Ameliorative Effect of Gastrodin on Aging and Inflammation of BV2 Cells by Regulating SIRT3
-
摘要: 目的:探讨天麻素对D-半乳糖诱导的BV2细胞衰老的保护作用及机制。方法:使用不同浓度(10、20、30和40 μg/mL)的D-半乳糖刺激BV2细胞24 h,建立细胞衰老模型,并用CCK-8法筛选出D-半乳糖的最佳造模浓度;实验分为4组:正常组、模型组、Silent mating type information regulation 2 homolog 3(SIRT3)抑制剂+天麻素组和天麻素组;用CCK-8法检测不同浓度(10、20、30、40和50 μmol/L)的天麻素对D-半乳糖刺激的BV2细胞活力的影响,并筛选出最佳的天麻素浓度;使用β-半乳糖苷酶(Senescence β-Galactosidase,SA-β-Gal)染色检测细胞衰老面积;使用生化法检测各组细胞活性氧(Reactive oxygen species,ROS)水平;使用Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay(ELISA)法检测各组细胞神经炎症因子IL-1β(Interleukin 1β,IL-1β)、IL-6(Interleukin 6,IL-6)和TNF-α(Tumor necrosis factor α,TNF-α)水平;使用免疫荧光法检测各组细胞SIRT3荧光强度;使用Western Blot法检测细胞SIRT3、P16和P21的蛋白表达水平。结果:30 μg/mL的D-半乳糖刺激BV2细胞活力极显著降低(P<0.01),引起BV2细胞中SA-β-Gal染色面积和衰老蛋白P16和P21表达极显著增加(P<0.01),细胞中ROS水平和炎症因子IL-1β、IL-6和TNF-α水平极显著增高(P<0.01),细胞内SIRT3蛋白表达极显著降低(P<0.01)。而30 μmol/L天麻素能极显著提高D-半乳糖刺激的BV2细胞活力(P<0.01),并且极显著降低细胞SA-β-Gal染色面积和衰老蛋白P16和P21表达水平(P<0.01),极显著降低ROS水平和神经炎症因子IL-1β、IL-6和TNF-α水平(P<0.01),极显著提高细胞内SIRT3蛋白荧光强度和表达水平(P<0.01)。结论:天麻素能够提高D-半乳糖刺激的BV2细胞活力,改善BV2细胞衰老染色和衰老蛋白表达,并降低ROS水平和减缓炎症反应,这可能与天麻素提高SIRT3蛋白表达有关。Abstract: Objective: In order to explore the protective effects and mechanism of gastrodin on BV2 cells treated with D-galactose. Methods: The BV2 cells were treated with D-galactose at different concentrations (10, 20, 30 and 40 μg/mL) for 24 h to establish a senescent cell model, and the optimum concentration of D-galactose was selected by CCK-8 method; The cells were divided into control group, model group, silent mating type information regulation 2 homolog 3 (SIRT3) inhibitor+gastrodin group and gastrodin group; and the optimum concentration of D-galactose was selected by CCK-8 method; The effects of different concentrations of gastrodin (10, 20, 30, 40 and 50 μg/mL) on the viability of BV2 cells treated with D-galactose were detected by CCK-8 method, and the best concentration of gastrodin was selected; The aging area of BV2 cells was detected by Senescence β-Galactosidase staining (SA-β-Gal); The level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in BV2 cells was detected by biochemical method; The levels of neuroinflammatory factor interleukin 1β (IL-1β), interleukin 6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) were detected by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA); The fluorescence intensity of SIRT3 was detected by immunofluorescence method; The protein expression levels of SIRT3, P16 and P21 were detected by Western blot. Results: Treatment with D-galactose at 30 μg/mL exerted a significant inhibitory effect on BV2 cell viability, resulting in SA-β-Gal staining area and the expression of aging proteins P16 and P21 increased (P<0.01), ROS level and inflammatory factor IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α significantly increased (P<0.01), and the expression of SIRT3 protein and fluorescence intensity decreased in BV2 cells (P<0.01). 30 μmol/L gastrodin significantly increased the of BV2 cells viability treated with D-galactose (P<0.01); Gastrodin reduced SA-β-Gal staining area and the expression levels of aging proteins P16 and P21 (P<0.01); Gastrodin significantly decreased the level of ROS and neuroinflammatory factor IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α; The expression level of SIRT3 protein in cells was significantly increased (P<0.01). Treatment with gastrodin increased the fluorescence intensity and protein levels of SIRT3. Conclusion: Gastrodin increased the viability of the BV2 cells treated with D-galactose, improved the SA-β-Gal staining area and aging protein P16 and P21 expression, reduced the ROS level and slowed down the inflammatory response, which may be related to its increasing effect on the expression of SIRT3 protein.
