Rosa roxburghii Fruit Wine Improves Glucose and Lipid Metabolism Disorder in Type 2 Diabetic Rats
-
摘要: 为探究刺梨果酒对2型糖尿病大鼠糖脂代谢紊乱的影响及可能机制。采用高脂高糖膳食联合腹腔注射链佐霉素(Streptozocin,STZ)建立2型糖尿病大鼠模型,将造模成功的大鼠分为刺梨果酒高(8 mL/kg)、中(4 mL/kg)、低(2 mL/kg)剂量组和模型组,并设空白对照组,给药期间每2周测一次空腹血糖,实验时间28 d。实验结束后测量血清和肝脏中高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(High-density lipoprotein cholesterol,HDL-C)、果糖胺(fructosamine,FMN)、甘油三酯(Triglyceride,TG)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol,LDL-C)、总胆固醇(Total cholesterol,TC)、肝糖原等含量;采用实时灾光定量PCR(real time polymerase chain reaction,RT-PCR)测定肝脏中腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶(AMP-activated protein kinase α,AMPK)、乙酰辅酶A羧化酶(Acetyl-CoA carboxylases alpha,ACACA)、β-羟-β-甲戊二酸单酰辅酶A还原酶(3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase,HMG-CoA)、脂肪酸合成酶(fatty acid synthetase,FASN)、和葡萄糖转运载体2(Glucose Transporter 2,GLUT2)、胆固醇7α-羟化酶(Cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase,CYP7A1)等mRNA相对表达量。结果表明,与模型组相比,刺梨果酒可减缓2型糖尿病大鼠体重减轻和多饮、多食的症状;高、中剂量刺梨果酒降低实验大鼠空腹血糖和果糖胺的效果显著(P<0.05);各剂量组均有降低实验大鼠血清和肝脏TC、TG、LDL-C的含量和升高HDL-C含量的作用,其中高、中剂量效果显著(P<0.05);低、中、高刺梨果酒均可显著(P<0.05)上调AMPK、GLUT2和ACACA mRNA表达量,低、中、高刺梨果酒均可上调FASN mRNA表达量,其中高、中剂量组上调FASN mRNA表达量显著(P<0.05);中、高剂量刺梨果酒可显著(P<0.05)下调G6Pase、PEPCK、HMG-COA和CYP7A1 mRNA表达量。结论:刺梨果酒改善2型糖尿病大鼠糖脂代谢紊乱的机制可能与通过抑制内源性胆固醇、增加脂肪的从头合成及提高葡萄糖跨膜转速率有关。Abstract: This study aimed to investigate the effect of Rosa roxburghii fruit wine on glucose and lipid metabolism disorder in type 2 diabetic rats and its possible mechanisms. The model of type 2 diabetic mice was established by high fat and high sugar diet combined with intraperitoneal injection of streptozocin (STZ). The rats were divided into high (8 mL/kg), medium (4 mL/kg), low (2 mL/kg) dose groups and model group, blank group. Fasting blood glucose was measured every two weeks for 28 d. After the experiment, the contents of High-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), fructosamine (FMN), triglyceride (TG), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), total cholesterol (TC) and hepatic glycogen were measured in serum and liver. The relative mRNA expressions of AMP-activated protein kinase α (AMPK), Acetyl-CoA carboxylases alpha (ACACA), 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase (HMG-CoA), fatty acid synthase (FASN), Glucose Transporter 2 (GLUT2) and Cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) in liver were measured by real time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). The results showed that compared with the model group, Rosa roxburghii fruit wine alleviated the symptoms of weight loss, polydipsia and polyphagia in type 2 diabetic rats. High and medium dose Rosa roxburghii fruit wine significantly reduced fasting blood glucose and fructosamine content in experimental rats (P<0.05). The contents of TC, TG and LDL-C in plasma and liver were decreased and the content of HDL-C was increased in each dose group. Among them, the high and medium dose showed significant effects (P<0.05). Each dose group significantly increased the relative expression of AMPK, GLUT2 and ACACA mRNA (P<0.05). High, medium and low dose increased the relative expression of FASN mRNA, and the high and medium dose had significant effects (P<0.05). High and medium dose also significantly decreased the relative expression of G6Pase, PEPCK, HMG-COA and CYP7A1 mRNA (P<0.05). Conclusion: The mechanisms of Rosa roxburghii fruit wine to improve glucose and lipid metabolism disorder in type 2 diabetic rats may be related to the inhibition of endogenous cholesterol, the increase of lipid de novo synthesis and the increase of glucose transmembrane rotational speed.
