Study on the Construction and Gel Properties of Plant Simulated Egg Liquid System
-
摘要: 本文以绿豆蛋白、甲基纤维素、κ-卡拉胶(κ-carrageenan,KC)和高酰基结冷胶(high acyl gellan gum,HA)等成分为原料,构建了以绿豆蛋白为基体的模拟蛋液体系。通过测定质构、动态流变、持水性和微观结构等指标,考察了主要凝胶剂KC和HA配比对模拟蛋液凝胶质构性质、流变性质、持水性和微观结构等的影响。质构分析和持水性测定结果表明,KC是模拟蛋液凝胶强度和硬度的决定性因素,而HA可提高凝胶的弹性、内聚性、咀嚼性和持水性。温度扫描结果显示模拟蛋液和天然蛋液在加热和冷却过程中储能模量(G′)始终大于损耗模量(G″),说明两者体系均以弹性为主体。随着HA质量比的提高,复合溶胶的黏度、储能模量(G′)和损耗模量(G″)增加,表明HA可改善模拟蛋液溶胶的黏性性质。扫描电镜结果显示,KC和HA可形成独立的互穿聚合物网络,具有一定的相容性和交联性。感官评定结果可知,当KC/HA配比为1.2:0.4时植物模拟煎蛋综合感官评分最高,和天然煎蛋在口感、组织结构和风味等方面最相近。综上所述,通过研究模拟蛋液体系中不同比例KC/HA的力学性能及相互作用机理,为植物基蛋类模拟制品的开发利用提供理论依据。Abstract: In this study, mung bean protein, methyl cellulose, κ-carrageenan (KC) and high acyl gellan gum (HA) were used as raw materials to construct a simulated egg liquid system based on mung bean protein. The effects of the ratios of KC and HA on the textural properties, rheological properties, water holding capacity (WHC) and microstructure of simulated egg liquid were investigated by measuring the textural results, dynamic rheology, WHC and microstructure. The textural analysis and WHC results suggested that KC was the decisive factor for the gel strength and hardness of the simulated egg liquid gels, HA contributed significantly to the springiness, cohesiveness, chewiness and WHC. The temperature scanning results showed that G′ and G" of the simulated egg liquid and natrual egg liquid increased gradually during heating and cooling, and G' was always greater than G", indicating that the two systems were dominated by elasticity. As the proportion of HA increased, the viscosity, the storage modulus (G′) and loss modulus (G″) of the compound sol system increased, showing that HA could improve viscoelasticity properties of the simulated egg liquid sol. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) results showed that KC and HA might form separate and interpenetrating polymer networks and the gel network structure was formed due to the certain compatibility and crosslinking between KC and HA. The sensory evaluation results showed that when the KC/HA ratio was 1.2:0.4, the comprehensive sensory score of the simulated fried egg was the highest, which was the closest to the natural fried egg in terms of taste, structure and flavor. In summary, this study could provide theoretical basis for the development and utilization of plant-based egg simulation products by investigating mechanical properties and interaction mechanism of simulated egg liquid system with different ratios of KC/HA.
-