-
Keywords:
- gastrodin /
- cell senescence /
- neuroinflammation /
- SIRT3 /
- D-galactose
-
随着世界人口老龄化,与衰老相关的神经退行性疾病的流行已成为一个严重的公共卫生问题,给社会带来了巨大的经济负担[1]。因此,研究大脑和神经细胞的衰老机制,将有助于制定有效的预防干预措施[2]。在衰老的大脑中,衰老的神经细胞也逐渐积累增加,加剧大脑的衰老,而改善脑中神经细胞的衰老则能够延缓大脑的衰老[3]。在脑老化过程中,衰老的小胶质细胞逐渐积累,大脑中的小胶质细胞占所有胶质细胞的5%~12%,在生理或病理条件下作为常驻的免疫细胞或巨噬细胞,是中枢神经系统的第一道防线,在感染、创伤、炎症、缺血性疾病以及神经退行性疾病中起着关键作用[4]。尽管激活的小胶质细胞能够吞噬细胞碎片和病原体来调节微环境的稳态,并分泌不同的神经营养因子以维持神经元的存活,但小胶质细胞的过度激活则会引起促炎介质以及细胞毒性物质如肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumor necrosis factor α,TNF-α)、白细胞介素-1β(interleukin 1β,IL-1β)、白细胞介素-6(interleukin 6,IL-6)、活性氧(reactive oxygen species,ROS)等的过度释放,加速神经炎症反应以及神经退行性变[5]。
NAD+依赖性脱乙酰酶蛋白Sirtuin3(silent mating type information regulation 2 homolog 3)属于Sirtuin基因家族,主要存在于线粒体中[6]。SIRT3参与能量代谢、线粒体功能和氧化应激以及炎症的调节,能够对抗与衰老相关的疾病[7]。同时,SIRT3已经被确定为几种炎症相关疾病中的关键调节因子[8]。研究发现,SIRT3可能是引发小胶质细胞炎症的关键上游启动因子,在炎症条件下,SIRT3蛋白表达下降。在之前的研究中,描述了SIRT3在神经炎症中的保护作用,但是很少有实验来研究SIRT3对衰老的小胶质细胞的作用。在本研究中,使用D-半乳糖诱导BV2细胞在体外建立一个衰老细胞模型,试图探讨SIRT3在衰老的BV2细胞中的具体作用。
天麻(Gastrodia)是兰科植物天麻的块茎,传统医学认为,天麻具有平肝息风、通络止痛的功效,能够广泛用于治疗头疼、癫痫、头晕、神经痛以及高血压等疾病[9]。天麻中有多种有效成分,但天麻素(Gastrodin)是其中最重要的一种天然酚类成分[10]。研究发现,天麻素具有抗氧化应激、抗炎和抗衰老的作用,由于天麻素能够穿越血脑屏障,通过清除活性氧,减少神经毒性促炎物质和脂质过氧化而在不同的神经系统疾病中发挥神经保护作用[11]。同时,天麻作为一种药食同源的中药材,有极高的营养保健价值,其明确指出的保健功能主要包括改善睡眠、增强机体免疫力,能够调节血压和血脂等[12]。以天麻为主要原料的保健产品也被广泛研究和开发,被CFDA批准的保健食品达30多种[13]。2019年11月,国家卫生健康委员会、国家市场监督管理总局联合发布对天麻等9种中药按照食药物质的标准进行研究,推进了中药材药食同源产业的发展[14]。然而目前关于天麻素对衰老的小胶质细胞的调控作用尚未有深入研究。由于神经炎症是神经退行性疾病的重要病理反应,而天麻素具有多种药理学作用,因此本项研究以D-半乳糖诱导的BV2细胞建立衰老细胞模型,探讨天麻素对衰老的BV2细胞中炎症反应的调节作用以及可能的机制,以期为开发治疗神经退行性疾病的新药和保健产品提供理论依据。
1. 材料和方法
1.1 材料与仪器
天麻素(纯度≥98%)(SG8080)、CCK-8试剂盒(CA1210)、TC处理细胞爬片(YA0350) 北京索莱宝生物科技有限公司;SIRT3抑制剂(50 mg)(120241-79-4) MedChemExpress公司;BV2小鼠小胶质细胞株(CL-0493)、BV2细胞专用培养基(CM-0493) 武汉普诺赛(Procell)生命科技有限公司;细胞衰老β-半乳糖苷酶(SA-β-Gal)染色试剂盒(C0602)、活性氧(ROS)检测试剂盒(S0033S)、小鼠白细胞介素1β(IL-1β)酶联免疫吸附检测试剂盒(PI301)、小鼠白细胞介素6(IL-6)酶联免疫吸附检测试剂盒(PI326)、小鼠肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)酶联免疫吸附检测试剂盒(PT512)、SIRT3兔抗蛋白(AF5303)、P16兔抗蛋白(AF1069)、P21兔抗蛋白(AF5252)、β-actin(AF0003)、Alexa Fluor 555标记驴抗兔IgG(H+L)(A0453)、辣根过氧化物酶标记山羊抗兔IgG(H+L)(A0208)、辣根过氧化物酶标记山羊抗小鼠IgG(H+L)(A0216)、抗荧光淬灭封片剂(P0131) 上海碧云天生物科技有效公司。
Multiskan FC酶标仪、BB150-2TCS二氧化碳培养箱、Sorvall Stratos低温冷冻高速离心机 美国Thermo Scientific公司;SDS-PAGE胶电泳转膜装置 美国Bio-Rad公司;Odyssey荧光成像系统 美国LI-COR Biosciences公司;CKX53倒置荧光显微镜 日本OLYMPUS公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 细胞培养
将BV2小胶质细胞置于含有10%胎牛血清、100 U/mL青霉素、链霉素的细胞培养基液中,在37 ℃,5% CO2培养箱中培养,隔天传代1次,当细胞生长状态良好时用于实验。
1.2.2 细胞分组
将BV2细胞分成4组:正常组,模型组,SIRT3抑制剂+天麻素组,天麻素组。正常组:给予细胞培养基培养;模型组:使用D-半乳糖(10、20、30和40 μg/mL)处理BV2细胞24 h;SIRT3抑制剂+天麻素组:先使用D-半乳糖处理BV2细胞24 h,然后同时使用10 μmol/L的SIRT3抑制剂和天麻素处理BV2细胞24 h;天麻素组:先使用D-半乳糖处理BV2细胞24 h,然后使用天麻素(10、20、30、40和50 μmol/L)处理BV2细胞24 h。
1.2.3 CCK-8法测量细胞活力
将细胞接种并培养在96孔板中,各组细胞用药干预结束后,弃去使用过的细胞培养基,每孔加入100 μL新鲜的细胞培养基,再加入10 μL CCK-8溶液,在细胞培养箱内继续培养2 h。培养结束后,使用酶标仪在450 nm处测定各组细胞吸光度值[15],实验结果用各组吸光度值与正常组吸光度的比值进行表示。
1.2.4 SA-β-Gal染色法检测细胞衰老面积
将细胞接种并培养在TC处理细胞爬片上,各组细胞在用药干预结束后,吸除使用过的细胞培养液。每孔加入400 μL PBS进行洗涤3次,每次3 min,洗涤结束后,每孔加入400 μL β-Gal染色固定液在室温固定15 min。染色固定结束后,每孔加入400 μL PBS洗涤3次,每次3 min。洗涤结束后,每孔加入400 μL染色工作液(每1 mL染色工作液中按照:β-Gal染色液A:B:C:X-Gal=10:10:930:50的比例配制)。使用保鲜膜封住24孔板以防止蒸发,放在37 ℃烘箱中孵育过夜。孵育结束后,在普通光学显微镜下观察,并拍照保存[16],实验结果用衰老细胞面积与总细胞面积进行表示。
1.2.5 ELISA法检测IL-1β、IL-6和TNF-α的含量
将细胞接种并培养在6孔板中并进行用药干预。各组用药干预结束后,首先根据试剂盒说明书配制标准品并绘制标准曲线。收集各组细胞进行离心(500 g,5 min),取上清。分别将100 μL样品和不同浓度的标准品加入到相应的反应孔中,用封板膜封住反应孔并室温孵育120 min。孵育结束后进行洗板,拍干后每孔加入400 μL辣根过氧化物酶标记Streptavidin,用封板膜封住反应孔后,室温下避光孵育20 min。孵育结束后,进行洗板5次。拍干反应板后,每孔加入100 μL显色剂TMB试剂。室温下避光孵育20 min,每孔加入50 μL终止液,混匀后立即测量A450值[17]。
1.2.6 生化法检测活性氧(ROS)水平
将细胞接种并培养在96孔板中,各组细胞用药干预结束后,弃掉细胞培养液,每孔加入100 μL 2,7-二氯二氢荧光素二乙酸酯(DCFH-DA)(按照1:1000比例稀释),37 ℃细胞培养箱内孵育20 min。孵育结束后,用无血清细胞培养液洗涤3次,每次5 min,洗涤结束后使用荧光酶标仪在激发波长488 nm,发射波长525 nm处检测荧光强度值[18]。
1.2.7 免疫荧光检测细胞中SIRT3蛋白表达水平
将细胞接种并培养在TC处理细胞爬片上并进行用药干预。各组干预结束后,吸尽使用过的细胞培养液,加入400 μL固定液室温下固定30 min。固定结束后,去除固定液,每孔加入400 μL PBS放入摇床进行摇动洗涤,每次5 min,洗涤3次。洗涤结束后用封闭液封闭60 min,封闭结束后加入稀释的一抗anti-SIRT3(1:500)。在4 ℃条件下孵育过夜,一抗孵育结束后,每孔加入400 μL PBS洗涤5次,每次5 min。洗涤结束后,每孔加入荧光标记的Alexa Fluor 555标记驴抗兔IgG(H+L)(1:1000)室温下避光孵育60 min,孵育结束后使用抗荧光淬灭封片剂(含DAPI)进行封片,在荧光显微镜下进行观察[18]。
1.2.8 Western Blot法检测SIRT3、P16、P21蛋白表达
将细胞接种并培养在24孔板中并进行用药干预。各组干预结束后,每孔加入400 μL PBS洗涤。洗涤结束后每孔加入100 μL裂解液,使用移液枪吹打,使裂解液与细胞充分接触。充分裂解后,离心(12000 g,5 min),取上清。使用BCA法测量蛋白浓度。使用12%分离胶和5%浓缩胶进行电泳和转膜,转膜结束后加入适量的封闭液,室温下封闭60 min,使用一抗稀释液稀释一抗anti-SIRT3(1:1000),anti-P16(1:1000),anti-P21(1:1000)和β-actin(1:1000),在4 ℃条件下孵育过夜,用Western洗涤液洗涤3次,每次10 min,加入二抗anti-rabbit(1:10000)、anti-mouse(1:10000),室温孵育60 min,洗涤3次,每次10 min。洗涤结束后将配置好的显影液滴加在PVDF膜上进行曝光成像[18]。
1.3 数据处理
使用 GraphPad Prism 8.0软件(GraphPad Software, Inc., An Diego, CA)对实验结果进行统计分析,数据采用均数±标准差表示。两组之间的比较采用独立样本t检验(Independent-Sample t Test),多组间比较采用单因素方差分析(One Way ANOVA),检验水准取双侧α=0.05,P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义,P<0.01为差异具有显著统计学意义。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 D-半乳糖对BV2细胞活力和衰老的影响
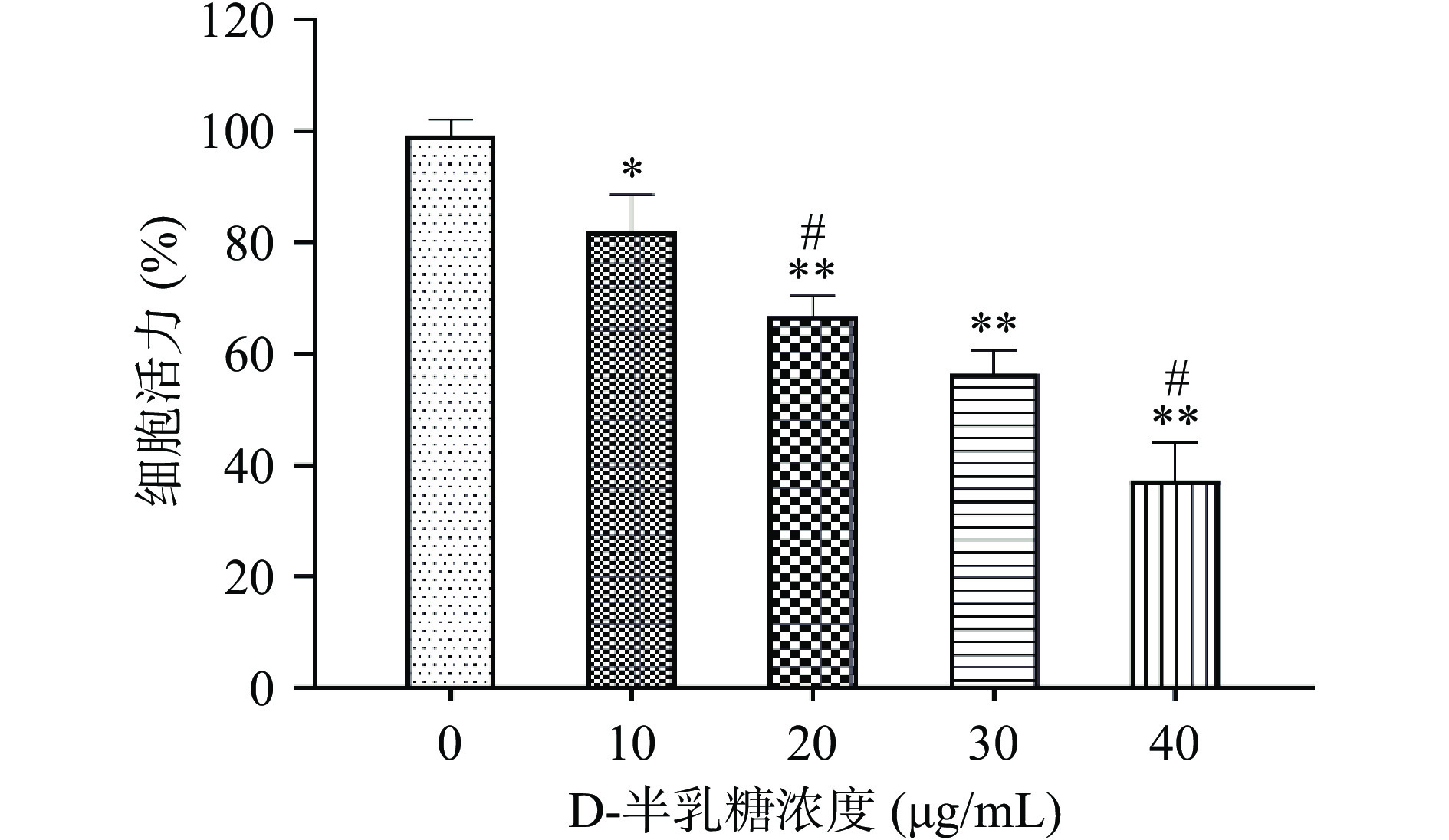
研究发现D-半乳糖在半乳糖氧化酶的催化作用下,会产生过氧化氢和醛糖,该产物又会刺激细胞,产生大量的自由基离子,从而进一步损伤细胞的生理功能,因此本实验使用D-半乳糖诱导BV2细胞衰老建立细胞模型[19]。如图1显示,不同剂量的D-半乳糖(10、20、30和40 μg/mL)均能够降低BV2细胞活力,并且呈剂量依赖性下降(P<0.05)。使用30 μg/mL的D-半乳糖诱导的BV2细胞存活率在50%~60%,比20 μg/mL的D-半乳糖诱导更为显著地降低细胞活力(P<0.05),高于使用40 μg/mL的D-半乳糖诱导的BV2细胞存活率(P<0.05)。为避免D-半乳糖处理的BV2细胞活力过度降低而产生不可逆性的损伤[20],本实验选择浓度30 μg/mL的D-半乳糖用于后续实验。本实验进一步检测30 μg/mL的D-半乳糖对BV2细胞衰老的影响,由于β-半乳糖苷酶染色阳性是细胞衰老的重要标志物,因此本实验使用SA-β-Gal染色法BV2细胞衰老面积。如图2显示:正常组细胞SA-β-Gal衰老染色面积小,30 μg/mL的D-半乳糖诱导的BV2细胞SA-β-Gal染色面积极显著增大(P<0.01)。这表明使用30 μg/mL的D-半乳糖处理BV2细胞能够降低BV2细胞活力,并且引起BV2细胞衰老。因此,在后续实验中使用30 μg/mL的D-半乳糖进行造模。
2.2 天麻素对D-半乳糖处理BV2细胞活力和衰老的影响
先前研究已证实天麻素具有抗衰老作用[21]。本实验中,使用不同浓度(10、20、30、40和50 μmol/L)的天麻素干预衰老的BV2细胞,然后检测各组细胞活力以测定天麻素的最佳干预浓度。如图3实验结果显示:浓度为20、30、40和50 μmol/L的天麻素均能提高D-半乳糖处理的BV2细胞活力,且呈剂量依赖性(P<0.05)。30 μmol/L的天麻素比20 μmol/L的天麻素更有效的提高细胞活力(P<0.05)。而30 μmol/L天麻素较之40 μmol/L天麻素与50 μmol/L天麻素的作用无统计学差异(P>0.05)。因此,本实验选择浓度为30 μmol/L的天麻素用做后续实验。进一步检测各组细胞的SA-β-Gal染色,如图4结果显示:与模型组相比,天麻素组中BV2细胞SA-β-Gal染色面积极显著减少(P<0.01)。与天麻素组相比,SIRT3抑制剂+天麻素组中BV2细胞的SA-β-Gal染色面积增加(P<0.05)。这提示天麻素能改善D-半乳糖诱导的BV2细胞衰老,而抑制SIRT3表达则会减弱天麻素对D-半乳糖处理的BV2细胞的抗衰老作用。
2.3 天麻素对D-半乳糖处理BV2细胞炎症因子IL-1β、IL-6和TNF-α水平的影响
如图5显示,与正常组相比,模型组BV2细胞培养液中炎症因子IL-1β、IL-6和TNF-α水平极显著增高(P<0.01)。与模型组相比,天麻素组BV2细胞培养液中炎症因子IL-1β、IL-6和TNF-α水平极显著降低(P<0.01)。与天麻素组细胞相比,SIRT3抑制剂加天麻素组中BV2细胞培养液中炎症因子IL-1β、IL-6和TNF-α水平增加(P<0.05)。这提示天麻素能改善D-半乳糖诱导的BV2炎症反应,而抑制SIRT3表达则会减弱天麻素对D-半乳糖处理的BV2细胞抗炎作用。
2.4 天麻素对D-半乳糖处理BV2细胞ROS水平的影响
由于线粒体产生的ROS与炎症反应密切相关[22],本实验检测了各组BV2细胞的ROS水平。如图6结果显示:与正常组相比,模型组细胞ROS水平极显著增高(P<0.01)。与模型组相比,天麻素组中细胞ROS水平极降低(P<0.01)。此外,与天麻素组相比,SIRT3抑制剂+天麻素组中细胞ROS水平显著升高(P<0.05)。这提示天麻素能降低D-半乳糖处理的BV2中ROS水平,而抑制SIRT3表达则会减弱天麻素降低BV2细胞中ROS的保护作用。
2.5 天麻素对D-半乳糖处理BV2细胞中SIRT3、P16和P21蛋白表达的影响
如图7和图8结果显示:与正常组相比,模型组BV2细胞中SIRT3荧光强度和蛋白表达水平极显著下降(P<0.01)。与模型组相比,天麻素组中细胞SIRT3荧光强度和蛋白表达水平极显著增高(P<0.01)。此外,与天麻素组相比,SIRT3抑制剂+天麻素组BV2细胞中SIRT3荧光强度和蛋白表达水平显著降低(P<0.05)。这提示天麻素能够增高D-半乳糖处理的BV2细胞中SIRT3蛋白表达。
细胞周期异常是细胞衰老的一个关键病理特征,衰老细胞表现出永久性细胞周期阻滞,并主要由P16INK4A蛋白和P53-P21-RB蛋白调节[23]。因此本实验检测了各组细胞中P16和P21蛋白表达水平。如图8结果显示:与正常组相比,模型组细胞P16和P21蛋白表达极显著增加(P<0.01)。与模型组相比,天麻素组细胞P16和P21蛋白表达极显著降低(P<0.01)。此外,与天麻素组相比,SIRT3抑制剂+天麻素组中细胞P16和P21蛋白表达显著增加(P<0.05)。这提示天麻素能够降低D-半乳糖处理的BV2细胞中P16和P21蛋白水平,但是抑制SIRT3表达后,天麻素降低BV2细胞中衰老相关蛋白P16和P21蛋白的作用被部分减弱,因此SIRT3可能是天麻素发挥抗衰老作用的重要靶点。
3. 讨论与结论
随着预期寿命的逐渐延长,人体各器官的生理机能状态渐进性下降,直至功能丧失。衰老通常不被视为一种疾病,但它却是心血管疾病、代谢性疾病,尤其是神经退行性疾病等慢性疾病的重要危险因素[24]。在衰老的组织器官中,衰老细胞大量积累,并以不可逆的方式失去增殖能力,导致组织的再生潜能丧失、导致炎症和器官功能障碍[25]。在正常的条件下,衰老细胞通常在一个称为免疫监视的过程中被免疫细胞清除,然而随着年龄的增长,衰老的免疫细胞也出现渐进性的功能失调,引起其他衰老的细胞清除减少,最终导致整个器官和系统功能水平障碍[26]。小胶质细胞作为中枢神经系统的常驻巨噬细胞,以持续和动态的方式监察健康的脑组织环境,并能够清除其他受损的神经细胞,在衰老大脑的神经炎症和神经退行性病变中起着关键作用[27]。研究发现,衰老的大脑呈现出低级炎症状态[28]。在大脑衰老的过程中,小胶质细胞也发生衰老并逐渐积累,产生大量的促炎细胞因子,如肿瘤坏死因子TNF-α、白细胞介素IL-1β和白细胞介素IL-6,引起神经炎症反应[29]。在本实验中,使用D-半乳糖处理BV2细胞以建立衰老细胞模型,证实衰老的小胶质细胞出现了β-半乳糖苷酶染色增加和细胞周期阻滞的典型衰老病理特征,并且衰老的小胶质细胞活力下降,释放的炎症因子IL-1β、IL-6和TNF-α水平增加,引起了神经炎症反应,实验结果与以往的研究结果一致。在对衰老的小胶质细胞进行干预的实验中,本实验使用前期研究已经证实具有抗炎和抗衰老作用的天麻素。本团队研究发现,改善衰老的小胶质细胞能够增加细胞活力,减少神经炎症反应。因此,调节衰老小胶质细胞的功能以减少炎症因子的释放,已经成为调节神经炎症、改善大脑衰老的一种重要策略。
NAD+依赖的脱乙酰蛋白SIRT3是主要的线粒体脱乙酰酶,能够调节线粒体功能和氧化应激,并保护细胞免受氧化应激损伤[30]。最近的研究进一步发现SIRT3与炎症的进展有关,研究结果显示LPS和TNF-α能够显著抑制人单核细胞/巨噬细胞中SIRT3的表达,引起小鼠心肺组织周细胞的丢失和炎性细胞浸润的增加[31]。在小鼠脑中敲低SIRT3表达则会增强IL-1β的表达和小胶质细胞的激活,加剧神经炎症反应,引起神经退行性变[32]。同时,SIRT3在衰老条件下表达受到抑制,恢复SIRT3表达能够通过恢复线粒体功能增加小胶质细胞的活力,改善神经炎症反应[33]。与之一致的是,本研究发现衰老的BV2细胞中SIRT3蛋白表达下降,进一步使用SIRT3抑制剂抑制SIRT3蛋白表达后,小胶质细胞的衰老细胞数量增加、细胞周期阻滞的程度加重,加剧了小胶质细胞的衰老进程,同时也引起了更多线粒体ROS水平产生和炎症因子IL-1β、IL-6和TNF-α水平增加,这也验证了SIRT3与神经炎症反应之间具有调控作用。
天麻素作为天麻的主要活性成分之一,大量的研究证明天麻素具有抗氧化应激、抗炎和抗衰老的作用,能够降低脂多糖诱导的小胶质细胞一氧化氮合酶(iNOS)、环氧合酶-2和促炎性细胞因子表达[34],并且能够通过调控TLR4/NFκB信号通路减少BV2细胞的过度激活[35]。本实验进一步研究天麻素对衰老的BV2细胞的保护作用,发现天麻素能够剂量依赖性改善衰老的BV2细胞活力,并且能够减少衰老的BV2细胞数量和改善细胞周期阻滞,进而发挥抗衰老作用。此外,天麻素还能通过降低衰老的BV2细胞中ROS水平和炎症因子IL-1β,IL-6和TNF-α水平发挥抗炎作用。本研究发现在同时给予SIRT3抑制剂和天麻素处理后,天麻素对衰老的小胶质细胞的抗炎和抗衰老作用减弱,表明天麻素可能通过增高SIRT3表达来发挥保护作用。
总之,本实验首次研究天麻素对衰老的小胶质细胞的抗炎和抗衰老作用,发现天麻素能增加衰老的小胶质细胞活力,减少β-半乳糖苷酶染色面积和衰老相关蛋白P16和P21表达水平。此外,天麻素还能降低衰老的小胶质细胞中ROS水平和神经炎症因子IL-1β、IL-6和TNF-α水平,提高SIRT3蛋白表达水平。由此推测天麻素对衰老的小胶质细胞的抗衰老和抗炎作用可能与上调SIRT3蛋白表达有关,为研究天麻素的神经保护作用提供了新的方向,但有关天麻素抗衰老和抗炎的具体作用机制仍然需要进一步阐明。
-
-
[1] CHRISTENSEN K, DOBLHAMMER G, RAU R, et al. Ageing populations: The challenges ahead[J]. The Lancet,2009,374(9696):1196−208. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61460-4
[2] DZIECHCIAZ M, FILIP R. Biological psychological and social determinants of old age: Bio-psycho-social aspects of human aging[J]. Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine,2014,21(4):835−838. doi: 10.5604/12321966.1129943
[3] ZIA A, POURBAGHER-SHAHRI A M, FARKHONDEH T, et al. Molecular and cellular pathways contributing to brain aging[J]. BBF,2021,17(1):6−36.
[4] HARRY G J, KRAFT A D. Microglia in the developing brain: A potential target with lifetime effects[J]. Neurotoxicology,2012,33(2):191−206. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2012.01.012
[5] MARIANI M M, KIELIAN T. Microglia in infectious diseases of the central nervous system[J]. Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology,2009,4(4):448−461. doi: 10.1007/s11481-009-9170-6
[6] ABDEL KHALEK W, CORTADE F, OLLENDORFF V, et al. SIRT3, a mitochondrial NAD+-dependent deacetylase, is involved in the regulation of myoblast differentiation[J]. PloS One,2014,9(12):e114388−e114408. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114388
[7] ANSARI A, RAHMAN M S, SAHA S K, et al. Function of the SIRT3 mitochondrial deacetylase in cellular physiology, cancer, and neurodegenerative disease[J]. Aging Cell,2017,16(1):4−16. doi: 10.1111/acel.12538
[8] ZHOU D, JIANG Y. Sirtuin 3 attenuates neuroinflammation-induced apoptosis in BV-2 microglia[J]. Aging,2019,11(20):9075−9089. doi: 10.18632/aging.102375
[9] 杨杰, 彭启伦, 张瑜. 天麻祛风通络活性成分研究概况[J]. 中医药学报,2018,46(2):120−123. [YANG J, PENG Q L, ZHANG Y. Research survey of active components of Gastrodia elata Blume for expelling wind and dredging collaterals[J]. Acta Chinese Medicine and Pharmacology,2018,46(2):120−123. doi: 10.19664/j.cnki.1002-2392.180065 YANG J, PENG Q L, ZHANG Y. Research survey of active components of Gastrodia elata Blume for expelling wind and dredging collaterals[J]. Acta Chinese Medicine and Pharmacology, 2018, 46(2): 120–123. doi: 10.19664/j.cnki.1002-2392.180065
[10] ZHANG Z L, GAO Y G, ZANG P, et al. Research progress on mechanism of gastrodin and p-hydroxybenzyl alcohol on central nervous system[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2020,45(2):312−320.
[11] LI J, HUANG J, HE Y, et al. The protective effect of gastrodin against the synergistic effect of HIV-Tat protein and METH on the blood-brain barrier via glucose transporter 1 and glucose transporter 3[J]. Toxicology Research,2021,10(1):91−101. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfaa102
[12] 程巧巧, 杨为民, 刘璇. 天麻对心血管及代谢性疾病的作用机制研究进展[J]. 上海中医药大学学报,2019,33(4):96−100. [CHENG Q Q, YANG W M, LIU X. Research progress on pharmacological mechanism of gastrodiae rhizoma in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases[J]. Academic Journal of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2019,33(4):96−100. doi: 10.16306/j.1008-861x.2019.04.015 CHENG Q Q, YANG W M, LIU X. Research progress on pharmacological mechanism of Gastrodiae Rhizoma in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases[J]. Academic Journal of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 33(4): 96-100. doi: 10.16306/j.1008-861x.2019.04.015
[13] 吴静澜. 天麻作为保健食品原料药的应用思考[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘,2017,17(39):103−104. [WU J L. Thoughts on the application of Gastrodia elata as a health food API[J]. World Latest Medical Information Digest,2017,17(39):103−104. WU J L. Thoughts on the application of Gastrodia elata as a health food API[J]. World Latest Medical Information Digest, 2017, 17(39): 103−104.
[14] 郭佳欣, 谢佳, 蒋丽施, 等. 天麻保健食品开发现状分析[J]. 中草药,2022,53(7):2247−2254. [GUO J X, XIE J, JIANG L S, et al. Analysis on development status of gastrodiae rhizoma health food[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2022,53(7):2247−2254. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2022.07.034 GUO J X, XIE J, JIANG L S, et al. Analysis on development status of Gastrodiae Rhizoma health food[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2022, 53(7): 2247-2254. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2022.07.034
[15] ZHANG J, ZHENG Y, LUO Y, et al. Curcumin inhibits LPS-induced neuroinflammation by promoting microglial M2 polarization via TREM2/TLR4/NF-κB pathways in BV2 cells[J]. Molecular Immunology,2019,116:29−37. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2019.09.020
[16] HU Y, HUANG Y, XING S, et al. Aβ promotes CD38 expression in senescent microglia in Alzheimer's disease[J]. Biological Research,2022,55(1):10−24. doi: 10.1186/s40659-022-00379-1
[17] HAN Q, YUAN Q, MENG X, et al. 6-Shogaol attenuates LPS-induced inflammation in BV2 microglia cells by activating PPAR-γ[J]. Oncotarget,2017,8(26):42001−42006. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16719
[18] HU Y R, XING S L, CHEN C, et al. Codonopsis pilosula polysaccharides alleviate Aβ 1-40-induced PC12 cells energy dysmetabolism via CD38/NAD+ signaling pathway[J]. Current Alzheimer Research,2021,18(3):208−221.
[19] ZHANG B, LIAN W, ZHAO J, et al. DL0410 alleviates memory impairment in D-galactose-induced aging rats by suppressing neuroinflammation via the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway[J]. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity,2021,2021:6521146−6521177.
[20] TSAKIRIS S, MARINOU K, SCHULPIS K H. The in vitro effects of galactose and its derivatives on rat brain Mg2+-ATPase activity[J]. Pharmacology & Toxicology,2002,91(5):254−257.
[21] HE J, LI X, YANG S, et al. Gastrodin extends the lifespan and protects against neurodegeneration in the Drosophila PINK1 model of Parkinson's disease[J]. Food Function,2021,12(17):7816−7824. doi: 10.1039/D1FO00847A
[22] SIMPSON D, OLIVER P L. ROS generation in microglia: Understanding oxidative stress and inflammation in neurodegenerative disease[J]. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland),2020,9(8):743−760.
[23] BAKER D J, WIJSHAKE T, TCHKONIA T, et al. Clearance of p16Ink4a-positive senescent cells delays ageing associated disorders[J]. Nature,2011,479(7372):232−236. doi: 10.1038/nature10600
[24] TOSATO M, ZAMBONI V, FERRINI A, et al. The aging process and potential interventions to extend life expectancy[J]. Clinical Interventions in Aging,2007,2(3):401−412.
[25] MOHAMAD KAMAL N S, SAFUAN S, SHAMSUDDIN S, et al. Aging of the cells: Insight into cellular senescence and detection methods[J]. European Journal of Cell Biology,2020,99(6):151108−151122. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2020.151108
[26] PRASNIKAR E, BORISEK J, PERDIH A. Senescent cells as promising targets to tackle age-related diseases[J]. Ageing Research Reviews,2021,66:101251−101284. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2020.101251
[27] PERRY V H, TEELING J. Microglia and macrophages of the central nervous system: The contribution of microglia priming and systemic inflammation to chronic neurodegeneration[J]. Seminars in Immunopathology,2013,35(5):601−612. doi: 10.1007/s00281-013-0382-8
[28] VON BERNHARDI R, TICHAUER J E, EUGENIN J. Aging-dependent changes of microglial cells and their relevance for neurodegenerative disorders[J]. Journal of Neurochemistry,2010,112(5):1099−1114. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06537.x
[29] BRAWEK B, SKOK M, GARASCHUK O. Changing functional signatures of microglia along the axis of brain aging[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2021,22(3):1091−1112. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031091
[30] SHEN Y, WU Q, SHI J, et al. Regulation of SIRT3 on mitochondrial functions and oxidative stress in Parkinson's disease[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy,2020,132:110928−110940.
[31] DU J, ZENG C, LI Q, et al. LPS and TNF-α induce expression of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor-2 in human microvascular endothelial cells[J]. Pathology, Research and Practice,2012,208(2):82−88. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2011.11.008
[32] LEE S, JEON Y M, JO M, et al. Overexpression of SIRT3 suppresses oxidative stress-induced neurotoxicity and mitochondrial dysfunction in dopaminergic neuronal cells[J]. Experimental Neurobiology,2021,30(5):341−355. doi: 10.5607/en21021
[33] THANGARAJ A, CHIVERO E T, TRIPATHI A, et al. HIV TAT-mediated microglial senescence: Role of SIRT3-dependent mitochondrial oxidative stress[J]. Redox Biology,2021,40:101843−101861. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101843
[34] DAI J N, ZONG Y, ZHONG L M, et al. Gastrodin inhibits expression of inducible NO synthase, cyclooxygenase-2 and proinflammatory cytokines in cultured LPS-stimulated microglia via MAPK pathways[J]. PLoS One,2011,6(7):e21891−e21902. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021891
[35] MAO X N, ZHOU H J, YANG X J, et al. Neuroprotective effect of a novel Gastrodin derivative against ischemic brain injury: Involvement of peroxiredoxin and TLR4 signaling inhibition[J]. Oncotarget,2017,8(53):90979−90995. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18773
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 徐柠檬,董仕豪,秦粉,申开泽,李为兰,华燕,郭磊. 基于UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS和网络药理学探讨天麻抗炎的物质基础及其作用机制. 食品科学. 2025(04): 30-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王剑涛,赵旭东,邓丽,葛梦君,高贝贝,李雷. 亚甲基蓝改善脑炎性衰老大鼠认知功能及机制探索. 中华老年心脑血管病杂志. 2024(03): 336-340 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘潇聪,张玉苗,潘亚磊. 天麻素药理作用及临床应用研究进展. 中南药学. 2024(06): 1615-1620 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 董欣,隋欣彤,胡力铭,王仁广,李占国,王景龙,王淑敏,梁磊. 米汤炮制天麻工艺的优化及抗炎作用. 食品工业科技. 2024(16): 358-367 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 应春苗,刘飞祥,潘小龙,樊飞燕,陈娜,张运克. 中药延缓神经血管单元衰老治疗神经退行性疾病的研究进展. 中国中药杂志. 2023(15): 4060-4071 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 宗芳,陈永华,代玉强. 真方白丸子联合注射用阿替普酶对急性缺血性卒中风痰入络证患者血清炎症因子及血管内皮活性物质的影响. 国际中医中药杂志. 2023(09): 1075-1080 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)





 下载:
下载:







 下载:
下载:



