Correlation Analysis between the Active Ingredients and the Antioxidant or Cholate-binding Ability of Ethanol Extracts from Psoralea corylifolia L.
-
摘要: 目的:在“成分-功效”关联模式下,探究补骨脂四种不同浓度乙醇提取物主要活性成分含量、抗氧化及胆酸盐结合能力差异。方法:以补骨脂为原料,采用无水乙醇、75%乙醇、50%乙醇、水进行提取,比较其总黄酮和总多酚含量,并分别通过3种抗氧化体系与胆酸盐结合能力进行体外抗氧化和降脂活性评价,并进行相关性分析。结果:无水乙醇提取物总黄酮含量(50.317±0.018 mg/g)和总多酚含量(3.860±0.045 mg/g)最高。补骨脂50%乙醇提取物对ABTS+·和DPPH·清除能力最强,IC50值分别为0.76和1.63 mg/mL,无水乙醇提取物还原能力最强,A0.5值为2.63 mg/mL。补骨脂水提物对胆酸钠的结合能力最强,IC50值为0.67 mg/mL,而50%乙醇提取物对牛磺胆酸钠和甘胺胆酸钠结合能力最强,IC50值分别为1.26和0.41 mg/mL。相关性结果表明,补骨脂不同浓度乙醇提取物中总黄酮含量与DPPH·清除率、牛磺胆酸钠结合率呈显著正相关性(P<0.05),总黄酮、总多酚含量与还原能力均呈极显著性正相关关系(P<0.01),而总多酚含量与胆酸钠结合率呈显著性负相关性(P<0.05)。结论:补骨脂50%乙醇提取物活性含量较高,抗氧化及结合胆酸盐能力最强,可以作为潜在的天然抗氧化及降脂活性物质的重要来源。Abstract: Objective: The contents of main active ingredients, antioxidant and cholate binding ability of different ethanol extracts from Psoralea corylifolia L. were explored based on the mode of correlation of “components-efficacy”. Methods: Psoralea corylifolia L. was extracted with anhydrous ethanol, 75% ethanol, 50% ethanol and water. The contents of total flavonoids and total polyphenols in Psoralea corylifolia L. were determined. The antioxidant and lipid-lowering activities in vitro of Psoralea corylifolia L. were evaluated by three antioxidant systems and the binding ability of cholate salts, respectively, and the correlation analysis was conducted. Results: The contents of total flavonoids and total polyphenols in anhydrous ethanol extract were the highest, (50.317±0.018) mg/g and (3.860±0.045) mg/g, respectively. The 50% ethanol extract showed the best ability to scavenge ABTS+· and DPPH·, the IC50 values were 0.76 and 1.63 mg/mL, respectively. The anhydrous ethanol extract showed the strongest reducing ability, the A0.5 value was 2.63 mg/mL. The water extract showed the strongest binding capacity to sodium cholate, the IC50 value was 0.67 mg/mL. The 50% ethanol extract showed the strongest binding capacity to sodium taurocholate and sodium glycinate, the IC50 values were 1.26 and 0.41 mg/mL, respectively. The correlation results showed that the content of total flavonoids of different ethanol extracts from Psoralea corylifolia L. had a significant positive correlation with DPPH· clearance rate and sodium taurocholate binding rate (P<0.05). And the content of total flavonoids and total polyphenols had a very significant positive correlation with reduction ability (P<0.01). While the content of total polyphenols had a significant negative correlation with sodium cholate binding rate (P<0.05). Conclusion : The 50% ethanol extract of Psoralea corylifolia L. has high content of active ingredients and the strongest antioxidant and cholate binding ability. It can be used as a potential important source of natural antioxidant and lipid-lowering active substances.
-
Keywords:
- Psoralea corylifolia L. /
- ethanol extracts /
- antioxidant /
- cholate /
- correlation analysis /
- hypolipidemic
-
补骨脂(Psoralea corylifolia L.)是一种豆科补骨脂属草本植物,主产于云南西双版纳和四川金沙江流域[1-3],被广泛应用于保健食品领域,如其乙醇提取物已作为食品添加剂用于泡菜等食品的加工生产[4-6]。其种子或果实具有重要的药理活性,中医临床常用其治疗由肾阳不足引起的阳痿遗精、遗尿尿频、腰膝酸痛等疾病[7]。文献调研表明其具有抗氧化、降胆固醇、抗炎和免疫调节等生理活性[2,8],这主要与其所含有的黄酮类、单萜酚类、酚类苯桂酸等成分有关[6,9]。不同极性溶剂可以显著地影响植物提取物的主要化学成分含量和功效[10-11],目前,国内外有对补骨脂总黄酮提取方法及提取工艺和补骨脂不同浓度乙醇提取物干预小鼠前列腺增生作用差异的研究[12-14],并有研究报道补骨脂乙醇提取物对α-葡萄糖苷酶具有抑制作用[15],但鲜有补骨脂不同浓度乙醇提取物中的主要活性成分含量及其体外抗氧化与降脂功效的比较研究。
中药成分复杂多样,通过将成分含量与生物活性进行关联分析,可以初步筛选活性组分和评价质量[16-17]。因此,本实验在“成分-功效”关联模式下,采用不同浓度乙醇分别提取补骨脂,进行总黄酮与总多酚含量比较,利用ABTS+·清除率、DPPH·清除率、还原能力和胆酸盐结合率体外实验开展抗氧化和降血脂能力评估,通过相关性分析建立补骨脂不同浓度乙醇提取物主要活性成分-体外抗氧化/降脂功效的评价模型,旨在为补骨脂在保健食品、药物等应用领域的进一步研究和资源利用提供必要的理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
补骨脂(四川) 安徽亳州中药材批发市场,经山东中医药大学张永清教授鉴定为豆科补骨脂属植物补骨脂Psoralea corylifolia L.的干燥成熟果实;2,2'-联氮双(3-乙基苯并噻唑啉-6-磺酸)二铵盐(ABTS) 纯度≥98%,上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(DPPH) 纯度≥97%,上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;铁氰化钾 纯度≥99.5%,天津市巴斯夫化工有限公司;胆酸钠、牛磺胆酸钠、甘氨胆酸钠盐 纯度≥98%,上海凯为化学科技有限公司;芦丁 纯度大于98%,上海源叶生物科技有限公司;没食子酸、硝酸铝、氢氧化钠、亚硝酸钠、三氯化铁、三氯乙酸、无水乙醇 均为国产分析纯。
KQ-500GVDV双频恒温数控超声波清洗器 昆山市超声仪器有限公司;X-5紫外可见分光光度计 上海元析仪器有限公司;RH-QG全温光照振荡器 常州市金坛精工仪器设备有限公司;FA1204B电子天平 上海佑科仪器仪表有限公司;ST16R高速冷冻离心机 赛默飞世尔科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 补骨脂不同浓度乙醇提取物制备
将补骨脂自然晾干,粉碎,过60目筛。准确称取补骨脂粉末4份,每份40 g,分别置于锥形瓶中,按1:40 g/mL料液比分别加入无水乙醇、75%乙醇、50%乙醇和水,参考鲁宪坤等[13]的方法进行提取,抽滤,滤液浓缩至浸膏状,分别用相应溶剂溶解定容至100 mL,即得提取物溶液(相当于原药材0.4 g/mL)。
1.2.2 总黄酮、总多酚含量测定
分别取无水乙醇、75%乙醇、50%乙醇、水提取液0.1 mL置于10 mL容量瓶中,参考裴文清等[18]的方法测定。配制质量浓度为0.00、0.01、0.02、0.04、0.06、0.08 mg/mL的芦丁标准溶液,绘制标准曲线,得回归方程为:A=12.416C+0.0092,r=0.9990(A为吸光度值;C为芦丁质量浓度:mg/mL)。结果以每克补骨脂粉末中所含芦丁当量(mg/g)表示。
分别移取无水乙醇、75%乙醇、50%乙醇、水提取液0.1 mL置于10 mL容量瓶中,参考崔施展等[19]的方法测定。配制质量浓度为0、0.001、0.003、0.005、0.007、0.009 mg/mL的没食子酸标准溶液,绘制标准曲线,得回归方程为:A=96.11C+0.0203,r=0.9991(A为吸光度值;C为没食子酸质量浓度:mg/mL)。结果以每克补骨脂粉末中所含没食子酸当量(mg/g)表示。
1.2.3 不同浓度乙醇提取物的抗氧化活性测定
1.2.3.1 ABTS+·清除能力测定
分别移取浓度为2、4、6、8、10 mg/mL无水乙醇、75%乙醇、50%乙醇、水提取液和VC溶液0.5 mL于10 mL的离心管中,参考杨美莲等[20]的方法测定。按式(1)计算清除率。
ABTS+⋅清除率(%)=A0−(A1−A2)A0×100 (1) 式中:A0为0.5 mL乙醇溶液代替样品溶液的吸光度值;A1为样品组吸光度值;A2为4 mL无水乙醇代替ABTS溶液的吸光度值。
1.2.3.2 DPPH·清除能力测定
分别移取浓度为2、4、6、8、10 mg/mL无水乙醇、75%乙醇、50%乙醇、水提取液和VC溶液2 mL于10 mL的离心管中,参考慕钰文等[21]的方法测定。按式(2)计算清除率。
DPPH⋅ 清除率 (%)=A0−(A1−A2)A0×100 (2) 式中:A0为2 mL DPPH溶液加入2 mL乙醇溶液的吸光度;A1为2 mL样品溶液加入2 mL DPPH溶液的吸光度;A2为2 mL样品溶液加入2 mL无水乙醇的吸光度。
1.2.3.3 还原能力的测定
分别移取浓度为2、4、6、8、10 mg/mL无水乙醇、75%乙醇、50%乙醇、水提取液和VC溶液0.5 mL于10 mL的离心管中,参照黎善铭等[22]的方法测定。吸光度值越高,表明其还原能力越强。
1.2.4 结合胆酸盐实验
分别移取质量浓度为2、4、6、8、10 mg/mL四种提取液0.5 mL于3支50 mL离心管中,各加入4 mL的胆酸钠、牛磺胆酸钠和甘氨胆酸钠溶液(0.6 mmol/L),参考李珊等[23]的方法测定。按式(3)计算结合率。
胆酸盐结合率(%)=A0−(A1−A2)A0×100 (3) 式中:A0为0.5 mL对应溶剂加入4 mL胆酸盐的吸光度;A1为0.5 mL样品溶液加入4 mL胆酸盐溶液的吸光度;A2为0.5 mL样品溶液加入4 mL磷酸缓冲液的吸光度。
1.3 数据处理
以上实验均平行操作三次,数据以
ˉX ±SD表示。采用SPSS 26.0,GraphPad Prism 8.0.1进行数据处理和绘图,使用Pearson相关性分析。2. 结果与分析
2.1 补骨脂不同浓度乙醇提取物中总黄酮和总多酚含量分析
由表1可知,补骨脂不同溶剂提取物中总黄酮和总多酚含量存在显著性差异(P<0.05),总黄酮和总多酚含量随着溶剂极性的增大而降低,与慕钰文等[21]研究花椒籽不同浓度乙醇提取物中总多酚含量变化规律相似,根据相似相溶原理推测此变化趋势是由于补骨脂中黄酮和多酚多属于低极性物质所致。总黄酮含量范围为(5.980±0.023)~(50.317±0.018)mg/g,其中,无水乙醇提取物中总黄酮含量最高,达到(50.317±0.018)mg/g,其次是75%乙醇提取物和50%乙醇提取物,水提取物总黄酮含量最少,四者之间差异性显著(P<0.05),与李婧雯等[24]研究的蒲公英根不同溶剂提取物黄酮含量变化规律相似;总多酚含量范围为(3.860±0.045)~(1.877±0.003)mg/g,无水乙醇和75%乙醇提取物中总多酚含量相近,分别为(3.860±0.045)和(3.670±0.007)mg/g,显著高于50%乙醇提取物和水提取物(P<0.05)。
表 1 补骨脂不同浓度乙醇提取物中总黄酮和总多酚含量Table 1. Contents of total flavonoids and polyphenols of different ethanol extracts from Psoralea corylifolia L.含量(mg/g) 溶剂类型 无水乙醇 75%乙醇 50%乙醇 水 总黄酮 50.317±0.018a 40.390±0.046b 30.943±0.051c 5.980±0.023d 总多酚 3.860±0.045a 3.670±0.007a 2.810±0.041b 1.877±0.003c 注:同行不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 2.2 补骨脂不同浓度乙醇提取物抗氧化活性分析
2.2.1 补骨脂不同浓度乙醇提取物对ABTS+·清除作用的比较
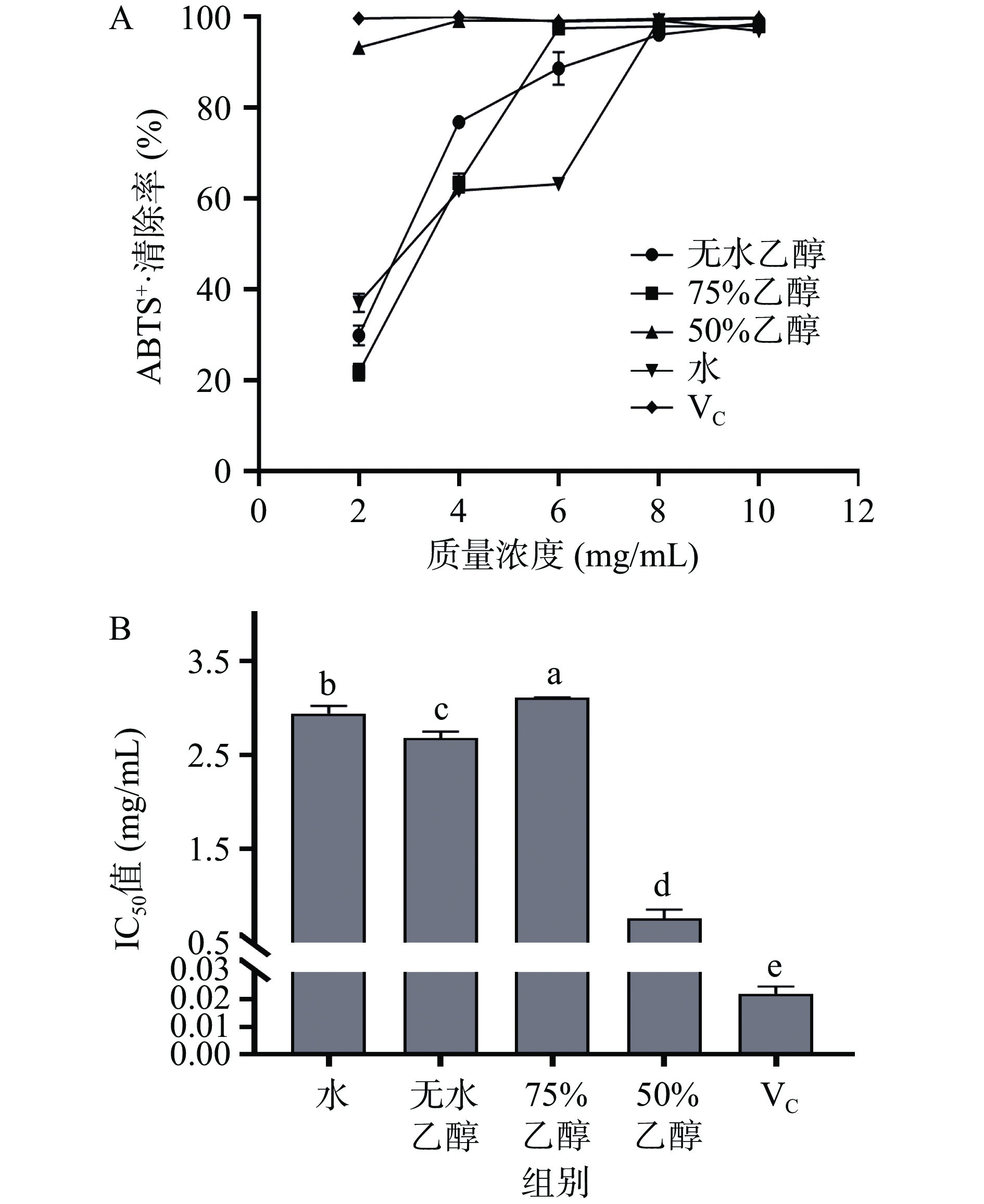
由图1-A可以看出,补骨脂不同浓度乙醇提取物对ABTS+·均具有一定的清除能力,当样品溶液浓度在2~8 mg/mL时,各提取物对ABTS+·清除率随浓度的增大而增大,在8~10 mg/mL范围内,清除率达到平稳状态。当质量浓度为10 mg/mL时,各提取物清除率均达到97%左右,但小于VC对照组。由图1-B可知,各提取物清除ABTS+·的IC50值均大于VC对照组,50%乙醇提取物清除ABTS+·的IC50值为0.76 mg/mL,显著低于其他三种溶剂的IC50值(P<0.05),其次是无水乙醇、水、75%乙醇提取物,其IC50值分别为2.68、2.94、3.11 mg/mL,因此,50%乙醇提取物清除ABTS+·能力最强,经分析可能是由于50%乙醇提取物存在多糖等其他活性成分,导致其总活性成分含量较高更易于清除ABTS+·,这与师聪等[25]的实验结果一致,即50%乙醇草果提取物清除ABTS+·能力最强。
2.2.2 补骨脂不同浓度乙醇提取物对DPPH·清除作用的比较
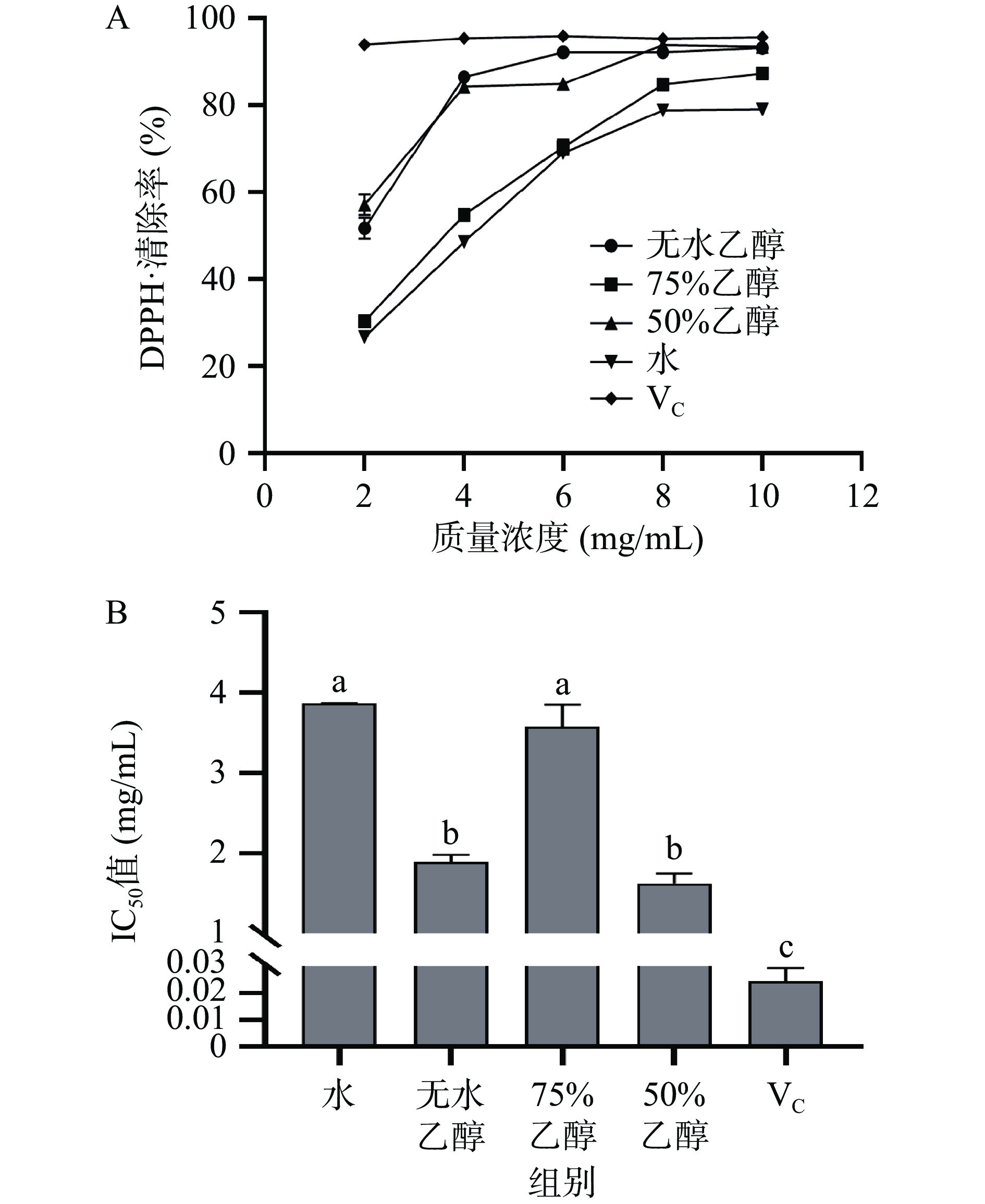
由图2-A可知,提取物的DPPH·清除率均小于VC对照组且相互之间差异性显著(P<0.05),在浓度为2~8 mg/mL范围内,各提取物对DPPH·清除率随着浓度的增大具有上升趋势,在8~10 mg/mL范围内,清除率增加缓慢。当浓度为10 mg/mL时,无水乙醇和50%乙醇提取物对DPPH·清除率分别达到93.21%和92.64%,其次为75%乙醇和水提取物,清除率分别达到87.37%和79.15%。由图2-B可知,各提取物清除DPPH·的IC50值均大于VC对照组,无水乙醇和50%乙醇提取物清除DPPH·的IC50值最小,分别是1.89和1.63 mg/mL,其次是75%乙醇和水提取物,IC50值分别为3.58和3.89 mg/mL,因此,50%乙醇提取物对DPPH·清除能力最强,这与覆盆子50%乙醇提取物清除DPPH·能力最强报道结果一致[26],此结果可能是由于除黄酮多酚外,其他活性物质也参与抗氧化体系所导致。
2.2.3 补骨脂不同浓度乙醇提取物还原能力的比较
由图3-A可知,VC的还原能力最大,VC浓度为2~10 mg/mL时,还原能力基本维持在3.5以上。在浓度为2~10 mg/mL时,各提取物的还原能力随提取物浓度的增加而升高。当样品浓度为10 mg/mL时,无水乙醇、75%乙醇和50%乙醇提取物的还原力分别为0.84、0.82、0.65,而水提取物还原能力较弱,还原力基本维持在0.1~0.25之间。由图3-B可知,各提取物还原力为0.5时对应的提取物质量浓度(A0.5)均大于VC对照组,不同浓度乙醇提取物还原能力的A0.5值大小顺序为:水>50%乙醇>75%乙醇>无水乙醇,这表明无水乙醇提取物还原能力最好,A0.5值为2.63 mg/mL,显著低于其他三种溶剂提取物的A0.5(P<0.05),这与李春爱等[27]对橄榄果渣还原能力的研究结果相似,即随着提取物乙醇浓度增大还原能力逐渐增大,这可能是由于乙醇含量较多的提取物中总黄酮和总多酚含量较多导致其还原能力较强。
2.3 补骨脂不同浓度乙醇提取物对胆酸盐结合能力比较
胆酸盐可以通过“肝肠循环”进行再利用,通过结合胆酸盐,胆酸盐无法完成“肝肠循环”,肝脏将更多的胆固醇转化成胆汁酸,因而间接地降低胆固醇,进而达到降脂目的[28-29]。胆酸盐可分为游离型胆酸盐和结合型胆酸盐[30],本实验选择游离型胆酸盐(胆酸钠)和结合型胆酸盐(牛磺胆酸钠,甘胺胆酸钠)开展研究。
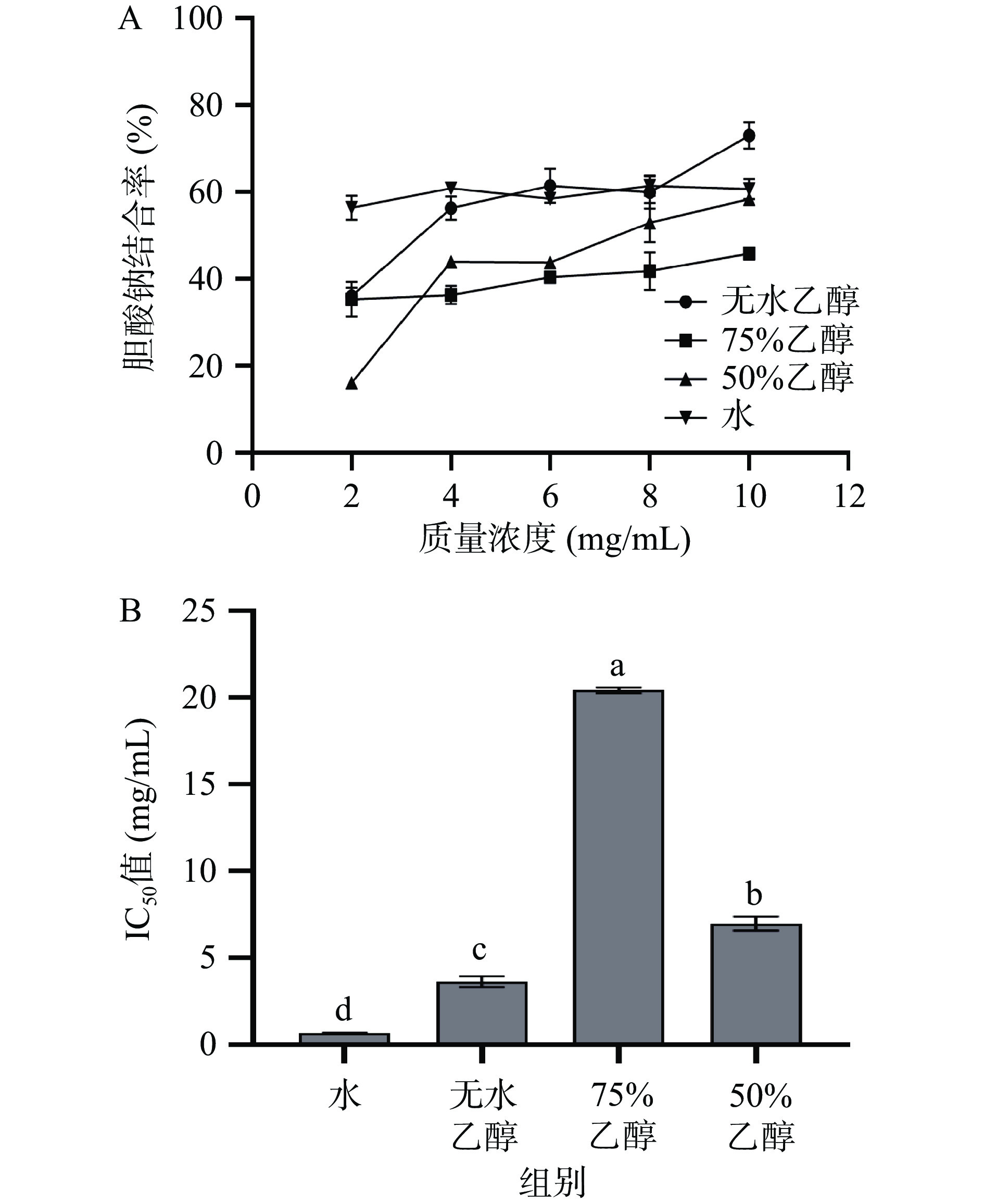
如图4-A所示,各提取物对胆酸钠都具有一定的结合能力,结合率随着样品浓度的增加而升高,当样品浓度达到10 mg/mL时,无水乙醇提取物对胆酸钠的结合能力较大,结合率达到73.14%,其次为水、50%乙醇和75%乙醇提取物,结合率分别为61.98%、58.30%和46.09%。由图4-B可以看出,无水乙醇、75%乙醇和50%乙醇、水提取物对胆酸钠的IC50值分别为3.63、20.42、6.98和0.67 mg/mL,所以水提取物对胆酸钠的结合能力最强,其次为无水乙醇提取物、50%乙醇提取物和75%乙醇提取物,并且四种溶剂胆酸钠结合能力存在显著性差异(P<0.05),可能与水提取物中多糖成分含量较高更易与游离胆酸盐结合有关,这与林沛纯等[31]的研究结果相似,即岩藻聚糖粗多糖对三种胆酸盐中的水合胆酸钠结合能力最大。
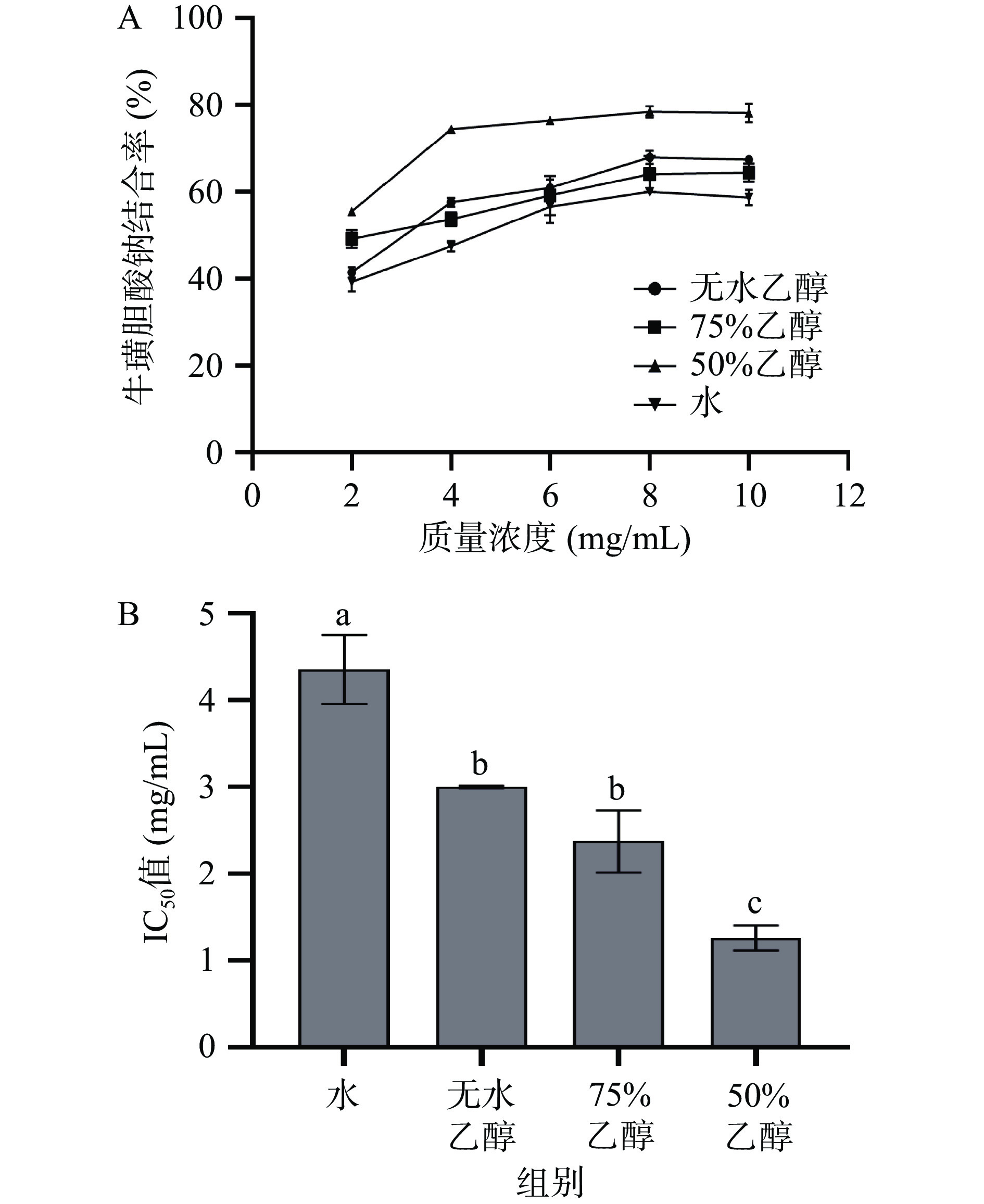
从图5-A可以看出,各提取物对牛磺胆酸钠均有一定的结合能力,并且在2~10 mg/mL浓度范围内,随实验浓度提高结合率逐步增大。当浓度为10 mg/mL时,50%乙醇提取物对牛磺胆酸钠的结合率达到79.56%,并高于10 mg/mL裙带菜多糖对牛磺胆酸盐的结合率(52.3%)[32]。由图5-B可知,不同溶剂提取物结合牛磺胆酸钠的IC50值大小顺序:水提取物>无水乙醇提取物>75%乙醇提取物>50%乙醇提取物,表明50%乙醇提取物对牛璜胆酸钠的结合能力最强,IC50值为1.26 mg/mL,显著低于水提取物的IC50值为4.36 mg/mL(P<0.05),但其余两种提取物之间差异并不显著(P>0.05)。经分析可能是由于50%乙醇提取物中除总黄酮和总多酚外,还有多糖等其他活性成分也参与了牛磺胆酸钠的结合体系[29,33]。
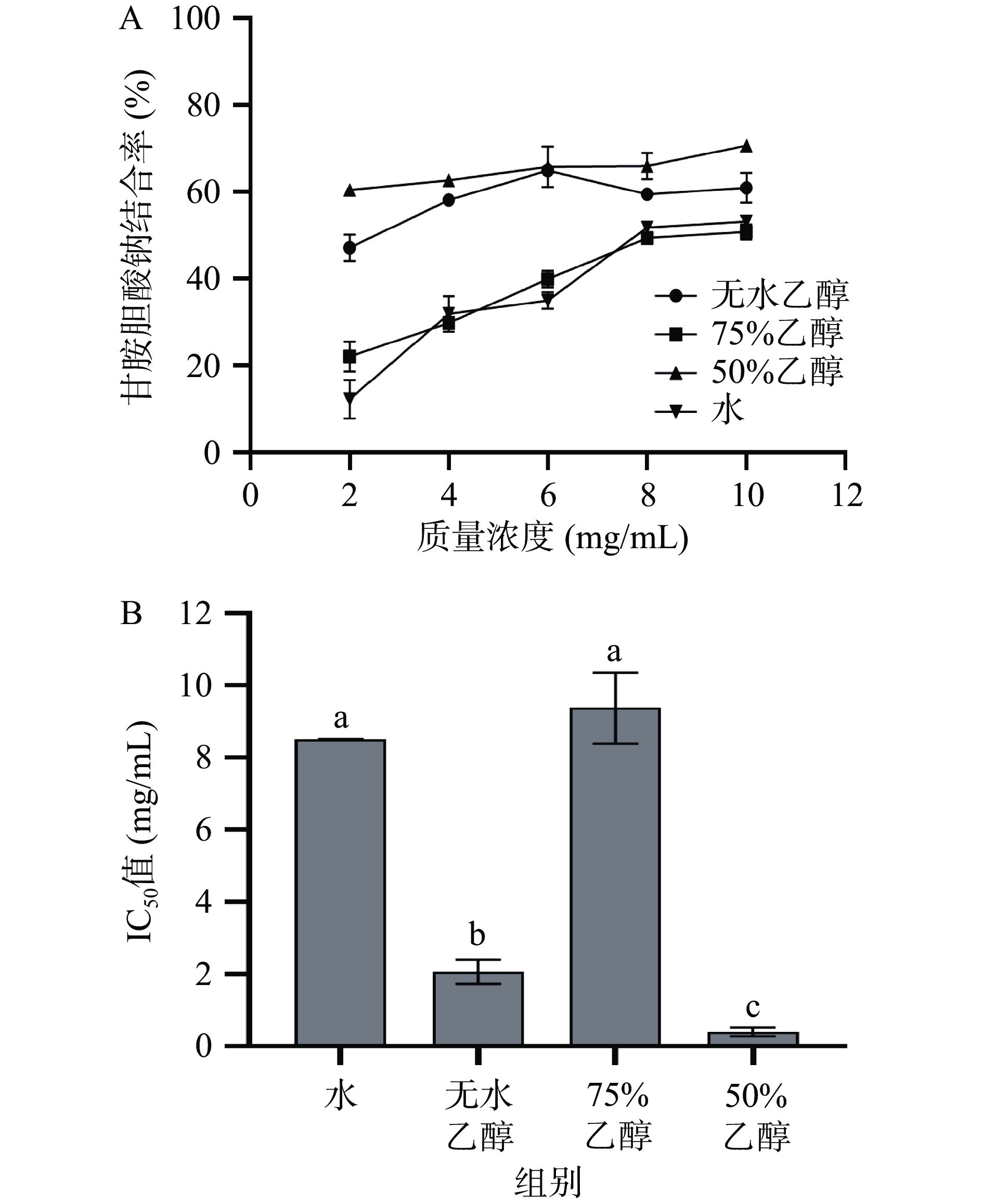
由图6-A可以看出,各提取物对甘胺胆酸钠均有一定结合能力,并且在2~10 mg/mL浓度范围内,随实验浓度提高结合率逐步增大。当浓度为10 mg/mL时,50%乙醇提取物对甘胺胆酸钠的结合能力最强,结合率达到70.97%,与体积浓度为1.0 mL/mL的药桑葡萄酒对甘胺胆酸钠结合率69.36%结果相近[34]。由图6-B可以看出,50%乙醇提取物和无水乙醇提取物对甘胺胆酸钠的IC50值较小,分别为0.41 mg/mL和2.07 mg/mL,显著低于其他两种溶剂(P<0.05),所以50%乙醇提取物对甘胺胆酸钠结合能力最强,其次是无水乙醇提取物,其余两种提取物结合能力相对较弱。
2.4 补骨脂不同浓度乙醇提取物中活性成分与抗氧化及胆酸盐结合能力的相关性分析
测定不同浓度乙醇提取物中总黄酮和总多酚含量,通过相关性分析探究活性成分含量与抗氧化及胆酸盐结合能力的关联性,初步建立补骨脂不同浓度乙醇提取物主要活性成分-体外抗氧化/降脂功效评价模型。从表2可以看出,总黄酮含量与DPPH·清除率、牛磺胆酸钠结合率呈显著性正相关(P<0.05);总黄酮、总多酚含量与还原能力均呈极显著正相关(P<0.01),与张天凤等[35]的研究报道亚麻籽粕提取物总黄酮、总多酚含量与还原能力均呈显著性正相关结果一致;总多酚含量与胆酸钠结合率呈显著性负相关(P<0.05);ABTS+·清除率和甘胺胆酸钠结合率与总黄酮和总多酚含量相关性较低。上述结果表明,补骨脂中总黄酮和总多酚均有一定的抗氧化和降脂活性,总黄酮的抗氧化和结合胆酸盐能力更强。
表 2 补骨脂活性成分含量与抗氧化活性和胆酸盐结合率的相关性分析Table 2. Correlation analysis between the contents of active components and antioxidant activity and cholate binding rate of Psoralea corylifolia L.指标 总黄酮 总多酚 ABTS+· DPPH· 还原能力 胆酸钠 牛磺胆酸钠 甘胺胆酸钠 总黄酮 1.000 0.972** 0.019 0.553* 0.948** −0.433 0.514* 0.389 总多酚 1.000 −0.139 0.383 0.912** −0.545* 0.433 0.210 ABTS+· 1.000 0.735 0.244 0.190 0.729** 0.787** DPPH· 1.000 0.616** 0.232 0.653* 0.970** 还原能力 1.000 −0.551* 0.744** 0.540 胆酸钠 1.000 −0.456 0.403 牛磺胆酸钠 1.000 0.569* 甘胺胆酸钠 1.000 注:**表示在0.01水平上相关性显著,*表示在0.05水平上显著相关。 3. 结论
本研究选用不同浓度乙醇溶剂提取补骨脂,其主要活性成分含量、体外抗氧化活性及胆酸盐结合能力之间差异显著(P<0.05)。实验结果表明,补骨脂不同乙醇浓度提取物的总黄酮和总多酚含量范围分别为(5.980±0.023)~(50.317±0.018)mg/g和(1.877±0.003)~(3.860±0.045)mg/g,其中,无水乙醇提取物总黄酮和总多酚含量均最高。50%乙醇提取物具有最强的ABTS+·和DPPH·清除能力,其次是无水乙醇提取物,而无水乙醇提取物还原能力最强。补骨脂水提取物对胆酸钠的结合能力最强,50%乙醇提取物对牛磺胆酸钠和甘胺胆酸钠的结合能力最强。相关性分析表明,补骨脂不同浓度乙醇提取物中总黄酮含量与DPPH·清除率、牛磺胆酸钠结合率呈显著正相关性(P<0.05),总黄酮、总多酚含量与还原能力均呈极显著性正相关关系(P<0.01),总多酚含量与胆酸钠结合率呈显著性负相关(P<0.05),总黄酮和总多酚含量与ABTS+·清除率和甘胺胆酸钠结合率相关性较低。同时,推测补骨脂中除黄酮和多酚外,多糖等其他重要活性成分也具有良好的抗氧化及降脂活性,需要进一步测定补骨脂中其他活性成分含量并进行分析,为补骨脂作为抗氧化和降脂物质提供一定的指导作用。
-
表 1 补骨脂不同浓度乙醇提取物中总黄酮和总多酚含量
Table 1 Contents of total flavonoids and polyphenols of different ethanol extracts from Psoralea corylifolia L.
含量(mg/g) 溶剂类型 无水乙醇 75%乙醇 50%乙醇 水 总黄酮 50.317±0.018a 40.390±0.046b 30.943±0.051c 5.980±0.023d 总多酚 3.860±0.045a 3.670±0.007a 2.810±0.041b 1.877±0.003c 注:同行不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 2 补骨脂活性成分含量与抗氧化活性和胆酸盐结合率的相关性分析
Table 2 Correlation analysis between the contents of active components and antioxidant activity and cholate binding rate of Psoralea corylifolia L.
指标 总黄酮 总多酚 ABTS+· DPPH· 还原能力 胆酸钠 牛磺胆酸钠 甘胺胆酸钠 总黄酮 1.000 0.972** 0.019 0.553* 0.948** −0.433 0.514* 0.389 总多酚 1.000 −0.139 0.383 0.912** −0.545* 0.433 0.210 ABTS+· 1.000 0.735 0.244 0.190 0.729** 0.787** DPPH· 1.000 0.616** 0.232 0.653* 0.970** 还原能力 1.000 −0.551* 0.744** 0.540 胆酸钠 1.000 −0.456 0.403 牛磺胆酸钠 1.000 0.569* 甘胺胆酸钠 1.000 注:**表示在0.01水平上相关性显著,*表示在0.05水平上显著相关。 -
[1] GAO H T Y, LANG G Z, ZANG Y D, et al. Bioactive monoterpene phenol dimers from the fruits of Psoralea corylifolia L.[J]. Bioorg Chem,2021,112:104924. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.104924
[2] CHOPRA B, DHINGRA A K, DHAR K L. Psoralea corylifolia L. (Buguchi)-folklore to modern evidence: Review[J]. Fitoterapia,2013,90:44−56. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2013.06.016
[3] ZHANG X N, ZHAO W W, WANG Y, et al. The chemical constituents and bioactivities of Psoralea corylifolia Linn. : A review[J]. Am J Chin Med,2016,44:35−60. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X16500038
[4] QIAO C F, HAN Q B, SONG J Z, et al. Chemical fingerprint and quantitative analysis of fructus psoraleae by high-performance liquid chromatography[J]. J Sep Sci,2007,30:813−818. doi: 10.1002/jssc.200600339
[5] 陈建平, 谢皓玥, 周际宇. 高效液相色谱-串联质谱法同时测定保健食品中淫羊藿苷、金丝桃苷、补骨脂素[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2021,12(1):192−196. [CHEN J P, XIE H Y, ZHOU J Y. Simultaneous determination of icariin, hyperoside and psoralen in functional food by high performance liquid chromatographytandem mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2021,12(1):192−196. CHEN J P, XIE H Y, ZHOU J Y. Simultaneous determination of icariin, hyperoside and psoralen in functional food by high performance liquid chromatographytandem mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality, 2021, 12(1): 192-196.
[6] 鲁亚奇, 张晓, 王金金, 等. 补骨脂化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2019,25(3):180−189. [LU Y Q, ZHANG X, WANG J J, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Psoraleae Fructus[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Chinese Medicine,2019,25(3):180−189. LU Y Q, ZHANG X, WANG J J, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Psoraleae Fructus[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 25(3): 180-189.
[7] 魏蒙蒙, 王树瑶, 杨维, 等. 补骨脂的化学成分及主要毒性研究进展[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2019,25(7):207−219. [WEI M M, WANG S Y, YANG W, et al. Chemical constituents of Psoraleae Fructus and its main toxic ingredients[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Formulae,2019,25(7):207−219. WEI M M, WANG S Y, YANG W, et al. Chemical constituents of Psoraleae Fructus and its main toxic ingredients[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Formulae, 2019, 25(7): 207-219.
[8] RAJENDRA P N, ANANDI C, BALASUBRAMANIAN S, et al. Antidermatophytic activity of extracts from Psoralea corylifolia (Fabaceae) correlated with the presence of a flavonoid compound[J]. J Ethnopharmacol,2004,91:21−24. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2003.11.010
[9] KOUL B, TAAK P, KUMAR A, et al. Genus Psoralea: A review of the traditional and modern uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology[J]. J Ethnopharmacol,2019,232:201−226. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.11.036
[10] 胡栋宝, 罗丽昌, 杨猛, 等. 不同溶剂提取黑牛肝菌中的多酚及抗氧化活性的比较研究[J]. 食用菌,2020,42(6):69−72. [HU D B, LUO L C, YANG M, et al. A comparative study on extracting polyphenol and antioxidant activity of polyphenol from Boletus aereus by different solvents[J]. Edible Fungi,2020,42(6):69−72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8357.2020.06.026 HU D B, LUO L C, YANG M, et al. A comparative study on extracting polyphenol and antioxidant activity of polyphenol from Boletus aereus by different solvents[J]. Edible fungi, 2020, 42(6): 69-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8357.2020.06.026
[11] 廖霞, 吴振, 杨勇, 等. 乌天麻不同溶剂提取物的总多酚、总黄酮含量及其抗氧化能力评价[J/OL]. 食品与发酵工业: 1−9 [2022-01-22]. DOI: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.027943. LIAO X, WU Z, YANG Y, et al. Total polyphenols, total flavonoids contents and antioxidant capacities of different solvents extracts from Gastrodia elata Bl. f. glauca S. Chow[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries: 1−9 [2022-01-22]. DOI: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.027943.
[12] 赵益业, 蔡宇, 冯笑珍, 等. 回流法与超声法提取补骨脂总黄酮的比较研究[J]. 中药材,2008(5):769−770. [ZHAO Y Y, CAI Y, FENG X Z, et al. Comparative study on extraction of total flavonoids from psoralen by reflux method and ultrasonic method[J]. Chinese Medicinal Materials,2008(5):769−770. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4454.2008.05.049 ZHAO Y Y, CAI Y, FENG X Z, et al. Comparative study on extraction of total flavonoids from psoralen by reflux method and ultrasonic method[J]. Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2008(5): 769-770. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-4454.2008.05.049
[13] 鲁宪坤, 翟鑫源, 李方红, 等. 补骨脂总黄酮提取工艺的优化[J]. 中成药,2022,44(1):193−197. [LU X K, ZHAI X Y, LI F H, et al. Optimization of extraction process of total flavonoids from psoralen[J]. Chinese Patent Medicine,2022,44(1):193−197. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2022.01.036 LU X K, ZHAI X Y, LI F H, et al. Optimization of extraction process of total flavonoids from psoralen[J]. Chinese Patent Medicine, 2022, 44(1): 193-197. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2022.01.036
[14] 王凯燕, 耿子凯, 刘莉, 等. 补骨脂不同溶剂提取物对前列腺增生小鼠干预作用比较[J]. 山东中医药大学学报,2019,43(6):594−598. [WANG K Y, GENG Z K, LIU L, et al. Comparison of intervention effect of different solvent extracts of buguzhi (Psoraleae Fructus) on mice with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2019,43(6):594−598. WANG K Y, GENG Z K, LIU L, et al. Comparison of intervention effect of different solvent extracts of buguzhi(Psoraleae Fructus)on mice with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 43(6): 594-598.
[15] 林萍萍, 陈明珠, 张吟. 补骨脂及其主要化学成分降糖机制的研究进展[J/OL]. 中国中药杂志: 1−10 [2022-03-02]. DOI:10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm. 20211229.701. LIN P P, CHEN M Z, ZHANG Y. Hypoglycemic mechanism of Psoraleae Fructus and its main chemical constituents[J/OL]. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine: 1−10 [2022-03-02]. DOI: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20211229.701.
[16] 常爱冰, 刘妍如, 王梅, 等. 基于“甾酮类化学成分-抗氧化生物活性”关联分析评价牛膝药材商品等级[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2020,32(10):1737−1746. [CHANG A B, LIU Y R, WANG M, et al. Commercial grade evaluation of Achyranthes bidentata based on "phytoecdysones components-antioxidant biological activity" correlation[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2020,32(10):1737−1746. CHANG A B, LIU Y R, WANG M, et al. Commercial grade evaluation of Achyranthes bidentata based on "phytoecdysones components-antioxidant biological activity" correlation[J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 2020, 32(10): 1737 -1746.
[17] 秦月雯, 侯金丽, 王萍, 等. 马齿苋“成分-活性-中药功效-疾病”研究进展及关联分析[J]. 中草药,2020,51(7):1924−1938. [QIN Y W, HOU J L, WANG P, et al. Research progress and correlation analysis on “phytochemistry-pharmacological effects-CMM efficacy-diseases”of Portulaca oleracea[J]. Chinese Herbal Medicine,2020,51(7):1924−1938. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2020.07.030 QIN Y W, HOU J L, WANG P, et al. Research progress and correlation analysis on “phytochemistry-pharmacological effects-CMM efficacy-diseases”of Portulaca oleracea[J]. Chinese Herbal Medicine, 2020, 51(7): 1924-1938. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2020.07.030
[18] 裴文清, 吕泸楠, 王靖宇, 等. 木瓜皮多酚和黄酮提取工艺优化及酪氨酸酶与胰脂肪酶抑制活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(1):188−195. [PEI W Q, LYU L N, WANG J Y, et al. Optimization of extraction of polyphenols and flavonoids from papaya peel and its anti-tyrosinase and anti-pancreatic lipase[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(1):188−195. PEI W Q, LU L N, WANG J Y, et al. Optimization of extraction of polyphenols and flavonoids from papaya peel and its anti-tyrosinase and anti-pancreatic lipase[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(1): 188-195.
[19] 崔施展, 谢晓亮, 贾东升, 等. 黑枸杞不同溶剂提取物抗氧化活性[J]. 食品研究与开发,2017,38(9):38−41. [CUI S Z, XIE X L, JIA D S, et al. Antioxidant activity of extracts from different solvents of black wolfberry[J]. Food Research and Development,2017,38(9):38−41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2017.09.009 CUI S Z, XIE X L, JIA D S, et al. Antioxidant activity of extracts from different solvents of black wolfberry[J]. Food Research and Development, 2017, 38(9): 38-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2017.09.009
[20] 杨美莲, 程桂广, 蔡圣宝, 等. 朝鲜蓟叶多酚提取及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 现代食品科技,2019,35(4):157−165, 21. [YANG M L, CHENG G G, CAI S B, et al. Extraction and antioxidant activity of polyphenols from Artichoke leaves[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2019,35(4):157−165, 21. YANG M L, CHENG G G, CAI S B, et al. Extraction and antioxidant activity of polyphenols from Artichoke leaves[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2019, 35(4): 157-165, 21.
[21] 慕钰文, 黄玉龙, 张辉元. 花椒籽不同溶剂提取物的活性成分及抗氧化性比较[J]. 包装与食品机械,2021,39(3):21−26. [MU Y W, HUANG Y L, ZHANG H Y. Bioactive compounds extracted with different solvents from Zanthoxylum bungeanum Maxim. seeds and comparison of their antioxidant activities[J]. Packaging and Food Machinery,2021,39(3):21−26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1295.2021.03.004 MU Y W, HUANG Y L, ZHANG H Y. Bioactive compounds extracted with different solvents from Zanthoxylum Bungeanum Maxim. seeds and comparison of their antioxidant activities[J]. Packaging and Food Machinery, 2021, 39(3): 21-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1295.2021.03.004
[22] 黎善铭, 桂海霞, 梅朋飞, 等. 毛薯多糖提取分离工艺优化及抗氧化活性研究[J/OL]. 热带作物学报: 1−11 [2022-01-23]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1019.S.20211026.2212.002.html. LI S M, GUI H X, MEI P F, et al. Extraction, isolation, process optimization and anti-oxidant activity of polysaccharides from Dioscorea esculenta[J/OL]. Journal of tropical crops: 1−11 [2022-01-23]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/46.1019.S.20211026.2212.002.html.
[23] 李珊, 刘耀耀, 刘哲, 等. 狭果茶藨子黄酮提取工艺优化及其体外降血脂活性[J]. 食品研究与开发,2021,42(3):73−79. [LI S, LIU Y Y, LIU Z, et al. Optimization of the extraction process of flavonoids from Ribes stenocarpum Maxim. and its hypolipidemic activity in vitro[J]. Food Research and Development,2021,42(3):73−79. LI S , LIU Y Y, LIU Z, et al. Optimization of the extraction process of flavonoids from Ribes stenocarpum Maxim. and its hypolipidemic activity in vitro[J]. Food Research and Development, 2021, 42(3): 73-79.
[24] 李婧雯, 包怡红. 不同溶剂的蒲公英根提取物的抗氧化活性及降糖能力比较分析[J]. 现代食品科技,2020,36(5):64−72. [LI J W, BAO Y H. Comparative analysis of antioxidant and hypoglycemic aapabilities of Taraxacum mongolicum root extracts in different solvents[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2020,36(5):64−72. LI J W, BAO Y H. Comparative analysis of antioxidant and hypoglycemic aapabilities of Taraxacum Mongolicum root extracts in different solvents[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2020, 36(5): 64-72.
[25] 师聪, 宫号, 李茹, 等. 草果不同极性萃取物总黄酮、总多酚含量与其抗氧化活性的相关性[J]. 化学试剂,2022,44(1):84−89. [SHI C, GONG H, LI R, et al. Correlation between total flavonoids, total polyphenols and antioxidant activity of different extracts fromFructus herba[J]. Chemical Reagents,2022,44(1):84−89. SHI C, GONG H, LI R, et al. Correlation between total flavonoids, total polyphenols and antioxidant activity of different extracts from Fructus herba[J]. Chemical Reagents, 2022, 44(1): 84-89.
[26] 师聪, 解春芝, 张建萍, 等. 覆盆子不同极性溶剂提取物的抗氧化活性比较[J]. 食品科技,2021,46(1):220−224. [SHI C, XIE C Z, ZHANG J P, et al. Comparison of antioxidant activities of different solvent extracts from raspberry[J]. Food Science and Technology,2021,46(1):220−224. SHI C, XIE C Z, ZHANG J P, et al. Comparison of antioxidant activities of different solvent extracts from Raspberry[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2021, 46(1): 220-224.
[27] 李春爱, 田立鹏, 蔡梦, 等. 橄榄果渣乙醇提取物成分分析及抗氧化和抑菌性能研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2022,34(1):7−15. [LI C A, TIAN L P, CAI M, et al. Study on the component, antioxidant and antibacterial properties of ethanol extract from olive pomace[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2022,34(1):7−15. LI C A, TIAN L P, CAI M, et al. Study on the component, antioxidant and antibacterial properties of ethanol extract from olive pomace[J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 2022, 34(1): 7-15.
[28] 姚旭, 郦萍, 顾青. 4种甜橙皮黄酮类化合物体外抗氧化活性及降糖降脂功能研究[J]. 中国食品学报,2022,22(1):49−57. [YAO X, LI P, GU Q. Studies on antioxidant activity, hypoglycemic and lipid-lowering capacity of flavonoids in sweet orange peels in vitro[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Science,2022,22(1):49−57. YAO X, LI P, GU Q. Studies on antioxidant activity, hypoglycemic and lipid-lowering capacity of flavonoids in sweet orange peels in vitro[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Science, 2022, 22(1): 49-57.
[29] 李井雷, 刘玉婷, 宗帅, 等. 羊肚菌胞外多糖体外降血糖降血脂活性研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2020,41(16):39−45. [LI J L, LIU Y T, ZONG S, et al. In vitro hyperglycemic and hypolipidemic activity of Morchella esculenta extracellular polysaccharides[J]. Food Research and Development,2020,41(16):39−45. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2020.16.006 LI J L, LIU Y T, ZONG S, et al. In vitro hyperglycemic and hypolipidemic activity of Morchella esculenta extracellular polysaccharides[J]. Food Research and Development, 2020, 41(16): 39-45. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2020.16.006
[30] 吕冰冰, 谢笔钧, 孙智达. 红肉番石榴果胶的理化特性及其体外降脂作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(20):51−60. [LYV B B, XIE B J, SUN Z D. Physical and chemical properties of red-flesh guava pectin and its lipid-lowering effect in vitro[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(20):51−60. LV B B, XIE B J, SUN Z D. Physical and chemical properties of red-flesh guava pectin and its lipid-lowering effect in vitro[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(20): 51-60.
[31] 林沛纯, 谌素华, 郑素丽. 亨氏马尾藻岩藻聚糖的提取及体外吸附胆酸盐的作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(17):58−61, 67. [LIN P C, CHEN S H, ZHENG S L. Extraction of fucoidan from Sargassum henslowianum and its binding effect on binding bile salts in vitro[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(17):58−61, 67. LIN P C, CHEN S H, ZHENG S L. Extraction of fucoidan from Sargassum henslowianum and its binding effect on binding bile salts in vitro[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(17): 58-61, 67.
[32] 唐茹萌, 焦文雅, 桑亚新, 等. 裙带菜多糖体外和体内降血脂活性[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(1):142−149. [TANG R M, JIAO W Y, SANG Y X, et al. In vitro and in vivo hypolipidemic effect of Undaria pinnatifida polysaccharide[J]. Food Science,2022,43(1):142−149. TANG R M, JIAO W Y, SANG Y X, et al. In vitro and in vivo hypolipidemic effect of Undaria pinnatifida polysaccharide[J]. Food Science, 2022, 43(1): 142-149.
[33] 赵有伟, 李德海. 超声微波协同制备粗毛纤孔菌多糖及体外降脂作用的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(20):191−198. [ZHAO Y W, LI D H. Ultrasonic and microwave synergistic preparation of polysaccharide from Inonotus hispidus and its effect on lowering lipid in vitro[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2021,42(20):191−198. ZHAO Y W, LI D H. Ultrasonic and microwave synergistic preparation of polysaccharide from Inonotus hispidus and its effect on lowering lipid in vitro[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2021, 42(20): 191-198.
[34] 古丽米热·祖努纳, 王伟雄, 吕泽, 等. 药桑葡萄酒发酵工艺优化及体外抗氧化与结合胆酸盐能力研究[J/OL]. 食品工业科技: 1−17 [2022-01-23]. DOI: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021060236 GULEMIRE Z, WANG W X, LYU Z, et al. Optimization of fermentation process of grape medicine mulberry wine and its antioxidant and bile acid binding capacity in vitro[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry: 1−17 [2022-01-23]. DOI: 10.13386/j.isssn1002-0306.2021060236.
[35] 张天凤, 张振山, 王帅, 等. 亚麻籽粕提取物抗氧化成分及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 粮食与油脂,2021,34(12):137−141. [ZHANG T F, ZHANG Z S, WANG S, et al. Study on antioxidant components and antioxidant activity of flaxseed meal extract[J]. Grain and Oil,2021,34(12):137−141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2021.12.032 ZHANG T F, ZHANG Z S, WANG S, et al. Study on antioxidant components and antioxidant activity of flaxseed meal extract[J]. Grain and Oil, 2021, 34(12): 137-141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2021.12.032
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)









 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