随着素食饮食的兴起,人们对素食食品的需求不断增长。近年来素食食品在全球范围内的上市数量增长了21%,如素肉饼[1]、素肉松[2]、素米肠[3]等食品应运而生。蛋类模拟制品作为食品工业中的新兴食品,是以植物基元素为主要原料,在口感、外观和组织结构等方面模拟天然鸡蛋。绿豆中含有丰富的蛋白质,目前对绿豆的加工主要以淀粉为主,对绿豆蛋白利用程度低,造成了资源的浪费。绿豆蛋白具有多种功能特性,如良好的溶解性、发泡性、凝胶性和乳化性等[4]。同时绿豆蛋白颜色为黄绿色,与天然蛋液凝胶相近,含有极少的过敏原,适宜大多数人食用[5]。因此,绿豆蛋白可作为一种良好的基体材料用于模拟蛋液的构建。甲基纤维素可使重组类食品在加热时和加热后较长时间保持食品所需的结实质构和多汁的口感,同时甲基纤维素还具有增稠、乳化、成膜等特性,因此,在食品加工领域应用广泛[6-7]。但二者的黏度和凝胶特性难以形成完整形态的凝胶,因此,有必要对具有黏度和凝胶特性的多糖进行筛选,以构建模拟蛋液体系。
多糖具有良好的凝胶特性,可将不同类型的多糖复配使用,构成性质不同的复合凝胶体系。κ-卡拉胶(κ-carrageenan,KC)和高酰基结冷胶(high acyl gellan gum,HA)作为冷凝胶多糖,在加热后可以形成凝胶,赋予模拟蛋液在加热后完整的质构性质。KC作为一种线性多糖,其单独形成的凝胶不仅脆度大、弹性小,且析水现象严重[8]。HA形成的凝胶柔软、富有弹性和黏着力,但凝胶硬度和凝胶强度较差[9]。因此,在模拟蛋液体系中,在植物蛋白和甲基纤维素含量确定的条件下,KC和HA这两种冷凝胶多糖对模拟蛋液加热后的形态发挥重要作用,可将这两种多糖以一定比例复配来改善蛋类替代品在加热冷却后的质构性质。目前,国内外对蛋类模拟制品的开发主要以植物蛋白和多糖为主。向宁等[10]以大豆分离蛋白为基体,利用谷氨酰胺转移酶与大豆分离蛋白的共价交联作用,在特定温度下,解决了植物类蛋白凝胶制品结构松散、不易成型的问题。Mahadevan等[11]发明了一种重组卵清蛋白,具有胶凝、起泡、成膜、乳化、粘结、增稠等特性,可代替鸡蛋用于焙烤食品。Keys等[12]提供了一种低胆固醇含量的鸡蛋替代品组合物,包括淀粉、脂肪和水胶体体系(水胶体和交联剂的混合物),可用于炒鸡蛋、煎蛋卷、煎蛋饼等。但是这些蛋类替代品在制备时需要复杂的加工工艺过程或者需要昂贵的仪器设备,制作成本较高。
本研究以绿豆蛋白、甲基纤维素、KC和HA作为主要成分,构建了模拟蛋液体系。该体系不仅加工工艺简单,不需要复杂或昂贵的仪器设备,成本相较传统鸡蛋也具有优势,同时具有高蛋白、低脂肪、零胆固醇等特点,为消费者提供一条新的素食选择。本文采用动态流变仪研究模拟蛋液凝胶过程中的动态黏弹性变化,以此来反映模拟蛋液随温度变化其弹性和黏性的变化规律。通过TPA、低场核磁、扫描电镜研究不同比例KC/HA复配对模拟蛋液凝胶体系的力学性能及相互作用机理进行表征,以期为植物基蛋类模拟制品的开发提供一定的理论参考和科学依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
天然鸡蛋 青岛市凌珊妈便利店;绿豆蛋白(纯度80%,未变性) 烟台双塔食品有限公司;甲基纤维素(粘度:50 mPa·s) 山东赫达股份有限公司;高酰基结冷胶(食品级) 浙江一诺生物科技有限公司;κ-卡拉胶(食品级) 浙江上方生物科技有限公司。
PX223ZH电子天平 奥豪斯仪器常州有限公司;TMS-PRO质构仪 美国Food Technology公司;MCR-101流变仪 德国Anton-Par公司;JSM-840电子扫描显微镜 日本JEOL株式会社;PQ001低场核磁共振分析仪 上海纽迈电子科技有限公司;Neofuge 18R高速冷冻离心机 上海力申科学仪器有限公司;HH-2电热恒温水浴锅 国华电器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 凝胶样品制备
植物模拟蛋液凝胶制备:称取12 g绿豆蛋白于烧杯中加入100 mL蒸馏水,以600 r/min搅拌30 min,静置过夜使绿豆蛋白充分溶胀。加入2 g甲基纤维素和质量比分别为(1.6:0、1.4:0.2、1.2:0.4、1.0:0.6、0.8:0.8)KC/HA复配多糖,冷凝胶多糖总浓度为1.6%,继续以600 r/min搅拌30 min。将制备好的混合溶胶样品装入直径为3 cm的塑料肠衣中,放入恒温水浴锅在100 ℃下水浴加热30 min,流水冷却至常温,在4 ℃下放置24 h待测[13]。天然蛋液凝胶制备:将鸡蛋液于烧杯中充分搅打使蛋黄和蛋清混合均匀,将其装入塑料肠衣中,在恒温水浴锅于100 ℃下水浴加热30 min,流水冷却至常温,在4 ℃下放置24 h待测。
1.2.2 质构特性测定
凝胶强度测定:参照黄远芬等[14]的方法,并稍作改动。将模拟蛋液凝胶和天然蛋液凝胶样品切成2~3 cm高的圆柱体,注意切面均匀平整。采用直径为12.7 mm圆柱塑胶探头(TMS 12.7 mm Black Aoetate),测试速度:60 mm/min,穿刺距离:4 mm,触发力:5 g。破断力代表样品的硬度,单位为g;破断距离代表样品的弹性,单位为mm;两者的乘积用来表征凝胶样品的凝胶强度,单位为g·cm。质地剖面分析(Texture profile analysis,TPA)测定:参照姜帅等[15]的方法,将模拟蛋液凝胶和天然蛋液凝胶凝胶样品分别置于TMS-PRO质构仪分析测试平台上,采用P-50探头对样品进行硬度、弹性等指标测定。测量参数如下:测试前速度和测试速度均为60 mm/min,测试后速度为50 mm/min,压缩程度为50%,触发力为5 g,间隔时间为5 s。
1.2.3 动态流变学测定
1.2.3.1 黏度测定
参照王小庆等[16]的方法,将模拟蛋液和天然蛋液置于测试平台上,使用MCR 101流变仪进行测定,测试温度为25 ℃,剪切速率为0.1~100 s−1。测试前用二甲基硅油密封样品以防止水分蒸发。
1.2.3.2 温度扫描
参照Anton等[17]的方法,取2~3 mL模拟蛋液和天然蛋液置于测试平台上,对样品进行温度扫描。以6 ℃/min的加热速率从25 ℃加热至100 ℃,然后从100 ℃降低至25 ℃,频率恒定为1 Hz,应变为1%。在加热和冷却的过程中,储能模量G′、损耗模量G″被记录下来。测试前用二甲基硅油密封样品以防止水分蒸发。
1.2.3.3 频率扫描
分别对热凝胶前后的模拟蛋液和天然蛋液在线性区域内(固定应变为1%)进行频率扫描,频率扫描的范围为0.01~25 Hz,测试温度为25 ℃。在这个过程中,G′、G″和损耗角正切Tanδ随频率的变化被记录下来。每组样品测试三次,取平均值进行分析。
1.2.4 持水性测定
持水性测定参照Chen等[18]的试验方法,将模拟蛋液凝胶和天然蛋液凝胶样品(约1.00 g)切成小块,并置于具有两层滤纸的离心管(直径10 mm)中,在25 ℃下以5000 r/min离心10 min,离心前后分别对样品进行称重,其持水性(WHC)计算公式如下:
WHC(\%) =m2m1×100 式中:m1:离心前凝胶样品的质量,g;m2:离心后凝胶样品的质量,g。
1.2.5 低场核磁测定
参照Li等[19]的方法并略作修改,将模拟蛋液凝胶样品切成5 mm×5 mm×10 mm的长方体,置于15 cm长的专用核磁玻璃管中,并插入NMR探针中。质子共振频率为22.7 MHz,测定时重复扫描4次,采用Carr-Purcell-Meiboom-Gill(CPMG)序列测量自旋-自旋弛豫时间(T2)。利用MultiExp InvAnalysis软件进行多指数拟合,得到模拟蛋液凝胶的横向弛豫图谱。
1.2.6 扫描电镜观察微观结构
参照Wang等[13]方法,将模拟蛋液凝胶和天然蛋液凝胶样品切成小块置于10 mL离心管中,在−80 ℃下预冻12 h,立即转移至真空冷冻干燥机中冷冻干燥2~3 d,将冷冻干燥后的凝胶放在铜网上并用金粉溅射涂覆。使用扫描电子显微镜在15 kV的加速电压下观察样品。
1.2.7 感官评价
参照姜帅等[15]的方法并稍作修改。在不粘锅中加入少量植物油,将含有不同比例KC/HA复配的植物模拟蛋液和天然鸡蛋液分别于不粘锅中以中小火煎5 min左右,得到植物煎蛋和天然煎蛋。邀请10名从事食品专业且经过专门感官训练培训的研究生,其中,5男5女,组成评定小组,采用双盲法进行检验。主要对产品的色泽、风味、组织状态、口感进行评定,每项指标的最高得分为10分,最低为1分,其中,色泽占比20%,风味占比20%,组织状态占比30%,口感占比30%,综合得分为这四项指标的加权平均数。评价标准如表1所示。
表 1 感官评价标准Table 1. The standard of sensory evaluation评价指标 评分标准(10分) 8~10 5~7 1~4 色泽 颜色为金黄色,有光泽 颜色略黄或略淡黄色,光泽一般 颜色较黄或较淡,光泽较差 风味 具有良好的煎鸡蛋特有的香味,
香味浓郁煎鸡蛋香味略淡或有轻微豆腥味 无煎鸡蛋特有的香味或豆腥味较浓或出现异味 组织状态 形状完整,连接性好,结构蓬松性好 形状较完整,连接性一般,蓬松性较好 形状不完整,连接性较差,蓬松性较差 口感 硬度适中,弹性和咀嚼性适中,
口感接近于天然煎鸡蛋硬度略大或略小,弹性和咀嚼性略大或略小,
口感与天然煎鸡蛋相比有略微差别硬度较大或较小,弹性和咀嚼性较大或较小,
口感与天然煎鸡蛋相比差别较大1.3 数据处理
所有实验数据采用Excel 2016进行数据统计,利用SPSS 20.0软件进行数据分析,实验指标采用平均值±标准差表示,采用Origin 9.0软件绘图。每组样品测量三次取平均值作为最终结果。不同字母表示差异性显著(P<0.05)。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同质量比KC/HA复配模拟蛋液凝胶质构分析
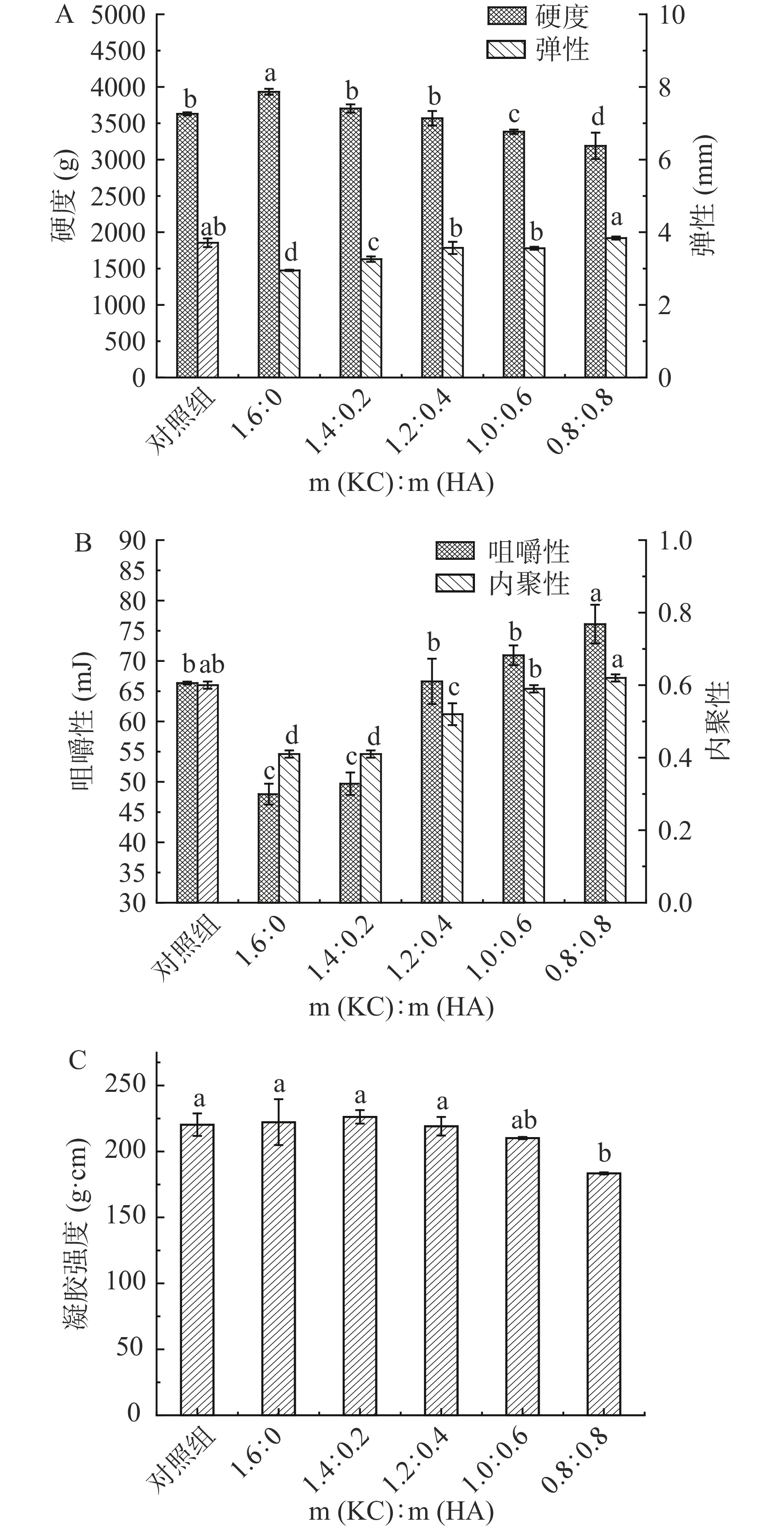
以天然蛋液凝胶为对照组,不同比例KC/HA复配植物模拟蛋液凝胶为实验组,质构测定结果如图1所示。随着HA比例的增加,模拟蛋液凝胶的硬度和凝胶强度呈降低趋势(图1A和图1C),这说明在模拟蛋液凝胶过程中,KC是决定模拟蛋液凝胶硬度和凝胶强度的关键性胶体,同时也说明凝胶硬度主要来自KC的网络结构,而不是聚合物的重排。郭琦等[20]在研究KC比例对明胶凝胶特性的影响时也发现随着KC比例的增加,混合凝胶的凝胶强度、硬度呈现升高趋势。同时HA的添加显著增加了模拟蛋液凝胶的弹性、咀嚼性和内聚性(P<0.05)(图1A和图1B),这主要是由于HA有庞大的乙酰基和甘油基阻碍了聚合物链的紧密结合,易形成柔软有弹性的凝胶[21];而KC则形成坚硬脆性大的凝胶,易破裂,将二者复配之后KC与HA分子间的缠绕作用有效改善了模拟蛋液凝胶的弹性、内聚性和咀嚼性。袁妍等[22]发现随着高酰基/低酰基结冷胶复配比例的增大,复合凝胶的硬度减小,内聚性和咀嚼性增大。由此可见,由于KC与低酰基结冷胶都属于双螺旋线性多糖,二者在与HA复配时有一定相似之处。同时可以看出,当KC/HA复配比例为1.2:0.4时,模拟蛋液凝胶的硬度、凝胶强度和咀嚼性与天然蛋液凝胶无显著差异(P>0.05),质构最为接近。
![]() 图 1 不同比例KC/HA复配模拟蛋液凝胶和天然蛋液凝胶质构性质注:不同字母表示同一指标差异显著(P<0.05);图5同。Figure 1. Textural properties of KC/HA mixtures at different mass ratios of simulated egg liquid gels and natural egg liquid gels
图 1 不同比例KC/HA复配模拟蛋液凝胶和天然蛋液凝胶质构性质注:不同字母表示同一指标差异显著(P<0.05);图5同。Figure 1. Textural properties of KC/HA mixtures at different mass ratios of simulated egg liquid gels and natural egg liquid gels2.2 动态流变学测定
2.2.1 黏度测定
图2为25 ℃时不同比例KC/HA复配植物模拟蛋液和天然蛋液黏度随剪切速率变化关系图。以天然蛋液为对照组,不同比例KC/HA复配植物模拟蛋液为实验组,由图2可知,各比例KC/HA复配模拟蛋液和天然蛋液的黏度随剪切速率的增加均逐渐下降,呈现假塑性,具有剪切稀化的特点。与天然蛋液黏度相比,植物模拟蛋液黏度较大,随着HA比例的增加,模拟蛋液的黏度逐渐增强,这可能是由于HA具有较高的持水性和黏性性质,提高了复配体系中连续相的黏弹性,增强了模拟蛋液的抗剪切能力[23]。
2.2.2 温度扫描
以天然蛋液为对照组,不同比例KC/HA复配模拟蛋液为实验组。图3A和图3B反映了各处理组随温度改变其动态黏弹性的变化,在升温和降温过程中,各比例KC/HA复配模拟蛋液G′和G″随温度变化趋势相似。在加热初期,各比例KC/HA复配模拟蛋液G′和G″变化趋势较为平缓。当温度大于45 ℃时,随温度继续升高,不同比例KC/HA复合模拟蛋液溶胶G′和G″急剧升高,这主要是由于体系中甲基纤维素具有热凝胶特性,可以使复合模拟蛋液实现溶胶到凝胶的转变[7]。在降温过程中(图中上方曲线),模拟蛋液G′和G″仍然继续增加,并且G′明显大于G″,说明模拟蛋液凝胶以弹性为主体,KC和HA作为冷凝胶多糖在加热后冷却可以形成凝胶,从而赋予模拟蛋类制品完整的质构特性。另外,随着HA比例的增加,冷却至常温时模拟蛋液凝胶G′呈逐渐降低的趋势,说明HA的添加降低了模拟蛋液凝胶的弹性模量,这与凝胶强度和硬度测定结果相一致。对于对照组,在加热初期,G′和G″明显低于模拟蛋液,其变化趋势与模拟蛋液相近。天然蛋液中既含有蛋清中的卵白蛋白、卵伴白蛋白和卵类黏蛋白等,同时也包含了蛋黄中的低密度脂蛋白,共同影响全蛋液的凝胶性[24]。在加热至50 ℃时,G′和G″急剧升高,说明此时蛋白质凝胶开始形成。在冷却过程中G′和G″持续升高,在冷却至25 ℃时,天然蛋液G′与KC/HA配比为1.2:0.4的模拟蛋液接近,这与凝胶强度测定结果一致。
2.2.3 频率扫描
图4反映了不同比例KC/HA复配模拟蛋液和天然蛋液的黏弹性行为。储能模量G′能反映黏弹性物质的类固体性质即弹性和刚性,损耗模量G″能反映黏弹性物质的类液体性质即黏性和流动性[25-26]。在0.01~25 Hz范围内,对于不同比例KC/HA复配模拟蛋液和天然蛋液溶胶体系,G′与G″均随频率的增加而增加(图4A和图4B);植物模拟蛋液的G′与G″均高于天然蛋液,且随着HA比例的增加,模拟蛋液溶胶的G″呈现升高趋势,说明HA可以提高模拟蛋液溶胶的黏性性质,这与黏度测定结果一致。在加热形成凝胶后,模拟蛋液凝胶和天然蛋液凝胶G′与G″几乎平行,G′明显高于G″,说明形成的凝胶为强凝胶。随着HA比例的增加,植物模拟蛋液凝胶G′呈降低趋势,与凝胶强度测定结果一致。Tanδ(G″/G′)来描述凝胶的相对粘弹性,Tanδ值越低,表明凝胶形成了更强的三维网络结构,弹性性质更优良[27]。由图4可以看出,所有处理组的Tanδ值均小于0.5(图4C),这说明所有组别均形成凝胶网络结构较强的热不可逆凝胶。添加HA的植物模拟蛋液凝胶,Tanδ值较低,说明其凝胶网络密度较大,内聚性较强,表现出更好的黏弹性特征。
2.3 持水性测定
持水能力影响食品凝胶的质地和感官性质,是评价食品凝胶可接受性的重要标准。由图5可知,随着HA比例的增加,植物模拟蛋液凝胶持水能力显著增加(P<0.05),均优于KC/HA为1.6:0时凝胶的持水性能。当KC/HA为1.2:0.4时,模拟蛋液凝胶持水性超过80%,当KC/HA比例为1.0:0.6时,模拟蛋液凝胶持水性与天然蛋液凝胶持水性无显著差异(P>0.05)。由此结果可知,HA可以提高模拟蛋液凝胶的持水性能,这是因为HA所含有的甘油酯基团对凝胶三维网络结构的稳定作用,可以束缚更多的水分[28];一般情况下,脆性多糖凝胶比弹性多糖凝胶更容易脱水收缩[29]。Huang等[21]研究低酰基结冷胶与高酰基结冷胶复配结构性能时也发现随着HA比例的增加其复合凝胶持水性也随之增加。在本研究中,添加HA后模拟蛋液凝胶弹性和内聚性增强,可以改善凝胶的持水能力。
2.4 低场核磁测定
低场核磁共振技术可以通过测定横向弛豫时间T2来判定食品中水分的结合状态。图6和表2反映了多指数拟合氢质子弛豫时间T2分布情况,在模拟蛋液凝胶中发现了三个峰,其中,T21(0.1~10 ms)为凝胶中与大分子紧密结合的结合水,T22(10~100 ms)为不易流动水,是被紧密束缚在凝胶网络空间中的水,T23(100~1000 ms)为自由水[30-31]。A21、A22和A23分别为T21、T22、T23的弛豫峰面积,弛豫峰面积与其对应的水分分数成比例[32]。从图6可知,植物模拟蛋液凝胶中的水主要为自由水。从表2可知随着HA比例的增加,T22和T23弛豫时间分别从14.06、108.28 ms降低至8.36、48.81 ms,具有显著性差异(P<0.05),表明模拟蛋液凝胶对水的结合能力增强,可能是由于KC与HA之间存在一定的相互作用,增强了凝胶间的分子作用力,增大了氢质子迁移的弛豫速率,使得弛豫时间降低[33]。由表3可以看出随着HA比例增加,A23峰面积比例从93.14%降低至87.18%,具有显著性差异(P<0.05),A21和A22峰面积比例分别从3.03%、3.80%增加至5.16%、7.09%,具有显著性差异(P<0.05),说明HA比例较大时,植物模拟蛋液凝胶对水分的束缚能力较强,可以使更多的自由水向不易流动水和结合水迁移。总而言之,HA的加入可以增强模拟蛋液凝胶的水分束缚能力,这与持水性测定结果相一致。
表 2 不同比例KC/HA复配模拟蛋液凝胶弛豫时间T2的变化Table 2. Changes in relation time T2 of KC/HA mixtures at different mass ratios of simulated egg liquid gels样品 T21(ms) T22(ms) T23(ms) 1.6:0 0.83±0.05a 14.06±0.30b 108.28±6.64a 1.4:0.2 0.91±0.09a 16.02±0.36a 92.17±1.26b 1.2:0.4 0.90±0.19a 11.42±0.53c 71.72±1.51c 1.0:0.6 0.92±0.07a 8.34±0.20d 49.16±0.81d 0.8:0.8 0.84±0.07a 8.36±0.25d 48.81±0.77d 注:同列不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);表3同。 