J, XIAO M L, et al. The spectrum-effect relationship-a rational approach to screening effective compounds, reflecting the internal quality of Chinese herbal medicine[J]. Chinese Journal of Natural Medicines,2016,14(3):177−184. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(16)30014-0
[22] 周文杰, 王鹏, 詹萍, 等. 香气活度值法结合PLSR用于梨酒特征香气物质筛选与鉴定[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(14):138−143. [ZHOU W J, WANG P, ZHAN P, et al. Screening and identification of flavor characteristics of three pear wines based on odor activity value using partial least squares regression[J]. Food Science,2017,38(14):138−143. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201714021 [23] 叶日英, 孙力军, 王雅玲, 等. 冷藏凡纳滨对虾色差值与若干典型质量性状的灰色关联分析[J]. 中国食品学报,2018,18(3):205−210. [YE R Y, SUN L J, WANG Y L, et al. Grey correlation analysis between color difference value of refrigeratedLitopenaeus vannamei and some typical quality traits[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2018,18(3):205−210. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2018.03.027 [24] 刘月新, 林艳, 谢菁琛, 等. 基于夏枯草不同生长发育时期化学成分的动态监测阐释“夏枯质优”的科学内涵[J]. 中草药,2021,52(7):2802−2090. [LIU Y X, LIN Y, XIE J C, et al. Scientific connotation of "summer withering with good quality" based on dynamic monitoring of chemical constituents at different growth and development stages of Prunella vulgaris[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2021,52(7):2802−2090. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2021.07.025 [25] 刘光敏, 贾晓斌, 陈彦, 等. HPLC法比较不同产地夏枯草属药材中成分组成的差异性[J]. 中草药,2010,41(8):1384−1386. [LIU G M, JIAO X B, CHEN Y, et al. Comparison of components in Prunella L. from different habitats by HPLC[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2010,41(8):1384−1386. [26] HU Y, DENG L, CHEN J, et al. An analytical pipeline to compare and characterise the anthocyanin antioxidant activities of purple sweet potato cultivars[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,194:46−54. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.07.133
[27] LIU X, WANG Y, GE W, et al. Spectrum-effect relationship between ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography fingerprints and antioxidant activities of Lophatherum gracile Brongn[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2022,10(5):1592−1601.
[28] 王颂萍, 钟强, 杨欣悦, 等. 多酚抑制脂肪氧化的作用机理及其在肉制品中应用的研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(10):417−425. [WANG S P, ZHONG Q, YANG X Y, et al. Mechanism of polyphenols inhibiting lipid oxidation and its development in meat products[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(10):417−425. [29] 党斌. 青海藜麦资源酚类物质及其抗氧化活性分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(17):30−37. [DANG B. Analysis on phenols and antioxidant activities of quinoa resources in Qinghai[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(17):30−37. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2019.17.006





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



