Analysis of the Physicochemical Properties and Osteocyte Proliferative Activity of the Enzymatic Hydrolysis Products of Chinese Soft-shelled Turtle
-
摘要: 本文使用碱性蛋白酶、胃蛋白酶和胰蛋白酶水解中华鳖骨和肉、壳和裙边制备中华鳖功能性肽,并对其主要构象变化、粒度等理化性质进行分析。同时通过测定各酶解物对MC3T3-E1细胞增殖情况的影响对其潜在的骨密度调节活性进行评价。结果显示,中华鳖壳和裙边干粉蛋白含量为54.18%,骨和肉干粉蛋白质含量为80.38%。酶解2 h后,碱性蛋白酶和胰蛋白酶的酶解产物分子量集中分布于1000 Da以下,胃蛋白酶酶解产物分子量分布较为均匀。酶解产物的结构以无规则卷曲为主,粒径集中分布于20和200 nm区域,说明酶解较为充分。酶解产物中赖氨酸、缬氨酸、苯丙氨酸、亮氨酸和苏氨酸等必需氨基酸的含量较高,非必需氨基酸中甘氨酸、丙氨酸和脯氨酸的含量相对较高。其中,胃蛋白酶酶解中华鳖骨和肉后必需氨基酸的总量达39.81%。细胞实验结果显示,六种酶解产物均有一定的促成骨细胞增殖活性,壳和裙边酶解物的增殖活性强于骨肉酶解物,其中胃蛋白酶酶解的壳和裙边产物活性最强,说明中华鳖酶解产物具有潜在的骨密度调节活性。本研究对于中华鳖等产品的深加工提供了可行性分析和理论参考。Abstract: Alkaline protease, pepsin and trypsin were used to hydrolyze the bones and meat, shell and skirt of Chinese soft-shelled turtle to prepare functional peptides, and their physical and chemical properties such as main conformational changes and particle size were analyzed. The potential bone mineral density-regulating activity of each enzymatic hydrolyzate was evaluated by measuring the effect on proliferation of MC3T3-E1 cells. The results showed that the protein content of Chinese soft-shelled turtle shell and skirt dry powder was 54.18%, and the protein content of bone and meat dry powder was 80.38%. After 2 h of enzymatic hydrolysis, the molecular weights of alkaline protease and trypsin hydrolyzed products were concentrated below 1000 Da, and the molecular weight distribution of pepsin hydrolyzed products was relatively uniform. The structure of the enzymatic hydrolysis products was dominated by random coil, and the particle sizes were concentrated in the 20 and 200 nm regions, indicating that the enzymatic hydrolysis was sufficient. The content of essential amino acids such as lysine, valine, phenylalanine, leucine and threonine in the enzymatic hydrolysis products was relatively high, and the content of glycine, alanine and proline in non-essential amino acids was relatively high. Among them, the total amount of essential amino acids after enzymatic hydrolysis of Chinese soft-shelled turtle bones and meat by pepsin reached 39.81%. The results of cell experiments showed that the six enzymatic hydrolysates had a certain pro-osteogenic activity, and the proliferative activities of the enzymatic hydrolysates of shell and skirt were stronger than those of bone meat, and the activity of the shell and skirt products of pepsin enzymatic hydrolysis was the best. The above data showed that the enzymatic hydrolysate of Chinese soft-shelled turtle had potential bone density regulation activity. This research provides feasibility analysis and theoretical reference for deep processing of Chinese soft-shelled turtle products.