表 3 不同比例KC/HA复配模拟蛋液凝胶弛豫时间T2峰面积的变化Table 3. Changes in T2 peak area of KC/HA mixtures at different mass ratios of simulated egg liquid gels样品 A21(%) A22(%) A23(%) 1.6:0 3.03±0.16d 3.80±0.13c 93.14±0.14a 1.4:0.2 4.49±0.18c 4.87±0.08b 91.51±0.26b 1.2:0.4 4.78±0.17b 4.99±0.14b 89.07±0.75c 1.0:0.6 5.13±0.10a 6.96±0.06a 87.77±0.37d 0.8:0.8 5.16±0.06a 7.09±0.15a 87.18±0.22d 2.5 微观结构分析
如图7所示,不同比例KC/HA复配植物模拟蛋液凝胶和天然蛋液凝胶微观结构具有一定的差异。单一KC凝胶结构主要是由丝状链和小颗粒组成的网状平面,扫描电子显微镜下没有观察到明显立体的空间结构(图7A)。随着HA比例的增加,模拟蛋液凝胶结构发生明显变化。当KC/HA比例为1.2:0.4时凝胶网络结构空隙较大,形成立体蜂窝状结构(图7C)。随着HA比例继续增加,凝胶网络结构更加均匀、有序且致密,孔隙变小(图7D和图7E)。由KC与HA形成的复合凝胶体系可以形成独立的互穿聚合物网络[34-35]。当两种聚合物链互相交联时可形成全互穿网络,如果一种聚合物链交联,另一种聚合物链为线性时则为半互穿网络[36]。研究表明,由全互穿网络形成的凝胶结构比半互穿网络更致密[37]。因此,当KC/HA为1.2:0.4时,离散的KC聚合物分散在连续的HA基质中,形成的网络结构为半互穿网络。当KC/HA为0.8:0.8时,这两种生物聚合物之间可以形成连续的网络。KC和HA之间具有很好的相容性和交联性,形成全互穿网络结构。由图7F 可知,在天然蛋液凝胶中由于蛋白质变性发生相互缔合作用,形成较大的聚集物,进而形成立体的空间网络结构[38]。同时也可以看出有油滴附着在天然蛋液凝胶表面,而模拟蛋液凝胶结构中无明显油滴。
2.6 感官评价
以天然煎蛋为评价标准,由图8可以看出,当KC/HA配比为1.6:0时植物煎蛋的感官评分最低,主要是由于当KC比例较高时,植物煎蛋的硬度较大,弹性较小,在口感方面与天然煎蛋差别较大。随着HA比例的增加,植物煎蛋的感官评分呈现先升高后降低的趋势。当KC/HA比例为1.2:0.4时,植物煎蛋的口感、组织状态、色泽和风味达到最佳水平,因此综合感官评分最高。图9为天然煎蛋和KC/HA比例为1.2:0.4时植物煎蛋对比图,可以看出植物煎蛋颜色为金黄色,与天然煎蛋颜色相近。与天然煎蛋相比,植物煎蛋表面较平整,褶皱纹理少,这是二者在外观上较大的区别。
3. 结论
本实验对不同KC/HA配比(1.6:0、1.4:0.2、1.2:0.4、1.0:0.6、0.8:0.8)的模拟蛋液和天然蛋液的流变和凝胶性质进行研究。结果表明,KC可增强模拟蛋液凝胶的硬度和凝胶强度;随着HA比例的增加,复合凝胶的弹性、咀嚼性和内聚性增强,当KC/HA比例为1.2:0.4时模拟蛋液凝胶的质构特性与天然蛋液凝胶最相近。低场核磁和持水性研究结果表明HA可通过改变水分迁移速率来提高凝胶的持水能力。黏度测定结果表明HA对模拟蛋液的黏性性质起决定作用,增强了体系的抗剪切能力。温度扫描结果显示模拟蛋液和天然蛋液随温度上升和下降过程中G′始终大于G″,说明两者的弹性性质大于黏性性质。频率扫描结果显示KC提高了模拟蛋液凝胶的G′和G″,而HA可降低损耗角正切值Tanδ,这是因为HA含有的甘油酯基团对凝胶三维网络结构起到稳定的作用,可改善网络结构的致密性。扫描电镜结果显示,在模拟蛋液凝胶中KC和HA可形成独立的互穿聚合物网络,而天然蛋液凝胶由于蛋白质交联作用可形成三维空间凝胶网络,并有油滴附着。感官评定结果表明当KC/HA比例为1.2:0.4时,植物模拟煎蛋在口感、组织结构和颜色上与天然煎蛋最相近。因此,在蛋类模拟制品中可通过调节KC/HA复配比例,来满足消费者对植物基蛋类模拟制品质地、口感和外观等方面的需求。
-
图 1 不同比例KC/HA复配模拟蛋液凝胶和天然蛋液凝胶质构性质
注:不同字母表示同一指标差异显著(P<0.05);图5同。
Figure 1. Textural properties of KC/HA mixtures at different mass ratios of simulated egg liquid gels and natural egg liquid gels
表 1 感官评价标准
Table 1 The standard of sensory evaluation
评价指标 评分标准(10分) 8~10 5~7 1~4 色泽 颜色为金黄色,有光泽 颜色略黄或略淡黄色,光泽一般 颜色较黄或较淡,光泽较差 风味 具有良好的煎鸡蛋特有的香味,
香味浓郁煎鸡蛋香味略淡或有轻微豆腥味 无煎鸡蛋特有的香味或豆腥味较浓或出现异味 组织状态 形状完整,连接性好,结构蓬松性好 形状较完整,连接性一般,蓬松性较好 形状不完整,连接性较差,蓬松性较差 口感 硬度适中,弹性和咀嚼性适中,
口感接近于天然煎鸡蛋硬度略大或略小,弹性和咀嚼性略大或略小,
口感与天然煎鸡蛋相比有略微差别硬度较大或较小,弹性和咀嚼性较大或较小,
口感与天然煎鸡蛋相比差别较大表 2 不同比例KC/HA复配模拟蛋液凝胶弛豫时间T2的变化
Table 2 Changes in relation time T2 of KC/HA mixtures at different mass ratios of simulated egg liquid gels
样品 T21(ms) T22(ms) T23(ms) 1.6:0 0.83±0.05a 14.06±0.30b 108.28±6.64a 1.4:0.2 0.91±0.09a 16.02±0.36a 92.17±1.26b 1.2:0.4 0.90±0.19a 11.42±0.53c 71.72±1.51c 1.0:0.6 0.92±0.07a 8.34±0.20d 49.16±0.81d 0.8:0.8 0.84±0.07a 8.36±0.25d 48.81±0.77d 注:同列不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05);表3同。 表 3 不同比例KC/HA复配模拟蛋液凝胶弛豫时间T2峰面积的变化
Table 3 Changes in T2 peak area of KC/HA mixtures at different mass ratios of simulated egg liquid gels
样品 A21(%) A22(%) A23(%) 1.6:0 3.03±0.16d 3.80±0.13c 93.14±0.14a 1.4:0.2 4.49±0.18c 4.87±0.08b 91.51±0.26b 1.2:0.4 4.78±0.17b 4.99±0.14b 89.07±0.75c 1.0:0.6 5.13±0.10a 6.96±0.06a 87.77±0.37d 0.8:0.8 5.16±0.06a 7.09±0.15a 87.18±0.22d -
[1] 肖志刚, 霍金杰, 王哲, 等. 模糊数学评价法优化素肉饼工艺及其品质研究[J]. 粮食与油脂,2021,34(6):118−123. [XIAO Zhigang, HUO Jinjie, WANG Zhe, et al. Study on optimization of the process and quality of plain meat pie by fuzzy mathematical evaluation[J]. Journal of Cereals & Oils,2021,34(6):118−123. [2] 雷叶斯, 杨巨鹏, 谢依霖, 等. 素肉松产品贮藏特性的研究[J]. 农产品加工,2017,9(17):6−10. [LEI Yesi, YANG Jupeng, XIE Yilin, et al. Research on the storage characteristics of vegetarian meat products[J]. Farm Products Processing,2017,9(17):6−10. [3] 刘金波, 马文庆, 张广春, 等. 一种新型蛋白素肠的研究[J]. 肉类加工,2020(12):1−3. [LIU Jinbo, MA Wenqing, ZHANG Guangchun, et al. Study on a new type of protein vegetarian sausage[J]. Meat Industry,2020(12):1−3. [4] ZHU Y S, SUN S, RICHARD F G. Mung bean proteins and peptides: Nutritional, functional and bioactive properties[J]. Food & Nutrition Research,2018,62:1−11.
[5] 杜梦霞, 李璇, 谢建华, 等. 绿豆蛋白与多肽理化性质及其生物活性研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2016,37(21):363−367. [DU Mengxia, LI Xuan, XIE Jianhua, et al. Research progress in physicochemical and bioactivities of protein and peptide from mung bean[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2016,37(21):363−367. [6] FORD J L. Thermal analysis of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose and methylcellulose: Powders, gels and matrix tablets[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics,1999,179(2):209−228. doi: 10.1016/S0378-5173(98)00339-1
[7] 颜正勇, 孙子重, SOO W, 等. 超级热凝胶的甲基纤维素在食品中的应用[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2012,4(S1):278−286. [YAN Zhengyong, SUN Zizhong, SOO W, et al. Supergelling methylcellulose’s food applications[J]. China Food Additives,2012,4(S1):278−286. [8] 浦庆琳. 酵母葡聚糖与其他大分子物质交互作用的研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2006. PU Qinglin. Study on the interaction between spent brewer’s yeast β-glucans and other macromolecules[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2006.
[9] TONG K F, XIAO G P, CHENG W F, et al. Large amplitude oscillatory shear behavior and gelation procedure of high and low acyl gellan gum in aqueous solution[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2018,199:397−405. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.07.043
[10] 向宁, 吴思弘, 夏久洁, 等. 一种基于大豆分离蛋白制备蛋类替代品的方法及产品: 中国, CN111436576A[P]. 2020-07-24. XIANG Ning, WU Sihong, XIA Jiujie, et al. A method and product for preparing egg substitute based on soybean protein isolate: China, CN111436576A[P]. 2020-07-24.
[11] MAHADEVAN K, AYOUGHI F, JOSHI I. et al. Ingredient composition for producing an egg-less food item, comprises a recombinant ovalbumin: The United States, WO2021034980-A1[P]. 2021-02-25.
[12] KEYS E, MONICA S, GOLDBERG R, et al. Plant-based egg substitute compositions: The United States, US10070654[P]. 2018-9-11.
[13] WANG W J, SHEN M Y, LIU S C, et al. Gel properties and interactions of Mesona blumes polysaccharide-soy protein isolates mixed gel: The effect of salt addition[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2018,192:193−201. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.03.064
[14] 黄远芬, 王欣, 刘宝林. 明胶-蔗糖/NaCl体系的LF-NMR弛豫特性及主成分分析[J]. 现代食品科技,2015,31(10):45−52,162. [HUANG Yuanfen, WANG Xin, LIU Baolin. Low-field nuclear magnetic resonance relaxation properties and principal component analysis of gelatin-sucrose/sodium chloride systems[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2015,31(10):45−52,162. [15] 姜帅, 牛海力, 刘骞, 等. 添加可得然胶对法兰克福香肠品质特性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(19):218−226. [JIANG Shuai, NIU Haili, LIU Qian, et al. Effect of curdlan addition on the quality of frankfurt sausage[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(19):218−226. [16] 王小庆, 任健. 不同油相比例对黑豆分离蛋白乳液凝胶特性的影响[J]. 中国油脂,2018,43(1):103−106. [WANG Xiaoqing, REN Jian. Influences of oil volume fraction on properties of black bean protein isolate emulsion gel[J]. China Oils and Fats,2018,43(1):103−106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7969.2018.01.026 [17] ANTON M, DENMAT M L, BEAUMAL V, et al. Filler effects of oil droplets on the rheology of heat-set emulsion gels prepared with egg yolk and egg yolk fractions[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces,2001,21(1-3):137−147. doi: 10.1016/S0927-7765(01)00167-9
[18] CHEN J, CHEN W T, DUAN F X, et al. The synergistic gelation of okra polysaccharides with kappa-carrageenan and its influence on gel rheology, texture behaviour and microstructures[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2019,87:425−435. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.08.003
[19] LI J H, XU L L, SU Y J, et al. Flocculation behavior and gel properties of egg yolk/κ-carrageenan composite aqueous and emulsion systems: Effect of NaCl[J]. Food Research International,2020,132:1−8.
[20] 郭琦, 王欣, 刘宝林. κ-卡拉胶比例对明胶凝胶体系凝胶特性、水分分布及微观结构的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(9):81−88. [GUO Qi, WANG Xin, LIU Baolin. Effects of κ-carrageenan ratio on gel properties, water distribution, and microstructure of a gelatin-gel system[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2019,45(9):81−88. [21] HUANG Y Q, TANG J M, SWANSON B G, et al. Effect of calcium concentration on textural properties of high and low acyl mixed gellan gels[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2003,54(4):517−522. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2003.08.006
[22] 袁妍, 李懋鸣, 李成倍, 等. 高酰基/低酰基结冷胶复合凝胶凝胶特性的研究[J]. 食品工业,2013,34(3):103−106. [YUAN Yan, LI Maoming, LI Chengbei, et al. Study on gel properties of high and low acyl mixed gellan gels[J]. Food Industry,2013,34(3):103−106. [23] MORRIS E R, NISHINARI K, RINAUDO M. Gelation of gellan-A review[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2012,28(2):373−411. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2012.01.004
[24] 辛楠. 蛋液凝胶形成影响因素分析及其产品创制[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2018. XIN Nan. Analysis on influencing factors of egg hot gel formation and its product development[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2018.
[25] ANDRADE I G, SOUKI N, MORAES I C F, et al. Rheology of emulsion-filled gels applied to the development of food materials[J]. Gels,2016,2(3):1−18.
[26] 刘婷婷, 杨嘉丹, 曹宸瑀, 等. 银耳多糖与结冷胶复配体系的流变及凝胶特性[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(17):72−78. [LIU Tingting, YANG Jiadan, CAO Chenyu, et al. Rheological and gelling properties of Tremella fuciformis polysaccharide and gellan gum mixtures[J]. Food Science,2019,40(17):72−78. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190122-257 [27] JIANG Shuai, CAO Chuan-ai, XIA Xiufang, et al. Enhancement of the textural and gel properties of frankfurters by adding thermo-reversible or thermo-irreversible curdlan gels[J]. Journal of Food Science,2019,84(5):1068−1077. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.14595
[28] YANG X, HOU Y J, GONG T, et al. Concentration-dependent rheological behavior and gelation mechanism of high acyl gellan aqueous solutions[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,131:959−970. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.137
[29] MAO R, TANG J, SWANSON B G. Water holding capacity and microstructure of gellan gels[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2001,46(4):365−371. doi: 10.1016/S0144-8617(00)00337-4
[30] GLICKSMAN M. Gelling hydrocolloids in food product applications[J]. Canadian Institute of Food Science and Technology Journal,1979,12(1):5−22.
[31] 段云霞, 赵英, 迟玉杰. 基于低场核磁共振技术分析不同贮藏条件下白煮蛋水分分布及品质变化[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(9):26−32. [DUAN Yunxia, ZHAO Ying, CHI Yujie. Low field nuclear magnetic resonance analysis of moisture distribution and quality variation in boiled eggs under different storage conditions[J]. Food Science,2018,39(9):26−32. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201809005 [32] LI J H, LI X, WANG C Y, et al. Characteristics of gelling and water holding properties of hen egg white/yolk gel with NaCl addition[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,77:887−893. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.11.034
[33] TANG H R, GODWARD J, HILLS B. The distribution of water in native starch granules-A multinuclear NMR study[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2000,43(4):375−387. doi: 10.1016/S0144-8617(00)00183-1
[34] DERKACH S, ZHABYKO I, VORONKO N G, et al. Stability and the rheological properties of concentrated emulsions containing gelatin-κ-carrageenan polyelectrolyte complexes[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2015,483:216−223.
[35] 马彩霞, 祝根平, 边界. 结冷胶与卡拉胶/魔芋胶的复配机理研究[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2007,4(2):102−106. [MA Caixia, ZHU Genping, BIAN Jie. Compound mechanism of gellan gum, carrageenan and konjac gum[J]. China Food Additives,2007,4(2):102−106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2513.2007.02.021 [36] MAO R S, TANG J M, SWANSON B G. Texture properties of high and low acyl mixed gellan gels[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2000,41(4):331−338. doi: 10.1016/S0144-8617(99)00108-3
[37] MANSON J A, SPERLING L H. Polymer blends and composites[M]. New York/London: Plenum Press, 1976: 121-151.
[38] 邓利玲, 张帅, 宋倩, 等. 添加魔芋葡甘聚糖对鸡蛋干品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(23):106−112. [DENG Liling, ZHANG Shuai, SONG Qian, et al. Effect of addition of konjac glucomannan to egg curd on its quality[J]. Food Science,2017,38(23):106−112. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201723018 -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 史文锦,刘仁慧. 山药在糖尿病及其并发症治疗中的作用机制研究进展. 山东医药. 2025(01): 144-149 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)






 下载:
下载:








 下载:
下载:



