Identification of Volatile Flavor Compounds of Zaobaijian Black Tea Harvested in Different Seasons Based on HS-SPME-GC-MS and PLS-DA
-
摘要: 采集四川省筠连县春、夏、秋三季共15份早白尖红茶样品,采用顶空固相萃取-气相色谱-质谱技术对红茶样品的香气成分进行测定,运用偏最小二乘-判别分析(partial least square-discriminant analysis,PLS-DA)建立不同季节茶叶判别模型,绘制层次聚类的树状热图确定关键香气成分在不同季节样品中的分布规律。结果表明,春季样品醇类(113.05 μg/g)和酯类物质(34.92 μg/g)含量明显高于夏秋两季样品,而醛类物质(23.85 μg/g)明显低于夏秋两季样品,且所建PLS-DA模型可将春和夏秋两季样品明显区分。进一步分析后的分层聚类的树状热图显示,苯乙醛、橙花醇和香叶醇是春季样品区别于其它两季茶样的特征香气化合物,在此基础上可通过芳樟醇、芳樟醇氧化物Ⅰ和Ⅱ对夏、秋两季样品进行进一步区分。该研究为解析不同季节早白尖红茶香气物质提供基础研究数据,也为进一步探究筠连早白尖红茶关键香气形成机制奠定基础。Abstract: By using headspace-solid phase microextraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (HS-SPME-GC-MS), the volatile flavor compounds were determined for 15 Zaobaijian black tea samples harvested in spring, summer and autumn in Junlian, Sichuan Province. Subsequently, a discriminant model partial least square-discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) was used and a hierarchical cluster analysis of the dendroid heat map was drawn to determine the distribution of key aroma components from different harvest seasons. Results showed that the alcohol content (113.05 μg/g) and esters (34.92 μg/g) in the spring samples were significantly higher than those from the summer and autumn samples, while the aldehydes (23.85 μg/g) were significantly lower than those in the summer and autumn samples. The established PLS-DA model could distinguish between tea samples harvested in spring and those harvested in summer and autumn. Moreover, the heat map cluster analysis showed that hyacinthin, nerol and (Z)-geraniol were the key aroma component that distinguished the spring tea samples from the summer and autumn tea samples. Cis-linalool oxide and trans-linalool oxide (furanoid) were the key aroma components that distinguished the summer tea samples from autumn tea samples. This study provides basic research data for analyzing the aroma components of Zaobaijian black tea from different seasons and lays a foundation for further exploration into the key aroma formation mechanism of Junlian Zaobaijian black tea.
-
筠连早白尖红茶是四川工夫红茶的优质代表,为国家地理标识产品。早白尖品种是由四川筠连本地川小叶群体种经多年选育出的国家级良种,种植区海拔760~1200 m,土壤为黄或棕壤且偏酸性,腐殖质含量较高,茶树成活率高,生长优势强,全年采摘期长达7个月,鲜叶具有“早、嫩、快、好”的优良品质[1]。筠连早白尖红茶条索显金毫,汤色浓亮,滋味醇厚鲜爽,带桔糖香,深受消费者喜爱。
茶的香气是其最重要的感官属性之一,对茶叶的品质和市场价格具有重要影响,而红茶是挥发性风味物质浓度最高,香气感知度最强烈的茶型[2-4],因此有关各地红茶香气物质方面的研究越来越受到关注。红茶香气的形成主要受茶树品种和加工工艺的影响[5-7],另外采摘季节、土壤条件、栽培海拔高度等也显著影响红茶中香气物质的组成和含量,进而产生不同红茶类型的香气品质[8-11]。目前对早白尖红茶香气的研究仅有少量感官香型描述[12],对不同季节筠连早白尖红茶香气成分的研究鲜见报道。
在分析茶中挥发性化合物方面,顶空-固相微萃取(HS-SPME)已被证明是一种无溶剂、快速、简单且方便的方法[13],其通常与气相色谱-质谱联用(GC-MS)结合进行分析,通过标准质谱库和保留指数来鉴定和定量单个挥发性化合物[14-16]。同时,为了最大程度地从挥发性成分分析的大数据中提取有用信息,应用化学计量学方法如主成分分析(PCA)、偏最小二乘-判别分析(PLS-DA)、层次聚类分析(HCA)等对数据进行处理和分析是非常必要的[17-18]。目前,HS-SPME-GC-MS与这些化学计量学方法相结合的模式已在分析不同类型茶样品中获得了越来越多的成功[19-20]。然而,相关研究模式尚未用于筠连早白尖红茶挥发性成分研究。
为了解筠连早白尖红茶的主要香气成分,解析不同季节早白尖红茶关键香气物质及差异,本研究采用HS-SPME-GC-MS定性定量分析春、夏、秋茶中各香气成分,采用PLS-DA以茶样中香气成分的相对含量建立不同季节判别模型,确定对分类起关键作用的香气成分,最后通过聚类分析的树状热图来确定各关键香气成分在不同季节筠连早白尖红茶中的分布规律,为更加科学和客观地评价筠连早白尖红茶的香气品质和地方优质红茶品牌塑造提供一些参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
供试早白尖红茶 由四川筠连县农产品品牌办公室提供,于2019年采自筠连县茶园,春、夏、秋茶分别于3、6、9月份采集,采摘标准为一芽二叶,当季从不同的茶园(位于北纬27°,东经104°,其中,H和L茶园海拔1100~1200 m,W、S和Y茶园海拔600~700 m)共采集5个茶样,鲜叶收集到同一加工厂,按照“萎凋-揉捻-发酵-干燥”[21]的传统川红工艺制得红茶成品,每个茶样3个重复,所有工艺参数一致。当季红茶成品研磨过60目筛,自封袋封装后常温保存,随后送至实验室3 d内完成测试分析。每季均从相同的茶园获得同样数量的鲜叶用于成品制作,三季共测试分析15个茶样。
FA1104分析天平 上海舜宇恒平科学仪器有限公司;气相色谱(7890A)-质谱(5975C)联用仪 美国安捷伦科技有限公司;65 μm PDMS/DVB固相微萃取头 美国Supelco公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品前处理
称取0.4 g磨碎茶样于样品瓶中,添加10 μL内标溶液(1-辛醇 10 μg/mL),加入0.6 g NaCl和2 mL 100 ℃蒸馏水,加盖密封,60 ℃水浴中平衡15 min[22]。使用65 μm PDMS/DVB固相微萃取头60 ℃顶空吸附60 min,进样口240 ℃,解析5 min。
1.2.2 色谱条件
采用HP-5MS石英毛细管色谱柱(30 m×0.32 mm,0.25 μm);进样口温度240 ℃,载气为高纯度氦气,流速0.8 mL/min,不分流进样;梯度升温程序:柱温为0 ℃,保持3 min,以 2 ℃/min升至 90 ℃,保持 5 min,再以 3 ℃/min 升至 160 ℃,以10 ℃/min升至250 ℃,保持5 min。
1.2.3 质谱条件
离子源为EI源,温度230 ℃,电子能量70 eV,四极杆温度150 ℃,接口温度280 ℃,电子倍增器电压1680 V,扫描范围44~350 m/z。
1.2.4 挥发性成分的定性和定量
根据样品总离子流图,结合NIST 98.L谱库和前人的相关研究,对不同季节茶叶中挥发性成分进行鉴定,筛选匹配度达到90%以上的化合物,同时排除柱流失等干扰性化合物。以1-辛醇为内标作为峰面积对照,参照汪鹏等[23]的研究方法采用归一法计算相对含量和内标法半定量计算其余组分含量,计算公式如下:
各组分含量(μg/g)=各组分的峰面积(A)×内标物含量(μg)内标峰面积(A)×样品量(g) 1.3 数据处理
原始数据用Microsoft Excel 2019进行预处理;采用SPSS 22.0进行单因素方差分析;采用SIMCA-P14.1进行偏最小二乘(PLS-DA)分析;采用Origin 2019进行图表绘制。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同季节筠连早白尖红茶挥发性成分分析
早白尖红茶样品色谱图见图1。如表1所示,对不同季节共15个早白尖红茶样品中挥发性成分分析表明,总共鉴定出44种化合物,包括醛类、醇类、酮类、酯类、碳氢化合物、杂环类及其他类化合物。其中醇类物质相对含量最丰富,共检出11种,各样品相对含量35.34%~64.42%之间,样品平均相对含量为53.65%;其次是醛类物质,共检测出12种,各样品相对含量在10.57%~36.88%之间,样品平均相对含量为20.29%;酯类物质为第三大类挥发性成分,共检测出2种,各样品相对含量在5.09%~20.92%之间,样品平均相对含量为12.28%;酮类、碳氢化合物和杂环类及其他类物质相对含量均非常低,分别检测出8种、6种、5种,样品平均相对含量分别只有0.55%、0.19%和3.93%。马玉青等[24]研究云南滇红香气组成包含醇类、酯类、醛类、萜烯类、酮类,其中醇类接近香气总量的43%,远高于其它种类化合物占比。章港等[25]利用SPME-GC-MS技术研究祁门红茶,发现醇类、醛类与酯类成分是主要挥发性香气物质,分别占总含量的67.54%、16.93%和11.36%。筠连早白尖红茶香气组成与前人研究基本一致,即红茶香气物质主要是醇类、醛类和酯类,由鲜叶中的糖苷类、氨基酸、脂肪酸、β-胡萝卜素等香气前体物质在萎凋、揉捻、发酵、干燥的加工过程中通过一系列生物化学反应逐渐形成[26]。
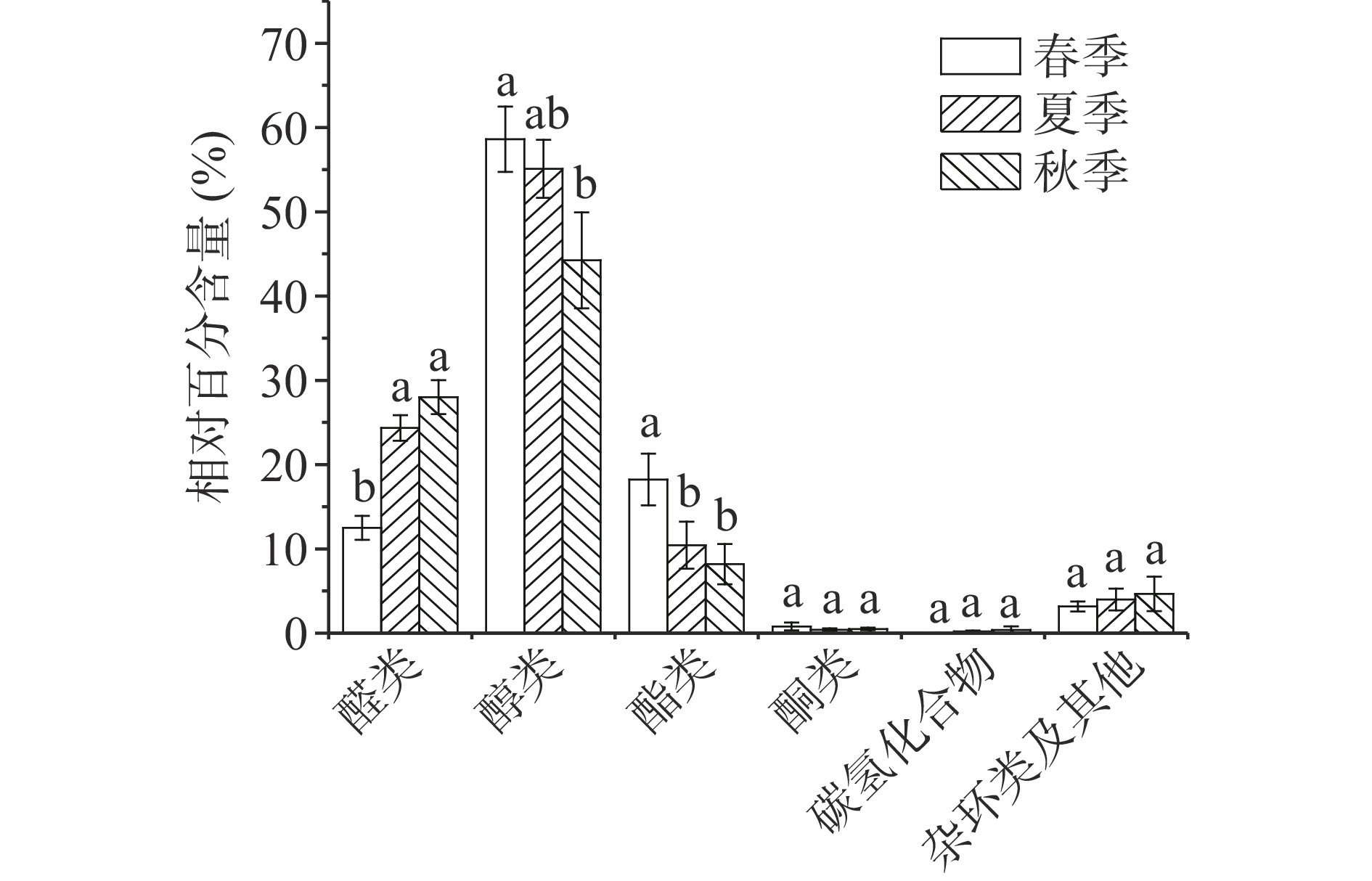
表 1 各季节样品挥发性成分(μg/g)Table 1. Volatile components of each tea sample collected from different seasons (μg/g)化合物 春季 夏季 秋季 显著性 糠醛 0.13±0.26 0.07±0.14 0.84±0.58 * 己烯醛 1.61±1.55 1.42±0.53 2.63±1.53 苯甲醛 12.58±2.43 19.87±6.97 14.38±11.37 2,4-庚二烯醛 0.19±0.21 0.53±0.76 4.30±5.79 辛醛 \ \ 0.14±0.28 苯乙醛 6.81±1.19 21.38±4.70 15.42±5.48 * 葵醛 0.11±0.22 0.06±0.13 0.21±0.18 β-环柠檬醛 0.05±0.09 0.25±0.20 0.41±0.41 β-柠檬醛 2.23±0.99 \ 0.72±1.13 * 2-苯基巴豆醛 \ 0.24±0.49 0.99±1.21 甲基苯基-2-戊烯醛 0.07±0.14 0.77±0.51 0.41±0.38 甲基苯基-2-己烯醛 0.07±0.09 0.13±0.09 0.18±0.18 醛类总计 23.85 44.72 40.63 顺-己烯-1-醇 1.12±1.23 3.04±2.36 2.74±3.08 苯甲醇 15.10±6.58 10.90±2.15 10.00±3.04 芳樟醇氧化物Ⅱ 4.03±2.71 13.66±7.33 4.44±3.61 * 芳樟醇氧化物Ⅰ 13.08±7.05 22.44±9.89 8.16±2.31 芳樟醇 13.83±8.15 9.09±4.50 1.76±1.49 苯乙醇 20.93±6.58 31.45±6.27 27.71±7.00 环氧芳樟醇 \ 1.82±3.64 \ α-松油醇 0.41±0.82 \ \ 香叶醇 44.38±22.69 \ \ * 橙花醇 \ 11.78±8.11 18.59±11.11 雪松醇 0.18±0.35 0.34±0.35 0.75±0.77 醇类总计 113.05 104.52 74.15 2-庚酮 0.02±0.05 \ 0.10±0.14 3,5-辛二烯酮 0.21±0.42 \ \ 2-莰酮 \ 0.04±0.09 \ 茉莉酮 0.95±0.55 \ \ * 顺-香叶基丙酮 \ \ 0.04±0.07 β-大马烯酮 \ 0.28±0.26 0.14±0.13 β-紫罗兰酮 0.33±0.06 0.29±0.20 0.57±0.31 α-紫罗兰酮 \ 0.09±0.11 0.02±0.05 酮类总计 1.51 0.70 0.87 乙酸苯甲酯 0.20±0.19 \ \ * 水杨酸甲酯 34.72±5.67 18.14±7.23 13.64±2.97 * 酯类总计 34.92 18.14 13.64 柠檬烯 \ 0.06±0.12 \ 十二烷 \ \ 0.21±0.31 2-莰烯 \ 0.17±0.22 0.06±0.12 3-蒈烯 \ 0.09±0.18 \ 十三烷 \ \ 0.22±0.23 * 十七烷 0.05±0.10 \ 0.06±0.07 碳氢化合物总计 0.05 0.32 0.55 2-戊基呋喃 \ 0.43±0.85 0.44±0.45 乙基-1H-吡咯-2-甲醛 \ \ 0.51±1.02 苯乙腈 \ 0.51±0.45 \ * 2,4-二叔丁基苯酚 5.74±1.03 6.22±1.80 6.79±3.00 咖啡因 0.31±0.39 \ 0.04±0.08 杂环类及其他总计 6.05 7.16 7.78 总含量 179.43 175.56 137.62 注:“\”为未检出;“*”表示不同季节样品组间差异显著(P<0.05)。 根据各样品挥发性成分(表1),春季样品平均挥发性成分最高(179.43 μg/g),夏季样品次之(175.56 μg/g),秋季样品最低(137.62 μg/g),但三季样品之间差异不显著(P>0.05)。从季节来看(图2),春季样品酯类物质含量显著高于(P<0.05)夏季和秋季样品,醇类物质显著高于(P<0.05)秋季,醇类物质主要差异来自香叶醇,春季5个样品中均检出了含量丰富的香叶醇,平均含量达到了44.38 μg/g,而夏季和秋季样品检出的是橙花醇(顺-香叶醇),平均含量分别为11.78和18.59 μg/g。香叶醇主要由鲜叶中萜烯醇类糖苷在加工过程中水解形成,具有典型的玫瑰花香和甜香,是“祁门香”的主要香气物质之一[25]。王梦琪等[26]研究发现不同季节鲜叶中各类糖苷含量的是不同的,春季以萜烯醇类糖苷为主,其含量可以达到70%以上,而夏季和秋季萜烯醇类糖苷大幅减少,芳香族醇和脂肪族醇糖苷含量明显增多。酯类物质的主要差异来自于水杨酸甲酯,具有典型的冬青香气,春季样品平均含量高达34.72 μg/g,而夏季和秋季样品分别为18.14 μg/g和13.64 μg/g。秋季样品的醛类物质最丰富,且显著高于(P<0.05)春季样品;本实验检出的醛类物质除了β-柠檬醛以外,其余醛类在秋季样品中的平均含量均高于春季样品,尤其是苯乙醛,夏季和秋季样品平均含量分别为21.38 μg/g和15.42 μg/g,而春季样品只有6.81 μg/g。另外,春季样品酮类物质相对含量最高,秋季样品碳氢类和杂环类物质相对含量最高,但其含量在样品中均极低,且三季节样品之间无显著性差异(P>0.05),而夏季样品各类物质相对含量大多处于春季和秋季样品之间,只有酮类物质含量最低。
从所有样品的平均化合物含量来看,苯乙醇(26.69 μg/g)、水杨酸甲酯(22.17 μg/g)、苯甲醛(15.61 μg/g)、苯乙醛(14.54 μg/g)、芳樟醇氧化物Ⅰ(14.56 μg/g)、苯甲醇(12.00 μg/g)、2,4-二叔丁基苯酚(6.25 μg/g)在所有样品中均可发现,另外香叶醇(或橙花醇)、芳樟醇(8.23 μg/g)、芳樟醇氧化物Ⅱ(7.38 μg/g)、顺-己烯-1-醇(2.30 μg/g)、己烯醛(1.89 μg/g)等化合物也在超过80%的样品中发现且大部分含量较高,表明这些挥发性成分是构成筠连早白尖红茶香气的重要成分。Chen等[27]发现芳樟醇氧化物I、II和III、E,E-2,4-壬二烯醛、4,5-二甲基-3-羟基-2,5-二氢呋喃-2-酮、1-辛烯-3-酮、E,E-2,6-壬二烯醛和双(2-甲基-3-呋喃基)二硫化物是陕西汉中红茶的主要香气化合物;Kang等[28]发现己烯醇、1-辛烯-3-醇、苯甲醇、芳樟醇、脱氢芳樟醇、苯乙醇、己醛、苯乙醛、2-壬酮、β-月桂烯、柠檬烯、2-戊基呋喃、庚酸和甲基吡嗪是祁门红茶的主要香气化合物,这与筠连早白尖红茶存在一定差异;而Wang等[29]对云南滇红的研究发现芳樟醇、香叶醇、芳樟醇氧化物II、反-橙花叔醇、氧化芳樟醇III和氧化芳樟醇I、苯甲醛、苯乙醛、β-环柠檬醛、水杨酸甲酯、β-紫罗兰酮是主要香气化合物,这与本研究结果高度相似。推测可能是由于筠连早白尖红茶在加工工艺上与云南滇红有更好的一致性,其差异则可能来自原料及生态环境的不同。
本实验在春季样品中均检测到茉莉酮(0.95 μg/g),而夏秋季样品均未检出。茉莉酮是由鲜叶中不饱和脂肪酸如亚麻酸经脂质氧化形成的环状挥发性芳香化合物,具有浓郁的茉莉花香[30],虽然其在样品中含量不高,但其香气阈值低,推测其对红茶整体香气仍有一定影响。以上结果表明,筠连早白尖红茶香气化合物组成与云南滇红比较一致,表现出明显的花香和果香,但不同季节样品之间存在差异,尤其是春季样品具有极高含量的醇类和酯类,整体香气组成与夏秋样品明显不同。
2.2 不同季节筠连早白尖红茶香气成分的PLS-DA
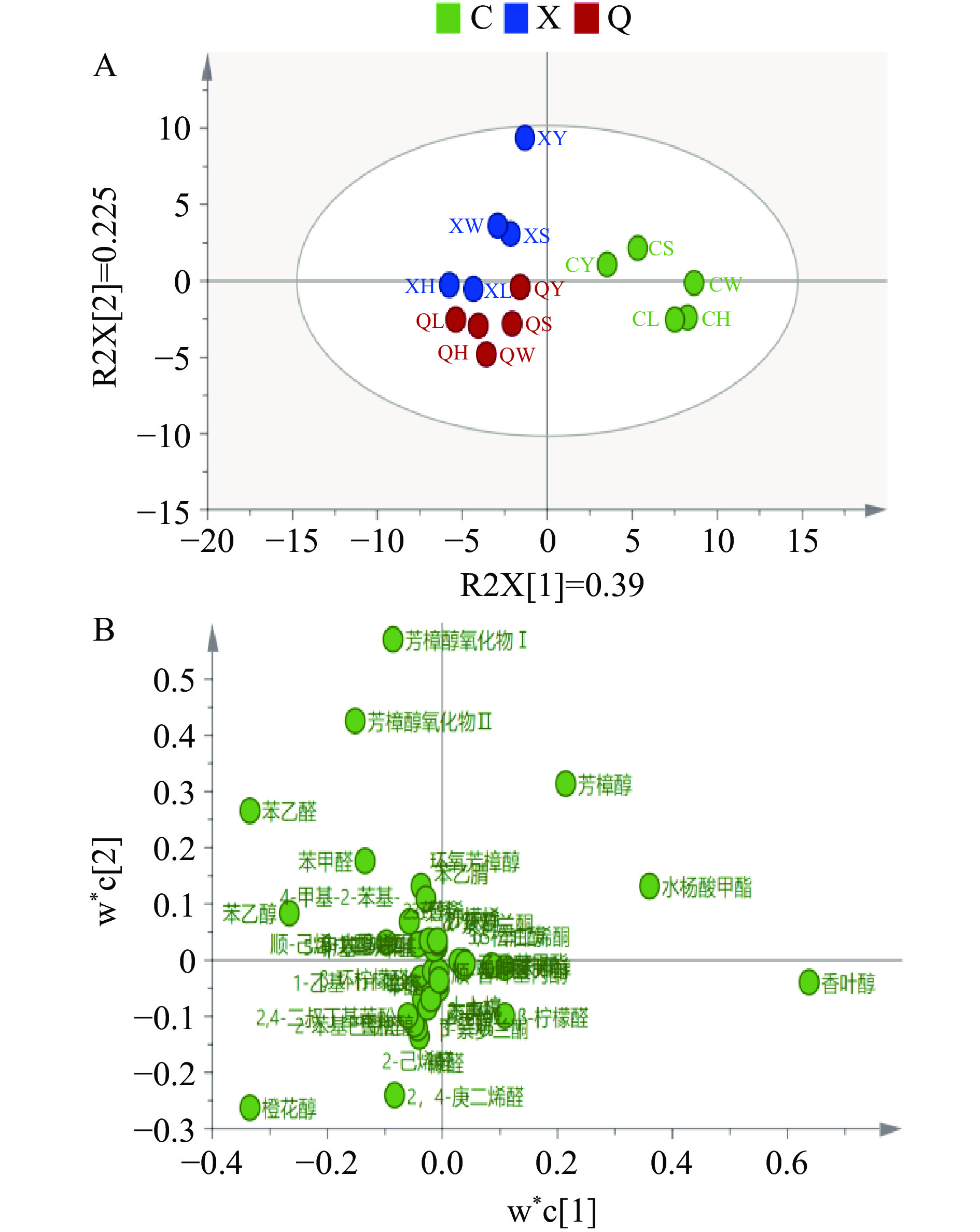
为了更好地进行三个季节红茶风味识别,以筠连早白尖红茶挥发性化合物为X变量,季节属性为Y变量,利用SMICA14.1软件进行PLS-DA分析,所建立的PLSR模型提取3个主成分可以解释82%的原始变量,说明该模型能够成功地反映样品的整体信息。以第一主成分和第二主成分为横纵坐标建立样品和挥发性化合物的相关性得分图和载荷图(图3),15个茶样的相似度在95%的置信区间内,各茶样表现出明显的聚类趋势,未发现离群样本点,说明建立的PLS-DA模型可对15个茶样进行分类。由图3A可以看出,春季茶和夏秋两季茶可以在主成分1上明显区分,夏季和秋季茶在主成分2上具有一定的区分度,但不能完全进行区分。各主成分的载荷值代表该主成分对该类物质反映程度的大小,由图3B可知,香叶醇、水杨酸甲酯、橙花醇、苯乙醛等物质在第一主成分的载荷值较大,芳樟醇氧化物Ⅰ和Ⅱ、2,4-庚二烯醛在第二成分上的载荷值较大。
通过PLS-DA 的变量投影重要度(variable importance for the projection,VIP)分析可知(表2),香叶醇、芳樟氧化物Ⅰ、苯乙醛、橙花醇、水杨酸甲酯、芳樟醇氧化物Ⅱ、2,4-庚二烯醛、芳樟醇、苯乙醇、苯甲醛的VIP值均>1,是不同季节筠连早白尖红茶相互判别的主要特征标志物。付静[31]发现香叶醇、水杨酸甲酯、β-芳樟醇、苯乙醇、苯甲醛和苯乙醛是不同季节陕西工夫红茶的主要呈香物质组分,其中春季茶香叶醇含量能达到40%以上,夏秋季茶则呈明显降低趋势,而水杨酸甲酯和芳樟醇类在春季茶中含量较低,从夏季开始则有增加趋势,说明通过检测红茶中香叶醇、水杨酸甲酯、β-芳樟醇、苯乙醇、苯甲醛和苯乙醛的含量可以区分不同季节样品,这与本文的研究结果相似;黄浩等[32]研究发现保靖黄金1号工夫红茶的秋季茶香气指数最高,夏、春季茶次之,不同季节的标志差异性化合物为水杨酸甲酯、苯甲醛、月桂烯、2,6-二甲基-3,7-辛二烯-2,6-二醇、1-乙基-2-甲酰吡咯、藏红花醛、反-橙叔醇、苯乙烯、2-辛烯-1-醛、反-2-癸烯醛、苯乙醇、反-芳樟醇氧化物(吡喃型)、反-2-壬烯醛,则与本文研究结果存在一定差异,这可能是由于茶叶品种以及工艺不同导致的。
表 2 PLS-DA分析中关键香气成分的VIP值、P值和香气特征Table 2. VIP value, P value and aroma characteristics of key aroma components in PLS-DA analysis序号 挥发性化合物 VIP值 P值 香气特征[33] 1 香叶醇 3.24838 0.000** 玫瑰花香,甜香 2 芳樟醇氧化物Ⅰ 2.11871 0.040* 花果香,柠檬香 3 苯乙醛 2.09512 0.001** 水果甜香 4 橙花醇 2.00904 0.019* 玫瑰花香,甜香 5 水杨酸甲酯 1.93897 0.001** 冬青香,薄荷香 6 芳樟醇氧化物Ⅱ 1.785 0.028* 花果香,柠檬香 7 2,4-庚二烯醛 1.57082 0.203 清香,肉香 8 芳樟醇 1.56885 0.028* 花果香,柠檬香 9 苯乙醇 1.47787 0.089 玫瑰花香,蜜香 10 苯甲醛 1.08978 0.388 坚果味,苦杏仁味 注:“**”表示不同季节间差异极显著(P<0.01);“*”表示不同季节间差异显著(P<0.05)。 为更好地了解10种关键香气成分分别在不同季节筠连早白尖红茶中的分布情况,将10种香气成分在样品中的含量进行单因素方差分析,发现不同季节茶样中香叶醇、水杨酸甲酯、苯乙醛具有极显著差异(P<0.01),芳樟醇氧化物Ⅰ和Ⅱ、橙花醇、芳樟醇具有显著差异(P<0.05),而苯乙醇、2,4-庚二烯醛和苯甲醛无显著差异(P>0.05)。
2.3 关键特征标志物在不同季节筠连早白尖红茶中的聚类分析
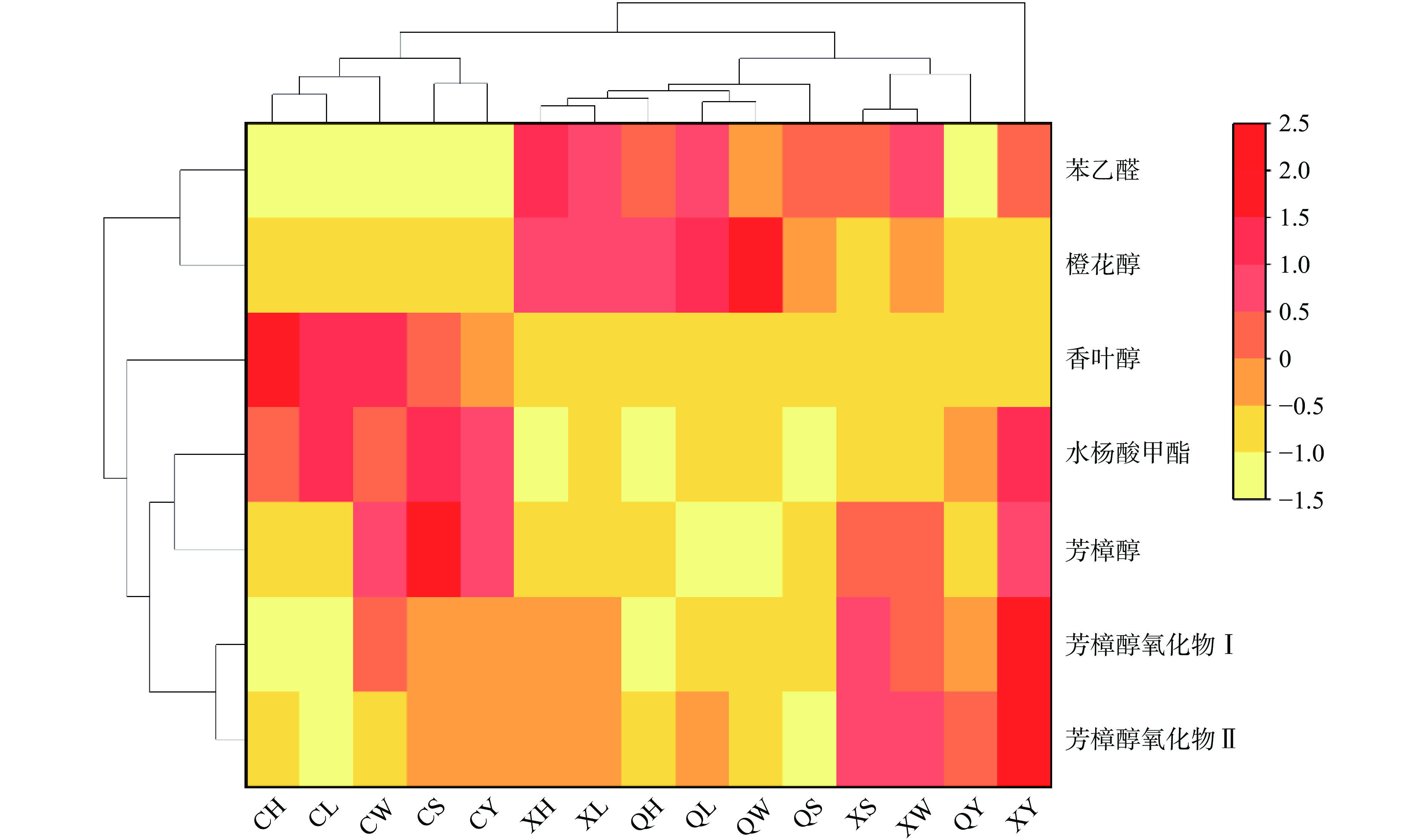
本实验将VIP>1且差异显著的7种关键特征标志物在不同季节样品中的相对含量分布情况进行分层聚类并绘制热图,如图4所示,颜色由黄色到红色,代表相对含量由低到高。苯乙醛和橙花醇聚为第一种香气类型,主要表现为玫瑰花香和水果甜香,平均相对含量在秋季样品中最高,夏季次之,春季样品中含量最低,但苯乙醛在夏季样品中平均相对含量也较高,与秋季样品无显著性差异(P>0.05);香叶醇单独聚为第二种香气类型,前文已讨论到其只在春季样品中出现且相对含量较高,主要表现为玫瑰花香;水杨酸甲酯和芳樟醇聚为第三种香气类型,主要表现为花果香、柠檬香、冬青味、薄荷味,在春季样品中平均相对含量最高,秋季最低,但芳樟醇在夏季样品中平均相对含量也较高,与春季样品无显著性差异(P>0.05);最后是芳樟醇氧化物Ⅰ和芳樟醇氧化物Ⅱ聚为第四种香气类型,主要表现为花果香和柠檬香,在夏季样品中相对含量最高,秋季最低。
综上所述,苯乙醛、橙花醇和香叶醇可以作为区分春季和夏秋两季茶样的特征标志物,特别是橙花醇可以进一步区分秋季和夏季茶样,表明筠连早白尖秋季红茶更突出玫瑰花香和水果甜香;在此基础上,芳樟醇氧化物Ⅰ和Ⅱ可以作为进一步区别夏、秋两季茶样的特征标志物,表明筠连早白尖夏季红茶更突出花果香和柠檬香。值得注意的是,本实验发现部分关键特征标志物即使在同一季节的不同早白尖红茶样品中分布也存在较大差异,比如芳樟醇,在春季和夏季样品中均是低海拔茶园含量显著高于高海拔茶园含量,推测可能是由于海拔差异(海拔高度相差超过500 m),海拔差异会带来气候条件的差异,进而影响茶叶初级、次级代谢物,研究发现[9]与高海拔茶叶相比,低海拔茶叶含有更多的丙氨酸、异亮氨酸和苹果酸等,这也成为影响茶叶香气成分的重要因素[34],具体影响规律还有待进一步研究。
3. 结论
本研究对不同季节筠连早白尖红茶香气成分进行研究,共鉴定出44种香气化合物,筠连红茶香气成分与云南滇红香气成分具有一定的相似性,表现出明显的花香和果香特征。但不同季节筠连早白尖红茶挥发性风味物质具有显著差异,通过PLS-DA 的变量投影重要度分析明确了10种主要特征香气成分,可以明显区分春季与夏秋两季茶样。其中,苯乙醛、橙花醇和香叶醇可以区别春季与其它两季茶样;在此基础上可通过芳樟醇、芳樟醇氧化物Ⅰ和Ⅱ对夏、秋两季样品进行进一步区分,进而实现以筠连早白尖红茶样品的香气成分来对原料采收期进行溯源,并为筠连早白尖红茶的开发提供了理论依据,为地方优质红茶品牌塑造提供参考;也为今后进一步探索筠连早白尖红茶关键香气成分形成机制,以及继续研究茶园海拔、加工工艺、采收年份等因素对筠连早白尖红茶香气成分的影响奠定基础。
-
表 1 各季节样品挥发性成分(μg/g)
Table 1 Volatile components of each tea sample collected from different seasons (μg/g)
化合物 春季 夏季 秋季 显著性 糠醛 0.13±0.26 0.07±0.14 0.84±0.58 * 己烯醛 1.61±1.55 1.42±0.53 2.63±1.53 苯甲醛 12.58±2.43 19.87±6.97 14.38±11.37 2,4-庚二烯醛 0.19±0.21 0.53±0.76 4.30±5.79 辛醛 \ \ 0.14±0.28 苯乙醛 6.81±1.19 21.38±4.70 15.42±5.48 * 葵醛 0.11±0.22 0.06±0.13 0.21±0.18 β-环柠檬醛 0.05±0.09 0.25±0.20 0.41±0.41 β-柠檬醛 2.23±0.99 \ 0.72±1.13 * 2-苯基巴豆醛 \ 0.24±0.49 0.99±1.21 甲基苯基-2-戊烯醛 0.07±0.14 0.77±0.51 0.41±0.38 甲基苯基-2-己烯醛 0.07±0.09 0.13±0.09 0.18±0.18 醛类总计 23.85 44.72 40.63 顺-己烯-1-醇 1.12±1.23 3.04±2.36 2.74±3.08 苯甲醇 15.10±6.58 10.90±2.15 10.00±3.04 芳樟醇氧化物Ⅱ 4.03±2.71 13.66±7.33 4.44±3.61 * 芳樟醇氧化物Ⅰ 13.08±7.05 22.44±9.89 8.16±2.31 芳樟醇 13.83±8.15 9.09±4.50 1.76±1.49 苯乙醇 20.93±6.58 31.45±6.27 27.71±7.00 环氧芳樟醇 \ 1.82±3.64 \ α-松油醇 0.41±0.82 \ \ 香叶醇 44.38±22.69 \ \ * 橙花醇 \ 11.78±8.11 18.59±11.11 雪松醇 0.18±0.35 0.34±0.35 0.75±0.77 醇类总计 113.05 104.52 74.15 2-庚酮 0.02±0.05 \ 0.10±0.14 3,5-辛二烯酮 0.21±0.42 \ \ 2-莰酮 \ 0.04±0.09 \ 茉莉酮 0.95±0.55 \ \ * 顺-香叶基丙酮 \ \ 0.04±0.07 β-大马烯酮 \ 0.28±0.26 0.14±0.13 β-紫罗兰酮 0.33±0.06 0.29±0.20 0.57±0.31 α-紫罗兰酮 \ 0.09±0.11 0.02±0.05 酮类总计 1.51 0.70 0.87 乙酸苯甲酯 0.20±0.19 \ \ * 水杨酸甲酯 34.72±5.67 18.14±7.23 13.64±2.97 * 酯类总计 34.92 18.14 13.64 柠檬烯 \ 0.06±0.12 \ 十二烷 \ \ 0.21±0.31 2-莰烯 \ 0.17±0.22 0.06±0.12 3-蒈烯 \ 0.09±0.18 \ 十三烷 \ \ 0.22±0.23 * 十七烷 0.05±0.10 \ 0.06±0.07 碳氢化合物总计 0.05 0.32 0.55 2-戊基呋喃 \ 0.43±0.85 0.44±0.45 乙基-1H-吡咯-2-甲醛 \ \ 0.51±1.02 苯乙腈 \ 0.51±0.45 \ * 2,4-二叔丁基苯酚 5.74±1.03 6.22±1.80 6.79±3.00 咖啡因 0.31±0.39 \ 0.04±0.08 杂环类及其他总计 6.05 7.16 7.78 总含量 179.43 175.56 137.62 注:“\”为未检出;“*”表示不同季节样品组间差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 2 PLS-DA分析中关键香气成分的VIP值、P值和香气特征
Table 2 VIP value, P value and aroma characteristics of key aroma components in PLS-DA analysis
序号 挥发性化合物 VIP值 P值 香气特征[33] 1 香叶醇 3.24838 0.000** 玫瑰花香,甜香 2 芳樟醇氧化物Ⅰ 2.11871 0.040* 花果香,柠檬香 3 苯乙醛 2.09512 0.001** 水果甜香 4 橙花醇 2.00904 0.019* 玫瑰花香,甜香 5 水杨酸甲酯 1.93897 0.001** 冬青香,薄荷香 6 芳樟醇氧化物Ⅱ 1.785 0.028* 花果香,柠檬香 7 2,4-庚二烯醛 1.57082 0.203 清香,肉香 8 芳樟醇 1.56885 0.028* 花果香,柠檬香 9 苯乙醇 1.47787 0.089 玫瑰花香,蜜香 10 苯甲醛 1.08978 0.388 坚果味,苦杏仁味 注:“**”表示不同季节间差异极显著(P<0.01);“*”表示不同季节间差异显著(P<0.05)。 -
[1] 余丽辰, 游玲, 王锐樯, 等. 茶树品种对筠连红茶品质的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(8):43−48. [YU Lichen, YOU Ling, WANG Ruiqiang, et al. Effect of tea cultivars on the quality of Junlian black tea[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(8):43−48. [2] FENG Z, LI Y, LI M, et al. Tea aroma formation from six model manufacturing processes[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,285:347−354. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.01.174
[3] WANG B, CHEN H, QU F, et al. Identification of aroma-active components in black teas produced by six Chinese tea cultivars in high-latitude region by GC-MS and GC-O analysis[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2022,248(3):647−657. doi: 10.1007/s00217-021-03911-x
[4] LI Y, RAN W, HE C, et al. Effects of different tea tree varieties on the color, aroma, and taste of Chinese Enshi green tea[J]. Food Chemistry,2022:100289.
[5] 王秋霜, 凌彩金, 乔小燕, 等. 萎凋及发酵时间对广东丹霞红茶香气及品质的影响[J]. 茶叶科学,2019,39(3):342−354. [WANG Qiushaung, LING Caijin, QIAO Xiaoyan, et al. Effect of withering and fermentation duration on aroma and qualities in Guangdong Danxia black tea[J]. Journal of Tea Science,2019,39(3):342−354. [6] 仇方方, 曾维超, 曲凤凤, 等. 提香方式对工夫红茶品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(11):82−87. [QIU Fangfang, ZENG Weichao, QU Fengfeng, et al. Effect of aroma enhancement methods on the quality of Congou black tea[J]. Food Science,2019,40(11):82−87. [7] MA L, GAO M, ZHANG L, et al. Characterization of the key aroma-active compounds in high-grade Dianhong tea using GC-MS and GC-O combined with sensory-directed flavor analysis[J]. Food Chemistry,2022:132058.
[8] CHEN X H, SUN H Y, QU D, et al. Identification and characterization of key aroma compounds in Chinese high altitude and northernmost black tea (Camellia sinensis) using distillation extraction and sensory analysis methods[J]. Flavour and Fragrance Journal,2020,35(6):666−673.
[9] FEDERICO S, GIULIA T, CARLO B, et al. Climate and processing effects on tea (Camellia sinensis L. Kuntze) metabolome: Accurate profiling and fingerprinting by comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry[J]. Molecules,2020,25(10):67−85.
[10] SU D, HE J J, ZHOU Y Z, et al. Aroma effects of key volatile compounds in Keemun black tea at different grades: HS-SPME-GC-MS, sensory evaluation, and chemometrics[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,373:131587. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131587
[11] FENG Z, LI M, LI Y, et al. Characterization of the key aroma compounds in infusions of four white teas by the sensomics approach[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2022:1−11.
[12] 杨娟, 王杰, 李中林, 等. 重庆工夫红茶加工过程中生化成分及香气组分变化[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(13):166−171. [YANG Juan, WANG Jie, LI Zhonglin, et al. Change of biochemical and aroma components during processing of Chongqing Congou[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(13):166−171. [13] DU L, LI J, LI W, et al. Characterization of volatile compounds of Pu-erh tea using solid-phase microextraction and simultaneous distillation-extraction coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. Research International,2014,57:61−70. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2014.01.008
[14] MA C Y, LI J X, CHEN W, et al. Study of the aroma formation and transformation during the manufacturing process of oolong tea by solid-phase micro-extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry combined with chemometrics[J]. Food Research International,2018,108:413−422.
[15] MA L, GAO M, HU J, et al. Characterization of the key active aroma compounds in Pu-erh tea using gas chromatography-time of flight/mass spectrometry-olfactometry combined with five different evaluation methods[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2022,248(1):45−56. doi: 10.1007/s00217-021-03847-2
[16] YAN T, LIN J, ZHU J, et al. Aroma analysis of Fuyun 6 and Jinguanyin black tea in the Fu'an area based on E-nose and GC–MS[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2022,248(4):947−961.
[17] MARCELA B A, GUSTAVO G M, ROY E B, et al. Spectroscopic and chromatographic fingerprints for discrimination of specialty and traditional coffees by integrated chemometric methods[J]. Food Analytical Methods,2020,13(12):1−9.
[18] CHEN Q, ZHU Y, LIU Y, et al. Black tea aroma formation during the fermentation period[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,374:131640. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131640
[19] 程超, 杜芬妮, 李伟, 等. 基于9种风味物质的利川红SPME优化及PLS-DA风味识别[J]. 食品科学,2020,42(6):215−221. [CHENG Chao, DU Fenni, LI Wei, et al. Optimization of solid phase microextraction for GC-MS analysis of nine flavor compounds in Lichuan Hong tea and flavor discrimination by partial least squares-discriminant analysis[J]. Food Science,2020,42(6):215−221. [20] WANG Q, JIANG X, QIN D, et al. Metabolic profiling of flavor compounds in black teas with almond odor during processing[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2020,246(3):2039−2053.
[21] 杨娟, 王杰, 王奕, 等. 萎凋叶含水量对四川中小叶群体种工夫红茶品质形成的影响[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2020,11(13):4379−4386. [YANG Juan, WANG Jie, WANG Yi, et al. Effect of water content of withered leaves on the quality of Congou black tea processed by Sichuan small and medium leaf group species[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2020,11(13):4379−4386. [22] 冯花, 王飞权, 张渤, 等. 不同茶树品种白牡丹茶香气成分的HS-SPME-GC-MS分析[J]. 现代食品科技,2021,37(12):252−264, 251. [FENG Hua, WANG Feiquan, ZHANG Bo, et al. Analysis of aroma components of Baimudan tea from different tea plant varieties using HS-SPME-GC-MS[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2021,37(12):252−264, 251. [23] 汪鹏, 王璐, 陈杰博, 等. 以4-叔丁基环己醇为内标物定量分析茶叶的香气成分[J]. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版),2021,50(2):198−205. [WANG Peng, WANG Lu, CHEN Jiebo, et al. Quantitative analysis of aroma components in tea by 4-tert-butylcyclohexanol as internal standard[J]. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition),2021,50(2):198−205. [24] 马玉青, 方成刚, 夏丽飞, 等. 不同发酵程度对重萎凋“云抗10号”红茶香气成分的影响[J]. 西南农业学报,2020,33(4):760−768. [MA Yuqing, FANG Chenggang XIA Lifei, et al. Effect of different fermentation degree on aroma components of heavy withered ‘Yunkang No.10' black tea[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences,2020,33(4):760−768. [25] 章港, 黄文静, 徐珩, 等. 基于气质联用技术的“祁门香”特征性成分分析[J]. 茶叶通讯,2020,47(1):96−101. [ZHANG Gang, HUANG Wenjing, XU Heng, et al. Analysis of the characteristic components of Keemun aroma based on gas chromatography-mass spectrometer[J]. Journal of Tea Communication,2020,47(1):96−101. [26] 王梦琪, 朱荫, 张悦, 等. 茶叶挥发性成分中关键呈香成分研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(23):341−349. [WANG Mengqi, ZHU Yin, ZHANG Yue, et al. A review of recent research on key aroma compounds in tea[J]. Food Science,2019,40(23):341−349. [27] CHEN X H, CHEN D J, JIANG H, et al. Aroma characterization of Hanzhong black tea (Camellia sinensis) using solid phase extraction coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and olfactometry and sensory analysis[J]. Food chemistry,2019,274:130−136. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.08.124
[28] KANG S, YAN H, ZHU Y, et al. Identification and quantification of key odorants in the world's four most famous black teas[J]. Food Research International,2019,121:73−83. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.03.009
[29] WANG C, ZHANG C, KONG Y, et al. A comparative study of volatile components in Dianhong teas from fresh leaves of four tea cultivars by using chromatography-mass spectrometry, multivariate data analysis, and descriptive sensory analysis[J]. Food Research International,2017,100:267−275. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2017.07.013
[30] 刘飞, 王云, 张厅, 等. 红茶加工过程香气变化研究进展[J]. 茶叶科学,2018,38(1):9−19. [LIU Fei, WANG Yun, ZHANG Ting, et al. Review on aroma change during black tea processing[J]. Journal of Tea Science,2018,38(1):9−19. [31] 付静. 不同采摘季节工夫红茶品质的研究[J]. 食品科技,2017,42(11):90−95. [FU Jing. The effects of different plucking seasons of fresh tea leaves on congou black tea quality[J]. Food Science and Technology,2017,42(11):90−95. [32] 黄浩, 余鹏辉, 赵熙, 等. 不同季节保靖黄金茶1号工夫红茶挥发性成分的HS-SPME-GC-MS分析[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(12):188−196. [HUANG Hao, YU Penghui, ZHAO Xi, et al. HS-SPME-GC-MS analysis of volatile components of Congou black tea processed from Baojing Huangjincha No.1 from different harvesting seasons[J]. Food Science,2020,41(12):188−196. [33] 蒋青香, 李慧雪, 李利君, 等. 基于感官检验和气相色谱-质谱联用对白芽奇兰茶叶香气分级[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(20):98−106. [JIANG Qingxiang, LI Huixue, LI Lijun, et al. Aroma classification of Baiyaqilan tea by sensory test and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. Food Science,2021,42(20):98−106. [34] FANG S M, NING J M, HUANG W J, et al. Identification of geographical origin of Keemun black tea based on its volatile composition coupled with multivariate statistical analyses[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2019,99(9):4344−4345. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.9668
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 陈佳妮,罗耀华,孔慧,丁可,葛帅,丁胜华. 热激处理对鲜切百合鳞茎片贮藏品质的影响. 食品科学. 2024(09): 163-172 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)






 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