-
中华鳖(Pelodiscus sinensis),又名水鱼、团鱼、甲鱼,属于卵生两栖类爬行动物,外形似龟,背部没有条纹,呈军绿色,是一种高蛋白、低脂肪的水产品[1]。中华鳖的营养丰富且风味独特,经研究,中华鳖可增强人体的免疫力,降低血糖血脂,且具有抗氧化活性[2-5],含多糖、维生素、牛磺酸和矿物质等,人体必需氨基酸组成合理[6]。
中华鳖全身的利用价值极高,目前,国内对中华鳖加工方面的研究主要有对中华鳖裙边胶原蛋白的制备、鉴定[7];对酶解法制备中华鳖蛋白条件的优化及分析[8]。张丹等[9]分析了中华鳖蛋白质含量、氨基酸组成,并评价中华鳖氨基酸的营养价值,马梦娇等[1]对中华鳖腿肉蛋白的结构组成及理化性质进行了分析,以上研究均证明了中华鳖是良好的蛋白质来源。Li等[2]使用胃蛋白酶利用鳖甲制备胶原蛋白作为哺乳动物胶原蛋白的新替代品,并对其理化性质进行了分析,研究发现其有较高的热稳定性。
本研究以中华鳖蛋白质为原料,充分利用肌肉、裙边、骨和鳖甲,提高了原料利用率。使用酶解法制备多肽混合物,并研究其理化性质和促成骨细胞增殖活性,为甲鱼蛋白的深入研究开发提供了一定的理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
冷冻中华鳖 江西神农氏生态农业开发有限公司提供;MC3T3-E1成骨细胞 中国科学院上海细胞库;MTT生化试剂 美国Sigma公司;二甲基亚砜 美国Gibso公司;碱性蛋白酶(酶活为2×105 U/g)、胃蛋白酶(酶活为5×105 U/g) 北京Solarbio公司;胰蛋白酶(酶活为2.5×105 U/g) Amresco公司;TEMED生化试剂 美国Bio-Rad公司。
Eon酶标仪 美国伯腾仪器有限公司;SKD-1000全自动凯式定氮仪 上海沛欧分析仪器有限公司;SCIENTZ-10ND冷冻干燥机 宁波新芝生物科技有限公司;CF16RN离心机 日本日立公司;LC-10Avp高效液相色谱 日本岛津公司;3000HSA激光粒度仪 英国马尔文仪器有限公司;J1500圆二色光谱仪 日本JASCO分光公司;F2700荧光光谱仪 日本日立公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 中华鳖的预处理
将冷冻中华鳖自然解冻。根据处理方式的选择,便于工厂加工处理,将解冻后的中华鳖分为骨和肉、壳和裙边两级。分级后的骨和肉用破壁器粉碎2 min,煮沸15 min;分级后的壳和裙边依据热压提取法[10],在电压力锅中按照115.34 ℃,70 kPa,料液比1:3处理对中华鳖的壳和裙边进行软化。处理后仍无法软化的胸骨,背甲放入60 ℃烘箱烘干4 h,粉碎,与软化的部分混合,再次使用破壁机打碎1 min,使原料分布均匀。
1.2.2 中华鳖蛋白质含量的测定
将分级处理后的中华鳖分别在冻干机中冻干成粉,采用GB 5009.5-2016中的自动凯氏定氮法[11]测定中华鳖蛋白质含量。
1.2.3 中华鳖蛋白质的酶解
对中华鳖的肌肉、裙边分别进行酶解,酶的最适条件如表1所示,料液比为1:3。按5000 U/g酶添加量解蛋白2 h,每5 min记录一次pH变化。酶解结束后将pH调至7.0,在100 ℃条件下灭酶10 min,冷却后在10000×g下离心15 min,取上清,500 Da透析袋透析48 h,冻干成粉,分装后放入干燥皿,保存备用。
表 1 酶的最适pH和温度Table 1. Optimal pH and temperature for enzymes名称 pH 最适温度(℃) 碱性蛋白酶 10.0 50 胃蛋白酶 2.0 37 胰蛋白酶 8.5 45 1.2.4 排阻色谱法测定酶解产物分子量分布
通过尺寸排阻色谱分析不同酶解条件制备的酶解产物的分子量[12]。使用纯净水稀释样品至5 mg/mL,0.22 μm水系膜过滤,色谱柱型号为TSK gel G2000SWXL,安捷伦1260高效液相色谱。流动相为45%的乙腈,0.1%三氟乙酸的水溶液,将流速设置为0.5 mL/min,70 min,等梯度洗脱,柱温设定25 ℃,进样量采用10 μL,于214 nm处进行检测。
1.2.5 圆二光谱法分析酶解产物构象
根据蛋白质具有圆二色性,使用圆二色光谱仪在远紫外区对酶解产物的构象扫描分析[13]。将多肽配制成0.25 mg/mL的溶液,CD光谱仪使用0.1 cm光程的石英池,通过改变波长λ,在190~250 nm得到样品的椭圆度。
1.2.6 内源荧光光谱分析酶解物结构变化
将多肽溶液浓度配制为2 mg/mL。将激发波长设置为290 nm,发射波长设置为250~400 nm,激发和发射的带宽均设定为5 nm。使用荧光分光光度计测定不同酶解产物样品的内置荧光光谱,用于观察活性肽内部荧光基团的微活性进而得知多肽的结构变化[14]。
1.2.7 动态光散射分析酶解产物粒度
采用粒度分布仪,利用斯托克斯-爱因斯坦方程将颗粒的扩散与粒度结合起来,从而检测出酶解产物中颗粒的粒度[15]。在酶解产物中加入10 mmol/L碳酸缓冲液(pH7.0),将样品溶液稀释至2 mg/mL,0.22 μm水系膜过滤,取1.2 mL样品进行测定。
1.2.8 酶解产物的氨基酸分析
用0.02 mol/L HCl将样品稀释至10 mg/mL,按体积比1:1加丙酮,混匀。10000×g,10 min离心后取1 mL上清,旋蒸后用0.02 mol/L HCl复溶,用于游离氨基酸测定。取10 mg样品于安培瓶中,加3 mL 6 mol/L盐酸,放入110 ℃烘箱水解22 h。取出1 mL水解后的样品,旋蒸,蒸干后用0.02 mol/L盐酸复溶,稀释20倍,用于总氨基酸测定。使用氨基酸分析仪对游离氨基酸和总氨基酸进行测定[16]。
1.2.9 MTT法测定酶解产物促成骨细胞增殖活性
MTT法测定中华鳖多肽对MC3T3-E1前成骨细胞的增殖情况[17-18]。将原代细胞传代三次备用。在添加了1%的双抗的α-MEM培养基中加入10%体积分数的胎牛血清(FBS)作为细胞培养基。首先,于96孔板中以密度为10000个/孔对细胞进行接种,培养箱环境为5% CO2,37 ℃;培养24 h后,空白对照组更换新鲜的完全培养基,实验组分别加入浓度为1、10和100 μg/mL的酶解产物(完全培养基配制),继续培养24、48和72 h。培养结束后,每孔细胞中加入10 μL四甲基偶氮唑蓝(MTT)溶液(浓度为5 mg/mL,PBS溶解),继续培养4 h。吸出培养基,避光加入150 μL二甲基亚砜(DMSO),置于摇床摇动15 min。使用酶标仪在490 nm处测吸光度值。计算每个孔中MC3T3-E1细胞的活力作为活细胞的百分比。
1.3 数据处理
所有实验数据均通过Excel 2016进行统计分析。Origin 2021进行图形绘制。凯式定氮法测量中华鳖蛋白质含量,促成骨细胞增殖实验有3组平行。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 中华鳖不同部位蛋白质含量
将中华鳖壳和裙边、骨和肉两部分分别进行匀浆后获得的提取物经冷冻干燥获得干粉。经凯式定氮法测得中华鳖壳和裙边干粉蛋白含量为54.18%,骨和肉干粉蛋白质含量为80.38%。
2.2 中华鳖不同部位蛋白质酶解过程中pH的变化规律
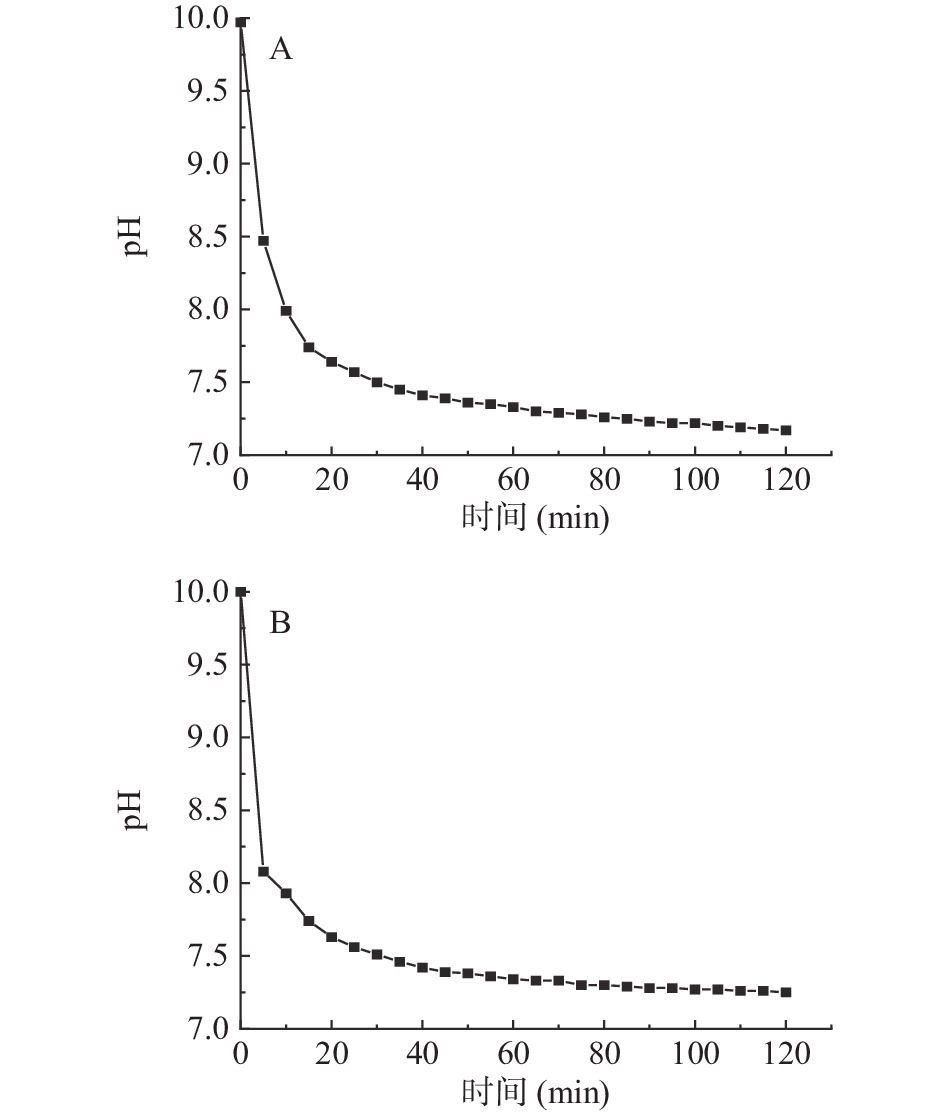
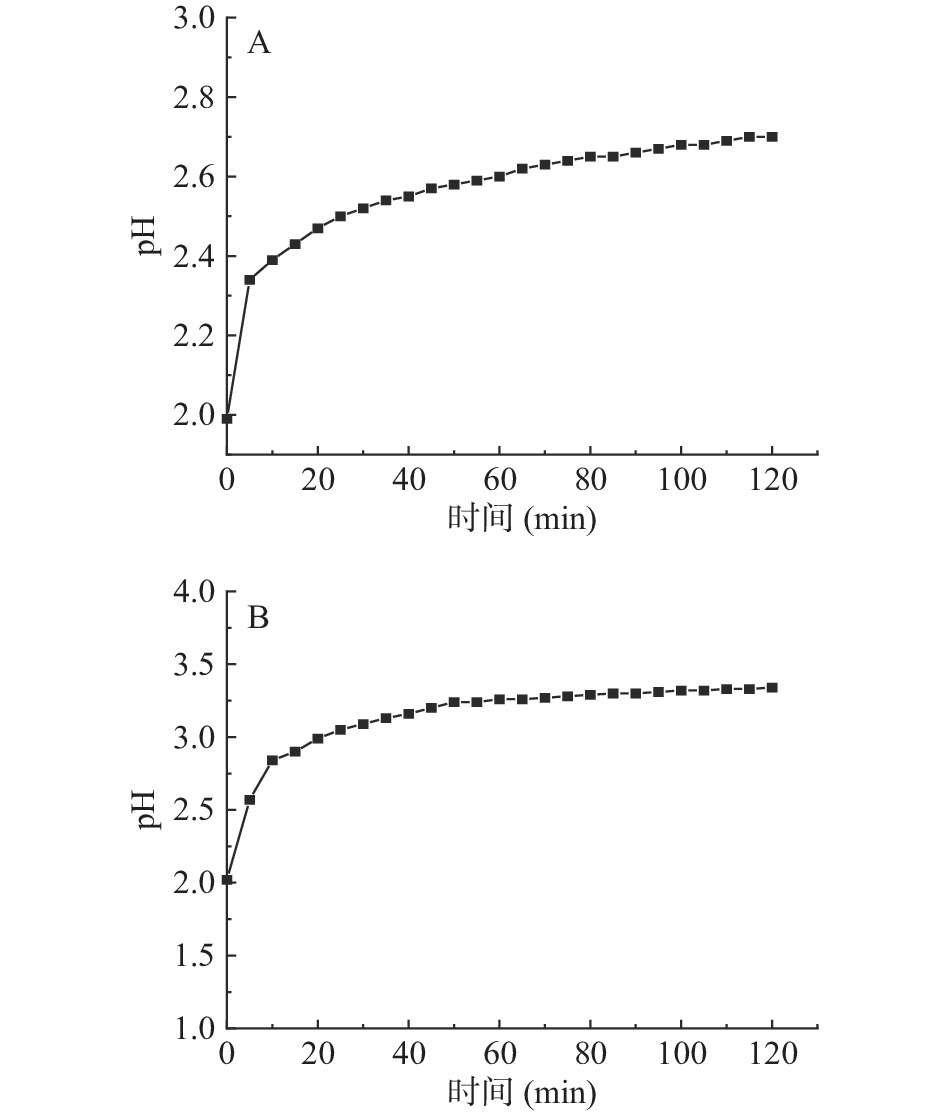
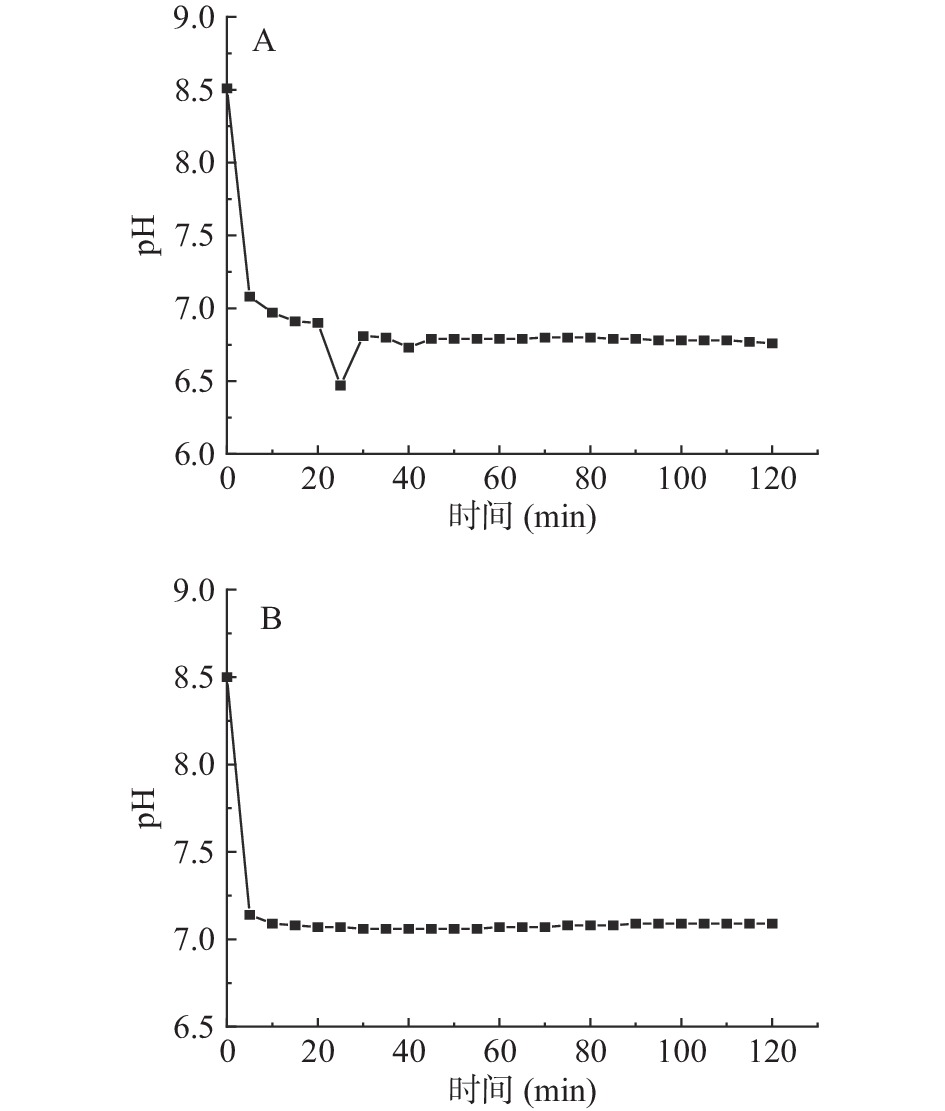
图1~图3分别显示了碱性蛋白酶、胃蛋白酶、胰蛋白酶酶解骨和肉、壳和裙边的pH变化,以及酶解程度[19]。由图1可知,酶解的前5~10 min,由于酶切位点较多,酶解速率较快,pH变化幅度较大,10 min后水解速率逐渐降低,100 min后酶解速率逐渐降为0,曲线不再变化,碱性蛋白酶酶解骨和肉、壳和裙边的pH分别稳定在7.17和7.26;胃蛋白酶酶解骨和肉、壳和裙边的pH分别稳定在2.70和3.30(图2);胰蛋白酶酶解骨和肉、壳和裙边的pH稳定在6.83和7.17(图3)。碱性蛋白酶酶解效率较好,pH变化幅度较大,胰蛋白酶在20 min后酶解速率逐渐降低;而碱性蛋白酶、胃蛋白酶在50 min后酶解速率逐渐保持不变。三种酶酶解壳和裙边时,pH均在前10 min内具有较大的变化幅度,推测壳和裙边中的部分蛋白经过热压提取法处理后,具有更高的溶解性,与酶的结合更加敏感[20],也有文献指出在酶解草鳖时,pH对酶解度有一定的影响[21]。
2.3 酶解产物分子量分布规律
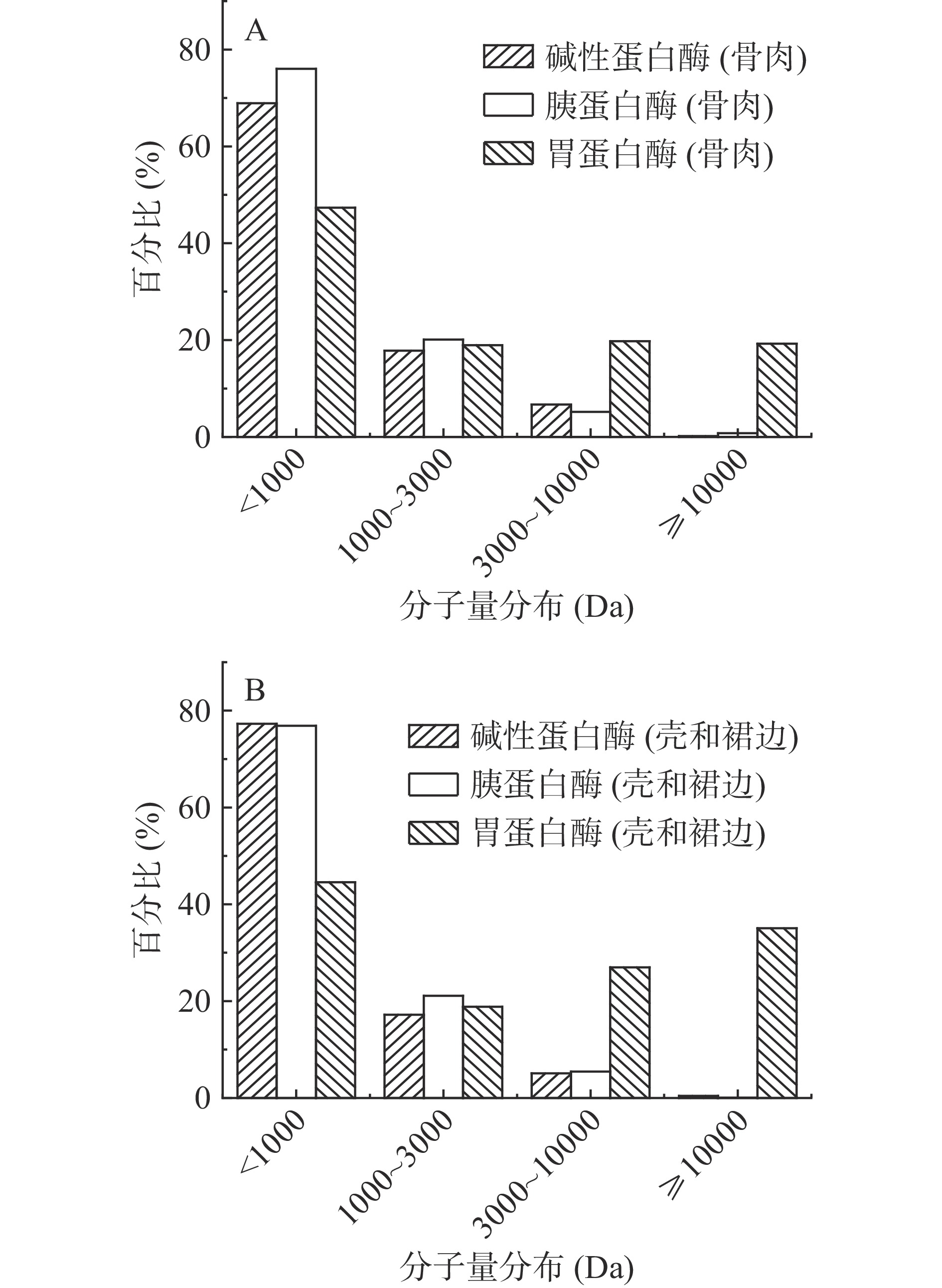
酶解中华鳖蛋白的分子量分布如图4所示。对于骨和肉、壳和裙边来说,经胰蛋白酶解后,分子量大于10000 Da的比例分别为0.77%、0.09%,小于1000 Da的比例分别为76.02%和76.88%。碱性蛋白酶酶解后,分子量大于10000 Da的比例分别为0.19%、0.43%,小于1000 Da的比例分别为68.93%和77.27%。胃蛋白酶酶解后,分子量大于10000 Da的比例分别为19.27%和35.05%,其中小于1000 Da的比例分别为47.33%和44.57%。
酶解壳和裙边得到的产物中分子量大于10000 Da和小于1000 Da的比例略大于骨和肉。碱性蛋白酶和胰蛋白酶的酶解产物分子量集中分布于1000 Da以下,胃蛋白酶酶解产物中分子量分布较为均匀。说明pH、酶的种类和温度对酶解产物的分子量存在一定影响。小于1000 Da的肽更容易被吸收利用,从这个角度出发,碱性蛋白酶和胰蛋白酶酶解产物中易被人体吸收的部分更多。
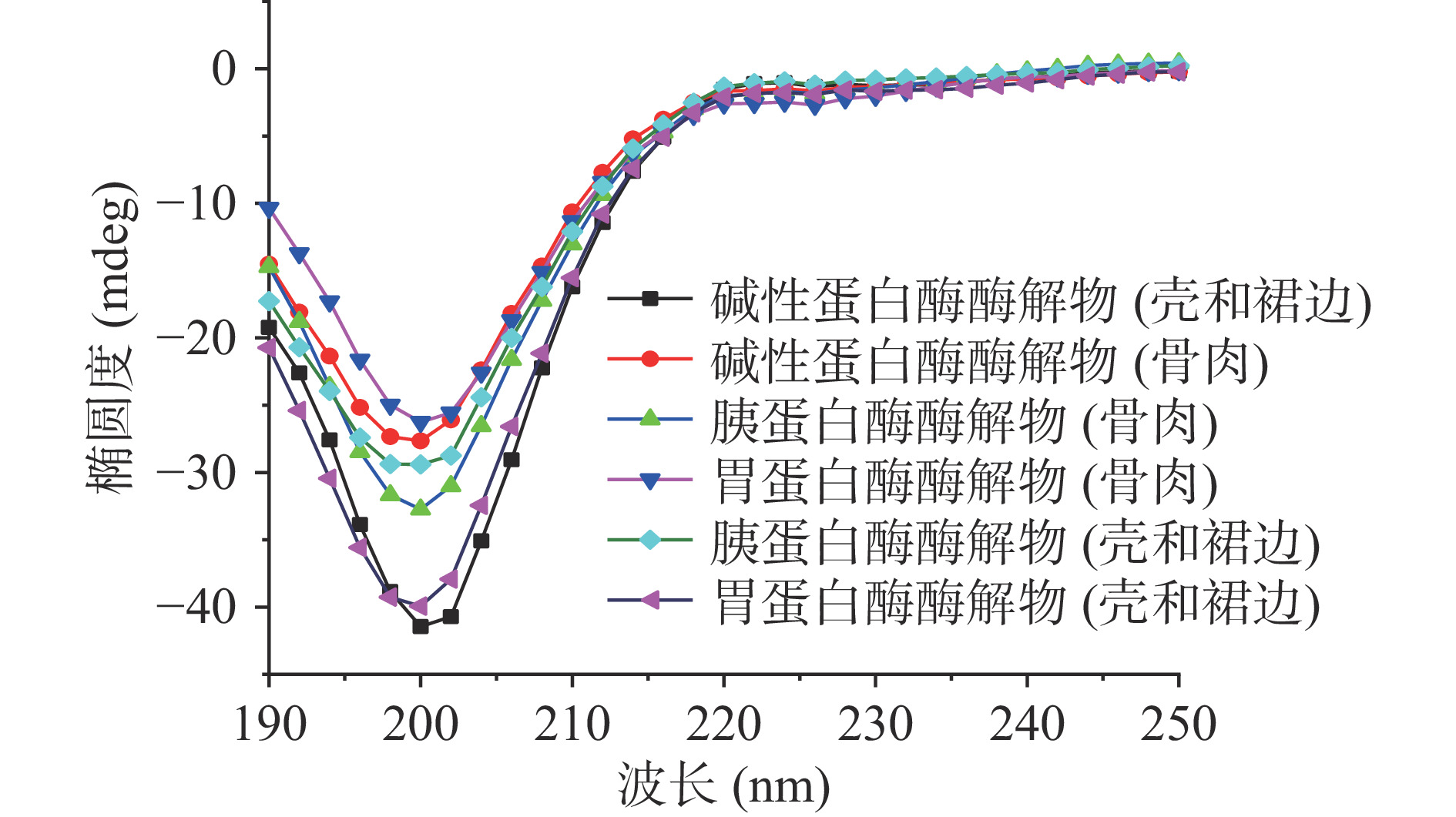
2.4 酶解产物中肽的二级结构变化规律
远紫外区圆二色光谱分析结果显示(图5),六种肽混合物在200 nm左右均有一个负峰,说明各酶解产物的二级结构均以无规则卷曲为主。通过对圆二色光谱的峰谱进行指认发现各酶解物中还存在一定的β折叠和β转角结构,且两者占比均为27%和9%左右,不同的酶解条件并未造成酶解物二级结构的显著变化。β折叠与水解产物二级结构的展开程度有关,氢键是维持β折叠结构的作用力,在多肽结构中起关键作用,研究表明,蛋白质的β折叠与其凝胶性和持水性呈正相关[22-23],该结果表明中华鳖酶解产物可能具有较好的凝胶性和持水性。
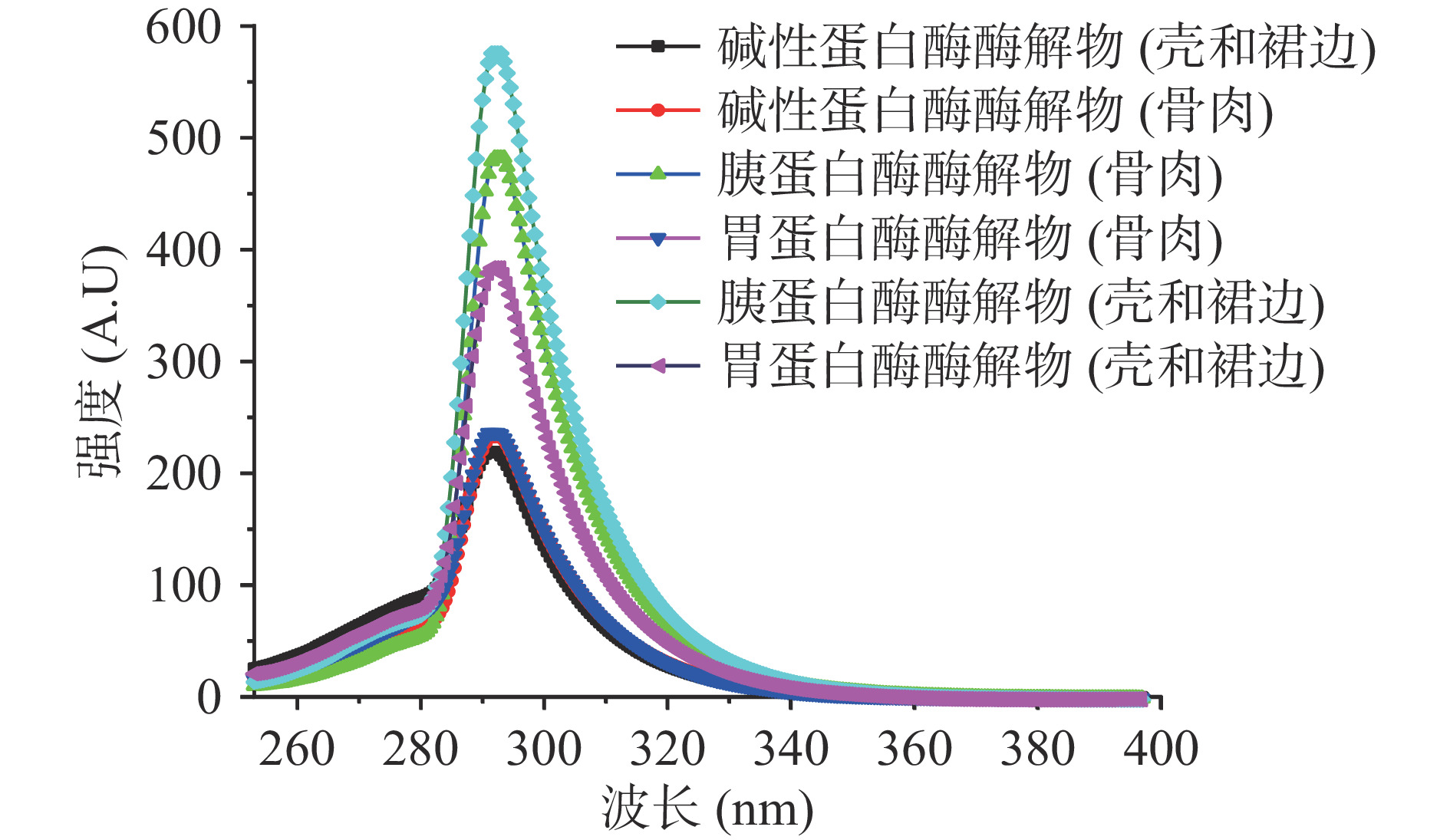
2.5 酶解产物分子表面荧光变化规律
