Composition Analysis of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Portulaca oleracea and Its Effect on Lipid Accumulation in HepG2 Cells
-
摘要: 目的:掌握马齿苋多不饱和脂肪酸(polyunsaturated fatty acids,PUFAs)各成分相对含量并探究马齿苋纯化油对HepG2细胞脂质堆积的影响程度。方法:采用气相色谱-质谱联用手段对马齿苋全草油以及纯化油的脂肪酸成分进行分析。利用MTT法测定不同马齿苋纯化油浓度对细胞存活率的影响并选定适宜浓度范围进行后续试验。通过油红O染色法判断油酸诱导建造的脂质堆积模型是否造模成功,并采用试剂盒测定方法明确低、中、高剂量组(即60、80、100 μg/mL)纯化油浓度对高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(high density lipoprotein-cholesterol,HDL-C)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(low density lipoprotein-cholesterol,LDL-C)、总胆固醇(total cholesterol,TC)、甘油三酯(triglyceride,TG)水平的影响。结果:马齿苋全草中的PUFAs组成有三种:亚油酸、α-亚麻酸和γ-亚麻酸。马齿苋全草油中PUFAs相对含量为27.6104%,富集纯化后纯化油相对含量高达73.9015%。MTT法选定的纯化油浓度范围为60~100 μg/mL,且马齿苋纯化油高剂量组(100 μg/mL)与模型组相比,HDL-C浓度极显著升高,LDL-C、TC以及TG浓度均极显著降低(P<0.01)。结论:马齿苋纯化油中PUFAs相对含量较高基本达到纯化目的,马齿苋PUFAs对脂肪肝有较好的缓解效果,表现出较强的体外降脂能力。Abstract: Objective: To investigate the relative content of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in Portulaca oleracea and the effect of Portulaca oleracea purified oil on lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells. Methods: The fatty acid composition of whole herb oil and purified oil were analyzed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. MTT method was used to determine the effect of different concentrations of Portulaca oleracea purified oil on cell viability and the suitable concentration range was selected for subsequent experiments. Oil red O staining was used to determine whether the oleic acid-induced lipid accumulation model was successfully established. The kit method was used to determine the effects of purified oil concentration on high density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C), low density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C), total cholesterol (TC) and triglyceride (TG) levels in low, medium and high dose groups (60、80、100 μg/mL). Results: There were three kinds of PUFAs in Portulaca oleracea include linoleic acid, α-linolenic acid and γ-linolenic acid. The relative content of PUFAs in the whole herb oil of Portulaca oleracea was 27.6104%, and the relative content of purified oil after enrichment and purification was as high as 73.9015%. The concentration range of purified oil selected by MTT method was 60~100 μg/mL. Compared with the model group, the concentration of HDL-C in the high-dose group (100 μg/mL) of Portulaca oleracea purified oil was significantly increased, and the concentrations of LDL-C, TC and TG were significantly decreased (P<0.01). Conclusion: The relative content of PUFAs in purified oil of Portulaca oleracea was relatively high, which basically achieved the purpose of purification. PUFAs of Portulaca oleracea had good relief effect on fatty liver, showing strong lipid-lowering ability in vitro.
-
Keywords:
- homology of medicine and food /
- Portulaca oleracea /
- PUFAs /
- HepG2 cells /
- lipid accumulation
-
非过量饮酒以及其他损害肝脏因素造成肝细胞脂肪沉积变性等特征的综合病症被称之为非酒精性脂肪肝(nonalcoholic fatty liver disease,NAFLD)[1]。全球肥胖的流行显著增加了NAFLD的患病率,使NAFLD成为西方国家最常见的慢性肝病病因,据统计肥胖成年人病发率已达到50.7%[2-3],长此以往NAFLD将会与糖尿病、高胰岛素血症、高血压等病症结合逐渐演变为脂肪性肝炎,从而增加肝硬化、门静脉高压症以及肝癌等疾病高发风险[4-6]。近年来国内外对NAFLD的治疗方式逐渐从对药物的全部依赖转变为调整饮食习惯[7-10],有利于功能食品以及药食同源中药材的长远发展。
脂肪酸(fatty acid,FA)是具有长的碳氢链和1个羧基末端的有机化合物的总称。自然界中约有70多种不同种类的脂肪酸,其碳链长度范围为C12~C18。按照脂肪酸碳链结构中双键数的多少可将其划分为饱和脂肪酸(saturated fatty acid,SFA)、单不饱和脂肪酸(monounsaturated fatty acid,MUFA)和多不饱和脂肪酸PUFAs。近年来研究发现,PUFAs在抗炎、抗氧化、抗癌、调节血脂、增强免疫、改善记忆力以及促进生长发育等方面具有显著的效果[11-14]。石计朋[15]通过实验研究推测ω-3系列PUFAs可以通过激活PI3K/AKT/β-catenin信号轴间接促进神经细胞的增殖和迁移、抑制神经细胞的凋亡,从而发挥对受损脑组织和神经细胞的治疗作用。PUFAs同时具有抗炎和炎症消退作用,陈英杰等[16-17]通过酶联免疫吸附测定法检测血清中肿瘤坏死因子(TNF)-α、白细胞介素(IL)-1、IL-6等指标判断PUFAs是否对重型颅脑损伤患者炎症反应以及神经细胞有影响,结果表明ω-3系列PUFAs可以减轻伤后发生炎症反应,减少神经胶质和神经元细胞损害,从而起到抗炎和神经保护作用。Ayumi等[18]研究认为PUFAs具有抗癌、抗肿瘤作用是由于肿瘤相关成纤维细胞(CAFs)中的基质金属蛋白酶(MMP)-9在体内外均会受到ω-3系列PUFAs的抑制造成的。胡慧芸[19]认为PUFAs具有显著的降血脂功效,并将实验室制备的PUFAs软胶囊通过动物试验研究进行验证,证实了PUFAs可以显著降低混合型高脂血症大鼠的血脂水平、明显减轻混合型高脂血症大鼠的炎症反应,其作用机制可能分别与脂质代谢相关基因HMGR、PPARα、SREBP-1c的表达有关、与调节验证信号通路AMPK/SIRT1/NF-κB及VCAM-1的表达有关。而马齿苋作为药食同源植物资源之一,性味酸寒,具有清热解毒,凉血止血等功效,现代药理学作用研究也表明马齿苋在抗炎、抗氧化、抗肿瘤等方面有显著效果[20],由于近年来国内外学者对药食同源马齿苋中药材中的脂肪酸成分研究较少以及国内对PUFAs作用逐步重视,因此本试验基于国内外各学者以及本实验室人员前期试验基础对马齿苋脂肪酸成分进行深入创新研究。
本试验通过对比马齿苋全草油和纯化油脂肪酸成分相对含量,明确纯化油的纯化程度,并将纯化油作用于油酸诱导成功的脂质堆积肝癌细胞模型,在检测血脂指标HDL-C、LDL-C、TC、TG水平变化后明确马齿苋纯化油对脂质沉积的影响,进而初探马齿苋纯化油中PUFAs的降脂能力。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
新鲜马齿苋全草 山东滨州种植基地;人肝癌细胞HepG2 上海泛柯实业有限公司;MTT、HDL-C、LDL-C、TC、TG试剂盒 南京建成生物科技有限公司;石油醚、尿素、无水乙醇、异丙醇、盐酸、无水硫酸钠、正己烷、浓硫酸(以上试剂均为分析纯)、甲醇(色谱纯) 天津市科密欧化学试剂有限公司;胰酶、优级胎牛血清、DMED高糖培养基、牛血清白蛋白(不含脂肪酸)、多聚甲醛固定液 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;苏丹红、油酸(分析纯) 上海麦克林生化科技有限公司。
YM-828H多功能加热破壁料理机 中山市优盟电器有限公司;SB25-120超声波清洗机 宁波新芝生物科技股份有限公司;SHZ-D(Ⅲ)循环水式真空泵 巩义市予华仪器有限责任公司;SY-2000旋转蒸发仪 上海亚荣生化仪器厂;GZX-9140MBE电热鼓风干燥箱 上海博讯实业有限公司医疗设备厂;AR223CN电子天平 奥豪斯仪器有限公司;Agilent Technologies 7890B/5977B气相色谱-质谱联用仪 郑州泽铭科技有限公司;BDS400倒置生物显微镜 重庆奥特光学仪器有限责任公司;SPECTRA MAX190酶标仪 北京生原诚业科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 马齿苋全草油的制备
将山东滨州种植基地的新鲜马齿苋全草洗净、破壁后适当沥干。准确称取10.00 g左右沥干物于平底烧瓶中,按照料液比1:22(m:V)加入60~90 ℃石油醚220 mL,并于超声温度70 ℃、超声时间61 min、超声功率500 W条件下进行提取,提取液浓缩(比例为49:1,V:V)干燥恒重后即得马齿苋全草油样品[21]。
1.2.2 马齿苋纯化油的制备
准确称取12.00 g尿素于60 ℃水浴条件下溶于120 mL 95%乙醇溶液中,即得样液A。将样液A趁热迅速置于1.00 g马齿苋全草油样品中使样品溶解,在60 ℃水浴条件下持续搅拌10 min后冷却至室温,置于−20 ℃条件下进行下一步结晶,6 h后取出迅速抽滤,将滤液旋转蒸发后恒重,即得浸膏物。将浸膏物中加入5 mL蒸馏水,用HCl调节pH至5~6后加10 mL石油醚进行萃取,用蒸馏水洗涤石油醚层直至尿素试纸检测无尿素即可停止,无水硫酸钠干燥4 h后,即可得到马齿苋纯化油[21]。
1.2.3 马齿苋脂肪酸纯化前后组成分析
1.2.3.1 马齿苋全草油、纯化油样品的甲酯化
称量马齿苋全草油、纯化油样品各100 mg,向其中各依次加入3 mL正己烷和2 mL 5% H2SO4-甲醇溶液,摇匀3 min后置于60 ℃条件下水浴30 min,再次各加入3 mL蒸馏水,摇匀2 min,等分层清晰后取上清液,经0.45 μm有机滤膜过滤后备用。
1.2.3.2 气相色谱-质谱联用仪检测条件
GC条件:PEG-20M弹性石英毛细管柱,30 m×0.25 m×0.25 μm,载气为N2,载气流速为0.8 mL·min−1,程序升温从180 ℃开始(保持2 min),以3 ℃·min−1升温到230 ℃,保持10 min,进样口温度250 ℃,出样口温度200 ℃,检测电压350 V,不分流进样。
MS条件:EI离子源,电子能量70 eV,发射电流200 μA,扫描范围20~550 amu,全离子扫描。
1.2.4 马齿苋纯化油对HepG2细胞增殖和脂质堆积的影响
1.2.4.1 不同马齿苋纯化油浓度对HepG2细胞存活率的影响
将培养的HepG2细胞用胰酶消化后接种于96孔板中,使每孔细胞数量大致为1×104个后,置于CO2培养箱贴壁培养24 h,各个孔分别加入100 μL用5% BSA配制的浓度分别为0、10、20、40、60、80、100、200、400、800、1600 μg/mL的马齿苋纯化油,最后用完全培养基补足体积,使得每孔总体积为200 μL,各给药浓度设置5个重复。置于CO2培养箱中作用24 h后,参照MTT试剂盒用法测定不同马齿苋纯化油浓度所对应的细胞存活率。
存活率(%)=实验组OD值空白组OD值×100 1.2.4.2 油红O染色法观察油酸诱导的HepG2细胞内脂滴形成情况
将正常培养的HepG2细胞用胰酶消化后接种于6孔板中,加入培养基正常培养24 h后弃去培养液并用PBS清洗。将6孔板分为两组:0.5%不含脂肪酸的牛血清白蛋白(fatty acid-free bovine serum albumin,BSA)组和0.5 mmol/L油酸(使用0.5% BSA配制而成)组,各设置3个复孔。各孔板中加入对应组别溶液3 mL,放入培养箱培养24 h。取出6孔板弃去培养液,用PBS清洗2遍后每孔加入2 mL 4%多聚甲醛细胞固定液固定30 min。固定结束后弃去固定液,用PBS清洗2遍,静置30 s,再向每孔加入2 mL现配的60%异丙醇滴洗20~30 s,弃去异丙醇后静置1 min。之后每孔加入油红O染色液(油红原液:蒸馏水=3:2,V:V)2 mL,密闭染色20 min后将染色液弃去,加入2 mL 60%异丙醇分化10 s,静置1 min,再加入PBS清洗2遍,各孔再加入3 mL PBS即可置于倒置显微镜下观察。
1.2.4.3 造模后不同组别细胞内血脂指标水平变化情况
将正常培养的HepG2细胞用胰酶消化后接种于96孔板中,置于CO2培养箱贴壁培养24 h,并将接种细胞的孔分为5组(每组设置5个重复):对照组、模型组、低剂量组、中剂量组和高剂量组。造模:对照组中加入0.5% BSA溶液200 μL,其余组别各加入200 μL 0.5 mmol/L的油酸进行诱导造模,放入培养箱培养24 h。给药:取出细胞后弃去溶液并用PBS清洗,在对照组和模型组中各加入0.5% BSA溶液200 μL,低、中、高剂量组分别加入60、80、100 μg/mL的马齿苋纯化油各200 μL,置于CO2培养箱中作用24 h后取出,并参照HDL-C、LDL-C、TC、TG各试剂盒说明书进行浓度测定。
1.3 数据处理
各组数据均采用Graphpad Prism V6.01软件进行分析并通过t检验的方法进行统计学分析,P<0.05表示差异具有统计学意义。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 马齿苋脂肪酸纯化前后成分对比
对马齿苋脂肪酸成分进行分析有利于掌握每种成分的相对含量,且可以明确富集纯化的程度,从而得到马齿苋脂肪酸富集前后PUFAs的纯度变化。由表1脂肪酸成分分析表可以得知,马齿苋全草油中含有的PUFAs相对含量为27.6104%,PUFAs种类主要为亚油酸和α-亚麻酸。除PUFAs之外还有SFA:月桂酸、肉豆蔻酸、十五碳酸、棕榈酸、花生酸、十七碳酸、硬脂酸、二十二碳酸、二十三碳酸和二十四碳酸共10种,相对含量总和为67.1861%;MUFA:棕榈油酸和油酸共两种,相对含量总和为5.2035%。而马齿苋纯化油中的PUFAs相对含量高达73.9015%,其中的PUFAs种类除亚油酸和α-亚麻酸外还增添了γ-亚麻酸,在全草油中未检测出此物质的原因可能是全草油中γ-亚麻酸含量低于仪器检测下限,而纯化后马齿苋纯化油中的γ-亚麻酸浓度明显升高,高于检测下限使得此物质被检出。而且马齿苋纯化油中SFA相对含量总和为18.7997%,MUFA相对含量总和为7.2988%,与马齿苋全草油相比,除MUFA中的油酸外,马齿苋纯化油中各SFA以及MUFA相对含量均有不同程度降低,且马齿苋纯化油中已经无二十三碳酸出现。因此,由表1可以得出结论:马齿苋纯化油PUFAs纯度(73.9015%)高于全草油PUFAs纯度(27.6104%),且高出46.2911%,纯化后纯度基本达到实验预期设想,因此可以纯化油进行后续PUFAs的体外降脂作用研究。
表 1 马齿苋脂肪酸成分含量分析Table 1. Analysis of fatty acid composition in Portulaca oleracea脂肪酸类型 类别 脂肪酸 马齿苋全草油
(相对含量,%)马齿苋纯化油
(相对含量,%)SFA C12:0 月桂酸 0.3306 0.0666 SFA C14:0 肉豆蔻酸 0.8413 0.1643 SFA C15:0 十五碳酸 0.1679 0.0398 SFA C16:0 棕榈酸 18.9987 15.2286 SFA C20:0 花生酸 3.1683 0.2870 SFA C17:0 十七碳酸 0.3587 0.0986 SFA C18:0 硬脂酸 4.5147 1.9866 SFA C22:0 二十二碳酸 11.3741 0.2749 SFA C23:0 二十三碳酸 0.5415 − SFA C24:0 二十四碳酸 26.8902 0.5446 MUFA C16:1 棕榈油酸 0.2338 0.1686 MUFA C18:1n9c 油酸 4.9697 7.1302 PUFAs C18:2n6c 亚油酸 14.1019 37.5822 PUFAs C18:3n3 α-亚麻酸 13.5085 36.3192 PUFAs C18:3n6 γ-亚麻酸 − 0.1089 总PUFAs 27.6104 73.9015 2.2 不同马齿苋纯化油浓度对细胞存活率的影响
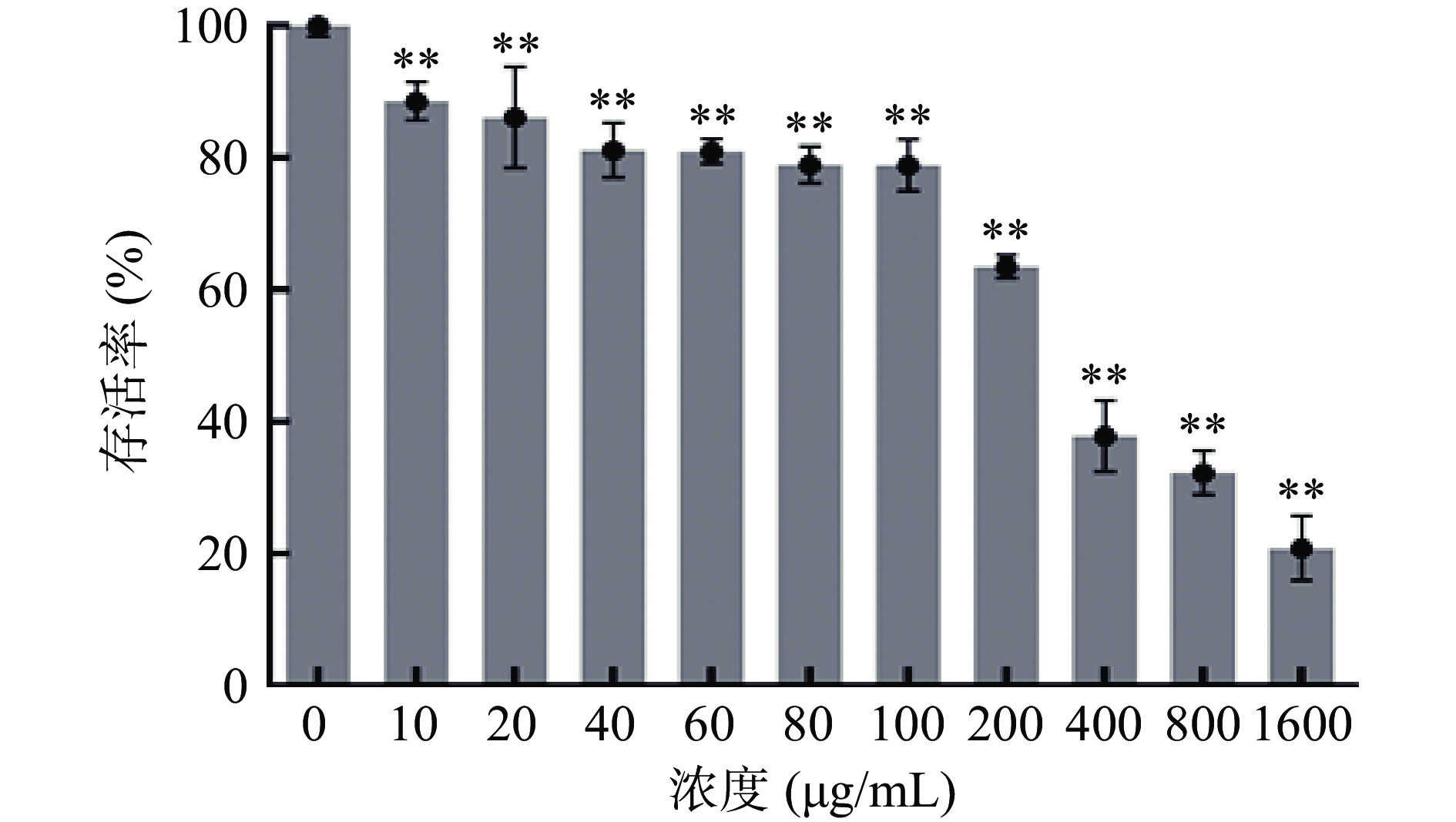
不同给药浓度对人肝癌HepG2细胞有一定的影响,在一定程度上可能对细胞造成毒性作用,因此本试验将采用MTT法考察不同马齿苋纯化油浓度对细胞存活率的影响,从而确定适宜细胞生长的纯化油浓度,避免在后续试验过程中浓度太高对细胞造成毒性作用。如图1所示,不同浓度组别与对照组相比细胞存活率均极显著降低,当马齿苋纯化油浓度为0~10 μg/mL时,细胞存活率由100%±1.61%缓慢下降为88.57%±2.88%,浓度在20~100 μg/mL内时,存活率由86.11%±7.65%缓慢下降为78.89%±3.93%,而当纯化油浓度处于200~1600 μg/mL时,细胞存活率急剧下降,由63.50%±1.72%下降至最低点20.90%±4.87%。结果表明,不同浓度马齿苋纯化油对细胞存活率影响不同,10~60 μg/mL纯化油浓度范围内虽然细胞存活率较高,但是此范围内细胞存活率波动幅度不如60~100 μg/mL浓度范围内波动幅度稳定,为排除其他因素干扰试验最终结果且综合考虑细胞存活率在80%左右以及细胞存活率稳定性较好等情况,本试验选用纯化油浓度在60~100 μg/mL左右范围进行后续试验。
2.3 油红O染色法观察油酸诱导的HepG2细胞内脂滴形成结果
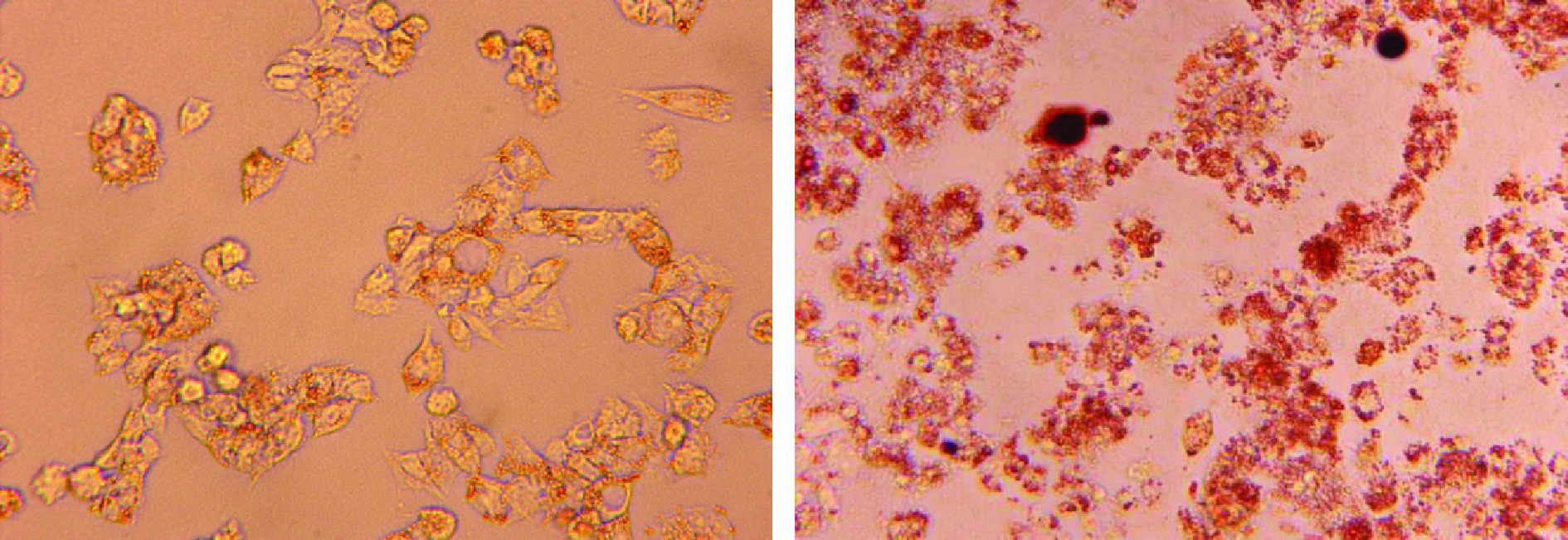
油红O为脂溶性染料,在脂肪中溶解性较强,可特异性与细胞以及动物组织内TG等中性脂肪着色,因此本试验采用油红O染色法来判断细胞脂质堆积模型的建立情况。本试验参照张蕾等[22]的方法采用0.5 mmol/L油酸诱导肝癌细胞脂肪变性模型。由图2可知,经过油红O染色后对照组的HepG2细胞形态正常,细胞呈现不规则形状且细胞边缘出现鲜少的粉色脂滴。与对照组相比,模型组细胞在视野范围内可大致观察到细胞的形态基本保持正常,并且在细胞外侧呈现大量红色粒状脂滴。表明使用0.5 mmol/L油酸诱导肝细胞脂肪变性造模成功,可以采用此油酸浓度进行后续试验。
2.4 造模后不同组别细胞内血脂指标水平变化结果
脂肪是构成身体细胞的重要成分之一,在人体脑神经、肝脏、肾脏等重要器官中含有很多脂肪。本试验选用HepG2肝癌细胞进行脂质堆积模型的建造而非选用其他脂肪细胞的原因如下:肝脏为HDL-C、LDL-C、TC、TG合成的重要器官;建造脂肪变性细胞模型时大部分学者均以HepG2肝癌细胞作为对象[22-23]。
本试验为了解不同浓度的马齿苋纯化油对HepG2细胞内脂质堆积的影响,在明确纯化油浓度范围为60~100 μg/mL后,将马齿苋纯化油浓度划分为低、中、高剂量(即60、80、100 μg/mL)进行细胞内血脂指标HDL-C、LDL-C、TC以及TG浓度的测定。
HDL-C为强大的血管扩张剂,人体内此浓度的升高有利于预防冠心病等发生,对心血管具有保护作用[24]。由表2可知,与对照组相比,模型组HDL-C浓度由0.2330 mmol/L急剧降为0.0100 mmol/L(P<0.01),而LDL-C、TC、TG浓度均有极显著提高(P<0.01),再次证实HepG2细胞脂质堆积模型被成功建立。同时随着给药浓度的升高,实验组HDL-C浓度由0.0100 mmol/L逐渐升高到0.1754 mmol/L(低剂量组)、0.2178 mmol/L(中剂量组)以及0.4325 mmol/L(高剂量组),且均具有极显著差异(P<0.01),初步表明了马齿苋纯化油中的PUFAs可以促进HDL-C合成,此结果与Xie等[25]学者所得结论“PUFAs可通过调节参与肝HDL-C合成的关键基因、蛋白和mRNA表达促进HDL-C合成”相一致。
表 2 HepG2细胞内HDL-C、LDL-C、TC、TG浓度结果Table 2. Results of HDL-C, LDL-C, TC and TG in HepG2 cells浓度(μg/mL) HDL-C
(mmol/L)LDL-C (mmol/L) TC
(mmol/L)TG
(mmol/L)对照组 − 0.2330±0.0873** 0.1041±0.0149** 0.1150±0.0065** 0.5997±0.0201** 模型组 − 0.0100±0.0060## 0.2677±0.0430## 0.2865±0.0345## 0.9115±0.0118## 低剂量组 60 0.1754±0.0791** 0.2627±0.0220## 0.2687±0.0159## 0.8575±0.0304**## 中剂量组 80 0.2178±0.0214** 0.1809±0.0375 0.2094±0.0121**## 0.7736±0.0070**## 高剂量组 100 0.4325±0.0167**# 0.1537±0.0239** 0.1926±0.0066**## 0.6333±0.0292** 注:**表示与模型组相比,差异极显著(P<0.01);#表示与对照组相比,差异显著(P<0.05);##表示与对照组相比,差异极显著(P<0.01)。 LDL-C是一种运送血液中脂类的一种脂蛋白颗粒,它可以将脂类物质从肝脏运送至血管内皮细胞中从而有效减少脏器内脂质堆积,但是LDL-C过高会导致过量脂类被运送后沉积于血管内皮细胞造成动脉粥样硬化等疾病,因此适量的LDL-C可以有效降低冠心病、血栓等心脑血管疾病发生率[24,26]。由表2结果可以得出:与模型组相比,高剂量组LDL-C浓度极显著降低(P<0.01),其余组别与模型组相比浓度无显著性差异;而与对照组相比,中、高剂量组LDL-C浓度无显著差异。结果表明高剂量马齿苋纯化油可以通过显著降低LDL-C浓度缓解细胞脂质堆积作用,从而使细胞恢复正常生理活动。
TC是人体血液中所有脂蛋白中所含胆固醇的总和,TC与人类冠心病、脑卒中、动脉粥样硬化等疾病息息相关,TC浓度的减少表明人体内胆固醇堆积较少,一定程度上此物质的降低有利于减少脂质堆积从而达到降血脂作用。由表2可知,中、高剂量组马齿苋纯化油可通过极显著降低模型组TC浓度来缓解脂质堆积作用(P<0.01),但中、高剂量组给药后的TC浓度极显著高于对照组(P<0.01)。结果表明中、高剂量马齿苋纯化油给药后虽可以缓解细胞脂质堆积但却无法达到HepG2细胞正常TG浓度水平,猜测可能是给药时间太短造成的。
TG为人体供能源之一,此物质在肝脏代谢后可被人体吸收成为营养物质,但过多的TG在体内聚集会造成高脂血症、非酒精性脂肪肝等,因此适量的TG可增加人体对营养物质的吸收能力,从而保障人体内分泌平衡[27]。从表2可以看出,低、中、高剂量组TG浓度与模型组相比均呈现出极显著降低现象(P<0.01)且高剂量组TC浓度与对照组浓度相比无显著变化,证实马齿苋纯化油中PUFAs可以通过此条途径缓解模型组脂质堆积现象,且高剂量纯化油给药后可以使细胞恢复至原始TG浓度水平。
综上所述,高剂量组(100 μg/mL)马齿苋纯化油浓度对各项血脂指标均有极显著影响,且与对照组正常HepG2细胞内TG、LDL-C浓度相比无显著变化,因此可以认为此浓度的马齿苋纯化油对肝脏内脂质堆积具有较好的缓解效果。
3. 讨论与结论
经过本试验对马齿苋全草油和纯化油脂肪酸成分的对比,发现马齿苋全草油中PUFAs相对含量为27.6104%,经富集纯化后的马齿苋纯化油中的PUFAs含量高达73.9015%,表明尿素包合法富集纯化马齿苋全草油是有显著效果的。而敬思群等[28]试验结果表明尿素包合法纯化马齿苋全草油后PUFAs含量可由68.12%升高到91.35%,本试验结果PUFAs含量73.9015% <91.35%,造成此现象的原因可能是本试验耗材选用新鲜马齿苋而非马齿苋干药材;选用马齿苋的产地不同[29];提取马齿苋全草中PUFAs时所用溶剂、技术不同造成的[30-31]。将马齿苋纯化油应用于HepG2细胞,发现经100 μg/mL马齿苋纯化油干预后细胞内HDL-C、LDL-C、TC、TG浓度与模型组相比均有显著变化,其中HDL-C浓度显著升高,其余浓度显著降低,初步表明马齿苋纯化油对脂质堆积具有缓解作用,为下一步深入研究降脂机制等的试验安排奠定了较好的实践基础。
-
表 1 马齿苋脂肪酸成分含量分析
Table 1 Analysis of fatty acid composition in Portulaca oleracea
脂肪酸类型 类别 脂肪酸 马齿苋全草油
(相对含量,%)马齿苋纯化油
(相对含量,%)SFA C12:0 月桂酸 0.3306 0.0666 SFA C14:0 肉豆蔻酸 0.8413 0.1643 SFA C15:0 十五碳酸 0.1679 0.0398 SFA C16:0 棕榈酸 18.9987 15.2286 SFA C20:0 花生酸 3.1683 0.2870 SFA C17:0 十七碳酸 0.3587 0.0986 SFA C18:0 硬脂酸 4.5147 1.9866 SFA C22:0 二十二碳酸 11.3741 0.2749 SFA C23:0 二十三碳酸 0.5415 − SFA C24:0 二十四碳酸 26.8902 0.5446 MUFA C16:1 棕榈油酸 0.2338 0.1686 MUFA C18:1n9c 油酸 4.9697 7.1302 PUFAs C18:2n6c 亚油酸 14.1019 37.5822 PUFAs C18:3n3 α-亚麻酸 13.5085 36.3192 PUFAs C18:3n6 γ-亚麻酸 − 0.1089 总PUFAs 27.6104 73.9015 表 2 HepG2细胞内HDL-C、LDL-C、TC、TG浓度结果
Table 2 Results of HDL-C, LDL-C, TC and TG in HepG2 cells
浓度(μg/mL) HDL-C
(mmol/L)LDL-C (mmol/L) TC
(mmol/L)TG
(mmol/L)对照组 − 0.2330±0.0873** 0.1041±0.0149** 0.1150±0.0065** 0.5997±0.0201** 模型组 − 0.0100±0.0060## 0.2677±0.0430## 0.2865±0.0345## 0.9115±0.0118## 低剂量组 60 0.1754±0.0791** 0.2627±0.0220## 0.2687±0.0159## 0.8575±0.0304**## 中剂量组 80 0.2178±0.0214** 0.1809±0.0375 0.2094±0.0121**## 0.7736±0.0070**## 高剂量组 100 0.4325±0.0167**# 0.1537±0.0239** 0.1926±0.0066**## 0.6333±0.0292** 注:**表示与模型组相比,差异极显著(P<0.01);#表示与对照组相比,差异显著(P<0.05);##表示与对照组相比,差异极显著(P<0.01)。 -
[1] 刘琪, 张玉梅. 非酒精性脂肪肝与认知功能障碍的研究进展[J]. 中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2021,23(10):1115−1117. [LIU Q, ZHANG Y M. Research progress on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and cognitive dysfunction[J]. Chinese Journal of Elderly Cardiocerebral Vascular Disease,2021,23(10):1115−1117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0126.2021.10.030 LIU Q, ZHANG Y M. Research progress on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and cognitive dysfunction[J]. Chinese Journal of Elderly Cardiocerebral Vascular Disease, 2021, 23(10): 1115-1117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0126.2021.10.030
[2] WADHWA R, GOSAVI D, RAVINDRANATH A. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: New epidemic[J]. APIK Journal of Internal Medicine,2021,9(3):139−145.
[3] 钟明月, 刘春妍, 颜妍, 等. 乳双歧杆菌V9对高脂饮食诱导的NAFLD大鼠的改善作用[J]. 生物技术通报,2022,38(3):181−187. [ZHONG M Y, LIU C Y, YAN Y, et al. Improvement of Bifidobacterium lactis V9 on NAFLD rats induced by high fat diet[J]. Biotechnology Briefing,2022,38(3):181−187. doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2021-0630 ZHONG M Y, LIU C Y, YAN Y, et al. Improvement of Bifidobacterium lactis V9 on NAFLD rats induced by high fat diet[J]. Biotechnology Briefing,2022,38(3):181-187. doi: 10.13560/j.cnki.biotech.bull.1985.2021-0630
[4] GIANLUIGI M, SALVATORE D C, TOMMASO M. The biological clock: A pivotal hub in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease pathogenesis[J]. Frontiers in Physiology,2018,9:193. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00193
[5] LEE C O, LI H L, TSOI M F, et al. Association between the liver fat score (LFS) and cardiovascular diseases in the national health and nutrition examination survey 1999-2016.[J]. Annals of Medicine,2021,53(1):1065−1073.
[6] 刘小珊. 高脂血症血清脂肪酸标志物的筛选研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉轻工大学, 2015. LIU X S. Screening of serum fatty acid markers for hyperlipidemia[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Light Industry, 2015.
[7] 刘金泉, 冯凭. 膳食脂肪酸与肥胖、2型糖尿病和心血管疾病关系的研究进展[J]. 医学综述,2014,20(20):3760−3762. [LIU J Q, FENG P. Research progress on the relationship between dietary fatty acids and obesity, type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases[J]. Medical Review,2014,20(20):3760−3762. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2014.20.044 LIU J Q, FENG P. Research progress on the relationship between dietary fatty acids and obesity, type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases[J]. Medical Review, 2014, 20(20): 3760-3762. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2084.2014.20.044
[8] 岳崟, 王丽梅, 刘仁禄, 等. 多不饱和脂肪酸与学习记忆关系的研究进展[J]. 中国油脂,2015,40(4):38−41. [YUE Y, WANG L M, LIU R L, et al. Advances in studies on the relationship between polyunsaturated fatty acids and learning and memory[J]. Chinese Oil,2015,40(4):38−41. YUE Y, WANG L M, LIU R L, et al. Advances in studies on the relationship between polyunsaturated fatty acids and learning and memory[J]. Chinese Oil, 2015, 40(4): 38-41.
[9] CUTHBERTSON D J, KOSKINEN J, BROWN E, et al. Fatty liver index predicts incident risk of prediabetes, type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).[J]. Annals of medicine,2021,53(1):1256−1264.
[10] MARCHESINI G, TAYLOR R. Genes and lifestyle: Which of the two is more relevant in driving NAFLD progression?[J]. Digestive and Liver Disease,2021,53(11):1433−1434. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2021.08.011
[11] 刘莉丹, 刘晏. 健脾利湿法治疗非酒精性脂肪肝的研究进展[J]. 中成药,2021,43(9):2452−2456. [LIU L D, LIU Y. Research progress in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with Jianpi Lishi method[J]. Chinese Patent Medicine,2021,43(9):2452−2456. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2021.09.032 LIU L D, LIU Y. Research progress in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with Jianpi Lishi method[J]. Chinese Patent Medicine, 2021, 43(9): 2452-2456. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2021.09.032
[12] S P, SMB H, H A. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) evaluation and management[J]. Bangladesh Journal of Medicine,2013,24(1):25−28. doi: 10.3329/bjmed.v24i1.15032
[13] DEL B M, BARATTA F, PASTORI D, et al. The challenge of cardiovascular prevention in NAFLD[J]. The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology,2021,6(11):877−878.
[14] 吴洪号, 张慧, 贾佳, 等. 功能性多不饱和脂肪酸的生理功能及应用研究进展[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2021,32(8):134−140. [WU H H, ZHANG H, JIA J, et al. Advances in physiological functions and applications of functional polyunsaturated fatty acids[J]. Chinese Food Additives,2021,32(8):134−140. WU H H, ZHANG H, JIA J, et al. Advances in physiological functions and applications of functional polyunsaturated fatty acids[J]. Chinese FoodAdditives, 2021, 32(8): 134-140.
[15] 石计朋. ω-3多不饱和脂肪酸对脂多糖所致新生大鼠脑损伤的保护作用[D]. 广州: 南方医科大学, 2020. SHI J P. Protective effect of ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on brain injury in neonatal rats induced by lipopolysaccharide[D]. Guangzhou: South Medical University, 2020.
[16] 陈英杰, 谢良杰, 庄耀东, 等. ω-3多不饱和脂肪酸对重型颅脑损伤患者伤后炎症反应和神经损害的影响[J]. 中华临床营养杂志,2015,23(4):224−228. [CHEN Y J, XIE L J, ZHUANG Y D, et al. Effect of ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on inflammatory response and nerve damage in patients with severe craniocerebral injury after injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Nutrition,2015,23(4):224−228. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-635X.2015.04.006 CHEN Y J, XIE L J, ZHUANG Y D, et al. Effect of ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on inflammatory response and nerve damage in patients with severe craniocerebral injury after injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2015, 23(4): 224-228. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-635X.2015.04.006
[17] 弓剑, 晓敏. 多不饱和脂肪酸代谢及其对炎症的调节[J]. 动物营养学报,2017,29(1):1−7. [GONG J, XIAO M. Polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolism and its regulation of inflammation[J]. Animal Nutrition Journal,2017,29(1):1−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2017.01.001 GONG J, XIAO M. Polyunsaturated fatty acid metabolism and its regulation of inflammation[J]. Animal Nutrition Journal, 2017, 29(1): 1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2017.01.001
[18] AYUMI T, KEI K, KENSUKE T, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 in cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) is suppressed by omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids in vitro and in vivo[J]. PLoS One,2017,9(2):e89605.
[19] 胡慧芸. 一种新型多不饱和脂肪酸混合物的软胶囊制备和对混合型高脂血症大鼠的降脂、抗炎作用及其机制研究[D]. 武汉:湖北中医药大学, 2019. HU H Y. Preparation of a new soft capsule of polyunsaturated fatty acid mixture and its lipid-lowering, anti-inflammatory effects and mechanism on mixed hyperlipidemia rats[D].Wuhan: Hubei University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019.
[20] 秦月雯, 侯金丽, 王萍, 等. 马齿苋“成分-活性-中药功效-疾病”研究进展及关联分析[J]. 中草药,2020,51(7):1924−1938. [QIN Y W, HOU J L, WANG P, et al. Research progress and correlation analysis of Portulaca oleracea “composition-activity-efficacy-disease”[J]. Chinese Herbal Medicine,2020,51(7):1924−1938. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2020.07.030 QIN Y W, HOU J L, WANG P, et al. Research progress and correlation analysis of Portulaca oleracea “composition-activity-efficacy-disease”[J]. Chinese Herbal Medicine, 2020, 51(7): 1924-1938. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2020.07.030
[21] 李冠文, 王辉敏, 杨金梅, 等. 尿素包合法富集纯化马齿苋中多不饱和脂肪酸的工艺优化[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2021,12(15):6185−6191. [LI G W, WANG H M, YANG J M, et al. Process optimization of enrichment and purification of polyunsaturated fatty acids in purslane by urea inclusion method[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Testing,2021,12(15):6185−6191. doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2021.15.040 LI G W, WANG H M, YANG J M, et al. Process optimization of enrichment and purification of polyunsaturated fatty acids in purslane by urea inclusion method[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Testing, 2021, 12(15): 6185-6191. doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2021.15.040
[22] 张蕾, 郝婧玮, 宛春雷, 等. 桦褐孔菌多糖的提取工艺优化及对人肝癌细胞HepG2脂肪堆积的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学,2019,47(10):201−204. [ZHANG L, HAO J W, WAN C L, et al. Optimization of extraction process of polysaccharide from Inonotus obliquus and its effect on fat accumulation of human hepatoma cell HepG2[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Science,2019,47(10):201−204. ZHANG L, HAO J W, WAN C L, et al. Optimization of extraction process of polysaccharide from Inonotus obliquus and its effect on fat accumulation of human hepatoma cell HepG2[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Science, 2019, 47(10): 201-204.
[23] 毛雨葳. 绞股蓝皂苷缓解油酸诱导的HepG2细胞脂肪堆积的作用[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2017. MAO Y W. Effect of Gynostemma pentaphyllum saponins on oleic acid-induced fat accumulation in HepG2 cells[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2017.
[24] 梁群, 薛鸿征, 冯文佳. 脂蛋白在脓毒症中作用的研究进展[J]. 中国急救医学,2021,41(8):729−733. [LIANG Q, XUE H Z, FENG W J. Research progress on the role of lipoprotein in sepsis[J]. Emergency Medicine in China,2021,41(8):729−733. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1949.2021.08.016 LIANG Q, XUE H Z, FENG W J. Research progress on the role of lipoprotein in sepsis[J]. Emergency Medicine in China, 2021, 41(8): 729-733. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1949.2021.08.016
[25] XIE X X, ZHANG T, ZHAO S, et al. Effects of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids high fat diet intervention on the synthesis of hepatic high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in obesity-insulin resistance rats[J]. Lipids in Health and Disease,2016,15(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s12944-016-0250-3
[26] MANABU O, KATSUMI M, AKIRA O, et al. Development of accelerated coronary atherosclerosis model using low density lipoprotein receptor knock-out swine with balloon injury[J]. PLoS ONE,2017,11(9):0163055.
[27] 杜宇忠, 苏洁, 颜美秋, 等. 陈皮醇提物对高脂血症模型大鼠甘油三酯的改善作用及其机制研究[J]. 中国中药杂志,2021,46(1):190−195. [DU Y Z, SU J, YAN M Q, et al. The improvement effect and mechanism of ethanol extract from Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae on triglycerides in hyperlipidemia rats[J]. Chinese Jour-nal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2021,46(1):190−195. DU Y Z, SU J, YAN M Q, et al. The improvement effect and mechanism of ethanol extract from Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae on triglycerides in hyperlipidemia rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 46(1): 190-195.
[28] 敬思群, 陈婧萱. 尿素包合法富集马齿苋全草油多不饱和脂肪酸及脂肪酸分析[J]. 粮食与油脂,2015(2):33−36. [JING S Q, CHEN J X. Enrichment of polyunsaturated fatty acids and fatty acid analysis of whole herb oil of purslane by urea inclusion method[J]. Grain and Oil,2015(2):33−36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2015.02.009 JING S Q, CHEN J X. Enrichment of polyunsaturated fatty acids and fatty acid analysis of whole herb oil of purslane by urea inclusion method[J]. Grain and oil, 2015(2): 33-36. DOI:10.3969 / j.issn.1008-9578.2015.02.009.
[29] 张雯雯, 郑必胜, 刘瑞海, 等. 不同产地马齿苋的抗衰老活性比较[J]. 现代食品科技,2020,36(5):57−63. [ZHANG W W, ZHEN B S, LIU R H, et al. Comparison of anti-aging activity of purslane from different habitats[J]. Modern Food Technology,2020,36(5):57−63. doi: 10.13982/j.mfst.1673-9078.2020.5.009 ZHANG W W, ZHEN B S, LIU R H, et al. Comparison of anti-aging activity of purslane from different habitats[J]. Modern Food Technology, 2020, 36(5): 57-63. DOI:10.13982/ j.mfst.1673-9078.2020.5.009.
[30] 陈凌, 陈召桂, 骆卢佳, 等. 不同方法提取马齿苋多糖的抗氧活性比较[J]. 食品研究与开发,2015,36(22):14−18. [CHEN L, CHEN Z G, LUO L J, et al. Comparison of antioxidant activities of polysaccharides extracted by different methods[J]. Food Research and Development,2015,36(22):14−18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2015.22.004 CHEN L, CHEN Z G, LUO L J, et al. Comparison of antioxidant activities of polysaccharides extracted by different methods[J]. Food research and development, 2015, 36(22): 14-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2015.22.004
[31] 徐琳. 不同提取方法对马齿苋水提物自由基清除和抗菌活性影响的研究[J]. 安徽农业科学,2015,43(27):53−54,66. [XU L. Study on the effects of different extraction methods on free radical scavenging and antibacterial activity of purslane aqueous extract[J]. Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2015,43(27):53−54,66. doi: 10.13989/j.cnki.0517-6611.2015.27.021 XU L. Study on the effects of different extraction methods on free radical scavenging and antibacterial activity of purslane aqueous extract[J]. Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 43(27): 53-54, 66. DOI:10.13989/ j.cnki.0517-6611.2015.27.021.





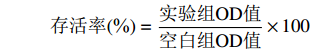
 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
