Induction of Melatonin Treatment on the Priming Resistance in Postharvest Plum Fruit
-
摘要: 研究了褪黑素(melatonin,MT)处理诱导采后李果实抗病反应的特征和效力。“凤凰”李果实经10 mmol/L褪黑素(melatonin,MT)处理及病原菌匍枝根霉(Rhizopus stolonifer)接种后,于20 ℃下贮藏5 d,期间观察果实病害发展情况,并测定果实H2O2、总酚、木质素含量以及抗性相关酶活性。结果显示,10 mmol/L MT处理能有效降低李果实采后R. stolonifer导致的根霉病发病率并延缓增加其病斑直径。单一MT处理能诱导李果实中苯丙烷类代谢酶活性及总酚和木质素含量的上升;但MT处理复合R. stolonifer接种则最显著的诱导果实H2O2迸发,同时提升几丁质酶、β-1,3-葡聚糖酶、苯丙氨酸解氨酶、肉桂酸-4-羟基化酶、4-香豆酸辅酶A连接酶、过氧化物酶和多酚氧化酶等抗病相关酶活性以及总酚和木质素含量。通过这些结果可推测,MT处理可诱导李果实priming反应,使果实在遭受病原菌侵染时展现更强烈的抗病反应,从而维持果实贮藏期间的商品性。Abstract: This study aimed to research the effectiveness and mode of the disease resistance induced by melatonin (MT) treatment in postharvest plum fruit. Plum fruit Cv ‘Fenghuang’ were treated with 10 mmol/L MT and/or inoculated with R. stolonifer, then stored for 5 days (20 ℃). Disease development, the contents of H2O2, total phenol and lignin and the activities of resistance-related enzyme were determined during the storage. The results showed that 10 mmol/L treatment effectively lowered the disease incidence and delayed the increase of lesion diameter of Rhizopus rot caused by R. stolonifer in plums. Single MT treatment could induce the activities of phenylpropanoid metabolic enzymes and the contents of total phenol and lignin in plums. MT treatment combined with R. tolonifer inoculation showed most significantly effects on the induction of H2O2 burst, and the activities of disease-resistance related enzymes such as chitinase, β-1,3-glucanase, phenylalanine ammonialyase (PAL), cinnamate-4-hydroxylase (C4H), 4-coumaric acid coenzyme A ligase (4-CL), peroxidase (POD) and polyphenol oxidase (PPO) as well as contents of total phenol and lignin in the samples during the storage. These results suggested that the MT treatment could activate the strong and rapid disease resistance upon the pathogenic infection by an induction of priming defence, by which the treatment resultantly maintained the overall quality in plums during the postharvest storage.
-
Keywords:
- melatonin /
- plum /
- induced resistance /
- priming /
- Rhizopus stolonifer
-
李(Prunus salicina Lindl.)为蔷薇科李属植物,其成熟果实的果色多样,口感酸甜多汁且富含诸多有益人体健康的生物活性化合物,如多酚类化合物、类胡萝卜素和抗坏血酸等,因此深受大众欢迎[1]。但李果实属于呼吸跃变型果实,且采摘期又逢高温季节(6~8月),采后呼吸和乙烯释放速率高,果实在贮藏期间迅速软化,因此易受到病原菌侵染而加速果实腐烂,从而失去商业性,其中,匍枝根霉(Rhizopus stolonifer)是主要的致病菌,极易引起李果实采后品质劣变,造成严重的经济损失[2]。以化学杀菌剂(如噻菌灵、仲丁胺、扑海因等)来控制李果实采后病害的效果极为显著,但化学残留及病原菌耐药性等问题严重限制了药剂保鲜的应用[3]。现阶段,众多绿色环保的化学激发子如水杨酸、茉莉酸及其甲酯衍生物、苯丙噻唑硫代乙酸甲酯(BTH)、β-氨基丁酸(BABA)、油菜素内酯等均被证实可有效诱导果蔬抗病性,降低病害发生率[4]。因此,采用激发子诱导果实采后抗性是替代化学杀菌剂的可能途径。诱导抗病性包括直接诱导作用和敏化(Priming)反应,Priming反应是指植物经激发子处理后只有受到病原菌侵染时才展现出更快、更强的抗病性反应,包括抗病基因表达、植保素合成等,是一种低成本、高效的抗病防御机制[5]。
褪黑素(melatonin,MT)是动植物中广泛存在的一种吲哚胺类激素,可参与众多信号传导过程从而调控细胞抗逆性反应以及能量和物质代谢[6]。研究表明,采后MT处理可显著抑制采后香蕉[7]和梨果实[8]中乙烯合成,并维持桃[9]、荔枝[10]、石榴[11]等果实活性氧代谢平衡,进而延缓这些果实在贮藏期间的品质劣变速度。此外,外源MT还可诱导模式作物拟南芥和烟草中水杨酸和乙烯介导的一系列防御基因的表达,激活植株防卫反应[12]。但MT处理对采后果实抗病性的具体诱导模式仍不明确。本研究以“凤凰”李果实为试材,通过研究MT处理对李果实贮藏期间H2O2、抗性相关酶活性及苯丙烷类代谢的影响,分析MT对李果实抗病性的诱导作用,为MT处理在李果实实际保鲜中的推广提供数据支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
八分熟的“凤凰”李(Prunus salicina cv ‘Fenghuang’) 于2020年6月采自四川省遂宁市船山区仁里镇有机李种植基地,采摘后2 h内运回实验室,先将有病虫害和机械伤的李果实去除,挑选转色均匀、大小一致的果实摊于实验台,经自然风散去田间热;匍枝根霉(Rhizopus stolonifer)参考Li等[13]的方法进行分离、纯化及鉴定,以传代培养后的菌丝体为材料,用无菌生理盐水缓慢冲洗出成熟根霉孢子,并将孢子浓度稀释为1.0×105 个/mL(血球计数板),现配现用;褪黑素(MT)、几丁质、Follin试剂、4-香豆酸 美国Sigma公司;邻苯二酚、亚油酸钠、L-苯丙氨酸、N-乙酰葡萄糖胺、亚硫酸钠、三羟甲基氨基甲烷(Tris)、愈创木酚 重庆拓世众和生物技术有限公司;3, 5-二硝基水杨酸(DNS)、昆布多糖、对二甲氨基甲醛(DMAB) 上海源叶有限公司。
PAL-1型数显折光仪 日本爱拓公司;DW-86L328型超低温冰箱 浙江捷胜设备有限公司;HWS-P400C恒温恒湿培养箱 合肥达斯卡特科技有限公司;UT-1900型全波长分光光度计 北京普析通用仪器有限责任公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品处理
MT处理浓度参考Bal[14]的实验结果进行确定。李果实以75%(v/v)乙醇溶液表面擦拭并晾干,随后用无菌解剖针在果实最大横截面处对称穿孔2个(2 mm×2 mm),随后随机划分为4份:对照组:用移液枪在李果实穿刺部位注入15 μL无菌蒸馏水;MT处理组:将10 μL浓度为10 mmol/L的MT溶液注入李果实穿刺部位;R. stolonifer接种组:每个穿刺部位注入15 μL的1.0×105 个/mL的孢子悬浮液;MT+R. stolonifer处理组:先在李果实穿刺部位注入15 μL 10 mmol/L的MT溶液,于20 ℃放置6 h,随后在各穿刺处接种15 μL的1.0×105 个/mL R. stolonifer孢子悬浮液。以上处理完成后,用PE塑料盒进行分装,每盒6颗果实,每个处理组共15盒,置于(20±1)℃、80 %~90% RH条件下贮藏5 d。在此期间每天观察李果实根霉病的发病情况,同时取样用无菌手术刀切取健康果肉组织于液氮速冻再置于−80 ℃超低温冰箱中保存,用于后续指标测定。各处理均重复3次,整个实验重复2次。
1.2.2 发病率和病斑直径的测定
李果实病斑直径超过2 mm时,则可认为是发病果;病果病斑直径用游标卡尺直接确定。
1.2.3 H2O2含量的测定
称取1 g果实冻样,加入5 mL冷丙酮匀浆,匀浆液超声提取1 h后于2 ℃,10000×g离心10 min。收集上清液根据Patterson等[15]的方法测定H2O2含量,结果以nmol/g FW表示。
1.2.4 细胞壁水解酶活性的测定
根据Abeles等[16]的方法测定几丁质酶和β-1,3-葡聚糖酶活性,以每小时催化生成1 mg N-乙酰葡萄糖胺为1个几丁质酶活单位,以每小时形成1 mg葡萄糖为1个β-1,3-葡聚糖酶活单位;以上酶活性结果均以U/g FW表示。
1.2.5 苯丙烷类代谢途径关键酶活性的测定
根据Zucker[17]的方法测定苯丙氨酸解氨酶(PAL)活性,每小时反应液在290 nm处吸光度增加0.01为1个酶活力单位;根据范存斐等[18]的方法测定肉桂酸-4-羟基化酶(C4H)和4-香豆酸辅酶A连接酶(4-CL)活性,以每小时反应液在340 nm处吸光度增加0.01为1个C4H酶活性单位,以每分钟反应液在333 nm处吸光度增加0.01为1个4-CL酶活性单位;根据Cao等[19]的方法测定过氧化物酶(POD)活性,以每分钟酶促反应体系在470 nm处吸光度增加0.01为1个酶活性单位;以上酶活性结果均以U/g FW表示。
1.2.6 总酚及木质素含量的测定
根据Flion-Ciocalteu法[20]测定总酚含量;木质素含量则参照Wang等[21]的方法进行测定。总酚和木质素含量结果均以mg/g FW表示。
1.2.7 脂氧合酶(LOX)和多酚氧化酶(PPO)活性的测定
根据Lin等[22]的方法测定LOX活性,略有修改;用4 ℃预冷的磷酸缓冲液(0.1 mol/L、pH6.8)冰浴提取LOX粗酶液。取2.75 mL 0.1 mol/L、pH5.5乙酸-乙酸钠缓冲液、0.05 mL浓度为0.1 mol/L的亚油酸钠溶液,在30 ℃保温10 min后加入0.2 mL粗酶液混匀,以反应液每分钟在234 nm处吸光度增加0.01为1个LOX活性单位;根据Cao等[19]的方法测定PPO活性,以每分钟酶促反应体系420 nm处吸光度增加0.01为1个酶活性单位;以上酶活性结果均以U/g FW表示。
1.3 数据处理
除果实根霉病发病率和病斑直径重复测定5次外,其余各指标均重复测定3次。绘图采用Excel 2010,差异显著性检验采用SPSS26.0(Duncan多重比较法),其中显著水平设定为5%。
2. 结果与分析
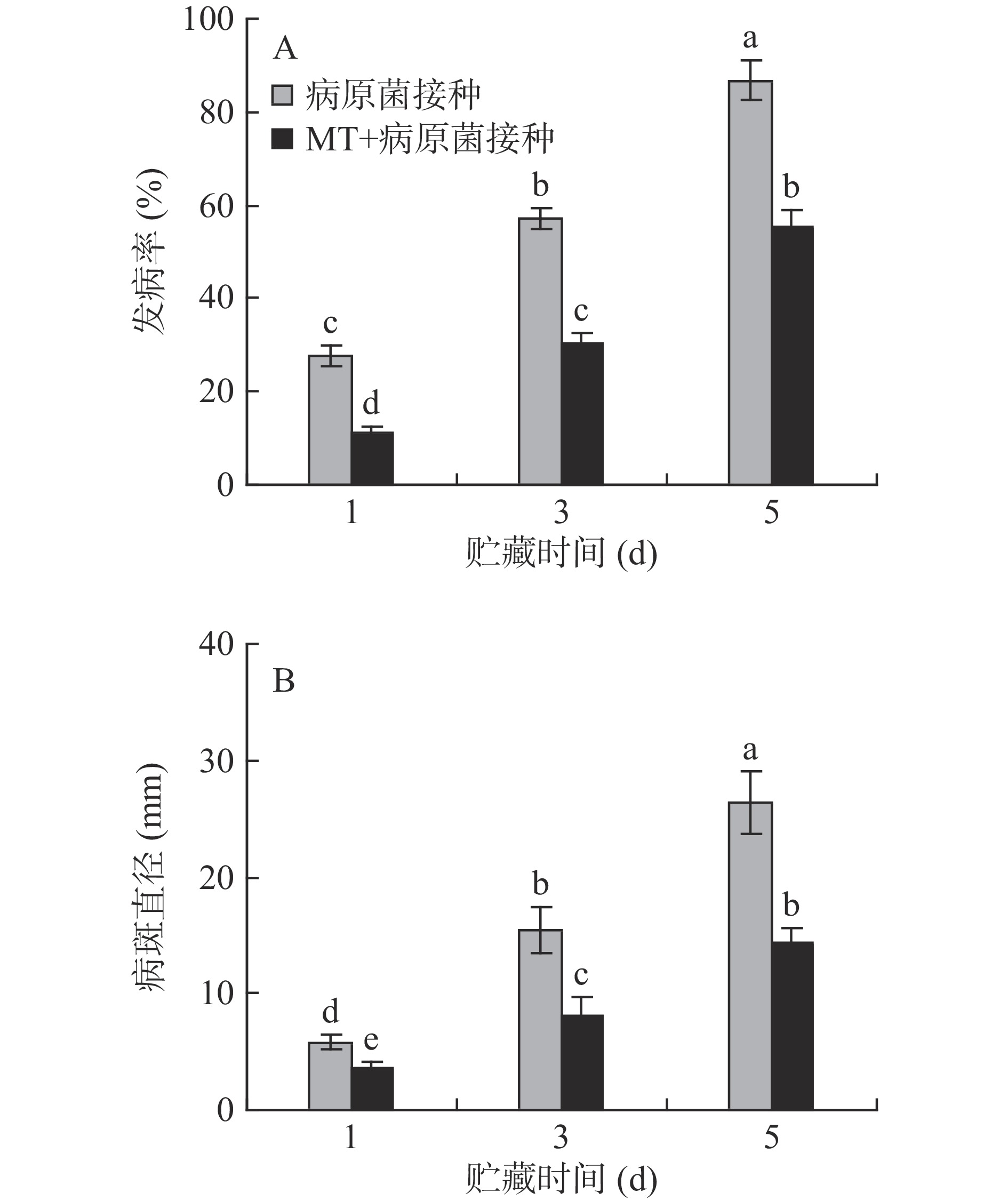
2.1 MT处理和R. stolonifer接种对采后李果实根霉病的影响
对照组和MT处理组李果实的表观无明显变化,未见明显的发病果实;李果实接种R. stolonifer后发病率不断上升,同时病斑直径也急剧增加。贮藏5 d后,MT+R. stolonifer接种组的果实发病率为55.35%,病斑直径为14.31 mm,较只接种R. stolonifer的果实分别下降了36.24%和45.65%,说明MT处理能够有效控制李果实采后病害的发生(图1A、B)。
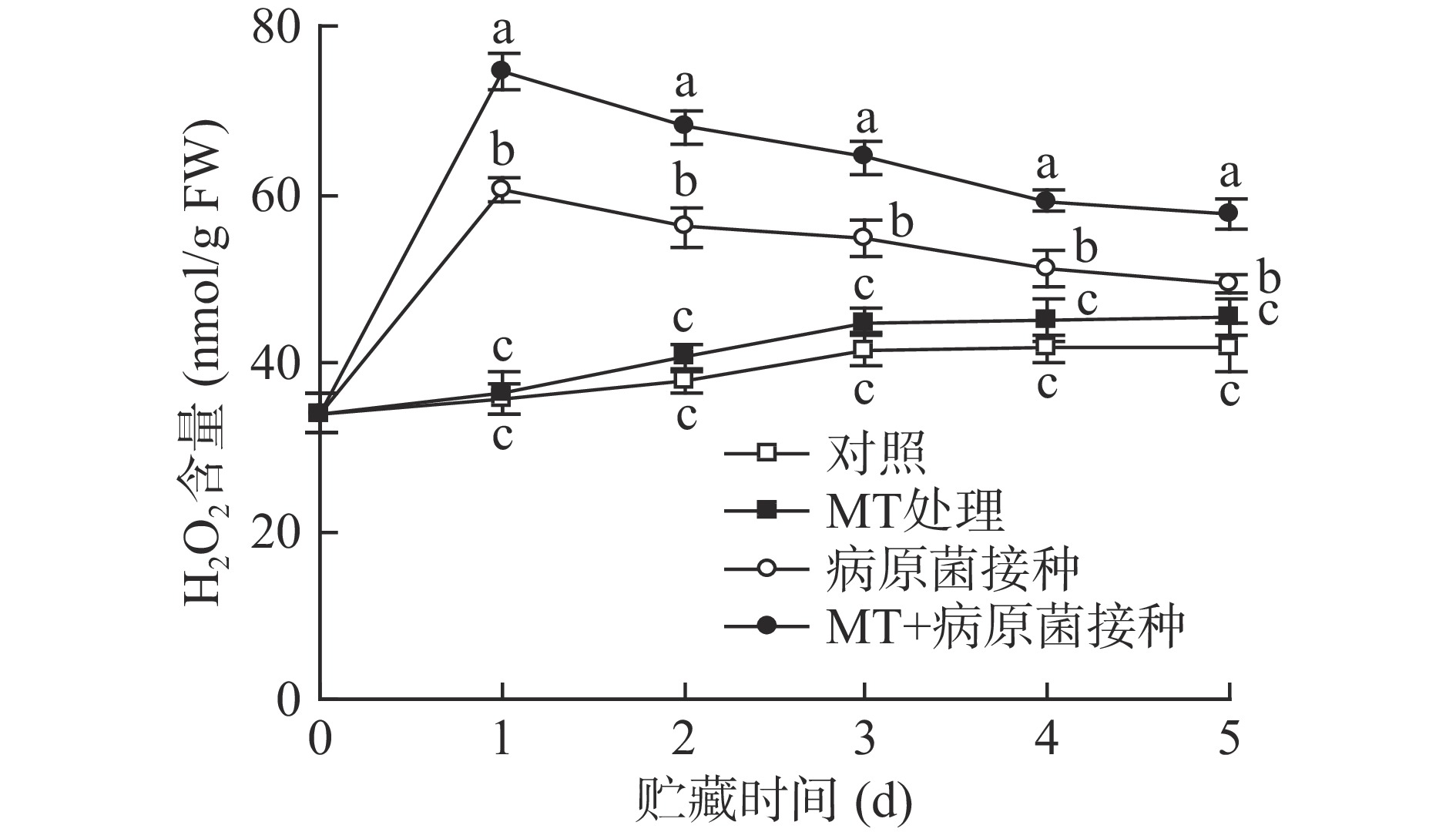
2.2 MT处理和R. stolonifer接种对采后李果实H2O2含量的影响
如图2所示,对照李果实在20 ℃贮藏期间H2O2含量呈缓慢上升趋势。单一MT处理组与对照组之间的H2O2含量无显著差异(P>0.05),而接种R. stolonifer的李果实H2O2含量大幅上升,并在贮藏第1 d达峰值,随后不断下降,由于果蔬在受到病原菌侵染时会产生应激反应,H2O2迸发是典型的应激反应,所以在接种后会大量生成。与单一接种R. stolonifer的果实相比,MT+R. stolonifer接种则更为显著(P<0.05)的诱导了李果实中H2O2的生成,其含量峰值较单一接种组上升了31.90%。
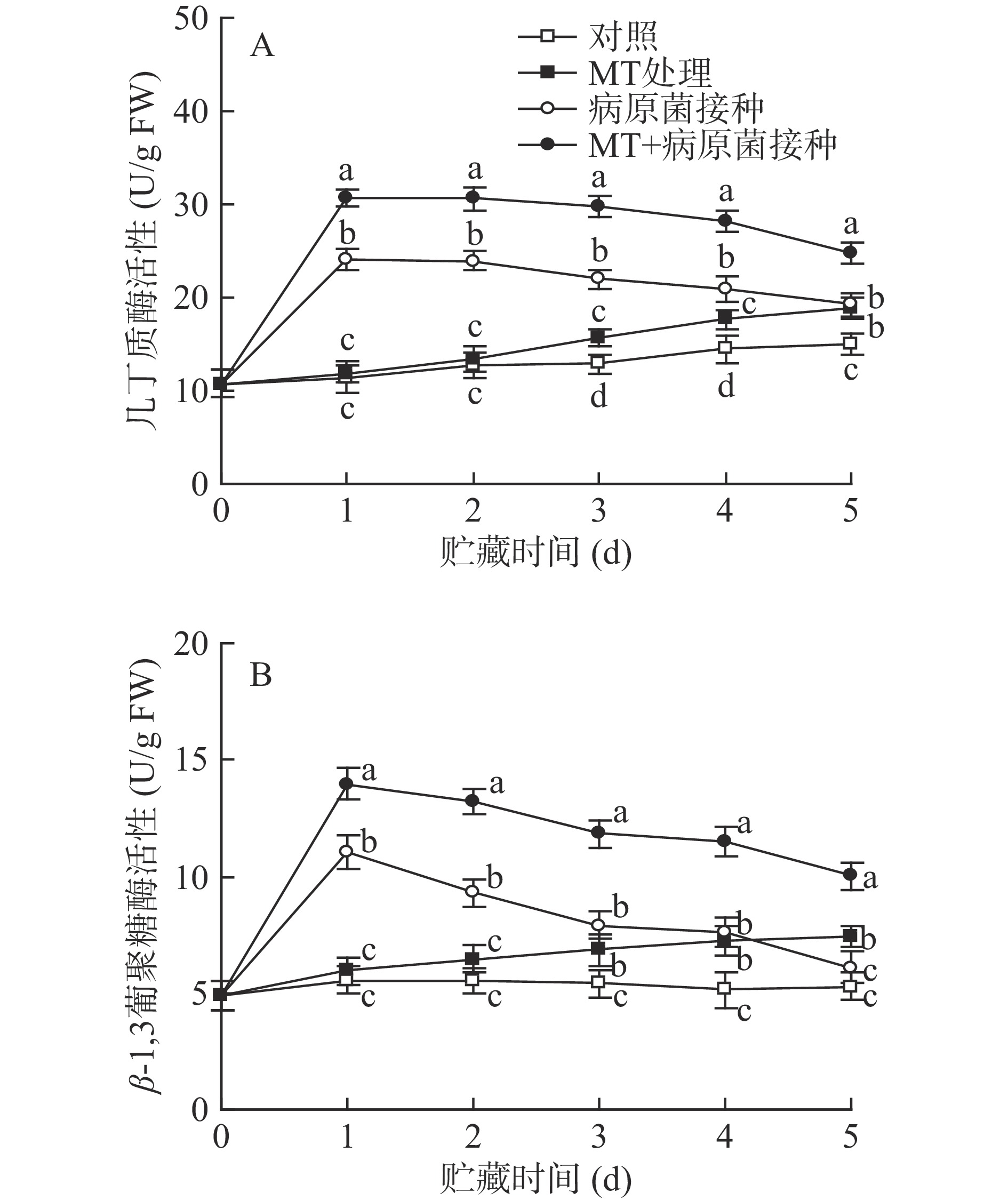
2.3 MT处理和R. stolonifer接种对采后李果实细胞壁水解酶活性的影响
如图3所示,对照李果实中几丁质酶和β-1,3-葡聚糖酶的活性在整个贮藏期间保持稳定。经单一MT处理的果实中几丁质酶和β-1,3-葡聚糖酶活性在贮藏期间逐渐上升,在贮藏3 d后其活性显著(P<0.05)高于对照组水平;接种R. stolonifer后,几丁质酶和β-1,3-葡聚糖酶活性迅速上升,并在第1 d达到峰值水平,随后呈逐渐下降趋势,因为几丁质酶和β-1,3-葡聚糖酶对病原菌有抑制作用,是植物中典型的抗病相关酶,所以当葡萄果实遭受病原菌侵染时,其活性被立即诱导。MT+R. stolonifer接种处理可明显诱导两种酶在整个贮藏期间保持较高活性,其活性值在各取样点均显著(P<0.05)高于单一接种R. stolonifer果实。
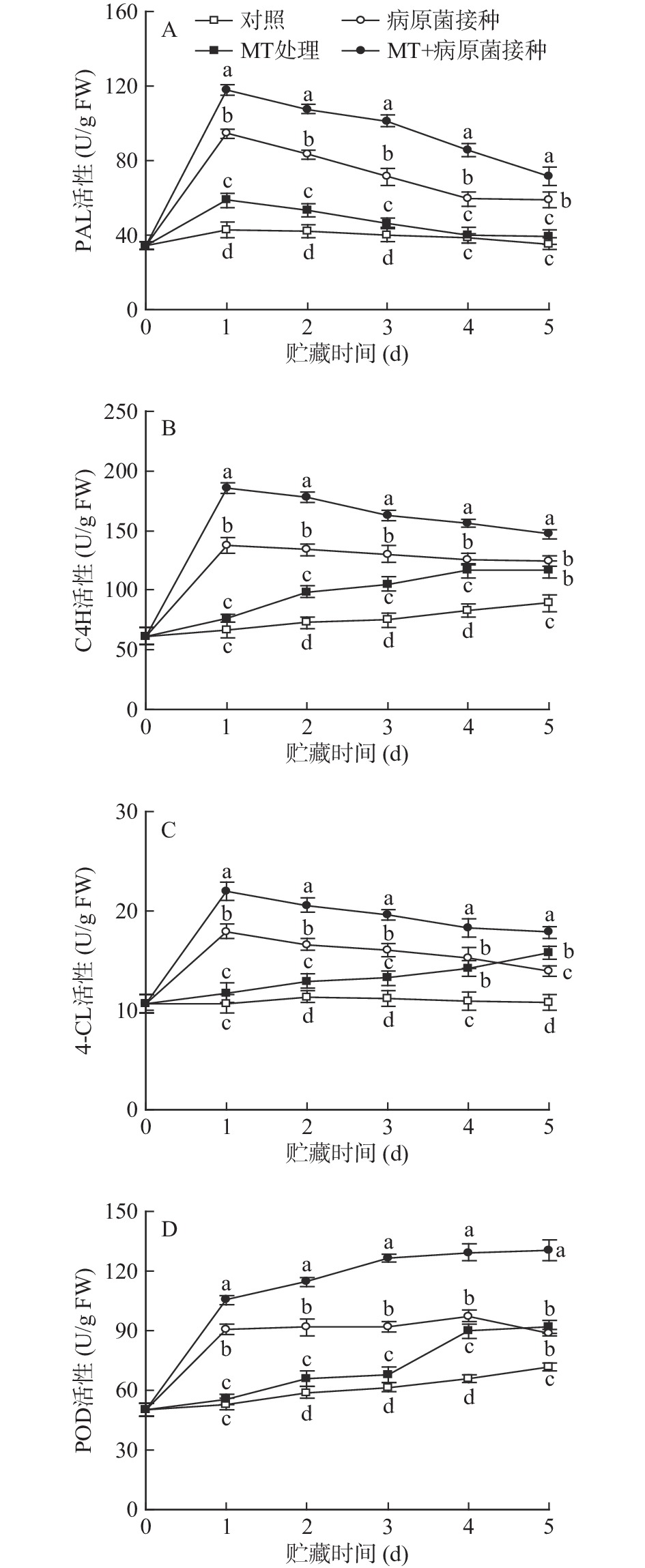
2.4 MT处理和R. stolonifer接种对采后李果实苯丙烷类代谢途径关键酶活性的影响
如图4所示,在贮藏期间,对照组李果实中PAL和4-CL的活性基本维持稳定,C4H和POD活性则缓慢上升。MT处理可有效提高上述苯丙烷类代谢途径关键酶活性。李果实接种R. stolonifer后,PAL、C4H、4-CL和POD活性迅速上升;MT+R. stolonifer接种处理可更为显著诱导李果实中PAL、C4H、4-CL和POD活性的上升,使酶活性在整个贮藏期间均显著(P<0.05)高于单一接种处理水平。
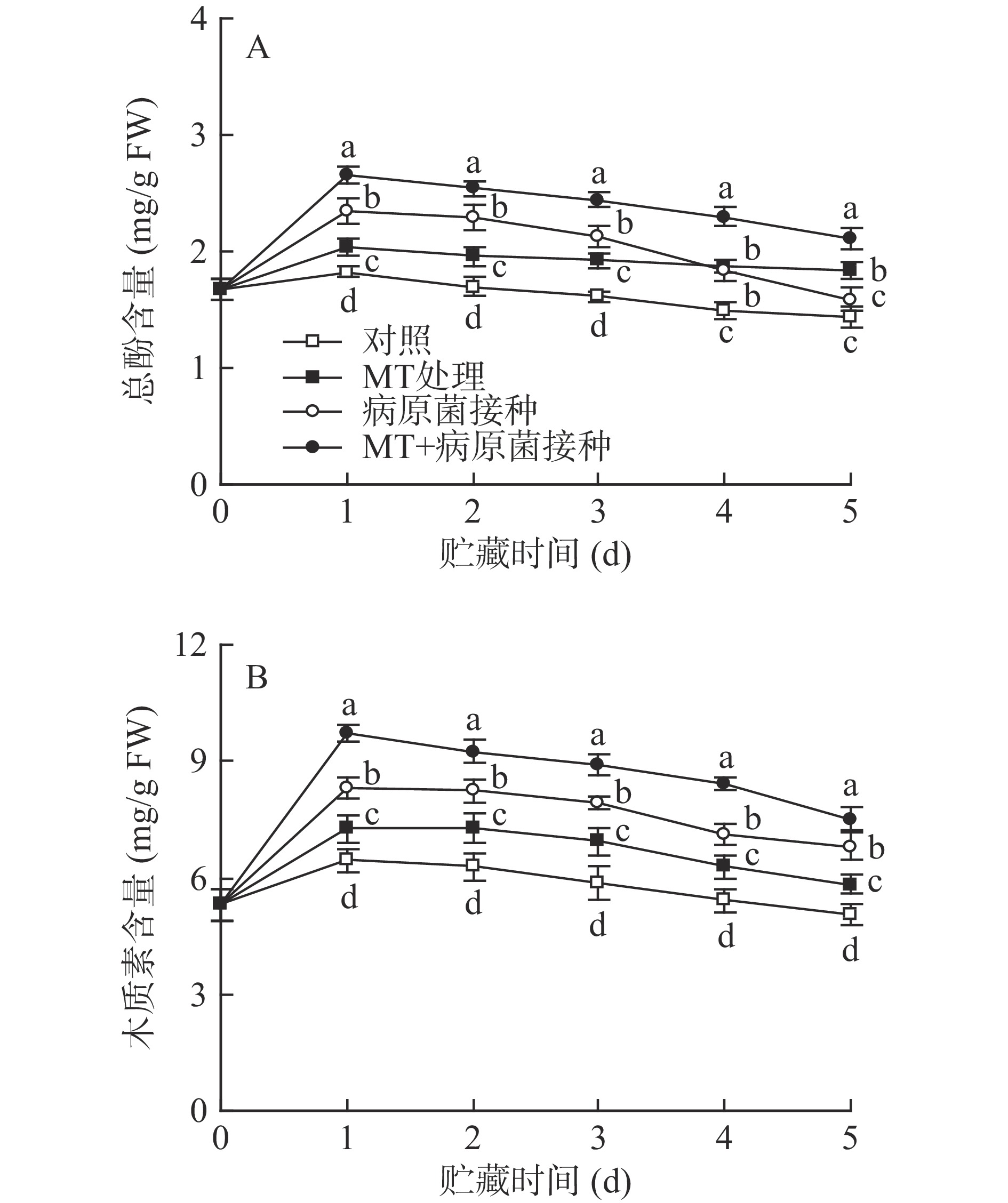
2.5 MT处理和R. stolonifer接种对采后李果实总酚及木质素含量的影响
如图5所示,对照组李果实在20 ℃贮藏过程中,其总酚和木质素含量在第1 d达峰值,随后逐渐降低。MT处理有效促进了李果实总酚和木质素含量的积累,使两者含量在贮藏期间显著(P<0.05)高于对照水平。R. stolonifer接种显著提高了李果实总酚和木质素的含量,但经MT+R. stolonifer接种处理的果实中总酚及木质素含量在整个贮藏期间均显著(P<0.05)高于单一接种组水平。
2.6 MT处理和R. stolonifer接种对采后李果实LOX和PPO活性的影响
如图6所示,采后贮藏期间,对照组李果实中LOX活性随贮藏时间的延长而缓慢上升,同时PPO活性基本维持稳定。单一MT处理组李果实中LOX活性在贮藏期间缓慢上升,PPO活性保持稳定。R. stolonifer接种显著(P<0.05)诱导李果实LOX和PPO活性水平的上升;而与单一R. stolonifer接种组相比,MT+R. stolonifer接种处理可更显著(P<0.05)提升李果实贮藏期间这两种酶的活性水平,使其保持在较高水平。
3. 讨论
MT为植物内源吲哚类激素,其通过信号传导作用参与植物的众多抗逆反应[23]。外源MT处理可有效延缓番茄[24]、水蜜桃[9]、樱桃[25]和草莓[26]等多种果实的采后衰老进程,维持果实综合品质。在本研究中,10 mmol/L MT处理可有效诱导李果实中活性氧迸发、提高抗病相关酶活性并促进总酚和木质素的合成,从而抑制采后贮藏期间果实根霉病的发生,维持果实的综合品质。
根据植物诱导抗性理论,抗病性的表达是一种典型植物应激反应,可调动组织和细胞内的底物和能量从正常的代谢途径转入病程相关基因(pathogenesis-related genes,PRs)的表达和抑菌物质的合成,因此可能限制植物的生长和发育;priming反应是植物免疫系统的共同特征,也是植物诱导抗病性的重要细胞机制,是一种基于代谢平衡和防卫反应的植物抗性模式,可显著减少植物的适应度损失[27]。研究表明,多种物理、化学和生物等激发子在低浓度状态下使用时,均可有效诱导果实的priming反应,从而使果实在受到病原菌严重侵染时表达强烈抗性。团队前期研究也证明,BABA(10~50 mmol/L)、BTH(0.1 mmol/L)和茉莉酸甲酯(10 μmol/L)等激发子均可通过诱导杨梅[21]、草莓[28]和葡萄[29]等果实的priming反应,来提升果实采后抗性,同时也促进了可溶性糖的积累。此外,H2O2迸发是植物受到病原微生物侵染的典型应激反应,其充当信号分子启动植物超敏反应,从而提升果实抗性反应[30];几丁质酶和β-1,3-葡聚糖酶为植物重要的细胞壁水解酶,其可特异性水解真菌细胞壁,阻碍病原菌的进一步侵染[16];植物苯丙烷类代谢途径是合成酚类和木质素等抗菌物质的主要途径,PAL、4-CL、C4H和POD是该途径的关键酶类[31]。LOX不仅参与调节植物的生长发育、成熟衰老等过程,在乙烯介导的抗病反应中也起着重要的调控作用[22]。在本研究中,经单一10 mmol/L MT处理的李果实中苯丙烷类代谢酶以及总酚和木质素含量在整个贮藏期间均高于对照果实,但MT处理对抗病相关酶的诱导作用有限;当经MT处理的果实再接种R. stolonifer后,果实内H2O2含量、几丁质酶和β-1,3-葡聚糖活性以及苯丙烷类代谢酶(PAL、4-CL、C4H和POD)活性、木质素和总酚含量在贮藏第1 d均出现明显峰值,并在整个贮藏期间均显著高于单一接种水平。这些结果说明,MT处理诱导的李果实抗病反应可归为priming反应类型,即单一MT处理可使果实处于防御准备(primed)状态,随后病原菌侵染时则迅速激活并放大防卫反应,阻止病原菌的进一步侵染,从而降低腐烂率并缩小病斑直径。此外,MT+R. stolonifer处理也能显著诱导LOX活性的上升,暗示MT诱导的李果实priming反应可能是由乙烯介导的ISR(induced systemic resistance,诱导系统抗性)类型。与本研究相类似,众多根瘤菌也可通过乙烯或茉莉酸途径诱导植物的priming反应[32]。但同时,MT也可通过水杨酸(SA)途径诱导采后草莓果实SAR(systemic acquired resistance,系统获得性抗性)反应从而提高抗病性[26]。因此,MT调控不同信号传导路径防卫反应的相关分子机理有待进一步阐明。
4. 结论
a.10 mmol/ L MT可有效诱导采后李果实抗病相关酶活性以及总酚和木质素含量的提高,从而提升抗病性,减少采后贮藏期间根霉病的发生。
b.经MT诱导的李果实在遭受病原菌侵染时可展现出强烈的活性氧迸发、较高的抗病相关酶活性及抗病相关物质含量增加,暗示该防卫反应归因于一种典型的priming反应机制。
-
-
[1] MARTÍNEZ-ESPLÁ A, ZAPATA P J, VALERO D, et al. Preharvest treatments with salicylates enhance nutrient and antioxidant compounds in plum at harvest and after storage[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2018,98(7):2742−2750. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.8770
[2] ANDRADE S C A, BARETTO T A, ARCANJO N M O, et al. Control of Rhizopus soft rot and quality responses in plums (Prunus domestica L.) coated with gum arabic, oregano and rosemary essential oils[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation,2017,41(6):e13251. doi: 10.1111/jfpp.13251
[3] LUCAS J A, HAWKINS N J, FRAAIJE B A. The evolution of fungicide resistance[J]. Advances in Applied Microbiology,2015,90:29−92.
[4] YASSIN M, TON J, ROLFE S A. The rise, fall and resurrection of chemical-induced resistance agents[J]. Pest Management Science,2021,77(9):3900−3909. doi: 10.1002/ps.6370
[5] CONRATH U, BECKERS G J, FLORS V, et al. Priming: Getting ready for battle[J]. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions,2006,19(10):1062−1071. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-19-1062
[6] ARNAO M B, HERNANDEZRUIZ J. Melatonin and its relationship to plant hormones[J]. Annals of Botany,2018,121(2):195−207. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcx114
[7] HU W, YANG H, TIE W W, et al. Natural variation in banana varieties highlights the role of melatonin in postharvest ripening and quality[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2017,65(46):9987−9994. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b03354
[8] ZHAI R, LIU J L, LIU F X, et al. Melatonin limited ethylene production, softening and reduced physiology disorder in pear (Pyrus communis L.) fruit during senescence[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2018,139:38−46. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2018.01.017
[9] GAO H, ZHANG Z K, CHAI H K, et al. Melatonin treatment delays postharvest senescence and regulates reactive oxygen species metabolism in peach fruit[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2016,118:103−110. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2016.03.006
[10] WANG T, HU M, YUAN D, et al. Melatonin alleviates pericarp browning in litchi fruit by regulating membrane lipid and energy metabolisms[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2020,160:111066. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2019.111066
[11] AGHDAM M S, LUO Z, LI L, et al. Melatonin treatment maintains nutraceutical properties of pomegranate fruits during cold storage[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,303:125385. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125385
[12] LEE H Y, BYEON Y, BACK K, et al. Melatonin as a signal molecule triggering defense responses against pathogen attack in Arabidopsis and tobacco[J]. Journal of Pineal Research,2014,57(3):262−268. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12165
[13] LI C H, CAO S F, WANG K T, et al. Heat shock protein HSP24 is involved in the baba-induced resistance to fungal pathogen in postharvest grapes underlying an npr1-dependent manner[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science,2021,12:292.
[14] BAL E. Physicochemical changes in ‘Santa Rosa’ plum fruit treated with melatonin during cold storage[J]. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization,2019,13(3):1713−1720. doi: 10.1007/s11694-019-00088-6
[15] PATTERSON B D, MACRAE E A, FERGUSON I B, et al. Estimation of hydrogen peroxide in plant extracts using titanium (IV)[J]. Analytical Biochemistry,1984,139(2):487−492. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90039-3
[16] ABELES F B, BOSSHART R P, FORRENCE L E, et al. Preparation and purification of glucanase and chitinase from bean leaves[J]. Plant Physiology,1971,47(1):129−134. doi: 10.1104/pp.47.1.129
[17] ZUCKER M. Sequential induction of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and a lyase-inactivating system in potato tuber disks[J]. Plant Physiology,1968,43(3):365−374. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.3.365
[18] 范存斐, 毕阳, 王云飞, 等. 水杨酸对厚皮甜瓜采后病害及苯丙烷代谢的影响[J]. 中国农业科学,2012,45(3):584−589. [FAN C F, BI Y, WANG Y F, et al. Effect of salicylic acid dipping on postharvest diseases and phenylpropanoid pathway in muskmelon fruits[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2012,45(3):584−589. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2012.03.022 FAN C F, BI Y, WANG Y F, et al. Effect of salicylic acid dipping on postharvest diseases and phenylpropanoid pathway in muskmelon fruits[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica , 2012, 45(3): 584-589. doi: 10.3864/j.issn.0578-1752.2012.03.022
[19] CAO S F, ZHENG Y H, YANG Z F, et al. Effect of methyl jasmonate on the inhibition of Colletotrichum acutatum infection in loquat fruit and the possible mechanisms[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2008,49(2):301−307. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2007.12.007
[20] SLINKARD K, SINGLETON V L. Total phenol analysis: Auto-mation and comparison with manual methods[J]. American Journal of Enology and Viticulture,1977,28(1):49−55.
[21] WANG K T, JIN P, HAN L, et al. Methyl jasmonate induces resistance against Penicillium citrinum in Chinese bayberry by priming of defense responses[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2014,98:90−97. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2014.07.009
[22] LIN Y F, LIN H T, LIN Y X, et al. The roles of metabolism of membrane lipids and phenolics in hydrogen peroxide-induced pericarp browning of harvested longan fruit[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2016,111:53−61. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2015.07.030
[23] FENG X, WANG M, ZHAO Y, et al. Melatonin from different fruit sources, functional roles, and analytical methods[J]. Trends in Food Science and Technology,2014,37(1):21−31. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgs.2014.02.001
[24] SUN Q, ZHANG N, WANG J, et al. Melatonin promotes ripening and improves quality of tomato fruit during postharvest life[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany,2015,66(3):657−668. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eru332
[25] XIA H, SHEN Y, SHEN T, et al. Melatonin accumulation in sweet cherry and its influence on fruit quality and antioxidant properties[J]. Molecules,2020,25(3):753. doi: 10.3390/molecules25030753
[26] LIU C H, ZHENG H H, SHENG K L, et al. Effects of melatonin treatment on the postharvest quality of strawberry fruit[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2018,139:47−55. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2018.01.016
[27] CONRATH U, BECKERS G J, LANGENBACH C J, et al. Priming for enhanced defense[J]. Annual Review of Phytopathology,2015,53:97−119. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-080614-120132
[28] WANG K T, LIAO Y X, XIONG Q, et al. Induction of direct or priming resistance against Botrytis cinerea in strawberries by β-aminobutyric acid and their effects on sucrose metabolism[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2016,64(29):5855−5865. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b00947
[29] WANG K T, LIAO Y X, CAO S F, et al. Effects of benzothiadiazole on disease resistance and soluble sugar accumulation in grape berries and its possible cellular mechanisms involved[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2015,102:51−60. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2015.02.011
[30] SMIRNOFF N, ARNAUD D. Hydrogen peroxide metabolism and functions in plants[J]. New Phytologist,2019,221(3):1197−1214. doi: 10.1111/nph.15488
[31] LIMA M C, De SOUSA C P, FERNANDEZ-PRADA C, et al. A review of the current evidence of fruit phenolic compounds as potential antimicrobials against pathogenic bacteria[J]. Microbial Pathogenesis,2019,130:259−270. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.03.025
[32] GARCÍA-CRISTOBAL J, GARCÍA-VILLARACO A, RA-MOS B, et al. Priming of pathogenesis related-proteins and enzymes related to oxidative stress by plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on rice plants upon abiotic and biotic stress challenge[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology,2015,188:72−79. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2015.09.011
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 徐冯莲,许锐鹏,张沂,王子昱,李煜龙,陈贵浩,方伟蓉. 植物乳杆菌RG-034对大鼠腹泻型肠易激综合征的治疗作用. 现代药物与临床. 2024(04): 816-825 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 施丰成,李天笑,许春平,国旭丹,冀晓龙,宋光富. 粗细支卷烟烟气对小鼠肠道菌群及代谢产物的影响. 食品工业. 2024(11): 91-97 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘玉鑫,韩迎香,王雅菲,郝艳萍,萨仁娜,托娅. 植物乳植杆菌LP-315对DSS诱导的小鼠炎症性肠病模型免疫应答调控研究. 中国微生态学杂志. 2024(12): 1365-1373 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