蛋白质的内源荧光性主要由芳香族氨基酸决定,其中色氨酸残基为最主要的发色基团。酶解过程中多肽色氨酸残基的荧光强度因酶解环境的pH、温度、酶种类以及酶解部位的变化而改变[24],通过蛋白自身所含有的内源荧光性色氨酸的特征峰峰谱位置,可以表征蛋白内部结构的松散程度,进而可以分析蛋白的三级结构。
如图6所示,胰蛋白酶处理的壳和裙边制备的肽荧光强度最高,胰蛋白酶处理的骨和肉次之。然而,碱性蛋白酶处理壳和裙边制备的肽荧光强度最低。这些结果表明,对于酶解制备的肽,碱性蛋白酶效果和其他酶效果相比,多肽的展开程度较大,色氨酸暴露发生淬灭反应,导致荧光强度降低。
从图中可以看出,不同酶解条件下的酶解产物中,峰出现的位置均在293 nm附近,表示微环境中色氨酸疏水性强弱并无明显变化,酶解产物的高级结构之间并无明显差别[25]。
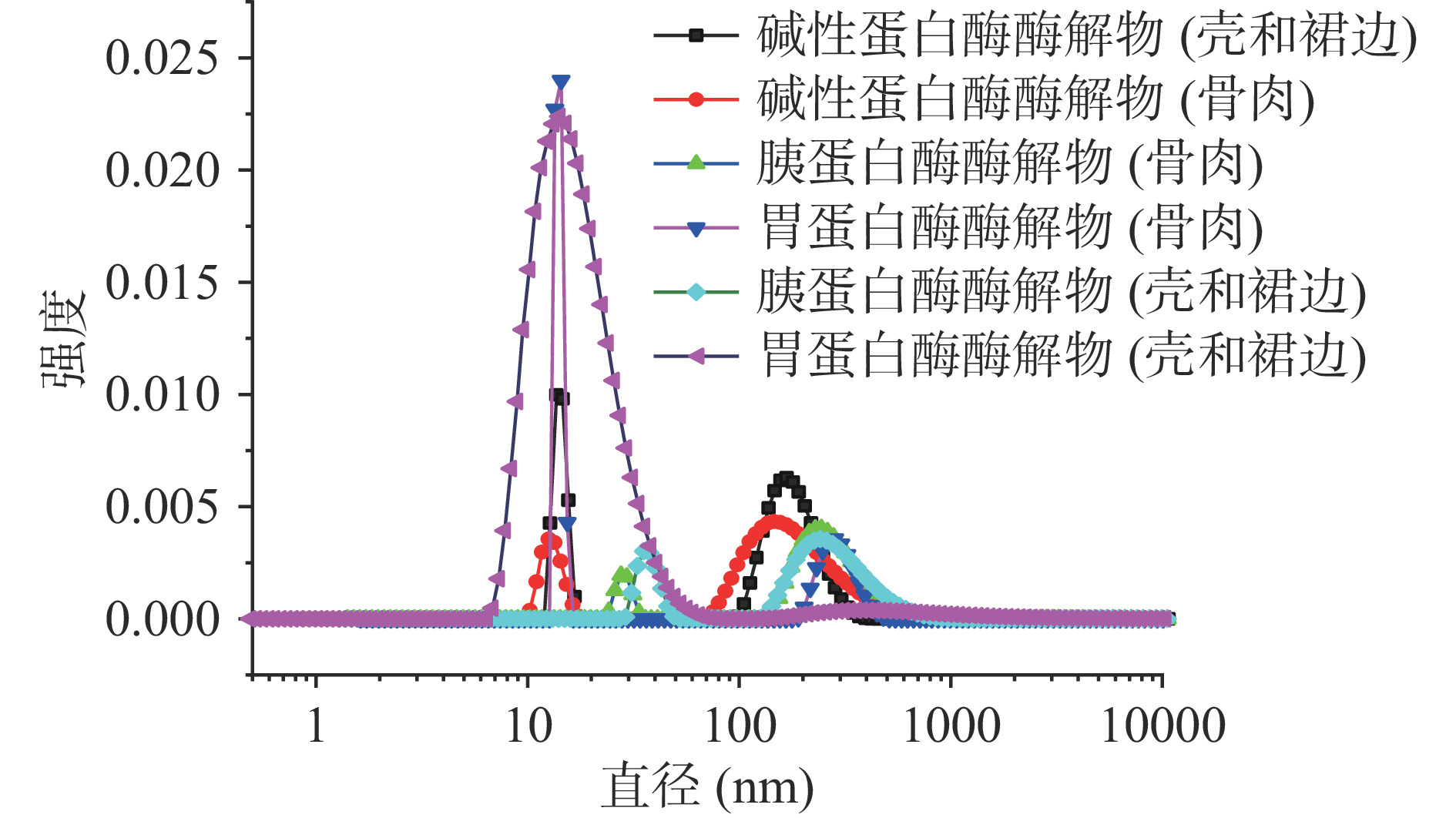
2.6 动态光散射分析结果
由图7可知,每种酶解产物内显示有两种峰,集中分布于20和200 nm区域内,原因是酶解后蛋白质的分子结构发生改变,酶解产物的分子重新凝集,形成小的粒度分布区域[26]。
不同酶解条件制备的肽有不同的粒径分布情况。胰蛋白酶处理壳和裙边、骨和肉制备的酶解产物粒径较大,碱性蛋白酶、胃蛋白酶制备的酶解产物粒径较小。谢雯雯等[27]研究发现,蛋白酶解混合物的粒径对于钙的吸收率有一定的影响,推测是由于随着粒径减小,与受体的接触面积增大,加强了钙的吸收。由此推测,碱性蛋白酶和胃蛋白酶制备的酶解产物可能相较于其他酶解物更能促进钙的吸收。
2.7 酶解产物的总氨基酸分析
由表2可知,在六种酶解产物中,胃蛋白酶酶解中华鳖骨和肉的总氨基酸含量最高,达到945.10 mg/g,其中必需氨基酸的总量占39.81%;胃蛋白酶酶解壳和裙边的总氨基酸含量最低,仅有139.52 mg/g,但必需氨基酸比例仍有29.89%。胰蛋白酶酶解骨和肉、壳和裙边的必需氨基酸占比分别为33.2%和23.82%。碱性蛋白酶酶解骨和肉、壳和裙边的必需氨基酸占比分别为21.49%和30.9%。不同酶解产物中总氨基酸发生差别的原因是酶解后将溶液pH调至7,离心取上清液,经透析,冻干两步,部分氨基酸被除去。对三种酶解产物的总氨基酸分析发现,必需氨基酸中赖氨酸、缬氨酸、苯丙氨酸、亮氨酸、苏氨酸含量较高,非必需氨基酸中甘氨酸、丙氨酸、脯氨酸的含量较高。胶原蛋白中甘氨酸、脯氨酸、丙氨酸为主要氨基酸[28],在骨中起到保护作用,因此也与骨质疏松的发生密切相关[29],有文献证明牦牛骨胶原蛋白肽可以显著促成骨细胞增殖[30],说明中华鳖酶解产物具有预防骨质疏松的潜力。
表 2 中华鳖蛋白酶解物的总氨基酸含量Table 2. Total amino acid content of enzymatic hydrolysate of Chinese soft-shelled turtle protein氨基酸种类 氨基酸含量(mg/g酶解物) 必需氨基酸 非必需氨基酸 壳和裙边 骨和肉 胰蛋白酶 胃蛋白酶 碱性蛋白酶 胰蛋白酶 胃蛋白酶 碱性蛋白酶 苏氨酸 26.49 3.68 36.18 34.21 31.76 26.10 半胱氨酸 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 85.79 0.00 赖氨酸 25.61 4.38 37.73 45.52 57.21 24.90 蛋氨酸 0.00 0.00 2.14 2.65 0.00 4.40 苯丙氨酸 34.71 9.78 42.64 40.41 54.35 28.76 异亮氨酸 9.76 1.00 15.61 15.66 13.81 9.53 亮氨酸 20.73 2.16 33.48 30.92 27.93 19.40 组氨酸 10.53 1.62 15.15 16.72 21.73 9.37 色氨酸 — — — — — — 酪氨酸 28.31 10.78 49.02 47.65 54.72 19.36 缬氨酸 30.06 6.89 32.55 30.81 28.98 30.45 丝氨酸 42.31 6.22 45.20 39.73 44.66 42.39 精氨酸 48.78 7.99 40.80 57.49 61.49 73.75 天冬氨酸 67.85 11.98 90.88 78.12 98.00 61.37 甘氨酸 142.82 23.61 103.17 90.06 130.70 156.78 谷氨酸 102.14 17.52 146.88 127.03 145.70 98.51 丙氨酸 95.22 15.78 88.94 78.63 0.00 97.61 脯氨酸 96.53 16.11 75.30 61.15 88.25 98.81 必需氨基酸总值 186.20 40.30 264.51 264.55 376.29 172.27 非必需氨基酸总值 595.66 99.22 591.15 532.22 568.81 629.22 注:“—”表示未检出,表3同。 同时酶解产物中天冬氨酸和谷氨酸含量也较高,天冬氨酸为鸟氨酸循环的重要代谢产物,可降低血液中氮和CO2的量,从而消除疲劳。谷氨酸则主要用于制造化学调味料、香料、生物化学试剂等[31],说明中华鳖酶解产物在食品领域及医疗领域都有潜在的应用前景。
2.8 酶解产物的游离氨基酸分析
由表3可知,经过2 h水解后,碱性蛋白酶水解壳和裙边制备的功能性肽中游离氨基酸如苯丙氨酸含量较高;水解骨和肉制备的活性肽中酪氨酸和苯丙氨酸含量较高。胰蛋白酶的水解产物和胃蛋白酶处理骨和肉后苯丙氨酸含量较高。胃蛋白酶水解壳和裙边后均没有发现较高的游离氨基酸。出现上述现象的原因主要是不同酶的酶切位点不同以及不同部位氨基酸的含量差异。在六种酶解产物中,均未检测出色氨酸和脯氨酸,可能原因是酶解物中这两种氨基酸含量较低,未检测到。主要风味物质中,苦味物质要多于甜味和香味物质,其中,碱性蛋白酶的酶解产物中苦味氨基酸要多于胰蛋白酶和胃蛋白酶,可能是由于酶切位点不同,从而导致碱性蛋白酶的酶解物中苦味氨基酸数量更多。
