Construction of PMP-HPLC Fingerprint of Partial Acid Hydrolysate of Polygonatum cyrtonema Polysaccharides Based on the Chemometric Methods
-
摘要: 本文通过构建多花黄精HPLC指纹图谱,结合多种化学计量学方法探讨不同产地多花黄精药材多糖的差异。采用1-苯基-3-甲基-5-吡唑啉酮柱前衍生化-HPLC法,建立多花黄精多糖类成分的指纹图谱,对其单糖组成、总多糖含量进行分析,并采用相似度评价(SA)、聚类分析(HCA)和主成分分析(PCA)方法,对多花黄精指纹图谱进行模式识别研究。结果显示,不同产地多花黄精均含有半乳糖醛酸,葡萄糖醛酸,半乳糖,葡萄糖和木糖;13批多花黄精药材相似度在0.781~0.945之间,总多糖含量为7.18%~16.27%,HCA和PCA将不同产地的多花黄精分为2类,采集于湖南省慈利县的样本单独为一支。以上研究结果表明多花黄精药材多糖指纹差异较大,为保障黄精药材临床用药的有效和安全,有必要建立多花黄精的规范化栽培技术体系。Abstract: In this paper, the polysaccharides fingerprints of Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua. were constructed, combined with various chemometric methods, to evaluate the differences of P. cyrtonema polysaccharides from different origins. The 1-pheny-3-methyl-5-pyrazolone (PMP) pre-column derivatization-HPLC method was applied to analyze the monosaccharide composition and total polysaccharide content of P. cyrtonema. Furthermore, the fingerprints were further evaluated by chemometric methods, including similarity analysis (SA), cluster analysis (HCA), and principal component analysis (PCA). The results showed that the composition of monosaccharides was galacturonic acid, glucuronic acid, galactose, glucose, and xylose. The similarities were ranged from 0.781 to 0.945. In addition, the content of total polysaccharides was in the range of 7.18% to 16.27%. HCA and PCA all divided P. cyrtonema polysaccharides from different origins into two categories, the samples collected in Cili County, Hunan Province were a separate one. These results indicated that the polysaccharide fingerprints of P. cyrtonema were quite different. Establishing the standardized cultivation technology system of P. cyrtonema is necessary to ensure clinical efficacy and safety.
-
多花黄精为百合科黄精属植物Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua.,又名姜状黄精,为2020年版《中华人民共和国药典》黄精药材的基原植物之一,是目前市场上黄精的主流栽培品种,具有补气养阴,健脾,润肺,益肾之功能[1],多花黄精为重要的药食同源资源,由于其良好的功效,近年来被广泛用于食品和保健品开发[2]。现代研究表明,多花黄精化学成分主要包括多糖,甾体皂苷、黄酮等成分[3-5],其中多糖是多花黄精中的质量标志物,也是中国药典黄精的质量控制指标[1],具有抗衰老、降血糖、降血脂、抗菌等药理作用[6-8]。据对保健食品原料的调查发现,黄精在中药类原料的使用频率排名靠前[9],目前市场上存在大量的黄精多糖产品如黄精膏、黄精饮料等产品,因此判定多花黄精产品的质量好坏和原料真伪极为重要。现有方法一般采用苯酚-硫酸法和蒽酮-硫酸法测定总多糖含量[10],用于控制多花黄精多糖产品质量,但此类方法选择性较差,不能有效地鉴别出掺假品;因此,迫切需要制定有效可靠的评价标准,以便科学地评价多花黄精多糖的质量,对黄精多糖保健食品的应用开发具有深远意义。
指纹图谱是近年来用于中药质量控制的一种有效、可行的方法,已广泛用于中药质量控制、药效成分研究领域[11-13]。由于黄精多糖为非单一分子化合物,结构复杂,且不含有共轭结构,使用常规高效液相二极管阵列检测法(High-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection,HPLC-DAD)方法无法有效检测。已有学者采用高效液相色谱-蒸发光散射法、高效阴离子交换色谱-脉冲安培法和电喷雾式检测器(Charged aerosol detector,CAD)对植物多糖的单糖组成进行了研究[14-16],但蒸发光散射检测的耐用性和稳定性欠佳[17-18],脉冲安培检测的成本较高、稳定性差且对色谱条件要求较为严格[16],CAD检测仪器价格昂贵,使用受到一定的限制[19-21]。有关黄精法定基原植物的指纹图谱研究方面,目前已有学者对滇黄精P. kingianum Coll. Et Hemsl.和黄精P. sibiricum Red.多糖的指纹图谱进行了研究[22-23];而对于多花黄精P. cyrtonema的指纹图谱研究方面,仅见周宝珍,杨青等对多花黄精乙醇提取物的指纹图谱研究[24-25],尚未见多花黄精中的多糖组分的指纹图谱的报道。因此,建立能表征多花黄精中多糖指纹的方法具有重要意义。鉴于此,本文采用柱前衍生化-HPLC对多花黄精药材的指纹图谱和单糖组成进行研究,并结合相似度分析(Similarity analysis,SA)、聚类分析(Hi-erarchical cluster analysis,HCA)和主成分分析(Prin-cipal component analysis,PCA)等化学计量学[26-28]手段,以期为多花黄精药材的质量控制奠定科学基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
黄精药材 13批样品 购于安徽、四川、湖南等地,均为栽培品,经大理大学段宝忠教授鉴定为百合科植物多花黄精P. cyrtonema Hua.,新鲜根茎切片后于40 ℃烘箱烘干,样品信息详见表1,凭证标本保存于大理大学中药标本馆;葡萄糖(批号171106)、甘露糖(批号170921)、盐酸氨基葡萄糖(批号171210)、半乳糖(批号171206)、L-鼠李糖(批号171024)、L-岩藻糖(批号170813)、葡萄糖醛酸(批号170730)、木糖(批号170912)、半乳糖醛酸(批号170903)、核糖(批号171103)、阿拉伯糖(批号171219) 以上单糖纯度≥98%,购自上海融禾医药科技有限公司;1-苯基-3-甲基-5-吡唑啉酮(1-pheny-3-methyl-5-pyrazolone,PMP) 阿拉丁;色谱级乙腈(批号085884) Fisher Scientific;水为超纯水,其他试剂为国产分析纯。
Agilent 1200高效液相色谱仪 美国安捷伦科技有限公司;GH-252电子天平 日本AND公司;AL204电子天平 梅特勒-托利多仪器(上海)有限公司;SB25-12D超声波清洗机 宁波新芝生物科技股份有限公司。
表 1 样品信息Table 1. Information of samples编号 来源 编号 来源 S1 安徽省金寨县 S8 贵州省赤水市 S2 四川省成都市 S9 湖南省怀化市 S3 湖南省祁阳县 S10 安徽省祁门县 S4 四川省遂宁市 S11 福建省建宁县 S5 广西省全州县 S12 江西省安福县 S6 重庆市江津区 S13 湖南省慈利县 S7 浙江省遂昌县 1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 色谱条件
Agilent Zorbax SB-C18色谱柱(250 mm×4.6 mm,5 μm);流动相:乙腈(A)−0.025 mol·L−1磷酸盐缓冲溶液(B)(pH7.5);梯度洗脱(0~10 min,15%~17% A;10~18.5 min,17%~22.5% A;18.5~20 min,22.5%~23.5% A;20~32 min,23.5%~30% A);流速:0.8 mL·min−1;柱温:35 ℃;检测波长:250 nm;进样量:20 μL。
1.2.2 衍生化对照品溶液制备
精密称取各单糖对照品适量,用蒸馏水配制成浓度约为0.5 mg·mL−1的单糖对照品溶液。精密吸取上述对照品溶液400 μL,置于5 mL的安瓿瓶中,精密加入200 μL 0.6 mol·L−1 NaOH和0.5 mol·L−1 PMP溶液,置70 ℃条件下反应60 min。取出,放冷,精密加入200 μL 0.6 mol·L−1 HCl溶液,混匀。加入等体积的三氯甲烷,混匀,离心10 min(4000 r·min−1),去掉三氯甲烷层,重复多次至三氯甲烷层无色,即得衍生化对照品溶液。
1.2.3 供试品溶液制备
1.2.3.1 粗多糖制备
取多花黄精样品于40 ℃烘箱干燥12 h至恒重,粉碎,过80目筛,取粉末5.0 g,精密称定,根据预实验得到最优工艺制备粗多糖,即加入100 mL水于80 ℃下超声提取,重复3次,每次1 h,抽滤,洗净滤渣,浓缩至10 mL,放入离心机离心20 min(4000 r·min−1)。取上清液转移至分液漏斗,加入3倍体积的石油醚进行萃取,直至石油醚层无色,静置分层,取下层水相,调节pH至6,加入体积分数为2%的木瓜蛋白酶溶液(80万U/g),水浴温度60 ℃,酶解4 h,待反应完成,沸水浴灭酶10 min。取上清液采用Sevage法(正丁醇:氯仿=1:5)脱去蛋白,直至无絮状物生成,离心10 min(4000 r·min−1),再取上清液转至烧杯中,精密缓慢的加入6倍量的无水乙醇,快速搅拌,于4 ℃冰箱中放置12 h,离心,向沉淀中加10 mL 95%乙醇,洗涤2次,再离心,加热水使沉淀溶解,转移至10 mL量瓶中,室温下放冷,后定容,再将溶液置于烧杯中冷冻干燥,最后得粗多糖粉末。
1.2.3.2 衍生化供试品溶液制备
精密称取5 mg粗多糖粉末,置于5 mL的安瓿瓶中,精密加入2 mL 4 mol·L−1三氟乙酸(TFA)溶液,封口,置于110 ℃条件下7 h,进行水解,取出,室温放冷,后水浴蒸干,向残渣中加入甲醇1 mL,烘干,重复多次,直至三氟乙酸除尽。再加热水适量,使沉淀溶解,转移至1 mL容量瓶中,室温放冷,定容摇匀,得供试品酸水解溶液。取酸水解溶液400 μL,按1.2.2项下衍生化方法制备,得衍生化供试品溶液,每批样品重复3次。
1.2.4 总多糖含量测定
按课题组已发表文献方法,对13批多花黄精总多糖含量进行测定[10]。
1.3 数据处理
相似度分析采用《中药色谱指纹图谱相似度评价系统》(2.0版),聚类分析采用SPSS 20.0软件进行,主成分分析采用SIMCA 13.0软件进行。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 色谱条件的选择
本研究比较了以下4种色谱柱:Zorbax SB-C18(4.6 mm×250 mm,5 μm),Zorbax Extend-C18(4.6 mm×250 mm,5 μm),Zorbax SB-Aq-C18(4.6 mm×250 mm,5 μm),Zorbax XDB-C18(4.6 mm×250 mm,5 μm)。实验结果表明,Agilent Zorbax SB-C18色谱柱(4.6 mm×250 mm,5 μm)出峰较多,各成分分离较好。同时,当流动相为纯水时,部分色谱峰产生了拖尾情况,因此,在实验中考察不同浓度磷酸盐缓冲溶液(0.01、0.02、0.025 mol·L−1)对色谱峰分离效果的影响,结果显示,当磷酸盐缓冲溶液浓度为0.025 mol·L−1时,所得色谱峰峰形及分离度较好,故选择0.025 mol·L−1的磷酸盐缓冲溶液作为洗脱溶剂。
2.2 方法学考察
2.2.1 精密度试验
取同一批供试品溶液(S2),按1.2.1项下方法连续进样6次,测得各共有峰相对保留时间和相对峰面积的RSD均小于2.10%,表明精密度良好。
2.2.2 重复性试验
取同一批S2样品6份,按1.2.3项下方法进行制备,在1.2.1项色谱条件下进样分析。测得结果显示,各共有峰的相对保留时间与相对峰面积的RSD均小于2.60%,表明重复性良好。
2.2.3 稳定性试验
取同一批S2供试品溶液,分别在0、4、8、12、18、24、48 h进样测定,测得结果显示,各共有峰的相对保留时间与相对峰面积的RSD均小于2.70%,表明供试品溶液在48 h内稳定。
2.3 指纹图谱的构建
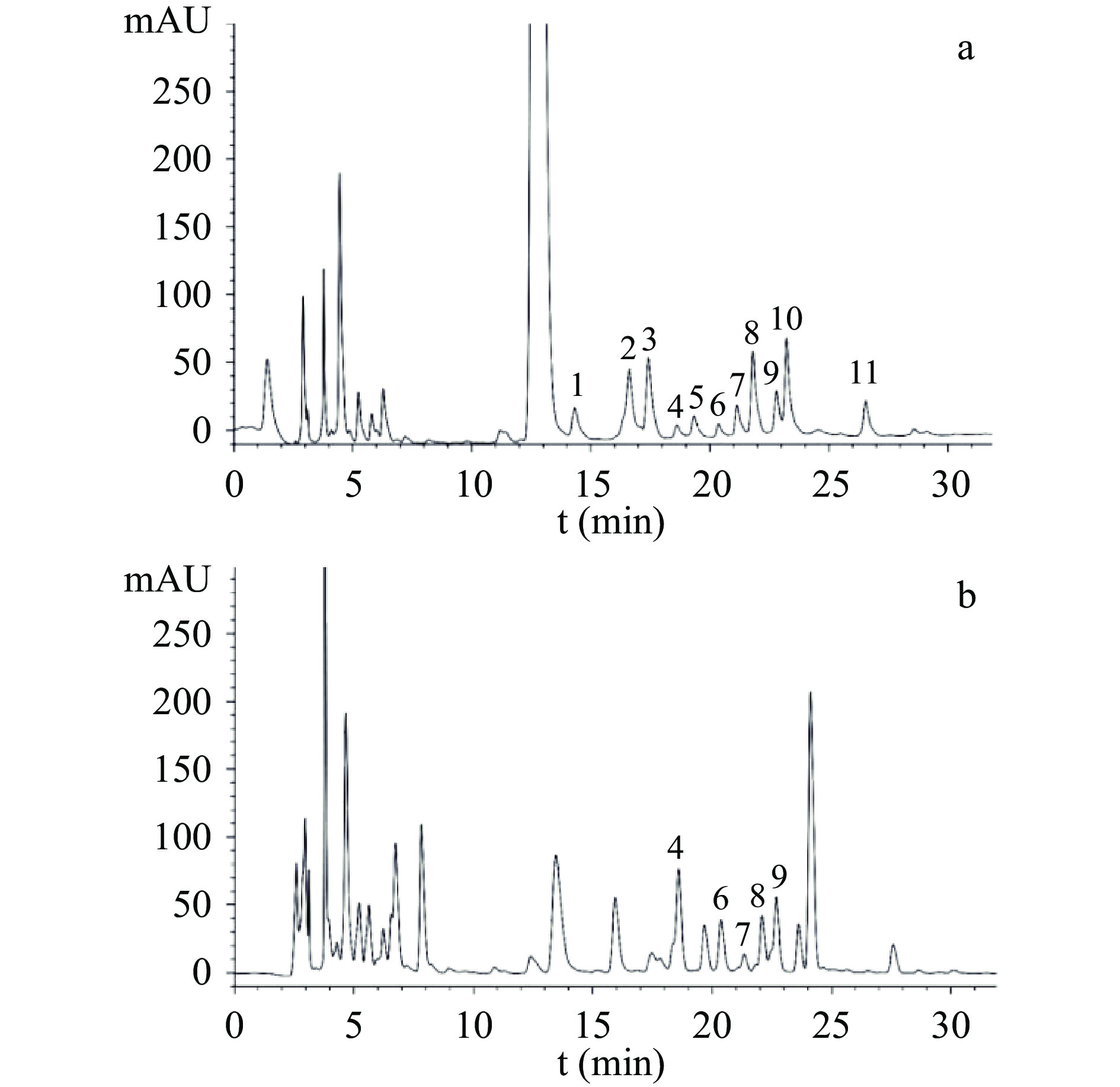
将13批多花黄精样品按1.2.3方法制备供试品溶液,按1.2.1项色谱条件下检测,记录色谱图,色谱数据导入《中药色谱指纹图谱相似度评价系统2.0版》软件,采用中位数法,以S1批样品作为参照谱进行指纹匹配,生成共有模式指纹图谱(图1),可见共有10个共有峰。相似度结果见表2,13批多花黄精的指纹图谱相似度在0.781~0.945之间,其中S1(安徽省金寨县)、S3(湖南省祁阳县)、S8(贵州省赤水市)、S11(福建省建宁县)和S12(江西省安福县)5批样本相似度大于0.90,其它样品低于0.90,占61.5%,这一结果与黄精P. sibiricum Red.和滇黄精P. kingianum Coll. et Hemsl.的HPLC指纹图谱研究结果不一致[22-23],其原因是否是产地或生长年限等影响了其多糖组成,还有待进一步深入研究。本研究中采集自湖南省慈利县的S13号相似度最低为0.781,观察发现与其他样品相比,S13号样品根茎较幼嫩,已有研究表明黄精幼嫩部位的多糖含量较成熟部位低[29],这可能是其相似度较低的原因。
表 2 13批不同产地多花黄精相似度Table 2. Similarity evaluation of 13 batches of P. cyrtonema from different localities样品编号 S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S6 S7 S8 S9 S10 S11 S12 S13 S1 1.000 S2 0.951 1.000 S3 0.854 0.706 1.000 S4 0.888 0.862 0.617 1.000 S5 0.952 0.862 0.832 0.941 1.000 S6 0.590 0.485 0.819 0.247 0.469 1.000 S7 0.596 0.445 0.895 0.221 0.508 0.924 1.000 S8 0.744 0.718 0.797 0.446 0.580 0.925 0.807 1.000 S9 0.634 0.469 0.928 0.288 0.568 0.916 0.994 0.806 1.000 S10 0.975 0.979 0.765 0.910 0.920 0.524 0.483 0.737 0.523 1.000 S11 0.813 0.716 0.939 0.490 0.702 0.887 0.927 0.879 0.928 0.730 1.000 S12 0.963 0.858 0.899 0.895 0.989 0.585 0.621 0.670 0.676 0.919 0.793 1.000 S13 0.534 0.515 0.637 0.218 0.358 0.919 0.746 0.896 0.719 0.497 0.792 0.464 1.000 R 0.929 0.857 0.935 0.805 0.845 0.841 0.808 0.907 0.829 0.884 0.945 0.905 0.781 2.4 单糖定性鉴定
样品及单糖对照品的PMP-HPLC色谱图见图2。通过与对照品的保留时间比对,发现10个共有峰中,5个与单糖对照品保留时间一致,即4号峰(18.80 min)为半乳糖醛酸,6号峰(20.13 min)为葡萄糖醛酸,7号峰(21.50 min)为半乳糖,8号峰(22.22 min)为葡萄糖,9号峰(22.84 min)为木糖,单糖研究结果与王坤等[30]对多花黄精单糖组成研究结果基本一致。在前期研究中,何连军等[14]采用高效阴离子交换色谱-脉冲安培检测法,检测到多花黄精含有果糖,而本研究未检测到果糖,主要原因是由于PMP仅能与醛糖发生衍生化反应,果糖属于酮糖,不发生衍生反应[31]。
2.5 总多糖含量
多糖是黄精药材的重要质量标志物[32],按2020年版《中华人民共和国药典》含量测定项规定,其干燥品含多糖以无水葡萄糖(C6H12O6)计,不得少于7.0%。本研究显示,13批多花黄精药材的多糖含量符合要求,在7.18%~16.27%范围内,结果见表3。可见总多糖含量最高的S3号(湖南省祁阳县),最低是S9号(湖南省怀化市),约相差1倍,表明不同产地多花黄精多糖含量有明显差异,与相似度分析结果一致。已有研究表明,产地和生长年限是影响黄精多糖含量的重要影响因素[29,33],本研究中,样品为随机采集,产地和生长年限可能是形成其多糖差异的原因。
表 3 13批多花黄精的总多糖含量测定结果Table 3. Determination results of total polysaccharide content of 13 batches of P. cyrtonema编号 吸光度(Abs) 百分含量(%) 编号 吸光度(Abs) 百分含量(%) S1 0.654 14.11 S8 0.579 12.30 S2 0.516 10.78 S9 0.367 7.18 S3 0.743 16.27 S10 0.441 8.97 S4 0.471 9.69 S11 0.432 8.75 S5 0.390 7.73 S12 0.584 12.43 S6 0.559 11.82 S13 0.388 7.69 S7 0.418 8.42 2.6 聚类分析
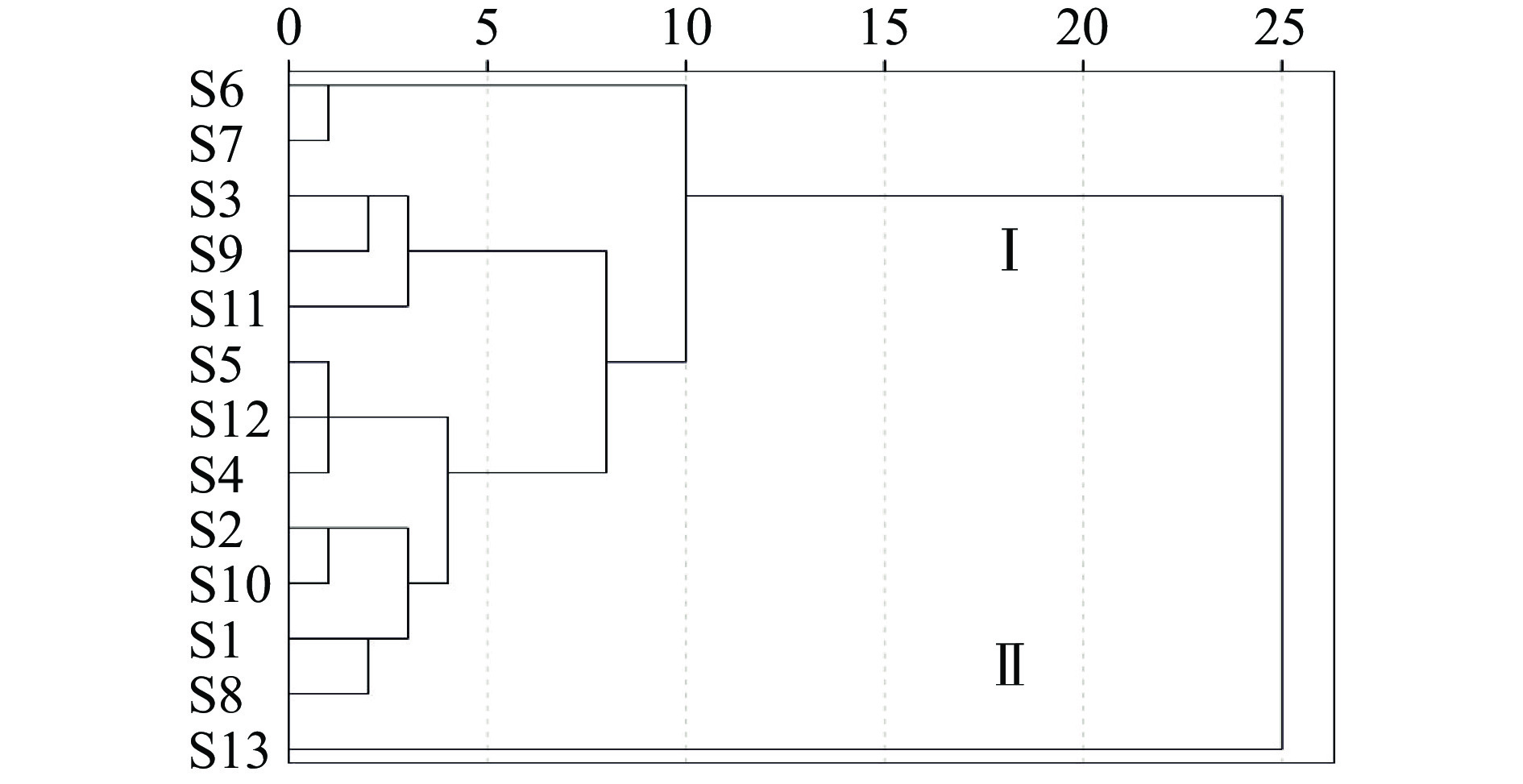
聚类分析(HCA)是按照个体数据特征对样本进行分类的一种方法,其同一类别个体间具有较高的相似度[11]。将13批样品单位质量药材峰面积进行量化,得到13×10阶的数据矩阵,采用SPSS 20.0版软件,瓦尔德法(Ward)进行分析,结果见图3。可见当判别条件距离为10时,13批多花黄精药材被分成两类,I类包括12个样品,为S1~S12号,II类仅有S13号(湖南省慈利县),若以相似度0.80为界限,聚类结果与相似度和多糖含量结果一致。不同产地的样品在聚类图上无明显区分,表明栽培多花黄精药材的多糖成分类别差异不大,S13号样本偏离的原因可能是采收年限、种质资源或栽培技术差异造成的[34]。
2.7 主成分分析
主成分分析(PCA)是将多维具有相关性的数据压缩为少数几个相互独立数据的统计方法,其在不损失主要信息的前提下实现降维,扩大样本之间的差异,可解决由于中成药成分复杂所致的普带重叠分析困难[35]。为了更加全面、系统地分析13批多花黄精之间的差异,揭示其内在关系,将上述13×10数据矩阵采用SPSS 20.0软件计算特征值和方差贡献率,见表4,以主成分的特征值大于1和累计方差贡献率大于85%,作为选择主成分因子依据[36],结果显示前三个主成分可代表89.364%的信息量。采用SIMCA-P13.0计算PCA得分图,结果见图4,13个样品被分成两类,其中采集于湖南省慈利县的S13号样品单独聚为一类,与HCA结果一致,观察发现与其他样品相比,S13号样本较为幼嫩,可能是其单独聚为一支的原因。
表 4 特征值和方差贡献率Table 4. Characteristic value and variance contribution rate成份 特征值 方差贡献率(%) 累计方差贡献率(%) 1 4.551 50.565 50.565 2 1.950 21.668 72.234 3 1.542 17.131 89.364 4 0.296 2.277 98.624 5 0.125 0.963 99.587 6 0.027 0.21 99.797 7 0.018 0.137 99.933 8 0.009 0.067 100 9 3.21E-16 2.47E-15 100 3. 结论
本实验首次建立了不同产地多花黄精中多糖成分的PMP-HPLC指纹图谱,并对其单糖组成进行了研究,在此基础上,结合指纹图谱技术,采用相似度分析,聚类分析和主成分分析对其指纹图谱进行了研究,并对其总多糖含量进行了测定。实验结果表明,13批多花黄精单糖组成均含半乳糖醛酸、葡萄糖醛酸、半乳糖、葡萄糖、木糖,其总多糖含量范围在7.18%~16.27%之间,HCA和PCA分析结果一致,样本被分为2类,其次,13批多花黄精的指纹图谱相似度较低,在0.781~0.945之间,其中相似度低于0.90的样品占所研究样品的61.5%,从一定程度反映了多花黄精药材质量的不均一,这一结果与黄精其他基原物种研究结果不一致[22-23],其原因可能是种质资源、产地或生长年限等影响了其多糖生成,还有待进一步深入研究。综合产地与指纹图谱相似度、总多糖含量、单糖组成等分析,未发现明显的规律,已有研究表明,多花黄精不同龄节间的有效成分含量差异较大[37],不同生长年限的黄精药材其多糖成分亦存在一定差异[29],提示采收年限和栽培技术可能是造成多花黄精品质差异的原因。因此,为确保黄精药材临床用药的有效和安全,有必要建立多花黄精的规范化栽培技术体系,以确保多花黄精药材品质的一致性。
-
表 1 样品信息
Table 1 Information of samples
编号 来源 编号 来源 S1 安徽省金寨县 S8 贵州省赤水市 S2 四川省成都市 S9 湖南省怀化市 S3 湖南省祁阳县 S10 安徽省祁门县 S4 四川省遂宁市 S11 福建省建宁县 S5 广西省全州县 S12 江西省安福县 S6 重庆市江津区 S13 湖南省慈利县 S7 浙江省遂昌县 表 2 13批不同产地多花黄精相似度
Table 2 Similarity evaluation of 13 batches of P. cyrtonema from different localities
样品编号 S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 S6 S7 S8 S9 S10 S11 S12 S13 S1 1.000 S2 0.951 1.000 S3 0.854 0.706 1.000 S4 0.888 0.862 0.617 1.000 S5 0.952 0.862 0.832 0.941 1.000 S6 0.590 0.485 0.819 0.247 0.469 1.000 S7 0.596 0.445 0.895 0.221 0.508 0.924 1.000 S8 0.744 0.718 0.797 0.446 0.580 0.925 0.807 1.000 S9 0.634 0.469 0.928 0.288 0.568 0.916 0.994 0.806 1.000 S10 0.975 0.979 0.765 0.910 0.920 0.524 0.483 0.737 0.523 1.000 S11 0.813 0.716 0.939 0.490 0.702 0.887 0.927 0.879 0.928 0.730 1.000 S12 0.963 0.858 0.899 0.895 0.989 0.585 0.621 0.670 0.676 0.919 0.793 1.000 S13 0.534 0.515 0.637 0.218 0.358 0.919 0.746 0.896 0.719 0.497 0.792 0.464 1.000 R 0.929 0.857 0.935 0.805 0.845 0.841 0.808 0.907 0.829 0.884 0.945 0.905 0.781 表 3 13批多花黄精的总多糖含量测定结果
Table 3 Determination results of total polysaccharide content of 13 batches of P. cyrtonema
编号 吸光度(Abs) 百分含量(%) 编号 吸光度(Abs) 百分含量(%) S1 0.654 14.11 S8 0.579 12.30 S2 0.516 10.78 S9 0.367 7.18 S3 0.743 16.27 S10 0.441 8.97 S4 0.471 9.69 S11 0.432 8.75 S5 0.390 7.73 S12 0.584 12.43 S6 0.559 11.82 S13 0.388 7.69 S7 0.418 8.42 表 4 特征值和方差贡献率
Table 4 Characteristic value and variance contribution rate
成份 特征值 方差贡献率(%) 累计方差贡献率(%) 1 4.551 50.565 50.565 2 1.950 21.668 72.234 3 1.542 17.131 89.364 4 0.296 2.277 98.624 5 0.125 0.963 99.587 6 0.027 0.21 99.797 7 0.018 0.137 99.933 8 0.009 0.067 100 9 3.21E-16 2.47E-15 100 -
[1] 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典[S]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020: 319 National Pharmacopoeia Committee. Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China[S]. Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press, 2020: 319.
[2] 宋艺君, 郭涛, 刘世军, 等. 响应面法优化黄精-大枣果酒发酵工艺及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(1):156−161. [SONG Yijun, GUO Tao, LIU Shijun, et al. Optimization of fermentation process and antioxidant activity of Polygonati Rhizoma-Jujubae Fructus fruit wine by response surface methodology[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(1):156−161. SONG Yijun, GUO Tao, LIU Shijun, et al. Optimization of fermentation process and antioxidant activity of Polygonati Rhizoma-Jujubae Fructus fruit wine by response surface methodology[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(1): 156−161.
[3] LI R S, TAO A E, YANG R M, et al. Structural characterization, hypoglycemic effects and antidiabetic mechanism of a novel polysaccharides from Polygonatum kingianum Coll. et Hemsl[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy,2020,131:1−8.
[4] XIE S Z, YANG G, JIANG X M, et al. Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua polysaccharide promotes GLP-1 secretion from enteroendocrine L-Cells through sweet taste receptor-mediated camp signaling[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2020,68(25):6864−68721. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c02058
[5] HUANG Z Z, DU X, MA C D, et al. Identification of antitumor active constituents in Polygonatum sibiricum flower by UPLC-Q-TOF-MSE and network pharmacology[J]. ACS Omega,2020,5(46):29755−29764. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c03582
[6] 杜泽飞, 陶爱恩, 夏从龙, 等. 基于PMP-HPLC和化学计量学的黄精基原物种多糖差异分析[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2019,15(25):25−29. [DU Zefei, TAO Aien, XIA Conglong, et al. Approach based on PMP-HPLC fingerprint and chemometrics to compare difference of polysaccharide in Polygonati Rhizoma[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2019,15(25):25−29. DU Zefei, TAO Aien, XIA Conglong, et al. Approach based on PMP-HPLC fingerprint and chemometrics to compare difference of polysaccharide in Polygonati Rhizoma[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2019, 15(25): 25−29.
[7] 吴丰鹏, 李芹英, 吴彦超, 等. 九蒸九制对黄精多糖单糖组成及其抗氧化性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(2):42−46. [WU Fengpeng, LI Qinying, WU Yanchao, et al. Effects of nine-steam-nine-bask on the monosaccharide composition and antioxidant activities of Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharide[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(2):42−46. WU Fengpeng, LI Qinying, WU Yanchao, et al. Effects of nine-steam-nine-bask on the monosaccharide composition and antioxidant activities of Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharide[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(2): 42−46.
[8] ZHAO P, ZHAO C C, LI X, et al. The genus Polygonatum: A review on ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2017,378(17):274−291.
[9] 杨紫玉, 杨科, 朱晓新, 等. 黄精保健食品的开发现状及产业发展分析[J]. 湖南中医药大学学报,2020,40(7):853−859. [YANG Ziyu, YANG Ke, ZHU Xiaoxin, et al. Development status and industry development analysis of Polygonati Rhizoma health-care food[J]. Journal of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine,2020,40(7):853−859. YANG Ziyu, YANG Ke, ZHU Xiaoxin, et al. Development status and industry development analysis of Polygonati Rhizoma health-care food[J]. Journal of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(7): 853−859.
[10] 王彩步, 段宝忠. 云南不同种植基地滇黄精中多糖含量测定分析[J]. 大理大学学报,2018,3(2):14−17. [WANG Caibu, DUAN Baozhong. Determination and analysis of polysaccharide in Polygonatum kingianum from different planting bases in Yunnan[J]. Journal of Dali University,2018,3(2):14−17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-2266.2018.02.004 WANG Caibu, DUAN Baozhong. Determination and analysis of polysaccharide in Polygonatum kingianum from different planting bases in Yunnan[J]. Journal of Dali University, 2018, 3(2): 14−17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-2266.2018.02.004
[11] 张晓灿, 罗丹丹, 陶爱恩, 等. 基于指纹图谱和化学计量学的丹参及紫丹参质量评价研究[J]. 中药材,2017,40(5):1061−1065. [ZHANG Xiaocan, LUO Dandan, TAO Aien, et al. Species differentiation and quality assessment of Salvia miltiorrhiza and Salvia trijuga by HPLC fingerprint[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials,2017,40(5):1061−1065. ZHANG Xiaocan, LUO Dandan, TAO Aien, et al. Species differentiation and quality assessment of Salvia miltiorrhiza and Salvia trijuga by HPLC fingerprint[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2017: 40(5): 1061−1065.
[12] 段宝忠, 黄林芳, 尚飞能, 等. 云南野生抚育粗茎秦艽药材的品质评价[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2013,19(21):82−86. [DUAN Baozhong, HUANG Linfang, SHANG Feineng, et al. Quality evaluation of wildlife tending Gentiana crassicaulis in Yunnan Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2013,19(21):82−86. DUAN Baozhong, HUANG Linfang, SHANG Feineng, et al. Quality evaluation of wildlife tending Gentiana crassicaulis in Yunnan Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2013, 19(21): 82−86.
[13] DUAN B Z, HUANG L F CHEN S L. Chemical fingerprint analysis of Fritillaria delavayi Franch. by high-performance liquid chromatography[J]. Journal of Separation Science,2015,35(4):513−518.
[14] 何连军, 干雅平, 吕伟德, 等. 高效阴离子交换色谱-脉冲安培检测法测定多花黄精多糖的单糖组成[J]. 中草药,2017,48(8):1671−1676. [HE Lianjun, GAN Yaping, LÜ Weide, et al. Monosaccharide composition analysis on polysaccharides in Polygonatum cyrtonema by high performance anion-exchange chromatography with pulsed amperometric detection[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2017,48(8):1671−1676. HE Lianjun, GAN Yaping, LÜ Weide, et al. Monosaccharide composition analysis on polysaccharides in Polygonatum cyrtonema by high performance anion-exchange chromatography with pulsed amperometric detection[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2017, 48(8): 1671−1676.
[15] 张雪, 李铮, 张英涛, 等. HPLC-CAD法同时测定白及中单糖、双糖的含量[J]. 国际药学研究杂志,2018,45(2):1547−157. [ZHANG Xue, LI Zheng, ZHANG Yingtao, et al. Simultaneous quantification of monosaccharides and disaccharides in Rhizoma Bletillae by HPLC-CAD[J]. Journal of International Pharmaceutical Research,2018,45(2):1547−157. ZHANG Xue, LI Zheng, ZHANG Yingtao, et al. Simultaneous quantification of monosaccharides and disaccharides in Rhizoma Bletillae by HPLC-CAD[J]. Journal of International Pharmaceutical Research, 2018, 45(2): 1547−157.
[16] MCGREGOR N, ARNAL G, BRUMER H. Quantitative kinetic characterization of glycoside hydrolases using high-performance anion-exchange chromatography (HPAEC)[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology,2017,1588:15−24.
[17] LIU J, ZHOU J, ZHANG Q Q, et al. Monosaccharide analysis and fingerprinting identification of polysaccharides from Poria cocos and Polyporus umbellatus by HPLC combined with chemometrics methods[J]. Chinese Herbal Medicines,2019,11(4):406−411. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2019.05.008
[18] LI H, YANG Z Z, WANG J J, et al. Chemical fingerprint for identification and quality control of saccharides in Danhong injection based on HPLC-ELSD with chemometrics[J]. Chemical Research in Chinese Universities,2019,35(5):782−787. doi: 10.1007/s40242-019-9030-8
[19] XIE M, YU Y, ZHU Z, et al. Simultaneous determination of six main components in Bushen Huoxue prescription by HPLC-CAD[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis,2021,201(2):1−9.
[20] 罗昌明, 吴雪松, 雷明珠, 等. 风湿定片中8种指标成分的HPLC-CAD含量测定研究[J]. 中南药学,2019,17(6):863−867. [LUO Changming, WU Xuesong, LEI Mingzhu, et al. Simultaneous determination of 8 ingredients in Fengshiding tablets by HPLC-CAD[J]. Central South Pharmacy,2019,17(6):863−867. LUO Changming, WU Xuesong, LEI Mingzhu, et al. Simultaneous determination of 8 ingredients in Fengshiding tablets by HPLC-CAD[J]. Central South Pharmacy, 2019, 17(6): 863−867.
[21] 闫丽, 吴莹, 高慧. HPLC-CAD法测定知母盐炙前后4种皂苷含量[J]. 现代中药研究与实践,2019,33(1):46−49. [YAN Li, WU Ying, GAO Hui. Determination of 4 kinds of saponins in Rhizoma Anemarrhenae before and after processing by HPLC-CAD[J]. Research and Practice on Chinese Medicines,2019,33(1):46−49. YAN Li, WU Ying, GAO Hui. Determination of 4 kinds of saponins in Rhizoma Anemarrhenae before and after processing by HPLC-CAD[J]. Research and Practice on Chinese Medicines, 2019, 33(1): 46−49.
[22] 王海洋, 高阳, 高其品, 等. 黄精多糖的柱前衍生化HPLC指纹图谱研究[J]. 湖北农业科学,2016,55(13):3462−3464. [WANG Haiyang, GAO Yang, GAO Qipin, et al. Study on pre-column derivatives HPLC fingerprint of Polygonati polysaccharide[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences,2016,55(13):3462−3464. WANG Haiyang, GAO Yang, GAO Qipin, et al. Study on pre-column derivatives HPLC fingerprint of Polygonati polysaccharide[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 55(13): 3462−3464.
[23] 秦垂新, 曹子丰, 黄绮敏, 等. 黄精多糖水解物柱前衍生HPLC指纹图谱[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2015,21(11):65−68. [QIN Chuixin, CAO Zifeng, HUANG Qimin, et al. Pre-column derivatives HPLC fingerprint of Polygonati Rhizoma polysaccharide hydrolysate[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2015,21(11):65−68. QIN Chuixin, CAO Zifeng, HUANG Qimin, et al. Pre-column derivatives HPLC fingerprint of Polygonati Rhizoma polysaccharide hydrolysate[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2015, 21(11): 65−68.
[24] 周宝珍. UPLC法在不同黄精指纹图谱研究中的应用[J]. 陕西农业科学,2017,63(7):36−39. [ZHOU Baozhen. Application of UPLC method in the study of fingerprints of different Polygonatum[J]. Shaanxi Journal of Agricultural Sciences,2017,63(7):36−39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0488-5368.2017.07.011 ZHOU Baozhen. Application of UPLC method in the study of fingerprints of different Polygonatum[J]. Shaanxi Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 63(7): 36−39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0488-5368.2017.07.011
[25] 杨青, 高华春, 陈红丽, 等. 武夷山及周边地区黄精植物ISSR分子标记鉴定及HPLC指纹图谱研究[J]. 亚热带植物科学,2017,46(1):25−29. [YANG Qing, GAO Huachun, CHEN Hongli, et al. Identification of Polygonatum from Wuyishan and its surrounding areas by ISSR molecular markers and their HPLC fingerprints[J]. Subtropical Plant Science,2017,46(1):25−29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7791.2017.01.005 YANG Qing, GAO Huachun, CHEN Hongli, et al. Identification of Polygonatum from Wuyishan and its surrounding areas by ISSR molecular markers and their HPLC fingerprints[J]. Subtropical Plant Science, 2017, 46(1): 25−29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7791.2017.01.005
[26] SONG J H, CHEN F Z, LIU J, et al. Combinative method using multi-components quantitation and HPLC fingerprint for comprehensive evaluation of Gentiana crassicaulis[J]. Pharmacognosy Magazine,2017,13(49):180−187.
[27] ARYANI S, MOHAMAD R, LATIFAH K. D, et al. Discrimination of red and white rice bran from Indonesia using HPLC fingerprint analysis combined with chemometrics[J]. Food Chemistry,2017,221:1717−1722. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.10.114
[28] LIU X Y, JIANG W W, SU M, et al. Quality evaluation of traditional Chinese medicines based on fingerprinting[J]. Journal of Separation Science,2019,43(1):6−17.
[29] 潘德芳, 吕杨, 陈伟民, 等. 紫外可见分光光度法测定不同年份黄精中多糖含量[J]. 安徽农业科学,2011,39(10):5790−5795. [PAN Defang, LÜ Yang, CHEN Weimin, et al. Test of the content of the polysaccharide in the Polygonatum with different ages with the method of UV-visible spectrophotometry[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2011,39(10):5790−5795. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2011.10.048 PAN Defang, LÜ Yang, CHEN Weimin, et al. Test of the content of the polysaccharide in the Polygonatum with different ages with the method of UV-visible spectrophotometry[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 39(10): 5790−5795. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2011.10.048
[30] 王坤, 岳永德, 汤锋, 等. 多花黄精多糖的分级提取及结构初步分析[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2014,26(3):364−369. [WANG Kun, YUE Yongde, TANG Feng, et al. Sequential extraction and structural analysis of polysaccharides from Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2014,26(3):364−369. [WANG Kun, YUE Yongde, TANG Feng, et al. Sequential extraction and structural analysis of polysaccharides from Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua[J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 2014, 26(3): 364-369.
[31] 茅蕾蕾, 陈颖, 胡碧原, 等. 银杏外种皮多糖的单糖组成分析[J]. 中国中药杂志,2014,39(2):262−266. [MAO Leilei, CHEN Ying, HU Biyuan, et al. Analysis of monosaccharide composition of exotesta polysaccharides of Ginkgo biloba[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2014,39(2):262−266. MAO Leilei, CHEN Ying, HU Biyuan, et al. Analysis of monosaccharide composition of exotesta polysaccharides of Ginkgo biloba[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2014, 39(2): 262−266.
[32] 姜程曦, 张铁军, 陈常青, 等. 黄精的研究进展及其质量标志物的预测分析[J]. 中草药,2017,48(1):1−16. [JIANG Chengxi, ZHANG Tiejun, CHEN Changqing, et al. Research progress of Polygonatum and prediction and analysis of its quality markers[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2017,48(1):1−16. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2017.01.001 JIANG Chengxi, ZHANG Tiejun, CHEN Changqing, et al. Research progress of Polygonatum and prediction and analysis of its quality markers[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2017, 48(1): 1−16. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2017.01.001
[33] 张洪洋, 李叶丹, 王义, 等. 不同产地黄精主要化学成分比较及主成分分析[J]. 黑龙江科技信息,2017,10:87. [ZHANG Hongyang, LI Yedan, WANG Yi, et al. Comparison and principal component analysis of main chemical components of Polygonatum from different producing areas[J]. Heilongjiang Science and Technology Information,2017,10:87. ZHANG Hongyang, LI Yedan, WANG Yi, et al. Comparison and principal component analysis of main chemical components of Polygonatum from different producing areas[J]. Heilongjiang Science and Technology Information, 2017, 10: 87.
[34] 肖琳婧, 刘莹莹, 赵禹, 等. HPLC指纹图谱结合化学计量学的不同产地灯盏花药材和近缘种样品的质量评价[J]. 中草药,2019,50(14):3438−3443. [XIAO Linjing, LIU Yingying, ZHAO Yu, et al. Quality evaluation of Erigeron breviscapus from different origins and its related species by HPLC coupled with chemometrics[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2019,50(14):3438−3443. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2019.14.026 XIAO Linjing, LIU Yingying, ZHAO Yu, et al. Quality evaluation of Erigeron breviscapus from different origins and its related species by HPLC coupled with chemometrics[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2019, 50(14): 3438−3443. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2019.14.026
[35] 胡建勇, 缪明锦, 闻焜, 等. 基于红外光谱结合化学计量学及HPLC色谱的紫丹参及其近缘种成分差异[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2019,25(15):8−14. [HU Jianyong, MIAO Mingjin, WEN Kun, et al. Identification of Salviae yunnanensis Radix et Rhizoma and its allied species based on chemical composition by FTIR with chemometric analysis and HPLC fingerprint[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2019,25(15):8−14. HU Jianyong, MIAO Mingjin, WEN Kun, et al. Identification of Salviae yunnanensis Radix et Rhizoma and its allied species based on chemical composition by FTIR with chemometric analysis and HPLC fingerprint[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2019, 25(15): 8−14.
[36] 卢森华, 黎强, 樊文研, 等. HPLC特征指纹图谱结合化学计量学评价不同产地消瘤藤的药材质量[J]. 现代中药研究与实践,2020,34(6):52−56. [LU Senhua, LI Qiang, FAN Wenyan, et al. HPLC fingerprint combined with chemometrics to evaluate the quality of Pileostegia tomentella from different areas[J]. Research and Practice on Chinese Medicines,2020,34(6):52−56. LU Senhua, LI Qiang, FAN Wenyan, et al. HPLC fingerprint combined with chemometrics to evaluate the quality of Pileostegia tomentella from different areas[J]. Research and Practice on Chinese Medicines, 2020, 34(6): 52−56.
[37] 刘佳, 朱翔, 叶宏达, 等. 云南多花黄精适宜采收期初步研究[J]. 中国农学通报,2017,33(27):88−91. [LIU Jia, ZHU Xiang, YE Hongda, et al. The appropriate collection period of Polygonatum cyrtonema in Yunnan[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2017,33(27):88−91. doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb17060006 LIU Jia, ZHU Xiang, YE Hongda, et al. The appropriate collection period of Polygonatum cyrtonema in Yunnan[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2017, 33(27): 88−91. doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb17060006
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 王玉净,都治香,张霞,王旭,王娜. 沙棘黄酮通过调控TLR4/NF-κB信号通路改善大鼠多囊卵巢综合征的作用. 食品工业科技. 2024(16): 340-347 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 王杰,常晨城,杨彦达,郭丽丽,张景萍,付绍印,石彩霞,张文广. 黄酮在反刍动物生产中的应用研究进展. 饲料研究. 2023(12): 144-147 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 陈美庆,朱卫丰,管咏梅,冯育林,张艳丽,景秀村,彭万钱,欧阳辉,李琼. 基于UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS技术分析葛根配方颗粒的化学成分. 中国实验方剂学杂志. 2023(19): 176-186 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