-
糖尿病(Diabetes mellitus, DM),主要包括1-型、2-型和妊娠性糖尿病,是以持续性高血糖、脂质和蛋白代谢异常的一种复杂的代谢综合征[1-4],其中2型糖尿病是主要类型,约占DM的90%~95%[5-6],2017年的流行病学研究表明,中国糖尿病患病率11.2%,总人数约为1.164亿,居世界首位[7-9]。糖尿病已经给人们生活质量及健康带来严重负担,随着DM患病率的逐年增加,防治任务十分艰巨。因此,如何有效延缓糖尿病的发生与发展,已成为世界性的公共卫生问题。
刺梨(Rosa roxbunghii)为蔷薇科(Rosaceae)缫丝花的果实[10],目前贵州省刺梨栽培面积(500万亩以上)和产量(1500万kg以上)均居世界之首;刺梨作为我国药食同源水果,富含VC、SOD、单宁类、三萜皂苷类和黄酮类等活性成分[11]。近年来,刺梨汁在解酒护肝[12]、抗氧化、降血糖[13]、减肥[14]等方面的研究越来越受到人们的关注。陈超等[15]研究表明刺梨冻干粉、刺梨总黄酮提取物、刺梨总多糖提取物可显著改善2型糖尿病(T2DM)小鼠糖脂代谢紊乱的作用;Yu等[16]研究表明刺梨三萜类物质具有抑制肝癌细胞的增殖和分化作用。综合以上文献,刺梨及其活性成分在降血糖、减肥、抗氧化、增加免疫等功效方面均取得了一定的成果,而将刺梨经发酵制成果酒后的功效方面的研究报道较少。许立伟等[17]表明,5种浆果果酒的抗氧化活性排序为野生蓝莓果酒>野生蓝靛果果酒>蓓蕾蓝靛果果酒>不老莓果酒>北陆蓝莓果酒;Rtss等[18]对百香果果酒的理化特征、生物活性、体外抗氧化活性进行了详细研究。然而,在刺梨果酒功效方面的研究才刚刚起步,本课题组前期的研究发现,刺梨果酒可通过胰岛素介导的PI3K途径改善1型糖尿病大鼠机体糖代谢紊乱[19]及对高脂诱导的小鼠肥胖具有预防作用,其机制与减少体内脂肪堆积,改善脂代谢紊乱有关[20]。而刺梨果酒对2型糖尿病糖脂代谢影响的研究未见报道。
因此,本实验通过长期高脂高糖膳食并联合腹腔STZ构建2型糖尿病模型后,给予不同剂量刺梨果酒干预,分别从大鼠生长情况、生理生化指标等考察刺梨果酒对2型糖尿病大鼠糖、脂水平的影响;并从胆固醇、脂肪合成与分解、葡萄糖跨膜转运关键基因mRNA水平探讨刺梨果酒对2型糖尿病大鼠机体糖脂代谢的作用机制,以期为刺梨果酒市场化、工业化提供科学的数据支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
刺梨 由贵州十里刺梨示范园区财满园基地提供;刺梨果酒 实验室自制;雄性SD大鼠[SCXK(渝)20120008]和基础饲料 重庆滕鑫比尔实验动物销售有限公司;Loading buffer、DNA marker DL2000、荧光定量试剂盒、RNA逆转录试剂盒、Total RNA提取试剂 宝生物工程有限公司;果糖胺、甘油三酯、总胆固醇、低密度脂蛋白、高密度脂蛋白等测定试剂盒 南京建成生物科技有限公司;BCA蛋白测定试剂盒 碧云天生物技术研究所;全蛋白提取试剂盒 生工生物工程股份有限公司;胆固醇(食品级)、蛋黄粉(食品级) 河南大田食品添加剂;猪油(食品级)、蔗糖(食品级) 永辉超市股份有限公司;胆盐(分析纯) 成都市科龙化工试剂厂;其它试剂 均为分析纯。
KQ5200DB超声波清洗器 昆山市超声仪器有限公司;3-18k冷冻离心机 德国Sigma公司;FSH-2可调高速均浆器 江苏省金坛市环宇科学仪器厂;XW-80漩涡混合器 上海青浦沪西仪器厂;HITACHI-7020全自动生化分析仪 日本株式会社日立制作所;H1MG酶标仪 美国基因有限公司;Nano Drop 1000微量紫外分光光度 美国Thermo公司;S1000梯度PCR仪 美国BIO-RAD公司;Tissue Lyser II组织研磨仪 德国Qiagen公司;荧光定量PCR仪 Light Cycler Nan美国罗氏公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 刺梨果酒
参照李劲松[21]的方法并做适当改进,其主要步骤为:挑选适宜成熟度、无病虫害的刺梨鲜果进行清洗、揉搓,装入容器,调整糖度(21.0 Brix%),pH3.5,控温(25~28 ℃)发酵6 d,陈酿,过滤,密封后存储于温度18±2 ℃、相对湿度75%~80%的冷藏库中。因新酿的刺梨果酒涩味较重,滋味弱,而2年陈酿的刺梨果酒涩味及滋味均较好,市场接受度也是最好的,故选取2年陈酿的刺梨果酒进行本试验[19-20]。
1.2.2 动物饲养与分组
将50只120~140 g健康雄性大鼠饲养于相对湿度50%~55%、室温25±2 ℃、12 h/12 h明暗交换的实验动物房中,适应性饲喂1周后。称量质量并作好标记后,按体质量随机分为空白组(n=10)和模型组(n=40),空白组饲喂基础饲料,而模型组采用高脂高糖饲喂30 d后,禁食不禁水12 h后,模型组按体质量腹腔注射STZ 45 mg/kg(0.1 mol/L柠檬酸盐缓冲液,pH4.2),而空白组大鼠腹腔注射等量柠檬酸盐缓冲液,注射7 d后,禁食不禁水12 h后,检测其空腹血糖,选了空腹血糖≥11.1 mmol·L−1[22]的大鼠,并按血糖和体质量随机分为模型对照组(MC)、刺梨果酒低(2 mL/kg, LD)、中(4 mL/kg, MD)、高剂量组(8 mL/kg, HD),为了排除酒精对实验结果的干扰,空白组与模型组灌胃与中剂量等酒度(蒸馏水稀释)、等剂量(4 mL/kg)的红星二锅头,空白组给予基础饲料,其余各组给予高脂高糖饲料。参考《保健食品功能学评价程序和检验方法》配制高脂高糖饲料,配方(%)为:基础饲料+1.5%胆固醇+10%蛋黄粉+10%猪油+0.25%胆盐+5%蔗糖。实验期间,每3 d称一次体质量,并根据体质量调整灌胃剂量,实验期间自由饮水和摄食,实验时间28 d。实验第28 d时,各组禁食不禁水12 h后,采用乙醚麻醉、断头处死颈部采血,血液在4000 r/min,4 ℃的条件下离心15 min,−80 ℃冻存,待用。迅速解剖各组织、称重、分装后置于−80 ℃保存,备用。
1.2.3 指标测定
1.2.3.1 空腹血糖测定
在给药处理第0、14、28 d,大鼠禁食不禁水12 h后,尾部静脉采血,采用血糖仪测定其空腹血糖。
1.2.3.2 生理生化指标的测定
血浆、肝脏组织中甘油三酯(TG)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)、血浆果糖胺、总胆固醇(TC)、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-C)等严格按照试剂盒方法进行检测。
1.2.3.3 RT-PCR的分析
从组织样品中提取总RNA,使用Qiagen提取并反转录得cDNA,使用紫外分光光度计测定RNA浓度。以β-actin为内参并采用2−ΔCt法计算各基因相对表达,操作步骤如下[2-4]:总RNA提取,检测其纯度,再经过反转录、cDNA的合成及检测(具体为95 ℃预变性30 s;95 ℃变性5 s,60 ℃退火20 s,72 ℃延伸50 s,45个循环)。各基因的引物序列如表1。
表 1 用于RT-PCR引物序列Table 1. Primer sequences for RT-PCR基因名 引物序列(5’~3’) 上游 下游 HMG-COA GACCAACCTTCTACCTCAGCAAG ACAACTCACCAGCCATCACAGT CYP7A1 GAGGGATTGAAGCACAAGAACC ATGCCCAGAGAATAGCGAGGT ACACA CATCCGGCGACTTACGTTC AAACTTATCCCTTGCTCGGAA FASN TCAACCTGCTCCTGAAGCCGAA GCCTCAGAGCGACAATATCCAC AMPK CGGGGTCATTCTCTATGCTT TTTAAACCACTCGTGTTCCCT PEPCK GACAGACTCGCCCTATGTGGTG GGTTGCAGGCCCAGTTGTTG G6Pase GGCTCACTTTCCCCATCAGGT CCAAGTGCGAAACCAAACAGG GLUT2 CCAGCACATACGACACCAGACG CCAAAGAACGAGGCGACCAT β-actin ACGTCAGGTCATCACTATCG GGCATAGAGGTCTTTACGGATG 1.3 数据处理
实验数据采用SPSS 21.0及Origin 8.1进行数据统计处理,多组间比较采用One-way ANOVA进行Duncan分析、两组间比较采用Student’s t检验,以P<0.05为有统计学差异。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 刺梨果酒对2型糖尿病大鼠生长状况的影响
刺梨果酒对2型糖尿病大鼠生长状况的影响如表2。由表2可知,与空白组相比,经过28 d高脂高糖饲养后,模型组和各试量组初体质量均显著(P<0.05)高于空白组;而采用STZ联合高脂高糖构建2型糖尿病模型后,由末体重和体重增加量可知,模型组和各试量组体重增加缓慢;与空白组相比,模型组末体重显著(P<0.05)降低了13.70%;而经过28 d不同剂量刺梨果酒灌胃后,与模型组相比,刺梨果酒均可增加试验大鼠体重的增加量,其中低、中、高各显著(P<0.05)增加了49.01%、50.36%和48.29%。与空白相比,模型组采食量和饮水量均显著增加,分别增加了40.88%和59.35%(P<0.05),而给予刺梨果酒后,均可改善实验大鼠“多饮、多食”的症状,其中高、中剂量改善显著(P<0.05)。说明刺梨果酒可减缓2型糖尿病大鼠体重减轻和多饮、多食的糖尿病典型症状。
表 2 刺梨果酒对大鼠生长状况的影响(n=10)Table 2. Effect of Rosa roxburghii fruit wine on growth of rats (n=10)组别 初体重(g) 末体重(g) 体重增加量(g) 采食量(g/4 w) 饮水量(mL/4 w) Control 207.92±8.54 319.44±10.21 111.52±5.05 510.033±15.99 528.21±4.21 MC 256.32±6.21*a 275.69±12.62*b 19.37±4.43*c 862.83±10.93*a 1299.48±10.32*a LD 252.74±7.23a 281.69±7.62b 28.95±3.43b 847.09±14.21a 1178.90±12.91b MD 257.33±5.32a 296.35±5.61a 39.02±5.31b 819.32±18.32b 928.19±14.21c HD 253.08±8.77a 291.07±8.16a 37.99±5.83a 792.99±12.61b 891.19±17.21c 注:不同字母a、b、c表示各试剂量与模型组之间存在显著性差异(P<0.05);*表示MC组与Control组间存在显著性差异(P<0.05)。Control:空白对照组;MC:模型对照组;LD:刺梨果酒低剂量组(2 mL/kg);MD:刺梨果酒中剂量组(4 mL/kg);HD:刺梨果酒高剂量组(8 mL/kg);图1~图4同。 2.2 对大鼠空腹血糖(FBG)和果糖胺(FMN)的影响
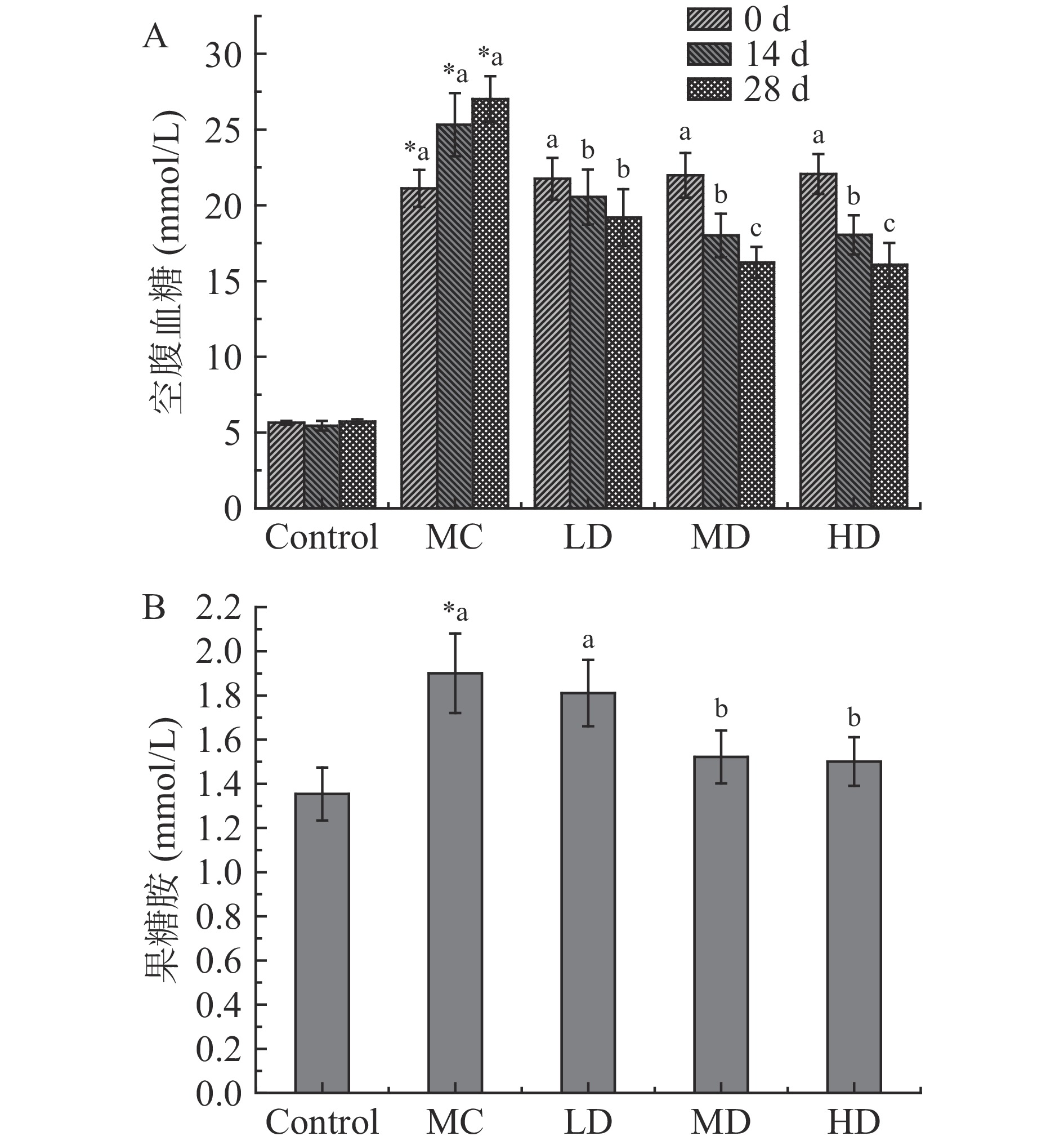
刺梨果酒对2型糖尿病大鼠空腹血糖(FBG)和果糖胺(FMN)的影响如图1。由图1A可知,实验期间空白组血糖值始终处在正常值内,而模型组实验期间空腹血糖值始终≥11.1mmol·L−1,说明模型稳定。然而,随着刺梨果酒灌胃时间的延长,大鼠空腹血糖值逐渐降低;不同剂量刺梨果酒灌胃14 d后,高、中、低剂量组大鼠空腹血糖值分别降低了28.71%、28.87%和18.84%;给28 d后,高、中、低剂量组空腹血糖值分别下降了28.95%、39.91%和40.47%。
由图1B可知,与正常对照大鼠比,模型组大鼠果糖胺显著(P<0.05)升高了28.77%;与模型组相比,刺梨果酒均有降低大鼠果糖胺的作用,其中高、中剂量组降低显著(P<0.05),分别降低了19.94%和21.04%。以上结果表明,刺梨果酒高剂量和中剂量不仅可以降低实验大鼠即时血糖,对长期血糖(果糖胺)也有显著(P<0.05)的降低效果。
2.3 刺梨果酒对2型糖尿病血脂和肝脂的影响
刺梨果酒对2型糖尿病血脂和肝脂的影响如图2。由图2可知,与空白组相比,模型组血清和肝脏TC和TG显著(P<0.05)升高,其中TC分别升高了34.20%和44.78%,TG分别升高了46.51%和40.45%,HDL-C显著(P<0.05)下降了28.32%和54.83%。与模型组相比,灌胃刺梨果酒后,大鼠血清中TC分别下降6.49%、24.68%和27.71%,TG分别下降9.86%、26.68%和30.89%,其中高剂量和中剂量显著(P<0.05)降低大鼠血清TC和TG含量;各试剂组均有升高HDL-C和降低LDL-C的趋势,但不显著(P>0.05)。大鼠肝脏TC分别降低了9.63%、16.99%和18.21%,TG分别降低了9.99%、24.21%和20.84%,其中高剂量和中剂量降低肝脏TC和TG的效果显著。有升高大鼠肝脏HDL-C和降低LDL-C的趋势,但不显著(P>0.05)。说明刺梨果酒有改善2型糖尿病大鼠的脂质代谢紊乱,这与以往研究结果相一致[13-14]。
2.4 对肝脏糖代谢关键基因mRNA水平的影响
刺梨果酒对肝脏糖代谢关键基因mRNA水平的影响如图3。由图3可知,与空白组相比,模型组PEPCK和G6Pase mRNA表达量显著(P<0.05)上调,分别上调了54.70%和53.15%,显著(P<0.05)下调AMPK和GLUT2 mRNA表达量,分别下调了53.37%和56.55%。与模型组相比,刺梨果酒可显著(P<0.05)上调AMPK mRNA表达量,分别上调了16.96%、19.12%和18.78%,但各剂量组间差异不显著(P>0.05);可显著(P<0.05)下调G6Pase mRNA表达量,分别下调了9.08%、34.46%和39.39%;可下调PEPCK mRNA表达量,其中高、中剂量组显著(P<0.05)下调了16.38%和17.24%;可显著(P<0.05)上调GLUT2 mRNA表达量,分别下调了17.90%、38.97%和39.47%。说明刺梨果酒可通过减少2型糖尿病大鼠肝脏糖异生作用和增加葡萄糖转运速率来降低机体血糖水平。
2.5 对肝脏脂代谢关键基因mRNA水平的影响
刺梨果酒对肝脏脂代谢关键基因mRNA水平的影响如图4。由图4可知,与空白组相比,模型组HMG-COA和CYP7A1 mRNA水平显著(P<0.05)上调了46.05%和70.72%;显著(P<0.05)下调ACACA和FASN mRNA水平,分别下调了79.38%和40.47%。与模型组相比,刺梨果酒均可下调HMG-COA和CYP7A1 mRNA表达量,其中高、中剂量组显著(P<0.05)下调HMG-COA和CYP7A1 mRNA表达量,其中HMG-COA mRNA分别下调了14.91%和15.58%,CYP7A1 mRNA表达量分别下调了22.56%和12.42%。低、中、高剂量均可显著(P<0.05)上调ACACA mRNA表达量,分别上调了45.30%、66.81%和68.43%;有上调FASN mRNA表达量,其中高、中剂量组分别显著(P<0.05)上调了29.71%和32.11%。以上结果表明,刺梨果酒可通过抑制机体肝脏内源性胆固醇的合成、加速胆汁酸排泄,增加脂肪酸的从头合成的作用。
3. 讨论
糖尿病临床表现的典型症状为多尿、多食、多饮、消瘦,即“三多一少”症状。目前长期高脂高糖诱导联合低剂量STZ腹腔注射是世界公认的构建2型糖尿病动物模型方式[23]。本实验过程中模型组空腹血糖值始终≥11.1 mmol·L−1,而且大鼠出现精神萎靡、活动量少、多尿、多饮、多食等糖尿病典型症状,说明模型构建成功,这与前人的研究结果一致[24]。而给予刺梨果酒后,可改善实验大鼠“多饮、多食”的症状,说明刺梨果酒可减缓2型糖尿病大鼠体重减轻和多饮、多食的糖尿病典型症状,这与刺梨果酒在1型糖尿病的效果相似[19]。空腹血糖是临床诊断糖尿病的关键指标,可反映机体即时血糖[25],但空腹血糖不能反映机体长期血糖的变化情况,而果糖胺可以反映机体2~3周内的平均血糖情况[26]。实验结果表明,刺梨果酒不仅可以降低实验大鼠即时血糖,对长期血糖(果糖胺)也有显著的降低效果。这可能与刺梨果酒中总黄酮、多酚、多糖、槲皮素、VC等功能性物质有关。Wang等[27]研究表明,槲皮素可抑制肝脏细胞氧化应激的调节因子硫氧还蛋白(thioredoxin interaction protein, TXNIP)的表达量,降低高血糖条件下的肝脏炎症和脂质积累;陈超等[15]研究发现,刺梨黄酮、多糖均可改善2型糖尿病小鼠糖脂代谢紊乱,而且刺梨多糖的效果大于刺梨黄酮;周艺[28]研究表明,刺梨茶中多酚、黄酮也可有效降低糖尿病小鼠FBG值。汪磊[29]从体外化学、细胞及动物在体实验研究表明,刺梨多糖具有显著的降血糖和血脂的效果。
血脂水平是判断机体脂代谢是否正常的重要指标[30],而脂质代谢异常作为糖尿病常见并发症之一。肝脏是负责脂肪酸的重头合成、转化、重新分布等的重要代谢器官[31]。因此,动物实验往往采用血脂和肝脂水平作为判断机体脂代谢情况。实验结果表明,刺梨果酒可降低大鼠血浆TC、TG和LDL-C含量,和升高HDL-C的含量。表明刺梨果酒有改善2型糖尿病大鼠的脂质代谢紊乱。陈萍等[14]研究表明,刺梨汁可降低高脂膳食小鼠肝脏血清和肝脏TC、TG和LDL-C含量,升高HDL-C的含量,说明刺梨汁具有降血脂的效果。梁敏[32]研究表明,蓝靛果酒加工工艺会影响其营养成分,但其体外抗氧化和降脂能力一直处于较高水平;陈珍等[20]研究表明,刺梨果酒可有效降低高脂血症大胆固醇代谢和脂肪酸的从头合成。综合以上文献和本实验结果推测,刺梨果酒改善2型糖尿病大鼠的脂质代谢可能与增加机体抗氧化、促进胆固醇代谢和脂肪酸从头合成有关,但其具体机制还有待进一步研究。
现已研究表明,胰岛素信号通信调节许多肝脏基因的表达速率,包括葡萄糖-6-磷酸酶(G6Pase)、磷酸烯醇式丙酮酸羧化酶(PEPCK)和葡萄糖-6-磷酸脱氢酶(G6PDHase)[33],这些酶的基因的表达在2型糖尿病中也受到异常调节[34],其中PEPCK和G6Pase是肝脏糖异生的关键限速酶,其活性直接影响糖异生的速度[35]。实验结果表明,刺梨果酒可下调G6Pase和PEPCK mRNA表达量,说明刺梨果酒可减缓肝脏糖异生的作用,降低血糖水平。而葡萄糖转运蛋白2(glucose transporter 2,GLUT2)在肝脏中具有高表达量,与葡萄糖的跨膜转位水平正相关[36]。而刺梨果酒可增加GLUT2 mRNA表达量,说明刺梨果酒提高机体葡萄糖的跨膜转位水平,促进葡萄糖的转移。现已研究表明,腺苷单磷酸依赖蛋白激酶(adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase,AMPK)在胰岛素抵抗的发生中起作重要作用,其参与能量代谢、脂代谢和糖代谢过程[2-3,37]。HMG-CoA是肝脏合成胆固醇的第一个限速酶/关键酶[38],目前临床上用的他汀类药物是HMG-CoA的抑制剂[39];CYP7A1是肝脏催化胆汁酸合成途径中的限速酶,其活性的增加能够加速机体胆固醇向胆汁酸转化[40-41];实验结果表明,刺梨果酒可下调HMG-COA和CYP7A1 mRNA表达量,说明刺梨果酒可降低肝脏胆固醇合成的速率和减缓肝脏胆固醇向胆汁酸转化。而ACACA作为肝脏脂肪酸合成关键酶,其活性与脂肪酸的合成速度相关,而ACACA经AMPK磷酸化后可抑制脂肪酸合成;脂肪酸合成酶(Fatty acid synthase, FASN)是一种关键的脂肪酸代谢酶,其催化长链饱和脂肪酸合成的终端步骤[42]。刺梨果酒可上调ACACA和FASN mRNA表达量。以上结果表明,刺梨果酒可通过抑制机体肝脏内源性胆固醇的合成、加速胆汁酸排泄,增加脂肪酸的从头合成的作用。
4. 结论
实验结果表明,刺梨果酒有减缓2型糖尿病症状,可降低2型糖尿病空腹血糖和果糖胺的水平,可有效降低大鼠血清和肝脏脂质水平;其机制与刺梨果酒上调肝脏组织中AMPK、GLUT2、ACACA、FASN mRNA表达量和下调G6Pase、PEPCK、HMG-COA、CYP7A1 mRNA表达量有关。从生理生化及mRNA结果表明,刺梨果酒改善2型糖尿病大鼠的症状可能是调节脂代谢和糖代谢的综合结果,但其机制的探索还需从蛋白水平、代谢组学、转录组学、代谢网络等深入研究。
-
表 1 用于RT-PCR引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences for RT-PCR
基因名 引物序列(5’~3’) 上游 下游 HMG-COA GACCAACCTTCTACCTCAGCAAG ACAACTCACCAGCCATCACAGT CYP7A1 GAGGGATTGAAGCACAAGAACC ATGCCCAGAGAATAGCGAGGT ACACA CATCCGGCGACTTACGTTC AAACTTATCCCTTGCTCGGAA FASN TCAACCTGCTCCTGAAGCCGAA GCCTCAGAGCGACAATATCCAC AMPK CGGGGTCATTCTCTATGCTT TTTAAACCACTCGTGTTCCCT PEPCK GACAGACTCGCCCTATGTGGTG GGTTGCAGGCCCAGTTGTTG G6Pase GGCTCACTTTCCCCATCAGGT CCAAGTGCGAAACCAAACAGG GLUT2 CCAGCACATACGACACCAGACG CCAAAGAACGAGGCGACCAT β-actin ACGTCAGGTCATCACTATCG GGCATAGAGGTCTTTACGGATG 表 2 刺梨果酒对大鼠生长状况的影响(n=10)
Table 2 Effect of Rosa roxburghii fruit wine on growth of rats (n=10)
组别 初体重(g) 末体重(g) 体重增加量(g) 采食量(g/4 w) 饮水量(mL/4 w) Control 207.92±8.54 319.44±10.21 111.52±5.05 510.033±15.99 528.21±4.21 MC 256.32±6.21*a 275.69±12.62*b 19.37±4.43*c 862.83±10.93*a 1299.48±10.32*a LD 252.74±7.23a 281.69±7.62b 28.95±3.43b 847.09±14.21a 1178.90±12.91b MD 257.33±5.32a 296.35±5.61a 39.02±5.31b 819.32±18.32b 928.19±14.21c HD 253.08±8.77a 291.07±8.16a 37.99±5.83a 792.99±12.61b 891.19±17.21c 注:不同字母a、b、c表示各试剂量与模型组之间存在显著性差异(P<0.05);*表示MC组与Control组间存在显著性差异(P<0.05)。Control:空白对照组;MC:模型对照组;LD:刺梨果酒低剂量组(2 mL/kg);MD:刺梨果酒中剂量组(4 mL/kg);HD:刺梨果酒高剂量组(8 mL/kg);图1~图4同。 -
[1] GOLDENBERG R, PUNTHAKEE Z. Definition, classification and diagnosis of diabetes, prediabetes and metabolic syndrome[J]. Canadian Journal of Diabetes,2013,37(suppS1):S8−S11.
[2] REN T, ZHU Y, KAN J. Zanthoxylum alkylamides activate phosphorylated AMPK and ameliorate glycolipid metabolism in the streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats[J]. Clinical and Experimental Hypertension (New York, NY:1993),2017,39(4):330−338. doi: 10.1080/10641963.2016.1259332
[3] REN T, ZHU Y, XIA X, et al. Zanthoxylum alkylamides ameliorate protein metabolism disorder in STZ-induced diabetic rats[J]. Journal of Molecular Endocrinology,2017,58(3):113−125. doi: 10.1530/JME-16-0218
[4] YOU Y M, REN T, ZHANG S Q, et al. Hypoglycemic effects of Zanthoxylum alkylamides by enhancing glucose metabolism and ameliorating pancreatic dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats[J]. Food & Function,2015,6(9):3144−3154.
[5] DENNIS J M. Precision medicine in type 2 diabetes: Using individualized prediction models to optimize selection of treatment[J]. Diabetes,2020,69(10):dbi200002.
[6] POUYA S, INGA P, PARASKEVI S, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the international diabetes federation diabetes atlas, 9th edition[J]. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice,2019,157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843
[7] 中华医学会糖尿病学分会. 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版)[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志,2021,13(4):315−409. [Chinese Diabetes Society. Guideline for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in China (2020 edition)[J]. Chinese Journal of Diabetes Mellitus,2021,13(4):315−409. Chinese Diabetes Society. Guideline for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus in China (2020 edition)[J]. Chinese Journal of Diabetes Mellitus, 2021, 13(4): 315-409.
[8] LIY Z, FU C, WANG W, et al. Prevalence of chronic complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus in outpatients-a cross-sectional hospital based survey in urban China[J]. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes,2010,8(1):62. doi: 10.1186/1477-7525-8-62
[9] KISA A, KISA S, COLLABORATORS G S. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990~2019: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019[J]. The Lancet Neurology,2021:1−26.
[10] YOSHIDA T, CHEN X M, HATANO T, et al. Tannins and related polyphenols of rosaceous medicinal plants. IV. Roxbins A and B from Rosa roxburghii fruits[J]. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin,1987,35(5):1817−1822.
[11] 白静, 张宗泽, 鲁敏, 等. 贵州不同地区野生刺梨果实品质分析[J]. 贵州农业科学,2016,44(3):43−46. [BAI J, ZHANG Z Z, LU M, et al. Fruit quality of wild Rosa roxburghii germplasm resources from different regions in Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences,2016,44(3):43−46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2016.03.011 BAI J, ZHANG Z Z, LU M, et al. Fruit quality of wild Rosa roxburghii germplasm resources from different regions in Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 44(3): 43-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2016.03.011
[12] 黄颖, 谭书明, 陈小敏, 等. 刺梨口服液对急性醉酒小鼠的解酒护肝作用[J]. 现代食品科技,2019,35(7):18−23. [HUANG Y, TAN S M, CHEN X M, et al. Antialcoholism effects of Rosa roxburghii Tratt oral liquid in acute drunkenness mice[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2019,35(7):18−23. HUANG Y, TAN S M, CHEN X M, et al. Antialcoholism effects of Rosa roxburghii Tratt oral liquid in acute drunkenness mice[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2019, 35(7): 18-23.
[13] 陈小敏, 谭书明, 黄颖, 等. 刺梨汁对Ⅰ型糖尿病小鼠的降糖作用[J]. 现代食品科技,2019,35(8):13−20. [CHEN X M, TAN S M, HUANG Y, et al. Hypoglycemic effect of Rosa roxburghii juice on type I diabetic mice[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2019,35(8):13−20. CHEN X M, TAN S M, HUANG Y, et al. Hypoglycemic effect of Rosa roxburghii juice on type I diabetic mice[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2019, 35(8): 13-20.
[14] 陈萍, 谭书明, 陈小敏, 等. 刺梨、蜂胶、山楂口服液的降血脂功能研究[J]. 现代食品科技,2019,35(8):78−83. [CHEN P, TAN S M, CHEN X M, et al. Study on hypolipidemic activity of Rosa roxburghii Tratt, propolis and crataegus oral liquid[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2019,35(8):78−83. CHEN P, TAN S M, CHEN X M, et al. Study on hypolipidemic activity of Rosa roxburghii Tratt, propolis and crataegus oral liquid[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2019, 35(8): 78-83.
[15] 陈超, 谭书明, 王画, 等. 刺梨及其活性成分对2型糖尿病小鼠糖脂代谢的影响[J/OL]. 食品科学: 1−14[2021-10-21]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2206.ts.20210723. 1740.028. htm. CHEN C, TAN S M, WANG H, et al. Effects of Rosa roxburghii Tratt and its active ingredients on glucose and lipid metabolism in type 2 diabetic mice[J/OL]. Food science: 1−14[2021-10-21]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/ detail/11.2206.ts.20210723. 1740.028. htm.
[16] YU L M, FANG N, YANG X S, et al. Effects of Rosa roxburghii extract on proliferation and differentiation in human hepatoma SMMC-7721 cells and CD34(+) haematopoietic cells[J]. Journal of Health Scienc,2007,53(1):10−15. doi: 10.1248/jhs.53.10
[17] 许立伟, 王炳宇, 杨馨悦, 等. 5种浆果果酒抗氧化活性差异及综合评价[J]. 中国酿造,2021,40(9):200−205. [XU L W, WANG B Y, YANG X Y, et al. Difference and comprehensive evaluation of antioxidant activity of 5 kinds of fruit wine[J]. China Brewing,2021,40(9):200−205. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2021.09.036 XU L W, WANG B Y, YANG X Y, et al. Difference and comprehensive evaluation of antioxidant activity of 5 kinds of fruit wine[J]. China Brewing, 2021, 40(9): 200-205. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2021.09.036
[18] RTSS A, ACTB B, ACPR B, et al. Physicochemical characterization, bioactive compounds, in vitro antioxidant activity, sensory profile and consumer acceptability of fermented alcoholic beverage obtained from Caatinga passion fruit (Passiflora cincinnata Mast. )[J]. LWT,2021,148:111714. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111714
[19] 安玉红, 陆敏涛, 卢秀, 等. 刺梨果酒通过胰岛素介导的PI3K途径改善1-型糖尿病大鼠机体糖代谢紊乱[J]. 现代食品科技,2020,36(7):25−33. [AN Y H, LU M T, LU X, et al. Rosa roxburghii Tratt wine can improve glucose metabolism disorder in type 1 diabetic rats through insulin-PI3K pathway[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2020,36(7):25−33. AN Y H, LU M T, LU X, et al. Rosa roxburghii Tratt wine can improve glucose metabolism disorder in type 1 diabetic rats through insulin-PI3K pathway[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2020, 36(7): 25-33.
[20] 陈珍, 陆敏涛, 徐方艳, 等. 刺梨果酒对高脂诱导肥胖小鼠脂代谢的影响[J/OL]. 食品工业科技: 1−16 [2021-10-21]. https: //doi. org/10.13386/j. issn1002-0306.2021050264. CHEN Z, LU M T, XU F Y, et al. Effects of Rosa roxburghii Tratt wine on lipid metabolism in hyperlipid-induced obesity mice[J/OL]. Science and Technology of Food Industry: 1−16 [2021-10-21]. https://doi.org/10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021050264.
[21] 李劲松. 刺梨果酒的酿造方法: CN 105331481B[P]. 2018. LI J S. Brewing method of Rosa roxburghii Tratt wine: CN 105331481B[P]. 2018.
[22] BEGORRE M A, DIB A, HABCHI K, et al. Microvascular vasodilator properties of the angiotensin II type 2 receptor in a mouse model of type 1 diabetes[J]. Scientific Reports,2017,7(1):45625. doi: 10.1038/srep45625
[23] KIM H J, CHAE I G, LEE S G, et al. Effects of fermented red ginseng extracts on hyperglycemia in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats[J]. Journal of Ginseng Research,2010,34(2):104−112. doi: 10.5142/jgr.2010.34.2.104
[24] SARAVANAN R, KV BABU, V RAMACHANDRAN. Effect of rebaudioside A, a diterpenoid on glucose homeostasis in STZ-induced diabetic rats[J]. Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry,2012,68(3):421−431. doi: 10.1007/s13105-012-0156-0
[25] RUSHFORTH N B, BENNETT P H, STEINBERG A G, et al. Diabetes in the pima indians. Evidence of bimodality in glucose tolerance distributions[J]. Diabetes,1971,20(11):756−758. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.11.756
[26] H MALMSTRÖM, WALLDIUS G, GRILL V, et al. Fructosamine is a useful indicator of hyperglycaemia and glucose control in clinical and epidemiological studies–cross-sectional and longitudinal experience from the AMORIS cohort[J]. PloS One,2014,9(10):e111463. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111463
[27] WANG W, WANG C, DING X Q, et al. Quercetin and allopurinol reduce liver thioredoxin-interacting protein to alleviate inflammation and lipid accumulation in diabetic rats[J]. Brit J Pharmacol,2013,169(6):1352−1371. doi: 10.1111/bph.12226
[28] 周艺. 刺梨茶对实验小鼠降血糖、血脂及抗氧化作用研究[D]. 贵州: 贵州大学, 2017. ZHOU Y. The study on the hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic and antioxidant activity effect from the tea of Rosa roxbugrhii Tratt[D]. Guizhou: Guizhou University, 2017.
[29] 汪磊. 刺梨多糖的分离纯化、降血糖作用及其对肠道微生态的影响[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2019. WANG L. Isolation, purification and hypoglycemic activity of polysaccharides from Rosa roxburghii Tratt fruit and their effect on gut microflora[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2019.
[30] ZHANG Y, WANG X, WANG W, et al. Effects of grape seed proanthocyanins on high-fat and high-sugar diet-induced metabolic syndrome in rats[J]. Food Science,2020,41(1):112−120.
[31] NGUYEN P, LERAY V, DIEZ M, et al. Liver lipid metabolism[J]. Journal of Animal Physiology & Animal Nutrition,2010,92(3):272−283.
[32] 梁敏. 蓝靛果酒酿造工艺对花色苷及功能性质的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北林业大学, 2018. LIANG M. Effect of brewing technology of blue honeysuckle wine on anthocyanins and functional properties[D]. Harbin: Northeast Forestry University, 2018.
[33] 杜国慧, 刘博伟, 尹福在, 等. 利拉鲁肽对糖尿病小鼠肝糖异生关键酶PEPCK及G6pase的表达影响及机制探讨[J]. 中国比较医学杂志,2020,30(12):98−102. [DU G H, LIU B W, YIN F Z, et al. Mechanistic analysis of liraglutide effects on the expression levels of PEPCK and G6pase in the diabetic mouse liver[J]. Chinese Journal of Comparative Modicine,2020,30(12):98−102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7856.2020.12.015 DU G H, LIU B W, YIN F Z, et al. Mechanistic analysis of liraglutide effects on the expression levels of PEPCK and G6pase in the diabetic mouse liver[J]. Chinese Journal of Comparative Modicine, 2020, 30(12): 98-102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7856.2020.12.015
[34] LOCHHEAD P A, SALT I P, WALKER K S, et al. 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide riboside mimics the effects of insulin on the expression of the 2 key gluconeogenic genes PEPCK and glucose-6-phosphatase[J]. Diabetes,2000,49(6):896−903. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.49.6.896
[35] HE L, LI Y, ZENG N, et al. Regulation of basal expression of hepatic PEPCK and G6Pase by AKT2[J]. Biochemical Journal,2020,477(5):1−19.
[36] DING L, HAN L, DUBE J, et al. WASH regulates glucose homeostasis by facilitating Glut2 receptor recycling in pancreatic β-cells[J]. Diabetes,2019,68(2):377−386. doi: 10.2337/db18-0189
[37] ILBEIGI D, NOURBAKHSH M, PASALAR P, et al. Nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase knockdown leads to lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells through the SIRT1-AMPK pathway[J]. Cell Journal, 2020, 22(Suppl 1): 125-132.
[38] KIM Y J, HOUNG S J, KIM J H, et al. Nanoemulsified green tea extract shows improved hypocholesterolemic effects in C57BL/6 mice[J]. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry,2012,23(2):186−191. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2010.11.015
[39] FESSLER, MICHAEL B. Regulation of adaptive immunity in health and disease by cholesterol metabolism[J]. Current Allergy & Asthma Reports,2015,15(8):42−48.
[40] MITRO N, GODIO C, FABIANI E D, et al. Insights in the regulation of cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase gene reveal a target for modulating bile acid synthesis[J]. Hepatology,2010,46(3):885−897.
[41] HANDSCHIN C, GNERRE. Species-specific mechanisms for cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) regulation by drugs and bile acids[J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics,2005,434(1):75−85. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2004.10.010
[42] SANDE T, SCHRIJVER E D, HEYNS W, et al. Role of the phosphatidylinositol 3’-Kinase/PTEN/Akt Kinase pathway in the overexpression of fatty acid synthase in LNCaP prostate cancer cells[J]. Cancer Research,2002,62(3):642−646.





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