表 3 中华鳖蛋白的酶解物游离氨基酸含量Table 3. Free amino acid content of enzymatic hydrolysate of Chinese soft-shelled turtle protein氨基酸种类 氨基酸含量(mg/g酶解物) 必需氨基酸 非必需氨基酸 壳和裙边 骨和肉 胰蛋白酶 胃蛋白酶 碱性蛋白酶 胰蛋白酶 胃蛋白酶 碱性蛋白酶 苏氨酸 0.00 0.15 0.00 0.00 0.26 0.44 半胱氨酸 0.18 0.16 0.24 0.00 0.30 0.88 赖氨酸 0.90 0.07 1.63 1.35 1.69 2.03 蛋氨酸 0.42 0.00 0.00 0.59 0.00 0.82 苯丙氨酸 5.25 1.80 10.31 5.83 8.05 10.18 异亮氨酸 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 亮氨酸 0.03 0.00 0.03 0.00 0.00 0.00 组氨酸 0.00 0.02 1.85 0.00 0.01 0.92 色氨酸 — — — — — — 酪氨酸 1.22 0.11 1.85 1.14 1.69 23.49 缬氨酸 1.08 0.19 0.93 0.58 0.37 0.63 丝氨酸 0.46 0.16 0.00 0.57 0.19 0.00 精氨酸 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.46 0.00 0.08 天冬氨酸 1.01 0.17 0.58 1.26 0.41 0.74 甘氨酸 0.02 0.01 0.00 0.04 0.06 0.01 谷氨酸 1.21 0.27 0.81 1.17 0.39 0.62 丙氨酸 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.10 0.00 0.00 脯氨酸 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 总游离氨基酸 11.78 3.13 18.22 13.07 13.40 40.83 苦味氨基酸 6.78 2.02 13.12 6.99 8.43 12.55 香味氨基酸 2.21 0.44 1.39 2.42 0.79 1.36 甜味氨基酸 0.49 0.32 0.00 0.71 0.50 0.45 2.9 成骨细胞增殖活性
由图8可知,使用三种不同酶酶解甲鱼骨肉、壳和裙边得到的六种酶解产物在1~100 μg/mL下对MC3T3-E1细胞无毒副作用。酶解产物作用于细胞24 h时,中华鳖壳和裙边的酶解物、碱性蛋白酶酶解骨和肉的酶解产物在100 μg/mL下对成骨细胞均有一定的促增殖活性,胰蛋白酶和胃蛋白酶酶解壳和裙边的酶解产物在10 μg/mL下对成骨细胞有一定的促增殖活性,与空白对照组相比,有显著性差异(P<0.05)。作用时间达到48、72 h后,该促增殖活性也变得更加显著(P<0.05)。干预至48 h时,除胃蛋白酶酶解的骨肉酶解产物外,其他酶解物在100 μg/mL下均能显著促进成骨细胞增殖(P<0.05)。培养至72 h后,中华鳖不同酶酶解物均显示出显著的促成骨细胞增殖活性(P<0.05)。其中,中华鳖壳的酶解物活性均优于骨肉部分的,且胃蛋白酶酶解肽的促成骨细胞增殖活性略优于胰蛋白酶和碱性蛋白酶的酶解物。总的来说,中华鳖各酶解物均具有一定的促骨细胞增殖活性,有潜在的骨密度调节活性[32]。
3. 结论
本研究测定的中华鳖壳和裙边干粉蛋白含量为54.18%,骨和肉干粉蛋白质含量为80.38%。经胰蛋白酶,碱性蛋白酶酶解后产物分子量分布集中于1000 Da以下,更适合人体吸收,经过胃蛋白酶酶解后产物分子量分布较为均匀,中华鳖骨和肉的酶解产物中必需氨基酸总量达到39.81%,显示了中华鳖蛋白酶解物的营养特性。三种酶解产物中甘氨酸、脯氨酸、丙氨酸含量较高。同时,由壳和裙边制备的酶解产物在100 μg/mL浓度时能显著促进成骨细胞增殖(P<0.05),提示其具有潜在的骨密度调节活性。本研究从实际应用出发,为工厂精深加工中华鳖以及中华鳖增强骨密度肽的深入研发提供了一定的理论依据。
-
表 1 酶的最适pH和温度
Table 1 Optimal pH and temperature for enzymes
名称 pH 最适温度(℃) 碱性蛋白酶 10.0 50 胃蛋白酶 2.0 37 胰蛋白酶 8.5 45 表 2 中华鳖蛋白酶解物的总氨基酸含量
Table 2 Total amino acid content of enzymatic hydrolysate of Chinese soft-shelled turtle protein
氨基酸种类 氨基酸含量(mg/g酶解物) 必需氨基酸 非必需氨基酸 壳和裙边 骨和肉 胰蛋白酶 胃蛋白酶 碱性蛋白酶 胰蛋白酶 胃蛋白酶 碱性蛋白酶 苏氨酸 26.49 3.68 36.18 34.21 31.76 26.10 半胱氨酸 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 85.79 0.00 赖氨酸 25.61 4.38 37.73 45.52 57.21 24.90 蛋氨酸 0.00 0.00 2.14 2.65 0.00 4.40 苯丙氨酸 34.71 9.78 42.64 40.41 54.35 28.76 异亮氨酸 9.76 1.00 15.61 15.66 13.81 9.53 亮氨酸 20.73 2.16 33.48 30.92 27.93 19.40 组氨酸 10.53 1.62 15.15 16.72 21.73 9.37 色氨酸 — — — — — — 酪氨酸 28.31 10.78 49.02 47.65 54.72 19.36 缬氨酸 30.06 6.89 32.55 30.81 28.98 30.45 丝氨酸 42.31 6.22 45.20 39.73 44.66 42.39 精氨酸 48.78 7.99 40.80 57.49 61.49 73.75 天冬氨酸 67.85 11.98 90.88 78.12 98.00 61.37 甘氨酸 142.82 23.61 103.17 90.06 130.70 156.78 谷氨酸 102.14 17.52 146.88 127.03 145.70 98.51 丙氨酸 95.22 15.78 88.94 78.63 0.00 97.61 脯氨酸 96.53 16.11 75.30 61.15 88.25 98.81 必需氨基酸总值 186.20 40.30 264.51 264.55 376.29 172.27 非必需氨基酸总值 595.66 99.22 591.15 532.22 568.81 629.22 注:“—”表示未检出,表3同。 表 3 中华鳖蛋白的酶解物游离氨基酸含量
Table 3 Free amino acid content of enzymatic hydrolysate of Chinese soft-shelled turtle protein
氨基酸种类 氨基酸含量(mg/g酶解物) 必需氨基酸 非必需氨基酸 壳和裙边 骨和肉 胰蛋白酶 胃蛋白酶 碱性蛋白酶 胰蛋白酶 胃蛋白酶 碱性蛋白酶 苏氨酸 0.00 0.15 0.00 0.00 0.26 0.44 半胱氨酸 0.18 0.16 0.24 0.00 0.30 0.88 赖氨酸 0.90 0.07 1.63 1.35 1.69 2.03 蛋氨酸 0.42 0.00 0.00 0.59 0.00 0.82 苯丙氨酸 5.25 1.80 10.31 5.83 8.05 10.18 异亮氨酸 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 亮氨酸 0.03 0.00 0.03 0.00 0.00 0.00 组氨酸 0.00 0.02 1.85 0.00 0.01 0.92 色氨酸 — — — — — — 酪氨酸 1.22 0.11 1.85 1.14 1.69 23.49 缬氨酸 1.08 0.19 0.93 0.58 0.37 0.63 丝氨酸 0.46 0.16 0.00 0.57 0.19 0.00 精氨酸 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.46 0.00 0.08 天冬氨酸 1.01 0.17 0.58 1.26 0.41 0.74 甘氨酸 0.02 0.01 0.00 0.04 0.06 0.01 谷氨酸 1.21 0.27 0.81 1.17 0.39 0.62 丙氨酸 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.10 0.00 0.00 脯氨酸 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 总游离氨基酸 11.78 3.13 18.22 13.07 13.40 40.83 苦味氨基酸 6.78 2.02 13.12 6.99 8.43 12.55 香味氨基酸 2.21 0.44 1.39 2.42 0.79 1.36 甜味氨基酸 0.49 0.32 0.00 0.71 0.50 0.45 -
[1] 马梦娇, 荆慧娟, 符安卫, 等. 中华鳖腿肉蛋白的理化性质[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(22):110−116. [MA Mengjiao, JING Huijuan, FU Anwei, et al. Physicochemical properties of Chinese soft-shelled turtle protein[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2019,45(22):110−116. MA Mengjiao, JING Huijuan, FU Anwei, et al. Physicochemical properties of Chinese soft-shelled turtle protein[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2019, 45(22): 110-116.
[2] LI Caiyan, SONG Wei, WU Jianping, et al. Thermal stable characteristics of acid- and pepsin-soluble collagens from the carapace tissue of Chinese soft-shelled turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis)[J]. Tissue and Cell,2020,67:101424. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2020.101424
[3] HARWANTO D, LEE G H, PARK S M, et al. Oral administration of a hot water extract of the softshell turtle (Trionyx sinensis) improves exercise performance[J]. Preventive Nutrition and Food Science,2015,20(2):133−136. doi: 10.3746/pnf.2015.20.2.133
[4] 张靖彬, 申松, 罗永康, 等. 甲鱼裙边蛋白酶解物的加工特性及抗氧化性[J]. 肉类研究,2017,31(6):1−6. [ZHANG Jingshan, SHEN Song, LUO Yongkang, et al. Processing properties and antioxidant activities of soft-shelled turtle (Trionyx sinensis) calipash protein hydrolysates[J]. Meat Research,2017,31(6):1−6. ZHANG Jingsong, SHEN Song, LUO Yongkang, et al. Processing properties and antioxidant activities of soft-shelled turtle (Trionyx sinensis) calipash protein hydrolysates[J]. Meat Research, 2017, 31(6): 1-6.
[5] 张君, 陈露, 余鹏, 等. 中华鳖4个品系营养成分分析与比较[J]. 水生生物学报,2018,42(4):770−778. [ZHANG Jun, CHEN Lu, YU Peng, et al. Analysis on nutrient compositions in the muscles of four strains of Pelodiscus sinensis[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica,2018,42(4):770−778. doi: 10.7541/2018.094 ZHANG Jun, CHEN Lu, YU Peng, et al. Analysis on nutrient compositions in the muscles of four strains of Pelodiscus sinensis[J]. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica, 2018, 42(4): 770-778. doi: 10.7541/2018.094
[6] 杨公明, 徐怀德, 段旭昌, 等. 甲鱼营养成分分析研究[J]. 营养学报,2003,25(4):443−445. [YANG Gongming, XU Huaide, DUAN Xuchang, et al. Study on the nutritional components of soft-shelled turtle[J]. Acta Nutrimenta Sinica,2003,25(4):443−445. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0512-7955.2003.04.028 YANG Gongming, XU Huaide, DUAN Xuchang, et al. Study on the nutritional components of soft-shelled turtle[J]. Acta Nutrimenta Sinica, 2003, 25(4): 443-445. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0512-7955.2003.04.028
[7] 张强, 黄鑫, 符安卫, 等. 中华鳖裙边胶原蛋白的提取、鉴定及其理化性质[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(12):176−182. [ZHANG Qiang, HUANG Xin, FU Anwei, et al. Extraction and characterization of collagens in Chinese sturgeon calipash[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2019,45(12):176−182. ZHANG Qiang, HUANG Xin, FU Anwei, et al. Extraction and characterization of collagens in Chinese sturgeon calipash[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2019, 45(12): 176-182.
[8] 王楠, 王伟, 周虹, 等. 甲鱼蛋白抗氧化肽的中性蛋白酶酶解条件优化[J]. 浙江农业学报,2014,26(2):303−308. [WANG Nan, WANG Wei, ZHOU Hong, et al. Condition optimization of the neutral protease hydrolyzing turtle protein into antioxidant activity peptides[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis,2014,26(2):303−308. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2014.02.08 WANG Nan, WANG Wei, ZHOU Hong, et al. Condition optimization of the neutral protease hydrolyzing turtle protein into antioxidant activity peptides[J]. Acta Agriculturae ZheJiangensis, 2014, 26(2): 303-308. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2014.02.08
[9] 张丹, 王锡昌. 中华鳖肉蛋白质营养特征分析及评价[J]. 食品工业科技,2014,35(15):356−359. [ZHANG Dan, WANG Xichang. Characteristics of protein from Chinese soft-shelled turtle meat (Trionyx sinensis)[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2014,35(15):356−359. ZHANG Dan, WANG Xichang. Characteristics of protein from Chinese soft-shelled turtle meat (Trionyx sinensis)[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2014, 35(15): 356-359.
[10] YUE Jianying, WANG Jinzhi, ZHANG Chunhui, et al. Effects of hot-pressure extraction time on composition and gelatin properties of chicken bone extracts[J]. Journal of Food Science,2017,82(5):1066−1075. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.13687
[11] 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.5-2016 食品中蛋白质的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017: 1-3. China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.5-2016 Determination of protein in foods[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2017: 1-3.
[12] ASPMO S I, HORN S J, EIJSINK V G H. Enzymatic hydrolysis of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.) viscera[J]. Process Biochemistry,2005,40(5):1957−1966. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2004.07.011
[13] MICSONAI A, BULYÁKI É, KARDOS J. From secondary structure analysis to protein fold prediction by circular dichroism spectroscopy[J]. Methods Mol Biol,2021,2199:175−189.
[14] MORO A, BÁEZ G D, BUSTI P A, et al. Emulsifying and foaming properties of β-lactoglobulin modified by heat treatment[J]. Food Research International,2013,51(1):1−7. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2012.11.011
[15] HENESTROSA R, PIZONES V M, PATINO M J, et al. A dynamic light scattering study on the complex assembly of glycinin soy globulin in aqueous solutions[J]. Journal of the American OiChemists' Society,2012,89(7):1183−1191.
[16] 国家食品药品监督管理总局. GB 5009.124-2016食品安全国家标准 食品中氨基酸的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017: 1−4. China Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.124-2016 National standard of the people’s republic of China, Determination of amino acids in foods[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2017: 1−4.
[17] BONCLER M, RÓŻALSKI M, KRAJEWSKA U, et al. Comparison of prestoblue and MTT assays of cellular viability in the assessment of anti-proliferative effects of plant extracts on human endothelial cells[J]. Journal of Pharmacological and Toxicological Methods,2014,69(1):9−16. doi: 10.1016/j.vascn.2013.09.003
[18] LI Yigen, HUANG Wenjin, HUANG Shenyuan, et al. Screening of anti-cancer agent using zebrafish: Comparison with the MTT assay[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2012,422(1):85−90. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.04.110
[19] 李琦, 贡佳欣, 唐善虎, 等. 无花果蛋白酶对牦牛肉糜理化和凝胶特性的影响[J]. 食品科技,2020,45(1):161−166. [LI Qi, GONG Jiaxin, TANG Shanhu, et al. Effect of ficin on physico-chemical and gelation properties of yak meat patties[J]. Food Science and Technology,2020,45(1):161−166. LI Qi, GONG Jiaxin, TANG Shanhu, et al. Effect of ficin on physico-chemical and gelation properties of yak meat patties[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2020, 45(1): 161-166.
[20] HICKMAN D, SIMS T J, MILES C A, et al. Lsinglass/collagen: Denaturation and functionality[J]. Journal of Biotechnology,2000,79(3):245−257. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1656(00)00241-8
[21] ISLAM M S, WANG Hongxin, ADMASSU H, et al. Degree of hydrolysis, functional and antioxidant properties of protein hydrolysates from grass turtle (Chinemys reevesii) as influenced by enzymatic hydrolysis conditions[J]. Food Sci Nutr,2021,9(8):4031−4047. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.1903
[22] 曹莹莹, 张亮, 王鹏, 等. 超高压结合热处理对肌球蛋白凝胶特性及蛋白二级结构的影响[J]. 肉类研究,2013,27(1):1−7. [CAO Yingying, ZHANG Liang, WANG Peng, et al. Combined effect of ultra high pressure and heating on gel properties and secondary structure of myosin[J]. Meat Research,2013,27(1):1−7. CAO Yingying, ZHANG Liang, WANG Peng, et al. Combined effect of ultra high pressure and heating on gel properties and secondary structure of myosin[J]. Meat Research, 2013, 27(1): 1-7.
[23] CHOI S M, MA C Y. Structural characterization of globulin from common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) using circular dichroism and Raman spectroscopy[J]. Food Chemistry,2007,102(1):150−160. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.05.011
[24] HELLMANN N, SCHNEIDER D. Hands on: Using tryptophan fluorescence spectroscopy to study protein structure[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology,2019,1958:379−401.
[25] 李萌, 王娟, 魏子凯, 等. 圆二色光谱、红外光谱法解析羊乳和牛乳β-酪蛋白结构及性质差异[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2020,40(3):770−776. [LI Meng, WANG Juan, WEI Zikai, et al. Analyzing structure and properties of goat milk β-casein and bovine milk β-casein by circular dichroism and fourier transformation infrared spectroscopy[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2020,40(3):770−776. LI Meng, WANG Juan, WEI Zikai, et al. Analyzing structure and properties of goat milk β-casein and bovine milk β-casein by circular dichroism and fourier transformation infrared spectroscopy[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2020, 40(3): 770-776.
[26] LEU M, MARCINIAK A, CHAMBERLAND J, et al. Effect of skim milk treated with high hydrostatic pressure on permeate flux and fouling during ultrafiltration[J]. J Dairy Sci,2017,100(9):7071−7082. doi: 10.3168/jds.2017-12774
[27] 谢雯雯, 尹涛, 张晋, 等. 鱼骨粉粒径对鱼骨粉-鱼蛋白酶解物混合物中钙生物利用率的影响[J]. 食品科学,2014,35(7):211−216. [XIE Wenwen, YIN Tao, ZHANG Jin, et al. Effects of fish bone powder particle size on calcium bioavailability of fish bone powder-fish protein hydrolysate mixture[J]. Food Science,2014,35(7):211−216. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201407042 XIE Wenwen, YIN Tao, ZHANG Jin, et al. Effects of fish bone powder particle size on calcium bioavailability of fish bone powder-fish protein hydrolysate mixture[J]. Food Science, 2014, 35(7): 211-216. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201407042
[28] HONG Hui, FAN Hongbing, CHALAMAIAH M, et al. Preparation of low-molecular-weight, collagen hydrolysates (peptides): Current progress, challenges, and future perspectives[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,301:125222. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125222
[29] SHUSTER S. Osteoporosis, like skin ageing, is caused by collagen loss which is reversible[J]. Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine,2020,113(4):158−160. doi: 10.1177/0141076820910315
[30] YE Mengliang, ZHANG Chunhui, ZHU Lingyu, et al. Yak (Bos grunniens) bones collagen-derived peptides stimulate osteoblastic proliferation and differentiation via the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2020,100(6):2600−2609. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10286
[31] FAN Weiwei, TAN Xiaoyi, TU Maolin, et al. Preparation of the rainbow trout bone peptides directed by nutritional properties and flavor analyses[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2018,6(4):925−933.
[32] 刘猛, 樊凤娇, 石璞洁, 等. 不同浓度牛乳铁蛋白对成骨细胞与破骨细胞共培养的影响[J]. 食品研究与开发,2017,38(24):1−6. [LIU Meng, FAN Fengjiao, SHI Pujie, et al. Effects of different concentrations of bovine lactoferrin on osteoblast/osteoclast co-cultures[J]. Food Research and Development,2017,38(24):1−6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2017.24.001 LIU Meng, FAN Fengjiao, SHI Pujie, et al. Effects of different concentrations of bovine lactoferrin on osteoblast/osteoclast co-cultures[J]. Food Research and Development, 2017, 38(24): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2017.24.001





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



