Effects of Anthocyanins from Opuntia ficus-indica on Gut Microbiota and Metabolites SCFAs Based on Fermentation in Vitro
-
摘要: 仙人掌果中富含多种活性物质,其中含有的花色苷在调节肠道菌群中起着重要作用,为了进一步探讨仙人掌果实中花色苷与人体肠道内菌群的关系,本文研究了仙人掌果实花色苷体外模拟消化和体外厌氧发酵K组(空白)、花色苷H组(高剂量15 mg/mL)、M组(中剂量10 mg/mL)、L组(低剂量5 mg/mL)对人体肠道微生物和代谢物短链脂肪酸(SCFAs)的影响。结果表明:采用pH示差法,以消化率为指标,仙人掌果实花色苷(10 mg/mL),经胃消化3 h后消化率为11.4%;经肠消化4 h后消化率为23.5%;剩余65.1%的花色苷未经胃肠道消化。采用高通量测序方法,通过α多样性和β多样性分析,与K组相比,花色苷H、M、L组均能显著提高肠道菌群多样性(P<0.05)。在菌群组成上,基于门水平分析,与空白组比较,花色苷各剂量组,变形菌门(Proteobacteria)相对丰度显著降低(P<0.05),厚壁菌门/拟干菌门(Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes,F/B值)的比例均显著减少(P<0.05);基于属水平中,与K组相比H、M、L组均能显著降低大肠杆菌志贺属(Escherichia-Shigella)、脱硫弧菌属(Desulfovibrio)致病菌相对丰度(P<0.05),能够显著增高有益菌的丰度(P<0.05),其中,中剂量组中普氏菌属(Prevotella)相对丰度最高,达到41.8%。高剂量组中乳酸杆菌属(Lactobacillus)、双歧杆菌属(Bifidobacterium)相对丰度最高,分别达到7.9%、5.9%,低剂量组中光冈菌属(Mitsuokella)相对丰度大幅提高,达到37.7%。通过气相色谱分析短链脂肪酸变化,与K组相比,H、M、L组总短链脂肪酸含量均显著提升(P<0.05),且分别为K组的7.8、5.0和1.1倍。其中乙酸、丙酸、丁酸含量上升最显著(P<0.05),乙酸上升最高为K组的10.0倍,丙酸为4.6倍,丁酸为10.7倍。综上,仙人掌果实花色苷在胃中少量消化,在小肠中大量消化,绝大部分剩余,其能够改变肠道的微生物的多样性及菌群组成,促进短链脂肪酸的产生,为后续花色苷对肠道微生物群的调节作用以及开发功能性食品建立基础。Abstract: Opuntia ficus-indica is rich in a variety of active substances, and the anthocyanins contained in it play an important role in regulating gut microbiota. In this paper, the simulated digestion and in vitro anaerobic fermentation of Opuntia ficus-indica anthocyanins were studied in K group (blank), anthocyanin H (high dose 15 mg/mL), M group (medium dose 10 mg/mL), L group (low dose 5 mg/mL) on human gut microbes and metabolites short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). The results showed that, using the pH test and difference method, and taking the digestibility as an indicator, the anthocyanins of Opuntia ficus-indica (10 mg/mL) were obtained, the digestibility was 11.4% after 3 h of gastric digestion, 23.5% after 4 h of intestinal digestion, the remaining 65.1% of anthocyanins were not digested by the gastrointestinal tract. Using high-throughput sequencing method, through α diversity and β diversity analysis, compared with K group, anthocyanin H, M, L group could significantly improve the diversity of gut microbiota (P<0.05). In terms of microbiota composition, based on phylum-level analysis, compared with blank group, the relative abundance of Proteobacteria in each anthocyanin dose group significantly decreased (P<0.05). The ratio of phylum Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes (F/B value) was significantly reduced (P<0.05). At the genus level, compared with the K group, the H, M and L dose groups could significantly reduce the relative abundance of Escherichia-Shigella and Desulfovibrio pathogens (P<0.05), and could significantly increase the beneficial effects. The abundance of bacteria, among which, the abundance of Prevotella in the middle-dose group was the highest, reaching 41.8%. The abundance of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium in the high-dose group was the highest, reaching 7.9% and 5.9%, respectively. The relative abundance of Mitsuokella in the low-dose group was greatly increased, reaching 37.7%. The changes of short-chain fatty acids were analyzed by gas chromatography (GC). Compared with the K group, the total short-chain fatty acid content of the high, medium and low dose groups significantly increased (P<0.05), and were 7.8, 5.0 and 1.1 times that of the blank group, respectively. Among them, the contents of acetic acid, propionic acid and butyric acid increased most significantly (P<0.05), the highest increased in acetic acid was 10.0 times that of the K group, 4.6 times for propionic acid and 10.7 times for butyric acid. In summary, Opuntia ficus-indica anthocyanins were digested in a small amount in the stomach, and a large amount was digested in the small intestine, and most of them were left. They could change the diversity and composition of microbes in the intestinal tract, and promote the production of short-chain fatty acids. This study would establish the foundation for the regulatory role of the microbiota and the development of functional foods.
-
Keywords:
- Opuntia ficus-indica /
- anthocyanins /
- digestion in vitro /
- fermentation in vitro
-
仙人掌果(Opuntia ficus-indica)是仙人掌属(Opuntia)植物的果实,源自美洲大陆的一种多浆植物,广泛分布于南非,该植物主产于我国热带地区,例如海南、云南、广西,具有气候耐受性。仙人掌果具有较高的营养价值,但是其鲜销和保存都比较困难,所以为了最大限度利用仙人掌果,提取其生物活性物质进行产品化利于保存与运输。仙人掌果中存在大量的生物活性物质如花色苷、多糖类、蛋白质等。花色苷在浆果中含量最为丰富,它是花色素与糖以糖苷键结合而成,属于类黄酮类化合物,是天然水溶性物质[1]。
近年来花色苷通过调节肠道微生物从而促进人体健康已成为研究热点[2]。花色苷在摄入后经历复杂的代谢,未被消化的花色苷和花色苷的分解代谢产物到达结肠对肠道微生物进行作用[3]。花色苷对肠道微生物的调节作用表现在两方面,一是肠道菌群通过代谢活动,使其具有直接的生理活性功能(例如调节糖尿病、肥胖症)[4],二是改变了肠道微生物的数量与构成,对人体发挥健康促进作用[5],对此研究者们进行大量研究。Wu等[6]研究发现,从桑葚中提取得到的花色苷能够显著抑制高脂膳食诱导引起的C578BL/6小鼠体重的增加并同时降低痩素和脂联素分泌以及胰岛素抵抗。Norberto等[7]通过对比研究发现,习惯性摄入蓝莓花色苷会减少二型糖尿病的发作把血糖控制在安全的水平。Gowd等[8]通过建立体外消化模型模拟口腔、胃-肠道消化来研究花色苷的消化吸收的程度,结果表明花色苷与肠道细菌相互作用使其呈现出剂量梯度。Walujkar等[9]研究了溃疡性结肠炎患者肠道菌群的变化,发现溃疡性结肠炎患者肠道存在生态失调和专性厌氧菌失调。
迄今为止,花色苷的生物利用度和健康益处已被广泛记载[10],但是由于目前研究者们普便利用蓝莓、蓝靛果、紫马铃薯等研究花色苷,而利用仙人掌果少之又少,对于仙人掌果中花色苷的研究还不够完全和深入[11],所以为了进一步预估仙人掌果花色苷在人体中发生的潜在作用,本文以仙人掌果果实为原料,从中提取花色苷进行模拟体外消化实验和体外发酵实验。通过pH示差法,评价消化过程中仙人掌果花色苷的消化率,Novaseq 6000测序和气相色谱(GC)分析肠道菌群以及短链脂肪酸的变化,为仙人掌果果实中花色苷作为膳食补充剂调节人体健康提供理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
无水乙醇、磷酸氢二钾、磷酸二氢钾、碳酸氢钠、七水合硫酸镁、六水合氯化钙、吐温80、硫酸、乙醚、氯化钾、氯化钠、六水合氯化镁、碳酸铵、浓盐酸、氢氧化钠 分析纯,天津市光复科技发展有限公司;蛋白胨、酵母膏、猪胆盐 分析纯,北京奥博星生物技术有限公司;氯化血红素、维生素K1、L-半胱氨酸、α-淀粉酶(4000 U/g)、胃蛋白酶(250 U/mg)、胰蛋白酶(3000 U/mg) 分析纯,上海源叶生物科技有限公司;6种水溶性脂肪酸混标 色谱纯,坛墨质检科技股份有限公司;粪便DNA试剂盒 型号D3141,广州美基生物科技有限公司;仙人掌果 购买于海南;粪便样品 来源于2位健康的志愿者,过去三个月内没有消化系统疾病、没有使用任何的抗生素和益生菌(18~30岁、1位女士和1位男士),实验前已经和志愿者阐述利害关系,试验均在志愿者同意下进行。
Magnetic stirrer磁力搅拌器 意大利Velp公司;Allegra 64R Compact Centrifuge离心机 贝克曼库尔特公司;UV1800紫外可见分光光度计 上海棱光技术有限公司;RE-25AA旋转蒸发仪 上海亚荣生化有限公司;FDU-1100真空冷冻干燥机 日本东京理化仪器有限公司;BSD-TX345摇床 上海启闵生物技术有限公司;7890A气相色谱 安捷伦科技有限公司;Vortex.Genie2漩涡振荡 上海迈旗环保科技有限公司;Bactron Ⅱ厌氧培养箱 美国Shellab公司;ABI StepOnePlus RealTime PCR System Life Technologies 美国ABI。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 仙人掌果花色苷提取物的制备
准确称取一定质量过40目筛的原料粉末,用51%的乙醇溶液(pH2)进行提取,料液比为1:25 g/mL,于55 ℃磁力搅拌提取70 min。4500 r/min,15 min离心,取上清液于50 ℃减压浓缩得到花色苷溶液,冻干成粉末[12]。
1.2.2 体外消化模型的建立
以Minekus等[13]的方法为基础稍做调整,制备模拟唾液(SSF)、模拟胃液(SGF)和模拟肠液(SIF)电解质储备溶液,如表1。
表 1 消化电解质液原液的配制Table 1. Configuration of digestive juice成分 基础液(g/L) SSF SGF SIF 基础液中吸取(mL)
pH7基础液中吸取(mL)
pH3基础液中吸取(mL)
pH7KCl 37.3 15.1 6.9 6.8 KH2PO4 68 3.7 0.9 0.8 NaHCO3 84 6.8 12.5 42.5 NaCl 117 − 11.8 9.6 MgCl2(H2O)6 30.5 0.5 0.4 1.1 (NH4)2CO3 48 0.06 0.5 − 模拟口腔消化:取10 mg/mL的仙人掌果花色苷粗提物5 mL,依次加入3.5 mL SSF电解质液、25 μL CaCl2·2H2O、0.5 mL活力值为1200 U/mL的α-淀粉酶,最后用超纯水定容至10 mL。在恒温摇床37 ℃、120 r/min、避光进行2 min。消化完成后立即转入−80 ℃冰箱灭酶。
体外模拟胃消化:将口腔消化产物(10 mL)加入7.5 mL SGF电解质液、1.6 mL活力值为24000 U/mL的胃蛋白酶、5 μL CaCl2·2H2O溶液,用HCl调pH为3后,加超纯水至20 mL。对照组:仅将模拟未消化中1.6 mL胃蛋白酶使用SGF电解质液等量代替。在恒温摇床37 ℃、120 r/min、避光进行胃消化,分别在1、2、3 h,取消化产物于−80 ℃冰箱灭酶。
体外模拟肠消化:将胃消化产物(20 mL)中加入11 mL SIF电解液、5 mL活力值为1000 U/mL的胰蛋白酶、4%猪胆盐2.5 mL、40 μL 0.3 mol/L CaCl2·2H2O溶液,用NaOH调pH为7后,加超纯水至40 mL。对照组:仅将模拟肠消化中肠蛋白酶和猪胆盐用7.5 mL SIF电解液代替。在恒温摇床37 ℃、120 r/min避光进行肠消化,分别在1、2、3 h,取肠消化产物于−80 ℃冰箱灭酶[14-17]。
1.2.3 模拟体外消化过程中花色苷含量和消化率的测定
采用pH示差法对消化过程中仙人掌果花色苷含量变化的测定,取两份2.0 mL的仙人掌果花色苷溶液,分别用0.025 mol/L,pH1.0氯化钾缓冲液和0.4 mol/L,pH4.5醋酸钠缓冲液定容至25 mL的容量瓶中。静置60 min,分别在535和700 nm下测定吸光值,根据公式,计算出花色苷的含量[18],公式如下:
W=A×MW×DF×Vε×L×M 式中:W为花色苷的含量,mg/g;Mw为矢车菊素-3-葡萄糖苷的摩尔质量,449.2 g/moL;A为花色苷吸光度,A=(A535pH1.0−A700pH1.0)−(A535pH4.5−A700pH4.5);DF为稀释倍数;V为定容的体积,mL;ε为矢车菊素-3-葡萄糖苷的摩尔消光系数,26900 L/(mol·cm);L为比色皿的宽度(1 cm);M为样品质量,g。
消化率的计算公式如下:
花色苷消化率(%)=已消化花色苷食入花色苷×100 1.2.4 仙人掌果实花色苷体外发酵实验
基础厌氧培养基配制[19]:酵母提取物(2.0 g)、蛋白胨(2.0 g)、NaHCO3(2.0 g)、胆汁盐(0.5 g)、L-半胱氨酸(0.5 g)、NaCl(0.1 g)、K2HPO4(0.04 g)、KH2PO4(0.04 g)、氯化血红素(0.02 g)、MgSO4·7H2O(0.01 g)、CaCl2(0.01 g)、维生素K1(10 μL)、吐温80(2.0 mL)溶于1.0 mL蒸馏水,将基础营养培养基的pH调节至7.0,121 ℃高压蒸汽灭菌15 min。
磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS)配制:氯化钠(2.0 g)、磷酸二氢钾(0.2 g)、磷酸氢二钠(2.9 g)、氯化钾(0.2 g),溶于1 L超纯水中,灭菌冷却调节pH7.4,于4 ℃冷藏备用。
试验当天取健康成年人(1男1女)(身体健康,无胃肠道疾病且近三个月未服用过抗生素)粪便,将收集好的粪便样品转入厌氧培养箱进行处理,在电子天平上称取粪便样品各10 g,与磷酸盐缓冲溶液以1:10(w/v)的比例混匀(采用一男一女得到更丰富的菌群,以构建肠道菌群模型),纱布过滤备用。在三角瓶中加入27 mL厌氧培养基,3 mL过滤的粪便悬浊液,1 mL不同浓度的花色苷溶液分为L组(低剂量5 mg/mL)、M组(中剂量10 mg/mL)、H组(高剂量15 mg/mL),K组(空白)使用等量无菌水代替花色苷溶液。于37 ℃恒温厌氧培养箱中培养24 h[19-20]。
1.2.5 气相色谱检测体外发酵后短链脂肪酸含量
前处理:将发酵24 h后的样品在条件为12000 r/min、4 ℃、5 min下离心,沉淀于冰箱保存备用。取上清液5 mL依次加入0.5 mL 50%的硫酸溶液以及5 mL乙醚,混匀旋涡振荡2 min后,于4 ℃,10000 r/min,5 min下进行离心,取上层乙醚层,过0.22 μm有机相滤膜后存于气相小瓶进行检测[21]。
气相色谱条件:色谱柱为10mDB-WAX毛细管柱,进样口温度为220 ℃,分流比为10:1,柱流量为1.5 mL/min,氮气横流,程序升温第一阶段为70 ℃,1 min;第二阶段以15 ℃/min升至160 ℃,6 min;第三阶段以30 ℃/ min升至210 ℃保持5 min,采用氢火焰检测器(FID)检测器温度为250 ℃[20-21]。
1.2.6 菌群多样性构成分析
K组、L组、M组以及H组共12例人类粪便与花色苷厌氧培养物样品中肠道微生物总DNA提取以及高通量测序委托广州基迪奥生物科技有限公司进行;采用粪便DNA试剂盒提取DNA;对目标片段16S rDNA V3~V4区域进行PCR扩增,以第一个引物中的barcode作为特异引物扩增得到目标产物;将目标片段中PCR扩增的产物经电泳检测后,切胶回收目标片段,采用荧光定量PCR扩增产物;使用AMPure XP Beads对第二轮扩增产物进行纯化,用ABI StepOnePlus RealTime PCR System(Life Technologies,产地美国)进行定量;根据Novaseq 6000的PE250模式pooling上机测序。
1.3 数据处理
采用SPSS 17.0软件对数据进行统计分析(P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义),Origin 2021进行作图。高通量测序的原始数据进行质控、过滤、去嵌合体,得到的有效数据,进行分类操作单元的划分以及系统发育学分析,菌群结构差异及差异微生物种类采用Usearch分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 模拟消化过程对花色苷含量的变化
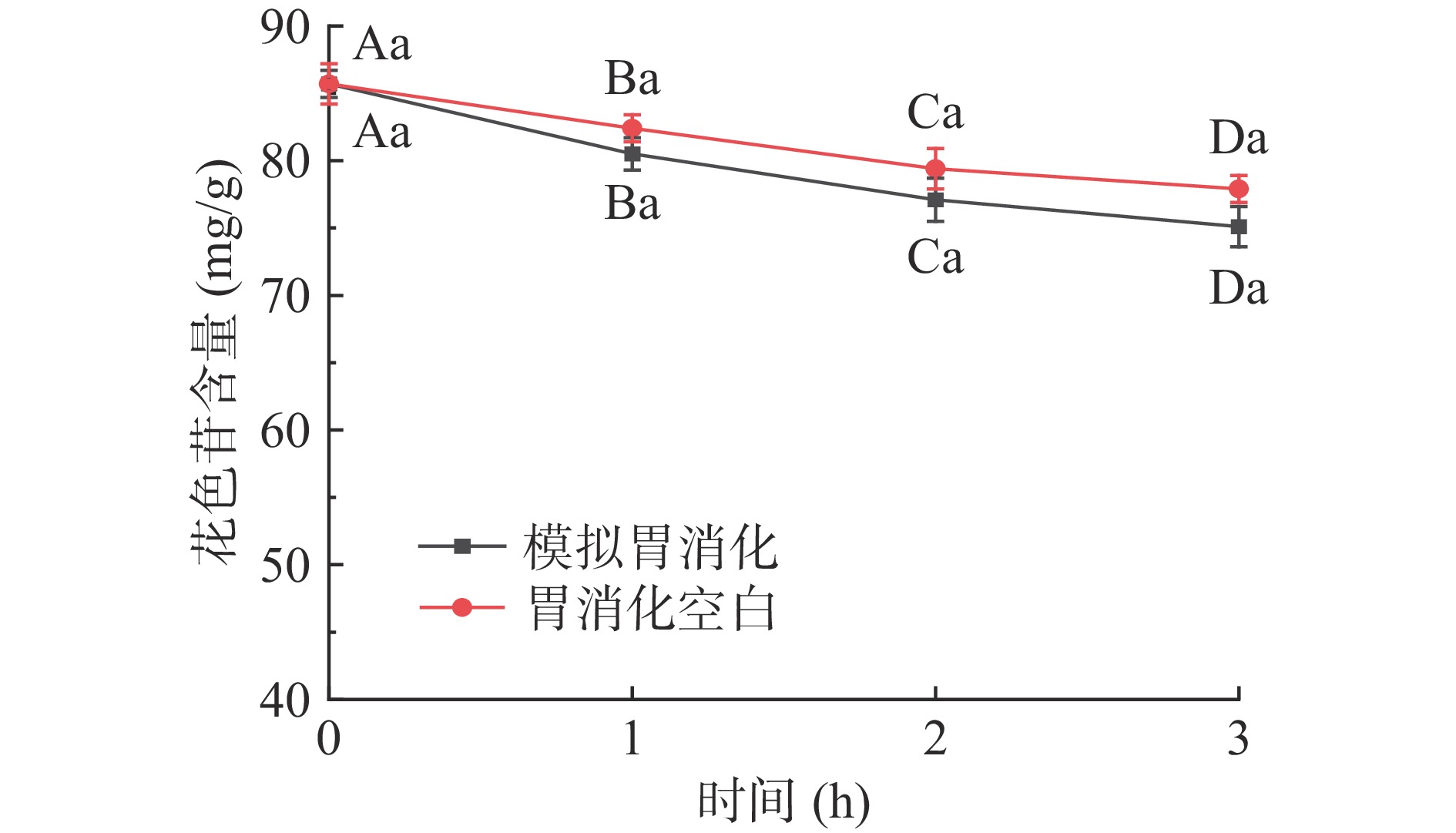
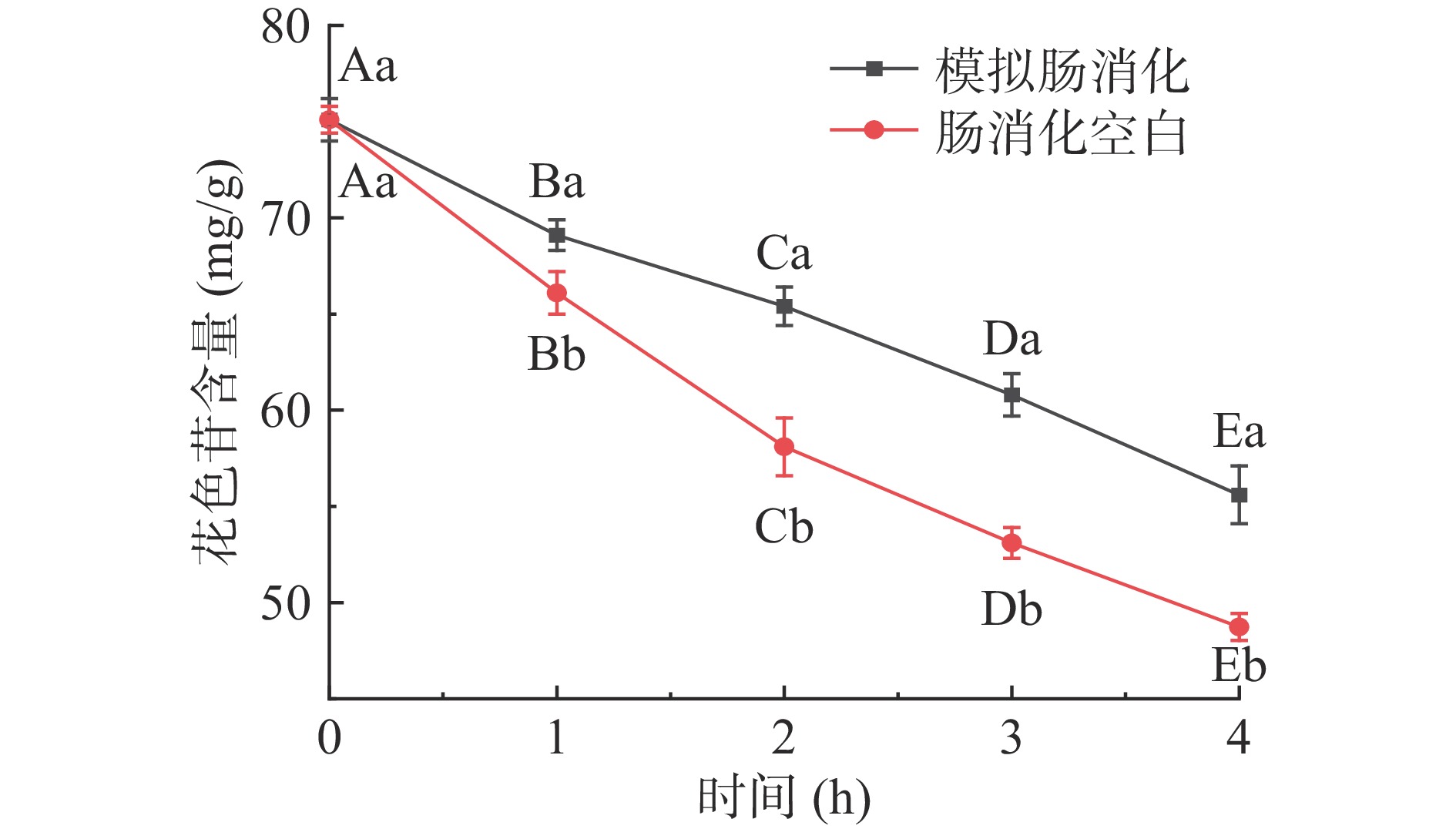
仙人掌果花色苷在模拟胃消化过程中含量的变化结果见图1。经胃消化3 h后花色苷含量与初始量相比显著下降(P<0.05),其消化率为11.4%;模拟胃消化组与胃消化空白组相比,花色苷含量稍有降低,但不具有显著性差异(P>0.05)。由于胃消化空白组未添加胃蛋白酶,因此该结果表明花色苷在消化过程中不受胃蛋白酶的影响,但受胃酸和胃液的影响较大[22]。仙人掌果花色苷在模拟肠消化过程中含量的变化结果见图2,经肠消化4 h后花色苷含量急剧下降(P<0.05),其消化率为23.5%;模拟肠消化组与肠消化空白组相比,花色苷含量具有显著性差异(P<0.05)。肠消化空白组未添加胰蛋白酶和胆盐,因此该结果表明花色苷在肠消化过程中受胆汁、胰蛋白酶的影响较大,花色苷在pH较高的肠液中不稳定,易被消化[22-23]。仙人掌果实花色苷经由胃-肠的总消化率为34.9%。绝大部分花色苷剩余,不会被上消化道消化[24]。
![]() 图 1 仙人掌果花色苷在模拟胃消化过程中含量的变化注:不同大写字母表示组内不同时间相比差异显著(P<0.05);不同小写字母表示同一时间不同组间差异显著(P<0.05);图2同。Figure 1. Changes of anthocyanins in Opuntia ficus-indica during simulated gastric digestion
图 1 仙人掌果花色苷在模拟胃消化过程中含量的变化注:不同大写字母表示组内不同时间相比差异显著(P<0.05);不同小写字母表示同一时间不同组间差异显著(P<0.05);图2同。Figure 1. Changes of anthocyanins in Opuntia ficus-indica during simulated gastric digestion2.2 气相色谱检测体外发酵后短链脂肪酸含量的变化
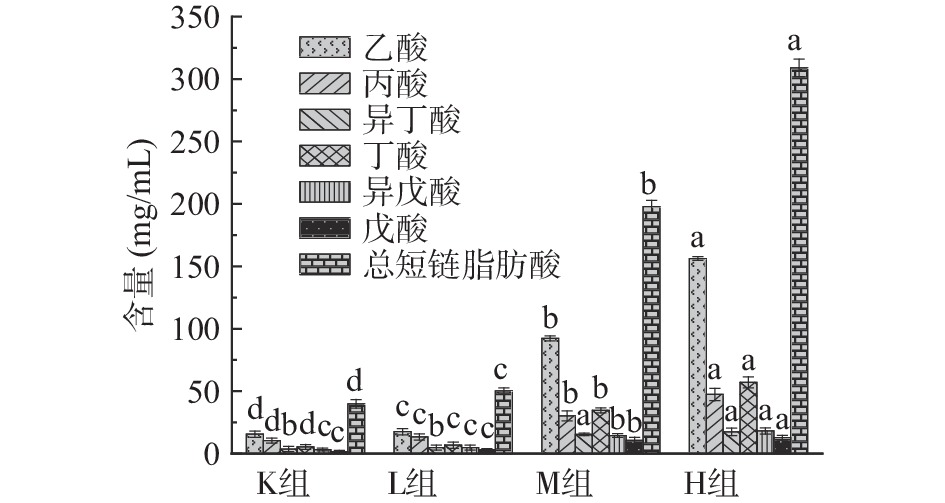
短链脂肪酸(Short chain fatty acids,SCFAs)是由肠道微生物在结肠内发酵未被消化的物质,包括碳水化合物、多糖低聚糖、膳食纤维以及其他植物营养素在肠道中获得的碳原子数为1~6个的饱和脂肪酸[25]。由图3可知与K组相比,H组、M组、L组总短链脂肪酸含量均显著升高(P<0.05),分别为K组的7.8、5.0和1.1倍。与K组相比,L组乙酸、丙酸和丁酸含量上具有显著差异性(P<0.05),分别上升1.1、1.3和1.2倍,异丁酸、异戊酸和戊酸含量无显著性差异(P>0.05)。与K组相比M组、H组均具有显著差异性(P<0.05),M组在乙酸、丙酸、丁酸、异丁酸、异戊酸和戊酸的含量均明显升高,分别为空白组的5.9、2.9、6.5、4.2、4.4和6.5倍;H组在乙酸、丙酸、丁酸、异丁酸、异戊酸和戊酸的含量均明显升高,分别为K组的10.0、4.6、10.7、4.7、5.6和7.8倍。从图3中还可知,仙人掌果实花色苷与人类粪便共培养后产生的乙酸、丙酸、丁酸其含量比较高。分析得出花色苷在一定程度上会影响短链脂肪酸的产生,拟杆菌门促进乙酸的产生,厚壁菌门促进丁酸的产生,放线菌门促进丙酸的产生[26]。随着花色苷浓度的增加短链脂肪酸含量升高,可能是由于花色苷与肠道上的微生物进行相互作用[25-27]。
2.3 体外发酵仙人掌果实花色苷对肠道菌群的影响
2.3.1 菌群Alpha多样性分析
Alpha多样性与物种数目也就是均匀度以及生态系统内的多样性两个因素有关,描述群落均匀度的指标主要包括Chao1、ACE指数,指数越小,群落均匀度低,多样性就越高;描述群落多样性的指数有Shannon、Simpson指数,指数其值越高,表明群落多样性越高。由表2所示,与K组相比L组、M组以及H组Chao1与ACE指数均显著减少(P<0.05),而Shannon指数与Simpson指数均显著增加(P<0.05)。使得肠道菌群内丰多样性的升高,表明添加花色苷会改变肠道内的菌群的多样性。
表 2 花色苷对肠道微生物群α多样性指数的影响Table 2. Effects of anthocyanins on the alpha diversity index of gut microbiota组别 Chao1 ACE Shannon Simpson K组 547.32±13.27 565.65±14.86 3.69±0.07 0.78±0.005 L组 535.33±8.15* 556.51±9.84* 4.17±0.08* 0.88±0.006* M组 511.14±0.18* 532.71±2.57* 3.84±0.06* 0.86±0.004* H组 508.01±11.64* 526.38±13.69* 3.97±0.07* 0.87±0.013* 注:*表示与空白组相比具有显著性差异,P<0.05。 2.3.2 菌群Beta多样性分析
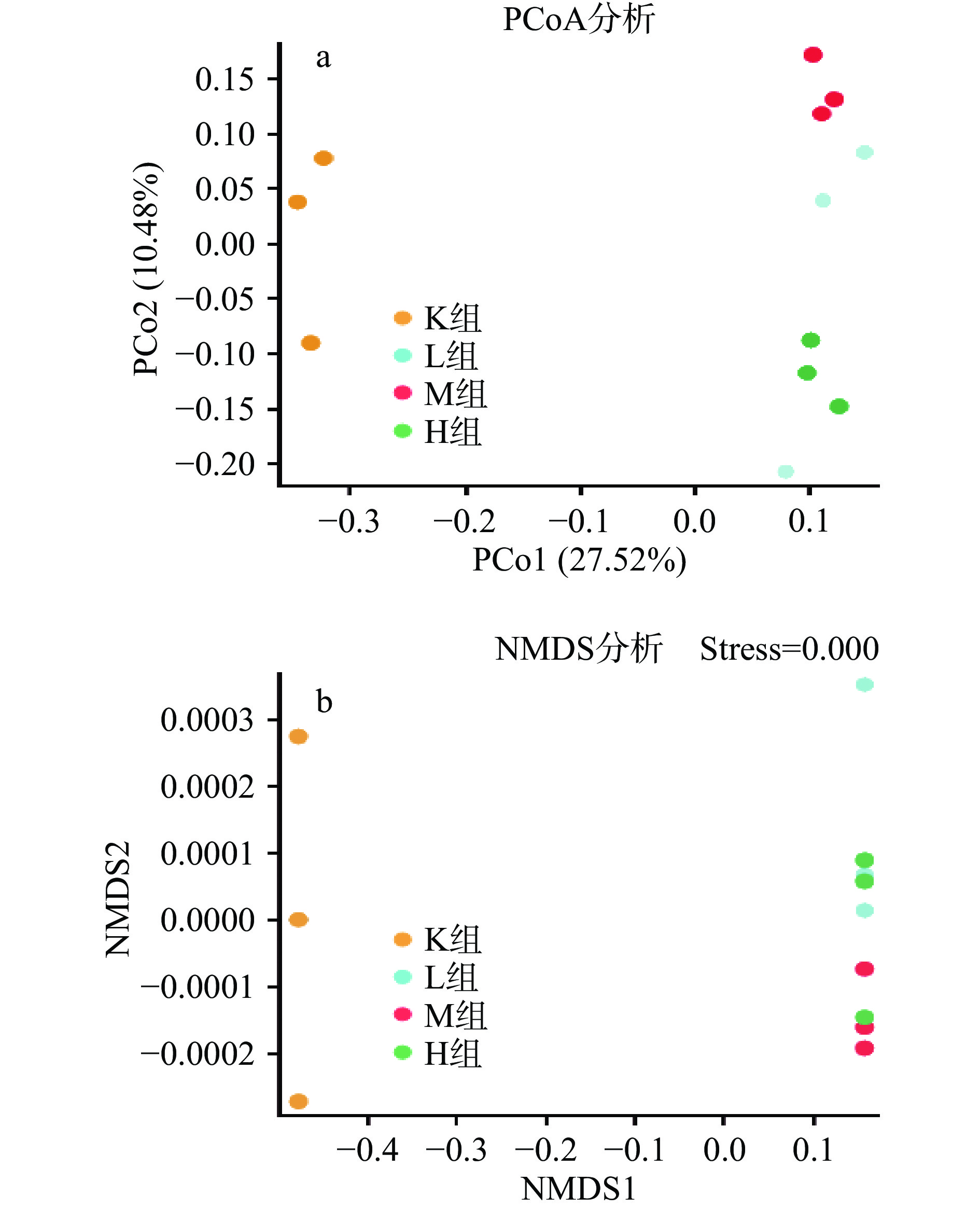
PCoA(principal co-ordinates analysis)是样本间的差异分析。每一个点代表一个样本,相同颜色的点来自同一个分组,两点之间距离越近表明两者的群落构成差异越小,距离越远,差异比例越大。由图4a可以得出,各个样本之间完全分离,说明各个样品中微生物菌落发生改变且差异明显,表明此次结果能够较好的描述样本特征,M组与K组距离最远,相似度最低,表明微生物群落相似度最低差异大,而L组与H组距离最近相似度最大,微生物群落相似度差异小。NMDS(Non-metric multidimensional scaling)由图4b可以得出应力函数值strees=0.00<0.05表明具有很好的代表性。
2.4 仙人掌果实花色苷对肠道菌群物种组成的影响
2.4.1 物种组成分析
通过四组样品每组三个样本共12个样品,这12个样品的平均测序深度为128163±3388 reads,按照97%的相似性下每个样本有476±33 OTUs,VENN图表示样品之间共有和差异物种或基因的情况,反映了各组之间共有的和特有的OTUs数目。根据图5所示L组、M组以及H组共同拥有而K组未出现的为92个OTU。L组、M组、H组以及K组共有177个OTU。K组和L组、M组、H组独特OTU分别为282、130、121、135。表明仙人掌果花色苷改变了粪便肠道微生物群的组成。
2.4.2 门水平下物种组成分析
由图6可知,各样本的肠道微生物主要有厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)、拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes)、变形菌门(Proteobacteria)、放线菌门(Actinobacteria)、疣微菌门(Verrucomicrobia)这5大门类[20-21],占样本丰富度的97%以上。其中K组变形菌门含量占比最多,添加仙人掌果实花色苷后L组、M组、H组分别显著降低43.5%、44.0%、43.4%(P<0.05),变形菌门包括绝大多数病原菌,如大肠杆菌、埃希氏菌、沙门氏菌、幽门螺旋杆菌、空肠弯曲杆菌[27]。与K组相比,L组、M组、H组的拟杆菌门增加43.5%、30.4%、28.1%,拟杆菌门促进乙酸以及异戊酸的产生,参与人体结肠中的代谢活动,通过代谢获得碳源与能量,厚壁菌门促进丁酸的产生,加花色苷组丁酸含量增多与厚壁菌门占比增加有关[8]。如图7所示,与K组相比,L组、M组以及H组厚壁菌门/拟干菌门(Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes,F/B值)的比例均显著降低74.1%、35.1%、35.5%(P<0.05),有利于减少肥胖的发生,高脂饮食、暴饮暴食会引起F/B值过高,该值越高表明发生肥胖的几率就越高,被作为肥胖的有效生物标记物[28-31]。Wu等[25]利用黄秋葵多糖进行体外发酵,发现能够降低变形菌门,增加拟杆菌门的丰富度,F/B值降低7.2%。Chen等[32]利用黑米花色苷,研究抑郁症小鼠,发拟杆菌属、厚壁菌门的水平增加,和变形菌门减少,其F/B值降低23.5%。由此可知,仙人掌果实中的花色苷的对肠道菌群的调节具有更好的作用。
2.4.3 属水平下物种组成分析
由图8可知,在仙人掌果实花色苷厌氧发酵下,K组主要有大肠杆菌志贺属(Escherichia-Shigella)、链型杆菌属(Catenibacterium)、脱硫弧菌属(Desulfovibrio)占比较多。而在加入花色苷后,则以普氏菌属(Prevotella)、光冈菌属(Mitsuokella)、乳酸杆菌属(Lactobacillus)、双歧杆菌属(Bifidobacterium)为主。
从图9中可以得到,与K组相比,L组、M组以及H组大肠杆菌志贺属占比显著下降41.0%、41.2%、41.1%(P<0.05),但L组、M组以及H组之间变化差异不大,大肠杆菌志贺属中存在着很多已发现的病原体,会引起肠道炎症等,对人体肠道菌群危害很大[33-34]。脱硫弧菌属也被称为硫酸盐还原菌(SRB)属于变形菌门。这类细菌可以“呼吸”硫酸盐而不是氧气。由于硫化氢(H2S)的产生,SRB被认为会对肠道上皮细胞具产生毒性,导致胃肠道疾病[35-36],与K组相比,L组、M组以及H组脱硫弧菌占比显著下降18.9%、19.6%以及19.9%(P<0.05),花色苷可能通过破坏细菌细胞膜/细胞壁,促进其裂解死亡,从而抑制致病菌的生长。
与K相比,L组、M组以及H组普氏菌属占比显著上升24.1%、40.7%、38.2%(P<0.05),普氏菌属存在于人类中,帮助分解蛋白质和碳水化合物食物,可以参与合成多种维生素,促进人体健康[26,37-38]。与K相比,L组、M组以及H组乳酸杆菌属和双歧杆菌属的总含量增加(P<0.05),分别增加了4.6%、5.8%、12.88%,L组、M组以及H组之间变化呈梯度增加,乳酸杆菌与双歧杆菌作为公认的益生菌,可以使肠道微生物维持稳定状态,乳酸杆菌属可利用精氨酸生产L-鸟氨酸,促进肠粘膜形成,调节肠道粘膜稳态[39-42]。与K组相比,L组、M组以及H组光冈菌属均增加,分别增加了36.0%、27.7%、27.2%(P<0.05),而光冈菌属丰富度的增加,能提高机体发酵碳水化合物、多糖的能力,对于减轻肥胖有很大益处[27,41]。
3. 结论
仙人掌果实花色苷在在模拟体外消化过程中,经胃部少量消化,在肠中大量消化,经过胃-肠的消化率34.9%,最终65.1%到达大肠。表明大部分的仙人掌果实花色苷,不会被人体消化,可能抵达大肠被肠道菌群所利用。
在体外厌氧发酵24 h后,仙人掌果实花色苷促使乙酸、丙酸、异丁酸、丁酸、异戊酸和戊酸六种短链脂肪酸含量显著上升(P<0.05),呈现剂量关系,其中仙人掌果实花色苷对乙酸、丙酸、丁酸的促进作用最为明显。表明添加仙人掌果实花色苷能够增加短链脂肪酸的产生,可能是使肠道菌群发生改变,从而促进了该短链脂肪酸产生菌的生长。
仙人掌果实花色苷干预可以改变肠道微生物群的多样性和组成。在门水平上,主要是减少了变形菌门,增加了拟杆菌门、厚壁菌门以及放线菌门的增长。在属水平上,增加了普氏菌属、乳酸杆菌属、双歧杆菌属、光冈菌属等肠道有益菌的相对丰度,降低了大肠埃希菌和脱硫弧菌属肠道有害菌的相对丰度。因此,仙人掌果实花色苷能够调节肠道微生物的组成与多样性,抑制有害菌,促进有益菌生长。仙人掌果实花色苷具有促进肠道健康的潜力,可以作为益生元进行探索。
-
图 1 仙人掌果花色苷在模拟胃消化过程中含量的变化
注:不同大写字母表示组内不同时间相比差异显著(P<0.05);不同小写字母表示同一时间不同组间差异显著(P<0.05);图2同。
Figure 1. Changes of anthocyanins in Opuntia ficus-indica during simulated gastric digestion
表 1 消化电解质液原液的配制
Table 1 Configuration of digestive juice
成分 基础液(g/L) SSF SGF SIF 基础液中吸取(mL)
pH7基础液中吸取(mL)
pH3基础液中吸取(mL)
pH7KCl 37.3 15.1 6.9 6.8 KH2PO4 68 3.7 0.9 0.8 NaHCO3 84 6.8 12.5 42.5 NaCl 117 − 11.8 9.6 MgCl2(H2O)6 30.5 0.5 0.4 1.1 (NH4)2CO3 48 0.06 0.5 − 表 2 花色苷对肠道微生物群α多样性指数的影响
Table 2 Effects of anthocyanins on the alpha diversity index of gut microbiota
组别 Chao1 ACE Shannon Simpson K组 547.32±13.27 565.65±14.86 3.69±0.07 0.78±0.005 L组 535.33±8.15* 556.51±9.84* 4.17±0.08* 0.88±0.006* M组 511.14±0.18* 532.71±2.57* 3.84±0.06* 0.86±0.004* H组 508.01±11.64* 526.38±13.69* 3.97±0.07* 0.87±0.013* 注:*表示与空白组相比具有显著性差异,P<0.05。 -
[1] 陈曦, 仝争, 王渝, 等. 花色苷的功能及其稳态化保持技术研究进展[J]. 农产品加工,2021(22):57−60. [CHEN X, TONG ZH, WANG Y, et al. Research progress of the health function of anthocyanins and its stable maintenance technology[J]. Farm Products Processing,2021(22):57−60. [2] BLESSO C N. Dietary anthocyanins and human health[J]. Nutrients,2019,11(9):2107−2112. doi: 10.3390/nu11092107
[3] KALT W, CASSIDY A, HOWARD L R, et al. Recent research on the health benefits of blueberries and their anthocyanins[J]. Advances in Nutrition,2019,11(5):224−236.
[4] LIU X, SHI J, YI J, et al. The effect of in vitro simulated gastrointestinal digestion on phenolic bioaccessibility and bioactivities of Prinsepia utilis Royle fruits[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2020,138(1):110782.
[5] 杨平. 花色苷与肠道微生物的相互作用[C]//2017第十届国际葡萄与葡萄酒学术研讨会论文集[A]. 宁夏: 中国食品工业协会, 2017: 231-243. YANG P. Interaction of anthocyanins with gut microbes[C]//Proceedings of the 10th International Symposium on Vine and Wine 2017[A]. Ningxia: CNFIA, 2017: 231-243.
[6] WU T, TANG Q, GAO Z, et al. Blueberry and mulberry juice prevent obesity development in C57BL/6 mice[J]. PLoS One,2013,8(10):77585−77592. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077585
[7] NORBERTO S, SILVA S, MEIRELES M, et al. Blueberry anthocyanins in health promotion: A metabolic overview[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2013,5(4):1518−1528. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2013.08.015
[8] GOWD V, TAO B, WEI C, et al. Antioxidant potential and phenolic profile of blackberry anthocyanin extract followed by human gut microbiota fermentation[J]. Food Research International,2019,120(1):523−533.
[9] WALUJKAR S A, DHOTRE D P, MARATHE N P, et al. Characterization of bacterial community shift in human ulcerative colitis patients revealed by Illumina based 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing[J]. Gut Pathogens,2014,6(22):22.
[10] LINGMIN T, YISHA T, CHEN G W, et al. Metabolism of anthocyanins and consequent effects on the gut microbiota[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2018,42(19):102−110.
[11] 苟莎, 曹洁, 万千帆, 等. 仙人掌果的综合开发利用研究进展[J]. 现代食品,2021(22):37−39. [GOU S, CAO J, WANG Q F, et al. Progress in comprehensive development and utilization of cacti fruit[J]. Modern Food,2021(22):37−39. doi: 10.16736/j.cnki.cn41-1434/ts.2021.22.010 [12] 吉雪慧, 张筠, 刘术明, 等. 响应面法优化仙人掌果花色苷的提取工艺[J]. 食品研究与开发,2018,39(18):77−82. [JI X H, ZHANG Y, LIU S M, et al. Optimization of extraction process of anthocyanins from cactus fruit by response surface methodology[J]. Food Research and Development,2018,39(18):77−82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2018.18.014 [13] MINEKUS M, AIMINGERl M, ALVITOl P, et al. A standardised static in vitro digestion method suitable for food-an international consensus[J]. Food & Function,2014,5(6):1113−1124.
[14] 刘楚. 山竹果皮中原花青素经体外消化后抗氧化性及对肠道菌群影响的研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江工商大学, 2020. LIU C. Antioxidative activity of proanthocyanidins in mangosteen peel after digestion in vitro and its effect on intestinal flora[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Gongshang University, 2020.
[15] 周笑犁, 吴珊珊, 林栋, 等. 体外模拟消化对蓝莓皮渣粗提物抗氧化成分及其活性的影响[J]. 食品研究与开发,2018,39(4):26−32. [ZHOU X L, WU S S, LIN D, et al. Effects of simulated digestion in vitro on antioxidant components and activity of crude extract from blueberry peel residue[J]. Food Research and Development,2018,39(4):26−32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2018.04.005 [16] WANG Y, BIN L I, MWNG X, et al. Effect of in vitro simulated digestion on anthocyanin composition and antioxidant activity of Lonicera caerulea berry extracts[J]. Food Science,2016,37(19):100−105.
[17] FLORES F P, SINGHh R K, KERR W L, et al. Total phenolics content and antioxidant capacities of microencapsulated blueberry anthocyanins during in vitro digestion[J]. Food Chemistry,2014,153(15):272−278.
[18] 高霄. 黑提过渣中花色苷提取、纯化、微胶囊化的研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江工商大学, 2017. GAO X. Study on extraction, purification and microencapsulation of anthocyanins from black tea residue[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Gongshang University, 2017.
[19] VEMANA G, TAO B, CHEN W, et al. Antioxidant potential and phenolic profile of blackberry anthocyanin extract followed by human gut microbiota fermentation[J]. Food Research International,2019,11(23):121−127.
[20] ROCIO G B, EDWARDS C A, CROZIER A, et al. Colonic catabolism of ellagitannins, ellagic acid, and raspberry anthocyanins: In vivo and in vitro studies[J]. Drug Metabolism & Disposition the Biological Fate of Chemicals,2011,39(9):1680−1688.
[21] 贾益群, 叶福媛, 王双, 等. 生物样品中短链脂肪酸的快速提取与分析方法[J]. 实验室研究与探索,2012,31(7):262−264. [JIA Y Q, YE F Y, WANG S, et al. Rapid extraction and analysis of short-chain fatty acids in biological samples[J]. Research and Exploration in Laboratory,2012,31(7):262−264. [22] DOUGALL G, DOBSON P, SMITH P, et al. Assessing potential bioavailability of raspberry anthocyanins using an in vitro digestion system[J]. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry,2005,53:5896−5904. doi: 10.1021/jf050131p
[23] MOHANNED M S. 微胶囊对红树莓花色苷的稳定性、特性、体外消化特性和相互作用方式的影响[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2020 MOHANNED M S. Effects of microcapsules on the stability, characteristics, in vitro digestibility and interaction mode of anthocyanins from red raspberry[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2020.
[24] TAKANORI T. Anthocyanins as functional food factors-chemistry, nutrition and health promotion[J]. Food Science & Technology Research,2018,12(3):315−324.
[25] WU D T, NIE X R, GAN R Y, et al. In vitro digestion and fecal fermentation behaviors of a pectic polysaccharide from okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) and its impacts on human gut microbiota[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2020,114(3):106577.
[26] 郭慧慧, 黄帅, 王璐璐, 等. 肠道菌群对机体营养物质的代谢研究[J]. 中国医药生物技术,2016(4):6. [GUO H H, HUANG S, WANG L L, et al. Study on metabolism of nutrients by intestinal flora[J]. China Med Bioteenol,2016(4):6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-713X.2016.04.010 [27] HAN F, WANG Y, HAN Y, et al. Effects of whole-grain rice and wheat on composition of gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acids in rats[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2018,66(25):6326−6335. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b01891
[28] ZHENG G, DENG J, WEN L, et al. Release of phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity of Chinese hawthorn “Crataegus pinnatifida” during in vitro digestion[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2018,40:76−85. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2017.10.039
[29] 龚梦鹃, 李春苑, 巫圣乾, 等. 16S rRNA高通量测序研究藿香正气口服液对湿困脾胃证大鼠肠道菌群的影响[J]. 中药新药与临床药理,2019,30(4):7−11. [GONG M J, LI C Y, WU S Q, et al. 16S rRNA high-throughput sequencing to study the effect of Huoxiangzhengqi oral liquid on intestinal flora in rats with dampness trapped in the spleen and stomach syndrome[J]. Traditional Chinese Drug Research and Clinical Pharmacology,2019,30(4):7−11. [30] LIU L, WANG Q, WU X, et al. Vancomycin exposure caused opportunistic pathogens bloom in intestinal microbiome by simulator of the human intestinal microbial ecosystem (SHIME)[J]. Environmental Pollution,2020,265:114399. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114399
[31] TURNBAUGH P J, LEY R E, MAHOWALD M A, et al. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest[J]. Nature,2006,444(7122):1027−1031. doi: 10.1038/nature05414
[32] CHEN Z, CHEN X, ZHAI Y, et al. Effects of black rice anthocyanins on the behavior and intestinal microbiota of mice with chronic unpredictable mild stress[J]. IOP Conference Series:Earth and Environmental Science,2021,792(1):012005. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/792/1/012005
[33] DE F C, CAVALIERI D, DI P M, et al. Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2010,107(33):14691−14696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1005963107
[34] WANG L, LIU L, LIU X, et al. The gut microbes, Enterococcus and Escherichia-Shigella, affect the responses of heart valve replacement patients to the anticoagulant warfarin[J]. Pharmacological Research,2020,159(22):104979.
[35] LLOYD J R, THOMAS G H, FINLAY J A, et al. Microbial reduction of technetium by Escherichia coli and Desulfovibrio desulfuricans: Enhancement via the use of high-activity strains and effect of process parameters[J]. Biotechnology & Bioengineering,2015,66(2):122−130.
[36] SAWIN E A, WOLFE T, AKTAS B, et al. Glycomacropeptide is a prebiotic that reduces Desulfovibrio bacteria, increases cecal short-chain fatty acids, and is anti-inflammatory in mice[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol,2015,309(7):590−601. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00211.2015
[37] QI H, LI Y, YUN H, et al. Lactobacillus maintains healthy gut mucosa by producing L-Ornithine[J]. Communications Biology,2019,2(1):1667−1679.
[38] KONG Q, ZHANG R, YOU L, et al. In vitro fermentation characteristics of polysaccharide from Sargassum fusiforme and its modulation effects on gut microbiota[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2021,151(20):112145.
[39] 柳岩. 茶叶提取物通过调节肠道微生物缓解葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的小鼠结肠炎症[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2020. LIU Y. Tea extract alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colonic inflammation in mice by modulating gut microbes[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2020.
[40] MOREMI N, OTHMAN A S, MSAKI B P, et al. Prevalence and antimicrobial sensitivity of Shiga-toxin-producing Escherichia coli among underfives presenting with diarrhoea at hospitals in Mwanza City, Tanzania[J]. Tanzania Journal of Health Research,2017,19(1):143−152.
[41] PALMAS V, PISANU S, MADAU V, et al. Gut microbiota markers associated with obesity and overweight in Italian adults[J]. Scientific Reports,2021,11(1):5532−5539. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84928-w
[42] PRESTI I, DORAZIO G, LABRA M, et al. Evaluation of the probiotic properties of new Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains and their in vitro effect[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2015,99(13):5613−5620. doi: 10.1007/s00253-015-6482-8
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 杜康,花扬扬,魏帅飞,王婷婷,曲冠男,赵猛,蔡红星. 基于内标法的低质量浓度葡萄糖溶液拉曼测定研究. 光学学报(网络版). 2024(05): 4-10 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 韩春然,岳振歌,遇世友,王鑫,张丝瑶. 检测葡萄糖的Ni基电化学传感器研究进展. 食品工业科技. 2023(14): 482-489 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:







 下载:
下载:



