Microbial Diversity Analysis of Sufu from Different Origins Based on High-throughput Sequencing
-
摘要: 为了解我国不同产地及风味腐乳中微生物的多样性。本研究基于高通量测序(high throughput sequencing,HTS)技术,对16种不同产地的腐乳样品中的微生物群落的多样性和差异性展开分析研究。细菌多样性结果显示,在属水平上,腐乳中含量最丰富的是芽孢杆菌属(Bacillus)和乳酸菌属(Lactobacillus),这两个属也分别代表了腐乳发酵后期的优势菌群;真菌多样性结果显示,腐乳中含有大量曲霉属(Aspergillus)和放射毛霉属(Actinmucor sp.)等水解酶产生菌;化学成分测定结果显示,不同产地对于腐乳中的化学成分具有一定的影响,腐乳中可溶性蛋白含量以及氨基氮含量与样品中的芽孢杆菌分布呈现正相关;主坐标分析结果显示,16种产地的腐乳样品中的真菌菌群结构与地区存在一定的聚类关系,具体表现为中国东部地区的真菌(ZJ2、ZJ4、ZJ5、ZJ6、SH9、AH11和JX12)可以归为一组,说明腐乳的真菌群落可能受地理因素的影响。本研究加深了对腐乳中微生物群落多样性的了解,为提高传统发酵调味品的品质提供理论支持。Abstract: To learn about the diversity of microorganisms in different flavor sufu from different origins in China. Based on high throughput sequencing (HTS), the microbial diversity differences and chemical properties of 16 sufu samples from different origins in China were analyzed in this study. The results of bacterial diversity showed that the most abundant bacteria in sufu were Lactobacillus sp and Bacillus sp, which also represented the dominant bacterial communities in different stages of sufu fermentation. The results of fungal diversity showed that sufu contained a large number of Aspergillus, Actinmucor sp. and other hydrolase producing bacteria. The results of chemical composition determination showed that different origins had certain influence on the chemical composition of sufu. The soluble protein content and amino nitrogen content in curd showed positive correlation with the distribution of Bacillus in the samples. The results of principal coordinate analysis showed that the fungal consortium structure in sufu samples from 16 origins had certain clustering relationship with regions, specifically the fungi from eastern China (ZJ2, ZJ4, ZJ5, ZJ6, SH9, AH11 and JX12) could be grouped together, which stated that the fungal consortium of sufu may be influenced by geographical factors. This study deepened the understanding of microbial community diversity in sufu and would provide theoretical support for the quality improvement of traditional fermented condiments.
-
腐乳,又称为“东方奶酪”,是我国一种传统的发酵豆制品,它起源于我国大约两千年前的魏朝,因其独特的营养和功能成分、芳香和风味特性而被国人广泛用作调味品和开胃菜[1]。经过微生物发酵后的腐乳以其低胆固醇、高蛋白和高钙等营养特点而被人们认为是一种健康食品。根据参与发酵的微生物类型不同,可将腐乳分为细菌发酵、霉菌发酵和自然发酵等三种类型。其中,以放线菌、毛霉和根霉为发酵剂的霉菌发酵法最为普遍[2]。
腐乳中的微生物可代谢合成产生多种风味物质,其群落构成在调节腐乳产品风味方面发挥着重要作用,被认为是决定腐乳最终质量的关键因素[3-5]。腐乳发酵前期,葡萄球菌属、明串珠菌属和毛霉属占据了优势,其酶系分泌活跃,使得产品中谷氨酸、缬氨酸、苯丙氨酸和亮氨酸等含量有较大幅度增长,苯丙氨酸和亮氨酸可进一步形成醇类化合物,这些醇类化合物可和霉菌分泌的脂肪酶降解豆腐中粗脂肪所产生的脂肪酸以及细菌代谢产生的乙酸、乳酸等发生酯化反应,进而产生乳酸乙酯、乙酸乙酯等风味物质[6]。芽孢杆菌属和假单胞菌属也可分解蛋白和脂肪,在腐乳后发酵阶段产生醇类、酯类和吡嗪类等风味物质;这些微生物通过合成代谢产生各种风味物质。不同的微生物组成受其产地的环境群落及气候特点等多种因素的影响,这导致不同产地的腐乳中微生物群落存在复杂多样的差异[7]。因此,阐明腐乳发酵过程中微生物的组成及其与食品性质的关系,并在此基础上对腐乳发酵进行合理的菌群设计是进一步提高腐乳发酵质量的必要条件。当前,有许多研究使用纯培养技术来揭示腐乳中的优势菌群,但这种技术受限于纯培养,对于含量较低、没有菌株分离、培养和鉴定过程的情况无法对腐乳中的整体微生物概况进行全面分析[8]。
近年来,随着测序技术的不断发展,高通量测序(high-throughput sequencing,HTS)作为新一代测序技术以其价格低廉、可读量大等优点被广泛用于探索各种豆豉、醋和米酒等生态系统中微生物的多样性,徐琼等[9]采用高通量测序技术分析不同地区红腐乳的细菌多样性,然而关于腐乳细菌及真菌的微生物群落同其产地和化学成分之间关系的研究还鲜见报道。
基于此,本研究以我国东部、南部和北部等不同地区所产的16种腐乳为研究对象,采用高通量测序(high-throughput sequencing,HTS)技术对腐乳中的细菌16S rRNA基因和真菌内部转录间隔区2(ITS2)基因进行测序,并针对腐乳中微生物多样性、关键微生物种属与腐乳化学性质、区域分布和调味处理的相关性展开研究,以期为提高传统发酵调味品的品质提供理论支持。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
16种腐乳样品 通过京东、淘宝等线上平台购自国内华东、华南和华北地区,具体编号、品牌、产地及调味方式如表1所示;实验中所用试剂 均购自郑州优吉生物科技有限公司,所有试剂纯度均为分析纯;磁珠法通用型基因组DNA提取试剂盒(DP705) 天根生化科技有限公司。
表 1 腐乳16种样品的产地信息Table 1. Origin information of 16 sufu samples产品编号 品牌 产地 调味方式 地域 ZJ1 **香酥玫瑰豆腐乳 浙江 花香 华东 ZJ2 **糟方豆腐乳 浙江 酒香 华东 ZJ4 **玫瑰腐乳 浙江 花香 华东 ZJ5 **玫瑰腐乳 浙江 花香 华东 ZJ6 **香酥红方腐乳 浙江 酒香 华东 SH8 **红腐乳 上海 酒香 华东 SH9 **玫瑰腐乳 上海 花香 华东 AH11 **五香腐乳 安徽 酒香 华东 JX12 **辣豆乳 江西 香辛 华东 GD14 **微辣腐乳 广东 香辛 华南 GL15 **豆腐乳 桂林 酒香 华南 GZ16 **红油腐乳 贵州 香辛 华南 JL17 **红腐乳 吉林 酒香 华北 BJ18 **红方大块腐乳 北京 香辛 华北 BJ19 **玫瑰腐乳 北京 花香 华北 BJ20 **糟方腐乳 北京 酒香 华北 注:**表示不同的产品品牌名称未显示。 欧莱博9830凯氏定氮仪 济南欧莱博科技有限公司;TGL-16M台式高速冷冻离心机 上海卢湘仪离心机有限公司;Sub-Cell GT电泳仪 美国伯乐;NanoPhotometer N60分光光度计 德国implen;Gene Amp 9700PCR仪 成都东胜科创;GelSMART凝胶成像仪 北京海鹏翔;Illumina Miseq高通量测序平台 上海派森诺生物科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 DNA提取和高通量测序
1.2.1.1 DNA提取
从16种不同的腐乳产品中各取1.0 g腐乳样品,使用基因组DNA提取试剂盒进行基因组DNA的提取和纯化。参考余巨全等[10]的方法,对所得到的基因组DNA进行纯度和浓度检测。吸取1.0 μL的DNA将其加至分光光度计中以检测所得基因组DNA中A260与A280的比值,以检测所得DNA的纯度;吸取2.5 μL的DNA将其加至1%的琼脂糖凝胶中,并将所得结果置于凝胶成像系统下进行成像以检测所得DNA的浓度。
1.2.1.2 PCR扩增
针对细菌16S rDNA基因的V3和V4区域合成带barcode的引物338F 5'-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3'、806R 5'-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3',针对真菌rRNA ITS2的保守序列合成带barcode的引物5'-TCCGTAGGTGGAACCTGCGG-3'、5'-TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC-3'。以所提取的DNA为模板,使用Gene Amp 9700PCR仪进行PCR扩增,PCR扩增体系:基因组模板DNA 2 μL,5×PCR Master Mix 5 μL,正反引物各0.5 μL,用双蒸水补足至25 μL。细菌PCR扩增条件:94 ℃预处理3 min;30循环(94 ℃变性25 s,56 ℃退火40 s,72 ℃延伸40 s),72 ℃延伸5 min。真菌PCR扩增条件:94 ℃预处理3 min;32循环(94 ℃变性30 s,56 ℃退火35 s,72 ℃延伸40 s),72 ℃延伸5 min。用0.01 g/mL琼脂糖凝胶电泳进行检测扩增出的PCR产物并使用PCR产物纯化试剂盒纯化回收PCR产物,而后使用Illumina Miseq进行高通量测序。
1.2.2 腐乳样品的化学成分测定
1.2.2.1 样品处理
取腐乳样品20 g并将其分别置于研钵中,用杵磨成糊状,然后用80 mL去离子水在60 ℃下溶解。将混合物轻轻搅拌并煮沸,然后转入200 mL的容量瓶中,用水稀释至总体积200 mL。将制备好的腐乳悬浮液过滤,取滤液进行化学成分的测定。
1.2.2.2 氨基酸态氮含量的测定
以蒸馏水为空白对照,吸取10 mL的样品滤液,将其加入盛有90 mL蒸馏水的三角瓶(250 mL)中,将其充分混匀后,再加入10 mL的甲醛溶液(浓度为0.36 g/mL),用浓度为0.05 mol/L的氢氧化钠溶液进行滴定,直至pH为9.2,通过计算氢氧化钠溶液的消耗量来计算腐乳样品中的氨基氮含量[11]。
1.2.2.3 水溶性蛋白质含量的测定
以蒸馏水为空白对照,吸取10 mL的样品滤液,将其加入盛有50 mL蒸馏水的三角瓶(150 mL)中,充分混匀后100 ℃水浴加热10 min,待温度降至室温后将其转入容量瓶(100 mL)中,参照GB 5009.5-2016中的第一法进行水溶性蛋白质的测定,其中蛋白质的换算系数为5.71[12]。
1.3 数据处理
用测序数据质控软件Trimmomatic对原始FASTQ文件进行质量控制。使用UPARSE7.1软件(http://drive5.com/uparse/)对操作分类单元(operational taxonomic unit,OTUs)进行预聚类,其序列一致性截断率为97%。真菌ITS和细菌16S rRNA的所有操作分类单元均采用核糖体数据库程序(RDP)分类器(http://rdp.cme.msu.edu/)对Silva(SSU128)数据库进行分类,置信阈值为70%。
使用美吉生物云平台的(www.majorbio.com)的免费在线平台对所获序列进行生信统计分析。使用QIIME(Quantitative Insights Into Microbial Ecology)的α多样性模块对样品中Shannon、Simpson、Coverage和Chao1指数进行alpha多样性统计与分析,其中Shannon指数和Simpson指数代表样品中的菌落多样性,coverage代表样品文库的覆盖率、Chao1指数代表菌落丰度。使用Mann-Whitney检验对样本间各操作分类单元(OTU)相对丰度进行统计差异分析,P<0.05表示差异显著。使用Majorbio Cloud platform(www.majorbio.com)的免费在线平台进行主坐标分析(Principal coordinate analysis,PCoA)和层次聚类分析(Hierarchical Cluster Analysis,HCA)。最后使用R语言进行微生物群落组成与腐乳化学成分之间的典范对应分析(Canonical correspondence analysis,CCA)和冗余分析(Redundancy analysis,RDA)。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 腐乳样品的文库构建及测序数据分析
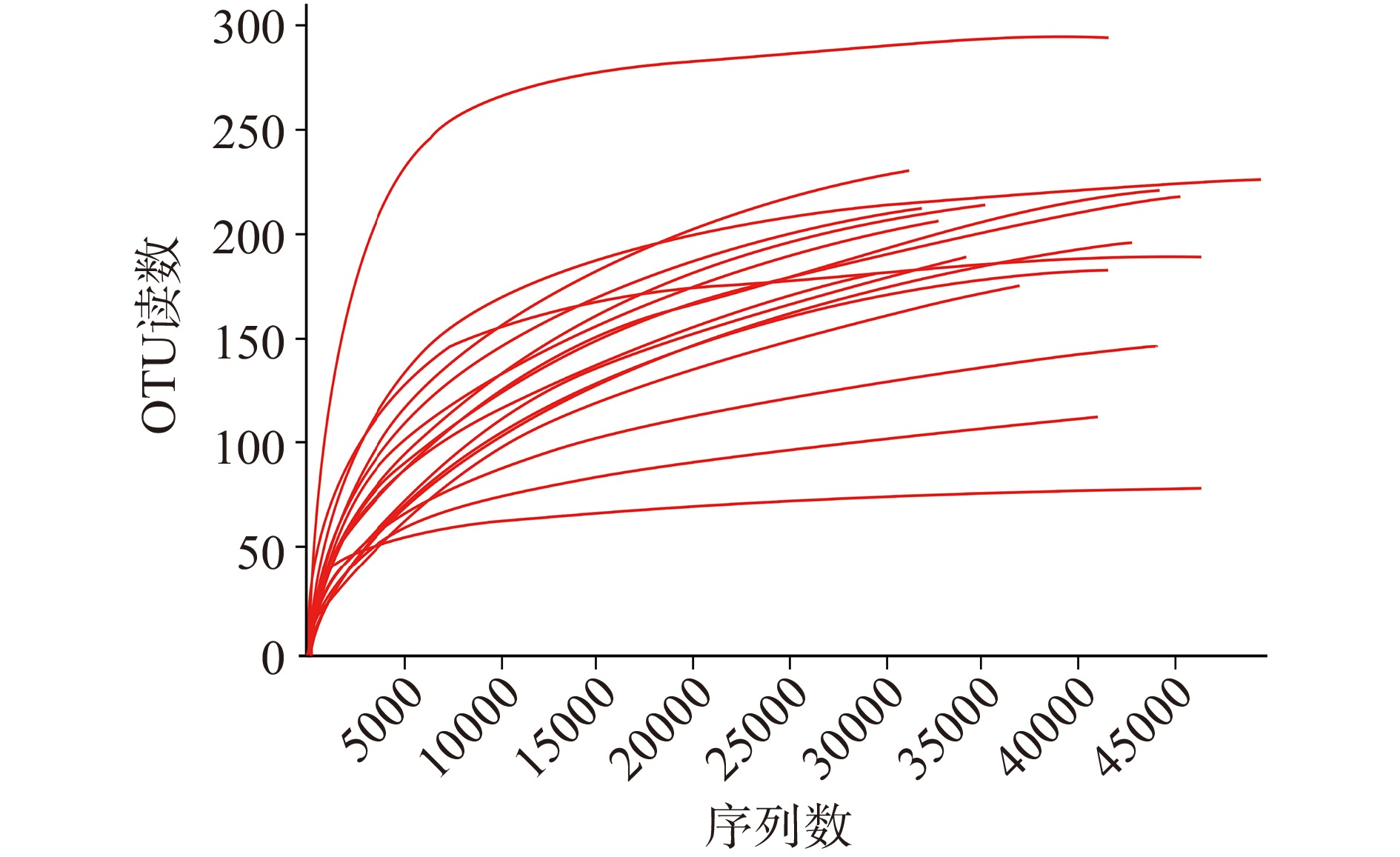
使用高通量测序技术,对来自不同地区的16份腐乳样品进行微生物多样性分析。共获得1032656个真菌群落的读数(OTU范围从22到239)以及689359个细菌群落的读数(OTU范围从68到289),样品中真菌ITS和细菌16S rRNA序列的覆盖度均大于99.90%,具有较好的微生物群落代表性。对所得样本序列进行随机取样,将抽到的样本序列与其代表的OTU数目构建稀释曲线,并以此来对测序数据量的合理性予以说明。所得结果如图1所示,由图1可知,16个腐乳样本的稀释曲线均趋于平缓,说明测序数据量合理,文库构建合理,测序深度可较好地反映微生物群落的信息[13]。
2.2 腐乳样品的真菌多样性分析
α多样性分析可反映测序样本中微生物群落的物种丰度和多样性,本研究采用ACE、Chao1、Shannon指数、Simpson指数对对腐乳样本中的真菌α-多样性进行评价,所得结果如表2及图2~图3所示。
表 2 16种腐乳样品中真菌的α多样性分析Table 2. α diversity analysis of fungi in 16 sofu samples编号 ACE值 Chao1值 Shannon值 Simpson值 覆盖率(%) ZJ1 165.677 167.000 2.583 0.268 99.994 ZJ2 62.029 61.333 2.863 0.139 99.997 ZJ4 67.813 65.000 2.470 0.192 99.991 ZJ5 81.609 81.500 2.748 0.147 99.998 ZJ6 62.392 42.000 2.183 0.231 99.993 SH8 46.035 45.333 0.710 0.706 99.997 SH9 62.441 62.000 2.706 0.166 99.999 AH11 46.410 45.500 2.307 0.207 99.997 JX12 102.523 102.500 3.232 0.101 99.995 GD14 180.480 179.500 3.810 0.054 99.995 GL15 139.440 139.500 2.386 0.245 99.997 GZ16 96.795 95.000 3.322 0.089 99.992 JL17 117.212 115.000 2.514 0.238 99.994 BJ18 246.280 242.667 4.231 0.046 99.989 BJ19 27.057 25.667 0.819 0.557 99.993 BJ20 207.013 203.000 3.286 0.113 99.970 其中,表2中的ACE指数和Chao1指数代表的是样本中微生物菌落的丰度,Shannon指数和Simpson指数代表的是样本中微生物菌落的多样性,但具体代表的值有所差别。Shannon指数值越大,代表微生物群落的多样性越高;Simpson指数越大,却代表微生物群落多样性越低。Coverage指的是所测样本文库的覆盖率,其数值的高低反映了所得到的测序结果是否完全代表样本的微生物群落[9]。从表2中可看到,所有样本的覆盖率均大于99%,说明文库的覆盖率基本涵盖样本中所有序列,本次测序结果可以代表样本中微生物的真实情况。
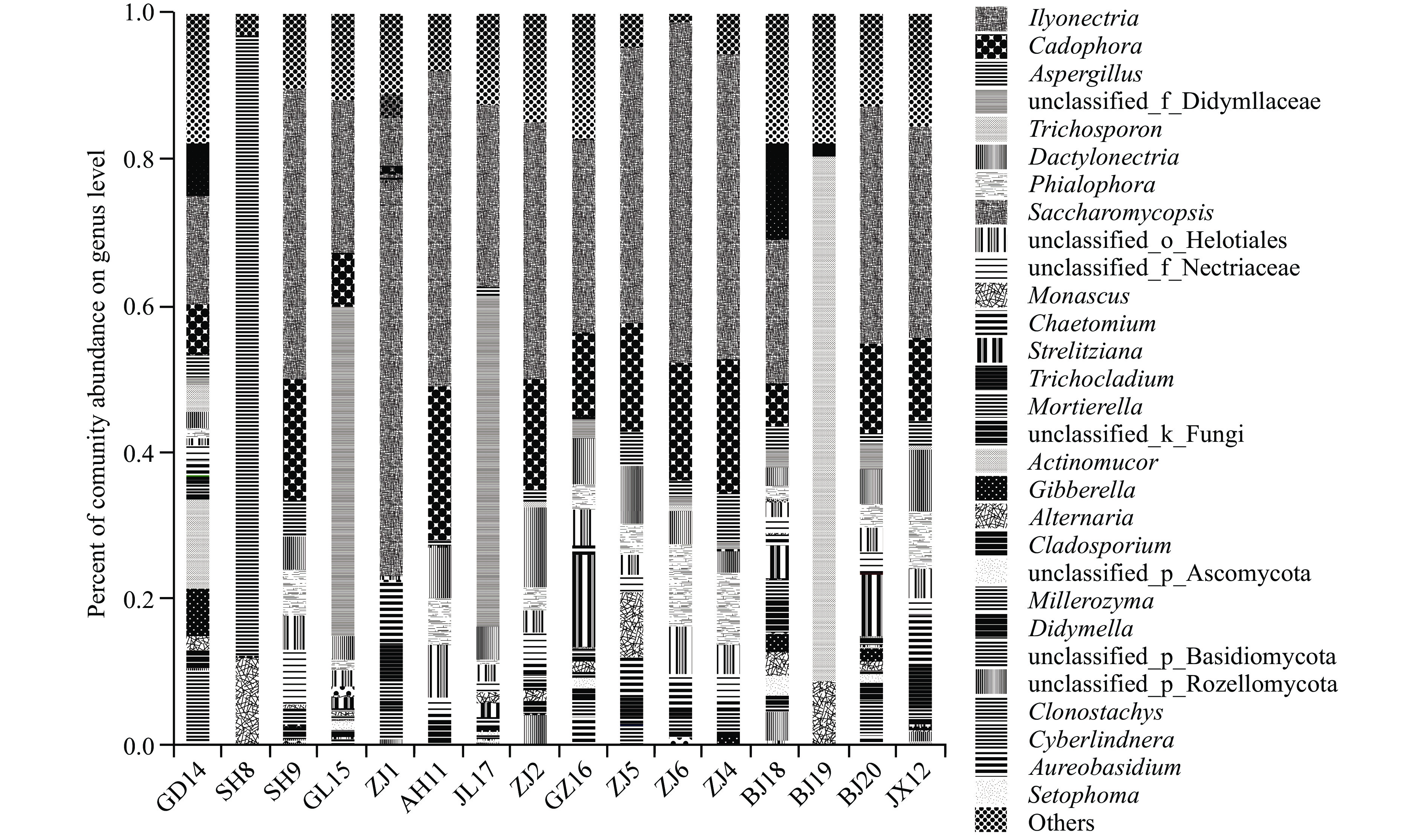
在真菌多样性方面,16个样本中的BJ18以最高的ACE(246.280)、Chao1(242.667)、Shannon指数(4.231)和最低的Simpson指数(0.046)而展现出最高的真菌丰度和多样性。BJ19和SH8分别以较低的ACE(27.057和46.035)和Chao(25.667和45.333)以及较高的Simpson指数(0.557和0.706)展现出较低的真菌丰度和多样性。在腐乳样品中,数量最多的5个真菌属分别为土赤壳属(Ilyonectria sp.)、刚毛藻属(Cadophora sp.)、曲霉属(Aspergillus sp.)、指趾藤属(Dactylonectria sp.)和瓶霉菌属(Phialophora sp.)(图2),平均占真菌群落组成的56.08%。此外,不同的腐乳样品在真菌属成分上存在显著差异,这可能与腐乳产地、发酵原料和发酵工艺的不同有关[14]。
高通量测序(high-throughput sequencing,HTS)腐乳16个样品所得到的真菌属相对丰度百分比如图2所示。16种腐乳样品中的微生物群落主要由土赤壳属( Ilyonectria sp.)、曲霉属(Aspergillus sp.)、酵母属(Saccharomycopsis sp.)、放射毛霉属(Actinomucor sp.)、假丝酵母属(Candida sp.)、根霉属(Rhizopus sp.)等胞外水解酶产生菌组成。此外,还存在刚毛藻属(Cadophora sp.)、枝孢属(Cladosporium sp.)、束毛藻属(Trichomerium sp.)、瓶霉属(Phialophora sp.)和镰刀菌属(Fusarium sp.)等大量的大豆共生体和病原菌。在产生水解酶的属中,放射毛霉属(Actinomucor sp.)在除了SH8和BJ19的其余14个腐乳样本中均有分布,而根霉(Rhizopus sp.)分布比较有限,仅在ZJ1(2.11%)中被检测出;综合对比各样本中的真菌多样性,推测放射毛霉属(Actinomucor sp.)比其他丝状属更适合作为腐乳生产发酵剂中的水解酶生产菌[15]。此外,在16个腐乳样品中均检测到了曲霉属(Aspergillus sp.),平均占所有属的8.65%,在样本SH8中更是以85.32%的比例占绝对优势。有报道称曲霉在腐乳生产过程中的后发酵中非常重要并占主导地位[16],这与本研究的结果一致。
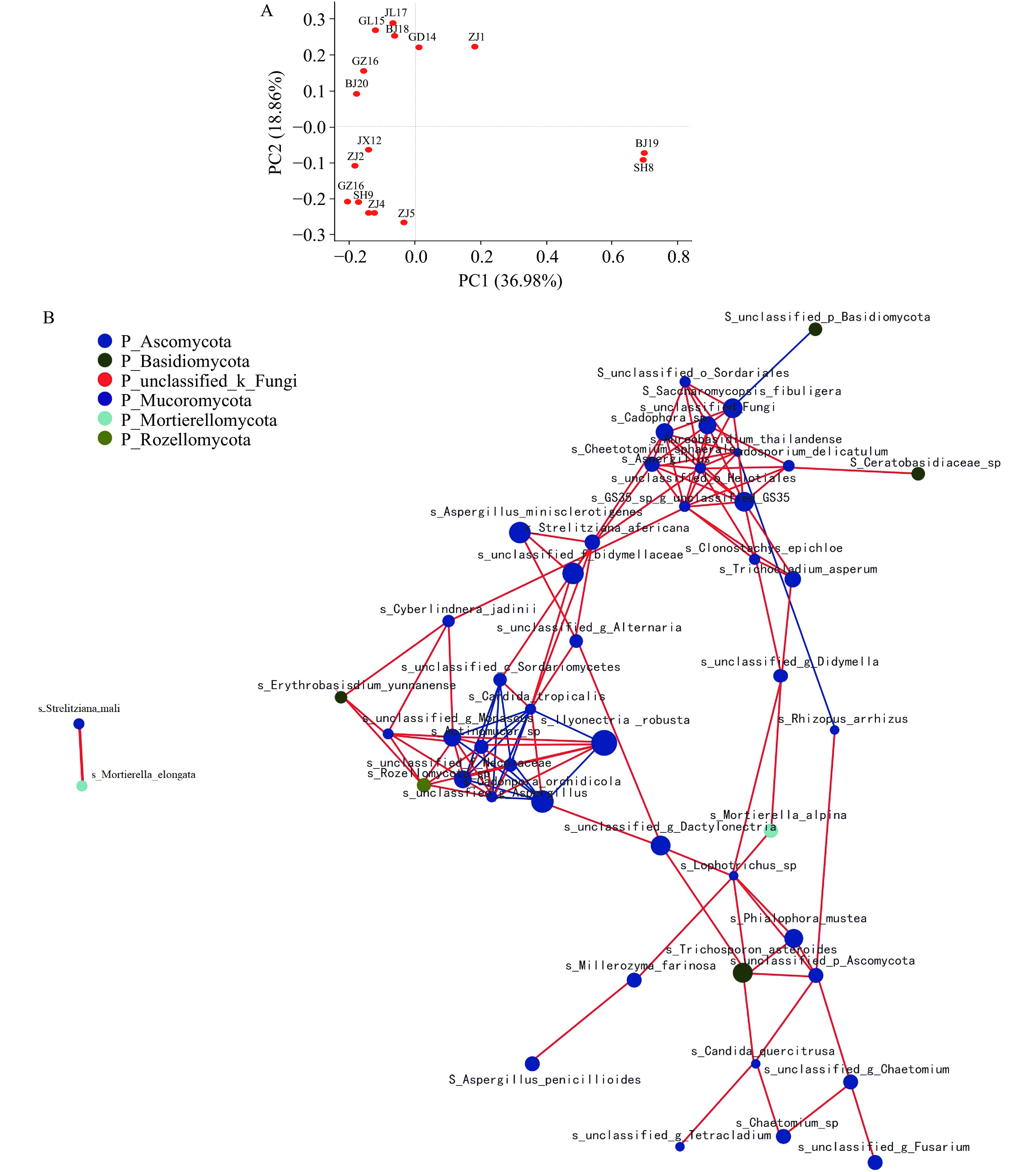
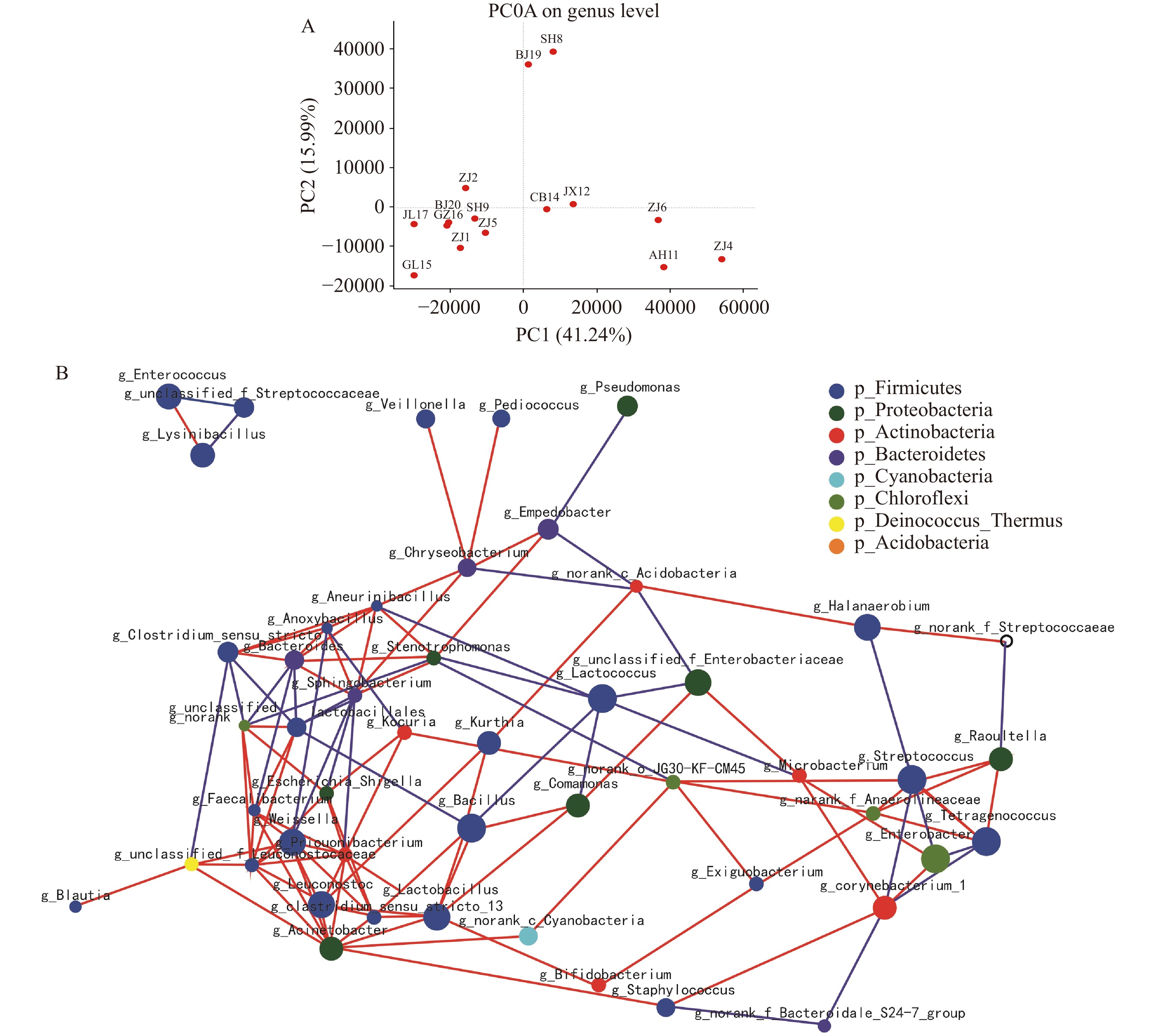
利用主坐标分析(Principal coordinate analysis,PCoA)和层次聚类分析(Hierarchical Cluster Analysis,HCA)对16种腐乳中真菌组成的异同进行了分析,所得结果如图3所示。根据PCoA图,主坐标成分PC1和PC2分别占真菌群落方差的36.98%和18.86%。中国东部地区的真菌(ZJ2、ZJ4、ZJ5、ZJ6、SH9、AH11和JX12)可以归为一组,说明腐乳的真菌群落可能受地理因素的影响,因为来自同一地区的样品在进行腐乳发酵制备时通常具有相似的温度和水分条件[17]。除此之外,课题组研究发现,中国南方(GD14、GL15、LGM16)和中国北方(JL17、BJ18和BJ20)各样本间的距离均比较近,表明这些样本之间的菌群差异性较小,可归为一类,这表明除了地理因素之外,还有其它因素可影响腐乳真菌的多样性。这些腐乳产品可能使用类似的接种发酵剂、大豆原料或预发酵工艺[18],这还需要进一步确认。另一方面,花香调味的ZJ1、ZJ4、ZJ5、SH9、BJ19以及酒香调味的ZJ2、ZJ6、SH8、AH11、GL15、JL17、BJ20和香辛调味的JX12、GD14、GZ16、BJ18这3组不同调味香料的样品在PCoA图中呈现不规则的分布,这表明调味香料不是影响腐乳中真菌群落组成的主要因素。
2.3 腐乳样品中的细菌多样性分析
16种腐乳样品的细菌α多样性检测结果如表3所示。在细菌多样性方面,16个样本中的ZJ1以最高的ACE(230.465)、Chao(186.895)、Shannon指数(1.117)和最低的Simpson指数(0.297)而展现出最高的细菌丰度和多样性。BJ19和GZ16分别以较低的ACE(39.697和86.113)和Chao(39.500和85.857)以及较高的Simpson指数(0.523和0.565)展现出较低的细菌丰度和多样性。对比真菌的α多样性结果,BJ19的细菌α多样性与真菌的α多样性结果一致,说明该产品在腐乳的发酵过程中应该是选用了特殊的发酵或加工方法[19]。此外,ZJ2和JX12的Shannon值最高,分别为2.187和2.162,Simpson值最低,分别为0.321和0.153,说明其菌群分布较其他样本更为均匀。而AH11的Shannon值最低(0.844),Simpson值最高(0.677),表明该样品中以少数物种为主[20]。
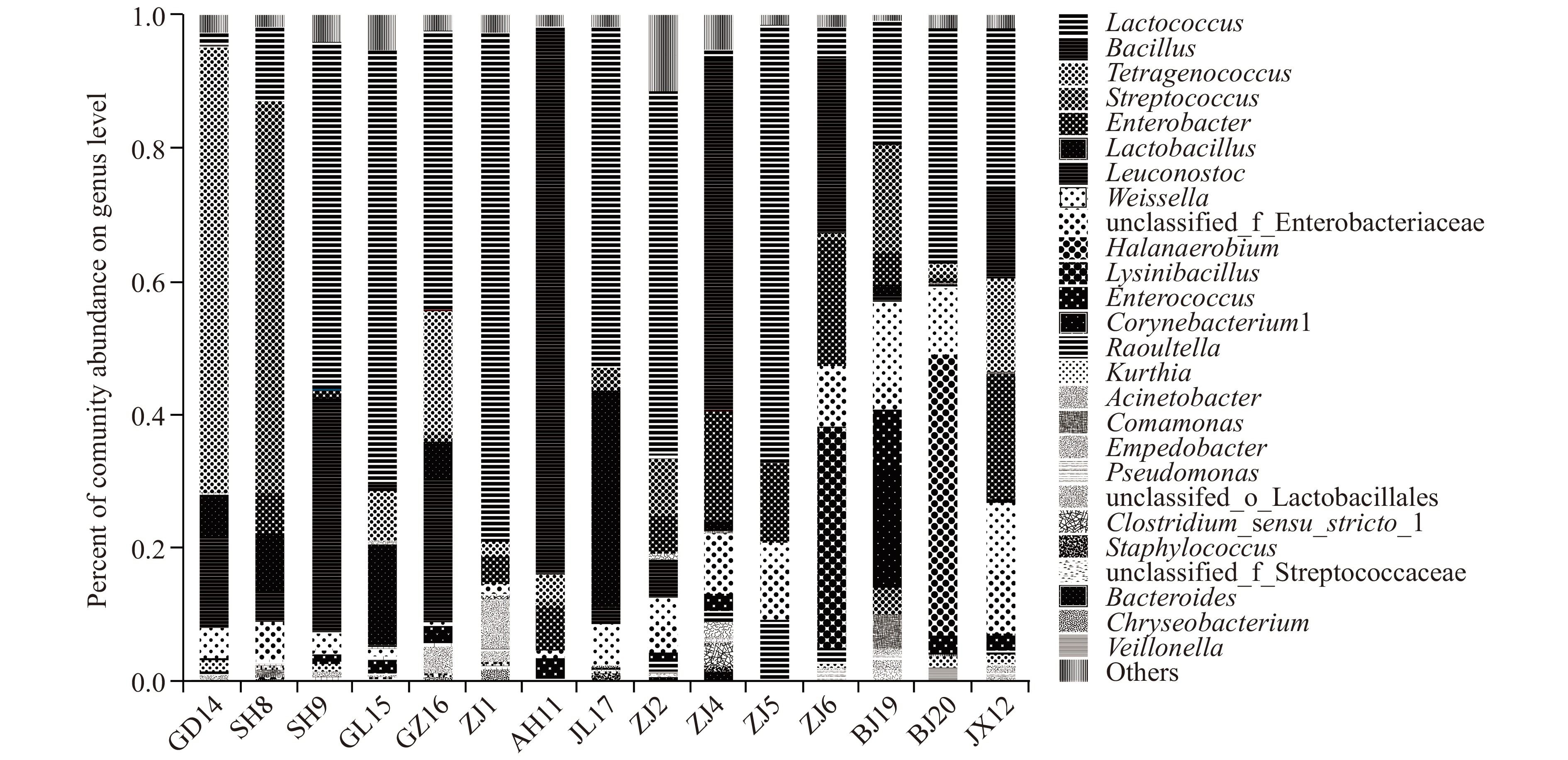
表 3 16种腐乳样品中细菌的α多样性分析Table 3. α diversity analysis of bacteria in 16 sufu samples编号 ACE值 Chao值 Shannon值 Simpson值 覆盖率(%) ZJ1 230.465 186.895 1.117 0.297 99.862 ZJ2 203.239 203.625 2.187 0.321 99.983 ZJ4 132.783 132.333 1.890 0.320 99.985 ZJ5 150.432 142.885 1.213 0.464 99.905 ZJ6 183.545 181.043 1.814 0.228 99.868 SH8 135.596 145.500 1.527 0.378 99.929 SH9 174.172 183.000 1.373 0.401 99.897 AH11 156.862 165.000 0.844 0.677 99.871 JX12 176.136 173.000 2.162 0.153 99.880 GD14 150.109 150.105 1.315 0.475 99.925 GL15 171.329 174.545 1.439 0.459 99.970 GZ16 86.113 85.857 1.725 0.565 99.956 JL17 179.003 176.875 1.354 0.375 99.914 BJ18 153.025 147.276 1.029 0.323 99.902 BJ19 39.697 39.500 2.348 0.523 99.996 BJ20 165.899 160.120 1.580 0.313 99.927 16个腐乳样品中细菌属的相对丰度百分比如图4所示,16份腐乳样品中平均菌群含量排名前6位的是乳球菌属(Lactococcus sp.)(33.83%)、芽孢杆菌(Bacillus sp.)(11.79%)、四联球菌(Tetragenococus sp.)(7.72%)、肠杆菌(Enterobacter sp.)(6.36%)、链球菌(Streptococcua sp.)(6.10%)和明串珠菌(Leuconostoc sp.)(5.72%),占菌群组成的71.52%,这与alpha多样性分析结果一致,即细菌群落倾向于以少数物种为主[21]。
从图4中还可以看到,腐乳样品中的细菌群落由可水解蛋白的芽孢杆菌属(Bacillus sp.)、乳杆菌属(Lactobacillus sp.)、魏斯氏菌属(Weissella sp.)、梭菌属(Clostridium sp.)、肠球菌属(Enterococcus sp.)、棒状杆菌属(Corynebacterium sp.)等增味菌和不动杆菌属(Acinetobacter sp.)、葡萄球菌属(Staphylococcus sp.)等潜在的致病性或腐败菌株组成。所有腐乳产品中,乳球菌属(Lactococcus sp.)最占优势,在腐乳样本ZJ1、GL15、SH9、JL17、ZJ2、ZJ5和GZ16中分布范围高达42.28%~76.69%。链球菌(Streptococcus sp.)在SH8和BJ19中分布范围高达59.04%和16.36%。明串珠菌属(Leuconostoc sp.)在样品SH9、GZ16和GD14中分别为35.21%、21.47%和13.67%。魏斯氏菌属(Weissella sp.)在BJ19、JX12和BJ20中的分布占12.68%、10.14%和10.00%。样品JL17中以乳酸菌(Lactobacillus sp.)含量较高,为32.66%。这些不同样品中的微生物组成支持了乳酸菌在腐乳发酵中的重要性和复杂机制。此外,从图4中看到,芽孢杆菌菌株广泛存在于样品AH11、JX12和GD14中,但在许多其他腐乳样品中分布较少。
利用主坐标分析(Principal coordinate analysis,PCoA)和层次聚类分析(Hierarchical Cluster Analysis,HCA)对16种腐乳中细菌组成的异同进行了分析,所得结果如图5所示。与真菌群落相似,不同腐乳样品的细菌群落差异显著。16种腐乳样品大体可分为乳酸杆菌类进化支(ZJ2、ZJ5、SH9、ZJ1、GL17、BJ20)和芽孢杆菌进化支(ZJ4、ZJ6、AH11、JX12、GD14)。这与之前对黄酒发酵的研究一致,8种发酵剂中有4种菌群以乳酸菌为主,而其余4个以芽孢杆菌为主。芽孢杆菌能提供多种水解酶,加速发酵物质中蛋白质、脂类和碳水化合物的降解,但芽孢杆菌对腐乳发酵的起源、影响及意义有待进一步研究。与真菌群落不同的是,样品中的细菌群落没有按区域进行聚类,说明腐乳样品中的细菌群落具有较强的变异性,可能受到多种因素的影响。与真菌群落相似,16种不同产品的菌群在发酵后也不能很好地按照调味方式进行聚类。因此可得出以下结论:腐乳中的细菌群落比真菌群落变化更大,其群落多样性在发酵后可能受到气候变化、浸泡和盐渍等高渗处理等多种因素的影响。
2.4 腐乳样品中的化学成分分析
对选自华东、华南、华北等不同产地的16份腐乳样品中可溶性蛋白和氨基氮含量等化学成分进行检测,所得结果如表4所示。从表中可以看出,不同产地对于腐乳中的化学成分具有一定的影响,比如,华东产区中,产自浙江的腐乳样品(ZJ1、ZJ2、ZJ4、ZJ5、ZJ6)和产自上海的腐乳样品(SH8和SH9)中的可溶性蛋白含量和氨基氮含量彼此间比较接近,说明这些腐乳样品中所使用的发酵剂菌种具有较为相近的产蛋白酶能力。同时,产自安徽和江西的腐乳样品(AH11)和(JX12)可溶性蛋白含量和氨基氮含量明显高于其它华东地区的腐乳样品,结合前边的细菌丰度检验结果,推测是由于这两种样品中含量较为丰富的芽孢杆菌作用所致,为验证该推测,课题组又检测了也具有高丰度的芽孢杆菌分布的产自华南地区GD14样品中的可溶性蛋白和氨基氮含量,发现该腐乳样品也具有较高的可溶性蛋白和氨基氮含量,这说明芽孢杆菌在腐乳发酵的蛋白质分解中扮演极为重要的角色。
表 4 16种腐乳样品的化学成分测定Table 4. Chemical determination of 16 different sufu samples编号 可溶性蛋白含量(g/100 g) 氨基氮含量(g/kg) ZJ1 6.29±0.11 5.79±0.07 ZJ2 5.89±0.12 4.81±0.08 ZJ4 5.39±0.09 4.93±0.09 ZJ5 5.68±0.13 4.80±0.18 ZJ6 5.12±0.08 4.91±0.22 SH 8 4.89±0.01 4.89±0.01 SH9 5.09±0.01 4.29±0.12 AH11 12.36±0.17 9.78±0.39 JX12 12.52±0.07 9.66±0.18 GD14 9.09±0.11 8.91±0.08 GL15 5.49±0.09 4.79±0.12 GZ16 7.71±0.21 6.92±0.31 JL17 5.12±0.12 4.71±0.09 BJ18 5.70±0.06 4.61±0.09 BJ19 4.91±0.16 3.79±0.01 BJ20 6.73±0.13 5.16±0.06 3. 讨论
研究表明,酱油、醋、腐乳等发酵调味品中的微生物组成是决定其最终质量的关键因素[22]。本研究基于高通量测序技术,将腐乳发酵过程中微生物群落、化学成分、产地及风味相关性进行了探讨分析,以期揭示腐乳发酵过程中微生物多样性的影响因素及潜在后果。
研究中课题组发现华东地区所产的腐乳样本中的真菌群落可大致分为一类,这说明了地理因素在腐乳发酵过程中的重要作用。然而,腐乳样品中的细菌群落就不能很好地按照地域进行聚类,这表明细菌群落在腐乳发酵过程中的变异性更大,除去地理条件之外,还可能受到加工技术及发酵环境因素的影响,这和前人的报道相一致[23]。
微生物多样性分析有助于揭示腐乳发酵的关键菌群和功能菌群,为今后腐乳发酵菌群的合理设计提供依据。结果表明,放射毛霉属(Actinomucor sp.)作为产水解酶的真菌,在腐乳发酵过程中起着极为重要的作用,通过分析16种腐乳样品的真菌多样性,发现放射毛霉属(Actinomucor sp.)作为优势菌以较高的丰度百分比广泛分布于华南、华东和华北等多个产地的腐乳样品样本(GD14、ZJ1、AH11、BJ20)中;此外,课题组也在16种腐乳样品中检测到大量的可产蛋白酶、脂肪酶和淀粉酶等水解酶的曲霉属(Aspergillus sp.),这些曲霉因其可广泛增加可溶性蛋白含量和氨基氮水平等特点被广泛用于豆制品的食品发酵中,腐乳样品的真菌多样性分析结果说明毛霉和曲霉对于腐乳的发酵生产具有极为重要的作用。陈卓等发现放射毛霉属是红腐乳发酵前期的主要菌种之一,红曲霉在发酵后占主导地位,该观点和本研究所得结果一致[24]。
本研究中根据细菌属的丰度,可将16种腐乳样品的细菌群落分为两大进化支:乳酸菌进化支和芽孢杆菌进化支。这两个分支的存在引起了课题组对于芽孢杆菌在豆制品发酵中的潜在作用的关注。芽孢杆菌是对食品发酵至关重要的菌种[25],它可以产蛋白酶等水解酶,因而在腐乳的发酵和成熟中发挥重要作用;本研究通过对比AH11、JX12和GD14这三个产地的细菌多样性结果和化学成分的关联,发现腐乳样品中可溶性蛋白和氨基氮的含量同芽孢杆菌的含量呈现正相关,这为后期针对不同用户需求设计生产腐乳发酵剂提供了理论依据。此外,腐乳样品中的细菌多样性分析结果显示,包括乳球菌属(lactococcus sp.)和链球菌(Streptococcua sp.)在内的乳酸菌广泛地存在于16种腐乳样品中,研究显示,这些菌群腐乳pH及风味的维持及生物防腐等方面发挥着重要影响[26]。
HTS技术可有效地揭示腐霉样品中细菌和真菌生态系统的整体状况。采用高通量测序,不仅检测出毛霉、曲霉和芽孢杆菌以及乳酸菌等优势菌群在各样品中的分布丰度,也检测出短梗霉(Aureobasidium sp.)、聚孢霉(Clonostachys sp.)和金黄杆菌属(Chrysobacterium sp.)等腐乳中的一些稀有属在AH11、ZJ2、SH9、ZJ5、ZJ6和ZJ4等样本中具有丰富的含量。研究表明,这些稀有属均来自于大豆材料[27],且其存在会影响腐乳发酵微生物群落的组成[28-29],具体影响机制还需要对腐乳发酵过程中微生物多样性及其特性的动态变化做进一步的研究。
-
表 1 腐乳16种样品的产地信息
Table 1 Origin information of 16 sufu samples
产品编号 品牌 产地 调味方式 地域 ZJ1 **香酥玫瑰豆腐乳 浙江 花香 华东 ZJ2 **糟方豆腐乳 浙江 酒香 华东 ZJ4 **玫瑰腐乳 浙江 花香 华东 ZJ5 **玫瑰腐乳 浙江 花香 华东 ZJ6 **香酥红方腐乳 浙江 酒香 华东 SH8 **红腐乳 上海 酒香 华东 SH9 **玫瑰腐乳 上海 花香 华东 AH11 **五香腐乳 安徽 酒香 华东 JX12 **辣豆乳 江西 香辛 华东 GD14 **微辣腐乳 广东 香辛 华南 GL15 **豆腐乳 桂林 酒香 华南 GZ16 **红油腐乳 贵州 香辛 华南 JL17 **红腐乳 吉林 酒香 华北 BJ18 **红方大块腐乳 北京 香辛 华北 BJ19 **玫瑰腐乳 北京 花香 华北 BJ20 **糟方腐乳 北京 酒香 华北 注:**表示不同的产品品牌名称未显示。 表 2 16种腐乳样品中真菌的α多样性分析
Table 2 α diversity analysis of fungi in 16 sofu samples
编号 ACE值 Chao1值 Shannon值 Simpson值 覆盖率(%) ZJ1 165.677 167.000 2.583 0.268 99.994 ZJ2 62.029 61.333 2.863 0.139 99.997 ZJ4 67.813 65.000 2.470 0.192 99.991 ZJ5 81.609 81.500 2.748 0.147 99.998 ZJ6 62.392 42.000 2.183 0.231 99.993 SH8 46.035 45.333 0.710 0.706 99.997 SH9 62.441 62.000 2.706 0.166 99.999 AH11 46.410 45.500 2.307 0.207 99.997 JX12 102.523 102.500 3.232 0.101 99.995 GD14 180.480 179.500 3.810 0.054 99.995 GL15 139.440 139.500 2.386 0.245 99.997 GZ16 96.795 95.000 3.322 0.089 99.992 JL17 117.212 115.000 2.514 0.238 99.994 BJ18 246.280 242.667 4.231 0.046 99.989 BJ19 27.057 25.667 0.819 0.557 99.993 BJ20 207.013 203.000 3.286 0.113 99.970 表 3 16种腐乳样品中细菌的α多样性分析
Table 3 α diversity analysis of bacteria in 16 sufu samples
编号 ACE值 Chao值 Shannon值 Simpson值 覆盖率(%) ZJ1 230.465 186.895 1.117 0.297 99.862 ZJ2 203.239 203.625 2.187 0.321 99.983 ZJ4 132.783 132.333 1.890 0.320 99.985 ZJ5 150.432 142.885 1.213 0.464 99.905 ZJ6 183.545 181.043 1.814 0.228 99.868 SH8 135.596 145.500 1.527 0.378 99.929 SH9 174.172 183.000 1.373 0.401 99.897 AH11 156.862 165.000 0.844 0.677 99.871 JX12 176.136 173.000 2.162 0.153 99.880 GD14 150.109 150.105 1.315 0.475 99.925 GL15 171.329 174.545 1.439 0.459 99.970 GZ16 86.113 85.857 1.725 0.565 99.956 JL17 179.003 176.875 1.354 0.375 99.914 BJ18 153.025 147.276 1.029 0.323 99.902 BJ19 39.697 39.500 2.348 0.523 99.996 BJ20 165.899 160.120 1.580 0.313 99.927 表 4 16种腐乳样品的化学成分测定
Table 4 Chemical determination of 16 different sufu samples
编号 可溶性蛋白含量(g/100 g) 氨基氮含量(g/kg) ZJ1 6.29±0.11 5.79±0.07 ZJ2 5.89±0.12 4.81±0.08 ZJ4 5.39±0.09 4.93±0.09 ZJ5 5.68±0.13 4.80±0.18 ZJ6 5.12±0.08 4.91±0.22 SH 8 4.89±0.01 4.89±0.01 SH9 5.09±0.01 4.29±0.12 AH11 12.36±0.17 9.78±0.39 JX12 12.52±0.07 9.66±0.18 GD14 9.09±0.11 8.91±0.08 GL15 5.49±0.09 4.79±0.12 GZ16 7.71±0.21 6.92±0.31 JL17 5.12±0.12 4.71±0.09 BJ18 5.70±0.06 4.61±0.09 BJ19 4.91±0.16 3.79±0.01 BJ20 6.73±0.13 5.16±0.06 -
[1] 张鹏飞, 乌日娜, 武俊瑞. 传统发酵大豆制品挥发性成分和微生物多样性的研究进展[J]. 中国酿造,2018,37(12):1−6. [ZHANG Pengfei, WU Rina, WU Junrui. Research advance on volatile components and microbial diversity of traditional fermented soybean products[J]. China Brewing,2018,37(12):1−6. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2018.12.001 [2] 孙娜, 张雅婷, 于寒松, 等. 发酵型青腐乳菌群结构与风味物质及其相关性分析[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(22):177−183. [SUN Na, ZHANG Yating, YU Hansong, et al. Microflora structure and flavor components and correlation between them in fermented stinky tofu[J]. Food Science,2020,41(22):177−183. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190929-360 [3] TAN G, HU M, LI X, et al. High-throughput sequencing and metabolomics reveal differences in bacterial diversity and metabolites between red and white sufu[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2020,11:758−760. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00758
[4] LIU S, QIAO J. Bacterial diversity of Anshun sufu, a traditional fermented tofu in Guizhou province of China[J]. Transactions of Tianjin University,2019,25(5):497−503. doi: 10.1007/s12209-019-00198-8
[5] YAO D, XU L, WU M, et al. Effects of microbial community succession on flavor compounds and physicochemical properties during CS sufu fermentation[J]. LWT,2021,152:112313. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112313
[6] TAN G, HU M, LI X, et al. Metagenomics reveals the diversity and taxonomy of antibiotic resistance genes in sufu bacterial communities[J]. Food Control,2021,121:107641. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107641
[7] LAW K K L, MAKINO S, MO R, et al. Antagonistic and cooperative actions of Kif7 and sufu define graded intracellular Gli activities in Hedgehog signaling[J]. PloS One,2012,7(11):e50193. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050193
[8] HE W, CHUNG H Y. Exploring core functional microbiota related with flavor compounds involved in the fermentation of a natural fermented plain sufu (Chinese fermented soybean curd)[J]. Food Microbiology,2020,90:103408. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2019.103408
[9] 徐琼, 刘洋, 曲勤凤, 等. 高通量测序分析不同地区红腐乳细菌多样性[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(10):110−116. [XU Qiong, LIU Yang, QU Qinfeng, et al. High-throughput sequencing analysis of bacterial diversity in red sufu from different regions[J]. Food Science,2020,41(10):110−116. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190408-087 [10] 余巨全, 巩建华, 柯尊伟. 对中国黄牛毛囊DNA六种提取方法的研究[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学,2020,39(4):1540−1548. [YU Juquan, GONG Jianhua, KE Zunwei. Study on six methods of extracting DNA from hair follicle of Bos taurina[J]. Genetics and Applied Biology,2020,39(4):1540−1548. [11] WAN Y, WANG Y, SHI Z, et al. Wheat amino acid transporters highly expressed in grain cells regulate amino acid accumulation in grain[J]. PloS One,2021,16(2):e0246763. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246763
[12] 蒋丽婷, 李理. 白腐乳质构与其成分相关性研究[J]. 现代食品科技,2010,26(8):797−800. [JIANG Liting, LI Li. The relation of chemical component to texture of white sufu[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2010,26(8):797−800. [13] 代来鑫, 卢红梅, 张丽平, 等. 影响腐乳结晶物产生的因素[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2013,39(7):114−119. [DAI Laixin, LU Hongmei, ZHANG Liping, et al. Effectors that influence the generation of crystal in sufu[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2013,39(7):114−119. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.2013.07.042 [14] 陶康, 吴凌伟, 金晓芳, 等. 基于高通量基因测序分析腐乳微生物多样性[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(8):143−149. [TAO Kang, WU Lingwei, JIN Xiaofang, et al. Analysis of microbial diversity in sufu using high-throughput sequencing[J]. Food Science,2021,42(8):143−149. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191230-362 [15] LIANG J, LI D, SHI R, et al. Effects of microbial community succession on volatile profiles and biogenic amine during sufu fermentation[J]. LWT,2019,114:108379. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108379
[16] XIE C, ZENG H, WANG C, et al. Volatile flavour components, microbiota and their correlations in different sufu, a Chinese fermented soybean food[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology,2018,125(6):1761−1773. doi: 10.1111/jam.14078
[17] FENG Z, GAO W, REN D, et al. Evaluation of bacterial flora during the ripening of Kedong sufu, a typical Chinese traditional bacteria-fermented soybean product[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2013,93(6):1471−1478. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.5918
[18] 张雅婷, 孙娜, 于寒松, 等. 红腐乳发酵过程中菌群结构与风味相关性研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(1):287−294. [ZHANG Yating, SUN Na, YU Hansong, et al. Advances in research on correlation between flora structure and product flavor during red sufu fermentation[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(1):287−294. [19] YAO D, XU L, WU M, et al. Microbial community succession and metabolite changes during fermentation of BS sufu, the fermented black soybean curd by Rhizopus microsporus, Rhizopus oryzae, and Actinomucor elegans[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2021,12:1505−1506.
[20] 周小虎, 李理. 白腐乳发酵过程中细菌群落演替规律研究[J]. 中国酿造,2020,39(5):168−172. [ZHOU Xiaohu, LI li. Succession regulations of bacterial community in the fermentation process of white sufu[J]. China Brewing,2020,39(5):168−172. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2020.05.032 [21] ZHEN D Z, Y R W, FAN S X, et al. Distinct bacterial community of a solid-state fermented Chinese traditional food huase sufu revealed by high-throughput sequencing[J]. Food Science and Biotechnology,2021,30(9):1233−1241. doi: 10.1007/s10068-021-00963-3
[22] SHI C, LIU M, ZHAO H, et al. Formation and control of biogenic amines in sufu-a traditional Chinese fermented soybean product: A critical review[J]. Food Reviews International,2021:1−22.
[23] XU D, WANG P, ZHANG X, et al. High-throughput sequencing approach to characterize dynamic changes of the fungal and bacterial communities during the production of sufu, a traditional Chinese fermented soybean food[J]. Food Microbiology,2020,86:103340. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2019.103340
[24] 陈卓, 吴学凤, 穆冬冬, 等. 红腐乳后酵期风味物质与细菌菌群分析[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(6):118−125. [CHEN Zhuo, WU Xuefeng, MU Dongdong, et al. Determination and correlation analysis of flavor components with bacterial community in post-fermented red sufu[J]. Food Science,2021,42(6):118−125. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191203-043 [25] LI K, TANG J, ZHANG Z, et al. Correlation between flavor compounds and microorganisms of chaling natural fermented red sufu[J]. LWT,2022,154:112873. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112873
[26] 万红芳, 赵勇, 王正全, 等. 生产菌种及环境微生物与腐乳品质关系研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(6):255−261. [WAN Hongfang, ZHAO Yong, WANG Zhengquan, et al. Research progress on the relationship between sufu quality and microorganisms from starters and environment[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2019,45(6):255−261. [27] 李娜, 崔梦君, 马佳佳, 等. 自然发酵腐乳中细菌多样性评价[J]. 食品研究与开发,2019,40(16):165−171. [LI Na, CUI Mengjun, MA Jiajia, et al. Evaluation of bacterial diversity in natural fermented sufu[J]. Food Research and Development,2019,40(16):165−171. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2019.16.029 [28] GU J S, LIU T J, HOU J, et al. Analysis of bacterial diversity and biogenic amines content during the fermentation processing of stinky tofu[J]. Food Research International,2018,111:689−698. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.05.065
[29] LI X, HE Y, YANG W, et al. Comparative analysis of the microbial community and nutritional quality of sufu[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2021,9(8):4117−4126.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 龙正玉,邹金浩,杨怀谷,任国谱,曹清明,唐道邦. 肉制品发酵技术对肉品品质的调控及应用研究进展. 食品工业科技. 2024(03): 354-362 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 白婷,王卫,吉莉莉,张佳敏,刘达玉. 浅发酵香肠产品特性及其与中式香肠和西式发酵肠的比较. 成都大学学报(自然科学版). 2022(02): 137-145 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张佳敏,袁波,王卫,叶富云,唐春,翁德晖. 品质改良剂对浅发酵腊肠产品特性的影响及主成分分析. 食品工业科技. 2021(18): 244-251 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



